WO2014013781A1 - 無線通信システムおよび通信制御方法 - Google Patents
無線通信システムおよび通信制御方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014013781A1 WO2014013781A1 PCT/JP2013/063547 JP2013063547W WO2014013781A1 WO 2014013781 A1 WO2014013781 A1 WO 2014013781A1 JP 2013063547 W JP2013063547 W JP 2013063547W WO 2014013781 A1 WO2014013781 A1 WO 2014013781A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- base station
- unit
- base stations
- list
- user apparatus
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W56/00—Synchronisation arrangements
- H04W56/001—Synchronization between nodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/08—Access restriction or access information delivery, e.g. discovery data delivery
- H04W48/12—Access restriction or access information delivery, e.g. discovery data delivery using downlink control channel
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/16—Discovering, processing access restriction or access information
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W16/00—Network planning, e.g. coverage or traffic planning tools; Network deployment, e.g. resource partitioning or cells structures
- H04W16/24—Cell structures
- H04W16/32—Hierarchical cell structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W24/00—Supervisory, monitoring or testing arrangements
- H04W24/02—Arrangements for optimising operational condition
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a wireless communication system and a communication control method.
- a plurality of base stations can cooperate to perform radio communication with a user apparatus.
- the plurality of base stations include, for example, a large-scale radio base station (macro base station) having a wide communicable area and a small-scale radio base station (pico base) having a communicable area narrower than the large-scale radio base station. Station, femto base station, etc.).
- Patent Document 1 discloses that a group of a plurality of femto base stations is grouped according to a geographical reference (geographic proximity), so that a macro base station and a femto base station group are grouped. It is disclosed that the handover is realized.
- the communication state for example, the quality of wireless communication between the user apparatus and the base station, the amount of traffic to be processed by the base station, etc.
- the selection of base stations included in the group may not be appropriate.
- the above problems caused by the fixed grouping are not only in a radio communication system (so-called heterogeneous network) including both large-scale radio base stations and small-scale radio base stations, but only in radio base stations of the same scale. It is understood that this can also occur in a wireless communication system including a so-called homogeneous network.
- an object of the present invention is to appropriately select a base station capable of performing wireless communication with a user apparatus in a wireless communication system including a plurality of base stations.
- the wireless communication system of the present invention includes a plurality of base stations each identified by an identifier, a user device capable of performing wireless communication with each of the plurality of base stations, and a plurality of the base stations and the user devices.
- a communication control device that controls wireless communication, and the user device is capable of wireless communication with the user device acquired by synchronization acquisition and a level measurement unit that measures a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from the base station.
- a storage unit that stores a first list that includes identifiers of active base stations and a second list that includes identifiers of base stations to which the user apparatus should maintain a synchronization state
- the communication control device includes: A selection information generation unit configured to generate selection information used for selecting a base station in which the user apparatus should maintain a synchronization state; and a selection information notification unit configured to notify the user apparatus of the selection information.
- the user apparatus further includes a plurality of user apparatuses that should hold a synchronization state from a plurality of base stations corresponding to identifiers included in the first list, based on the selection information notified from the communication control apparatus.
- a base station selection unit that selects a plurality of selected base stations and stores the identifiers of the selected base stations in the second list, and a plurality of the bases selected by the base station selection unit and included in the second list
- a base station information reporting unit for reporting the identifier of the station and the reception level of the radio wave transmitted from the base station corresponding to the identifier to the communication control device, and the identifier included in the second list
- a synchronization holding unit that holds a synchronization state with each of the plurality of base stations.
- the level measurement unit of the user apparatus measures a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from a base station corresponding to the identifier included in the first list for each base station, and performs the communication control.
- the selection information generation unit of the device generates the maximum number of the identifiers that can be included in the second list as the selection information, and the base station selection unit of the user device receives the reception measured by the level measurement unit
- the base stations up to the maximum number of the identifiers indicated by the selection information are selected as the base stations that should maintain the synchronization state in descending order of level.
- the level measurement unit of the user apparatus measures a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from a base station corresponding to the identifier included in the first list for each base station, and performs the communication control.
- the selection information generation unit of the device generates the maximum number of the identifiers that can be included in the second list as the selection information, and the user device further determines that the second list is based on the state of the user device.
- a determination unit that determines a maximum number of identifiers that can be included, wherein the base station selection unit of the user apparatus includes the maximum number of identifiers indicated by the selection information and the maximum number of identifiers determined by the determination unit The base stations up to the smaller maximum number are selected as the base stations that should maintain the synchronization state in descending order of the reception levels measured by the level measurement unit.
- the level measurement unit of the user apparatus measures a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from a base station corresponding to the identifier included in the first list for each base station, and the user apparatus
- the base station information report unit reports an identifier of a base station corresponding to the highest reception level among the reception levels measured by the level measurement unit to the communication control device, and the selection information of the communication control device
- the generation unit generates, as the selection information, a candidate list of identifiers of a plurality of base stations that should be included in the second list, based on the identifier reported from the base station information report unit of the user device.
- the base station selection unit of the apparatus selects a base station corresponding to the plurality of identifiers indicated by the selection information as a base station that should maintain a synchronization state.
- the level measurement unit of the user apparatus measures a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from a base station corresponding to the identifier included in the first list for each base station, and the user apparatus
- the base station information report unit reports an identifier of a base station corresponding to the highest reception level among the reception levels measured by the level measurement unit to the communication control device, and the selection information of the communication control device
- the generation unit selects the candidate list in which candidates for identifiers of a plurality of base stations to be included in the second list are arranged in order of priority based on the identifier reported from the base station information report unit of the user apparatus.
- the user apparatus further includes a determination unit that determines a maximum number of the identifiers that can be included in the second list based on a state of the user apparatus.
- the base station selection unit of the apparatus indicates the base station up to the maximum number of the identifiers determined by the determination unit among the base stations corresponding to the plurality of identifiers indicated by the selection information. In order of priority, the base stations are selected as base stations that should maintain the synchronization state.
- the level measurement unit of the user apparatus measures a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from a base station corresponding to the identifier included in the first list at a first frequency, and The reception level of the radio wave transmitted from the base station corresponding to the identifier included in the two lists is measured at a second frequency higher than the first frequency.
- the plurality of base stations include a first base station that forms a first cell and a second base station that forms a second cell having a smaller radius than the first cell,
- the second base station is connected to the communication control apparatus, and the communication control apparatus controls wireless communication between the second base station and the user apparatus.
- the first base station performs radio communication with the user apparatus using radio waves in a first frequency band
- the second base station has a frequency higher than that of the first frequency band.
- Wireless communication with the user apparatus is performed using radio waves in two frequency bands.
- the communication control method of the present invention includes a plurality of base stations each identified by an identifier, a user apparatus capable of performing wireless communication with each of the plurality of base stations, and a plurality of the base stations and the user apparatus.
- a communication control method in a wireless communication system comprising a communication control device for controlling wireless communication, wherein the user device is obtained by measuring a reception level of a radio wave transmitted from the base station and acquiring synchronization Storing a first list including an identifier of a base station capable of wireless communication with the user apparatus and a second list including an identifier of a base station with which the user apparatus should maintain a synchronization state;
- the user device In the control device, the user device generates selection information used to select a base station that should maintain a synchronization state, and the selection information is transmitted to the user device.
- the user apparatus based on the selection information notified from the communication control apparatus, the user apparatus maintains a synchronization state from a plurality of base stations corresponding to identifiers included in the first list. Selecting a plurality of base stations to be stored, storing the identifiers of the selected plurality of base stations in the second list, the identifiers of the plurality of base stations included in the second list, and the identifiers Reporting the reception level of the radio wave transmitted from the corresponding base station to the communication control device, and maintaining the synchronization state with each of the plurality of base stations corresponding to the identifier included in the second list To prepare.
- an identifier is acquired by synchronization acquisition based on selection information notified from a communication control device, and a base station capable of wireless communication with a user device (a base station corresponding to an identifier included in the first list) ), A plurality of base stations with which the user apparatus should maintain the synchronization state are selected. Therefore, more appropriate base station selection based on the selection information is realized.
- 1 is a block diagram showing a wireless communication system according to a first embodiment of the present invention. It is a figure which shows the example of the cell which a base station forms around a self-station. It is a block diagram which shows the structure of the user apparatus of 1st Embodiment. It is a block diagram which shows the structure of the macro base station of 1st Embodiment. It is a block diagram which shows the structure of the small base station of 1st Embodiment. It is a block diagram which shows the structure of the aggregation unit of 1st Embodiment. It is a figure which shows the 1st example of the dynamic selection operation
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a radio communication system CS according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- the radio communication system CS includes a macro base station eNB, a small base station TP, a small cell aggregation unit PhNB, and a user apparatus UE as elements (hereinafter, the macro base station eNB and the small base station TP are included in the base station NB). In some cases).
- the radio communication system CS may include elements other than those described above, for example, an exchange, a serving gateway, a PDN gateway, and the like.
- the network NW may include all elements other than the user apparatus UE among the elements included in the radio communication system CS.
- Each element in the radio communication system CS performs communication according to a predetermined access technology (LTE / SAE (Long Term Evolution / System Architecture Evolution) standard in 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project) standard).
- LTE / SAE Long Term Evolution / System Architecture Evolution
- 3GPP Third Generation Partnership Project
- the user equipment UE is User Equipment
- the macro base station eNB is evolved Node B
- the switching center is a Mobile Management Entity
- the serving gateway is a Serving Gateway
- the PDN gateway is Packet Data Network Gateway.
- the small base station TP Transmission Point
- PhNB Phantom Node B
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB includes a plurality of small base stations TP and user devices UE.
- the user apparatus UE can wirelessly communicate with the macro base station eNB and the small base station TP.
- a method of radio communication between the user apparatus UE and the base station NB is arbitrary.
- OFDMA Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access
- SC-FDMA Single-Carrier Frequency Division Multiple Access
- a configuration in which a wireless communication method (for example, LTE, LTE-Advanced, etc.) used by the macro base station eNB and a wireless communication method used by the small base station TP are different can be employed.
- the macro base station eNB and the small base station TP are connected to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB and the user apparatus UE perform communication (for example, transmission / reception of control signals) via the macro base station eNB or the small base station TP.
- the macro base station eNB can be connected to an upper node (switching station, serving gateway, etc.) in a core network (for example, Evolved Packet Core defined in the 3GPP standard).
- the above connection is typically a wired connection, but may be a wireless connection.
- the S1 interface exists between the macro base station eNB and the upper node
- the X3 interface exists between the macro base station eNB and the small cell aggregation unit PhNB
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB There is an X4 interface with the small base station TP.
- the S1 interface is already defined by the 3GPP standard (for example, 3GPP TS 36.300 V10.6.0 (2011-12) 4.6.3 Interfaces).
- the X3 interface and the X4 interface are interfaces not defined in the 3GPP standard, and are based on the X2 interface already defined as an interface between the macro base stations eNB.
- the names X3 interface and X4 interface described above are provisional names, and it is understood that arbitrary names can be adopted in the future.
- the identification information may include the IP address of the node, TEID (tunnel endpoint identifier), and the like. Further, the identification information of the macro base station eNB may include a physical cell identifier PCI (Physical Cell Identity) for identifying the cell C formed by the base station.
- the identification information of the small cell aggregation unit PhNB may include physical cell identifiers PCI for identifying the plurality of cells C formed by the plurality of small base stations TP accommodated by the small cell aggregation unit PhNB.
- the identification information of the small base station TP may include a transmission point identifier TPI (Transmission Point Identity) for identifying the cell C formed by the base station.
- TPI Transmission Point Identity
- the physical cell identifier PCI may be adopted as the transmission point identifier TPI of the small base station TP.
- the IP address is an address value that uniquely identifies the node in the radio communication system CS.
- the TEID is an identifier that identifies an end point of a bearer that logically connects nodes. A node in the wireless communication system CS can identify another node based on the identification information of the other node, and can transmit / receive a signal to / from the identified node.
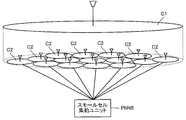
- FIG. 2 shows an example of a cell C formed by the base station NB around the own station.
- the macro base station eNB forms a macro cell C1 around it
- the small base station TP forms a small cell C2 around it.
- the antenna of each base station is schematically shown.
- the plane in which the macro cell C1 is shown and the plane in which the small cell C2 are shown are drawn separately, but in reality, the macro cell C1 and the small cell C2 are superimposed on the same plane (the ground surface or the like). Can be done.
- Cell C is a range in which radio waves from each base station NB reach the user apparatus UE effectively.
- the user apparatus UE can perform radio communication with the base station NB corresponding to the cell C in which the user apparatus UE is located.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB is connected to each small base station TP, and can perform scheduling of radio communication (allocation of radio resources) between the small base station TP and the user apparatus UE.
- the small base station TP is smaller than the macro base station eNB and has a small radio transmission capability (average transmission power, maximum transmission power, etc.).
- the frequency band (second frequency band, for example, 3.5 GHz band) used by the small base station TP for radio communication is higher than the frequency band (first frequency band, for example, 2 GHz band) used by the macro base station eNB for radio communication.
- High frequency and large propagation loss. Therefore, the small cell C2 has a smaller area than the macro cell C1.
- wireless communication using the frequency band common by macro base station eNB and small base station TP is also employable.
- FIG. 3 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the user device UE according to the first embodiment.
- the user apparatus UE includes a radio communication unit 110, a storage unit 120, and a control unit 130. Illustrations of an output device that outputs audio, video, and the like and an input device that receives an instruction from the user are omitted for convenience.
- the wireless communication unit 110 is an element for performing wireless communication with the macro base station eNB and the small base station TP, a transmission / reception antenna, a reception circuit that receives a radio signal (radio wave) and converts it into an electrical signal, and a control A transmission circuit that converts electric signals such as signals and user signals into radio signals (radio waves) and transmits the signals.
- the storage unit 120 stores information related to communication control, in particular, a first list L1 and a second list L2 each including a transmission point identifier TPI of a plurality of small base stations TP (details will be described later).
- the control unit 130 includes a synchronization acquisition unit 132, a level measurement unit 134, a determination unit 136, a base station selection unit 138, a base station information report unit 140, and a synchronization holding unit 142. Details of the operation of each element in the control unit 130 will be described later.
- the control unit 130 and each element in the control unit 130 are configured by a CPU (Central Processing Unit) (not shown) in the user apparatus UE executing a computer program stored in the storage unit 120 and functioning according to the computer program. It is a functional block that is realized.
- a CPU Central Processing Unit
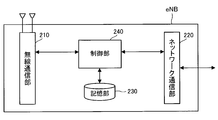
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the macro base station eNB according to the first embodiment.
- the macro base station eNB includes a radio communication unit 210, a network communication unit 220, a storage unit 230, and a control unit 240.
- the radio communication unit 210 is an element for executing radio communication with the user apparatus UE, and has the same configuration as the radio communication unit 110 of the user apparatus UE.
- the network communication unit 220 is an element for executing communication with other nodes (such as the small cell aggregation unit PhNB and the exchange) in the network NW, and transmits and receives electrical signals to and from other nodes.
- the storage unit 230 stores information related to communication control.
- the control unit 240 executes communication control by the wireless communication unit 210 and the network communication unit 220.
- the wireless communication unit 210 is controlled to transmit the physical cell identifier PCI of the own station using the control channel.
- the control unit 240 is a functional block realized by a CPU (not shown) in the macro base station eNB executing a computer program stored in the storage unit 230 and functioning according to the computer program.
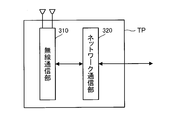
- FIG. 5 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the small base station TP according to the first embodiment.
- the small base station TP includes a wireless communication unit 310 and a network communication unit 320.
- the wireless communication unit 310 is an element for performing wireless communication with the user apparatus UE, such as a transmission / reception antenna, a reception circuit that receives a radio signal (radio wave) and converts it into an electrical signal, a control signal, a user signal, and the like.
- a transmission circuit that converts an electrical signal into a radio signal (radio wave) and transmits the signal.
- the wireless communication unit 310 can transmit its own transmission point identifier TPI as a wireless signal.
- the network communication unit 320 is an element for performing communication with the small cell aggregation unit PhNB, and transmits and receives electrical signals to and from the small cell aggregation unit PhNB. That is, the small base station TP converts the radio signal received from the user apparatus UE into an electric signal and transfers (transmits) the signal to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB, and the electric signal received from the small cell aggregation unit PhNB as a radio signal. And the function of transferring (transmitting) to the user apparatus UE. It should be understood that the network communication unit 320 may be omitted when the small base station TP and the small cell aggregation unit PhNB are connected by radio.
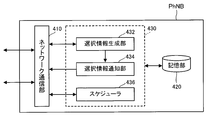
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the small cell aggregation unit PhNB according to the first embodiment.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB includes a network communication unit 410, a storage unit 420, and a control unit 430.
- the network communication unit 410 is an element for executing communication with other nodes (macro base station eNB, small base station TP, etc.) in the network NW, and has the same configuration as the network communication unit 220 of the macro base station eNB. Have.
- the storage unit 420 stores information related to communication control.
- the control unit 430 includes a selection information generation unit 432, a selection information notification unit 434, and a scheduler 436.
- control unit 430 executes unified control of a plurality of small base stations TP accommodated in the small cell aggregation unit PhNB.
- the above-described elements included in the control unit 430 and the control unit 430 are realized by a CPU (not illustrated) in the exchange MME executing a computer program stored in the storage unit 420 and functioning according to the computer program. Functional block.
- RM set Resource Management Set
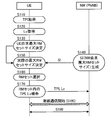
- the user apparatus UE receives radio waves transmitted from the small base station TP, executes synchronization acquisition, acquires the transmission point identifier TPI of the small base station TP, and stores it in the first list L1 in the storage unit 120. (S110). More specifically, the synchronization acquisition unit 132 of the user apparatus UE performs a correlation operation between each of the plurality of synchronization signal sequences stored in the storage unit 120 and the synchronization signal transmitted from the small base station TP, The transmission point identifier TPI indicated by the synchronization signal sequence from which the correlation peak is acquired (that is, corresponding to the synchronization signal from the small base station TP) is acquired as the transmission point identifier TPI of the small base station TP.
- the above operation is executed for a plurality of small base stations TP from which the user apparatus UE can receive radio waves.
- a known stepwise synchronization method for example, a synchronization method using the first synchronization signal and the second synchronization signal in the LTE standard
- a known stepwise synchronization method may be employed.
- the set of small base stations TP corresponding to the transmission point identifier TPI stored in the first list L1 is a set of small base stations TP capable of wireless communication with the user apparatus UE.
- SCM set Small Cell Measurement Set
- the level measuring unit 134 of the user apparatus UE uses the reception level Lv (for example, reference signal received power) of the radio wave transmitted from the small base station TP in the SCM set and received by the wireless communication unit 110 as the small base station TP.
- Lv for example, reference signal received power
- the storage unit 120 stores the transmission point identifier TPI of the small base station TP capable of wireless communication with the user apparatus UE, and the reception level Lv of the radio wave from the small base station TP. Are stored in association with each other.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB generates selection information SI used to select a small base station TP (a base station included in the RM set) in which the user apparatus UE should maintain a synchronization state, and notifies the user apparatus UE of the selection information SI. (S140). More specifically, the selection information generation unit 432 of the small cell aggregation unit PhNB determines, based on the state of the network NW, the maximum number of small base stations TP that can be included in the RM set (ie, transmissions that the second list L2 may include).
- the maximum number of point identifiers TPI (hereinafter may be referred to as “maximum RM set size”) is generated, and the selection information notification unit 434 notifies (transmits) the generated selection information SI to the user apparatus UE.
- the selection information SI described above may be determined for each user apparatus UE, may be determined for each small cell aggregation unit PhNB, or may be determined in other units (for example, for each of a plurality of user apparatuses UE). ) May be determined.
- the “network NW state” referred to when the selection information generation unit 432 generates the selection information SI in step S140 is arbitrary.
- the maximum RM set size may be reduced as the number of user apparatuses UE to be controlled by the scheduler 436 included in the small cell aggregation unit PhNB increases (that is, as the processing load on the scheduler 436 increases).
- the maximum RM set size may be increased as the moving speed of the user apparatus UE to be supported increases.
- the maximum RM set size may be reduced as the amount of traffic to be processed on the network NW side increases.
- the maximum RM set size may be determined based on a plurality of determination criteria including any of the above criteria.
- the above selection information SI is transmitted to the user apparatus UE as a control signal.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB selection information notification unit 434. transmits a control signal (selection information SI) to the user apparatus UE via the base station NB. More specifically, a control signal may be transmitted via a control plane (C-plane) path established between the macro base station eNB and the user apparatus UE, or all the subordinates thereof may be transmitted from the small base station TP.
- the control signal may be transmitted using a broadcast channel for broadcasting the broadcast signal to the user apparatus UE.
- the small base station TP having the highest radio wave reception level Lv and the user apparatus UE establish a wireless connection, and a control signal is transmitted via the small base station TP in which the wireless connection is established. May be.
- the base station selection unit 138 of the user apparatus UE selects and selects a plurality of small base stations TP (RM sets) that should maintain the synchronization state.
- the transmission point identifiers TPI of a plurality of small base stations TP are stored in the second list L2 (S160). More specifically, the base station selection unit 138 should maintain the synchronization state of the small base stations TP up to the maximum RM set size indicated by the selection information SI according to the descending order of the reception level Lv measured by the level measurement unit 134. Select as small base station TP.
- the base station selection unit 138 selects five small reception stations Lv from the small base stations TP included in the first list L1 in descending order.
- the small base stations TP (RM set) are selected and their transmission point identifiers TPI are stored in the second list L2. If the number of transmission point identifiers TPI of small base stations TP included in the first list L1 (that is, the number of small base stations TP included in the SCM set) is smaller than the maximum RM set size, it is included in the RM set.
- the number of small base stations TP may be smaller than the maximum RM set size.
- the base station information reporting unit 140 of the user apparatus UE includes the transmission point identifier TPI selected in step S160 and included in the second list L2, and the radio wave transmitted from the small base station TP corresponding to each of the above transmission point identifiers TPI.
- the reception level Lv is reported (transmitted) to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB (S170). More information than reported (TPI, Lv) is supplied to the scheduler 436.
- the number of transmission point identifiers TPI actually included in the second list L2 (hereinafter sometimes referred to as “actual RM set size”) is reported to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB (scheduler 436). , May be used for scheduling.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB counts the reported transmission point identifier TPI, which may be different from the maximum RM set size. "RM set size" can be obtained. As understood from the above, in the reporting operation in step S170, information indicating the actual RM set size is reported to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB either explicitly or implicitly.
- step S170 ends, under the control of the small cell aggregation unit PhNB (scheduler 436), connection processing between the small base station TP included in the RM set and the user apparatus UE is executed, and radio communication is started (S180). . While the wireless communication is performed, the user apparatus UE maintains a synchronization state with each of the plurality of small base stations TP included in the RM set (S190). That is, during the execution of wireless communication, the synchronization holding unit 142 of the user apparatus UE synchronizes with a plurality of small base stations TP in the RM set including the small base station TP that is not performing wireless communication with the user apparatus UE.
- the synchronization signal from each small base station TP is continuously detected so as to maintain the state, and the reception timing is updated frequently.
- the level measurement unit 134 frequently measures the reception level Lv of radio waves from the small base station TP included in the RM set, and reports the measured reception level Lv to the base station information report.
- the unit 140 reports to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB.
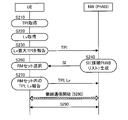
- FIG. 8 is another example (second example) of the dynamic selection operation of the small base station TP of the present embodiment. Since the operations in steps S110 and S120 are the same as those in the first example described above, description thereof will be omitted.
- the determination unit 136 of the user apparatus UE determines the maximum number (maximum RM set size) of small base stations TP that can be included in the RM set based on the state of the user apparatus UE (S130).
- the “state of the user apparatus UE” that is referred to when the determining unit 136 determines the maximum RM set size is arbitrary.
- the determination unit 136 may reduce the maximum RM set size as the remaining amount of the battery of the user apparatus UE is smaller, and suppress the synchronization holding processing load to be executed by the user apparatus UE.
- the determination unit 136 may increase the maximum RM set size as the processing performance of the user apparatus UE is higher.
- the maximum RM set size may be determined based on a plurality of determination criteria including any of the above criteria.
- step S140 the generation of the selection information SI (maximum RM set size) and the notification to the user apparatus UE by the small cell aggregation unit PhNB are the same as in the first example. Therefore, when step S140 ends, the user apparatus UE includes a maximum RM set size based on the state of the user apparatus UE determined in step S130 (hereinafter, may be referred to as “UE-derived maximum RM set size”), Both the maximum RM set size based on the state of the network NW generated in S140 (hereinafter sometimes referred to as “NW-derived maximum RM set size”).
- UE-derived maximum RM set size Both the maximum RM set size based on the state of the network NW generated in S140.
- the base station selection unit 138 of the user apparatus UE determines the smaller one of the NW-derived maximum RM set size and the UE-derived maximum RM set size as the actual maximum RM set size (S150). Then, the base station selection unit 138 selects the small base station TP up to the actual maximum RM set size as the small base station TP that should maintain the synchronization state in the descending order of the reception level Lv measured by the level measurement unit 134.
- the transmission point identifiers TPI of the plurality of selected small base stations TP are stored in the second list L2 (S160).
- the base station selection unit 138 determines a smaller “4” as the actual RM set size. Then, the base station selection unit 138 selects four small base stations TP (RM sets) in descending order of the measured reception level Lv from the small base stations TP included in the first list L1, and transmits them.
- the point identifier TPI is stored in the second list L2.
- the operations after step S170 are the same as in the first example described above.
- the user apparatus UE From the plurality of small base stations TP (SCM sets) from which the transmission point identifier TPI has been acquired by synchronization acquisition (that is, capable of wireless communication with the user apparatus UE), the user apparatus UE A plurality of small base stations TP (RM sets) to be kept in synchronization are selected.
- SCM sets small base stations
- RM sets small base stations
- the small base stations TP up to the number indicated by the smaller maximum RM set size are selected from the NW-derived maximum RM set size and the UE-derived maximum RM set size.
- the number of small base stations TP selected as the holding target becomes more appropriate.
- the size of the RM set (the transmission point identifier TPI included in the second list L2) Is appropriately set.
- a set of small base stations TP is selected in two stages, a more appropriate small base station TP is compared with a configuration in which a base station set is selected based on a single criterion (for example, only a geographical position). Is selected.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB In the dynamic selection operation of the small base station TP of the first embodiment, the small cell aggregation unit PhNB generates a maximum RM set size (NW-derived maximum RM set size) as the selection information SI and notifies the user apparatus UE of it. In the second embodiment, the small cell aggregation unit PhNB notifies the candidate of the small base station TP to be included in the RM set as the selection information SI.
- NW-derived maximum RM set size NW-derived maximum RM set size
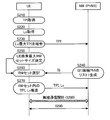
- step S220 the base station information report unit 140 of the user apparatus UE receives the highest reception level Lv of radio waves received from the small base station TP measured by the level measurement unit 134 and stored in the storage unit 120. The level Lv is specified. Then, the base station information report unit 140 reads the transmission point identifier TPI of the small base station TP corresponding to the highest reception level Lv from the storage unit 120 and reports it to the small cell aggregation unit PhNB (S230).
- the selection information generation unit 432 of the small cell aggregation unit PhNB selects a candidate for the small base station TP to be included in the RM set based on the transmission point identifier TPI of the small base station TP reported from the user apparatus UE, and A list (candidate list) of transmission point identifiers TPI of the small base station TP (ie, candidates for transmission point identifiers TPI of the small base station TP to be included in the second list L2) as selection information SI, and the generated selection
- the selection information notification unit 434 notifies (transmits) the information SI to the user apparatus UE (S240). Note that the size of the candidate list included in the selection information SI is the same as the NW-derived maximum RM set size generated in the first embodiment (step S140).
- the selection information generation unit 432 can select a candidate small base station TP on an arbitrary basis. For example, the selection information generation unit 432 may select, as candidates, a small base station TP that has a geographical location close to the small base station TP corresponding to the transmission point identifier TPI reported from the user apparatus UE. The selection information generation unit 432 uses, as candidates, the small base station TP that is synchronized with the small base station TP corresponding to the transmission point identifier TPI reported from the user apparatus UE (or whose synchronization timing shift is less than a predetermined value). You may choose. In addition, a small base station TP with a smaller traffic load may be selected as a candidate.
- a plurality of small base stations TP grouped according to specific conditions may be selected as candidates. For example, a plurality of small base stations TP temporarily installed in an event venue such as a concert may be selected as candidates, or a plurality of small base stations TP installed in a moving vehicle such as a train are selected as candidates. Also good. Further, the candidate small base station TP may be selected based on a plurality of determination criteria including any of the above criteria.
- the base station selection unit 138 of the user apparatus UE selects the small base station TP corresponding to the plurality of transmission point identifiers TPI indicated by the selection information SI (candidate list) as the small base station TP that should maintain the synchronization state (S260). ). That is, the base station selection unit 138 selects a candidate for the small base station TP that should be included in the RM set indicated by the candidate list notified from the small cell aggregation unit PhNB as the small base station TP that should maintain the synchronization state. And the base station selection part 138 memorize
- the operations after Step S270 are the same as the operations after Step S170 in the first embodiment described above, and thus description thereof is omitted.
- FIG. 10 is another example (second example) of the dynamic selection operation of the small base station TP of the present embodiment. Since the operations in steps S210 to S230 are the same as those in the first example described above, description thereof will be omitted.
- the selection information generation unit 432 of the small cell aggregation unit PhNB A candidate for the small base station TP to be included is selected.
- the selection information generation unit 432 selects candidate candidates from the small base stations TP that are candidates based on a predetermined criterion, as in the first example of the present embodiment, and then selects a plurality of selected small base stations TP. Arrange candidates in priority order (sort). That is, the selection information generation unit 432 generates a candidate list in which candidates for transmission point identifiers TPI of a plurality of small base stations TP that should be included in the second list L2 are arranged in order of priority based on the reported transmission point identifiers TPI. It generates as selection information SI (S240). The selection information notification unit 434 notifies the generated selection information SI to the user apparatus UE.
- Priority order of each small base station TP can be determined according to any standard. For example, when the candidate small base station TP is selected based on the proximity of the geographical position with the small base station TP having the maximum reception level Lv, a higher priority is assigned to the closer small base station TP. Also good. When the candidate small base station TP is selected based on the synchronization timing, a higher priority may be assigned to the small base station TP that is closer to the synchronization timing of the small base station TP having the maximum reception level Lv. When the candidate small base station TP is selected based on the traffic load, a higher priority may be assigned to the small base station TP having a smaller traffic load. A priority may be assigned to the small base station TP based on any other criterion, and a priority may be assigned based on a plurality of determination criteria including any of the above criteria.
- the determination unit 136 of the user apparatus UE determines the UE-derived maximum RM set size (S250).
- the base station selection unit 138 selects small base stations TP up to the UE-derived maximum RM set size among the small base stations TP corresponding to the plurality of transmission point identifiers TPI indicated by the selection information SI (candidate list).
- the small base stations TP that should hold the synchronization state are selected in the order of priority indicated by the selection information SI (candidate list).
- the base station selection unit 138 stores the transmission point identifiers TPI of the selected plurality of small base stations TP in the second list L2. Since the operation after step S270 is the same as the operation after step S170 of the first embodiment described above, description thereof will be omitted.
- the small cell aggregation unit PhNB that is, the node on the network NW side selects the candidates for the small base stations TP that should be included in the RM set, so only the number (maximum RM set size) is selected. Is compared with the configuration in which the network NW side determines the small base station TP selected as the RM set is more suitable for the state on the network NW side.
- the wireless communication system CS (network NW) of the above embodiment is a heterogeneous network including a macro base station eNB and a small base station TP, but a homogeneous network including only a single type of base station NB is employed. May be.
- the two selection operations exemplified in the first embodiment and the two selection operations exemplified in the second embodiment may be any combination of two or more selection operations.
- the determination unit 136 of the user apparatus UE is not an essential component. Therefore, when only the configuration of the first example of the first embodiment and only the configuration of the first example of the second embodiment are to be realized, the determination unit 136 of the user apparatus UE can be omitted.
- the level measurement unit 134 of the user apparatus UE transmits radio waves transmitted from the small base station TP corresponding to the transmission point identifier TPI included in the first list L1 (that is, the small base station TP of the SCM set). While measuring the reception level Lv with the first frequency F1, the reception level of the radio wave transmitted from the small base station TP corresponding to the transmission point identifier TPI included in the second list L2 (that is, the small base station TP of the RM set) It is preferable to measure Lv at a second frequency F2 that exceeds the first frequency F1. According to the above configuration, the radio wave reception level Lv from the small base station TP included in the RM set is measured more frequently. Therefore, more appropriate scheduling of wireless communication via the small base station TP included in the RM set can be realized.
- the user apparatus UE is an arbitrary apparatus that can perform radio communication with the macro base station eNB and the small base station TP.
- the user apparatus UE may be, for example, a mobile phone terminal such as a feature phone or a smartphone, a desktop personal computer, a notebook personal computer, a UMPC (Ultra-Mobile Personal Computer), or a portable game machine. Other wireless terminals may be used.
- Each function executed by the CPU in each element (user apparatus UE, macro base station eNB, small base station TP, small cell aggregation unit PhNB) in the radio communication system CS may be executed by hardware instead of the CPU. Alternatively, it may be executed by a programmable logic device such as an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) or a DSP (Digital Signal Processor).
- a programmable logic device such as an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) or a DSP (Digital Signal Processor).
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/403,788 US9699745B2 (en) | 2012-07-20 | 2013-05-15 | Radio communication system and communication control method |
| EP13819287.7A EP2876940B1 (en) | 2012-07-20 | 2013-05-15 | Radio communication system and communication control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012161243A JP5715599B2 (ja) | 2012-07-20 | 2012-07-20 | 無線通信システムおよび通信制御方法 |
| JP2012-161243 | 2012-07-20 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014013781A1 true WO2014013781A1 (ja) | 2014-01-23 |
Family
ID=49948617
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/063547 Ceased WO2014013781A1 (ja) | 2012-07-20 | 2013-05-15 | 無線通信システムおよび通信制御方法 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9699745B2 (enExample) |
| EP (1) | EP2876940B1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP5715599B2 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014013781A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019027791A (ja) * | 2017-07-25 | 2019-02-21 | Kddi株式会社 | 携帯電話端末の位置範囲を検出する方法、移動基地局及びプログラム |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5758352B2 (ja) * | 2012-06-22 | 2015-08-05 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | 無線通信システムおよび基地局 |
| US9722725B2 (en) * | 2014-07-29 | 2017-08-01 | Nec Corporation | System and method for resource management in heterogeneous wireless networks |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008103858A2 (en) * | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Wireless node search procedure |
| JP2009303221A (ja) | 2008-06-13 | 2009-12-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | 無線通信システム及び方法 |
| JP2010028665A (ja) * | 2008-07-23 | 2010-02-04 | Toshiba Corp | 移動通信システムの無線通信装置 |
| JP2010537478A (ja) * | 2007-08-16 | 2010-12-02 | テレフオンアクチーボラゲット エル エム エリクソン(パブル) | ユーザ端末用の隣接セルリスト管理 |
| JP2012070074A (ja) * | 2010-09-21 | 2012-04-05 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | 隣接セル処理装置および隣接セル処理方法 |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6044272A (en) * | 1997-02-25 | 2000-03-28 | Sbc Technology Resources, Inc. | Mobile assisted handoff system and method |
| FI20021042A0 (fi) | 2002-05-31 | 2002-05-31 | Sonera Oyj | Menetelmä ja ohjain tilaajapäätelaitteen aktiivisetin päivittämiseen solukkoradiojärjestelmässä |
| JP2004289226A (ja) * | 2003-03-19 | 2004-10-14 | Nec Corp | 携帯情報端末及びハンドオーバー解決方法 |
| US7853215B2 (en) | 2003-10-10 | 2010-12-14 | Motorola, Inc. | Communication circuit and method for selecting a reference link |
| US20080207245A1 (en) | 2005-08-04 | 2008-08-28 | Mitsubish Electric Corporation | Mobile Communications System, Base Station Control Apparatus, and Mobile Terminal |
| KR100725056B1 (ko) * | 2005-11-09 | 2007-06-08 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이동통신 단말기의 인접 셀 관리 방법 |
| KR100796850B1 (ko) * | 2005-12-30 | 2008-01-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Gsm 통신 장치의 총 배터리 수명을 개선하는 시스템 |
| US9247515B2 (en) * | 2006-04-25 | 2016-01-26 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Enhanced mobility support for wireless communication |
| US9648523B2 (en) * | 2007-11-21 | 2017-05-09 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Target access point initiated communication handover |
| KR20090074454A (ko) * | 2008-01-02 | 2009-07-07 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이동통신 단말에서 인접 셀 관리 방법 및 장치 |
| KR20100088855A (ko) * | 2009-02-02 | 2010-08-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 매크로 및 펨토 셀들을 가지는 무선 통신 네트워크의 측정 보고 방법 및 이를 위한 시스템 |
| US8588787B2 (en) | 2010-05-28 | 2013-11-19 | Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. | Neighboring cell processing device, wireless base station device, neighboring cell processing method and data structure |
| US8526906B1 (en) * | 2010-06-04 | 2013-09-03 | Sprint Spectrum L.P. | Active set management based on mobile station battery power |
| US9426685B2 (en) * | 2010-07-16 | 2016-08-23 | Broadcom Corporation | Method and system for mitigation of unlisted cell impacts in idle mode of cellular systems |
| WO2014113075A1 (en) * | 2013-01-17 | 2014-07-24 | Intel IP Corporation | Fast small cell discovery |
-
2012
- 2012-07-20 JP JP2012161243A patent/JP5715599B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-05-15 US US14/403,788 patent/US9699745B2/en active Active
- 2013-05-15 EP EP13819287.7A patent/EP2876940B1/en active Active
- 2013-05-15 WO PCT/JP2013/063547 patent/WO2014013781A1/ja not_active Ceased
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008103858A2 (en) * | 2007-02-21 | 2008-08-28 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Wireless node search procedure |
| JP2010537478A (ja) * | 2007-08-16 | 2010-12-02 | テレフオンアクチーボラゲット エル エム エリクソン(パブル) | ユーザ端末用の隣接セルリスト管理 |
| JP2009303221A (ja) | 2008-06-13 | 2009-12-24 | Fujitsu Ltd | 無線通信システム及び方法 |
| JP2010028665A (ja) * | 2008-07-23 | 2010-02-04 | Toshiba Corp | 移動通信システムの無線通信装置 |
| JP2012070074A (ja) * | 2010-09-21 | 2012-04-05 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | 隣接セル処理装置および隣接セル処理方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 3GPP TS 36.300, vol. 10.6.0, December 2011 (2011-12-01) |
| See also references of EP2876940A4 * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019027791A (ja) * | 2017-07-25 | 2019-02-21 | Kddi株式会社 | 携帯電話端末の位置範囲を検出する方法、移動基地局及びプログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2876940A1 (en) | 2015-05-27 |
| JP5715599B2 (ja) | 2015-05-07 |
| US20150156737A1 (en) | 2015-06-04 |
| EP2876940B1 (en) | 2016-12-28 |
| JP2014023011A (ja) | 2014-02-03 |
| US9699745B2 (en) | 2017-07-04 |
| EP2876940A4 (en) | 2016-04-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11388658B2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and a program for information processing for performing measurement of first and second frequency bands based on first and second discovery reference signals within first and second periods respectively | |
| CN106376082B (zh) | 用于无线通信的电子设备以及无线通信方法 | |
| US9973980B2 (en) | Communications methods and apparatus that facilitate handover decisions and related measurements | |
| CN106664171B (zh) | 用于管理小区参考符号的传输的网络节点和方法 | |
| HK1244156A1 (zh) | 特定於小区的概率负载均衡的设备、系统和方法 | |
| WO2018029041A1 (en) | Network controlled sharing of measurement gaps for intra and inter frequency measurements for wireless networks | |
| US11528632B2 (en) | Device for measuring channel quality on primary cell and secondary cell | |
| JP6516914B2 (ja) | モビリティ参照信号割り当て | |
| US11601894B2 (en) | Network node and method for managing power of cell reference symbols | |
| JP6295964B2 (ja) | 無線通信方法、無線通信システム、および無線基地局 | |
| JP5715599B2 (ja) | 無線通信システムおよび通信制御方法 | |
| US20160295444A1 (en) | Network node, wireless device and methods for handling evaluation of a secondary cell for a wireless device | |
| JP7570361B2 (ja) | 端末装置及び無線通信方法 | |
| TW201906449A (zh) | 利用接收器分集提高短距離無線網路通道掃描的效能 | |
| TW201715904A (zh) | 對頻率間量測的管理 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13819287 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14403788 Country of ref document: US |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2013819287 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013819287 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |