CN108008974B - 基于动态随机存取存储器的处理单元架构 - Google Patents
基于动态随机存取存储器的处理单元架构 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN108008974B CN108008974B CN201710823568.7A CN201710823568A CN108008974B CN 108008974 B CN108008974 B CN 108008974B CN 201710823568 A CN201710823568 A CN 201710823568A CN 108008974 B CN108008974 B CN 108008974B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- column
- dram
- computing
- dpu
- array
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/30—Arrangements for executing machine instructions, e.g. instruction decode
- G06F9/38—Concurrent instruction execution, e.g. pipeline or look ahead
- G06F9/3885—Concurrent instruction execution, e.g. pipeline or look ahead using a plurality of independent parallel functional units
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F13/00—Interconnection of, or transfer of information or other signals between, memories, input/output devices or central processing units
- G06F13/14—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer
- G06F13/16—Handling requests for interconnection or transfer for access to memory bus
- G06F13/1668—Details of memory controller
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/406—Management or control of the refreshing or charge-regeneration cycles
- G11C11/40622—Partial refresh of memory arrays
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F12/00—Accessing, addressing or allocating within memory systems or architectures
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F15/00—Digital computers in general; Data processing equipment in general
- G06F15/76—Architectures of general purpose stored program computers
- G06F15/78—Architectures of general purpose stored program computers comprising a single central processing unit
- G06F15/7807—System on chip, i.e. computer system on a single chip; System in package, i.e. computer system on one or more chips in a single package
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F15/00—Digital computers in general; Data processing equipment in general
- G06F15/76—Architectures of general purpose stored program computers
- G06F15/78—Architectures of general purpose stored program computers comprising a single central processing unit
- G06F15/7807—System on chip, i.e. computer system on a single chip; System in package, i.e. computer system on one or more chips in a single package
- G06F15/7821—Tightly coupled to memory, e.g. computational memory, smart memory, processor in memory
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F15/00—Digital computers in general; Data processing equipment in general
- G06F15/76—Architectures of general purpose stored program computers
- G06F15/80—Architectures of general purpose stored program computers comprising an array of processing units with common control, e.g. single instruction multiple data processors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/403—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells with charge regeneration common to a multiplicity of memory cells, i.e. external refresh
- G11C11/405—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells with charge regeneration common to a multiplicity of memory cells, i.e. external refresh with three charge-transfer gates, e.g. MOS transistors, per cell
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/4076—Timing circuits
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/409—Read-write [R-W] circuits
- G11C11/4091—Sense or sense/refresh amplifiers, or associated sense circuitry, e.g. for coupled bit-line precharging, equalising or isolating
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C11/00—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor
- G11C11/21—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements
- G11C11/34—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices
- G11C11/40—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors
- G11C11/401—Digital stores characterised by the use of particular electric or magnetic storage elements; Storage elements therefor using electric elements using semiconductor devices using transistors forming cells needing refreshing or charge regeneration, i.e. dynamic cells
- G11C11/4063—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing
- G11C11/407—Auxiliary circuits, e.g. for addressing, decoding, driving, writing, sensing or timing for memory cells of the field-effect type
- G11C11/409—Read-write [R-W] circuits
- G11C11/4096—Input/output [I/O] data management or control circuits, e.g. reading or writing circuits, I/O drivers or bit-line switches
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C7/00—Arrangements for writing information into, or reading information out from, a digital store
- G11C7/10—Input/output [I/O] data interface arrangements, e.g. I/O data control circuits, I/O data buffers
- G11C7/1006—Data managing, e.g. manipulating data before writing or reading out, data bus switches or control circuits therefor
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C7/00—Arrangements for writing information into, or reading information out from, a digital store
- G11C7/10—Input/output [I/O] data interface arrangements, e.g. I/O data control circuits, I/O data buffers
- G11C7/1006—Data managing, e.g. manipulating data before writing or reading out, data bus switches or control circuits therefor
- G11C7/1012—Data reordering during input/output, e.g. crossbars, layers of multiplexers, shifting or rotating
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Dram (AREA)
- Memory System (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201662413977P | 2016-10-27 | 2016-10-27 | |
| US62/413,977 | 2016-10-27 | ||
| US201662418155P | 2016-11-04 | 2016-11-04 | |
| US62/418,155 | 2016-11-04 | ||
| US15/426,033 | 2017-02-06 | ||
| US15/426,033 US10242728B2 (en) | 2016-10-27 | 2017-02-06 | DPU architecture |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN108008974A CN108008974A (zh) | 2018-05-08 |
| CN108008974B true CN108008974B (zh) | 2023-05-26 |
Family
ID=62022501
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710823568.7A Active CN108008974B (zh) | 2016-10-27 | 2017-09-13 | 基于动态随机存取存储器的处理单元架构 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10242728B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6799520B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR102139213B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN108008974B (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI714806B (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10777262B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-09-15 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Read data processing circuits and methods associated memory cells |
| US10998040B2 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2021-05-04 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Computational memory cell and processing array device using the memory cells for XOR and XNOR computations |
| US10847212B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-11-24 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Read and write data processing circuits and methods associated with computational memory cells using two read multiplexers |
| US10943648B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2021-03-09 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Ultra low VDD memory cell with ratioless write port |
| US10770133B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-09-08 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Read and write data processing circuits and methods associated with computational memory cells that provides write inhibits and read bit line pre-charge inhibits |
| US10891076B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2021-01-12 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Results processing circuits and methods associated with computational memory cells |
| US10854284B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-12-01 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Computational memory cell and processing array device with ratioless write port |
| US10725777B2 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-07-28 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Computational memory cell and processing array device using memory cells |
| US11227653B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2022-01-18 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Storage array circuits and methods for computational memory cells |
| US10860320B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-12-08 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Orthogonal data transposition system and method during data transfers to/from a processing array |
| US10847213B1 (en) | 2016-12-06 | 2020-11-24 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Write data processing circuits and methods associated with computational memory cells |
| US10614875B2 (en) * | 2018-01-30 | 2020-04-07 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Logical operations using memory cells |
| CN108985449B (zh) * | 2018-06-28 | 2021-03-09 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | 一种对卷积神经网络处理器的控制方法及装置 |
| US10755766B2 (en) | 2018-09-04 | 2020-08-25 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Performing logical operations using a logical operation component based on a rate at which a digit line is discharged |
| KR20200057475A (ko) | 2018-11-16 | 2020-05-26 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 연산 회로를 포함하는 메모리 장치 및 그것을 포함하는 뉴럴 네트워크 시스템 |
| US11157692B2 (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2021-10-26 | Western Digital Technologies, Inc. | Neural networks using data processing units |
| US10949214B2 (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2021-03-16 | Intel Corporation | Technologies for efficient exit from hyper dimensional space in the presence of errors |
| US11074008B2 (en) * | 2019-03-29 | 2021-07-27 | Intel Corporation | Technologies for providing stochastic key-value storage |
| US10777253B1 (en) * | 2019-04-16 | 2020-09-15 | International Business Machines Corporation | Memory array for processing an N-bit word |
| US10958272B2 (en) | 2019-06-18 | 2021-03-23 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Computational memory cell and processing array device using complementary exclusive or memory cells |
| US10930341B1 (en) | 2019-06-18 | 2021-02-23 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Processing array device that performs one cycle full adder operation and bit line read/write logic features |
| US10877731B1 (en) | 2019-06-18 | 2020-12-29 | Gsi Technology, Inc. | Processing array device that performs one cycle full adder operation and bit line read/write logic features |
| US11409527B2 (en) * | 2019-07-15 | 2022-08-09 | Cornell University | Parallel processor in associative content addressable memory |
| US12061971B2 (en) | 2019-08-12 | 2024-08-13 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Predictive maintenance of automotive engines |
| US12249189B2 (en) | 2019-08-12 | 2025-03-11 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Predictive maintenance of automotive lighting |
| US11042350B2 (en) | 2019-08-21 | 2021-06-22 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Intelligent audio control in vehicles |
| US12210401B2 (en) | 2019-09-05 | 2025-01-28 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Temperature based optimization of data storage operations |
| US11435946B2 (en) * | 2019-09-05 | 2022-09-06 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Intelligent wear leveling with reduced write-amplification for data storage devices configured on autonomous vehicles |
| US11562205B2 (en) * | 2019-09-19 | 2023-01-24 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Parallel processing of a convolutional layer of a neural network with compute-in-memory array |
| DE112020004469T5 (de) * | 2019-09-20 | 2022-08-04 | Semiconductor Energy Laboratory Co., Ltd. | Halbleitervorrichtung |
| KR102831057B1 (ko) * | 2020-01-20 | 2025-07-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 고대역폭 메모리 및 이를 포함하는 시스템 |
| US11226816B2 (en) | 2020-02-12 | 2022-01-18 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Systems and methods for data placement for in-memory-compute |
| US12159219B2 (en) * | 2020-08-19 | 2024-12-03 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Neuron using posits |
| CN116136835B (zh) * | 2023-04-19 | 2023-07-18 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | 一种三进二出数值获取方法、装置及介质 |
| CN119993237B (zh) * | 2025-04-10 | 2025-08-05 | 北京大学 | 存储模块、存储阵列、存储装置及存内计算编程方法 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015187771A2 (en) * | 2014-06-05 | 2015-12-10 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for performing an exclusive or operation using sensing circuitry |
| CN105703765A (zh) * | 2014-12-16 | 2016-06-22 | 三星电子株式会社 | 基于dram的可重构逻辑 |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5838165A (en) * | 1996-08-21 | 1998-11-17 | Chatter; Mukesh | High performance self modifying on-the-fly alterable logic FPGA, architecture and method |
| EP1537486A1 (de) * | 2002-09-06 | 2005-06-08 | PACT XPP Technologies AG | Rekonfigurierbare sequenzerstruktur |
| US20110026323A1 (en) * | 2009-07-30 | 2011-02-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Gated Diode Memory Cells |
| US8238173B2 (en) * | 2009-07-16 | 2012-08-07 | Zikbit Ltd | Using storage cells to perform computation |
| US8379433B2 (en) * | 2010-09-15 | 2013-02-19 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | 3T DRAM cell with added capacitance on storage node |
| JP6106043B2 (ja) * | 2013-07-25 | 2017-03-29 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体集積回路装置 |
| US8971124B1 (en) * | 2013-08-08 | 2015-03-03 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for performing logical operations using sensing circuitry |
| US9019785B2 (en) * | 2013-09-19 | 2015-04-28 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Data shifting via a number of isolation devices |
| US10420200B2 (en) | 2014-07-28 | 2019-09-17 | Victor Equipment Company | Automated gas cutting system with auxiliary torch |
| US9697877B2 (en) * | 2015-02-05 | 2017-07-04 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Illinois | Compute memory |
-
2017
- 2017-02-06 US US15/426,033 patent/US10242728B2/en active Active
- 2017-05-12 KR KR1020170059482A patent/KR102139213B1/ko active Active
- 2017-09-13 CN CN201710823568.7A patent/CN108008974B/zh active Active
- 2017-09-18 TW TW106131867A patent/TWI714806B/zh active
- 2017-10-17 JP JP2017201264A patent/JP6799520B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015187771A2 (en) * | 2014-06-05 | 2015-12-10 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for performing an exclusive or operation using sensing circuitry |
| CN105703765A (zh) * | 2014-12-16 | 2016-06-22 | 三星电子株式会社 | 基于dram的可重构逻辑 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TWI714806B (zh) | 2021-01-01 |
| US10242728B2 (en) | 2019-03-26 |
| CN108008974A (zh) | 2018-05-08 |
| JP6799520B2 (ja) | 2020-12-16 |
| KR102139213B1 (ko) | 2020-07-29 |
| US20180122456A1 (en) | 2018-05-03 |
| JP2018073402A (ja) | 2018-05-10 |
| KR20180046345A (ko) | 2018-05-08 |
| TW201816592A (zh) | 2018-05-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
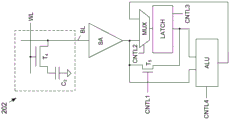
| CN108008974B (zh) | 基于动态随机存取存储器的处理单元架构 | |
| CN108010551B (zh) | 用于dpu运算的软件栈和编程 | |
| CN108022615B (zh) | 动态随机存取存储器处理单元 | |
| Asifuzzaman et al. | A survey on processing-in-memory techniques: Advances and challenges | |
| CN111338601B (zh) | 用于存储器内乘法及累加运算的电路及其方法 | |
| Talati et al. | mmpu—a real processing-in-memory architecture to combat the von neumann bottleneck | |
| CN110222818B (zh) | 一种用于卷积神经网络数据存储的多bank行列交织读写方法 | |
| US20220366968A1 (en) | Sram-based in-memory computing macro using analog computation scheme | |
| TWI861682B (zh) | 用於記憶體內運算之加速器架構之二維網格 | |
| US20230385624A1 (en) | Computing in memory with artificial neurons | |
| Gauchi | Exploration of reconfigurable tiles of computing-in-memory architecture for data-intensive applications | |
| Sim et al. | Mapim: Mat parallelism for high performance processing in non-volatile memory architecture | |
| US20240329930A1 (en) | Heterogeneous multi-functional reconfigurable processing-in-memory architecture | |
| Ogbogu et al. | Heterogeneous Manycore In-Memory Computing Architectures | |
| Nag | Enabling Near Data Processing for Emerging Workloads | |
| WO2025085124A2 (en) | Systolic ai processor compiler | |
| CN119312855A (zh) | 一种基于eDRAM存内计算的神经网络加速器及其控制方法 | |
| Kim et al. | DRAM-Based Processing-in-Memory |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |