EP0016735A2 - Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Produktes für die Diagnose von Karzinomen - Google Patents
Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Produktes für die Diagnose von Karzinomen Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0016735A2 EP0016735A2 EP80830003A EP80830003A EP0016735A2 EP 0016735 A2 EP0016735 A2 EP 0016735A2 EP 80830003 A EP80830003 A EP 80830003A EP 80830003 A EP80830003 A EP 80830003A EP 0016735 A2 EP0016735 A2 EP 0016735A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- antigen
- process according
- cells
- tests
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N33/00—Investigating or analysing materials by specific methods not covered by groups G01N1/00 - G01N31/00
- G01N33/48—Biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Haemocytometers
- G01N33/50—Chemical analysis of biological material, e.g. blood, urine; Testing involving biospecific ligand binding methods; Immunological testing
- G01N33/53—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor
- G01N33/569—Immunoassay; Biospecific binding assay; Materials therefor for microorganisms, e.g. protozoa, bacteria, viruses
- G01N33/56983—Viruses
- G01N33/56994—Herpetoviridae, e.g. cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N2474/00—Immunochemical assays or immunoassays characterised by detection mode or means of detection
- G01N2474/20—Immunohistochemistry assay
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S435/00—Chemistry: molecular biology and microbiology
- Y10S435/803—Physical recovery methods, e.g. chromatography, grinding
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S436/00—Chemistry: analytical and immunological testing
- Y10S436/811—Test for named disease, body condition or organ function
- Y10S436/813—Cancer
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S530/00—Chemistry: natural resins or derivatives; peptides or proteins; lignins or reaction products thereof
- Y10S530/806—Antigenic peptides or proteins
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a process for the industrial production of a product which is designed to be used in the early diagnosis of the tumours of the fleshy parts or carcinomata of the human body, said product consisting of an antigen obtained by infection with Herpes Simplex Virus of cells of three guinea-pig kidneys said process comprising three treatment sections, in the first of which the antigen production is performed in the second section biochemical treatments of purification are carried out, while in the third section the product is prepared in preservable condition and confection.
- tumours of the epithelial tissues or carcinoma which are localized, in particular, in the lip, mouth cavity, pharynx, nose-pharynx, larynx, skin, kidney, bladder, prostate, penis, anus, cervix uteri, vulva, vagina, and rectum can be considered about the third part of the known tumours.
- HSV Herpes Simplex Virus
- tumours due to the said Virus promote in the blood of the patients the formation of specific antibodies directed against said tumours.
- the present invention provides a process for the industrial production of such a product. This process permits to obtain a programmed industrial production, based upon the application of repeatable and controllable operarations within predetermined limits, of a product in a lyophilized form for the best preservation of the product in perfect conditions and for long time periods.
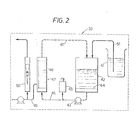
- the block 1 indicates the first section of the process where the antigen is prepared
- the section 2 includes the blocks concerning the biochemical purification treatments
- the block 3 indicates the third section in which the preparation and confectioning of the finished product take place.
- the section 1 is, in turn, divided in a main subsection A, in which the cells for the antigen are prepared, said section A operating in parallel with a main subsection B, in which the virus is prepared, as well as with an auxiliary subsection C which is necessary only for the purpose of providing an industrial complete production line.
- a unit 4 forms a part of this subsection C, in which means are provided for the washing of the containers used for the inoculation of the cells with HSV in order to obtain the antigen.
- These containers are preferably of the known type, named "Spinner Flasks".
- the unit 7 of the subsection A is the unit in which the ky- dneys are drawn from guinea-pigs or any other suitable type of cavy.
- the material which will be obtained in the following unit 8 is trypsinized; i.e. an addition of sterile trypsin is performed which has been obtained in the unit 8 by a filtering step, using special membrane filters, preferably of the "Seitz" type.
- the material from the unit 8 then passes through the unit 10, into which are conveyed the sterile and well dried containers coming out from unit 6.
- the material will be now distributed into said containers with an addition of a culture medium prepared in unit 11 and which consists of lactalbumin and serum of calf blood, filtered in sterile condition and kept inside this unit 12 for about two days at 4°C so that there is the time necessary for performing sterility tests.
- the tests are carried out on samples of cells taken from unit 10 in presence of an amount of culture medium taken from unit 11. If the sterility test will be positive, the controlled material can be supplied into the dosing unit 13 in which the material is distributed in constant volumes into containers of the aforementioned types.
- an industrial plant has to be planned in order to produce each day at least 48.000 gamma of activity. That is to say, a simple repeatition of that technique which is used in a laboratory production would require to handle more than 24.000 bottles in this cell section. To this number of bottle is also necessary to add the number of bottles which are required for receiving the virus (about 12.000) and those in course of preparation and emptying so that a total number of about 40.000 Roux bottles would be necessary and the handling and control of a so high number of bottles would be very problematic and burdensome on an economic stan- d point and also would require a prohibitive number of attendants.
- this invention provides the use of containers of the "Spinner Flask” type, which are well known on the market and which have each a capacity of 5000 ml and are each provided with an inner magnetically driven stirrer.
- the growth step requires about only four days, said growth step being performed in the unit 15 inside ma- crothermostats so adjusted as to maintain a temperature of 37° C .
- the unit 15 is associated with a unit 16, in which, after the second day of treatment, the culture medium is restored; in particular, it is hydrolized with lactoalbumin and calf serum.
- HEP2 cells Human Epidermoid Carcinoma
- BME Basal Medium Eagle
- these cells are infected with the HSV virus (Herpes Simplex Virus) and then the infected cells are transferred into the unit 19 in which the growth takes place inside an incubation cell at a temperature of 37° for about 24 to 48 hours.
- HSV virus Herpes Simplex Virus
- the infected cells will be then collected into the unit 20 and stored inside a freezer in the unit 21 at a temperature of about -80°C, The material is drawn out of the unit 21 in the required quantity and then conveyed into the unit 22 in which it is titrated with rabbit kidney according to the well known "plaque method".
- the cells coming from unit 15 are joined to the virus coming from unit 22; this operation is performed according to such a ratio so as to obtain from said combination the production of the antigen.
- this production correctly takes place, but also that it is attained with a desired ponderal yield, after repeated studies and tests has been found that the optimum ratio between HSV and the cells must be equal or higher than 1, but not higher than 100.
- Another operative condition of primary importance consists of the fact that it has been found that the antigen production is strongly and substantially positively affected by the contact time between the HSV virus and the cells. Several tests and qualitative and quantitative data obtained in said tests have proved that said optimal time is of about 3 hours.
- the subsequent unit 24 the cells are collected for the production of the antigen; this unit 24 serves for the feeding of the Section 2 of the plant in which the biochemical treatments are performed for the purification of the obtained antigen.
- the biochemical Section 2 of the process is-the second main part which permits to produce a product in industrial quantities, with the highest efficiency, and which is perfectly pure and of a high preservability.
- This second part of the process is designed to insulate and purify the product, by the removing of all the nonspecific proteins and the various impurities which could negatively affect the tests.
- the product which has been obtained in the unit 24 of the operative unit 1, is now conveyed into the unit 25, in which sequential freezing and defreezing steps which are repeated at least three times, are carried out for the purpose of breaking the cellular membranes and for starting the solubilization of the antigen, also applying a treatment by means of ultra-udible vibrations so as to promote breakage of the cellular membranes and; as a result thereof, so as to promote the complete dissolution of the antigen, thus permitting the subsequent operations, since the completely solubilized antigen can be easily separated from its heavier fractions by means of sequential centrifugation steps.
- a further dilution of the material is carried out using Tris - HC1 20 mM,pH 7.2 as buffer said buffer solution being added to a 40% of saturation by volume.
- the cellular liquid is brought into the unit 27, in which a ultracentrifuge operates at a maximum speed of about 50.000 r.p.m. and which imparts to the liquid a thrust force higher than about 100.000 times the force of gravity so that on the bottom of the used containers, for instance, test tubes of polycarbonate, a precipitate in the form of sediment is settled out which will be removed, while the liquid phase or supernatant containing the antigen is subjected to sequential purification steps.
- the liquid is saturated to 80% with powdered ammonium sulphate. Then it is subjected in the unit 29 to a further centrifugation inside a centrifuge rotating at about 15.000 r.p.m. Since the various proteins present in the solution, together with the antigen protein, are caused to precipitate in presence of the ammonium sulphate, these proteins can be separated by centrifugation in the unit 29. After the removal c f the liquid phase obtained by this centrifugation step, the process provides the dilution of the residual solids in the unit 30 with a buffer consisting of Tris-HCl 20 mM (pH 7.2), at a dilution of about 1:2,5 where 1 is the volume of the residual solids.
- the separation on gel is carried out at ambient temperature.
- the proteins of the different mclecular weights as well as the antigen protein which is a protein of' the molecular weight of 70.000 so that at first will be separated the proteins of highest weight and then ordinately those which have a lower and lower molecular weight.
- each column is provided with an automatic collecting means of the sequentially eluted fractions as well as with an optical reader capable of readings of 280 um, as for instance, the well known Dual Path Monitor UV 2 and respective recorder providing two independent recordings, and with stream deflectors with a peristaltic pump or the like and with a container of suitable capacity for the preparation of the required Sephadex G100 resin.
- the DEAE-Sephadex A 50 resin is used of the class including organic gellified copolymers having electric surface charges.
- Said device includes an open container 4l containing distilled water; a second closed container 42 in which is fed the liquid to be filtered; a pump 43 the suction pipe of which sucks the liquid from the bottom of the container 42, said liquid passing through the filtering section 44 before coming out of the container 42.
- This liquid is then conveyed through the pipe 45 to which is connected a manometer 46 designed to control the pressure of the liquid which is caused to pass through a filter device 47, in which are inserted filtering hollow crossing fibers 48.
- At 49 is indicated the outlet pipe coming from the filter device 47 and through which the filtrate is conveyed up to pass through a flowmeter 50 the outlet pipe of which ends inside the successive 30 unit 34.
- the non-glycosilated proteins are removed in the successive unit 34 by affinity chromatography on a column filled with an organic gellified copolymer, in particular the resin known under the Trade mark Sepharose, which is bound to the product, named "concanavalin A" by a metal-protein.
- an organic gellified copolymer in particular the resin known under the Trade mark Sepharose, which is bound to the product, named "concanavalin A" by a metal-protein.
- the third part of the process takes place in the section 3 and concerns the preparation and preservation or curing of the product in a form ready for the sale and use.
- an automatic dosing is carried out so as to fill each container, as for instance, a tiny bottle, with a predetermined volume of said liquid. Provision can be made, for instance that each tiny bottle has to contain 2.4 ml of solution which corresponds to a single dose adapted for carrying out twelve tests, for each of them 0,2 ml of said water solution is required which contains 2 gamma (mmg) of antigen.
- the tiny bottles will be closed by capsules by a capsuling machine in the unit 39; then the tiny bottles are conveyed through conventional labelling and confectioning machines.
- kit confection which comprises:
- This kit serves for performing n laboratory tests according to the use instructions which will accompany said kit confection.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Tropical Medicine & Parasitology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging Apparatus (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
- Preparation Of Compounds By Using Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Apparatus Associated With Microorganisms And Enzymes (AREA)
- Manufacture Of Macromolecular Shaped Articles (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Plant Substances (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT4908279 | 1979-05-18 | ||
| IT4908279A IT1117218B (it) | 1979-05-18 | 1979-05-18 | Procedimento per la produzione di un prodotto per la diagnosi dei tumori delle parti molli o carcinomi e prodotto ottenuto |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0016735A2 true EP0016735A2 (de) | 1980-10-01 |
| EP0016735A3 EP0016735A3 (en) | 1981-04-15 |
| EP0016735B1 EP0016735B1 (de) | 1984-10-31 |
Family
ID=11269590
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP19800830003 Expired EP0016735B1 (de) | 1979-05-18 | 1980-01-14 | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Produktes für die Diagnose von Karzinomen |
Country Status (13)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4391911A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0016735B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPS55158559A (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE10102T1 (de) |
| BR (1) | BR8003165A (de) |
| CA (1) | CA1172562A (de) |
| DE (1) | DE3069536D1 (de) |
| EG (1) | EG14898A (de) |
| ES (1) | ES491553A0 (de) |
| IL (1) | IL59539A (de) |
| IT (1) | IT1117218B (de) |
| SU (1) | SU1213974A3 (de) |
| ZA (1) | ZA802935B (de) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT1117218B (it) * | 1979-05-18 | 1986-02-17 | Depa Sas | Procedimento per la produzione di un prodotto per la diagnosi dei tumori delle parti molli o carcinomi e prodotto ottenuto |
| US4452734A (en) * | 1980-02-11 | 1984-06-05 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Herpes subunit vaccine |
| US4572896A (en) * | 1980-08-27 | 1986-02-25 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Department Of Health And Human Services | Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type I polypeptides |
| JPS6051120A (ja) * | 1983-08-31 | 1985-03-22 | Chemo Sero Therapeut Res Inst | 単純ヘルペスサブユニットワクチン |
| EP0200767B1 (de) * | 1984-10-31 | 1994-06-01 | Alcon Laboratories, Inc. | Sandwich-immunotestverfahren für antigene bei ophthalmischen störungen |
| US4786590A (en) * | 1985-01-15 | 1988-11-22 | California Institute Of Technology | Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of receptor-mediated leukemogenesis |
| ATE411809T1 (de) * | 1993-04-30 | 2008-11-15 | Wellstat Biologics Corp | Zusuammensetzungen zur behandlung von krebs mittels viren |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1535317A (en) * | 1976-02-20 | 1978-12-13 | Mun Hon Ng W | Anti-cancer vaccines |
| IT1117218B (it) * | 1979-05-18 | 1986-02-17 | Depa Sas | Procedimento per la produzione di un prodotto per la diagnosi dei tumori delle parti molli o carcinomi e prodotto ottenuto |
-
1979
- 1979-05-18 IT IT4908279A patent/IT1117218B/it active
-
1980
- 1980-01-14 AT AT80830003T patent/ATE10102T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1980-01-14 DE DE8080830003T patent/DE3069536D1/de not_active Expired
- 1980-01-14 EP EP19800830003 patent/EP0016735B1/de not_active Expired
- 1980-01-25 US US06/115,375 patent/US4391911A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1980-03-06 IL IL5953980A patent/IL59539A/xx unknown
- 1980-04-24 CA CA000350584A patent/CA1172562A/en not_active Expired
- 1980-05-13 SU SU802918702A patent/SU1213974A3/ru active
- 1980-05-15 JP JP6346480A patent/JPS55158559A/ja active Pending
- 1980-05-16 ES ES491553A patent/ES491553A0/es active Granted
- 1980-05-16 ZA ZA00802935A patent/ZA802935B/xx unknown
- 1980-05-18 EG EG31080A patent/EG14898A/xx active
- 1980-05-19 BR BR8003165A patent/BR8003165A/pt unknown
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CA1172562A (en) | 1984-08-14 |
| SU1213974A3 (ru) | 1986-02-23 |
| IT1117218B (it) | 1986-02-17 |
| DE3069536D1 (en) | 1984-12-06 |
| ATE10102T1 (de) | 1984-11-15 |
| EP0016735A3 (en) | 1981-04-15 |
| IT7949082A0 (it) | 1979-05-18 |
| ES8104404A1 (es) | 1981-04-16 |
| BR8003165A (pt) | 1980-12-30 |
| ES491553A0 (es) | 1981-04-16 |
| IL59539A (en) | 1983-10-31 |
| ZA802935B (en) | 1981-06-24 |
| US4391911A (en) | 1983-07-05 |
| IL59539A0 (en) | 1980-06-30 |
| EG14898A (en) | 1985-06-30 |
| EP0016735B1 (de) | 1984-10-31 |
| JPS55158559A (en) | 1980-12-10 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Malmquist et al. | Isolation, immunodiffusion, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy of a syncytial virus of lymphosarcomatous and apparently normal cattle | |
| Gerber | Activation of Epstein-Barr virus by 5-bromodeoxyuridine in “virus-free” human cells | |
| US4511653A (en) | Process for the industrial preparation of collagenous materials from human placental tissues, human collagenous materials obtained and their application as biomaterials | |
| Ahmed et al. | Demonstration of a blocking factor in the plasma and spinal fluid of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: I. Partial characterization | |
| EP0016735B1 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Produktes für die Diagnose von Karzinomen | |
| Ohtsuki et al. | Neocarzinostatin-induced breakdown of deoxyribonucleic acid in HeLa-S3 cells | |
| CN116854828A (zh) | 一种幽门螺杆菌融合多肽抗原及其应用 | |
| Baron et al. | A culture strain (LAC) of human epithelial-like cells from an adenocarcinoma of the lung | |
| JPS6176422A (ja) | 百日ぜきコンポ−ネントワクチンおよび百日ぜき・ジフテリア・破傷風混合ワクチンの製造方法 | |
| EP0133200B1 (de) | Diagnostisches Antigen für Träger der durch Pseudorabiesviren verursachten Krankheit bei Schweinen | |
| Goldblum et al. | Production of formalinized poliomyelitis vaccine (Salk-type) on a semi-industrial scale | |
| CN112341540B (zh) | 用于治疗covid-19感染的抗s1蛋白受体结合域多克隆抗体 | |
| CN108467434A (zh) | 哌拉西林单克隆抗体的制备方法及应用 | |
| Frothingham | Further observations on cell cultures infected concurrently with mumps and Sindbis viruses | |
| CN111748042B (zh) | 一种含有内毒素的非洲猪瘟融合蛋白及其制备方法和应用 | |
| Davies et al. | The typing of bluetongue virus | |
| Ubertini et al. | Process report: Large‐scale production of foot‐and‐mouth disease virus | |
| CN114075551B (zh) | 沙林鼠种布鲁氏菌脂多糖的单克隆抗体及应用 | |
| Kurup et al. | Indirect immunofluorescent detection of antibodies against thermophilic actinomycetes in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis | |
| Sato et al. | Herpes zoster of the maxillary branch of the trigeminus nerve: virological and serological studies | |
| CN112094344B (zh) | 从covid-19康复者血浆中纯化抗s1蛋白受体结合域多克隆抗体的方法 | |
| KR920010872B1 (ko) | Dna 비루스에 대한 백신의 제조방법 | |
| EP0308717B1 (de) | Methode für die Behandlung von viraler Gehirnentzündung | |
| Hübschle et al. | Purification of the group-specific antigen of bluetongue virus by chromatofocusing | |
| JPH03504856A (ja) | がん腫瘍細胞に対する肺増殖刺激因子および肺増殖阻害因子 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19810406 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE FR GB LU NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 10102 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19841115 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 3069536 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19841206 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19850131 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Effective date: 19860115 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee | ||
| NLXE | Nl: other communications concerning ep-patents (part 3 heading xe) |
Free format text: IN PAT.BUL.07/85,PAGE 799:SHOULD BE MODIFIED INTO:790518 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Effective date: 19881118 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19890131 Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 19900704 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 19900710 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19900712 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 19900713 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19910114 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Effective date: 19910131 Ref country code: BE Effective date: 19910131 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 19910313 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19910801 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Effective date: 19910930 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Effective date: 19921001 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed |
Ref document number: 80830003.2 Effective date: 19861023 |