EP1892457B1 - Procédé et dispositif destinés à l'enregistrement de gaz combustible, en particulier de gaz naturel - Google Patents
Procédé et dispositif destinés à l'enregistrement de gaz combustible, en particulier de gaz naturel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1892457B1 EP1892457B1 EP07114847A EP07114847A EP1892457B1 EP 1892457 B1 EP1892457 B1 EP 1892457B1 EP 07114847 A EP07114847 A EP 07114847A EP 07114847 A EP07114847 A EP 07114847A EP 1892457 B1 EP1892457 B1 EP 1892457B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- gas stream
- partial gas
- partial
- compressed
- compressor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000002737 fuel gas Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 26
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 24
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims description 66
- 239000003345 natural gas Substances 0.000 title claims description 22
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 167
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 claims description 25
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 claims 8
- 239000000112 cooling gas Substances 0.000 claims 3
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000002040 relaxant effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003949 liquefied natural gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001932 seasonal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J1/00—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures
- F25J1/02—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures requiring the use of refrigeration, e.g. of helium or hydrogen ; Details and kind of the refrigeration system used; Integration with other units or processes; Controlling aspects of the process
- F25J1/0201—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures requiring the use of refrigeration, e.g. of helium or hydrogen ; Details and kind of the refrigeration system used; Integration with other units or processes; Controlling aspects of the process using only internal refrigeration means, i.e. without external refrigeration
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C6/00—Methods and apparatus for filling vessels not under pressure with liquefied or solidified gases
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C7/00—Methods or apparatus for discharging liquefied, solidified, or compressed gases from pressure vessels, not covered by another subclass
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J1/00—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures
- F25J1/0002—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the fluid to be liquefied
- F25J1/0022—Hydrocarbons, e.g. natural gas
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J1/00—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures
- F25J1/003—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the kind of cold generation within the liquefaction unit for compensating heat leaks and liquid production
- F25J1/0032—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the kind of cold generation within the liquefaction unit for compensating heat leaks and liquid production using the feed stream itself or separated fractions from it, i.e. "internal refrigeration"
- F25J1/0035—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the kind of cold generation within the liquefaction unit for compensating heat leaks and liquid production using the feed stream itself or separated fractions from it, i.e. "internal refrigeration" by gas expansion with extraction of work
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J1/00—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures
- F25J1/003—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the kind of cold generation within the liquefaction unit for compensating heat leaks and liquid production
- F25J1/0032—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the kind of cold generation within the liquefaction unit for compensating heat leaks and liquid production using the feed stream itself or separated fractions from it, i.e. "internal refrigeration"
- F25J1/004—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures characterised by the kind of cold generation within the liquefaction unit for compensating heat leaks and liquid production using the feed stream itself or separated fractions from it, i.e. "internal refrigeration" by flash gas recovery
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J1/00—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures
- F25J1/02—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures requiring the use of refrigeration, e.g. of helium or hydrogen ; Details and kind of the refrigeration system used; Integration with other units or processes; Controlling aspects of the process
- F25J1/0228—Coupling of the liquefaction unit to other units or processes, so-called integrated processes
- F25J1/0232—Coupling of the liquefaction unit to other units or processes, so-called integrated processes integration within a pressure letdown station of a high pressure pipeline system
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J1/00—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures
- F25J1/02—Processes or apparatus for liquefying or solidifying gases or gaseous mixtures requiring the use of refrigeration, e.g. of helium or hydrogen ; Details and kind of the refrigeration system used; Integration with other units or processes; Controlling aspects of the process
- F25J1/0228—Coupling of the liquefaction unit to other units or processes, so-called integrated processes
- F25J1/0235—Heat exchange integration
- F25J1/0242—Waste heat recovery, e.g. from heat of compression
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2221/00—Handled fluid, in particular type of fluid
- F17C2221/03—Mixtures
- F17C2221/032—Hydrocarbons
- F17C2221/033—Methane, e.g. natural gas, CNG, LNG, GNL, GNC, PLNG
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2223/00—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel
- F17C2223/01—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel characterised by the phase
- F17C2223/0107—Single phase
- F17C2223/0123—Single phase gaseous, e.g. CNG, GNC
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2223/00—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel
- F17C2223/03—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel characterised by the pressure level
- F17C2223/035—High pressure (>10 bar)
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2225/00—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel
- F17C2225/01—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel characterised by the phase
- F17C2225/0146—Two-phase
- F17C2225/0153—Liquefied gas, e.g. LPG, GPL
- F17C2225/0161—Liquefied gas, e.g. LPG, GPL cryogenic, e.g. LNG, GNL, PLNG
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2225/00—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel
- F17C2225/03—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel characterised by the pressure level
- F17C2225/033—Small pressure, e.g. for liquefied gas
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/01—Propulsion of the fluid
- F17C2227/0128—Propulsion of the fluid with pumps or compressors
- F17C2227/0157—Compressors
- F17C2227/0164—Compressors with specified compressor type, e.g. piston or impulsive type
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/01—Propulsion of the fluid
- F17C2227/0128—Propulsion of the fluid with pumps or compressors
- F17C2227/0171—Arrangement
- F17C2227/0185—Arrangement comprising several pumps or compressors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/03—Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/0337—Heat exchange with the fluid by cooling
- F17C2227/0341—Heat exchange with the fluid by cooling using another fluid
- F17C2227/0348—Water cooling
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/03—Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/0337—Heat exchange with the fluid by cooling
- F17C2227/0358—Heat exchange with the fluid by cooling by expansion
- F17C2227/036—"Joule-Thompson" effect
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/03—Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/0367—Localisation of heat exchange
- F17C2227/0388—Localisation of heat exchange separate
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/01—Applications for fluid transport or storage
- F17C2270/0134—Applications for fluid transport or storage placed above the ground
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2210/00—Processes characterised by the type or other details of the feed stream
- F25J2210/06—Splitting of the feed stream, e.g. for treating or cooling in different ways
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2210/00—Processes characterised by the type or other details of the feed stream
- F25J2210/60—Natural gas or synthetic natural gas [SNG]
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2220/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for the removal of impurities
- F25J2220/60—Separating impurities from natural gas, e.g. mercury, cyclic hydrocarbons
- F25J2220/68—Separating water or hydrates
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2230/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams
- F25J2230/04—Compressor cooling arrangement, e.g. inter- or after-stage cooling or condensate removal
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2230/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams
- F25J2230/20—Integrated compressor and process expander; Gear box arrangement; Multiple compressors on a common shaft
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2230/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams
- F25J2230/30—Compression of the feed stream
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2230/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams
- F25J2230/60—Processes or apparatus involving steps for increasing the pressure of gaseous process streams the fluid being hydrocarbons or a mixture of hydrocarbons
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2240/00—Processes or apparatus involving steps for expanding of process streams
- F25J2240/90—Hot gas waste turbine of an indirect heated gas for power generation
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25J—LIQUEFACTION, SOLIDIFICATION OR SEPARATION OF GASES OR GASEOUS OR LIQUEFIED GASEOUS MIXTURES BY PRESSURE AND COLD TREATMENT OR BY BRINGING THEM INTO THE SUPERCRITICAL STATE
- F25J2270/00—Refrigeration techniques used
- F25J2270/04—Internal refrigeration with work-producing gas expansion loop
- F25J2270/06—Internal refrigeration with work-producing gas expansion loop with multiple gas expansion loops
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method and apparatus for storing fuel gas, in particular methane (natural gas), as well as, for example, from the WO 03/07991 are known.
- the natural gas demand of private and industrial consumers is characterized by seasonal and daily fluctuations.
- Natural gas storage facilities are operated to compensate for the fluctuations in consumption.
- To cover the peak consumption in particular to cover the high natural gas demand for heating purposes at low winter temperatures correspondingly high capacities are provided in gas transmission networks municipal gas supplier.
- large underground natural gas storage facilities for buffering consumption peaks such as tube storage and ball container are known.
- the capacities of the latter gas storage are limited to several hours Eintechnisch- or Aus Grandezeit and therefore suitable only to compensate for daily consumption fluctuations.
- the specific investment costs of such gas storage are high.
- the supply of natural gas is therefore burdened with a relatively high transport or performance price.
- conventional gas storage relatively large volumes and thus a lot of space.
- the present invention has for its object to provide a method and an apparatus that allow a more cost-effective gas supply, especially natural gas supply.
- the invention has for its object to provide a method and an apparatus that allow space-saving gas storage.
- the invention proposes a method for storing fuel gas, in particular natural gas (methane), in which compressed fuel gas supplied by means of a supply line, in particular natural gas, is divided by means of a dividing device into a first partial gas stream and at least one second partial gas stream, in which the first partial gas stream is expanded by means of at least one working machine, in particular an expansion turbine, wherein the first partial gas stream is previously heated by means of at least one heat exchanger so that this partial gas stream after relaxation in the at least one working machine a temperature still above 5 ° C, preferably greater than or equal to 8 ° C, in which the second partial gas stream is compressed by means of at least one compressor driven by the at least one working machine, heat dissipated in the second partial gas stream by its compression being removed and being used to heat the first Gas partial flow is used in the at least one heat exchanger, in which the compressed, cooled by heat removal second partial gas stream is so far relaxed that at least 10%, preferably more than 50% of the second partial gas stream incurred in the liquid state, and in which
- the first partial gas stream is preferably introduced into a municipal supply network.
- the device according to the invention accordingly comprises a dividing device for dividing compressed, supplied by a supply line fuel gas, in particular natural gas, in a first partial gas flow and at least one second partial gas flow, at least one working machine, in particular an expansion turbine, for relaxing the first partial gas flow, at least one compressor for compressing the second partial gas flow, wherein the compressor is driven by the at least one working machine, at least one heat exchanger, which transfers heat, which arises in the second partial gas flow by the compression thereof, to the first gas partial flow before its expansion in the at least one working machine, at least one expansion device for relaxation and at least partial liquefaction of the compressed, cooled by heat removal second partial gas flow, and at least one heat-insulated container for storing fuel gas liquefied by means of the expansion device.
- a dividing device for dividing compressed, supplied by a supply line fuel gas, in particular natural gas, in a first partial gas flow and at least one second partial gas flow
- at least one working machine in particular an expansion turbine
- the compressor for compressing the second partial gas
- heat exchanger can also be used in the present context, the term "heat exchanger”.
- An essential feature of the invention is the use of one or more heat exchangers to use the heat generated in the one partial gas flow during the compression, for the heating of the other, relaxing gas partial flow, and the drive of the at least one compressor by the at least one Working machine, by means of which said partial gas stream is expanded.
- part of the pressure energy of the compressed fuel gas supplied via the supply line (high-pressure line) is used for the further compression and liquefaction of a partial gas stream.
- the coupling according to the invention of the at least one compressor with the at least one working machine (for example expansion turbine) which relaxes the other partial gas stream does not require any additional drive energy, which is economically advantageous.
- Another economic advantage of the invention is that it does not require any additional heat energy, which is usually required to heat (heat) natural gas as it is being expanded from a high pressure supply line to medium or low pressure for further distribution to prevent possible icing of the expansion plants due to the Joule-Thompson effect.
- liquefying the fuel gas can be a space-saving gas storage achieve.
- natural gas compressed to 20 bar occupies about 5% of the volume of natural gas
- liquefied natural gas (methane) cooled to -162 ° C requires only about 0.17% of the volume of the standard gas.
- fuel gas methane
- other methods for which the use of a particularly low temperature level is advantageous include, for example, the decomposition of air, the production of crystalline CO 2 , as well as the direct use of liquid methane, for example, for power generation by direct injection in diesel combined heat and power plants or the pre-cooling sucked in gas turbines air.
- the high temperature gradient between liquefied fuel gas (methane) and the usual ambient temperature (outside temperature) can be used to vaporize gas quantities and gain further energy.
- An advantageous embodiment of the method according to the invention provides that the partial gas flow from which liquefied gas is to be produced is compressed in several stages and cooled between the compression stages becomes. In this way, the efficiency of the compression process can be improved.
- the compressed and cooled partial gas flow is partially relaxed before its leading to liquefaction relaxation in another working machine, in particular another expansion turbine.
- the power generated in this further work machine is preferably used to drive the compressor, a generator and / or another machine.
- At least part of the compressed, cooled and relaxed for the purpose of liquefaction partial gas flow is used for cooling of even at a higher pressure level gas of the same partial gas flow.
- the part of the partial gas stream used for cooling is then fed to the expanded, first partial gas stream, i. the non-liquefied gas partial stream added.
- heat which is generated in the further compressed partial gas flow through its compression, is used by means of at least one heat exchanger to the relaxed by means of the working machine partial gas flow (ie the non-liquefied partial gas stream) after its relaxation to warm up.
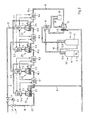
- the apparatus described comprises a dividing device 1 for dividing a gas flow supplied by means of a supply line (high-pressure line) into a first partial gas stream A and at least one second partial gas stream B.
- the gas available in the high-pressure line usually has a pressure in the range from 30 to 100 bar, for example about 50 bar.
- the dividing device 1 consists for example of a pipe branch provided with a control valve.
- the inventive device further comprises a working machine 2 for relaxing the first partial gas flow A and a compressor 3 for compressing the second partial gas flow B, wherein the compressor 3 is driven by the working machine 2.
- the working machine 2 preferably consists of an expansion turbine, while the compressor. 3 is preferably designed as a compression turbine.
- the working machine 2 and the compressor 3 are arranged on a common shaft 4.
- the control valve of the dividing device 1 is set as a function of the prevailing in the high-pressure line (gas pipeline) gas pressure.
- the gas stream is preferably divided so that 50 to 70%, in particular about 60% of the gas is supplied to the compressor 3.
- the quantitative ratio of the first partial gas flow A to the second partial gas flow B is, for example, about 40% to 60%.
- the partial gas flow A is heated before the almost isentropic relaxation in the expansion turbine 2 by means of a heat exchanger 5 so far that it has a temperature even above 8 ° C after the almost isentropic relaxation.
- the released during the relaxation work (rotational energy) is transmitted via the shaft 4 to the compression turbine 3.
- a part of the work thus released can be used to drive a generator 7, wherein missing drive power can optionally be generated by a motor 6.
- the second partial gas stream B is compressed in the compression turbine 3 to about 100 bar, whereby the gas heats up very strongly.
- the temperature of the compressed partial gas stream B can be up to 1000 ° C.
- Heat energy generated by the compression of the second partial gas stream B is discharged via a heat exchanger 8 and the heat exchanger 5 is supplied to the low pressure side via a water circuit 9.
- a multi-stage compression with respective intermediate cooling is provided.
- the compressor 3 has two compression stages 3.1, 3.2, wherein between the compression stages 3.1, 3.2 of the connected to the heat exchanger 5 via the water circuit 9 heat exchanger 8 is arranged.
- a further heat exchanger 10 is provided, with which the compressed gas is cooled.
- the heat exchanger 10 is connected via a water circuit 11 with a heat exchanger 12, which is arranged behind the expansion turbine 2 and the heating of the first partial gas flow A is used after its relaxation.
- the compressed and cooled second partial gas stream B is fed to an expansion device 13 and expanded there to a low pressure, wherein the greater part of the gas (methane) is liquefied.
- the liquefied gas B f is stored in one or more thermally insulated containers 14.
- the storage volume of these containers is for example 600 to 800 m 3 . Such a storage volume is sufficient to cover the gas demand for a severe winter day or the peak demand of several days in a gas central plant of medium size.
- the expansion device 13 is formed in the illustrated embodiment of at least one expansion valve. A part of the second partial gas stream B is still in the gaseous state after the flow through the expansion device 13 and is used for further cooling of even at a higher pressure level gas of the second partial gas stream B.
- the expansion device 13 is provided with a cooling device (heat exchanger device) 15 in which non-liquefied gas of the expanded second partial gas stream B is passed in countercurrent to the gas which is still at a higher pressure level. Subsequently, this part of the expanded second partial gas stream B used for cooling is preferably added to the expanded first partial gas stream A.
- the cooling device 15 is connected to a pipeline 16, which conducts the relaxed first partial gas flow A, so that non-liquefied gas of the expanded second partial gas stream B is fed to the expanded first partial gas stream A.
- the expansion valve 13 is preferably preceded by an expansion turbine 17 in order to extract additional enthalpy from the compressed second gas flow B.
- the further expansion turbine 17 can - as shown - either be arranged on the same shaft 4 in order to integrate their energy in the overall energy balance of the device according to the invention, or it can drive a generator via another shaft.
- the device according to the invention can be arbitrarily extended in terms of their storage capacity.
- Fig. 2 is shown a further embodiment of the device according to the invention.
- the apparatus sketched in turn comprises a dividing device 1 for dividing a gas stream fed by means of a supply line (high-pressure line) into a first partial gas stream A and at least one second partial gas stream B.
- the dividing device 1 comprises a fork (pipeline branch), wherein the high-pressure lines 21, 22 branching off there respectively a valve 1.1, 1.2 is integrated.
- the valves 1.1 and 1.2 is assigned a common actuator 1.3.
- the device has a plurality of turbine compressors 23, which are also referred to as a turbo compressor set.
- Each turbine compressor (turbo compressor set) 23 comprises a compressor 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 or 3.4 and a turbine (expansion turbine) 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.4, which are mechanically coupled to each other.
- a turbine compressor (expansion turbine) 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 and 2.4 which are mechanically coupled to each other.
- Fig. 2 For example, four turbine compressors 23 are connected in series.
- the partial gas flow A is gradually reduced in the turbines 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 of the turbo compressor sets 23. Before the partial gas flow A flows into the turbine of the respective turbo-compressor set, it is first heated by means of an upstream heat exchanger 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4 respectively.
- the construction volume of the turbines 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 increases in the flow direction of the gas to be expanded. The gas to be expanded thus flows through the turbines from that of a relatively compact turbine 2.1 to a relatively large-volume turbine 2.4.
- the partial gas flow B in stages in the compressors 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 of the turbo compressor sets 23 compacted.
- the construction volume of the compressors 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 decreases in the flow direction of the gas to be compressed.
- the gas to be compressed thus flows through the compressors from a relatively large-volume compressor 3.1 to a relatively compact compressor 3.4.
- the temperature or heat energy of the partial gas stream B increases due to the compression.
- a portion of the heat that arises in the partial gas stream B by the compression is dissipated by means of heat exchangers 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4 and used to heat the partial gas stream A in the heat exchangers 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4.
- each of the compressors 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, a heat exchanger 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 and 8.4 downstream the heat is delivered to one of the heat exchanger 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, which one of the turbines 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 or 2.4 is upstream and the heating of the partial gas stream A to be expanded is used.
- the heat exchangers 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 and 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4 form several cycles in groups.
- four of the eight heat exchangers are each connected to two circuits.
- the last compressor 3.4 in the series of compressors downstream heat exchanger 8.4 is connected to the heat exchanger 5.2, which is upstream of the second turbine 2.2 in the series of turbines.
- the downstream of the penultimate compressor 3.3 in the series of compressors heat exchanger 8.3 is connected to the heat exchanger 5.1, which is connected upstream of the first turbine 2.1.
- the compressed, cooled by heat removal gas partial flow B is relaxed by means of an expansion turbine 17 to a pressure which is in a range greater than 20 bar.
- the temperature of the so relaxed gas partial stream B is in the range of about 5 to 8 ° C.
- the expansion turbine 17 is a throttle 19 and a liquid separator 20 downstream for driving through the dew point.
- the liquid separator 20 is followed by a heat exchanger 15 ', with which the gas partial stream B withdrew further heat.
- the temperature of the partial gas stream B is after the heat exchanger 15 'just before the dew point of methane.
- the compressed, cooled by heat removal partial gas flow B is relaxed so far that at least 10 to 30%, preferably more than 50% of the second partial gas stream B incurred in the liquid state.
- the liquefaction takes place in several stages, for example in two stages.
- a first expansion device 13 ' comprising a heat exchanger tube, a pressure vessel (boiler) 14' and at least one throttle 13.1
- the expanded gas is present at a pressure in the range of 10 - 30 bar.
- the gas is then expanded by the first expansion device 13 'into a second expansion device 13 ", which also comprises a heat exchanger tube, a boiler (container) 14 "and at least one throttle 13.2 In the boiler 14", the expanded gas has a pressure of about 1 bar.
- the amounts of gas not liquefied during expansion are brought by means of at least one throttle 18 to a common pressure level and fed to the heat exchanger 15 ', where they extract the gas partial stream B - as mentioned above - further heat.
- the non-liquefied gas quantities are compressed, so that they have the pressure level of a downstream distribution network, in which also the relaxed partial gas flow A is fed.
- the liquefied fuel gas B f is finally discharged from the boiler (container) 14 ''.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Filling Or Discharging Of Gas Storage Vessels (AREA)
- Separation By Low-Temperature Treatments (AREA)
Claims (23)
- Procédé d'accumulation de gaz combustible, en particulier de gaz naturel,
dans lequel le gaz combustible, en particulier le gaz naturel, comprimé, alimenté avec une conduite d'alimentation, est divisé à l'aide d'un dispositif de division en un premier courant partiel de gaz (A) et au moins un deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B),
dans lequel le premier courant partiel de gaz (A) est détendu à l'aide d'au moins une machine de travail (2), en particulier une turbine de détente, où le premier courant partiel de gaz (A) est chauffé à l'aide d'au moins un échangeur de chaleur (5) de sorte que ce courant partiel de gaz (A) présente après la détente dans la au moins une machine de travail (2), une température encore supérieure à 5°C, de préférence supérieure ou égale à 8°C,
dans lequel le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) est comprimé à l'aide d'au moins un compresseur (3) entraîné par la au moins une machine de travail (2), où la chaleur, qui se forme dans le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) par cette compression, est extraite et utilisée pour le chauffage du premier courant partiel de gaz (A) dans le au moins un échangeur de chaleur,
dans lequel le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par l'extraction de chaleur, est détendu dans la mesure où au moins 10%, de préférence plus de 50% du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) se trouve à l'état liquide, et
dans lequel le gaz combustible (Bf) ainsi liquéfié est accumulé dans au moins un récipient isolé thermiquement (14) . - Procédé selon la revendication 1, caractérisé en ce que le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par extraction de la chaleur, est détendu à l'aide d'une ou de plusieurs turbines de détente et/ou soupapes de détente, de sorte qu'au moins 10%, de préférence plus de 50% du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) se trouve à l'état liquide.
- Procédé selon la revendication 1 ou 2, caractérisé en ce que le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) est comprimé en plusieurs étapes et refroidi entre les étapes de compression (3.1, 3.2).
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, caractérisé en ce que le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par extraction de la chaleur, est partiellement détendu dans une autre machine de travail (17), en particulier une autre turbine de détente, avant la détente dans laquelle au moins 10%, de préférence plus de 50% du deuxième courant partiel de gaz se trouve à l'état liquide.
- Procédé selon la revendication 4, caractérisé en ce que la puissance de l'autre machine de travail (17), produite par la détente partielle du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par extraction de chaleur, est utilisée pour le fonctionnement du compresseur (3), un générateur (7) et/ou une machine.
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, caractérisé en ce qu'au moins une partie du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par extraction de chaleur, puis détendu, est utilisée pour le refroidissement du gaz se trouvant encore à un niveau élevé de pression du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B).
- Procédé selon la revendication 6, caractérisé en ce que la partie utilisée pour le refroidissement du gaz se trouvant encore à un niveau élevé de pression du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B), du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) détendu, est ajoutée au premier courant partiel de gaz (A) détendu.
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 7, caractérisé en ce que la chaleur, qui se forme dans le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) par sa compression, est utilisée à l'aide d'au moins un échangeur de chaleur (10, 12) pour chauffer le premier courant partiel de gaz (A) détendu à l'aide de la machine de travail (2).
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 8, caractérisé en ce que le gaz combustible comprimé est divisé à l'aide du dispositif de division (1), de sorte que 50% à 70% du gaz combustible est alimenté comme deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) au compresseur (3).
- Dispositif d'accumulation de gaz combustible, en particulier de gaz naturel, comprenant un dispositif de division (1) pour la division du gaz combustible, en particulier du gaz naturel, comprimé, amené à l'aide d'une conduite d'alimentation, en un premier courant partiel de gaz (A) et au moins un deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B),
au moins une machine de travail (2), en particulier une turbine de détente, pour la détente du premier courant partiel de gaz (A),
au moins un compresseur (3), pour la compression du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B), où le compresseur (3) est entraîné par la au moins une machine de travail (2),
au moins un échangeur de chaleur (5), qui transfère la chaleur, qui se forme dans le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) par sa compression, vers le premier courant partiel de gaz (A) avant sa détente dans la au moins une machine de travail (2),
au moins un dispositif de détente (13) pour la détente et la liquéfaction au moins partielle du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par échange de chaleur, et
au moins un récipient isolé thermiquement (14) pour l'accumulation du gaz combustible liquéfié (Bf) à l'aide du dispositif de détente. - Dispositif selon la revendication 10, caractérisé en ce que le au moins un dispositif de détente (13) est formé d'une ou de plusieurs soupapes de détente.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 10 ou 11, caractérisé en ce que le compresseur (3) présente au moins deux étapes de compression (3.1, 3.2), où entre les étapes de compression (3.1, 3.2), au moins un échangeur de chaleur (8) servant au refroidissement du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B), est agencé.
- Dispositif selon l'une des revendications 10 à 12, caractérisé en ce que la machine de travail (2) pour la détente du premier courant partiel de gaz (A) et le condenseur (3) sont couplés mécaniquement l'un à l'autre.
- Dispositif selon l'une des revendications 10 à 13, caractérisé en ce que la machine de travail (2) pour la détente du premier courant partiel de gaz (A) et le compresseur (3) sont couplés mécaniquement l'un à l'autre par un arbre (4) commun.
- Dispositif selon l'une des revendications 10 à 14, caractérisé en ce que le compresseur (3) suit une autre machine de travail (17), en particulier une autre turbine de détente, pour la détente partielle du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par extraction de chaleur.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 15, caractérisé en ce que l'autre machine de travail (17) entraîne le compresseur (3), un générateur (7) et/ou une machine.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 15 ou 16, caractérisé en ce que l'autre machine de travail (17) est couplée mécaniquement au compresseur (3), au générateur (7) et/ou à la machine.
- Dispositif selon la revendication 15 ou 16, caractérisé en ce que l'autre machine de travail (17) le compresseur (3), le générateur (7) et/ou la machine sont couplés mécaniquement l'un à l'autre avec un arbre (4) commun.
- Dispositif selon l'une des revendications 15 à 18, caractérisé en ce qu'entre le compresseur (3) et l'autre machine de travail (17), est agencé au moins un échangeur de chaleur (10) servant au refroidissement du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) et/ou au chauffage du premier courant partiel de gaz (A).
- Dispositif selon l'une des revendications 10 à 19, caractérisé en ce qu'au moins un autre échangeur de chaleur (12) est présent, et transfère la chaleur, qui se forme par la compression du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B), au premier courant partiel de gaz (A) après sa détente dans la machine de travail (2).
- Dispositif selon l'une des revendications 10 à 20, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de détente (13), à l'aide duquel le deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) comprimé, refroidi par extraction de chaleur, est partiellement liquéfié, est muni d'un dispositif de refroidissement (15), dans lequel le gaz non liquéfié du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) détendu est utilisé pour le refroidissement du gaz de trouvant encore à un niveau élevé de pression du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B).
- Dispositif selon la revendication 21, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de refroidissement (15) est formé de sorte que le gaz non liquéfié du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) détendu est conduit à contre-courant du gaz se trouvant encore à un niveau élevé de pression du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B).
- Dispositif selon la revendication 21 ou 22, caractérisé en ce que le dispositif de refroidissement (15) est relié à une conduite tubulaire (16), qui conduit le premier courant partiel de gaz (A) détendu, de sorte que le gaz non liquéfié du deuxième courant partiel de gaz (B) détendu est conduit est alimenté au premier courant partiel de gaz (A) détendu.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102006039616A DE102006039616B3 (de) | 2006-08-24 | 2006-08-24 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Speicherung von Brenngas, insbesondere Erdgas |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1892457A1 EP1892457A1 (fr) | 2008-02-27 |
| EP1892457B1 true EP1892457B1 (fr) | 2009-01-14 |
Family
ID=38616385
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP07114847A Active EP1892457B1 (fr) | 2006-08-24 | 2007-08-23 | Procédé et dispositif destinés à l'enregistrement de gaz combustible, en particulier de gaz naturel |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1892457B1 (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE421068T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE102006039616B3 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HUE025791T2 (en) * | 2012-12-20 | 2016-05-30 | Linde Ag | Compression and cooling of gas |
| CN103775239B (zh) * | 2013-01-17 | 2017-01-04 | 摩尔动力(北京)技术股份有限公司 | 近恒温压冷源热机 |
| FR3002311B1 (fr) * | 2013-02-20 | 2016-08-26 | Cryostar Sas | Dispositif de liquefaction de gaz, notamment de gaz naturel |
| RU2707349C1 (ru) * | 2019-01-18 | 2019-11-26 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "АПА-КАНДТ СИБИРЬ" (ООО "АПА-КАНДТ СИБИРЬ") | Рекуперативный способ наполнения метаном баллонов высокого давления и устройство для его осуществления |
| WO2022187781A1 (fr) * | 2021-03-04 | 2022-09-09 | Exxonmobil Upstream Research Company | Systèmes et procédés de liquéfaction de gaz naturel |
| CN113606499B (zh) * | 2021-08-13 | 2023-05-05 | 上海氢枫能源技术有限公司 | 一种适用于加氢站的冷水机组及其使用方法 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3503220A (en) * | 1967-07-27 | 1970-03-31 | Chicago Bridge & Iron Co | Expander cycle for natural gas liquefication with split feed stream |
| US3735600A (en) * | 1970-05-11 | 1973-05-29 | Gulf Research Development Co | Apparatus and process for liquefaction of natural gases |
| FR2165729B1 (fr) * | 1971-12-27 | 1976-02-13 | Technigaz Fr | |
| GB1538477A (en) * | 1975-05-28 | 1979-01-17 | Gutehoffnungshuette Sterkrade | Evaporation of liquified natural gas |
| US5611218A (en) * | 1995-12-18 | 1997-03-18 | The Boc Group, Inc. | Nitrogen generation method and apparatus |
| FR2774158B1 (fr) * | 1998-01-23 | 2000-03-17 | Air Liquide | Installation combinee d'un four et d'un appareil de distillation d'air et procede de mise en oeuvre |
| US6006545A (en) * | 1998-08-14 | 1999-12-28 | L'air Liquide, Societe Anonyme Pour L'etude Et L'exploitation Des Procedes | Liquefier process |
| US6220053B1 (en) * | 2000-01-10 | 2001-04-24 | Praxair Technology, Inc. | Cryogenic industrial gas liquefaction system |
| US6581409B2 (en) * | 2001-05-04 | 2003-06-24 | Bechtel Bwxt Idaho, Llc | Apparatus for the liquefaction of natural gas and methods related to same |
| US6672104B2 (en) * | 2002-03-28 | 2004-01-06 | Exxonmobil Upstream Research Company | Reliquefaction of boil-off from liquefied natural gas |
| NO323496B1 (no) * | 2004-01-23 | 2007-05-29 | Hamwrothy Kse Gas System As | Fremgangsmate for rekondensering av avkoksgass |
-
2006
- 2006-08-24 DE DE102006039616A patent/DE102006039616B3/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2007
- 2007-08-23 DE DE502007000381T patent/DE502007000381D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2007-08-23 EP EP07114847A patent/EP1892457B1/fr active Active
- 2007-08-23 AT AT07114847T patent/ATE421068T1/de active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE502007000381D1 (de) | 2009-03-05 |
| EP1892457A1 (fr) | 2008-02-27 |
| DE102006039616B3 (de) | 2008-04-03 |
| ATE421068T1 (de) | 2009-01-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3362739B1 (fr) | Production de vapeur industrielle au moyen d'une pompe à chaleur haute température | |
| EP1892457B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif destinés à l'enregistrement de gaz combustible, en particulier de gaz naturel | |
| DE102015109898A1 (de) | Dampfkraftwerk und Verfahren zu dessen Betrieb | |
| EP0874188B2 (fr) | Procédé pour le traitement d'un gaz liquéfié cryogénique | |
| EP1562013A1 (fr) | Procédé de re-liquéfaction d'un gaz | |
| EP2880267A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour produire de l'énergie électrique | |
| WO2014000882A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de production d'une énergie électrique | |
| DE69819366T2 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur verflüssigung | |
| WO2010108464A2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour faire fonctionner un moteur d'entraînement d'un navire destiné au transport de gaz liquide | |
| WO2006136269A1 (fr) | Procede de liquefaction d'un courant riche en hydrocarbures | |
| WO2013156284A1 (fr) | Installation d'accumulation et de distribution d'énergie thermique au moyen d'un accumulateur de chaleur et d'un accumulateur de froid et procédé de fonctionnement de ladite installation | |
| DE102015002164A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Verflüssigen von Erdgas | |
| DE102012020469A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Abtrennung von Methan aus einem Synthesegas | |
| DE102006046246A1 (de) | Verfahren und Anlage zum Verdampfen von verflüssigtem Erdgas und Entspannen von Erdgas | |
| DE102007006370A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Verflüssigen eines Kohlenwasserstoff-reichen Stromes | |
| EP1913319A2 (fr) | Procede et installation pour liquefier un courant riche en hydrocarbure | |
| DE102016009254A1 (de) | Verfahren zur Speicherung und Rückgewinnung von Energie | |
| WO2018029371A1 (fr) | Échangeur de chaleur destiné à être utilisé dans une partie chaude d'une centrale de stockage d'énergie par air liquide, partie chaude et procédé permettant de faire fonctionner ledit échangeur de chaleur dans ladite partie chaude | |
| EP2902604A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de stockage d'énergie | |
| EP3948122A1 (fr) | Procédé et système de liquéfaction d'un gaz | |
| EP3293475A1 (fr) | Procédé et appareil de stockage et de récupération d'énergie | |
| DE602004001004T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Stickstoffverflüssigung durch Ausnutzung der Verdampfungskälte von flüssigem Methan | |
| EP3795885A1 (fr) | Installation de détente de gaz pourvue d'installation de fabrication de gnl | |
| DE102022205134B3 (de) | Druckaufbausystem und Druckaufbauverfahren zum Entnehmen eines Druckgases aus einer Speichervorrichtung zur Aufbewahrung eines Flüssiggases | |
| WO2005111522A1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif de liquefaction d'un flux riche en carbure d'hydrogene |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20071121 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK YU |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502007000381 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20090305 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090425 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090615 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090414 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090514 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20090925 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20091015 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090414 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100302 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090415 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090715 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090114 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 20110817 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20110817 Year of fee payment: 5 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20110826 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20110819 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20110902 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: OTTEN, EBERHARD Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: V1 Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20120823 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130301 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20130430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120823 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 421068 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120823 |