EP0100293A1 - Satzbetriebene Holzschnitzelaufschlussverfahren - Google Patents
Satzbetriebene Holzschnitzelaufschlussverfahren Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0100293A1 EP0100293A1 EP83630112A EP83630112A EP0100293A1 EP 0100293 A1 EP0100293 A1 EP 0100293A1 EP 83630112 A EP83630112 A EP 83630112A EP 83630112 A EP83630112 A EP 83630112A EP 0100293 A1 EP0100293 A1 EP 0100293A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- digester
- chips
- cooking
- cooked
- mass
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D21—PAPER-MAKING; PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE
- D21C—PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE BY REMOVING NON-CELLULOSE SUBSTANCES FROM CELLULOSE-CONTAINING MATERIALS; REGENERATION OF PULPING LIQUORS; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- D21C3/00—Pulping cellulose-containing materials
- D21C3/22—Other features of pulping processes
Definitions
- the present invention is in the field of cooking wood chips under alkaline conditions and seeks to improve the economy of the process and the heat utilization by pressurizing the cooked chips in the digester under a curtain of relatively cool air to discharge the same from the digester effectively.
- the prior art contains numerous examples of digesting wood chips in a batch type process. Such digestion usually takes place in a digester specifically built for that purpose, the digester being partially filled with the wood chips and then charged with hot solutions of sodium hydroxide alone or in admixture with sodium sulfide.
- the temperature of the digester is controlled through the introduction of steam and after maintaining the chips in contact with the cooking liquor for a predetermined period of time, a blow-valve in the digester is opened, to dump the contents thereof into a blow-tank. It was determined that there is a great deal of heat loss associated with the dumping of the contents. While various systems were attempted for minimizing this heat loss, none to my knowledge was particularly effective. Indeed, some paper manufacturers have gone to continuous digesting processes in order to avoid this drawback of a batch process, but the equipment costs for a continuous digesting system are very high.
- Hot black liquor from the accumulator is pumped into the bottom of the digester where it heats the chips.
- an excess of black liquor is employed, more than the capacity of the digester so that excess black liquor is discharged from the top of the digester and is transferred to a weak black liquor tank.
- Fresh white liquor is then used to displace the black liquor from the bottom of the digester and the resulting spent liquor is passed to a weak black liquor storage space.
- the contents of the digester are then heated with steam to the desired cooking temperatures and held there for the required cooking times. When the contents of the digester have reached the cooking temperature, the steam introduction stops. After cooking, the hot liquor is removed as in the originally described step, and the cycle starts over again.
- the present invention provides an improved, more efficient means of treating wood chips with strong cooking solutions.
- the digester after the cooking operation is completed, is emptied by providing a curtain of compressed, relatively cool air at the top of the digester to force the pulp out through a blow valve and into a blow tank.
- Particularly effective results are obtained when the air curtain is introduced at an initial pressure of from 0.5 to 1.0 MPa.
- the curtain of air has been found to be capable of discharging the cooked chips at a rate which is significantly faster than could be achieved with steam as the blowing agent. What is more, the operation proceeds very smoothly, without the hammering or erratic operation that was frequently noticed using steam as a blowing agent.
- the subject invention can be used to improve-the processes for wood chips digesting referred to above, namely:
- the improvement according to the invention comprises establishing a blanket of air over the mass of cooked chips in said digester at sufficient pressure to discharge the mass of cooked chips from said digester.
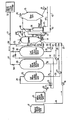
- reference numeral 10 has been applied to a digester of the conventional type including a removable lid 11.
- a steam line 12 is provided for introducing steam into the base of the digester in order to achieve the appropriate cooking temperature.
- an air curtain is provided to discharge the chips through an air inlet conduit 13.
- the chips are discharged from the digester through a conventional blow valve 14 which directs the blown pulp into a conventional blow tank identified at reference numeral 15. Discharge from the blow tank is controlled by means of a pump 16 in the usual manner.
- a washer filtrate liquor tank 17 which contains a filtrate from one of the washing steps of the pulp making operation. This filtrate is used as a displacement liquid during operation of the digester and proceeds by means of a conduit 18, a pump 19 and a valve 20 into an inlet point at the base of the digester 10.
- a white liquor storage tank 21 which houses the concentrated cooking solution consisting normally of a mixture of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide in concentrated aqueous solution.
- This white liquor from the tank 21 is delivered by means of a pump 22 through a heat exchanger 23 and a valve 24 into a hot white liquor accumulator 25.
- the contents of the hot white liquor accumulator 25 are delivered through a conduit 26 by means of a pump 27 and a valve 28 into the lower inlet end of the digester 10.
- a hot black liquor accumulator 29 in which hot black liquor is kept under pressure.
- a portion of the hot black liquor contained in-the accumulator 29 is delivered by means of a discharge line 30 into heat exchange relationship with the white liquor circulating through heat exchanger 23 by means of a line 31.
- Cooled black liquor is then delivered by means of a conduit 32 and a valve 33 into a cool black liquor accumulator 34.
- a valve 35 is provided to control the input to the cool black liquid accumulator 34.
- the discharge of the cool black liquor accumulator 34 is taken through a discharge conduit 36 through a pump 37 and a valve 38 for introduction into the lower end of the digester 10.
- a heat exchanger 39 to keep the cooking liquor at a substantially uniform temperature.
- the cooking liquor going to the digester 10 is preferably subjected to a forced liquid circulation.
- a portion of the cooking liquor is continuously withdrawn by means of a discharge line 40 and passed by means of a pump 41 into the heat exchanger 39 where it comes into heat exchange relationship with steam delivered from a steam line 42 through a valve 43.
- a condensate line 44 controlled by a valve 45 recirculates condensate to the steam generating source.
- the output of the heat exchanger 39 is split with one portion going by means of a branch line 46 and a valve 47 into the lower end of the digester 10, and another portion going by means of line 48 and a valve 49 into the upper end of the digester 10.
- a weak black liquor may be discharged from the digester through a line 50 and a valve 51 to a weak black liquor storage tank 52.
- the weak black liquor may be discharged as an overflow from the cool black liquor accumulator 34.
- the operation of the system proceeds substantially as follows.
- An appropriate amount of wood chips is introduced into the digester 10 through the removable lid 11. These chips may be compacted as required to provide a uniform density throughout the portion of the digester in which the chips are located.
- the digester 10 is first filled from the bottom with cool black liquor from the accumulator 34 through conduit 36, pump 37 and valve 38. This cool black liquor serves to preheat and to condition the chips.
- the cool black liquor is then displaced by hot black liquor from the accumulator 29 which is pumped by means of a pump 53 and valve 54 into the lower end of digester 10.
- the amount of hot black liquor introduced at this time is in excess of the capacity of the digester 10, the excess passing to the cool black liquor accumulator 34 through valve 35.
- white liquor from accumulator 25 is introduced into the base of the digester 10 by means of pump 27 and valve 28.
- the fresh white liquor serves to displace the remaining black liquor without substantial intermixing of the liquids.
- the contents of the digester are heated by steam introduced through line 12 to a cooking temperature of about 160° to 171 °C.
- the cooking, liquor is circulated in a forced circulation path, being introduced into the bottom of the digester 10 by means of the line 46, and into the top of the digester by means of the line 48.
- the cooking liquor is withdrawn by means of the line 40 and is circulated by the pump 41 through the heat exchanger 39 which serves to keep the cooking liquor up to temperature.
- the steam introduction through the line 12 is terminated.
- the digester is held at the cooking temperature for the required time which may run from 30 to 90 minutes.
- the hot black liquor which has resulted in the digester is discharged threfrom by displacing it with the washer filtrate from the liquor tank 17, the discharge line 18, pump 19, and valve 20.
- This hot spent liquor is pushed up through the chip column and is directed into the pressurized hot black liquor accumulator through a line 57 and a valve 58.
- the digester 10 is then closed and relatively cool air at approximately room temperature is injected into the top of the digester 10 by means of the air inlet line 13.
- the air blanket which is thus introduced is preferably at a pressure of about 0.5 to 1 MPa.
- the blow valve 14 is opened and the pressure of the air quickly serves to force the pulp through the blow valve 14 into the blow tank 15.
- the air is exhausted through flow valve 14 into blow tank 15 and out through a vent 62 at the top of the blow tank.
Landscapes
- Paper (AREA)
- Cookers (AREA)
- Commercial Cooking Devices (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US40263682A | 1982-07-28 | 1982-07-28 | |
| US402636 | 1982-07-28 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0100293A1 true EP0100293A1 (de) | 1984-02-08 |
Family
ID=23592723
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP83630112A Withdrawn EP0100293A1 (de) | 1982-07-28 | 1983-07-04 | Satzbetriebene Holzschnitzelaufschlussverfahren |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0100293A1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS5943181A (de) |
| BR (1) | BR8303886A (de) |
| FI (1) | FI831781L (de) |
| NO (1) | NO832694L (de) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0135461A1 (de) * | 1983-08-24 | 1985-03-27 | Beloit Corporation | Mehrstufiges Aufschlussverfahren in einem satzweise arbeitenden Kocher |
| DE3941551A1 (de) * | 1988-12-16 | 1990-06-21 | Amada Co | Vorrichtung zum positionieren von plattenfoermigen werkstuecken |
| WO1991005907A1 (en) * | 1989-10-17 | 1991-05-02 | Sunds Defibrator Industries Aktiebolag | Method for discharging a digester |
| WO1997038157A1 (en) * | 1996-04-04 | 1997-10-16 | Impco-Voest-Alpine Pulping Technologies Gmbh | Process for continuously guiding liquids when digesting pulp in a digester |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0543870Y2 (de) * | 1988-02-02 | 1993-11-05 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE388215C (de) * | 1924-01-10 | Erik L Haegg | Verfahren und Einrichtung zum Entleeren von Massenbehaeltern aller Art | |
| US1872548A (en) * | 1928-12-15 | 1932-08-16 | American Bemberg Corp | Method of clearing fibers out of a vessel |
| DE898707C (de) * | 1951-12-24 | 1953-12-03 | Waldhof Zellstoff Fab | Kocherentleerung unter Zuhilfenahme von Druckluft od. dgl. |
| GB900880A (en) * | 1960-02-03 | 1962-07-11 | Allen Edward Chittenden | Improvements in and relating to the cold caustic pulping process |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI63268C (fi) * | 1979-04-11 | 1989-06-21 | Sunds Defibrator | Foerfaringssaett foer toemning av en satsvis cellulosakokare. |
-
1983
- 1983-05-19 FI FI831781A patent/FI831781L/fi not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1983-07-04 EP EP83630112A patent/EP0100293A1/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1983-07-20 BR BR8303886A patent/BR8303886A/pt unknown
- 1983-07-25 NO NO832694A patent/NO832694L/no unknown
- 1983-07-27 JP JP13600683A patent/JPS5943181A/ja active Granted
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE388215C (de) * | 1924-01-10 | Erik L Haegg | Verfahren und Einrichtung zum Entleeren von Massenbehaeltern aller Art | |
| US1872548A (en) * | 1928-12-15 | 1932-08-16 | American Bemberg Corp | Method of clearing fibers out of a vessel |
| DE898707C (de) * | 1951-12-24 | 1953-12-03 | Waldhof Zellstoff Fab | Kocherentleerung unter Zuhilfenahme von Druckluft od. dgl. |
| GB900880A (en) * | 1960-02-03 | 1962-07-11 | Allen Edward Chittenden | Improvements in and relating to the cold caustic pulping process |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| TAPPI J. TECHN. ASS. PULP PAPER INDUSTRY, vol. 63, no. 9, September 1980, pages 65-68, Atlanta, Georgia, USA * |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0135461A1 (de) * | 1983-08-24 | 1985-03-27 | Beloit Corporation | Mehrstufiges Aufschlussverfahren in einem satzweise arbeitenden Kocher |
| DE3941551A1 (de) * | 1988-12-16 | 1990-06-21 | Amada Co | Vorrichtung zum positionieren von plattenfoermigen werkstuecken |
| WO1991005907A1 (en) * | 1989-10-17 | 1991-05-02 | Sunds Defibrator Industries Aktiebolag | Method for discharging a digester |
| US5116475A (en) * | 1989-10-17 | 1992-05-26 | Sunds Defibrator Industries Aktiebolag | Method for discharging a digester |
| WO1997038157A1 (en) * | 1996-04-04 | 1997-10-16 | Impco-Voest-Alpine Pulping Technologies Gmbh | Process for continuously guiding liquids when digesting pulp in a digester |
| WO1997038156A1 (de) * | 1996-04-04 | 1997-10-16 | Impco-Voest-Alpine Pulping Technologies Gmbh | Kontinuierliche flüssigkeitsführung bei der kochung von zellstoff in einem kocher |
| US6261413B1 (en) | 1996-04-04 | 2001-07-17 | Impco-Voest-Alpine Pulping Technologies Gmbh | Continuously guiding liquids in a digester during pulp digestion |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPS6328159B2 (de) | 1988-06-07 |
| NO832694L (no) | 1984-01-30 |
| FI831781L (fi) | 1984-01-29 |
| JPS5943181A (ja) | 1984-03-10 |
| BR8303886A (pt) | 1984-02-28 |
| FI831781A0 (fi) | 1983-05-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4274913A (en) | Process for producing alkali pulp | |
| US4849052A (en) | Batch digester multi-stage pulping process | |
| EP0502852B1 (de) | Heizung mit verschiebung in kontinuierlichen zellstoffkochern | |
| US4578149A (en) | Process for digesting cellulosic material with heat recovery | |
| JPH03130482A (ja) | セルロースの連続蒸解方法及び装置 | |
| US4236961A (en) | Pulping lignocellulose in continuous pressurized batch digesters | |
| US5643410A (en) | Batch process for preparing kraft pulp in a batch digesting process | |
| EP0135461B1 (de) | Mehrstufiges Aufschlussverfahren in einem satzweise arbeitenden Kocher | |
| US3215587A (en) | Continuous process and apparatus for delignification of cellulosic material | |
| EP0498821B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur versetzung von ablaugen in einem kocher | |
| EP0100293A1 (de) | Satzbetriebene Holzschnitzelaufschlussverfahren | |
| JP4280636B2 (ja) | セルロースパルプの製造方法 | |
| US2008635A (en) | Process of and apparatus for producing pulp | |
| EP1702101B1 (de) | Diskontinuierliches verfahren zur herstellung von zellstoff | |
| US5080757A (en) | Method to displace a digester from both ends | |
| EP0554391B1 (de) | Aufschlussverfahren | |
| US6939439B1 (en) | Batch process for producing chemical pulp by removing and reintroducing calcium-containing spent liquor in the digester | |
| WO1985002423A1 (en) | A method for the production of cellulose by the batch cooking process | |
| EP1268925B1 (de) | Verfahren zur verbesserten terpentinrückgewinnung in einer modernen kochanlage | |
| US2882148A (en) | Method of charging cellulose digesters | |
| US1885918A (en) | Recovery of relief material | |
| JPS636188A (ja) | バツチ式蒸解釜からの原料排出方法 | |
| US2216649A (en) | Process of and apparatus for digesting fibrous materials | |
| JPH0514191U (ja) | 蒸解装置 | |
| JPH0244957B2 (de) |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): DE FR GB IT NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19840625 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19850803 |
|
| RIN1 | Information on inventor provided before grant (corrected) |
Inventor name: GRANT, RALPH SMYTHE |