WO2024023923A1 - 分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 - Google Patents
分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024023923A1 WO2024023923A1 PCT/JP2022/028760 JP2022028760W WO2024023923A1 WO 2024023923 A1 WO2024023923 A1 WO 2024023923A1 JP 2022028760 W JP2022028760 W JP 2022028760W WO 2024023923 A1 WO2024023923 A1 WO 2024023923A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- candidate
- communication
- communication devices
- wireless communication
- antennas
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/02—Diversity systems; Multi-antenna system, i.e. transmission or reception using multiple antennas
- H04B7/022—Site diversity; Macro-diversity
- H04B7/024—Co-operative use of antennas of several sites, e.g. in co-ordinated multipoint or co-operative multiple-input multiple-output [MIMO] systems
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04B—TRANSMISSION
- H04B7/00—Radio transmission systems, i.e. using radiation field
- H04B7/02—Diversity systems; Multi-antenna system, i.e. transmission or reception using multiple antennas
- H04B7/04—Diversity systems; Multi-antenna system, i.e. transmission or reception using multiple antennas using two or more spaced independent antennas
- H04B7/0413—MIMO systems
- H04B7/0452—Multi-user MIMO systems
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a distributed antenna system, a wireless communication method, and a wireless communication device.
- MIMO Multiple-Input Multiple-Output
- MIMO technology is widely used as a technology that can improve frequency usage efficiency and greatly improve capacity and throughput.
- MIMO technology multiple antennas are provided on the transmitting side and the receiving side, and spatial multiplex transmission is performed at the same time and at the same frequency.
- MINO includes SU-MIMO (Single User MIMO), which uses multiple antennas in one-to-one communication, and one-to-many or many-to-many communication, such as between a base station (BS) and a terminal (UE: user equipment).
- BS base station
- UE terminal
- MU-MIMO Multi-User MIMO
- MIMO Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output
- CSI channel state information
- MIMO using a distributed antenna system in which base station antennas are distributed in a distributed manner is also widely considered as a configuration that is expected to reduce the spatial correlation between the base station antenna and the terminal antenna (for example, Non-Patent Document 1 reference).
- clustering methods are also being considered to reduce the processing load by limiting the range of distributed antennas used by each terminal.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a technology that can reduce spatial correlation when performing spatial multiplex transmission and improve communication efficiency without acquiring CSI between all antennas. It is said that
- One aspect of the present invention is a distributed antenna system including a first communication device and a plurality of antennas that communicate with a plurality of second communication devices by spatial multiplexing according to control of the first communication device
- the first communication device includes an extraction unit that extracts a plurality of candidate second communication devices that are candidates for performing spatial multiplexing from among the plurality of second communication devices; , the distance between the candidate second communication devices is equal to or greater than the first threshold, and the duplication rate of each antenna assigned to each candidate second communication device is less than the second threshold.
- an allocation unit that allocates a communication opportunity to a candidate second communication device as a target for communication by spatial multiplexing, the two or more candidate second communication devices to which a communication opportunity is allocated among the plurality of antennas.
- Each antenna assigned to is a distributed antenna system that performs spatial multiplexing transmission to the two or more candidate second communication devices.
- One aspect of the present invention is a wireless communication method in a distributed antenna system including a first communication device and a plurality of antennas that communicate with a plurality of second communication devices by spatial multiplexing according to control of the first communication device.
- the first communication device extracts a plurality of candidate second communication devices that are candidates for spatial multiplexing from among the plurality of second communication devices, and extracts a plurality of candidate second communication devices that are candidates for performing spatial multiplexing.
- a communication opportunity is allocated to the two or more candidate second communication devices as targets for communication by spatial multiplexing, and the communication opportunity is allocated to the two or more candidate second communication devices to which the communication opportunity is allocated among the plurality of antennas.
- each antenna performs spatial multiplex transmission to the two or more candidate second communication devices.
- One aspect of the present invention includes a plurality of antennas that perform spatial multiplexing transmission to a plurality of communication devices, and an extraction unit that extracts a plurality of candidate communication devices that are candidates for spatial multiplexing from among the plurality of communication devices. , from among the plurality of extracted candidate communication devices, the distance between the candidate communication devices is greater than or equal to a first threshold, and the overlap rate of each antenna assigned to each candidate communication device is less than a second threshold; an allocation unit that allocates a communication opportunity as a target for communication by spatial multiplexing to two or more candidate communication devices that satisfy a condition, the two or more of the plurality of antennas to which the communication opportunity is allocated.
- Each antenna assigned to the candidate second communication device is a wireless communication device that performs spatial multiplex transmission to the two or more candidate communication devices.
- the present invention it is possible to reduce spatial correlation when performing spatial multiplex transmission without acquiring CSI between all antennas, and it is possible to improve communication efficiency.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an example of a distributed antenna system in this embodiment. It is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of a base station in this embodiment. It is a figure showing an example of composition of a control part in this embodiment. It is a flowchart which shows the flow of processing of a base station in this embodiment.
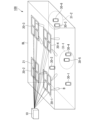
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an example of a distributed antenna system 100 in this embodiment.
- Distributed antenna system 100 includes a base station 10 and a plurality of antennas 20-1 to 20-4.
- the base station 10 and the plurality of antennas 20-1 to 20-4 are connected by optical transmission lines. Communication between the base station 10 and the plurality of antennas 20-1 to 20-4 is performed, for example, by RoF (Radio over Fiber).
- the base station 10 and the plurality of antennas 20-1 to 20-4 are one aspect of a wireless communication device.
- the plurality of antennas 20-1 to 20-4 are installed on the ceiling in the building BL, and are connected to the plurality of wireless communication terminals 30-1 to 30-6 located in the building BL. communicate.
- the plurality of antennas 20-1 to 20-4 are arranged apart from each other as shown in FIG.
- Each antenna 20 is configured to include a plurality of subarrays 21. Note that the numbers of antennas 20, wireless communication terminals 30, and subarrays 21 are not limited to the numbers shown in FIG. In the following description, unless the antennas 20-1 to 20-4 are particularly distinguished, they will simply be referred to as antennas 20.
- the base station 10 controls each of the distributed antennas 20 through centralized control.
- the base station 10 simultaneously realizes communication with a plurality of wireless communication terminals 30 through spatial multiplexing by controlling each antenna 20.
- the base station 10 performs MU-MIMO by simultaneously transmitting multiple streams from multiple antennas 20 to multiple wireless communication terminals 30.
- Each antenna 20 communicates with each wireless communication terminal 30.
- Each antenna 20 is configured to include a plurality of subarrays 21.
- Each sub-array 21 emits radio waves under control from the base station 10.
- the antenna 20 communicates with the wireless communication terminal 30 with which it communicates by performing beamforming using a plurality of array elements to ensure gain in a high frequency band. Note that a portion of each antenna 20 may not include the subarray 21.
- Each wireless communication terminal 30 includes one or more antennas and communicates with each antenna 20.
- the wireless communication terminal 30 equipped with a plurality of antennas can also perform SU-MIMO communication with the antenna 20.
- the wireless communication terminal 30 may perform beamforming.
- Each wireless communication terminal 30 has a function of acquiring its own location information, and acquires its own location information upon request from the base station 10 or at a predetermined timing.
- Each wireless communication terminal 30 notifies the base station 10 of the acquired position information via the antenna 20.
- Methods for each wireless communication terminal 30 to acquire location information include GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) such as GPS (Global Positioning System), three-point positioning or single-point positioning using communication radio waves, sonic positioning, visible light positioning, etc. Either method may be used.
- GNSS Global Navigation Satellite System
- GPS Global Positioning System
- three-point positioning or single-point positioning using communication radio waves sonic positioning, visible light positioning, etc. Either method may be used.
- wireless communication using another frequency band may be used.
- the distributed antenna system 100 When performing spatial multiplexing transmission simultaneously with a plurality of wireless communication terminals 30 using distributed antennas 20 as in the distributed antenna system 100, the spatial correlation of the propagation path may vary depending on how the wireless communication terminals 30 are selected. changes. Therefore, the communicable capacity and throughput also change depending on the selection of the wireless communication terminal 30. Therefore, in the distributed antenna system 100 in this embodiment, based on the position information of each wireless communication terminal 30, wireless communication terminals 30 that are not expected to have high spatial correlation are spatially multiplexed simultaneously. Select as. That is, in the distributed antenna system 100 according to the present embodiment, communication opportunities are allocated to wireless communication terminals 30 that are not expected to have a high spatial correlation as targets for spatial multiplexing.
- the distributed antenna system 100 uses the position information of one selected wireless communication terminal 30 as a reference to communicate with other wireless communication terminals 30 located within a predetermined distance from the selected wireless communication terminal 30. By removing them from opportunity allocation targets, nearby wireless communication terminals 30 that are likely to have a high spatial correlation are excluded from selection candidates.
- wireless communication terminals 30-1 to 30-6 are located in a building BL, and wireless communication terminals 30-5 and 30-6 are assigned wireless communication opportunities. Assume that the terminal is 30.
- the area 31-1 shown in FIG. 1 represents a range that is a predetermined distance away from the wireless communication terminal 30-5, based on the position of the wireless communication terminal 30-5.
- the area 31-2 shown in FIG. 1 represents a range that is a predetermined distance away from the wireless communication terminal 30-6, with the position of the wireless communication terminal 30-6 as a reference.
- the base station 10 excludes other wireless communication terminals 30-3 and 30-4 located within these areas 31-1 and 31-2 from being allocated communication opportunities. This makes it possible to avoid combinations of wireless communication terminals 30 that result in high spatial correlation. As a result, it is possible to reduce spatial correlation between wireless communication terminals 30 that are targets of simultaneous communication through spatial multiplexing.
- the antennas 20 allocated to each wireless communication terminal 30 are spatially multiplexed.
- a wireless communication terminal 30 with a low duplication rate is selected.
- the duplication rate is, for example, the number of identical antennas 20 allocated to different wireless communication terminals 30 out of the total number of antennas allocated to each of a plurality of wireless communication terminals 30 (for example, two wireless communication terminals 30).
- the duplication rate refers to, for example, the number of identical subarrays allocated to different wireless communication terminals 30 out of the total number of subarrays allocated to each of two wireless communication terminals 30. It is determined by the ratio of the number of subarrays 21. As a result, it is possible to expect an increase in the number of streams allocated per device.
- the base station 10 excludes nearby wireless communication terminals 30 that are likely to have a high spatial correlation from selection candidates, and adjusts the duplication rate of the antennas 20 assigned to each wireless communication terminal 30 to be spatially multiplexed.
- a communication opportunity is assigned to a plurality of wireless communication terminals 30 with a low value as a combination of wireless communication terminals 30 that perform spatial multiplex transmission.
- the base station 10 allocates communication opportunities to the wireless communication terminals 30-1, 30-2, 30-5, and 30-6 as a combination of wireless communication terminals 30 that perform spatial multiplex transmission. .
- the distributed antenna system 100 can reduce spatial correlation when performing spatial multiplex transmission without acquiring CSI between all antennas, and can improve communication efficiency. .
- a specific configuration for realizing the above processing will be described below.
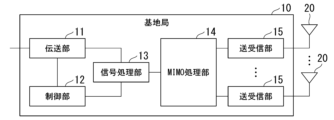
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the base station 10 in this embodiment.
- the base station 10 includes a transmission section 11 , a control section 12 , a signal processing section 13 , a MIMO processing section 14 , a plurality of transmitting/receiving sections 15 , and a plurality of antennas 20 .
- the transmission unit 11 performs signal transmission with higher-level devices on the network, other wireless communication devices, and the like.
- the control unit 12 controls the operation of the base station 10 as a whole. For example, the control unit 12 performs scheduling such as allocation of each antenna 20 and each wireless communication terminal 30 for performing spatial multiplex transmission.
- the signal processing unit 13 performs signal processing related to wireless communication.
- the MIMO processing unit 14 performs MIMO processing such as precoding and postcoding. Note that the MIMO processing unit 14 may be controlled to perform analog beamforming or hybrid beamforming instead of precoding or postcoding.
- the transmitting/receiving unit 15 performs processing related to transmitting and receiving wireless signals. Specifically, the transmitter/receiver 15 controls each antenna 20 to communicate with each wireless communication terminal 30. For example, the transmitting/receiving unit 15 controls the antenna 20 assigned to a wireless communication terminal 30 (hereinafter referred to as a "candidate terminal station") that is a candidate for spatial multiplexing by MU-MIMO, and performs communication between the candidate terminal station and the candidate terminal station. communicate.
- a wireless communication terminal 30 hereinafter referred to as a "candidate terminal station”
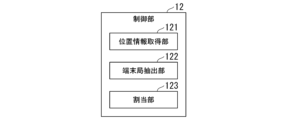
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of the configuration of the control section 12 in this embodiment.
- the control unit 12 includes a location information acquisition unit 121, a terminal station extraction unit 122, and an allocation unit 123.
- the location information acquisition unit 121 acquires location information from each of the plurality of wireless communication terminals 30.
- the terminal station extraction unit 122 extracts a plurality of candidate terminal stations from among the plurality of wireless communication terminals 30.
- Methods for extracting candidate terminal stations include methods of selecting candidate terminal stations based on indicators such as RI (Rank Indicator) through various types of scheduling, methods of selecting candidate terminal stations based on PF (Proportional Fair) norms, and methods of selecting candidate terminal stations based on the PF (Proportional Fair) norm. Any of the following methods may be used: a method of selecting candidate terminal stations based on , or a method of selecting wireless communication terminals 30 such that interference between the wireless communication terminals 30 is reduced based on positional relationships or the like.
- Methods of selecting candidate terminal stations based on received power include a method of checking the received power of each wireless communication terminal 30 and selecting wireless communication terminals 30 in order from the highest received power, and a method of selecting wireless communication terminals 30 with similar received power. For example, there is a method of selecting the same.
- the terminal station extraction unit 122 is one aspect of an extraction unit.
- the allocation unit 123 allocates the antenna 20 to each wireless communication terminal 30 based on reception quality, terminal accommodation status, etc. in the phase in which the wireless communication terminal 30 entering the area (for example, the building BL) connects to the base station 10. .
- the allocation unit 123 allocates the sub-arrays 21 of the antenna 20 based on reception quality, terminal accommodation status, etc. in the phase in which the wireless communication terminal 30 connects to the base station 10. Allocated to each wireless communication terminal 30.
- the allocation unit 123 may allocate, for each candidate terminal station extracted by the terminal station extraction unit 122, the antenna 20 that communicates with the candidate terminal station.
- a plurality of antennas 20 or a sub-array 21 of antennas 20 may be allocated to the wireless communication terminal 30.
- the allocation unit 123 allocates, for each candidate terminal station extracted by the terminal station extraction unit 122, the sub-array 21 that communicates with the candidate terminal station. good.
- the allocation unit 123 allocates communication opportunities to two or more candidate terminal stations as targets for communication by spatial multiplexing. More specifically, from among the plurality of candidate terminal stations extracted by the terminal station extraction unit 122, the allocation unit 123 selects a candidate terminal station whose distance between the candidate terminal stations is equal to or greater than a first threshold, and for each candidate terminal station. A communication opportunity is assigned to two or more candidate terminal stations that satisfy the condition that the duplication rate of each antenna assigned to the antenna is less than a second threshold value as targets for communication by spatial multiplexing.
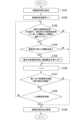
- FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing the process flow of the base station 10 in this embodiment. It is assumed that the base station 10 has acquired the position information of each wireless communication terminal 30 when the process in FIG. 4 is started. For example, the base station 10 may acquire the location information of each wireless communication terminal 30 by each wireless communication terminal 30 including the location information in a connection request signal and transmitting it to the base station 10. Further, at the start of the process in FIG. 4, the antenna 20 is allocated to each wireless communication terminal 30, and the allocation unit 123 assigns one or more antennas 20 or one or more subarrays 21 to each wireless communication terminal 30. It is assumed that information regarding the sets is held as clustering information.
- the terminal station extraction unit 122 extracts candidate terminal stations from among the plurality of wireless communication terminals 30 (step S101).
- the allocation unit 123 allocates a number to each extracted candidate terminal station. For example, the allocation unit 123 sequentially allocates a number starting from 1 as a candidate terminal station number to each candidate terminal station.
- the allocation unit 123 assigns 1 to the candidate terminal station number i (step S102).
- the allocation unit 123 determines whether the position of the i-th candidate terminal station is allocated to the communication opportunity based on the position information of the i-th candidate terminal station and the position information of the candidate terminal station to which the communication opportunity has been allocated. It is determined whether the distance is a distance equal to or more than a first threshold value from the position of the candidate terminal station that has been completed (step S103). At the start of the process, since i is 1, there is no candidate terminal station to which a communication opportunity has been allocated. Therefore, here, the allocation unit 123 determines that the position of the i-th candidate terminal station is separated by a distance equal to or more than the first threshold value from the position of the candidate terminal station to which the communication opportunity has been allocated.
- the allocation unit 123 determines the overlap rate. It is determined whether or not is less than a second threshold (step S104). Specifically, first, the allocation unit 123 refers to the clustering information held for each candidate terminal station and assigns the clustering information of the i-th candidate terminal station and the clustering information of the candidate terminal stations to which communication opportunities have been allocated. Read out. Next, the allocation unit 123 compares the pieces of read clustering information and calculates the duplication rate. Here, since i is 1, there is no candidate terminal station to which a communication opportunity has been allocated. Therefore, the allocation unit 123 determines that the duplication rate is less than the second threshold.
- the allocation unit 123 determines whether the number of candidate terminal stations to which communication opportunities have been allocated is less than the maximum allocatable number (step S107).
- the maximum allocatable number is determined depending on, for example, the number of antennas 20 and sub-arrays 21, the processing capacity of the base station 10, or the corresponding maximum number of MIMO layers.
- the allocation unit 123 determines whether the value of i is greater than the number of candidate terminal stations. (Step S108). That is, the allocation unit 123 determines whether allocation determination has been made for all of the candidate terminal stations extracted in step S101.
- step S108-NO allocation determination is not made for all of the candidate terminal stations extracted in step S101. Therefore, the allocation unit 123 executes the process of step S103.
- the allocation unit 123 determines whether the position of the second candidate terminal station is a candidate to which a communication opportunity has been allocated, based on the position information of the second candidate terminal station and the position information of the candidate terminal station to which the communication opportunity has been allocated. It is determined whether the distance from the terminal station is greater than or equal to a first threshold (step S103).
- the allocation unit 123 determines that the location of the second candidate terminal station is the location of the first candidate terminal station based on the location information of the second candidate terminal station and the location information of the first candidate terminal station. It is determined whether the distance is greater than or equal to a first threshold value from the position.
- step S103-NO If the allocation unit 123 determines that the position of the second candidate terminal station is not more than the first threshold distance from the position of the first candidate terminal station (step S103-NO), the allocation unit 123 performs the process of step S106. After adding 1 to i, the process of step S107 is executed.
- step S104 if the allocation unit 123 determines that the position of the second candidate terminal station is away from the position of the first candidate terminal station by a distance equal to or more than the first threshold value (step S103-YES) ), it is determined whether the duplication rate is less than a second threshold (step S104). Specifically, first, the allocation unit 123 refers to the clustering information held for each candidate terminal station and assigns the clustering information of the second candidate terminal station and the candidate terminal station to which the communication opportunity has been allocated (for example, The clustering information of the first candidate terminal station) is read out. Next, the allocation unit 123 compares each piece of read clustering information and calculates an overlap rate.
- the allocation unit 123 determines that the overlap rate is less than the second threshold (step S104-YES)
- the allocation unit 123 allocates a communication opportunity to the i-th candidate terminal station (for example, the second candidate terminal station) (step S105). ). That is, the allocation unit 123 adds the i-th candidate terminal station to the targets for spatial multiplexing. If the allocation unit 123 determines that the duplication rate is equal to or higher than the second threshold (step S104-NO), or after the process in step S105, it adds 1 to i (step S106).
- the allocation unit 123 assigns the position of the third candidate terminal station in the process of step S103. However, it is determined whether the distance is a distance equal to or more than a first threshold value from the positions of candidate terminal stations to which communication opportunities have been allocated (for example, the first candidate terminal station and the second candidate terminal station).
- the allocation unit 123 determines that the position of the third candidate terminal station in the process of step S103 is the position of the candidate terminal stations (for example, the first candidate terminal station and the second candidate terminal station) to which the communication opportunity has been allocated. If it is determined that the distance is greater than or equal to the first threshold, it is determined in step S104 whether the overlap rate is less than the second threshold. Specifically, first, the allocation unit 123 refers to the clustering information held for each candidate terminal station, and selects the clustering information of the third candidate terminal station and the candidate terminal station to which communication opportunities have been allocated (for example, The clustering information of the first candidate terminal station and the second candidate terminal station) is read out. Next, the allocation unit 123 compares the pieces of read clustering information and calculates the duplication rate. In this way, as the number of candidate terminal stations to which communication opportunities have been allocated increases, the number of objects to be compared increases.
- step S107 if the allocation unit 123 determines that the number of candidate terminal stations to which communication opportunities have been allocated is greater than or equal to the maximum allocatable number (step S107-NO), the base station 10 Spatial multiplex transmission is performed with the added candidate terminal station (step S109).
- step S108 if the allocation unit 123 determines that the value of i is greater than the number of candidate terminal stations (step S108-YES), the allocation determination has been made for all the candidate terminal stations extracted in step S101. Become. In this case, the base station 10 performs spatial multiplexing transmission with the candidate terminal station added as a target for spatial multiplexing (step S109). In this way, the base station 10 repeatedly performs the process shown in FIG. 4 until the maximum number of candidate terminal stations that can be allocated is reached or there are no more candidate terminal stations that are candidates for spatial multiplexing. Note that when the base station 10 runs out of candidate terminal stations that are candidates for spatial multiplexing, if the maximum allocatable number is not satisfied, even if a new candidate terminal station that is a candidate for spatial multiplexing is added. good.
- the base station 10 includes a terminal station extraction unit 122 that extracts a plurality of candidate terminal stations from among the plurality of wireless communication terminals 30, and a , two or more candidates that satisfy the conditions that the distance between the candidate terminal stations is equal to or greater than the first threshold, and the duplication rate of each antenna assigned to each candidate second communication device is less than the second threshold.
- an allocation unit 123 that allocates a communication opportunity to a second communication device as a target for communication by spatial multiplexing, and the communication opportunity is allocated to two or more candidate terminal stations among the plurality of antennas 20;
- Each antenna 20 performs spatial multiplex transmission to two or more candidate terminal stations.
- the number can be increased. Therefore, it is possible to reduce spatial correlation when performing spatial multiplex transmission without acquiring CSI between all antennas, and it is possible to improve communication efficiency.
- the distributed antenna system 100 is expected to reduce the processing load by avoiding interference between wireless communication terminals using only analog beamforming without performing precoding or postcoding processing in high frequency bands. Can be done.
- Each functional unit included in the base station 10 may be divided and arranged into a CU (Centralized Unit), a DU (Distributed Unit), and an RU (Radio Unit) in 5G NR.
- the transmission section 11 is arranged in the CU
- the control section 12 the signal processing section 13, and the MIMO processing section 14 are arranged in the DU
- the transmitting/receiving section 15 and the antenna 20 are arranged in the RU. be done.
- Modification 2 In the above embodiment, the configuration in the downlink from the base station 10 to the wireless communication terminal 30 was shown, but the above processing in the distributed antenna system 100 is also applicable to the uplink from the wireless communication terminal 30 to the base station 10. It is possible.
- the distributed antenna system 100 may perform MU-MIMO by simultaneously transmitting multiple streams from multiple wireless communication terminals 30 to multiple antennas 20.
- the base station 10 may consider not only spatial correlation but also other factors such as fairness of communication opportunities and traffic volume, and performs scheduling control that takes into account location information and/or clustering information of wireless communication terminals. Good too.
- the base station 10 is one aspect of a first communication device, a second communication device, and a wireless communication device.
- the wireless communication terminal 30 is one aspect of a first communication device, a second communication device, and a wireless communication device.
- the wireless communication terminal 30 is the second communication device, and when the base station 10 is the second communication device, the wireless communication terminal 30 is the first communication device.
- some or all of the functional units of the base station 10 and the wireless communication terminal 30 are configured such that one or more processors such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit) It is realized as software by executing a program stored in a storage device having a storage medium (media) and a memory.
- the program may be recorded on a computer-readable non-transitory recording medium.
- Computer-readable non-temporary recording media include, for example, portable media such as flexible disks, magneto-optical disks, ROM (Read Only Memory), and CD-ROM (Compact Disc-ROM), and storage such as hard disks built into computer systems. It is a non-temporary recording medium such as a device.
- Some or all of the functional units of the base station 10 and the wireless communication terminal 30 are, for example, LSI (Large Scale Integrated circuit), ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit), PLD (Programmable Logic Device), or FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array). ), etc., may be realized using hardware including an electronic circuit or circuitry.
- LSI Large Scale Integrated circuit
- ASIC Application Specific Integrated Circuit
- PLD Programmable Logic Device
- FPGA Field Programmable Gate Array
- the present invention can be applied to a wireless communication system using MIMO.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2024536589A JP7755213B2 (ja) | 2022-07-26 | 2022-07-26 | 分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 |
| PCT/JP2022/028760 WO2024023923A1 (ja) | 2022-07-26 | 2022-07-26 | 分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/028760 WO2024023923A1 (ja) | 2022-07-26 | 2022-07-26 | 分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024023923A1 true WO2024023923A1 (ja) | 2024-02-01 |
Family
ID=89705619
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2022/028760 Ceased WO2024023923A1 (ja) | 2022-07-26 | 2022-07-26 | 分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7755213B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2024023923A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20240063850A1 (en) * | 2021-01-07 | 2024-02-22 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Distributed antenna system, wireless communication method, and centralized station |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010193189A (ja) * | 2009-02-18 | 2010-09-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | 分散アンテナシステムおよび分散アンテナ制御方法 |
| JP2014086786A (ja) * | 2012-10-19 | 2014-05-12 | Sharp Corp | 基地局装置、およびプロセッサ |
| JP2018518104A (ja) * | 2015-05-22 | 2018-07-05 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッドQualcomm Incorporated | マルチユーザ多入力/多出力局に関するスマートグループ化 |
| JP2020031306A (ja) * | 2018-08-21 | 2020-02-27 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 分散アンテナを用いた無線基地局およびスケジューリング方法 |
| US10771128B1 (en) * | 2019-06-24 | 2020-09-08 | Sprint Communcations Company L.P. | Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) user equipment (UE) grouping with geographic correlation factors |
-
2022
- 2022-07-26 JP JP2024536589A patent/JP7755213B2/ja active Active
- 2022-07-26 WO PCT/JP2022/028760 patent/WO2024023923A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010193189A (ja) * | 2009-02-18 | 2010-09-02 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | 分散アンテナシステムおよび分散アンテナ制御方法 |
| JP2014086786A (ja) * | 2012-10-19 | 2014-05-12 | Sharp Corp | 基地局装置、およびプロセッサ |
| JP2018518104A (ja) * | 2015-05-22 | 2018-07-05 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッドQualcomm Incorporated | マルチユーザ多入力/多出力局に関するスマートグループ化 |
| JP2020031306A (ja) * | 2018-08-21 | 2020-02-27 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 分散アンテナを用いた無線基地局およびスケジューリング方法 |
| US10771128B1 (en) * | 2019-06-24 | 2020-09-08 | Sprint Communcations Company L.P. | Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) user equipment (UE) grouping with geographic correlation factors |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20240063850A1 (en) * | 2021-01-07 | 2024-02-22 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Distributed antenna system, wireless communication method, and centralized station |
| US12250034B2 (en) * | 2021-01-07 | 2025-03-11 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Distributed antenna system, wireless communication method, and centralized station |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7755213B2 (ja) | 2025-10-16 |
| JPWO2024023923A1 (enExample) | 2024-02-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12177825B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving beam information in wireless communication system | |
| JP7097385B2 (ja) | 送信ビーム情報を取得する方法と装置、および送信ビーム情報をフィードバックする方法と装置 | |
| JP6498762B2 (ja) | 高周波無線ネットワーク用の効率的なビーム走査 | |
| US10897286B2 (en) | Adaptive MU-MIMO beamforming | |
| US10560180B2 (en) | Ground radio station (GRS) apparatus and radio station apparatus included in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) | |
| US8027702B2 (en) | Combined omni- and directional- communications in high-frequency wireless networks | |
| WO2020065818A1 (ja) | 送信装置、受信装置および無線通信システム | |
| EP3285422A1 (en) | Antenna apparatus | |
| CN102545989B (zh) | 用于分布式天线系统的通信方法、装置和系统 | |
| EP4030636A2 (en) | Beamforming of beams | |
| KR20160147499A (ko) | 무선 통신 시스템에서 안테나 어레이를 사용한 빔포밍 장치 및 방법 | |
| WO2024064857A1 (en) | Integrated sensing and communication with millimeter wave full duplex hybrid beamforming | |
| US12483305B2 (en) | Multiple spatial data streams via a re-configurable reflective device | |
| US20160360531A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for configuring virtual beam identifier, and method and apparatus for allocating resources using the virtual beam identifier | |
| WO2018231646A1 (en) | Massive multiple-input multiple-output (m-mimo) wireless distribution system (wds) and related methods for optimizing the m-mimo wds | |
| US20160183228A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for transmitting physical channel | |
| JP7755213B2 (ja) | 分散アンテナシステム、無線通信方法及び無線通信装置 | |
| CN114079490A (zh) | 一种通信方法及装置 | |
| JP2005136967A (ja) | 多重ビーム・スケジューリングを提供するためのシステムおよび方法 | |
| JP3620779B2 (ja) | チャネル割当装置 | |
| KR20060081194A (ko) | 다중 안테나 시스템에서 섹터 구성 장치 및 방법 | |
| JP7755204B2 (ja) | 無線通信方法及び分散アンテナシステム | |
| CN109982330B (zh) | 频谱资源调度方法及装置 | |
| US12040872B2 (en) | Beam-index based data distribution for scalable distributed radio systems | |
| KR102085901B1 (ko) | 차세대 이동통신 서비스 기지국 운용 시스템 및 방법 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22953020 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2024536589 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 22953020 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |