WO2019029320A1 - 一种配置管理方法、装置及设备 - Google Patents
一种配置管理方法、装置及设备 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019029320A1 WO2019029320A1 PCT/CN2018/095631 CN2018095631W WO2019029320A1 WO 2019029320 A1 WO2019029320 A1 WO 2019029320A1 CN 2018095631 W CN2018095631 W CN 2018095631W WO 2019029320 A1 WO2019029320 A1 WO 2019029320A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- terminal
- gateway
- identifier
- message
- mqtt
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/54—Interprogram communication
- G06F9/546—Message passing systems or structures, e.g. queues
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F15/00—Digital computers in general; Data processing equipment in general
- G06F15/16—Combinations of two or more digital computers each having at least an arithmetic unit, a program unit and a register, e.g. for a simultaneous processing of several programs
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/24—Querying
- G06F16/245—Query processing
- G06F16/2455—Query execution
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/54—Interprogram communication
- G06F9/542—Event management; Broadcasting; Multicasting; Notifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L12/00—Data switching networks
- H04L12/66—Arrangements for connecting between networks having differing types of switching systems, e.g. gateways
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
- H04L41/0889—Techniques to speed-up the configuration process
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
- H04L41/0893—Assignment of logical groups to network elements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/12—Protocols specially adapted for proprietary or special-purpose networking environments, e.g. medical networks, sensor networks, networks in vehicles or remote metering networks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/50—Network services
- H04L67/55—Push-based network services
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L69/00—Network arrangements, protocols or services independent of the application payload and not provided for in the other groups of this subclass
- H04L69/22—Parsing or analysis of headers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04Q—SELECTING
- H04Q9/00—Arrangements in telecontrol or telemetry systems for selectively calling a substation from a main station, in which substation desired apparatus is selected for applying a control signal thereto or for obtaining measured values therefrom
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L41/00—Arrangements for maintenance, administration or management of data switching networks, e.g. of packet switching networks
- H04L41/08—Configuration management of networks or network elements
- H04L41/0894—Policy-based network configuration management
Definitions
- the present application relates to the field of computer technologies, and in particular, to a configuration management method, apparatus, and device.
- the control device can manage a large number of network access devices or provide various services for a mass network access device by interacting with a mass network access device.
- the management device can manage the massive network access devices, including device configuration management, device performance management, device fault management, application deployment management, virtual machine deployment management, radio frequency tuning, terminal location analysis, user admission control, and mobile operation and maintenance.
- the control device can provide services for massive network access devices, including WIFI access, data exchange, network security and other network services; in addition, the control device can also provide data-level services, such as system log, performance indicator data collection and storage;
- the device can also provide application-level services, such as providing application analysis reports with industry attributes for public operation services, etc., to meet a variety of equipment management and service needs of users.
- the control device releases the application message to the mass network access device, the efficiency of the application is low, which adversely affects device management and service quality.
- the control device sends a configuration update message to multiple network access devices, the speed of the transmission is The network access device cannot update the configuration information in time, causing the network access device to fail to interact with other devices. Therefore, how to improve the efficiency of the control device to release application messages to a mass network access device is an urgent problem to be solved in the current computer network field.
- the invention provides a configuration management method, device and device, which can send a message according to a packet sending manner, so as to improve the efficiency of the control device to publish an application message to a mass network access device.
- an embodiment of the present invention provides a configuration management method, which is applied to a control device.
- the control device determines that the application message needs to be distributed to the target logical group, obtains the identifier of the target logical group, and queries the gateway connected to each target terminal in the target logical group according to the gateway mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, to obtain at least A target gateway.
- the control device generates an MQTT advertisement message according to the application message, and sends the MQTT advertisement message to the at least one target gateway, where the MQTT advertisement message is used to indicate that the target gateway that receives the MQTT advertisement message is sent to the target gateway.
- the connected target terminals belonging to the target logical group send corresponding application messages.
- the target logical grouping includes at least one target terminal.
- the gateway mapping table records identifiers of multiple gateways, identifiers of terminals connected to each of the multiple gateways, and identifiers of logical groups to which each terminal belongs.
- the MQTT publish message includes an identifier of the target logical group and the application message.
- the control device may send the MQTT advertisement message including the application message to the gateway connected to the terminal in the packet in a packet manner, and instruct the gateway to send the application message to each terminal, which can improve the efficiency of sending the message.
- the subscription/distribution mechanism of the MQTT protocol is adopted between the control device and the terminal, and the long-term connection between the control device and the terminal does not need to be established, and the control device can be connected in cascade with multiple gateways, so the connection can be increased exponentially. The number of terminals entered.
- the control device receives the MQTT subscription message carrying the subscription topic, and parses the MQTT subscription message to obtain the flag data. If the flag data includes the subscription flag and the identifier of the gateway, the control device determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway, and records the identifier of the gateway to the gateway mapping table; if the flag data includes a forwarding flag, an identifier of the terminal, and a gateway And the control device determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal, and determines that the terminal is connected to the gateway, and records the identifier of the terminal into an entry corresponding to the identifier of the gateway in the gateway mapping table.
- control device can parse the MQTT subscription message, obtain the flag data, determine the connection relationship between the gateway and the terminal according to the flag data, or determine the connection relationship between the control device and the gateway, that is, the control device can determine to send to the terminal. Apply the path of the message and support the gateway subscription topic or gateway forwarding subscription topic to make the subscription mechanism more flexible.
- the control device groups the multiple terminals according to the subscription topic of the multiple terminals connected to the multiple gateways, or randomly groups the multiple terminals, or according to the multiple gateways
- the plurality of terminals are grouped to obtain a plurality of logical packets.
- the control device configures an identifier for each logical group, and records the identifier of each logical group into an entry corresponding to the identifier of each terminal in the logical grouping in the gateway mapping table.
- control device can group the terminals connected to the multiple gateways according to the subscription theme, the gateway or the random manner of the terminal, and can flexibly group the terminals, so that the control device can group the terminals according to the grouping manner.
- control device detects at least one application message that matches the subscription topic of the at least one target terminal within the target logical group; or if the historical behavior data of the at least one target terminal is detected Matching at least one application message to determine that an application message needs to be published to the target logical group.
- control device may determine, according to the subscription topic of each terminal in the target logical group or the historical behavior data of each terminal, whether it is necessary to issue an application message to each target terminal in the target logical group.
- control device generates a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the target logical group, and generates a payload of the MQTT format according to the application message, and encapsulates the variable header and the payload into the MQTT release report. Text.
- control device may encapsulate the identifier of the target logical group and the at least one application message in an MQTT advertisement message, so that the gateway may send an application message to each target terminal according to the MQTT advertisement message.
- the second aspect provides another configuration management method, which is applied to a gateway.
- the method includes: the gateway receives the first message queue telemetry transmission MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device, and parses the first MQTT release message to obtain a target.
- the gateway determines, according to the packet mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, at least one target terminal that is connected to the gateway and belongs to the target logical group, and subscription topic or historical behavior data of each target terminal in the at least one target terminal.
- the packet mapping table records the identifiers of the terminals connected to the gateway, the identifiers of the logical groups to which the terminals belong, and the subscription topic or historical behavior data of each terminal.
- the gateway can receive the MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device in a group manner, and send the application message in the MQTT advertisement message to the terminal in the packet, so that the control device can be used to release the application to the mass network access device.
- the efficiency of the message can be performed by the control device in a group manner, and send the application message in the MQTT advertisement message to the terminal in the packet, so that the control device can be used to release the application to the mass network access device.
- the gateway receives the subscription request of the terminal, and parses the subscription request, obtains the identifier of the terminal, and the subscription topic of the terminal, and further determines that the terminal is connected to the gateway.
- the gateway records the identifier of the terminal and the subscription topic of the terminal into an entry of the packet mapping table, and receives the packet message sent by the control device.
- the gateway records the identifier of the logical group to which the terminal belongs included in the packet message to the entry corresponding to the identifier of the terminal in the packet mapping table.
- the packet message includes an identifier of the terminal and an identifier of a logical group to which the terminal belongs.
- the gateway may determine each terminal connected to the gateway according to the subscription request of the terminal, and determine, according to the packet message sent by the control device, the logical group identifier to which each terminal belongs, so that the gateway may determine to send to each terminal in the packet. The path to the message.
- the gateway obtains the historical behavior data of the terminal, and records the historical behavior data of the terminal into the entry corresponding to the identifier of the terminal in the packet mapping table.
- the gateway can obtain the historical behavior data of each terminal, and record the historical behavior data of the terminal in the packet mapping table, so that the application message can be sent when receiving the application message that matches the historical behavior data of the terminal. Give the terminal.
- the gateway generates a variable header in the MQTT format according to the identifier of the terminal and the identifier of the gateway, generates a payload in the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the terminal, and generates a fixed header in the MQTT format according to the forwarding flag.
- the gateway may encapsulate the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header into an MQTT subscription packet, and send the MQTT subscription packet to the control device.
- the MQTT subscription message is used to indicate that the control device determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal, and determines that the terminal is connected to the gateway, and records the identifier of the terminal to the gateway mapping table of the control device. In the table entry.
- the gateway can forward the subscription request of the terminal connected to the gateway, and the control device can determine the path for sending the application message to each terminal according to the subscription request, and can also support the gateway to forward the subscription topic, and enhance the subscription mechanism. flexibility.
- the gateway generates a variable header in the MQTT format according to the identifier of the gateway, generates a payload in the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the gateway, and generates a fixed header in the MQTT format according to the subscription flag.
- the gateway may encapsulate the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header into an MQTT subscription packet, and send the MQTT subscription packet to the control device.
- the MQTT subscription message is used to instruct the control device to determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway, and record the identity of the gateway to the gateway mapping table of the control device.
- the gateway can send a subscription request to the control device, can support the gateway subscription topic, and enhance the flexibility of the subscription mechanism.
- a configuration management apparatus for use in a control device having a function to implement the behavior of the first aspect or the possible implementation of the first aspect.
- This function can be implemented in hardware or in hardware by executing the corresponding software.
- the hardware or software includes one or more modules corresponding to the functions described above. This module can be software and/or hardware.
- a gateway having a function of implementing the behavior of the second aspect or the possible implementation of the second aspect.
- This function can be implemented in hardware or in hardware by executing the corresponding software.
- the hardware or software includes one or more modules corresponding to the functions described above. This module can be software and/or hardware.
- a control device comprising: a memory for storing one or more programs; and a processor for calling a program stored in the memory to implement the method design of the first aspect above In the program.
- a gateway comprising: a memory for storing one or more programs; and a processor for calling a program stored in the memory to implement the method design of the second aspect above Program.
- a computer readable storage medium having stored thereon a computer program, which, when executed by at least one processor, implements the first aspect, the second aspect, and the first aspect of the first aspect And possible implementations and benefits of the second aspect.
- an embodiment of the present invention provides a computer program product, where the computer program product includes a non-transitory computer readable storage medium storing a computer program, the computer program being executed to cause a computer to implement the first aspect and
- the steps of the method of the second aspect, the implementation of the problem and the beneficial effects of the computer program product can be seen in the above first aspect, the second aspect, the possible aspects of the first aspect, and the implementation of each possible method of the second aspect and Benefits, repetitions are not repeated.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a network structure for configuration management according to an embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 2 is a schematic flowchart of a configuration management method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a schematic flowchart of another configuration management method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a configuration management apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of another configuration management apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic structural diagram of a control device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of a gateway according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the control device can implement management of massive network access devices or provide various services for mass network access devices, such as implementing configuration management of devices and providing data exchange services.
- the control device releases the application message to the mass network access device, the efficiency of the device management and service quality is adversely affected.
- a configuration management method, apparatus, and device are provided, which enable a control device to send a message to a network access device based on a packet transmission manner, so as to improve the efficiency of message transmission.
- the present invention can be applied to application scenarios such as telemetry, vehicle monitoring, smart home, energy monitoring, chat application, smart meter reading, notification service, or health care to implement management of terminals in an application scenario or provide services for terminals.
- application scenarios such as telemetry, vehicle monitoring, smart home, energy monitoring, chat application, smart meter reading, notification service, or health care to implement management of terminals in an application scenario or provide services for terminals.
- the control device in the embodiment of the present invention may be a server that is applied to various application scenarios, and the terminal may be a terminal that is applied to various application scenarios.
- the control device in the vehicle supervision application scenario, the control device may refer to the vehicle monitoring server, and the terminal may refer to the vehicle terminal; in the smart meter reading application scenario, the control device may refer to a power meter reading server, and the terminal may refer to a smart meter.
- the control device can be applied to multiple application scenarios, and the terminal can also be applied to multiple application scenarios.
- the gateway in the embodiment of the present invention may refer to an access router (AR).
- AR access router
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a network structure of configuration management according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the network architecture of the configuration management shown in FIG. 1 may include a control device 101 and one or more gateways (FIG. 1 Two are examples, labeled as gateway 102 and gateway 103).
- the control device 101 can be deployed in the cloud and connected to the gateway 102 and the gateway 103 through the Internet in the public network.
- the gateway has the capability of converting the public network IP address into the private network IP address or the private network IP address into the public network IP address. Therefore, the terminal 1, the terminal 2, the terminal 3, and the terminal 4 distributed on the private network can pass through the gateway.
- the network architecture shown in FIG. 1 can implement sending a subscription request and publishing an application message, thereby implementing management of the terminal or providing services for the terminal.
- the gateway 102 or the gateway 103 may send a subscription request carrying a subscription flag to the control device 101, where the subscription request includes a subscription topic, and after receiving the subscription request carrying the subscription flag, the control device 101 parses the subscription request, and if the subscription flag is obtained, And the identifier of the gateway is 102, then the gateway 102 can be determined to be connected to the control device 101. Similarly, if the identifier of the subscription and the identifier of the gateway are 103, the gateway 103 and the control device 101 can be determined.
- the terminal 1 may send a subscription request to the gateway 102, where the subscription request includes the subscription topic and the identifier of the terminal. After receiving the subscription request, the gateway 102 parses the subscription request.
- the terminal 1 and the gateway 102 may be determined. connection.
- the gateway 102 may encapsulate the subscription request into a subscription request carrying a forwarding flag, and forward the subscription request carrying the forwarding flag to the control device 101.
- the control device 101 parses the subscription request, and obtains a forwarding flag, a subscription topic, and a gateway.
- the identifier 102 and the identifier 1 of the terminal may determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal 1, and may determine that the terminal 1 is connected to the gateway 102.
- the control device 101 may determine that the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 are connected to the gateway 102.
- control device 101 issues an application message to the terminal 1 to the terminal 4, the application message needs to be sent to the gateway 102 and forwarded by the gateway 102 to the terminal 1 to the terminal 4.
- the control device 101 can forward the subscription request of the terminal 5 to the terminal 8 by parsing the received gateway 103, and determine that the terminal 5 to the terminal 8 are connected to the gateway 103.
- the control device may group the terminals connected to each gateway, obtain a plurality of logical groups, and configure an identifier for each logical group, and may carry the grouping message of the identifier of the logical group and the identifier of the terminal included in each logical group.
- the gateway 102 and the gateway 103 are sent to the gateway 102 to determine the identity of the logical group to which the terminal 1, the terminal 2, the terminal 3, and the terminal 4 belong, and the gateway 103 determines that the terminal 5, the terminal 6, the terminal 7, and the terminal 8 belong to each other.
- the identity of the logical grouping may be used to determine the identity of the logical group to which the terminal 1, the terminal 2, the terminal 3, and the terminal 4 belong.
- the foregoing logical grouping may refer to grouping of each terminal according to a subscription topic, a gateway, or a random manner of each terminal.
- the control device may divide the terminal with the same subscription topic into one logical group.
- the control device may divide the terminal 2 to the terminal 8 into the first logical group, the identifier of the first logical group is 1, the terminal 1 is divided into the second logical group, the identifier of the second logical group is 2, and may be carried
- the identifier of the logical group to which each terminal belongs and the packet message of the identity of each terminal are respectively sent to the gateway 102 and the gateway 103, so that the gateway 102 can determine and record the belonging of the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 in the packet mapping table of the gateway 102.
- the logical group identifier is 1, and the logical group identifier to which the terminal 1 belongs is 2, and the gateway 103 can determine and record in the packet mapping table of the gateway 103 that the logical group identifier to which the terminal 5 to the terminal 8 belong is 1.
- the control device can query, by using the determined connection relationship between the terminal and the gateway, that the gateway connected to the terminal in the first logical group is the gateway 102 and The gateway 103, in turn, may send the MQTT advertisement message carrying the logical group identifier to the gateway 102 and the gateway 103, where the MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device to the gateway 102 includes at least the subscription topic matching the terminal 2 to the terminal 4.
- An application message, the MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device to the gateway 103 includes at least one application message matching the subscription topic of the terminal 5 to the terminal 8.
- the gateway 102 may parse the MQTT advertisement packet, obtain a logical group identifier, and at least one application message, and determine, according to the foregoing packet mapping table, that the application message needs to be sent to the terminal 2 to the terminal 4, The application messages matching the subscription topics of the respective terminals are respectively determined in the at least one application message, and the determined application messages are respectively sent to the terminal 2 to the terminal 4.
- the gateway 103 can parse the MQTT advertisement packet, obtain a logical group identifier, and at least one application message, and determine, according to the packet mapping table, that the application message needs to be sent to the terminal 5 to the terminal 8. Then, the application messages that match the subscription topics of the respective terminals are respectively determined from the at least one application message, and the determined application messages are respectively sent to the terminal 5 to the terminal 8.
- the gateway 102 or the gateway 103 in the network architecture may be used to forward the subscription request of the terminal or forward the application message advertised by the control device 101 to the connected terminal. Therefore, the gateway 102 and the gateway 103 may be regarded as
- the MQTT broker in the MQTT mechanism can regard the control device 101 as a broker for issuing messages in the MQTT mechanism, and can treat each terminal as a subscriber in the MQTT mechanism.
- the MQTT publishing message and the subscription request are transmitted based on the MQTT protocol.
- the Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) protocol is an instant messaging protocol, and the protocol has the following advantages: 1) reliable transmission .
- the MQTT protocol guarantees reliable and secure transmission of messages and can be easily integrated with enterprise applications; 2) message push. Support real-time notification of messages, rich push content, flexible subscription/release and message storage and filtering; 3) low bandwidth, low power consumption and low cost. Occupy mobile applications have low bandwidth, high bandwidth utilization, and low power consumption. Therefore, the protocol is widely used in telemetry, automotive, smart home, energy monitoring, chat applications, notification services, health care applications and other application scenarios.
- the MQTT protocol combined with the proxy can implement the publish/subscribe mechanism.
- the publisher such as the control device
- the subscriber such as the terminal
- the proxy such as The presence of a gateway can interact directly with the agent, and the agent forwards the subscribed or published message to the publisher or subscriber.
- the release and subscription mechanism of the MQTT protocol can completely decouple publishers and subscribers from the following three aspects: 1) Spatial decoupling: Publishers and subscribers do not need to know the existence of the other party (communication through IP address and port); 2) Time decoupling: subscribers and publishers do not need to be connected at the same time; 3) synchronous decoupling: when posting or receiving messages, the components on the subscriber and the publisher will operate synchronously, based on the complete decoupling of the above three aspects. Subscribers and publishers interact more easily.
- subscribers and publishers mainly use MQTT subscription messages and MQTT publish messages to interact.
- the MQTT subscription message refers to a message type that the subscriber sends to the publisher in order to create one or more subscriptions, and each MQTT subscription message carries one or more interested parties that the subscriber registers with the publisher. Subscribe to the topic. If the publisher publishes a message that matches the subject that the subscriber subscribes to, the publisher can send a message that matches the subscriber's subscription topic to the subscriber.
- the MQTT subscription message includes three parts: a fixed header, a variable header, and a payload.
- the fixed header of the MQTT subscription packet is as shown in Table 1.
- the fixed header includes the MQTT control packet type and is reserved. Bit and remaining length, the value of the field of the MQTT control message type is used to describe the type of the MQTT message. For example, if the value is 8, the MQTT message is an MQTT subscription message, and the remaining length is used to indicate the MQTT subscription.
- the reserved field can be set according to the needs of the application scenario.
- the variable header can be used to describe information such as the identity of the device (such as the subscriber's device identity); the payload is used to describe the subscription topic.
- An MQTT-published message is a type of message carrying an application message sent by the publisher to the subscriber, and is mainly used for the issuance of the message.
- the MQTT-published message also includes a fixed header, a variable header, and a payload.
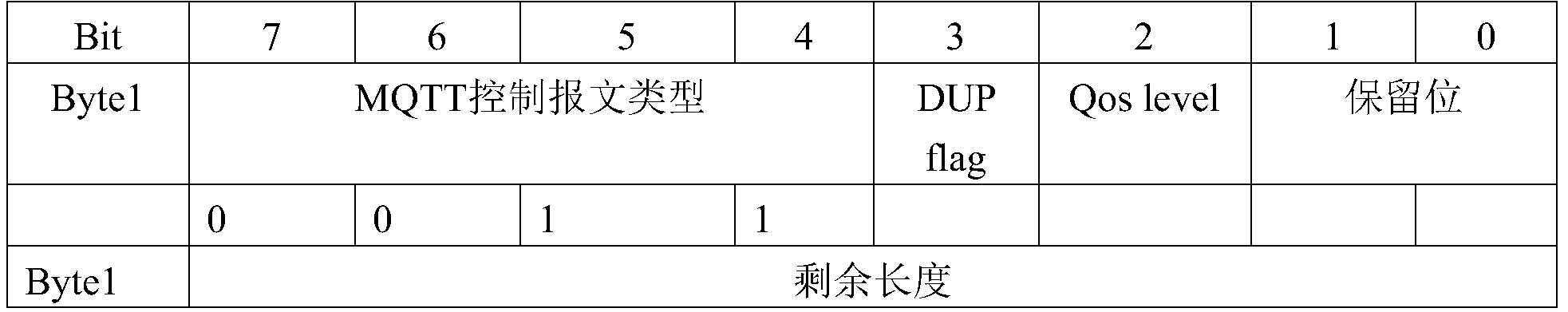
- the fixed header of the MQTT-published message is shown in Table 2.
- the fixed header of the MQTT-published message includes the MQTT control packet type and the retransmission identifier. Duplicate delivery, DUP) flag, quality of service (QoS) level, remaining length, and reserved bits.
- the value of the field of the MQTT control packet type is used to describe the type of the MQTT packet. If the value is 3, the MQTT packet is sent to the MQTT.
- the DUP flag is used to describe whether the MQTT advertisement is retransmitted. If the value of the DUP flag is 0, the value of the DUT flag is the first one. If the value of the DUP flag is 1, it indicates that the MQTT is the retransmitted message.
- the QoS level is used to describe the quality of service level of the published application message; the remaining length is used to indicate the total number of bytes of the variable header and payload of the MQTT-issued message, and the reserved bit field can be set according to the needs of the application scenario.
- the variable header of the MQTT publication message is shown in Table 3.
- the variable header includes subscription topic information (such as the length of the subscription topic, the subscription topic name) and the message identifier.
- the fields in Byte1 to Byte2 in Table 3 are used to describe The length of the subscription topic, the fields in Byte3 to Byte5 are used to describe the subscription topic name, and the fields in Byte6 to Byte7 can be used to describe the message identifier.
- the message identifier can be used to uniquely indicate the MQTT release message, the most significant bit ( Most significant bit (MSB), least significant bit (LSB).
- the payload of the MQTT publish message is used to describe the published application message.
- the gateway and the control device may agree to use the reserved bits of the fixed header of the MQTT subscription message shown in Table 1 to indicate the subscription flag or the forwarding flag. If the value of the reserved bit is set to 1, the subscription flag is used to indicate the The subscription topic carried in the MQTT subscription message is subscribed by the gateway. The subscription is set to 2 to indicate the forwarding flag, which is used to indicate that the subscription topic carried in the MQTT subscription message is subscribed by the terminal.
- the value of the reserved bit of the fixed header of the MQTT subscription packet sent to the control device may be set to a subscription flag (such as 1), and is used to indicate that the MQTT subscription packet is carried in the message.
- the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway.
- the value of the reserved bit of the fixed header of the MQTT subscription packet sent to the control device may be set to a forwarding flag (such as 2) for indicating the MQTT subscription packet.
- a forwarding flag such as 2
- the value of the reserved bit of the fixed header of the MQTT subscription message sent to the control device may be set to be null, that is, consistent with the original MQTT protocol.
- the gateway and the control device may stipulate the identifier of the logical packet of the 2 Bytes of the variable header of the MQTT-issued message as shown in Table 3, and indicate that the application message carried in the MQTT-published message is sent to the logical grouping or sending To the gateway, the variable header of the modified MQTT publication message is as shown in Table 4.
- the Byte 8 to Byte 9 added in the table are used to indicate the identifier of the logical group.
- the terminal sends an MQTT advertisement message that does not carry the flag of the logical group, that is, the original MQTT protocol is consistent.
- the identifier of the logical group of the variable header of the MQTT advertisement message sent to the gateway may be set to 1 to indicate that the application message carried by the MQTT advertisement packet is sent. To the gateway.
- control device needs to send an application message to the terminal through the gateway, there are two cases:
- the subscription topic of the variable header of the MQTT publication message sent to the gateway may be set as the subscription topic of the terminal, and the identifier of the logical group of the variable header is set. The bit is set to 0.
- the gateway After receiving the MQTT advertisement message, the gateway removes the identifier of the logical packet of the variable header of the MQTT advertisement packet, and obtains the MQTT advertisement packet that does not carry the identifier of the logical packet.
- the MQTT release message is sent to the terminal.
- the subscription topic of the variable header of the MQTT publishing message sent to the gateway may be set as the subscription topic of each target terminal in the target logical group, and the variable header is The identification bit of the logical grouping is set to the identifier of the target logical grouping, and the payload is set to at least one application message matching the subscription topic of each target terminal.
- the gateway After receiving the MQTT advertisement message, the gateway removes the identifier of the logical group of the variable header of the MQTT publication message, replaces the subscription topic of the variable header with the subscription topic of the target terminal, and replaces the application message in the payload.
- the subscription topic mentioned above is a UTF-8 format string used by the gateway to process the filtering message for the subscriber (such as the terminal), and each subscription topic may have only one layer or multiple levels. Each level is divided by "/". Since the subscription topic is relatively lightweight (that is, the number of bytes is small), the gateway does not need to perform the initial initialization process before receiving the subscription topic, and thus, the control device does not need to create the terminal before performing the publishing or subscription step. The subscription topic you need.
- UTF-8 is a variable length character encoding for the unified character encoding standard Unicode.
- the control device may send an application message to the gateway connected to each terminal in the packet by using the packet to send the MQTT to send the packet, and instruct the gateway to send the application message to each terminal, which can improve the efficiency of message issuance.
- the gateway may send a subscription request to the control device, or may send a subscription request of the terminal to the control device, that is, the gateway subscription mechanism and the gateway forwarding subscription mechanism are added, so that the subscription mechanism is more flexible, and the control device is
- the subscription/distribution mechanism of the MQTT protocol is adopted between the terminals, and the long-term connection between the control device and the terminal does not need to be established.
- the control device can be connected to multiple gateways in a cascade manner, so the number of terminals that can be accessed can be increased exponentially. .
- the present invention provides a configuration management method, which is applied to a control device, a target gateway, and a target terminal. Referring to FIG. 2, the method shown in FIG. 2 is used.
- Can include:
- the control device determines that an application message needs to be released to the target logical group.
- the foregoing specific manner of determining that the application message needs to be distributed to the target logical group includes: determining, if the at least one application message that matches the subscription topic of the at least one target terminal in the target logical group is detected, determining The application message needs to be published to the target logical group; or, if at least one application message matching the historical behavior data of the at least one target terminal is detected, it is determined that an application message needs to be issued to the target logical group.
- the control device detects the system configuration update message of each target terminal, it is determined that the application message needs to be published to the target logical group.
- the at least one target gateway may report the behavior data of the at least one target terminal to the control device. If the control device detects the updated technology video, it is determined that the application message needs to be released to the target logical group.
- control device may detect whether there is at least one application message that matches the subscription topic of the at least one target terminal in the target logical group, or detect whether there is at least a match with the behavior data of the at least one target terminal.
- An application message if any, determines that the application message needs to be published to the target logical group.
- the application message may include a configuration management message, a news message, or a notification service message.
- the configuration management message may include a configuration message of a network security policy, a data collection policy configuration message, or an application deployment policy configuration message.
- the subscription topic may refer to a label of the application message. For example, if the application message is a news message, the subscription topic may be military news, financial news, or health news.
- the subscription theme of each target terminal may be the same or different, and the present invention does not limit this.
- the control device may receive historical behavior data reported by the gateway to the one of the target terminals, and the historical behavior data of the at least one target terminal may be determined by the gateway according to the collected running log of an application of the target terminal. For example, the running log of the web browser application in the preset time period, the running log of the video playing application in the preset time period, or the running log of the shopping application in the preset time period.
- the control device acquires an identifier of the target logical group, where the target logical group includes at least one target terminal.
- the control device queries, according to the gateway mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, a gateway connected to each target terminal in the at least one target terminal to obtain at least one target gateway.
- the control device 101 when the control device 101 needs to issue an application message to the first logical group, the control device acquires the target logical group identifier as 1, and the control device may identify the target logical group according to the gateway mapping table.
- the target gateway connected to the at least one target terminal is queried as the gateway 102 and the gateway 103.
- the control device can send an MQTT publish message to the gateway 102 and the gateway 103.
- the gateway mapping table records identifiers of multiple gateways, identifiers of terminals connected to the multiple gateways, and identifiers of logical groups to which each terminal belongs.
- the control device may dynamically adjust the gateway mapping table according to the grouping result of the multiple terminals by the device or the control device in the network architecture. For example, if the control device detects that a terminal is newly accessed in the network architecture, the terminal may be used. The identifier of the terminal is recorded in the gateway mapping table; if the control device detects that a terminal in the network architecture disconnects from the gateway, the identifier of the terminal may be removed from the gateway mapping table.
- the logical group identifier may be composed of one or more of a letter, a value or a symbol.
- the control device may query, according to the gateway mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, a gateway connected to each target terminal in the at least one target terminal to obtain at least one target gateway, so that the control device may follow the grouping manner. Sending the first MQTT packet to each target gateway can improve the efficiency of message publishing.
- the identifier of the gateway may refer to the MAC address of the gateway, or other identifiers that may uniquely indicate the gateway.
- the identifier of the terminal may refer to a MAC address, or other identifier that can uniquely indicate the terminal.
- the control device generates a first message queue telemetry transmission MQTT advertisement packet according to the application message, where the first MQTT advertisement message includes an identifier of the target logical group and the application message.
- control device may generate the first MQTT publishing message according to the application message and the identifier of the target logical group, so that the target gateway device may send the application message to the at least one target terminal, and further the at least one Management of the target terminal or providing various application services for the target terminals.
- control device may generate a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the target logical group, generate a payload of the MQTT format according to the application message, and encapsulate the variable header and the payload into the first
- the MQTT publishes a message.
- control device may add an identifier of a logical packet of 2 bytes in the variable header of the first MQTT advertisement message, and is used to indicate that the first MQTT advertisement packet is sent to the logical group or the gateway.
- the subscription message needs to be sent to each terminal with the logical group identifier of 1, for example, the subscription topic name of each terminal is a/b, the length of the subscription topic is 3, and the identifier of the packet is 10, and the control device can Adding a 2 Byte field to the variable header of the first MQTT release message to indicate a logical group identifier, such as adding a field in Byte8 to Byte9 to the variable header to indicate the identifier of the logical group, and the control device may subscribe the topic name of each terminal.
- the subject length, the packet identifier, and the logical grouping identifier are encapsulated in the variable header of the MQTT format, and the variable header of the encapsulated first MQTT publishing message as shown in Table 5 is obtained.
- 'a' (0x61) in Table 5 means that the letter a can be expressed as 61 in hexadecimal, and the same as '/' (0x2F) means that the symbol / can be expressed in hexadecimal as 2F, 'b' ( 0x62) means that the letter b can be expressed as 62 in hexadecimal.
- the control device may generate a payload in the MQTT format according to the application message that matches the subscription topic of each terminal, where the format of the payload of the first MQTT advertisement packet is not fixed, and may be set according to factors such as an application scenario of the application message.
- the variable header and the payload may be encapsulated into the first MQTT advertisement packet, so that the first MQTT advertisement message may be sent to each target gateway.
- the control device and the target gateway may agree in advance to encapsulate the identifier of the logical group and the application message in a certain position in the MQTT format, such as an agreement to encapsulate the identifier of the logical group in a variable header of the MQTT format, and apply the message.
- the variable encapsulated in the MQTT format that is, the control device may generate a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the target logical group, generate a payload of the MQTT format according to the application message, and encapsulate the variable header and the payload into the first MQTT.
- the message is published so that the first MQTT publication message can be sent to each target gateway.
- the first MQTT advertisement message further includes a fixed header, and the fixed header may include a type field, where the type field is used to indicate the type of the first MQTT advertisement message, for example, the type field indicates the first
- the type of the MQTT-published message is the message that advertises the message.
- the control device sends the first MQTT publish message to the at least one target gateway.
- the first MQTT advertisement message is used to indicate that the target gateway that receives the first MQTT advertisement message sends a corresponding application message to each target terminal that is connected to the target gateway and belongs to the target logical group.
- control device may send the first MQTT advertisement message to the at least one target gateway, so that the at least one target gateway may send the application message in the first MQTT advertisement message to the at least one target terminal.
- the number of the application messages carried in the first MQTT advertisement packet may be one, or may be multiple, that is, if the subscription topic or behavior data of each target terminal in the at least one target terminal is consistent,
- the number of the application messages carried in the first MQTT advertisement packet may be one, that is, the foregoing application message is sent to each target terminal that is connected to the target gateway and belongs to the target logical group, and may refer to the target gateway to each The target terminal sends the same application message, which matches the subscription topic or behavior data of the target terminal.
- the number of the application messages carried in the first MQTT advertisement packet may be multiple, that is, the foregoing connection to the target gateway belongs to the Each target terminal of the target logical group sends a corresponding application message, which may be that the target gateway sends an application message that matches the subscription topic or behavior data of the target terminal to each target terminal of the at least one target terminal.
- the subscription topic of the terminal 1 is a wide area network (WAN) configuration
- the target gateway sends an application message matching the WAN configuration to the terminal 1;
- the subscription topic of the terminal 2 is a network security configuration
- the target gateway sends the terminal gateway to the terminal 2.
- the at least one target gateway parses the first MQTT advertisement packet, and obtains an identifier of the target logical group and at least one application message.
- the at least one target gateway may parse the variable header of the first MQTT-published message, obtain the identifier of the target logical group, and parse the payload of the MQTT-published message to obtain at least one application message.
- the at least one target gateway may further receive the first message queue telemetry transmission MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device.
- the at least one target gateway determines, according to the packet mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, at least one target terminal that is connected to the target logical group and belongs to the target logical group, and a subscription topic of each target terminal in the at least one target terminal or Historical behavior data.
- the gateway 10 and the gateway 103 receive the first MQTT advertisement packet, and the first MQTT advertisement packet can be parsed to obtain at least one application message and the identifier of the target logical group (such as 1).
- the gateway 102 determines that the at least one target terminal is the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 according to the packet mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, and determines that the subscription topic of the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 is a configuration of the network traffic policy;
- the gateway 103 according to the packet mapping table and The identifier of the target logical group determines that the at least one target terminal is the terminal 5 to the terminal 8, determines that the subscription topic of the terminal 5 is a configuration of the network traffic policy, and determines that the subscription topic of the terminal 6 to the terminal 8 is performance indicator data (such as network quality indicator data). ).
- the packet mapping table records the identifiers of the terminals connected to the gateway, the identifiers of the logical groups to which the terminals belong, and the subscription topic or historical behavior data of each terminal.
- the gateway may dynamically adjust the packet mapping table according to the grouping result of the device or the control device in the network architecture, for example, if the gateway detects that a terminal is newly accessed in the network architecture, the identifier of the terminal may be Recorded in the packet mapping table; if the gateway detects that a terminal in the network architecture disconnects from the gateway, the identifier of the terminal may be removed from the packet mapping table.
- the at least one target gateway determines, according to the packet mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, the subscription topic or historical behavior data of the at least one target terminal and each terminal of the at least one target terminal, so that the target gateway can Each target terminal of at least one target terminal transmits an application message that matches the subscription topic or historical behavior data.
- the at least one target gateway determines, from the at least one application message, a target application message that matches historical behavior data or a subscription topic of each target terminal of the at least one target terminal, and generates a second MQTT release report according to the target application message. And sending the second MQTT advertisement message carrying the target application message to the target terminal.
- the gateway 102 may identifier the logical group of the variable header of the received first MQTT release message. The bit is removed, and the subscription topic of the variable header of the first MQTT release message is replaced with the subscription topic of the terminal 2 (ie, the configuration of the network traffic policy), and the application message of the payload of the first MQTT release message is replaced with The configuration of the network traffic policy matches the target application message, and the second MQTT advertisement message carrying the target application message is obtained.
- the gateway 102 can send the second MQTT advertisement message to the terminal 2 to the terminal 4, and the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 can parse the second MQTT after receiving the MQTT advertisement message.
- the message is sent to obtain the target application message, and the network of the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 can be configured according to the target application message, that is, the control device can implement configuration management of the terminal 2 to the terminal 4.
- the gateway 103 may remove the identifier of the logical group of the variable header of the received first MQTT release message, and change the identifier of the first MQTT release message.
- the subscription topic of the header is replaced with the subscription topic of the terminal 5 (that is, the configuration of the network traffic policy), and the application message of the payload of the first MQTT advertisement packet is replaced with the target application message matching the configuration of the network traffic policy, thereby being carried.
- the second MQTT issuance message of the target application message, and the gateway 103 can send the second MQTT release message to the device 5.
- the terminal 5 After receiving the second MQTT advertisement packet, the terminal 5 can parse the MQTT advertisement packet to obtain the target application message, and can configure the network of the terminal 5 according to the target application message, that is, the control device can implement the terminal. 5 configuration management.
- the gateway 103 may remove the identifier of the logical group of the variable header of the received first MQTT release message, which will be The subject of the variable header of an MQTT-published message is replaced with the subscription topic of the terminal 6 (ie, the network quality indicator data), and the application message of the payload of the first MQTT-published message is replaced with the target that matches the network quality indicator data. Applying a message, and then obtaining a second MQTT publish message carrying the target application message. The gateway 103 can send the second MQTT advertisement message to the terminal 6 to the terminal 8, and the control device can implement the collection service of the performance indicator data for the terminal 6 to the terminal 8.
- performance indicator data such as network quality indicator data
- At least one target gateway may determine, from the at least one application message, a target application message that matches historical behavior data or a subscription topic of each target terminal in the at least one target terminal, and carries the target application message.
- the second MQTT publication message is sent to the target terminal, so that management of each target terminal within the target logical group or service for each target terminal can be implemented.
- control device may send the MQTT publishing message carrying the application message to the terminal; or send the MQTT publishing message carrying the application message to the gateway.
- control device may send an MQTT advertisement message carrying the application message to the terminal connected to the control device, or send an MQTT advertisement message carrying the application message to the gateway, such as sending a system configuration update message or grouping to the gateway. Messages, etc.
- the identifier of the logical group may be added to the variable header of the MQTT release message, for example, the fields in Byte8 to Byte9 in Table 5 are all set to 1. The flag is used to indicate that the MQTT advertisement message is sent to the gateway.
- the gateway may receive the MQTT publishing message that is sent by the control device and that carries the application message.
- the gateway may receive the MQTT advertisement message that is sent by the control device and carries the application message, so that the corresponding operation may be performed according to the MQTT release message, for example, the system configuration update message sent by the control device, the gateway may System update information is used for system updates.
- the gateway 102 receives the MQTT advertisement message that is sent by the control device 101 and carries the application message, and can parse the MQTT advertisement message to obtain the Byte 8 to Byte 9 of the variable header of the MQTT release message.
- the fields are all 1, and it can be determined that the MQTT publish message is sent to the gateway 102.
- control device may send the MQTT advertisement packet to the gateway connected to each terminal in the packet in a packet manner, and instruct the gateway to send the application message to each terminal, thereby improving the efficiency of message transmission, and thus Implementing management of individual terminals within a packet or providing services for terminals within a packet.
- the present invention provides another configuration management method, which is applied to a control device, a target gateway, and a target terminal, as shown in FIG. 3, as shown in FIG. 3, based on the description of the network architecture of a configuration management.
- Methods can include:
- the control device receives the MQTT subscription message carrying the subscription topic, and parses the MQTT subscription message to obtain the flag data.
- control device may receive the MQTT subscription message carrying the subscription topic, and parse the MQTT subscription message to obtain the flag data, so that it may be determined according to the flag data, which device is subscribed by the device, or may be determined.
- the connection between the gateway and the terminal may be determined according to the flag data, which device is subscribed by the device, or may be determined.
- the control device determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal, and determines that the terminal is connected to the gateway, and records the identifier of the terminal to the gateway mapping.
- the identifier of the gateway corresponds to the entry.
- the control device may determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal, and determine that the terminal is connected to the gateway, and the identifier of the terminal is Recording the entry corresponding to the identifier of the gateway in the gateway mapping table can not only determine the connection relationship between the gateway and the terminal, but also support the gateway to forward the subscription topic, so that the subscription mechanism is more flexible.
- the MQTT subscription message carrying the subscription topic is received, and the MQTT subscription message is parsed to obtain the flag data. If the flag data includes the subscription identifier and the identifier of the gateway, determining the subscription topic by the gateway. Subscribed, the identity of the gateway is recorded to the gateway mapping table.
- the control device receives the MQTT subscription message carrying the subscription topic, and then parses the MQTT subscription message to obtain the flag data. If the flag data includes the subscription flag and the identifier of the gateway, determining that the subscription topic is determined by the The gateway subscribes to record the identity of the gateway to the gateway mapping table, so that the control device can determine the connection with the gateway, and determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway, and can support the gateway subscription topic, so that the subscription mechanism is more flexible.
- the gateway and the control device may agree to use the field in the reserved bit of the fixed header of the MQTT subscription message to indicate the forwarding flag or the subscription flag.
- the reserved value of the reserved bit is 1 to indicate the subscription flag, and is used to indicate the subscription flag. Indicates that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway; if the agreement retains the value of the reserved bit to 2, it indicates a forwarding flag indicating that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal.
- the control device 101 receives the MQTT subscription packet, and can parse the payload of the MQTT subscription packet, obtain a subscription topic, and parse the fixed header of the MQTT subscription packet to obtain a reserved bit of the fixed header. If the value is 1, it is determined that the flag data includes a subscription flag, and the variable header of the MQTT subscription message is parsed, and the identifier of the gateway is 102, and the control device 101 can determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway 102, and the gateway can be used. The identity of the record is recorded in the gateway mapping table shown in Table 6.
- the control device 101 receives the MQTT subscription packet, and can parse the payload of the MQTT subscription packet to obtain a subscription topic, and parse the fixed header of the MQTT subscription packet to obtain a reserved bit of the fixed header. If the value is 2, it is determined that the flag data includes a forwarding flag, and the variable header of the MQTT subscription packet is parsed, and the identifier of the terminal is 1 and the identifier of the gateway is 102.
- the control device 101 may determine that the subscription topic is determined by the terminal. 1, and the terminal 1 is connected to the gateway 102, and the identifier 1 of the terminal is recorded in the entry corresponding to the identifier 102 of the gateway in the gateway mapping table shown in Table 1.
- control device can The connection between the gateway 102 and the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 is determined, and the connection between the gateway 103 and the terminal 5 to the terminal 8 is determined, and the identity of each gateway and the identifier of the terminal are recorded in the gateway mapping table as shown in Table 6.
- control device may group the multiple terminals according to the subscription topic of the multiple terminals connected to the multiple gateways, or randomly group the multiple terminals, or according to the multiple
- the gateways group the plurality of terminals to obtain a plurality of logical groups, and configure an identifier for each logical group, and record the identifier of each logical group to the corresponding identifier of each terminal in the logical grouping in the gateway mapping table. In the table entry.
- the control device may group the terminals according to the subscription topics of the multiple terminals connected to the multiple gateways. For example, the control device may group the terminals with the same subscription topic into a group; Multiple terminals are grouped; the multiple terminals may be grouped according to the multiple gateways, for example, the terminals connected to the same gateway are grouped into one group; thereby, multiple logical groups are obtained, and identifiers are configured for each logical group.
- the identifier of each logical group is recorded into a corresponding entry of the identifier of each terminal in the logical grouping in the gateway mapping table, so that the terminals in each logical group can be determined according to the group identifier.
- the control device 101 may group terminals connected to respective gateways, such as dividing the terminals 2 to 8 into first logical packets, and may identify the logical grouping of the first logical group.
- the terminal 1 is divided into second logical grouping, the identifier of the logical grouping of the second logical grouping can be set to 2, and the identifier of the logical grouping of each group is recorded in the gateway mapping table as shown in Table 6. .
- the gateway may generate a variable header in the MQTT format according to the identifier of the terminal, the identifier of the gateway, generate a payload in the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the terminal, and generate a fixed header in the MQTT format according to the forwarding flag.
- the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header are encapsulated into an MQTT subscription message, and the MQTT subscription message is sent to the control device, where the MQTT subscription message is used to indicate that the control device determines that the subscription topic is determined by the terminal.
- the subscriber is subscribed to, and the terminal is connected to the gateway, and the identifier of the terminal is recorded in the entry corresponding to the identifier of the gateway in the gateway mapping table.
- the gateway 102 may generate a variable header in the MQTT format according to the identifier of the terminal 1, the identifier 102 of the gateway, and generate a payload in the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the terminal, according to the forwarding flag (eg, 2) generating a reserved bit of the fixed header in the MQTT format, and encapsulating the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header into an MQTT subscription message, and sending the MQTT subscription message to the control device 101, to indicate the control
- the device 101 determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal 1, and determines that the terminal 1 is connected to the gateway 102, and records the identifier 1 of the terminal in the entry corresponding to the identifier 102 of the gateway in the gateway mapping table.
- the gateway may generate a variable header in the MQTT format according to the identifier of the gateway, generate a payload in the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the gateway, generate a fixed header in the MQTT format according to the subscription flag, and change the variable.
- the header, the payload, and the fixed header are encapsulated into an MQTT subscription message, and the MQTT subscription message is sent to the control device, to indicate that the control device determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway, and records the identifier of the gateway to The gateway maps the table.
- the gateway 102 may generate a variable header in the MQTT format according to the identifier 102 of the gateway, generate a payload in the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the gateway, and generate an MQTT format according to the subscription flag (such as 1). a fixed bit of the fixed header, the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header are encapsulated into an MQTT subscription message, and the MQTT subscription message is sent to the control device 101, to indicate that the control device 101 determines that the subscription topic is determined by The gateway 102 subscribes to record the identity 102 of the gateway into the gateway mapping table.
- the control device determines that an application message needs to be released to the target logical group.
- the control device acquires an identifier of the target logical group, where the target logical group includes at least one target terminal.
- the control device queries, according to the gateway mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, a gateway connected to each target terminal of the at least one target terminal to obtain at least one target gateway.
- the control device generates a first message queue telemetry transmission MQTT advertisement packet according to the application message, where the first MQTT advertisement message includes an identifier of the target logical group and the application message.
- the control device sends the first MQTT publish message to the at least one target gateway.
- the at least one target gateway parses the first MQTT advertisement packet, and obtains an identifier of the target logical group and at least one application message.
- the at least one target gateway determines, according to the packet mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, at least one target terminal that is connected to the gateway and belongs to the target logical group, and a subscription topic or history of each target terminal in the at least one target terminal. Behavioral data.
- the gateway may receive the subscription request of the terminal, parse the subscription request, obtain the identifier of the terminal, and the subscription topic of the terminal, and determine that the terminal is connected to the gateway.
- the gateway may record the identifier of the terminal and the subscription topic of the terminal to an entry of the packet mapping table, and receive a packet message sent by the control device, where the packet message includes an identifier of the terminal and a logical group to which the terminal belongs.
- logo The gateway may record the identifier of the logical group to which the terminal belongs to the entry corresponding to the identifier of the terminal in the packet mapping table.
- the gateway 102 of the terminal of FIG. 1 receives the subscription request of the terminal 1 to the terminal 4, and can parse the subscription request, and obtain the subscription theme of the terminal 1 as a WAN configuration, and the subscription theme of the terminal 2 is a network security configuration, and the terminal 3
- the subscription topic is the network traffic policy configuration
- the subscription theme of the terminal 4 is the device maintenance configuration
- the identifiers of the terminals 1 to 4 are 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively, and the identifiers of the respective terminals and the subscription topic records of the respective terminals can be recorded.
- the packet message when receiving the packet message sent by the control device 101, the packet message may be parsed to obtain the identifier of the terminal connected to the gateway 102, and each terminal
- the associated logical group identifier for example, the identifier of the terminal connected to the gateway is 1, 2, 3, 4, and the logical group identifier of the terminal 2 to the terminal 4 belongs to 1, and the logical group identifier of the terminal 1 belongs to 2.
- the logical group identifiers to which the respective terminals belong may be recorded in the entries corresponding to the identifiers of the respective terminals in the packet mapping table, as shown in Table 7.
- the gateway may obtain the historical behavior data of the terminal connected to the gateway, and record the historical behavior data of the terminal into the entry corresponding to the terminal identifier in the packet mapping table.
- the gateway may collect the running log of an application in the terminal, for example, the running log of the web browser application in the preset time period, the running log of the video playing application in the preset time period, or the preset time period.
- the running log of the shopping application is used, and the behavior data of the terminal is determined according to the running log of the application, and the historical behavior data of the terminal is recorded in the entry corresponding to the terminal identifier in the packet mapping table.
- the at least one target gateway determines, from the at least one application message, a target application message that matches historical behavior data or a subscription topic of each of the at least one target terminal, and generates a second MQTT release report according to the target application message. And sending the second MQTT advertisement message carrying the target application message to the target terminal.
- the control device may send an MQTT release message to the gateway connected to the terminal, and may set the identifier of the logical group in the variable header of the MQTT release message. Bit, if the fields in Byte8 to Byte9 in FIG. 5 are all set to 0, the flag is used to indicate that the application message is sent to a single terminal, and the gateway parses the MQTT release when receiving the MQTT publishing message.
- the message which is an application message, can be sent to the terminal.
- the control device may send an application message to the gateway connected to each terminal in the packet by using a packet sending message, and instruct the gateway to send the application message to each terminal, which can improve the efficiency of message publishing, and the gateway can control
- the device sends a subscription request, and may also send a subscription request of the terminal to the control device, that is, the subscription mechanism of the gateway and the forwarding and subscription mechanism of the gateway are added, so that the subscription mechanism is more flexible, and the MQTT protocol is adopted between the control device and the terminal.
- the subscription/release mechanism does not need to establish a long-term connection between the control device and the terminal, and the control device can be connected in cascade with multiple gateways, so the number of terminals accessed can be increased exponentially.
- the present invention provides a configuration management device, which is applied to a control device.
- the configuration management device shown in FIG. 4 may include a determining module 401.
- the determining module 401 is configured to determine that an application message needs to be published to the target logical group.
- the obtaining module 402 is configured to obtain an identifier of the target logical grouping, where the target logical grouping includes at least one target terminal.
- the querying module 403 is configured to query, according to the gateway mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, a gateway connected to each target terminal in the at least one target terminal to obtain at least one target gateway, where the gateway mapping table records An identifier of the plurality of gateways, an identifier of the terminal connected to each of the plurality of gateways, and an identifier of the logical group to which each terminal belongs.
- the generating module 404 is configured to generate a message queue telemetry transmission MQTT publishing message according to the application message, where the MQTT publishing message includes an identifier of the target logical group and the application message.
- the sending module 405 is configured to send the MQTT publishing message to the at least one target gateway, where the MQTT publishing message is used to indicate that the target gateway that receives the MQTT publishing message is connected to the target gateway.
- Each target terminal of the target logical grouping sends a corresponding application message.
- the receiving module 406 is configured to receive the MQTT subscription message that carries the subscription topic.
- the parsing module 407 is configured to parse the MQTT subscription packet to obtain the flag data.
- the determining module 401 is further configured to: if the identifier data includes a subscription identifier and an identifier of the gateway, determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway.
- the recording module 408 is configured to record the identifier of the gateway into the gateway mapping table.
- the determining module 401 is further configured to: if the identifier data includes a forwarding identifier, an identifier of the terminal, and an identifier of the gateway, determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal, and determine the terminal and the The gateway connection.
- the recording module 408 is further configured to record the identifier of the terminal into an entry corresponding to the identifier of the gateway in the gateway mapping table.
- the grouping module 409 is configured to group the multiple terminals according to a subscription topic of multiple terminals connected to the multiple gateways, or randomly group the multiple terminals, or The plurality of gateways group the plurality of terminals to obtain a plurality of logical packets.
- the configuration module 410 is configured to configure an identifier for each logical group.
- the recording module 408 is further configured to record an identifier of each logical group into a corresponding entry of an identifier of each terminal in the logical group in the gateway mapping table.
- the determining module 401 is specifically configured to: if it is detected that at least one application message that matches a subscription topic of the at least one target terminal in the target logical group, determine that an application needs to be released to the target logical group The message, or if at least one application message matching the historical behavior data of the at least one target terminal is detected, determines that an application message needs to be issued to the target logical group.
- the generating module 404 is configured to generate a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the target logical group; generate a payload of the MQTT format according to the application message; and use the variable header and the payload Encapsulation is the publication of the MQTT message.
- the sending module 405 is further configured to send an MQTT publishing message that carries the application message to the terminal, or send an MQTT publishing message that carries the application message to the gateway.
- the configuration management apparatus has a function of implementing corresponding steps performed by the control device in the configuration management method in the foregoing embodiments of FIG. 2 and FIG. 3.
- This function can be implemented in hardware or in hardware by executing the corresponding software.
- the hardware or software includes one or more modules corresponding to the functions described above.
- the above modules may be software and/or hardware.
- the configuration management apparatus solves the problem and the beneficial effects, reference may be made to the implementation manner of the configuration management method described in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 and the beneficial effects. Therefore, the implementation manner of the configuration management apparatus may be Referring to the implementation manner of the configuration management method described in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 above, the repeated description is not repeated.
- the control device may send an application message to the gateway connected to each terminal in the packet by using a packet sending message, and instruct the gateway to send the application message to each terminal, which can improve the efficiency of message publishing.
- the gateway may send a subscription request to the control device, or may send a subscription request of the terminal to the control device, that is, the gateway subscription mechanism and the gateway forwarding subscription mechanism are added, so that the subscription mechanism is more flexible, and between the control device and the terminal.
- the subscription/release mechanism of the MQTT protocol there is no need to establish a long-term connection between the control device and the terminal, and the control device can be connected in cascade with multiple gateways, so the number of terminals accessed can be increased exponentially.
- the configuration management device shown in FIG. 5 may include a receiving module 501.
- the receiving module 501 is configured to receive a first message queue telemetry transmission MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device.
- the parsing module 502 is configured to parse the first MQTT publishing message to obtain an identifier of the target logical group and at least one application message.
- a determining module 503 configured to determine, according to the packet mapping table and the identifier of the target logical group, at least one target terminal that is connected to the gateway and belongs to the target logical group, and each target terminal of the at least one target terminal Subscribing to topic or historical behavior data, wherein the packet mapping table records an identity of each terminal connected to the gateway, an identifier of a logical group to which each terminal belongs, and a subscription topic or historical behavior data of each terminal.
- the determining module 503 is further configured to determine, from the at least one application message, a target application message that matches historical behavior data or a subscription topic of each target terminal in the at least one target terminal.
- the generating module 504 is configured to generate a second MQTT publishing message according to the target application message.
- the sending module 505 is configured to send the second MQTT publishing message that carries the target application message to the target terminal.
- the receiving module 501 is further configured to receive a subscription request of the terminal.
- the parsing module 502 is further configured to parse the subscription request, obtain an identifier of the terminal, and a subscription topic of the terminal.
- the determining module 503 is further configured to determine that the terminal is connected to the gateway.
- the recording module 506 is configured to record the identifier of the terminal and the subscription topic of the terminal into an entry of the packet mapping table.
- the receiving module 501 is further configured to receive a packet message sent by the control device, where the packet message includes an identifier of the terminal and an identifier of a logical group to which the terminal belongs.
- the recording module 506 is further configured to record an identifier of the logical group to which the terminal belongs to an entry corresponding to the identifier of the terminal in the packet mapping table.
- the obtaining module 507 is configured to obtain historical behavior data of the terminal.
- the recording module 506 is further configured to record the historical behavior data of the terminal into an entry corresponding to the identifier of the terminal in the packet mapping table.
- the generating module 504 is further configured to generate a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the terminal and the identifier of the gateway, generate a payload of the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the terminal, and generate a payload according to the forwarding flag.
- a fixed header in the MQTT format is further configured to generate a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the terminal and the identifier of the gateway, generate a payload of the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the terminal, and generate a payload according to the forwarding flag.
- the first encapsulating module 508 is configured to encapsulate the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header into an MQTT subscription message.
- the sending module 505 is further configured to send the MQTT subscription message to the control device, where the MQTT subscription message is used to indicate that the control device determines that the subscription topic is subscribed by the terminal. And determining that the terminal is connected to the gateway, and the identifier of the terminal is recorded in an entry corresponding to the identifier of the gateway in the gateway mapping table of the control device.
- the generating module 504 is further configured to generate a variable header of the MQTT format according to the identifier of the gateway; generate a payload of the MQTT format according to the subscription topic of the gateway; and generate a fixed header of the MQTT format according to the subscription flag.
- the second encapsulating module 509 is configured to encapsulate the variable header, the payload, and the fixed header into an MQTT subscription message.
- the sending module 505 is further configured to send the MQTT subscription message to the control device, where the MQTT subscription message is used to instruct the control device to determine that the subscription topic is subscribed by the gateway. And recording the identifier of the gateway to a gateway mapping table of the control device.
- the receiving module 501 is configured to receive an MQTT publishing message that is sent by the control device and that carries an application message.
- the configuration management apparatus has a function of implementing corresponding steps performed by the gateway in the configuration management method in the foregoing embodiments of FIG. 2 and FIG. 3.
- This function can be implemented in hardware or in hardware by executing the corresponding software.
- the hardware or software includes one or more modules corresponding to the functions described above.
- the above modules may be software and/or hardware.
- the configuration management apparatus solves the problem and the beneficial effects, reference may be made to the implementation manner of the configuration management method described in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 and the beneficial effects. Therefore, the implementation manner of the configuration management apparatus may be Referring to the implementation manner of the configuration management method described in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3 above, the repeated description is not repeated.
- the gateway may receive the MQTT advertisement message sent by the control device in a group manner, and send the application message carried in the MQTT advertisement message to the terminal in the packet, so as to improve the efficiency of message advertisement.
- the gateway may send a subscription request to the control device, or may forward the subscription request of the terminal to the control device, that is, the subscription mechanism of the gateway and the forwarding and subscription mechanism of the gateway are added, so that the subscription mechanism is more flexible.
- the present invention provides a control device based on the above description of a configuration management device.
- the control device shown in FIG. 6 may include: a processor 601, a memory 602, and a communication interface 603.
- the processor 601, the memory 602, and the communication interface 603 are connected to each other through a bus.
- the processor 601 may be one or more central processing units (English: central processing unit, CPU for short). In the case that the processor 601 is a CPU, the CPU may be a single core CPU or a multi-core CPU.
- the memory 602 includes, but is not limited to, a random access memory (English: random access memory, abbreviated as: RAM), a read-only memory (English: read-only memory, abbreviated as: ROM), an erasable programmable read-only memory (English: Erasable programmable read only memory (abbreviation: EPROM), or portable read-only memory (English: compact disc read-only memory, CD-ROM for short), the memory 602 is used to store instructions and data, such as storage and connection with the control device The identity of the gateway, etc.
- RAM random access memory
- ROM read-only memory
- EPROM erasable programmable read-only memory
- portable read-only memory English: compact disc read-only memory, CD-ROM for short
- the above communication interface 603 is connected to other network devices.
- the communication interface 603 includes a plurality of interfaces that are respectively connected to a plurality of gateways.
- Communication interface 603 can be a wired interface, a wireless interface, or a combination thereof.
- the wired interface can for example be an Ethernet interface.
- the Ethernet interface can be an optical interface, an electrical interface, or a combination thereof.
- the wireless interface may be, for example, a wireless local area network (abbreviation: WLAN) interface, a cellular network interface, or a combination thereof.
- the communication interface 603 is configured to receive or send data under the control of the controller, such as receiving an MQTT subscription message or sending an MQTT release message.
- the above memory 602 is also used to store program instructions.
- the processor 601 can invoke the program instructions stored in the memory 602 to implement the configuration management method as shown in the foregoing embodiments of the present application.
- the processor 601 in the embodiment of the present invention may implement the determining module 401, the obtaining module 402, the querying module 403, the generating module 404, the parsing module 407, the recording module 408, and the grouping module 409 in FIG.
- the function of the memory 602 can implement the function of the recording module 408 in FIG. 4, and the communication interface 603 can implement the functions of the sending module 405 and the receiving module 406 in FIG. 4, which are not limited in the embodiment of the present invention.
- control device provided in the embodiment of the present invention.
- the implementation of the control device and the beneficial effects can be seen in the foregoing method embodiments. Let me repeat.
- the present invention provides a gateway based on the foregoing description of a configuration management apparatus.
- the gateway shown in FIG. 7 may include a processor 701, a memory 702, and a communication interface 703.
- the 701, the memory 702, and the communication interface 703 are connected to each other through a bus.
- the processor 701 may be one or more CPUs.
- the processor 701 is a CPU
- the CPU may be a single-core CPU or a multi-core CPU
- the processor 701 is configured to control various functional modules in the gateway. Processing the signal, the processor 701 can include a modem for modulating or demodulating the signal received by the communication interface 703.
- the memory 702 includes, but is not limited to, a RAM, a ROM, an EPROM, a CD-ROM for storing instructions, an operating system, various applications, and data, such as storing an identifier of a terminal connected to the gateway and a subscription topic of the terminal, and the like. .
- the above communication interface 703 is connected to other network devices or terminals.
- the communication interface 703 includes a plurality of interfaces that are respectively connected to a plurality of terminals or connected to a control device.
- Communication interface 703 can be a wired interface, a wireless interface, or a combination thereof.
- the wired interface can for example be an Ethernet interface.
- the Ethernet interface can be an optical interface, an electrical interface, or a combination thereof.
- the wireless interface can be, for example, a wireless local area network (WLAN) interface, a cellular network interface, or a combination thereof.
- the communication interface 703 is configured to receive or send data under the control of the controller, such as receiving an MQTT subscription message or sending an MQTT release message.
- the above memory 702 is also used to store program instructions.
- the processor 701 can invoke the program instructions stored in the memory 702 to implement the configuration management method as shown in the foregoing embodiments of the present application.
- the processor 701 in the embodiment of the present invention may implement the functions of the parsing module 502, the determining module 503, the generating module 504, the obtaining module 507, the first encapsulating module 508, and the second encapsulating module 509 in FIG.
- the function of the recording module 506 in FIG. 5 can be implemented.
- the communication interface 703 can implement the functions of the receiving module 501 and the sending module 505 in FIG. 5, which are not limited in the embodiment of the present invention.
- the principle of the gateway to solve the problem in the embodiment of the present invention is similar to the method embodiment of the present invention. Therefore, the implementation and beneficial effects of the gateway may be referred to as well as the beneficial effects. For brevity, the details are not described herein.
- the present invention also provides a computer readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and an implementation and a beneficial effect of the program for solving the problem can be referred to the embodiment and the beneficial effects of the configuration management method of FIG. 2 and FIG. It will not be repeated here.
- the present invention also provides a computer program product comprising a non-transitory computer readable storage medium storing a computer program, the computer program being executed to cause a computer to execute the above-described embodiments of FIGS. 2 and 3
- the steps of the configuration management method, the implementation of the problem and the beneficial effects of the computer program product can be referred to the embodiments and the beneficial effects of the configuration management method of FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, and the repeated description is not repeated.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
本发明实施例公开了一种配置管理方法、装置及设备,其中,所述方法包括:确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息;获取所述目标逻辑分组的标识,其中,所述目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端;根据网关映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识查询与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关,根据所述应用消息生成消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文;向所述至少一个目标网关发送所述MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文用于指示接收到所述MQTT发布报文的目标网关向所述目标网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息。采用本发明实施例,可以提高控制设备向海量网络接入设备发布应用消息的效率。
Description
本申请要求于2017年8月11日提交中国专利局、申请号为201710684907.8、发明名称为“一种配置管理方法、装置及设备”的中国专利申请的优先权,其全部内容通过引用结合在本申请中。
本申请涉及计算机技术领域,尤其涉及一种配置管理方法、装置及设备。
控制设备通过与海量网络接入设备进行交互,可以实现对海量网络接入设备的管理或为海量网络接入设备提供各种服务。控制设备对海量网络接入设备的管理可以包括设备配置管理、设备性能管理、设备故障管理、应用部署管理、虚拟机部署管理、射频调优、终端位置分析、用户准入控制、移动运维等。控制设备可以为海量网络接入设备提供的服务包括WIFI接入、数据交换、网络安全等网络业务;此外,控制设备还可以提供数据级服务,如系统日志、性能指标数据的采集和存储;控制设备也能够提供应用级别服务,如针对公共运行业务提供具有行业属性的应用分析报表等等,可以满足用户多种多样的设备管理及服务需求。
但是,由于控制设备向海量网络接入设备发布应用消息的效率较低,对设备管理及服务质量造成不利影响,例如,控制设备向多个网络接入设备发送配置更新消息时,由于发送的速度较慢,造成网络接入设备不能及时更新配置信息,进而导致网络接入设备不能与其他设备进行交互。因此,如何提高控制设备向海量网络接入设备发布应用消息的效率是当前计算机网络领域亟待解决的问题。
发明内容
本发明提供一种配置管理方法、装置及设备,可基于分组发送的方式发送消息,以提高控制设备向海量网络接入设备发布应用消息的效率。
第一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种配置管理方法,应用于控制设备。控制设备确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息,并获取该目标逻辑分组的标识,根据网关映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识查询与该目标逻辑分组内的每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关。控制设备根据该应用消息生成MQTT发布报文,将该MQTT发布报文发送至该至少一个目标网关,该MQTT发布报文用于指示接收到该MQTT发布报文的目标网关,向与该目标网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的各个目标终端发送对应的应用消息。
其中,该目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端。
其中,该网关映射表记录了多个网关的标识,与该多个网关中每个网关连接的终端的标识,以及每个终端所属的逻辑分组的标识。
其中,该MQTT发布报文包括该目标逻辑分组的标识以及该应用消息。
在该技术方案中,控制设备可以以分组的方式将包括应用消息的MQTT发布报文发 送给与分组内终端连接的网关,并指示网关将应用消息发送给各个终端,可以提高发送消息的效率。在控制设备与终端之间采用MQTT协议的订阅/发布机制,不需要建立控制设备与终端之间的长时间连接,控制设备可以与多个网关以级联方式连接,所以可以指数级的增加接入的终端数。
作为一种可能的实施方案,控制设备接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文,并解析该MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据。若该标志数据包括订阅标志及网关的标识,则控制设备确定该订阅主题由该网关所订阅,将该网关的标识记录到该网关映射表;若该标志数据包括转发标志、终端的标识以及网关的标识,则控制设备确定该订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与该网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到该网关映射表中该网关的标识对应的表项中。
在该技术方案中,控制设备可以对MQTT订阅报文解析,得到标志数据,可以根据标志数据确定网关与终端的连接关系,或者确定控制设备与网关的连接关系,即控制设备可以确定向终端发送应用消息的路径,并可以支持网关订阅主题或网关转发订阅主题,使订阅机制更加灵活。
作为一种可能的实施方案,控制设备根据与该多个网关连接的多个终端的订阅主题对该多个终端进行分组,或者,随机对该多个终端进行分组,或者,按照该多个网关对该多个终端进行分组,得到多个逻辑分组。控制设备为每个逻辑分组配置标识,并将每个逻辑分组的标识记录到该网关映射表中该逻辑分组中每个终端的标识对应的表项中。
该技术方案中,控制设备可以根据终端的订阅主题、网关或随机的方式对与多个网关连接的终端进行分组,可以灵活地对各个终端进行分组,以便控制设备可以按照分组的方式向各个终端发送应用消息,提高消息发送的效率。
作为一种可能的实施方案,如果控制设备检测到与该目标逻辑分组内该至少一个目标终端的订阅主题相匹配的至少一条应用消息;或者如果检测到与该至少一个目标终端的历史行为数据相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向该目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
该技术方案中,控制设备可以根据该目标逻辑分组内的各个终端的订阅主题或者各个终端的历史行为数据,判断是否需要向该目标逻辑分组内的各个目标终端发布应用消息。
作为一种可能的实施方案,控制设备根据该目标逻辑分组的标识生成MQTT格式的可变报头,并根据该应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷,将该可变报头及该载荷封装为该MQTT发布报文。
该技术方案中,控制设备可以将该目标逻辑分组的标识、该至少一条应用消息封装在MQTT发布报文中,以便网关可以根据该MQTT发布报文向各个目标终端发送应用消息。
第二方面,提供了另一种配置管理方法,应用于网关,该方法包括:网关接收控制设备发送的第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,并解析该第一MQTT发布报文,得到目标逻辑分组的标识及至少一条应用消息。网关根据分组映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识确定与该网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据。网关从该至少一条应用消息中确 定与该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息,根据该目标应用消息生成第二MQTT发布报文,并将携带该目标应用消息的该第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端。
其中,该分组映射表记录了与该网关连接的各终端的标识,各终端所属的逻辑分组的标识,以及各终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据。
该技术方案中,网关可以接收控制设备以分组方式发送的MQTT发布报文,并该将MQTT发布报文中的应用消息发送给分组内的终端,可以提高控制设备向海量网络接入设备发布应用消息的效率。
作为一种可能的实施方案,网关接收终端的订阅请求,并解析该订阅请求,获得该终端的标识及该终端的订阅主题,进而,确定该终端与该网关连接。网关将该终端的标识及该终端的订阅主题记录到该分组映射表的一个表项中,并接收该控制设备发送的分组消息。网关将分组消息中包括的该终端所属的逻辑分组的标识记录到该分组映射表中该终端的标识对应的表项中。
其中,该分组消息包括该终端的标识以及该终端所属的逻辑分组的标识。
该技术方案中,网关可以根据终端的订阅请求确定与该网关连接的各个终端,可以根据控制设备发送的分组消息确定该各个终端所属的逻辑分组标识,以便网关可以确定向分组内的各个终端发送消息的路径。
作为一种可能的实施方案,网关获取该终端的历史行为数据,将该终端的历史行为数据记录到该分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
该技术方案中,网关可以获取各个终端的历史行为数据,并将终端的历史行为数据记录在分组映射表中,以便在接收到与终端的历史行为数据匹配的应用消息时,可以将应用消息发送给的终端。
作为一种可能的实施方案,网关根据该终端的标识、该网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头,根据该终端的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷,并根据转发标志生成MQTT格式的固定头。网关可以将该可变头、该载荷及该固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向该控制设备发送该MQTT订阅报文。该MQTT订阅报文用于指示该控制设备确定该订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与该网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到该控制设备的网关映射表中该网关的标识对应的表项中。
该技术方案中,网关可以转发与该网关连接的终端的订阅请求,不仅可以使控制设备可以根据订阅请求确定向各个终端发送应用消息的路径,还可以支持网关转发订阅主题,增强了订阅机制的灵活性。
作为一种可能的实施方案,网关根据该网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头,根据该网关的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷,并根据订阅标志生成MQTT格式的固定头。网关可以将该可变头、该载荷及该固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向该控制设备发送该MQTT订阅报文。该MQTT订阅报文用于指示该控制设备确定该订阅主题由该网关所订阅,将该网关的标识记录到该控制设备的网关映射表。
该技术方案中,网关可以向控制设备发送订阅请求,可以支持网关订阅主题,增强了订阅机制的灵活性。
第三方面,提供了一种配置管理装置,应用于控制设备,该配置管理装置具有实现 上述第一方面或第一方面可能的实现方式中行为的功能。该功能可以通过硬件实现,也可以通过硬件执行相应的软件实现。该硬件或软件包括一个或多个与上述功能相对应的模块。该模块可以是软件和/或硬件。
第四方面,提供了另一种配置管理装置,应用于网关,该配置管理装置具有实现上述第二方面或第二方面可能的实现方式中行为的功能。该功能可以通过硬件实现,也可以通过硬件执行相应的软件实现。该硬件或软件包括一个或多个与上述功能相对应的模块。该模块可以是软件和/或硬件。
第五方面,提供了一种控制设备,该控制设备包括:存储器,用于存储一个或多个程序;处理器,用于调用存储在该存储器中的程序,以实现上述第一方面的方法设计中的方案。
第六方面,提供了一种网关,该网关包括:存储器,用于存储一个或多个程序;处理器,用于调用存储在该存储器中的程序,以实现上述第二方面的方法设计中的方案。
第七方面,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序被至少一个处理器执行时,可以实现上述第一方面、第二方面、第一方面的各可能的和第二方面各可能的实施方式以及有益效果。
第八方面,本发明实施例提供了一种计算机程序产品,该计算机程序产品包括存储了计算机程序的非易失性计算机可读存储介质,该计算机程序被执行时使计算机实现上述第一方面及第二方面的方法的步骤,该计算机程序产品解决问题的实施方式以及有益效果可以参见上述第一方面、第二方面、第一方面的各可能的和第二方面各可能的方法的实施方式以及有益效果,重复之处不再赘述。
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例中的技术方案,下面将对本发明实施例中所需要使用的附图进行说明。
图1是本发明实施例提供的一种配置管理的网络构架的示意图;
图2是本发明实施例提供的一种配置管理方法的流程示意图;
图3是本发明实施例提供的另一种配置管理方法的流程示意图;
图4是本发明实施例提供的一种配置管理装置的结构示意图;
图5是本发明实施例提供的另一种配置管理装置的结构示意图;
图6是本发明实施例提供的一种控制设备的结构示意图;
图7是本发明实施例提供的一种网关的结构示意图。
下面结合本发明实施例中的附图对本发明实施例进行描述。
控制设备通过与海量网络接入设备进行交互,可以实现对海量网络接入设备的管理或为海量网络接入设备提供各种服务,如实现对设备的配置管理,提供数据交换的服务等。但是,由于控制设备向海量网络接入设备的发布应用消息的效率较低,对设备管理及服务质量造成不利影响。基于此本发明提出一种配置管理方法、装置及设备,可使控制设备基于分组发送的方式向网络接入设备发送消息,以提高消息发送的效率。
本发明可以应用于遥测、车辆监控、智能家居、能源监控、聊天应用、智能抄表、通知服务或健康医疗等应用场景,以实现对应用场景中的终端的管理或为终端提供服务。
本发明实施例中的控制设备可以是指应用于各种应用场景中的服务器,终端可以是应用于各种应用场景中的终端。例如在车辆监管应用场景中,控制设备可以是指车辆监控服务器,终端可以是指车载终端;在智能抄表应用场景中,控制设备可以是指电力抄表服务器,终端可以是指智能电表。另外,控制设备可以应用于多种应用场景中,终端也可以应用于多种应用场景中。
本发明实施例中的网关可以是指接入路由器(access router,简称:AR)。
本发明的说明书和权利要求书及附图中的术语“第一”和“第二”等是用于区别不同对象,而不是用于描述特定顺序。
为了更好理解本发明实施例提供的一种配置管理方法、装置及设备,下面先描述本发明实施例的网络构架。
请参见图1,图1是本发明实施例提供的一种配置管理的网络构架示意图,在图1中所示的配置管理的网络构架可包括控制设备101及一个或多个网关(图1以两个为例,标示为网关102及网关103)。其中,控制设备101可部署在云端,通过公网中的Internet分别与网关102及网关103连接。网关具备将公网IP地址转换私网的IP地址,或者将私网IP地址转换为公网IP地址的能力,因此,分布于私网的终端1、终端2、终端3、终端4可以通过网关102与Internet连接;同理,分布于私网的终端5、终端6、终端7、终端8可以通过网关103与Internet连接。基于图1所示的网络构架可以实现发送订阅请求和发布应用消息,进而实现对终端的管理或为终端提供服务。
具体的,网关102或网关103可以向控制设备101发送携带订阅标志的订阅请求,该订阅请求包括订阅主题,控制设备101接收到携带订阅标志的订阅请求后,解析该订阅请求,若得到订阅标志及网关的标识为102,则可以确定网关102与控制设备101连接;同理,若得到订阅标志及网关的标识为103,则可以确定网关103与控制设备101。终端1可以向网关102发送订阅请求,该订阅请求包括订阅主题、终端的标识,网关102接收到订阅请求后,解析该订阅请求,若得到终端的标识为1,则可以确定终端1与网关102连接。网关102可以将订阅请求封装成携带转发标志的订阅请求,将携带转发标志的订阅请求转发至控制设备101,控制设备101接收到订阅请求后,解析该订阅请求,得到转发标志、订阅主题、网关的标识102及终端的标识1,则可以确定该订阅主题由终端1所订阅,并可以确定终端1与网关102连接,同理,控制设备101可以确定终端2至终端4与网关102连接。也就是说,若控制设备101向终端1至终端4发布应用消息时,需要将应用消息发送至网关102,并由网关102转发至终端1至终端4。同理,控制设备101可以通过解析接收到的网关103转发终端5至终端8的订阅请求,确定终端5至终端8与网关103连接。
控制设备可以对与每个网关连接的终端进行分组,得到多个逻辑分组,并为每个逻辑分组配置标识,可以将携带逻辑分组的标识及每个逻辑分组所包括的终端的标识的分组消息发送至网关102及网关103,以使网关102确定终端1、终端2、终端3、终端4分别所属的逻辑分组的标识,并使网关103确定终端5、终端6、终端7、终端8分别所 属的逻辑分组的标识。
其中,上述逻辑分组可以是指根据各个终端的订阅主题、网关或随机的方式对各个终端进行的分组,如,控制设备可以将订阅主题相同的终端划分为一个逻辑分组。例如,控制设备可以将终端2至终端8分到第一逻辑分组,第一逻辑分组的标识为1,将终端1分到第二逻辑分组,第二逻辑分组的标识为2,并可以将携带每个终端所属的逻辑分组的标识及每个终端的标识的分组消息分别发送至网关102及网关103,以使网关102可以确定并在网关102的分组映射表中记录终端2至终端4的所属的逻辑分组标识为1,终端1所属的逻辑分组标识为2,并使网关103可以确定并在网关103的分组映射表中记录终端5至终端8所属的逻辑分组标识为1。
在需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息时,如目标逻辑分组标识为1,控制设备可以通过上述确定的终端与网关的连接关系查询到与第一逻辑分组内的终端连接的网关分别为网关102及网关103,进而可以分别向网关102及网关103发送携带逻辑分组标识的MQTT发布报文,其中,控制设备发送给网关102的MQTT发布报文中包括与终端2至终端4的订阅主题匹配的至少一条应用消息,控制设备发送给网关103的MQTT发布报文中包括与终端5至终端8的订阅主题匹配的至少一条应用消息。
在网关102接收到MQTT发布报文后,可以解析该MQTT发布报文,得到逻辑分组标识,及至少一条应用消息,并根据上述分组映射表确定需要向终端2至终端4发送应用消息,则从该至少一条应用消息中分别确定出与各个终端的订阅主题匹配的应用消息,将确定出的应用消息分别发送至终端2至终端4。
同理,网关103接收到MQTT发布报文后,可以解析该MQTT发布报文,得到逻辑分组标识,及至少一条应用消息,并根据上述分组映射表确定需要向终端5至终端8发送应用消息,则从该至少一条应用消息中分别确定出与各个终端的订阅主题匹配的应用消息,将确定出的应用消息分别发送至终端5至终端8。
需要说明的是,该网络构架中的网关102或网关103,可以用于转发终端的订阅请求或者将控制设备101发布的应用消息转发至连接的终端,因此,可以将网关102及网关103看作MQTT机制中的MQTT代理(broker),可以将控制设备101看作MQTT机制中发布消息的代理(broker),可以将各个终端看作MQTT机制中订阅者(subscriber)。
需要说明的是,上述MQTT发布报文及订阅请求是基于MQTT协议传输的,消息队列遥测传输(Message Queuing Telemetry Transport,MQTT)协议是一种即时通讯协议,该协议具有以下优点:1)可靠传输。MQTT协议可以保证消息可靠安全的传输,并可以与企业应用简易集成;2)消息推送。支持消息实时通知、丰富的推送内容、灵活的订阅/发布以及消息存储和过滤;3)低带宽、低耗能、低成本。占用移动应用程序带宽小,并且带宽利用率高,耗电量较少。因此,该协议广泛应用于遥测、汽车、智能家居、能源监控、聊天应用、通知服务、健康医疗应用等等应用场景。
MQTT协议结合代理可以实现发布/订阅机制,在发布或订阅的过程中,发布者(如控制设备)或订阅者(如终端)无需知晓对方的存在,发布者或者订阅者仅需知道代理(如网关)的存在,可以与代理直接交互,并由代理将订阅的消息或发布的消息转发到发布者或订阅者。
MQTT协议的发布、订阅机制可以做到从以下三方面完全解耦发布者和订阅者:1) 空间解耦:发布者和订阅者无需知道对方的存在(通过IP地址和端口即可通信);2)时间解耦:订阅者和发布者无需同时连接;3)同步解耦:发布消息或接收消息时,订阅者和发布者上的组件会同步操作,基于以上三方面的完全解耦可以使订阅者和发布者更加便捷地交互。
MQTT协议的发布、订阅机制中,订阅者与发布者主要采用MQTT订阅(subscribe)报文及MQTT发布(publish)报文进行交互。
其中,MQTT订阅报文是指订阅者为了创建一个或多个订阅而发送往发布者的一种消息类型,每一个MQTT订阅报文携带订阅者向发布者去注册的一个或多个感兴趣的订阅主题。如果发布者发布的消息与订阅者所订阅的主题相匹配,发布者可以将与订阅者的订阅主题相匹配的消息发送至订阅者。
表1:MQTT订阅报文的固定头
MQTT订阅报文包括固定头(fixed header)、可变头(variable header)、载荷(payload)三部分,MQTT订阅报文的固定头如表1所示,固定报头包括MQTT控制报文类型、保留位及剩余长度,MQTT控制报文类型的字段的取值用于描述MQTT报文的类型,如,取值为8,则指示MQTT报文为MQTT订阅报文,剩余长度用于指示该MQTT订阅报文的可变头和载荷的数据总字节数,保留位的字段可以根据应用场景的需要设置。可变头可以用于描述设备的标识(如订阅者的设备标识)等信息;载荷用于描述订阅主题。
表2:MQTT发布报文的固定头
MQTT发布报文是由发布者发往订阅者的一种携带应用消息的报文,主要用于消息的发布。同样,MQTT发布报文也包括固定头、可变头、载荷三部分,MQTT发布报文的固定头如表2所示,MQTT发布报文的固定头包含MQTT控制报文类型、重发标识(duplicate delivery,DUP)flag、服务质量(quality of service,QoS)等级(level)、剩余长度以及保留位。MQTT控制报文类型的字段的取值用于描述MQTT报文的类型,如取值为3,则指示MQTT报文为MQTT发布报文;DUP flag用于描述该MQTT发布报文是否为重发的报文,如DUP flag的取值为0,则表示该MQTT发布报文为第一次发送的报文,DUP flag的取值为1,则表示该MQTT发布报文为重发的报文;QoS level用于描述发布应用消息的服务质量等级;剩余长度用于指示该MQTT发布报文的可变头和载荷的数据总字节数,保留位的字段可以根据应用场景的需要设置。
MQTT发布报文的可变头如表3所示,可变头包括订阅主题信息(如订阅主题的长度、 订阅主题名)和报文标识,表3中的Byte1至Byte2中的字段用于描述订阅主题的长度,Byte3至Byte5中的字段用于描述订阅主题名,Byte6至Byte7中的字段可以用于描述报文标识,报文标识可以用于唯一指示该MQTT发布报文,最高有效位(most significant bit,MSB),最低有效位(least significant bit,LSB)。
MQTT发布报文的载荷用于描述发布的应用消息。
表3:MQTT发布报文的可变头
为了实现本发明提出的一种配置管理方法,将MQTT订阅报文作出以下修改:
网关与控制设备可以约定采用表1所示的MQTT订阅报文的固定头的保留位来表示订阅标志或转发标志,如约定将保留位的取值设置为1来表示订阅标志,用于指示该MQTT订阅报文中携带的订阅主题由网关订阅;约定将保留位的取值设置为2来表示转发标志,用于指示该MQTT订阅报文中携带的订阅主题由终端订阅。
对MQTT订阅报文修改后,对MQTT协议规则作出以下约定:
若网关需要向控制设备发送订阅请求,则可以将发往控制设备的MQTT订阅报文的固定头的保留位的取值设置为订阅标志(如1),用于指示该MQTT订阅报文中携带的订阅主题由网关订阅。
若网关需要向控制设备转发终端的订阅请求,则可以将发往控制设备的MQTT订阅报文的固定头的保留位的取值设置为转发标志(如2),用于指示该MQTT订阅报文中携带的订阅主题由终端订阅。
若终端需要向控制设备发送订阅请求,则可以将发往控制设备的MQTT订阅报文的固定头的保留位的取值设置为空,即与原MQTT协议保持一致。
表4:修改后的MQTT发布报文的可变头
同理,为了实现本发明提出的一种配置管理方法,将MQTT发布报文作出以下修改:
网关与控制设备可以约定在如表3所示的MQTT发布报文的可变头增加2Bytes的逻辑分组的标识位,用于指示该MQTT发布报文中携带的应用消息是发给逻辑分组或发给网关,修改后的MQTT发布报文的可变头如表4所示,表中增加的Byte8至Byte9用于表示逻辑分组的标识。
对MQTT发布报文修改后,对MQTT协议规则作出以下约定:
若控制设备需要向终端发布应用消息,则向终端发送不携带逻辑分组的标志位的MQTT发布报文,即与原MQTT协议保持一致。
若控制设备需要向网关发布应用消息,则可以将发往网关的MQTT发布报文的可变头的逻辑分组的标识位都设置为1,用于指示该MQTT发布报文携带的应用消息是发送至网关。
若控制设备需要通过网关向终端发布应用消息,这里分为两种情况:
(1)若控制设备需要向单独的终端发布应用消息,则可以将发往网关的MQTT发布报文的可变头的订阅主题设置为该终端的订阅主题,将可变头的逻辑分组的标识位都设置为0,网关接收到该MQTT发布报文后,移除该MQTT发布报文的可变头的逻辑分组的标识位,得到不携带逻辑分组的标识位的MQTT发布报文,将得到的MQTT发布报文发送给终端。
(2)若控制设备需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息,则可以将发往网关的MQTT发布报文的可变头的订阅主题设置为目标逻辑分组内各目标终端的订阅主题,将可变头的逻辑分组的标识位设置为该目标逻辑分组的标识,将载荷设置为与各目标终端的订阅主题匹配的至少一条应用消息。网关接收到该MQTT发布报文后,移除该MQTT发布报文的可变头的逻辑分组的标识位,将可变头的订阅主题替换为目标终端的订阅主题,将载荷中的应用消息替换为与该目标终端的订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息,将携带该目标应用消息的MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端,该目标逻辑分组包括至少一个目标终端。
需要说明的是,上述的订阅主题是网关用于为订阅者(如终端)处理过滤消息而用到的UTF-8格式的字符串,每一个订阅主题可以只有一层,也可以有多个层级,每个层级用“/”来分割。由于订阅主题比较轻量级(即占的字节数较少),因此网关在接收到订阅主题之前无需做前期的初始化处理,进而,在执行发布或者订阅步骤之前,控制设备也无需创建终端所需的订阅主题。
其中,UTF-8为一种针对统一的字符编码标准Unicode的可变长度字符编码。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以采用分组发送MQTT发布报文的方式向与分组内各个终端连接的网关发布应用消息,并指示网关将应用消息发送给各个终端,可以提高消息发布的效率。并且,网关可以向控制设备发送订阅请求,也可以向控制设备发送终端的订阅请求,也就是增加了网关的订阅机制及网关的转发订阅机制,可以使订阅机制更加灵活,另外,在控制设备与终端之间采用MQTT协议的订阅/发布机制,不需要建立控制设备与终端之间的长时间连接,控制设备可以与多个网关采用级联方式连接,所以可以指数级的增加接入的终端数。
基于上述对一种配置管理的网络构架的描述,本发明实施提供了一种配置管理方法,该方法应用于控制设备、目标网关、目标终端,请参见图2,如图2所示所述方法可以包括:
S201、控制设备确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
作为一种可选的实施方式,上述确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息的具体方式包括:如果检测到与该目标逻辑分组内的至少一个目标终端的订阅主题相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向该目标逻辑分组发布应用消息;或者,如果检测到与该至少一个目标终端的历史行为数据相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向该目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
举例来说,若至少一个目标终端的订阅主题为配置更新消息,控制设备检测到各个目标终端的系统配置更新消息,则确定需要向该目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
再举例来说,若至少一个目标网关根据至少一个目标终端在预设时间段内视频播放应用的运行日志,确定该至少一个目标终端播放科技类的视频的时长大于其他类型的视频,该至少一个目标网关可以将该至少一个目标终端的行为数据上报给控制设备,若控制设备检测到更新的科技类视频,确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以检测是否存在与该目标逻辑分组内的至少一个目标终端的订阅主题相匹配的至少一条应用消息,或者检测是否存在与该至少一个目标终端的行为数据匹配的至少一条应用消息,若存在,则确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布该应用消息。
其中,应用消息可以包括配置管理消息、新闻消息或通知服务消息等等,配置管理消息可以包括网络安全策略的配置消息、数据采集策略配置消息或应用部署策略配置消息等。其中,订阅主题可以是指应用消息的标签,如,若应用消息为新闻消息,则订阅主题可以为军事类新闻、财经类新闻或健康类新闻等。
其中,各个目标终端的订阅主题可以相同,也可以不相同,本发明对此不做限定。
其中,控制设备可以接收网关上报的至该少一个目标终端的历史行为数据,该至少一个目标终端的历史行为数据可以是由网关根据采集到的该目标终端中的某个应用的运行日志确定,如,预设时间段内网页浏览器应用的运行日志、预设时间段内视频播放应用的运行日志或者预设时间段内的购物应用的运行日志等。
S202、控制设备获取该目标逻辑分组的标识,其中,该目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端。
S203、控制设备根据网关映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识查询与该至少一个目标终 端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关。
举例来说,如图1中所示,控制设备101需要向第一逻辑分组发布应用消息时,控制设备获取到该目标逻辑分组标识为1,控制设备可以根据网关映射表及该目标逻辑分组标识查询到与该至少一个目标终端连接的目标网关为网关102及网关103。控制设备可以向网关102及网关103发送MQTT发布报文。
其中,该网关映射表记录了多个网关的标识,与该多个网关连接的终端的标识,以及每个终端所属的逻辑分组的标识。另外,控制设备可以根据网络构架中的设备或控制设备对多个终端的分组结果动态调整该网关映射表,例如,若控制设备检测到网络构架中新接入了一个终端,则可以将该终端的标识记录到该网关映射表中;若控制设备检测到网络构架中某个终端断开了与网关的连接,则可以将该终端的标识从该网关映射表中移除。
其中,该逻辑分组标识可以由字母、数值或符号中的一种或多种组成。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以根据网关映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识查询与该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关,以便控制设备可以按照分组的方式向各个目标网关的发送第一MQTT报文,可以提高消息发布的效率。
需要说明的是,网关的标识可以是指该网关的MAC地址,或者其他可以唯一指示该网关的标识,终端的标识可以是指MAC地址,或其他可以唯一指示该终端的标识。
S204、控制设备根据该应用消息生成第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,该第一MQTT发布报文包括该目标逻辑分组的标识以及该应用消息。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以根据该应用消息及该目标逻辑分组的标识生成第一MQTT发布报文,以便目标网关设设备可以将该应用消息发送到至少一个目标终端,进而对该至少一个目标终端的管理或者为该各目标终端提供各种应用服务。
作为一种可选的实施方式,控制设备可以根据该目标逻辑分组的标识生成MQTT格式的可变报头,根据该应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷,将该可变报头及该载荷封装为该第一MQTT发布报文。
需要说明的是,控制设备可以在第一MQTT发布报文的可变头增加2Bytes的逻辑分组的标识位,用于指示该第一MQTT发布报文发往逻辑分组或网关。
举例来说,若需要向逻辑分组标识为1的各个终端发布订阅报文,如各个终端的订阅主题名为a/b,订阅主题的长度为3,报文的标识为10,控制设备可以在第一MQTT发布报文的可变头中增加2Byte字段来表示逻辑分组标识,如在可变头中增加Byte8至Byte9中的字段来表示逻辑分组的标识,控制设备可以将各个终端的订阅主题名、订阅主题长度、报文标识、逻辑分组的标识封装在MQTT格式的可变头,得到如表5所示的封装后的第一MQTT发布报文的可变头。
表5中的‘a’(0x61)是指字母a可以用十六进制表示为61,同理‘/’(0x2F)是指符号/可以用十六进制表示为2F,‘b’(0x62)是指字母b可以用十六进制表示为62。
表5:封装后的第一MQTT发布报文的可变头
控制设备可以根据与各个终端的订阅主题匹配的应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷,其中第一MQTT发布报文的载荷的格式是不固定的,可以根据该应用消息的应用场景等因素设置。在获得可变报头和载荷后,可以将变报头和载荷封装为该第一MQTT发布报文,以便可以将该第一MQTT发布报文发送至各目标网关。
本发明实施例中,控制设备与目标网关可以事先约定将逻辑分组的标识及应用消息封装在MQTT格式的某个位置,如约定将逻辑分组的标识封装在MQTT格式的可变报头,将应用消息封装在MQTT格式的载荷,即控制设备可以根据该目标逻辑分组的标识生成MQTT格式的可变报头,根据该应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷,将该可变报头及该载荷封装为该第一MQTT发布报文,以便可以将第一MQTT发布报文发送至各个目标网关。
需要说明的是,第一MQTT发布报文还包括固定头部,固定头部可以包括类型字段,该类型字段用于指示该第一MQTT发布报文的类型,如,该类型字段指示该第一MQTT发布报文的类型为发布消息的报文。
S205、控制设备向该至少一个目标网关发送该第一MQTT发布报文。
其中,该第一MQTT发布报文用于指示接收到该第一MQTT发布报文的目标网关,向与该目标网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以向该至少一个目标网关发送该第一MQTT发布报文,以便该至少一个目标网关可以将第一MQTT发布报文中的应用消息发送至该至少一个目标终端。
其中,第一MQTT发布报文中携带的应用消息的条数可以是一条,也可以是多条,也就是说,若该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或行为数据一致,则第一MQTT发布报文中携带的应用消息的条数可以是一条,即上述向与该目标网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息,可以是指该目标网关向各目标终 端发送同一条应用消息,该应用消息与目标终端的订阅主题或行为数据匹配。若该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或行为数据不一致,则第一MQTT发布报文中携带的应用消息的条数可以是多条,即上述向与该目标网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息,可以是指该目标网关向该至少一个目标终端中的每个目标终端发送与该目标终端的订阅主题或行为数据匹配的应用消息。如终端1的订阅主题为广域网(wide area network,WAN)配置,则目标网关向终端1发送与WAN配置匹配的应用消息;若终端2的订阅主题为网络安全配置,则目标网关向终端2发送与网络安全配置匹配的应用消息。
S206、至少一个目标网关解析该第一MQTT发布报文,得到目标逻辑分组的标识及至少一条应用消息。
本发明实施例中,至少一个目标网关可以解析该第一MQTT发布报文的可变头,得到目标逻辑分组的标识,可以解析该MQTT发布报文的载荷,得到至少一条应用消息。
作为一种可选的实施例,该至少一个目标网关执行步骤S206之前,还可以接收控制设备发送的第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文。
S207、至少一个目标网关根据分组映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识确定与该目标网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据。
举例来说,如图1所示,在网关102及网关103接收到第一MQTT发布报文,可以解析该第一MQTT发布报文,获得至少一条应用消息及该目标逻辑分组的标识(如1),网关102根据分组映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识确定至少一个目标终端为终端2至终端4,确定终端2至终端4的订阅主题为网络流量策略的配置;网关103根据分组映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识确定至少一个目标终端为终端5至终端8,确定终端5的订阅主题为网络流量策略的配置,确定终端6至终端8的订阅主题为性能指标数据(如网络质量指标数据)。
其中,该分组映射表记录了与该网关连接的各终端的标识,各终端所属的逻辑分组的标识,以及各终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据。另外,网关可以根据网络构架中的设备或者控制设备对多个终端的分组结果动态调整该分组映射表,例如,若网关检测到网络构架中新接入了一个终端,则可以将该终端的标识记录到该分组映射表中;若网关检测到网络构架中某个终端断开了与该网关的连接,则可以将该终端的标识从该分组映射表中移除。
本发明实施例中,至少一个目标网关根据分组映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识确定至少一个目标终端,及该至少一个目标终端中的每个终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据,以便可以向该至少一个目标终端的每个目标终端发送与订阅主题或历史行为数据匹配的应用消息。
S208、至少一个目标网关从该至少一条应用消息中确定与该至少一个目标终端中每个该目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息,根据该目标应用消息生成第二MQTT发布报文,并将携带该目标应用消息的该第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端。
举例来说,如图1所示,若终端2至终端4的订阅主题为网络流量策略的配置,则 网关102可以将接收到的第一MQTT发布报文的可变头部的逻辑分组的标识位移除,将第一MQTT发布报文的可变头部的订阅主题替换为终端2的订阅主题(即网络流量策略的配置),将第一MQTT发布报文的载荷的应用消息替换为与网络流量策略的配置匹配的目标应用消息,进而得到携带该目标应用消息的第二MQTT发布报文。由于终端2至终端4的订阅主题相同,网关102可以将该第二MQTT发布报文发送给终端2至终端4,终端2至终端4接收到该MQTT发布报文后,可以解析该第二MQTT发布报文,得到该目标应用消息,可以根据该目标应用消息对终端2至终端4的网络进行配置,也就说控制设备可以实现对终端2至终端4的配置管理。
若终端5的订阅主题为网络流量策略的配置,网关103可以将接收到的第一MQTT发布报文的可变头部的逻辑分组的标识位移除,将第一MQTT发布报文的可变头部的订阅主题替换为终端5的订阅主题(即网络流量策略的配置),将第一MQTT发布报文的载荷的应用消息替换为与网络流量策略的配置匹配的目标应用消息,进而得到携带该目标应用消息的第二MQTT发布报文,网关103可以将该第二MQTT发布报文发送给设备5。终端5接收到该第二MQTT发布报文后,可以解析该MQTT发布报文,得到该目标应用消息,可以根据该目标应用消息对终端5的网络进行配置,也就说控制设备可以实现对终端5的配置管理。
若终端6至终端8的订阅主题为性能指标数据(如网络质量指标数据),网关103可以将接收到的第一MQTT发布报文的可变头部的逻辑分组的标识位移除,将第一MQTT发布报文的可变头部的订阅主题替换为终端6的订阅主题(即网络质量指标数据),将第一MQTT发布报文的载荷的应用消息替换为与网络质量指标数据匹配的目标应用消息,进而得到携带该目标应用消息的第二MQTT发布报文。由于终端6至终端8的订阅主题相同,网关103可以将该第二MQTT发布报文发送给终端6至终端8,控制设备可以实现为终端6至终端8提供性能指标数据的采集服务。
本发明实施例中,至少一个目标网关可以从该至少一条应用消息中确定与该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息,并将携带该目标应用消息的第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端,以便可以实现对该目标逻辑分组内的各个目标终端的管理或为各个目标终端提供服务。
作为一种可选的实施方式,控制设备可以向终端发送携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文;或者,向网关发送携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文。
本发明实施中,控制设备可以向与该控制设备连接的终端发送携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文,或者,向网关发送携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文,如向网关发送系统配置更新消息或者分组消息等。
需要说明的是,控制设备在向网关发布MQTT发布报文时,可以在该MQTT发布报文的可变头增加逻辑分组的标识位,如将表5中Byte8至Byte9中的字段都设置为1,该标志用于指示该MQTT发布报文是发送给网关的。
作为一种可选的实施方式,网关可以接收该控制设备发送的携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文。
本发明实施例中,网关可以接收该控制设备发送的携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文,以便可以根据该MQTT发布报文做出相应的操作,如,控制设备发送的系统配置 更新消息,网关可以采用系统配置更新消息进行系统更新。
举例来说,如图1所示,网关102接收到控制设备101发送的携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文,可以解析该MQTT发布报文,得到MQTT发布报文的可变头的Byte8至Byte9中的字段都1,可以确定该MQTT发布报文是发给该网关102的。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以以分组的方式向与分组内的各个终端的连接的网关发送MQTT发布报文,并指示网关将应用消息发送给各个终端,可以提高消息发送的效率,进而可以实现对分组内的各个终端的管理或为分组内的终端提供服务。
基于上述对一种配置管理的网络构架的描述,本发明实施提供了另一种配置管理方法,该方法应用于控制设备、目标网关、目标终端,请参见图3,如图3所示所述方法可以包括:
S301、控制设备接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文,解析该MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文,并解析该MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据,以便可以根据标志数据确定该订阅主题是由哪个设备所订阅,也可以确定网关与终端的连接关系。
S302、若该标志数据包括转发标志、终端的标识以及网关的标识,则控制设备确定该订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与该网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到该网关映射表中该网关的标识对应的表项中。
本发明实施例中,若该标志数据包括转发标志、终端的标识以及网关的标识,则控制设备可以确定该订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与该网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到该网关映射表中该网关的标识对应的表项中,不仅可以确定网关与终端之间的连接关系,还可以支持网关转发订阅主题,使订阅机制更加灵活。
作为一种可选的实施例,接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文,解析该MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据,若该标志数据包括订阅标志及网关的标识,则确定该订阅主题由该网关所订阅,将该网关的标识记录到网关映射表。
本发明实施例中,控制设备接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文,则可以解析该MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据,若该标志数据包括订阅标志及网关的标识,则确定该订阅主题由该网关所订阅,将该网关的标识记录到该网关映射表,以便控制设备可以确定与该网关的连接,并确定该订阅主题是由该网关所订阅的,可支持网关订阅主题,使订阅机制更加灵活。
需要说明的是,网关与控制设备可以约定采用MQTT订阅报文的固定头的保留位中的字段来表示转发标志或订阅标志,如约定将保留位的取值为1来表示订阅标志,用于指示订阅主题由网关订阅;如约定将保留位的取值为2时,表示转发标志,用于指示该订阅主题由终端订阅。
举例来说,如图1所示,控制设备101接收MQTT订阅报文,可以解析该MQTT订阅报文的载荷,得到订阅主题,解析该MQTT订阅报文的固定报头,得到固定头的保留位的取值为1,则确定该标志数据包括订阅标志,解析该MQTT订阅报文的可变头,得到网关的标识为102,则控制设备101可以确定该订阅主题由网关102所订阅,可以 将网关的标识记录到如表6所示网关映射表中。
再举例来说,如图1所示,控制设备101接收MQTT订阅报文,可以解析该MQTT订阅报文的载荷,得到订阅主题,解析该MQTT订阅报文的固定报头,得到固定头的保留位的取值为2,则确定该标志数据包括转发标志,解析该MQTT订阅报文的可变头,得到终端的标识为1以及网关的标识为102,则控制设备101可以确定该订阅主题由终端1所订阅,并确定该终端1与该网关102连接,将该终端的标识1记录到如表1所示的网关映射表中该网关的标识102对应的表项中,同理,控制设备可以确定网关102与终端2至终端4的连接,并确定网关103与终端5至终端8的连接,将各个网关的标识及终端的标识记录到如表6所示的网关映射表中。
作为一种可选的实施方式,控制设备可以根据与该多个网关连接的多个终端的订阅主题对该多个终端进行分组,或者,随机对该多个终端进行分组,或者,按照该多个网关对该多个终端进行分组,得到多个逻辑分组,为每个逻辑分组配置标识,将每个逻辑分组的标识记录到该网关映射表中该逻辑分组中每个终端的标识的对应的表项中。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以根据与该多个网关连接的多个终端的订阅主题对各个终端进行分组,如,控制设备可以将订阅主题相同的终端分为一组;还可以随机对该多个终端进行分组;也可以按照该多个网关对该多个终端进行分组,如将连接在同一个网关的终端分为一组;进而得到多个逻辑分组,并为各个逻辑分组配置标识,将每个逻辑分组的标识记录到该网关映射表中该逻辑分组中每个终端的标识的对应的表项中,以便可以根据分组标识确定各个逻辑分组内的终端。
举例来说,如图1所示,控制设备101可以对与各个网关连接的终端进行分组,如将终端2至终端8分为第一逻辑分组,可将该第一逻辑分组的逻辑分组的标识设置为1,将终端1分为第二逻辑分组,可以将该第二逻辑分组的逻辑分组的标识设置2,并将各个分组的逻辑分组的标识记录到如表6所示的网关映射表中。
表6:网关映射表
作为一种可选的实施方式,网关可以根据该终端的标识、该网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头,根据该终端的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷,根据转发标志生成MQTT格式的固定头,将该可变头、该载荷及该固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向该控制设备发送该MQTT订阅报文,该MQTT订阅报文用于指示该控制设备确定该订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与该网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到该网关映 射表中该网关的标识对应的表项中。
举例来说,如图1所示,网关102可以根据该终端的标识1、该网关的标识102生成MQTT格式的可变头,根据该终端的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷,根据转发标志(如2)生成MQTT格式的固定头的保留位,将该可变头、该载荷及该固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向该控制设备101发送所述MQTT订阅报文,用于指示该控制设备101确定该订阅主题由该终端1所订阅,并确定该终端1与该网关102连接,将该终端的标识1记录到该网关映射表中该网关的标识102对应的表项中。
作为一种可选的实施方式,网关可以根据该网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头,根据该网关的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷,根据订阅标志生成MQTT格式的固定头,将该可变头、该载荷及该固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向该控制设备发送该MQTT订阅报文,用于指示该控制设备确定该订阅主题由该网关所订阅,将该网关的标识记录到该网关映射表中。
举例来说,如图1所示,网关102可以根据该网关的标识102生成MQTT格式的可变头,根据该网关的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷,根据订阅标志(如1)生成MQTT格式的固定头的保留位,将该可变头、该载荷及该固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向该控制设备101发送该MQTT订阅报文,用于指示该控制设备101确定该订阅主题由该网关102所订阅,将该网关的标识102记录到该网关映射表中。
S303、控制设备确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
S304、控制设备获取该目标逻辑分组的标识,其中,该目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端。
S305、控制设备根据网关映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识查询与该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关。
S306、控制设备根据该应用消息生成第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,该第一MQTT发布报文包括该目标逻辑分组的标识以及该应用消息。
S307、控制设备向该至少一个目标网关发送该第一MQTT发布报文。
S308、至少一个目标网关解析该第一MQTT发布报文,得到目标逻辑分组的标识及至少一条应用消息。
S309、至少一个目标网关根据分组映射表及该目标逻辑分组的标识确定与该网关连接的属于该目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及该至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据。
作为一种可选的实施方式,网关可以接收终端的订阅请求,解析该订阅请求,获得该终端的标识及该终端的订阅主题,并确定该终端与该网关连接。网关可以将该终端的标识及该终端的订阅主题记录到该分组映射表的一个表项中,接收该控制设备发送的分组消息,该分组消息包括该终端的标识以及该终端所属的逻辑分组的标识。网关可以将该终端所属的逻辑分组的标识记录到该分组映射表中该终端的标识对应的表项中。
表7:分组映射表
举例来说,如图1终端的网关102接收到终端1至终端4的订阅请求,可以解析该订阅请求,获得终端1的订阅主题为WAN配置,终端2的订阅主题为网络安全配置,终端3的订阅主题为网络流量策略配置,终端4的订阅主题为设备维护配置,终端1至终端4的标识分别为1、2、3、4,可以将该各个终端的标识及各个终端的订阅主题记录到该分组映射表中该网关的标识对应的表项中,在接收到该控制设备101发送的分组消息时,可以解析该分组消息,获得与该网关102的连接的终端的标识,及各个终端所属的逻辑分组标识,如与获得该网关连接的终端的标识分别为1、2、3、4,及终端2至终端4所属的逻辑分组标识为1,终端1所属的逻辑分组标识为2,可以将该各个终端所属的逻辑分组标识记录到该分组映射表中该各个终端的标识对应的表项中,如表7所示。
作为一种可选的实施例,网关可以获取与该网关连接的终端的历史行为数据,将该终端的历史行为数据记录到该分组映射表中该终端标识对应的表项中。
本发明实施例中,网关可以采集终端中的某个应用的运行日志,如,预设时间段内网页浏览器应用的运行日志、预设时间段内视频播放应用的运行日志或者预设时间段内的购物应用的运行日志等,并根据应用的运行日志确定该终端的行为数据,并将该终端的历史行为数据记录到该分组映射表中该终端标识对应的表项中。
S310、至少一个目标网关从该至少一条应用消息中确定与该至少一个目标终端中每个该目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息,根据该目标应用消息生成第二MQTT发布报文,并将携带该目标应用消息的该第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端。
需要说明的是,若控制设备需要向单个终端发布应用消息,则控制设备可以向与该终端连接的网关发送MQTT发布报文,并可以在该MQTT发布报文的可变头设置逻辑分组的标识位,如可将图5中的Byte8至Byte9中的字段都设置为0,该标志位用于指示该应用消息是发送给单个终端的,网关接收到该MQTT发布报文时,解析该MQTT发布报文,得到应用消息,可以将该应用消息发送给该终端。
需要说明的是,本发明实施例中对步骤S303~S310的解释说明可以参考图2中对步骤S201至S208的解释说明,重复之处不在赘述。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以采用分组发送消息的方式向与分组内各个终端连接的网关发布应用消息,并指示网关将应用消息发送给各个终端,可以提高消息发布的效率,网关可以向控制设备发送订阅请求,也可以向控制设备发送终端的订阅请求,即增加了网关的订阅机制及网关的转发订阅机制,可以使订阅机制更加灵活,另外,在控制设备与终端之间采用MQTT协议的订阅/发布机制,不需要建立控制设备与终端之间的长时间连接,控制设备可以与多个网关采用级联方式连接,所以可以指数级的增加接入的终端数。
基于上述对一种配置管理的方法的描述,本发明实施提供了一种配置管理装置,该装置应用于控制设备,请参见图4,如图4所示的配置管理装置可以包括确定模块401、获取模块402、查询模块403、生成模块404、发送模块405、接收模块406、解析模块407、记录模块408及分组模块409,配置模块410,其中:
确定模块401,用于确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
获取模块402,用于获取所述目标逻辑分组的标识,其中,所述目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端。
查询模块403,用于根据网关映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识查询与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关,其中,所述网关映射表记录了多个网关的标识,与所述多个网关中每个网关连接的终端的标识,以及每个终端所属的逻辑分组的标识。
生成模块404,用于根据所述应用消息生成消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文包括所述目标逻辑分组的标识以及所述应用消息。
发送模块405,用于向所述至少一个目标网关发送所述MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文用于指示接收到所述MQTT发布报文的目标网关向所述目标网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息。
可选的,接收模块406,用于接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文。
可选的,解析模块407,用于解析所述MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据。
可选的,所述确定模块401,还用于若所述标志数据包括订阅标志及网关的标识,则确定所述订阅主题由所述网关所订阅。
可选的,记录模块408,用于将所述网关的标识记录到所述网关映射表中。
可选的,所述确定模块401,还用于若所述标志数据包括转发标志、终端的标识以及网关的标识,则确定所述订阅主题由所述终端所订阅,并确定所述终端与所述网关连接。
可选的,所述记录模块408,还用于将所述终端的标识记录到所述网关映射表中所述网关的标识对应的表项中。
可选的,分组模块409,用于根据与所述多个网关连接的多个终端的订阅主题对所述多个终端进行分组,或者,随机对所述多个终端进行分组,或者,按照所述多个网关对所述多个终端进行分组,得到多个逻辑分组。
可选的,配置模块410,用于为每个逻辑分组配置标识。
可选的,所述记录模块408,还用于将每个逻辑分组的标识记录到所述网关映射表中所述逻辑分组中每个终端的标识的对应的表项中。
可选的,所述确定模块401,具体用于如果检测到与所述目标逻辑分组内所述至少一个目标终端的订阅主题相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向所述目标逻辑分组发布应用消息,或者,如果检测到与所述至少一个目标终端的历史行为数据相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向所述目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
可选的,所述生成模块404,具体用于根据所述目标逻辑分组的标识生成MQTT格式的可变报头;根据所述应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷;将所述可变报头及所述载荷封装为所述MQTT发布报文。
可选的,所述发送模块405,还用于向终端发送携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文;或者,向网关发送携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文。
本发明实施例中,该配置管理装置具有实现上述图2和图3对应实施例中的配置管理方法中控制设备执行的相应步骤的功能。该功能可以通过硬件实现,也可以通过硬件执行相应的软件实现。该硬件或软件包括一个或多个与上述功能相对应的模块。上述模块可以是软件和/或硬件。
基于同一发明构思,由于该配置管理装置解决问题的原理以及有益效果可以参见上述图2和图3所述配置管理方法的实施方式以及所带来的有益效果,因此该配置管理装置的实施方式可以参见上述图2和图3所述配置管理方法的实施方式,重复之处不再赘述。
本发明实施例中,控制设备可以采用分组发送消息的方式向与分组内各个终端连接的网关发布应用消息,并指示网关将应用消息发送给各个终端,可以提高消息发布的效率。网关可以向控制设备发送订阅请求,也可以向控制设备发送终端的订阅请求,即增加了网关的订阅机制及网关的转发订阅机制,可以使订阅机制更加灵活,另外,在控制设备与终端之间采用MQTT协议的订阅/发布机制,不需要建立控制设备与终端之间的长时间连接,控制设备可以与多个网关采用级联方式连接,所以可以指数级的增加接入的终端数。
基于上述对一种配置管理的方法的描述,本发明实施提供了另一种配置管理装置,该装置应用于网关,请参见图5,如图5所示的配置管理装置可以包括接收模块501、解析模块502、确定模块503、生成模块504、发送模块505、记录模块506、获取模块507、第一封装模块508及第二封装模块509,其中:
接收模块501,用于接收控制设备发送的第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文。
解析模块502,用于解析所述第一MQTT发布报文,得到目标逻辑分组的标识及至少一条应用消息。
确定模块503,用于根据分组映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识确定与所述网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据,其中,所述分组映射表记录了与所述网关连接的各终端的标识,各终端所属的逻辑分组的标识,以及各终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据。
所述确定模块503,还用于从所述至少一条应用消息中确定与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息。
生成模块504,用于根据所述目标应用消息生成第二MQTT发布报文。
发送模块505,用于将携带所述目标应用消息的所述第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端。
可选的,所述接收模块501,还用于接收终端的订阅请求。
可选的,所述解析模块502,还用于解析所述订阅请求,获得所述终端的标识及所述终端的订阅主题。
可选的,所述确定模块503,还用于确定所述终端与所述网关连接。
可选的,记录模块506,用于将所述终端的标识及所述终端的订阅主题记录到所述 分组映射表的一个表项中。
可选的,所述接收模块501,还用于接收所述控制设备发送的分组消息,所述分组消息包括所述终端的标识以及所述终端所属的逻辑分组的标识。
可选的,所述记录模块506,还用于将所述终端所属的逻辑分组的标识记录到所述分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
可选的,获取模块507,用于获取所述终端的历史行为数据。
可选的,所述记录模块506,还用于将所述终端的历史行为数据记录到所述分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
可选的,所述生成模块504,还用于根据所述终端的标识、所述网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头;根据所述终端的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷;根据转发标志生成MQTT格式的固定头。
可选的,第一封装模块508,用于将所述可变头、所述载荷及所述固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文。
可选的,所述发送模块505,还用于向所述控制设备发送所述MQTT订阅报文,所述MQTT订阅报文用于指示所述控制设备确定所述订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与所述网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到所述控制设备的网关映射表中所述网关的标识对应的表项中。
可选的,所述生成模块504,还用于根据所述网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头;根据所述网关的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷;根据订阅标志生成MQTT格式的固定头。
可选的,第二封装模块509,用于将所述可变头、所述载荷及所述固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文。
可选的,所述发送模块505,还用于向所述控制设备发送所述MQTT订阅报文,所述MQTT订阅报文用于指示所述控制设备确定所述订阅主题由所述网关所订阅,将所述网关的标识记录到所述控制设备的网关映射表。
可选的,接收模块501,用于接收所述控制设备发送的携带应用消息的MQTT发布报文。
本发明实施例中,该配置管理装置具有实现上述图2和图3对应实施例中的配置管理方法中网关执行的相应步骤的功能。该功能可以通过硬件实现,也可以通过硬件执行相应的软件实现。该硬件或软件包括一个或多个与上述功能相对应的模块。上述模块可以是软件和/或硬件。
基于同一发明构思,由于该配置管理装置解决问题的原理以及有益效果可以参见上述图2和图3所述配置管理方法的实施方式以及所带来的有益效果,因此该配置管理装置的实施方式可以参见上述图2和图3所述配置管理方法的实施方式,重复之处不再赘述。
本发明实施例中,网关可以接收控制设备以分组方式发送的MQTT发布报文,并将该MQTT发布报文中携带的应用消息发送给该分组内的终端,可以提高消息发布的效率。网关可以向控制设备发送订阅请求,也可以向控制设备转发终端的订阅请求,即增加了网关的订阅机制及网关的转发订阅机制,可以使订阅机制更加灵活。
基于上述对一种配置管理装置的描述,本发明实施提供了一种控制设备,请参见图6,如图6所示的控制设备可以包括:包括处理器601、存储器602和通信接口603,所述处理器601、存储器602和通信接口603通过总线相互连接。
处理器601可以是一个或多个中央处理器(英文:central processing unit,简称:CPU),在处理器601是一个CPU的情况下,该CPU可以是单核CPU,也可以是多核CPU。
存储器602包括但不限于是随机存储记忆体(英文:random access memory,简称:RAM)、只读存储器(英文:read-only memory,简称:ROM)、可擦除可编程只读存储器(英文:erasable programmable read only memory,简称:EPROM)、或便携式只读存储器(英文:compact disc read-only memory,简称:CD-ROM),该存储器602用于存储指令及数据,如存储与该控制设备连接的网关的标识等。
上述通信接口603与其他网络设备相连。例如,通信接口603包括多个接口,分别与多个网关相连。通信接口603可以是有线接口,无线接口或其组合。有线接口例如可以为以太网接口。以太网接口可以是光接口,电接口或其组合。无线接口例如可以为无线局域网(英文:wireless local area network,缩写:WLAN)接口,蜂窝网络接口或其组合。通信接口603用于在控制器的控制下接收或者发送数据,如接收MQTT订阅报文或发送MQTT发布报文。
上述存储器602还用于存储程序指令。上述处理器601可以调用上述存储器602存储的程序指令,实现如本申请上述各实施例所示的配置管理方法。
可选的,本发明实施例中的处理器601可以实现图4中的确定模块401、获取模块402、查询模块403、生成模块404、解析模块407、记录模块408及分组模块409,配置模块410中的功能,存储器602可以实现图4中的记录模块408的功能,通信接口603可以实现图4中的发送模块405及接收模块406的功能,本发明实施例不做限定。
基于同一发明构思,本发明实施例中提供的控制设备解决问题的原理与本发明方法实施例相似,因此该控制设备的实施以及有益效果可以参见上述各方法实施例,为简洁描述,在这里不再赘述。
基于上述对一种配置管理装置的描述,本发明实施提供了一种网关,请参见图7,如图7所示的网关可以包括:包括处理器701、存储器702和通信接口703,所述处理器701、存储器702和通信接口703通过总线相互连接。
处理器701可以是一个或多个CPU,在处理器701是一个CPU的情况下,该CPU可以是单核CPU,也可以是多核CPU,处理器701,用于控制网关中的各个功能模块以及处理信号,处理器701可以包括调制解调器,用于对通信接口703接收到的信号进行调制或解调处理。
存储器702包括但不限于是RAM、ROM、EPROM、CD-ROM,该存储器702用于存储指令、操作系统、各种应用及数据,如存储与该网关连接的终端的标识及终端的订阅主题等。
上述通信接口703与其他网络设备或终端相连。例如,通信接口703包括多个接口,分别与多个终端相连或者与控制设备相连接。通信接口703可以是有线接口,无线接口 或其组合。有线接口例如可以为以太网接口。以太网接口可以是光接口,电接口或其组合。无线接口例如可以为无线局域网(英文:wireless local area network,WLAN)接口,蜂窝网络接口或其组合。通信接口703用于在控制器的控制下接收或者发送数据,如接收MQTT订阅报文或发送MQTT发布报文。
上述存储器702还用于存储程序指令。上述处理器701可以调用上述存储器702存储的程序指令,实现如本申请上述各实施例所示的配置管理方法。
可选的,本发明实施例中的处理器701可以实现图5中的解析模块502、确定模块503、生成模块504、获取模块507、第一封装模块508及第二封装模块509的功能,存储器702可以实现图5中的记录模块506的功能,通信接口703可以实现图5中的接收模块501及发送模块505的功能,本发明实施例不做限定。
基于同一发明构思,本发明实施例中提供的网关解决问题的原理与本发明方法实施例相似,因此该网关的实施以及有益效果可以参见以及有益效果,为简洁描述,在这里不再赘述。
本发明还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,该程序解决问题的实施方式以及有益效果可以参见上述图2及图3的配置管理方法的实施方式以及有益效果,重复之处不再赘述。
本发明实施还提供了一种计算机程序产品,该计算机程序产品包括存储了计算机程序的非易失性计算机可读存储介质,该计算机程序被执行时使计算机执行上述图2及图3对应实施例中的配置管理方法的步骤,该计算机程序产品解决问题的实施方式以及有益效果可以参见上述图2及图3的配置管理方法的实施方式以及有益效果,重复之处不再赘述。
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例方法中的全部或部分流程,是可以通过计算机程序来指令相关的硬件来完成,上述的程序可存储于一计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,可包括如上述各方法的实施例的流程。
Claims (24)
- 一种配置管理方法,应用于控制设备,其特征在于,包括:确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息;获取所述目标逻辑分组的标识,其中,所述目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端;根据网关映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识查询与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关,其中,所述网关映射表记录了多个网关的标识,与所述多个网关中每个网关连接的终端的标识,以及每个终端所属的逻辑分组的标识;根据所述应用消息生成消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文包括所述目标逻辑分组的标识以及所述应用消息;向所述至少一个目标网关发送所述MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文用于指示接收到所述MQTT发布报文的目标网关,向与所述目标网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息。
- 如权利要求1所述的方法,其特征在于,所述方法还包括:接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文;解析所述MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据;若所述标志数据包括订阅标志及网关的标识,则确定所述订阅主题由所述网关所订阅,将所述网关的标识记录到所述网关映射表中;若所述标志数据包括转发标志、终端的标识以及网关的标识,则确定所述订阅主题由所述终端所订阅,并确定所述终端与所述网关连接,将所述终端的标识记录到所述网关映射表中所述网关的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求2所述的方法,其特征在于,所述根据网关映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识查询与所述至少一个目标终端中的每个目标终端连接的网关之前,所述方法还包括:根据与所述多个网关连接的多个终端的订阅主题对所述多个终端进行分组,或者,随机对所述多个终端进行分组,或者,按照所述多个网关对所述多个终端进行分组,得到多个逻辑分组;为每个逻辑分组配置标识,将每个逻辑分组的标识记录到所述网关映射表中所述逻辑分组中每个终端的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求2或3所述的方法,其特征在于,所述确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息,包括:如果检测到与所述目标逻辑分组内所述至少一个目标终端的订阅主题相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向所述目标逻辑分组发布应用消息;或者,如果检测到与所述至少一个目标终端的历史行为数据相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向所述目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
- 如权利要求4所述的方法,其特征在于,所述根据所述应用消息生成消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,包括:根据所述目标逻辑分组的标识生成MQTT格式的可变报头;根据所述应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷;将所述可变报头及所述载荷封装为所述MQTT发布报文。
- 一种配置管理方法,应用于网关,其特征在于,包括:接收控制设备发送的第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文;解析所述第一MQTT发布报文,得到目标逻辑分组的标识及至少一条应用消息;根据分组映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识确定与所述网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据,其中,所述分组映射表记录了与所述网关连接的各终端的标识,各终端所属的逻辑分组的标识,以及各终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据;从所述至少一条应用消息中确定与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息,根据所述目标应用消息生成第二MQTT发布报文,并将携带所述目标应用消息的所述第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端。
- 如权利要求6所述的方法,其特征在于,所述根据分组映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识确定与所述网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据之前,所述方法还包括:接收终端的订阅请求,解析所述订阅请求,获得所述终端的标识及所述终端的订阅主题,并确定所述终端与所述网关连接;将所述终端的标识及所述终端的订阅主题记录到所述分组映射表的一个表项中;接收所述控制设备发送的分组消息,所述分组消息包括所述终端的标识以及所述终端所属的逻辑分组的标识;将所述终端所属的逻辑分组的标识记录到所述分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求7所述的方法,其特征在于,所述方法还包括:获取所述终端的历史行为数据;将所述终端的历史行为数据记录到所述分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求7所述的方法,其特征在于,所述确定所述终端与所述网关连接之后,所述方法还包括:根据所述终端的标识、所述网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头;根据所述终端的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷;根据转发标志生成MQTT格式的固定头;将所述可变头、所述载荷及所述固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向所述控制设备发送所述MQTT订阅报文,所述MQTT订阅报文用于指示所述控制设备确定所述订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与所述网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到所述控制设备的网关映射表中所述网关的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求6所述的方法,其特征在于,所述方法还包括:根据所述网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头;根据所述网关的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷;根据订阅标志生成MQTT格式的固定头;将所述可变头、所述载荷及所述固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文,并向所述控制设备发送所述MQTT订阅报文,所述MQTT订阅报文用于指示所述控制设备确定所述订阅主题由所述网关所订阅,将所述网关的标识记录到所述控制设备的网关映射表中。
- 一种配置管理装置,应用于控制设备,其特征在于,包括:确定模块,用于确定需要向目标逻辑分组发布应用消息;获取模块,用于获取所述目标逻辑分组的标识,其中,所述目标逻辑分组包含至少一个目标终端;查询模块,用于根据网关映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识查询与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端连接的网关,得到至少一个目标网关,其中,所述网关映射表记录了多个网关的标识,与所述多个网关中每个网关连接的终端的标识,以及每个终端所属的逻辑分组的标识;生成模块,用于根据所述应用消息生成消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文包括所述目标逻辑分组的标识以及所述应用消息;发送模块,用于向所述至少一个目标网关发送所述MQTT发布报文,所述MQTT发布报文用于指示接收到所述MQTT发布报文的目标网关,向与所述目标网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的各目标终端发送对应的应用消息。
- 如权利要求11所述的装置,其特征在于,所述配置管理装置还包括:接收模块,用于接收携带订阅主题的MQTT订阅报文;解析模块,用于解析所述MQTT订阅报文,得到标志数据;所述确定模块,还用于若所述标志数据包括订阅标志及网关的标识,则确定所述订阅主题由所述网关所订阅;记录模块,用于将所述网关的标识记录到所述网关映射表中;所述确定模块,还用于若所述标志数据包括转发标志、终端的标识以及网关的标识,则确定所述订阅主题由所述终端所订阅,并确定所述终端与所述网关连接;所述记录模块,还用于将所述终端的标识记录到所述网关映射表中所述网关的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求12所述的装置,其特征在于,所述配置管理装置还包括:分组模块,用于根据与所述多个网关连接的多个终端的订阅主题对所述多个终端进行分组,或者,随机对所述多个终端进行分组,或者,按照所述多个网关对所述多个终端进行分组,得到多个逻辑分组;配置模块,用于为每个逻辑分组配置标识;所述记录模块,还用于将每个逻辑分组的标识记录到所述网关映射表中所述逻辑分组中每个终端的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求12或13所述的装置,其特征在于,所述确定模块,具体用于如果检测到与所述目标逻辑分组内所述至少一个目标终端的订阅主题相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向所述目标逻辑分组发布应用消息;或者,如果检测到与所述至少一个目标终端的历史行为数据相匹配的至少一条应用消息,确定需要向所述目标逻辑分组发布应用消息。
- 如权利要求14所述的装置,其特征在于,所述生成模块,具体用于根据所述目标逻辑分组的标识生成MQTT格式的可变报头;根据所述应用消息生成MQTT格式的载荷;将所述可变报头及所述载荷封装为所述MQTT发布报文。
- 一种配置管理装置,应用于网关,其特征在于,包括:接收模块,用于接收控制设备发送的第一消息队列遥测传输MQTT发布报文;解析模块,用于解析所述第一MQTT发布报文,得到目标逻辑分组的标识及至少一条应用消息;确定模块,用于根据分组映射表及所述目标逻辑分组的标识确定与所述网关连接的属于所述目标逻辑分组的至少一个目标终端,以及所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据,其中,所述分组映射表记录了与所述网关连接的各终端的标识,各终端所属的逻辑分组的标识,以及各终端的订阅主题或历史行为数据;所述确定模块,还用于从所述至少一条应用消息中确定与所述至少一个目标终端中每个目标终端的历史行为数据或订阅主题匹配的目标应用消息;生成模块,用于根据所述目标应用消息生成第二MQTT发布报文;发送模块,用于将携带所述目标应用消息的所述第二MQTT发布报文发送至该目标终端。
- 如权利要求16所述的装置,其特征在于,所述接收模块,还用于接收终端的订阅请求;所述解析模块,还用于解析所述订阅请求,获得所述终端的标识及所述终端的订阅主题;所述确定模块,还用于确定所述终端与所述网关连接;所述配置管理装置还包括:记录模块,用于将所述终端的标识及所述终端的订阅主题记录到所述分组映射表的一个表项中;所述接收模块,还用于接收所述控制设备发送的分组消息,所述分组消息包括所述终端的标识以及所述终端所属的逻辑分组的标识;所述记录模块,还用于将所述终端所属的逻辑分组的标识记录到所述分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求17所述的装置,其特征在于,所述配置管理装置还包括:获取模块,用于获取所述终端的历史行为数据;所述记录模块,还用于将所述终端的历史行为数据记录到所述分组映射表中所述终端的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求17所述的装置,其特征在于,所述生成模块,还用于根据所述终端的标识、所述网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头;根据所述终端的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷;根据转发标志生成MQTT格式的固定头;所述配置管理装置还包括:第一封装模块,用于将所述可变头、所述载荷及所述固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文;所述发送模块,还用于向所述控制设备发送所述MQTT订阅报文,所述MQTT订阅报文用于指示所述控制设备确定所述订阅主题由该终端所订阅,并确定该终端与所述网关连接,将该终端的标识记录到所述控制设备的网关映射表中所述网关的标识对应的表项中。
- 如权利要求16所述的装置,其特征在于,所述生成模块,还用于根据所述网关的标识生成MQTT格式的可变头;根据所述网关的订阅主题生成MQTT格式的载荷;根据订阅标志生成MQTT格式的固定头;所述配置管理装置还包括:第二封装模块,用于将所述可变头、所述载荷及所述固定头封装成MQTT订阅报文;所述发送模块,还用于向所述控制设备发送所述MQTT订阅报文,所述MQTT订阅报文用于指示所述控制设备确定所述订阅主题由所述网关所订阅,将所述网关的标识记录到所述控制设备的网关映射表。
- 一种控制设备,所述控制设备包括至少一个处理器、存储器及存储在所述存储器上并可被所述至少一个处理器执行的指令,其特征在于,所述至少一个处理器执行所述指令,以实现权利要求1至5中任一项所述的配置管理方法的步骤。
- 一种网关,所述网关包括至少一个处理器、存储器及存储在所述存储器上并可 被所述至少一个处理器执行的指令,其特征在于,所述至少一个处理器执行所述指令,以实现权利要求6至10中任一项所述的配置管理方法的步骤。
- 一种计算机可读存储介质,其特征在于,所述计算机存储介质存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序包括程序指令,所述程序指令当被处理器执行时使所述处理器执行如权利要求1至10中任一项所述的配置管理方法的步骤。
- 一种计算机程序产品,其特征在于,所述计算机程序产品包括存储了计算机程序的非易失性计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机程序被执行时使计算机实现权利要求1至10中任一项所述的配置管理方法的步骤。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP18843153.0A EP3654192B1 (en) | 2017-08-11 | 2018-07-13 | Configuration management method, apparatus and device |
| US16/786,598 US11265218B2 (en) | 2017-08-11 | 2020-02-10 | Configuration management method and apparatus, and device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201710684907.8 | 2017-08-11 | ||
| CN201710684907.8A CN109391500B (zh) | 2017-08-11 | 2017-08-11 | 一种配置管理方法、装置及设备 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/786,598 Continuation US11265218B2 (en) | 2017-08-11 | 2020-02-10 | Configuration management method and apparatus, and device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019029320A1 true WO2019029320A1 (zh) | 2019-02-14 |
Family
ID=65270825
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2018/095631 WO2019029320A1 (zh) | 2017-08-11 | 2018-07-13 | 一种配置管理方法、装置及设备 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11265218B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP3654192B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN109391500B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2019029320A1 (zh) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113127217A (zh) * | 2019-12-30 | 2021-07-16 | 中移(成都)信息通信科技有限公司 | 数据发布方法、装置、设备及存储介质 |
| CN114095502A (zh) * | 2021-10-08 | 2022-02-25 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | 一种业务处理方法、系统、装置及介质 |
| CN114157692A (zh) * | 2021-11-30 | 2022-03-08 | 广东电网有限责任公司广州供电局 | 多源多态海量异构终端泛接入互联协议转换方法及系统 |
| CN115580534A (zh) * | 2022-11-24 | 2023-01-06 | 锱云(上海)物联网科技有限公司 | 一种数据采集发送方法、系统、设备及网关 |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10853391B2 (en) * | 2018-09-20 | 2020-12-01 | Dell Products L.P. | Device identification and control in a computing environment |
| CN110266801B (zh) * | 2019-06-24 | 2021-10-29 | 宁波中车时代传感技术有限公司 | 一种基于订阅发布模型的站台门监控系统及方法 |
| CN112202700B (zh) * | 2019-07-08 | 2023-04-07 | 中国移动通信集团浙江有限公司 | 业务评价方法、装置、计算设备及计算机存储介质 |
| CN110401592B (zh) * | 2019-07-30 | 2022-03-04 | 三体云智能科技有限公司 | 一种消息通道中数据流转的方法及设备 |
| CN112671697B (zh) * | 2019-10-16 | 2022-03-18 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | 综合监控系统的数据处理方法、装置和系统 |
| CN110855774B (zh) * | 2019-11-11 | 2021-08-10 | 卡乐电子(苏州)有限责任公司 | 基于mqtt协议的自动配置的物联网系统 |
| CN111212135A (zh) * | 2019-12-31 | 2020-05-29 | 北京金山云网络技术有限公司 | 消息订阅方法、装置、系统、电子设备及存储介质 |
| US20230119073A1 (en) * | 2020-02-25 | 2023-04-20 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Communication apparatus, receiving side communication apparatus, communication method and program |
| CN112104720B (zh) * | 2020-09-03 | 2024-04-26 | 国电南瑞科技股份有限公司 | 适用于边缘物联终端的MQTT双Broker数据交互方法及系统 |
| CN112350850A (zh) * | 2020-09-29 | 2021-02-09 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | 日志文件的上报方法、装置、存储介质及电子设备 |
| CN112351080B (zh) * | 2020-10-23 | 2023-05-02 | 许继集团有限公司 | 一种配电系统物联终端及其与外接装置通讯方法 |
| CN112995321A (zh) * | 2021-03-04 | 2021-06-18 | 华录智达科技股份有限公司 | 基于mqtt协议远程即时更新客户端的方法 |
| US11563827B1 (en) * | 2021-07-12 | 2023-01-24 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Method and system for network performance optimization service |
| CN114095546B (zh) * | 2021-10-27 | 2024-03-01 | 许昌许继软件技术有限公司 | 一种基于mqtt协议的报文监视方法及装置 |
| CN114285699B (zh) * | 2021-12-20 | 2023-06-06 | 徐工汉云技术股份有限公司 | 一种实现终端在分布式网关session唯一的方法及装置 |
| CN114124649B (zh) * | 2022-01-26 | 2022-05-06 | 山东融为信息科技有限公司 | 基于mqtt和报文约定的网关通信方法、系统及网关设备 |
| CN115065595B (zh) * | 2022-08-17 | 2022-12-02 | 湖南云畅网络科技有限公司 | 一种自动化发布部署方法 |
| CN117135011B (zh) * | 2023-10-27 | 2024-02-09 | 深圳市天思智慧科技有限公司 | 让网关适配多个基于mqtt通讯的云平台的方法及网关系统 |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080133541A1 (en) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-05 | International Business Machines Corporation | Flexible Topic Identification in a Publish/Subscribe System |
| CN102640137A (zh) * | 2009-10-30 | 2012-08-15 | 弗里塞恩公司 | 分级发布和订阅系统 |
| CN104836723A (zh) * | 2015-03-31 | 2015-08-12 | 青岛海尔智能家电科技有限公司 | 基于mqtt主题订阅机制的通信方法以及接入网关 |
Family Cites Families (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7406537B2 (en) * | 2002-11-26 | 2008-07-29 | Progress Software Corporation | Dynamic subscription and message routing on a topic between publishing nodes and subscribing nodes |
| GB2417160B (en) * | 2003-02-06 | 2006-12-20 | Progress Software Corp | Dynamic subscription and message routing on a topic between a publishig node and subscribing nodes |
| JP6067732B2 (ja) * | 2011-11-18 | 2017-01-25 | トムソン ライセンシングThomson Licensing | エンドユーザデバイス、およびそれぞれのエンドユーザデバイスの遠隔管理のためのパブリッシュ/サブスクライブブローカを備えるシステム |
| US9882950B2 (en) * | 2012-06-13 | 2018-01-30 | All Purpose Networks LLC | Methods and systems of an all purpose broadband network |
| US10257287B2 (en) * | 2013-08-28 | 2019-04-09 | Physio-Control, Inc. | Real-time data distribution system for patient monitoring devices, cardiac defibrillators and associated information delivery systems |
| CN105531711B (zh) * | 2013-09-28 | 2018-10-02 | 迈克菲股份有限公司 | 数据交换层上的上下文感知网络 |
| US10171594B2 (en) * | 2013-09-28 | 2019-01-01 | Mcafee, Llc | Service-oriented architecture |
| CN105493047A (zh) * | 2013-09-28 | 2016-04-13 | 迈克菲股份有限公司 | 在数据交换层上合并多个系统树 |
| US10148695B2 (en) * | 2013-09-28 | 2018-12-04 | Mcafee, Llc | Real-time policy distribution |
| CN105659554A (zh) * | 2013-09-29 | 2016-06-08 | 迈克菲公司 | 基于普遍度的信誉 |
| US10356085B2 (en) * | 2015-05-01 | 2019-07-16 | Graco Minnesota Inc. | Remote pump monitoring and control |
| US10630731B2 (en) * | 2015-10-08 | 2020-04-21 | Verizon Patent And Licensing Inc. | Establishing media sessions via MQTT and SIP |
| TWI599260B (zh) * | 2016-04-13 | 2017-09-11 | 正文科技股份有限公司 | 具區域通訊之無線網路系統及其通訊方法 |
| US10503581B2 (en) * | 2016-08-25 | 2019-12-10 | Intel Corporation | Profiling and diagnostics for internet of things |
| US10568524B2 (en) * | 2016-08-25 | 2020-02-25 | Intel Corporation | Compliance checker for service agreement |
| US11463526B2 (en) * | 2016-08-25 | 2022-10-04 | Intel Corporation | Future proofing and prototyping an internet of things network |
| US10623240B2 (en) * | 2016-08-25 | 2020-04-14 | Intel Corporation | IoT solution sizing |
| US10645181B2 (en) * | 2016-12-12 | 2020-05-05 | Sap Se | Meta broker for publish-subscribe-based messaging |
| US10432535B2 (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2019-10-01 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Performing a specific action on a network packet identified as a message queuing telemetry transport (MQTT) packet |
| US10708360B2 (en) * | 2017-03-14 | 2020-07-07 | Infiswift Technologies, Inc. | Method for transport agnostic communication between internet of things client and broker |
| US10756983B2 (en) * | 2017-12-08 | 2020-08-25 | Apstra, Inc. | Intent-based analytics |
| EP3662370B1 (en) * | 2018-01-08 | 2023-12-27 | All Purpose Networks, Inc. | Internet of things system with efficient and secure communications network |
| DE102018216111A1 (de) * | 2018-09-21 | 2020-03-26 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Übertragungsverfahren |
-
2017
- 2017-08-11 CN CN201710684907.8A patent/CN109391500B/zh active Active
-
2018
- 2018-07-13 WO PCT/CN2018/095631 patent/WO2019029320A1/zh unknown
- 2018-07-13 EP EP18843153.0A patent/EP3654192B1/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-02-10 US US16/786,598 patent/US11265218B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080133541A1 (en) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-05 | International Business Machines Corporation | Flexible Topic Identification in a Publish/Subscribe System |
| CN102640137A (zh) * | 2009-10-30 | 2012-08-15 | 弗里塞恩公司 | 分级发布和订阅系统 |
| CN104836723A (zh) * | 2015-03-31 | 2015-08-12 | 青岛海尔智能家电科技有限公司 | 基于mqtt主题订阅机制的通信方法以及接入网关 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP3654192A4 |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113127217A (zh) * | 2019-12-30 | 2021-07-16 | 中移(成都)信息通信科技有限公司 | 数据发布方法、装置、设备及存储介质 |
| CN114095502A (zh) * | 2021-10-08 | 2022-02-25 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | 一种业务处理方法、系统、装置及介质 |
| CN114095502B (zh) * | 2021-10-08 | 2023-11-03 | 浙江吉利控股集团有限公司 | 一种业务处理方法、系统、装置及介质 |
| CN114157692A (zh) * | 2021-11-30 | 2022-03-08 | 广东电网有限责任公司广州供电局 | 多源多态海量异构终端泛接入互联协议转换方法及系统 |
| CN115580534A (zh) * | 2022-11-24 | 2023-01-06 | 锱云(上海)物联网科技有限公司 | 一种数据采集发送方法、系统、设备及网关 |
| CN115580534B (zh) * | 2022-11-24 | 2023-02-21 | 锱云(上海)物联网科技有限公司 | 一种数据采集发送方法、系统、设备及网关 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3654192A4 (en) | 2020-05-20 |
| EP3654192B1 (en) | 2023-11-22 |
| EP3654192A1 (en) | 2020-05-20 |
| US11265218B2 (en) | 2022-03-01 |
| US20200177461A1 (en) | 2020-06-04 |
| CN109391500B (zh) | 2021-08-31 |
| CN109391500A (zh) | 2019-02-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2019029320A1 (zh) | 一种配置管理方法、装置及设备 | |
| Chen et al. | Copss: An efficient content oriented publish/subscribe system | |
| WO2019141111A1 (zh) | 通信方法和通信装置 | |
| US10708376B2 (en) | Message bus service directory | |
| US10313858B2 (en) | Service layer interworking using MQTT protocol | |
| KR101806257B1 (ko) | 가입 통지를 구현하기 위한 방법 및 장치 | |
| CN102790776B (zh) | 心跳连接归一处理方法、终端、服务器及通信系统 | |
| WO2017054576A1 (zh) | 单播隧道建立方法、装置和系统 | |
| CN109451804B (zh) | cNAP以及由cNAP、sNAP执行的方法 | |
| WO2014180407A1 (zh) | 推送方法及装置 | |
| CN106921578B (zh) | 一种转发表项的生成方法和装置 | |
| Batalla et al. | ID-based service-oriented communications for unified access to IoT | |
| CN105637819A (zh) | 用于传输广播数据的方法和系统 | |
| Elmangoush et al. | Application-derived communication protocol selection in M2M platforms for smart cities | |
| WO2021169291A1 (zh) | 发布路由的方法、网元、系统及设备 | |
| US10225367B2 (en) | Method and device for generating forwarding information | |
| CN108512669A (zh) | 用于传输广播数据的方法和系统 | |
| CN107347100B (zh) | 一种内容分发网络的透明代理转发方法 | |
| US9015309B2 (en) | Networked probe system | |
| Sharma et al. | Networking models and protocols for/on edge computing | |
| Hmissi et al. | A review of application protocol enhancements for internet of things | |
| Hmissi et al. | A Survey on Application Layer Protocols for IoT Networks | |
| US8402474B2 (en) | Message sending method, message sending device and message transmission system | |
| Ma et al. | Design of p2p application layer protocol | |
| Tseng et al. | SPaaS-NFV: Enabling Stream-Processing-as-a-Service for NFV |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18843153 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2018843153 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20200212 |