WO2019003631A1 - Object detection device for vehicle and method for determining horizontal axial deviation of object detection device for vehicle - Google Patents
Object detection device for vehicle and method for determining horizontal axial deviation of object detection device for vehicle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2019003631A1 WO2019003631A1 PCT/JP2018/017403 JP2018017403W WO2019003631A1 WO 2019003631 A1 WO2019003631 A1 WO 2019003631A1 JP 2018017403 W JP2018017403 W JP 2018017403W WO 2019003631 A1 WO2019003631 A1 WO 2019003631A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- object detection
- detectors
- amount
- millimeter wave
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/87—Combinations of radar systems, e.g. primary radar and secondary radar
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S13/93—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S7/00—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00
- G01S7/02—Details of systems according to groups G01S13/00, G01S15/00, G01S17/00 of systems according to group G01S13/00
- G01S7/40—Means for monitoring or calibrating
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to an object detection apparatus for a vehicle and a method for determining a horizontal axis deviation in an object detection apparatus for a vehicle.
- a detector for detecting an object around the vehicle for example, a camera or a radar, is mounted on the vehicle in order to realize braking assistance and steering assistance in the vehicle.
- the radar's axis offsets the radar's axis in the horizontal direction based on the angle difference between the leading vehicle and the vehicle obtained by the camera and the angle obtained by the radar.
- Techniques for determining the amount of misalignment, and techniques for estimating the amount of radar misalignment in the horizontal direction using a target with a relative velocity of 0 km / h, for example, an angle when a wall is detected for example, JP-A-2016-65759, JP-A-2014-153256).
- a first aspect provides an object detection device for a vehicle.
- the object detection device for a vehicle according to the first aspect is a plurality of detectors for detecting a plurality of detection points representing an object using a reflected wave, and a part of the detection points overlap.
- a plurality of detectors disposed in a vehicle and the detection points input from two of the plurality of detectors relative offset amounts of the two detectors in the horizontal direction are calculated.
- a detector identification unit that identifies a detector whose horizontal axis is offset using the calculated and calculated relative axis offset amount.
- the time shift based on the determination of the axis shift of the detector in the horizontal direction is shortened, and the axis shift is determined using only the detector that detects the reflected wave. be able to.
- a second aspect provides a method for determining a horizontal axis deviation in an object detection device for a vehicle.
- the method for determining an axis deviation in the horizontal direction according to the second aspect is a plurality of detectors for detecting a plurality of detection points representing an object using a reflected wave, in which some of the detection points overlap.
- the relative offset amount between the two detectors in the horizontal direction is calculated using the detection points input from the two detectors among the plurality of detectors arranged in the vehicle, and the calculated relative Identifying a detector whose horizontal axis is offset using a typical amount of offset.
- the present disclosure can also be realized as a horizontal axis offset determination program in an object detection device for a vehicle or a computer readable recording medium for recording the program.
- Explanatory drawing which shows typically the detection range of several detectors mounted in the vehicle in 1st Embodiment, An explanatory view showing an example of relative angle difference of a plurality of detectors carried in vehicles in a 1st embodiment, An explanatory view schematically showing superposition of a detection point group of the first millimeter wave radar and a detection point group of the second millimeter wave radar in the first embodiment.
- a flowchart showing a processing flow for correcting an axis deviation of a specified detector and a detector having a horizontal axis deviation which is executed by the object detection device according to the second embodiment.
- the flowchart which shows the processing flow which specifies the detector which has carried out axis offset in the horizontal direction performed by the object detection device concerning a 3rd embodiment.
- An object detection device for a vehicle and a method for determining a horizontal axis deviation in a vehicle in the object detection device according to the present disclosure will be described below based on some embodiments.
- the object detection device 10 is mounted on a vehicle 500 and used.
- Vehicle 500 is not limited to four or more wheels, and may be a two or three wheel vehicle.
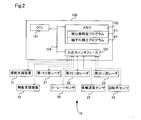
- the object detection device 10 includes a control device 100, a first millimeter wave radar 21, a second millimeter wave radar 22, a third millimeter wave radar 23, a rotation angle sensor 24, a wheel speed sensor 25, and a yaw rate sensor 26.
- the vehicle 500 includes a steering assist device 31, a braking assist device 32, a steering device 42, wheels 501, a braking device 502, a braking line 503, a steering wheel 504, a windshield 510, and a front bumper 520.
- the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are detection units that detect a plurality of detection points representing an object.
- the vehicle may further include a monocular camera or a stereo camera as a detection unit.
- the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are sensors as detectors that emit millimeter waves and detect the position and distance of an object by receiving a reflected wave reflected by the object.
- Each of the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 has, for example, an axis defining an emission direction of the millimeter wave at the center of the front view, that is, an emission axis, and a direction desired for detection and the emission axis Are matched and placed in the vehicle 500.
- the first millimeter wave radar 21 is disposed at the center of the front bumper 520
- the second millimeter wave radar 22 is disposed on the left side of the front bumper 520 in the traveling direction of the vehicle 500.
- the radar 23 is disposed on the right side of the front bumper 520 in the traveling direction of the vehicle 500.
- the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are arranged such that the detection ranges overlap each other.
- Each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 may be provided with an actuator capable of horizontally rotating the radar, for example, an electric motor.
- the detection signals output from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are, for example, signals consisting of point trains indicating a plurality of representative positions of the object for which the reception wave has been processed in the processing circuit included in each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23. It may be a signal indicating an unprocessed received wave.
- the detector may be any detector that detects an object by emitting an electromagnetic wave and detecting a reflected wave reflected by the object.
- a lidar LIDAR: laser radar
- an ultrasonic sensor May be used.
- Each wheel 501 of the vehicle 500 is provided with a braking device 502.
- Each braking device 502 realizes braking of each wheel 501 by the brake fluid pressure supplied via a braking line 503 including a brake fluid line and a brake piston that generates a brake fluid pressure in accordance with a driver's brake pedal operation.
- a brake assisting device 32 including an actuator for generating a brake fluid pressure is disposed on the brake line 503, and fluid pressure control can be performed independently of the brake pedal operation, whereby each millimeter wave radar 21 to 23 is provided.
- the braking assistance is realized according to the detection result by the.
- a braking control actuator which has already been introduced as a skid prevention device or an antilock braking system may be used as an actuator of the braking assistance device 32.
- the steering wheel 504 is connected to the front wheel 501 via a steering device 42 including a steering rod and a steering mechanism.
- a steering assist device 31 capable of driving the steering device 42 by an actuator, for example, an electric motor, is disposed in the steering device 42.
- the steering assist device 31 can perform drive control of the steering device 42 independently of the operation of the steering wheel 504, whereby steering assist according to the detection result of each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 is realized.
- the steering assist device 31 is also drive-controlled to reduce the steering force by the steering wheel 504.
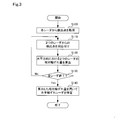
- the control device 100 includes a central processing unit (CPU) 101, a memory 102, an input / output interface 103, and a bus 104.
- the CPU 101, the memory 102, and the input / output interface 103 are bi-directionally connected via a bus.
- the memory 102 is a non-volatile detector specification program P1 for identifying a millimeter wave radar causing an axis offset in the horizontal direction and an axis offset correction program P2 for correcting an axis offset in the horizontal direction of the identified millimeter wave radar. It includes a memory that is stored read only, such as a ROM, and a memory that can be read and written by the CPU 101, such as a RAM.
- the CPU 101 functions as a detector identification unit by expanding and executing the detector identification program P1 stored in the memory 102 in a readable / writable memory, and similarly as a correction unit by executing the axis deviation correction program P2. Function.
- the correction program P2 may not be included in the first embodiment.
- the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, the steering angle sensor 24, the wheel speed sensor 25, the yaw rate sensor 26, the steering assist device 31, and the brake assist device 32 are connected to the input / output interface 103 via signal lines, respectively. It is connected. Detection information is input from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, the steering angle sensor 24, the wheel speed sensor 25, and the yaw rate sensor 26, and a drive control signal is output to the steering assist device 31 and the brake assist device 32. .
- a drive control signal can be transmitted from the input / output interface 103 through the signal line.
- the steering angle sensor 24 is a torque sensor that detects a twist amount generated on the stearin rod by steering of the steering wheel 504, that is, a steering torque, and detects a steering angle of the steering wheel 504.
- the steering angle sensor 24 is provided on a steering rod connecting the steering wheel 504 and the steering mechanism.
- the detection signal output from the steering angle sensor 24 is a voltage value proportional to the amount of twist.
- the wheel speed sensor 25 is a sensor that detects the rotational speed of the wheel 501, and is provided to each wheel 501.
- the detection signal output from the wheel speed sensor 25 is a voltage value proportional to the wheel speed or a pulse wave indicating an interval according to the wheel speed.
- the yaw rate sensor 26 is a sensor that detects the rotational angular velocity of the vehicle 500.
- the yaw rate sensor 26 is disposed, for example, at a central portion of the vehicle.
- the detection signal output from the yaw rate sensor 26 is a voltage value proportional to the rotation direction and the angular velocity.
- the detector identification process executed by the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 5.
- the processing routine shown in FIG. 3 is executed, for example, after the start of the control system of the vehicle or waiting for a request input from the driver via the execution switch by the CPU 101 executing the detector identification program P1. .
- the control system of the vehicle When the control system of the vehicle is triggered by the start of the control system, the control system may be repeatedly executed until the control system ends after the control system is started, or may be executed once every time the control system is started.
- the present invention may be executed every predetermined number of starting times or at a predetermined traveling time interval.
- the CPU 101 acquires detection points from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 (step S100).
- the detection points to be acquired are a detection point group composed of a plurality of detection points, for example, 10 to 1000 points.
- the detection signals input from the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 to the control device 100 include information on a plurality of detection points representing the detection target, for example, (x, y, z) coordinate information as position information, and the vehicle Relative velocity information of the detection point, signal strength or reception power, and the like.
- the detection ranges A1, A2 and A3 of the first, second and third millimeter wave radars 21, 22 and 23 are at least partially, as shown in FIG. 4, a first overlap area DA1 and a second overlap area DA2.
- the millimeter wave radars other than the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, that is, the millimeter wave radar 20 s disposed on the side of the vehicle 500 and the millimeter disposed on the rear of the vehicle 500 Wave radar 20b is illustrated for reference.
- the detection ranges of the other millimeter wave radars 20b and 20s also overlap. That is, in the present embodiment, each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, 20b, and 20s is disposed with respect to the vehicle 500 so that its own detection range and the detection range of the adjacent millimeter wave radar overlap.
- the CPU 101 associates detection points obtained from two millimeter wave radars whose detection ranges overlap with each other (step S110).
- the CPU 101 first executes, for example, association of a plurality of detection points obtained respectively from the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the second millimeter wave radar 22.
- detection point groups obtained from the respective millimeter wave radars 21 and 22 in the first overlapping area DA1 shown in FIG. 4 are associated with each other.
- the association of each detection point constituting the detection point group is performed, for example, using a known ICP (Iterative Closest Point) method.
- ICP Intelligent Closest Point
- each detection point of the second detection point group obtained by the second millimeter wave radar 22 The association is performed by searching for the closest point from. Incidentally, the correspondence between the detection points constituting the detection point group is omitted even when the detection points constituting the detection point groups are close to each other, that is, when the nearest points can be easily determined. good.
- the CPU 101 calculates the amount of relative axis deviation of the two millimeter wave radars in the horizontal direction using each pair of detection points that have been associated (step S120).
- the ICP method by repeating the minimization of the distance between each detection point that has been matched, that is, the distance such that each detection point of the second detection point group overlaps each detection point of the first detection point group
- the three-dimensional, ie the amount of deviation in the XYZ axis direction between the first detection point group and the second detection point group is calculated.
- the shift amount in the X axis direction is the relative horizontal between the first detection point group and the second detection point group It is calculated as the amount of axial deviation in the direction.
- the detection accuracy in the vehicle height direction may not be used because the azimuth accuracy in the Y-axis direction is often low.
- the amount of rotation (deg) in the X-axis direction necessary to overlap each detection point pair of the first detection point group and the second detection point group is calculated as the amount of axial deviation.
- the amount of deviation in the XYZ axial directions may be calculated by repeating the minimization of the distance such that each detection point of the first detection point group overlaps each detection point of the second detection point group.
- the relative horizontal axis offset between the first detection point group and the second detection point group, that is, the shift amount in the X-axis direction can be calculated.
- step S130 determines whether or not the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount has been completed for the combination of all adjacent millimeter wave radars (step S130), and if not completed (step S130: No), step 110 And step S120 is repeatedly executed.
- steps S110 and S120 are performed until the combination of the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the second millimeter wave radar 22, and the combination of the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the third millimeter wave radar 23 are performed. Is repeatedly executed.
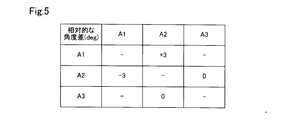
- the amount of horizontal axis offset between the adjacent millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 is calculated, for example, as shown in FIG. 5 and FIG.
- “ ⁇ ” means a counterclockwise direction and “+” means a horizontal angle in the clockwise direction, with reference to the horizontal axis not causing the horizontal axis deviation.
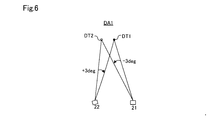
- superposition of the detection point group DT1 of the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the detection point group DT2 of the second millimeter wave radar 22 in the overlapping area DA1 is schematically shown. As shown in FIG.
- the amount of horizontal axis deviation of the second millimeter wave radar 22 (A2) with respect to the first millimeter wave radar 21 (A1) that is, the detection point group DT1 of the first millimeter wave radar 21
- the amount of rotation to match the detection point group DT2 of the millimeter wave radar 22 of No. 2 is -3 deg
- the horizontal axis deviation of the first millimeter wave radar 21 (A1) with respect to the second millimeter wave radar 22 (A2) That is, the amount of rotation for causing the detection point group DT2 of the second millimeter wave radar 22 to coincide with the detection point group DT1 of the first millimeter wave radar 21 is 3 degrees.
- the horizontal axis deviation of the third millimeter wave radar 23 (A3) with respect to the first millimeter wave radar 21 (A1) is 0 degree, and the first millimeter wave radar 21 (with the third millimeter wave radar 23 (A3)
- the amount of horizontal axis deviation of A1) is 0 deg.
- the CPU 101 determines that the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount has been completed for all combinations of adjacent millimeter wave radars (Yes at step S130), the horizontal axis is calculated using the calculated relative axis shift amount in the horizontal axis direction.
- the deviation radar is specified (step S140), and this processing routine is ended.
- the CPU 101 is horizontal based on a combination of the relative axis deviation between the first and second millimeter wave radars 21 and 22 and the relative axis deviation between the first and third millimeter wave radars 21 and 23. Identify the millimeter wave radar that is causing the axis shift.
- the CPU 101 determines It is possible to determine that the third millimeter wave radars 21 and 23 do not cause the horizontal axis deviation.
- a relative angle difference of 3 degrees is generated between the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the second millimeter wave radar 22, and either the first or second millimeter wave radars 21 and 22 There is a horizontal offset.
- the CPU 101 causes the second millimeter wave radar 22 to generate a horizontal axis deviation.
- the second millimeter wave radar 22 can be identified as a horizontal axis offset radar.
- the first millimeter-wave radar 21 to the third millimeter-wave radar 23 are used to determine the axis offset of the radar in the horizontal direction, and the horizontal axis Deviation radar can be identified. Therefore, it is possible to determine the axis shift using the shortening of time based on the determination of the axis shift of the radar in the horizontal direction and using only the radar. That is, when using both a front camera and a radar, image processing for detecting a preceding vehicle is performed using a captured image, and then an axial deviation is determined in combination with the detection result of the radar.
- the object detection device 10 only the millimeter wave radar is used without using the front camera, so it does not require time for detecting a leading vehicle using a captured image. Further, since the horizontal axis offset of the radar can be determined without being affected by the horizontal axis offset of the front camera, the determination accuracy can be improved. Furthermore, when using a target with a relative radar velocity of 0, the presence of a target with a relative velocity of 0 is a condition, and if the condition is not met, it is not possible to determine the horizontal axis offset of the radar. . According to the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment, it is possible to use a detection point whose relative velocity is not 0, and it is possible to determine the off-axis of the radar under more conditions. . As a result, the determination time can be shortened.
- the horizontal axis shift amount is calculated using a combination of all adjacent millimeter wave radars
- a millimeter wave radar that can be used without using a combination of all adjacent millimeter wave radars.
- the horizontal axis shift amount may be calculated using a combination of the above. For example, the case where four millimeter wave radars are arranged at the front center, the left side center and the rear center of the vehicle 500 so that the detection ranges overlap between adjacent millimeter wave radars will be described.
- the horizontal axis of the combination of the rear center millimeter wave radar and the left side center center millimeter wave, and the rear center center millimeter wave radar and the right side surface center millimeter wave radar The deviation can not be calculated.
- the horizontal axis offset is obtained for the combination of the millimeter wave radar at the front center and the millimeter wave radar at the center at the left side, and the millimeter wave radar at the center at the front center and the millimeter wave
- the amount may be obtained, and the horizontal axis offset radar may be specified using the calculated relative axis offset amount in the horizontal axis direction.
- the horizontal axis deviation radar can be used without waiting for the input of the detection point from the millimeter wave radar. It is possible to identify Therefore, it is possible to suppress or prevent the delay of the time required to specify the horizontal axis offset radar.
- Second embodiment In the first embodiment, only the millimeter wave radar in which the horizontal axis deviation has occurred is identified. However, in the second embodiment, the first correction is made in that the calculated horizontal axis deviation is further corrected. It differs from the embodiment of In addition, since the object detection apparatus according to the second embodiment has the same configuration as the object detection apparatus 10 according to the first embodiment, the respective components are denoted using the reference numerals used in the first embodiment. Description of the configuration is omitted.
- the detector identification process and the axis offset correction process executed by the object detection device 10 according to the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 7.
- the processing routine shown in FIG. 7 is executed at the timing described in the first embodiment as the CPU 101 executes the detector identification program P1 and the axis deviation correction program P2.
- the same reference numerals are given to the processing steps described in the first embodiment, and the description thereof is omitted.
- the CPU 101 determines the correction amount for the horizontal axis deviation radar (step S150).
- the CPU 101 determines the correction amount so as to eliminate or reduce the relative axis deviation amount of the horizontal axis deviation radar identified in step S140. For example, in the example of FIG. 5, since the second millimeter wave radar 22 is identified as a radar causing a horizontal axis shift, a rotation angle of +3 deg or +3 deg to 0 deg is determined as the correction amount.
- the CPU 101 executes the correction (step S160), and ends the processing routine.
- the execution of the correction by the CPU 101 has, for example, the following two modes.
- the CPU 101 performs software conversion processing by rotating the detection point obtained from the second millimeter wave radar 22, that is, (x, y, z) coordinates horizontally by +3 deg. Correction can be performed.
- the CPU 101 transmits a drive control signal to rotate the detection unit of the second millimeter wave radar 22 or the second millimeter wave radar 22 by +3 degrees with respect to the actuator included in the second millimeter wave radar 22. By doing this, the horizontal axis deviation of the second millimeter wave radar 22 can be corrected in hardware.
- the execution of the horizontal axis offset correction may be performed, for example, when the calculated absolute value of the horizontal axis offset amount is a predetermined first correction reference value, for example, 3 ° or more.
- a predetermined first correction reference value for example, 3 ° or more.
- the millimeter wave radar in which the horizontal axis shift is specified can be corrected by software or hardware. It is possible to suppress or prevent the decrease in detection accuracy. As a result, it is possible to suppress or prevent the accuracy reduction of the steering assistance by the steering assistance device 31 using the detection result from the millimeter wave radar and the braking assistance by the braking assistance device 32.
- the vehicle 500 is provided with second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 arranged so that detection ranges overlap. That is, in the third embodiment, the process of specifying the horizontal axis offset radar in the case where two millimeter wave radars having overlapping detection ranges are provided.
- the object detection device according to the third embodiment has the same configuration as the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment, from the point that the first millimeter wave radar 21 is not provided. The description of each configuration will be omitted using the reference numerals used in the first embodiment.
- the detector identification process executed by the object detection device 10 according to the third embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the processing routine shown in FIG. 8 is executed at the timing described in the first embodiment as the CPU 101 executes the detector identification program P1.
- the CPU 101 acquires detection points from each of the millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 (step S200).
- the detection points to be acquired are a detection point group composed of a plurality of detection points, for example, 10 to 1000 points.
- the detection signals input from the millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 to the control device 100 include information on the detection points described above.
- the detection ranges of the second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 at least partially overlap.
- the CPU 101 associates detection points obtained from two millimeter wave radars whose detection ranges overlap with each other (step S210). The association of detection points is performed by the method described in the first embodiment.
- the CPU 101 calculates the amount of relative axis deviation of the two millimeter wave radars in the horizontal direction using each pair of detection points that have been associated (step S220). The calculation of the relative axis deviation amount is performed by the method described in the first embodiment.
- the CPU 101 calculates the absolute axis deviation of each of the millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 in the horizontal direction (step S230). That is, without using the detection results from the two adjacent millimeter wave radars whose detection ranges overlap with each other, using the detection results obtained by the respective millimeter wave radars 22 and 23, the axial deviation amounts of the respective millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 alone Is calculated.
- the direction of the zero speed detection point is calculated as the detection point at which the relative speed to be present at the 90 ° azimuth with respect to the longitudinal direction of the vehicle 500 is zero.
- the horizontal direction of the millimeter wave radar that is, the amount of axis deviation can be determined. More specifically, the azimuth (angle) of the zero velocity detection point with respect to the emission axis of the millimeter wave radar, that is, the azimuth (90 °) perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the vehicle 500, ie, the vehicle coordinate
- the misorientation with the system is calculated as the amount of axis deviation.
- the lateral distance of the stationary object relative to the host vehicle is determined using the distance and orientation angle of the stationary object detected by the millimeter wave radar, and the trajectory of the stationary object is calculated using the determined lateral distance.
- the amount of horizontal axis deviation may be calculated from the angle difference between the determined trajectory of the stationary object and the line segment of the azimuth angle 0.
- the azimuth angle 0 is an azimuth angle parallel to the traveling direction of the vehicle 500.
- the CPU 101 specifies the horizontal axis offset radar using the relative axis offset amount and the absolute axis offset amount (step S240), and ends this processing routine.
- the calculated relative axis deviation is a relative value, and even if the relative axis deviation is calculated, it is determined which millimeter wave radar actually causes the horizontal axis deviation. Can not. Therefore, it is possible to determine which of the millimeter wave radars is causing the horizontal axis shift by using the absolute axis shift amount obtained by each millimeter wave radar alone.
- the object detection device 10 even in the case where two millimeter wave radars are provided, it is possible to determine the off-axis of the radar in the horizontal direction and specify the off-axis radar. . Therefore, it is possible to determine the axis shift using the shortening of time based on the determination of the axis shift of the radar in the horizontal direction and using only the radar.
- the relative axis deviation amount is calculated to determine the presence or absence of the horizontal axis deviation, it becomes possible to determine the horizontal axis deviation using a detection point at which the relative velocity is not 0, and the case of using only the absolute axis deviation amount In comparison, it is possible to increase the frequency with which the horizontal axis deviation can be determined, and the horizontal axis deviation state of the millimeter wave radar can be determined more quickly. That is, when the relative axis deviation amount is 0 or less than the reference amount, it can be determined that the axis deviation of the millimeter wave radar is determined without using the absolute axis deviation amount. It can be managed precisely.
- the correction process described in the second embodiment may be executed subsequent to the specification of the horizontal axis offset radar in the third embodiment.
- the correspondence between detection points and the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount may be performed by a method other than the ICP method. For example, when the nearest detection points included in two detection point groups are associated with each other as a temporary detection point pair, the relative velocity difference between the temporary detection point pair is smaller than a predetermined reference difference. A method of determining the correspondence as a determined detection point pair may be used. Instead of or in addition to the relative speed difference, the received power difference may be used as well. After the correspondence is determined, the orientation difference of each detection point pair can be obtained, and the average value of the orientation difference of each detection point pair included in the detection point group can be used as the horizontal axis offset amount.
- the temporary The detection point pairs when associating the detection points, if the relative speed difference between the pair of temporary detection points and the received power difference is larger than a predetermined reference, the temporary The detection point pairs may be excluded from the definite detection point pairs.
- the relative speed difference or the reception power difference when calculating the average value of the azimuth difference, the relative speed difference or the reception power difference is predetermined rather than the azimuth difference of the determined detection point pair whose relative speed difference or reception power difference is larger than a predetermined reference.
- the horizontal axis shift amount may be determined from the average value of the ICP method or the azimuth angle by increasing the weighting of the misorientation of the determined detection point pair smaller than the reference.
- the temporary detection point pair when the temporary detection point pair is the detection point pair on the moving object, it may be excluded from the final detection point pair.
- the azimuth angle tends to shift, and the calculation accuracy of the horizontal axis shift amount decreases. Therefore, by excluding the moving detection point pair, the decrease in the calculation accuracy can be prevented or reduced.
- the ICP weighting is performed by increasing the weight for the orientation difference of the detection point pair closer to the center orientation of the overlap region than the orientation difference of the detection point pair closer to the peripheral orientation of the overlap region.
- the amount of horizontal axis offset may be determined from the mean value of the modulus or the azimuth angle.
- the accuracy of millimeter wave radar is better in azimuth accuracy in the narrow angle area than in the wide angle area, and by using a detection point pair close to the central direction of the overlapping area located near the narrow angle, The calculation accuracy can be improved.
- the horizontal axis shift amount is calculated using one detection point obtained from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, that is, it is calculated instantaneously,
- the horizontal axis shift amount may be calculated using the average value of the rotation amounts obtained using the detection points detected for a predetermined time, and the millimeter wave radar causing the horizontal axis shift may be identified.
- the detection points obtained while the vehicle 500 is turning may not be used. Since azimuth deviation is likely to occur during turning of the vehicle 500, calculation accuracy of the horizontal axis deviation amount and identification accuracy of the horizontal axis deviation radar can be improved by not using the detection point during turning. Whether or not the vehicle 500 is turning is, for example, whether or not the traveling locus of the own vehicle draws a turning locus using a detection signal input from at least one of the rotation angle sensor 24 and the yaw rate sensor 26 It can be determined by In addition, the detection point obtained when the vehicle 500 is stopped may not be used.
- the vehicle 500 While the position of the detection point group is stabilized when the vehicle 500 is stopped, there is a possibility that a certain target object is to be detected and the detection result is biased. That is, by randomly changing the detection target, the bias of the reflected wave caused by the target is dispersed and eliminated, and a more reliable detection result can be obtained. Note that whether or not the vehicle 500 is stopped can be determined, for example, based on whether or not the wheel speed input from the wheel speed sensor 25 is 0 km / h.
- the single axis deviation amount by each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 is used
- the horizontal offset radar may be identified. For example, when the second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 are offset in the same direction in the horizontal direction, it can be determined that the first millimeter wave radar 21 is in the horizontal offset. Therefore, as described in the third embodiment, absolute axis offset amounts may be obtained for each of the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, and the result of the determination of horizontal axis offset alone may be taken into consideration.
- the absolute axis shift amount of the first millimeter wave radar 21 is 0 or less than the reference value, it is determined that both the second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 cause horizontal axis shift. it can. Furthermore, the relative axis deviation amount and the absolute axis deviation amount may be respectively weighted, and then weighted average axis deviation amount may be used to determine the horizontal axis deviation of each millimeter wave radar. By adopting the above means, it is possible to eliminate or reduce the erroneous determination that may occur when three millimeter wave radars are used.
- the difference between the absolute axis deviation amount and the relative axis deviation amount described in the third embodiment is a second correction reference value, for example, 1 °. It may be executed in the following cases. Further, the correction amount may be changed according to the difference between the absolute axis deviation amount and the relative axis deviation amount. For example, as the difference increases, the correction amount for the absolute axis deviation amount, the relative axis deviation amount, or the average deviation amount of the both is reduced. If the difference is large, it is possible that one of the absolute axis offset amount or the relative axis offset amount is an abnormal value, so by gradually eliminating the horizontal axis offset amount, the influence of the correction of an inappropriate horizontal axis offset Is reduced.
- the CPU 101 executes the detector identification program P1 and the axis offset correction program P2 to realize the detector identification unit and the correction unit in software. It may be realized in hardware by a preprogrammed integrated circuit or discrete circuit.
- the embodiment of the invention described above is for the purpose of facilitating the understanding of the present disclosure and does not limit the present disclosure.
- the present disclosure can be modified and improved without departing from the spirit and the claims, and the present disclosure includes the equivalents thereof.
- the technical features in the embodiments corresponding to the technical features in the respective forms described in the section of the summary of the invention, and the technical features in the modified examples are for solving some or all of the problems described above, or Replacements or combinations can be made as appropriate to achieve part or all of the effects.
- the technical features are not described as essential in the present specification, they can be deleted as appropriate.
- the object detection device for a vehicle according to the first aspect is an application example 1, Application Example 2 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to Application Example 1,
- the plurality of detectors are three or more detectors,
- the detector specifying unit calculates the relative amount of axial deviation for all combinations of two detectors, and uses a combination of the calculated relative amount of axial deviation to detect a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated.
- Application Example 3 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Example 1,
- the plurality of detectors are two detectors,
- the detector specifying unit is a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated using the relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated using the detection points input from the respective detectors.
- An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it.
- Application Example 4 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Examples 1 to 3, The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is turning.
- Application Example 5 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 4, The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is stationary.
- Application Example 6 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 5, further, A vehicle comprising: a correction unit that corrects the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector by correcting the detection signal from the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount; Object detection device.
- the plurality of detectors may include a drive and may be horizontally rotatable.
- the object detection device for a vehicle further includes a correction unit that drives the drive unit to correct the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount.
- Application Example 8 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Example 6 or 7, The said correction
- Application Example 9 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle described in Application Example 6 or 7, The correction unit is configured such that a difference between the calculated relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated for each of the detectors using the detection point is equal to or less than a predetermined second correction reference value.
- An object detection device for a vehicle that makes corrections in the case.
- Application Example 10 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 6 to 9, The said correction
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Provided is an object detection device 10 for a vehicle. This object detection device 10 comprises: a plurality of detectors 21, 22, 23 that are for using reflected waves to detect a plurality of detection points indicating an object and are disposed in the vehicle such that some of the detection points overlap; and a detector specification unit 101, P1 for calculating the amount of relative horizontal axial deviation between two detectors from among the plurality of detectors 21, 22, 23 using detection points input from the two detectors and using the calculated amount of relative axial deviation to specify a detector having a deviant horizontal axis.
Description
本願は、その全ての開示が参照によりここに組み込まれる、2017年6月29日に出願された、日本国特許出願 出願番号2017-126827に基づく優先権を主張する。
The present application claims priority based on Japanese Patent Application No. 2017-126827, filed on June 29, 2017, the entire disclosure of which is incorporated herein by reference.
本開示は車両用の対象物検出装置および車両用の対象物検出装置における水平方向の軸ずれ判定方法に関する。
The present disclosure relates to an object detection apparatus for a vehicle and a method for determining a horizontal axis deviation in an object detection apparatus for a vehicle.
車両における制動支援や操舵支援を実現するために車両周囲の対象物を検出するための検出器、例えば、カメラやレーダが車両に搭載されている。レーダの軸ずれは、対象物の検出精度を低下させるため、カメラにより得られる先行車両と自車両とのなす角度を用いてレーダにより得られる角度との角度差に基づいて水平方向におけるレーダの軸ずれ量を判定する技術や、相対速度が0km/hとなる物標、例えば、壁を検出した際における角度を用いて水平方向におけるレーダの軸ずれ量を推定する技術が提案されている(例えば、特開2016-65759号公報、特開2014-153256号公報)。
A detector for detecting an object around the vehicle, for example, a camera or a radar, is mounted on the vehicle in order to realize braking assistance and steering assistance in the vehicle. In order to reduce the detection accuracy of the object, the radar's axis offsets the radar's axis in the horizontal direction based on the angle difference between the leading vehicle and the vehicle obtained by the camera and the angle obtained by the radar. Techniques for determining the amount of misalignment, and techniques for estimating the amount of radar misalignment in the horizontal direction using a target with a relative velocity of 0 km / h, for example, an angle when a wall is detected (for example, JP-A-2016-65759, JP-A-2014-153256).
しかしながら、先行車両と自車両とのなす角度を用いる技術では、先行車両が存在しない場合、軸ずれを判定することができず、また、カメラの軸ずれに起因してレーダの軸ずれが誤判定される場合がある。相対速度が0km/hとなる物標を用いる技術では、自車両の横方向に壁が存在しなければ軸ずれ量を推定できないという問題がある。
However, with the technology that uses the angle formed by the leading vehicle and the host vehicle, it is not possible to determine the axis shift when there is no preceding vehicle, and the axis shift of the radar is erroneously determined due to the axis shift of the camera. May be In the technology using a target whose relative velocity is 0 km / h, there is a problem that it is not possible to estimate the amount of axial deviation if there is no wall in the lateral direction of the vehicle.
したがって、水平方向における検出器の軸ずれの判定によるする時間の短縮化、反射波を検出する検出器のみを用いて軸ずれを判定することが望まれている。
Therefore, it is desirable to shorten the time based on the determination of the axis offset of the detector in the horizontal direction and to determine the axis offset using only the detector that detects the reflected wave.
本開示は、以下の態様として実現することが可能である。
The present disclosure can be implemented as the following aspects.
第1の態様は、車両用の対象物検出装置を提供する。第1の態様に係る車両用の対象物検出装置は、反射波を用いて対象物を表す複数の検出点を検出する複数の検出器であって、一部の前記検出点が重複するように車両に配置されている複数の検出器と、前記複数の検出器のうち2つの検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて、前記2つの検出器の水平方向における相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、検出器特定部と、を備える。
A first aspect provides an object detection device for a vehicle. The object detection device for a vehicle according to the first aspect is a plurality of detectors for detecting a plurality of detection points representing an object using a reflected wave, and a part of the detection points overlap. Using a plurality of detectors disposed in a vehicle and the detection points input from two of the plurality of detectors, relative offset amounts of the two detectors in the horizontal direction are calculated. And a detector identification unit that identifies a detector whose horizontal axis is offset using the calculated and calculated relative axis offset amount.
第1の態様に係る車両用の対象物検出装置によれば、水平方向における検出器の軸ずれの判定によるする時間の短縮化、反射波を検出する検出器のみを用いて軸ずれを判定することができる。
According to the object detection device for a vehicle according to the first aspect, the time shift based on the determination of the axis shift of the detector in the horizontal direction is shortened, and the axis shift is determined using only the detector that detects the reflected wave. be able to.
第2の態様は、車両用の対象物検出装置における水平方向の軸ずれ判定方法を提供する。第2の態様に係る水平方向の軸ずれ判定方法は、反射波を用いて対象物を表す複数の検出点を検出する複数の検出器であって、一部の前記検出点が重複するように車両に配置されている複数の検出器のうち2つの検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて、前記2つの検出器の水平方向における相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、ことを備える。
A second aspect provides a method for determining a horizontal axis deviation in an object detection device for a vehicle. The method for determining an axis deviation in the horizontal direction according to the second aspect is a plurality of detectors for detecting a plurality of detection points representing an object using a reflected wave, in which some of the detection points overlap. The relative offset amount between the two detectors in the horizontal direction is calculated using the detection points input from the two detectors among the plurality of detectors arranged in the vehicle, and the calculated relative Identifying a detector whose horizontal axis is offset using a typical amount of offset.
第2の態様に係る車両用の対象物検出装置における水平方向の軸ずれ判定方法によれば、水平方向における検出器の軸ずれの判定によるする時間の短縮化、反射波を検出する検出器のみを用いて軸ずれを判定することができる。なお、本開示は、車両用の対象物検出装置における水平方向の軸ずれ判定プログラムまたは当該プログラムを記録するコンピュータ読み取り可能記録媒体としても実現可能である。
According to the method of determining an axis shift in the horizontal direction in the object detection device for a vehicle according to the second aspect, shortening of the time based on the determination of the axis shift of the detector in the horizontal direction, only the detector that detects the reflected wave The axis offset can be determined using Note that the present disclosure can also be realized as a horizontal axis offset determination program in an object detection device for a vehicle or a computer readable recording medium for recording the program.
本開示に係る車両用の対象物検出装置および対象物検出装置における車両における水平方向の軸ずれ判定方法について、いくつかの実施形態に基づいて以下説明する。
An object detection device for a vehicle and a method for determining a horizontal axis deviation in a vehicle in the object detection device according to the present disclosure will be described below based on some embodiments.
第1の実施形態:
図1に示すように、第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10は、車両500に搭載されて用いられる。なお、車両500は、四輪以上の車両に限られず、二輪または三輪の車両であっても良い。対象物検出装置10は、制御装置100、第1のミリ波レーダ21、第2のミリ波レーダ22、第3のミリ波レーダ23、回転角センサ24、車輪速度センサ25およびヨーレートセンサ26を備えている。車両500は、操舵支援装置31、制動支援装置32、操舵装置42、車輪501、制動装置502、制動ライン503、ステアリングホイール504、フロントガラス510およびフロントバンパ520を備えている。第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23は、対象物を表す複数の検出点を検出する検出部である。車両は、検出部として、この他に、単眼カメラやステレオカメラを備えていても良い。 First embodiment:
As shown in FIG. 1, theobject detection device 10 according to the first embodiment is mounted on a vehicle 500 and used. Vehicle 500 is not limited to four or more wheels, and may be a two or three wheel vehicle. The object detection device 10 includes a control device 100, a first millimeter wave radar 21, a second millimeter wave radar 22, a third millimeter wave radar 23, a rotation angle sensor 24, a wheel speed sensor 25, and a yaw rate sensor 26. ing. The vehicle 500 includes a steering assist device 31, a braking assist device 32, a steering device 42, wheels 501, a braking device 502, a braking line 503, a steering wheel 504, a windshield 510, and a front bumper 520. The first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are detection units that detect a plurality of detection points representing an object. The vehicle may further include a monocular camera or a stereo camera as a detection unit.
図1に示すように、第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10は、車両500に搭載されて用いられる。なお、車両500は、四輪以上の車両に限られず、二輪または三輪の車両であっても良い。対象物検出装置10は、制御装置100、第1のミリ波レーダ21、第2のミリ波レーダ22、第3のミリ波レーダ23、回転角センサ24、車輪速度センサ25およびヨーレートセンサ26を備えている。車両500は、操舵支援装置31、制動支援装置32、操舵装置42、車輪501、制動装置502、制動ライン503、ステアリングホイール504、フロントガラス510およびフロントバンパ520を備えている。第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23は、対象物を表す複数の検出点を検出する検出部である。車両は、検出部として、この他に、単眼カメラやステレオカメラを備えていても良い。 First embodiment:
As shown in FIG. 1, the
第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23は、ミリ波を射出し、対象物によって反射された反射波を受信することによって対象物の位置および距離を検出する検出器としてのセンサである。第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23は、例えば、正面視の中央にミリ波の射出方向を規定する軸、すなわち、射出軸を有しており、検出を所望する方向と射出軸とが一致されて車両500に配置される。本実施形態において、第1のミリ波レーダ21は、フロントバンパ520の中央に配置され、第2のミリ波レーダ22はフロントバンパ520の車両500の進行方向左側に配置され、第3のミリ波レーダ23はフロントバンパ520の車両500の進行方向右側に配置されている。各ミリ波レーダ21~23は、検出範囲が互いに重なるように配置されている。各ミリ波レーダ21~23には、レーダを水平方向に回転可能なアクチュエータ、例えば、電動モータが備えられていても良い。各ミリ波レーダ21~23から出力される検出信号は、例えば、各ミリ波レーダ21~23が備える処理回路において受信波が処理された対象物の複数の代表位置を示す点列からなる信号であっても良く、あるいは、未処理の受信波を示す信号であっても良い。未処理の受信波が検出信号として用いられる場合には、制御装置100において対象物の位置および距離を特定するための信号処理が実行される。なお、検出器としては、電磁波を射出し、対象物により反射された反射波を検出することで対象物を検出する検出器であればよく、例えば、ライダー(LIDAR:レーザレーダ)や超音波センサが用いられても良い。
The first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are sensors as detectors that emit millimeter waves and detect the position and distance of an object by receiving a reflected wave reflected by the object. Each of the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 has, for example, an axis defining an emission direction of the millimeter wave at the center of the front view, that is, an emission axis, and a direction desired for detection and the emission axis Are matched and placed in the vehicle 500. In the present embodiment, the first millimeter wave radar 21 is disposed at the center of the front bumper 520, and the second millimeter wave radar 22 is disposed on the left side of the front bumper 520 in the traveling direction of the vehicle 500. The radar 23 is disposed on the right side of the front bumper 520 in the traveling direction of the vehicle 500. The millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are arranged such that the detection ranges overlap each other. Each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 may be provided with an actuator capable of horizontally rotating the radar, for example, an electric motor. The detection signals output from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are, for example, signals consisting of point trains indicating a plurality of representative positions of the object for which the reception wave has been processed in the processing circuit included in each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23. It may be a signal indicating an unprocessed received wave. When an unprocessed received wave is used as a detection signal, signal processing for specifying the position and distance of an object is performed in the control device 100. The detector may be any detector that detects an object by emitting an electromagnetic wave and detecting a reflected wave reflected by the object. For example, a lidar (LIDAR: laser radar) or an ultrasonic sensor May be used.
車両500の各車輪501には、それぞれ制動装置502が備えられている。各制動装置502は、ブレーキ液ラインおよび運転者の制動ペダル操作に応じてブレーキ液圧を発生させるブレーキピストンを含む制動ライン503を介して供給されるブレーキ液圧によって各車輪501の制動を実現する。制動ライン503には、ブレーキ液圧を発生させるアクチュエータを含む制動支援装置32が配置されており、制動ペダル操作とは独立して液圧制御が可能であり、これにより各ミリ波レーダ21~23による検出結果に応じた制動支援が実現される。なお、制動支援装置32のアクチュエータには、横滑り防止装置、アンチロックブレーキシステムとして既に導入されている制動制御アクチュエータが用いられても良い。
Each wheel 501 of the vehicle 500 is provided with a braking device 502. Each braking device 502 realizes braking of each wheel 501 by the brake fluid pressure supplied via a braking line 503 including a brake fluid line and a brake piston that generates a brake fluid pressure in accordance with a driver's brake pedal operation. . A brake assisting device 32 including an actuator for generating a brake fluid pressure is disposed on the brake line 503, and fluid pressure control can be performed independently of the brake pedal operation, whereby each millimeter wave radar 21 to 23 is provided. The braking assistance is realized according to the detection result by the. In addition, as an actuator of the braking assistance device 32, a braking control actuator which has already been introduced as a skid prevention device or an antilock braking system may be used.
ステアリングホイール504は、ステアリングロッドおよび操舵機構を含む操舵装置42を介して前側の車輪501と接続されている。操舵装置42には、アクチュエータ、例えば、電動モータにより操舵装置42を駆動可能な操舵支援装置31が配置されている。操舵支援装置31は、ステアリングホイール504の操作とは独立して操舵装置42の駆動制御が可能であり、これにより各ミリ波レーダ21~23による検出結果に応じた操舵支援が実現される。操舵支援装置31は、ステアリングホイール504による操舵力を軽減するためにも駆動制御される。
The steering wheel 504 is connected to the front wheel 501 via a steering device 42 including a steering rod and a steering mechanism. A steering assist device 31 capable of driving the steering device 42 by an actuator, for example, an electric motor, is disposed in the steering device 42. The steering assist device 31 can perform drive control of the steering device 42 independently of the operation of the steering wheel 504, whereby steering assist according to the detection result of each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 is realized. The steering assist device 31 is also drive-controlled to reduce the steering force by the steering wheel 504.
図2に示すように、制御装置100は、中央処理装置(CPU)101、メモリ102、入出力インタフェース103およびバス104を備えている。CPU101、メモリ102および入出力インタフェース103はバスを介して双方向通信可能に接続されている。メモリ102は、水平方向に軸ずれを起こしているミリ波レーダを特定するための検出器特定プログラムP1および特定したミリ波レーダの水平方向の軸ずれを補正する軸ずれ補正プログラムP2を不揮発的且つ読み出し専用に格納するメモリ、例えばROMと、CPU101による読み書きが可能なメモリ、例えばRAMとを含んでいる。CPU101はメモリ102に格納されている検出器特定プログラムP1を読み書き可能なメモリに展開して実行することによって検出器特定部として機能し、同様に軸ずれ補正プログラムP2を実行することによって補正部として機能する。なお、補正プログラムP2は、第1の実施形態においては備えられていなくても良い。
As shown in FIG. 2, the control device 100 includes a central processing unit (CPU) 101, a memory 102, an input / output interface 103, and a bus 104. The CPU 101, the memory 102, and the input / output interface 103 are bi-directionally connected via a bus. The memory 102 is a non-volatile detector specification program P1 for identifying a millimeter wave radar causing an axis offset in the horizontal direction and an axis offset correction program P2 for correcting an axis offset in the horizontal direction of the identified millimeter wave radar. It includes a memory that is stored read only, such as a ROM, and a memory that can be read and written by the CPU 101, such as a RAM. The CPU 101 functions as a detector identification unit by expanding and executing the detector identification program P1 stored in the memory 102 in a readable / writable memory, and similarly as a correction unit by executing the axis deviation correction program P2. Function. The correction program P2 may not be included in the first embodiment.
入出力インタフェース103には、第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23、舵角センサ24、車輪速度センサ25、ヨーレートセンサ26、操舵支援装置31および制動支援装置32がそれぞれ信号線を介して接続されている。各ミリ波レーダ21~23、舵角センサ24、車輪速度センサ25およびヨーレートセンサ26からは、検出情報が入力され、操舵支援装置31および制動支援装置32に対しては駆動制御信号が出力される。なお、第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23にアクチュエータが備えられている場合には、入出力インタフェース103から信号線を介して駆動制御信号が送信され得る。
The first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, the steering angle sensor 24, the wheel speed sensor 25, the yaw rate sensor 26, the steering assist device 31, and the brake assist device 32 are connected to the input / output interface 103 via signal lines, respectively. It is connected. Detection information is input from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, the steering angle sensor 24, the wheel speed sensor 25, and the yaw rate sensor 26, and a drive control signal is output to the steering assist device 31 and the brake assist device 32. . When the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 are provided with an actuator, a drive control signal can be transmitted from the input / output interface 103 through the signal line.
舵角センサ24は、ステアリングホイール504の操舵によりステアリンロッドに生じるねじれ量、すなわち、操舵トルク、を検出するトルクセンサであり、ステアリングホイール504の操舵角を検出する。本実施形態において、舵角センサ24は、ステアリングホイール504と操舵機構とを接続するステアリングロッドに備えられている。舵角センサ24から出力される検出信号は、ねじれ量に比例する電圧値である。
The steering angle sensor 24 is a torque sensor that detects a twist amount generated on the stearin rod by steering of the steering wheel 504, that is, a steering torque, and detects a steering angle of the steering wheel 504. In the present embodiment, the steering angle sensor 24 is provided on a steering rod connecting the steering wheel 504 and the steering mechanism. The detection signal output from the steering angle sensor 24 is a voltage value proportional to the amount of twist.
車輪速度センサ25は、車輪501の回転速度を検出するセンサであり、各車輪501に備えられている。車輪速度センサ25から出力される検出信号は、車輪速度に比例する電圧値または車輪速度に応じた間隔を示すパルス波である。
The wheel speed sensor 25 is a sensor that detects the rotational speed of the wheel 501, and is provided to each wheel 501. The detection signal output from the wheel speed sensor 25 is a voltage value proportional to the wheel speed or a pulse wave indicating an interval according to the wheel speed.
ヨーレートセンサ26は、車両500の回転角速度を検出するセンサである。ヨーレートセンサ26は、例えば、車両の中央部に配置されている。ヨーレートセンサ26から出力される検出信号は、回転方向と角速度に比例する電圧値である。
The yaw rate sensor 26 is a sensor that detects the rotational angular velocity of the vehicle 500. The yaw rate sensor 26 is disposed, for example, at a central portion of the vehicle. The detection signal output from the yaw rate sensor 26 is a voltage value proportional to the rotation direction and the angular velocity.
図3~図5を参照して第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によって実行される、検出器特定処理について説明する。図3に示す処理ルーチンは、CPU101が検出器特定プログラムP1を実行することによって、例えば、車両の制御システムの始動後、または、実行スイッチを介した運転者からの要求入力を待って実行される。なお、車両の制御システムの始動をトリガにして実行される場合には、車両の制御システム始動後、制御システムが終了するまで繰り返し実行されても良く、制御システム始動後に毎回一度実行されても良く、所定の始動回数毎または所定走行時間間隔で実行されても良い。
The detector identification process executed by the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 3 to 5. The processing routine shown in FIG. 3 is executed, for example, after the start of the control system of the vehicle or waiting for a request input from the driver via the execution switch by the CPU 101 executing the detector identification program P1. . When the control system of the vehicle is triggered by the start of the control system, the control system may be repeatedly executed until the control system ends after the control system is started, or may be executed once every time the control system is started. The present invention may be executed every predetermined number of starting times or at a predetermined traveling time interval.
CPU101は、各ミリ波レーダ21~23から検出点を取得する(ステップS100)。取得される検出点は、複数の検出点、例えば、10~1000点、から構成される検出点群である。各ミリ波レーダ21~23から制御装置100に入力される検出信号には、検出対象物を表す複数の検出点の情報、例えば、位置情報としての(x、y、z)座標情報、自車両に対する検出点の相対速度情報、信号強度または受信電力、が含まれている。第1、第2および第3のミリ波レーダ21、22、23の検出範囲A1、A2、A3は、図4に示すように少なくとも一部、第1の重複領域DA1および第2の重複領域DA2において重複している。なお、図4では、第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23以外のミリ波レーダ、すなわち、車両500の側面に配置されているミリ波レーダ20s、車両500の後部に配置されているミリ波レーダ20bが参考のために図示されている。これら他のミリ波レーダ20b、20sについても、検出範囲の一部が重複している。すなわち、本実施形態において、各ミリ波レーダ21~23、20b、20sは、自身の検出範囲と隣接するミリ波レーダの検出範囲とが重複するように車両500に対して配置されている。
The CPU 101 acquires detection points from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 (step S100). The detection points to be acquired are a detection point group composed of a plurality of detection points, for example, 10 to 1000 points. The detection signals input from the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 to the control device 100 include information on a plurality of detection points representing the detection target, for example, (x, y, z) coordinate information as position information, and the vehicle Relative velocity information of the detection point, signal strength or reception power, and the like. The detection ranges A1, A2 and A3 of the first, second and third millimeter wave radars 21, 22 and 23 are at least partially, as shown in FIG. 4, a first overlap area DA1 and a second overlap area DA2. Overlap in In FIG. 4, the millimeter wave radars other than the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, that is, the millimeter wave radar 20 s disposed on the side of the vehicle 500 and the millimeter disposed on the rear of the vehicle 500 Wave radar 20b is illustrated for reference. The detection ranges of the other millimeter wave radars 20b and 20s also overlap. That is, in the present embodiment, each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, 20b, and 20s is disposed with respect to the vehicle 500 so that its own detection range and the detection range of the adjacent millimeter wave radar overlap.
CPU101は、検出範囲が重複する2つのミリ波レーダから得られた検出点を対応付けする(ステップS110)。CPU101は、例えば、先ず、第1のミリ波レーダ21および第2のミリ波レーダ22からそれぞれ得られた複数の検出点の対応付けを実行する。具体的には、図4に示す第1の重複領域DA1における各ミリ波レーダ21、22から得られた検出点群が対応付けられる。検出点群を構成する各検出点の対応付けは、例えば、既知のICP(Iterative Closest Point)法を用いて実行される。ICP法では、例えば、第1のミリ波レーダ21によって得られた第1検出点群の各検出点に対して、第2のミリ波レーダ22によって得られた第2検出点群の各検出点から最近傍点を探索することによって対応付けが実行される。なお、検出点群を構成する各検出点の対応付けは、各検出点群を構成する各検出点が互いに近接している場合、すなわち、最近傍点を容易に判別できる場合には省略されても良い。
The CPU 101 associates detection points obtained from two millimeter wave radars whose detection ranges overlap with each other (step S110). The CPU 101 first executes, for example, association of a plurality of detection points obtained respectively from the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the second millimeter wave radar 22. Specifically, detection point groups obtained from the respective millimeter wave radars 21 and 22 in the first overlapping area DA1 shown in FIG. 4 are associated with each other. The association of each detection point constituting the detection point group is performed, for example, using a known ICP (Iterative Closest Point) method. In the ICP method, for example, with respect to each detection point of the first detection point group obtained by the first millimeter wave radar 21, each detection point of the second detection point group obtained by the second millimeter wave radar 22 The association is performed by searching for the closest point from. Incidentally, the correspondence between the detection points constituting the detection point group is omitted even when the detection points constituting the detection point groups are close to each other, that is, when the nearest points can be easily determined. good.
CPU101は、対応付けを行った各検出点対を用いて、水平方向における2つのミリ波レーダの相対軸ずれ量を算出する(ステップS120)。ICP法では、対応付けを行った各検出点間の距離の最小化を繰り返すことによって、すなわち、第1検出点群の各検出点に対して第2検出点群の各検出点が重なり合うよう距離の最小化を繰り返すことによって、第1検出点群と第2検出点群との間の3次元、すなわち、XYZ軸方向のずれ量が算出される。X軸が車幅方向、Y軸が車高方向、Z軸が車長方向である場合、X軸方向のずれ量が第1検出点群と第2検出点群との間の相対的な水平方向の軸ずれ量として算出される。なお、第1検出点群と第2検出点群との間のずれ量の算出に際して、Y軸方向の方位精度は低いことが多いため、車高方向の検出情報は用いられなくても良い。本実施例では、軸ずれ量として、第1検出点群と第2検出点群の各検出点対を重ね合わせるために必要なX軸方向の回転量(deg)を算出する。あるいは、第2検出点群の各検出点に対して第1検出点群の各検出点が重なり合うよう距離の最小化を繰り返すことによってXYZ軸方向のずれ量が算出されても良い。いずれの場合にも、第1検出点群と第2検出点群との間の相対的な水平方向の軸ずれ量、すなわち、X軸方向のずれ量が算出され得る。
The CPU 101 calculates the amount of relative axis deviation of the two millimeter wave radars in the horizontal direction using each pair of detection points that have been associated (step S120). In the ICP method, by repeating the minimization of the distance between each detection point that has been matched, that is, the distance such that each detection point of the second detection point group overlaps each detection point of the first detection point group By repeating the above, the three-dimensional, ie, the amount of deviation in the XYZ axis direction between the first detection point group and the second detection point group is calculated. When the X axis is in the vehicle width direction, the Y axis is in the vehicle height direction, and the Z axis is in the vehicle length direction, the shift amount in the X axis direction is the relative horizontal between the first detection point group and the second detection point group It is calculated as the amount of axial deviation in the direction. In calculating the amount of deviation between the first detection point group and the second detection point group, the detection accuracy in the vehicle height direction may not be used because the azimuth accuracy in the Y-axis direction is often low. In the present embodiment, the amount of rotation (deg) in the X-axis direction necessary to overlap each detection point pair of the first detection point group and the second detection point group is calculated as the amount of axial deviation. Alternatively, the amount of deviation in the XYZ axial directions may be calculated by repeating the minimization of the distance such that each detection point of the first detection point group overlaps each detection point of the second detection point group. In any case, the relative horizontal axis offset between the first detection point group and the second detection point group, that is, the shift amount in the X-axis direction can be calculated.
CPU101は、隣接する全てのミリ波レーダの組み合わせについて水平軸ずれ量の算出が完了しているか否かを判定し(ステップS130)、完了していない場合には(ステップS130:No)、ステップ110およびステップS120を繰り返し実行する。実施形態においては、第1のミリ波レーダ21および第2のミリ波レーダ22の組み合わせ、第1のミリ波レーダ21および第3のミリ波レーダ23の各組み合わせについて実行されるまでステップS110およびS120が繰り返し実行される。
The CPU 101 determines whether or not the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount has been completed for the combination of all adjacent millimeter wave radars (step S130), and if not completed (step S130: No), step 110 And step S120 is repeatedly executed. In the embodiment, steps S110 and S120 are performed until the combination of the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the second millimeter wave radar 22, and the combination of the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the third millimeter wave radar 23 are performed. Is repeatedly executed.
隣接する各ミリ波レーダ21~23間の水平軸ずれ量は、例えば、図5および図6に示すように算出される。図5および図6において、水平軸ずれを起こしていない水平軸を基準として、「-」は反時計回り方向、「+」は時計回り方向の水平角度を意味する。図6では、例として、重複領域DA1における第1のミリ波レーダ21の検出点群DT1と第2のミリ波レーダ22の検出点群DT2との重ね合わせが模式的に示されている。図6に示すように、第1のミリ波レーダ21(A1)に対する第2のミリ波レーダ22(A2)の水平軸ずれ量、すなわち、第1のミリ波レーダ21の検出点群DT1を第2のミリ波レーダ22の検出点群DT2に一致させるための回転量は-3degであり、第2のミリ波レーダ22(A2)に対する第1のミリ波レーダ21(A1)の水平軸ずれ量、すなわち、第2のミリ波レーダ22の検出点群DT2を第1のミリ波レーダ21の検出点群DT1に一致させるための回転量は3degである。第1のミリ波レーダ21(A1)に対する第3のミリ波レーダ23(A3)の水平軸ずれ量は0degであり、第3のミリ波レーダ23(A3)に対する第1のミリ波レーダ21(A1)の水平軸ずれ量は0degである。
The amount of horizontal axis offset between the adjacent millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 is calculated, for example, as shown in FIG. 5 and FIG. In FIG. 5 and FIG. 6, “−” means a counterclockwise direction and “+” means a horizontal angle in the clockwise direction, with reference to the horizontal axis not causing the horizontal axis deviation. In FIG. 6, as an example, superposition of the detection point group DT1 of the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the detection point group DT2 of the second millimeter wave radar 22 in the overlapping area DA1 is schematically shown. As shown in FIG. 6, the amount of horizontal axis deviation of the second millimeter wave radar 22 (A2) with respect to the first millimeter wave radar 21 (A1), that is, the detection point group DT1 of the first millimeter wave radar 21 The amount of rotation to match the detection point group DT2 of the millimeter wave radar 22 of No. 2 is -3 deg, and the horizontal axis deviation of the first millimeter wave radar 21 (A1) with respect to the second millimeter wave radar 22 (A2) That is, the amount of rotation for causing the detection point group DT2 of the second millimeter wave radar 22 to coincide with the detection point group DT1 of the first millimeter wave radar 21 is 3 degrees. The horizontal axis deviation of the third millimeter wave radar 23 (A3) with respect to the first millimeter wave radar 21 (A1) is 0 degree, and the first millimeter wave radar 21 (with the third millimeter wave radar 23 (A3) The amount of horizontal axis deviation of A1) is 0 deg.
CPU101は、隣接するミリ波レーダの組み合わせの全てについて水平軸ずれ量の算出が完了していると判定した場合には(ステップS130Yes)、算出した水平軸方向における相対軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸ずれレーダを特定し(ステップS140)、本処理ルーチンを終了する。CPU101は、第1および第2のミリ波レーダ21、22の間の相対軸ずれ量と、第1および第3のミリ波レーダ21、23の間の相対軸ずれ量の組み合わせに基づいて、水平軸ずれを起こしているミリ波レーダを特定する。図5に示す相対軸ずれ量の結果が得られた場合、第1のミリ波レーダ21と第3のミリ波レーダ23との間では角度差は発生しておらず、CPU101は、第1および第3のミリ波レーダ21、23は水平軸ずれを起こしていないと判定することができる。一方、第1のミリ波レーダ21と第2のミリ波レーダ22との間では3degの相対的な角度差が発生しており、第1または第2のミリ波レーダ21、22のいずれかが水平軸ずれを起こしている。第3のミリ波レーダ23との関係において、第1のミリ波レーダ21には水平軸ずれは発生していないので、CPU101は、第2のミリ波レーダ22に水平軸ずれか発生していると判定し、第2のミリ波レーダ22を水平軸ずれレーダとして特定することができる。
If the CPU 101 determines that the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount has been completed for all combinations of adjacent millimeter wave radars (Yes at step S130), the horizontal axis is calculated using the calculated relative axis shift amount in the horizontal axis direction. The deviation radar is specified (step S140), and this processing routine is ended. The CPU 101 is horizontal based on a combination of the relative axis deviation between the first and second millimeter wave radars 21 and 22 and the relative axis deviation between the first and third millimeter wave radars 21 and 23. Identify the millimeter wave radar that is causing the axis shift. When the result of the relative axis deviation shown in FIG. 5 is obtained, no angular difference occurs between the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the third millimeter wave radar 23, and the CPU 101 determines It is possible to determine that the third millimeter wave radars 21 and 23 do not cause the horizontal axis deviation. On the other hand, a relative angle difference of 3 degrees is generated between the first millimeter wave radar 21 and the second millimeter wave radar 22, and either the first or second millimeter wave radars 21 and 22 There is a horizontal offset. In the relationship with the third millimeter wave radar 23, since the first millimeter wave radar 21 does not generate a horizontal axis deviation, the CPU 101 causes the second millimeter wave radar 22 to generate a horizontal axis deviation. Thus, the second millimeter wave radar 22 can be identified as a horizontal axis offset radar.
以上説明した第1の態様に係る対象物検出装置10によれば、第1のミリ波レーダ21~第3のミリ波レーダ23を用いて、水平方向におけるレーダの軸ずれを判定し、水平軸ずれレーダを特定することができる。したがって、水平方向におけるレーダの軸ずれの判定によるする時間の短縮化、レーダのみを用いて軸ずれを判定することができる。すなわち、前方カメラとレーダの双方を用いる場合には撮像画像を用いて先行車両を検出するための画像処理を行った上で、レーダの検出結果と組み合わせて軸ずれが判定される。第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によれば、前方カメラを用いることなくミリ波レーダのみを用いているので撮像画像を用いて先行車両を検出するための時間を要しない。また、前方カメラの水平軸ずれによる影響を受けることなくレーダの水平軸ずれを判定することができるので判定精度を向上させることができる。さらに、レーダ相対速度が0の対象物を利用する際には、相対速度が0である物標の存在が条件となり、条件が整わない場合にはレーダの水平軸ずれ判定を実行することができない。第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によれば、相対速度が0ではない検出点を利用することが可能となり、より多くの条件下においてレーダの軸ずれを判定することが可能となる。この結果、判定時間を短縮することができる。
According to the object detection device 10 according to the first aspect described above, the first millimeter-wave radar 21 to the third millimeter-wave radar 23 are used to determine the axis offset of the radar in the horizontal direction, and the horizontal axis Deviation radar can be identified. Therefore, it is possible to determine the axis shift using the shortening of time based on the determination of the axis shift of the radar in the horizontal direction and using only the radar. That is, when using both a front camera and a radar, image processing for detecting a preceding vehicle is performed using a captured image, and then an axial deviation is determined in combination with the detection result of the radar. According to the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment, only the millimeter wave radar is used without using the front camera, so it does not require time for detecting a leading vehicle using a captured image. Further, since the horizontal axis offset of the radar can be determined without being affected by the horizontal axis offset of the front camera, the determination accuracy can be improved. Furthermore, when using a target with a relative radar velocity of 0, the presence of a target with a relative velocity of 0 is a condition, and if the condition is not met, it is not possible to determine the horizontal axis offset of the radar. . According to the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment, it is possible to use a detection point whose relative velocity is not 0, and it is possible to determine the off-axis of the radar under more conditions. . As a result, the determination time can be shortened.
第1の実施形態において、隣接する全てのミリ波レーダの組み合わせを用いて水平軸ずれ量が算出されているが、隣接する全てのミリ波レーダの組み合わせが用いられることなく、利用できるミリ波レーダの組み合わせを用いて水平軸ずれ量が算出されても良い。例えば、車両500の前方中央、左右側面中央および後方中央に、隣接するミリ波レーダ間で検出範囲が重複するように4つのミリ波レーダが配置されている場合について説明する。後方中央のミリ波レーダにより検出点が検出されない場合には、後方中央のミリ波レーダと左側面中央のミリ波レーダ、後方中央のミリ波レーダと右側面中央のミリ波レーダの組み合わせについて水平軸ずれ量を算出できない。この場合には、予め定められた待機時間の経過後に、前方中央のミリ波レーダと左側面中央のミリ波レーダ、前方中央のミリ波レーダと右側面中央のミリ波レーダの組み合わせについて水平軸ずれ量を求め、算出した水平軸方向における相対軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸ずれレーダを特定しても良い。この場合には、車両500に備えられているいずれかのミリ波レーダによって検出点を検出できない場合であっても、当該ミリ波レーダからの検出点の入力を待機することなく、水平軸ずれレーダを特定することが可能となる。したがって、水平軸ずれレーダの特定に要する時間の遅延を抑制または防止することができる。
In the first embodiment, although the horizontal axis shift amount is calculated using a combination of all adjacent millimeter wave radars, a millimeter wave radar that can be used without using a combination of all adjacent millimeter wave radars. The horizontal axis shift amount may be calculated using a combination of the above. For example, the case where four millimeter wave radars are arranged at the front center, the left side center and the rear center of the vehicle 500 so that the detection ranges overlap between adjacent millimeter wave radars will be described. When the detection point is not detected by the rear center millimeter wave radar, the horizontal axis of the combination of the rear center millimeter wave radar and the left side center center millimeter wave, and the rear center center millimeter wave radar and the right side surface center millimeter wave radar The deviation can not be calculated. In this case, after a predetermined waiting time has elapsed, the horizontal axis offset is obtained for the combination of the millimeter wave radar at the front center and the millimeter wave radar at the center at the left side, and the millimeter wave radar at the center at the front center and the millimeter wave The amount may be obtained, and the horizontal axis offset radar may be specified using the calculated relative axis offset amount in the horizontal axis direction. In this case, even if the detection point can not be detected by any of the millimeter wave radars provided in the vehicle 500, the horizontal axis deviation radar can be used without waiting for the input of the detection point from the millimeter wave radar. It is possible to identify Therefore, it is possible to suppress or prevent the delay of the time required to specify the horizontal axis offset radar.
第2の実施形態:
第1の実施形態においては、水平軸ずれが生じているミリ波レーダを特定するに留まっているが、第2の実施形態においては、更に、算出された水平軸ずれを補正する点において第1の実施形態と異なっている。なお、第2の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置は、第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10と同様の構成を備えているので、第1の実施形態において用いた符号を用いて各構成についての説明は省略する。 Second embodiment:
In the first embodiment, only the millimeter wave radar in which the horizontal axis deviation has occurred is identified. However, in the second embodiment, the first correction is made in that the calculated horizontal axis deviation is further corrected. It differs from the embodiment of In addition, since the object detection apparatus according to the second embodiment has the same configuration as theobject detection apparatus 10 according to the first embodiment, the respective components are denoted using the reference numerals used in the first embodiment. Description of the configuration is omitted.
第1の実施形態においては、水平軸ずれが生じているミリ波レーダを特定するに留まっているが、第2の実施形態においては、更に、算出された水平軸ずれを補正する点において第1の実施形態と異なっている。なお、第2の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置は、第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10と同様の構成を備えているので、第1の実施形態において用いた符号を用いて各構成についての説明は省略する。 Second embodiment:
In the first embodiment, only the millimeter wave radar in which the horizontal axis deviation has occurred is identified. However, in the second embodiment, the first correction is made in that the calculated horizontal axis deviation is further corrected. It differs from the embodiment of In addition, since the object detection apparatus according to the second embodiment has the same configuration as the
図7を参照して第2の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によって実行される、検出器特定処理および軸ずれ補正処理について説明する。図7に示す処理ルーチンは、CPU101が検出器特定プログラムP1および軸ずれ補正プログラムP2を実行することによって、第1の実施形態において説明したタイミングにて実行される。なお、第1の実施形態において説明した処理ステップについては同一の符号を付して、その説明を省略する。
The detector identification process and the axis offset correction process executed by the object detection device 10 according to the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 7. The processing routine shown in FIG. 7 is executed at the timing described in the first embodiment as the CPU 101 executes the detector identification program P1 and the axis deviation correction program P2. The same reference numerals are given to the processing steps described in the first embodiment, and the description thereof is omitted.
CPU101は、ステップS100~S140を実行した後、水平軸ずれレーダに対する補正量を決定する(ステップS150)。CPU101は、ステップS140において特定した水平軸ずれレーダの相対軸ずれ量を解消または軽減するように補正量を決定する。例えば、図5の例では、第2のミリ波レーダ22が水平軸ずれを起こしているレーダとして特定されたので、+3degまたは+3deg~0degの回転角が補正量として決定される。
After executing steps S100 to S140, the CPU 101 determines the correction amount for the horizontal axis deviation radar (step S150). The CPU 101 determines the correction amount so as to eliminate or reduce the relative axis deviation amount of the horizontal axis deviation radar identified in step S140. For example, in the example of FIG. 5, since the second millimeter wave radar 22 is identified as a radar causing a horizontal axis shift, a rotation angle of +3 deg or +3 deg to 0 deg is determined as the correction amount.
CPU101は、補正を実行し(ステップS160)、本処理ルーチンを終了する。CPU101による補正の実行には、例えば、以下の2態様がある。第1の態様として、CPU101は、第2のミリ波レーダ22から得られた検出点、すなわち、(x、y、z)座標を水平方向に+3deg回転させる変換処理を実行することによりソフトウェア的な補正を実行できる。第2の態様として、CPU101は、第2のミリ波レーダ22が備えるアクチュエータに対して、第2のミリ波レーダ22または第2のミリ波レーダ22の検出部を+3deg回転させる駆動制御信号を送信することにより、ハードウェア的に第2のミリ波レーダ22の水平軸ずれを補正することができる。なお、水平軸ずれ補正の実行は、例えば、算出された水平軸ずれ量の絶対値が予め定められた第1補正基準値、例えば3°以上である場合に実行されても良い。水平軸ずれ量が第1補正基準値未満の場合には、ミリ波レーダからの検出結果を用いた操舵支援や制動支援に対して与える影響は低く、また、水平軸ずれ量の算出誤差の可能性もあるため、水平軸ずれの補正を行わないことに伴う不都合はなく、適切でない水平軸ずれの補正を回避することができる。
The CPU 101 executes the correction (step S160), and ends the processing routine. The execution of the correction by the CPU 101 has, for example, the following two modes. As a first aspect, the CPU 101 performs software conversion processing by rotating the detection point obtained from the second millimeter wave radar 22, that is, (x, y, z) coordinates horizontally by +3 deg. Correction can be performed. As a second aspect, the CPU 101 transmits a drive control signal to rotate the detection unit of the second millimeter wave radar 22 or the second millimeter wave radar 22 by +3 degrees with respect to the actuator included in the second millimeter wave radar 22. By doing this, the horizontal axis deviation of the second millimeter wave radar 22 can be corrected in hardware. Note that the execution of the horizontal axis offset correction may be performed, for example, when the calculated absolute value of the horizontal axis offset amount is a predetermined first correction reference value, for example, 3 ° or more. When the horizontal axis deviation is less than the first correction reference value, the influence on the steering assistance and the braking assistance using the detection result from the millimeter wave radar is low, and the calculation error of the horizontal axis deviation is possible Due to the nature, there is no inconvenience associated with not performing the correction of the horizontal axis deviation, and it is possible to avoid the correction of the inappropriate horizontal axis deviation.
第2の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によれば、水平軸ずれが特定されたミリ波レーダをソフトウェア的またはハードウェア的に補正することができるので、水平軸ずれに伴う、対象物の検出精度の低下を抑制または防止することができる。この結果、ミリ波レーダからの検出結果を用いる、操舵支援装置31による操舵支援や制動支援装置32による制動支援の精度低下を抑制または防止することができる。
According to the object detection device 10 according to the second embodiment, the millimeter wave radar in which the horizontal axis shift is specified can be corrected by software or hardware. It is possible to suppress or prevent the decrease in detection accuracy. As a result, it is possible to suppress or prevent the accuracy reduction of the steering assistance by the steering assistance device 31 using the detection result from the millimeter wave radar and the braking assistance by the braking assistance device 32.
第3の実施形態:
第3の実施形態において、車両500は検出範囲が重複する様に配置されている第2および第3のミリ波レーダ22、23を備えている。すなわち、第3の実施形態においては、検出範囲が重複する2つのミリ波レーダが備えられている場合における水平軸ずれレーダの特定処理が実行される。なお、第3の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置は、第1のミリ波レーダ21を備えない点を覗き、第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10と同様の構成を備えているので、第1の実施形態において用いた符号を用いて各構成についての説明は省略する。 Third embodiment:
In the third embodiment, thevehicle 500 is provided with second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 arranged so that detection ranges overlap. That is, in the third embodiment, the process of specifying the horizontal axis offset radar in the case where two millimeter wave radars having overlapping detection ranges are provided. Note that the object detection device according to the third embodiment has the same configuration as the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment, from the point that the first millimeter wave radar 21 is not provided. The description of each configuration will be omitted using the reference numerals used in the first embodiment.
第3の実施形態において、車両500は検出範囲が重複する様に配置されている第2および第3のミリ波レーダ22、23を備えている。すなわち、第3の実施形態においては、検出範囲が重複する2つのミリ波レーダが備えられている場合における水平軸ずれレーダの特定処理が実行される。なお、第3の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置は、第1のミリ波レーダ21を備えない点を覗き、第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10と同様の構成を備えているので、第1の実施形態において用いた符号を用いて各構成についての説明は省略する。 Third embodiment:
In the third embodiment, the
図8を参照して第3の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によって実行される、検出器特定処理について説明する。図8に示す処理ルーチンは、CPU101が検出器特定プログラムP1を実行することによって、第1の実施形態において説明したタイミングにて実行される。CPU101は、各ミリ波レーダ22、23から検出点を取得する(ステップS200)。取得される検出点は、複数の検出点、例えば、10~1000点、から構成される検出点群である。各ミリ波レーダ22、23から制御装置100に入力される検出信号には、既述の検出点の情報が含まれている。第2および第3のミリ波レーダ22、23の検出範囲は、少なくとも一部が重複している。
The detector identification process executed by the object detection device 10 according to the third embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. The processing routine shown in FIG. 8 is executed at the timing described in the first embodiment as the CPU 101 executes the detector identification program P1. The CPU 101 acquires detection points from each of the millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 (step S200). The detection points to be acquired are a detection point group composed of a plurality of detection points, for example, 10 to 1000 points. The detection signals input from the millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 to the control device 100 include information on the detection points described above. The detection ranges of the second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 at least partially overlap.
CPU101は、検出範囲が重複する2つのミリ波レーダから得られた検出点を対応付けする(ステップS210)。検出点の対応付けは、第1の実施形態において説明した方法により実行される。CPU101は、対応付けを行った各検出点対を用いて、水平方向における2つのミリ波レーダの相対軸ずれ量を算出する(ステップS220)。相対軸ずれ量を算出は、第1の実施形態において説明した方法により実行される。
The CPU 101 associates detection points obtained from two millimeter wave radars whose detection ranges overlap with each other (step S210). The association of detection points is performed by the method described in the first embodiment. The CPU 101 calculates the amount of relative axis deviation of the two millimeter wave radars in the horizontal direction using each pair of detection points that have been associated (step S220). The calculation of the relative axis deviation amount is performed by the method described in the first embodiment.
CPU101は、水平方向における各ミリ波レーダ22、23の絶対軸ずれ量を算出する(ステップS230)。すなわち、検出範囲が重複する隣接する2つのミリ波レーダからの検出結果を用いず、各ミリ波レーダ22、23によって得られた検出結果を用いて各ミリ波レーダ22、23単独で軸ずれ量が算出される。ミリ波レーダ単体で自身の軸ずれ量を検出する手法としては、車両500の前後方向に対して90°の方位に存在すべき相対速度が0となる検出点を速度0検出点の方位を算出してミリ波レーダの水平方向の向き、すなわち軸ずれ量を求めることができる。より具体的には、ミリ波レーダの射出軸に対する速度0検出点の方位(角度)、すなわち、レーダ座標系と、車両500の前後方向に対して直角な方位(90°)、すなわち、車両座標系との方位差が、軸ずれ量として算出される。あるいは、ミリ波レーダにより検出された静止対象物の距離と方位角度を用いて自車両に対する静止対象物の横方向の距離を求め、求められた横方向の距離を用いて静止対象物の軌跡を求め、求められた静止対象物の軌跡と方位角度0の線分の角度差から水平軸ずれ量が算出されても良い。なお、方位角度0は、車両500の進行方向と平行な方位角である。
The CPU 101 calculates the absolute axis deviation of each of the millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 in the horizontal direction (step S230). That is, without using the detection results from the two adjacent millimeter wave radars whose detection ranges overlap with each other, using the detection results obtained by the respective millimeter wave radars 22 and 23, the axial deviation amounts of the respective millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 alone Is calculated. As a method of detecting the amount of axis deviation of the millimeter wave radar alone, the direction of the zero speed detection point is calculated as the detection point at which the relative speed to be present at the 90 ° azimuth with respect to the longitudinal direction of the vehicle 500 is zero. Then, the horizontal direction of the millimeter wave radar, that is, the amount of axis deviation can be determined. More specifically, the azimuth (angle) of the zero velocity detection point with respect to the emission axis of the millimeter wave radar, that is, the azimuth (90 °) perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the vehicle 500, ie, the vehicle coordinate The misorientation with the system is calculated as the amount of axis deviation. Alternatively, the lateral distance of the stationary object relative to the host vehicle is determined using the distance and orientation angle of the stationary object detected by the millimeter wave radar, and the trajectory of the stationary object is calculated using the determined lateral distance. The amount of horizontal axis deviation may be calculated from the angle difference between the determined trajectory of the stationary object and the line segment of the azimuth angle 0. Note that the azimuth angle 0 is an azimuth angle parallel to the traveling direction of the vehicle 500.
CPU101は、相対軸ずれ量と絶対軸ずれ量とを用いて水平軸ずれレーダを特定し(ステップS240)、本処理ルーチンを終了する。2つのミリ波レーダを用いる場合には、求められる相対軸ずれ量は相対値であり、相対軸ずれ量が算出された場合でもいずれのミリ波レーダが実際に水平軸ずれを起こしているのか決定できない。そこで、各ミリ波レーダ単独で求められた絶対軸ずれ量を用いることによっていずれのミリ波レーダが水平軸ずれを起こしているのかを決定することができる。
The CPU 101 specifies the horizontal axis offset radar using the relative axis offset amount and the absolute axis offset amount (step S240), and ends this processing routine. When two millimeter wave radars are used, the calculated relative axis deviation is a relative value, and even if the relative axis deviation is calculated, it is determined which millimeter wave radar actually causes the horizontal axis deviation. Can not. Therefore, it is possible to determine which of the millimeter wave radars is causing the horizontal axis shift by using the absolute axis shift amount obtained by each millimeter wave radar alone.
第3の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10によれば、2つのミリ波レーダを備える場合であっても、水平方向におけるレーダの軸ずれを判定し、水平軸ずれレーダを特定することができる。したがって、水平方向におけるレーダの軸ずれの判定によるする時間の短縮化、レーダのみを用いて軸ずれを判定することができる。また、相対軸ずれ量を算出して水平軸ずれの有無を判定するので、相対速度が0でない検出点を用いて水平軸ずれを判定することが可能となり、絶対軸ずれ量のみを用いる場合と比較して、水平軸ずれを判定することができる頻度を増大させることが可能となり、ミリ波レーダの水平軸ずれ状態をより早く判定することができる。すなわち、相対軸ずれ量が0または基準量以下の場合には、絶対軸ずれ量を用いることなくミリ波レーダの軸ずれなしを確定することが確定できるので、ミリ波レーダの水平軸ずれ状態を精度良く管理することができる。なお、第3の実施形態における水平軸ずれレーダの特定に続いて第2の実施形態において説明した補正処理が実行されても良い。
According to the object detection device 10 according to the third embodiment, even in the case where two millimeter wave radars are provided, it is possible to determine the off-axis of the radar in the horizontal direction and specify the off-axis radar. . Therefore, it is possible to determine the axis shift using the shortening of time based on the determination of the axis shift of the radar in the horizontal direction and using only the radar. Further, since the relative axis deviation amount is calculated to determine the presence or absence of the horizontal axis deviation, it becomes possible to determine the horizontal axis deviation using a detection point at which the relative velocity is not 0, and the case of using only the absolute axis deviation amount In comparison, it is possible to increase the frequency with which the horizontal axis deviation can be determined, and the horizontal axis deviation state of the millimeter wave radar can be determined more quickly. That is, when the relative axis deviation amount is 0 or less than the reference amount, it can be determined that the axis deviation of the millimeter wave radar is determined without using the absolute axis deviation amount. It can be managed precisely. The correction process described in the second embodiment may be executed subsequent to the specification of the horizontal axis offset radar in the third embodiment.
その他の実施形態:
(1)第1~第3の実施形態において、検出点の対応付けおよび水平軸ずれ量の算出は、ICP法以外の手法によって行われても良い。例えば、2つの検出点群に含まれる最近傍の検出点同士を仮の検出点対として対応付けを行い、仮の検出点対の相対速度差が予め定められた基準差よりも小さい場合には、確定検出点対として対応付けを確定する手法が用いられ得る。相対速度差に代えて、あるいは、相対速度差に加えて受信電力差が同様に用いられても良い。対応付けが確定した後、各検出点対の方位差を求め、検出点群に含まれる各検出点対の方位差の平均値を水平軸ずれ量として用いることができる。 Other embodiments:
(1) In the first to third embodiments, the correspondence between detection points and the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount may be performed by a method other than the ICP method. For example, when the nearest detection points included in two detection point groups are associated with each other as a temporary detection point pair, the relative velocity difference between the temporary detection point pair is smaller than a predetermined reference difference. A method of determining the correspondence as a determined detection point pair may be used. Instead of or in addition to the relative speed difference, the received power difference may be used as well. After the correspondence is determined, the orientation difference of each detection point pair can be obtained, and the average value of the orientation difference of each detection point pair included in the detection point group can be used as the horizontal axis offset amount.
(1)第1~第3の実施形態において、検出点の対応付けおよび水平軸ずれ量の算出は、ICP法以外の手法によって行われても良い。例えば、2つの検出点群に含まれる最近傍の検出点同士を仮の検出点対として対応付けを行い、仮の検出点対の相対速度差が予め定められた基準差よりも小さい場合には、確定検出点対として対応付けを確定する手法が用いられ得る。相対速度差に代えて、あるいは、相対速度差に加えて受信電力差が同様に用いられても良い。対応付けが確定した後、各検出点対の方位差を求め、検出点群に含まれる各検出点対の方位差の平均値を水平軸ずれ量として用いることができる。 Other embodiments:
(1) In the first to third embodiments, the correspondence between detection points and the calculation of the horizontal axis shift amount may be performed by a method other than the ICP method. For example, when the nearest detection points included in two detection point groups are associated with each other as a temporary detection point pair, the relative velocity difference between the temporary detection point pair is smaller than a predetermined reference difference. A method of determining the correspondence as a determined detection point pair may be used. Instead of or in addition to the relative speed difference, the received power difference may be used as well. After the correspondence is determined, the orientation difference of each detection point pair can be obtained, and the average value of the orientation difference of each detection point pair included in the detection point group can be used as the horizontal axis offset amount.
(2)第1~第3の実施形態において、検出点を対応付けするに際して、仮の検出点対の相対速度差や受信電力差が予め定められた基準よりも大きい場合には、当該仮の検出点対は確定検出点対から除外されても良い。あるいは、方位差の平均値を算出するに際して、相対速度差や受信電力差が予め定められた基準よりも大きい確定検出点対の方位差よりも、相対速度差や受信電力差が予め定められた基準よりも小さい確定検出点対の方位差の重み付けを大きくして、ICP法や方位角の平均値から水平軸ずれ量が求められても良い。これらの手法を採用することのよって、水平軸ずれ量の算出精度が向上され、水平軸ずれレーダの特定制度が向上される。
(2) In the first to third embodiments, when associating the detection points, if the relative speed difference between the pair of temporary detection points and the received power difference is larger than a predetermined reference, the temporary The detection point pairs may be excluded from the definite detection point pairs. Alternatively, when calculating the average value of the azimuth difference, the relative speed difference or the reception power difference is predetermined rather than the azimuth difference of the determined detection point pair whose relative speed difference or reception power difference is larger than a predetermined reference. The horizontal axis shift amount may be determined from the average value of the ICP method or the azimuth angle by increasing the weighting of the misorientation of the determined detection point pair smaller than the reference. By adopting these methods, the calculation accuracy of the horizontal axis offset amount is improved, and the specification system of the horizontal axis offset radar is improved.
(3)第1~第3の実施形態において、仮の検出点対が移動体上の検出点対である場合には、確定検出点対から除外されても良い。移動する検出点対を用いる場合、方位角がずれやすく、水平軸ずれ量の算出精度が低下するので、移動する検出点対を除外することによって算出精度の低下を防止または低減することができる。
(3) In the first to third embodiments, when the temporary detection point pair is the detection point pair on the moving object, it may be excluded from the final detection point pair. When a moving detection point pair is used, the azimuth angle tends to shift, and the calculation accuracy of the horizontal axis shift amount decreases. Therefore, by excluding the moving detection point pair, the decrease in the calculation accuracy can be prevented or reduced.
(4)第1~第3の実施形態において、重複領域の周縁方位に近い検出点対の方位差よりも、重複領域の中心方位に近い検出点対の方位差に対する重み付けを大きくして、ICP法や方位角の平均値から水平軸ずれ量が求められても良い。一般的に、ミリ波レーダの精度は挟角域の方が広角域よりも方位精度が良く、挟角寄りに位置する重複領域の中心方位に近い検出点対を用いることにより水平軸ずれ量の算出精度を向上させることができる。
(4) In the first to third embodiments, the ICP weighting is performed by increasing the weight for the orientation difference of the detection point pair closer to the center orientation of the overlap region than the orientation difference of the detection point pair closer to the peripheral orientation of the overlap region. The amount of horizontal axis offset may be determined from the mean value of the modulus or the azimuth angle. Generally, the accuracy of millimeter wave radar is better in azimuth accuracy in the narrow angle area than in the wide angle area, and by using a detection point pair close to the central direction of the overlapping area located near the narrow angle, The calculation accuracy can be improved.
(5)第1~第3の実施形態においては、水平軸ずれ量は、各ミリ波レーダ21~23から得られた1回の検出点を用いて算出、すなわち、瞬時算出されているが、一定時間にわたり検出された検出点を用いて得られた回転量の平均値を用いて水平軸ずれ量を算出し、水平軸ずれを起こしているミリ波レーダが特定されても良い。
(5) In the first to third embodiments, the horizontal axis shift amount is calculated using one detection point obtained from each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, that is, it is calculated instantaneously, The horizontal axis shift amount may be calculated using the average value of the rotation amounts obtained using the detection points detected for a predetermined time, and the millimeter wave radar causing the horizontal axis shift may be identified.
(6)第1~第3の実施形態において、車両500が旋回中に得られる検出点は用いなくても良い。車両500の旋回中は方位ずれが発生しやすいので、旋回中の検出点を用いないことにより、水平軸ずれ量の算出精度および水平軸ずれレーダの特定精度を向上させることができる。車両500が旋回中であるか否かは、例えば、回転角センサ24およびヨーレートセンサ26の少なくともいずれか一方から入力された検出信号を用いて自車両の走行軌跡が旋回軌跡を描いているか否かにより判定可能である。また、車両500が停止している際に得られた検出点を用いないようにしても良い。車両500が停止している際には、検出点群の位置が安定する一方で、一定の対象物が検出対象となり検出結果に偏りが生じる可能性が有る。すなわち、検出対象物がランダムに変化することによって、対象物に起因する反射波の偏りが分散、解消され、より信頼性の高い検出結果を得ることができる。なお、車両500が停止しているか否かは、例えば、車輪速度センサ25から入力される車輪速度が0km/hであるか否かにより判定することができる。
(6) In the first to third embodiments, the detection points obtained while the vehicle 500 is turning may not be used. Since azimuth deviation is likely to occur during turning of the vehicle 500, calculation accuracy of the horizontal axis deviation amount and identification accuracy of the horizontal axis deviation radar can be improved by not using the detection point during turning. Whether or not the vehicle 500 is turning is, for example, whether or not the traveling locus of the own vehicle draws a turning locus using a detection signal input from at least one of the rotation angle sensor 24 and the yaw rate sensor 26 It can be determined by In addition, the detection point obtained when the vehicle 500 is stopped may not be used. While the position of the detection point group is stabilized when the vehicle 500 is stopped, there is a possibility that a certain target object is to be detected and the detection result is biased. That is, by randomly changing the detection target, the bias of the reflected wave caused by the target is dispersed and eliminated, and a more reliable detection result can be obtained. Note that whether or not the vehicle 500 is stopped can be determined, for example, based on whether or not the wheel speed input from the wheel speed sensor 25 is 0 km / h.
(7)第1の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10において、2つのミリ波レーダによる検出結果を用いる相対軸ずれ量に加えて、各ミリ波レーダ21~23による単独の軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸ずれレーダの特定が行われても良い。例えば、第2および第3のミリ波レーダ22、23が同一方向に水平軸ずれしている場合には、第1のミリ波レーダ21が水平軸ずれを起こしていると判定され得る。そこで、第3の実施形態において説明したように、第1~第3のミリ波レーダ21~23についてそれぞれ、絶対軸ずれ量を求め、単独での水平軸ずれ判定結果を加味しても良い。第1のミリ波レーダ21について絶対軸ずれ量が0または基準値以下の場合には、第2および第3のミリ波レーダ22、23が共に水平軸ずれを起こしていることを判定することができる。さらに、相対軸ずれ量および絶対軸ずれ量にそれぞれ重み付けをした上で加重平均した軸ずれ量を用いて各ミリ波レーダの水平軸ずれが判定されても良い。以上の手段を採用することによって、3つのミリ波レーダが用いられる際に発生し得る誤判定を解消または低減することができる。
(7) In the object detection device 10 according to the first embodiment, in addition to the relative axis deviation amount using the detection results of the two millimeter wave radars, the single axis deviation amount by each of the millimeter wave radars 21 to 23 is used The horizontal offset radar may be identified. For example, when the second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 are offset in the same direction in the horizontal direction, it can be determined that the first millimeter wave radar 21 is in the horizontal offset. Therefore, as described in the third embodiment, absolute axis offset amounts may be obtained for each of the first to third millimeter wave radars 21 to 23, and the result of the determination of horizontal axis offset alone may be taken into consideration. When the absolute axis shift amount of the first millimeter wave radar 21 is 0 or less than the reference value, it is determined that both the second and third millimeter wave radars 22 and 23 cause horizontal axis shift. it can. Furthermore, the relative axis deviation amount and the absolute axis deviation amount may be respectively weighted, and then weighted average axis deviation amount may be used to determine the horizontal axis deviation of each millimeter wave radar. By adopting the above means, it is possible to eliminate or reduce the erroneous determination that may occur when three millimeter wave radars are used.
(8)第2の実施形態に係る対象物検出装置10における補正は、第3の実施形態において説明した絶対軸ずれ量と相対軸ずれ量との差が第2補正基準値、例えば、1°以下の場合に実行されても良い。また、絶対軸ずれ量と相対軸ずれ量との差に応じて、補正量が変更されても良い。例えば、差が大きくなるに連れて、絶対軸ずれ量または相対軸ずれ量、あるいは、両者の平均ずれ量に対する補正量が小さくされる。差が大きい場合には、絶対軸ずれ量または相対軸ずれ量の一方が異常値であることも考えられるので、水平軸ずれ量を徐々に解消することにより、適当でない水平軸ずれの補正の影響が低減される。
(8) In the correction in the object detection device 10 according to the second embodiment, the difference between the absolute axis deviation amount and the relative axis deviation amount described in the third embodiment is a second correction reference value, for example, 1 °. It may be executed in the following cases. Further, the correction amount may be changed according to the difference between the absolute axis deviation amount and the relative axis deviation amount. For example, as the difference increases, the correction amount for the absolute axis deviation amount, the relative axis deviation amount, or the average deviation amount of the both is reduced. If the difference is large, it is possible that one of the absolute axis offset amount or the relative axis offset amount is an abnormal value, so by gradually eliminating the horizontal axis offset amount, the influence of the correction of an inappropriate horizontal axis offset Is reduced.
(9)第1~第3の実施形態においては、CPU101が検出器特定プログラムP1および軸ずれ補正プログラムP2を実行することによって、ソフトウェア的に検出器特定部および補正部が実現されているが、予めプログラムされた集積回路またはディスクリート回路によってハードウェア的に実現されても良い。
(9) In the first to third embodiments, the CPU 101 executes the detector identification program P1 and the axis offset correction program P2 to realize the detector identification unit and the correction unit in software. It may be realized in hardware by a preprogrammed integrated circuit or discrete circuit.
以上、実施形態、変形例に基づき本開示について説明してきたが、上記した発明の実施の形態は、本開示の理解を容易にするためのものであり、本開示を限定するものではない。本開示は、その趣旨並びに特許請求の範囲を逸脱することなく、変更、改良され得ると共に、本開示にはその等価物が含まれる。たとえば、発明の概要の欄に記載した各形態中の技術的特徴に対応する実施形態、変形例中の技術的特徴は、上述の課題の一部又は全部を解決するために、あるいは、上述の効果の一部又は全部を達成するために、適宜、差し替えや、組み合わせを行うことが可能である。また、その技術的特徴が本明細書中に必須なものとして説明されていなければ、適宜、削除することが可能である。例えば、上記第1の態様に係る車両用の対象物検出装置を適用例1とし、
[適用例2]適用例1に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は3以上の検出器であり、
前記検出器特定部は、2つの検出器の組み合わせの全てについて前記相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量の組み合わせを用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例3]適用例1に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は2つの検出器であり、
前記検出器特定部は、前記相対的な軸ずれ量と、各前記検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて算出される絶対軸ずれ量とを用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例4]適用例1から3に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記検出器特定部は、前記車両が旋回中に検出された検出点を用いない、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例5]適用例1から4のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記検出器特定部は、前記車両が静止中に検出された検出点を用いない、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例6]適用例1から5のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、さらに、
前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて、前記特定された検出器からの検出信号を補正することによって前記特定された検出器の水平軸ずれを補正する補正部を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例7]適用例1から5のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は駆動部を備え、水平方向に回転可能であり、
前記車両用の対象物検出装置はさらに、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて、前記駆動部を駆動させて前記特定された検出器の水平軸ずれを補正する補正部を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例8]適用例6または7に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量が予め定められた第1補正基準値以上の場合に補正を行う、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例9]適用例6または7に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量と、前記検出点を用いて各前記検出器について算出される絶対軸ずれ量との差が予め定められた第2補正基準値以下の場合に補正を行う、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例10]適用例6から9のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量に応じて補正量を決定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。としても良い。 Although the present disclosure has been described above based on the embodiment and the modification, the embodiment of the invention described above is for the purpose of facilitating the understanding of the present disclosure and does not limit the present disclosure. The present disclosure can be modified and improved without departing from the spirit and the claims, and the present disclosure includes the equivalents thereof. For example, the technical features in the embodiments corresponding to the technical features in the respective forms described in the section of the summary of the invention, and the technical features in the modified examples are for solving some or all of the problems described above, or Replacements or combinations can be made as appropriate to achieve part or all of the effects. Also, if the technical features are not described as essential in the present specification, they can be deleted as appropriate. For example, the object detection device for a vehicle according to the first aspect is an application example 1,
Application Example 2 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to Application Example 1,
The plurality of detectors are three or more detectors,
The detector specifying unit calculates the relative amount of axial deviation for all combinations of two detectors, and uses a combination of the calculated relative amount of axial deviation to detect a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated. An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it.
Application Example 3 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Example 1,
The plurality of detectors are two detectors,
The detector specifying unit is a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated using the relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated using the detection points input from the respective detectors. An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it.
Application Example 4 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Examples 1 to 3,
The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is turning.
Application Example 5 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 4,
The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is stationary.
Application Example 6 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 5, further,
A vehicle comprising: a correction unit that corrects the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector by correcting the detection signal from the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount; Object detection device.
Application Example 7 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 5,
The plurality of detectors may include a drive and may be horizontally rotatable.
The object detection device for a vehicle further includes a correction unit that drives the drive unit to correct the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount. Object detection device for vehicles.
Application Example 8 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Example 6 or 7,
The said correction | amendment part is a target object detection apparatus for vehicles which correct | amends when the calculated relative axis shift amount is more than a predetermined 1st correction | amendment reference value.
Application Example 9 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle described in Application Example 6 or 7,
The correction unit is configured such that a difference between the calculated relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated for each of the detectors using the detection point is equal to or less than a predetermined second correction reference value. An object detection device for a vehicle that makes corrections in the case.
Application Example 10 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 6 to 9,
The said correction | amendment part determines the correction amount according to the calculated relative axis shift amount, The target object detection apparatus for vehicles. As well.
[適用例2]適用例1に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は3以上の検出器であり、
前記検出器特定部は、2つの検出器の組み合わせの全てについて前記相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量の組み合わせを用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例3]適用例1に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は2つの検出器であり、
前記検出器特定部は、前記相対的な軸ずれ量と、各前記検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて算出される絶対軸ずれ量とを用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例4]適用例1から3に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記検出器特定部は、前記車両が旋回中に検出された検出点を用いない、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例5]適用例1から4のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記検出器特定部は、前記車両が静止中に検出された検出点を用いない、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例6]適用例1から5のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、さらに、
前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて、前記特定された検出器からの検出信号を補正することによって前記特定された検出器の水平軸ずれを補正する補正部を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例7]適用例1から5のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は駆動部を備え、水平方向に回転可能であり、
前記車両用の対象物検出装置はさらに、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて、前記駆動部を駆動させて前記特定された検出器の水平軸ずれを補正する補正部を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例8]適用例6または7に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量が予め定められた第1補正基準値以上の場合に補正を行う、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例9]適用例6または7に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量と、前記検出点を用いて各前記検出器について算出される絶対軸ずれ量との差が予め定められた第2補正基準値以下の場合に補正を行う、車両用の対象物検出装置。
[適用例10]適用例6から9のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量に応じて補正量を決定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。としても良い。 Although the present disclosure has been described above based on the embodiment and the modification, the embodiment of the invention described above is for the purpose of facilitating the understanding of the present disclosure and does not limit the present disclosure. The present disclosure can be modified and improved without departing from the spirit and the claims, and the present disclosure includes the equivalents thereof. For example, the technical features in the embodiments corresponding to the technical features in the respective forms described in the section of the summary of the invention, and the technical features in the modified examples are for solving some or all of the problems described above, or Replacements or combinations can be made as appropriate to achieve part or all of the effects. Also, if the technical features are not described as essential in the present specification, they can be deleted as appropriate. For example, the object detection device for a vehicle according to the first aspect is an application example 1,
Application Example 2 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to Application Example 1,
The plurality of detectors are three or more detectors,
The detector specifying unit calculates the relative amount of axial deviation for all combinations of two detectors, and uses a combination of the calculated relative amount of axial deviation to detect a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated. An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it.
Application Example 3 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Example 1,
The plurality of detectors are two detectors,
The detector specifying unit is a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated using the relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated using the detection points input from the respective detectors. An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it.
Application Example 4 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Examples 1 to 3,
The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is turning.
Application Example 5 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 4,
The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is stationary.
Application Example 6 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 5, further,
A vehicle comprising: a correction unit that corrects the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector by correcting the detection signal from the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount; Object detection device.
Application Example 7 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 1 to 5,
The plurality of detectors may include a drive and may be horizontally rotatable.
The object detection device for a vehicle further includes a correction unit that drives the drive unit to correct the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount. Object detection device for vehicles.
Application Example 8 In the object detection device for a vehicle according to Application Example 6 or 7,
The said correction | amendment part is a target object detection apparatus for vehicles which correct | amends when the calculated relative axis shift amount is more than a predetermined 1st correction | amendment reference value.
Application Example 9 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle described in Application Example 6 or 7,
The correction unit is configured such that a difference between the calculated relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated for each of the detectors using the detection point is equal to or less than a predetermined second correction reference value. An object detection device for a vehicle that makes corrections in the case.
Application Example 10 In the object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of Application Examples 6 to 9,
The said correction | amendment part determines the correction amount according to the calculated relative axis shift amount, The target object detection apparatus for vehicles. As well.
Claims (11)
- 車両用の対象物検出装置(10)であって、
反射波を用いて対象物を表す複数の検出点を検出する複数の検出器(21~23)であって、一部の前記検出点が重複するように車両に配置されている複数の検出器と、
前記複数の検出器のうち2つの検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて、前記2つの検出器の水平方向における相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、検出器特定部(101、P1)と、を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。 An object detection device (10) for a vehicle, wherein
A plurality of detectors (21 to 23) for detecting a plurality of detection points representing an object using a reflected wave, wherein the plurality of detectors are arranged on a vehicle such that a part of the detection points overlap. When,
The amount of relative axis deviation in the horizontal direction of the two detectors is calculated using the detection points input from the two detectors among the plurality of detectors, and the calculated amount of relative axis deviation An object detection apparatus for a vehicle, comprising: a detector identification unit (101, P1) for identifying a detector whose horizontal axis is offset using. - 請求項1に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は3以上の検出器であり、
前記検出器特定部は、2つの検出器の組み合わせの全てについて前記相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量の組み合わせを用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to claim 1,
The plurality of detectors are three or more detectors,
The detector specifying unit calculates the relative amount of axial deviation for all combinations of two detectors, and uses a combination of the calculated relative amount of axial deviation to detect a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated. An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it. - 請求項1に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は2つの検出器であり、
前記検出器特定部は、前記相対的な軸ずれ量と、各前記検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて算出される絶対軸ずれ量とを用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to claim 1,
The plurality of detectors are two detectors,
The detector specifying unit is a detector whose horizontal axis is deviated using the relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated using the detection points input from the respective detectors. An object detection device for a vehicle that identifies it. - 請求項1から3のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記検出器特定部は、前記車両が旋回中に検出された検出点を用いない、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is turning. - 請求項1から4のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記検出器特定部は、前記車両が静止中に検出された検出点を用いない、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
The object detection device for a vehicle, wherein the detector specifying unit does not use a detection point detected while the vehicle is stationary. - 請求項1から5のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、さらに、
前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて、前記特定された検出器からの検出信号を補正することによって前記特定された検出器の水平軸ずれを補正する補正部(101、P2)を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to any one of claims 1 to 5, further comprising:
A correction unit (101, P2) for correcting the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector by correcting the detection signal from the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount An object detection device for a vehicle, comprising: - 請求項1から5のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記複数の検出器は駆動部を備え、水平方向に回転可能であり、
前記車両用の対象物検出装置はさらに、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて、前記駆動部を駆動させて前記特定された検出器の水平軸ずれを補正する補正部を備える、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of claims 1 to 5.
The plurality of detectors may include a drive and may be horizontally rotatable.
The object detection device for a vehicle further includes a correction unit that drives the drive unit to correct the horizontal axis deviation of the specified detector using the calculated relative axis deviation amount. Object detection device for vehicles. - 請求項6または7に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量が予め定められた第1補正基準値以上の場合に補正を行う、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to claim 6 or 7
The said correction | amendment part is a target object detection apparatus for vehicles which correct | amends when the calculated relative axis shift amount is more than a predetermined 1st correction | amendment reference value. - 請求項6または7に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量と、前記検出点を用いて各前記検出器について算出される絶対軸ずれ量との差が予め定められた第2補正基準値以下の場合に補正を行う、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection apparatus for a vehicle according to claim 6 or 7
The correction unit is configured such that a difference between the calculated relative axis deviation amount and an absolute axis deviation amount calculated for each of the detectors using the detection point is equal to or less than a predetermined second correction reference value. An object detection device for a vehicle that makes corrections in the case. - 請求項6から9のいずれか一項に記載の車両用の対象物検出装置において、
前記補正部は、前記算出された相対的な軸ずれ量に応じて補正量を決定する、車両用の対象物検出装置。 The object detection device for a vehicle according to any one of claims 6 to 9.
The said correction | amendment part determines the correction amount according to the calculated relative axis shift amount, The target object detection apparatus for vehicles. - 車両用の対象物検出装置における水平方向の軸ずれ判定方法であって、
反射波を用いて対象物を表す複数の検出点を検出する複数の検出器であって、一部の前記検出点が重複するように車両に配置されている複数の検出器のうち2つの検出器から入力される前記検出点を用いて、前記2つの検出器の水平方向における相対的な軸ずれ量を算出し、
算出した前記相対的な軸ずれ量を用いて水平軸がずれている検出器を特定する、ことを備える、水平方向の軸ずれ量判定方法。 A method of determining an axis deviation in a horizontal direction in an object detection device for a vehicle, comprising:
A plurality of detectors for detecting a plurality of detection points representing an object using a reflected wave, wherein two detections among a plurality of detectors arranged on a vehicle such that a part of the detection points overlap Calculating the relative amount of offset between the two detectors in the horizontal direction using the detection point input from the
A method for determining the amount of off-axis misalignment in the horizontal direction, comprising: using the calculated relative amount of off-axis misalignment to identify a detector having a deviated horizontal axis.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017126827A JP6848725B2 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2017-06-29 | Horizontal axis deviation determination method in the object detection device for vehicles and the object detection device for vehicles |
| JP2017-126827 | 2017-06-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2019003631A1 true WO2019003631A1 (en) | 2019-01-03 |
Family
ID=64741411
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/017403 WO2019003631A1 (en) | 2017-06-29 | 2018-05-01 | Object detection device for vehicle and method for determining horizontal axial deviation of object detection device for vehicle |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6848725B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019003631A1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113447899A (en) * | 2021-06-29 | 2021-09-28 | 上海为彪汽配制造有限公司 | Installation test method and system for vehicle-mounted millimeter wave radar |
| US20220342068A1 (en) * | 2019-10-10 | 2022-10-27 | Kyocera Corporation | Electronic device, method for controlling electronic device, and program for controlling electronic device |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2020189685A1 (en) * | 2019-03-19 | 2020-09-24 | ||
| WO2021024289A1 (en) * | 2019-08-02 | 2021-02-11 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Vehicle-mounted object detection device |
| JP7546704B2 (en) | 2021-02-03 | 2024-09-06 | 日立Astemo株式会社 | Radar Signal Processing Device |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001166051A (en) * | 1999-12-10 | 2001-06-22 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | Axis deviation detection device for vehicular radar device |
| JP2002350532A (en) * | 2001-05-24 | 2002-12-04 | Tech Res & Dev Inst Of Japan Def Agency | Radar antenna adjustment error correcting method |
| JP2005257510A (en) * | 2004-03-12 | 2005-09-22 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Another car detection device and method |
| JP2008519246A (en) * | 2003-12-06 | 2008-06-05 | ローベルト ボツシユ ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | Radar sensor |
| JP2009281862A (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2009-12-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | Axis adjusting method of radar device and axis adjusting device |
| WO2010139446A1 (en) * | 2009-06-05 | 2010-12-09 | Valeo Schalter Und Sensoren Gmbh | Driver assistance device and method for correcting a target angle parameter characteristic curve |
| JP2014153211A (en) * | 2013-02-08 | 2014-08-25 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | Periphery monitoring system and misalignment detection method of periphery monitoring system |
| JP2015078925A (en) * | 2013-10-17 | 2015-04-23 | 株式会社デンソー | Periphery monitoring device and periphery monitoring system |
| JP2016053748A (en) * | 2014-09-02 | 2016-04-14 | 株式会社デンソー | Driving support device and driving support method |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5976027B2 (en) * | 2014-03-27 | 2016-08-23 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Sensor axis deviation detection device and sensor axis deviation detection method |
-
2017
- 2017-06-29 JP JP2017126827A patent/JP6848725B2/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-05-01 WO PCT/JP2018/017403 patent/WO2019003631A1/en active Application Filing
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001166051A (en) * | 1999-12-10 | 2001-06-22 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | Axis deviation detection device for vehicular radar device |
| JP2002350532A (en) * | 2001-05-24 | 2002-12-04 | Tech Res & Dev Inst Of Japan Def Agency | Radar antenna adjustment error correcting method |
| JP2008519246A (en) * | 2003-12-06 | 2008-06-05 | ローベルト ボツシユ ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | Radar sensor |
| JP2005257510A (en) * | 2004-03-12 | 2005-09-22 | Alpine Electronics Inc | Another car detection device and method |
| JP2009281862A (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2009-12-03 | Toyota Motor Corp | Axis adjusting method of radar device and axis adjusting device |
| WO2010139446A1 (en) * | 2009-06-05 | 2010-12-09 | Valeo Schalter Und Sensoren Gmbh | Driver assistance device and method for correcting a target angle parameter characteristic curve |
| JP2014153211A (en) * | 2013-02-08 | 2014-08-25 | Furukawa Electric Co Ltd:The | Periphery monitoring system and misalignment detection method of periphery monitoring system |
| JP2015078925A (en) * | 2013-10-17 | 2015-04-23 | 株式会社デンソー | Periphery monitoring device and periphery monitoring system |
| JP2016053748A (en) * | 2014-09-02 | 2016-04-14 | 株式会社デンソー | Driving support device and driving support method |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20220342068A1 (en) * | 2019-10-10 | 2022-10-27 | Kyocera Corporation | Electronic device, method for controlling electronic device, and program for controlling electronic device |
| CN113447899A (en) * | 2021-06-29 | 2021-09-28 | 上海为彪汽配制造有限公司 | Installation test method and system for vehicle-mounted millimeter wave radar |
| CN113447899B (en) * | 2021-06-29 | 2024-02-02 | 上海为彪汽配制造有限公司 | Method and system for mounting and testing vehicle-mounted millimeter wave radar |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6848725B2 (en) | 2021-03-24 |
| JP2019007934A (en) | 2019-01-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2019003631A1 (en) | Object detection device for vehicle and method for determining horizontal axial deviation of object detection device for vehicle | |
| CN108238047B (en) | Driving support device | |
| EP2127986B1 (en) | Parking assistance device | |
| WO2017111110A1 (en) | Travel support device and travel support method | |
| WO2017104503A1 (en) | Traveling-body control device and traveling-body control method | |
| WO2017145845A1 (en) | Collision prediction apparatus | |
| US10884125B2 (en) | Parking assistance device | |
| JP2015153165A (en) | preceding vehicle selection device | |
| WO2016158238A1 (en) | Vehicle control device in vehicle control method | |
| JP2007139665A (en) | Object detection device and object detection method | |
| WO2017142075A1 (en) | Estimation device | |
| WO2018092567A1 (en) | Traveling control apparatus | |
| JP2010108168A (en) | Collision prediction device | |
| JP2010008055A (en) | Parking assistance apparatus | |
| US20210405186A1 (en) | Obstacle detection system and method using distance sensor | |
| KR20160059823A (en) | System and Method for Lane Keep Asistance | |
| US11142187B2 (en) | Parking assistance device | |
| US11247671B2 (en) | Object recognition device | |
| WO2019065411A1 (en) | Vehicle sensing system | |
| WO2021070881A1 (en) | Control device | |
| JP2008195140A (en) | Radar system, target detection program and target detection method | |
| WO2016063533A1 (en) | In-vehicle object determining apparatus | |
| US11285946B2 (en) | Moving object detector, vehicle control system, method for detecting moving object, and method for controlling vehicle | |
| JP2018199458A (en) | Reverse parking assist device of combination vehicle | |
| JP6256795B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18824013 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18824013 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |