CN1011739B - 用于光纤传输系统的光学元件 - Google Patents
用于光纤传输系统的光学元件Info
- Publication number
- CN1011739B CN1011739B CN89101841A CN89101841A CN1011739B CN 1011739 B CN1011739 B CN 1011739B CN 89101841 A CN89101841 A CN 89101841A CN 89101841 A CN89101841 A CN 89101841A CN 1011739 B CN1011739 B CN 1011739B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- optical element
- guide
- optical
- adjustable plate
- plate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired
Links
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 74
- 239000013307 optical fiber Substances 0.000 title claims description 23
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 title abstract description 12
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000012780 transparent material Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000012634 optical imaging Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037361 pathway Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009738 saturating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B10/00—Transmission systems employing electromagnetic waves other than radio-waves, e.g. infrared, visible or ultraviolet light, or employing corpuscular radiation, e.g. quantum communication
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/35—Optical coupling means having switching means
- G02B6/3564—Mechanical details of the actuation mechanism associated with the moving element or mounting mechanism details
- G02B6/3568—Mechanical details of the actuation mechanism associated with the moving element or mounting mechanism details characterised by the actuating force
- G02B6/357—Electrostatic force
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B26/00—Optical devices or arrangements for the control of light using movable or deformable optical elements
- G02B26/02—Optical devices or arrangements for the control of light using movable or deformable optical elements for controlling the intensity of light
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B26/00—Optical devices or arrangements for the control of light using movable or deformable optical elements
- G02B26/08—Optical devices or arrangements for the control of light using movable or deformable optical elements for controlling the direction of light
- G02B26/0875—Optical devices or arrangements for the control of light using movable or deformable optical elements for controlling the direction of light by means of one or more refracting elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/264—Optical coupling means with optical elements between opposed fibre ends which perform a function other than beam splitting
- G02B6/266—Optical coupling means with optical elements between opposed fibre ends which perform a function other than beam splitting the optical element being an attenuator
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/28—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals
- G02B6/293—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means
- G02B6/29346—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means operating by wave or beam interference
- G02B6/29361—Interference filters, e.g. multilayer coatings, thin film filters, dichroic splitters or mirrors based on multilayers, WDM filters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/28—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals
- G02B6/293—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means
- G02B6/29379—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means characterised by the function or use of the complete device
- G02B6/29389—Bandpass filtering, e.g. 1x1 device rejecting or passing certain wavelengths
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/28—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals
- G02B6/293—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means
- G02B6/29379—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means characterised by the function or use of the complete device
- G02B6/29395—Optical coupling means having data bus means, i.e. plural waveguides interconnected and providing an inherently bidirectional system by mixing and splitting signals with wavelength selective means characterised by the function or use of the complete device configurable, e.g. tunable or reconfigurable
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/35—Optical coupling means having switching means
- G02B6/351—Optical coupling means having switching means involving stationary waveguides with moving interposed optical elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/35—Optical coupling means having switching means
- G02B6/351—Optical coupling means having switching means involving stationary waveguides with moving interposed optical elements
- G02B6/3532—Optical coupling means having switching means involving stationary waveguides with moving interposed optical elements the optical element being a wavelength independent filter or having spatially dependent transmission properties, e.g. neutral filter or neutral density wedge substrate with plurality of density filters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/35—Optical coupling means having switching means
- G02B6/354—Switching arrangements, i.e. number of input/output ports and interconnection types
- G02B6/3544—2D constellations, i.e. with switching elements and switched beams located in a plane
- G02B6/3548—1xN switch, i.e. one input and a selectable single output of N possible outputs
- G02B6/355—1x2 switch, i.e. one input and a selectable single output of two possible outputs
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B6/00—Light guides; Structural details of arrangements comprising light guides and other optical elements, e.g. couplings
- G02B6/24—Coupling light guides
- G02B6/26—Optical coupling means
- G02B6/35—Optical coupling means having switching means
- G02B6/354—Switching arrangements, i.e. number of input/output ports and interconnection types
- G02B6/3544—2D constellations, i.e. with switching elements and switched beams located in a plane
- G02B6/3548—1xN switch, i.e. one input and a selectable single output of N possible outputs
- G02B6/3552—1x1 switch, e.g. on/off switch
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mechanical Light Control Or Optical Switches (AREA)
- Light Guides In General And Applications Therefor (AREA)
- Optical Couplings Of Light Guides (AREA)
- Optical Fibers, Optical Fiber Cores, And Optical Fiber Bundles (AREA)
- Laser Surgery Devices (AREA)
- Glass Compositions (AREA)
- Dental Preparations (AREA)
- Treatments For Attaching Organic Compounds To Fibrous Goods (AREA)
- Chemical Or Physical Treatment Of Fibers (AREA)
- Optical Communication System (AREA)
- Devices For Conveying Motion By Means Of Endless Flexible Members (AREA)
- Cable Accessories (AREA)
- Optical Head (AREA)
Abstract
本发明涉及光纤传输系统中的光学元件,例如,衰减元件、滤光器、功率分配器。该光学元件至少由两个光纤支承件和一个可在支承件间移动的调节件构成。
由支承件构成导板,由调节件构成介电材料的调节板,调节板可在导板之间形成的导向空间中移动,至少在一个导板上带有至少两个用以形成介电场的电极表面,所述电极表面与电压供应控制系统相连。
Description
本发明涉及一种用于光纤传输系统的光学元件,例如衰减元件,滤光器、功率分配器或类似元件。该光学元件包含至少两个光纤支承件及一个可在支承件之间移动的调节件。
这种光学元件用作各种类型的衰减元件,滤光器、功率分配器及类似元件是人们熟知的。现有的一种光衰减元件包含一个盒式壳体,在壳体相对的侧壁上有做成光纤联接器的支承件。此外,用于扩展光束的球面透境成象系统设置在盒式壳体的内侧。在壳体内,一个圆盘装于侧壁的轴颈上。光纤的光轴与圆盘转轴彼此隔开。作为滤光器贮存盒的圆盘带有各种盘形滤光器,每种盘形滤光器有一个停止位置,转动圆盘可将其转到不同的停止位置,以便调整不同衰减值。上述衰减元件的缺点是,每调整一个不同的滤光器必须用手直接在衰减元件中完成,而不能遥控。与滤光器、功率分配器或类似元件具有相似结构的其它光学元件也存在相同的缺点。因此,本发明的目的就在于提供一种本文开始所说的光学元件。该光学元件可用简便的方式遥控,而无需目前的手动调整。
实现本发明目的的解决方案是:光学元件至少由两个光纤支承件和一个可在两个支承件之间移动的调节件构成;支承件构成为导板,调节件做成为介电材料作的调节板,调节板可在导板之间的导向空间中移动,至少有一个导板带有形成至少一个介电场的电极表面,所述电极表面与一个可调电压供应源相连。本发明的光学元件依照下述原理进行遥控调节:控制系统根据确定的输入信号使光纤导板(如果合适,同时又是光纤和其光学成象系统共同的支承件或承载体)之间的电场
产生局部移动。借助电场,将有不同光学特性的调节板置于光纤之间,以使不同的衰减值、不同的滤光器曲线、不同的功率分配器等有可能实现。本发明的光学元件也可用作电控光换向开关。
由从属权利要求中可得出本发明更多的有用实施例。
下面结合附图所示光学元件的各实施例详述本发明。其中:
图1 光学元件的工作原理图;
图2 光学元件第一实施例的垂直剖面图;
图3 图2所示光学元件的侧视图;
图4 光学元件第二实施例的水平剖面图;
图5 光学元件第三实施例的水平剖面图;
图6 光学元件第四实施例的水平剖面图;
图7 光学元件第五实施例的水平剖面图;
图8 图7的俯视图;
图9 一种光学成象系统的原理图;
图10 光学元件第六实施例,即电控光学功率分配器的原理图;
图11 光学元件第七实施例(电控光学功率分配器);
图12 光学元件第八实施例(电控光学滤光器)的水平剖面图;
图13 图12所示光学滤光器的光传输功率曲线,是波长和调节板调整的函数;
图14 作为电控光换向开关的光学元件第九实施例。
本发明光学元件的物理基础是:如图1所示,如果介电体最初有一部分是在电场作用以外,那么,在平板电容器2电场中的可移动介电体1被吸入电场(逐渐变为最小能量状态)。作用于介电体1的力F与电容器板2上恒量电荷Q的等量关系式为:
FQ= 1/2 · (ε-εo)/([εoa+(ε-εo)x]2) · (d)/(h) Q2
其中:X<a,
εo环境空间的介电常数
ε 介电体1的介电常数
h 系统在垂直于图面方向的尺寸
其余数值根据图1引入。
对于恒定电压u,作用于介电体1上的力为:
Fu= 1/2 (ε-εo)·u2· (h)/(d)
其中:x<a。
基于上述原理的本发明光学元件可借助电容器板2之间的电场将介电体准确地置于不同位置。
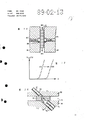
图2和图3所示第一实施例中,光学元件由间隔距离为d的两平行导板10、11和在它们之间可移动的调节板12组成。带有光学成象系统19的光纤13、14插入导板10、11,它们的自由前表面与可动调节板12相对。导板10、11和调节板12由介电材料(例如玻璃板)构成。在导板10、11的内侧装有平行的导电条状电极15、16。条状电极可由蒸镀的透明材料组成。每个板10、11上的单个条状电极15、16均带有与控制系统相连的引线18(控制系统未示出),所述控制系统完成单个条状电极15、16之间的电压换向。
由导板10、11以及调节板12组成的完整的光学元件置于密
封的壳体内,壳体中充满具有合适指数的液体。
分别施加电压于电极15、16或它们的引线18(标记字符Bi到Bj)及分别切断电极15、16或它们的引线18的电压(标记字符Ai到Ak),则电场移动。由于上述的基本工作原理,介电调节板12可移动到新的位置,并且根据电极15、16的数目、距离和尺寸调节板12可被移到多种不同的位置。由于添加了具有合适指数的液体,调节板移动的摩擦阻力极小。
要将电压施加到两个导板10、11的条状电极15、16上,须利用装于导板10、11之一的用玻璃芯片(Chip-on-glass)技术制造的固体元件实现所需的换向。玻璃芯片技术对于LCD元件属于一种普通技术。然后,仅须将在一端形成电场的电压和所需的控制信号加到固体元件上。
将调节板12移到新位置所需能量很小,因此功率消耗极低,仅只部分电容器需要充电。调节板12在新位置的定位时间周期为毫秒级,所说的时间周期还取决于调节板12的惯量。
在实施例中,由于调节板12的移动仅沿一个直线座标,因此调节板12必须被电场本身或被一个凹槽或被一个隔挡件定位。由于需要在切断电压时仍能保持调节板12的定位,因此使用机械式定位是有利的。
调节板的原点位置必须借助电惯量或机械装置实现,例如,借助在整个移动范围内的一个移动电场,再通过不同的移动达到确定的原点。
在图4所示的第二实施例中,光学元件由两个导板20、21和调节板22组成,调节板22可在导板21中的自由导向空间27内
移动。条状电极25、26分装于导板20、21的表面,在调节板22的移动区域内。光成象系统29装于光纤23、24上。
图5所示为第三实施例。这个实施例的突出优点是制造简便。光成象系统39分别装于光纤33、34上。在介电导板31上为调节板32的移动留有自由导向空间37。只在导板31上导向空间37的两侧蒸镀有两排条状电极35、36。也可按照同样的方式为导板31装上用玻璃芯片技术制作的固体元件以取代条状电极35、36。本实施例实现同样力的作用所需的电压比前两个实施例要大。
图6所示是第四实施例。该实施例由平面导板40、带有为调节板42所设的导向空间47的第二导板41以及两排条状电极45、46组成。光纤43、44借助光成象系统49插入所述导板41;两排条状电极45、46置于导板41上的导向空间47两侧。本实施可用作电控光衰减元件。
图7和图8所示为光学元件的第五实施例。与第四实施例不同,本实施例为调节板52设置的导向空间57均等地位于导板50、51内。条状电极55、56分别位于导板50、51的外侧,在导向空间57区域内或调节板52于导向空间57中移动的区域内。光纤53、54端接于光学成象系统59,后者插在导板50、51中。
图9所示为位于准直光纤束53与另一光纤54端部之间的光学成象系统59。
下面,对专用的光学元件作更详细的说明。所说的光学元件均基于前述的基本工作原理并在图2~图7的实施例中分别用于定位调节板或形成电场。所说的光学元件仅仅作为举例,从原则上说,就像任何实施例都是可能的一样。
在光传输通路上,路径衰减必须调整到一个规定值,并在一个长时间周期内保持稳定。根据接收电平,将一个遥侧信号送入发送器,并用一个控制信号调节一个光学衰减元件,以使衰减值与规定值的偏差低于予定阈值。图7和图8所示的用作电控光衰减元件的第五实施例可完成上述功能。其中,调节板52,即一个可沿纵向变化传送的介电盘,基于前述的基本工作原理在光纤53、54的前工作面之间移动。根据调节板52的位置、条状电极55、56的数量以及连续变动传送调节板52的次数,可将衰减量在最大与最小值之间以固定间隔调整。导向空间57的深度与调节板52的宽度相适应。
图10和图11所示分别是光学元件第六、七实施例的基本形式。图中的光学元件是能够电控分配比率的光学功率分配器。在具有光传输的通讯网络中,从传输通路中耦合输出确定的一部分光功率是一项重要功能。
在图10、11所示的电控光学功率分配器的基本形式中,调节板62或72根据干涉滤光器分段不同,并按照前述光学元件的实施例分别被置于输入光纤60、70和两根输出光纤61、61′或71、71′之间的光路中。利用电控信号,以大小不等的间隔将调节板置于带有条状电极的导板间的选定位置(条状电极和导板在图中未示出)。由此,可变透射或反射滤光器在光束路径中分别起作用。所说的滤光器分别由调节板62或72充当。被反射的光功率在半透明反射镜68处被耦合输出到输出光纤61′(图10)
图12所示的光学元件第八实施例是一个电控滤光器。在多路波长传输系统中,滤光器应置于光路的末端用以选择具有特定波长的信号。用可调滤光器能方便地识别具有不同波长的信号。图中调节板82
是一个滤光器,它的位置由电控制。滤光器可在导板80、81之间移动,根据前述的工作原理,是在输入光纤83和输出光纤84的工作面之间移动。
图13所示是对于不同波长λ和调节板82沿箭头A(曲线A)或箭头B(曲线B)方向移动时耦合输出光功率的基本曲线。
最后,图14所示光学元件第九实施例是一个电控光换向开关。在有光传输的网络中,当某个元件或分支网络(例如,带环形结构的局部网络)发生故障时,启动替换光路是合理的。为此,需使用光换向开关将输入光纤93的信号耦合到两个输出光纤94、94′中的一个。已知的用于此目的的开关是利用光纤的直接机械移动或压电控制移动。通过在两个导板90、91(每个导板都由介电材料构成)之间配置调节板92,当调节板92材料的折射率n2选成与周围其它材料的折射率n1明显不同时,便可构成一个带有透明介电调节板92的简单的换向开关。此外,也可在光学交换网络中形成光学矩阵。
如果图7和图8中所示第五实施例的调节板52换为在具有合适指数的液体中移动的非透明调节板,则也可构成与第五实施例结构相同的光学开关。这种(甚至带有大直径光纤芯的)光学开关可在具有光纤光波导的显示系统中应用并取代那些低效率的光学开关。根据符号或影象的大小排列光学开关是有益的。
Claims (11)
1、一种用于两根或多根光纤的光学元件,例如衰减元件,滤光器,功率分配器或类似元件,至少由两个光纤支承件和一个可在两个支承件之间移动的调节件构成,其特征在于,支承件做成为导板,调节件做成为介电材料作的调节板,调节板可在导板之间的导向空间中移动,至少有一个导板带有形成至少一个介电场的电极表面,所述电极表面与一个可调电压供应源相连。
2、如权利要求1所述的光学元件,其特征在于,介电材料是玻璃。
3、如权利要求1或2所述的光学元件,其特征在于,电极表面由彼此间隔的条状电极构成。
4、如权利要求3所述的光学元件,其特征在于,条状电极由导电的透明材料构成。
5、如权利要求3所述的光学元件,其特征在于,条状电极是蒸镀到导板内表面上的。
6、如权利要求1或2所述的光学元件,其特征在于,调节板的导向空间位于一个导板的一个凹槽中。
7、如权利要求3所述的光学元件,其特征在于,条状电极以平行的两排设置在确定导向空间的导板的表面上。
8、如权利要求3所述的光学元件,其特征在于,条状电极以平行的两排位于一个导板(31;41)的导向空间(37;47)旁边的表面上。
9、如权利要求1或2所述的光学元件,其特征在于,以调节板的厚度确定导向空间的深度。
10、如权利要求1或2所述的光学元件,其特征在于,以调节板(42)的宽度确定导向空间(47)的深度。
11、如权利要求3所述的光学元件,其特征在于,导向空间(57)由两个导板(50,51)表面上的两个凹槽构成,条状电极(55,56)置于导板(50,51)外侧,在调节板(52)的移动区域内。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE3804822A DE3804822C1 (zh) | 1988-02-12 | 1988-02-12 | |
| DEP38048221 | 1988-02-12 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1036841A CN1036841A (zh) | 1989-11-01 |
| CN1011739B true CN1011739B (zh) | 1991-02-20 |
Family
ID=6347531
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN89101841A Expired CN1011739B (zh) | 1988-02-12 | 1989-02-11 | 用于光纤传输系统的光学元件 |
Country Status (25)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US4919503A (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP0328738B1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JPH024208A (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR920005876B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1011739B (zh) |
| AT (1) | ATE61672T1 (zh) |
| AU (1) | AU604995B2 (zh) |
| CA (1) | CA1311822C (zh) |
| DD (1) | DD283465A5 (zh) |
| DE (2) | DE3804822C1 (zh) |
| DK (1) | DK63789A (zh) |
| ES (1) | ES2021128B3 (zh) |
| FI (1) | FI89310C (zh) |
| GR (1) | GR3001599T3 (zh) |
| HK (1) | HK106691A (zh) |
| IE (1) | IE60842B1 (zh) |
| IL (1) | IL88221A (zh) |
| MX (1) | MX170460B (zh) |
| NO (1) | NO173036C (zh) |
| NZ (1) | NZ227942A (zh) |
| PT (1) | PT89685B (zh) |
| RU (1) | RU1828550C (zh) |
| SG (1) | SG64891G (zh) |
| TR (1) | TR24475A (zh) |
| ZA (1) | ZA891050B (zh) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5953426A (ja) * | 1982-09-21 | 1984-03-28 | Wakunaga Seiyaku Kk | 心因性性行動障害回復剤 |
| US4945229A (en) * | 1988-12-29 | 1990-07-31 | Thomas & Betts Corporation | Fiber optic receiver and transceiver |
| GB2295687A (en) * | 1994-12-01 | 1996-06-05 | Ford Motor Co | Manually operable optical switch with encoded shutter |
| DE19520167B4 (de) * | 1995-06-01 | 2006-08-24 | Sick Ag | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur opto-elektronischen Entfernungsmessung nach dem Laufzeitverfahren |
| DE69909828T2 (de) * | 1998-12-09 | 2004-05-27 | Steris Inc., Temecula | Faseroptische zusatzlampe für deckenoperationsleuchte mit optischem gelenk und handobjektivlinse |
| AU2059600A (en) * | 1998-12-31 | 2000-07-31 | Optical Coating Laboratory, Inc. | Wavelength selective optical switch |
| CA2403689A1 (en) * | 1999-11-23 | 2001-05-31 | Nanovation Technologies, Inc. | Waveguide optical phase shifter |
| US6587608B2 (en) * | 2000-11-14 | 2003-07-01 | Chameleon Optics, Inc. | Reconfigurable, all optical add/drop nodes using non-interrupting switching apparatus and methods |
| WO2002086596A1 (en) | 2001-04-20 | 2002-10-31 | Cormack Robert H | Polarization insensitive tunable optical filters |
| US6807356B2 (en) * | 2001-12-10 | 2004-10-19 | Jds Uniphase Corporation | Fiber-coupled optical attenuator |
| JP2003241120A (ja) | 2002-02-22 | 2003-08-27 | Japan Aviation Electronics Industry Ltd | 光デバイス |
| CA2477490A1 (en) | 2002-02-26 | 2003-09-04 | Martin G. Selbrede | Enhancements to optical flat panel displays |
| US7015458B2 (en) * | 2002-10-10 | 2006-03-21 | Emerging Manufacturing Technology, Inc. | High density fiber optic output interface and system |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4223217A (en) * | 1977-05-12 | 1980-09-16 | Eaton Corporation | Fiber optic electric switch |
| JPS5526558A (en) * | 1978-08-15 | 1980-02-26 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Photo switch |
| DE2936463A1 (de) * | 1979-09-10 | 1981-03-19 | Siemens AG, 1000 Berlin und 8000 München | Vorrichtung zum erzeugen bewegter lichtstrahlengaenge |
| DE3138968A1 (de) * | 1981-09-30 | 1983-04-14 | Siemens AG, 1000 Berlin und 8000 München | Optische steuervorrichtung zum steuern der in einem optischen wellenleiter gefuehrten strahlung, insbesondere optischer schalter |
| DE3206919A1 (de) * | 1982-02-26 | 1983-09-15 | Philips Patentverwaltung Gmbh, 2000 Hamburg | Vorrichtung zum optischen trennen und verbinden von lichtleitern |
| DE3223898C2 (de) * | 1982-06-26 | 1984-04-19 | Standard Elektrik Lorenz Ag, 7000 Stuttgart | Einstellbares optisches Dämpfungsglied |
| CA1258786A (en) * | 1985-04-11 | 1989-08-29 | Omur M. Sezerman | Tilt adjustable optical fibre connectors |
| JPS61275717A (ja) * | 1985-05-31 | 1986-12-05 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 光シヤツタ−装置 |
| JPS61285419A (ja) * | 1985-06-13 | 1986-12-16 | Seiko Epson Corp | 光書込プリンタ |
| US4753507A (en) * | 1986-01-07 | 1988-06-28 | Litton Systems, Inc. | Piezoelectric loading housing and method |
-
1988
- 1988-02-12 DE DE3804822A patent/DE3804822C1/de not_active Expired
- 1988-10-20 AT AT88117463T patent/ATE61672T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1988-10-20 DE DE8888117463T patent/DE3862024D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-10-20 ES ES88117463T patent/ES2021128B3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-10-20 EP EP88117463A patent/EP0328738B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-10-28 IL IL88221A patent/IL88221A/xx not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1988-11-23 CA CA000583925A patent/CA1311822C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1988-11-30 AU AU26428/88A patent/AU604995B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1988-12-09 JP JP63311823A patent/JPH024208A/ja active Pending
- 1988-12-27 US US07/291,536 patent/US4919503A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
1989
- 1989-02-08 IE IE40889A patent/IE60842B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1989-02-09 DD DD89325657A patent/DD283465A5/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1989-02-09 NO NO890550A patent/NO173036C/no unknown
- 1989-02-10 MX MX014880A patent/MX170460B/es unknown
- 1989-02-10 NZ NZ227942A patent/NZ227942A/en unknown
- 1989-02-10 PT PT89685A patent/PT89685B/pt not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1989-02-10 FI FI890667A patent/FI89310C/fi not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1989-02-10 TR TR89/0149A patent/TR24475A/xx unknown
- 1989-02-10 ZA ZA891050A patent/ZA891050B/xx unknown
- 1989-02-10 DK DK063789A patent/DK63789A/da not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1989-02-10 RU SU894613536A patent/RU1828550C/ru active
- 1989-02-11 CN CN89101841A patent/CN1011739B/zh not_active Expired
- 1989-02-13 KR KR1019890001624A patent/KR920005876B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
-
1991
- 1991-03-14 GR GR91400198T patent/GR3001599T3/el unknown
- 1991-08-12 SG SG64891A patent/SG64891G/en unknown
- 1991-12-23 HK HK1066/91A patent/HK106691A/xx unknown
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN1011739B (zh) | 用于光纤传输系统的光学元件 | |
| US3931518A (en) | Optical fiber power taps employing mode coupling means | |
| US4720171A (en) | Liquid crystal optical switching device having reduced crosstalk | |
| BR9803400A (pt) | Guia de onda óptica de baixa atenuação. | |
| EP0488708B1 (en) | Optical switching device | |
| AU543708B2 (en) | A lens having a high refractive index with a low dispersion | |
| US4722583A (en) | Modulators | |
| CA2149267A1 (en) | Electric field sensor | |
| GB2031609A (en) | Coupling arrangements for optical fibres | |
| CN1266536C (zh) | 使用光子带间隙装置切换光信号的方法与设备 | |
| CN115808744A (zh) | 一种高一致性的光纤光开关 | |
| US4033669A (en) | Precision optical fiber switch | |
| US4720174A (en) | Liquid crystal optical switching device with integrally attached optical fibers | |
| KR100501195B1 (ko) | 이동식 광도파로를 구비한 mems 가변 광감쇄기 및이동식 광도파로의 구동방법 | |
| CN1555146A (zh) | 集成式光功率可调型光波分复用器 | |
| CN218782434U (zh) | 一种高一致性的光纤光开关 | |
| JPS6375726A (ja) | 光減衰器 | |
| CN209590484U (zh) | 一种基于正交液晶的可调谐光滤波器 | |
| GB2327773A (en) | Planar optical segmented waveguide for attenuation | |
| US20020009280A1 (en) | Variable optical attenuator | |
| CN110174781B (zh) | 一种网状结构微环电光开关阵列器件 | |
| CA1245087A (en) | Light by-passing device | |
| CN100368840C (zh) | 光纤开关 | |
| US6633721B2 (en) | Variable optical attenuator | |
| EP0223466A3 (en) | Improved optical fiber |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C13 | Decision | ||
| GR02 | Examined patent application | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C19 | Lapse of patent right due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |