CN108010551B - 用于dpu运算的软件栈和编程 - Google Patents
用于dpu运算的软件栈和编程 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN108010551B CN108010551B CN201710684841.2A CN201710684841A CN108010551B CN 108010551 B CN108010551 B CN 108010551B CN 201710684841 A CN201710684841 A CN 201710684841A CN 108010551 B CN108010551 B CN 108010551B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- dram
- dpu
- row
- rows
- random
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/408—Address circuits
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0646—Horizontal data movement in storage systems, i.e. moving data in between storage devices or systems
- G06F3/0647—Migration mechanisms
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/38—Information transfer, e.g. on bus
- G06F13/40—Bus structure
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C7/00—Arrangements for writing information into, or reading information out from, a digital store
- G11C7/10—Input/output [I/O] data interface arrangements, e.g. I/O data control circuits, I/O data buffers
- G11C7/1006—Data managing, e.g. manipulating data before writing or reading out, data bus switches or control circuits therefor
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/14—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer
- G06F13/16—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to memory bus
- G06F13/1668—Details of memory controller
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0668—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems adopting a particular infrastructure
- G06F3/0671—In-line storage system
- G06F3/0683—Plurality of storage devices
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/402—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells with charge regeneration individual to each memory cell, i.e. internal refresh
- G11C11/4023—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells with charge regeneration individual to each memory cell, i.e. internal refresh using field effect transistors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/403—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells with charge regeneration common to a multiplicity of memory cells, i.e. external refresh
- G11C11/405—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells with charge regeneration common to a multiplicity of memory cells, i.e. external refresh with three charge-transfer gates, e.g. MOS transistors, per cell
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/409—Read-write [R-W] circuits
- G11C11/4091—Sense or sense/refresh amplifiers, or associated sense circuitry, e.g. for coupled bit-line precharging, equalising or isolating
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/409—Read-write [R-W] circuits
- G11C11/4094—Bit-line management or control circuits
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/409—Read-write [R-W] circuits
- G11C11/4097—Bit-line organisation, e.g. bit-line layout, folded bit lines
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Dram (AREA)
- Advance Control (AREA)
- Memory System (AREA)
- Logic Circuits (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201662413973P | 2016-10-27 | 2016-10-27 | |
| US62/413,973 | 2016-10-27 | ||
| US15/426,015 | 2017-02-06 | ||
| US15/426,015 US10180808B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2017-02-06 | Software stack and programming for DPU operations |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN108010551A CN108010551A (zh) | 2018-05-08 |
| CN108010551B true CN108010551B (zh) | 2023-05-02 |
Family
ID=62021467
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710684841.2A Active CN108010551B (zh) | 2016-10-27 | 2017-08-11 | 用于dpu运算的软件栈和编程 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10180808B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6920169B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102268179B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN108010551B (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI718336B (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10249362B2 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2019-04-02 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Computational memory cell and processing array device using the memory cells for XOR and XNOR computations |
| US10860320B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-12-08 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Orthogonal data transposition system and method during data transfers to/from a processing array |
| KR20200057475A (ko) | 2018-11-16 | 2020-05-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 연산 회로를 포함하는 메모리 장치 및 그것을 포함하는 뉴럴 네트워크 시스템 |
| WO2020159800A1 (en) | 2019-01-28 | 2020-08-06 | Rambus Inc. | Memory-integrated neural network |
| US10949214B2 (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2021-03-16 | Intel Corporation | Technologies for efficient exit from hyper dimensional space in the presence of errors |
| US11157692B2 (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2021-10-26 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Neural networks using data processing units |
| US11074008B2 (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2021-07-27 | Intel Corporation | Technologies for providing stochastic key-value storage |
| CN110275498A (zh) * | 2019-06-28 | 2019-09-24 | 泉州信息工程学院 | 一种基于互联网与深度学习的智能制造方法和系统及设备 |
| CN112684977B (zh) * | 2019-10-18 | 2024-05-28 | 旺宏电子股份有限公司 | 存储器装置及其存储器内计算方法 |
| KR102813842B1 (ko) * | 2020-06-29 | 2025-05-28 | 마이크론 테크놀로지, 인크 | 포지트를 사용하는 뉴로모픽 연산 |
| US12159219B2 (en) * | 2020-08-19 | 2024-12-03 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Neuron using posits |
| CN114201421B (zh) | 2022-02-17 | 2022-05-10 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | 一种数据流处理方法、存储控制节点及可读存储介质 |
| US12517711B2 (en) * | 2023-03-07 | 2026-01-06 | Lemon Inc. | Computation architecture synthesis |
| KR102733671B1 (ko) | 2023-08-14 | 2024-11-25 | 서울과학기술대학교 산학협력단 | 반도체 소자, 이를 포함하는 반도체 장치 및 그의 제조 방법 |
| KR102752637B1 (ko) * | 2023-12-05 | 2025-01-10 | 경북대학교 산학협력단 | 스토캐스틱 컴퓨팅 기반의 확률수 생성기 및 이를 이용한 스토캐스틱 컴퓨팅 회로 |
| KR20250145258A (ko) | 2024-03-28 | 2025-10-13 | 경희대학교 산학협력단 | Dram의 비트 단위 논리 연산을 수행하는 pim 연산 장치 및 pim 연산 방법 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11338767A (ja) * | 1998-05-22 | 1999-12-10 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 画像処理用機能メモリ装置 |
| CN103907157A (zh) * | 2011-10-28 | 2014-07-02 | 惠普发展公司,有限责任合伙企业 | 进行行移位的可移位存储器 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA2158467A1 (en) * | 1993-03-17 | 1994-09-29 | Richard D. Freeman | Random access memory (ram) based configurable arrays |
| US5847577A (en) * | 1995-02-24 | 1998-12-08 | Xilinx, Inc. | DRAM memory cell for programmable logic devices |
| US6745219B1 (en) | 2000-06-05 | 2004-06-01 | Boris Zelkin | Arithmetic unit using stochastic data processing |
| US9552047B2 (en) * | 2001-03-05 | 2017-01-24 | Pact Xpp Technologies Ag | Multiprocessor having runtime adjustable clock and clock dependent power supply |
| US6507530B1 (en) * | 2001-09-28 | 2003-01-14 | Intel Corporation | Weighted throttling mechanism with rank based throttling for a memory system |
| US8127075B2 (en) | 2007-07-20 | 2012-02-28 | Seagate Technology Llc | Non-linear stochastic processing storage device |
| US8352384B2 (en) | 2008-03-04 | 2013-01-08 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Combinational stochastic logic |
| US8341362B2 (en) * | 2008-04-02 | 2012-12-25 | Zikbit Ltd. | System, method and apparatus for memory with embedded associative section for computations |
| US8103598B2 (en) | 2008-06-20 | 2012-01-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Compiler for probabilistic programs |
| WO2011103587A2 (en) | 2010-02-22 | 2011-08-25 | Benjamin Vigoda | Superscalar control for a probability computer |
| US8645286B2 (en) | 2010-02-23 | 2014-02-04 | Prior Knowledge, Inc. | Configurable circuitry for solving stochastic problems |
| US9251467B2 (en) | 2013-03-03 | 2016-02-02 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Probabilistic parsing |
| KR102168652B1 (ko) * | 2013-12-16 | 2020-10-23 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 감지 증폭기, 그것을 포함하는 반도체 메모리 장치 및 그것의 읽기 방법 |
| US9455020B2 (en) * | 2014-06-05 | 2016-09-27 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for performing an exclusive or operation using sensing circuitry |
| US9954533B2 (en) * | 2014-12-16 | 2018-04-24 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | DRAM-based reconfigurable logic |
| US9697877B2 (en) * | 2015-02-05 | 2017-07-04 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Illinois | Compute memory |
| US9922696B1 (en) * | 2016-10-28 | 2018-03-20 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Circuits and micro-architecture for a DRAM-based processing unit |
-
2017
- 2017-02-06 US US15/426,015 patent/US10180808B2/en active Active
- 2017-05-31 KR KR1020170067968A patent/KR102268179B1/ko active Active
- 2017-08-11 CN CN201710684841.2A patent/CN108010551B/zh active Active
- 2017-09-06 TW TW106130354A patent/TWI718336B/zh active
- 2017-10-23 JP JP2017204581A patent/JP6920169B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11338767A (ja) * | 1998-05-22 | 1999-12-10 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 画像処理用機能メモリ装置 |
| CN103907157A (zh) * | 2011-10-28 | 2014-07-02 | 惠普发展公司,有限责任合伙企业 | 进行行移位的可移位存储器 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW201816619A (zh) | 2018-05-01 |
| TWI718336B (zh) | 2021-02-11 |
| US20180121130A1 (en) | 2018-05-03 |
| JP2018073413A (ja) | 2018-05-10 |
| KR20180046346A (ko) | 2018-05-08 |
| KR102268179B1 (ko) | 2021-06-23 |
| US10180808B2 (en) | 2019-01-15 |
| JP6920169B2 (ja) | 2021-08-18 |
| CN108010551A (zh) | 2018-05-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108010551B (zh) | 用于dpu运算的软件栈和编程 | |
| CN108022615B (zh) | 动态随机存取存储器处理单元 | |
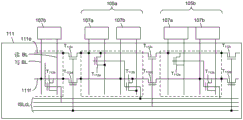
| CN108008974B (zh) | 基于动态随机存取存储器的处理单元架构 | |
| Talati et al. | mmpu—a real processing-in-memory architecture to combat the von neumann bottleneck | |
| JP7173709B2 (ja) | ニューラルネットワーク回路 | |
| TW202024898A (zh) | 用於記憶體內乘法及累加運算的電路及其方法 | |
| US7073039B2 (en) | Providing a register file memory with local addressing in a SIMD parallel processor | |
| CN108885887A (zh) | 用于数据移动的设备及方法 | |
| US10956813B2 (en) | Compute-in-memory circuit having a multi-level read wire with isolated voltage distributions | |
| CN110462738A (zh) | 用于数据路径内计算操作的设备及方法 | |
| CN115552523A (zh) | 使用存储器内处理的基于计数器的乘法 | |
| CN110476212A (zh) | 用于存储器中数据交换网络的设备及方法 | |
| US20210225429A1 (en) | High bandwidth memory and system having the same | |
| US20230385624A1 (en) | Computing in memory with artificial neurons | |
| Zhou et al. | Flexidram: A flexible in-dram framework to enable parallel general-purpose computation | |
| Sudarshan et al. | A critical assessment of dram-pim architectures-trends, challenges and solutions | |
| EP3933605B1 (en) | Memory device for performing in-memory processing | |
| Sim et al. | Mapim: Mat parallelism for high performance processing in non-volatile memory architecture | |
| Kulkarni et al. | Neuromorphic Accelerator for Deep Spiking Neural Networks with NVM Crossbar Arrays | |
| Bottleneck | mMPU-A Real Processing-in-Memory | |
| 신현승 | McDRAM: Low Latency and Energy-Efficient Matrix Computation in DRAM | |
| Kim et al. | DRAM-Based Processing-in-Memory |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |