EP0215752A2 - Piston pump, particularly for inflating tyres, mattresses, sports equipment and the like - Google Patents
Piston pump, particularly for inflating tyres, mattresses, sports equipment and the like Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0215752A2 EP0215752A2 EP86830256A EP86830256A EP0215752A2 EP 0215752 A2 EP0215752 A2 EP 0215752A2 EP 86830256 A EP86830256 A EP 86830256A EP 86830256 A EP86830256 A EP 86830256A EP 0215752 A2 EP0215752 A2 EP 0215752A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- piston
- cylinder
- chambers
- opening
- valve member
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F01—MACHINES OR ENGINES IN GENERAL; ENGINE PLANTS IN GENERAL; STEAM ENGINES
- F01L—CYCLICALLY OPERATING VALVES FOR MACHINES OR ENGINES
- F01L21/00—Use of working pistons or pistons-rods as fluid-distributing valves or as valve-supporting elements, e.g. in free-piston machines
- F01L21/02—Piston or piston-rod used as valve members
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B33/00—Pumps actuated by muscle power, e.g. for inflating
- F04B33/02—Pumps actuated by muscle power, e.g. for inflating with intermediate gearing
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B39/00—Component parts, details, or accessories, of pumps or pumping systems specially adapted for elastic fluids, not otherwise provided for in, or of interest apart from, groups F04B25/00 - F04B37/00
- F04B39/0005—Component parts, details, or accessories, of pumps or pumping systems specially adapted for elastic fluids, not otherwise provided for in, or of interest apart from, groups F04B25/00 - F04B37/00 adaptations of pistons
- F04B39/0016—Component parts, details, or accessories, of pumps or pumping systems specially adapted for elastic fluids, not otherwise provided for in, or of interest apart from, groups F04B25/00 - F04B37/00 adaptations of pistons with valve arranged in the piston
Definitions
- the present invention refers to piston pumps and relates particularly to a piston pump for pumping fluids, comprising:
- a pump of the above-specified type is known in which the rod comprises two co-axial ducts, intake and delivery respectively, and in which two one-way disc valves are mounted on each of the two faces of the piston, operating in opposite directions and communicating respectively with the intake duct and the delivery duct.
- the present invention has the object of providing a piston pump of the above-specified type, which is improved in terms of efficiency and convenience of use, and does not give rise to the drawbacks in use described above.
- this object is achieved by means of a piston pump of the type specified above, characterised in that it includes a further valve member associated with one of the two chambers and selectively openable so as to put the said one of the two chambers into free communication with the outside of the cylinder.
- the decrease in the volume of the corresponding pumping chamber causes only the discharge of the pumped fluid (typically air) from the cylinder and not the supply of the delivery duct. Under such conditions, the pump actually behaves as a single-action pump.
- the pumped fluid typically air
- the further valve member will be associated with the chamber which is in the upper position in use.
- the user will be able to actuate the further valve element so as to cause the pump to operate as a single-acting pump and perform the pumping action only when the piston is pushed downwardly towards the ground.
- the raising of the piston (which does not involve the performance of a pumping action) may be carried out easily without excessive effort.
- a piston pump preferably intended to be used for the inflation of tyres, mattresses, sports equipment, and the like is generally indicated 1.
- the pump 1 comprises, as component parts:
- the rod 5 has two internal ducts 8 and 9, intake and delivery respectively, which open into two corresponding inlet and outlet openings 10, 11 at the upper end of the rod 5.
- a pipe union is normally associated with the latter opening which enables the pump 1 to be connected to a tube or sleeve for connection to the inflatable article (tyre, mattress, item of sports equipment, etc) to be inflated.
- the opening 10 may also have a pipe union which it is possible to connect to a tube or sleeve ending at an inflatable item whose deflation it is desired to speed up.
- the intake and delivery ducts 8, 9 may be constructed in different ways, account being taken of the structure of the rod 5 which is normally cylindrical.
- the ducts 8 and 9 may be two ducts of semi-circular section placed side by side. It is also possible to adopt a coaxial arrangement, with an inner duct of circular section and an outer duct of annular section.
- the arrangement of the openings 10 and 11, which are shown side by side for convenience of representation, is adapted to the structure of ducts 8 and 9.
- the piston 4 is generally hollow and has internal septa or partitions which divide it into two volumes 12, 13 sealed from each other.
- the piston 9 divides the cylinder 1 into two chambers 14, 15 which are superposed in the normal arrangement of use of the pump 1.
- the intake volume 12 of piston 4 communicates with the lower chamber 15 of the cylinder 2 through an opening in which a one-way valve 16 with disc or discoidal shutter is interposed.
- the function of the valve 16 is to allow the flow of pumping fluid (normally air) from the volume 12 to the chamber 15 but to prevent flow in the opposite direction.
- the movement of the shutter of the valve 16 is controlled by the pressure gradient established between the volume 12 and the chamber 15 in such a manner that the valve 16 closes when the pressure in the chamber 15 exceeds the pressure in the volume 12 and opens when the pressure gradient is reversed.
- the volume 13 of the piston 4 communicates with the upper chamber 14 through an opening in which a one-way valve 17 is interposed and with the lower chamber 15 through a further opening in which a one-way valve 18 is interposed.
- the valves 17 and 18 also are of the disc-shutter type and are preferably fitted with a single common shutter 178 of cylindrical shape, one end of which acts as a shutter for the valve 17 and the opposite end of which acts as a shutter for valve 18.
- the valves 17 and 18 are mounted on the piston 4 in such a manner as to allow the pumping fluid to flow towards the delivery duct 9 from the chamber 14 or the chamber 15 in alternation, preventing flow in the opposite direction in each case.
- valves 17 and 18 The mounting arrangement of the valves 17 and 18 on the piston 4 is, so to speak, reversed with respect to the valve 16. This result is normally obtained by arranging the disc shutter of the valve 16 outside piston 4 and the common shutter 178 of the valves 17 and 18 inside the piston.
- a further valve with a disc or discoidal shutter is indicated 19 and is mounted on the cover or end 6 which closes cylinder 2 at its upper end.
- valve 19 is associated with an opening 20 which allows communication between the chamber 14 and the outside of the pump.
- a pin-shaped body, indicated 21 extends through the opening 20 and is movable between a first operating position, shown in full outline and indicated A in Figure 2, and a second operating position, shown in broken outline and indicated B in Figure 2.
- the pin 21 is slidably mounted within a tubular sleeve 22 held in a central position relative to the opening 20 by radial spokes, not clearly shown in the drawings.
- a disc shutter 24 similar in every respect to the shutters of the valves 16, 17 and 18.
- the movement of the shutter 24 is controlled by the pressure gradient established through the respective opening 20.
- the shutter 24 is moved away from the opening 20 so as to open it.
- the amplitude of the movement of the shutter 20 between the position of closure of the opening 20 and the position of disengagement from the opening 20 is chosen so that, when the pin 21 is pressed inwardly of the cylinder 2 towards position B, the shutter 24 is any case disengaged from the opening 20 so as always to keep it open.
- the shutter of the valve 16 is pushed into its closure position to interrupt the communication between the intake duct 8 and the chamber 15.
- the shutter 24 of the valve 19 moves into its open position, whereby air can flow freely into the chamber 14 from the outside.
- the shutter 178 is pushed into the position of opening of the valve 18 to put the chamber 15 (which acts at this time as a pumping chamber) into communication with the volume 13 and the delivery duct 9. At the same time, the shutter 178 closes the valve 17 to interrupt communication between the chamber 14 and the delivery duct 9.
- the pressure level in the latter thus tends to increase, while the pressure level in the chamber 15,whose dimensions increase, tends to decrease.
- the shutter of the valve 16 is brought into its open position, whereby the pumping fluid from the intake duct 8 can pass freely into the chamber 15.
- the shutter 24 of the valve 19 is pressed into its closure position to close the opening 20.
- the shutter 178 is pushed into the position of opening the valve 17, which puts the chamber 14 into communication between the chamber 15 and the delivery duct 9.
- valves 16, 17 and 18 take up the same positions of operation as described above.
- valve 19, which is in the open position during the downstroke of the piston 4 are also reproduced, so that the pump performs the normal pumping action.
- valves 16 and 18 are brought respectively to the open and closed positions (as in the case of double-acting operation), and the pumping fluid flows in through the intake duct 8 towards the chamber 15.
- the raising of the piston 4 does not therefore involve the considerable effort which would be required, however, if the pump were operating as a double-acting pump.
- the user has the means for selectively limiting the pumping action to only the downstroke of the piston 4 which, being performed with the user's weight bearing on the rod 5, is less tiring for the back muscles.
- the further valve member 19 enables the selective control of the intake of air into the chamber 14, without the need to provide a corresponding valve on the piston 4 for this purpose.
- the one-way valve 17 which selectively controls the communication between the chamber 14 and the delivery duct 9 is in fact mounted on the face of the piston 4 facing the chamber 14. In this way, a further advantage is obtained over the double-acting pumps of known type, deriving from the elimination of one of the valves mounted on the piston.
- a piston pump has thus been described which can be operated selectively in two modes or types of operation, it being switched selectively from use as a double-acting pump to use as a single-acting pump.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Reciprocating Pumps (AREA)
- Compressors, Vaccum Pumps And Other Relevant Systems (AREA)
Abstract
A piston pump for pumping fluids, in which at least one intake duct (8) and a delivery duct (9) for the pumping fluid are provided in the rod (5) for effecting the reciprocating sliding of the piston (4), includes valve members (16-18) at least partly associated with the piston (4) and selectively closable and openable with the movement of the piston (4) to put that (14 or 15) of the two chambers whose dimensions are decreasing at the particular time into communication with the delivery duct (9). A further valve member (19) associated with one (14) of the two chambers (14, 15) permits the said one (14) of the two chambers (14,15) to be put into free communication with the outside of the cylinder (2).
Description
- The present invention refers to piston pumps and relates particularly to a piston pump for pumping fluids, comprising:
- - a pumping cylinder;
- - a piston sealingly slidable in the cylinder and dividing the cylinder into two chambers whose dimensions increase and decrease alternately as a result of the sliding of the piston in the cylinder;
- - a rod for effecting the reciprocating sliding of the piston in the cylinder, having at least one intake duct and a delivery duct for the pumping fluid, and
- - valve members at least partly associated with the piston and alternately closable and openable with the movement of the piston to put that of the two chambers whose dimensions are decreasing at the particular time into communication with the delivery duct.
- This is a design of pump which is currently used for the inflation of tyres, mattresses; sports equipment, etc.
- A pump of the above-specified type is known in which the rod comprises two co-axial ducts, intake and delivery respectively, and in which two one-way disc valves are mounted on each of the two faces of the piston, operating in opposite directions and communicating respectively with the intake duct and the delivery duct.
- The principal advantage deriving from the use of pumps of this type, which are commonly called "double-acting pumps", consists in the possibility of exercising a continuous pumping action which is not interrupted as a result of the change of the direction of movement of the piston within the cylinder.
- However, particularly during the inflation of tyres and the like when the pump is operated in a vertical disposition, this advantage becomes a drawback in the final stages of the inflation operation. As a result of the high pressure created therein, the tyre does in fact exercise considerable resistance to the pumping action, increasing the effort of the person operating the pump. This effort is felt particularly during the upstroke of the piston, that is, when the person operating the pump must pull the rod of the pump upwards by acting on the handle at its top end. This effort, normally exerted by the muscles of the back, may be found to be excessive in certain cases and even produce muscular lesions, in addition to appreciable fatigue.
- The present invention has the object of providing a piston pump of the above-specified type, which is improved in terms of efficiency and convenience of use, and does not give rise to the drawbacks in use described above.
- According to the present invention, this object is achieved by means of a piston pump of the type specified above, characterised in that it includes a further valve member associated with one of the two chambers and selectively openable so as to put the said one of the two chambers into free communication with the outside of the cylinder.
- When one of the two chambers is put into communication with the outside of the cylinder, the decrease in the volume of the corresponding pumping chamber causes only the discharge of the pumped fluid (typically air) from the cylinder and not the supply of the delivery duct. Under such conditions, the pump actually behaves as a single-action pump.
- In the preferred application to the inflation of tyres, in which the pump is used in a generally vertical position with the two pumping chambers superposed, it is envisaged that the further valve member will be associated with the chamber which is in the upper position in use.
- In this way, after the first part of the pumping operation has been performed with the pump used as a double-acting pump, the user will be able to actuate the further valve element so as to cause the pump to operate as a single-acting pump and perform the pumping action only when the piston is pushed downwardly towards the ground. When the pump is single-acting, the raising of the piston (which does not involve the performance of a pumping action) may be carried out easily without excessive effort.
- Further characteristics and advantages of the invention will be apparent from the following description, given purely by way of non-limiting example with reference to the appended drawings, in which:
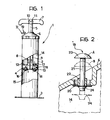
- Figure 1 is a partially cut-away and sectioned vertical elevational view of a pump according to the invention, and
- Figure 2 is a sectional view, on an enlarged scale, of the part of pump indicated by the arrow in Figure 1.
- In Figure 1, a piston pump preferably intended to be used for the inflation of tyres, mattresses, sports equipment, and the like is generally indicated 1.
- The pump 1 comprises, as component parts:
- - a light metal or
plastics cylinder 2 defining the pumping chamber of the pump and provided at its bottom end with a widenedfoot part 3 intended to facilitate the resting of the pump on the ground; - - a piston 4 sealingly slidable in the
cylinder 2 in axial direction relative to the cylinder, and - - a
rod 5 slidably mounted in anend part 6 which closes the end of thecylinder 2 opposite thefoot 3 and connected at the opposite end to the piston 4; therod 5 is operable to reciprocate the piston 4 within thecylinder 2, and for the purpose it is provided, at its end opposite the piston 4, with a handle 7 on which the user exerts a pulling and pushing action. - Generally, and according to a construction known in itself, the
rod 5 has twointernal ducts outlet openings rod 5. A pipe union is normally associated with the latter opening which enables the pump 1 to be connected to a tube or sleeve for connection to the inflatable article (tyre, mattress, item of sports equipment, etc) to be inflated. To advantage, the opening 10 may also have a pipe union which it is possible to connect to a tube or sleeve ending at an inflatable item whose deflation it is desired to speed up. - The intake and
delivery ducts rod 5 which is normally cylindrical. For example, theducts openings ducts - The piston 4 is generally hollow and has internal septa or partitions which divide it into two
volumes - The
volume 12, called the intake volume, communicates with theintake duct 8, while thevolume 13, called the delivery volume, communicates with thedelivery duct 12. - The communication of the
volumes respective ducts - The
piston 9 divides the cylinder 1 into twochambers - As a result of the reciprocation of the piston 4, which is effected by working the
rod 5 by means of the handle 7, the dimensions of thechambers - The
intake volume 12 of piston 4 communicates with thelower chamber 15 of thecylinder 2 through an opening in which a one-way valve 16 with disc or discoidal shutter is interposed. The function of thevalve 16 is to allow the flow of pumping fluid (normally air) from thevolume 12 to thechamber 15 but to prevent flow in the opposite direction. - The movement of the shutter of the
valve 16 is controlled by the pressure gradient established between thevolume 12 and thechamber 15 in such a manner that thevalve 16 closes when the pressure in thechamber 15 exceeds the pressure in thevolume 12 and opens when the pressure gradient is reversed. - According to a structurally-similar manner of assembly, the
volume 13 of the piston 4 communicates with theupper chamber 14 through an opening in which a one-way valve 17 is interposed and with thelower chamber 15 through a further opening in which a one-way valve 18 is interposed. - The
valves common shutter 178 of cylindrical shape, one end of which acts as a shutter for thevalve 17 and the opposite end of which acts as a shutter forvalve 18. Thevalves delivery duct 9 from thechamber 14 or thechamber 15 in alternation, preventing flow in the opposite direction in each case. - The mounting arrangement of the
valves valve 16. This result is normally obtained by arranging the disc shutter of thevalve 16 outside piston 4 and thecommon shutter 178 of thevalves - A further valve with a disc or discoidal shutter is indicated 19 and is mounted on the cover or
end 6 which closescylinder 2 at its upper end. - As can be seen better in the enlarged view of Figure 2, the
valve 19 is associated with anopening 20 which allows communication between thechamber 14 and the outside of the pump. A pin-shaped body, indicated 21, extends through theopening 20 and is movable between a first operating position, shown in full outline and indicated A in Figure 2, and a second operating position, shown in broken outline and indicated B in Figure 2. - More precisely, the
pin 21 is slidably mounted within atubular sleeve 22 held in a central position relative to the opening 20 by radial spokes, not clearly shown in the drawings. - The translational movement of the
pin 21 between the position of partial withdrawal from the cylinder, indicated A, and the position of insertion within the cylinder, indicated B, is easily effected by acting on amushroom head 23 provided on the end of thepin 21 facing outwardly of thecylinder 2. - On the opposite end of the
pin 21 is mounted adisc shutter 24 similar in every respect to the shutters of thevalves - In this case also, the movement of the
shutter 24 is controlled by the pressure gradient established through therespective opening 20. - More precisely, when the
pin 21 is in position A, the establishment of a pressure in thechamber 14 higher than that of the external environment causes theshutter 24 to be pressed against the opening 20 to close it. - On the other hand, when the pressure in the
chamber 14 is lower than that of the external environment, theshutter 24 is moved away from the opening 20 so as to open it. - The amplitude of the movement of the
shutter 20 between the position of closure of theopening 20 and the position of disengagement from theopening 20 is chosen so that, when thepin 21 is pressed inwardly of thecylinder 2 towards position B, theshutter 24 is any case disengaged from the opening 20 so as always to keep it open. - In order to illustrate the operation of the pump according to the invention, reference will be made to an initial condition of use in which the
valve member 19 is in the operating position A, wherein theshutter 24 selectively controls the flow of air through opening 20. - When the piston 4 is lowered towards the
bottom 3 of the cylinder, the pressure level in thechamber 14 tends to decrease, while the pressure level in thechamber 15 tends to increase. - Consequently, the shutter of the
valve 16 is pushed into its closure position to interrupt the communication between theintake duct 8 and thechamber 15. On the other hand, theshutter 24 of thevalve 19 moves into its open position, whereby air can flow freely into thechamber 14 from the outside. - The
shutter 178 is pushed into the position of opening of thevalve 18 to put the chamber 15 (which acts at this time as a pumping chamber) into communication with thevolume 13 and thedelivery duct 9. At the same time, theshutter 178 closes thevalve 17 to interrupt communication between thechamber 14 and thedelivery duct 9. - When the piston 4 is raised to move it back towards the upper end of the
cylinder 2, the functions of thechambers - The
chamber 14, whose dimensions decrease, acts as a pumping chamber. The pressure level in the latter thus tends to increase, while the pressure level in thechamber 15,whose dimensions increase, tends to decrease. - Consequently, the shutter of the
valve 16 is brought into its open position, whereby the pumping fluid from theintake duct 8 can pass freely into thechamber 15. At the same time, theshutter 24 of thevalve 19 is pressed into its closure position to close theopening 20. Theshutter 178 is pushed into the position of opening thevalve 17, which puts thechamber 14 into communication between thechamber 15 and thedelivery duct 9. - The operating conditions described above with reference respectively to the lowering and raising of the piston 4 alternate until the
valve member 19 is held in its first operating position corresponding to the location of thepin 21 in its partially withdrawn position, indicated A in Figure 2. Under such conditions, the pump 1 acts as a double-acting pump, ensuring a pumping action (intake through theduct 8, delivery through the duct 9) which is continuous and is not interrupted by the change in the direction of movement of the piston 4. - The pushing of the
pin 21 into the operating position B, in which theshutter 24 is always disengaged from theopening 20, renders the latter continuously open and the pump 1 goes over to a single-acting mode of operation. - Under such conditions, during the downstroke of piston 4, the
valves valve 19, which is in the open position during the downstroke of the piston 4, are also reproduced, so that the pump performs the normal pumping action. - When piston 4 is returned upwardly, the
valves intake duct 8 towards thechamber 15. - On the other hand (unlike what takes place in the case of double-acting operation) even if the
valve 17 moves to the open position to establish communication between thechamber 14 and thedelivery duct 9, the movement of piston 4 does not cause any substantial pumping action, since the fluid which is compressed within thechamber 14, the dimensions of which gradually decrease, flows out through theopening 20 left free by theshutter 24. Naturally, as there is no pumping action, the piston 4, and hence therod 5 and the handle 7, does not exert any appreciable resistance to the raising movement. - Moreover, during the final stages of the inflation of an article such as a tyre, the raising of the piston 4 does not therefore involve the considerable effort which would be required, however, if the pump were operating as a double-acting pump. Thus, the user has the means for selectively limiting the pumping action to only the downstroke of the piston 4 which, being performed with the user's weight bearing on the
rod 5, is less tiring for the back muscles. - It may also be seen that, during the double-acting operation, the
further valve member 19 enables the selective control of the intake of air into thechamber 14, without the need to provide a corresponding valve on the piston 4 for this purpose. In the pump according to the invention, only the one-way valve 17 which selectively controls the communication between thechamber 14 and thedelivery duct 9 is in fact mounted on the face of the piston 4 facing thechamber 14. In this way, a further advantage is obtained over the double-acting pumps of known type, deriving from the elimination of one of the valves mounted on the piston. - A piston pump has thus been described which can be operated selectively in two modes or types of operation, it being switched selectively from use as a double-acting pump to use as a single-acting pump.
Claims (4)
1. A piston pump for pumping fluids, comprising:
- a pumping cylinder (2);
- a piston (4) sealingly slidable in the cylinder (2) and dividing the cylinder (2) into two chambers (14, 15) whose dimensions increase and decrease alternately as a result of the sliding of the piston (4) in the cylinder (2);
- a rod (5) for effecting the reciprocating sliding of the piston (4) in the cylinder (2), having at least one intake duct (8) and a delivery duct (9) for the pumping fluid, and
- valve members ( 16 - 18 ) at least partly associated with the piston (4). and selectively closable and openable with the movement of the piston - ( 4 ) to put and that of the two chambers ( 14 or 15) whose dimensions are decreasing at the particular time into communication with the delivery duct (9), characterised in that it includes a further valve member (19) associated with one (14) of the two chambers (14, 15) and selectively openable to put the said one (14) of the two chambers (14, 15) into free communication with the outside of the cylinder (2).
2. A piston pump according to Claim 1, intended for use in a generally vertical position with the two chambers (14, 15) located one above the other, characterised in that the further valve member (19) is associated with the chamber (14) which is in the upper position in use.
3. A piston pump according to Claim 1 or Claim 2, characterised in that, on the face of the piston (4) facing the said one (14) of the two chambers (14, 15), there are only mounted one-way valve members (17) for putting the said one chamber (14) selectively into communication with the delivery duct (9), and in that the further valve member (19) is selectively switchable between first (A) and second (B) operating positions, the arrangement being such that in the first operating position (A) the further valve member (19) acts as a one-way valve member to permit the flow of pumping fluid toward the said one (14) of the chambers and to prevent the flow of the fluid in the opposite direction, and in the second operating position (B) the further valve member permits the free communication of the said one chamber (14) with the outside of the cylinder (2).
4. A pump according to Claim 3, characterised in that the further valve member (19) is substantially defined by:
- an opening (20) in the wall of the cylinder (2);
- a pin-shaped body (21) extending through the opening (20) between a position of partial withdrawal from the opening (20), which defines the first position (A), and a position of insertion into the cylinder (2), which defines thesecond position (B), and
- a disc or discoidal shutter (24) for closing the opening (20), which is fitted onto the pin-shaped body (21) within the cylinder (2) and is able to effect a sliding movement of given amplitude relative to the pin-shaped body (21) as a result of the pressure gradient established within the opening (20), the amplitude of the sliding movement of the shutter (24) being selected in such a manner that, with the pin-shaped body (21) in the partially withdrawn position (A), the shutter (24) is able selectively to open and to close the opening (20) and, with the pin-shaped body (21) in the inserted position (B), the shutter is always disengaged from the opening (20).
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT5382785U | 1985-09-20 | ||
| IT5382785U IT8553827V0 (en) | 1985-09-20 | 1985-09-20 | PISTON PUMP PARTICULARLY FOR INFLATION OF INFLATABLE MATTRESSES SPORTS EQUIPMENT AND SIMILAR |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0215752A2 true EP0215752A2 (en) | 1987-03-25 |
| EP0215752A3 EP0215752A3 (en) | 1989-03-08 |
Family
ID=11285424
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP86830256A Withdrawn EP0215752A3 (en) | 1985-09-20 | 1986-09-17 | Piston pump, particularly for inflating tyres, mattresses, sports equipment and the like |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0215752A3 (en) |
| IT (1) | IT8553827V0 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2190150B (en) * | 1986-04-04 | 1989-11-29 | Lucisano F & C Srs Snc | Hand-operated pump |
| AP505A (en) * | 1992-11-20 | 1996-07-12 | VAN NIEKERK Hendrik Cornelius | Pump. |
| CN103953525A (en) * | 2014-04-21 | 2014-07-30 | 侯如升 | Anti-slipping base for inflator |
| CN104196697A (en) * | 2014-07-14 | 2014-12-10 | 格力休闲体育用品有限公司 | Bi-directional hand inflator piston |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1697734A (en) * | 1927-07-25 | 1929-01-01 | William Kuhrt | Air pump |
| DE1703474A1 (en) * | 1967-05-29 | 1972-02-03 | Stiga Verken Ab | Double-acting piston pump for gaseous or liquid media |
| DE2005339C3 (en) * | 1969-02-11 | 1978-06-01 | Ferdinando Mailand Castiglioni (Italien) | Hand piston pump |
-
1985
- 1985-09-20 IT IT5382785U patent/IT8553827V0/en unknown
-
1986
- 1986-09-17 EP EP86830256A patent/EP0215752A3/en not_active Withdrawn
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US1697734A (en) * | 1927-07-25 | 1929-01-01 | William Kuhrt | Air pump |
| DE1703474A1 (en) * | 1967-05-29 | 1972-02-03 | Stiga Verken Ab | Double-acting piston pump for gaseous or liquid media |
| DE2005339C3 (en) * | 1969-02-11 | 1978-06-01 | Ferdinando Mailand Castiglioni (Italien) | Hand piston pump |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2190150B (en) * | 1986-04-04 | 1989-11-29 | Lucisano F & C Srs Snc | Hand-operated pump |
| AP505A (en) * | 1992-11-20 | 1996-07-12 | VAN NIEKERK Hendrik Cornelius | Pump. |
| CN103953525A (en) * | 2014-04-21 | 2014-07-30 | 侯如升 | Anti-slipping base for inflator |
| CN104196697A (en) * | 2014-07-14 | 2014-12-10 | 格力休闲体育用品有限公司 | Bi-directional hand inflator piston |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| IT8553827V0 (en) | 1985-09-20 |
| EP0215752A3 (en) | 1989-03-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5450924A (en) | Portable oil suction device | |
| US4749337A (en) | Reciprocating bladder pump, and methods of constructing and utilizing same | |
| US4008008A (en) | Pumps | |
| US4628994A (en) | Oil wells | |
| US4593951A (en) | Hydraulic chair lift mechanism | |
| US1754975A (en) | Nonreturn valve | |
| US5431229A (en) | Method and apparatus for utilizing the pressure of a fluid column generated by a pump to assist in reciprocating the pump plunger | |
| EP0215752A2 (en) | Piston pump, particularly for inflating tyres, mattresses, sports equipment and the like | |
| US5885061A (en) | Pneumatic pump | |
| US4842489A (en) | Hand-operated pump changeable from dual action to single action | |
| US5322101A (en) | Balloon stuffing device | |
| US7648348B2 (en) | Dewatering apparatus | |
| CA2310525C (en) | Pilot control valve for controlling a reciprocating pump | |
| US2262128A (en) | Double acting pump | |
| US4221551A (en) | Sliding valve pump | |
| US4243361A (en) | Standing valve assembly for an oil well pump | |
| GB2100362A (en) | Submersible hydraulic bore and pressure or negative pressure is well pump | |
| KR20180033427A (en) | Suspension fork for bicyle | |
| US2180864A (en) | Deep well pump | |
| US2250419A (en) | Fluid pump | |
| US5328339A (en) | Pump driven by air pressure | |
| US2214343A (en) | Well pump | |
| US184603A (en) | Improvement in pumps | |
| US1771070A (en) | Pump | |
| US1721127A (en) | Pump |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19890331 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: STROPPIANA, FIORINDO |