WO2015115305A1 - 排ガス処理装置 - Google Patents
排ガス処理装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015115305A1 WO2015115305A1 PCT/JP2015/051726 JP2015051726W WO2015115305A1 WO 2015115305 A1 WO2015115305 A1 WO 2015115305A1 JP 2015051726 W JP2015051726 W JP 2015051726W WO 2015115305 A1 WO2015115305 A1 WO 2015115305A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- exhaust gas
- gas
- flue
- dust collector
- supplying
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/46—Removing components of defined structure
- B01D53/48—Sulfur compounds
- B01D53/50—Sulfur oxides
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J15/00—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes
- F23J15/003—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes for supplying chemicals to fumes, e.g. using injection devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/46—Removing components of defined structure
- B01D53/48—Sulfur compounds
- B01D53/50—Sulfur oxides
- B01D53/501—Sulfur oxides by treating the gases with a solution or a suspension of an alkali or earth-alkali or ammonium compound
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/46—Removing components of defined structure
- B01D53/54—Nitrogen compounds
- B01D53/56—Nitrogen oxides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/46—Removing components of defined structure
- B01D53/64—Heavy metals or compounds thereof, e.g. mercury
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/74—General processes for purification of waste gases; Apparatus or devices specially adapted therefor
- B01D53/75—Multi-step processes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J15/00—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes
- F23J15/02—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes of purifiers, e.g. for removing noxious material
- F23J15/04—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes of purifiers, e.g. for removing noxious material using washing fluids
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J15/00—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes
- F23J15/06—Arrangements of devices for treating smoke or fumes of coolers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23L—SUPPLYING AIR OR NON-COMBUSTIBLE LIQUIDS OR GASES TO COMBUSTION APPARATUS IN GENERAL ; VALVES OR DAMPERS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR CONTROLLING AIR SUPPLY OR DRAUGHT IN COMBUSTION APPARATUS; INDUCING DRAUGHT IN COMBUSTION APPARATUS; TOPS FOR CHIMNEYS OR VENTILATING SHAFTS; TERMINALS FOR FLUES
- F23L15/00—Heating of air supplied for combustion
- F23L15/04—Arrangements of recuperators
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2251/00—Reactants
- B01D2251/40—Alkaline earth metal or magnesium compounds
- B01D2251/404—Alkaline earth metal or magnesium compounds of calcium
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2251/00—Reactants
- B01D2251/60—Inorganic bases or salts
- B01D2251/602—Oxides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2251/00—Reactants
- B01D2251/60—Inorganic bases or salts
- B01D2251/604—Hydroxides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2251/00—Reactants
- B01D2251/60—Inorganic bases or salts
- B01D2251/606—Carbonates
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2257/00—Components to be removed
- B01D2257/30—Sulfur compounds
- B01D2257/302—Sulfur oxides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2257/00—Components to be removed
- B01D2257/40—Nitrogen compounds
- B01D2257/404—Nitrogen oxides other than dinitrogen oxide
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/34—Chemical or biological purification of waste gases
- B01D53/74—General processes for purification of waste gases; Apparatus or devices specially adapted therefor
- B01D53/86—Catalytic processes
- B01D53/869—Multiple step processes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J2215/00—Preventing emissions
- F23J2215/10—Nitrogen; Compounds thereof
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J2215/00—Preventing emissions
- F23J2215/20—Sulfur; Compounds thereof
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J2219/00—Treatment devices
- F23J2219/10—Catalytic reduction devices
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F23—COMBUSTION APPARATUS; COMBUSTION PROCESSES
- F23J—REMOVAL OR TREATMENT OF COMBUSTION PRODUCTS OR COMBUSTION RESIDUES; FLUES
- F23J2219/00—Treatment devices
- F23J2219/60—Sorption with dry devices, e.g. beds
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/20—Air quality improvement or preservation, e.g. vehicle emission control or emission reduction by using catalytic converters
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E20/00—Combustion technologies with mitigation potential
- Y02E20/34—Indirect CO2mitigation, i.e. by acting on non CO2directly related matters of the process, e.g. pre-heating or heat recovery
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an exhaust gas treatment apparatus that can follow fluctuations in SO 3 concentration in exhaust gas.
- SO x sulfur oxides
- SO 2 sulfur dioxide
- SO 3 sulfur trioxide
- the sulfur (S) content derived from the fuel of a thermal power plant is oxidized by the catalyst component in the fuel or the catalyst of the denitration device, and from sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) to sulfur trioxide (SO 3 ) component Convert to
- the converted SO 3 concentration may reach a maximum of about 30 to 50 ppm in the exhaust gas from coal-fired boilers, and may reach a maximum of around 180 ppm for oil-fired and heavy fuels, depending on the boiler fouling condition and combustion conditions.
- the SO 3 in the exhaust gas causes troubles such as equipment corrosion and blockage due to increased ash adhesion in the low-temperature equipment downstream of the air heater, and increases maintenance costs for power plant users.
- SO 3 is known as a typical causative component of purple smoke from the chimney, and the plant may be forced to stop when the purple smoke is dark.
- SO 3 is the fuel property, contamination of the boiler furnace, although over time the concentration by the active state of the denitration catalyst varies from that on-line measurements of SO 3 concentration was difficult, the conventional CaCO 3
- the SO 3 concentration at the time of trial operation was measured by a chemical analysis method, or it was often sprayed excessively with respect to this SO 3 concentration assuming the maximum SO 3 concentration. For this reason, when the plant operating conditions fluctuate and increase to an unexpected SO 3 concentration, there is a problem that the chemical becomes insufficient, the SO 3 removal performance decreases, and pressure loss increase due to ash adhesion and corrosion is promoted. .
- the SO 3 concentration is lower than expected, it is also a factor in injecting an excessive amount of chemicals and introducing wasteful costs.
- an object of the present invention is to provide an exhaust gas treatment apparatus that can adjust the supply amount of the SO 3 removal agent and follow the variation in the SO 3 concentration in the exhaust gas.
- a first invention of the present invention for solving the above-described problems includes a denitration device for removing nitrogen oxides in exhaust gas from a boiler, an air preheater for recovering heat in the exhaust gas after removing nitrogen oxides, A dust collector that removes soot and dust in the exhaust gas after heat recovery, a gas-liquid contact type desulfurization device that removes sulfur oxide in the exhaust gas after dust removal, a chimney that discharges the exhaust gas after desulfurization to the outside, and SO 3 removing agent supply device for supplying the exhaust gas flue of SO 3 removal agent into the exhaust gas at the feed section of the upstream side of the dust collector, in the downstream side of the air preheater, the SO 3 removal agent
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus includes a wet state treatment unit that supplies moisture to a part of the exhaust gas to make it wet in the exhaust gas flue on the upstream side of the supply unit that supplies the exhaust gas flue.
- the wet state processing unit rises in a direction orthogonal to the flue gas flue for discharging the exhaust gas, a gas ascending passage and a gas in the riser
- An exhaust gas treatment apparatus comprising: a partition section that partitions into a descending passage; and a droplet supply section that supplies droplets in the gas descending passage partitioned by the partition section.
- the third invention is the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the first or second invention, wherein a hopper is provided below the rising portion.
- a fourth invention is the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to any one of the first to third inventions, wherein the desulfurization waste water or the dehydrated filtrate from the desulfurization apparatus is supplied to the wet state treatment unit.
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus further comprises an Hg removal agent supply means for supplying an Hg removal agent into the exhaust gas on the front side of the dust collector. is there.
- the sixth invention in any one invention of the first to fifth, a part of the fly ash containing SO 3 removing agent recovered by the dust collector, the dust collector of the front SO 3 removal agent
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus is provided with a return line for supplying the exhaust gas in the vicinity of the exhaust gas.
- a seventh aspect of the invention is the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to any one of the first to sixth aspects, further comprising a gas gas heater between the supply unit that supplies the SO 3 removing agent and the dust collector. It is in.
- the eighth invention is a denitration device that removes nitrogen oxides in exhaust gas from a boiler, an air preheater that recovers heat in the exhaust gas after removing nitrogen oxides, and heat exchange of the heat of the exhaust gas after heat recovery Gas gas heater, dust collector that removes dust in exhaust gas after heat recovery, gas-liquid contact type desulfurization device that removes sulfur oxide in exhaust gas after dust removal, and exhaust gas after desulfurization to the outside A chimney, an SO 3 removal agent supply device for supplying an SO 3 removal agent into the exhaust gas in the exhaust gas at a supply portion on the downstream side of the air preheater and the upstream side of the gas gas heater, and the gas
- An exhaust gas treatment comprising: a wet state treatment unit which supplies moisture to a part of the exhaust gas in a flue gas flue on the downstream side of the gas heater and on the upstream side of the dust collector. In the device.
- the wet state treatment unit rises in a direction orthogonal to the flue gas flue from which the exhaust gas is discharged, a gas ascending passage and a gas in the riser
- An exhaust gas treatment apparatus comprising: a partition section that partitions into a descending passage; and a droplet supply section that supplies droplets in the gas descending passage partitioned by the partition section.
- a tenth aspect of the invention is an exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the eighth or ninth aspect of the invention, further comprising a hopper below the rising portion.
- An eleventh aspect of the invention is an exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to any one of the eighth to tenth aspects of the invention, wherein desulfurization waste water or dehydrated filtrate from the desulfurization apparatus is supplied to the wet state treatment unit.
- a twelfth aspect of the present invention is the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to any one of the eighth to eleventh aspects, further comprising an Hg removal agent supply means for supplying an Hg removal agent into the exhaust gas on the front side of the dust collector. is there.
- a thirteenth invention in any one invention of the eighth to 12, a part of the fly ash containing SO 3 removing agent recovered by the dust collector, the dust collector of the front SO 3 removal agent
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus is provided with a return line for supplying the exhaust gas in the vicinity of the exhaust gas.
- moisture is actively supplied by supplying moisture to the exhaust gas, so that water is present at the interface near the powder surface of the supplied SO 3 removing agent.
- a chemical reaction in which SO 3 in the exhaust gas is absorbed on the surface of the SO 3 removing agent powder can be actively promoted.
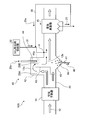
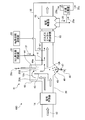
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to a first embodiment.
- FIG. 2 is a schematic view of the calcium carbonate in a wet state.
- FIG. 3 is a schematic view of an exhaust gas flue according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas processing apparatus according to the second embodiment.
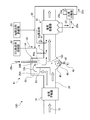
- FIG. 5 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the third embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the fourth embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the fifth embodiment.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to a first embodiment.
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus 10A recovers heat in the exhaust gas 12 after removing the nitrogen oxide in the exhaust gas 12 from the boiler 11 and the nitrogen oxide removed.
- the SO 3 removal agent 31 is supplied into the exhaust gas flue in the exhaust gas 12 by the contact-type desulfurization device 16, the chimney 17 that discharges the exhaust gas after desulfurization to the outside, and the supply section X on the upstream side of the dust collector 15.
- a wet state processing unit 41 for supplying moisture to a part of the water Is shall.
- symbol F is fuel supplied to the boiler
- A is air
- 25 is dust collection ash from the dust collector
- 26 is desulfurization drainage
- 27 is a belt filter that separates the gypsum 28 from the desulfurization drainage
- 29 is The dehydrated filtrate from which the gypsum 28 has been separated by the belt filter 27 is illustrated.
- a part 29a of the dehydrated filtrate 29 is used in the exhaust gas 12 as water supplied from the outside.
- the exhaust gas flue 20 is provided with the wet state treatment unit 41 that partially wets the exhaust gas, the amount of water finely sprayed on the exhaust gas 12 increases and the gas temperature also decreases.
- FIG. 2 is a schematic view of the calcium carbonate in a wet state.
- the gas temperature of the exhaust gas 12 is after passing through the air preheater 14, when the gas temperature of the exhaust gas 12 after passing through the denitration device 13 is 350 ° C., for example, it becomes about 180 ° C., for example.
- the outer surface gas film 52 of the wet CaCO 3 water film film 51 covered with the water film film film 51 is about 180 ° C., which is the same as the gas temperature. In 51, it becomes about 70 degreeC (wet bulb temperature of water), and a big temperature gradient arises in both boundary films by this temperature difference. Due to this temperature gradient, the exhaust gas 12 containing gaseous SO 3 entering the calcium carbonate becomes lower than the acid dew point temperature (140 to 150 ° C.).
- the portion 29a of the dehydrated filtrate 29 is supplied to the exhaust gas 12 so as to be actively moistened.
- a temperature gradient involving water is generated, and a chemical reaction in which SO 3 in the exhaust gas 12 becomes calcium sulfate is actively performed on the surface of calcium carbonate.
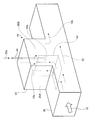
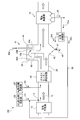
- FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram of an exhaust gas flue according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 4 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas processing apparatus according to the second embodiment.
- symbol is attached
- FIG. 4 shows only the main part of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus shown in FIG. 1, and others are omitted (the same applies to the following examples). As shown in FIGS.
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus 10 ⁇ / b> B of the present embodiment, as the wet state treatment unit 41, a startup unit 42 that rises in a direction perpendicular to the exhaust gas flue 20 that exhausts the exhaust gas 12 from the boiler 11.
- the rising portion 42 is divided into a gas rising passage 20A and a gas lowering passage 20B, an inverted L-shaped partitioning portion 43, and a gas dropping passage 20B partitioned by the partitioning portion 43 into a droplet 44a.
- a part 25a of the dust collection ash 25 containing the unreacted SO 3 removal agent 31 collected by the dust collectors 15 in the three sections 15-1 to 15-3 is disposed on the front side of the dust collector 15.
- a return line 35 for supplying the SO 3 removing agent 31 in the vicinity of the exhaust gas 12 is provided to join the SO 3 removing agent 31 supplied from the SO 3 removing agent supply unit 32 and sprayed into the exhaust flue 20.
- the supply of the part 25a of the dust collection ash 25 is merged with the SO 3 removal agent 31 and sprayed into the flue gas flue 20, but the part 25a of the dust collection ash 25 is separated. You may make it spray in the exhaust gas flue 20 separately separately in a line.
- the droplet supply unit 44 sprays fine droplets using a spray nozzle or the like that sprays the dehydrated filtrate 29a.
- a spray nozzle it is considered that a two-fluid nozzle capable of miniaturizing droplets can be applied.
- the present invention is not limited to this.
- the wet exhaust gas 12b merges with the exhaust gas 12 that has passed through the lower side of the partition portion 43.
- a hopper 45 is provided on the bottom surface side of the flue gas flue 20 of the start-up portion 42, and when the droplets 44a are sprayed or when the solid matter 46 adhering to the vicinity of the nozzle falls, it enters the flue. Prevents accumulation.
- a rotary valve 47 is provided at the bottom of the hopper 45 so that the solid matter 46 is periodically removed.
- Ca ions, SO 4 ions, Cl ions, etc. in the dehydrated filtrate 29a are evaporated to form a salt form, or a part of the reaction gypsum / unreacted calcium carbonate or accompanying substances. And a mixture of combustion ash.
- droplets when droplets are sprayed, they are sprayed in the gas descending passage 20B of the rising portion 42 and sprayed in the same direction as the gas flow direction (left and right direction in the figure) in the exhaust gas flue 20. Not done.
- coarse solids 46 adhering to and dropping out from the nozzle periphery and surrounding structures may accumulate in the flue and obstruct the droplet spraying operation.
- the droplets 44a are sprayed along the descending flow of the rising portion.
- the solid matter 46 adhering to the periphery of the nozzle may obstruct the miniaturization of the droplets, it may be removed by intermittent beating or removal air by installing a removal device.
- the dehydrated filtrate 29a is used as water for supplying droplets, but the present invention is not limited to this.
- a part of the desulfurization waste water 26 before separating the gypsum 28 may be used.
- the gypsum slurry concentration may be adjusted using water.
- a part of the dust collection ash 25 collected by the electric dust collector 15 is returned again into the flue through the dust collection ash supply line.
- FIG. 5 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the third embodiment.
- the exhaust gas treatment apparatus 10 ⁇ / b> C according to the present embodiment further includes an Hg removal agent supply unit 62 that supplies an Hg removal agent 61 into the exhaust gas on the front side of the dust collector 15 in the second embodiment. SO 3 in the exhaust gas is removed and mercury in the exhaust gas is removed.
- the Hg removing agent is supplied on the upstream side of the dust collector 15 and on the downstream side of the supply unit X that supplies the SO 3 removing agent 31 into the exhaust gas flue 20.
- activated carbon (AC) can be exemplified.
- the SO 3 concentration in the exhaust gas 12 is reduced, so that the amount of activated carbon necessary for mercury-removing activated carbon (AC) is reduced, and the activated carbon necessary for Hg removal is reduced.
- the amount of addition can be minimized.
- the return line 35 for supplying the separated product 25c of the SO 3 remover 31 and the Hg remover 61 into the exhaust gas 12 is provided.
- the SO 3 remover 31 and the Hg remover are provided in the return line.
- a specific gravity separator 63 that separates a portion 25 a of the dust collection ash 25 including the agent 61 into fly ash 25 b and a separated product 25 c of the SO 3 removal agent 31 and the Hg removal agent 61 is provided. Then, the separated product 25c of the SO 3 removing agent 31 and the Hg removing agent 61 excluding the fly ash 25b separated by specific gravity is supplied into the exhaust gas 12. This makes it possible to reuse only the SO 3 removal agent 31 and Hg-removing agent 61 unreacted during SO 3 removal and Hg removal.
- FIG. 6 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the fourth embodiment.
- symbol is attached
- a gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery device 65 is further provided on the front side of the dust collector 15 to recover the heat of the exhaust gas 12.
- the heat medium after heat recovery is supplied for low-pressure turbine side feed water heating, and the cooled heat medium is returned to the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery device 65 and circulated ( The circulation line is omitted).
- GGH gas gas heater
- the exhaust gas temperature is further lowered. Therefore, the condensed SO 3 mist in the exhaust gas 12 after passing through the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery unit 65 is It is made to react with the unreacted calcium carbonate (CaCO 3 ) that is entrained in the catalyst to further improve the SO 3 removal efficiency.
- CaCO 3 unreacted calcium carbonate
- FIG. 7 is a schematic flowchart of the exhaust gas treatment apparatus according to the fifth embodiment.
- symbol is attached
- the exhaust gas treatment device 10E of this embodiment includes a denitration device 13 that removes nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gas 12 from the boiler, and air that recovers heat in the exhaust gas 12 after the removal of nitrogen oxides.
- the upstream side supply unit Y is the downstream side of the SO 3 removal agent supply unit 32 for supplying the SO 3 removal agent 31 into the exhaust gas flue 20 and the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery unit 65 in the upstream side.
- a wet state processing unit 41 for making a part of the exhaust gas 12 into a wet state.
- the wet state processing unit 41 is installed on the downstream side of the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery unit 65, so that the gas temperature of the exhaust gas 12 after passing through the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery unit 65 is 100 ° C.
- the gas temperature of the exhaust gas 12 after passing through the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery unit 65 is 100 ° C.
- SO 3 remaining in the exhaust gas after passing through the gas gas heater (GGH) heat recovery device 65 is reacted with unreacted calcium carbonate, Further, the SO 3 removal efficiency is improved.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Treating Waste Gases (AREA)
- Chimneys And Flues (AREA)
- Exhaust Gas Treatment By Means Of Catalyst (AREA)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/025,783 US9925490B2 (en) | 2014-01-31 | 2015-01-22 | Flue gas treatment device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014-018080 | 2014-01-31 | ||
| JP2014018080A JP6212401B2 (ja) | 2014-01-31 | 2014-01-31 | 排ガス処理装置 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015115305A1 true WO2015115305A1 (ja) | 2015-08-06 |
Family
ID=53756881
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/051726 Ceased WO2015115305A1 (ja) | 2014-01-31 | 2015-01-22 | 排ガス処理装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9925490B2 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6212401B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2015115305A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105498535A (zh) * | 2015-12-01 | 2016-04-20 | 大连海事大学 | 一种使用亚氯酸钠海水溶液脱除船舶柴油机废气中氮氧化物的方法及装置 |
| CN105771575A (zh) * | 2016-03-24 | 2016-07-20 | 上海蓝科石化环保科技股份有限公司 | 一种烟气多组分污染物一体化干式净化方法及系统 |
| CN106958936A (zh) * | 2016-01-12 | 2017-07-18 | 沈阳兰昊新能源科技有限公司 | 环保型生物质秸秆燃料锅炉 |
| CN107631290A (zh) * | 2017-09-14 | 2018-01-26 | 北京建筑大学 | 一种基于膜吸收的烟气余热回收系统 |
| CN107930359A (zh) * | 2017-12-21 | 2018-04-20 | 华北电力大学(保定) | 利用脱硫废水脱除燃煤烟气中元素态汞的装置和方法 |
| CN108730942A (zh) * | 2018-06-06 | 2018-11-02 | 安徽亿达新能源科技有限公司 | 一种可利用烟气加热的蒸汽发生器 |
| CN110529872A (zh) * | 2018-07-24 | 2019-12-03 | 青岛科技大学 | 基于入口烟气温度通信控制的电站锅炉余热利用系统 |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9724638B2 (en) | 2014-01-02 | 2017-08-08 | General Electric Technology Gmbh | Apparatus and method for evaporating waste water and reducing acid gas emissions |
| US9352274B2 (en) * | 2014-01-02 | 2016-05-31 | Alstom Technology Ltd | Apparatus and method for evaporating waste water and reducing acid gas emissions |
| US10267517B2 (en) * | 2016-07-08 | 2019-04-23 | Arvos Ljungstrom Llc | Method and system for improving boiler effectiveness |
| CN106322415A (zh) * | 2016-09-29 | 2017-01-11 | 杭州创屹机电科技有限公司 | 烟气污染物协同深度净化系统 |
| CN110366443A (zh) * | 2017-03-08 | 2019-10-22 | 国际壳牌研究有限公司 | 从so2含量暂时非常高的气体中除去so2的方法 |
| US11300292B2 (en) * | 2018-09-14 | 2022-04-12 | Minplus B.V. | Method of operating an incinerator comprising a device for capturing ash entrained by flue gas |
| CN111974207A (zh) * | 2019-05-23 | 2020-11-24 | 同正环保集团有限公司 | 一种烟气低温scr脱硝工艺 |
| CN111059561B (zh) * | 2019-12-25 | 2022-07-01 | 东莞市建安管桩有限公司 | 一种管桩锅炉蒸汽系统 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS51152043U (enExample) * | 1975-01-07 | 1976-12-04 | ||
| JPS6135827A (ja) * | 1984-07-27 | 1986-02-20 | Hitachi Zosen Corp | 乾式石灰法による排ガスの浄化方法 |
| JPH04135618A (ja) * | 1990-09-26 | 1992-05-11 | Babcock Hitachi Kk | 排煙脱硫方法 |
| JPH09141050A (ja) * | 1995-11-24 | 1997-06-03 | Chiyoda Corp | 排煙脱硫プラントのガス吸収装置内部の洗浄方法および洗浄装置 |
| JPH10272335A (ja) * | 1997-03-31 | 1998-10-13 | Kawasaki Heavy Ind Ltd | 湿式排煙脱硫方法及びスプレー式吸収塔 |
| JP2000121032A (ja) * | 1998-10-16 | 2000-04-28 | Nkk Corp | 排ガス処理方法および装置 |
| WO2008078721A1 (ja) * | 2006-12-27 | 2008-07-03 | Babcock-Hitachi Kabushiki Kaisha | 排ガス処理方法と装置 |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04300624A (ja) | 1991-03-28 | 1992-10-23 | Babcock Hitachi Kk | 使用済み脱硫剤の再生方法および装置 |
| JPH0914050A (ja) * | 1995-06-30 | 1997-01-14 | Suzuki Motor Corp | クランクプーリのオイルシール構造 |
| JPH10118446A (ja) | 1996-10-17 | 1998-05-12 | Ishikawajima Harima Heavy Ind Co Ltd | 高濃度so2ガス排煙処理装置 |
-
2014
- 2014-01-31 JP JP2014018080A patent/JP6212401B2/ja active Active
-
2015
- 2015-01-22 US US15/025,783 patent/US9925490B2/en active Active
- 2015-01-22 WO PCT/JP2015/051726 patent/WO2015115305A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS51152043U (enExample) * | 1975-01-07 | 1976-12-04 | ||
| JPS6135827A (ja) * | 1984-07-27 | 1986-02-20 | Hitachi Zosen Corp | 乾式石灰法による排ガスの浄化方法 |
| JPH04135618A (ja) * | 1990-09-26 | 1992-05-11 | Babcock Hitachi Kk | 排煙脱硫方法 |
| JPH09141050A (ja) * | 1995-11-24 | 1997-06-03 | Chiyoda Corp | 排煙脱硫プラントのガス吸収装置内部の洗浄方法および洗浄装置 |
| JPH10272335A (ja) * | 1997-03-31 | 1998-10-13 | Kawasaki Heavy Ind Ltd | 湿式排煙脱硫方法及びスプレー式吸収塔 |
| JP2000121032A (ja) * | 1998-10-16 | 2000-04-28 | Nkk Corp | 排ガス処理方法および装置 |
| WO2008078721A1 (ja) * | 2006-12-27 | 2008-07-03 | Babcock-Hitachi Kabushiki Kaisha | 排ガス処理方法と装置 |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105498535A (zh) * | 2015-12-01 | 2016-04-20 | 大连海事大学 | 一种使用亚氯酸钠海水溶液脱除船舶柴油机废气中氮氧化物的方法及装置 |
| CN106958936A (zh) * | 2016-01-12 | 2017-07-18 | 沈阳兰昊新能源科技有限公司 | 环保型生物质秸秆燃料锅炉 |
| CN105771575A (zh) * | 2016-03-24 | 2016-07-20 | 上海蓝科石化环保科技股份有限公司 | 一种烟气多组分污染物一体化干式净化方法及系统 |
| CN105771575B (zh) * | 2016-03-24 | 2018-10-30 | 上海蓝科石化环保科技股份有限公司 | 一种烟气多组分污染物一体化干式净化方法及系统 |
| CN107631290A (zh) * | 2017-09-14 | 2018-01-26 | 北京建筑大学 | 一种基于膜吸收的烟气余热回收系统 |
| CN107631290B (zh) * | 2017-09-14 | 2019-01-25 | 北京建筑大学 | 一种基于膜吸收的烟气余热回收系统 |
| CN107930359A (zh) * | 2017-12-21 | 2018-04-20 | 华北电力大学(保定) | 利用脱硫废水脱除燃煤烟气中元素态汞的装置和方法 |
| CN108730942A (zh) * | 2018-06-06 | 2018-11-02 | 安徽亿达新能源科技有限公司 | 一种可利用烟气加热的蒸汽发生器 |
| CN110529872A (zh) * | 2018-07-24 | 2019-12-03 | 青岛科技大学 | 基于入口烟气温度通信控制的电站锅炉余热利用系统 |
| CN110529872B (zh) * | 2018-07-24 | 2020-11-17 | 苏州海陆重工股份有限公司 | 基于入口烟气温度通信控制的电站锅炉余热利用系统 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20160243498A1 (en) | 2016-08-25 |
| JP6212401B2 (ja) | 2017-10-11 |
| US9925490B2 (en) | 2018-03-27 |
| JP2015144986A (ja) | 2015-08-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6212401B2 (ja) | 排ガス処理装置 | |
| JP7390431B2 (ja) | 無排水化排ガス処理システム及び無排水化排ガス処理方法 | |
| JP5984712B2 (ja) | 排ガス処理システム及び排ガス処理方法 | |
| JP6230818B2 (ja) | 排ガス処理装置及び排ガス処理方法 | |
| US7625537B2 (en) | Integrated dry and wet flue gas cleaning process and system | |
| KR100288993B1 (ko) | 연도가스 처리 방법 및 시스템 | |
| EP2891630B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for evaporating waste water and reducing acid gas emissions | |
| US10247414B2 (en) | Coal-fired boiler exhaust gas treatment apparatus and coal-fired boiler exhaust gas treatment method | |
| JP2009166012A (ja) | 石炭焚ボイラの排ガス処理システム及びその運転方法 | |
| US9650269B2 (en) | System and method for reducing gas emissions from wet flue gas desulfurization waste water | |
| JP2013039511A (ja) | 湿式排煙脱硫装置およびそれを備えた火力発電プラント | |
| KR20170124106A (ko) | 폐수를 증발시키고 산성 가스 배출을 감소시키기 위한 장치 및 방법 | |
| BRPI0616068A2 (pt) | métodos de remoção de so3 de uma corrente de gás de combustão, e de fornecimento de um sorvente seco para injeção de gás de combustão | |
| JP3621822B2 (ja) | 排煙処理方法及び設備 | |
| JP2016120438A (ja) | 湿式脱硫装置及び湿式脱硫方法 | |
| US10005026B2 (en) | Limestone supply device and air pollution control system | |
| WO2016110828A2 (en) | Method and apparatus to increase industrial combustion efficiency | |
| EP0862939B1 (en) | Flue gas treating process | |
| JP5859244B2 (ja) | 排煙処理設備と排煙処理方法 | |
| US10617999B2 (en) | Process for removing SO2 from flue gases using liquid sorbent injection | |
| BR112020002489A2 (pt) | processo para tratar gases de combustão em tratamento de gás de combustão de cds |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15743405 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15025783 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15743405 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |