EP1245708B1 - Multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use and method to manufacture same - Google Patents
Multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use and method to manufacture same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1245708B1 EP1245708B1 EP02007003A EP02007003A EP1245708B1 EP 1245708 B1 EP1245708 B1 EP 1245708B1 EP 02007003 A EP02007003 A EP 02007003A EP 02007003 A EP02007003 A EP 02007003A EP 1245708 B1 EP1245708 B1 EP 1245708B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- weft
- elements
- yarn
- bundles
- warp
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 34
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 10
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title description 3
- 238000009954 braiding Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000009940 knitting Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000009795 derivation Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052500 inorganic mineral Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011707 mineral Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005470 impregnation Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 7
- -1 polyvinyl chloride Chemical compound 0.000 description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003628 erosive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920002239 polyacrylonitrile Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 244000025254 Cannabis sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000012766 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000012765 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. spontanea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 description 1
- DQXBYHZEEUGOBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N but-3-enoic acid;ethene Chemical compound C=C.OC(=O)CC=C DQXBYHZEEUGOBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000009120 camo Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000005607 chanvre indien Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007596 consolidation process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000005038 ethylene vinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011487 hemp Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003993 interaction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001200 poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000915 polyvinyl chloride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004800 polyvinyl chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04B—KNITTING
- D04B21/00—Warp knitting processes for the production of fabrics or articles not dependent on the use of particular machines; Fabrics or articles defined by such processes
- D04B21/14—Fabrics characterised by the incorporation by knitting, in one or more thread, fleece, or fabric layers, of reinforcing, binding, or decorative threads; Fabrics incorporating small auxiliary elements, e.g. for decorative purposes
Definitions
- the invention concerns a multi-axial textile grid, for technical or geotechnical use, characterized by a mesh structure which allows it to resist both cutting forces acting on several axes in the same plane as the grid, and also torque forces acting thereon.
- Such grids if used in the geotechnical field, are called "geogrids”.
- the textile grid according to the invention has a multi-axial structure reinforced and stabilized both along two axes orthogonal to each other and also along two further axes oblique and rotated with respect to the first two.
- the invention also concerns the method to manufacture said multi-axial grids.
- the state of the art includes bi-axial textile grids used to impart stability and compactness to elements which are disconnected, incoherent and liable to slide or similar.
- Such grids generally include a structure with orthogonal elements defined by a plurality of apertures which allow them to interact with the relative surfaces or supports on which they rest.
- US-A-5,795,835 a bonded composite knitted structural textile formed of knitted polymeric components.
- the first component is a high tenacity, high modulus, low elongation mono- or multifilament yarn.
- the second component is a fusible polymer in yarn which encapsulates and bonds adjacent load bearing yarns.
- the third component is an optional effect or bulking yarn.
- the fourth component is a multifilament warp knit stitch forming yarn to form the ground structure of the knitted textile.
- This structural textile has the disadvantage not to provide sufficient free area between the different links and not to have great features of resistance to the cutting forces in several directions and to the torque forces admiring on the same plane.
- the purpose of the invention is to achieve a textile grid characterized by great planar stability on a plurality of axes, and therefore suitable to guarantee great efficiency of use even in conditions of stress and high cutting forces and considerable torque forces.
- the purpose of the invention is to achieve a multi-axial textile grid or geogrid suitable to considerably increase, with respect to the conventional multi-axial textile, the anchorage of the surface on which it rests, or of the elements incorporated therein and also to increase the friction coefficient or cohesion, in order to obtain extremely good results of dimensional stability, also with respect to conventional bi-axial grids.
- the multi-axial textile grid according to the invention can be employed in every type of intervention where planning resistance and flexibility are required in the case of composite materials, both active and passive processes of protection and consolidation in the geotechnical field or in other technical solutions concerned.
- This grid is therefore applied in achieving interventions of flexibility or resistance, reinforcement or stabilization in the field of industry, roads, railways, or airports and similar, reclamation and protection against the erosion of banks of rivers, streams, canals, water courses and similar, reinforcement and protection against sea and wind erosion.
- the invention provides to make this multi-axial textile grid by means of using the technology "warp knitting with weft insertion”.
- the multi-axial textile grid according to the invention is achieved by means of sequences of "three-hinge arches", and therefore absolutely stable, arranged in such a manner as to obtain and therefore exploit an ample area, open and free, which allows to apply the grid for the specific functions, of a technical and geotechnical type, which it has to perform.
- the multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use comprises a first mesh structure formed by the orthogonal braiding of a plurality of weft elements and a corresponding plurality of warp elements, and a second mesh structure formed by further bundles of yarn disposed obliquely with respect to said weft elements and to said warp elements.
- Such further bundles of yarn are orthogonal to each other and are disposed in such a manner that said second mesh structure together with said first mesh structure define groups of three-hinge arches located checkerwise inside the apertures of said first mesh structure, with respect to apertures of said first mesh structure, which are free from any of said further bundles of yarn.
- the weft and warp elements and the bundles of yarn are attached to each other by another yarn disposed according to a joining chain.
- the multi-axial textile grid is made with apertures with a minimum dimension of about 10x10 mm of free area, with a thickness varying from a minimum of about 0.2 mm to a maximum of about 10 mm, and with a resistance varying from about 10 kN/m to about 10,000 kN/m and more, with the materials and yarns available today.
- the invention provides to use, as a basic material, the following types of yarns:
- the production process of said multi-axial textile grids advantageously provides finishing and enhancing steps, by means of the impregnation of the yarns mentioned above with resins, whether they be polyolefin in origin, such as ethylene vinyl acetate, polyurethane, polystyrene, polyvinyl, such as polyvinyl chloride, or other types, or by means of heat treatments or otherwise.
- finishing and enhancing steps allow to obtain a specific arrangement of the multi-axial textile grid according to the different purposes of use.
- the multi-axial textile grid according to the invention combines, in a non-obvious fashion, the advantages of conventional bi-axial textile grids, such as the quality of cohesion, with the advantages of multi-axial textile, such as the resistance to cutting and torque forces, at the same time eliminating the shortcomings of both, such as weakness for bi-axial textile grids and low cohesion for multi-axial textiles.
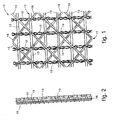
- a multi-axial textile grid 10 comprises a first mesh structure 11 formed by the orthogonal braiding of a plurality of weft yarns 13 and a corresponding plurality of warp yarns 12.
- yarns is intended to mean both yarns as such, and also strands, straps and any other element suitable to be woven.
- the yarns with which the weft 13 and warp 12 is formed are chosen from among various solutions of synthetic yarns of differing polymeric derivation, such as for example polyester, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (PA), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), liquid crystal polymers (LCP), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), oxidized polyacrylonitril (PAN), carbon fibre, polyethylene naphthalene (PEN) or similar, natural yarns of mineral derivation (glass fibre, ceramic yarns, metal yarns) or natural yarns of biological derivation (cotton, hemp, animal fleeces) or their combinations.
- Advantageously synthetic yarns and yarns of mineral derivation are mainly used.
- the weft 13 and warp 12 yarns are grouped together in bundles, separated from each other so as to form a net with apertures which can vary according to the field of use of the grid 10 and are indicatively greater than or equal to 10 x 10 mm.
- the grid 10 in addition comprises further bundles of yarns 15 and 16 disposed obliquely at 45°, with respect to the bundles of weft 13 and warp 12, in particular arranged so as to be aligned with determinate crossing points of the bundles of weft 13 and warp 12.
- the method used to achieve this crossing is known as "warp knitting with multi-axial DOS (Directionally oriented structures) system weft insertion".
- the bundles of weft 13 and warp 12 yarns, and the diagonal yarns 15 and 16, are attached to each other by a yarn 14 shaped so as to form a joining chain, intended to obtain a textile structure formed by three-hinge arches, which confers on the first mesh structure 11 characteristics of great resistance to the cutting forces in several directions and to the torque forces acting on the same plane.
- the further bundles of yarn 15 and 16 are orthogonal to each other and form a second mesh structure 17 which defines groups of three-hinge arches located checkerwise inside the apertures of the first meshstructure formed by the bundles of weft 13 and warp 12, leaving the adjacent areas free.
- the grid 10 can also be subjected to subsequent finishing and/or enhancing steps, as shown above.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Knitting Of Fabric (AREA)
- Woven Fabrics (AREA)
- Braiding, Manufacturing Of Bobbin-Net Or Lace, And Manufacturing Of Nets By Knotting (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
- Details Of Garments (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- The invention concerns a multi-axial textile grid, for technical or geotechnical use, characterized by a mesh structure which allows it to resist both cutting forces acting on several axes in the same plane as the grid, and also torque forces acting thereon. Such grids, if used in the geotechnical field, are called "geogrids".
- To be more exact, the textile grid according to the invention has a multi-axial structure reinforced and stabilized both along two axes orthogonal to each other and also along two further axes oblique and rotated with respect to the first two.
- The invention also concerns the method to manufacture said multi-axial grids.
- The state of the art includes bi-axial textile grids used to impart stability and compactness to elements which are disconnected, incoherent and liable to slide or similar.
- Such grids generally include a structure with orthogonal elements defined by a plurality of apertures which allow them to interact with the relative surfaces or supports on which they rest.
- Conventional bi-axial textile grids, however, are not generally resistant either to cutting forces distributed over several axes or to torque forces on the plane, inasmuch as their mesh structures form a repetition of "articulated parallelograms" which resist the cutting forces only on two axes of geometry, that is, those along which the warp and weft elements are arranged, and yield to the torque forces which are in any case arranged on their plane.
- Such bi-axial textile grids, in certain conditions of use, are therefore subject to limited efficiency.
- It is known from
US-A-5,795,835 a bonded composite knitted structural textile formed of knitted polymeric components. The first component is a high tenacity, high modulus, low elongation mono- or multifilament yarn. The second component is a fusible polymer in yarn which encapsulates and bonds adjacent load bearing yarns. The third component is an optional effect or bulking yarn. The fourth component is a multifilament warp knit stitch forming yarn to form the ground structure of the knitted textile. This structural textile has the disadvantage not to provide sufficient free area between the different links and not to have great features of resistance to the cutting forces in several directions and to the torque forces insisting on the same plane. - It is known from
US-A-2, 244,835 a textile material for foundations which has woven therein a component of hair to increase the rigidity or stiffness. The resultant fabric is formed by the classic weave of weft yarns and warp yarns and by an additional yarn. The three yarns define a woven structure having a plurality of substantially square apertures, on which the point of crossing of weft yarns and warp yarns are disposed, which square apertures are separated, checker-wise, by a plurality of substantially hexagonal openings. - The present Applicant has devised and embodied this invention to overcome the shortcomings of the state of the art and to obtain further advantages.
- The invention is set forth and characterized in the respective main claims, while the dependent claims describe other innovative characteristics of the invention.
- The purpose of the invention is to achieve a textile grid characterized by great planar stability on a plurality of axes, and therefore suitable to guarantee great efficiency of use even in conditions of stress and high cutting forces and considerable torque forces.
- To be more exact, the purpose of the invention is to achieve a multi-axial textile grid or geogrid suitable to considerably increase, with respect to the conventional multi-axial textile, the anchorage of the surface on which it rests, or of the elements incorporated therein and also to increase the friction coefficient or cohesion, in order to obtain extremely good results of dimensional stability, also with respect to conventional bi-axial grids.
- The multi-axial textile grid according to the invention can be employed in every type of intervention where planning resistance and flexibility are required in the case of composite materials, both active and passive processes of protection and consolidation in the geotechnical field or in other technical solutions concerned.
- This grid is therefore applied in achieving interventions of flexibility or resistance, reinforcement or stabilization in the field of industry, roads, railways, or airports and similar, reclamation and protection against the erosion of banks of rivers, streams, canals, water courses and similar, reinforcement and protection against sea and wind erosion.
- The invention provides to make this multi-axial textile grid by means of using the technology "warp knitting with weft insertion".
- To be more exact, the multi-axial textile grid according to the invention is achieved by means of sequences of "three-hinge arches", and therefore absolutely stable, arranged in such a manner as to obtain and therefore exploit an ample area, open and free, which allows to apply the grid for the specific functions, of a technical and geotechnical type, which it has to perform.
- The multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use according to the present invention comprises a first mesh structure formed by the orthogonal braiding of a plurality of weft elements and a corresponding plurality of warp elements, and a second mesh structure formed by further bundles of yarn disposed obliquely with respect to said weft elements and to said warp elements. Such further bundles of yarn are orthogonal to each other and are disposed in such a manner that said second mesh structure together with said first mesh structure define groups of three-hinge arches located checkerwise inside the apertures of said first mesh structure, with respect to apertures of said first mesh structure, which are free from any of said further bundles of yarn. Moreover, the weft and warp elements and the bundles of yarn are attached to each other by another yarn disposed according to a joining chain.
- According to the invention, the multi-axial textile grid is made with apertures with a minimum dimension of about 10x10 mm of free area, with a thickness varying from a minimum of about 0.2 mm to a maximum of about 10 mm, and with a resistance varying from about 10 kN/m to about 10,000 kN/m and more, with the materials and yarns available today.
- In making said multi-axial textile grids, the invention provides to use, as a basic material, the following types of yarns:
- synthetic yarns of different polymeric derivation and/or their combinations;
- composite yarns characterized by a heat sensitive or heat opponent cuticle;
- natural yarns of mineral derivation;
- natural yarns of biological derivation.
- The choice of using the various types of yarns, synthetic and non-synthetic, satisfies the capacity which they have of meeting the specific planning requirements, since the physical/chemical characteristics of the various materials mentioned, and their interactions with the environment for which they are mainly intended, are known.
- The production process of said multi-axial textile grids advantageously provides finishing and enhancing steps, by means of the impregnation of the yarns mentioned above with resins, whether they be polyolefin in origin, such as ethylene vinyl acetate, polyurethane, polystyrene, polyvinyl, such as polyvinyl chloride, or other types, or by means of heat treatments or otherwise. These finishing and enhancing steps allow to obtain a specific arrangement of the multi-axial textile grid according to the different purposes of use.
- In all cases, the result is to obtain, thanks to the specific nature of the invention, a greater suitability both of use and of durability in the specific fields and sectors indicated above.
- Therefore, the multi-axial textile grid according to the invention combines, in a non-obvious fashion, the advantages of conventional bi-axial textile grids, such as the quality of cohesion, with the advantages of multi-axial textile, such as the resistance to cutting and torque forces, at the same time eliminating the shortcomings of both, such as weakness for bi-axial textile grids and low cohesion for multi-axial textiles.
- These and other characteristics of the invention will be apparent from the description of a preferential form of embodiment of the invention, given as a non-restrictive example with reference to the attached drawings wherein:
- Fig. 1
- shows a schematic plane view of a multi-axial textile grid according to the invention;
- Fig. 2
- shows a schematic side view of the grid in Fig. 1 showing the multi-axial DOS textile.
- With reference to Figs. 1 and 2, a
multi-axial textile grid 10 according to the invention comprises afirst mesh structure 11 formed by the orthogonal braiding of a plurality ofweft yarns 13 and a corresponding plurality ofwarp yarns 12. We hereby specify that in this description the term yarns is intended to mean both yarns as such, and also strands, straps and any other element suitable to be woven. - The yarns with which the
weft 13 andwarp 12 is formed are chosen from among various solutions of synthetic yarns of differing polymeric derivation, such as for example polyester, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), polyamide (PA), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), liquid crystal polymers (LCP), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), oxidized polyacrylonitril (PAN), carbon fibre, polyethylene naphthalene (PEN) or similar, natural yarns of mineral derivation (glass fibre, ceramic yarns, metal yarns) or natural yarns of biological derivation (cotton, hemp, animal fleeces) or their combinations. Advantageously synthetic yarns and yarns of mineral derivation are mainly used. - The
weft 13 andwarp 12 yarns are grouped together in bundles, separated from each other so as to form a net with apertures which can vary according to the field of use of thegrid 10 and are indicatively greater than or equal to 10 x 10 mm. - The
grid 10 in addition comprises further bundles ofyarns weft 13 andwarp 12, in particular arranged so as to be aligned with determinate crossing points of the bundles ofweft 13 andwarp 12. The method used to achieve this crossing is known as "warp knitting with multi-axial DOS (Directionally oriented structures) system weft insertion". - The bundles of
weft 13 andwarp 12 yarns, and thediagonal yarns yarn 14 shaped so as to form a joining chain, intended to obtain a textile structure formed by three-hinge arches, which confers on thefirst mesh structure 11 characteristics of great resistance to the cutting forces in several directions and to the torque forces acting on the same plane. - In fact, the further bundles of
yarn second mesh structure 17 which defines groups of three-hinge arches located checkerwise inside the apertures of the first meshstructure formed by the bundles ofweft 13 andwarp 12, leaving the adjacent areas free. - The
grid 10 can also be subjected to subsequent finishing and/or enhancing steps, as shown above.
Claims (8)
- - Multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use, comprising a first mesh structure (11) formed by the orthogonal braiding of a plurality of weft elements (13) and a corresponding plurality of warp elements (12), and a second mesh structure (17) formed by further bundles of yarn (15, 16) disposed obliquely with respect to said weft elements (13) and to said warp elements (12), wherein said weft elements (13) and said warp elements (12) are grouped together in bundles and separated from each other in such a manner that said weft elements (13) lie on a first plane and said warp elements (12) lie on a second plane parallel and adjacent to said first plane, so as to form a net with apertures, and wherein said further bundles of yarn (15, 16) are orthogonal to each other and are disposed on two adjacent different planes parallel to said first and second planes, characterized in that said further bundles of yarn (15, 16) are disposed with respect to said first mesh structure (11) so as to be aligned with the points of crossing of said weft (13) and warp elements (12), so that the crossing points of said second mesh structure (17) are disposed inside said apertures of said net, in such a manner that said second mesh structure (17) together with said first mesh structure (11), define groups of three-hinge arches inside apertures of said net ; located checker-wisewith respect to apertures of said net, which are free from any of said further bundles of yarn (15, 16), and in that said weft (13) and warp elements (12) and said bundles of yarn (15, 16) are attached to each other by another yarn (14) disposed according to a chain stitch along said weft (13), said warp elements (12), or said bundles of yarn (15, 16), provided that said another yarn (14) crosses said points of crossing of said weft (13) and warp elements (12).
- - Grid as in claim 1, characterized in that each of said apertures of said net has a minimum dimension of about 10 x 10 mm.
- - Grid as in claim 1, characterized in that said weft and warp elements (12, 13) comprise at least one of the following types of yarn: synthetic yarns of differing polymeric derivation and/or their combinations; composite yarns having heat sensitive or heat opponent cuticle; natural yarns of mineral derivation; natural yarns of biological derivation.
- - Method to make a multi-axial textile grid for technical and geotechnical use, comprising a first step to make a first mesh structure (11) formed by the orthogonal braiding of a plurality of weft elements (13) and a corresponding plurality of warp elements (12), wherein said weft elements (13) and said warp elements (12) are grouped together in bundles and separated from each other in such a manner that said weft elements (13) lie on a first plane and said warp elements (12) lie on a second plane parallel and adjacent to said first plane, so as to form a net with apertures, and a second step to make a second mesh structure (17) formed by further bundles of yarn (15, 16) disposed obliquely with respect to said weft elements (13) and to said warp elements (12), wherein said further bundles of yarn (15, 16) are arranged orthogonal to each other and are disposed on two adjacent different planes parallel to said first and second planes, characterized in that said second step provides that said further bundles of yarn (15, 16) are disposed with respect to said first mesh structure (11) so as to be aligned with the points of crossing of said weft (13) and warp elements (12), so that the crossing points of said second mesh structure (17) are disposed inside said apertures of said net, in such a manner that said second mesh structure (17) together with said first mesh structure (11), define, groups of three-hinge arches inside said apertures of said net, located checker-wise, with respect to apertures of said net, which are free from any of said further bundles of yarn (15, 16), and in that said method further comprises a third step wherein said weft (13) said warp elements (12) and said bundles of yarn (15, 16) are attached to each other by another yarn (14) disposed according to a chain stitch along said weft (13), said warp elements (12) or said bundles of yarn (15, 16), provided that said another yarn (14) crosses said points of crossing of said weft (13) and warp elements (12).
- - Method as in claim 4, characterized in that the methodology used to make the braiding of said weft elements (13) and warp elements (12) and said further bundles of yarn (15, 16) is that known as warp knitting with multi-axial DOS system weft insertion.
- - Method as in claim 4, characterized in that it comprises finishing and enhancing steps, by means of the impregnation of said elements or yarns with resins or by means of heat treatments.
- - Method as in claim 6, characterized in that said resins are indifferently polyolefines, polyurethanes, polystyrenes, or polyvinyls.
- - Use of a multi-axial textile grid as in any claim from 1 to 3 inclusive, for a geotechnical field.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT2001UD000059A ITUD20010059A1 (en) | 2001-03-30 | 2001-03-30 | MULTI-AXIAL TEXTILE GRID FOR TECHNICAL OR GEOTECHNICAL USE AND PROCEDURE FOR ITS MANUFACTURE |
| ITUD010059 | 2001-03-30 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1245708A1 EP1245708A1 (en) | 2002-10-02 |
| EP1245708B1 true EP1245708B1 (en) | 2008-01-16 |
| EP1245708B8 EP1245708B8 (en) | 2008-03-19 |
Family
ID=11460553
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP02007003A Expired - Lifetime EP1245708B8 (en) | 2001-03-30 | 2002-03-27 | Multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use and method to manufacture same |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP1245708B8 (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE384153T1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE60224604T2 (en) |
| IT (1) | ITUD20010059A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102085762B1 (en) * | 2018-11-06 | 2020-03-06 | 윤태용 | Textile geogrid |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN100441758C (en) * | 2004-10-20 | 2008-12-10 | 东华大学 | A kind of knitting structure, knitting method and special device thereof |
| CN101994209A (en) * | 2010-12-08 | 2011-03-30 | 浙江高达新材料有限公司 | Biaxial warp-knitted special garment liner |
| CN105839285A (en) * | 2016-03-24 | 2016-08-10 | 江苏工程职业技术学院 | High-strength bi-axial warp-knitting composite earthwork cloth production method |
| CN106884425B (en) * | 2017-04-17 | 2022-08-09 | 泰安路德工程材料有限公司 | Four-way grating and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN107099927B (en) * | 2017-05-02 | 2019-07-26 | 常州市宏发纵横新材料科技股份有限公司 | Warp-knitting unidirectional fabric and its production technology |
| CN107151859B (en) * | 2017-07-12 | 2023-07-21 | 浙江恒石纤维基业有限公司 | Fabric with high saturation rate and preparation method and application thereof |
| FR3078346B1 (en) * | 2018-02-23 | 2020-02-14 | Serge Ferrari Sas | TEXTILE WITH REINFORCEMENT THREADS |
| DE102020103451B4 (en) | 2020-02-11 | 2024-12-05 | Hitexbau Gmbh | Reinforcing grid, process for its manufacture and reinforced element made of concrete and/or mortar |
| KR102651115B1 (en) * | 2023-08-16 | 2024-03-25 | 김창환 | geogrid manufacturing method for preventing loosening and deformation |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2244835A (en) * | 1939-05-18 | 1941-06-10 | Jacob Rothman | Textile material |
| US4518640A (en) * | 1983-02-09 | 1985-05-21 | Karl Mayer Textilmaschinenfabrik Gmbh | Warp knitted ware with reinforcing threads |
| US6074722A (en) * | 1994-09-30 | 2000-06-13 | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Flexible material for use in an inflatable structure |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4340174C2 (en) * | 1993-11-25 | 2000-06-21 | Saechsisches Textilforsch Inst | Multi-layer, voluminous geotextile |
| US5795835A (en) * | 1995-08-28 | 1998-08-18 | The Tensar Corporation | Bonded composite knitted structural textiles |
| US6171984B1 (en) * | 1997-12-03 | 2001-01-09 | Ppg Industries Ohio, Inc. | Fiber glass based geosynthetic material |
| DE19915722A1 (en) * | 1999-04-08 | 2000-10-12 | Huesker Synthetic Gmbh & Co | Textile lattice structure, especially geogrid |
-
2001
- 2001-03-30 IT IT2001UD000059A patent/ITUD20010059A1/en unknown
-
2002
- 2002-03-27 DE DE60224604T patent/DE60224604T2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-03-27 EP EP02007003A patent/EP1245708B8/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2002-03-27 AT AT02007003T patent/ATE384153T1/en active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2244835A (en) * | 1939-05-18 | 1941-06-10 | Jacob Rothman | Textile material |
| US4518640A (en) * | 1983-02-09 | 1985-05-21 | Karl Mayer Textilmaschinenfabrik Gmbh | Warp knitted ware with reinforcing threads |
| US6074722A (en) * | 1994-09-30 | 2000-06-13 | Lockheed Martin Corporation | Flexible material for use in an inflatable structure |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102085762B1 (en) * | 2018-11-06 | 2020-03-06 | 윤태용 | Textile geogrid |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE60224604D1 (en) | 2008-03-06 |
| EP1245708A1 (en) | 2002-10-02 |
| EP1245708B8 (en) | 2008-03-19 |
| ITUD20010059A1 (en) | 2002-09-30 |
| ATE384153T1 (en) | 2008-02-15 |
| DE60224604T2 (en) | 2009-01-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6056479A (en) | Bonded composite open mesh structural textiles | |
| US7279436B2 (en) | Grid fabric | |
| US4472086A (en) | Geotextile fabric construction | |
| EP2423359B1 (en) | Industrial fabric | |
| US11174612B2 (en) | Turf reinforcement mats | |
| EP1245708B1 (en) | Multi-axial textile grid for technical or geotechnical use and method to manufacture same | |
| WO1997009476A2 (en) | Bonded composite knitted structural textiles | |
| US4540311A (en) | Geotextile fabric construction | |
| US6429153B1 (en) | Textile composite material | |
| WO1998006570A1 (en) | Bonded composite engineered mesh structural textiles | |
| JP6593767B2 (en) | High-strength warp knitted mesh sheet | |
| CN108431315A (en) | Knitted fabric | |
| KR101732153B1 (en) | textile geogrid for ground reinforcement | |
| CA2533179C (en) | Reinforcing non-woven base fabric | |
| AU775644B2 (en) | Mesh fabric | |
| JPH0217030Y2 (en) | ||
| US6918412B2 (en) | Grid mat | |
| KR20010096241A (en) | Textile geogrid | |
| CA2217536C (en) | Bonded composite open mesh structural textiles | |
| JP4824488B2 (en) | Mesh sheet | |
| CN212834362U (en) | Carbon fiber weft yarn dividing reed for multi-axial warp knitting machine | |
| JP2008144330A (en) | Mesh sheet with holes | |
| RU2249066C2 (en) | Cord fabric | |
| CA2957754C (en) | Turf reinforcement mats | |
| JPH0632977Y2 (en) | Civil engineering sheet |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20030331 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AXX | Extension fees paid |
Extension state: AL Payment date: 20030331 Extension state: LT Payment date: 20030331 Extension state: RO Payment date: 20030331 Extension state: LV Payment date: 20030331 Extension state: MK Payment date: 20030331 Extension state: SI Payment date: 20030331 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20050414 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL LT LV MK RO SI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: ALPE ADRIA TEXTIL SRL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 60224604 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20080306 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| NLT2 | Nl: modifications (of names), taken from the european patent patent bulletin |
Owner name: ALPE ADRIA TEXTIL SRL Effective date: 20080220 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: R. A. EGLI & CO. PATENTANWAELTE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080116 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080427 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080116 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080616 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080116 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080416 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080331 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20081017 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080327 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080116 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080327 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080116 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20080417 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20190115 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20190320 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20190322 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20190326 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20190321 Year of fee payment: 18 Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20190320 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R119 Ref document number: 60224604 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20200401 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 384153 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20200327 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200401 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200331 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200331 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20201001 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200327 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200331 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20200327 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20200327 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20210301 Year of fee payment: 20 |