WO2019039149A1 - Air-conditioning control device - Google Patents
Air-conditioning control device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019039149A1 WO2019039149A1 PCT/JP2018/027163 JP2018027163W WO2019039149A1 WO 2019039149 A1 WO2019039149 A1 WO 2019039149A1 JP 2018027163 W JP2018027163 W JP 2018027163W WO 2019039149 A1 WO2019039149 A1 WO 2019039149A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- condensation
- dust
- dust concentration
- air conditioning
- dust sensor
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/24—Devices purely for ventilating or where the heating or cooling is irrelevant
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F24—HEATING; RANGES; VENTILATING
- F24F—AIR-CONDITIONING; AIR-HUMIDIFICATION; VENTILATION; USE OF AIR CURRENTS FOR SCREENING
- F24F11/00—Control or safety arrangements
- F24F11/89—Arrangement or mounting of control or safety devices
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to an air conditioning control device used in an air conditioning unit.
- Patent Document 1 describes a ventilator having a dust sensor.
- the dust sensor has a light receiving unit and a light emitting unit, and detects suspended particles by reflection of light.
- a dust sensor and a sensor storage unit for storing the dust sensor are provided inside a housing of the ventilation device.
- the sensor storage unit is provided facing the air passage inside the housing. Further, a shutter that can be opened and closed is provided at the boundary between the air passage and the sensor storage unit.
- the shutter is normally closed and opened only when the dust sensor detects it.
- Patent Document 1 it is supposed that the time for which the dust sensor is exposed to the air in the air passage can be shortened and the dirt of the lens of the dust sensor can be alleviated.
- Patent Document 1 As described in Patent Document 1, if condensation occurs on the dust sensor, the dust sensor may cause erroneous detection. And if the shutter of patent document 1 is used, it is thought that dew condensation of a dust sensor can be suppressed. However, Patent Document 1 has not described how to avoid an inappropriate situation caused by dew condensation on a dust sensor when condensation occurs. As a result of the inventors' detailed studies, the above was found.
- the present disclosure aims to provide an air conditioning control device capable of avoiding an inappropriate situation caused by dew condensation of a dust sensor when dew condensation occurs.
- an air conditioning control device includes: Used in an air conditioning unit that has an air conditioning case in which a ventilating passage through which air is blown into the vehicle compartment is formed, and a dust sensor that detects the dust concentration in the ventilating passage when the light receiving unit receives light emitted from the light emitting unit.
- Air conditioning control device A dew condensation determination unit that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor; When it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the dust concentration value detected during condensation that is treated as the concentration of dust during condensation is the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor before condensation occurs on the dust sensor And a value determination unit that determines based on the detection value before condensation which is the detection value of.
- the dust concentration is grasped as a size that is far from the actual value due to an inappropriate situation caused by the condensation, for example, an erroneous detection of the dust sensor. This can be avoided by using the dust concentration value during condensation.
- the air conditioning control device Used in an air conditioning unit that has an air conditioning case in which a ventilating passage through which air is blown into the vehicle compartment is formed, and a dust sensor that detects the dust concentration in the ventilating passage when the light receiving unit receives light emitted from the light emitting unit.
- Air conditioning control device A dew condensation determination unit that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor; A factor determination unit that determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to increase when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor; And a control execution unit that executes dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that a dust concentration increase factor has occurred.
- the dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit such that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control.
- FIG. 1 It is the block diagram which showed typically schematic structure with an air-conditioning unit and an air-conditioning control apparatus in 1st Embodiment. It is explanatory drawing for demonstrating easily the principle in which the dust sensor of FIG. 1 detects dust concentration. It is sectional drawing which showed typically schematic structure of the dust sensor of FIG. FIG. 2 is a block diagram simply showing an electrical configuration until the dust sensor of FIG. 1 detects a dust concentration and outputs a signal representing the dust concentration. In 1st Embodiment, it is the flowchart which showed the control processing which an air-conditioning control apparatus performs. FIG.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram exemplifying a waveform of a dust concentration detection value with an elapsed time taken as a horizontal axis in order to explain the control processing of FIG. 5 in the first embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a view exemplifying a waveform of the dust concentration detection value when the change ratio of the dust concentration detection value with respect to the elapsed time suddenly changes to a side where the change processing of the dust concentration detection value increases with time in order to explain the control process of FIG.
- FIG. 6 is a view exemplifying a waveform of the dust concentration detection value when the change ratio of the dust concentration detection value with respect to the elapsed time suddenly changes to a smaller side in order to explain the control process of FIG. 5 in the first embodiment.
- FIG. 11 it is a diagram illustrating the waveform of the dust concentration detection value with the elapsed time as the horizontal axis, and an enlarged view of the same portion as the portion shown in FIG. It is.
- FIG. 14 is a diagram showing an addition amount map used to determine the addition amount based on the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value before the occurrence of condensation in the second embodiment.
- FIG. 15 is a flowchart showing control processing executed by the air conditioning control device in the fourth embodiment, which corresponds to FIG. 14. It is the block diagram which showed the structure of the display apparatus in 4th Embodiment.
- 5th Embodiment it is the flowchart which showed the control processing which an air-conditioning control apparatus performs, Comprising: It is a figure corresponded in FIG.
- 6th Embodiment it is the flowchart which showed the control processing which an air-conditioning control apparatus performs, Comprising: It is a figure corresponded in FIG.
- the vehicle air conditioner 1 includes an air conditioning unit 2 and an air conditioning control device 40 used in the air conditioning unit 2.
- the air conditioning unit 2 is a vehicle air conditioning unit installed in a vehicle compartment and performing air conditioning of the vehicle interior.
- the air conditioning unit 2 is installed in an instrument panel disposed forward of the vehicle in the vehicle compartment.
- Arrows DR1 and DR2 in FIG. 1 indicate the direction of the vehicle on which the air conditioning unit 2 is mounted. That is, the arrow DR1 in FIG. 1 indicates the vehicle longitudinal direction DR1, and the arrow DR2 indicates the vehicle vertical direction DR2.
- These directions DR1 and DR2 are directions crossing each other, strictly speaking, directions perpendicular to each other.
- the air conditioning unit 2 includes an air conditioning case 21, an inside / outside air switching door 22, a blower 23, an evaporator 26, a heater core 27, an air mix door 28, an air filter 30, an outlet door 254, 255, 256, And a dust sensor 32 and the like.
- the air conditioning case 21 has a certain degree of elasticity and is formed of a resin excellent in strength.
- the resin that forms the air conditioning case 21 include polypropylene.
- the air conditioning case 21 forms an outer shell of the air conditioning unit 2, and an air passage, that is, an air passage 24 through which the air blown into the vehicle compartment flows is formed inside the air conditioning case 21. Further, the air conditioning case 21 introduces outside air into the air flow path 24 from the outside of the vehicle, inside air introduction port 241 for introducing the inside air into the air flow path 24 from a predetermined location in the vehicle room on the air flow direction upstream side of the air flow path 24 And an external air inlet 242 for Here, the inside air is the air inside the vehicle cabin, and the outside air is the air outside the vehicle cabin.
- the air conditioning case 21 has a plurality of outlet openings 251, 252, 253 for blowing air from the air passage 24 to the front seat area of the vehicle compartment on the downstream side of the air passage 24 in the air flow direction.
- the plurality of blowout openings 251, 252, 253 include a face blowout opening 251, a foot blowout opening 252, and a defroster blowout opening 253.
- the face blowout opening 251 is an opening that blows conditioned air toward the upper body of the occupant seated in the front seat.
- the foot blowing opening 252 is an opening that blows the conditioned air toward the feet of the occupant.
- the defroster blowout opening 253 is an opening that blows conditioned air toward the front window of the vehicle.
- an inside / outside air switching door 22 Inside the air conditioning case 21, an inside / outside air switching door 22, a blower 23, an evaporator 26, a heater core 27, an air mix door 28, an air filter 30, and the like are provided.
- the inside / outside air switching door 22 continuously adjusts the opening area of the inside air introduction port 241 and the opening area of the outside air introduction port 242.
- the inside / outside air switching door 22 is driven by an actuator such as a servomotor (not shown).
- the inside / outside air switching door 22 rotates so as to close one of the inside air introduction port 241 and the outside air introduction port 242 as the other introduction port is opened.
- the inside / outside air switching door 22 can adjust the ratio between the air volume of the inside air introduced into the air passage 24 and the air volume of the outside air.
- the inside / outside air switching door 22 is positioned at an operation position where the inside air introduction port 241 is opened and the outside air introduction port 242 is closed.
- the inside / outside air switching door 22 is positioned at an operation position in which the outside air introduction port 242 is opened while the inside air introduction port 241 is closed.
- the blower 23 is a centrifugal blower, and includes a centrifugal fan 231 disposed in the air passage 24 and a motor (not shown) that rotationally drives the centrifugal fan 231.
- a centrifugal fan 231 of the blower 23 When the centrifugal fan 231 of the blower 23 is rotationally driven, an air flow is formed in the air passage 24.
- the air introduced into the ventilation path 24 from the inside air introduction port 241 or the outside air introduction port 242 flows through the ventilation path 24, and any of the face outlet 251, the foot outlet 252 and the defroster outlet 253. It is blown out from the heel.
- the face blowout opening door 254 is provided in the face blowout opening 251 and adjusts the opening area of the face blowout opening 251.
- the foot blowout opening door 255 is provided in the foot blowout opening 252 and adjusts the opening area of the foot blowout opening 252.
- the defroster blowout opening door 256 is provided in the defroster blowout opening 253 and adjusts the opening area of the defroster blowout opening 253.
- the evaporator 26 is a heat exchanger for cooling the air flowing through the air passage 24.
- the evaporator 26 exchanges heat between the air passing through the evaporator 26 and the refrigerant, thereby cooling the air and evaporating the refrigerant.
- the heater core 27 is a heat exchanger for heating the air flowing through the air passage 24.
- the heater core 27 exchanges heat between, for example, the engine cooling water and the air passing through the heater core 27, and heats the air with the heat of the engine cooling water.
- the heater core 27 is disposed downstream of the evaporator 26 in the air flow direction.
- the air passage 24 of the air conditioning case 21 is formed in parallel to the heater core 27 and includes a bypass passage 24 a for bypassing the heater core 27 to allow air to flow.
- An air mix door 28 is provided between the evaporator 26 and the heater core 27 of the air conditioning unit 2.
- the air mix door 28 adjusts the ratio of the air volume passing through the evaporator 26 and bypassing the heater core 27 (that is, the air volume flowing through the bypass passage 24 a) and the air volume passing through the heater core 27 after passing through the evaporator 26 .
- the air filter 30 is disposed between the blower 23 and the evaporator 26 in the air passage 24 of the air conditioning case 21. In other words, the air filter 30 is disposed downstream of the blower 23 in the air flow direction and upstream of the evaporator 26 in the air flow direction.
- the air filter 30 captures dust and the like contained in the air passing through the air filter 30. Therefore, the air blown out from the blower 23 flows into the evaporator 26 after dust and the like in the air are removed to some extent by the air filter 30.
- the air conditioning control device 40 can operate the air conditioning unit 2 so as to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment. In the case of such operation, the air conditioning control device 40 operates the blower 23 after, for example, setting the air conditioning unit 2 to the inside air mode. And, the larger the air flow rate of the blower 23, the higher the dust removal ability of the air conditioning unit 2 for removing the dust in the passenger compartment.
- the dust sensor 32 is a detection device that detects the dust concentration at a predetermined sensing location. Then, the dust sensor 32 outputs a detection signal indicating the dust concentration to the air conditioning control device 40.
- the dust concentration is also referred to as dust concentration, and more specifically, is the mass concentration of dust contained in the air, and the unit of dust concentration is, for example, " ⁇ g / m 3 ". In short, the dust concentration is the mass of dust contained in a unit volume of air.
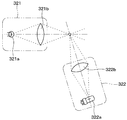
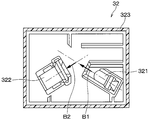
- the dust sensor 32 of the present embodiment is an optical dust sensor configured to detect dust concentration by a light scattering method. That is, as shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the dust sensor 32 accommodates the light emitting unit 321 that emits light, the light receiving unit 322 that receives the light emitted by the light emitting unit 321, and the light emitting unit 321 and the light receiving unit 322. And a sensor case 323. The dust sensor 32 detects the dust concentration of the air passage 24 by the light receiving portion 322 receiving the light emitted from the light emitting portion 321.
- the dust sensor 32 is disposed downstream of the centrifugal fan 231 of the blower 23 in the air flow direction and upstream of the air filter 30 in the air flow direction. Therefore, air is introduced into the sensor case 323 from between the centrifugal fan 231 and the air filter 30 in the air passage 24. That is, in the present embodiment, a portion between the centrifugal fan 231 and the air filter 30 in the ventilation path 24 is a sensing portion of the dust sensor 32.
- the light emitting portion 321 of the dust sensor 32 has a light emitting element 321 a formed of, for example, a light emitting diode, and an irradiation light lens 321 b.
- the light receiving section 322 has a light receiving element 322a configured by, for example, a photodiode, and a condensing lens 322b.
- the light emitted from the light emitting element 321a as shown by the arrow B1 in FIG. 3 and passing through the irradiation light lens 321b is reflected by the dust in the air introduced into the sensor case 323, and the reflected light is as shown by the arrow B2.
- the light is received by the light receiving element 322a through the condenser lens 322b.
- the light receiving element 322a generates a current by receiving light.
- the dust sensor 32 has a sensor circuit 324.
- the sensor circuit 324 amplifies the current of the light receiving element 322a and outputs it as a voltage output through an amplifier. The voltage output is converted to dust concentration.
- the dust sensor 32 detects the dust concentration in the air passage 24 in this manner.
- the vertical axis of the graph GF in FIG. 4 represents the dust concentration converted from the voltage value, that is, the density conversion value, and the horizontal axis of the graph GF represents the elapsed time.
- the air conditioning control device 40 illustrated in FIG. 1 is a control device that controls the air conditioning unit 2.
- the air-conditioning control apparatus 40 is an electronic control apparatus including a storage unit configured by a non-transitional tangible storage medium such as a semiconductor memory and a processor.
- the air conditioning control device 40 executes a computer program stored in the storage unit.
- the computer program is executed to execute a method corresponding to the computer program. That is, according to the computer program, the air conditioning control device 40 executes various control processes such as the control process of FIG. 5 described later.
- the air conditioning control device 40 controls the operation of each actuator by outputting a control signal to each actuator included in the air conditioning unit 2.
- the air conditioning control device 40 performs various air conditioning control in the air conditioning unit 2.
- the air conditioner control device 40 drives and controls the blower 23, the inside / outside air switching door 22, the air mix door 28, the face outlet door 254, the foot outlet door 255, and the defroster outlet door 256 described above. .
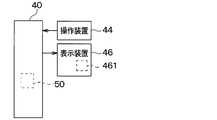
- an operation device 44 and a display device 46 are electrically connected to the air conditioning control device 40, for example.
- the operating device 44 is an operating unit operated by the occupant when adjusting the air volume, temperature, and the like of the conditioned air blown out from the air conditioning unit 2.
- the operating device 44 is disposed, for example, on an instrument panel of a vehicle.
- the air volume of the conditioned air, the target room temperature in the vehicle compartment, the outlet of the conditioned air, and the like can be set.
- the operating device 44 outputs, to the air conditioning control device 40, information indicating these settings, that is, operation information indicating an occupant operation performed on the operating device 44.
- the air conditioning control device 40 inputs the air flow of the blower 23 and the operation of the respective doors 22, 28, 254, 255, 256 from a plurality of sensors. Adjust or control automatically based on the signal.
- the display device 46 is a display unit that displays various information of the air conditioning unit 2. That is, a signal indicating various information of the air conditioning unit 2 is input from the air conditioning control device 40 to the display device 46, and the display device 46 performs display according to the input signal from the air conditioning control device 40.
- the display device 46 is disposed, for example, at a position where a passenger in the vehicle compartment can easily view, such as an instrument panel of a vehicle.
- the display device 46 may be included in the display device of another car-mounted device such as a car navigation device, or may be configured exclusively for the air conditioning unit 2.
- the air conditioning control device 40 functionally includes a dust sensor control unit 50 that performs control related to the dust sensor 32.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 executes, for example, the control process of FIG.
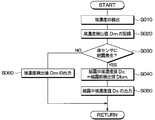
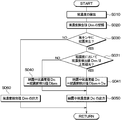
- FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing control processing executed by the dust sensor control unit 50.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 periodically and repeatedly executes the flowchart of FIG. 5 while the air conditioning unit 2 is operating, for example. As described above, being repeatedly and periodically executed during operation of the air conditioning unit 2 is the same as in the flowcharts of FIGS. 11, 14, 15, 17, and 18 described later.
- step S010 the dust sensor control unit 50 acquires the detection value Dm of the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor 32, that is, the dust concentration detection value Dm based on the detection signal from the dust sensor 32. . In short, the dust sensor control unit 50 performs the detection of the dust concentration in accordance with the detection signal from the dust sensor 32. After step S010, the process proceeds to step S020.
- step S020 the dust sensor control unit 50 records the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained in step S010.
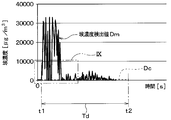
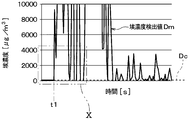
- the dust concentration detection value Dm is stored, for example, in a storage unit configured of a semiconductor memory or the like. By repeatedly executing this step S020, it is possible to obtain a time change of the dust concentration detection value Dm as shown in FIG.
- the horizontal axis in FIG. 6 indicates the elapsed time, and the vertical axis in FIG. 6 indicates the dust concentration.
- step S030 the process proceeds to step S030.
- step S030 the dust sensor control unit 50 determines whether condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 or not. For example, as shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, when the change rate of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time, that is, the slope of the dust concentration detection value Dm suddenly changes beyond a predetermined limit, condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 It is determined that When dew condensation occurs on the dust sensor 32, the light emitted from the light emitting unit 321 is also reflected to the dew condensation water in the sensor case 323. That is, in step S030, it is determined whether the dust concentration detection value Dm is affected by condensation of the dust sensor 32. If the dust concentration detection value Dm is affected by condensation, the dust sensor 32 is detected.
- the time t1 is the dew condensation start time when dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has started.
- the condensation elimination time point t2 at which the condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated is recognized based on the elapsed time from the condensation start time point t1. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 6, when the elapsed time from the condensation start time t1 reaches the condensation continuation time Td experimentally set in advance, the dust sensor control unit 50 causes the condensation of the dust sensor 32 to Is determined to be eliminated. In short, the point at which the dew condensation continuation time Td has elapsed from the dew condensation start time t1 is recognized as the dew condensation elimination time t2.
- step S030 if condensation is determined to occur in the dust sensor 32 from the change in the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm, the condensation continuation time Td elapses from the condensation start time t1 regardless of the dust concentration detection value Dm. Until then, the determination that the dew sensor 32 has generated condensation is continued.
- step S030 If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. For example, in the period from the dew condensation start time t1 to the dew condensation elimination time t2 in FIG. 6, the process proceeds from step S030 to step S040.
- step S030 when it is determined in step S030 that condensation does not occur on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S060. For example, before the condensation start time t1 and after the condensation elimination time t2 in FIG. 6, the process proceeds from step S030 to step S060.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc to be treated as the dust concentration in the occurrence of condensation based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm.
- the pre-condensation detected value Dbm is a detected value Dm of the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor 32 before condensation occurs (that is, immediately before the condensation start time t1). Specifically, since the detection of the dust concentration by the dust sensor 32 is periodically and repeatedly performed in step S010 of FIG. 5, the pre-condensation detected value Dbm is the previous detection with respect to the condensation start time t1 of the dust sensor 32. It is the obtained dust concentration detection value Dm. In short, the pre-condensation detected value Dbm is the latest dust concentration detected value Dm among the dust concentration detected values Dm sequentially obtained before the condensation start time t1.
- the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is determined based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm, the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is determined regardless of the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained during condensation occurrence. .
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc so that the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc becomes the pre-condensation detection value Dbm.
- the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is made the same value as the detection value before condensation Dbm.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the dust concentration value during condensation Dc based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm.
- step S ⁇ b> 050 the dust sensor control unit 50 outputs the dust concentration value during condensation Dc determined in step S ⁇ b> 040 as the dust concentration of the air passage 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32.
- the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is output to the control unit other than the dust sensor control unit 50 in the air conditioning control device 40, for example, a control unit that controls a plurality of doors of the air conditioning unit 2 and the blower 23.
- the dust concentration in the air passage 24 can be obtained during the dew condensation occurrence in the air conditioning control device 40 by executing this step S050.
- the dust concentration detection value Dm it is recognized that the dust concentration value during condensation is Dc.
- step S060 the dust sensor control unit 50 outputs the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained in step S010 as it is as the dust concentration of the air passage 24.
- the flowchart of FIG. 5 starts again from step S010 when step S050 or step S060 is completed.
- Step S030 in FIG. 2 corresponds to the condensation determination unit
- step S040 corresponds to the value determination unit.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40 functionally includes the condensation determination unit and the value determination unit.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32. Then, as shown in FIG. 6 and FIG. 10, when the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, the dust concentration value Dc during condensation treated as the dust concentration in the dew condensation occurrence is , And is determined based on the detection value before condensation Dbm.
- the dust concentration at the sensing location is grasped as a size far from the actual value due to an inappropriate situation caused by the dew condensation, for example, erroneous detection of the dust sensor 32. Can be avoided by using the dust concentration value Dc during condensation.
- the dust concentration close to the actual value during condensation is regarded as the dust concentration value Dc during condensation while avoiding the influence of erroneous detection of the dust sensor 32 caused by the condensation. It is possible to get.
- the dust removal capability for removing the dust in the vehicle interior by the air conditioning unit 2 is dust concentration It is possible to avoid a shortage due to false detection.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc so that the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc becomes the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. . Therefore, it is possible to easily determine the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc so that the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc does not become a value far from the actual value of the dust concentration at the sensing location.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines whether condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 or not. For example, as shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 when the change ratio of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time changes beyond a predetermined limit. judge. Therefore, there is an advantage that no special device is required to determine the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32.
- control processing executed by the air conditioning control device 40 is different from that of the first embodiment. Specifically, steps S031 and S041 of the flowchart of FIG. 11 are added to the flowchart of FIG. In the flowchart of FIG. 11, steps S010, S020, S030, S040, S050, and S060, which are the other steps, are the same as the flowchart of FIG.
- the control process of FIG. 11 is also executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40, similarly to the control process of FIG. 5 described above.
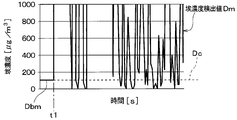
- step S031 the dust sensor control unit 50 determines whether the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 (that is, before the condensation start time t1 in FIG. 12). In other words, it is determined whether the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of the condensation tends to increase. For example, in the waveform of the dust concentration detection value Dm in FIG. 12, as shown in the A1 portion, the dust concentration detection value Dm rises before the condensation start time t1. In this case, the dust sensor control unit 50 It is determined that the concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32.
- the dew condensation start time t1 is the end time of the predetermined rise determination period, and in the transition of the dust concentration detection value Dm in the rise determination period up to the dew condensation start time t1, the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time Is calculated by a known method.
- the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before the condensation start time t1. Is determined.
- step S031 in FIG. 11 If it is determined in step S031 in FIG. 11 that the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before dew condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S041. On the other hand, when it is determined that the dust concentration detection value Dm has not risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040.
- the case where the dust concentration detection value Dm is not rising means the case where the dust concentration detection value Dm is falling or the dust concentration detection value Dm is not changing.
- step S041 the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc so that the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc has a value larger than the pre-condensation detection value Dbm.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 of the present embodiment determines the dust concentration value Dc during condensation as such, specifically, based on the increase rate of the dust concentration detection value Dm within the increase determination period, as shown in FIG.
- the amount of addition Dx is determined using 13 addition amount maps.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 sets a value obtained by adding the determined predetermined addition amount Dx to the pre-condensation detection value Dbm as a dust concentration value Dc during condensation.
- the horizontal axis indicates the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before dew condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32, that is, the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm within the increase determination period, and the vertical axis indicates the rate of increase
- An addition amount Dx is shown.
- the added amount Dx is set larger as the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 is larger. If the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm is larger than zero, the addition amount Dx is always larger than zero.
- step S040 in FIG. 11 the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is set to the same value as the pre-condensation detection value Dbm, as in step S040 in FIG. 5 of the first embodiment. Therefore, in step S040, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that the dust concentration value Dc during condensation is smaller than in the case where it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32.
- the dust concentration value Dc during dew condensation is determined so as to The case where it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 is, in other words, the case where the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is determined in step S041.
- step S040 the process proceeds to step S050.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 controls the dust concentration value Dc during condensation determined in step S040 or S041 in the dust of the air passage 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32, as in the first embodiment. Output as concentration.
- step S010 The flowchart of FIG. 11 is started again from step S010 when step S050 or step S060 ends.
- Steps S040 and S041 in FIG. 11 correspond to the value determination unit, and step S031 corresponds to the dust concentration increase determination unit.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40 functionally includes a value determination unit and a dust concentration increase determination unit in addition to the condensation determination unit similar to the first embodiment.
- the present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except for the above description. And in this embodiment, the effect show
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that condensation is generated in the dust sensor 32, and the dust concentration detection value Dm is before condensation generation of the dust sensor 32. If it is determined that the temperature is rising, the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc is determined so as to make the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc larger than the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. Therefore, it is possible to determine the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc so as to increase the accuracy of the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc with respect to the actual value of the dust concentration at the sensing location.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, it is assumed that the dust concentration detection value Dm has not risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32. If it is determined, the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc is determined so as to make the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc smaller than in the case where it is determined that the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before the occurrence of condensation. Therefore, depending on whether the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor, it is possible to appropriately make a difference in the magnitude of the dust concentration value during condensation Dc.
- the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc may be determined so that the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc does not easily fall below the actual value of the dust concentration. it can.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 sets the dust concentration value during condensation so that the dust concentration value during condensation Dc becomes a value larger than the detection value before condensation Dbm. Determine Dc.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 adds a predetermined addition amount Dx to the detection value before condensation Dbm to obtain a dust concentration value Dc during condensation. I assume. Then, as shown in FIG. 13, as the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 increases, the addition amount Dx for calculating the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is set larger. Therefore, it is possible to increase the accuracy of the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc with respect to the actual value of the dust concentration at the sensing location, as compared to the case where the added amount Dx is constant, for example.
- control processing executed by the air conditioning control device 40 is different from that of the first embodiment. Specifically, steps S072, S082, S092, and S102 of the flowchart of FIG. 14 are added to the flowchart of FIG.
- the flowchart of FIG. 14 does not include steps S020, S040, and S050 of FIG. Steps S010, S030, and S060 in FIG. 14 are the same as those in the flowchart in FIG.
- control process of FIG. 14 is executed by the air conditioning control device 40. More specifically, steps S010, S030 and S060 of FIG. 14 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40. Be done.
- step S030 If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S072. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S030 that condensation does not occur in the dust sensor 32, the flowchart of FIG. 14 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
- step S072 the air-conditioning control device 40 determines whether an instruction to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment has been issued from the occupant (ie, the user). That is, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is instructed by the manual operation of the occupant.
- the dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit 2 so that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control.
- the air conditioning unit 2 is set to the inside air mode, and the air flow of the blower 23 is This is the maximum air flow rate within the variable range of the air flow rate.
- the operating device 44 of FIG. 1 includes, for example, a dust removing switch manually operated by the occupant.
- the occupant can instruct the execution of the dust concentration reduction control by turning on the dust removal switch manually.
- step S072 in FIG. 14 If it is determined in step S072 in FIG. 14 that the execution of the dust concentration reduction control has been instructed, for example, if the on operation for turning on the dust removal switch is performed, the process proceeds to step S092. On the other hand, if it is determined that execution of dust concentration reduction control is not instructed, for example, if the dust removal switch is not turned on, the process proceeds to step S082.
- the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor has occurred. Specifically, it is determined whether the dust concentration increase factor has occurred after the condensation start time t1 of FIG.
- the dust concentration rise factor is a situation that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to rise, and is predetermined. As an example of the dust concentration rising factor, it can be mentioned that any door of the vehicle is opened and that any window glass of the vehicle is opened. This is because dust may easily intrude from the outside of the vehicle compartment into the vehicle compartment if any of these things occur.
- the opening and closing of the above-described vehicle door can be recognized based on a signal from a door sensor that detects the opening and closing of the door. Further, the opening and closing of the window glass of the vehicle can be recognized based on the operation information of the power window switch operated by the occupant in order to open and close the window glass.
- step S082 If it is determined in step S082 that a dust concentration increase cause has occurred, the process proceeds to step S092. On the other hand, when it is determined that the dust concentration increase cause is not generated, the flowchart of FIG. 14 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
- step S092 the air conditioning control device 40 carries out the dust concentration reduction control to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment.
- This dust concentration reduction control is performed regardless of the magnitude of the dust concentration detection value Dm, as can be understood from the implementation in accordance with the determination results of the above steps S030, S072, and S082.
- the dust concentration reduction control is performed to forcibly remove dust in the vehicle interior.
- step S102 the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has been eliminated. This determination is performed in the same manner as the determination of condensation elimination of the dust sensor 32 in step S030. Then, if the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether or not a predetermined time has elapsed from the condensation elimination time at which the condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated. The predetermined time is set experimentally in advance to a time that is sufficient to prevent the dust concentration reduction control in step S092 from ending before condensation is eliminated.
- step S102 If it is determined in step S102 that the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has not been eliminated yet, or if it is determined that the predetermined time has not yet elapsed from the condensation clearing of the dust sensor 32, the process returns to step S092. . That is, in this case, the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is continued in step S092.
- step S102 when it is determined in step S102 that the predetermined time has elapsed from the time when the condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated, the flowchart of FIG. 14 is ended and the process is started again from step S010. That is, in this case, the dust concentration reduction control ends.
- Step S082 in FIG. 14 corresponds to the factor determination unit, and steps S092 and S102 correspond to the control execution unit.
- the air-conditioning control apparatus 40 is functionally provided with the factor determination part and control implementation part other than the condensation determination part similar to 1st Embodiment.
- the present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except for the above description. And in this embodiment, the effect show
- the air conditioning control device 40 determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32
- the air conditioning control device 40 causes the dust concentration in the vehicle interior to increase. It is determined whether a dust concentration increase factor has occurred. Then, when it is determined that the dust concentration increase factor has occurred, the air conditioning control device 40 performs dust concentration reduction control.
- the dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit 2 so that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. Therefore, when dew condensation occurs on the dust sensor 32, an inappropriate situation caused by the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32, for example, an incorrect detection of the dust sensor 32, can not accurately grasp the dust concentration, and the dust concentration in the vehicle cabin increases. It is possible to avoid the situation of the problem by implementing the dust concentration reduction control.
- the dust concentration reduction control is performed even when the air conditioning control device 40 instructs the execution of the dust concentration reduction control by the manual operation of the occupant. Therefore, the occupant can reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment by the air conditioning unit 2 at any timing.
- control processing executed by the air conditioning control device 40 is different from that of the third embodiment. Specifically, steps S043, S053, S063 and S073 of the flowchart of FIG. 15 are added to the flowchart of FIG. Steps S010, S030, S060, S072, S082, S092, and S102 in FIG. 15 are the same as those in the flowchart of FIG.
- control process of FIG. Steps S010, S030, and S060 in FIG. 15 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40.
- step S030 If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S043. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S030 that condensation does not occur in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S063.
- step S ⁇ b> 043 the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether it is possible to notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32 by the dew condensation indicator 461 of FIG. 16.
- the dew condensation indicator 461 is a notification device for notifying the occupant of the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32, and constitutes a part of the display device 46.
- the dew condensation indicator 461 is provided in a vehicle mounted with the air conditioning control device 40, it is determined that the dew condensation indicator 461 can notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32.
- step S043 in FIG. 15 If it is determined in step S043 in FIG. 15 that the dew condensation indicator 461 can notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S053. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S043 that the dew condensation indicator 461 can not notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S073.
- step S 053 the air conditioning control device 40 notifies the occupant of the occurrence of dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 by the dew condensation indicator 461. Specifically, the air conditioning control device 40 turns on the dew condensation indicator 461 to thereby notify the occupant of the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32. If the condensation indicator 461 is already on, it will continue to be on. To turn on the condensation indicator 461 is, for example, to turn on or blink the condensation indicator 461. After step S053, the process proceeds to step S072.
- step S063 the air conditioning control device 40 switches the dew condensation indicator 461 off. If the condensation indicator 461 is already off, it will continue to be off. To turn off the condensation indicator 461 is, for example, to turn off the condensation indicator 461.
- the flowchart of FIG. 15 is started again from step S010 when step S063 is completed.
- step S073 the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether the air conditioning unit 2 is operated in the automatic air conditioning mode (in other words, the auto mode).
- step S092 when the dust concentration reduction control of step S092 is performed, the air conditioning unit 2 is automatically set to the inside air mode, and the air flow rate of the blower 23 is automatically adjusted. Therefore, this step S073 is provided to confirm in advance whether the occupant recognizes that the air conditioning unit 2 is in a state where the inside air mode and the outside air mode are automatically switched and the air flow rate is automatically adjusted. It is done.
- step S073 When it is determined in step S073 that the air conditioning unit 2 is operated in the automatic air conditioning mode, the process proceeds to step S082.
- the flowchart of FIG. It starts from step S010.
- the manual mode is an air conditioning mode in which the air volume adjustment of the air conditioning air, the temperature adjustment of the air conditioning air, and the selection of the inside air circulation or the outside air introduction are performed by the manual operation of the occupant on the operation device 44.
- step S072 of FIG. 15 the determination is made in the same manner as step S072 of FIG.
- the process proceeds to step S092.
- the flowchart of FIG. 15 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
- step S082 of FIG. 15 the determination is performed in the same manner as step S082 of FIG. 14.
- step S092 the flowchart of FIG. 15 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
- step S092 in FIG. 15 dust concentration reduction control is performed as in step S092 in FIG. After step S092 in FIG. 15, the process proceeds to step S102.
- step S102 of FIG. 15 the determination is made in the same manner as step S102 of FIG. That is, if it is determined in step S102 in FIG. 15 that the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has not been eliminated yet, or if it is determined that the predetermined time has not yet elapsed from the condensation elimination time of the dust sensor 32.
- step S092 the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is continued.
- the dust concentration reduction control ends.
- Steps S053 and S063 in FIG. 15 correspond to the dew condensation notification unit.
- the air-conditioning control device 40 functionally includes a condensation notification unit in addition to the condensation determination unit, the factor determination unit, and the control execution unit as in the third embodiment.
- the present embodiment is the same as the third embodiment except for the points described above. And in this embodiment, the effect show
- the air conditioning control device 40 determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32
- the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32 is given to the occupant by the dew condensation indicator 461. Inform. Therefore, it is possible to make the occupant recognize that the dust sensor 32 may not function properly due to condensation.
- the present embodiment is an embodiment roughly combining the first embodiment and the fourth embodiment described above. So, in this embodiment, points different from the above first embodiment and fourth embodiment will be mainly described.
- steps S010, S020, S030 and S040 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 17 are the same as the flowchart of FIG.
- Steps S043, S053, S063, S073, S072, S082, S092 and S102 in the flowchart shown in FIG. 17 are the same as those in the flowchart of FIG.
- control process of FIG. 17 is executed by the air conditioning control device 40 as in the fourth embodiment. Then, steps S010, S020, S030, and S040 in FIG. 17 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40.
- step S030 If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S030 that condensation is not generated in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S054.
- step S040 in FIG. 17 the same process as step S040 in FIG. 5 is performed. Then, after step S040, the process proceeds to step S044.
- step S044 in FIG. 17 the air-conditioning control device 40 regards the dew-in-condensing dust concentration value Dc determined in step S040 as the dust concentration of the air passage 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32. Then, the air conditioning control device 40 controls the air conditioning unit 2 so that dust is removed according to the dust concentration. If control of this air conditioning unit 2 is already implemented, it will be continued as it is. For example, in the control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration in step S044, the air conditioning unit 2 is set to the inside air mode, and the air flow of the blower 23 is increased as the dust concentration is higher. After step S044, the process proceeds to step S043.
- step S054 in FIG. 17 the control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration is performed as in step S044 described above.
- the air-conditioning control device 40 regards the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained in step S010 as the dust concentration at the sensing location of the dust sensor 32, not the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc.
- step S044 control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration value Dc during condensation is carried out in the above-mentioned step S044, but control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration detection value Dm is carried out in this step S054 .
- step S054 the process proceeds to step S063.
- step S092 the dust concentration reduction control in step S092 is performed prior to the control of the air conditioning unit 2 performed in step S044 or S054. That is, when the control process of FIG. 17 proceeds to step S092 while the control of the air conditioning unit 2 in step S044 or S054 is being carried out, instead of the control of the air conditioning unit 2 in step S044 or S054, Dust concentration reduction control is implemented.
- the present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment or the fourth embodiment except for what has been described above. And in this embodiment, the effect show
- FIG. 18 A flowchart of this embodiment is shown in FIG. 18, and steps S010, S020, S030, S040, S031, and S041 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 18 are the same as the flowchart of FIG. Steps S043, S053, S063, S073, S072, S082, S092, S102, S044, and S054 in the flowchart shown in FIG. 18 are similar to the flowchart in FIG.
- step S030 If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S031. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S030 that condensation is not generated in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S054.
- step S031 When it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S041. Then, after step S041, the process proceeds to step S044. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm has not risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. Then, after step S040, the process proceeds to step S044.
- step S044 in FIG. 18 the air conditioning control device 40 controls the dust concentration value Dc during condensation determined in step S040 or step S041 in the ventilation path 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32 as in step S044 in FIG. 17. It is regarded as dust concentration. And control of the air-conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration is implemented. After step S044, the process proceeds to step S043.
- the present embodiment is the same as the second embodiment or the fifth embodiment except for what has been described above. And in this embodiment, the effect show
- the air filter 30 is disposed downstream of the dust sensor 32 in the air flow direction and upstream of the evaporator 26 in the air flow path 24 of the air conditioning case 21. Although arranged, this is an example. As long as all or most of the air flowing through the air passage 24 passes through the air filter 30, the arrangement of the air filter 30 in the air passage 24 is not limited.
- the air-conditioning control apparatus 40 functionally contains the dust sensor control part 50, this is an example.
- the air conditioning control device 40 may be configured of a plurality of physically separated control devices.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 may be a control device separate from the control unit that controls the doors and the blower 23 in the air conditioning control device 40.
- the dust sensor control unit 50 and the dust sensor 32 may be integrally configured to constitute one dust sensor unit.
- step S030 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 5 it is determined in step S030 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 5 whether condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, and the presence or absence of the condensation generation is the dust concentration detection value Dm. And the elapsed time, which is an example.
- the presence or absence of dew condensation may be determined using the temperature and relative humidity of the air introduced into the sensor case 323 of the dust sensor 32, the ambient temperature of the dust sensor 32, and the like. The same applies to each of the second and subsequent embodiments.
- the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is the same value as the pre-condensation detection value Dbm in step S040 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 5, the present invention is not limited thereto.
- the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc may be determined based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm.
- the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc may be a value obtained by adding a certain value to the detection value before condensation Dbm, or may be obtained by subtracting a certain value from the detection value before condensation Dbm. It may be a value. The same applies to the dust concentration value during dew condensation Dc in each of the second and subsequent embodiments.
- step S072 the flowchart of FIG. 14 includes step S072, but it may be assumed that step S072 is not included in the flowchart of FIG. In the flowchart without step S072, when it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S082.
- step S030 it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, and if an instruction to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is issued from the occupant, the process proceeds to step S072. If it is determined, dust concentration reduction control is performed in step S092. However, this is an example. For example, even if condensation is not generated in the dust sensor 32, the dust concentration reduction control may be performed when an instruction to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is issued from the occupant.
- the condensation indicator 461 is provided in the vehicle mounted with the air conditioning control device 40 in step S043 in FIG. It is determined that it is possible to notify the occupant by However, this is one example.
- the display device 46 is configured to be able to switch a plurality of display modes alternatively. When the display device 46 is turned on as such, when the display device 46 is switched to the display mode in which the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32 can be displayed by the dew condensation indicator 461, the dew condensation occurrence is displayed by the occupant using the dew condensation indicator 461. It is determined that it is possible to inform
- the condensation determination unit determines whether condensation has occurred in the dust sensor. If it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines the dust concentration value during condensation to be treated as the dust concentration during condensation generation before the condensation of the dust sensor occurs. It is determined based on the detection value before condensation which is the detection value of the dust concentration detected in
- the value determination unit determines the dust concentration value during condensation so as to set the dust concentration value during condensation to the detection value before condensation. Therefore, the dust concentration value during condensation can be easily determined so that the dust concentration value during condensation does not become a value far from the actual value of dust concentration at the sensing location of the dust sensor.
- the value determination unit determines that the detected value of the dust concentration is increased before condensation occurs in the dust sensor. If it is determined by the dust concentration increase determination unit, the in-condensation dust concentration value is determined so as to make the in-condensation dust concentration value larger than the pre-condensation detection value. Therefore, it is possible to determine the dust concentration value during condensation so as to increase the accuracy of the dust concentration value during condensation relative to the actual value of dust concentration.
- the value determination unit when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation occurs on the dust sensor, the value determination unit increases the detection value of the dust concentration before condensation occurs on the dust sensor. If it is determined by the dust concentration rise judging unit, the dust concentration value during condensation is set to a smaller value than when it is determined that the detection value of the dust concentration has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor. Determine the dust concentration value during condensation. Therefore, it is possible to appropriately differentiate the magnitude of the dust concentration value during condensation depending on whether the detection value of the dust concentration has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor.
- the detection of the dust concentration by the dust sensor is periodically and repeatedly performed.
- the detection value before condensation is a detection value of the dust concentration obtained by the previous detection with respect to the dew condensation start time of the dust sensor.
- the factor determination unit when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor, the factor determination unit is configured to increase the dust concentration in the vehicle interior by a predetermined dust concentration increase factor It is determined whether or not has occurred.
- the control execution unit implements dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that a dust concentration increase factor has occurred.
- the dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit so that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. The same applies to the seventh aspect.
- the condensation notification unit when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor, the condensation notification unit notifies the occupant of the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor by the notification device. Therefore, it is possible to make the occupant aware that the dust sensor may not function properly due to condensation.
- control execution unit executes the dust concentration reduction control even when the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is instructed by the manual operation of the occupant. Therefore, the occupant can reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment by the air conditioning unit at any timing.
- the dew condensation determining unit determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor when the change ratio of the detected value of the dust concentration to the elapsed time changes beyond a predetermined limit. Accordingly, there is an advantage that no special device is required to determine the occurrence of dew condensation on the dust sensor.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
Abstract
The purpose of the present invention is to provide an air-conditioning control device that can avoid an inappropriate situation caused by condensation on a dust sensor when condensation occurs on the dust sensor. An air-conditioning unit (2) includes: an air-conditioner case (21) in which an air passage (24), through which air blown out into a vehicle cabin passes, is formed; and a dust sensor (32) in which light emitted from a light emitting part (321) is received by a light receiving part (322), thus detecting the dust concentration in the air passage. An air-conditioning control device used in the air-conditioning unit includes a condensation determination unit (S030) and a value determination unit (S040, S041). The condensation determination unit determines whether condensation has occurred on the dust sensor. If it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines an condensation-present dust concentration value (Dc), which is treated as the dust concentration at which condensation is occurring, on the basis of a pre-condensation detection value (Dbm), which is the detection value of the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor before the condensation has occurred on the dust sensor.
Description
本出願は、2017年8月23日に出願された日本特許出願番号2017-160340号に基づくもので、ここにその記載内容が参照により組み入れられる。
This application is based on Japanese Patent Application No. 2017-160340 filed on August 23, 2017, the contents of which are incorporated herein by reference.
本開示は、空調ユニットにおいて用いられる空調制御装置に関するものである。
The present disclosure relates to an air conditioning control device used in an air conditioning unit.
特許文献1には、埃センサを有する換気装置が記載されている。その埃センサは受光部と発光部とを有し、光の反射により浮遊粒子を検知する。換気装置の筐体内部には、埃センサと、この埃センサを格納するセンサ格納部とが設けられている。このセンサ格納部は、筐体内部の風路に面して設けられている。更に、その風路とセンサ格納部との境界には、開閉可能なシャッターが設けられている。
Patent Document 1 describes a ventilator having a dust sensor. The dust sensor has a light receiving unit and a light emitting unit, and detects suspended particles by reflection of light. A dust sensor and a sensor storage unit for storing the dust sensor are provided inside a housing of the ventilation device. The sensor storage unit is provided facing the air passage inside the housing. Further, a shutter that can be opened and closed is provided at the boundary between the air passage and the sensor storage unit.
このシャッターは通常時には閉じられ、埃センサが検知する時にのみ開かれる。これにより、特許文献1では、埃センサが風路内の空気に晒される時間を短縮し埃センサのレンズの汚れを緩和することができるとされている。
The shutter is normally closed and opened only when the dust sensor detects it. Thus, according to Patent Document 1, it is supposed that the time for which the dust sensor is exposed to the air in the air passage can be shortened and the dirt of the lens of the dust sensor can be alleviated.
特許文献1に記載されているように、埃センサに結露が発生すると、埃センサが誤検出を生じる場合がある。そして、特許文献1のシャッターを用いれば埃センサの結露を抑制できると思われる。しかしながら、埃センサに結露が発生した場合にその埃センサの結露に起因した不適切な事態を如何に回避するかということは、特許文献1には記載されていなかった。発明者らの詳細な検討の結果、以上のようなことが見出された。
As described in Patent Document 1, if condensation occurs on the dust sensor, the dust sensor may cause erroneous detection. And if the shutter of patent document 1 is used, it is thought that dew condensation of a dust sensor can be suppressed. However, Patent Document 1 has not described how to avoid an inappropriate situation caused by dew condensation on a dust sensor when condensation occurs. As a result of the inventors' detailed studies, the above was found.
本開示は上記点に鑑みて、埃センサに結露が発生した場合にその埃センサの結露に起因した不適切な事態を回避することが可能な空調制御装置を提供することを目的とする。
In view of the above-described point, the present disclosure aims to provide an air conditioning control device capable of avoiding an inappropriate situation caused by dew condensation of a dust sensor when dew condensation occurs.
上記目的を達成するため、本開示の1つの観点によれば、空調制御装置は、
車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する通風路が形成された空調ケースと、発光部から発せされた光を受光部が受光することにより通風路の埃濃度を検出する埃センサとを有する空調ユニットにおいて用いられる空調制御装置であって、
埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する結露判定部と、
埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合には、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値を、埃センサがその埃センサの結露発生前に検出した埃濃度の検出値である結露前検出値に基づいて決定する値決定部とを備えている。 In order to achieve the above object, according to one aspect of the present disclosure, an air conditioning control device includes:
Used in an air conditioning unit that has an air conditioning case in which a ventilating passage through which air is blown into the vehicle compartment is formed, and a dust sensor that detects the dust concentration in the ventilating passage when the light receiving unit receives light emitted from the light emitting unit. Air conditioning control device,
A dew condensation determination unit that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
When it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the dust concentration value detected during condensation that is treated as the concentration of dust during condensation is the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor before condensation occurs on the dust sensor And a value determination unit that determines based on the detection value before condensation which is the detection value of.
車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する通風路が形成された空調ケースと、発光部から発せされた光を受光部が受光することにより通風路の埃濃度を検出する埃センサとを有する空調ユニットにおいて用いられる空調制御装置であって、
埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する結露判定部と、
埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合には、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値を、埃センサがその埃センサの結露発生前に検出した埃濃度の検出値である結露前検出値に基づいて決定する値決定部とを備えている。 In order to achieve the above object, according to one aspect of the present disclosure, an air conditioning control device includes:
Used in an air conditioning unit that has an air conditioning case in which a ventilating passage through which air is blown into the vehicle compartment is formed, and a dust sensor that detects the dust concentration in the ventilating passage when the light receiving unit receives light emitted from the light emitting unit. Air conditioning control device,
A dew condensation determination unit that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
When it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the dust concentration value detected during condensation that is treated as the concentration of dust during condensation is the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor before condensation occurs on the dust sensor And a value determination unit that determines based on the detection value before condensation which is the detection value of.
このようにすれば、埃センサに結露が発生した場合に、その結露に起因した不適切な事態、例えば埃センサの誤検出に起因して埃濃度が実際値から懸け離れた大きさとして把握されるという事態を、結露中埃濃度値を用いることで回避することが可能である。
In this way, when condensation occurs on the dust sensor, the dust concentration is grasped as a size that is far from the actual value due to an inappropriate situation caused by the condensation, for example, an erroneous detection of the dust sensor. This can be avoided by using the dust concentration value during condensation.
また、本開示の別の観点によれば、空調制御装置は、
車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する通風路が形成された空調ケースと、発光部から発せされた光を受光部が受光することにより通風路の埃濃度を検出する埃センサとを有する空調ユニットにおいて用いられる空調制御装置であって、
埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する結露判定部と、
埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合に、車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する要因判定部と、
埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと要因判定部により判定された場合に埃濃度低減制御を実施する制御実施部とを備え、
埃濃度低減制御は、その埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように空調ユニットを作動させる制御である。 Also, according to another aspect of the present disclosure, the air conditioning control device
Used in an air conditioning unit that has an air conditioning case in which a ventilating passage through which air is blown into the vehicle compartment is formed, and a dust sensor that detects the dust concentration in the ventilating passage when the light receiving unit receives light emitted from the light emitting unit. Air conditioning control device,
A dew condensation determination unit that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
A factor determination unit that determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to increase when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
And a control execution unit that executes dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that a dust concentration increase factor has occurred.
The dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit such that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control.
車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する通風路が形成された空調ケースと、発光部から発せされた光を受光部が受光することにより通風路の埃濃度を検出する埃センサとを有する空調ユニットにおいて用いられる空調制御装置であって、
埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する結露判定部と、
埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合に、車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する要因判定部と、
埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと要因判定部により判定された場合に埃濃度低減制御を実施する制御実施部とを備え、
埃濃度低減制御は、その埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように空調ユニットを作動させる制御である。 Also, according to another aspect of the present disclosure, the air conditioning control device
Used in an air conditioning unit that has an air conditioning case in which a ventilating passage through which air is blown into the vehicle compartment is formed, and a dust sensor that detects the dust concentration in the ventilating passage when the light receiving unit receives light emitted from the light emitting unit. Air conditioning control device,
A dew condensation determination unit that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
A factor determination unit that determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to increase when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
And a control execution unit that executes dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that a dust concentration increase factor has occurred.
The dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit such that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control.
このようにすれば、埃センサに結露が発生した場合に、その埃センサの結露に起因した不適切な事態、例えば埃センサの誤検出で埃濃度を正確に把握できず車室内の埃濃度が上昇するという事態を、埃濃度低減制御の実施により回避することが可能である。
In this way, when dew condensation occurs on the dust sensor, an inappropriate situation caused by the dew condensation on the dust sensor, for example, the false detection of the dust sensor can not accurately grasp the dust concentration, and the dust concentration in the vehicle interior It is possible to prevent the situation of rising by implementing the dust concentration reduction control.
なお、各構成要素等に付された括弧付きの参照符号は、その構成要素等と後述する実施形態に記載の具体的な構成要素等との対応関係の一例を示すものである。
The reference numerals in parentheses attached to each component, etc., shows an example of a relationship of the specific component such as described in the following embodiments and their components, and the like.
以下、図面を参照しながら、各実施形態を説明する。なお、以下の各実施形態相互において、互いに同一もしくは均等である部分には、図中、同一符号を付してある。
Hereinafter, each embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. In the following embodiments, parts identical or equivalent to each other are denoted by the same reference numerals in the drawings.
(第1実施形態)
図1に示すように本実施形態では、車両用空調装置1は、空調ユニット2と、その空調ユニット2において用いられる空調制御装置40とを備えている。その空調ユニット2は、車室内に設置され車室内の空調を行う車両用空調ユニットである。例えば、空調ユニット2は、車室内のうち車両前方側に配置されたインストルメントパネル内に設置される。なお、図1の各矢印DR1、DR2は、空調ユニット2が搭載される車両の向きを示す。すなわち、図1の矢印DR1は車両前後方向DR1を示し、矢印DR2は車両上下方向DR2を示している。これらの方向DR1、DR2は互いに交差する方向、厳密に言えば互いに直交する方向である。 First Embodiment
As shown in FIG. 1, in the present embodiment, thevehicle air conditioner 1 includes an air conditioning unit 2 and an air conditioning control device 40 used in the air conditioning unit 2. The air conditioning unit 2 is a vehicle air conditioning unit installed in a vehicle compartment and performing air conditioning of the vehicle interior. For example, the air conditioning unit 2 is installed in an instrument panel disposed forward of the vehicle in the vehicle compartment. Arrows DR1 and DR2 in FIG. 1 indicate the direction of the vehicle on which the air conditioning unit 2 is mounted. That is, the arrow DR1 in FIG. 1 indicates the vehicle longitudinal direction DR1, and the arrow DR2 indicates the vehicle vertical direction DR2. These directions DR1 and DR2 are directions crossing each other, strictly speaking, directions perpendicular to each other.
図1に示すように本実施形態では、車両用空調装置1は、空調ユニット2と、その空調ユニット2において用いられる空調制御装置40とを備えている。その空調ユニット2は、車室内に設置され車室内の空調を行う車両用空調ユニットである。例えば、空調ユニット2は、車室内のうち車両前方側に配置されたインストルメントパネル内に設置される。なお、図1の各矢印DR1、DR2は、空調ユニット2が搭載される車両の向きを示す。すなわち、図1の矢印DR1は車両前後方向DR1を示し、矢印DR2は車両上下方向DR2を示している。これらの方向DR1、DR2は互いに交差する方向、厳密に言えば互いに直交する方向である。 First Embodiment
As shown in FIG. 1, in the present embodiment, the
図1に示すように、空調ユニット2は、空調ケース21、内外気切替ドア22、送風機23、エバポレータ26、ヒータコア27、エアミックスドア28、空気フィルタ30、吹出開口部ドア254、255、256、および埃センサ32などを有している。
As shown in FIG. 1, the air conditioning unit 2 includes an air conditioning case 21, an inside / outside air switching door 22, a blower 23, an evaporator 26, a heater core 27, an air mix door 28, an air filter 30, an outlet door 254, 255, 256, And a dust sensor 32 and the like.
空調ケース21は、ある程度の弾性を有し、強度的にも優れた樹脂にて形成されている。空調ケース21を形成する樹脂として、例えばポリプロピレンが挙げられる。空調ケース21は空調ユニット2の外殻を成し、空調ケース21の内側には、車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する空気通路すなわち通風路24が形成されている。また、空調ケース21は、通風路24の空気流れ方向上流側に、車室内の所定箇所から通風路24に内気を導入するための内気導入口241と、車外から通風路24に外気を導入するための外気導入口242とを有している。ここで、内気とは車室内の空気であり、外気とは車室外の空気である。
The air conditioning case 21 has a certain degree of elasticity and is formed of a resin excellent in strength. Examples of the resin that forms the air conditioning case 21 include polypropylene. The air conditioning case 21 forms an outer shell of the air conditioning unit 2, and an air passage, that is, an air passage 24 through which the air blown into the vehicle compartment flows is formed inside the air conditioning case 21. Further, the air conditioning case 21 introduces outside air into the air flow path 24 from the outside of the vehicle, inside air introduction port 241 for introducing the inside air into the air flow path 24 from a predetermined location in the vehicle room on the air flow direction upstream side of the air flow path 24 And an external air inlet 242 for Here, the inside air is the air inside the vehicle cabin, and the outside air is the air outside the vehicle cabin.
また、空調ケース21は、通風路24の空気流れ方向下流側に、通風路24から車室内の前席領域に空気を送風するための複数の吹出開口部251、252、253を有している。その複数の吹出開口部251、252、253は、フェイス吹出開口部251とフット吹出開口部252とデフロスタ吹出開口部253とを含んでいる。
Further, the air conditioning case 21 has a plurality of outlet openings 251, 252, 253 for blowing air from the air passage 24 to the front seat area of the vehicle compartment on the downstream side of the air passage 24 in the air flow direction. . The plurality of blowout openings 251, 252, 253 include a face blowout opening 251, a foot blowout opening 252, and a defroster blowout opening 253.
フェイス吹出開口部251は、前座席に着座した乗員の上半身に向けて空調風を吹き出す開口部である。フット吹出開口部252は、その乗員の足元に向けて空調風を吹き出す開口部である。デフロスタ吹出開口部253は、車両のフロントウインドウに向けて空調風を吹き出す開口部である。
The face blowout opening 251 is an opening that blows conditioned air toward the upper body of the occupant seated in the front seat. The foot blowing opening 252 is an opening that blows the conditioned air toward the feet of the occupant. The defroster blowout opening 253 is an opening that blows conditioned air toward the front window of the vehicle.
空調ケース21の内部には、内外気切替ドア22、送風機23、エバポレータ26、ヒータコア27、エアミックスドア28、および空気フィルタ30などが設けられている。
Inside the air conditioning case 21, an inside / outside air switching door 22, a blower 23, an evaporator 26, a heater core 27, an air mix door 28, an air filter 30, and the like are provided.
内外気切替ドア22は、内気導入口241の開口面積と外気導入口242の開口面積とを連続的に調整するものである。内外気切替ドア22は、図示していないサーボモータなどのアクチュエータによって駆動される。内外気切替ドア22は、内気導入口241と外気導入口242とのうち一方の導入口を開くほど他方の導入口を閉じるように回転動作する。これにより、内外気切替ドア22は、通風路24に導入される内気の風量と外気の風量との割合を調整することが可能である。
The inside / outside air switching door 22 continuously adjusts the opening area of the inside air introduction port 241 and the opening area of the outside air introduction port 242. The inside / outside air switching door 22 is driven by an actuator such as a servomotor (not shown). The inside / outside air switching door 22 rotates so as to close one of the inside air introduction port 241 and the outside air introduction port 242 as the other introduction port is opened. As a result, the inside / outside air switching door 22 can adjust the ratio between the air volume of the inside air introduced into the air passage 24 and the air volume of the outside air.
例えば、通風路24に専ら内気が導入される内気モードでは、内外気切替ドア22は、内気導入口241を開く一方で外気導入口242を閉じる作動位置に位置決めされる。逆に、通風路24に専ら外気が導入される外気モードでは、内外気切替ドア22は、内気導入口241を閉じる一方で外気導入口242を開く作動位置に位置決めされる。
For example, in the inside air mode in which inside air is introduced exclusively into the air passage 24, the inside / outside air switching door 22 is positioned at an operation position where the inside air introduction port 241 is opened and the outside air introduction port 242 is closed. Conversely, in the outside air mode in which outside air is introduced into the air passage 24 exclusively, the inside / outside air switching door 22 is positioned at an operation position in which the outside air introduction port 242 is opened while the inside air introduction port 241 is closed.
送風機23は遠心送風機であり、通風路24に配置された遠心ファン231と、その遠心ファン231を回転駆動する不図示のモータとを有している。送風機23の遠心ファン231が回転駆動されると、通風路24に気流が形成される。これにより、内気導入口241または外気導入口242から通風路24に導入された空気は、その通風路24を流れ、フェイス吹出開口部251とフット吹出開口部252とデフロスタ吹出開口部253とのいずれかから吹き出される。なお、通風路24のうち遠心ファン231よりも空気流れ方向下流側では、大まかには矢印Arで示される方向に空気が流れる。
The blower 23 is a centrifugal blower, and includes a centrifugal fan 231 disposed in the air passage 24 and a motor (not shown) that rotationally drives the centrifugal fan 231. When the centrifugal fan 231 of the blower 23 is rotationally driven, an air flow is formed in the air passage 24. Thus, the air introduced into the ventilation path 24 from the inside air introduction port 241 or the outside air introduction port 242 flows through the ventilation path 24, and any of the face outlet 251, the foot outlet 252 and the defroster outlet 253. It is blown out from the heel. In the air flow direction downstream of the centrifugal fan 231 in the air passage 24, air flows roughly in the direction indicated by the arrow Ar.
フェイス吹出開口部ドア254はフェイス吹出開口部251に設けられており、そのフェイス吹出開口部251の開口面積を調整する。フット吹出開口部ドア255はフット吹出開口部252に設けられており、そのフット吹出開口部252の開口面積を調整する。デフロスタ吹出開口部ドア256はデフロスタ吹出開口部253に設けられており、そのデフロスタ吹出開口部253の開口面積を調整する。
The face blowout opening door 254 is provided in the face blowout opening 251 and adjusts the opening area of the face blowout opening 251. The foot blowout opening door 255 is provided in the foot blowout opening 252 and adjusts the opening area of the foot blowout opening 252. The defroster blowout opening door 256 is provided in the defroster blowout opening 253 and adjusts the opening area of the defroster blowout opening 253.
エバポレータ26は、通風路24を流れる空気を冷却するための熱交換器である。エバポレータ26は、エバポレータ26を通過する空気と冷媒とを熱交換させ、それにより、その空気を冷却すると共に冷媒を蒸発させる。
The evaporator 26 is a heat exchanger for cooling the air flowing through the air passage 24. The evaporator 26 exchanges heat between the air passing through the evaporator 26 and the refrigerant, thereby cooling the air and evaporating the refrigerant.
ヒータコア27は、通風路24を流れる空気を加熱するための熱交換器である。ヒータコア27は、例えばエンジン冷却水とヒータコア27を通過する空気とを熱交換させ、エンジン冷却水の熱で空気を加熱する。また、ヒータコア27は、エバポレータ26に対し空気流れ方向下流側に配置されている。
The heater core 27 is a heat exchanger for heating the air flowing through the air passage 24. The heater core 27 exchanges heat between, for example, the engine cooling water and the air passing through the heater core 27, and heats the air with the heat of the engine cooling water. The heater core 27 is disposed downstream of the evaporator 26 in the air flow direction.
また、空調ケース21の通風路24は、ヒータコア27に対し並列に形成されヒータコア27を迂回させて空気を流すバイパス通路24aを含んでいる。
Further, the air passage 24 of the air conditioning case 21 is formed in parallel to the heater core 27 and includes a bypass passage 24 a for bypassing the heater core 27 to allow air to flow.
空調ユニット2のエバポレータ26とヒータコア27との間には、エアミックスドア28が設けられている。エアミックスドア28は、エバポレータ26を通過し、ヒータコア27を迂回して流れる風量(すなわち、バイパス通路24aを流れる風量)と、エバポレータ26を通過した後にヒータコア27を通過する風量との割合を調整する。
An air mix door 28 is provided between the evaporator 26 and the heater core 27 of the air conditioning unit 2. The air mix door 28 adjusts the ratio of the air volume passing through the evaporator 26 and bypassing the heater core 27 (that is, the air volume flowing through the bypass passage 24 a) and the air volume passing through the heater core 27 after passing through the evaporator 26 .
空気フィルタ30は、空調ケース21の通風路24のうち送風機23とエバポレータ26との間に配置されている。言い換えれば、空気フィルタ30は、送風機23に対する空気流れ方向下流側で且つエバポレータ26に対する空気流れ方向上流側に配置されている。
The air filter 30 is disposed between the blower 23 and the evaporator 26 in the air passage 24 of the air conditioning case 21. In other words, the air filter 30 is disposed downstream of the blower 23 in the air flow direction and upstream of the evaporator 26 in the air flow direction.
空気フィルタ30は、その空気フィルタ30を通過する空気中に含まれる塵埃等を捕捉する。従って、送風機23から吹き出された空気は、その空気中の塵埃等が空気フィルタ30によって或る程度取り除かれてから、エバポレータ26へ流入する。
The air filter 30 captures dust and the like contained in the air passing through the air filter 30. Therefore, the air blown out from the blower 23 flows into the evaporator 26 after dust and the like in the air are removed to some extent by the air filter 30.
この空気フィルタ30が空調ケース21の通風路24に設けられているので、空調制御装置40は、車室内の埃濃度を低減するように空調ユニット2を運転することが可能である。そのように運転する場合、空調制御装置40は、例えば、空調ユニット2を内気モードとした上で、送風機23を作動させる。そして、送風機23の送風量が大きくなるほど、空調ユニット2が車室内の埃を除去する埃除去能力は高くなる。
Since the air filter 30 is provided in the ventilation path 24 of the air conditioning case 21, the air conditioning control device 40 can operate the air conditioning unit 2 so as to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment. In the case of such operation, the air conditioning control device 40 operates the blower 23 after, for example, setting the air conditioning unit 2 to the inside air mode. And, the larger the air flow rate of the blower 23, the higher the dust removal ability of the air conditioning unit 2 for removing the dust in the passenger compartment.
埃センサ32は、所定のセンシング箇所の埃濃度を検出する検出装置である。そして、埃センサ32は、埃濃度を示す検出信号を空調制御装置40へ出力する。その埃濃度は塵埃濃度とも言い、詳細に言えば、空気中に含まれる埃の質量濃度であり、埃濃度の単位は例えば「μg/m3」である。要するに、埃濃度とは、空気の単位体積に含まれる埃の質量である。
The dust sensor 32 is a detection device that detects the dust concentration at a predetermined sensing location. Then, the dust sensor 32 outputs a detection signal indicating the dust concentration to the air conditioning control device 40. The dust concentration is also referred to as dust concentration, and more specifically, is the mass concentration of dust contained in the air, and the unit of dust concentration is, for example, "μg / m 3 ". In short, the dust concentration is the mass of dust contained in a unit volume of air.
本実施形態の埃センサ32は、光散乱法により埃濃度を検出するように構成された光学式塵埃センサである。つまり、埃センサ32は、図2および図3に示すように、光を発する発光部321と、発光部321が発した光を受ける受光部322と、その発光部321と受光部322とを収容するセンサケース323とを備えている。埃センサ32は、その発光部321から発せされた光を受光部322が受光することにより、通風路24の埃濃度を検出する。
The dust sensor 32 of the present embodiment is an optical dust sensor configured to detect dust concentration by a light scattering method. That is, as shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the dust sensor 32 accommodates the light emitting unit 321 that emits light, the light receiving unit 322 that receives the light emitted by the light emitting unit 321, and the light emitting unit 321 and the light receiving unit 322. And a sensor case 323. The dust sensor 32 detects the dust concentration of the air passage 24 by the light receiving portion 322 receiving the light emitted from the light emitting portion 321.
従って、埃センサ32のセンサケース323内には空調ケース21の通風路24から空気が導入されるようになっている。具体的には、埃センサ32は、送風機23の遠心ファン231に対する空気流れ方向下流側で且つ空気フィルタ30に対する空気流れ方向上流側に配置されている。そのため、通風路24のうち遠心ファン231と空気フィルタ30との間から空気がセンサケース323内に導入される。すなわち、本実施形態では、通風路24のうち遠心ファン231と空気フィルタ30との間が、埃センサ32のセンシング箇所となっている。
Therefore, air is introduced into the sensor case 323 of the dust sensor 32 from the air passage 24 of the air conditioning case 21. Specifically, the dust sensor 32 is disposed downstream of the centrifugal fan 231 of the blower 23 in the air flow direction and upstream of the air filter 30 in the air flow direction. Therefore, air is introduced into the sensor case 323 from between the centrifugal fan 231 and the air filter 30 in the air passage 24. That is, in the present embodiment, a portion between the centrifugal fan 231 and the air filter 30 in the ventilation path 24 is a sensing portion of the dust sensor 32.
埃センサ32の発光部321は、例えば発光ダイオードで構成された発光素子321aと、照射光レンズ321bとを有している。受光部322は、例えばフォトダイオードで構成された受光素子322aと、集光レンズ322bとを有している。図3の矢印B1のように発光素子321aから発せられ照射光レンズ321bを通った光は、センサケース323内に導入された空気中の埃に反射し、その反射した光は、矢印B2のように集光レンズ322bを通って受光素子322aに受光される。受光素子322aは受光することにより電流を発生する。
The light emitting portion 321 of the dust sensor 32 has a light emitting element 321 a formed of, for example, a light emitting diode, and an irradiation light lens 321 b. The light receiving section 322 has a light receiving element 322a configured by, for example, a photodiode, and a condensing lens 322b. The light emitted from the light emitting element 321a as shown by the arrow B1 in FIG. 3 and passing through the irradiation light lens 321b is reflected by the dust in the air introduced into the sensor case 323, and the reflected light is as shown by the arrow B2. The light is received by the light receiving element 322a through the condenser lens 322b. The light receiving element 322a generates a current by receiving light.
そして、図4に示すように、埃センサ32はセンサ回路324を有しており、そのセンサ回路324は、受光素子322aの電流を増幅し、それをアンプを介し電圧出力とする。その電圧出力は埃濃度に換算される。埃センサ32は、このようにして通風路24の埃濃度を検出する。なお、図4のグラフGFの縦軸は、電圧値から換算された埃濃度すなわち濃度換算値を表し、グラフGFの横軸は経過時間を表している。
As shown in FIG. 4, the dust sensor 32 has a sensor circuit 324. The sensor circuit 324 amplifies the current of the light receiving element 322a and outputs it as a voltage output through an amplifier. The voltage output is converted to dust concentration. The dust sensor 32 detects the dust concentration in the air passage 24 in this manner. The vertical axis of the graph GF in FIG. 4 represents the dust concentration converted from the voltage value, that is, the density conversion value, and the horizontal axis of the graph GF represents the elapsed time.
図1に示す空調制御装置40は、空調ユニット2を制御する制御装置である。具体的に、空調制御装置40は、半導体メモリなどの非遷移的実体的記憶媒体で構成された記憶部とプロセッサとを含んだ電子制御装置である。空調制御装置40は、その記憶部に格納されたコンピュータプログラムを実行する。このコンピュータプログラムが実行されることで、コンピュータプログラムに対応する方法が実行される。すなわち、空調制御装置40は、そのコンピュータプログラムに従って、後述する図5の制御処理など、種々の制御処理を実行する。
The air conditioning control device 40 illustrated in FIG. 1 is a control device that controls the air conditioning unit 2. Specifically, the air-conditioning control apparatus 40 is an electronic control apparatus including a storage unit configured by a non-transitional tangible storage medium such as a semiconductor memory and a processor. The air conditioning control device 40 executes a computer program stored in the storage unit. The computer program is executed to execute a method corresponding to the computer program. That is, according to the computer program, the air conditioning control device 40 executes various control processes such as the control process of FIG. 5 described later.
また、空調制御装置40は空調ユニット2に含まれる各アクチュエータへ制御信号を出力することにより、各アクチュエータの作動を制御する。要するに、空調制御装置40は、空調ユニット2において種々の空調制御を行う。例えば、上述した送風機23、内外気切替ドア22、エアミックスドア28、フェイス吹出開口部ドア254、フット吹出開口部ドア255、およびデフロスタ吹出開口部ドア256は、空調制御装置40によって駆動制御される。
Further, the air conditioning control device 40 controls the operation of each actuator by outputting a control signal to each actuator included in the air conditioning unit 2. In short, the air conditioning control device 40 performs various air conditioning control in the air conditioning unit 2. For example, the air conditioner control device 40 drives and controls the blower 23, the inside / outside air switching door 22, the air mix door 28, the face outlet door 254, the foot outlet door 255, and the defroster outlet door 256 described above. .
また、図1に示すように、空調制御装置40には、例えば、埃センサ32などのセンサ類やドア等のアクチュエータのほか、操作装置44および表示装置46が電気的に接続されている。
Further, as shown in FIG. 1, in addition to sensors such as a dust sensor 32 and actuators such as a door, an operation device 44 and a display device 46 are electrically connected to the air conditioning control device 40, for example.
操作装置44は、空調ユニット2から吹き出される空調風の風量や温度等を調整する際に乗員により操作される操作部である。操作装置44は、例えば車両のインストルメントパネルに配置されている。操作装置44では、例えば空調風の風量、車室内の目標室温、及び空調風の吹出口等を設定することができる。また、操作装置44では、空調風の風量調整、空調風の温度調整、および内気循環または外気導入の選択が自動的に行われる自動空調モードを設定することもできる。操作装置44は、これらの設定を示す情報、すなわち操作装置44に対して為された乗員操作を示す操作情報を、空調制御装置40に出力する。
The operating device 44 is an operating unit operated by the occupant when adjusting the air volume, temperature, and the like of the conditioned air blown out from the air conditioning unit 2. The operating device 44 is disposed, for example, on an instrument panel of a vehicle. In the operation device 44, for example, the air volume of the conditioned air, the target room temperature in the vehicle compartment, the outlet of the conditioned air, and the like can be set. Further, in the operation device 44, it is possible to set an automatic air conditioning mode in which selection of the air volume adjustment of the air conditioning air, the temperature adjustment of the air conditioning air, and the inside air circulation or the outside air introduction is automatically performed. The operating device 44 outputs, to the air conditioning control device 40, information indicating these settings, that is, operation information indicating an occupant operation performed on the operating device 44.
例えば、操作装置44で自動空調モードが設定されると、空調制御装置40は、送風機23の送風量、および各ドア22、28、254、255、256の作動を、複数のセンサ類からの入力信号に基づいて自動的に調整または制御する。
For example, when the automatic air conditioning mode is set by the operation device 44, the air conditioning control device 40 inputs the air flow of the blower 23 and the operation of the respective doors 22, 28, 254, 255, 256 from a plurality of sensors. Adjust or control automatically based on the signal.
表示装置46は、空調ユニット2の各種情報を表示する表示部である。すなわち、表示装置46には、その空調ユニット2の各種情報を示す信号が空調制御装置40から入力され、表示装置46は、その空調制御装置40から入力信号に従った表示を行う。
The display device 46 is a display unit that displays various information of the air conditioning unit 2. That is, a signal indicating various information of the air conditioning unit 2 is input from the air conditioning control device 40 to the display device 46, and the display device 46 performs display according to the input signal from the air conditioning control device 40.
表示装置46は、例えば車両のインストルメントパネルなど車室内の乗員が見易い位置に配置されている。この表示装置46は、カーナビゲーション装置など他の車載機器の表示装置に含まれていてもよいし、空調ユニット2専用のものとして構成されていてもよい。
The display device 46 is disposed, for example, at a position where a passenger in the vehicle compartment can easily view, such as an instrument panel of a vehicle. The display device 46 may be included in the display device of another car-mounted device such as a car navigation device, or may be configured exclusively for the air conditioning unit 2.
空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32に関わる制御を行う埃センサ制御部50を機能的に含んでいる。その埃センサ制御部50は、例えば、図5の制御処理を実行する。
The air conditioning control device 40 functionally includes a dust sensor control unit 50 that performs control related to the dust sensor 32. The dust sensor control unit 50 executes, for example, the control process of FIG.
図5は、埃センサ制御部50が実行する制御処理を示したフローチャートである。埃センサ制御部50は、例えば空調ユニット2の作動中に、図5のフローチャートを周期的に繰り返し実行する。このように空調ユニット2の作動中に周期的に繰り返し実行されることは、後述する図11、図14、図15、図17、および図18のフローチャートについても同様である。
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing control processing executed by the dust sensor control unit 50. The dust sensor control unit 50 periodically and repeatedly executes the flowchart of FIG. 5 while the air conditioning unit 2 is operating, for example. As described above, being repeatedly and periodically executed during operation of the air conditioning unit 2 is the same as in the flowcharts of FIGS. 11, 14, 15, 17, and 18 described later.
図5に示すように、埃センサ制御部50は、まず、ステップS010では、埃センサ32からの検出信号により、埃センサ32が検出した埃濃度の検出値Dmすなわち埃濃度検出値Dmを取得する。要するに、埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32からの検出信号に従った埃濃度の検出を実施する。ステップS010の次はステップS020へ進む。
As shown in FIG. 5, first, in step S010, the dust sensor control unit 50 acquires the detection value Dm of the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor 32, that is, the dust concentration detection value Dm based on the detection signal from the dust sensor 32. . In short, the dust sensor control unit 50 performs the detection of the dust concentration in accordance with the detection signal from the dust sensor 32. After step S010, the process proceeds to step S020.
ステップS020では、埃センサ制御部50は、ステップS010で得られた埃濃度検出値Dmを記録する。その埃濃度検出値Dmは、例えば半導体メモリ等で構成された記憶部へ記憶され、これにより記録される。このステップS020が繰り返し実行されることにより、図6に示すような埃濃度検出値Dmの時間変化を得ることができる。なお、図6の横軸は経過時間を示し、図6の縦軸は埃濃度を示している。図5のステップS020の次はステップS030へ進む。
In step S020, the dust sensor control unit 50 records the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained in step S010. The dust concentration detection value Dm is stored, for example, in a storage unit configured of a semiconductor memory or the like. By repeatedly executing this step S020, it is possible to obtain a time change of the dust concentration detection value Dm as shown in FIG. The horizontal axis in FIG. 6 indicates the elapsed time, and the vertical axis in FIG. 6 indicates the dust concentration. After step S020 in FIG. 5, the process proceeds to step S030.
ステップS030では、埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したか否かを判定する。例えば図7および図8に示すように、経過時間に対する埃濃度検出値Dmの変化割合すなわち埃濃度検出値Dmの勾配が所定の限度を超えて急変した場合に、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定される。埃センサ32に結露が発生すると、センサケース323内において、その結露水にも、発光部321から発せられた光が反射するからである。つまり、このステップS030では、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露の影響を受けているか否かが判定され、その埃濃度検出値Dmが結露の影響を受けている場合に、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定される。なお、上記埃濃度検出値Dmの勾配の急変には、その勾配が図7のように大きくなる側への急変もあれば、図8のように小さくなる側への急変もある。
In step S030, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines whether condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 or not. For example, as shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, when the change rate of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time, that is, the slope of the dust concentration detection value Dm suddenly changes beyond a predetermined limit, condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 It is determined that When dew condensation occurs on the dust sensor 32, the light emitted from the light emitting unit 321 is also reflected to the dew condensation water in the sensor case 323. That is, in step S030, it is determined whether the dust concentration detection value Dm is affected by condensation of the dust sensor 32. If the dust concentration detection value Dm is affected by condensation, the dust sensor 32 is detected. It is determined that condensation has occurred on the In the sudden change of the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm, if there is a sudden change to the side where the gradient becomes large as shown in FIG. 7, there is also a sudden change to the side where the gradient becomes small as shown in FIG.
そして、その埃濃度検出値Dmの勾配の急変が生じた時点t1から埃センサ32の結露が始まったと認識される。すなわち、図7および図8では、その時点t1が、埃センサ32の結露が始まった結露開始時点である。
Then, it is recognized that dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has started from time t1 when a sudden change of the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm occurs. That is, in FIG. 7 and FIG. 8, the time t1 is the dew condensation start time when dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has started.
また、ステップS030では、結露開始時点t1からの経過時間に基づいて、埃センサ32の結露が解消した結露解消時点t2が認定される。具体的には、図6に示すように、埃センサ制御部50は、結露開始時点t1からの経過時間が予め実験的に設定された結露継続時間Tdに達した場合に、埃センサ32の結露が解消したと判定される。要するに、結露開始時点t1から結露継続時間Tdが経過した時点が、結露解消時点t2と認定される。
Further, at step S030, the condensation elimination time point t2 at which the condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated is recognized based on the elapsed time from the condensation start time point t1. Specifically, as shown in FIG. 6, when the elapsed time from the condensation start time t1 reaches the condensation continuation time Td experimentally set in advance, the dust sensor control unit 50 causes the condensation of the dust sensor 32 to Is determined to be eliminated. In short, the point at which the dew condensation continuation time Td has elapsed from the dew condensation start time t1 is recognized as the dew condensation elimination time t2.
従って、ステップS030では、埃濃度検出値Dmの勾配の変化から、埃センサ32に結露が発生と判定されると、埃濃度検出値Dmに拘わらず、結露開始時点t1から結露継続時間Tdが経過するまで、埃センサ32に結露が発生したという判定が継続される。
Therefore, in step S030, if condensation is determined to occur in the dust sensor 32 from the change in the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm, the condensation continuation time Td elapses from the condensation start time t1 regardless of the dust concentration detection value Dm. Until then, the determination that the dew sensor 32 has generated condensation is continued.
ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS040へ進む。例えば図6の結露開始時点t1から結露解消時点t2までの間においては、このステップS030からステップS040へ進む。
If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. For example, in the period from the dew condensation start time t1 to the dew condensation elimination time t2 in FIG. 6, the process proceeds from step S030 to step S040.
その一方で、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、ステップS060へ進む。例えば図6の結露開始時点t1の前、および結露解消時点t2の後においては、このステップS030からステップS060へ進む。
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S030 that condensation does not occur on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S060. For example, before the condensation start time t1 and after the condensation elimination time t2 in FIG. 6, the process proceeds from step S030 to step S060.
ステップS040では、埃センサ制御部50は、図9および図10に示すように、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値Dcを、結露前検出値Dbmに基づいて決定する。その結露前検出値Dbmとは、埃センサ32がその埃センサ32の結露発生前(すなわち、結露開始時点t1の直前)に検出した埃濃度の検出値Dmである。具体的に言えば、埃センサ32による埃濃度の検出は図5のステップS010で周期的に繰り返し実行されるので、結露前検出値Dbmは、埃センサ32の結露開始時点t1に対する前回の検出で得られた埃濃度検出値Dmである。要するに、その結露前検出値Dbmは、結露開始時点t1の前において逐次得られた埃濃度検出値Dmのうち最新の埃濃度検出値Dmである。
In step S040, as shown in FIGS. 9 and 10, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc to be treated as the dust concentration in the occurrence of condensation based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. The pre-condensation detected value Dbm is a detected value Dm of the dust concentration detected by the dust sensor 32 before condensation occurs (that is, immediately before the condensation start time t1). Specifically, since the detection of the dust concentration by the dust sensor 32 is periodically and repeatedly performed in step S010 of FIG. 5, the pre-condensation detected value Dbm is the previous detection with respect to the condensation start time t1 of the dust sensor 32. It is the obtained dust concentration detection value Dm. In short, the pre-condensation detected value Dbm is the latest dust concentration detected value Dm among the dust concentration detected values Dm sequentially obtained before the condensation start time t1.
上記のように結露中埃濃度値Dcは結露前検出値Dbmに基づいて決定されるので、その結露中埃濃度値Dcは、結露発生中に得られる埃濃度検出値Dmに拘わらず決定される。
As described above, since the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is determined based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm, the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is determined regardless of the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained during condensation occurrence. .
例えば本実施形態では、埃センサ制御部50は、結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmにするように、その結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。要するに、結露中埃濃度値Dcは結露前検出値Dbmと同じ値とされる。このようにして、埃センサ制御部50は結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmに基づいて決定する。なお、図9は図6のIX部分を拡大した拡大図であり、図10はその図9のX部分を拡大した拡大図である。図5のステップS040の次はステップS050へ進む。
For example, in the present embodiment, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc so that the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc becomes the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. In short, the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is made the same value as the detection value before condensation Dbm. Thus, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the dust concentration value during condensation Dc based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. 9 is an enlarged view of a portion IX in FIG. 6, and FIG. 10 is an enlarged view of a portion X in FIG. After step S040 in FIG. 5, the process proceeds to step S050.
ステップS050では、埃センサ制御部50は、ステップS040で決定した結露中埃濃度値Dcを、埃センサ32のセンシング箇所である通風路24の埃濃度として出力する。例えば、その結露中埃濃度値Dcは、空調制御装置40のうち、埃センサ制御部50以外の制御部、例えば空調ユニット2の複数のドアおよび送風機23を制御する制御部へ出力される。例えば図6に示すように、結露開始時点t1から結露解消時点t2までの期間中には、このステップS050の実行により、空調制御装置40において通風路24の埃濃度は、結露発生中に得られる埃濃度検出値Dmに拘わらず結露中埃濃度値Dcであると認識される。
In step S <b> 050, the dust sensor control unit 50 outputs the dust concentration value during condensation Dc determined in step S <b> 040 as the dust concentration of the air passage 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32. For example, the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is output to the control unit other than the dust sensor control unit 50 in the air conditioning control device 40, for example, a control unit that controls a plurality of doors of the air conditioning unit 2 and the blower 23. For example, as shown in FIG. 6, during the period from the dew condensation start time t1 to the dew condensation elimination time t2, the dust concentration in the air passage 24 can be obtained during the dew condensation occurrence in the air conditioning control device 40 by executing this step S050. Regardless of the dust concentration detection value Dm, it is recognized that the dust concentration value during condensation is Dc.
ステップS060では、埃センサ制御部50は、ステップS010で得られた埃濃度検出値Dmをそのまま、通風路24の埃濃度として出力する。図5のフローチャートは、ステップS050またはステップS060が終了すると、再びステップS010から開始される。
In step S060, the dust sensor control unit 50 outputs the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained in step S010 as it is as the dust concentration of the air passage 24. The flowchart of FIG. 5 starts again from step S010 when step S050 or step S060 is completed.
なお、上述した図5の各ステップでの処理は、それぞれの機能を実現する機能部を構成している。後述する図11、図14、図15、図17、および図18のフローチャートでも同様である。
The processing in each step of FIG. 5 described above constitutes a functional unit that implements each function. The same applies to the flowcharts of FIG. 11, FIG. 14, FIG. 15, FIG. 17, and FIG.
また、図2のステップS030は結露判定部に対応し、ステップS040は値決定部に対応する。そして、空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50は、その結露判定部と値決定部とを機能的に備えている。
Step S030 in FIG. 2 corresponds to the condensation determination unit, and step S040 corresponds to the value determination unit. The dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40 functionally includes the condensation determination unit and the value determination unit.
上述したように、本実施形態によれば、図5に示すように、空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したか否かを判定する。そして、図6および図10に示すように、埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定した場合には、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値Dcを、結露前検出値Dbmに基づいて決定する。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 5, the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32. Then, as shown in FIG. 6 and FIG. 10, when the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, the dust concentration value Dc during condensation treated as the dust concentration in the dew condensation occurrence is , And is determined based on the detection value before condensation Dbm.
従って、埃センサ32に結露が発生した場合に、その結露に起因した不適切な事態、例えば埃センサ32の誤検出に起因してセンシング箇所の埃濃度が実際値から懸け離れた大きさとして把握されるという事態を、結露中埃濃度値Dcを用いることで回避することが可能である。
Therefore, when dew condensation occurs on the dust sensor 32, the dust concentration at the sensing location is grasped as a size far from the actual value due to an inappropriate situation caused by the dew condensation, for example, erroneous detection of the dust sensor 32. Can be avoided by using the dust concentration value Dc during condensation.
別言すれば、埃センサ32に結露が発生した場合に、その結露に起因した埃センサ32の誤検出の影響を避けつつ、結露中の実際値に近い埃濃度を結露中埃濃度値Dcとして得ることが可能である。
In other words, when condensation occurs on the dust sensor 32, the dust concentration close to the actual value during condensation is regarded as the dust concentration value Dc during condensation while avoiding the influence of erroneous detection of the dust sensor 32 caused by the condensation. It is possible to get.
例えば車室内の埃濃度を低減する空調ユニット2の運転制御がセンシング箇所の埃濃度に応じて実施される場合には、その空調ユニット2が車室内の埃を除去する埃除去能力が埃濃度の誤検出に起因して不足するという事態を回避することが可能である。
For example, when the operation control of the air conditioning unit 2 for reducing the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is performed according to the dust concentration at the sensing location, the dust removal capability for removing the dust in the vehicle interior by the air conditioning unit 2 is dust concentration It is possible to avoid a shortage due to false detection.
また、本実施形態によれば、図5のステップS040において、埃センサ制御部50は、結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmにするように、その結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。従って、結露中埃濃度値Dcがセンシング箇所の埃濃度の実際値から懸け離れた値にならないように、結露中埃濃度値Dcを簡単に定めることが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, in step S040 in FIG. 5, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc so that the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc becomes the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. . Therefore, it is possible to easily determine the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc so that the in-condensation dust concentration value Dc does not become a value far from the actual value of the dust concentration at the sensing location.
また、本実施形態によれば、図5のステップS030では、埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したか否かを判定する。例えば図7および図8に示すように、埃センサ制御部50は、経過時間に対する埃濃度検出値Dmの変化割合が所定の限度を超えて変化した場合に、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定する。従って、埃センサ32の結露発生を判定するために特別な装置を必要とはしないというメリットがある。
Further, according to the present embodiment, in step S030 of FIG. 5, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines whether condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 or not. For example, as shown in FIGS. 7 and 8, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32 when the change ratio of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time changes beyond a predetermined limit. judge. Therefore, there is an advantage that no special device is required to determine the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32.
(第2実施形態)
次に、第2実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。また、前述の実施形態と同一または均等な部分については省略または簡略化して説明する。このことは後述の実施形態の説明においても同様である。 Second Embodiment
Next, a second embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, points different from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described. In addition, the same or equivalent parts as those of the above-described embodiment will be described with omission or simplification. The same applies to the description of the embodiments described later.
次に、第2実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。また、前述の実施形態と同一または均等な部分については省略または簡略化して説明する。このことは後述の実施形態の説明においても同様である。 Second Embodiment
Next, a second embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, points different from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described. In addition, the same or equivalent parts as those of the above-described embodiment will be described with omission or simplification. The same applies to the description of the embodiments described later.
図11に示すように、本実施形態では、空調制御装置40が実行する制御処理が第1実施形態と異なる。具体的には、図11のフローチャートのステップS031、S041が、図5のフローチャートに対して追加されている。図11のフローチャートにおいて、それら以外のステップであるステップS010、S020、S030、S040、S050、S060は、図5のフローチャートと同様である。なお、この図11の制御処理も、前述の図5の制御処理と同様に、空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50によって実行される。
As shown in FIG. 11, in the present embodiment, control processing executed by the air conditioning control device 40 is different from that of the first embodiment. Specifically, steps S031 and S041 of the flowchart of FIG. 11 are added to the flowchart of FIG. In the flowchart of FIG. 11, steps S010, S020, S030, S040, S050, and S060, which are the other steps, are the same as the flowchart of FIG. The control process of FIG. 11 is also executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40, similarly to the control process of FIG. 5 described above.
図11のフローチャートでは、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS031へ進む。そのステップS031では、埃センサ制御部50は、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前(すなわち、図12の結露開始時点t1の前)に上昇していたか否かを判定する。言い換えれば、その結露発生前の埃濃度検出値Dmが上昇傾向か否かを判定する。例えば図12の埃濃度検出値Dmの波形では、A1部分に示すように、埃濃度検出値Dmが結露開始時点t1の前に上昇しているので、この場合、埃センサ制御部50は、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇していたと判定する。
In the flowchart of FIG. 11, when it is determined in step S030 that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S031. In step S031, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines whether the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 (that is, before the condensation start time t1 in FIG. 12). In other words, it is determined whether the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of the condensation tends to increase. For example, in the waveform of the dust concentration detection value Dm in FIG. 12, as shown in the A1 portion, the dust concentration detection value Dm rises before the condensation start time t1. In this case, the dust sensor control unit 50 It is determined that the concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32.
具体的に、その埃濃度検出値Dmが上昇していたか否かを認識する方法は種々考えられる。例えば、埃濃度検出値Dmが経過時間と線形関係にあると仮定する。そして、結露開始時点t1が所定の上昇判定期間の終了時点とされ、その結露開始時点t1までの上昇判定期間内での埃濃度検出値Dmの推移において、経過時間に対する埃濃度検出値Dmの勾配が周知の方法によって算出される。その結果、その経過時間に対する埃濃度検出値Dmの勾配(すなわち、埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率)が正の値であれば、埃濃度検出値Dmが結露開始時点t1の前に上昇していたと判定される。
Specifically, there are various conceivable methods for recognizing whether or not the dust concentration detection value Dm has increased. For example, it is assumed that the dust concentration detection value Dm has a linear relationship with the elapsed time. The dew condensation start time t1 is the end time of the predetermined rise determination period, and in the transition of the dust concentration detection value Dm in the rise determination period up to the dew condensation start time t1, the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time Is calculated by a known method. As a result, if the gradient of the dust concentration detection value Dm with respect to the elapsed time (that is, the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm) is a positive value, the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before the condensation start time t1. Is determined.
図11のステップS031において、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇していたと判定された場合には、ステップS041へ進む。その一方で、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇してはいないと判定された場合には、ステップS040へ進む。なお、埃濃度検出値Dmが上昇してはいない場合とは、埃濃度検出値Dmが下降していた場合または埃濃度検出値Dmが変化していない場合である。
If it is determined in step S031 in FIG. 11 that the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before dew condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S041. On the other hand, when it is determined that the dust concentration detection value Dm has not risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. The case where the dust concentration detection value Dm is not rising means the case where the dust concentration detection value Dm is falling or the dust concentration detection value Dm is not changing.
ステップS041では、埃センサ制御部50は、結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmよりも大きい値にするように、その結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。本実施形態の埃センサ制御部50は、そのように結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する場合には、具体的に、上記上昇判定期間内での埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率に基づき、図13の加算量マップを用いて加算量Dxを決定する。そして、図12に示すように、埃センサ制御部50は、その決定した所定の加算量Dxを結露前検出値Dbmに加算して得た値を結露中埃濃度値Dcとする。
In step S041, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc so that the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc has a value larger than the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. When the dust sensor control unit 50 of the present embodiment determines the dust concentration value Dc during condensation as such, specifically, based on the increase rate of the dust concentration detection value Dm within the increase determination period, as shown in FIG. The amount of addition Dx is determined using 13 addition amount maps. Then, as shown in FIG. 12, the dust sensor control unit 50 sets a value obtained by adding the determined predetermined addition amount Dx to the pre-condensation detection value Dbm as a dust concentration value Dc during condensation.
図13の加算量マップでは、横軸が、埃センサ32の結露発生前における埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率すなわち上記上昇判定期間内での埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率を示し、縦軸が加算量Dxを示している。この加算量マップから判るように、本実施形態では、埃センサ32の結露発生前における埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率が大きいほど、加算量Dxは大きく設定される。そして、埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率が零よりも大きければ、加算量Dxは常に零よりも大きくなる。図11のステップS041の次はステップS050へ進む。
In the additive amount map of FIG. 13, the horizontal axis indicates the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before dew condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32, that is, the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm within the increase determination period, and the vertical axis indicates the rate of increase An addition amount Dx is shown. As can be seen from the added amount map, in the present embodiment, the added amount Dx is set larger as the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 is larger. If the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm is larger than zero, the addition amount Dx is always larger than zero. After step S041 in FIG. 11, the process proceeds to step S050.
図11のステップS040では、第1実施形態の図5のステップS040と同様に、結露中埃濃度値Dcは結露前検出値Dbmと同じ値とされる。従って、このステップS040では、埃センサ制御部50は、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇していたとステップS031で判定される場合よりも結露中埃濃度値Dcを小さい値にするように、その結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。その埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇していたとステップS031で判定される場合とは、言い換えれば、ステップS041にて結露中埃濃度値Dcが決定される場合である。ステップS040の次はステップS050へ進む。
In step S040 in FIG. 11, the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is set to the same value as the pre-condensation detection value Dbm, as in step S040 in FIG. 5 of the first embodiment. Therefore, in step S040, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that the dust concentration value Dc during condensation is smaller than in the case where it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before condensation occurs in the dust sensor 32. The dust concentration value Dc during dew condensation is determined so as to The case where it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 is, in other words, the case where the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is determined in step S041. After step S040, the process proceeds to step S050.
図11のステップS050では、第1実施形態と同様に、埃センサ制御部50は、ステップS040またはS041で決定した結露中埃濃度値Dcを、埃センサ32のセンシング箇所である通風路24の埃濃度として出力する。
In step S050 in FIG. 11, the dust sensor control unit 50 controls the dust concentration value Dc during condensation determined in step S040 or S041 in the dust of the air passage 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32, as in the first embodiment. Output as concentration.
図11のフローチャートは、ステップS050またはステップS060が終了すると、再びステップS010から開始される。
The flowchart of FIG. 11 is started again from step S010 when step S050 or step S060 ends.
なお、図11のステップS040およびS041は値決定部に対応し、ステップS031は埃濃度上昇判定部に対応する。そして、空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50は、第1実施形態と同様の結露判定部のほかに、その値決定部と埃濃度上昇判定部とを機能的に備えている。
Steps S040 and S041 in FIG. 11 correspond to the value determination unit, and step S031 corresponds to the dust concentration increase determination unit. The dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40 functionally includes a value determination unit and a dust concentration increase determination unit in addition to the condensation determination unit similar to the first embodiment.
以上説明したことを除き、本実施形態は第1実施形態と同様である。そして、本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態と共通の構成から奏される効果を第1実施形態と同様に得ることができる。
The present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except for the above description. And in this embodiment, the effect show | played from the structure common to above-mentioned 1st Embodiment can be acquired similarly to 1st Embodiment.
また、本実施形態によれば、図11に示すように、埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定し、且つ埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇していたと判定した場合には、結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmよりも大きい値にするように結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。従って、センシング箇所の埃濃度の実際値に対する結露中埃濃度値Dcの正確性を高くするようにその結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定することが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 11, the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that condensation is generated in the dust sensor 32, and the dust concentration detection value Dm is before condensation generation of the dust sensor 32. If it is determined that the temperature is rising, the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc is determined so as to make the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc larger than the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. Therefore, it is possible to determine the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc so as to increase the accuracy of the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc with respect to the actual value of the dust concentration at the sensing location.
また、本実施形態によれば、埃センサ制御部50は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定した場合において、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇してはいないと判定した場合には、埃濃度検出値Dmがその結露発生前に上昇していたと判定する場合よりも結露中埃濃度値Dcを小さい値にするように結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。従って、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたか否かに応じて、結露中埃濃度値Dcの大きさに適切に差異を設けることが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, when the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, it is assumed that the dust concentration detection value Dm has not risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32. If it is determined, the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc is determined so as to make the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc smaller than in the case where it is determined that the dust concentration detection value Dm is rising before the occurrence of condensation. Therefore, depending on whether the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor, it is possible to appropriately make a difference in the magnitude of the dust concentration value during condensation Dc.
具体的には、埃センサ制御部50は、そのように埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇してはいないと判定した場合には、結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmと同じ値にする。従って、例えば埃濃度検出値Dmがその結露発生前に下降していた場合において、結露中埃濃度値Dcが埃濃度の実際値を下回りにくいようにその結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定することができる。
Specifically, when the dust sensor control unit 50 determines that the dust concentration detection value Dm does not rise before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 as described above, the condensation during dust concentration value Dc is performed before condensation. Make it the same value as the detection value Dbm. Therefore, for example, when the dust concentration detection value Dm is falling before the dew condensation occurs, the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc may be determined so that the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc does not easily fall below the actual value of the dust concentration. it can.
また、本実施形態によれば、図11のフローチャートのステップS041では、埃センサ制御部50は、結露中埃濃度値Dcを結露前検出値Dbmよりも大きい値にするように結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する。そのように結露中埃濃度値Dcを決定する場合、埃センサ制御部50は、具体的に、結露前検出値Dbmに所定の加算量Dxを加算して得た値を結露中埃濃度値Dcとする。そして、図13に示すように、埃センサ32の結露発生前における埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率が大きいほど、結露中埃濃度値Dcを算出するための上記加算量Dxは大きく設定される。従って、その加算量Dxが例えば一定である場合と比較して、センシング箇所の埃濃度の実際値に対する結露中埃濃度値Dcの正確性を高くすることが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, in step S041 of the flowchart of FIG. 11, the dust sensor control unit 50 sets the dust concentration value during condensation so that the dust concentration value during condensation Dc becomes a value larger than the detection value before condensation Dbm. Determine Dc. When the dust concentration value Dc during condensation is determined as such, specifically, the dust sensor control unit 50 adds a predetermined addition amount Dx to the detection value before condensation Dbm to obtain a dust concentration value Dc during condensation. I assume. Then, as shown in FIG. 13, as the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 increases, the addition amount Dx for calculating the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is set larger. Therefore, it is possible to increase the accuracy of the in-condensing dust concentration value Dc with respect to the actual value of the dust concentration at the sensing location, as compared to the case where the added amount Dx is constant, for example.
(第3実施形態)
次に、第3実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Third Embodiment
Next, a third embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, points different from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described.
次に、第3実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Third Embodiment
Next, a third embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, points different from the first embodiment described above will be mainly described.
図14に示すように、本実施形態では、空調制御装置40が実行する制御処理が第1実施形態と異なる。具体的には、図14のフローチャートのステップS072、S082、S092、S102が、図5のフローチャートに対して追加されている。そして、図14のフローチャートは、図5のステップS020、S040、S050を含んでいない。なお、図14のステップS010、S030、S060は、図5のフローチャートと同様である。
As shown in FIG. 14, in the present embodiment, control processing executed by the air conditioning control device 40 is different from that of the first embodiment. Specifically, steps S072, S082, S092, and S102 of the flowchart of FIG. 14 are added to the flowchart of FIG. The flowchart of FIG. 14 does not include steps S020, S040, and S050 of FIG. Steps S010, S030, and S060 in FIG. 14 are the same as those in the flowchart in FIG.
本実施形態において図14の制御処理は空調制御装置40によって実行されるが、詳細には、図14のステップS010、S030、S060は、その空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50によって実行される。
In the present embodiment, the control process of FIG. 14 is executed by the air conditioning control device 40. More specifically, steps S010, S030 and S060 of FIG. 14 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40. Be done.
図14に示すように、制御処理が開始されると、ステップS010、S060、S030の順に進む。
As shown in FIG. 14, when the control process is started, the process proceeds in the order of steps S010, S060 and S030.
ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS072へ進む。その一方で、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、図14のフローチャートは終了し再びステップS010から開始される。
If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S072. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S030 that condensation does not occur in the dust sensor 32, the flowchart of FIG. 14 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
ステップS072では、空調制御装置40は、車室内の埃濃度を低減する指示が乗員(すなわち、ユーザ)から為されたか否かを判定する。すなわち、空調制御装置40は、乗員の手動操作により埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示されたか否かを判定する。埃濃度低減制御とは、その埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように空調ユニット2を作動させる制御である。この埃濃度低減制御における空調ユニット2の作動内容は種々想定されうるが、本実施形態の埃濃度低減制御においては、空調ユニット2が内気モードとされ、それと共に、送風機23の送風量が、その送風量の可変範囲のうちの最大送風量とされる。
In step S072, the air-conditioning control device 40 determines whether an instruction to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment has been issued from the occupant (ie, the user). That is, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is instructed by the manual operation of the occupant. The dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit 2 so that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. Although various operation contents of the air conditioning unit 2 in this dust concentration reduction control can be assumed, in the dust concentration reduction control of this embodiment, the air conditioning unit 2 is set to the inside air mode, and the air flow of the blower 23 is This is the maximum air flow rate within the variable range of the air flow rate.
また、図1の操作装置44には、例えば、乗員に手動操作される埃除去スイッチが含まれている。乗員は手動操作でその埃除去スイッチをオンにすることにより埃濃度低減制御の実施を指示することができる。
Further, the operating device 44 of FIG. 1 includes, for example, a dust removing switch manually operated by the occupant. The occupant can instruct the execution of the dust concentration reduction control by turning on the dust removal switch manually.
図14のステップS072において、埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示されたと判定された場合、例えば埃除去スイッチをオンにするオン操作が為された場合には、ステップS092へ進む。その一方で、埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示されてはいないと判定された場合、例えばその埃除去スイッチのオン操作が為されていない場合には、ステップS082へ進む。
If it is determined in step S072 in FIG. 14 that the execution of the dust concentration reduction control has been instructed, for example, if the on operation for turning on the dust removal switch is performed, the process proceeds to step S092. On the other hand, if it is determined that execution of dust concentration reduction control is not instructed, for example, if the dust removal switch is not turned on, the process proceeds to step S082.
ステップS082では、空調制御装置40は、所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する。詳細には、その埃濃度上昇要因が図12の結露開始時点t1以後に発生したか否かを判定する。その埃濃度上昇要因とは、車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる事態であり、予め定められている。埃濃度上昇要因の例としては、車両の何れかのドアが開かれること、および、車両の何れかの窓ガラスが開けられること等を挙げることができる。このようなことの何れかが生じると、車室外から車室内へ埃が侵入しやすくなるからである。
In step S082, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor has occurred. Specifically, it is determined whether the dust concentration increase factor has occurred after the condensation start time t1 of FIG. The dust concentration rise factor is a situation that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to rise, and is predetermined. As an example of the dust concentration rising factor, it can be mentioned that any door of the vehicle is opened and that any window glass of the vehicle is opened. This is because dust may easily intrude from the outside of the vehicle compartment into the vehicle compartment if any of these things occur.
上記の車両のドアの開閉については、そのドアの開閉を検出するドアセンサからの信号に基づき認識することができる。また、車両の窓ガラスの開閉については、その窓ガラスを開閉作動させるために乗員に操作されるパワーウインドゥスイッチの操作情報に基づき認識することができる。なお、確認的に述べるが、埃濃度上昇要因として上述したように複数の事態が定められている場合には、その複数の事態のうちの1つの事態が発生すれば、埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと判定される。
The opening and closing of the above-described vehicle door can be recognized based on a signal from a door sensor that detects the opening and closing of the door. Further, the opening and closing of the window glass of the vehicle can be recognized based on the operation information of the power window switch operated by the occupant in order to open and close the window glass. In addition, although stated convincingly, when a plurality of situations are determined as described above as a factor of increasing the dust concentration, if one of the plurality of situations occurs, the factor of increasing the dust concentration occurs It is determined that the
ステップS082において、埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS092へ進む。その一方で、埃濃度上昇要因が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、図14のフローチャートは終了し再びステップS010から開始される。
If it is determined in step S082 that a dust concentration increase cause has occurred, the process proceeds to step S092. On the other hand, when it is determined that the dust concentration increase cause is not generated, the flowchart of FIG. 14 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
ステップS092では、空調制御装置40は、車室内の埃濃度を低減する上記埃濃度低減制御を実施する。この埃濃度低減制御は、上記のステップS030、S072、S082の判定結果に応じて実施されることから判るように、埃濃度検出値Dmの大小に拘わらず実施される。要するに、このステップS092では、埃濃度検出値Dmの大小に拘わらず、埃濃度低減制御の実施により強制的に車室内の埃の除去が行われる。ステップS092の次はステップS102へ進む。
In step S092, the air conditioning control device 40 carries out the dust concentration reduction control to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment. This dust concentration reduction control is performed regardless of the magnitude of the dust concentration detection value Dm, as can be understood from the implementation in accordance with the determination results of the above steps S030, S072, and S082. In short, in this step S092, regardless of the magnitude of the dust concentration detection value Dm, the dust concentration reduction control is performed to forcibly remove dust in the vehicle interior. After step S092, the process proceeds to step S102.
ステップS102では、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32の結露が解消したか否かを判定する。この判定は、ステップS030における埃センサ32の結露解消の判定と同様に行われる。そして、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32の結露が解消していれば、埃センサ32の結露が解消した結露解消時から所定時間が経過したか否かを判定する。その所定時間は、ステップS092の埃濃度低減制御が結露解消前に終了しないように過不足無い時間に予め実験的に設定されている。
In step S102, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has been eliminated. This determination is performed in the same manner as the determination of condensation elimination of the dust sensor 32 in step S030. Then, if the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether or not a predetermined time has elapsed from the condensation elimination time at which the condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated. The predetermined time is set experimentally in advance to a time that is sufficient to prevent the dust concentration reduction control in step S092 from ending before condensation is eliminated.
ステップS102において、埃センサ32の結露が未だ解消していないと判定された場合、または埃センサ32の結露解消時から所定時間が未だ経過していないと判定された場合には、ステップS092へ戻る。すなわち、この場合には、ステップS092で埃濃度低減制御の実施が継続される。
If it is determined in step S102 that the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has not been eliminated yet, or if it is determined that the predetermined time has not yet elapsed from the condensation clearing of the dust sensor 32, the process returns to step S092. . That is, in this case, the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is continued in step S092.
その一方で、ステップS102において、埃センサ32の結露解消時から所定時間が経過したと判定された場合には、図14のフローチャートは終了し再びステップS010から開始される。すなわち、この場合には、埃濃度低減制御が終了する。
On the other hand, when it is determined in step S102 that the predetermined time has elapsed from the time when the condensation of the dust sensor 32 is eliminated, the flowchart of FIG. 14 is ended and the process is started again from step S010. That is, in this case, the dust concentration reduction control ends.
なお、図14のステップS082は要因判定部に対応し、ステップS092、S102は制御実施部に対応する。そして、空調制御装置40は、第1実施形態と同様の結露判定部のほかに、その要因判定部と制御実施部とを機能的に備えている。
Step S082 in FIG. 14 corresponds to the factor determination unit, and steps S092 and S102 correspond to the control execution unit. And the air-conditioning control apparatus 40 is functionally provided with the factor determination part and control implementation part other than the condensation determination part similar to 1st Embodiment.
以上説明したことを除き、本実施形態は第1実施形態と同様である。そして、本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態と共通の構成から奏される効果を第1実施形態と同様に得ることができる。
The present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except for the above description. And in this embodiment, the effect show | played from the structure common to above-mentioned 1st Embodiment can be acquired similarly to 1st Embodiment.
また、本実施形態によれば、図14に示すように、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定した場合には、車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する。そして、空調制御装置40は、その埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと判定した場合には埃濃度低減制御を実施する。そして、その埃濃度低減制御とは、その埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように空調ユニット2を作動させる制御である。従って、埃センサ32に結露が発生した場合に、その埃センサ32の結露に起因した不適切な事態、例えば埃センサ32の誤検出で埃濃度を正確に把握できず車室内の埃濃度が上昇するという事態を、埃濃度低減制御の実施により回避することが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 14, when the air conditioning control device 40 determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, the air conditioning control device 40 causes the dust concentration in the vehicle interior to increase. It is determined whether a dust concentration increase factor has occurred. Then, when it is determined that the dust concentration increase factor has occurred, the air conditioning control device 40 performs dust concentration reduction control. The dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit 2 so that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. Therefore, when dew condensation occurs on the dust sensor 32, an inappropriate situation caused by the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32, for example, an incorrect detection of the dust sensor 32, can not accurately grasp the dust concentration, and the dust concentration in the vehicle cabin increases. It is possible to avoid the situation of the problem by implementing the dust concentration reduction control.
また、本実施形態によれば、空調制御装置40、乗員の手動操作により埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示された場合にも、埃濃度低減制御を実施する。従って、乗員は任意のタイミングで車室内の埃濃度を空調ユニット2により低減することが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, the dust concentration reduction control is performed even when the air conditioning control device 40 instructs the execution of the dust concentration reduction control by the manual operation of the occupant. Therefore, the occupant can reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment by the air conditioning unit 2 at any timing.
(第4実施形態)
次に、第4実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、前述の第3実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Fourth Embodiment
Next, a fourth embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, differences from the above-described third embodiment will be mainly described.
次に、第4実施形態について説明する。本実施形態では、前述の第3実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Fourth Embodiment
Next, a fourth embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, differences from the above-described third embodiment will be mainly described.
図15に示すように、本実施形態では、空調制御装置40が実行する制御処理が第3実施形態と異なる。具体的には、図15のフローチャートのステップS043、S053、S063、S073が、図14のフローチャートに対して追加されている。なお、図15のステップS010、S030、S060、S072、S082、S092、S102は、図14のフローチャートと同様である。
As shown in FIG. 15, in the present embodiment, control processing executed by the air conditioning control device 40 is different from that of the third embodiment. Specifically, steps S043, S053, S063 and S073 of the flowchart of FIG. 15 are added to the flowchart of FIG. Steps S010, S030, S060, S072, S082, S092, and S102 in FIG. 15 are the same as those in the flowchart of FIG.
本実施形態では第3実施形態と同様に、図15の制御処理は空調制御装置40によって実行される。そして、図15のステップS010、S030、S060は、その空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50によって実行される。
In the present embodiment, as in the third embodiment, the control process of FIG. Steps S010, S030, and S060 in FIG. 15 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40.
図15に示すように、制御処理が開始されると、ステップS010、S060、S030の順に進む。
As shown in FIG. 15, when the control process is started, the process proceeds in the order of steps S010, S060, and S030.
ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS043へ進む。その一方で、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、ステップS063へ進む。
If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S043. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S030 that condensation does not occur in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S063.
ステップS043では、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32の結露発生を図16の結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせることが可能であるか否かを判定する。その結露インジケータ461は、埃センサ32の結露発生を乗員へ通知する通知装置であり、表示装置46の一部を構成している。
In step S <b> 043, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether it is possible to notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32 by the dew condensation indicator 461 of FIG. 16. The dew condensation indicator 461 is a notification device for notifying the occupant of the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32, and constitutes a part of the display device 46.
例えば、空調制御装置40が搭載された車両に結露インジケータ461が設けられていれば、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせることが可能であると判定される。
For example, if the dew condensation indicator 461 is provided in a vehicle mounted with the air conditioning control device 40, it is determined that the dew condensation indicator 461 can notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32.
図15のステップS043において、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせることが可能であると判定された場合には、ステップS053へ進む。その一方で、ステップS043において、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせることが不可能であると判定された場合には、ステップS073へ進む。
If it is determined in step S043 in FIG. 15 that the dew condensation indicator 461 can notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S053. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S043 that the dew condensation indicator 461 can not notify the occupant of dew condensation occurrence in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S073.
ステップS053では、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせる。具体的には、空調制御装置40は、結露インジケータ461をオンに切り替え、それにより、埃センサ32の結露発生を乗員へ知らせる。既に結露インジケータ461がオンであれば、オンのまま継続される。その結露インジケータ461をオンにすることとは、例えば、結露インジケータ461を点灯または点滅させることである。ステップS053の次はステップS072へ進む。
In step S 053, the air conditioning control device 40 notifies the occupant of the occurrence of dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 by the dew condensation indicator 461. Specifically, the air conditioning control device 40 turns on the dew condensation indicator 461 to thereby notify the occupant of the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32. If the condensation indicator 461 is already on, it will continue to be on. To turn on the condensation indicator 461 is, for example, to turn on or blink the condensation indicator 461. After step S053, the process proceeds to step S072.
ステップS063では、空調制御装置40は、結露インジケータ461をオフに切り替える。既に結露インジケータ461がオフであれば、オフのまま継続される。その結露インジケータ461をオフにすることとは、例えば、結露インジケータ461を消灯させることである。図15のフローチャートは、ステップS063が終了すると、再びステップS010から開始される。
In step S063, the air conditioning control device 40 switches the dew condensation indicator 461 off. If the condensation indicator 461 is already off, it will continue to be off. To turn off the condensation indicator 461 is, for example, to turn off the condensation indicator 461. The flowchart of FIG. 15 is started again from step S010 when step S063 is completed.
ステップS073では、空調制御装置40は、空調ユニット2が自動空調モード(別言すれば、オートモード)で運転されているか否かを判定する。
In step S073, the air conditioning control device 40 determines whether the air conditioning unit 2 is operated in the automatic air conditioning mode (in other words, the auto mode).
ここで、ステップS092の埃濃度低減制御が実施されると、空調ユニット2が自動的に内気モードになり、送風機23の送風量が自動調整される。そのため、内気モードと外気モードとが自動切替えで且つ送風量が自動調整される状況に空調ユニット2があるということを乗員が認識しているか否かを予め確認するために、このステップS073が設けられている。
Here, when the dust concentration reduction control of step S092 is performed, the air conditioning unit 2 is automatically set to the inside air mode, and the air flow rate of the blower 23 is automatically adjusted. Therefore, this step S073 is provided to confirm in advance whether the occupant recognizes that the air conditioning unit 2 is in a state where the inside air mode and the outside air mode are automatically switched and the air flow rate is automatically adjusted. It is done.
ステップS073において、空調ユニット2が自動空調モードで運転されていると判定された場合には、ステップS082へ進む。その一方で、空調ユニット2が自動空調モードでは運転されていないと判定された場合、例えば空調ユニット2がマニュアルモードで運転されていると判定された場合には、図15のフローチャートは終了し再びステップS010から開始される。そのマニュアルモードとは、空調風の風量調整、空調風の温度調整、および内気循環または外気導入の選択が操作装置44に対する乗員の手動操作により行われる空調モードである。
When it is determined in step S073 that the air conditioning unit 2 is operated in the automatic air conditioning mode, the process proceeds to step S082. On the other hand, when it is determined that the air conditioning unit 2 is not operated in the automatic air conditioning mode, for example, when it is determined that the air conditioning unit 2 is operated in the manual mode, the flowchart of FIG. It starts from step S010. The manual mode is an air conditioning mode in which the air volume adjustment of the air conditioning air, the temperature adjustment of the air conditioning air, and the selection of the inside air circulation or the outside air introduction are performed by the manual operation of the occupant on the operation device 44.
図15のステップS072では、図14のステップS072と同様に判定される。そして、図15のステップS072において、埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示されたと判定された場合には、ステップS092へ進む。その一方で、埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示されてはいないと判定された場合には、図15のフローチャートは終了し再びステップS010から開始される。
In step S072 of FIG. 15, the determination is made in the same manner as step S072 of FIG. When it is determined in step S072 in FIG. 15 that the execution of the dust concentration reduction control has been instructed, the process proceeds to step S092. On the other hand, when it is determined that execution of dust concentration reduction control is not instructed, the flowchart of FIG. 15 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
図15のステップS082では、図14のステップS082と同様に判定される。そして、図15のステップS082において、埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS092へ進む。その一方で、埃濃度上昇要因が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、図15のフローチャートは終了し再びステップS010から開始される。
In step S082 of FIG. 15, the determination is performed in the same manner as step S082 of FIG. 14. When it is determined in step S082 in FIG. 15 that a dust concentration increase factor has occurred, the process proceeds to step S092. On the other hand, when it is determined that the dust concentration increase factor has not occurred, the flowchart of FIG. 15 is ended and the process is started again from step S010.
図15のステップS092では、図14のステップS092と同様に埃濃度低減制御が実施される。図15のステップS092の次はステップS102へ進む。
In step S092 in FIG. 15, dust concentration reduction control is performed as in step S092 in FIG. After step S092 in FIG. 15, the process proceeds to step S102.
図15のステップS102では、図14のステップS102と同様に判定される。すなわち、図15のステップS102において、埃センサ32の結露が未だ解消していないと判定された場合、または埃センサ32の結露解消時から所定時間が未だ経過していないと判定された場合には、ステップS092で埃濃度低減制御の実施が継続される。その一方で、ステップS102において、埃センサ32の結露解消時から所定時間が経過したと判定された場合には、埃濃度低減制御が終了する。
In step S102 of FIG. 15, the determination is made in the same manner as step S102 of FIG. That is, if it is determined in step S102 in FIG. 15 that the dew condensation of the dust sensor 32 has not been eliminated yet, or if it is determined that the predetermined time has not yet elapsed from the condensation elimination time of the dust sensor 32. At step S092, the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is continued. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S102 that the predetermined time has elapsed from the time when the condensation of the dust sensor 32 has been eliminated, the dust concentration reduction control ends.
なお、図15のステップS053、S063は結露通知部に対応する。そして、空調制御装置40は、第3実施形態と同様の結露判定部と要因判定部と制御実施部とのほかに、その結露通知部を機能的に備えている。
Steps S053 and S063 in FIG. 15 correspond to the dew condensation notification unit. The air-conditioning control device 40 functionally includes a condensation notification unit in addition to the condensation determination unit, the factor determination unit, and the control execution unit as in the third embodiment.
以上説明したことを除き、本実施形態は第3実施形態と同様である。そして、本実施形態では、前述の第3実施形態と共通の構成から奏される効果を第3実施形態と同様に得ることができる。
The present embodiment is the same as the third embodiment except for the points described above. And in this embodiment, the effect show | played from the structure common to above-mentioned 3rd Embodiment can be acquired similarly to 3rd Embodiment.
また、本実施形態によれば、図15に示すように、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定した場合には、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせる。従って、埃センサ32が結露に起因して正常に機能しないおそれがあることを乗員に認識させることが可能である。
Further, according to the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 15, when the air conditioning control device 40 determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32 is given to the occupant by the dew condensation indicator 461. Inform. Therefore, it is possible to make the occupant recognize that the dust sensor 32 may not function properly due to condensation.
(第5実施形態)
次に、第5実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、大まかには、前述の第1実施形態と第4実施形態とを組み合わせた実施形態である。そこで、本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態および第4実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Fifth Embodiment
Next, a fifth embodiment will be described. The present embodiment is an embodiment roughly combining the first embodiment and the fourth embodiment described above. So, in this embodiment, points different from the above first embodiment and fourth embodiment will be mainly described.
次に、第5実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、大まかには、前述の第1実施形態と第4実施形態とを組み合わせた実施形態である。そこで、本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態および第4実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Fifth Embodiment
Next, a fifth embodiment will be described. The present embodiment is an embodiment roughly combining the first embodiment and the fourth embodiment described above. So, in this embodiment, points different from the above first embodiment and fourth embodiment will be mainly described.
本実施形態のフローチャートは図17に示されており、その図17に示すフローチャートのステップS010、S020、S030、S040は、図5のフローチャートと同様である。また、図17に示すフローチャートのステップS043、S053、S063、S073、S072、S082、S092、S102は、図15のフローチャートと同様である。
The flowchart of this embodiment is shown in FIG. 17, and steps S010, S020, S030 and S040 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 17 are the same as the flowchart of FIG. Steps S043, S053, S063, S073, S072, S082, S092 and S102 in the flowchart shown in FIG. 17 are the same as those in the flowchart of FIG.
本実施形態では第4実施形態と同様に、図17の制御処理は空調制御装置40によって実行される。そして、図17のステップS010、S020、S030、S040は、その空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50によって実行される。
In the present embodiment, the control process of FIG. 17 is executed by the air conditioning control device 40 as in the fourth embodiment. Then, steps S010, S020, S030, and S040 in FIG. 17 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40.
図17に示すように、制御処理が開始されると、ステップS010、S020、S030の順に進む。
As shown in FIG. 17, when the control process is started, the process proceeds in the order of steps S010, S020 and S030.
ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS040へ進む。その一方で、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、ステップS054へ進む。
If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S030 that condensation is not generated in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S054.
図17のステップS040では、図5のステップS040と同様の処理が為される。そして、ステップS040の次はステップS044へ進む。
In step S040 in FIG. 17, the same process as step S040 in FIG. 5 is performed. Then, after step S040, the process proceeds to step S044.
図17のステップS044では、空調制御装置40は、ステップS040で決定した結露中埃濃度値Dcを、埃センサ32のセンシング箇所である通風路24の埃濃度とみなす。そして、空調制御装置40は、その埃濃度に応じて、埃が除去されるように空調ユニット2を制御する。この空調ユニット2の制御は既に実施されていれば、そのまま継続される。例えば、このステップS044における埃濃度に応じた空調ユニット2の制御では、空調ユニット2が内気モードとされ、それと共に、その埃濃度が高いほど送風機23の送風量が大きくされる。ステップS044の次はステップS043へ進む。
In step S044 in FIG. 17, the air-conditioning control device 40 regards the dew-in-condensing dust concentration value Dc determined in step S040 as the dust concentration of the air passage 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32. Then, the air conditioning control device 40 controls the air conditioning unit 2 so that dust is removed according to the dust concentration. If control of this air conditioning unit 2 is already implemented, it will be continued as it is. For example, in the control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration in step S044, the air conditioning unit 2 is set to the inside air mode, and the air flow of the blower 23 is increased as the dust concentration is higher. After step S044, the process proceeds to step S043.
図17のステップS054では、上記のステップS044と同様に、埃濃度に応じた空調ユニット2の制御が実施される。但し、空調制御装置40は、結露中埃濃度値Dcではなく、ステップS010で得られた埃濃度検出値Dmを、埃センサ32のセンシング箇所の埃濃度とみなす。
In step S054 in FIG. 17, the control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration is performed as in step S044 described above. However, the air-conditioning control device 40 regards the dust concentration detection value Dm obtained in step S010 as the dust concentration at the sensing location of the dust sensor 32, not the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc.
要するに、上記のステップS044では、結露中埃濃度値Dcに応じた空調ユニット2の制御が実施されるが、このステップS054では、埃濃度検出値Dmに応じた空調ユニット2の制御が実施される。ステップS054の次はステップS063へ進む。
In short, control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration value Dc during condensation is carried out in the above-mentioned step S044, but control of the air conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration detection value Dm is carried out in this step S054 . After step S054, the process proceeds to step S063.
ここで、ステップS092の埃濃度低減制御は、ステップS044またはS054で実施される空調ユニット2の制御に対し優先して実施される。すなわち、ステップS044またはS054における空調ユニット2の制御が実施されている最中に、図17の制御処理がステップS092へ進んだ場合には、ステップS044またはS054における空調ユニット2の制御に替えて、埃濃度低減制御が実施される。
Here, the dust concentration reduction control in step S092 is performed prior to the control of the air conditioning unit 2 performed in step S044 or S054. That is, when the control process of FIG. 17 proceeds to step S092 while the control of the air conditioning unit 2 in step S044 or S054 is being carried out, instead of the control of the air conditioning unit 2 in step S044 or S054, Dust concentration reduction control is implemented.
なお、図17のフローチャートにおいてステップS043以降の流れおよびステップS063以降の流れは、図15のフローチャートと同様である。
In the flowchart of FIG. 17, the flow after step S043 and the flow after step S063 are the same as the flowchart of FIG.
以上説明したことを除き、本実施形態は第1実施形態または第4実施形態と同様である。そして、本実施形態では、前述の第1実施形態または第4実施形態と共通の構成から奏される効果を、その共通の構成を有する実施形態と同様に得ることができる。
The present embodiment is the same as the first embodiment or the fourth embodiment except for what has been described above. And in this embodiment, the effect show | played from a structure common to above-mentioned 1st Embodiment or 4th Embodiment can be acquired similarly to the embodiment which has the common structure.
(第6実施形態)
次に、第6実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、大まかには、前述の第2実施形態と第5実施形態とを組み合わせた実施形態である。そこで、本実施形態では、前述の第2実施形態および第5実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Sixth Embodiment
Next, a sixth embodiment will be described. This embodiment is an embodiment roughly combining the second embodiment and the fifth embodiment described above. Thus, in the present embodiment, points different from the above-described second embodiment and fifth embodiment will be mainly described.
次に、第6実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、大まかには、前述の第2実施形態と第5実施形態とを組み合わせた実施形態である。そこで、本実施形態では、前述の第2実施形態および第5実施形態と異なる点を主として説明する。 Sixth Embodiment
Next, a sixth embodiment will be described. This embodiment is an embodiment roughly combining the second embodiment and the fifth embodiment described above. Thus, in the present embodiment, points different from the above-described second embodiment and fifth embodiment will be mainly described.
本実施形態のフローチャートは図18に示されており、その図18に示すフローチャートのステップS010、S020、S030、S040、S031、S041は、図11のフローチャートと同様である。また、図18に示すフローチャートのステップS043、S053、S063、S073、S072、S082、S092、S102、S044、S054は、図17のフローチャートと同様である。
A flowchart of this embodiment is shown in FIG. 18, and steps S010, S020, S030, S040, S031, and S041 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 18 are the same as the flowchart of FIG. Steps S043, S053, S063, S073, S072, S082, S092, S102, S044, and S054 in the flowchart shown in FIG. 18 are similar to the flowchart in FIG.
本実施形態では第5実施形態と同様に、図18の制御処理は空調制御装置40によって実行される。そして、図18のステップS010、S020、S030、S040、S031、S041は、その空調制御装置40に含まれる埃センサ制御部50によって実行される。
In the present embodiment, as in the fifth embodiment, the control processing of FIG. Steps S010, S020, S030, S040, S031, and S041 in FIG. 18 are executed by the dust sensor control unit 50 included in the air conditioning control device 40.
図18に示すように、制御処理が開始されると、ステップS010、S020、S030の順に進む。
As shown in FIG. 18, when the control process is started, the process proceeds in the order of steps S010, S020, and S030.
ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS031へ進む。その一方で、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生してはいないと判定された場合には、ステップS054へ進む。
If it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S031. On the other hand, if it is determined in step S030 that condensation is not generated in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S054.
また、ステップS031において、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇していたと判定された場合には、ステップS041へ進む。そして、ステップS041の次はステップS044へ進む。その一方で、ステップS031において、埃濃度検出値Dmが埃センサ32の結露発生前に上昇してはいないと判定された場合には、ステップS040へ進む。そして、ステップS040の次はステップS044へ進む。
When it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S041. Then, after step S041, the process proceeds to step S044. On the other hand, when it is determined in step S031 that the dust concentration detection value Dm has not risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S040. Then, after step S040, the process proceeds to step S044.
図18のステップS044では、図17のステップS044と同様に、空調制御装置40は、ステップS040またはステップS041で決定した結露中埃濃度値Dcを、埃センサ32のセンシング箇所である通風路24の埃濃度とみなす。そして、その埃濃度に応じた空調ユニット2の制御を実施する。ステップS044の次はステップS043へ進む。
In step S044 in FIG. 18, the air conditioning control device 40 controls the dust concentration value Dc during condensation determined in step S040 or step S041 in the ventilation path 24 which is the sensing location of the dust sensor 32 as in step S044 in FIG. 17. It is regarded as dust concentration. And control of the air-conditioning unit 2 according to the dust concentration is implemented. After step S044, the process proceeds to step S043.
なお、図18のフローチャートにおいてステップS043以降の流れおよびステップS054以降の流れは、図17のフローチャートと同様である。
In the flowchart of FIG. 18, the flow after step S043 and the flow after step S054 are the same as the flow of FIG.
以上説明したことを除き、本実施形態は第2実施形態または第5実施形態と同様である。そして、本実施形態では、前述の第2実施形態または第5実施形態と共通の構成から奏される効果を、その共通の構成を有する実施形態と同様に得ることができる。
The present embodiment is the same as the second embodiment or the fifth embodiment except for what has been described above. And in this embodiment, the effect show | played from the structure common to above-mentioned 2nd Embodiment or 5th Embodiment can be acquired similarly to the embodiment which has the common structure.
(他の実施形態)
(1)上述の各実施形態では図1に示すように、空気フィルタ30は、空調ケース21の通風路24において、埃センサ32に対する空気流れ方向下流側で且つエバポレータ26に対する空気流れ方向上流側に配置されているが、これは一例である。通風路24を流れる空気の全部または大部分が空気フィルタ30を通過するようになっていれば、通風路24内における空気フィルタ30の配置に限定はない。 (Other embodiments)
(1) In each embodiment described above, as shown in FIG. 1, theair filter 30 is disposed downstream of the dust sensor 32 in the air flow direction and upstream of the evaporator 26 in the air flow path 24 of the air conditioning case 21. Although arranged, this is an example. As long as all or most of the air flowing through the air passage 24 passes through the air filter 30, the arrangement of the air filter 30 in the air passage 24 is not limited.
(1)上述の各実施形態では図1に示すように、空気フィルタ30は、空調ケース21の通風路24において、埃センサ32に対する空気流れ方向下流側で且つエバポレータ26に対する空気流れ方向上流側に配置されているが、これは一例である。通風路24を流れる空気の全部または大部分が空気フィルタ30を通過するようになっていれば、通風路24内における空気フィルタ30の配置に限定はない。 (Other embodiments)
(1) In each embodiment described above, as shown in FIG. 1, the
(2)上述の各実施形態では図1に示すように、空調制御装置40は、埃センサ制御部50を機能的に含んでいるが、これは一例である。その空調制御装置40は、物理的に分離した複数の制御装置から構成されていてもよい。例えば、埃センサ制御部50は、空調制御装置40のうちドア類や送風機23を制御する制御部とは別個の制御装置になっていてもよい。その場合さらに、その埃センサ制御部50と埃センサ32とが一体構成となって1つの埃センサユニットを構成していてもよい。
(2) As shown in FIG. 1 in the above-mentioned each embodiment, although the air-conditioning control apparatus 40 functionally contains the dust sensor control part 50, this is an example. The air conditioning control device 40 may be configured of a plurality of physically separated control devices. For example, the dust sensor control unit 50 may be a control device separate from the control unit that controls the doors and the blower 23 in the air conditioning control device 40. In that case, the dust sensor control unit 50 and the dust sensor 32 may be integrally configured to constitute one dust sensor unit.
(3)上述の第1実施形態において、図5に示すフローチャートのステップS030では、埃センサ32に結露が発生したか否かが判定されており、その結露発生の有無は、埃濃度検出値Dmと経過時間とを用いて判定されるが、これは一例である。埃センサ32の結露発生の有無を判定する方法に限定はない。例えば、その結露発生の有無は、埃センサ32のセンサケース323内に導入される空気の温度と相対湿度、埃センサ32の周辺温度などを用いて判定されても差し支えない。このことは、第2実施形態以降の各実施形態においても同様である。
(3) In the first embodiment described above, it is determined in step S030 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 5 whether condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, and the presence or absence of the condensation generation is the dust concentration detection value Dm. And the elapsed time, which is an example. There is no limitation on the method of determining the presence or absence of dew condensation on the dust sensor 32. For example, the presence or absence of dew condensation may be determined using the temperature and relative humidity of the air introduced into the sensor case 323 of the dust sensor 32, the ambient temperature of the dust sensor 32, and the like. The same applies to each of the second and subsequent embodiments.
(4)上述の第1実施形態において、図5に示すフローチャートのステップS040では、結露中埃濃度値Dcは結露前検出値Dbmと同じ値とされるが、これに限らない。そのステップS040では、結露中埃濃度値Dcが結露前検出値Dbmに基づいて決定されればよい。例えば、結露中埃濃度値Dcは、結露前検出値Dbmに対し或る値を加算して得られた値とされてもよいし、結露前検出値Dbmから或る値を差し引いて得られた値とされてもよい。このことは、第2実施形態以降の各実施形態における結露中埃濃度値Dcについても同様である。
(4) In the first embodiment described above, although the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc is the same value as the pre-condensation detection value Dbm in step S040 of the flowchart shown in FIG. 5, the present invention is not limited thereto. In step S040, the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc may be determined based on the pre-condensation detection value Dbm. For example, the dew condensation dust concentration value Dc may be a value obtained by adding a certain value to the detection value before condensation Dbm, or may be obtained by subtracting a certain value from the detection value before condensation Dbm. It may be a value. The same applies to the dust concentration value during dew condensation Dc in each of the second and subsequent embodiments.
(5)上述の第2実施形態において、図13に示すように、埃センサ32の結露発生前における埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率が大きいほど、結露中埃濃度値Dcを算出するための加算量Dxは大きく設定されるが、これは一例である。例えば、その埃濃度検出値Dmの上昇率に拘わらず加算量Dxは一定値であるとすることも考え得る。
(5) In the second embodiment described above, as shown in FIG. 13, as the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor 32 is larger, addition for calculating the dust concentration value during condensation Dc is performed. Although the amount Dx is set large, this is an example. For example, it can be considered that the addition amount Dx is a constant value regardless of the rate of increase of the dust concentration detection value Dm.
(6)上述の第3実施形態において、図14のフローチャートはステップS072を含んでいるが、その図14のフローチャートにステップS072が無いことも想定できる。そのステップS072が無いフローチャートでは、ステップS030において、埃センサ32に結露が発生したと判定された場合には、ステップS082へ進む。
(6) In the third embodiment described above, the flowchart of FIG. 14 includes step S072, but it may be assumed that step S072 is not included in the flowchart of FIG. In the flowchart without step S072, when it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, the process proceeds to step S082.
(7)上述の第3実施形態の図14のフローチャートでは、埃センサ32に結露が発生したとステップS030にて判定され、車室内の埃濃度を低減する指示が乗員から為されたとステップS072にて判定された場合には、埃濃度低減制御がステップS092にて実施される。しかしながら、これは一例である。例えば、埃センサ32に結露が発生していなくても、埃濃度低減制御は、車室内の埃濃度を低減する指示が乗員から為された場合に実施されて差し支えない。
(7) In the flowchart of FIG. 14 of the third embodiment described above, it is determined in step S030 that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor 32, and if an instruction to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is issued from the occupant, the process proceeds to step S072. If it is determined, dust concentration reduction control is performed in step S092. However, this is an example. For example, even if condensation is not generated in the dust sensor 32, the dust concentration reduction control may be performed when an instruction to reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is issued from the occupant.
(8)上述の第4実施形態において、図15のステップS043では、例えば、空調制御装置40が搭載された車両に結露インジケータ461が設けられていれば、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせることが可能であると判定される。しかしながら、これは1つの例示である。例えば、複数の表示モードを択一的に切替え可能な構成に表示装置46がなっている場合が想定される。そのように表示装置46がなっている場合においては、埃センサ32の結露発生を結露インジケータ461により表示可能な表示モードに表示装置46が切り替わっている場合に、その結露発生を結露インジケータ461により乗員へ知らせることが可能であると判定される。
(8) In the fourth embodiment described above, for example, if the condensation indicator 461 is provided in the vehicle mounted with the air conditioning control device 40 in step S043 in FIG. It is determined that it is possible to notify the occupant by However, this is one example. For example, it is assumed that the display device 46 is configured to be able to switch a plurality of display modes alternatively. When the display device 46 is turned on as such, when the display device 46 is switched to the display mode in which the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor 32 can be displayed by the dew condensation indicator 461, the dew condensation occurrence is displayed by the occupant using the dew condensation indicator 461. It is determined that it is possible to inform
(9)上述の各実施形態において、図5、図11、図14、図15、図17、および図18のフローチャートに示す各ステップの処理はコンピュータプログラムによって実現されるものであるが、ハードウェアで実現されるものであっても差し支えない。
(9) In the above-described embodiments, the processing of each step shown in the flowcharts of FIGS. 5, 11, 14, 15, 17, and 18 is realized by a computer program, but hardware It may be realized by
(10)なお、本開示は、上述の実施形態に限定されることなく、種々変形して実施することができる。また、上記各実施形態において、実施形態を構成する要素は、特に必須であると明示した場合および原理的に明らかに必須であると考えられる場合等を除き、必ずしも必須のものではないことは言うまでもない。
(10) In addition, this indication can be variously deformed and implemented, without being limited to the above-mentioned embodiment. Further, in each of the above-described embodiments, it is needless to say that the elements constituting the embodiment are not necessarily essential except when clearly indicated as being essential and when it is considered to be obviously essential in principle. Yes.
また、上記各実施形態において、実施形態の構成要素の個数、数値、量、範囲等の数値が言及されている場合、特に必須であると明示した場合および原理的に明らかに特定の数に限定される場合等を除き、その特定の数に限定されるものではない。また、上記各実施形態において、構成要素等の材質、形状、位置関係等に言及するときは、特に明示した場合および原理的に特定の材質、形状、位置関係等に限定される場合等を除き、その材質、形状、位置関係等に限定されるものではない。
Further, in the above embodiments, when numerical values such as the number, numerical value, amount, range, etc. of constituent elements of the embodiment are mentioned, it is clearly indicated that they are particularly essential and clearly limited to a specific number in principle. It is not limited to the specific number except when it is done. Further, in the above embodiments, when referring to materials, shapes, positional relationships, etc. of constituent elements etc., unless specifically stated otherwise or in principle when limited to a specific material, shape, positional relationship, etc., etc. It is not limited to the material, the shape, the positional relationship, etc.
(まとめ)
上記各実施形態の一部または全部で示された第1の観点によれば、結露判定部は、埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する。埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合には、値決定部は、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値を、埃センサがその埃センサの結露発生前に検出した埃濃度の検出値である結露前検出値に基づいて決定する。 (Summary)
According to the first aspect shown in part or all of the above-described embodiments, the condensation determination unit determines whether condensation has occurred in the dust sensor. If it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines the dust concentration value during condensation to be treated as the dust concentration during condensation generation before the condensation of the dust sensor occurs. It is determined based on the detection value before condensation which is the detection value of the dust concentration detected in
上記各実施形態の一部または全部で示された第1の観点によれば、結露判定部は、埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する。埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合には、値決定部は、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値を、埃センサがその埃センサの結露発生前に検出した埃濃度の検出値である結露前検出値に基づいて決定する。 (Summary)
According to the first aspect shown in part or all of the above-described embodiments, the condensation determination unit determines whether condensation has occurred in the dust sensor. If it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines the dust concentration value during condensation to be treated as the dust concentration during condensation generation before the condensation of the dust sensor occurs. It is determined based on the detection value before condensation which is the detection value of the dust concentration detected in
また、第2の観点によれば、値決定部は、結露中埃濃度値を結露前検出値にするようにその結露中埃濃度値を決定する。従って、結露中埃濃度値が埃センサのセンシング箇所における埃濃度の実際値から懸け離れた値にならないように、結露中埃濃度値を簡単に定めることが可能である。
Further, according to the second aspect, the value determination unit determines the dust concentration value during condensation so as to set the dust concentration value during condensation to the detection value before condensation. Therefore, the dust concentration value during condensation can be easily determined so that the dust concentration value during condensation does not become a value far from the actual value of dust concentration at the sensing location of the dust sensor.
また、第3の観点によれば、埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合において、値決定部は、埃濃度の検出値が埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたと埃濃度上昇判定部により判定された場合には、結露中埃濃度値を結露前検出値よりも大きい値にするように結露中埃濃度値を決定する。従って、埃濃度の実際値に対する結露中埃濃度値の正確性を高くするようにその結露中埃濃度値を決定することが可能である。
Further, according to the third aspect, when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines that the detected value of the dust concentration is increased before condensation occurs in the dust sensor. If it is determined by the dust concentration increase determination unit, the in-condensation dust concentration value is determined so as to make the in-condensation dust concentration value larger than the pre-condensation detection value. Therefore, it is possible to determine the dust concentration value during condensation so as to increase the accuracy of the dust concentration value during condensation relative to the actual value of dust concentration.
また、第4の観点によれば、埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合において、値決定部は、埃濃度の検出値が埃センサの結露発生前に上昇してはいないと埃濃度上昇判定部により判定された場合には、埃濃度の検出値が埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたと判定される場合よりも結露中埃濃度値を小さい値にするように結露中埃濃度値を決定する。従って、埃濃度の検出値が埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたか否かに応じて、結露中埃濃度値の大きさに適切に差異を設けることが可能である。
Further, according to the fourth aspect, when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation occurs on the dust sensor, the value determination unit increases the detection value of the dust concentration before condensation occurs on the dust sensor. If it is determined by the dust concentration rise judging unit, the dust concentration value during condensation is set to a smaller value than when it is determined that the detection value of the dust concentration has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor. Determine the dust concentration value during condensation. Therefore, it is possible to appropriately differentiate the magnitude of the dust concentration value during condensation depending on whether the detection value of the dust concentration has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor.
また、第5の観点によれば、埃センサによる埃濃度の検出は周期的に繰り返し実行される。そして、結露前検出値は、埃センサの結露開始時点に対する前回の検出で得られた埃濃度の検出値である。
Further, according to the fifth aspect, the detection of the dust concentration by the dust sensor is periodically and repeatedly performed. And the detection value before condensation is a detection value of the dust concentration obtained by the previous detection with respect to the dew condensation start time of the dust sensor.
また、第6の観点によれば、埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合に、要因判定部は、車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する。制御実施部は、埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと要因判定部により判定された場合に埃濃度低減制御を実施する。そして、その埃濃度低減制御は、その埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように空調ユニットを作動させる制御である。このことは、第7の観点においても同様である。
Further, according to the sixth aspect, when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor, the factor determination unit is configured to increase the dust concentration in the vehicle interior by a predetermined dust concentration increase factor It is determined whether or not has occurred. The control execution unit implements dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that a dust concentration increase factor has occurred. The dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit so that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. The same applies to the seventh aspect.
また、第8の観点によれば、埃センサに結露が発生したと結露判定部により判定された場合に、結露通知部は、埃センサの結露発生を通知装置により乗員へ知らせる。従って、埃センサが結露に起因して正常に機能しないおそれがあることを乗員に認識させることが可能である。
Further, according to the eighth aspect, when it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred in the dust sensor, the condensation notification unit notifies the occupant of the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor by the notification device. Therefore, it is possible to make the occupant aware that the dust sensor may not function properly due to condensation.
また、第9の観点によれば、制御実施部は、乗員の手動操作により埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示された場合にも、埃濃度低減制御を実施する。従って、乗員は任意のタイミングで車室内の埃濃度を空調ユニットにより低減することが可能である。
Further, according to the ninth aspect, the control execution unit executes the dust concentration reduction control even when the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is instructed by the manual operation of the occupant. Therefore, the occupant can reduce the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment by the air conditioning unit at any timing.
また、第10の観点によれば、結露判定部は、経過時間に対する埃濃度の検出値の変化割合が所定の限度を超えて変化した場合に、埃センサに結露が発生したと判定する。従って、埃センサの結露発生を判定するために特別な装置を必要とはしないというメリットがある。
Further, according to the tenth aspect, the dew condensation determining unit determines that dew condensation has occurred in the dust sensor when the change ratio of the detected value of the dust concentration to the elapsed time changes beyond a predetermined limit. Accordingly, there is an advantage that no special device is required to determine the occurrence of dew condensation on the dust sensor.
Claims (10)
- 車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する通風路(24)が形成された空調ケース(21)と、発光部(321)から発せされた光を受光部(322)が受光することにより前記通風路の埃濃度を検出する埃センサ(32)とを有する空調ユニット(2)において用いられる空調制御装置であって、
前記埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する結露判定部(S030)と、
前記埃センサに結露が発生したと前記結露判定部により判定された場合には、結露発生中の埃濃度として取り扱われる結露中埃濃度値(Dc)を、前記埃センサが該埃センサの結露発生前に検出した埃濃度の検出値である結露前検出値(Dbm)に基づいて決定する値決定部(S040、S041)とを備えている、空調制御装置。 An air conditioning case (21) in which a ventilating passage (24) through which air blown out into a vehicle compartment is formed, and light emitted from the light emitting unit (321) are received by the light receiving unit (322). An air conditioning control device used in an air conditioning unit (2) having a dust sensor (32) for detecting a concentration, comprising:
A dew condensation determination unit (S030) that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
If it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the dust sensor generates the dew concentration of the dust sensor during condensation that is treated as the dust concentration during condensation occurrence. An air conditioning control device comprising: a value determination unit (S040, S041) to determine based on a pre-condensation detection value (Dbm) that is a detection value of dust concentration detected before. - 前記値決定部(S040)は、前記結露中埃濃度値を前記結露前検出値にするように該結露中埃濃度値を決定する、請求項1に記載の空調制御装置。 The air conditioning control device according to claim 1, wherein the value determination unit (S040) determines the dust concentration value during condensation so as to set the dust concentration value during condensation to the detection value before condensation.
- 前記埃濃度の検出値が前記埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたか否かを判定する埃濃度上昇判定部(S031)を備え、
前記埃センサに結露が発生したと前記結露判定部により判定された場合において、前記値決定部は、前記埃濃度の検出値が前記埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたと前記埃濃度上昇判定部により判定された場合には、前記結露中埃濃度値を前記結露前検出値よりも大きい値にするように該結露中埃濃度値を決定する、請求項1に記載の空調制御装置。 The dust concentration increase determination unit (S031) determines whether the detected value of the dust concentration has increased before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor,
When it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines that the dust concentration increase is determined that the detected value of the dust concentration has risen before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor. The air conditioning control device according to claim 1, wherein the dust concentration value during condensation is determined such that the dust concentration value during condensation is made larger than the detection value before condensation, when it is determined by the unit. - 前記埃センサに結露が発生したと前記結露判定部により判定された場合において、前記値決定部は、前記埃濃度の検出値が前記埃センサの結露発生前に上昇してはいないと前記埃濃度上昇判定部により判定された場合には、前記埃濃度の検出値が前記埃センサの結露発生前に上昇していたと判定される場合よりも前記結露中埃濃度値を小さい値にするように該結露中埃濃度値を決定する、請求項3に記載の空調制御装置。 When it is determined by the condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor, the value determination unit determines that the detected value of the dust concentration does not increase before condensation occurs on the dust sensor. When it is determined by the rise determination unit, the dust concentration value during condensation is set to a smaller value than when it is determined that the detection value of the dust concentration is rising before the occurrence of condensation of the dust sensor. The air conditioning control device according to claim 3, wherein the dust concentration value during condensation is determined.
- 前記埃センサによる前記埃濃度の検出は周期的に繰り返し実行され、
前記結露前検出値は、前記埃センサの結露開始時点に対する前回の検出で得られた前記埃濃度の検出値である、請求項1ないし4のいずれか1つに記載の空調制御装置。 The detection of the dust concentration by the dust sensor is periodically repeated.
The air conditioning control device according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein the pre-condensation detection value is a detection value of the dust concentration obtained by previous detection with respect to the condensation start time of the dust sensor. - 車室内へ吹き出る空気が流通する通風路(24)が形成された空調ケース(21)と、発光部(321)から発せされた光を受光部(322)が受光することにより前記通風路の埃濃度を検出する埃センサ(32)とを有する空調ユニット(2)において用いられる空調制御装置であって、
前記埃センサに結露が発生したか否かを判定する結露判定部(S030)と、
前記埃センサに結露が発生したと前記結露判定部により判定された場合に、前記車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する要因判定部(S082)と、
前記埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと前記要因判定部により判定された場合に埃濃度低減制御を実施する制御実施部(S092、S102)とを備え、
前記埃濃度低減制御は、該埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して前記車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように前記空調ユニットを作動させる制御である、空調制御装置。 An air conditioning case (21) in which a ventilating passage (24) through which air blown out into a vehicle compartment is formed, and light emitted from the light emitting unit (321) are received by the light receiving unit (322). An air conditioning control device used in an air conditioning unit (2) having a dust sensor (32) for detecting a concentration, comprising:
A dew condensation determination unit (S030) that determines whether dew condensation has occurred on the dust sensor;
A factor determination unit that determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to increase when the condensation determination unit determines that condensation occurs in the dust sensor (S082),
A control execution unit (S092, S102) for performing dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that the dust concentration increase factor has occurred;
The air conditioning control device, wherein the dust concentration reduction control is control for operating the air conditioning unit such that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. - 前記埃センサに結露が発生したと前記結露判定部により判定された場合に、前記車室内の埃濃度を上昇させる原因になる所定の埃濃度上昇要因が発生したか否かを判定する要因判定部(S082)と、
前記埃濃度上昇要因が発生したと前記要因判定部により判定された場合に埃濃度低減制御を実施する制御実施部(S092、S102)とを備え、
前記埃濃度低減制御は、該埃濃度低減制御の開始前に比して前記車室内の埃濃度が低減されるように前記空調ユニットを作動させる制御である、請求項1ないし5のいずれか1つに記載の空調制御装置。 A factor determination unit that determines whether or not a predetermined dust concentration increase factor that causes the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment to increase when the condensation determination unit determines that condensation occurs in the dust sensor (S082),
A control execution unit (S092, S102) for performing dust concentration reduction control when it is determined by the factor determination unit that the dust concentration increase factor has occurred;
The dust concentration reduction control according to any one of claims 1 to 5, wherein the air conditioning unit is operated such that the dust concentration in the vehicle compartment is reduced as compared to before the start of the dust concentration reduction control. Air conditioning control device according to the above. - 前記埃センサに結露が発生したと前記結露判定部により判定された場合に、前記埃センサの結露発生を通知装置(461)により乗員へ知らせる結露通知部(S053、S063)を備えている、請求項6または7に記載の空調制御装置。 The apparatus further comprises a dew condensation notification unit (S053, S063) for notifying the occupant of the dew condensation occurrence of the dust sensor by the notification device (461) when it is determined by the dew condensation determination unit that condensation has occurred on the dust sensor. Item 8. The air conditioning control device according to item 6 or 7.
- 前記制御実施部は、乗員の手動操作により前記埃濃度低減制御の実施が指示された場合にも、前記埃濃度低減制御を実施する、請求項6ないし8のいずれか1つに記載の空調制御装置。 The air conditioning control according to any one of claims 6 to 8, wherein the control execution unit executes the dust concentration reduction control even when the execution of the dust concentration reduction control is instructed by a manual operation of an occupant. apparatus.
- 前記結露判定部は、経過時間に対する前記埃濃度の検出値の変化割合が所定の限度を超えて変化した場合に、前記埃センサに結露が発生したと判定する、請求項1ないし9のいずれか1つに記載の空調制御装置。 10. The dew condensation determination unit according to any one of claims 1 to 9, wherein the dew condensation is determined to occur in the dust sensor when a change ratio of the detected value of the dust concentration to an elapsed time changes beyond a predetermined limit. Air conditioning control device according to one.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201880053974.2A CN111032388B (en) | 2017-08-23 | 2018-07-19 | Air conditioner control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017160340A JP6841187B2 (en) | 2017-08-23 | 2017-08-23 | Air conditioning controller |
| JP2017-160340 | 2017-08-23 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019039149A1 true WO2019039149A1 (en) | 2019-02-28 |
Family
ID=65438808
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/027163 WO2019039149A1 (en) | 2017-08-23 | 2018-07-19 | Air-conditioning control device |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6841187B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN111032388B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019039149A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112178869B (en) * | 2020-09-29 | 2021-12-21 | 重庆海尔空调器有限公司 | Method and device for detecting fault of air conditioner and air conditioner |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56163444A (en) * | 1980-05-21 | 1981-12-16 | Nippon Denso Co Ltd | Device for detecting blur on window glass |
| JPS59128432A (en) * | 1983-01-13 | 1984-07-24 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Gas concentration measuring device |
| JPH0360104U (en) * | 1989-10-18 | 1991-06-13 | ||
| JP2005153795A (en) * | 2003-11-27 | 2005-06-16 | Toshiba Corp | On-vehicle air cleaner |
| JP2005283507A (en) * | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-13 | Yamatake Corp | Apparatus for detecting state on specular surface, and moisture detector |
| JP2006230037A (en) * | 2005-02-15 | 2006-08-31 | Toyota Motor Corp | Actuator and control method of actuating apparatus |
| JP2009274603A (en) * | 2008-05-15 | 2009-11-26 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | Intake door control device for vehicle |
| JP2011168195A (en) * | 2010-02-19 | 2011-09-01 | Denso Corp | Air cleaner for vehicle |
| JP2017095086A (en) * | 2015-11-12 | 2017-06-01 | 株式会社デンソー | Vehicle air conditioner |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3012271B2 (en) * | 1990-03-15 | 2000-02-21 | 松下電工株式会社 | air purifier |
| CN101354332A (en) * | 2008-09-26 | 2009-01-28 | 北京绿林创新数码科技有限公司 | Laser powder dust detector with humidity continuous self-correcting function and detecting method thereof |
| JP6596283B2 (en) * | 2015-09-18 | 2019-10-23 | 株式会社デンソー | Air conditioner for vehicles |
| KR20170048789A (en) * | 2015-10-27 | 2017-05-10 | 현대자동차주식회사 | Device for removing dust of vehicle |
-
2017
- 2017-08-23 JP JP2017160340A patent/JP6841187B2/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-07-19 WO PCT/JP2018/027163 patent/WO2019039149A1/en active Application Filing
- 2018-07-19 CN CN201880053974.2A patent/CN111032388B/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56163444A (en) * | 1980-05-21 | 1981-12-16 | Nippon Denso Co Ltd | Device for detecting blur on window glass |
| JPS59128432A (en) * | 1983-01-13 | 1984-07-24 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Gas concentration measuring device |
| JPH0360104U (en) * | 1989-10-18 | 1991-06-13 | ||
| JP2005153795A (en) * | 2003-11-27 | 2005-06-16 | Toshiba Corp | On-vehicle air cleaner |
| JP2005283507A (en) * | 2004-03-30 | 2005-10-13 | Yamatake Corp | Apparatus for detecting state on specular surface, and moisture detector |
| JP2006230037A (en) * | 2005-02-15 | 2006-08-31 | Toyota Motor Corp | Actuator and control method of actuating apparatus |
| JP2009274603A (en) * | 2008-05-15 | 2009-11-26 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | Intake door control device for vehicle |
| JP2011168195A (en) * | 2010-02-19 | 2011-09-01 | Denso Corp | Air cleaner for vehicle |
| JP2017095086A (en) * | 2015-11-12 | 2017-06-01 | 株式会社デンソー | Vehicle air conditioner |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111032388B (en) | 2023-05-09 |
| JP2019038335A (en) | 2019-03-14 |
| JP6841187B2 (en) | 2021-03-10 |
| CN111032388A (en) | 2020-04-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110573861B (en) | Dust concentration detection device | |
| US20170113517A1 (en) | Automatic dust removal device for vehicle | |
| JP2010168026A (en) | Air conditioning system for vehicle | |
| CN110049888B (en) | Air conditioner for vehicle | |
| JP2020100294A (en) | Moving body | |
| WO2019039149A1 (en) | Air-conditioning control device | |
| WO2020149065A1 (en) | Pm sensor | |
| WO2018116683A1 (en) | Air-conditioning device for vehicle | |
| JP4967779B2 (en) | Air conditioner for vehicles | |
| CN111225811B (en) | Air conditioner for vehicle | |
| JP2009274603A (en) | Intake door control device for vehicle | |
| WO2018159479A1 (en) | Vehicle air-conditioning device | |
| JP5884682B2 (en) | Air conditioner for vehicles | |
| JP2000135918A (en) | Intake door control device | |
| KR101953688B1 (en) | Air conditioning system for automotive vehicles | |
| JP2000135917A (en) | Intake door control device | |
| JP2005112036A (en) | Swing louver control device | |
| CN113242807B (en) | Air conditioner for vehicle | |
| KR20160124459A (en) | Air conditioning system for vehicle and controlling method thereof | |
| JPH0622566Y2 (en) | Demist control device for vehicle air conditioner | |
| JP2000135919A (en) | Intake door control device | |
| KR20140034635A (en) | Air conditioner for vehicle and control method thereof | |
| JP2006290274A (en) | Vehicular air-conditioner | |
| JP2005161993A (en) | Air-conditioning control unit, and vehicular air-conditioner | |
| JP2005075165A (en) | Air conditioner for vehicle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18848453 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18848453 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |