EP0441573B1 - Hitzebeständige Legierung - Google Patents
Hitzebeständige Legierung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0441573B1 EP0441573B1 EP91300887A EP91300887A EP0441573B1 EP 0441573 B1 EP0441573 B1 EP 0441573B1 EP 91300887 A EP91300887 A EP 91300887A EP 91300887 A EP91300887 A EP 91300887A EP 0441573 B1 EP0441573 B1 EP 0441573B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- alloy
- heat
- skid
- oxide
- resistant
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F27—FURNACES; KILNS; OVENS; RETORTS
- F27D—DETAILS OR ACCESSORIES OF FURNACES, KILNS, OVENS OR RETORTS, IN SO FAR AS THEY ARE OF KINDS OCCURRING IN MORE THAN ONE KIND OF FURNACE
- F27D3/00—Charging; Discharging; Manipulation of charge
- F27D3/02—Skids or tracks for heavy objects
- F27D3/022—Skids
- F27D3/024—Details of skids, e.g. riders
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C32/00—Non-ferrous alloys containing at least 5% by weight but less than 50% by weight of oxides, carbides, borides, nitrides, silicides or other metal compounds, e.g. oxynitrides, sulfides, whether added as such or formed in situ
- C22C32/001—Non-ferrous alloys containing at least 5% by weight but less than 50% by weight of oxides, carbides, borides, nitrides, silicides or other metal compounds, e.g. oxynitrides, sulfides, whether added as such or formed in situ with only oxides
- C22C32/0015—Non-ferrous alloys containing at least 5% by weight but less than 50% by weight of oxides, carbides, borides, nitrides, silicides or other metal compounds, e.g. oxynitrides, sulfides, whether added as such or formed in situ with only oxides with only single oxides as main non-metallic constituents
- C22C32/0026—Matrix based on Ni, Co, Cr or alloys thereof
Definitions
- the present invention concerns a heat-resistant alloy having good strength and anti-corrosion properties at high temperature.
- the alloy of this invention is suitable as the material for skid rails of furnaces used in, for example, steel industry for heating steel pieces.
- Steel plates and steel wires are produced by rolling steel pieces called slabs or billets after uniformly heating them in a heating furnace such as a walking beam furnace or pusher furnace. If the temperature of the steel piece is lower at the position where the steel piece contacts the furnace bed than at the remaining positions, then uneven thickness of the rolled steel plate or even cracking may occur. In order to avoid these troubles, it is necessary to raise the temperature of the furnace bed at the position of contact with the heated piece to a temperature near the heating temperature. Thus, at the highest temperatures of use the furnace bed metal attains a temperature as high as 1300 o C or more.
- super alloys of the oxide-dispersion strengthened type i.e., Ni-based super alloys in which fine particles of an oxide having a high melting point such as Y 2 O 3 are dispersed
- find application in gas-turbines and jet-engines for example, Japanese Patent Publication No. 38665/1981.
- high temperature furnaces it has been proposed to use an oxide-dispersion strengthened type super alloy of the composition consisting of 12.5-20% Cr, up to 1% Al, up to 0.1% C and up to 0.5% (volume) Y 2 O 3 , the balance being Ni, as the material for mesh belts (Japanese Patent Publication No. 9610/1984).
- oxide-dispersion strengthened type super alloys As the material of the skid member of a skid rail, and as the result of research, it was discovered that an oxide-dispersion strengthened type super alloy consisting of 18-40% Cr, up to 5% Ti, the balance being substantially Ni, and containing 0.1-2% of fine particles of a high melting point metal oxide dispersed in the austenite matrix thereof is useful as a material for a skid rail.
- the discovery has been disclosed (Japanese Patent Application No. 14044/1989).
- Ni-based super alloys are easily corroded due to high temperature sulfidation attack by the sulfur in the heavy oil.
- the material having sufficient anti-corrosive properties is, for example, Fe-Ni-Cr-Co-W solid solution strengthened heat resistant cast alloy. If oxide-dispersion strengthened heat resistant alloy having the matrix composition similar thereto is obtained, then the alloy will be a material suitable for the furnace bed metal without the above drawback.
- Ni-based alloys are expensive, and therefore, it is desirable to construct the skid rails with a less expensive alloy, i.e. less Ni.
- the general object of the present invention is to provide an alloy having not only high temperature deformation resistance, anti-abrasion property and shock resistance, but also a good oxidation resistance, which are of the same rank as those of the above noted oxide-dispersion strengthened type Ni-based super alloy.
- a preferred object of the present invention is to provide a heat-resistant alloy of better performance by dispersing oxide particles in the matrix of the heat-resistant alloy of the composition giving the highest ranked high temperature strength and anti high temperature corrosion property as the solid solution strengthened type casting alloy so as to suppress plastic deformation of the matrix at high temperature with the oxide particles.
- Another aspect of the present invention is to provide furnace metals, particularly, skid rails, of higher performance by using the above mentioned heat-resistant alloy.
- the alloy according to the present invention is an oxide-dispersion strengthened type Fe-based alloy consisting, apart from impurities, of up to 0.2% C + N, up to 2.0% Si, up to 2.0% Mn, 15 to 35% Ni, 20-35% Cr, 5-50% Co, and one or more of 0.5 to 5% Mo, 0.5 to 5% W and 0.2 to 4% Ta; and at least 26.465% Fe; and containing 0.1-2% of fine particles of high melting point metal oxide dispersed in the austenite matrix of the alloy. Percentages are by weight.
- the high melting point metal oxide may be one or more selected from Y 2 O 3 , ZrO 2 and Al 2 O 3 .
- Y 2 O 3 gives the best results.
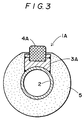
- FIG. 1 to Figure 3 illustrate a typical embodiment of a skid rail using an alloy according to the invention:
- the above mentioned oxide-dispersion strengthened type alloy so-called mechanical alloying technology developed by INCO (The International Nickel Co., Inc.) is useful.
- the technology comprises subjecting powders of metal components and fine crystals of a high melting point metal oxide in a ball mill, for example, a high kinetic energy type ball mill, so as to produce by repeated welding and fracturing a granular product comprising an intimate and uniform mixture of very fine particles of the components.
- the product prepared by mechanical alloying is then compacted and sintered by hot extrusion or hot isostatic pressing and, if necessary, machined to produce the skid member.
- a typical embodiment of a skid rail using an alloy of the present invention is, as shown in Figure 1 to Figure 3, a skid rail 1A made by welding metal saddles 3A on a water-cooled skid pipe 2, attaching skid members 4A made of the oxide-dispersion strengthened heat-resistant alloy to the saddles and covering all the members except for the skid members 4A with refractory insulator 5.
- the material of the skid member there is used the above oxide-dispersion strengthened type alloy.
- the skid rails may be of other configurations.
- a skid structure may use cylindrical saddles to attach button shaped skid members.
- nickel-basedoxide-dispersion strengthened type super alloys are stable even at a high temperature
- the above mentioned known nickel-base alloys have alloy compositions suitable for the use such as turbine blades (Japanese Patent Publication No. 56-38665) or mesh belts (Japanese Patent Publication No. 59-9610) and contain suitable amounts of oxide particles.
- these known nickel-base alloys do not have sufficient corrosion-resistance against the high temperature sulfidation attack occurring in furnaces having an atmosphere resulting from combustion of heavy oil.
- oxide-dispersion strengthened alloy according to the present invention it is possible to achieve a high compresssion creep strength, as shown in the working example described later, in addition to the heat-resistance and oxidation-resistance. Thus, less expensive, but more durable heat-resistant alloy is provided.
- Alloys embodying the invention have been found to show, when used as the material of the skid rails or other skid surfaces in various furnaces such as heating furnaces for hot processing of steel, excellent properties against hot deformation, oxidation resistance, abrasion resistance and thermal shock resistance, and therefore, can be used for a long period of time. This will decrease maintenance labor of the heating furnaces and facilitates continuous operation thereof. Decreased costs for energy and maintenance result in lowering production costs in the hot processing of steel.
- Oxide-dispersion strengthened type alloys of the composition as shown in Table 1 were prepared by the above mechanical alloying process, and the alloys were hot extruded and machined to give test samples.
- Test samples were subjected to compressive creep test and high temperature oxidation at very high temperature, and the durability and oxidation resistance thereof were compared with those of a conventional material for skid rails, TH101 (0.1C-32Cr-21Ni-23Co-2.5W, Bal. Fe).
- the compression creep test is carried out by cramping a columnar test piece of 3mm in diameter and 6.5mm in height between a fitting plate and a receiving plate, and applying compressing load at a high temperature. After a certain period of time, the height of the test piece is measured, and the deformation is calculated as the percentage of decrease in height.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Heat Treatments In General, Especially Conveying And Cooling (AREA)
- Furnace Charging Or Discharging (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Alloys Or Alloy Compounds (AREA)
- Ceramic Products (AREA)
- Powder Metallurgy (AREA)
Claims (6)
- Durch Oxiddispersion verstärkte, hitzebeständige Legierung auf Fe-Basis, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Legierung abgesehen von Verunreinigungen aus (bezogen auf Gewicht) bis zu 0,2% C + N, bis zu 2,0% Si, bis zu 2,0% Mn, 15 bis 35% Ni, 20 bis 35 % Cr, 5 bis 50% Co; und einem oder mehreren aus 0,5 bis 5 % Mo, 0,5 bis 5 % W und 0,2 bis 4% Ta; und zumindest 26,465% Fe besteht, und daß die Legierung weiters 0,1-2% feine Teilchen aus einem Metalloxid mit hohem Schmelzpunkt enthält, die in der Austenitmatrix dispergiert sind.
- Hitzebeständige Legierung nach Anspruch 1, worin die Legierung zwischen 5 und 23,9 Gew.-% Co enthält.
- Hitzebeständige Legierung nach Anspruch 1, worin das Metalloxid mit hohem Schmelzpunkt Y2O3 ist.
- Gleitschiene, bei der die hitzebeständige Legierung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3 verwendet ist.
- Gleitschiene nach Anspruch 4, die Gleitelemente (4A) aus der Legierung umfaßt, die durch Sättel (3A) entlang eines Gleitrohres (2) befestigt sind.
- Verwendung eines aus einer Legierung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3 gebildeten Gegenstands als ein Hitze und Abrasion ausgesetztes Element in einem Hochtemperatur-Ofen.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP26968/90 | 1990-02-06 | ||
| JP2026968A JP3002215B2 (ja) | 1990-02-06 | 1990-02-06 | 耐熱合金およびそれを使用したスキッドレール |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0441573A1 EP0441573A1 (de) | 1991-08-14 |
| EP0441573B1 true EP0441573B1 (de) | 1996-09-18 |
Family
ID=12207960
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP91300887A Expired - Lifetime EP0441573B1 (de) | 1990-02-06 | 1991-02-04 | Hitzebeständige Legierung |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0441573B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP3002215B2 (de) |
| KR (1) | KR100190552B1 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE143060T1 (de) |
| CA (1) | CA2035618A1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE69122138T2 (de) |
| TW (1) | TW200532B (de) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5372499A (en) * | 1993-08-24 | 1994-12-13 | Daido Tokushuko Kabushiki Kaisha | High-temperature gas blower impeller with vanes made of dispersion-strengthened alloy, gas blower using such impeller, and gas circulating furnace equipped with such gas blower |
| CN115198163B (zh) * | 2022-05-24 | 2023-04-25 | 北京科技大学 | 一种具有拉伸塑性的多纳米相强化ods合金的制备方法 |
| CN116159999A (zh) * | 2023-02-16 | 2023-05-26 | 成都美奢锐新材料有限公司 | 原料粉及用其制备得到的高温氧化环境使用的材料和模具 |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4111685A (en) * | 1976-11-04 | 1978-09-05 | Special Metals Corporation | Dispersion-strengthened cobalt-bearing metal |
| CA1329320C (en) * | 1988-01-26 | 1994-05-10 | Kazuto Terai | Skid rail |
-
1990
- 1990-02-06 JP JP2026968A patent/JP3002215B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1991
- 1991-02-02 TW TW080100844A patent/TW200532B/zh active
- 1991-02-04 AT AT91300887T patent/ATE143060T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1991-02-04 EP EP91300887A patent/EP0441573B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-02-04 CA CA002035618A patent/CA2035618A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1991-02-04 DE DE69122138T patent/DE69122138T2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1991-02-06 KR KR1019910002051A patent/KR100190552B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| CHEMICAL ABSTRACTS, vol. 109, no. 22, 28th November 1988, page 331, abstract no. 195479n, Columbus, Ohio, US; & JP- A-63 157 827 (SUMITOMO METAL INDUSTRIES) 30-06-1988 *Abstract; JP-A-63 157 827, page 144, table 1, examples E,F,G,H * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE69122138T2 (de) | 1997-02-27 |
| CA2035618A1 (en) | 1991-08-07 |
| ATE143060T1 (de) | 1996-10-15 |
| KR100190552B1 (ko) | 1999-06-01 |
| JPH03232945A (ja) | 1991-10-16 |
| TW200532B (de) | 1993-02-21 |
| JP3002215B2 (ja) | 2000-01-24 |
| EP0441573A1 (de) | 1991-08-14 |
| KR910015715A (ko) | 1991-09-30 |
| DE69122138D1 (de) | 1996-10-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6294131B1 (en) | Heat resistant steel | |
| EP1191117B1 (de) | Rostfreier Gussstahl mit guter Hitzebeständigkeit und guter Spannbarkeit | |
| EP0326371A1 (de) | Balken | |
| EP0441574B1 (de) | Gleitschienenteil benutzend dispersionsverstärkte Eisen-Chrom-Basis-Legierungen | |
| US5667379A (en) | Charging rack for firing objects composed of ceramic of glass ceramic materials | |
| EP0441573B1 (de) | Hitzebeständige Legierung | |
| JPS60200948A (ja) | 加熱炉の支持部材用複合材料 | |
| US5226980A (en) | Skid rail alloy | |
| CN1106467A (zh) | 铁-铝合金和它的应用 | |
| CA2215447C (en) | Heat-resistant alloy steel for hearth metal members of steel material heating furnaces | |
| JPS6221860B2 (de) | ||
| JPS6254388B2 (de) | ||
| JPS60145954A (ja) | 加熱炉の被加熱材支持面用炭化クロム焼結体 | |
| KR960010603B1 (ko) | 스키드 레일 | |
| Kazimierzak et al. | Fe Base ODS alloys with improved mechanical strength | |
| JPH04301049A (ja) | 加熱炉内被加熱鋼材支持面部材用耐熱合金 | |
| JPH04131344A (ja) | 加熱炉用スキッドレールとその製造方法 | |
| JPH04301048A (ja) | 加熱炉内被加熱鋼材支持面部材用耐熱合金 | |
| JP2802768B2 (ja) | 複合焼結合金および加熱炉内鋼材支持部材 | |
| JPS628497B2 (de) | ||
| JPH0693328A (ja) | 酸化物分散強化型合金を用いたハースロール | |
| AU737814B2 (en) | A heat resistant steel | |
| JPH10226841A (ja) | 超耐熱クロム基合金および鋼材加熱炉の炉床金物 | |
| JPH05463B2 (de) | ||
| JPH01222033A (ja) | 炉床部材用耐熱合金 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19920211 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19940606 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 143060 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19961015 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 69122138 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19961024 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19970124 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19970213 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19970217 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19970217 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19970219 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19970220 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19970304 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980204 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980204 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980205 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980228 Ref country code: FR Free format text: THE PATENT HAS BEEN ANNULLED BY A DECISION OF A NATIONAL AUTHORITY Effective date: 19980228 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980228 Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980228 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: INCO ALLOYS INTERNATIONAL INC. Effective date: 19980228 Owner name: DAIDO TOKUSHUKO K.K. Effective date: 19980228 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19980204 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 91300887.6 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19981103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES;WARNING: LAPSES OF ITALIAN PATENTS WITH EFFECTIVE DATE BEFORE 2007 MAY HAVE OCCURRED AT ANY TIME BEFORE 2007. THE CORRECT EFFECTIVE DATE MAY BE DIFFERENT FROM THE ONE RECORDED. Effective date: 20050204 |