WO2018079430A1 - 画像処理装置、画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム - Google Patents
画像処理装置、画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018079430A1 WO2018079430A1 PCT/JP2017/037978 JP2017037978W WO2018079430A1 WO 2018079430 A1 WO2018079430 A1 WO 2018079430A1 JP 2017037978 W JP2017037978 W JP 2017037978W WO 2018079430 A1 WO2018079430 A1 WO 2018079430A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- image
- virtual viewpoint
- viewpoint image
- processing apparatus
- generation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T17/00—Three dimensional [3D] modelling, e.g. data description of 3D objects
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/90—Arrangement of cameras or camera modules, e.g. multiple cameras in TV studios or sports stadiums
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T15/00—3D [Three Dimensional] image rendering
- G06T15/10—Geometric effects
- G06T15/20—Perspective computation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N13/00—Stereoscopic video systems; Multi-view video systems; Details thereof
- H04N13/10—Processing, recording or transmission of stereoscopic or multi-view image signals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/60—Control of cameras or camera modules
- H04N23/63—Control of cameras or camera modules by using electronic viewfinders
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N23/00—Cameras or camera modules comprising electronic image sensors; Control thereof
- H04N23/95—Computational photography systems, e.g. light-field imaging systems
- H04N23/951—Computational photography systems, e.g. light-field imaging systems by using two or more images to influence resolution, frame rate or aspect ratio
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N5/00—Details of television systems
- H04N5/222—Studio circuitry; Studio devices; Studio equipment
- H04N5/2224—Studio circuitry; Studio devices; Studio equipment related to virtual studio applications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N5/00—Details of television systems
- H04N5/222—Studio circuitry; Studio devices; Studio equipment
- H04N5/262—Studio circuits, e.g. for mixing, switching-over, change of character of image, other special effects ; Cameras specially adapted for the electronic generation of special effects
- H04N5/2628—Alteration of picture size, shape, position or orientation, e.g. zooming, rotation, rolling, perspective, translation
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a technique for generating a virtual viewpoint image.
- Patent Document 1 when a virtual viewpoint image is generated by synthesizing images taken from a plurality of viewpoints, the image quality of the virtual viewpoint image is improved by reducing the rendering unit in the boundary region of the object in the image. Is described.
- a virtual viewpoint image corresponding to a plurality of different requirements regarding image quality cannot be generated.
- the processing time for generation may be longer, making it difficult to meet a user's request to view the virtual viewpoint image in real time even if the image quality is low. There is a risk of becoming.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object thereof is to generate a virtual viewpoint image corresponding to a plurality of different requirements regarding image quality.
- an image processing apparatus has the following configuration, for example. That is, a receiving means for receiving a virtual viewpoint image generation instruction based on captured images photographed from different directions by a plurality of cameras and viewpoint information corresponding to the designation of the virtual viewpoint, and a first for allowing the user to designate a virtual viewpoint 1 virtual viewpoint image and the second virtual viewpoint image that is a second virtual viewpoint image generated based on designation of the virtual viewpoint by the user and has higher image quality than the first virtual viewpoint image, Control means for controlling the generation means in response to the reception of the generation instruction by the reception means so that the generation means is generated based on the captured image and the viewpoint information.
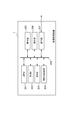
- FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining a configuration of an image processing system 10.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining a hardware configuration of an image processing apparatus 1.
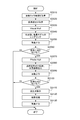
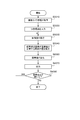
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart for explaining one mode of operation of the image processing apparatus 1.
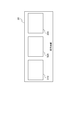
- 4 is a diagram for explaining a configuration of a display screen by the display device 3.
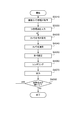
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart for explaining one mode of operation of the image processing apparatus 1.
- 3 is a flowchart for explaining one mode of operation of the image processing apparatus 1.
- the image processing system 10 in this embodiment includes an image processing device 1, a camera group 2, a display device 3, and a display device 4.
- the virtual viewpoint image in the present embodiment is an image obtained when a subject is photographed from a virtual viewpoint.
- the virtual viewpoint image is an image representing the appearance at the designated viewpoint.
- the virtual viewpoint may be specified by the user, or may be automatically specified based on the result of image analysis or the like. That is, the virtual viewpoint image includes an arbitrary viewpoint image (free viewpoint image) corresponding to the viewpoint arbitrarily designated by the user. An image corresponding to the viewpoint designated by the user from a plurality of candidates and an image corresponding to the viewpoint automatically designated by the apparatus are also included in the virtual viewpoint image.
- the virtual viewpoint image is a moving image will be mainly described.
- the virtual viewpoint image may be a still image.
- the camera group 2 includes a plurality of cameras, and each camera photographs a subject from different directions.
- each of the plurality of cameras included in the camera group 2 is connected to the image processing apparatus 1, and transmits a captured image, parameters of each camera, and the like to the image processing apparatus 1.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and a plurality of cameras included in the camera group 2 can communicate with each other. 1 may be transmitted.
- any camera included in the camera group 2 may transmit an image based on photographing by the camera group 2, such as an image generated based on a difference between photographed images by a plurality of cameras, instead of the photographed image. Good.
- the display device 3 accepts designation of a virtual viewpoint for generating a virtual viewpoint image, and transmits information corresponding to the designation to the image processing device 1.
- the display device 3 includes input units such as a joystick, a jog dial, a touch panel, a keyboard, and a mouse, and a user (operator) who specifies a virtual viewpoint specifies a virtual viewpoint by operating the input unit.
- the user in the present embodiment is an operator who operates the input unit of the display device 3 to specify a virtual viewpoint or a viewer who views a virtual viewpoint image displayed by the display device 4. When not distinguished, it is simply described as a user. In this embodiment, the case where the viewer and the operator are different will be mainly described.
- information according to the designation of the virtual viewpoint transmitted from the display device 3 to the image processing apparatus 1 is virtual viewpoint information indicating the position and orientation of the virtual viewpoint.
- the information according to the designation of the virtual viewpoint may be information indicating contents determined according to the virtual viewpoint such as the shape and orientation of the subject in the virtual viewpoint image.
- a virtual viewpoint image may be generated based on information according to the designation of the viewpoint.
- the display device 3 displays the virtual viewpoint image generated and output by the image processing device 1 based on the image based on the photographing by the camera group 2 and the designation of the virtual viewpoint accepted by the display device 3.
- the operator can specify the virtual viewpoint while viewing the virtual viewpoint image displayed on the display device 3.
- the display device 3 that displays the virtual viewpoint image accepts the designation of the virtual viewpoint, but is not limited thereto.
- a device that receives designation of a virtual viewpoint and a display device that displays a virtual viewpoint image for allowing an operator to designate a virtual viewpoint may be separate devices.
- the display device 3 gives a generation instruction for starting generation of a virtual viewpoint image to the image processing device 1 based on an operation by the operator.
- the generation instruction is not limited to this.
- the generation instruction may be an instruction for reserving generation of the virtual viewpoint image in the image processing apparatus 1 so that generation of the virtual viewpoint image is started at a predetermined time.
- an instruction for making a reservation so that generation of a virtual viewpoint image is started when a predetermined event occurs may be used.
- the device that instructs the image processing device 1 to generate a virtual viewpoint image may be a device different from the display device 3, or the user may directly input the generation instruction to the image processing device 1. .
- the display device 4 gives the virtual viewpoint image generated by the image processing device 1 based on the designation of the virtual viewpoint by the operator using the display device 3 to a user (viewer) different from the operator who designates the virtual viewpoint.
- the image processing system 10 may include a plurality of display devices 4, and the plurality of display devices 4 may display different virtual viewpoint images.
- the image processing system 10 includes a display device 4 that displays a virtual viewpoint image (live image) broadcast live and a display device 4 that displays a virtual viewpoint image (non-live image) broadcast after recording. May be.
- the image processing apparatus 1 includes a camera information acquisition unit 100, a virtual viewpoint information acquisition unit 110 (hereinafter referred to as a viewpoint acquisition unit 110), an image generation unit 120, and an output unit 130.
- the camera information acquisition unit 100 acquires, from the camera group 2, images based on shooting by the camera group 2, external parameters and internal parameters of each camera included in the camera group 2, and outputs them to the image generation unit 120.
- the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 acquires information according to the designation of the virtual viewpoint by the operator from the display device 3 and outputs the information to the image generation unit 120.
- the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 receives a virtual viewpoint image generation instruction from the display device 3.
- the image generation unit 120 is based on the image based on the shooting acquired by the camera information acquisition unit 100, information according to the designation acquired by the viewpoint acquisition unit 110, and the generation instruction received by the viewpoint acquisition unit 110. Then, a virtual viewpoint image is generated and output to the output unit 130.
- the output unit 130 outputs the virtual viewpoint image generated by the image generation unit 120 to an external device such as the display device 3 or the display device 4.
- the image processing apparatus 1 generates a plurality of virtual viewpoint images with different image quality and outputs them to an output destination corresponding to each virtual viewpoint image. For example, a low-quality virtual viewpoint image with a short processing time is generated to the display device 4 viewed by a viewer who desires a virtual viewpoint image in real time (low delay). On the other hand, a high-quality virtual viewpoint image with a long processing time is generated to the display device 4 viewed by a viewer who desires a high-quality virtual viewpoint image.
- the delay in the present embodiment corresponds to a period from when the camera group 2 performs shooting until a virtual viewpoint image based on the shooting is displayed. However, the definition of the delay is not limited to this. For example, a time difference between the time in the real world and the time corresponding to the display image may be used as the delay.
- the image processing apparatus 1 includes a CPU 201, ROM 202, RAM 203, auxiliary storage device 204, display unit 205, operation unit 206, communication unit 207, and bus 208.
- the CPU 201 controls the entire image processing apparatus 1 using computer programs and data stored in the ROM 202 and the RAM 203.
- the image processing apparatus 1 may have a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), and the GPU may perform at least a part of the processing by the CPU 201.
- the ROM 202 stores programs and parameters that do not need to be changed.
- the RAM 203 temporarily stores programs and data supplied from the auxiliary storage device 204 and data supplied from the outside via the communication unit 207.
- the auxiliary storage device 204 is composed of, for example, a hard disk drive and stores content data such as still images and moving images.
- the display unit 205 includes a liquid crystal display, for example, and displays a GUI (Graphical User Interface) for the user to operate the image processing apparatus 1.
- the operation unit 206 is composed of, for example, a keyboard and a mouse, and inputs various instructions to the CPU 201 in response to a user operation.
- the communication unit 207 communicates with external devices such as the camera group 2, the display device 3, and the display device 4. For example, when the image processing apparatus 1 is connected to an external apparatus by wire, a LAN cable or the like is connected to the communication unit 207. Note that when the image processing apparatus 1 has a function of performing wireless communication with an external apparatus, the communication unit 207 includes an antenna.
- a bus 208 connects each part of the image processing apparatus 1 and transmits information.
- the display unit 205 and the operation unit 206 exist in the image processing apparatus 1, but the image processing apparatus 1 may not include at least one of the display unit 205 and the operation unit 206. Further, at least one of the display unit 205 and the operation unit 206 exists as another device outside the image processing apparatus 1, and the CPU 201 controls the display control unit that controls the display unit 205 and the operation that controls the operation unit 206. It may operate as a control unit.
- the process shown in FIG. 3 is started at the timing when the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 receives an instruction to generate a virtual viewpoint image, and is repeated periodically (for example, every frame when the virtual viewpoint image is a moving image).
- the start timing of the process shown in FIG. 3 is not limited to the above timing.
- the processing shown in FIG. 3 is realized by the CPU 201 developing and executing a program stored in the ROM 202 on the RAM 203. Note that at least part of the processing illustrated in FIG. 3 may be realized by dedicated hardware different from the CPU 201.
- S2010 and S2020 correspond to processing for acquiring information
- S2030 to S2050 correspond to processing for generating and outputting a virtual viewpoint image (designation image) for allowing the operator to specify a virtual viewpoint.
- S2070 to S2100 correspond to processing for generating and outputting a live image.
- Steps S2110 to S2130 correspond to processing for generating and outputting a non-live image. Details of the processing in each step will be described below.
- the camera information acquisition unit 100 acquires a captured image of each camera based on shooting by the camera group 2, and external parameters and internal parameters of each camera.
- the external parameter is information related to the position and orientation of the camera
- the internal parameter is information related to the focal length of the camera and the image center.
- the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 acquires virtual viewpoint information as information according to the designation of the virtual viewpoint by the operator.
- the virtual viewpoint information corresponds to an external parameter and an internal parameter of a virtual camera that captures a subject from the virtual viewpoint, and one piece of virtual viewpoint information is required to generate one frame of the virtual viewpoint image.
- the image generation unit 120 estimates the three-dimensional shape of the object that is the subject based on the image captured by the camera group 2.
- the object that is the subject is, for example, a person or a moving object that exists within the shooting range of the camera group 2.
- the image generation unit 120 calculates a difference between the captured image acquired from the camera group 2 and a background image corresponding to each camera acquired in advance, thereby extracting a portion (foreground region) corresponding to the object in the captured image. Generate a silhouette image. Then, the image generation unit 120 estimates the three-dimensional shape of the object using the silhouette image corresponding to each camera and the parameters of each camera. For example, the Visual Hull method is used for the estimation of the three-dimensional shape.
- a 3D point group (a set of points having three-dimensional coordinates) expressing the three-dimensional shape of the object as the subject is obtained.
- the method of deriving the three-dimensional shape of the object from the image captured by the camera group 2 is not limited to this.
- the image generation unit 120 renders the 3D point group and the background 3D model based on the acquired virtual viewpoint information, and generates a virtual viewpoint image.
- the background 3D model is a CG model such as a stadium where the camera group 2 is installed, for example, and is created in advance and stored in the image processing system 10.
- the area corresponding to the object and the background area are each displayed in a predetermined color (for example, one color).
- the process of rendering the 3D point cloud and the background 3D model is known in the field of games and movies, and a method for performing high-speed processing such as a method of processing using a GPU is known. Therefore, the virtual viewpoint image generated by the processing up to S2040 can be generated at high speed according to the shooting by the camera group 2 and the designation of the virtual viewpoint by the operator.
- the output unit 130 outputs the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2040 by the image generation unit 120 to the display device 3 for allowing the operator to specify the virtual viewpoint.
- the display screen 30 includes an area 310, an area 320, and an area 330.
- the virtual viewpoint image generated as the designation image is displayed in the area 310
- the virtual viewpoint image generated as the live image is displayed in the area 320
- the virtual viewpoint image generated as the non-live image is displayed in the area 330. Is done. That is, the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2040 and output in S2050 is displayed in area 310.
- the operator designates the virtual viewpoint while looking at the screen of the area 310.
- the display device 3 only needs to display at least the designation image, and does not have to display a live image or a non-live image.
- the image generation unit 120 determines whether to perform a process of generating a virtual viewpoint image with a higher image quality than the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2040. For example, if only a low-quality image for specifying the virtual viewpoint is required, the process does not proceed to S2070 but ends. On the other hand, if a higher quality image is required, the process proceeds to S2070 and the process is continued.
- the image generation unit 120 further increases the accuracy of the shape model (3D point group) of the object estimated in S2030 using, for example, the PhotoHull method. Specifically, by projecting each point of the 3D point group onto the captured image of each camera and evaluating the degree of color matching in each captured image, whether or not the point is necessary for expressing the subject shape Determine. For example, if the variance of the projection target pixel value is larger than a threshold value for a certain point in the 3D point group, it is determined that the point is not correct as a point representing the shape of the subject, and the point is deleted from the 3D point group. . This processing is performed on all points in the 3D point group, thereby realizing high accuracy of the shape model of the object. Note that the method for increasing the accuracy of the shape model of the object is not limited to this.
- step S2080 the image generation unit 120 adds a color to the 3D point group that has been improved in step S2070, projects the image to the coordinates of the virtual viewpoint, and generates a foreground image corresponding to the foreground area.
- a process of generating a viewed background image is executed.
- the image generation unit 120 generates a virtual viewpoint image as a live image by superimposing the foreground image on the generated background image.
- a process of coloring the 3D point group is executed.
- the coloring process includes a point visibility determination and a color calculation process.
- the visibility determination it is possible to specify a camera that can be photographed for each point from the positional relationship between each point in the 3D point group and a plurality of cameras included in the camera group 2.
- the point is projected onto a captured image of a camera that can shoot the point, and the color of the pixel at the projection destination is set as the color of the point.
- a foreground image of a virtual viewpoint image can be generated by rendering the 3D point group that is colored in this way by an existing CG rendering method.
- the vertex of the background 3D model (for example, a point corresponding to the end of the playing field) is set. These vertices are projected onto the coordinate system of two cameras (referred to as the first camera and the second camera) close to the virtual viewpoint and the coordinate system of the virtual viewpoint.
- the first projection matrix between the virtual viewpoint and the first camera and the first projection matrix between the virtual viewpoint and the second camera using the corresponding points of the virtual viewpoint and the first camera and the corresponding points of the virtual viewpoint and the second camera.
- a two-projection matrix is calculated.
- each pixel of the background image is projected onto the captured image of the first camera and the captured image of the second camera, and the average of the two pixel values of the projection destination is calculated.
- the pixel value of the background image is determined. Note that the pixel value of the background image may be determined from the captured images of three or more cameras by a similar method.
- a colored virtual viewpoint image can be generated by superimposing the foreground image on the background image of the virtual viewpoint image obtained in this way. That is, the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2080 has higher image quality with respect to the number of color gradations than the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2040. In other words, the number of gradations of colors included in the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2040 is smaller than the number of gradations of colors included in the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2080. Note that the method of adding color information to the virtual viewpoint image is not limited to this.
- the output unit 130 outputs the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2080 by the image generation unit 120 to the display device 3 and the display device 4 as a live image.
- the image output to the display device 3 is displayed in the area 320 and can be viewed by the operator, and the image output to the display device 4 can be viewed by the viewer.
- the image generation unit 120 determines whether to perform a process of generating a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2080. For example, when the virtual viewpoint image is provided only to the viewer by live broadcasting, the process does not proceed to S2110 and the process ends. On the other hand, when a higher quality image is broadcast to the viewer after recording, the process proceeds to S2110 and the process is continued.
- the image generation unit 120 further increases the accuracy of the shape model of the object generated in S2070.
- high accuracy is realized by deleting isolated points of the shape model.
- isolated point removal first, with respect to the voxel set (3D point group) calculated by Photo Hull, it is checked whether another voxel exists around each voxel. If there are no surrounding voxels, it is determined that the voxel is an isolated point, and the voxel is deleted from the voxel set.
- a virtual viewpoint image in which the shape of the object is made more accurate than the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2080 is generated.
- the image generation unit 120 performs a smoothing process on the boundary between the foreground region and the background region of the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2110, and corrects the image so that the boundary region is displayed smoothly.
- the output unit 130 outputs the virtual viewpoint image generated in S2120 by the image generation unit 120 to the display device 3 and the display device 4 as a non-live image.
- the non-live image output to the display device 3 is displayed in the area 330.
- the image processing apparatus 1 uses the virtual viewpoint image as the designation image for allowing the operator to designate the virtual viewpoint, and the virtual viewpoint image for displaying to the viewer with higher image quality than the designation image.
- a live image is generated based on a set of captured images and virtual viewpoint information.
- the live image is generated based on the designation of the virtual viewpoint by the operator.
- the live image is a virtual viewpoint image corresponding to a virtual viewpoint determined according to a designation operation performed by the operator on the designation image.
- the image processing apparatus 1 also generates a non-live image that is a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the live image.
- the image processing device 1 outputs the generated live image and non-live image to the display device 4 so that the live image is displayed before the non-live image is displayed.
- the image processing apparatus 1 outputs the generated designation image to the display device 3 so that the designation image is displayed on the display device 3 before the live image is displayed on the display device 4.
- the display device 4 displays a low-quality designation image, a live image that is higher in quality than the designation image and is broadcast live, and a non-live image that is higher in quality than the live image and broadcast after recording. It becomes possible to do.
- the display device 4 may display only one of the live image and the non-live image.
- the image processing device 1 outputs a virtual viewpoint image suitable for the display device 4.
- the display device 3 has three types of virtual viewpoints: a low-quality virtual viewpoint image as a designation image, a medium-quality virtual viewpoint image as a live image, and a high-quality virtual viewpoint image as a non-live image.
- a viewpoint image can be displayed.
- the display device 3 may not display at least one of the live image and the non-live image.
- the image processing apparatus 1 outputs a designation image to the display device 3 for allowing the user to designate a virtual viewpoint.
- the image processing apparatus 1 displays at least one of a live image and a non-live image with higher image quality than the designation image on the display device 4 for displaying a virtual viewpoint image generated based on the designation of the virtual viewpoint by the user. Is output.
- a virtual viewpoint image is generated based on the image based on the photographing by the camera group 2 and information according to the designation of the virtual viewpoint, and a higher image quality is obtained based on the processing result for the generation.
- a virtual viewpoint image is generated. Therefore, the overall processing amount can be reduced as compared with the case where a low-quality virtual viewpoint image and a high-quality virtual viewpoint image are generated by independent processing.
- the low-quality virtual viewpoint image and the high-quality virtual viewpoint image may be generated by independent processing.
- the image processing apparatus 1 when the virtual viewpoint image is displayed on a display installed at a competition venue or a live venue or is broadcast live, and it is not necessary to broadcast after recording, the image processing apparatus 1 generates a non-live image. The processing to do is not performed. Thereby, the processing amount for generating a high-quality non-live image can be reduced.
- the image processing apparatus 1 may generate a replay image that is displayed after shooting, instead of or in addition to a live image that is broadcast live.
- the replay image is displayed on the display of the competition venue during half-time or after the match is over, for example, when the subject of shooting by the camera group 2 is a game such as soccer in the competition venue.
- the replay image has a higher image quality than the designation image, and is generated with an image quality that can be displayed after completion of the match or by the end of the game.
- the processing shown in FIG. 5 is started at the timing when the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 receives a virtual viewpoint image generation instruction.
- the start timing of the process of FIG. 5 is not limited to this.
- the image processing apparatus 1 acquires a captured image and virtual viewpoint information by each camera in the camera group 2 by the same processing as that described in FIG.
- the image generation unit 120 sets the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image used for generating the virtual viewpoint image.
- the image generation unit 120 sets the number of cameras so that the processing of S4050 to S4070 is completed within a processing time equal to or less than a predetermined threshold (for example, a time corresponding to one frame when the virtual viewpoint image is a moving image).
- a predetermined threshold for example, a time corresponding to one frame when the virtual viewpoint image is a moving image.
- a predetermined threshold for example, a time corresponding to one frame when the virtual viewpoint image is a moving image.
- the processing of S4050 to S4070 is executed in advance using images taken by 100 cameras, and the processing time is 0.5 seconds. In this case, if you want to complete the processing of S4050-S4070 within 0.016 seconds corresponding to one frame of the virtual viewpoint image with a frame rate of 60 fps (frame per second), set the number of cameras to three. .
- the process returns to S4030 to reset the number of cameras to be used.
- the permissible processing time is increased and the number of cameras is increased accordingly so that a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the previously output virtual viewpoint image is generated.
- the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image to be used is set to 20 so that the processing of S4050 to S4070 is completed in a processing time of 0.1 seconds or less.
- the image generation unit 120 selects a camera corresponding to the photographed image used for generating the virtual viewpoint image from the camera group 2 according to the number of cameras set in S4030. For example, when three cameras are selected from 100 cameras, the camera closest to the virtual viewpoint and the 34th camera and the 67th camera counted from the camera are selected.
- the shape model estimated in the first processing is further improved in accuracy.
- a camera other than the camera selected at the second time is selected. Specifically, when 20 cameras are selected from 100 cameras, the camera closest to the virtual viewpoint is first selected from the cameras not selected in the first processing, and then 5 cameras are selected at intervals of 5 cameras. Select the camera. At this time, the camera already selected in the first time is skipped and the next camera is selected. For example, when generating a virtual viewpoint image with the highest image quality as a non-live image, all the cameras included in the camera group 2 are selected, and the processes of S4050 to S4070 are executed using the captured images of each camera. To do.
- the method of selecting a camera corresponding to a captured image to be used is not limited to this.
- a camera close to the virtual viewpoint may be selected with priority.
- the accuracy of shape estimation of the rear region that cannot be seen from the virtual viewpoint in the shape estimation of the object that is the subject is lowered, but the accuracy of shape estimation of the front region that is visible from the virtual viewpoint is improved. That is, it is possible to preferentially improve the image quality of an area that is easily noticeable by the viewer in the virtual viewpoint image.
- the image generation unit 120 executes an object shape estimation process using the image captured by the camera selected in S4040.
- the process here is, for example, a combination of the process in S2030 (VisualHull) and the process in S2070 (PhotoHull) in FIG.
- the VisualHull process includes a process of calculating a logical product of the viewing volumes of a plurality of cameras corresponding to a plurality of captured images to be used.
- the PhotoHull process includes a process of projecting each point of the shape model onto a plurality of captured images and calculating the consistency of pixel values. Therefore, the smaller the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image to be used, the lower the accuracy of shape estimation and the shorter the processing time.
- the image generation unit 120 executes a rendering process.
- the processing here is the same as the processing in S2080 of FIG. 3, and includes 3D point group coloring processing and background image generation processing.
- Both the 3D point group coloring process and the background image generation process include a process of determining a color by calculation using pixel values of corresponding points of a plurality of captured images. Therefore, the smaller the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image to be used, the lower the rendering accuracy and the shorter the processing time.
- the output unit 130 outputs the virtual viewpoint image generated in S4060 by the image generation unit 120 to the display device 3 and the display device 4.
- the image generation unit 120 determines whether to perform a process of generating a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the virtual viewpoint image generated in S4060.
- the virtual viewpoint image generated in S4060 is an image for allowing the operator to specify a virtual viewpoint, and when further generating a live image, the process returns to S4030 to increase the number of cameras to be used and display the live image.
- the number of cameras is further increased to generate a virtual viewpoint image as a non-live image.
- Live images have higher image quality than designated images.
- the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image used for generating the virtual viewpoint image as the non-live image is larger than the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image used for generating the virtual viewpoint image as the live image.
- Non-live images have higher image quality than live images.
- the image processing apparatus 1 can generate and output a plurality of virtual viewpoint images with improved image quality in stages at appropriate timings. For example, by limiting the number of cameras used for generating the virtual viewpoint image to the number that can complete the generation process within the set processing time, it is possible to generate the designation image with a small delay. Further, when generating a live image or a non-live image, it is possible to generate a higher quality image by increasing the number of cameras used and performing the generation process.
- the image quality of the virtual viewpoint image is improved by increasing the number of cameras used for generating the virtual viewpoint image.
- the image quality of the virtual viewpoint image is improved by gradually increasing the resolution of the virtual viewpoint image.
- the description of the same part as the processing of FIG. 3 and FIG. 5 is omitted.
- the number of pixels of the generated virtual viewpoint image is always 4K (3840 ⁇ 2160), and whether the pixel value is calculated for each large pixel block or each small pixel block.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and the resolution may be controlled by changing the number of pixels of the generated virtual viewpoint image.
- the process shown in FIG. 6 is started at the timing when the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 receives a virtual viewpoint image generation instruction.
- the start timing of the process of FIG. 6 is not limited to this.
- the image processing apparatus 1 acquires a captured image and virtual viewpoint information by each camera in the camera group 2 by the same processing as that described in FIG.
- the image generation unit 120 sets the resolution of the generated virtual viewpoint image.
- the image generation unit 120 sets the resolution so that the processing of S5050 and S4070 is completed in a processing time equal to or less than a predetermined threshold.
- a predetermined threshold For example, it is assumed that the processing of S5050 and S4070 when generating a 4K resolution virtual viewpoint image in advance is performed and the processing time is 0.5 seconds.
- the process returns to S5030 to reset the resolution.
- the allowable processing time is increased and the resolution is increased accordingly so that a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the previously output virtual viewpoint image is generated.
- the resolution is set to 1/4 of the 4K resolution in the vertical and horizontal directions
- the processing of S5050 and S4070 is completed in a processing time of 0.1 second or less.
- the image generation unit 120 determines the position of the pixel whose pixel value is to be calculated in the virtual viewpoint image according to the resolution set in S5030.
- the resolution of the virtual viewpoint image is set to 1/8 of the 4K resolution
- pixel values are calculated every 8 pixels in the vertical and horizontal directions. Then, the same pixel value as that of the pixel (x, y) is set to the pixel existing between the pixel (x, y) for which the pixel value is calculated and the pixel (x + 8, y + 8).
- the pixel value calculated at the first time is skipped to calculate the pixel value.
- the resolution is set to 1/4 of the 4K resolution
- the pixel value of the pixel (x + 4, y + 4) is calculated, and the pixel existing between the pixel (x + 4, y + 4) and the pixel (x + 8, y + 8) is calculated.
- the same pixel value as the pixel (x + 4, y + 4) is set.
- the image generation unit 120 calculates the pixel value of the pixel at the position determined in S5040 and performs a coloring process on the virtual viewpoint image.
- a pixel value calculation method for example, an Image-Based Visual Hull method can be used. In this method, since the pixel value is calculated for each pixel, the processing time becomes shorter as the number of pixels for which the pixel value is to be calculated is smaller, that is, as the resolution of the virtual viewpoint image is lower.
- the output unit 130 outputs the virtual viewpoint image generated in S5050 by the image generation unit 120 to the display device 3 and the display device 4.
- the image generation unit 120 determines whether to perform a process of generating a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the virtual viewpoint image generated in S5050.
- the virtual viewpoint image generated in S5050 is an image for allowing the operator to specify a virtual viewpoint, and when generating a live image, the process returns to S5030 to generate a virtual viewpoint image with a higher resolution.
- a virtual viewpoint image as a non-live image having a higher resolution is generated. That is, since the virtual viewpoint image as the live image has a higher resolution than the virtual viewpoint image as the designation image, the live image has higher image quality than the designation image.
- the virtual viewpoint image as a non-live image has a higher resolution than the virtual viewpoint image as a live image, the non-live image has higher image quality than the live image.
- the image processing apparatus 1 can generate and output a plurality of virtual viewpoint images with improved resolution in stages at appropriate timings. For example, by setting the resolution of the virtual viewpoint image so that the generation process can be completed within the set processing time, it is possible to generate a designating image with little delay. Further, when generating a live image or a non-live image, a higher-quality image can be generated by performing generation processing with a high resolution.
- the image processing apparatus 1 generates a high-quality image (for example, a non-live image) by performing image processing for improving the image quality of the virtual viewpoint image. Further, the image processing apparatus 1 generates a low-quality image (for example, a live image) by a process that is a partial process included in the image process and is executed in a processing time that is equal to or less than a predetermined threshold. This makes it possible to generate and display both a virtual viewpoint image displayed with a delay of a predetermined time or less and a high-quality virtual viewpoint image.
- a high-quality image for example, a non-live image
- a low-quality image for example, a live image
- a generation parameter (resolution) for completing the generation process is estimated within a processing time equal to or less than a predetermined threshold, and a virtual viewpoint image is generated using the estimated generation parameter.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and the image processing apparatus 1 may improve the image quality of the virtual viewpoint image in stages, and output the generated virtual viewpoint image when the processing time reaches a predetermined threshold. For example, when the processing time reaches a predetermined threshold, a virtual viewpoint image whose resolution is 1/8 of 4K resolution has been generated, and a virtual viewpoint image whose resolution is 1/4 of 4K resolution has not been completed. In some cases, a virtual viewpoint image with 1/8 resolution may be output. Further, a virtual viewpoint image in which the process of improving the resolution from 1/8 resolution to 1/4 resolution is performed halfway may be output.
- the image generation unit 120 included in the image processing apparatus 1 controls generation of a virtual viewpoint image based on the image acquired by the camera information acquisition unit 100 and the virtual viewpoint information acquired by the viewpoint acquisition unit 110,
- the case where a plurality of virtual viewpoint images having different image quality are generated has been mainly described.
- the present invention is not limited to this, and a function for controlling generation of a virtual viewpoint image and a function for actually generating a virtual viewpoint image may be provided in different apparatuses.
- a generation device (not shown) that has the function of the image generation unit 120 and generates a virtual viewpoint image may exist in the image processing system 10. Then, the image processing apparatus 1 may control the generation of the virtual viewpoint image by the generation apparatus based on the image acquired by the camera information acquisition unit 100 and the information acquired by the viewpoint acquisition unit 110. Specifically, the image processing apparatus 1 transmits a captured image and virtual viewpoint information to the generation apparatus, and gives an instruction to control generation of the virtual viewpoint image.
- the generation apparatus is a first virtual viewpoint image and a second virtual viewpoint image that should be displayed at an earlier timing than the first virtual viewpoint image is displayed, and has a lower image quality than the first virtual viewpoint image.
- a second virtual viewpoint image is generated based on the received captured image and virtual viewpoint information.
- the first virtual viewpoint image is a non-live image, for example
- the second virtual viewpoint image is a live image, for example.
- the image processing apparatus 1 may perform control so that the first virtual viewpoint image and the second virtual viewpoint image are generated by different generation apparatuses.
- the image processing apparatus 1 may perform output control such as controlling the output destination and output timing of the virtual viewpoint image by the generation apparatus.
- the generation device has the functions of the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 and the image generation unit 120, and the image processing device 1 controls generation of a virtual viewpoint image by the generation device based on the image acquired by the camera information acquisition unit 100.
- the image acquired by the camera information acquisition unit 100 is an image based on shooting, such as a captured image captured by the camera group 2 or an image generated based on a difference between a plurality of captured images.
- the generation device has the functions of the camera information acquisition unit 100 and the image generation unit 120, and the image processing device 1 controls the generation of the virtual viewpoint image by the generation device based on the image acquired by the viewpoint acquisition unit 110. May be.
- the image acquired by the viewpoint acquisition unit 110 is information according to the designation of the virtual viewpoint, such as information indicating the contents determined according to the virtual viewpoint, such as the shape and orientation of the subject in the virtual viewpoint image, and virtual viewpoint information. That is, the image processing apparatus 1 acquires information related to generation of a virtual viewpoint image including at least one of an image based on shooting and information according to designation of the virtual viewpoint, and generates a virtual viewpoint image based on the acquired information. May be controlled.
- the generation apparatus existing in the image processing system 10 has the functions of the camera information acquisition unit 100, the viewpoint acquisition unit 110, and the image generation unit 120.
- the image processing apparatus 1 is information related to generation of a virtual viewpoint image.
- the generation of the virtual viewpoint image by the generation device may be controlled based on the above.
- the information related to the generation of the virtual viewpoint image in this case includes, for example, at least one of a parameter related to the image quality of the first virtual viewpoint image and a parameter related to the image quality of the second virtual viewpoint image generated by the generation device.
- Specific examples of the parameters relating to the image quality include the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image used for generating the virtual viewpoint image, the resolution of the virtual viewpoint image, and the time allowed as the processing time for generating the virtual viewpoint image.
- the image processing apparatus 1 controls the generation device based on the acquired parameters, for example, acquires parameters related to the image quality based on an input by the operator and transmits the parameters to the generation device. Accordingly, the operator can generate a plurality of virtual viewpoint images having different desired image quality.
- the image processing apparatus 1 accepts an instruction for generating a virtual viewpoint image based on an image based on photographing of a subject from different directions by a plurality of cameras and information according to designation of the virtual viewpoint. Then, the image processing apparatus 1 determines that the first virtual viewpoint image output to the first display apparatus and the second virtual viewpoint image output to the second display apparatus are based on the image based on the shooting and the designation of the virtual viewpoint. Control is performed in response to reception of the generation instruction so that the generation instruction is generated based on the received information.
- the second virtual viewpoint image is a virtual viewpoint image with higher image quality than the first virtual viewpoint image.
- a virtual suitable for the timing to be displayed A viewpoint image can be generated.
- the case of controlling the color gradation, the resolution, and the number of cameras corresponding to the captured image used for generating the virtual viewpoint image as the image quality of the virtual viewpoint image has been described. May be controlled. A plurality of parameters relating to image quality may be controlled simultaneously.
- the present invention supplies a program that realizes one or more functions of the above-described embodiments to a system or apparatus via a network or a storage medium, and one or more processors in a computer of the system or apparatus read and execute the program This process can be realized. It can also be realized by a circuit (for example, ASIC) that realizes one or more functions. Further, the program may be provided by being recorded on a computer-readable recording medium.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Graphics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
- Image Generation (AREA)
- Testing, Inspecting, Measuring Of Stereoscopic Televisions And Televisions (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
Priority Applications (16)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| BR112019008387-1A BR112019008387B1 (pt) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | sistema e método de processamento de imagem para gerar imagem de ponto de observação virtual, e meio de armazenamento |
| RU2019114982A RU2708437C1 (ru) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | Устройство обработки изображений, система обработки изображений, способ обработки изображений и носитель данных |
| AU2017351012A AU2017351012B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method and storage medium |
| EP22150472.3A EP4012661A1 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | Generation of virtual viewpoint images |
| KR1020207005390A KR102262731B1 (ko) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | 화상 처리 시스템, 화상 처리 방법 및 기억 매체 |
| CN201911223799.XA CN110944119B (zh) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | 图像处理系统、图像处理方法和存储介质 |
| KR1020197014181A KR102083767B1 (ko) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | 화상 처리 장치, 화상 처리 시스템, 화상 처리 방법 및 기억 매체 |
| EP17864980.2A EP3534337B1 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and program |
| CA3041976A CA3041976C (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and storage medium, for generating virtual viewpoint image |
| CN201780067201.5A CN109964253B (zh) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | 图像处理设备、图像处理系统、图像处理方法和存储介质 |
| ES17864980T ES2908243T3 (es) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | Aparato de procesamiento de imágenes, sistema de procesamiento de imágenes, procedimiento de procesamiento de imágenes y programa |
| KR1020217016990A KR102364052B1 (ko) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | 화상 처리 시스템, 화상 처리 방법 및 기억 매체 |
| US16/396,281 US11128813B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2019-04-26 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and storage medium |
| AU2020200831A AU2020200831A1 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2020-02-05 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and program |
| US17/373,469 US20210344848A1 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2021-07-12 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and storage medium |
| AU2021269399A AU2021269399B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2021-11-18 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016-211905 | 2016-10-28 | ||
| JP2016211905A JP6419128B2 (ja) | 2016-10-28 | 2016-10-28 | 画像処理装置、画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/396,281 Continuation US11128813B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2019-04-26 | Image processing apparatus, image processing system, image processing method, and storage medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018079430A1 true WO2018079430A1 (ja) | 2018-05-03 |
Family
ID=62023396
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/037978 Ceased WO2018079430A1 (ja) | 2016-10-28 | 2017-10-20 | 画像処理装置、画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US11128813B2 (enExample) |
| EP (2) | EP3534337B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6419128B2 (enExample) |
| KR (3) | KR102364052B1 (enExample) |
| CN (2) | CN109964253B (enExample) |
| AU (3) | AU2017351012B2 (enExample) |
| BR (1) | BR112019008387B1 (enExample) |
| CA (1) | CA3041976C (enExample) |
| ES (1) | ES2908243T3 (enExample) |
| RU (1) | RU2708437C1 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2018079430A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7212611B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-27 | 2023-01-25 | パナソニック インテレクチュアル プロパティ コーポレーション オブ アメリカ | 画像配信方法、画像表示方法、画像配信装置及び画像表示装置 |
| JP7027049B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-15 | 2022-03-01 | キヤノン株式会社 | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及びプログラム |
| JP7033865B2 (ja) * | 2017-08-10 | 2022-03-11 | キヤノン株式会社 | 画像生成装置、画像生成方法、及びプログラム |
| JP7030452B2 (ja) * | 2017-08-30 | 2022-03-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理装置の制御方法、情報処理システム及びプログラム |
| JP6868288B2 (ja) * | 2018-09-11 | 2021-05-12 | 株式会社アクセル | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法、及び画像処理プログラム |
| JP7353782B2 (ja) * | 2019-04-09 | 2023-10-02 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| JP7418101B2 (ja) * | 2019-07-26 | 2024-01-19 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| CN114762355B (zh) * | 2019-12-09 | 2024-08-02 | 索尼集团公司 | 信息处理装置和方法、程序以及信息处理系统 |
| WO2021131375A1 (ja) * | 2019-12-26 | 2021-07-01 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム |
| WO2021131365A1 (ja) * | 2019-12-26 | 2021-07-01 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理装置の作動方法、及びプログラム |
| JP6708917B1 (ja) * | 2020-02-05 | 2020-06-10 | リンクウィズ株式会社 | 形状検出方法、形状検出システム、プログラム |
| JP7476160B2 (ja) * | 2021-11-29 | 2024-04-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理システム、及びプログラム |
| CN115883792B (zh) * | 2023-02-15 | 2023-05-05 | 深圳市完美显示科技有限公司 | 一种利用5g和8k技术的跨空间实景用户体验系统 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007150747A (ja) * | 2005-11-28 | 2007-06-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 受信装置及び本線映像配信装置 |
| JP2011135138A (ja) * | 2009-12-22 | 2011-07-07 | Canon Inc | 映像再生装置及びその制御方法 |
Family Cites Families (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3486579B2 (ja) * | 1999-09-02 | 2004-01-13 | キヤノン株式会社 | 空間描画方法、仮想空間描画装置および記憶媒体 |
| US20020049979A1 (en) * | 2000-05-18 | 2002-04-25 | Patrick White | Multiple camera video system which displays selected images |
| US7085409B2 (en) * | 2000-10-18 | 2006-08-01 | Sarnoff Corporation | Method and apparatus for synthesizing new video and/or still imagery from a collection of real video and/or still imagery |
| US7307654B2 (en) * | 2002-10-31 | 2007-12-11 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Image capture and viewing system and method for generating a synthesized image |
| US8711923B2 (en) * | 2002-12-10 | 2014-04-29 | Ol2, Inc. | System and method for selecting a video encoding format based on feedback data |
| JP2004280250A (ja) * | 2003-03-13 | 2004-10-07 | Canon Inc | 情報処理装置および方法 |
| US7538774B2 (en) * | 2003-06-20 | 2009-05-26 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Virtual visual point image generating method and 3-d image display method and device |
| CN100355272C (zh) * | 2005-06-24 | 2007-12-12 | 清华大学 | 一种交互式多视点视频系统中虚拟视点的合成方法 |
| JP4727329B2 (ja) * | 2005-07-15 | 2011-07-20 | パナソニック株式会社 | 画像合成装置及び画像合成方法 |
| US8277316B2 (en) * | 2006-09-14 | 2012-10-02 | Nintendo Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for using a common pointing input to control 3D viewpoint and object targeting |
| JP4895042B2 (ja) | 2007-07-20 | 2012-03-14 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 画像圧縮装置、画像圧縮方法、及びプログラム |
| US9041722B2 (en) * | 2007-11-16 | 2015-05-26 | Sportvision, Inc. | Updating background texture for virtual viewpoint animations |
| US8270767B2 (en) * | 2008-04-16 | 2012-09-18 | Johnson Controls Technology Company | Systems and methods for providing immersive displays of video camera information from a plurality of cameras |
| US8819172B2 (en) * | 2010-11-04 | 2014-08-26 | Digimarc Corporation | Smartphone-based methods and systems |
| US8611674B1 (en) * | 2010-01-18 | 2013-12-17 | Disney Enterprises, Inc. | System and method for invariant-based normal estimation |
| US8823797B2 (en) * | 2010-06-03 | 2014-09-02 | Microsoft Corporation | Simulated video with extra viewpoints and enhanced resolution for traffic cameras |
| JP2012114816A (ja) * | 2010-11-26 | 2012-06-14 | Sony Corp | 画像処理装置、画像処理方法及び画像処理プログラム |
| CN107197226B (zh) * | 2011-03-18 | 2019-05-28 | 索尼公司 | 图像处理设备、图像处理方法和计算机可读存储介质 |
| EP2600316A1 (en) * | 2011-11-29 | 2013-06-05 | Inria Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et en Automatique | Method, system and software program for shooting and editing a film comprising at least one image of a 3D computer-generated animation |
| KR101265711B1 (ko) | 2011-11-30 | 2013-05-20 | 주식회사 이미지넥스트 | 3d 차량 주변 영상 생성 방법 및 장치 |
| JP5887994B2 (ja) * | 2012-02-27 | 2016-03-16 | 日本電気株式会社 | 映像送信装置、端末装置、映像送信方法及びプログラム |
| JP6128748B2 (ja) | 2012-04-13 | 2017-05-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | 画像処理装置及び方法 |
| KR101224221B1 (ko) * | 2012-05-10 | 2013-01-22 | 쉐어쉐어주식회사 | 응용프로그램을 이용한 콘텐츠 운영 시스템 |
| EP2860606B1 (en) | 2012-06-12 | 2018-01-10 | Sony Corporation | Information processing device, information processing method, and program for an augmented reality display |
| CN102801997B (zh) * | 2012-07-11 | 2014-06-11 | 天津大学 | 基于感兴趣深度的立体图像压缩方法 |
| US9769365B1 (en) * | 2013-02-15 | 2017-09-19 | Red.Com, Inc. | Dense field imaging |
| US9462301B2 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2016-10-04 | Google Inc. | Generating videos with multiple viewpoints |
| JP6432029B2 (ja) * | 2013-05-26 | 2018-12-05 | ピクセルロット エルティーディー.Pixellot Ltd. | 低コストでテレビ番組を制作する方法及びシステム |
| KR102098277B1 (ko) * | 2013-06-11 | 2020-04-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 시선 추적을 이용한 시인성 개선 방법, 저장 매체 및 전자 장치 |
| US9996974B2 (en) * | 2013-08-30 | 2018-06-12 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Method and apparatus for representing a physical scene |
| WO2015054235A1 (en) * | 2013-10-07 | 2015-04-16 | Vid Scale, Inc. | User adaptive 3d video rendering and delivery |
| JP6607433B2 (ja) | 2014-06-23 | 2019-11-20 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 映像配信方法及びサーバ |
| JP6299492B2 (ja) | 2014-07-03 | 2018-03-28 | ソニー株式会社 | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、およびプログラム |
| JP6477214B2 (ja) | 2015-05-01 | 2019-03-06 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 傾斜度測定方法及び装置並びに電子機器及びプログラム |
-
2016
- 2016-10-28 JP JP2016211905A patent/JP6419128B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-10-20 EP EP17864980.2A patent/EP3534337B1/en active Active
- 2017-10-20 AU AU2017351012A patent/AU2017351012B2/en active Active
- 2017-10-20 BR BR112019008387-1A patent/BR112019008387B1/pt active IP Right Grant
- 2017-10-20 EP EP22150472.3A patent/EP4012661A1/en active Pending
- 2017-10-20 KR KR1020217016990A patent/KR102364052B1/ko active Active
- 2017-10-20 WO PCT/JP2017/037978 patent/WO2018079430A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2017-10-20 KR KR1020197014181A patent/KR102083767B1/ko active Active
- 2017-10-20 CN CN201780067201.5A patent/CN109964253B/zh active Active
- 2017-10-20 ES ES17864980T patent/ES2908243T3/es active Active
- 2017-10-20 RU RU2019114982A patent/RU2708437C1/ru active
- 2017-10-20 CA CA3041976A patent/CA3041976C/en active Active
- 2017-10-20 CN CN201911223799.XA patent/CN110944119B/zh active Active
- 2017-10-20 KR KR1020207005390A patent/KR102262731B1/ko active Active
-
2019
- 2019-04-26 US US16/396,281 patent/US11128813B2/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-02-05 AU AU2020200831A patent/AU2020200831A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2021
- 2021-07-12 US US17/373,469 patent/US20210344848A1/en active Pending
- 2021-11-18 AU AU2021269399A patent/AU2021269399B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007150747A (ja) * | 2005-11-28 | 2007-06-14 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 受信装置及び本線映像配信装置 |
| JP2011135138A (ja) * | 2009-12-22 | 2011-07-07 | Canon Inc | 映像再生装置及びその制御方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| KITAHARA, ITARU ET AL.: "Real-time 3D video display of humans in a large-scale space", IEICE TECHNICAL REPORT. PRMU, vol. 102, no. 532, 13 December 2002 (2002-12-13), pages 43 - 48, XP009514214 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20190253639A1 (en) | 2019-08-15 |
| ES2908243T3 (es) | 2022-04-28 |
| US11128813B2 (en) | 2021-09-21 |
| AU2017351012A1 (en) | 2019-05-23 |
| RU2708437C1 (ru) | 2019-12-06 |
| JP2018073105A (ja) | 2018-05-10 |
| KR102262731B1 (ko) | 2021-06-10 |
| KR20190064649A (ko) | 2019-06-10 |
| CA3041976A1 (en) | 2018-05-03 |
| KR20200023513A (ko) | 2020-03-04 |
| CN110944119A (zh) | 2020-03-31 |
| EP3534337A4 (en) | 2020-08-26 |
| AU2017351012B2 (en) | 2019-11-14 |
| EP4012661A1 (en) | 2022-06-15 |
| JP6419128B2 (ja) | 2018-11-07 |
| CN110944119B (zh) | 2022-04-26 |
| AU2021269399A1 (en) | 2021-12-16 |
| CA3041976C (en) | 2020-07-28 |
| BR112019008387A2 (pt) | 2019-07-09 |
| AU2020200831A1 (en) | 2020-02-20 |
| KR20210068629A (ko) | 2021-06-09 |
| AU2021269399B2 (en) | 2023-09-28 |
| CN109964253A (zh) | 2019-07-02 |
| EP3534337A1 (en) | 2019-09-04 |
| KR102083767B1 (ko) | 2020-03-02 |
| CN109964253B (zh) | 2020-01-31 |
| EP3534337B1 (en) | 2022-02-16 |
| BR112019008387B1 (pt) | 2021-02-23 |
| KR102364052B1 (ko) | 2022-02-18 |
| US20210344848A1 (en) | 2021-11-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6419128B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム | |
| US10916048B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium | |
| JP7023696B2 (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2015230695A (ja) | 情報処理装置及び情報処理方法 | |
| JP7439146B2 (ja) | 画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2022110751A (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP6672417B2 (ja) | 画像処理装置、画像処理システム、画像処理方法及びプログラム | |
| JP6717486B1 (ja) | 拡張仮想空間提供システム | |
| EP4296961A1 (en) | Image processing device, image processing method, and program | |
| JP7182915B2 (ja) | 画像生成装置、画像生成方法、及びプログラム | |
| JP2022073648A (ja) | 情報処理装置、情報処理方法、及びプログラム | |
| JP2022094788A (ja) | 生成装置、生成方法、及び、プログラム | |
| JP2023026244A (ja) | 画像生成装置および画像生成方法、プログラム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17864980 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 3041976 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to national code |
Ref country code: BR Ref legal event code: B01A Ref document number: 112019008387 Country of ref document: BR |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20197014181 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017351012 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20171020 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017864980 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20190528 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 112019008387 Country of ref document: BR Kind code of ref document: A2 Effective date: 20190425 |