EP0054504B1 - Piezoelectric ignition system for a safety gas burner and apparatuses, in particular absorption refrigerators, using such a system - Google Patents
Piezoelectric ignition system for a safety gas burner and apparatuses, in particular absorption refrigerators, using such a system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0054504B1 EP0054504B1 EP19810420183 EP81420183A EP0054504B1 EP 0054504 B1 EP0054504 B1 EP 0054504B1 EP 19810420183 EP19810420183 EP 19810420183 EP 81420183 A EP81420183 A EP 81420183A EP 0054504 B1 EP0054504 B1 EP 0054504B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- piezo
- push
- electric mechanism
- actuating means
- safety shutter
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 title claims description 4
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 41
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000009527 percussion Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001960 triggered effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910000746 Structural steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000881 depressing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000994 depressogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008246 gaseous mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23Q—IGNITION; EXTINGUISHING-DEVICES
- F23Q3/00—Igniters using electrically-produced sparks
- F23Q3/002—Igniters using electrically-produced sparks using piezoelectric elements
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a gas burner ignition system, combining on the one hand a temperature sensitive safety valve and on the other hand a piezoelectric mechanism.
- a gas burner ignition system combining on the one hand a temperature sensitive safety valve and on the other hand a piezoelectric mechanism.
- Such systems can be used on various gas appliances, such as water heaters, heating stoves, absorption refrigerators.
- thermo-sensitive safety valve in the sense of the present invention, it is necessary to understand a valve with inlet (connected to a gas source), and outlet (connected directly or indirectly to a burner), comprising within it a thermo element -sensitive (itself connected to a sensor arranged so as to be in contact with the burner flame), as well as an elastically charged pusher, making it possible to open the valve at least partially, in the absence of excitation of the thermosensitive element; when the burner is operating, it is the heat-sensitive element which keeps the valve open, the pusher then being released to return to its initial position, under the effect of its elastic load; when the burner stops working, the heat-sensitive element no longer acts, which leads to the automatic closing of the valve.
- the thermosensitive element and the sensor consist respectively of an electromagnet and a thermoelectric couple.
- piezoelectric mechanism within the meaning of the present invention, it is necessary to understand a compact system, with electrical outlet (connected to an electrode arranged so as to ignite by sparks the gaseous mixture leaving the burner, the rest of the mechanism being at the mass), comprising within it a piezoelectric ceramic, as well as an elastically charged thrust member making it possible, from the start or during its stroke, to generate by action on the piezoelectric ceramic a high electric voltage (which generates at least one spark between the electrode and the burner); when the thrust member is released, it returns to its initial position, under the effect of its elastic load.
- Such mechanisms can be single-spark (percussion) or multi-spark (compression).
- This solution leads to placing the safety valve and the piezoelectric mechanism in a fixed manner relative to each other, and to providing a relatively complex actuation means, both in its construction and in its operation to act successively. on the safety valve and on the piezoelectric mechanism.
- This complexity can in certain cases hamper the normal operation of the safety valve, for example by preventing the return of the pusher to its rest position, which is obviously not desirable in the event of the burner going out.
- the actuating means is integral with the pushing member of the piezoelectric mechanism, which by its part opposite to said pushing member cooperates with the pusher, the safety valve, and d on the other hand the force required to actuate the piezoelectric mechanism is greater than the force required to at least partially open the safety valve by means of the pusher.
- actuation means integral with the pushing member of the piezoelectric mechanism
- the actuation means push button for example
- the same means is distinct from the same member and connected to the latter, for example in rotation, the actuating means being capable of rotating relative to the thrust member of the piezoelectric mechanism.
- force necessary for actuating the piezoelectric mechanism is meant the value of the thrust from which the piezoelectric mechanism is actuated or triggered, and therefore at least one electric shock is produced.
- the thrust exerted on the thrust member increases with the displacement of the latter, in particular as a function of the deflection imposed on the elastic return load (spring in
- force necessary to at least partially open the safety valve is meant the value of the thrust exerted on the pusher, making it possible to at least partially open said valve, and ensuring the passage of a gas flow at least sufficient to ignition of the burner, with which said valve communicates.
- the thrust exerted on the pusher of the safety valve increases with the displacement of the latter, in particular as a function of the deflection imposed on the elastic return load (spring in general).
- a security system in accordance with the invention brings together, behind and against each other, an actuating means 1, a piezoelectric mechanism 2, and a safety valve 3.
- the safety valve is retained by two brackets 4 and 5, the vertical wing of which has an orifice adjusted to receive the body 6 of the safety valve.
- the safety valve is blocked on the support constituted by the two brackets 4 and 5 is effected on the one hand by the shouldered nut 7 bearing against the bracket 5, and on the other hand by a ring of stop 8 forcibly mounted on the other side of the same bracket.
- An intermediate piece 9 encloses the piezoelectric mechanism, and the pushing member 10 belonging to the latter freely exits from this piece.
- the actuating means, or push button 1 consists of two differently colored parts 11 and 12, fitted one on the other.
- the push button 1 is fixed to the pushing member 10 of the mechanism 2, by means of a screw 13 retaining the part 11 of the actuating means 1.
- the rear part of the intermediate part 9, opposite to the the pushing member 10 is fixed to the pusher 14 of the safety valve 3, for example by means of a clip 15, which is received in two slots provided on the part 9 and a circular groove provided on the pusher 14.
- An angle iron 16 having a flared orifice 17 serves as a guide for the push-button 1.
- the piezoelectric mechanism comprises a housing 18, the thrust member 10, movable in translation, being capable of sinking into the housing.
- a piezoelectric ceramic 19 is contained in the housing 18.
- the displacement of the thrust member 10 in the housing 18 makes it possible both to load a return spring 20, and to project in translation a striker 21 against the ceramic 19 , under the effect of another spring 22, previously loaded during the same movement of the thrust member 10; the percussion is triggered when the lug 23 integral with the striker 21 escapes from its housing 24 provided on the housing 18, under the effect of the ramp 25 provided on the thrust member 10.
- the return to the initial position of the thrust member 10 and striker 21 takes place under the sole effect of the return spring 20, the counter-ramp 26 provided on the member 10 bringing the lug 23 back into its housing 24.
- the safety valve 3 comprises the tubular body 6, the end opposite the nut 7 is associated with the pusher 14, loaded elastically towards the outside by a compression spring 27.
- the interior end of the pusher 14 has a rod 28 capable of acting on a valve 29 pushed against its seat 6a by means of another spring 30.
- a heat-sensitive element 31, for example an electromagnet, keeps the valve 29 open if the sensor (not shown) ) connected to it by a wire 32, reaches a determined temperature.
- the pusher 14 can be maintained in an intermediate position, thanks to the presence of balls 33 loaded centrifugally and cooperating with a chamfer 6b of the body.
- the safety valve is provided with a gas inlet 34 (about) located upstream of the valve 29, and a gas outlet 35 located downstream of the valve.
- the force necessary to open it at least partially by means of the pusher 14, that is to say the force necessary to move the valve 29 and reach between the latter and the seat a passage section sufficient to ignite the burner is approximately equal to the elastic load of the spring 27, plus the elastic load of the spring 30, when said sufficient passage section is reached. According to the invention, it is this force which must remain less than the actuation force of the piezoelectric mechanism.
- the invention applies to any gas burner appliance, in particular absorption refrigerators equipped with such a burner.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Feeding And Controlling Fuel (AREA)
Description
La présente invention concerne un système d'allumage d'un brûleur à gaz, associant d'une part une vanne de sécurité thermo-sensible et d'autre part un méchanisme piézo-électrique. De tels systèmes, bien connus dans la pratique, peuvent être utilisés sur différents appareils à gaz, tels que chauffe-eau, réchauds de chauffage, réfrigérateurs à absorption.The present invention relates to a gas burner ignition system, combining on the one hand a temperature sensitive safety valve and on the other hand a piezoelectric mechanism. Such systems, well known in the art, can be used on various gas appliances, such as water heaters, heating stoves, absorption refrigerators.
Par vanne de sécurité thermo-sensible, au sens de la présente invention, il faut comprendre une vanne avec entrée (reliée à une source de gaz), et sortie (reliée directement ou indirectement à un brûleur), comprenant en son sein un élément thermo-sensible (lui-même relié à un capteur disposé de manière à être en contact avec la flamme du brûleur), ainsi qu'un poussoir chargé élastiquement, permettant d'ouvrir au moins partiellement la vanne, en l'absence d'excitation de l'élément thermo-sensible; lorsque le brûleur fonctionne, c'est l'élément thermo-sensible qui maintient la vanne ouverte, le poussoir étant alors relâché pour revenir à sa position initiale, sous l'effet de sa charge élastique; lorsque le brûleur cesse de fonctionner, l'élément thermosensible n'agit plus ce qui entraîne la fermeture automatique de la vanne. Le plus souvent l'élément thermo- sensible et le capteur consistent respectivement en un électro-aimant et un couple thermo-électrique.By thermo-sensitive safety valve, in the sense of the present invention, it is necessary to understand a valve with inlet (connected to a gas source), and outlet (connected directly or indirectly to a burner), comprising within it a thermo element -sensitive (itself connected to a sensor arranged so as to be in contact with the burner flame), as well as an elastically charged pusher, making it possible to open the valve at least partially, in the absence of excitation of the thermosensitive element; when the burner is operating, it is the heat-sensitive element which keeps the valve open, the pusher then being released to return to its initial position, under the effect of its elastic load; when the burner stops working, the heat-sensitive element no longer acts, which leads to the automatic closing of the valve. Most often the thermosensitive element and the sensor consist respectively of an electromagnet and a thermoelectric couple.
Par mécanisme piézo-électrique, au sens de la présente invention, il faut comprendre un système de faible encombrement, avec sortie électrique (reliée à une électrode disposée de manière à enflammer par étincelles le mélange gazeux sortant du brûleur, le reste du mécanisme étant à la masse), comprenant en son sein une céramique piézo-électrique, ainsi qu'un organe de poussée chargée élastiquement permettant, dès le début ou lors de sa course, de générer par action sur la céramique piézo-électrique une tension électrique élevée (laquelle engendre au moins une étincelle entre l'électrode et le brûleur); lorsqu'on relâche l'organe de poussée, celui-ci revient à sa position initiale, sous l'effet de sa charge élastique. De tels mécanismes peuvent être mono- étincelles (à percussion) ou multi-étincelles (à compression). Afin de simplifier le maniement des systèmes d'allumage envisagés par la présente invention, conformément «au document FR-A-2437575» «(numéro de dépôt» 78 28317 du 27/09/78) déposée par la Demanderesse, on a déjà proposé de rassembler la vanne de sécurité et le mécanisme piézo-électrique selon une disposition relative, par exemple alignement, dans laquelle un moyen unique d'actionnement permet d'agir, par exemple en translation, successivement sur le poussoir de la vanne de sécurité et sur l'organe de poussée du mécanisme piézo-électrique, le réarmement, ou retour à la position initiale du moyen unique d'actionnement, s'effectuant après relâchement sous le seul effet des charges élastiques ainsi libérées, disponibles dans la vanne de sécurité et le mécanisme piézo-électrique.By piezoelectric mechanism, within the meaning of the present invention, it is necessary to understand a compact system, with electrical outlet (connected to an electrode arranged so as to ignite by sparks the gaseous mixture leaving the burner, the rest of the mechanism being at the mass), comprising within it a piezoelectric ceramic, as well as an elastically charged thrust member making it possible, from the start or during its stroke, to generate by action on the piezoelectric ceramic a high electric voltage (which generates at least one spark between the electrode and the burner); when the thrust member is released, it returns to its initial position, under the effect of its elastic load. Such mechanisms can be single-spark (percussion) or multi-spark (compression). In order to simplify the handling of the ignition systems envisaged by the present invention, in accordance with “document FR-A-2437575” “(deposit number” 78 28317 of 09/27/78) filed by the Applicant, it has already been proposed to assemble the safety valve and the piezoelectric mechanism according to a relative arrangement, for example alignment, in which a single actuation means makes it possible to act, for example in translation, successively on the pusher of the safety valve and on the piezoelectric mechanism pushing member, resetting, or returning to the initial position of the single actuating means, taking place after release under the sole effect of the elastic loads thus released, available in the safety valve and the piezoelectric mechanism.
Cette solution conduit à disposer la vanne de sécurité et le mécanisme piézo-électrique de manière fixe l'un par rapport à l'autre, et à prévoir un moyen d'actionnement relativement complexe, tant dans sa construction que dans son fonctionnement pour agir successivement sur la vanne de sécurité et sur le mécanisme piézo-électrique. Cette complexité peut dans certains cas entraver le fonctionnement normal de la vanne de sécurité, par exemple en empêchant le retour du poussoir à sa position de repos, ce qui n'est évidemment pas souhaitable en cas d'extinction du brûleur.This solution leads to placing the safety valve and the piezoelectric mechanism in a fixed manner relative to each other, and to providing a relatively complex actuation means, both in its construction and in its operation to act successively. on the safety valve and on the piezoelectric mechanism. This complexity can in certain cases hamper the normal operation of the safety valve, for example by preventing the return of the pusher to its rest position, which is obviously not desirable in the event of the burner going out.
Tout ceci conduit à vouloir encore simplifier les systèmes d'allumage envisagés par la présente invention, de mainière à les rendre aisément réalisables au plan industriel, et parfaitement fiables au plan de leur utilisation quotidienne, domestique par exemple. Tel est le problème technique que vise à résoudre la présente invention.All this leads to wanting to further simplify the ignition systems envisaged by the present invention, so as to make them easily achievable on an industrial level, and perfectly reliable in terms of their daily use, domestic for example. This is the technical problem which the present invention aims to solve.
Selon la présente invention, d'une part le moyen d'actionnement est solidaire de l'organe de poussée du mécanisme piézo-électrique, lequel par sa partie opposée audit organe de poussée coopère avec le poussoir, de la vanne de sécurité, et d'autre part la force nécessaire à l'actionnement du mécanisme piézo-électrique est supérieure à la force nécessaire pour ouvrir au moins partiellement la vanne de sécurité au moyen du poussoir.According to the present invention, on the one hand the actuating means is integral with the pushing member of the piezoelectric mechanism, which by its part opposite to said pushing member cooperates with the pusher, the safety valve, and d on the other hand the force required to actuate the piezoelectric mechanism is greater than the force required to at least partially open the safety valve by means of the pusher.
Par moyen d'actionnement solidaire de l'organe de poussée du mécanisme piézo-électrique, il faut comprendre que soit le moyen d'actionnement, bouton-poussoir par exemple, s'identifie avec l'organe de poussée en question, soit le même moyen est distinct du même organe et relié à ce dernier, par exemple en rotation, le moyen d'actionnement étant susceptible de tourner par rapport à l'organe de poussée du mécanisme piézo-électrique.By actuation means integral with the pushing member of the piezoelectric mechanism, it should be understood that either the actuation means, push button for example, is identified with the pushing member in question, or the same means is distinct from the same member and connected to the latter, for example in rotation, the actuating means being capable of rotating relative to the thrust member of the piezoelectric mechanism.
Par coopération du mécanisme piézo-électrique avec le poussoir de la vanne de sécurité, il faut comprendre que la partie du mécanisme, opposée à l'organe de poussée agit sous l'effet du moyen d'actionnement, soit indirectement, par exemple grâce à un moyen mécanique intermédiaire transmettant au poussoir de la vanne la pousée exercée sur le mécanisme, soit directement, par exemple par appui contre le poussoir de la même vanne.By cooperation of the piezoelectric mechanism with the pusher of the safety valve, it should be understood that the part of the mechanism, opposite to the thrust member acts under the effect of the actuating means, either indirectly, for example thanks to an intermediate mechanical means transmitting the thrust exerted on the mechanism to the valve pusher, either directly, for example by pressing against the pusher of the same valve.
Par force nécessaire à l'actionnement du mécanisme piézo-électrique, on entend la valeur de la poussée à partir de laquelle on actionne ou déclenche le mécanisme piézo-électrique, et donc on produit au moins une décharge électrique. Ainsi dans le cas d'un mécanisme piézo-électrique à percussion, la poussée exercée sur l'organe de poussée croît avec le déplacement de ce dernier, notamment en fonction de la flèche imposée à la charge élastique de rappel (ressort enBy force necessary for actuating the piezoelectric mechanism is meant the value of the thrust from which the piezoelectric mechanism is actuated or triggered, and therefore at least one electric shock is produced. Thus in the case of a piezoelectric percussion mechanism, the thrust exerted on the thrust member increases with the displacement of the latter, in particular as a function of the deflection imposed on the elastic return load (spring in
général); passée une certaine valeur de cette poussée, le percuteur est projeté, sous l'effet de sa propre charge élastique, contre la céramique piézo-électrique, et c'est cette valeur qu'il convient de retenir comme étant la force nécessaire à l'actionnement du mécanisme piézo-électrique. Par force nécessaire pour ouvrir au moins partiellement la vanne de sécurité, on entend la valeur de la poussée exercée sur le poussoir, permettant d'ouvrir au moins partiellement ladite vanne, et d'assurer le passage d'un débit gazeux au moins suffisant à l'allumage du brûleur, avec lequel ladite vanne communique.general); past a certain value of this thrust, the striker is projected, under the effect of its own elastic load, against the piezoelectric ceramic, and it is this value which should be retained as being the force necessary for the actuation of the piezoelectric mechanism. By force necessary to at least partially open the safety valve is meant the value of the thrust exerted on the pusher, making it possible to at least partially open said valve, and ensuring the passage of a gas flow at least sufficient to ignition of the burner, with which said valve communicates.
Comme précédemment, la poussée exercée sur le poussoir de la vanne de sécurité croît avec le déplacement de ce dernier, notamment en fonction de la flèche imposée à la charge élastique de rappel (ressort en général).As before, the thrust exerted on the pusher of the safety valve increases with the displacement of the latter, in particular as a function of the deflection imposed on the elastic return load (spring in general).
Le dessin annexé, donné à titre d'exemple, permettra de mieux comprendre l'invention, les caractéristiques qu'elle présente et les avantages qu'elle est susceptible de procurer:
- 1 Fig. 1 représente une vue de dessus d'un système d'allumage conforme à la présente invention, avec coupe partielle, la vanne de sécurité et le mécanisme piézo-électrique étant en position de repos.
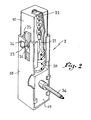
- Fig. 2 représente une vue en perspective, avec arrachements partiels, du mécanisme piézo-électrique faisant partie du système conforme à la fig. 1.
- 1 Fig. 1 shows a top view of an ignition system according to the present invention, with partial section, the safety valve and the piezoelectric mechanism being in the rest position.
- Fig. 2 shows a perspective view, with partial cutaway, of the piezoelectric mechanism forming part of the system according to FIG. 1.
Un système de sécurité conforme à l'invention regroupe de façon alignée, les uns derrière et contre les autres, un moyen d'actionnement 1, un mécanisme piézo-électrique 2, et une vanne de sécurité 3. La vanne de sécurité est retenue par deux équerres 4 et 5 dont l'aile verticale comporte un orifice ajusté pour recevoir le corps 6 de la vanne de sécurité. Le blocage de la vanne de sécurité sur le support constitué par les deux équerres 4 et 5 s'effectue grâce d'une part à l'écrou épaulé 7 en appui contre l'équerre 5, et d'autre part par un anneau d'arrêt 8 monté à force de l'autre côté de la même équerre. Une pièce intermédiaire 9 renferme le mécanisme piézo-électrique, et l'organe de poussée 10 appartenant à ce dernier sort librement de cette pièce. Le moyen d'actionnement, ou bouton-poussoir 1, est constitué de deux parties 11 et 12 colorées différemment, emboîtées l'une sur l'autre. Le bouton-poussoir 1 est fixé sur l'organe de poussée 10 du mécanisme 2, par l'intermédaire d'une vis 13 retenant la partie 11 du moyen d'actionnement 1. La partie arrière de la pièce intermédiaire 9, opposée à l'organe de poussée 10, est fixée sur le poussoir 14 de la vanne de sécurité 3, par exemple au moyen d'une agrafe 15, venant se loger dans deux fentes prévues sur la pièce 9 et une gorge circulaire prévue sur le poussoir 14. Ainsi, la partie arrière du mécanisme 2, opposée à l'organe de poussée 10, est constamment en appui contre le poussoir 14 de la vanne 3. Une cornière 16 comportant un orifice évasé 17 sert de guide au bouton-poussoir 1.A security system in accordance with the invention brings together, behind and against each other, an actuating means 1, a
Conformément à fig. 2, de manière en soi connue, le mécanisme piézo-électrique comporte un boîtier 18, l'organe de poussée 10, mobile en translation, étant susceptible de s'enfoncer dans le boîtier. Une céramique piézo-électrique 19 est contenue dans le boîtier 18. Le déplacement de l'organe de poussée 10 dans le boîtier 18 permet à la fois de charger un ressort de rappel 20, et de projeter en translation un percuteur 21 contre la céramique 19, sous l'effet d'un autre ressort 22, préalablement chargé lors du même déplacement de l'organe de poussée 10; la percussion se déclenche lorsque l'ergot 23 solidaire du percuteur 21 échappe de son logement 24 prévu sur le boîtier 18, sous l'effet de la rampe 25 prévue sur l'organe de poussée 10. Le retour à la position initiale de l'organe de poussée 10 et du percuteur 21 s'effectue sous le seul effet du ressort de rappel 20, la contre-rampe 26 prévue sur l'organe 10 ramenant l'ergot 23 dans son logement 24.In accordance with fig. 2, in a manner known per se, the piezoelectric mechanism comprises a
De la description à la fois de la constitution et du fonctionnement du mécanisme piézo-électrique 2, il résulte que la force nécessaire à son actionnement est égale à la somme de la charge élastique du ressort 20 et de celle du ressort 22, au moment où l'ergot 23 quitte son logement 24, c'est-à-dire approximativement en fin de course de l'organe de pousée 10.From the description of both the constitution and the operation of the
Conformément à la fig. 1, la vanne de sécurité 3 comporte le corps tubulaire 6 dont l'extrémité opposée à l'écrou 7 est associée au poussoir 14, chargé élastiquement vers l'extérieur par un ressort de compression 27. L'extrémité intérieure du poussoir 14 comporte une tige 28 propre à agir sur un clapet 29 repoussé contre son siège 6a par l'intermédaire d'un autre ressort 30. Un élément thermo-sensible 31, par exemple un électro-aimant, maintient le clapet 29 ouvert si le capteur (non représenté) relié à lui par un fil 32, atteint une température déterminée.In accordance with fig. 1, the safety valve 3 comprises the tubular body 6, the end opposite the nut 7 is associated with the
Le poussoir 14 peut-être maintenu à une position intermédaire, grâce à la présence de billes 33 chargées de manière centrifuge et coopérant avec un chanfrein 6b du corps. Bien entendu, la vanne de sécurité est pourvue d'une entrée de gaz 34 (about) située en amont du clapet 29, et d'une sortie de gaz 35 située en aval du clapet.The
D'après la description précédente de l'agencement et du fonctionnement de la vanne de sécurité, la force nécessaire pour l'ouvrir au moins partiellement au moyen du poussoir 14, c'est-à-dire la force nécessaire pour déplacer le clapet 29 et atteindre entre ce dernier et le siège une section de passage suffisante pour allumer le brûleur, est égale approximativement à la charge élastique du ressort 27, plus la charge élastique du ressort 30, lorsque ladite section de passage suffisante est atteinte. Selon l'invention, c'est cette force qui doit demeurer inférieure à la force d'actionnement du mécanisme piézo-électrique.According to the preceding description of the arrangement and operation of the safety valve, the force necessary to open it at least partially by means of the
Le fonctionnement du système d'allumage selon l'invention est en substance le suivant, en partant de la position de repos de la fig. 1, et en enfonçant progressivement le bouton-poussoir 1 :
- - Dans une première partie de la course, on enfonce le
poussoir 14 de la vanne de sécurité 3 sans enfoncer l'organe depoussée 10 du mécanisme piézo-électrique 2; à la fin de cette première partie, la poussée exercée sur le bouton-poussoir 1 atteint la force nécessaire pour ouvrir au moins partiellement la vanne de sécurité; - - Dans une deuxième partie de la course, la poussée exercée dépasse la force précitée, et on enfonce alors l'organe de
poussée 10 dumécanisme 2, tout en maintenant enfoncé ou en continuant d'enfoncer lepoussoir 14 de la vanne 3; à la fin de cette deuxième partie, la poussée exercée sur le bouton-poussoir 1 atteint la force d'actionnement du mécanisme piézo-électrique; on provoque alors une étincelle au brûleur, via lecâble 36 relié à lacéramique 19; - - Lorsqu'on relâche le bouton-poussoir 1, l'organe de
poussée 10 dumécanisme 2, et lepoussoir 14 de la vanne 3 co-agissent, sous l'effet de leurs charges élastiques respectives, devenues libres, pour ramener le bouton-poussoir 1, soit dans une position intermédiaire, correspondant à la retenue dupoussoir 14 sur l'épaulement 6b de la vanne de sécurité, dans laquelle lapartie 11 est cachée par lacornière 16, soit dans la position initiale, si la flame du brûleur n'est pas allumée, position dans laquelle les deuxparties 11 et 12 du bouton-poussoir 1 sont visibles.
- - In a first part of the stroke, the
pusher 14 of the safety valve 3 is depressed without depressing thethrust member 10 of thepiezoelectric mechanism 2; at the end of this first part, the thrust exerted on the push-button 1 reaches the force necessary to at least partially open the safety valve; - - In a second part of the stroke, the thrust exerted exceeds the aforementioned force, and then pushes the pushing
member 10 of themechanism 2, while holding down or continuing to push theplunger 14 of the valve 3; at the end of this second part, the thrust exerted on the push button 1 reaches the actuating force of the piezoelectric mechanism; a spark is then caused to the burner, via thecable 36 connected to the ceramic 19; - - When the push-button 1 is released, the pushing
member 10 of themechanism 2, and the push-button 14 of the valve 3 co-act, under the effect of their respective elastic loads, which have become free, to bring the button back -pusher 1, either in an intermediate position, corresponding to the retention of thepusher 14 on the shoulder 6b of the safety valve, in which thepart 11 is hidden by theangle 16, or in the initial position, if the flame of the burner is not lit, position in which the twoparts
L'invention s'applique à tout appareil à brûleur à gaz notamment les réfrigérateurs à absorption équipés d'un tel brûleur.The invention applies to any gas burner appliance, in particular absorption refrigerators equipped with such a burner.
Claims (8)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR8026988A FR2496233A1 (en) | 1980-12-15 | 1980-12-15 | PIEZOELECTRIC IGNITION SYSTEM OF A GAS BURNER WITH SAFETY, AND APPARATUSES, IN PARTICULAR ABSORPTION REFRIGERATORS, PROVIDED WITH SUCH A SYSTEM |
| FR8026988 | 1980-12-15 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0054504A1 EP0054504A1 (en) | 1982-06-23 |
| EP0054504B1 true EP0054504B1 (en) | 1983-11-23 |
Family
ID=9249272
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19810420183 Expired EP0054504B1 (en) | 1980-12-15 | 1981-12-11 | Piezoelectric ignition system for a safety gas burner and apparatuses, in particular absorption refrigerators, using such a system |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0054504B1 (en) |
| DE (1) | DE3161515D1 (en) |
| FR (1) | FR2496233A1 (en) |
| HU (1) | HU183737B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105674549B (en) * | 2016-04-01 | 2019-03-05 | 邓辉 | A kind of full-automatic piezoelectron sparking water heater |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NL6716173A (en) * | 1967-11-28 | 1969-05-30 | ||
| FR2099023A5 (en) * | 1970-10-27 | 1972-03-10 | Leblanc Marcel | |
| FR2112637A5 (en) * | 1970-11-03 | 1972-06-23 | Antargaz | |
| ES179600Y (en) * | 1972-04-22 | 1973-12-01 | Metalicas De Pamplona, S. A. | ACTUATING DEVICE APPLICABLE TO IGNITION OF GAS STOVES. |
-
1980
- 1980-12-15 FR FR8026988A patent/FR2496233A1/en active Granted
-
1981
- 1981-12-11 DE DE8181420183T patent/DE3161515D1/en not_active Expired
- 1981-12-11 EP EP19810420183 patent/EP0054504B1/en not_active Expired
- 1981-12-14 HU HU376181A patent/HU183737B/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| HU183737B (en) | 1984-05-28 |
| EP0054504A1 (en) | 1982-06-23 |
| DE3161515D1 (en) | 1983-12-29 |
| FR2496233A1 (en) | 1982-06-18 |
| FR2496233B1 (en) | 1983-02-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| FR2843327A1 (en) | SEALING TOOL ACTUATED BY INTERNAL COMBUSTION | |
| EP0054504B1 (en) | Piezoelectric ignition system for a safety gas burner and apparatuses, in particular absorption refrigerators, using such a system | |
| FR2875160A1 (en) | INTERNAL COMBUSTION SEALING TOOL | |
| FR2604510A1 (en) | GAS COOKING HAVING A COOKING BURNER LOCATED BELOW A PLATE OF VITROCERAM | |
| EP0333540B1 (en) | Gas valve with a thermocouple safety system, and apparatus using such a valve | |
| US2912841A (en) | Pyrophoric igniting device | |
| US2019165A (en) | Pyrophoric igniter | |
| EP1597534A1 (en) | Projectile fuze | |
| CH419899A (en) | Trigger device for firearm | |
| US3617160A (en) | Device for actuating the friction wheel of a pyrophoric lighter | |
| FR2667125A1 (en) | COMBINED CONTROL KNOB FOR GAS APPLIANCE. | |
| CH542163A (en) | Process for the production of a terpene mixture | |
| US1147784A (en) | Cigar-lighter. | |
| CH275000A (en) | Control device for gas burner. | |
| FR1464789A (en) | Automatic ignition device for gas burner | |
| WO1982003117A1 (en) | Control system for the power supply of a gas and electricity apparatus | |
| EP0165082A1 (en) | Regulating mechanism with variable rigidity for a gas-operated apparatus for the instantaneous production of warm water | |
| FR2561757A1 (en) | Gas water heater without a permanent pilot light | |
| CH266453A (en) | Flow rate and shutter adjustment device for lighters and gas lighters. | |
| EP0269509A1 (en) | Gas valve incorporating a security for a hot water apparatus without a permanent pilot flame | |
| CH368112A (en) | Control device of a gas burner | |
| FR2761459A1 (en) | Gas cooker burner safety system | |
| FR2489938A1 (en) | Rapid purge for gas appliance control - has purge pipe open during pilot ignition to evacuate inner valve chamber | |
| FR2642828A1 (en) | PERCUSSION SAFETY DEVICE IN THE EVENT OF DEVICE DROP ACTUATED BY EXPLOSION OF A CARTRIDGE | |
| FR2607907A1 (en) | Water heater |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19820630 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): BE CH DE FR GB IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19831123 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3161515 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19831229 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19831231 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19841116 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19841214 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19841231 Year of fee payment: 4 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19841231 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19850226 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19851231 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19861212 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Effective date: 19861231 Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19861231 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19861231 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: APPLICATION DES GAZ Effective date: 19861231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19870701 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19870831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19870901 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19881118 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 81420183.6 Effective date: 19870917 |