EP0573691A1 - Method for producing a PTC heating element - Google Patents
Method for producing a PTC heating element Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0573691A1 EP0573691A1 EP92109860A EP92109860A EP0573691A1 EP 0573691 A1 EP0573691 A1 EP 0573691A1 EP 92109860 A EP92109860 A EP 92109860A EP 92109860 A EP92109860 A EP 92109860A EP 0573691 A1 EP0573691 A1 EP 0573691A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- ptc
- pressing
- web
- hollow body
- heating element
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 7
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title description 3
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920003223 poly(pyromellitimide-1,4-diphenyl ether) Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B3/00—Ohmic-resistance heating
- H05B3/10—Heating elements characterised by the composition or nature of the materials or by the arrangement of the conductor
- H05B3/12—Heating elements characterised by the composition or nature of the materials or by the arrangement of the conductor characterised by the composition or nature of the conductive material
- H05B3/14—Heating elements characterised by the composition or nature of the materials or by the arrangement of the conductor characterised by the composition or nature of the conductive material the material being non-metallic
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B3/00—Ohmic-resistance heating
- H05B3/40—Heating elements having the shape of rods or tubes
- H05B3/42—Heating elements having the shape of rods or tubes non-flexible
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05B—ELECTRIC HEATING; ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS FOR ELECTRIC LIGHT SOURCES, IN GENERAL
- H05B2203/00—Aspects relating to Ohmic resistive heating covered by group H05B3/00
- H05B2203/02—Heaters using heating elements having a positive temperature coefficient
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a PTC radiator according to the preamble of claim 1.
- This radiator contains a PTC element, which is pressed into a hollow extruded profile.
- the narrow sides of the extruded profile are pressed together on both sides such that they assume an approximately bell-shaped contour in cross section.
- the deformed narrow sides create a spring effect between the top and bottom surface of the extruded profile and thus clamp the PTC element firmly.
- the present invention has for its object to provide a PTC radiator that can be easily manufactured with a well-defined contact pressure.
- the extruded profile Due to the shape of the extruded profile, it is achieved in a simple manner that even with dimensional tolerances in the PTC element and in the extruded profile and in tolerances in the movement of the die, only slight deviations in the contact pressure occur.
- the web and the outwardly curved sections give in upon pressing when a force is reached which is necessary to deform the material inelastically, without the force being increased significantly with a further movement of the die.
- a defined contact pressure is maintained, which is determined by the spring action of the web and the curved section.
- the hollow extrusion profile is pressed from the axis of symmetry, seen outside the webs in the region of the curved sections. Compression at this point is particularly favorable because it allows the webs to be deformed better by tilting them outward due to the deformation of the curved regions.
- the web has a height which corresponds approximately to half the clear height of the hollow body before the pressing.
- a radiator with the specified aspect ratio has sufficient rigidity in its structure so that the PTC element is not damaged during pressing.
- the inelastic deformation of the curved sections takes place in such a way that the spring action is particularly good.
- the curved section is at least the clear height of the hollow body laterally beyond the footbridge.
- the leg or. End points of the U-shaped to part-circular curved sections almost. This extremely strong curvature of the curved section leads to particularly good spring properties.
- the webs after the pressing are inclined to the outside by an angle of approximately 10 ° to 30 ° , preferably 20 ° , with respect to the vertical.
- the base area is provided with lateral flanges which protrude over the web and the curved section on both sides.
- the side flanges enlarge the base area of the PTC radiator, whereby better heat extraction is achieved.
- the top surface of the hollow body opposite the base surface is circular sector-shaped in cross-section, the rounded side being on the outside.
- a cover surface shaped in this way prevents the formation of waves during the pressing in the central region of the hollow body profile, which lies flat on the PTC element, thereby ensuring optimum heat extraction from the PTC element to the cover surface.
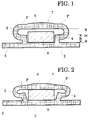
- the radiator has an extruded profile 1, with an essentially rectangular and flat base plate 2, which is provided with lateral flanges 3 along its long sides.
- the flanges 3 are formed in one piece with the base plate 2 and enlarge the base area of the PTC heating element.
- the base area has two vertical webs 4 running in the longitudinal direction. Each web 4 is followed by an approximately U-shaped to partially circular curved section 5.
- the lower leg ends of the curved sections 5 form an approximately right angle with the outer wall of the webs, as seen from the axis of symmetry.
- the curved sections 5 extend in the longitudinal direction over the entire length of the radiator.
- the two upper ends of the legs are connected to one another via a flat cover surface 6, which lies opposite the base surface.
- the top surface 6 has a circular sector shape in cross-section, the outer side being rounded.
- a cavity is formed in the interior of the extruded profile, the clear height H of which corresponds to the height h of the web before pressing in a ratio of about 2: 1.
- a PTC element is arranged in the cavity in the area between the webs 4.
- the PTC element is a cuboid plate, the dimensions of which are preferably chosen so that the space available between the webs is completely or almost completely filled.
- the thickness of the cuboid PTC element is somewhat larger (approx. 20%) than the height h of the webs 4, so that the PTC element projects somewhat vertically beyond the webs 4.
- the PTC element 8 is provided in a manner not shown on the top and bottom surface with a metallic electrode and this unit, consisting of PTC element 8 and electrodes, is encased in a tubular Kapton film.
- the PTC heater of Figure 1 is shown after the mechanical deformation (pressing).
- the pressing is carried out on the lines P, which are seen from the axis of symmetry on the edge of the webs 4 or just at the webs 5 outside the webs 4 in the region of the curved sections 5. Due to the pressure applied, the curved sections 5 are pressed together until their legs or end points almost touch. The pressing is continued even if the inner surfaces of the top surface have already applied to the PTC element. The central areas of the curved sections experience the greatest inelastic deformation. If the stamp is pressed further down, the lower leg ends are bent in the direction of the base plate. In this case, the webs 4 standing vertically before the pressing are inelastically deformed, namely bent outwards.
- a particularly favorable deformation of the webs is when the webs make an angle of preferably 20 ° with the vertical.
- the circular sector-shaped cross section of the top surface 6 of the extruded profile brings about reinforcement in the central region of the top surface. This reinforcement does not deform the top surface during pressing. This is extremely important, since the smooth support of the top surface on the top of the PTC element is a prerequisite for good heat extraction.
Landscapes
- Resistance Heating (AREA)
- Thermistors And Varistors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Die vorliegende Erfindung bezieht sich auf einen PTC-Heizkörper gemäß dem Oberbegriff des Anspruches 1.The present invention relates to a PTC radiator according to the preamble of claim 1.
Aus der DE GM 78 38 558 ist ein elektrischer Heizkörper der eingangs genannten Art bekannt. Dieser Heizkörper enthält ein PTC-Element, das in ein Hohlkörper-Strangpreßprofil eingepreßt ist. Bei der Herstellung eines solchen Heizkörpers werden die Schmalseiten des Strangpreßprofils beidseitig derart zusammengepreßt, daß sie im Querschnitt eine etwa glockenförmige Kontur annehmen. Die verformten Schmalseiten erzeugen zwischen der Deck- und Grundfläche des Strangpreßprofils eine Federwirkung und spannen damit das PTC-Element fest ein. Bei der Herstellung dieses Heizkörpers ist es jedoch schwierig, den Druck, mit dem das PTC-Element im Hohlprofil eingeklemmt ist, genau zu definieren. Es besteht sogar die Gefahr, daß das PTC-Element beim Zusammendrücken der Schmalseiten überbeansprucht wird und dadurch dauerhaft beschädigt wird. Bei zu geringem Anpreßdruck ist hingegen die Wärmeübertragung und eventuell auch der elektrische Kontakt ungenügend.From DE GM 78 38 558 an electric heater of the type mentioned is known. This radiator contains a PTC element, which is pressed into a hollow extruded profile. In the manufacture of such a radiator, the narrow sides of the extruded profile are pressed together on both sides such that they assume an approximately bell-shaped contour in cross section. The deformed narrow sides create a spring effect between the top and bottom surface of the extruded profile and thus clamp the PTC element firmly. When manufacturing this radiator, however, it is difficult to precisely define the pressure with which the PTC element is clamped in the hollow profile. There is even a risk that the PTC element will be overstressed when the narrow sides are pressed together and thereby permanently damaged. If the contact pressure is too low, however, the heat transfer and possibly the electrical contact is insufficient.
Der vorliegenden Erfindung liegt die Aufgabe zugrunde, einen PTC-Heizkörper anzugeben, der auf einfache Weise mit gut definiertem Anpreßdruck herstellbar ist.The present invention has for its object to provide a PTC radiator that can be easily manufactured with a well-defined contact pressure.
Diese Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß mit den kennzeichnenden Merkmalen des Anspruchs 1 gelöst.This object is achieved with the characterizing features of claim 1.
Durch die Formgebung des Strangpreßprofils wird es auf einfache Weise erreicht, daß auch bei Maßtoleranzen im PTC-Element und im Strangpreßprofil sowie in Toleranzen in der Bewegung des Prägestempels nur geringe Abweichungen im Anpreßdruck entstehen. Der Steg und die nach außen gekrümmten Abschnitte geben beim Verpressen bei Erreichen einer Kraft, die notwendig ist, um das Material unelastisch zu verformen, nach, ohne daß die Kraft bei einer weiteren Bewegung des Prägestempels wesentlich erhöht wird. Beim anschließenden Zurückziehen des Prägestempels bleibt ein definierter Anpreßdruck erhalten, der durch die Federwirkung des Stegs und des gekrümmten Abschnitts festgelegt ist.Due to the shape of the extruded profile, it is achieved in a simple manner that even with dimensional tolerances in the PTC element and in the extruded profile and in tolerances in the movement of the die, only slight deviations in the contact pressure occur. The web and the outwardly curved sections give in upon pressing when a force is reached which is necessary to deform the material inelastically, without the force being increased significantly with a further movement of the die. When the stamp is subsequently withdrawn, a defined contact pressure is maintained, which is determined by the spring action of the web and the curved section.
Bei dem PTC-Heizkörpern in einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform erfolgt die Verpressung des Hohlkörper-Strangpreßprofils von der Symmetrieachse aus gesehen außerhalb der Stege im Bereich der gekrümmten Abschnitte. Eine Verpressung an dieser Stelle ist besonders günstig, weil sich damit die Stege besser verformen lasen, indem sie durch die Verformung der gekrümmten Bereiche nach außen geneigt werden.In the case of the PTC heating element in a preferred embodiment, the hollow extrusion profile is pressed from the axis of symmetry, seen outside the webs in the region of the curved sections. Compression at this point is particularly favorable because it allows the webs to be deformed better by tilting them outward due to the deformation of the curved regions.
In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform weist der Steg eine Höhe auf, die in etwa der halben lichten Höhe des Hohlkörpers vor dem Verpressen entspricht. Ein Heizkörper mit dem angegebenen Längenverhältnis besitzt einerseits eine ausreichende Steifigkeit in seinem Aufbau, damit das PTC-Element beim Verpressen nicht beschädigt wird. Andererseits erfolgt die unelastische Verformung der gekrümmten Abschnitte derart, daß die Federwirkung besonders gut ist.In a further preferred embodiment, the web has a height which corresponds approximately to half the clear height of the hollow body before the pressing. On the one hand, a radiator with the specified aspect ratio has sufficient rigidity in its structure so that the PTC element is not damaged during pressing. On the other hand, the inelastic deformation of the curved sections takes place in such a way that the spring action is particularly good.
In einer vorteilhaften Ausgestaltung steht der gekrümmte Abschnitt um mindestens die lichte Höhe des Hohlkörpers seitlich über den Steg hinaus. Dadurch wird die Federwirkung eines so ausgeformten gekrümmten Abschnitts ebenfalls verbessert.In an advantageous embodiment, the curved section is at least the clear height of the hollow body laterally beyond the footbridge. As a result, the spring action of a curved section shaped in this way is also improved.
Gemäß einem Ausführungsbeispiel des erfindungsgemäßen Heizkörpers berühren sich nach dem Verpressen die Schenkel-bzw. Endpunkte der U-förmig bis teilkreisförmig gekrümmten Abschnitte nahezu. Diese extrem starke Krümmung des gekrümmten Abschnitts führt zu besonders guten Federeigenschaften.According to an embodiment of the radiator according to the invention, the leg or. End points of the U-shaped to part-circular curved sections almost. This extremely strong curvature of the curved section leads to particularly good spring properties.
Gemäß einer vorteilhaften Ausbildung sind die Stege nach dem Verpressen um einen Winkel von etwa 10o bis 30o, vorzugsweise 20o, gegenüber der Senkrechten nach außen geneigt.According to an advantageous embodiment, the webs after the pressing are inclined to the outside by an angle of approximately 10 ° to 30 ° , preferably 20 ° , with respect to the vertical.
In einer vorteilhaften Weiterbildung ist die Grundfläche mit seitlichen Flanschen versehen, welche auf beiden Seiten über den Steg und den gekrümmten Abschnitt überstehen. Die seitlichen Flansche vergrößern die Grundfläche des PTC-Heizkörpers, wobei eine bessere Wärmeauskopplung erzielt wird.In an advantageous further development, the base area is provided with lateral flanges which protrude over the web and the curved section on both sides. The side flanges enlarge the base area of the PTC radiator, whereby better heat extraction is achieved.
Gemäß einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform ist die der Grundfläche gegenüberliegende Deckfläche des Hohlkörpers im Querschnitt kreissektorförmig, wobei die abgerundete Seite außenliegt. Eine so geformte Deckfläche verhindert während des Verpressens eine Wellenbildung in dem mittigen Bereich des Hohlkörperprofils, der auf dem PTC-Element glatt aufliegt, wodurch eine optimale Wärmeauskopplung von dem PTC-Element zur Deckfläche sichergestellt ist.According to a preferred embodiment, the top surface of the hollow body opposite the base surface is circular sector-shaped in cross-section, the rounded side being on the outside. A cover surface shaped in this way prevents the formation of waves during the pressing in the central region of the hollow body profile, which lies flat on the PTC element, thereby ensuring optimum heat extraction from the PTC element to the cover surface.
Im folgenden wird ein bevorzugtes Ausführungsbeispiel der Erfindung anhand der beiliegenden Zeichnungen näher erläutert, welche zeigen:
- Fig. 1
- einen Querschnitt durch den erfindungsgemäßen PTC-Heizkörper vor dem Verpressen des Strangpreßprofils, und
- Fig. 2
- einen Querschnitt durch den erfindungsgemäßen PTC-Heizkörper nach dem Verpressen des Strangpreßprofils.
- Fig. 1
- a cross section through the PTC radiator according to the invention before pressing the extruded profile, and
- Fig. 2
- a cross section through the PTC radiator according to the invention after pressing the extruded profile.
Der Heizkörper weist ein Strangpreßprofil 1 auf, mit einer im wesentlichen rechteckförmigen und ebenen Grundplatte 2, die entlang ihrer Längsseiten mit seitlichen Flanschen 3 versehen ist. Die Flansche 3 sind einstückig mit der Grundplatte 2 ausgebildet und vergrößern die Grundfläche des PTC-Heizkörpers. Die Grundfläche weist zwei in Längsrichtung verlaufende senkrecht stehende Stege 4 auf. An jeden Steg 4 schließt sich ein etwa U-förmig bis teilkreisförmig gebildeter gekrümmter Abschnitt 5 an. Die unteren Schenkelenden der gekrümmten Abschnitte 5 bilden mit den von der Symmetrieachse aus gesehen außenliegenden Wand der Stege einen in etwa rechten Winkel. Die gekrümmten Abschnitte 5 erstrecken sich in Längsrichtung über die gesamte Länge des Heizkörpers. Die beiden oberen Schenkelenden sind über eine ebene Deckfläche 6, welche der Grundfläche gegenüberliegt, miteinander verbunden. Die Deckfläche 6 weist eine im Querschnitt kreissektorförmige Form auf, wobei die außenliegende Seite abgerundet ist.The radiator has an extruded profile 1, with an essentially rectangular and
Insgesamt gesehen ist das Strangpreßprofil spiegelsymmetrisch ausgebildet.Overall, the extruded profile is mirror-symmetrical.
Im Innern des Strangpreßprofils ist ein Hohlraum ausbildet, dessen lichte Höhe H zu der Höhe h des Steges vor dem Verpressen in einem Verhältnis von etwa 2:1 steht. In dem Hohlraum ist in dem Bereich zwischen den Stegen 4 ein PTC-Element angeordnet. Das PTC-Element ist eine quaderförmige Platte, deren Abmessungen vorzugsweise so gewählt sind, daß der zwischen den Stegen zur Verfügung stehende Zwischenraum vollständig oder nahezu vollständig ausgefüllt ist. Die Dicke des quaderförmigen PTC-Elements ist etwas größer (ca. 20 %) als die Höhe h der Stege 4, so daß das PTC-Element vertikal etwas über die Stege 4 hinaussteht. Das PTC-Element 8 ist in nicht näher dargestellter Weise auf der Deck- und Grundfläche noch mit je einer metallischen Elektrode versehen und diese Einheit, bestehend aus PTC-Element 8 und Elektroden, ist in eine schlauchförmige Kaptonfolie eingehüllt.A cavity is formed in the interior of the extruded profile, the clear height H of which corresponds to the height h of the web before pressing in a ratio of about 2: 1. A PTC element is arranged in the cavity in the area between the
In Figur 2 ist der PTC-Heizkörper der Figur 1 nach der mechanischen Verformung (Verpressung) dargestellt. Die Verpressung ist an den Linien P, welche sich von der Symmetrieachse aus gesehen am Rande der Stege 4 oder knapp an den Stegen 5 außerhalb der Stege 4 im Bereich der gekrümmten Abschnitte 5 befinden, erfolgt. Durch den angelegten Druck werden die gekrümmten Abschnitte 5 soweit zusammengepreßt, bis sich ihre Schenkel bzw. Endpunkte nahezu berühren. Die Verpressung wird auch dann noch weitergeführt, wenn sich die Innenflächen er Deckfläche bereits an das PTC-Element angelegt hat. Dabei erfahren die mittigen Bereiche der gekrümmten Abschnitte die größte unelastische Verformung. Wird der Prägestempel noch weiter nach unten gedrückt, werden die unteren Schenkelenden in Richtung der Bodenplatte abgebogen. Dabei werden auch die vor dem Verpressen senkrecht stehenden Stege 4 unelastisch verformt, nämlich nach außen gebogen. Eine besonders günstige Verformung der Stege ist diejenige, wenn die Stege einen Winkel von vorzugsweise 20o mit der Senkrechten einnehmen.In Figure 2, the PTC heater of Figure 1 is shown after the mechanical deformation (pressing). The pressing is carried out on the lines P, which are seen from the axis of symmetry on the edge of the
Durch die starke Verformung, nachdem sich die Deckfläche 6 bereits an das PTC-Element 8 angelegt hat, ergibt sich eine Federwirkung, die das PTC-Element 8 dauerhaft und fest umklammert. Trotzdem wird das PTC-Element 8 nicht mit zu hoher Kraft beim Verpressen beansprucht, da das Material durch den Gegendruck, den das PTC-Element 8 ausübt, nachgeben kann, was auf die hier vorliegende Formgebung zurückzuführen ist.The strong deformation after the
Der kreissektorförmige Querschnitt der Deckfläche 6 des Strangpreßprofils bewirkt eine Verstärkung in dem mittigen Bereich der Deckfläche. Durch diese Verstärkung wird die Deckfläche während des Verpressens nicht verformt. Dies ist von außerordentlicher Wichtigkeit, da die glatte Auflage der Deckfläche auf der Oberseite des PTC-Elements eine Voraussetzung für eine gute Wärmeauskopplung ist.The circular sector-shaped cross section of the
Claims (8)
die Schmalseiten einen auf der Grundfläche (2) des Strangpreßprofils (1) senkrecht stehenden Steg (4) aufweisen, an den sich ein etwa U-förmig bis halbkreisförmig ausgebildeter gekrümmter Abschnitt (5) anschließt.PTC heater with a hollow extruded profile made of metal, preferably aluminum, and with a PTC element pressed into the hollow body by squeezing the narrow sides together, the narrow sides having outwardly curved sections, characterized in that
the narrow sides have a web (4) standing vertically on the base surface (2) of the extruded profile (1), which is followed by an approximately U-shaped to semicircular curved section (5).
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES92109860T ES2099767T3 (en) | 1992-06-11 | 1992-06-11 | METHOD TO PRODUCE A HEATING RESISTANCE WITH POSITIVE TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT. |
| EP19920109860 EP0573691B1 (en) | 1992-06-11 | 1992-06-11 | Method for producing a PTC heating element |
| DE59207853T DE59207853D1 (en) | 1992-06-11 | 1992-06-11 | Process for the production of a PTC radiator |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19920109860 EP0573691B1 (en) | 1992-06-11 | 1992-06-11 | Method for producing a PTC heating element |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0573691A1 true EP0573691A1 (en) | 1993-12-15 |
| EP0573691B1 EP0573691B1 (en) | 1997-01-08 |
Family
ID=8209702
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19920109860 Expired - Lifetime EP0573691B1 (en) | 1992-06-11 | 1992-06-11 | Method for producing a PTC heating element |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0573691B1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE59207853D1 (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2099767T3 (en) |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2724874A1 (en) * | 1994-09-22 | 1996-03-29 | Behr Gmbh & Co | MOTOR VEHICLE HAVING ELECTRICAL HEATING IN SUPPLEMENT |
| FR2749645A1 (en) * | 1996-06-11 | 1997-12-12 | Suntec Ind France | REGULAR SELF-PROPELLED HEATER |
| FR2796120A1 (en) * | 1999-07-06 | 2001-01-12 | Eichenauer Gmbh & Co Kg F | Heater element for escaping gas from crankcase of internal combustion engine has shoulder for securing clamp and has ceramic valve seat with profiled section |
| US6455822B1 (en) * | 2000-10-11 | 2002-09-24 | Mega Dynamics Ltd. | Heat sink for a PTC heating element and a PTC heating member made thereof |
| EP1529470A1 (en) * | 2003-11-05 | 2005-05-11 | DBK David + Baader GmbH | Heating modul with heating surface and continuous flow heater and production method thereof |
| EP1532906A1 (en) * | 2003-11-24 | 2005-05-25 | DBK David + Baader GmbH | Electrical warming device |
| WO2008111101A1 (en) * | 2007-03-13 | 2008-09-18 | Rotfil S.R.L. | Cartridge heater |
| EP2506661A1 (en) * | 2011-04-02 | 2012-10-03 | Eichenauer Heizelemente GmbH & Co. KG | Electric heating device |
| JP2014523513A (en) * | 2011-06-21 | 2014-09-11 | ベール ゲーエムベーハー ウント コー カーゲー | Heat exchanger |
| CN104896746A (en) * | 2015-06-09 | 2015-09-09 | 广东美的环境电器制造有限公司 | Heating element installation structure of air heater and air heater |
| DE19922668B4 (en) * | 1999-05-18 | 2020-03-05 | Mahle International Gmbh | Radiators for automobiles |
| DE102012104917B4 (en) | 2012-06-06 | 2023-03-23 | Eichenauer Heizelemente Gmbh & Co. Kg | Electrical heating device |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10360159A1 (en) | 2003-12-20 | 2005-07-21 | Eichenauer Heizelemente Gmbh & Co. Kg | Profile tube and method for clamping functional elements in such |
| DE102006013271B4 (en) | 2006-03-21 | 2011-05-19 | Rittal Gmbh & Co. Kg | Kondensatverdunster |
| DE102008056083B4 (en) * | 2008-07-21 | 2021-08-12 | Borgwarner Ludwigsburg Gmbh | Method of making a heater and heater |
| DE102011057017A1 (en) | 2011-12-23 | 2013-06-27 | Dbk David + Baader Gmbh | Heating assembly for heating e.g. ammonia in ammonia storage and delivery system for diesel engine of lorry, has coupling layer arranged in circumference gap between sleeve wall and cartridge wall for thermal and/or mechanical coupling |
| DE102013103433A1 (en) | 2012-04-13 | 2013-10-17 | Dbk David + Baader Gmbh | Electric auxiliary heater for motor vehicle, has sealing unit has two form-seals, which sealingly surround control housing-side end portion and distal end portion of heating housing |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3996447A (en) * | 1974-11-29 | 1976-12-07 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | PTC resistance heater |
| EP0240447A2 (en) * | 1986-04-04 | 1987-10-07 | Emerson Electric Co. | PTC thermal protector |
| DE3942266C1 (en) * | 1989-12-21 | 1991-03-07 | Tuerk & Hillinger Gmbh | Electrical PTC heater ensuring even dissipation has leaf spring - has rectangular cavity in carrier to accommodate heating element and contact plates |
| DE4010620A1 (en) * | 1990-04-02 | 1991-10-10 | Petz Elektro Waerme Techn | Electric heating element for fan heater - has C-clips between longitudinal edges of opposing profile rails |
-
1992
- 1992-06-11 EP EP19920109860 patent/EP0573691B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1992-06-11 DE DE59207853T patent/DE59207853D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1992-06-11 ES ES92109860T patent/ES2099767T3/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3996447A (en) * | 1974-11-29 | 1976-12-07 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | PTC resistance heater |
| EP0240447A2 (en) * | 1986-04-04 | 1987-10-07 | Emerson Electric Co. | PTC thermal protector |
| DE3942266C1 (en) * | 1989-12-21 | 1991-03-07 | Tuerk & Hillinger Gmbh | Electrical PTC heater ensuring even dissipation has leaf spring - has rectangular cavity in carrier to accommodate heating element and contact plates |
| DE4010620A1 (en) * | 1990-04-02 | 1991-10-10 | Petz Elektro Waerme Techn | Electric heating element for fan heater - has C-clips between longitudinal edges of opposing profile rails |
Cited By (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2724874A1 (en) * | 1994-09-22 | 1996-03-29 | Behr Gmbh & Co | MOTOR VEHICLE HAVING ELECTRICAL HEATING IN SUPPLEMENT |
| FR2749645A1 (en) * | 1996-06-11 | 1997-12-12 | Suntec Ind France | REGULAR SELF-PROPELLED HEATER |
| EP0814302A1 (en) * | 1996-06-11 | 1997-12-29 | Suntec Industries France (Sa) | Self-regulating fuel oil heater |
| DE19922668B4 (en) * | 1999-05-18 | 2020-03-05 | Mahle International Gmbh | Radiators for automobiles |
| FR2796120A1 (en) * | 1999-07-06 | 2001-01-12 | Eichenauer Gmbh & Co Kg F | Heater element for escaping gas from crankcase of internal combustion engine has shoulder for securing clamp and has ceramic valve seat with profiled section |
| US6455822B1 (en) * | 2000-10-11 | 2002-09-24 | Mega Dynamics Ltd. | Heat sink for a PTC heating element and a PTC heating member made thereof |
| EP1529470A1 (en) * | 2003-11-05 | 2005-05-11 | DBK David + Baader GmbH | Heating modul with heating surface and continuous flow heater and production method thereof |
| WO2005046410A1 (en) * | 2003-11-05 | 2005-05-26 | Dbk David + Baader Gmbh | Heating module comprising a heating surface, flow heater, and method for the production thereof |
| US7865073B2 (en) | 2003-11-05 | 2011-01-04 | Dbk David + Baader Gmbh | Heating module comprising a heating surface, flow heater, and method for the production thereof |
| EP1532906A1 (en) * | 2003-11-24 | 2005-05-25 | DBK David + Baader GmbH | Electrical warming device |
| WO2008111101A1 (en) * | 2007-03-13 | 2008-09-18 | Rotfil S.R.L. | Cartridge heater |
| EP2506661A1 (en) * | 2011-04-02 | 2012-10-03 | Eichenauer Heizelemente GmbH & Co. KG | Electric heating device |
| JP2014523513A (en) * | 2011-06-21 | 2014-09-11 | ベール ゲーエムベーハー ウント コー カーゲー | Heat exchanger |
| US9863663B2 (en) | 2011-06-21 | 2018-01-09 | Mahle International Gmbh | Heat exchanger |
| EP2724086B1 (en) * | 2011-06-21 | 2018-10-03 | MAHLE Behr GmbH & Co. KG | Heat exchanger |
| EP2724086B2 (en) † | 2011-06-21 | 2024-10-30 | MAHLE Behr GmbH & Co. KG | Heat exchanger |
| DE102012104917B4 (en) | 2012-06-06 | 2023-03-23 | Eichenauer Heizelemente Gmbh & Co. Kg | Electrical heating device |
| CN104896746A (en) * | 2015-06-09 | 2015-09-09 | 广东美的环境电器制造有限公司 | Heating element installation structure of air heater and air heater |
| CN104896746B (en) * | 2015-06-09 | 2018-09-07 | 广东美的环境电器制造有限公司 | A kind of the heating element mounting structure and warm-air drier of warm-air drier |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP0573691B1 (en) | 1997-01-08 |
| DE59207853D1 (en) | 1997-02-20 |
| ES2099767T3 (en) | 1997-06-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0573691B1 (en) | Method for producing a PTC heating element | |
| DE2500556C2 (en) | Electrical flat conductor connection element | |
| DE3042420A1 (en) | Electric heater with flat heating elements - has sheet metal contact strips, with resilient fastening tags, as heater terminals | |
| DE20216509U1 (en) | Electric heater | |
| DE2236408B2 (en) | Method for producing pot-shaped housings, in particular housings for small electric motors | |
| DE2011859C3 (en) | Electrical crimp connector | |
| DE2319589C2 (en) | Method of manufacturing an aluminum capacitor for high frequencies | |
| DE202020101182U1 (en) | Electric heater | |
| DE2521754A1 (en) | HEATING DEVICE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A HEATING DEVICE | |
| EP1698840B1 (en) | PTC heater, especially for a vehicle | |
| EP1467597B1 (en) | Heating apparatus | |
| EP0254770A2 (en) | Electrical contact device | |
| EP0281996B1 (en) | Electrical connector with clamping screw | |
| DE1615578B2 (en) | Crimping clamp | |
| CH628185A5 (en) | Connecting part for penetrating the insulation of an insulated conductor, and an electrical connector having such a connecting part | |
| DE102020113402A1 (en) | Electric heater | |
| DE2240382C3 (en) | Electric heating element and process for its manufacture | |
| DE69617922T2 (en) | Electric heating device and its manufacturing process | |
| DE2402122A1 (en) | FIXED ELECTROLYTE CAPACITOR | |
| EP1213790A2 (en) | Electrical connecting terminal | |
| DE10035747A1 (en) | Temperature sensor such as negative temperature coefficient (NTC) sensor has thermally conducting element with molding facing into housing forming flat contact for sensor element | |
| DE29512310U1 (en) | Arrangement of a series resistor and a ceramic insulation surrounding it | |
| DE102021102894A1 (en) | Method for producing a tubular heating cartridge for electrical heating devices, heating element blank for such a heating cartridge and heating cartridge | |
| DE10351668B4 (en) | Device for heating or keeping food and drinks warm | |
| DE2626075A1 (en) | Bent insulated electric heating element mfr. - ensures that insulation on outside of bend requires no reinforcement after bending |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): CH DE ES FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19940614 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19960502 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): CH DE ES FR GB IT LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59207853 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19970220 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19970408 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2099767 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19970630 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19970630 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20080617 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20090612 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090612 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20100623 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20110630 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20110606 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20110627 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20110611 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 59207853 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 59207853 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20110611 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20120612 |