CN107055754B - Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage - Google Patents
Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN107055754B CN107055754B CN201710055117.3A CN201710055117A CN107055754B CN 107055754 B CN107055754 B CN 107055754B CN 201710055117 A CN201710055117 A CN 201710055117A CN 107055754 B CN107055754 B CN 107055754B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- zero
- valent iron
- sewage
- biological filter
- tank
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 136
- 239000010865 sewage Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 99
- 238000005728 strengthening Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 35
- 239000003673 groundwater Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000003621 irrigation water Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 53
- 239000010802 sludge Substances 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000003344 environmental pollutant Substances 0.000 claims description 14
- 244000005700 microbiome Species 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 13
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 231100000719 pollutant Toxicity 0.000 claims description 11
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910021536 Zeolite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 239000010457 zeolite Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010902 straw Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000571 coke Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000005189 flocculation Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000016615 flocculation Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- -1 pebbles Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002893 slag Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000002023 wood Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000813 microbial effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000005265 energy consumption Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000005416 organic matter Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007667 floating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 1
- 240000007594 Oryza sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000007164 Oryza sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006065 biodegradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011449 brick Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035425 carbon utilization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008239 natural water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002203 pretreatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004886 process control Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005067 remediation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000009566 rice Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003442 weekly effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/02—Aerobic processes
- C02F3/06—Aerobic processes using submerged filters
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/28—Anaerobic digestion processes
- C02F3/2826—Anaerobic digestion processes using anaerobic filters
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F3/00—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F3/30—Aerobic and anaerobic processes
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02W—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO WASTEWATER TREATMENT OR WASTE MANAGEMENT
- Y02W10/00—Technologies for wastewater treatment
- Y02W10/10—Biological treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Biodiversity & Conservation Biology (AREA)
- Hydrology & Water Resources (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Water Supply & Treatment (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Biological Treatment Of Waste Water (AREA)
Abstract
本发明公开了一种强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池,其结构是在地下设置多个污水处置单元;通过输水管道系统将农村生活污水收集至污水处置单元内进行循环和强化处理,处理后的生活污水用作农业灌溉用水或者补充地下水或者直接排放进入河道;所述的污水处置单元包括:预处理池,循环池以及零价铁生物滤池三部分,各处理单元构筑物相互独立,彼此间通过管道进行连通。优点:低维护,低能耗,抗水质水量冲击,污水处理效率高;仅通过一台泵耦合了集约和生态两种技术路线的各自优势,自如的应对农村地区复杂的排水情况,保证了出水水质的稳定;同时节省地表土地资源,简单适用,运行管理方便,造价低廉。
The invention discloses a circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for strengthening the treatment of rural domestic sewage. Its structure is that a plurality of sewage disposal units are arranged underground; Intensified treatment, the treated domestic sewage is used as agricultural irrigation water or supplements groundwater or is directly discharged into the river; the sewage treatment unit includes: pretreatment tank, circulation tank and zero-valent iron biological filter three parts, each treatment unit structure They are independent of each other and communicate with each other through pipes. Advantages: low maintenance, low energy consumption, resistance to water quality and quantity impact, and high sewage treatment efficiency; only one pump couples the respective advantages of the two technical routes of intensive and ecological, which can easily cope with the complex drainage situation in rural areas and ensure the quality of the effluent. At the same time, it saves surface land resources, is simple and applicable, easy to operate and manage, and low cost.
Description
技术领域technical field
本发明涉及的是一种强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池,可直接应用到农村生活污水或者村镇小型生活污水处理,同时也可用于农村面源污染物的降解和水质净化。属于环保污水处理领域。The invention relates to a circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for strengthening the treatment of rural domestic sewage, which can be directly applied to the treatment of rural domestic sewage or small-scale domestic sewage in villages and towns, and can also be used for the degradation of rural non-point source pollutants and water quality purification. It belongs to the field of environmental protection sewage treatment.
背景技术Background technique
农村污水由于地区分散,人口数量较大,收集难等原因造成农村污水成为河湖水体污染的重要污染源,也是农村面源污染的重要组成部分;农村污水中含有大量的有机物和氮、磷等有机盐类,未经处理的农村生活污水直接排放进入自然水体,不仅影响了作物产量,而且对生态环境和河湖水质带来严重危害。因此,农村生活污水的治理十分迫切,并且意义重大。Due to scattered areas, large population, and difficulty in collection, rural sewage has become an important source of pollution of rivers and lakes, as well as an important part of rural non-point source pollution; rural sewage contains a large amount of organic matter and nitrogen, phosphorus and other organic matter. Salt and untreated rural domestic sewage are directly discharged into natural water bodies, which not only affects crop yields, but also brings serious harm to the ecological environment and water quality of rivers and lakes. Therefore, the treatment of rural domestic sewage is very urgent and of great significance.
生活污水的处理模式包括集中处理与分散式处理模式;集中处理技术和工艺已经非常成熟,以城镇污水处理厂为主,其日常运行都可以达到较为稳定的处理效能;而农村一般处于偏远地区,污水收集管网难以覆盖,因此,农村污水一般采用分散式处理模式;国外对于农村生活污水采用的主流技术包括:生物接触氧化法,SBR活性污泥法以及膜生物反应器等;这些工艺,技术要求较高,工艺控制难度大,运行成本较高,不适于我国农村污水的处理模式;目前,我国农村污水采用的技术主要包括将污水厂工艺小型化的生物处理技术、以人工湿地为核心的生态处理技术以及两者相结合的耦合处理技术。同样,这些工艺也存在一些问题,比如污水处理厂工艺小型化单位能耗较高,农村地区缺少技术人员;人工湿地占地面积大,处理效果不稳定;并且我国农村水量水质变化大,高峰排水会短时间内对处理设施造成水量水质的冲击。另外,我国农村生活污水中氮、磷浓度相对较高,一般的处理工艺对总氮的去除效果不佳。如公开号为CN104098223B公开了一种农村分散式生活污水处理系统及方法,将“生物”与“生态”相耦合,集生态浮岛和人工湿地等技术之优势,创造性的提出了生态浮岛—人工湿地技术组合新工艺,充分利用水生植物的修复作用,无需占地、成本低廉且处理效果好,将污水有控制地投配到填料经常处于饱和状态填料中,污水沿一定方向流动的过程中,在填料的物理、化学协同作用下,污水中有机物通过过滤、吸附、吸收作用,促进兼性微生物分解来实现对污水的高效净化。但由于缺少碳源的供给和厌氧环境的营造,该系统反硝化能力较弱,并且出水效果不稳定。就目前来看,投入实际应用的农村生活污水处理系统尚存在一定的局限性。The treatment mode of domestic sewage includes centralized treatment and decentralized treatment mode; the centralized treatment technology and process are very mature, mainly urban sewage treatment plants, and their daily operation can achieve relatively stable treatment efficiency; while rural areas are generally located in remote areas, The sewage collection pipe network is difficult to cover. Therefore, the rural sewage generally adopts the decentralized treatment mode; the mainstream technologies used for rural domestic sewage abroad include: biological contact oxidation method, SBR activated sludge method and membrane bioreactor, etc.; these processes, technologies The requirements are high, the process control is difficult, and the operation cost is high, which is not suitable for the treatment mode of rural sewage in my country. At present, the technologies adopted for rural sewage in my country mainly include biological treatment technology that miniaturizes the process of sewage treatment plants, and artificial wetlands as the core. Ecological treatment technology and coupled treatment technology that combines the two. Similarly, these processes also have some problems, such as the high energy consumption per unit of the miniaturization of the sewage treatment plant process, and the lack of technical personnel in rural areas; the artificial wetland covers a large area, and the treatment effect is unstable; It will cause an impact on the water quality and quality of the treatment facilities in a short time. In addition, the concentration of nitrogen and phosphorus in rural domestic sewage in my country is relatively high, and the general treatment process is not effective in removing total nitrogen. For example, the publication number CN104098223B discloses a rural decentralized domestic sewage treatment system and method, which couples "biology" and "ecology", integrates the advantages of technologies such as ecological floating islands and artificial wetlands, and creatively proposes ecological floating islands— Constructed wetland technology combines new technology, makes full use of the remediation effect of aquatic plants, does not require land occupation, has low cost and good treatment effect, and controls the dosing of sewage into the filler that is often saturated, and the sewage flows in a certain direction. , Under the physical and chemical synergy of the filler, the organic matter in the sewage can effectively purify the sewage through filtration, adsorption and absorption, and promote the decomposition of facultative microorganisms. However, due to the lack of carbon source supply and the creation of anaerobic environment, the denitrification capacity of the system is weak, and the effluent effect is unstable. At present, the rural domestic sewage treatment system that has been put into practical application still has certain limitations.
本发明总结我国已有农村生活污水处理技术中的不足,充分考虑我国农村污水处理的需求和特点,创新性的提出了低维护,低能耗,抗水质水量冲击,并且出水效果稳定的耦合集约与水质强化处理的循环零价铁生物滤池技术。The invention summarizes the deficiencies in the existing rural domestic sewage treatment technology in China, fully considers the needs and characteristics of rural sewage treatment in my country, and innovatively proposes low maintenance, low energy consumption, resistance to water quality and water impact, and stable effluent effect. Coupling intensive and Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter technology for enhanced water quality treatment.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明提出的是一种强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池,其目的旨在克服现有农村生活污水处理技术中存在的不足,具有低维护,低能耗,抗水质水量冲击,污水处理效率高,出水水质稳定,同时简单适用,运行管理方便,造价低廉等特点,并可广泛应用于农村生活污水集约与强化处理的循环零价铁生物滤池。The invention proposes a circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for strengthening the treatment of rural domestic sewage. It has the characteristics of high sewage treatment efficiency, stable effluent quality, simple application, convenient operation and management, and low cost. It can be widely used in the circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for intensive and intensive treatment of rural domestic sewage.
本发明的技术解决方案:一种强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池,其特征在于:在地下设置多个污水处置单元;通过输水管道系统将农村生活污水收集至污水处置单元内进行循环和强化处理,处理后的生活污水用作农业灌溉用水或者补充地下水或者直接排放进入河道;所述的污水处置单元包括:预处理池,循环池以及零价铁生物滤池三部分,三部分依次相接;多个污水处置单元构筑物相互独立,彼此间通过管道进行连通;所述的零价铁生物滤池分为普通生物滤池和内置零价铁强化反应池两部分。The technical solution of the present invention: a circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for strengthening the treatment of rural domestic sewage, which is characterized in that: a plurality of sewage disposal units are arranged underground; rural domestic sewage is collected to the sewage disposal unit through a water pipeline system Circulation and intensive treatment are carried out inside the treated domestic sewage, and the treated domestic sewage is used as agricultural irrigation water or supplementary groundwater or directly discharged into the river; the sewage treatment unit includes: a pretreatment tank, a circulation tank and a zero-valent iron biological filter. The three parts are connected in sequence; multiple sewage treatment unit structures are independent of each other, and communicate with each other through pipelines; the zero-valent iron biological filter is divided into two parts: ordinary biological filter and built-in zero-valent iron enhanced reaction tank.
本发明的优点:Advantages of the present invention:
(1)仅通过一台泵耦合了集约和生态两种技术路线的各自优势,自如的应对农村地区复杂的排水情况,保证了出水水质的稳定;(1) Only one pump couples the respective advantages of the two technical routes of intensive and ecological, which can cope with the complex drainage situation in rural areas freely, and ensure the stability of the effluent quality;
(2)构建形成不同深度的好氧-缺氧-厌氧条件,利于总氮的去除,在厌氧区零价铁反应箱内,可以外加利用水稻秸秆或者木屑作为固体碳源,增强异养反硝化性能的微生物生长,最终形成零价铁/微生物耦合系统,强化了NO3 -的去除,同时生成的Fe3+/Fe2+有着良好的絮凝性能,强化了厌氧释放出来的磷的去除;(2) Construct aerobic-anoxic-anaerobic conditions of different depths, which are beneficial to the removal of total nitrogen. In the zero-valent iron reaction box in the anaerobic zone, rice straw or wood chips can be used as a solid carbon source to enhance heterotrophy. The growth of microorganisms with denitrification performance finally forms a zero-valent iron/microbial coupling system, which strengthens the removal of NO 3 - , and the generated Fe 3+ /Fe 2+ has good flocculation performance, which strengthens the anaerobic release of phosphorus. remove;
(3)零价铁反应箱上方设置沸石层,保障了出水水质,也为下层创造厌氧环境,延长了零价铁的使用寿命;(3) The zeolite layer is set above the zero-valent iron reaction box, which ensures the water quality of the effluent, creates an anaerobic environment for the lower layer, and prolongs the service life of the zero-valent iron;
(4)整个循环生物滤池低维护,低能耗,抗水质水量冲击,污水处理效率高;(4) The entire circulating biological filter has low maintenance, low energy consumption, resistance to water quality and water impact, and high sewage treatment efficiency;
(5)处理构筑物埋于地下,节省地面资源,在处置单元顶部铺设植生砖,营造良好的生态环境;(5) The treatment structure is buried underground to save ground resources, and planted bricks are laid on the top of the disposal unit to create a good ecological environment;
(6)零价铁反应箱容易检查更换,便于管理与维护;(6) The zero-valent iron reaction box is easy to check and replace, which is convenient for management and maintenance;
(7)整个工程材料价格低廉、易于获取且不会对环境产生二次污染;(7) The whole project materials are cheap, easy to obtain and will not cause secondary pollution to the environment;
(8)整个工程构造简单、施工方便、功能稳定、造价低廉、使用方便。(8) The whole project is simple in structure, convenient in construction, stable in function, low in cost and easy to use.
附图说明Description of drawings
附图1 是强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池示意图。Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for intensive treatment of rural domestic sewage.
附图2 是强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池平面示意图。Figure 2 is a schematic plan view of a circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for intensive treatment of rural domestic sewage.
附图3 是零价铁反应箱示意图。Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a zero-valent iron reaction box.
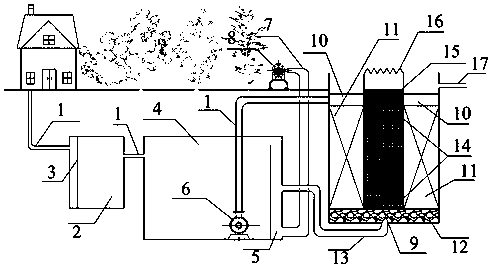
图中的1是输水管道、2是预处理池、3是10~40mm中格栅、4是循环池、5是污泥收集槽、6是循环溶气泵、7是排泥管、8是排泥泵、9是零价铁生物滤池、10是布水区、11是生物填料(碎石,卵石、炉渣或者焦炭中的一种)、12是卵石承托层、13是回流管道、14是零价铁反应箱、15是沸石填料、16是溢流板、17是排水管道、18是φ15的钢筋骨架、19是钢丝网面、20是零价铁填料(由海绵铁、铁刨花和废铁屑三种中的一种或者多种组合而成)、21是木屑(秸秆)、22是圆环挂钩。1 is the water pipeline, 2 is the pretreatment tank, 3 is the 10-40mm middle grid, 4 is the circulation tank, 5 is the sludge collection tank, 6 is the circulating dissolved air pump, 7 is the sludge discharge pipe, and 8 is the Sludge pump, 9 is zero-valent iron biological filter, 10 is water distribution area, 11 is biological filler (one of crushed stone, pebble, slag or coke), 12 is pebble support layer, 13 is return pipeline, 14 is zero-valent iron reaction box, 15 is zeolite filler, 16 is overflow plate, 17 is drainage pipe, 18 is steel frame of φ15, 19 is steel mesh surface, 20 is zero-valent iron filler (made of sponge iron, iron shavings) 21 is wood chips (straw), 22 is a ring hook.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
一种强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池,其结构是在地下设置多个污水处置单元;通过输水管道系统将农村生活污水收集至污水处置单元内进行循环和强化处理,处理后的生活污水用作农业灌溉用水或者补充地下水或者直接排放进入河道;所述的污水处置单元包括:预处理池,循环池以及零价铁生物滤池三部分,各处理单元构筑物相互独立,彼此间通过管道进行连通;所述的零价铁生物滤池分为普通生物滤池和内置零价铁强化反应池两部分。A circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for strengthening the treatment of rural domestic sewage, the structure of which is that a plurality of sewage disposal units are arranged underground; The latter domestic sewage is used as agricultural irrigation water or supplements groundwater or is directly discharged into the river; the sewage treatment unit includes three parts: a pretreatment tank, a circulation tank and a zero-valent iron biological filter, and the structures of each treatment unit are independent from each other. The said zero-valent iron biological filter is divided into two parts: ordinary biological filter and built-in zero-valent iron enhanced reaction tank.
所述多个污水处置单元是通过全埋式或者半埋式在地下设置。The plurality of sewage treatment units are arranged underground in a fully-buried or semi-buried type.
所述预处理池主要去除原污水中的悬浮物等能够堵塞滤料的污染物,并使水质均化;预处理池内置中格栅,拦截较大的生活垃圾和杂质。The pretreatment tank mainly removes the suspended solids in the raw sewage and other pollutants that can block the filter material, and homogenizes the water quality; the pretreatment tank has a built-in grille to intercept larger domestic garbage and impurities.
所述循环池内置一台循环溶气泵,进行污水循环和富氧;仅通过一台泵耦合了集约和生态两种技术路线的各自优势,自如的应对农村地区复杂的排水情况,保证了出水水质的稳定;同时溶气泵自带富氧功能,为普通生物滤池提供了好氧条件;在循环池内靠近零价铁生物滤池的侧壁设置污泥收集槽和排泥管;污泥收集槽主要用于富集和浓缩经回流管排出的脱落以及老化的生物膜,同时上层的清液回流进入循环池;在循环池的侧壁靠近收集槽的底部设置排泥管,通过排泥泵排出浓缩后的污泥。The circulating pool has a built-in circulating dissolved air pump for sewage circulation and oxygen enrichment; only one pump couples the respective advantages of the two technical routes of intensive and ecological, which can freely cope with the complex drainage situation in rural areas and ensure the quality of the effluent. At the same time, the dissolved air pump has its own oxygen-enriching function, which provides aerobic conditions for ordinary biological filters; a sludge collection tank and a sludge discharge pipe are set in the circulation tank near the side wall of the zero-valent iron biological filter; the sludge collection tank It is mainly used for enriching and concentrating the fallen off and aging biofilms discharged through the return pipe, and at the same time, the supernatant from the upper layer flows back into the circulation tank; a sludge discharge pipe is set on the side wall of the circulation tank near the bottom of the collection tank, and the sludge is discharged through the sludge discharge pump. Concentrated sludge.
所述零价铁生物滤池,外形为近圆形,圆形的设计可以消除“死角”;最外层的墙体经过防渗处理;中间是普通生物滤料池,内层是零价铁反应池;零价铁生物滤池的进出水方式为“周进中出”,污水通过输水管道进入布水区,经过布水器均匀喷洒分别进入普通生物填料池和零价铁强化反应池;普通生物滤料池的构建为:上层设置工作层,工作层的填料可为当地易于获取的碎石、卵石、炉渣或者焦炭中的一种,粒径为25~40mm,工作层的厚度为1.5~1.8m;下层设置承托层,粒径为70~100mm质地坚硬的卵石,承托层的厚度为0.2m。普通生物滤料池中填料表面附着生长了大量微生物,形成生物膜系统,对污水中的污染物起到生物降解的作用;并且由于溶解氧在污染物的生物降解过程中不断被消耗,从上至下逐渐形成好氧区和缺氧区。内圈为零价铁强化反应池,底部也为0.2m厚度的承托层;承托层的底部中心设置回流管道,回流管道的另一端与循环池相连,将回流的污水和脱落的生物膜排入到污泥收集槽内,另外,回流管设置零价铁反应区之前的好处在于可以保证进入厌氧零价铁反应区NO3 -的浓度;承托层上部依次装填数量不等的可移动式零价铁反应箱,零价铁反应箱为圆柱形,以φ15的钢筋作为支撑骨架,其直径等于零价铁强化反应池的内径,高度约为30cm,零价铁反应箱设置为可开启式,并且在上表面中心的位置设置圆环挂钩,以便检查更换;零价铁反应箱内填料由海绵铁、铁刨花和废铁屑三种中的一种或者多种组合而成,同时外加10%体积的木屑或者秸秆。零价铁反应箱是整个系统的核心区,其对污水中的污染物起到强化去除的作用,特别是氮、磷;零价铁反应箱处于整个生物滤池的厌氧区,外加碳源,有利于反硝化微生物的生长,在零价铁反应箱内微生物附着在铁质载体上形成了零价铁/微生物耦合系统,强化了NO3 -的去除,同时生成的Fe3+/Fe2+有着良好的絮凝性能,强化了厌氧释放出来的磷的去除;零价铁反应箱上层铺设沸石吸附出水中的微污染物,保障了出水水质,同时也为下层的零价铁反应箱创造了厌氧环境;零价铁反应池的出水采用溢流的形式。The zero-valent iron biological filter has a nearly circular shape, and the circular design can eliminate "dead corners"; the outermost wall is treated with anti-seepage; the middle is a common biological filter, and the inner layer is zero-valent iron Reaction tank; the water inlet and outlet of the zero-valent iron biological filter is "weekly in and out", the sewage enters the water distribution area through the water pipeline, and is evenly sprayed by the water distributor into the ordinary biological filler tank and the zero-valent iron enhanced reaction tank; ordinary The construction of the biological filter material tank is as follows: the upper layer is provided with a working layer, and the filler of the working layer can be one of crushed stone, pebbles, slag or coke that is easily obtained locally, with a particle size of 25~40mm, and the thickness of the working layer is 1.5~ 1.8m; the lower layer is provided with a supporting layer, the particle size is 70~100mm hard pebble, and the thickness of the supporting layer is 0.2m. A large number of microorganisms are attached to the surface of the filler in the ordinary biological filter tank, forming a biofilm system, which plays a role in biodegrading the pollutants in the sewage; and because the dissolved oxygen is continuously consumed in the biodegradation process of the pollutants, from the top Aerobic zone and anoxic zone are gradually formed to the bottom. The inner ring is a zero-valent iron-enhanced reaction pool, and the bottom is also a 0.2m-thick supporting layer; a return pipe is set in the center of the bottom of the supporting layer, and the other end of the return pipe is connected to the circulation tank to connect the returned sewage and the falling biofilm. It is discharged into the sludge collection tank. In addition, the advantage of setting the zero-valent iron reaction zone in the return pipe is that the concentration of NO 3 - in the anaerobic zero-valent iron reaction zone can be guaranteed; Mobile zero-valent iron reaction box, the zero-valent iron reaction box is cylindrical, with φ15 steel bar as the support frame, its diameter is equal to the inner diameter of the zero-valent iron-enhanced reaction pool, and the height is about 30cm. The zero-valent iron reaction box is set to be openable A ring hook is set at the center of the upper surface for inspection and replacement; the filler in the zero-valent iron reaction box is composed of one or more of sponge iron, iron shavings and scrap iron filings. 10% by volume sawdust or straw. The zero-valent iron reaction box is the core area of the whole system, which can strengthen the removal of pollutants in the sewage, especially nitrogen and phosphorus; the zero-valent iron reaction box is located in the anaerobic area of the entire biological filter, plus a carbon source , which is beneficial to the growth of denitrifying microorganisms. In the zero-valent iron reaction box, the microorganisms adhere to the iron carrier to form a zero-valent iron/microorganism coupling system, which strengthens the removal of NO 3 - and generates Fe 3+ /Fe 2 + has good flocculation performance, which strengthens the removal of phosphorus released by anaerobicity; the upper layer of the zero-valent iron reaction box is laid with zeolite to adsorb micro-pollutants in the effluent, which ensures the quality of the effluent, and also creates a new zero-valent iron reaction box for the lower layer. The anaerobic environment is adopted; the effluent of the zero-valent iron reaction tank is in the form of overflow.
下面结合附图进一步描述本发明的技术解决方案:The technical solutions of the present invention are further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings:
如附图1,附图2和附图3所示,在农村分散用户污水产生处铺设输水管道1用以收集农村生活污水;采用全埋或者半埋式在地下依次挖设预处理池2,循环池4和零价铁生物滤池9;预处理池2内部设置10~40mm的中格栅3;预处理池3的一侧通过输水管道1与循环池4连通;在循环池4内靠近零价铁生物滤池9的侧壁设置污泥收集槽5和排泥管7;污泥收集槽5内浓缩后的污泥通过排泥泵8排出;循环池内置一台循环溶气泵6(自带富氧功能),通过输水管道将循环池内的污水提升至零价铁生物滤池9;零价铁生物滤池9分为最外层的墙体,中间层的普通生物滤料池和内层的零价铁反应池,普通生物滤料池和零价铁反应池之间是经过防渗处理的墙体;输水管道的污水经过布水区10均匀撒布至中间层的普通生物滤料池的生物填料11表面;填料层11的设计高度约为1.5~1.8m,填料粒径为25~40mm,所选填料(碎石,卵石、炉渣或者焦炭中的一种)质地应均匀一致,并且就地取材,便与加工和运输;填料层11下方铺设0.2m的卵石承托层12,卵石承托层12的填料粒径介于70~100mm;承托层12的底部中心设置回流管道13,回流管道的另一端与循环池4中的污泥收集槽5相连;内层的零价铁反应池的构建是通过装填5~6个高度约为0.3m的零价铁反应箱14,零价铁反应箱14为圆柱形,以φ15的钢筋作为支撑骨架18,以钢丝网面19作为外表面,钢丝网面的孔径略小于铁质填料的粒径;零价铁反应箱的圆面直径等于零价铁反应池的内径,零价铁反应箱14内填料由零价铁填料20(海绵铁、铁刨花和废铁屑三种中的一种或者多种组合而成)和外加10%体积的木屑(秸秆)21组成;零价铁反应箱设置为可开启式,并且在上表面中心的位置设置圆环挂钩22,便于提携和检查更换;零价铁反应箱14的上层铺设0.3m的沸石填料15,零价铁反应池的出水口设置溢流板16;溢流出水通过排水管道17进行回收利用或者直接排放。在构筑物的上方可以种植花草和树木,营造良好的生态环境。As shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2 and Fig. 3,
一种强化处理农村生活污水的循环零价铁生物滤池,其处理污水的方法,包括如下步骤:A circulating zero-valent iron biological filter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage, and a method for treating sewage, comprising the following steps:
1)预处理池:农村散户排放的生活污水通过输水管道1进行收集并排入预处理池2,预处理池2内部设置10~40mm的中格栅3,用以拦截较大的生活垃圾和杂质;同时污水在预处理池内进行短暂停留,主要去除原污水中的悬浮物等能够堵塞滤料的污染物,并使水质均化;1) Pretreatment tank: The domestic sewage discharged by rural retail households is collected through the
2)循环池:经预处理池2均化后的污水,经过输水管道1进入循环池4;循环池4内置一台循环溶气泵6,进行污水循环和富氧,仅通过一台泵耦合了集约和生态两种技术路线的各自优势,自如的应对农村地区复杂的排水情况,保证了出水水质的稳定;同时溶气泵6自带富氧功能,为普通生物滤池提供好氧条件。在循环池近零价铁生物滤池9的侧壁设置污泥收集槽5,用于接受零价铁生物滤池的回流污水以及老化脱落的生物膜;浓缩后的生物膜通过排泥管7经由排泥泵8排出;2) Circulation pool: The sewage homogenized by the
3)零价铁生物滤池:循环池4的污水通过溶气泵6输送至零价铁生物滤池的上布水区10,通过布水器均匀向生物填料11上表面撒布污水,生物滤料池填料表面附着大量微生物,形成生物膜系统,对污水中的污染物起到生物降解的作用;由于进入生物滤料池的是富氧污水,滤料上层附着的主要为好氧微生物,而在污染物的微生物降解过程中需要消耗水中的溶解氧,从上至下污水中溶解氧逐渐减少,形成了下层的缺氧区;经过生物滤池处理后的污水通过承托层12进入中间的厌氧零价铁反应箱14;好氧-缺氧-厌氧的条件,利于总氮的去除,厌氧区的零价铁和微生物形成零价铁/微生物耦合系统,强化了NO3 -的去除,同时生成的Fe3+/Fe2+有着良好的絮凝性能,强化了厌氧释放出来的磷的去除;在零价铁反应区的上层布设沸石层15,吸附出水中的微污染物,保障了出水水质;在承托层12的底部中心处设有回流管13,用于回流污水和脱落的生物膜,回流管设置零价铁反应区之前的好处在于可以保证进入厌氧零价铁反应区NO3 -的浓度。3) Zero-valent iron biological filter: The sewage in the
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710055117.3A CN107055754B (en) | 2017-01-24 | 2017-01-24 | Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710055117.3A CN107055754B (en) | 2017-01-24 | 2017-01-24 | Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN107055754A CN107055754A (en) | 2017-08-18 |
| CN107055754B true CN107055754B (en) | 2020-09-01 |
Family
ID=59598130
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710055117.3A Active CN107055754B (en) | 2017-01-24 | 2017-01-24 | Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN107055754B (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN107973487B (en) * | 2017-11-14 | 2021-03-02 | 东华大学 | A kind of dyeing and finishing wastewater level treatment process and device |
| CN108059249B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2020-02-18 | 桂林理工大学 | A method for purifying sewage in artificial wetlands with externally generated electricity and internal converging water flow |
| CN108163982B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2019-11-26 | 桂林理工大学 | A kind of inner guide type bacterium algae one microbiological fuel cell ecological water body purification system |
| CN108191063B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2019-11-26 | 桂林理工大学 | A kind of week conduction bacterium algae one microbiological fuel cell ecological water body purification system |
| CN108059248B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2019-11-26 | 桂林理工大学 | A kind of inner guide type bacterium algae one microbiological fuel cell ecological water body purification method |
| CN108046411B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2020-02-18 | 桂林理工大学 | A sewage purification system for artificial wetlands with internal power generation and eversion type water flow |
| CN108147537B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2020-02-18 | 桂林理工大学 | A method for purifying sewage in artificial wetland with internal power generation and eversion type water flow |
| CN108217941B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2020-02-18 | 桂林理工大学 | A sewage purification system for artificial wetlands with external power generation and internal confluence type water flow |
| CN108046412B (en) * | 2018-01-05 | 2019-11-26 | 桂林理工大学 | A kind of week conduction bacterium algae one microbiological fuel cell ecological water body purification method |
| CN110357367A (en) * | 2019-08-15 | 2019-10-22 | 沈阳环境科学研究院 | Based on low-intensity magnetic field-sewage water denitrification dephosphorization apparatus associated with Zero-valent Iron-MABR |
| CN110759595B (en) * | 2019-11-07 | 2020-08-04 | 生态环境部环境规划院 | Repair system for underground water with composite pollution of ammonia nitrogen and inorganic phosphorus |
| CN113248082A (en) * | 2021-05-28 | 2021-08-13 | 浙江问源环保科技股份有限公司 | Device for promoting, transforming and strengthening phosphorus removal of rural domestic sewage by using iron shavings |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050016928A1 (en) * | 1999-08-06 | 2005-01-27 | Trustees Of Stevens Institute Of Technology | Apparatus and method for water treatment by a direct co-precipitation/filtration process |
| CN201648104U (en) * | 2010-01-15 | 2010-11-24 | 北京工业大学 | A sleeve filter device for sewage reuse |
| WO2016085754A1 (en) * | 2014-11-26 | 2016-06-02 | Atlanta Gold Corporation | System and method for treating contaminated wastewater |
| CN104817173A (en) * | 2015-03-27 | 2015-08-05 | 杭州师范大学 | Two-stage double-flow autotrophic denitrification biofilter |
| CN104773929B (en) * | 2015-05-04 | 2016-06-08 | 河海大学 | Zero-valent iron/microorganism composite filtration wall purification system for domestic sewage in irrigation areas |
| CN105347465B (en) * | 2015-12-12 | 2017-09-12 | 刘微 | The intensive aeration of modified form and vein formula biofilter |
| CN105439395A (en) * | 2016-01-04 | 2016-03-30 | 大唐国际化工技术研究院有限公司 | Zero-discharge treatment method of salt-containing organic wastewater |
-
2017
- 2017-01-24 CN CN201710055117.3A patent/CN107055754B/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107055754A (en) | 2017-08-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107055754B (en) | Circulating zero-valent iron biofilter for strengthening treatment of rural domestic sewage | |
| CN101973637B (en) | River channel purification system for processing rural domestic sewage | |
| CN107540094B (en) | Constructed wetland sewage treatment system | |
| CN105906159B (en) | A kind of double coupled systems for the processing of irrigated area reinforced sewage | |
| CN104773929B (en) | Zero-valent iron/microorganism composite filtration wall purification system for domestic sewage in irrigation areas | |
| CN201372233Y (en) | Unpowered Integrated Constructed Wetland Sewage Treatment System | |
| CN105084650B (en) | Micro- aeration cycle integrated sewage water biological and ecological processing system and method | |
| CN107352738B (en) | A composite artificial ecological bed sewage treatment system and method for strengthening nitrogen and phosphorus removal | |
| CN206308212U (en) | A kind of unpowered rural sewage treatment unit | |
| CN101973679B (en) | Distributed sewage treatment and regeneration technology | |
| CN102976548A (en) | Zero emission district sewage resource treatment apparatus | |
| CN111484206A (en) | Simulate natural environment biological sewage treatment system | |
| CN211644786U (en) | Biochemical wetland ecological purification system for new rural domestic sewage | |
| CN200974793Y (en) | Sewage composite artificial marshland ecological treatment system | |
| CN203212433U (en) | Rural sewage treatment system | |
| CN102701448A (en) | Rural domestic sewage reutilization treatment device | |
| CN104355490B (en) | The removal device of pollution substance and minimizing technology in a kind of domestic sewage in rural areas | |
| CN101585607B (en) | Preparation method for substrate of vertical-flow constructed wetlands | |
| CN112939381A (en) | Multi-efficiency combined biological filter | |
| CN206033519U (en) | Rural domestic sewage of solar energy drips and strains processing system | |
| CN203021402U (en) | Internal carbon sourced-oxygen enriched cascade-combination constructed wetland engineering reactor | |
| CN215049509U (en) | Multi-efficiency combined biological filter | |
| CN214142004U (en) | Treatment system of decentralized sewage | |
| CN114524589A (en) | Ecological low-energy-consumption high-efficiency laminated percolation sewage treatment system and method | |
| CN211255623U (en) | Distributed rural domestic sewage treatment system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |