CN111392323A - Conveying structure and conveying device - Google Patents
Conveying structure and conveying device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111392323A CN111392323A CN202010239570.1A CN202010239570A CN111392323A CN 111392323 A CN111392323 A CN 111392323A CN 202010239570 A CN202010239570 A CN 202010239570A CN 111392323 A CN111392323 A CN 111392323A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- conveyor belt
- axial direction
- rod
- along
- supporting
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G15/00—Conveyors having endless load-conveying surfaces, i.e. belts and like continuous members, to which tractive effort is transmitted by means other than endless driving elements of similar configuration
- B65G15/10—Conveyors having endless load-conveying surfaces, i.e. belts and like continuous members, to which tractive effort is transmitted by means other than endless driving elements of similar configuration comprising two or more co-operating endless surfaces with parallel longitudinal axes, or a multiplicity of parallel elements, e.g. ropes defining an endless surface
- B65G15/12—Conveyors having endless load-conveying surfaces, i.e. belts and like continuous members, to which tractive effort is transmitted by means other than endless driving elements of similar configuration comprising two or more co-operating endless surfaces with parallel longitudinal axes, or a multiplicity of parallel elements, e.g. ropes defining an endless surface with two or more endless belts
- B65G15/14—Conveyors having endless load-conveying surfaces, i.e. belts and like continuous members, to which tractive effort is transmitted by means other than endless driving elements of similar configuration comprising two or more co-operating endless surfaces with parallel longitudinal axes, or a multiplicity of parallel elements, e.g. ropes defining an endless surface with two or more endless belts the load being conveyed between the belts
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G21/00—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors
- B65G21/10—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors movable, or having interchangeable or relatively movable parts; Devices for moving framework or parts thereof
- B65G21/12—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors movable, or having interchangeable or relatively movable parts; Devices for moving framework or parts thereof to allow adjustment of position of load-carrier or traction element as a whole
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G21/00—Supporting or protective framework or housings for endless load-carriers or traction elements of belt or chain conveyors
- B65G21/20—Means incorporated in, or attached to, framework or housings for guiding load-carriers, traction elements or loads supported on moving surfaces
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65G—TRANSPORT OR STORAGE DEVICES, e.g. CONVEYORS FOR LOADING OR TIPPING, SHOP CONVEYOR SYSTEMS OR PNEUMATIC TUBE CONVEYORS
- B65G23/00—Driving gear for endless conveyors; Belt- or chain-tensioning arrangements
- B65G23/44—Belt or chain tensioning arrangements
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Structure Of Belt Conveyors (AREA)
Abstract
The embodiment of the invention provides a conveying device, which is characterized in that a certain distance is kept between a first conveying belt and a first limiting rod; and a certain distance is kept between the second conveyor belt and the second limiting rod, the protruding part of the article can be accommodated between the first conveyor belt and the first limiting rod, and the application range of the conveyor can be enlarged.
Description
Technical Field
The invention relates to the technical field of machinery, in particular to a conveying structure and a conveying device.
Background
In industrial production, a production line is generally used to improve production efficiency. The basic principle of the production line is to divide a repeated production process into a plurality of sub-processes, wherein the former sub-process creates execution conditions for the next sub-process, and each process can be performed simultaneously with other sub-processes. In short, it is "functional decomposition, sequential in space, parallel in time overlap".
In a production line, a conveyor is required to continuously convey goods on a certain line to complete the transfer of the goods from one process to the next. However, existing transfer devices are yet to be perfected.
Disclosure of Invention
In view of the above, the present invention provides a conveying structure and a conveying device to improve the conveying device.
In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a transmission structure, where the transmission structure includes:
the conveying device comprises a first conveyor belt and a second conveyor belt, wherein the first conveyor belt and the second conveyor belt are parallel to each other and are used for bearing and conveying articles along a first axial direction;
the first limiting rod is arranged on the outer side of the first conveyor belt and is spaced from the first conveyor belt by a preset distance;
the second limiting rod is arranged on the outer side of the second conveyor belt and is spaced from the second conveyor belt by a preset distance;
the distance between the first limiting rod and the second limiting rod is basically the same as the length of the article along the second axial direction;
wherein the first axis is perpendicular to the second axis.
Preferably, the first limiting rod and the second limiting rod are round rods.
Preferably, the distance between the first conveyor belt and the second conveyor belt is adjustable.
Preferably, the transfer structure further comprises:
the supporting rod is arranged along the first axial direction and is used for supporting the first conveyor belt and the second conveyor belt;
the connecting plate is arranged along the first axial direction and is fixedly connected with the supporting rod, and the connecting plate comprises a through hole along the second axial direction.
Preferably, the transfer structure further comprises:
the distance adjusting screw is arranged along the second axial direction, is matched with the through hole in the second axial direction and is used for adjusting the position of the first conveyor belt and/or the second conveyor belt in the second axial direction;
the adjusting block is fixedly connected to the connecting plate, is matched with the adjusting screw rod, moves along a second axial direction along with the rotation of the adjusting screw rod, and is used for driving the first conveyor belt and/or the second conveyor belt to move in the second axial direction;
the locking nut is used for fixing the adjusting block;
the supporting plate is arranged along the third axial direction, is fixedly connected with two ends of the interval adjusting screw rod and is used for supporting the interval adjusting screw rod;
wherein the third axial direction is perpendicular to the first and second axial directions.
Preferably, the connecting plate includes a guide hole in the second axial direction;
the transfer device further includes:
the guide rod is arranged along the second axial direction, and two ends of the guide rod are fixedly connected with the supporting plate and used for supporting the connecting plate;
and the outer periphery of the linear bearing is matched with the guide hole, and the inner periphery of the linear bearing is matched with the guide rod and used for enabling the connecting plate to slide along the guide rod.
Preferably, the transfer device further comprises:
the motor is used for providing power and driving the first conveyor belt and the second conveyor belt to move along the first axial direction;
the driving wheel is driven by the motor to rotate and is used for driving the first conveyor belt or the second conveyor belt to rotate;
and the idler wheel assembly is connected to the supporting rod, supports the first conveyor belt or the second conveyor belt and is used for realizing the reversing of the first conveyor belt and the second conveyor belt.
Preferably, the transfer structure further comprises:
a tensioning assembly for tensioning the first and second conveyor belts.
In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a transmission apparatus, including:
a plurality of transport structures as described in the first aspect.
Preferably, adjacent conveying structures share one first limiting rod or one second limiting rod.
The embodiment of the invention provides a conveying device, which is characterized in that a certain distance is kept between a first conveying belt and a first limiting rod; and a certain distance is kept between the second conveyor belt and the second limiting rod, the protruding part of the article can be accommodated between the first conveyor belt and the first limiting rod, and the application range of the conveyor can be enlarged.
Drawings
The above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention will become more apparent from the following description of the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which:
FIGS. 1 and 2 are schematic views of a conveyor apparatus according to an embodiment of the invention;
FIG. 3 is a schematic view of an article being conveyed by the conveyor of an embodiment of the present invention;
FIGS. 4 and 5 are schematic views of a second transfer assembly of the transfer apparatus of an embodiment of the present invention;
fig. 6 is a schematic view of a support assembly of a conveyor apparatus according to an embodiment of the invention.
Description of reference numerals:
01 item
011 plane area
012 convex
10a first transfer assembly
107a first conveyor belt
108a first stop lever
10b second transfer assembly
107b second conveyor belt
108b second stop lever
101 connecting plate
1011 through hole
1012 guide hole
102 connecting block
103 support rod
109 gag lever post connecting block
110 motor
111 motor fixing plate
112 driving wheel
104 idler assembly
104c top idler wheel fixing block
104b top idler spindle
104a top idler
114 tensioning assembly
20 support assembly
201 supporting plate
202 guide rod
203 linear bearing
204 spacing adjusting screw
205 regulating block
206 locking nut
Detailed Description
The present invention will be described below based on examples, but the present invention is not limited to only these examples. In the following detailed description of the present invention, certain specific details are set forth. It will be apparent to one skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without these specific details. Well-known methods, procedures, components and circuits have not been described in detail so as not to obscure the present invention.
Further, those of ordinary skill in the art will appreciate that the drawings provided herein are for illustrative purposes and are not necessarily drawn to scale.
Unless the context clearly requires otherwise, throughout the description, the words "comprise", "comprising", and the like are to be construed in an inclusive sense as opposed to an exclusive or exhaustive sense; that is, what is meant is "including, but not limited to".
In the description of the present invention, it is to be understood that the terms "first," "second," and the like are used for descriptive purposes only and are not to be construed as indicating or implying relative importance. In addition, in the description of the present invention, "a plurality" means two or more unless otherwise specified.
The existing conveying device is generally used for conveying articles with a plane bottom, and a limiting part is arranged on the outer side of a conveying belt to ensure that the articles move along the running direction of the conveying belt and prevent the articles from sliding off the conveying belt. However, in the existing structure, the limiting part is tightly attached to the outer edge of the conveying belt, so that the conveying device is limited to a certain extent when conveying objects with uneven bottoms. Meanwhile, in the existing conveying device, the distance between the conveying belts cannot be adjusted, and the application range of the conveying device is limited.
In view of this, the embodiment of the present invention provides a conveying device, which can be used for conveying multiple types of articles 01, so as to increase the application range of the conveying device.
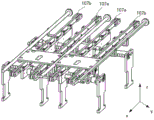
Fig. 1 and 2 are schematic views of a transfer apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in fig. 1 and 2, a transfer apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention includes: a first transfer assembly 10a, a second transfer assembly 10b and a support assembly 20.
In an alternative implementation, the first transfer assembly 10a is stationary and the second transfer assembly 10b is movable relative to the first transfer assembly 10 a. By adjustment, the conveyor can be used to convey articles 01 of various sizes.
In other alternative implementations, the second transfer assembly 10b may be stationary and the first transfer assembly 10a may move relative to the second transfer assembly 10 b.
In other alternative implementations, both the first 10a and second 10b conveyor assemblies may be movable.
In an alternative implementation, the transfer device comprises two pairs of first 10a and second 10b transfer assemblies. As shown in fig. 1, simultaneous conveyance of articles 01 of different sizes can be achieved by positioning the fixed first conveyor assembly 10a in an intermediate position and moving the movable second conveyor assembly 10b relative to the first conveyor assembly 10 a.
In an alternative implementation, the conveying device includes at least two sets of support assemblies 20, and the two sets of support assemblies 20 respectively support different positions of the conveying assembly to support and fix the conveying assembly. After the two groups of supporting components 20, the first conveying component 10a and the second conveying component 10b are fixedly connected, a rectangular bracket structure as shown in fig. 1 is formed.
FIG. 3 is a schematic view of article 01; fig. 4 and 5 are schematic views of a transfer assembly. Fig. 6 is a schematic view of the support assembly 20.
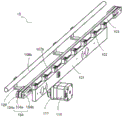
The first transfer assembly 10a may include: a first conveyor belt 107a and a first stopper rod 108 a. The second conveying assembly 10b includes a second stopper rod 108b, a second conveying belt 107b, a support rod 103, a connecting plate 101, a stopper rod connecting block 109 motor 110, a driving wheel 112, an idler assembly 104, and a tensioning assembly 114.
The first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107b are parallel to each other and are configured to carry and transport the article 01 in the first axial direction.
As shown in fig. 1, 2 and 3, the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107b are in contact with the plane area 011 of the bottom of the article 01, and the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107b move the article 01 in the first axial direction by friction force formed between the first conveyor belt 107a and the plane area 011 of the article 01. Wherein the first axial direction is the direction along the coordinate axis x in fig. 1.
In an alternative implementation, the conveyor includes two pairs of first and second conveyors 107a, 107 b. Further, as shown in fig. 1, the pair of first and second conveyor belts 107a and 107b may share one first stopper rod 108 a. Therefore, the fixed first conveying assembly 10a is arranged at the middle position, so that the utilization rate of the first limiting rod 108a can be improved, and the cost of the conveying device can be reduced.
The first stopper rod 108a and the second stopper rod 108b are respectively disposed on both sides of the article 01. The distance between the first stopper rod 108a and the second stopper rod 108b is substantially the same as the length of the article 01 in the second axial direction. The first and second stop bars 108a and 108b are used to ensure that the article 01 moves in the direction of belt travel, preventing the article 01 from sliding off the belt. Wherein the second axial direction is the direction along the coordinate axis y in fig. 1. The first axis is perpendicular to the second axis.
The first stopper rod 108a is disposed at an outer side of the first conveyor belt 107a, and spaced apart from the first conveyor belt 107a by a predetermined distance.
The second stopper rod 108b is disposed outside the second conveyor belt 107b, and is spaced apart from the second conveyor belt 107b by a predetermined distance.
The distance between the first stopper rod 108a and the first conveyor belt 107a is larger than the dimension of the projections 012 in the article 01 in the second axial direction. The gap between the first stopper rod 108a and the first conveyor belt 107a is used for accommodating the protrusion 012 of the article 01.
In other alternative implementations, the gap between the first stopper rod 108a and the first conveyor belt 107a may be adaptively adjusted according to the shape of the article 01.
In the embodiment of the present invention, a certain distance is provided between the first stopper rod 108a and the first conveyor belt 107a, so that the application range of the conveyor apparatus can be increased. Not only can the article with flat bottom be conveyed, but also the article with concavo-convex shape at the bottom can be conveyed.
As shown in fig. 1, 4 and 5, the first stopper rod 108a and the second stopper rod 108 b. Specifically, the first and second limit levers 108a and 108b are made of a solid round bar, such as 45# steel with a diameter of 50. Because solid round bar has better straightness accuracy, need not deep-processing again, only need confirm mounting hole etc. can improve machining efficiency, and the low price of round bar material can reduce production conveyer's cost.
The material of the first stopper rod 108a and the second stopper rod 108b may be various types of aluminum alloys, various types of carbon steels, various types of stainless steels, and the like.
In other alternative implementations, the first limiting rod 108a and the second limiting rod 108b may also be made of a section material such as a pipe, an i-steel, a C-steel, etc.
In an alternative implementation, the distance between the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107b is adjustable.
The support rod 103 is disposed along the first axial direction, and supports the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107 b.
The connecting plate 101 is arranged along the first axial direction and is fixedly connected with the supporting rod 103, and the connecting plate 101 comprises a through hole 1011 along the second axial direction and a guide hole 1012 along the second axial direction.
In an alternative implementation, the connecting plate 101 is fixedly connected to the supporting rod 103 through a connecting block 102.
The first limiting rod 108a or the second limiting rod 108b is fixedly connected with the connecting plate 101. In an alternative implementation manner, the first limiting rod 108a or the second limiting rod 108b is fixedly connected with the connecting plate 101 through three limiting rod connecting blocks 109. The distance between the first stopper rod 108a and the first conveyor belt 107a can be adjusted by adjusting the size of the stopper rod connection block 109. In an optional implementation manner, the limiting rod connecting block 109 is fixedly connected with the first limiting rod 108a through a bolt, and the limiting rod connecting block 109 is fixedly connected with the connecting plate 101 through a bolt, so that the limiting rod connecting block is convenient to detach and adjust.
In an alternative implementation, the transfer assembly includes a motor 110, a drive pulley 112, an idler assembly 104, and a tension assembly 114.
The motor is used for providing power and driving the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107b to move along the first axial direction.
And a motor fixing plate 111 for fixedly connecting the connecting plate 101 with the motor 110.
The driving wheel is driven by a motor to rotate and is used for driving the first conveying belt 107a or the second conveying belt 107b to rotate.
The idler assembly is connected to the supporting rod 103, and supports the first conveyor belt 107a or the second conveyor belt 107b, so as to realize the reversing of the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107 b.
The idler assembly includes a top idler mount block 104c, a top idler spindle 104b, and a top idler 104 a.
The top idler fixing block 104c is used for supporting and connecting the top idler 104a and the supporting rod 103.
The top idler shaft 104b is used to support and connect the top idler fixing block 104c and the top idler 104 a.
The top idler 104a is used to connect the rotating support of the first conveyor belt 107a or the second conveyor belt 107 b.
A tensioning assembly 114 for tensioning the first conveyor belt 107a and the second conveyor belt 107 b.
In an alternative implementation, as shown in fig. 6, the support assembly 20 may include: a spacing adjusting screw 204, an adjusting block 205, a locking nut 206, a support plate 201, a guide rod 202 and a linear bearing 203.
The spacing adjustment screw 204 is disposed along the second axial direction, and is matched with the through hole 1011 of the connecting plate 101 in the second axial direction, so as to adjust the position of the first conveyor belt 107a and/or the second conveyor belt 107b in the second axial direction.
The adjusting block 205 is fixedly connected to the connecting plate 101, and is matched with the adjusting screw to move along the second axial direction along with the rotation of the adjusting screw, so as to drive the first conveyor belt 107a and/or the second conveyor belt 107b to move along the second axial direction.
A lock nut 206 is used to fix the adjustment block 205.
The supporting plate 201 is arranged along the third axial direction, is fixedly connected with two ends of the interval adjusting screw 204, and is used for supporting the interval adjusting screw 204.
Specifically, the transfer device includes at least four support plates 201.
Wherein the third axial direction is perpendicular to the first and second axial directions. The third axis is the z-coordinate axis in fig. 1.
And the guide rod 202 is arranged along the second axial direction, and two ends of the guide rod 202 are fixedly connected with the supporting plate 201 and used for supporting the connecting plate 101.
And a linear bearing 203 having an outer circumference engaged with the guide hole 1012 and an inner circumference engaged with the guide bar 202 for sliding the link plate 101 along the guide bar 202.
The embodiment of the invention provides a conveying device, which is characterized in that a certain distance is kept between a first conveying belt and a first limiting rod; and a certain distance is kept between the second conveyor belt and the second limiting rod, the protruding part of the article can be accommodated between the first conveyor belt and the first limiting rod, and the application range of the conveyor can be enlarged.
The above description is only a preferred embodiment of the present invention and is not intended to limit the present invention, and various modifications and changes may be made by those skilled in the art. Any modification, equivalent replacement, or improvement made within the spirit and principle of the present invention should be included in the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
1. A conveying structure, characterized in that it comprises:
a first conveyor belt (107a) and a second conveyor belt (107b), said first conveyor belt (107a) and said second conveyor belt (107b) being parallel to each other for carrying and transporting articles (01) in a first axial direction;
a first stopper rod (108a) disposed outside the first conveyor belt (107a) and spaced apart from the first conveyor belt (107a) by a predetermined distance;
a second stopper rod (108b) provided outside the second conveyor belt (107b) and spaced apart from the second conveyor belt (107b) by a predetermined distance;
the distance between the first limiting rod (108a) and the second limiting rod (108b) is basically the same as the length of the article (01) along the second axial direction;
wherein the first axis is perpendicular to the second axis.
2. The conveying structure according to claim 1, wherein the first stopper rod (108a) and the second stopper rod (108b) are round rods.
3. The conveying structure according to any one of claims 1 or 2, characterized in that the distance between the first conveyor belt (107a) and the second conveyor belt (107b) is adjustable.
4. A transfer structure according to claim 3, characterized in that it further comprises:
a support bar (103) disposed along the first axial direction for supporting the first conveyor belt (107a) and the second conveyor belt (107 b);
the connecting plate (101) is arranged along the first axial direction and is fixedly connected with the supporting rod (103), and the connecting plate (101) comprises a through hole (1011) along the second axial direction.
5. The transfer structure of claim 4, further comprising:
the distance adjusting screw rod (204) is arranged along the second axial direction, is matched with the through hole (1011) of the second axial direction and is used for adjusting the position of the first conveyor belt (107a) and/or the second conveyor belt (107b) in the second axial direction;
the adjusting block (205) is fixedly connected to the connecting plate (101), is matched with the adjusting screw rod, moves along the second axial direction along with the rotation of the adjusting screw rod, and is used for driving the first conveyor belt (107a) and/or the second conveyor belt (107b) to move in the second axial direction;
a lock nut (206) for fixing the adjusting block (205);
the supporting plate (201) is arranged along a third axial direction, is fixedly connected with two ends of the spacing adjusting screw rod (204), and is used for supporting the spacing adjusting screw rod (204);
wherein the third axial direction is perpendicular to the first and second axial directions.
6. A transfer structure according to claim 5, characterized in that the connection plate (101) comprises guide holes (1012) in the second axial direction;
the transfer device further includes:
the guide rod (202) is arranged along the second axial direction, and two ends of the guide rod are fixedly connected with the supporting plate 201) and used for supporting the connecting plate (101);
and a linear bearing (203) having an outer periphery fitted to the guide hole (1012) and an inner periphery fitted to the guide bar (202) for sliding the link plate (101) along the guide bar (202).
7. The transfer structure of claim 4, wherein the transfer device further comprises:
the motor is used for providing power and driving the first conveyor belt (107a) and the second conveyor belt (107b) to move along the first axial direction;
the driving wheel is driven by a motor to rotate and is used for driving the first conveyor belt (107a) or the second conveyor belt (107b) to rotate;
an idler assembly connected to the support bar (103) supporting the first conveyor belt (107a) or the second conveyor belt (107b) for effecting a reversal of the first conveyor belt (107a) and the second conveyor belt (107 b).
8. The transfer structure of claim 1, further comprising:
a tensioning assembly for tensioning the first conveyor belt (107a) and the second conveyor belt (107 b).
9. A conveyor, characterized in that it comprises:
a plurality of the transfer structures of any of claims 1-8.
10. A conveyor as claimed in claim 9, wherein adjacent conveying structures share one of the first stop bar (108a) or the second stop bar (108 b).
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010239570.1A CN111392323A (en) | 2020-03-30 | 2020-03-30 | Conveying structure and conveying device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010239570.1A CN111392323A (en) | 2020-03-30 | 2020-03-30 | Conveying structure and conveying device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111392323A true CN111392323A (en) | 2020-07-10 |
Family
ID=71425898
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010239570.1A Pending CN111392323A (en) | 2020-03-30 | 2020-03-30 | Conveying structure and conveying device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111392323A (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT1169112B (en) * | 1983-02-24 | 1987-05-27 | Augusto Marchetti | TAPING MACHINE WITH ADJUSTABLE DISTANCE DRIVING UNIT |
| CN201901409U (en) * | 2010-11-29 | 2011-07-20 | 杨旸 | Roller type equal-height hydraulic stepping conveyor |
| CN202321618U (en) * | 2011-10-31 | 2012-07-11 | 东莞市新泽谷机械制造股份有限公司 | Parallelogram form connecting platform |
| CN107352258A (en) * | 2017-08-07 | 2017-11-17 | 安徽信盟装备股份有限公司 | A kind of forming machine feeding device |
| CN208647871U (en) * | 2018-07-27 | 2019-03-26 | 东莞市奥百特实业有限公司 | A PCB placement machine discharge mechanism |
| CN208994512U (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2019-06-18 | 无锡百晟科技有限公司 | A kind of conveying device of flexible circuit board |
| CN209367059U (en) * | 2018-09-19 | 2019-09-10 | 上海统然自动化科技有限公司 | A kind of adjustable belting |
| CN209853143U (en) * | 2019-05-10 | 2019-12-27 | 浙江聚成机械科技有限公司 | Flat plate type material conveyor with lateral positioning function |
| CN209939619U (en) * | 2019-05-05 | 2020-01-14 | 陈保成 | Single-shaft adjustable-interval conveying belt mechanism |
-
2020
- 2020-03-30 CN CN202010239570.1A patent/CN111392323A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IT1169112B (en) * | 1983-02-24 | 1987-05-27 | Augusto Marchetti | TAPING MACHINE WITH ADJUSTABLE DISTANCE DRIVING UNIT |
| CN201901409U (en) * | 2010-11-29 | 2011-07-20 | 杨旸 | Roller type equal-height hydraulic stepping conveyor |
| CN202321618U (en) * | 2011-10-31 | 2012-07-11 | 东莞市新泽谷机械制造股份有限公司 | Parallelogram form connecting platform |
| CN107352258A (en) * | 2017-08-07 | 2017-11-17 | 安徽信盟装备股份有限公司 | A kind of forming machine feeding device |
| CN208647871U (en) * | 2018-07-27 | 2019-03-26 | 东莞市奥百特实业有限公司 | A PCB placement machine discharge mechanism |
| CN209367059U (en) * | 2018-09-19 | 2019-09-10 | 上海统然自动化科技有限公司 | A kind of adjustable belting |
| CN208994512U (en) * | 2018-10-18 | 2019-06-18 | 无锡百晟科技有限公司 | A kind of conveying device of flexible circuit board |
| CN209939619U (en) * | 2019-05-05 | 2020-01-14 | 陈保成 | Single-shaft adjustable-interval conveying belt mechanism |
| CN209853143U (en) * | 2019-05-10 | 2019-12-27 | 浙江聚成机械科技有限公司 | Flat plate type material conveyor with lateral positioning function |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 周正军: "《工业机器人工装设计》", 31 July 2017 * |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101423940B1 (en) | conveyor | |
| US6533103B2 (en) | Transfer device for use between two conveyors | |
| US8640861B2 (en) | Vernier adjustor for conveyor systems | |
| SA112330387B1 (en) | Transport device for work pieces having a longitudinal axis | |
| KR20110020744A (en) | Heavy Load Carrying Support Device | |
| US10124960B2 (en) | Chain conveyor with adjustable distance between shafts | |
| CN202007030U (en) | Conveying and steering device for turnover box | |
| JP5064000B2 (en) | Auto palletizer | |
| US3870140A (en) | Feeding device for a carton forming machine | |
| US5207314A (en) | Device for horizontally holding loading bases moving circulatively in vertical plane | |
| CN111392323A (en) | Conveying structure and conveying device | |
| WO2017216825A1 (en) | Conveyor unit | |
| US10870541B2 (en) | Logistics trolley and production line using the same | |
| CN112192165A (en) | Unloader suitable for pipe fitting assembly line | |
| KR101211105B1 (en) | Conveyor system | |
| CN209814975U (en) | Three-degree-of-freedom adjustable belt conveyor | |
| US20020070101A1 (en) | Chain tensioning structure | |
| KR20170124263A (en) | Chain conveyer assembly | |
| CN220949678U (en) | Transfer equipment of production line | |
| JP5424449B2 (en) | Article conveying device | |
| CN213975812U (en) | Heavy-load large-angle transmission track | |
| JP5092709B2 (en) | Roller conveyor equipment | |
| JP2016008617A (en) | Carrier structure and processing method for guide rail | |
| KR101002350B1 (en) | Conveyor with width adjustment | |
| CN106185182B (en) | A kind of bracket tray positioning apparatus of annular pallet transfer equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |
Application publication date: 20200710 |