WO2017175548A1 - 端末装置、情報処理システム - Google Patents
端末装置、情報処理システム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017175548A1 WO2017175548A1 PCT/JP2017/010118 JP2017010118W WO2017175548A1 WO 2017175548 A1 WO2017175548 A1 WO 2017175548A1 JP 2017010118 W JP2017010118 W JP 2017010118W WO 2017175548 A1 WO2017175548 A1 WO 2017175548A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- terminal device
- information
- user
- server
- measurement data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H50/00—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics
- G16H50/20—ICT specially adapted for medical diagnosis, medical simulation or medical data mining; ICT specially adapted for detecting, monitoring or modelling epidemics or pandemics for computer-aided diagnosis, e.g. based on medical expert systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0002—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0002—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network
- A61B5/0015—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network characterised by features of the telemetry system
- A61B5/002—Monitoring the patient using a local or closed circuit, e.g. in a room or building
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0002—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network
- A61B5/0015—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network characterised by features of the telemetry system
- A61B5/0022—Monitoring a patient using a global network, e.g. telephone networks, internet
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
- A61B5/7264—Classification of physiological signals or data, e.g. using neural networks, statistical classifiers, expert systems or fuzzy systems
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7271—Specific aspects of physiological measurement analysis
- A61B5/7282—Event detection, e.g. detecting unique waveforms indicative of a medical condition
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/74—Details of notification to user or communication with user or patient; User input means
- A61B5/742—Details of notification to user or communication with user or patient; User input means using visual displays
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/74—Details of notification to user or communication with user or patient; User input means
- A61B5/746—Alarms related to a physiological condition, e.g. details of setting alarm thresholds or avoiding false alarms
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08B—SIGNALLING OR CALLING SYSTEMS; ORDER TELEGRAPHS; ALARM SYSTEMS
- G08B25/00—Alarm systems in which the location of the alarm condition is signalled to a central station, e.g. fire or police telegraphic systems
- G08B25/01—Alarm systems in which the location of the alarm condition is signalled to a central station, e.g. fire or police telegraphic systems characterised by the transmission medium
- G08B25/04—Alarm systems in which the location of the alarm condition is signalled to a central station, e.g. fire or police telegraphic systems characterised by the transmission medium using a single signalling line, e.g. in a closed loop
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H10/00—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data
- G16H10/60—ICT specially adapted for the handling or processing of patient-related medical or healthcare data for patient-specific data, e.g. for electronic patient records
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H40/00—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/60—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/63—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices for local operation
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H40/00—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/60—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/67—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices for remote operation
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B2505/00—Evaluating, monitoring or diagnosing in the context of a particular type of medical care
- A61B2505/07—Home care
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/48—Other medical applications
- A61B5/4842—Monitoring progression or stage of a disease
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04Q—SELECTING
- H04Q2209/00—Arrangements in telecontrol or telemetry systems
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04Q—SELECTING
- H04Q2209/00—Arrangements in telecontrol or telemetry systems
- H04Q2209/10—Arrangements in telecontrol or telemetry systems using a centralized architecture
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04Q—SELECTING
- H04Q9/00—Arrangements in telecontrol or telemetry systems for selectively calling a substation from a main station, in which substation desired apparatus is selected for applying a control signal thereto or for obtaining measured values therefrom
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to a terminal device and an information processing system.
- Various measuring devices for measuring various biological information indicating the current state of the human body such as body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, blood glucose level, etc. have been developed.
- Biological information measured by such a measuring device is taken into a terminal device such as a smartphone, and the health status of the user of the terminal device is confirmed.
- a biological information obtained by the measurement device is analyzed in a server for managing the measurement device, and the analysis result is provided to the terminal device.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a method for managing at least one external device connected to a host terminal via a management server. The method includes the steps of acquiring measurement information measured by an external device, requesting authentication from the management server, and transmitting acquired measurement information to the management server upon successful authentication. And receiving, at the management server, management information for managing at least one external device generated based on the measurement information, and managing at least one external device based on the received management information Including.
- the management server collects measurement information measured by an external device (for example, information related to the health of the user of the host terminal) via the authenticated host terminal and uses the measurement information. Judging the health status of the user of the host terminal is disclosed, but nothing is taught about the technology related to the above needs.
- the present disclosure has been made in view of the above, and an object in one aspect is to provide a terminal device and an information processing system capable of improving convenience when checking the health state of a user of another terminal device Is to provide.
- a terminal device configured to be able to communicate with a server having a database of biological information measured by a biological information measuring device.
- the database includes measurement data of biometric information of the user of the other terminal device transmitted from the other terminal device to the server.
- the terminal device includes a reception unit that receives measurement data from the server, a state determination unit that determines whether the user's health is normal or abnormal based on the measurement data received by the reception unit, and a state determination And an information output unit that outputs information related to the user's health status based at least on the determination result of the unit.
- the measurement data includes at least one of measurement time and measurement date of the user's biological information.
- the state determination unit determines that the user's health condition is abnormal when determining that the user's biological information is not measured at a predetermined timing based on at least one of the measurement time and the measurement date.
- the measurement data further includes a measurement value of the user's biological information.
- the state determination unit determines that the measured value is within a predetermined range, and if the state determination unit determines that the user's biological information is measured at a predetermined timing, the user's health state Is determined to be normal.
- the terminal device further includes an importance determination unit that determines whether the importance of the measurement data is equal to or higher than a reference level.
- the information output unit outputs abnormality information indicating that the user's health condition is abnormal when the user's health condition is abnormal and the importance is equal to or higher than a reference level.
- the output of abnormality information includes at least one of display of abnormality information on a display included in the terminal device and transmission of abnormality information to another terminal device different from other terminal devices.
- the terminal device further includes an information storage unit that stores pairing information for establishing a wireless communication connection between the terminal device and the biological information measurement device, and an information transmission unit that transmits the pairing information to the server. .
- An information processing system includes a server having a database of biological information measured by a biological information measuring device, and a first terminal device and a second terminal device configured to be able to communicate with the server.
- the second terminal device has a data acquisition unit that acquires measurement data of the biological information of the user of the second terminal device measured by the biological information measurement device from the biological information measurement device, and the measurement data acquired by the data acquisition unit.
- an information transmission unit to be transmitted to the server.
- the first terminal device includes: a receiving unit that receives measurement data from the server; a state determining unit that determines whether the user's health is normal based on the measurement data received by the receiving unit; And an information output unit that outputs information on the health status of the user based at least on the determination result.
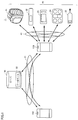
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an information processing system 1 according to the present embodiment.
- an information processing system 1 includes terminal devices 10A and 10B that are user terminals, a sphygmomanometer 21 that is an example of a biological information measurement device for measuring the biological information of the user, a sleep meter 22, and the number of steps It includes a total 23, a weight / body composition meter 24 and a thermometer 25, a server 30, and networks 41 and 43.
- the terminal device 10A is a user A terminal (terminal on the watching side)
- the terminal device 10B is a user B terminal (terminal on the watching target person side).
- the terminal devices 10A and 10B may be collectively referred to as “terminal device 10”.
- the biological information measuring device is not limited to the sphygmomanometer 21, the sleep meter 22, the pedometer 23, the body weight / body composition meter 24, and the thermometer 25, and may be any device for measuring the biological information of the user.
- the biological information measuring device may be an activity meter.
- the sphygmomanometer 21, the sleep meter 22, the pedometer 23, the weight / body composition meter 24, and the thermometer 25 may be collectively referred to as “measuring device 20”.
- sphygmomanometer 21 according to the present embodiment is a wristwatch-type sphygmomanometer in which a main body and a cuff (armband) are integrated.
- the sphygmomanometer 21 has a function of wearing a wrist for a long time like a wristwatch and measuring a pulsation every beat for 24 hours continuously, a function capable of being measured by simply wearing a wristwatch and pressing a measurement start button. . Thereby, the sphygmomanometer 21 can always measure the blood pressure of the user.
- the terminal device 10 is, for example, a smartphone including a touch panel.
- a smartphone will be described as a representative example of a “terminal device”.
- the terminal device may be another terminal device such as a foldable mobile phone, a tablet terminal device, a PC (personal computer), or a PDA (Personal Data Assistance).
- the network 41 for connecting to the terminal device 10A, the terminal device 10B, and the server 30 includes various networks such as the Internet and a mobile terminal communication network.
- the network 43 for connecting the terminal device 10B and the measuring device 20 employs a short-range wireless communication method, and typically employs BLE (Bluetooth (registered trademark) low energy).
- BLE Bluetooth (registered trademark) low energy
- the network 43 is not limited to this, and a wired communication method may be adopted, or another wireless communication method such as a wireless LAN (local area network) may be adopted.
- the server 30 stores various data transmitted from each terminal device 10. Specifically, the server 30 stores the group ID assigned to each group to which the terminal device 10 belongs in association with the identification information (terminal ID) of the terminal device 10 in the database 32. In addition, the server 30 manages various data transmitted from each terminal device 10 by group ID using the database 32.
- the terminal device 10A and the terminal device 10B belong to the same group X. Therefore, the group ID x of the group X is associated with the terminal IDa of the terminal device 10A and the terminal IDb of the terminal device 10B. Thereby, terminal device 10A and terminal device 10B can share various data stored in association with group IDx by accessing server 30 (database 32) using the same group IDx.
- server 30 database 32
- measurement data of the biological information of the user B transmitted from the terminal device 10B to the server 30 is stored.
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an outline of operation of information processing system 1 according to the present embodiment.
- terminal device 10A makes a registration (pairing) request to measuring device 20 (sequence SQ10).
- the registration request includes the terminal IDa of the terminal device 10A.
- Measuring instrument 20 transmits pairing information to terminal apparatus 10A in response to the registration request from terminal apparatus 10A (sequence SQ12).
- the pairing information is information necessary for the terminal device 10 to establish a wireless communication connection with the measurement device 20, and includes, for example, the device name, MAC address, service information, and the like of the measurement device 20.
- the terminal device 10 receives and stores a PIN code input required for pairing from the user. For example, the PIN code is printed on the casing of the measuring device 20 or displayed on the screen.
- Terminal device 10A registers the acquired pairing information in its own device and transmits the pairing information and terminal IDa to server 30 (sequence SQ14).
- the server 30 stores the pairing information transmitted from the terminal device 10A in the database 32 in association with the group ID x.
- Terminal apparatus 10B makes an acquisition request for data associated with group IDx (sequence SQ16).
- the acquisition request includes the terminal IDb of the terminal device 10B.
- Server 30 transmits pairing information to terminal apparatus 10B as a response to the acquisition request (sequence SQ18).
- Terminal device 10B establishes a wireless communication connection with measurement device 20 using the received pairing information (sequence SQ20).
- the user A acquires the pairing information of the measuring device 20 for the user B (person to be watched over) using his / her terminal device 10A, and the acquired pairing Information is stored in the server 30.
- User B can establish connection with the measuring device 20 by accessing the server 30 using the terminal device 10B and registering the pairing information in the terminal device 10B. Therefore, the user B can save the labor of the pairing work for establishing the wireless communication connection with the measuring device 20.
- Measurement device 20 measures biological information of user B (sequence SQ22). Measuring device 20 transmits the measurement data of the biological information of user B to terminal device 10B (sequence SQ24). Typically, when the measurement device 20 receives a data transfer request from the terminal device 10B within a predetermined time from the time of measurement, the measurement device 20 transmits the measurement data to the terminal device 10B. The measurement data may be transferred to the terminal device 10B by the user B operating the measuring device 20.
- Terminal device 10B stores the measurement data received from measurement device 20 in the internal memory and transmits the measurement data to server 30 (sequence SQ26).
- Terminal apparatus 10A requests acquisition of data associated with group ID x (sequence SQ28).
- the terminal device 10A executes a data acquisition request with respect to the server 30 periodically (for example, every several hours) or at a preset timing (for example, 7 am and 8 pm).
- the terminal device 10 ⁇ / b> A may make the acquisition request based on the reception of the data update notification associated with the group ID x from the server 30.
- the server 30 transmits the measurement data of the biological information of the user B received from the terminal device 10B to the terminal device 10A (sequence SQ30).
- Terminal apparatus 10A determines whether or not the health state of user B is normal based on the received measurement data (sequence SQ32).
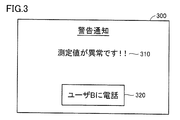
- terminal device 10A determines that health status of user B is abnormal, terminal device 10A notifies user A of the abnormal status (sequence SQ34). For example, the terminal device 10A displays a warning screen as shown in FIG. 3 on the display.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of a warning screen according to the present embodiment.
- warning screen 300 includes information 310 indicating that the measurement value of the biological information is abnormal, and a call button 320 to user B (terminal device 10B).
- terminal device 10A when terminal device 10A receives a selection operation of call button 320 from user A, terminal device 10A executes a call operation to terminal device 10B (sequence SQ36).
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing an example of a hardware configuration of terminal device 10 according to the present embodiment.
- the terminal device 10 includes, as main components, a processor 152, a memory 154, an input device 156, a display 158, a wireless communication unit 160, a memory interface (I / F) 164, A communication interface (I / F) 166, a speaker 168, and a microphone 170 are included.
- the processor 152 is typically an arithmetic processing unit such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit) or an MPU (Multi Processing Unit).
- the processor 152 functions as a control unit that controls the operation of each unit of the terminal device 10 by reading and executing the program stored in the memory 154.
- the processor 152 implements each process (step) of the terminal device 10 to be described later by executing the program.
- the memory 154 is realized by a RAM (Random Access Memory), a ROM (Read-Only Memory), a flash memory, or the like.
- the memory 154 stores a program executed by the processor 152, data used by the processor 152, and the like.
- the input device 156 accepts an operation input to the terminal device 10.
- the input device 156 is realized by a touch panel.
- the touch panel is provided on a display 158 having a function as a display unit, and is, for example, a capacitance type.
- the touch panel detects a touch operation on the touch panel by an external object every predetermined time, and inputs touch coordinates to the processor 152.
- the input device 156 may include a button or the like.
- the wireless communication unit 160 connects to the mobile communication network via the communication antenna 162 and transmits and receives signals for wireless communication.
- the terminal device 10 can communicate with other communication devices (for example, the server 30 and other terminal devices 10) via a mobile communication network such as LTE (Long Term Evolution).
- LTE Long Term Evolution
- Memory interface 164 reads data from external storage medium 165.
- the processor 152 reads data stored in the storage medium 165 via the memory interface 164 and stores the data in the memory 154.
- the processor 152 reads data from the memory 154 and stores the data in the external storage medium 165 via the memory interface 164.
- the storage medium 165 is non-volatile such as CD (Compact Disc), DVD (Digital Versatile Disk), BD (Blu-ray (registered trademark) Disc), USB (Universal Serial Bus) memory, SD (Secure Digital) memory card, etc. Includes media for storing programs.
- CD Compact Disc
- DVD Digital Versatile Disk
- BD Blu-ray (registered trademark) Disc
- USB Universal Serial Bus
- SD Secure Digital
- the communication interface (I / F) 166 is a communication interface for exchanging various data between the terminal device 10 and the measuring device 20, and is realized by an adapter, a connector, or the like.
- BLE Bluetooth (registered trademark) low energy) is adopted as a communication method.
- the communication method may be a wireless communication method using a wireless LAN or the like, or a wired communication method using USB (Universal Serial Bus) or the like.
- the speaker 168 converts the audio signal given from the processor 152 into audio and outputs it to the outside of the terminal device 10.
- the microphone 170 receives an audio input to the terminal device 10 and gives an audio signal corresponding to the audio input to the processor 152.
- the server 30 only needs to provide information processing as described above and below as a whole, and a known hardware configuration can be adopted.
- the server 30 receives a processor for executing various processes, a memory for storing programs and data, a communication interface for transmitting and receiving various data to and from the terminal device 10, and instructions from an administrator. Including an input interface.
- the measuring device 20 only needs to provide information processing as described above and below as a whole, and a known hardware configuration can be adopted.
- the measuring device 20 receives a processor for executing various processes, a memory for storing programs and data, a communication interface for transmitting and receiving various data to and from the terminal device 10, and instructions from the user. And an input interface for measuring biometric information.
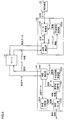
- FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of each of terminal devices 10A and 10B according to the present embodiment.
- terminal device 10A includes a registered information storage unit 202A, an information communication unit 204A, a state determination unit 206A, an importance level determination unit 208A, and an information output unit 210A.
- the terminal device 10B includes a registration information storage unit 202B, an information communication unit 204B, and a data acquisition unit 212B.
- Each function of the terminal devices 10A and 10B is realized, for example, when the processor 152 of each terminal device 10 executes a program stored in the memory 154. Note that some or all of these functions may be implemented by hardware.
- the registration information storage unit 202A of the terminal device 10A stores pairing information for establishing a wireless communication connection between the terminal device 10A and the measuring device 20.
- the information communication unit 204A transmits pairing information and the terminal IDa of the terminal device 10A to the server 30.
- the server 30 since the terminal IDa is associated with the group IDx (the terminal device 10A belongs to the group X), the server 30 stores the received pairing information in the database 32 in association with the group IDx.
- the information communication unit 204B of the terminal device 10B acquires pairing information from the server 30. Specifically, the information communication unit 204B transmits a data acquisition request including the terminal IDb of the terminal device 10B to the server 30.
- the terminal IDb is associated with the group IDx (the terminal device 10B belongs to the group X)
- the server 30 receives the data acquisition request
- the information associated with the group IDx (here Then, the pairing information) is transmitted to the information communication unit 204B.
- the information communication part 204B receives pairing information from the server 30, and stores it in the registration information storage part 202B.
- the information communication unit 204B may receive a user B instruction and make a data acquisition request to the server 30, or may make a data acquisition request periodically.
- the data acquisition unit 212B acquires the measurement data of the biological information measured by the measurement device 20 after establishing the wireless communication connection with the measurement device 20 using the pairing information. Specifically, the data acquisition unit 212B acquires measurement data of the biometric information of the user B.
- the measurement data includes information indicating the type of biological information (for example, blood pressure, body temperature, etc.), a measured value (numerical information) of biological information, and information indicating the measurement timing (for example, measurement date and time).
- the measurement data of the sphygmomanometer 21 includes the maximum blood pressure / minimum blood pressure, the pulse rate and the like (measurement value), and the measurement date and time.
- the measurement data of the sleep meter 22 includes the sleeping time and the number of times of turning (measured value) and the measurement date and time.
- the measurement data of the pedometer 23 includes the number of steps (measurement value) and the measurement date and time.
- the measurement data of the body weight / body composition meter 24 includes body weight, body fat and skeletal muscle rate (measured value), and measurement date and time.
- the measurement data of the thermometer 25 includes body temperature (measured value) and measurement date / time. Note that the information indicating the measurement timing may be only the measurement date or only the measurement time.
- the information communication unit 204B transmits the measurement data (hereinafter, also simply referred to as “measurement data Db”) of the biometric information of the user B acquired by the data acquisition unit 212B and the terminal IDb to the server 30.
- the server 30 stores the measurement data Db in the database 32 in association with the group IDx.
- the information communication unit 204A of the terminal device 10A receives the measurement data Db from the server 30. Specifically, the information communication unit 204A transmits a data acquisition request including the terminal IDa of the terminal device 10A to the server 30. When the server 30 receives the data acquisition request, the server 30 transmits information associated with the group ID x (here, measurement data Db) to the information communication unit 204A. Thereby, the information communication unit 204A receives the measurement data Db from the server 30. Note that the information communication unit 204A may receive a user A instruction and make a data acquisition request to the server 30, or may make a data acquisition request periodically.
- the state determination unit 206A determines whether the health state of the user B is normal or abnormal based on the measurement data Db received by the information communication unit 204A. Specifically, the state determination unit 206A determines the health state of the user B with reference to the information table 600 as illustrated in FIG.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram showing an information table 600 according to the present embodiment.
- information table 600 is information that is referred to in order to determine the health status of user B.
- the information table 600 associates the type of measurement data (the type of measured biological information) by each measuring device 20, the measurement timing, the normal range of the measurement value, and the importance of the measurement data. I remember it.
- the measurement timing is set to “always”, and the normal maximum blood pressure and the minimum blood pressure are set to less than 140 mmHg and less than 90 mmHg, respectively. In this case, it means that the blood pressure is measured every certain time (for example, every few minutes), and the measured blood pressure is preferably less than 140 mmHg / 90 mmHg.
- the measurement timing is set to “morning, night”, and the normal range is set to 3000 steps or more.
- the number of steps is preferably measured in a daytime period (for example, from 11:00 to 15:00) and a nighttime period (for example, from 19:00 to 23:00), and each measurement step number is preferably 3000 steps or more. It means that.
- the measurement data for example, three levels of importance of “high”, “medium”, and “low” are set according to the type.
- the importance of the measurement data of biological information that is considered to have a great influence on life is set high.
- the blood pressure and body temperature measurement data is set to the importance “high”
- the sleep time and step count measurement data is set to the “medium” importance
- the weight measurement data is set to the “low” importance. Is set. In general, it is necessary to monitor biological information that has a great influence on life more frequently.
- the measurement data of the biological information for example, blood pressure, body temperature
- the reference time for example, 1 hour
- the biological information for example, 1 hour
- the degree of importance is set higher than the measurement data of time, number of steps, and weight).
- the contents (type, measurement timing, normal range, and importance) of the information table 600 can be arbitrarily set by the user A according to the health condition of the user B who is the person to watch. Note that the user B may set the contents of the information table 600 himself.
- state determination unit 206A in one aspect, has a case where a measurement value included in measurement data Db is within a predetermined range (within a normal range in information table 600). Is determined to be normal for user B, and otherwise determined to be abnormal for user B.
- the state determination unit 206A determines whether the biological information of the user B is measured at a predetermined timing based on the measurement date and time included in the measurement data Db. Specifically, state determination unit 206A checks the measurement date and time included in measurement data Db, and determines whether or not the biological information is measured according to the measurement timing shown in information table 600.
- the state determination unit 206A determines whether or not the blood pressure is measured every predetermined time.
- the state determination unit 206A determines whether or not the step count is measured in the morning time zone and the night time zone. If the state determination unit 206A determines that the biological information of the user B is not measured at a predetermined timing, the state determination unit 206A determines that the health state of the user B is abnormal.
- state determination unit 206A has a case where the measurement value included in measurement data Db is within a predetermined range and the biological information of user B is measured at a predetermined timing. May determine that the health condition of the user B is normal.
- the importance determination unit 208A refers to the information table 600 and determines whether or not the importance of the measurement data Db is set to be equal to or higher than the reference level. For example, assume that the reference level is set to “medium”. In this case, the importance level determination unit 208A refers to the information table 600, and when the measurement data Db is any one of blood pressure, body temperature, sleep time, and number of steps, the importance level is the reference level. Judge that it is above. On the other hand, when the measurement data Db is weight data, the importance determination unit 208A determines that the importance is less than the reference level.
- the information output unit 210A outputs information related to the health state of the user B based at least on the determination result of the state determination unit 206A. Specifically, in a certain situation, when the state determination unit 206A determines that the health state of the user B is abnormal, the information output unit 210A outputs abnormality information indicating that the health state is abnormal. . When the state determination unit 206A determines that the health state of the user B is normal, the information output unit 210A may output normal information indicating that the health state is normal. For example, the information output unit 210 ⁇ / b> A displays abnormal information (or normal information) on the display 158, and outputs abnormal information (or normal information) via the speaker 168 as a sound.
- the information output unit 210A is the case where the state determination unit 206A determines that the health state of the user B is abnormal, and the importance determination unit 208A determines that the importance of the measurement data Db is the reference level.
- the abnormality information may be output. Specifically, for biological information of low importance (for example, weight), even if an abnormal value is measured, the level of abnormality of the health condition of the user B is not high enough to affect life. Often not. Therefore, in such a case, abnormality information is not output. Thereby, it is possible to reduce the processing load on the terminal device 10A on the watching side and the monitoring burden on the user A on the watching side.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing an example of the processing procedure of terminal apparatus 10A according to the present embodiment. Typically, each step in FIG. 7 is executed by the processor 152 of the terminal device 10A.
- terminal device 10 ⁇ / b> A transmits an acquisition request for measurement data Db of biometric information of user B to server 30 via communication interface 166 (step S ⁇ b> 100).
- the terminal device 10A determines whether or not the measurement data Db has been received from the server 30 (step S102). If measurement data Db has not been received (NO in step S102), terminal device 10A repeats the process of step S102.
- the terminal device 10A determines whether the biological information of the user B is measured at a predetermined timing based on the measurement data Db and the information table 600. Is determined (step S104). Specifically, the terminal device 10A makes the determination based on the information table 600 and at least one of the measurement time and the measurement date included in the measurement data Db.
- step S108 If not measured at a predetermined timing (NO in step S104), the process of step S108 described later is executed. If the measurement is performed at a predetermined timing (YES in step S104), terminal device 10A determines whether or not the measurement value included in measurement data Db is within the normal range (step S106). If the measured value is within the normal range (YES in step S106), terminal device 10A ends the process. That is, the terminal device 10A ends the process without outputting information related to the health status of the user B.
- the terminal device 10A determines whether or not the importance of the measurement data Db is equal to or higher than the reference level (step S108). If the importance level is less than the reference level (NO in step S108), terminal device 10A ends the process. On the other hand, if the importance level is equal to or higher than the reference level (YES in step S108), terminal device 10A displays the abnormality information on display 158 or outputs the sound via speaker 168 (step S110). Then, the process ends.
- the measurement data Db may be such that abnormality information is output regardless of the importance level. That is, the configuration may be such that step S108 in FIG. 7 is not executed. As a result, regardless of the abnormal level of user B's health condition, abnormal information is output when an unusual situation occurs, so user A must know in detail the health condition of user B. Can do.
- the health of the user B may be configured to output information indicating that the state is normal. Thereby, since the user A can immediately grasp that the health state of the user B is normal, the user A can be given a sense of security.
- the user A of the terminal device 10A can check the health state of the user B in real time by requesting the measurement data Db of the biological information of the user B of the terminal device 10B from the server 30. .
- the fact is notified to the user A via a display or the like, so that the user A can immediately grasp the abnormality of the user B.
- the pairing information acquired by the terminal device 10A is stored in the server 30, and the pairing information is acquired by the terminal device 10B. Therefore, the user B does not need to perform an operation for establishing a wireless communication connection with the measuring device 20.
- the terminal device 10 ⁇ / b> A has described the configuration in which the abnormality information is displayed on the display 158 or the abnormality information is output through the speaker 168 as an example of the abnormality information output.
- the configuration is not limited to this.
- the terminal device 10A may transmit abnormality information to another terminal device different from the terminal device 10B. According to this, even if the user A is not aware of the abnormality information notified in the terminal device 10A, the user of the other terminal device can grasp the abnormality of the health state of the user B.
- the terminal device 10A has a function of determining whether the health status of the user B is normal or abnormal (corresponding to the status determination unit 206A in FIG. 5).
- the server 30 may be configured to have the function. Specifically, the server 30 determines whether the health state of the user B is normal or abnormal based on the information table 600 stored in the internal memory and the measurement data Db received from the terminal device 10B. Then, the determination result is transmitted to the terminal device 10A. Note that the server 30 may transmit the determination result to the terminal device 10A only when the health state of the user B is abnormal.
- the terminal device 10A outputs the received determination result (abnormal information).
- the server 30 may also have the configuration of the importance determination unit 208A. Specifically, the server 30 refers to the information table 600, determines whether or not the importance of the measurement data Db is set to a reference level or higher, and transmits the determination result to the terminal device 10A.
- a program for causing a computer to function and executing control as described in the above flowchart is recorded on a non-temporary computer-readable recording medium such as a flexible disk attached to the computer, a CD (Compact Disk Read Only Memory), a secondary storage device, a main storage device, and a memory card. It can also be provided as a program product. Alternatively, the program can be provided by being recorded on a recording medium such as a hard disk built in the computer. A program can also be provided by downloading via a network.
- the program may be a program module that is provided as a part of an operating system (OS) of a computer and that calls necessary modules in a predetermined arrangement at a predetermined timing to execute processing.
- OS operating system
- the program itself does not include the module, and the process is executed in cooperation with the OS.
- a program that does not include such a module can also be included in the program according to the present embodiment.
- the program according to the present embodiment may be provided by being incorporated in a part of another program. Even in this case, the program itself does not include the module included in the other program, and the process is executed in cooperation with the other program. A program incorporated in such another program can also be included in the program according to the present embodiment.
- the configuration exemplified as the above-described embodiment is an example of the configuration of the present invention, and can be combined with another known technique, and a part thereof does not depart from the gist of the present invention. It is also possible to change and configure such as omitting. In the above-described embodiment, the processing and configuration described in the other embodiments may be adopted as appropriate.
- Information processing system 10A, 10B terminal device, 20 measuring device, 21 blood pressure monitor, 22 sleep meter, 23 pedometer, 24 body composition meter, 25 thermometer, 30 server, 32 database, 41, 43 network, 152 processor, 154 Memory, 156 input device, 158 display, 160 wireless communication unit, 162 communication antenna, 164 memory interface, 165 storage medium, 166 communication interface, 168 speaker, 170 microphone, 202A, 202B registration information storage unit, 204A, 204B information communication unit , 206A status determination unit, 208A importance determination unit, 210A information output unit, 212B data acquisition unit, 300 warning screen, 320 transmission button, 600 information table.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Emergency Management (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
- Alarm Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201780020469.3A CN109074855B (zh) | 2016-04-08 | 2017-03-14 | 终端装置、信息处理系统 |
| EP17778927.8A EP3432256B1 (en) | 2016-04-08 | 2017-03-14 | Terminal device and information processing system |
| US16/144,213 US10456037B2 (en) | 2016-04-08 | 2018-09-27 | Terminal device and information processing system |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016-077908 | 2016-04-08 | ||
| JP2016077908A JP2017188008A (ja) | 2016-04-08 | 2016-04-08 | 端末装置、情報処理システム |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/144,213 Continuation US10456037B2 (en) | 2016-04-08 | 2018-09-27 | Terminal device and information processing system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017175548A1 true WO2017175548A1 (ja) | 2017-10-12 |
Family
ID=60000449
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/010118 Ceased WO2017175548A1 (ja) | 2016-04-08 | 2017-03-14 | 端末装置、情報処理システム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10456037B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP3432256B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP2017188008A (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN109074855B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017175548A1 (enExample) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111341432B (zh) * | 2020-02-11 | 2024-04-30 | 深圳智裳科技有限公司 | 智能塑身服饰控制方法、装置、计算机设备及存储介质 |
| CN113545776A (zh) * | 2020-04-16 | 2021-10-26 | 智准生医科技股份有限公司 | 生物信息测量系统以及生物信息校正方法 |
| JP7520580B2 (ja) * | 2020-06-04 | 2024-07-23 | 株式会社東海理化電機製作所 | システム、処理装置、およびプログラム |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10155749A (ja) * | 1996-12-04 | 1998-06-16 | Hiyuunet Kk | 人の健康状態の監視通報システム |
| JP2006085390A (ja) * | 2004-09-15 | 2006-03-30 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | 固定型通信端末、携帯型通信端末、情報集約・蓄積サーバおよび見守り専用端末 |
| JP2015535411A (ja) * | 2012-10-19 | 2015-12-10 | マカフィー, インコーポレイテッド | 安否サービスおよび緊急サービス |
| JP2016042630A (ja) * | 2014-08-14 | 2016-03-31 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | 端末装置、情報処理装置及びプログラム |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6440066B1 (en) * | 1999-11-16 | 2002-08-27 | Cardiac Intelligence Corporation | Automated collection and analysis patient care system and method for ordering and prioritizing multiple health disorders to identify an index disorder |
| EP1319928A1 (en) * | 2001-12-14 | 2003-06-18 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Indicator for perishable goods with preceding period data input, interrupt, variable recording, Arrhenius equation, data transmission |
| US8740789B2 (en) * | 2005-03-03 | 2014-06-03 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Automatic etiology sequencing system and method |
| US20080021741A1 (en) * | 2006-07-19 | 2008-01-24 | Mdatalink, Llc | System For Remote Review Of Clinical Data |
| US9968266B2 (en) * | 2006-12-27 | 2018-05-15 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Risk stratification based heart failure detection algorithm |
| US8515547B2 (en) * | 2007-08-31 | 2013-08-20 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | Wireless patient communicator for use in a life critical network |
| EP2361035B1 (en) * | 2008-09-19 | 2014-12-31 | Cardiac Pacemakers, Inc. | System for determining a heart failure status |
| JP2010155749A (ja) * | 2008-12-26 | 2010-07-15 | Daikin Ind Ltd | 微細気泡発生装置 |
| KR102037416B1 (ko) | 2012-12-17 | 2019-10-28 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 외부 기기 관리 방법, 외부 기기의 동작 방법, 호스트 단말, 관리 서버 및 외부 기기 |
| US9585563B2 (en) * | 2012-12-31 | 2017-03-07 | Dexcom, Inc. | Remote monitoring of analyte measurements |
| US9724470B2 (en) * | 2014-06-16 | 2017-08-08 | Icu Medical, Inc. | System for monitoring and delivering medication to a patient and method of using the same to minimize the risks associated with automated therapy |
| CN204246115U (zh) * | 2014-07-15 | 2015-04-08 | 北京博实联创科技有限公司 | 一种生理信息采集和处理装置 |
-
2016
- 2016-04-08 JP JP2016077908A patent/JP2017188008A/ja active Pending
-
2017
- 2017-03-14 WO PCT/JP2017/010118 patent/WO2017175548A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2017-03-14 CN CN201780020469.3A patent/CN109074855B/zh active Active
- 2017-03-14 EP EP17778927.8A patent/EP3432256B1/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-09-27 US US16/144,213 patent/US10456037B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10155749A (ja) * | 1996-12-04 | 1998-06-16 | Hiyuunet Kk | 人の健康状態の監視通報システム |
| JP2006085390A (ja) * | 2004-09-15 | 2006-03-30 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | 固定型通信端末、携帯型通信端末、情報集約・蓄積サーバおよび見守り専用端末 |
| JP2015535411A (ja) * | 2012-10-19 | 2015-12-10 | マカフィー, インコーポレイテッド | 安否サービスおよび緊急サービス |
| JP2016042630A (ja) * | 2014-08-14 | 2016-03-31 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | 端末装置、情報処理装置及びプログラム |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP3432256A4 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN109074855A (zh) | 2018-12-21 |
| EP3432256A1 (en) | 2019-01-23 |
| EP3432256B1 (en) | 2024-07-31 |
| CN109074855B (zh) | 2021-11-26 |
| JP2017188008A (ja) | 2017-10-12 |
| EP3432256A4 (en) | 2019-11-20 |
| US20190021592A1 (en) | 2019-01-24 |
| US10456037B2 (en) | 2019-10-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8653965B1 (en) | Human health monitoring systems and methods | |
| US20130211265A1 (en) | Multifunctional medical device for telemedicine applications | |
| US20070010721A1 (en) | Apparatus and system of Internet-enabled wireless medical sensor scale | |
| JP2013146463A (ja) | 睡眠表示プログラム、睡眠表示方法及び睡眠表示装置 | |
| JP7073763B2 (ja) | 情報処理システム、情報処理方法、電子機器、サーバ装置及び情報処理プログラム | |
| US20180317780A1 (en) | Multi-Vital Sign Detector of SpO2 Blood Oxygenation and Heart Rate From a Photoplethysmogram Sensor and Respiration Rate, Heart Rate Variability and Blood Pressure from a Micro Dynamic Light Scattering Sensor in an Electronic Medical Records System | |
| WO2018123228A1 (ja) | 情報処理システム | |
| US10456037B2 (en) | Terminal device and information processing system | |
| KR19990065818A (ko) | 무선망에 연계되는 건강 진단장치 | |
| JP2010282414A (ja) | 携帯型検査端末と健康管理システム | |
| KR20090014481A (ko) | 건강 관리 시스템 및 방법 | |
| JP2014036781A (ja) | 情報処理装置、ナースコールシステム、ナースコール方法及びプログラム | |
| JP2008043702A (ja) | 生体データ計測システム及び生体データ計測方法、並びに生体データ計測センサ | |
| JP2008242502A (ja) | 総合医療支援システム | |
| KR20210047041A (ko) | 다중 디바이스 간의 생리적 데이터 통합 및 도시화 장치 및 그 방법 | |
| JP7570608B1 (ja) | ウェアラブル端末からブロードキャスト通信で送信される生体情報を管理する管理システム | |
| KR101810996B1 (ko) | 웨어러블 디바이스를 통한 응급 문자 전송 방법 및 이를 실행하는 장치 | |
| US20120157790A1 (en) | Physical examination method using mobile terminal, and gateway and mobile terminal for physical examination | |
| KR20010019660A (ko) | 원격 의료 진단망 및 원격 의료 진단망내의 휴대형 감시 장치 | |
| WO2017175547A1 (ja) | 端末装置 | |
| CN111263610B (zh) | 一种监护系统、数据传输方法、便携式监护仪及配置器 | |
| KR101220462B1 (ko) | 위치 정보를 이용한 응급상황알림시스템 | |
| JP5735848B2 (ja) | 電話機 | |
| KR20010037228A (ko) | 원격진료장치 및 이를 이용한 건강정보관리시스템 | |
| KR20040098982A (ko) | 원격 자동 검진/진단 무선 페이징 시스템 및 이를 이용한원격 자동 진단 방법 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2017778927 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2017778927 Country of ref document: EP Effective date: 20181015 |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17778927 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |