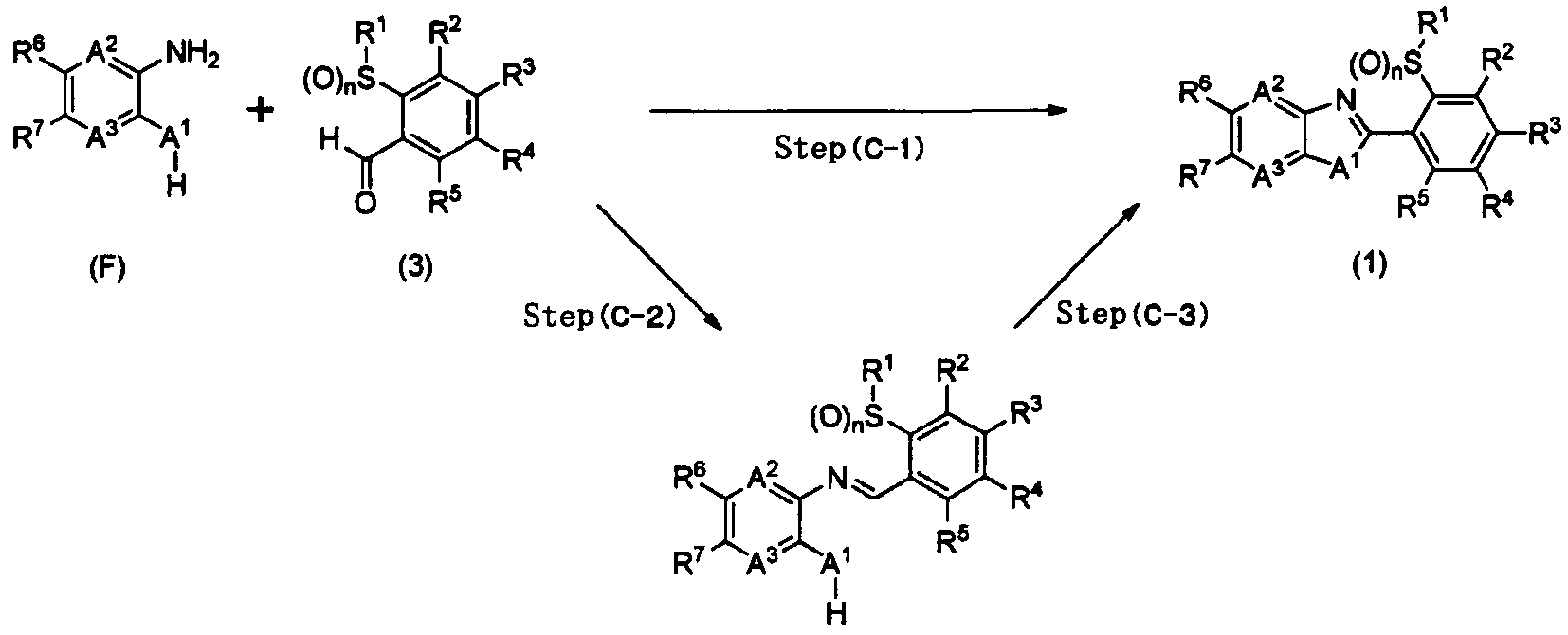
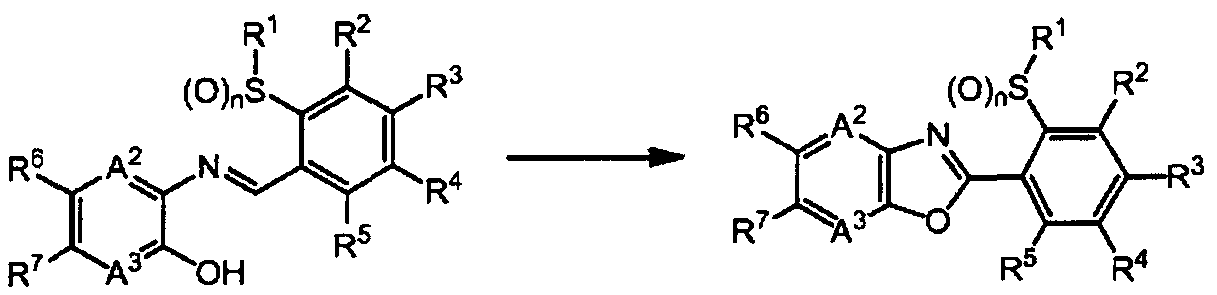
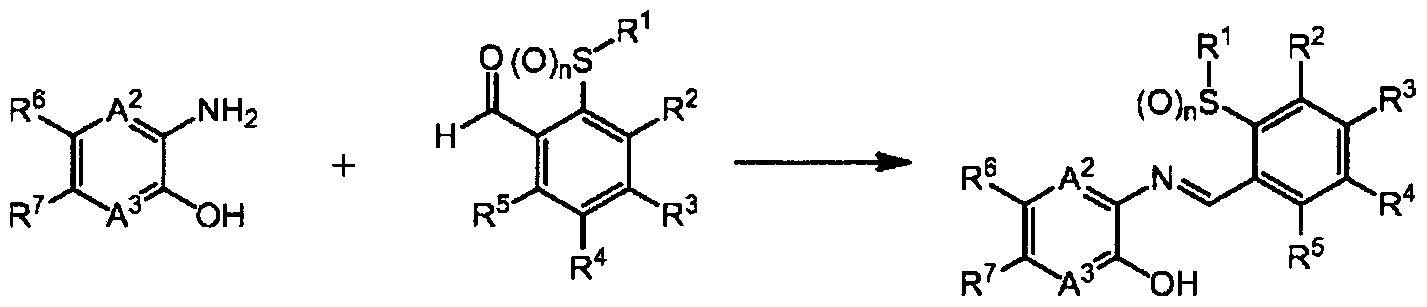
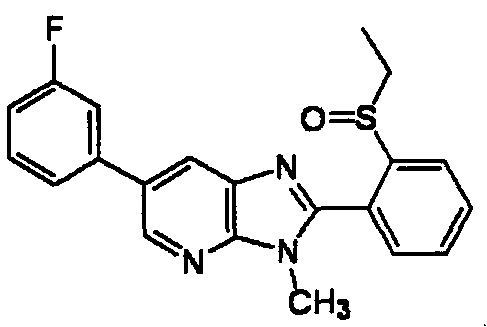
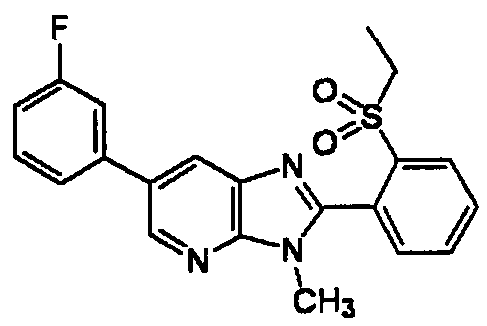
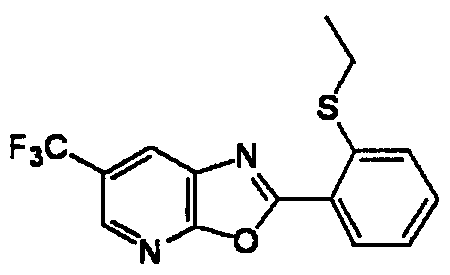
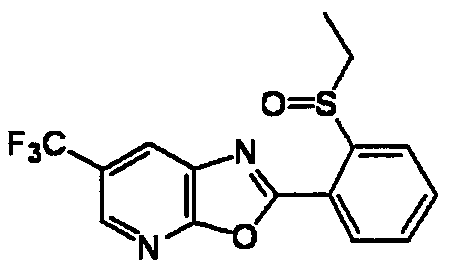
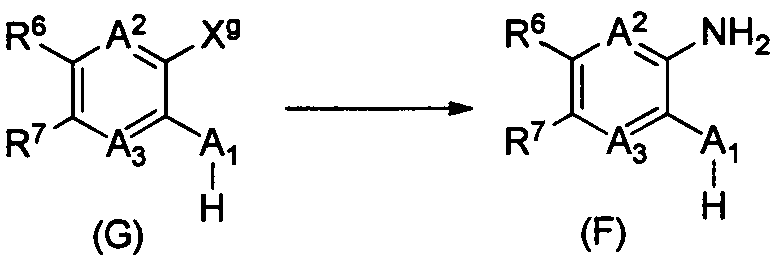DESCRIPTION
FUSED HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUND AND USE FOR PEST CONTROL
THEREOF
Technical Field
[0001]
The present invention relates to a certain fused heterocyclic compound and use for pest control thereof. Background Art
[0002]
For controlling pests, various compounds have heretofore been developed and used practically.
Certain fused heterocyclic compounds are known (see, Patent Literature 1) .
Citation List
[0003]
Patent Literature
Patent Literature 1: JP-A-01-501473
Summary of Invention
Technical Problem
[0004]
An object of the present invention is to provide a
compound having an excellent activity of controlling pests and a method of controlling pests using the compound.
Solution to Problem
[0005]
The present inventors have studied so as to resolve the above problem and found that a fused heterocyclic compound of the following formula (1) has an excellent activity of controlling pests, thus leading to the present invention .
[0006]
That is, the present invention provides:
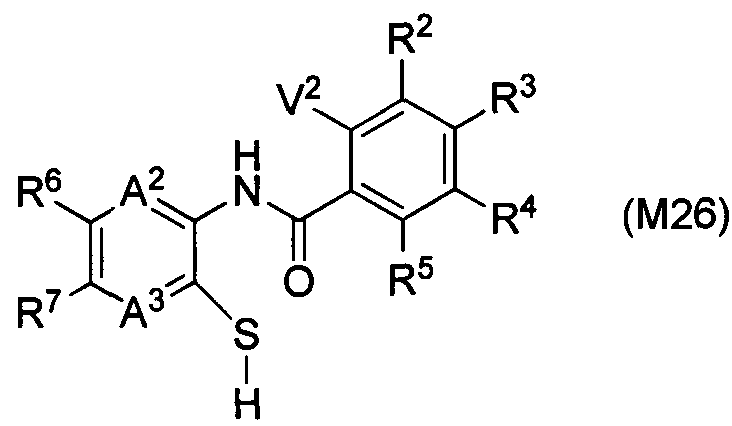
1] A fused heterocyclic compound of the formula (1):
A1 represents -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom; A2 represents a nitrogen atom or =CR9-;
A represents a nitrogen atom or =CR -;
R1 represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X, or a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Y;
R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 6- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, -OR11, -S (0) mR1:L, - NR11R12, -C02Ru, -C(0)Ru, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, -SF5, or a hydrogen atom, provided that at least two of R2, R3, R4, and R5 represent a hydrogen atom;
R6 and R7 are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X, a phenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, -OR11, - S(0)mRn, -S (0) 2NR11R12, -NR11R12, -NR^COsR12, · -NR C (0) R12,
CO2R11, -C(0)Rn, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, -SF5, or a hydrogen atom;
R8 represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group W, -CO2R11, -C(0)Rn, a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon
group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Y, or a hydrogen atom;
R9 and R10 are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRi:L, -NRnR12, -CO2R11, -C(0)R1:L, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R11 and R12 are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom; and
m represents 0, 1, or 2; and n represents 0, 1, or 2; (except in cases as follows: both R6 and R7 are a hydrogen atom; in -S(0)mRi:L, when m is 1 or 2, R11 is a hydrogen atom; and when A1 represents -NH- or -N(CH3)-, A2 and A3 represent =CH-, R1 represents a methyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 represent a hydrogen atom, and n is 0, 1, or 2, R6 and R7 are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X, a phenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 6- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, -OR11, -S(0)mRi:L, - S (0) 2NRnR12, -NR11R12, -NRn-C02R1 , -NRnC (0) R12, -C02H,
C(0)Rn, a cyano group, a nitro group, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, -SF5 or a hydrogen atom)
the Group X consists of a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkenyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkynyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkylcarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a cyano group, a hydroxy group, and a halogen atom;
the Group Y consists of a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkenyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkynyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a hydroxy group, and a halogen atom;
the Group Z consists of a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a
C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkylcarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylamino group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C8 dialkylamino group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, a cyano group, and a nitro group; and
the Group consists of a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkenyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkynyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkylcarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C3-C6 cycloalkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, a cyano group, and a hydroxy group (hereinafter referred to as the present compound) ;
[2] The fused heterocyclic compound according to the above
[1] wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mR1:L, -NR11R12, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
[3] The fused heterocyclic compound according to the above [1] or [2] wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S (0) mRi:L, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
[4] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[3] wherein A2 is =CH-;
[5] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[4] wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
[6] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[4] wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom;
[7] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [ 1 ]— [ 6 ] wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
[8] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[7] wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C6
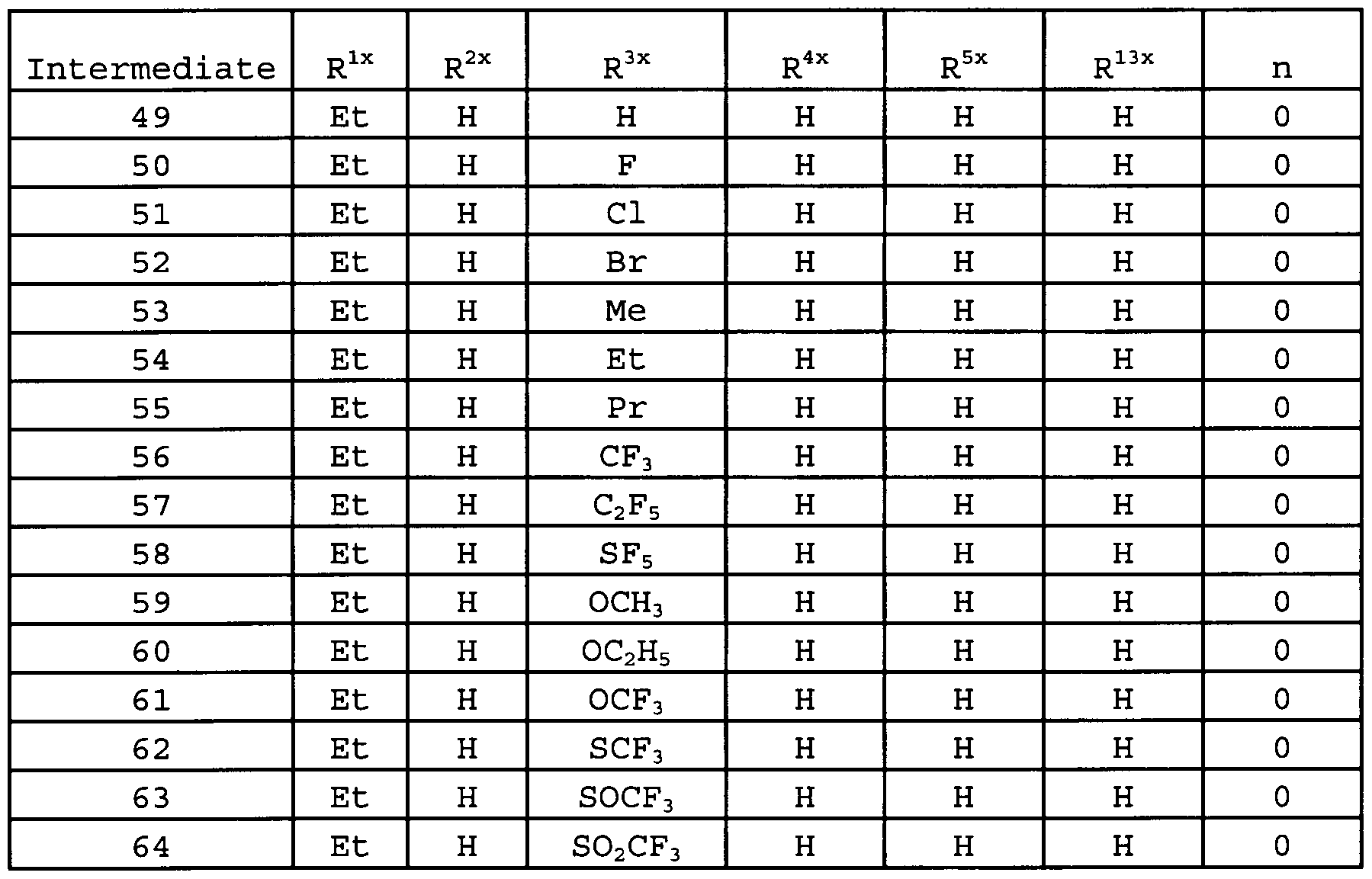
chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
[9] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[7] wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group;
[10] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[7] wherein A1 is an oxygen atom;
[11] The fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [l]-[7] wherein A1 is a sulfur atom;
[12] The fused heterocyclic compound according to the above
[1] which is represented by the formula (1-1) :
wherein :
Ala represents -NR8a- or a sulfur atom;
A3a represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10a-;
Rla represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
R2a, R4a, and R5a are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group
optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R3a represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlla, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R6a represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -0Rlla, S(0)mRlla, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
R8a represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
R10a represents a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
Rlla represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms; and
m represents 0, 1, or 2, and n represents 0, 1, or 2;
[13] The fused heterocyclic compound according to the above [12] wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a methyl group, A3a is a nitrogen atom, Rla is an ethyl group, R2a, R4a, and R5a are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R3a is a trifluoromethyl group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R6a is a Cl- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms,
or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
[14] A pest controlling composition which comprises the fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [1]-[13] and an inert carrier; and
[15] A method of controlling pests which comprises applying an effective amount of the fused heterocyclic compound according to any one of the above [1]-[13] to pests or habitats of pests.
Effect of Invention
[0007]
The present compound has an excellent activity of controlling pests and is useful as an active ingredient of a pest controlling agent.
Description of Embodiments
[0008]
Various substituents used in the present specification will be illustrated by way of examples.
In the present invention, the "halogen atom" includes a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, and an iodine atom.
[0009]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 chain
hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X" include a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X such as a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, an isobutyl group, a sec-butyl group, a tert-butyl group, a pentyl group, a neopentyl group, a hexyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, a propyloxymethyl group, an isopropyloxymethyl group, a butyloxymethyl group, a sec- butyloxymethyl group, a tert-butyloxymethyl group, a 2- methoxyethyl group, a 2-ethoxyethyl group, a 2- propyloxyethyl group, a 2-isopropyloxyethyl group, a 2- butyloxyethyl group, a 2-sec-butyloxyethyl group, a 2-tert- butyloxyethyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trichloromethyl group, a 2-fluoroethyl group, a 2,2- difluoroethyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a methylsulfanylethyl group, an ethylsulfanylethyl group, a methylsulfinylethyl group, and a methylsulfonylethyl group, a methoxycarbonylethyl group, a cyanomethyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl group, and a cyclobutylmethyl group;
a C2-C6 alkenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X such as a vinyl group, a 1- propenyl group, a 2-propenyl group, a 1-methylvinyl group, a 2-methyl-l-propenyl group, a 1-butenyl group, a 2-butenyl
group, a 3-butenyl group, a 1-pentenyl group, a 1-hexenyl group, a 1 , 1-difluoroallyl group, and a pentafluoroallyl group; and
a C2-C6 alkynyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X such as an ethinyl group, a propargyl group, a 2-butynyl group, a 3-butynyl group, a 1- pentynyl group, a 1-hexynyl group, and a 4 , 4 , 4-trifluoro-2- butynyl group.
[0010]
In the present compound, examples of the "C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Y" include a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a cyclopentyl group, a cyclohexyl group, a 1-cyclohexenyl group, a 2- cyclohexenyl group, a 3-cyclohexenyl group, a 1- methylcyclohexyl group, a 2-methylcyclohexyl group, a 3- methylcyclohexyl group, a 4-methylcyclohexyl group, a 2- methoxycyclohexyl group, a 3-methoxycyclohexyl group, a 4- methoxycyclohexyl group, a 1-fluorocyclohexyl group, a 2- fluorocyclohexyl group, a 3-fluorocyclohexyl group, and a 4-fluorocyclohexyl group.
[0011]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or
more halogen atoms such as a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, an isobutyl group, a sec-butyl group, a tert-butyl group, a pentyl group, a neopentyl group, a hexyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trichloromethyl group, a 2- fluoroethyl group, a 2 , 2-difluoroethyl group, a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, and a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
a C2-C6 alkenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms such as a vinyl group, a 1-propenyl group, a 2- propenyl group, a 1-methylvinyl group, a 2-methyl-l- propenyl group, a 1-butenyl group, a 2-butenyl group, a 3- butenyl group, a 1-pentenyl group, a 1-hexenyl group, a 1, 1-difluoroallyl group, and a pentafluoroallyl group; and a C2-C6 alkynyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms such as an ethinyl group, a propargyl group, a 2- butynyl group, a 3-butynyl group, a 1-pentynyl group, a 1- hexynyl group, and a 4 , 4 , 4-trifluoro-2-butynyl group.
[0012]
In the present compound, examples of the "phenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z" include a phenyl group, a 2-fluorophenyl group, a 3-fluorophenyl group, a 4-fluorophenyl group, a 2,3- difluorophenyl group, a 2 , 4-difluorophenyl group, a 2,5- difluorophenyl group, a 2 , 6-difluorophenyl group, a 3,4-
difluorophenyl group, a 3 , 5-difluorophenyl group, a 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6-pentafluorophenyl group, a 2-chlorophenyl group, a 3-chlorophenyl group, a 4-chlorophenyl group, a 2- bromophenyl group, a 3-bromophenyl group, a 4-bromophenyl group, a 2-iodophenyl group, a 3-iodophenyl group, a 4- iodophenyl group, a 2-trifluoromethylphenyl group, a 3- trifluoromethylphenyl group, a 4-trifluoromethylphenyl group, a 2-trifluoromethoxyphenyl group, a 3- trifluoromethoxyphenyl group, a 4-trifluoromethoxyphenyl group, a 2-trifluoromethylsulfanylphenyl group, a 3- trifluoromethylsulfanylphenyl group, a 4- trifluoromethylsulfanylphenyl group, a 4- methoxycarbonylphenyl group, a 4-nitrophenyl group, a 4- cyanophenyl group, a 4-methylaminophenyl group, a 4- dimethylaminophenyl group, a 4-methylsulfinylphenyl group, a 4-methylsulfonylphenyl group, a 4-acetylphenyl group, and 4-methoxycarbonylphenyl group.
[0013]
In the present compound, the "heterocyclic group" in the "5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z" represents a heterocyclic residue. Examples of "5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z" include a 5-membered saturated heterocyclic group optionally having one or more
atoms or groups selected from Group Z such as a pyrrolidin- 1-yl group and a tetrahydrof ran-2-yl group; and
a 5-membered unsaturated heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z such as a 2-pyrrolyl group, a 2-furyl group, a 3-furyl group, a 5-pyrazolyl group, a 4-pyrazolyl group, a 1- pyrrolyl group, a l-methyl-2-pyrrolyl group, a 5-bromo-2- furyl group, a 5-nitro-2-furyl group, a 2-methyl-3-furyl group, a 2 , 5-dimethyl-3-furyl group, a 2 , -dimethyl-3-furyl group, a 5-methyl-2-thienyl group, a 3-methyl-2-thienyl group, a l-methyl-3-trifluoromethyl-5-pyrazolyl group, a 5- chloro-1, 3-dimethyl-4-pyrazolyl group, a pyrazol-l-yl group, a 3-chloro-pyrazol-l-yl group, a 3-bromopyrazol-l-yl group, a 4-chloropyrazol-l-yl group, a 4-bromopyrazol-l-yl group, a imidazol-l-yl group, a pyrrol-l-yl group, a 1,2,4- triazol-l-yl group, a 3-chloro-l , 2 , 4-triazol-l-yl group, a 1, 2 , 3, 4-tetrazol-l-yl group, a 1 , 2 , 3 , 5-tetrazol-l-yl group, a 2-thienyl group, a 3-thienyl group, a 3-trifluoromethyl- 1 , 2 , 4-triazol-l-yl group, and a 4-trifluoromethylpyrazol-1- yl group.
[0014]
In the present compound, the "heterocyclic group" in the "6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z" represents a heterocyclic residue. Examples of the "6-membered
heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z" include a 6-membered saturated heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z such as a piperidyl group, a morpholinyl group, and a thiomorpholinyl group; and
a 6-membered aromatic heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z such as a pyrazinyl group, a 2-pyrimidyl group, a 4-pyrimidyl group, a 5-pyrimidyl group, a 2-pyridyl group, a 3-pyridyl group, a 4-pyridyl group, a 3-fluoro-2-pyridyl group, a 4-fluoro- 2-pyridyl group, a 5-fluoro-2-pyridyl group, a 6-fluoro-2- pyridyl group, a 2-pyrimidyl group, and a 5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl group .
[0015]
In the present compound, the "C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group W" include a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group W such as a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, an isobutyl group, a sec-butyl group, a tert-butyl group, a pentyl group, a neopentyl group, a hexyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trichloromethyl group, a 2-fluoroethyl group, a 2,2- difluoroethyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, a
pentafluoroethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, a propyloxymethyl group, an isopropyloxymethyl group, a butyloxymethyl group, a sec- butyloxymethyl group, an isobutyloxymethyl group, a tert- butyloxymethyl group, a methoxyethyl group, an ethoxyethyl group, a propyloxyethyl group, an isopropyloxyethyl group, a butyloxyethyl group, a sec-butyloxyethyl group, an isobutyloxyethyl group, a tert-butyloxyethyl group, a methylsulfanylethyl group, an ethylsulfanylethyl group, a methylsulfinylethyl group, a methylsulfonylethyl group, a methoxycarbonylmethyl group, a methoxycarbonylethyl group, a cyclopropylmethyl group, and a cyclohexylmethyl group; a C2-C6 alkenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group W such as a vinyl group, a 1- propenyl group, a 2-propenyl group, a 1-methylvinyl group, a 2-methyl-l-propenyl group, a 1-butenyl group, a 2-butenyl group, a 3-butenyl group, a 1-pentenyl group, a 1-hexenyl group, a 1 , 1-difluoroallyl group, and a pentafluoroallyl group; and
a C2-C6 alkynyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group such as an ethinyl group, a propargyl group, a 2-butynyl group, a 3-butynyl group, a 1- pentynyl group, a 1-hexynyl group, and a 4 , 4 , 4-trifluoro-2- butynyl group.
[0016]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methylsulfanyl group, an ethylsulfanyl group, a propylsulfanyl group, an isopropylsulfanyl group, a butylsulfanyl group, a pentylsulfanyl group, a hexylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethylsulfanyl group, and a pentafluoroethylsulfanyl group.
[0017]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methylsulfinyl group, an ethylsulfinyl group, a propylsulfinyl group, an isopropylsulfinyl group, a butylsulfinyl group, a pentylsulfinyl group, a hexylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethylsulfinyl group, and a pentafluoroethylsulfinyl group.
[0018]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methylsulfonyl group, an ethylsulfonyl group, a propylsulfonyl group, an isopropylsulfonyl group, a butylsulfonyl group, a pentylsulfonyl group, a hexylsulfonyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethylsulfonyl group, and a
pentafluoroethylsulfonyl group.
[0019]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methoxy group, a trifluoromethoxy group, an ethoxy group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethoxy group, a propyloxy group, an isopropyloxy group, a butyloxy group, an isobutyloxy group, a sec-butyloxy group, a tert-butyloxy group, a pentyloxy group, and a hexyloxy group.
[0020]
In the present compound, examples of the "C2-C6 alkenyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a 2-propenyloxy group, a 2-methyl-2- propenyloxy group, a 2-butenyloxy group, a 3-butenyloxy group, a 2-pentenyloxy group, a 2-hexenyloxy group, a 3,3- difluoroallyloxy group, and a 3 , 3-dichloroallyloxy group.
[0021]
In the present compound, examples of the "C2-C6 alkynyloxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a propargyloxy group, a 2-butynyloxy group, a 3-butynyloxy group, a 2-pentynyloxy group, a 2-hexynyloxy group, and a , 4 , 4-trifluoro-2-butynyloxy group.
[0022]
In the present compound, examples of the "C2-C6 alkylcarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen
atoms" include an acetyl group, a propionyl group, a propylcarbonyl group, a butylcarbonyl group, a pentylcarbonyl group, and a trifluoroacetyl group.
[0023]
In the present compound, examples of the "C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methoxycarbonyl group, an ethoxycarbonyl group, a propyloxycarbonyl group, a butyloxycarbonyl group, a pentyloxycarbonyl group, a tert-butyloxycarbonyl group, and a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethylcarbonyl group.
[0024]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C6 alkylamino group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methylamino group, an ethylamino group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethylamino group, a propylamino group, an isopropylamino group, and a butylamino group.
[0025]
In the present compound, examples of the "C2-C8 dialkylamino group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a dimethylamino group, a diethylamino group, a bis (2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl ) amino group, and a dipropylamino group .
[0026]
In the present compound, examples of the "C3-C6 cycloalkyl group optionally having one or more halogen
atoms" include a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a cyclopentyl group, and a cyclohexyl group.
[0027]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms" include a fluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trichloromethyl group, a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, and a heptafluoroisopropyl group.
[0028]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more a fluorine atoms" include a trifluoromethoxy group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethoxy group, and a pentafluoroethoxy group.
[0029]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms" include a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a 2,2,2- trifluoroethylsulfanyl group, a pentafluoroethylsulfanyl group, a heptafluoropropylsulfanyl group, and a heptafluoroisopropylsulfanyl group .
[0030]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms" include a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a 2,2,2-
trifluoroethylsulfinyl group, a pentafluoroethylsulfinyl group, a heptafluoropropylsulfinyl group, and a heptafluoroisopropylsulfinyl group .
[0031]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms" include a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a 2,2,2- trifluoroethylsulfonyl group, a pentafluoroethylsulfonyl group, a heptafluoropropylsulfonyl group, and a heptafluoroisopropylsulfonyl group.
[0032]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkyl group" include a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, and an isopropyl group.
[0033]
In the present compound, examples of the "C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms" include a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trichloroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, and a heptafluoroisopropyl group.
[0034]
Examples of the present compound include the following pyrimidine compounds.
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group, -CO2R11, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or
an oxygen atom, and R is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group, -CO2R11, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and
R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and
R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A is a sulfur atom;
[0035]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, and R9 is a C1-C3 chain hydrocarbon group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, and R9 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, and R9 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, and R9 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRn, -NR11R12, -C02Rn, - C(0)R1:L, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, and R9 is a C1-C3 chain hydrocarbon group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, and R9 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, and R9 is a hydrogen atom;
[0036]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a C1-C3 chain hydrocarbon group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is =CR10-, and R10 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRn, -NR11R12, -CO2R11, -C(0)R1:L, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is =CR10-, and R10 is a C1-C3 chain hydrocarbon group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A3 is =CR10-, and R10 is a hydrogen atom;
[0037]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group, -CO2R11, or a cyclopropyl group, A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, R9 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a cyclopropyl group, A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, R9 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, R8 is a methyl group, A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, R9 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, R8 is a methyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
[0038]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Y;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group,
a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, and a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, and a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, and R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, or a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group;
[0039]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and
R5 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -NR11R12, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and
R5 are same or different and are independently a methyl group, an ethyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a methoxy
group, an ethoxy group, a trifluoromethoxy group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently an amino group, a methylamino group, a dimethylamino group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a cyano group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a nitro group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, a methyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a methoxy group, a cyano group, a nitro group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5
are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkylcarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylamxno group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, C2-C8 dialkylamino group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, an aldehyde group, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a
hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
[0040]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRn, -NR11R12, -C02Rn, -C(0)Rn, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R11 and R12 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mR1:L, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom,
and R11 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, an aldehyde group, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, an aldehyde group, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mR11, or a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more halogen atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more a fluorine atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is -OR11, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is -S(0)mRn, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more halogen atoms, - OR11, -S(0)mRn, or a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a hydrogen
atom, and R7 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a bromine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a heptafluoroisopropyl group, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
[0041]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein n is 0;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein n is 1;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein n is 2;
[0042]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein m is 0;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein m is 1;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein m is 2;
[0043]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom,
A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, and R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
[0044]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, and R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group or an ethoxymethyl group, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, and R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
[0045]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8
is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R7 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
[0046]
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a
pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and n is 0;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a
propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and n is 1;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec- butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and n is 2;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, A2 is a nitrogen atom or =CR9-, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, an aldehyde group, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom, R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group, R9 and R10 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and Ru is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C2-C6 alkoxycarbonyl
group, -CO2R , a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or
more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and
R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and
R8 is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, and R8 is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a sulfur atom, and R8 is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, and R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, and
A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A is =CR -;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom, A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom, A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom, A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom, A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is =CR10-;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is a nitrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a
sulfur atom, R is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a sulfur atom, R8 is a methyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, and R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom, A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, and R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, and R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one- or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, or a cyclopentyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and
R5 are same or different and are independently a phenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a 2-pyridyl group, a 2-pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, a 3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently -SF5 or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and
R5 are same or different and are independently a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently -OR11 or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently -NR1:LR12 or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R3 is a phenyl group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R3 is a phenyl group optionally having
one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Z group, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Z;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5
are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and- R3 is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, or a 3-chloro- 5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 2-pyrimidyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5
are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C3
alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein R6 is -SF5, and
R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a sulfur atom, R8 is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom, R1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2, R4,
and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- or a sulfur atom, R8 is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom, R1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1
is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and n is 0;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and n is 1;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and n is 2;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a
pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, A3 is =CR10-, R9 and R10 are a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8-, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group,
or a 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9-, R9 is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a
bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
[0047]
A compound of the formula (1-1)
wherein;
Ala represents -NR8a- or a sulfur atom;
A3a represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10a-;
Rla represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
R2a, R4a, and R5a are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R3a represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlla, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R6a represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlla, S(0)mRlla, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
R8a represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
R10a represents a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
Rlla represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, m represents 0, 1, or 2, and n represents 0, 1 or 2;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A is -NR - or a sulfur atom, R8a is a methyl group, A3a is a nitrogen atom, Rla is an ethyl group, R2a, R4a, and R5a are a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R3a is a trifluoromethyl group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R6a is a C1-C3 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more a fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more a fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more a fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a methyl group, A3a is a nitrogen atom, Rla is an ethyl group, R2a, R4a, and R5a are a hydrogen atom, R3a is a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, a trifluoromethyl group, or a hydrogen atom, and R6a is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A is -NR -
or a sulfur atom, and R8a is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A is -NR -, and R8a is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Al is -NR8a-, and R8a is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is a sulfur atom;
[0048]
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A3a is a nitrogen atom or =CR10a-, and R10a is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A3a is =CR10a-, and R10a is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A3a is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, A3a is a nitrogen atom or =CR10a-, and R10a is a hydrogen atom;
[0049]
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, and A3a is a
nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A is -NR - or a sulfur atom, R8a is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, A3a is =CR10a-, and R10a is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a methyl group, and A3a is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, R8a is a methyl group, and A3a is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is a sulfur atom, and A3a is a nitrogen atom;
[0050]
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Rla is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Rla is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R2a, Ra, and R5a are same or different and are independently a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R3a is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R2a, Ra, and R5a are a hydrogen atom, and R3a is a fluorine atom, a
chlorine atom, a bromine atom, a methyl group, or a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A is -NR -, and R8a is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and R8a is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A3a is =CR10a-, and R10a is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a-, and A3a is =CR10a-;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is a sulfur atom, and A3a is =CR10a-;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- ,
and A3a is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein A is -NR -, R8a is a hydrogen atom group, and A3a is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Rla is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Rla is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Rla is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Rla is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R2a, R3a, Ra, and R5a are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein R6a is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A3a is =CR10a-, R10a is a hydrogen atom, Rla is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2a, R4a, and R5a are a hydrogen atom, R3a is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, and R6a is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more
fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1-1) wherein Ala is -NR8a- or a sulfur atom, R8a is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A3a is a nitrogen atom, Rla is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2a, R4a, and R5a are a hydrogen atom, R3a is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, and R6a is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
[0051]
A compound of the formula (1-0) :
wherein :
A represents -NR8j-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom;
A 3 represents a nitrogen atom or =CR -;
A3-" represents a nitrogen atom or =CR103-;
Rlj represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X3 , or a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group Y3 ;
R2j, R3j, Rj, and R5j are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11', -NRllj R12-* , a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom: provided that at least two of R2j, R3j, Rj, and R5j represent a hydrogen atom;
R6j and Rl3 are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllj, -S(0)mRllj, -NRllj R12j, -C02Rllj, -C(0)Rllj, an aldehyde group, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R8j represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one -OR11-', or a cyclopropyl group;
R9j and R103 are same or different and independently
represent a C1-C3 chain hydrocarbon group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
RLLJ and R12J are same or different and independently represent a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom; and
m represents 0, 1, or 2, and n represents 0, 1, or 2; (except in cases as follows: both R6J and R7J are a hydrogen atom; in -S(0)MRLLJ, when m is 1 or 2, RLLJ represents a hydrogen atom; and when A1-1 represents a methylimino group, A2j and A3j represent a methine group, RLJ represents a methyl group, Rz R3-5, R4J, and R5½epresent a hydrogen atom, and n represents 0 or 1, both R6J and R7J are a chlorine atom and one of R6 and R7J is a chlorine atom and the other is a hydrogen atom)
the Group Xj consists of -ORLLJ and a halogen atom; and the Group Yj consists of a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group, a -OR11-1, and a halogen atom.
[0052]
A com ound of the formula (Z) :
wherein, RLJ, R2J , R3J, R4J, R5J, R6J, Alj, A3j, and n are as defined in the formula (1-0) ;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8J-, an
oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom, and R 3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms ;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8:i- or a sulfur atom, and R8j is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j- or a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and R8;i is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and R8j is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1-" is -NR8:i-, and R8j is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-,
and R 3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1-* is -NR8j-, and R8j is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Α1· is -NR8j-, and R8j is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1^ is -NR8j-, and R8-1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1^ is -NR8-1-, and R83 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1^ is -NR8:I-, and R8j is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, a cyclopropyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1-* is -NR83-, and R8j is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a cyclopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and R8-5 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and R8j is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1^ is -NR8-1-,
and R 3 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is -NR83-, and R8j is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and R8j is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1-* is -NR83-, and R8j is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and R8j is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is -NR8j-, and R8j is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is an oxygen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR83- or a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j- or a sulfur atom, and R8j is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j- or a sulfur atom, and R8j is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A3j is a
nitrogen atom or =CR10j-, and R10j is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A33 is =CR10^-, and R10j is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A3j is =CR10j-, and R10-1 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A3j is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1 is -NR8^-, and A3j is =CR10j-;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is a sulfur atom, and A3j is =CR10j-;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j-, and A33 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A1-1 is a sulfur atom, and A3j is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j- or a sulfur atom, R8j is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, A33 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10j-, and R10j is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein 13 is -NR8]- or a sulfur atom, R8j is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, and A3j is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j- or
a sulfur atom, R 3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, A33 is =CR103-, and R10j is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Alj is -NR8j- or a sulfur atom, R8j is a methyl group, and A3j is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is -NR83-, R83 is a methyl group, and A33 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R1] is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rlj is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rlj is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a butyl group, a sec-butyl group, an isobutyl group, a tert-butyl group, a cyclopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a 2,2,2- trifluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R13 is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one ore more atoms or groups selected from Group Y-';
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein Rl3 is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, or a cyclopentyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R23 , Rj , and R53 are same or different and are independently a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R33 is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, a trifluoromethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R 3 , R], and R 3 are a hydrogen atom, R3-1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a optionally having one or more fluorine atoms C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3] is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3-1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, Rj, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, a trifluoromethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, Rj, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, Rj, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R33 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j are a hydrogen atom, and R3-1 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4j, and R5j
are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R4-1, and R53 are a hydrogen atom, and R3j is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2j, R3j, , and R5-5 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6^ is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6] is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6j is a
trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R6-1 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R63 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2:, R33, R43 , and R53 are same or different and are independently a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R6j is a trifluoromethyl group or a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2J, R3J, R4J, and
R53 are a hydrogen atom, and R63 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2J, R3J, R J, and R53 are a hydrogen atom, and R6J is a pentafluoroethyl group or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2J, R3J, R J, and
R5J are a hydrogen atom, and R6J is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein R2], R33, R43, and R5J are a hydrogen atom, and R63 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is -NR8J - or a sulfur atom, R8J is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A3j is =CR10J-, R10J is a hydrogen atom, RLJ is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2], R4-1, and
R5j are a hydrogen atom, R3j is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, and R6-1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom; and
A compound of the formula (Z) wherein A13 is -NR8j - or a sulfur atom, R8j is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A3j is a nitrogen atom, Rlj is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2j, R4-', and R5j are a hydrogen atom, R3j is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, and R6j is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom.
[0053]
The present compound can be produced, for example, by the following Production methods A-F.
[0054]
(Production method A)
The present compound (1) can be produced by reacting Compound (IF) with Compound (5) . Alternatively, the present compound (1) can be produced by reacting Compound (F) with Compound (5) to give Compound (B) , followed by cyclizing Compound (B) :
(B)
wherein, R1, RJ, RH R5, R6, R7, A1, A2 and n are as defined above
[0055]
(Production method B)
The present compound (1) can be produced by reacting Compound (IF) with Compound (M3) . Alternatively, the present compound (1) can be produced by reacting Compound
(F) with Compound (5) to give Compound (B) , followed by cyclizing Compound (B) :
(B)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3 and n are as defined above.
[0056]
(Production method C)
The present compound (1) can be produced by reacting Compound (F) with Compound (3) . Alternatively, the present compound (1) can be produced by reacting Compound (IF) with Compound (3) to give Compound (1J), followed by cyclizing Compound (1J) :
(U)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3, and n are as
defined above.
[0057]
(Production method D)
Compound (12) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting Compound (K) with a sulfating agent:
(K) (12)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
[0058]
(Production method E)
Compound (23) of the formula (1) wherein n is 0 can be produced, for example, by the following method:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3, and n are as defined above, and V2 represents a fluorine atom or a
chlorine atom.
[0059]
(Production method F)
Compound (23) of the formula (1) wherein n is 0 can be produced, for example, by the following method:
wherein, R
1, R
2, R
3, R
4, R
5, R
6, R
7, A
1, A
2, A
3, n, and V
2 are as defined above.
[0060]
The production method of the present compound is illustrated below.
[0061]
The production methods A-F of the present compound are further illustrated bellow. In addition, the production methods which the present compound is converted to other present compound are illustrated. The present compound can be produced, for example, by the following Production methods 1-26.
[0062]
(Production method 1) (Step (C-l) )
Compound (4) of the formula (1) wherein A
1 is -NR
8- can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound (3) :
(2) (3) (4)
wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a base, acid, sulfite, or disulfite.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrogen carbonates such as sodium hydrogen carbonate and potassium hydrogen carbonate; carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; and mixtures thereof .
Examples of the acid to be used in the reaction include sulfonic acids such as p-toluenesulfonic acid; and carboxylic acids such as acetic acid.
Examples of the sulfite to be used in the reaction include sodium sulfite and potassium sulfite.
Examples of the disulfite to be used in the reaction include sodium disulfite and potassium disulfite.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as tetrahydrofuran (hereinafter referred to as THF) , ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-
butyl methyl ether, and 1 , 4-dioxane ; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as N, -dimethylformamide (hereinafter referred to as DMF) and N-methylpyrrolidone (hereinafter referred to as N P) ; sulfoxides such as dimethylsulfoxide (hereinafter referred to as D SO) ; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
An oxidizing agent can be added to the reaction as necessary .
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include an oxygen, copper (II) oxide, and 2,3- dichloro-5 , 6-dicyano-p-benzoquinon .
The amount of Compound (3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the acid to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the sulfite to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the disulfite to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the
oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2).
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (4) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (4) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0063]
(Production method 2) (Step A-l)
Compound (4) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound (5) in the presence of a dehydration-condensing agent:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, tert-butyl methyl ether, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as 1-ethyl- 3- ( 3-dimethylaminopropyl ) carbodiimide hydrochloride
(hereinafter referred to as WSC) , and 1,3- dicyclohexylcarbodiimide; and (benzotriazol-1- yloxy) tris (dimethylamxno) phosphonium hexafluorophosphate
(hereinafter referred to as BOP reagent) .
A catalyst can be added to the reaction as necessary. Examples of the catalyst to be used in the reaction include 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (hereinafter referred to as HOBt) .
The amount of Compound (5) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (2) . The amount of the catalyst to be used in the reaction is usually 0.01 to 0.1 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (4) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (4) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
Alternatively, Compound (4) can be produced according to the above method using Compound (M3) instead of Compound (5) .
When Compound (M3) is used, the reaction is usually performed without a dehydration-condensing agent.
A base can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include carbonates of alkali metal such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen- containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4- dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound (M3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) .
[0064]
(Production method 3) (Step (A-3) , Step ( B-3))
Compound (4) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- can be produced by dehydration-condensing Compound (6):
(6) (4)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, and
pentanol; and mixtures thereof.
In the reaction, an acid or a dehydrating agent can be used as necessary. Examples of the acid to be used in the reaction include sulfonic acids such as p-toluenesulfonic acid, and carboxylic acids such as acetic acid. Examples of the dehydrating agent to be used in the reaction include phosphorous oxychloride, acetic anhydride, and trifluoroacetic anhydride.
The amount of the acid or the dehydrating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (6) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (4) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (4) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0065]
(Production method 4) (Step (A-3), Step (B-3) )
Compound (4) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- can be produced by reacting Compound (6) in the presence of a base:
wherein, R
1, R
2, R
3, R
4, R
5, R
6, R
7, R
8, A
2, A
3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as D F and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, tert-butanol, and pentanol; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include tripotassium phosphate.
The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (6) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (4) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (4) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0066]
(Production method 5)
Compound (4) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is -NR8- can be produced by reacting Compound (32) with Compound (33) in the presence of a base.
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and n are as defined above, and L represents a leaving group such as a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, a trifluoromethylsulfonyloxy group and a methylsulfonyloxy group .
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic
hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrides of alkali metal or alkali earth metal such as sodium hydride, potassium hydride, and calcium hydride; inorganic bases such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; and organic bases such as triethylamine .
The amount of Compound (33) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (32).
The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (32) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (4) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (4) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0067]
(Production method 6) (Step (A-l))
Compound (8) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom can be produced by reacting Compound (7) with
Compound (5) in the presence of an acid:
(7) (5) (8)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence or absence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene and dichlorobenzene; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the acid to be used in the reaction include polyphosphoric acid and trimethylsilyl polyphosphate .
When polyphosphoric acid is used as an acid, though the reaction is usually performed in the absence of a solvent, the reaction may be performed in the presence of a solvent.
The amount of Compound (5) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) .
The amount of the acid to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (8) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring the reaction mixture into water and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (8) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
Alternatively, Compound (8) can be produced according to the above method using Compound ( 3) instead of Compound (5) .
When Compound (M3) is used, the reaction is usually performed without a dehydration-condensing agent.
A base can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include carbonates of alkali metal such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen- containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4- dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound (M3) to be used in the reaction
is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) .
[0068]
(Production method 7) (Step (C-3))
Compound (8) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom can be produced by oxidizing Compound (9) :
(9) (8)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane , chloroform, and chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO; acetic acid; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include a metal oxidizing agent such as lead (IV) acetate and lead (IV) oxide, and a hypervalent iodine compound such as iodobenzene diacetate.
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 9) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (8) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (8) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0069]
(Production method 8) (Step (A-3), Step (B-3))
Compound (8) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom can be produced by reacting Compound (10) in the presence of a dehydration-condensing agent:
( 10) (8)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; and mixtures thereof. Among of them, carbon tetrachloride can be used as a dehydration-condensing agent.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include a mixture of triphenylphosphine , a base and carbon tetrachloride or carbon tetrabromide, and a mixture of triphenylphosphine and azodiesters such as diethyl azodicarboxylate ester.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine .
The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (10) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (10) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -30 to 100 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (8) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (8) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0070]
(Production method 9) (Step (A-3), Step (B-3))
Compound (8) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is an oxygen atom can be produced by reacting Compound (10) in the presence of an acid:
( 10) (8)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, -dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, and chlorobenzene; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the acid include sulfonic acids such as p- toluenesulfonic acid and polyphosphoric acid.
The amount of the acid to be used in the reaction is usually 0.1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (10) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (8) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (8) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0071]
(Production method 10) (Step (C-l))
Compound (12) of the formula (1) wherein A
1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting Compound (11) with Compound ( 3 ) :
(Π)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a base, acid, sulfite, or disulfite.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrogen carbonates such as sodium hydrogen carbonate and potassium hydrogen carbonate; carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; and mixtures thereof .
Examples of the acid to be used in the reaction include sulfonic acids such as p-toluenesulfonic acid; and carboxylic acids such as acetic acid.
Examples of the sulfite to be used in the reaction include sodium sulfite and potassium sulfite.
Examples of the disulfite to be used in the reaction include sodium disulfite and potassium disulfite.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic
hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as D F, and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene, xylene, nitrobenzene; and mixtures thereof.
An oxidizing agent can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include an oxygen, copper (II) oxide, and 2,3- dichloro-5 , 6-dicyano-p-benzoquinon .
The amount of Compound (3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the acid to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the sulfite to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the disulfite to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (12)
can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, adding the reaction mixture to water and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound
(12) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0072]
(Production method 11) (Step (C-l))
Compound (12) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting hydrochloride of Compound (11) with Compound (3) :
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is performed in the presence of a base and usually in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include tertiary amines such as diisopropylethylamine and triethylamine .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include sulfoxides such as DMSO; aromatic hydrocarbons such as nitrobenzene; and mixtures thereof.
The amount of Compound (3) to be used in the reaction is usually 0.5 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 2 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (12) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, adding the reaction mixture to water and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (12) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0073]
(Production method 12)
Compound (14) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a cyano group or a C1-C6 alkyl group can be produced by reacting Compound (13) with a cyanating agent or di(Cl-C6 alkyl) zinc in the presence of a palladium compound:
(13) ( 14)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, A1, A2, and A3 are as defined
above, V represents a leaving group such as a bromine atom and an iodine atom, and R6z represents a cyano group or a C1-C6 alkyl group.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the cyanating agent to be used in the reaction include zinc cyanide. Examples of di (C1-C6 alkyl) zinc to be used in the reaction include dimethyl zinc, diethyl zinc, and diisopropyl zinc.
Examples of the palladium compound to be used in the reaction include tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium.
The amount of the cyanating agent or di (C1-C6 alkyl) zinc to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of the palladium compound to be used in the reaction is usually 0.01 to 0.5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13).
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the
reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (14) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (14) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0074]
(Production method 13)
Compound (16) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is C(0)R6y can be produced by reacting Compound (15) with a organometallic agent, then a carbonylating agent:
(15) (16)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, A1, A2, and A3 are as defined above, R6y is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a hydrogen atom, or -OR11, and R11 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane.
Examples of the organometallic agent to be used in the reaction include alkyllithiums such as n-butyllithium and tert-butyllithium, organic magnesium halides such as isopropylmagnesium chloride.
Examples of the carbonylatxng agent to be used in the reaction include DMF, 1-formylpiperidine, 4- formylmorpholine, ethyl formate, ethyl acetate, methyl trifluoroacetate , methyl chloroformate, ethyl chloroformate, and carbon dioxide.
The amount of the organometallic agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (15) . The amount of the carbonylating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (15) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -100 to 0 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (16) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (16) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0075]
(Production method 14)
Compound (18) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a C1-C3 perfluoroalkyl group can be produced by reacting Compound (13) with Compound (17) in the presence of copper iodide:
(13) (17) (18)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, A1, A2, A3, and V1 are as defined above, and Rf represents a C1-C3 perfluoroalkyl group .
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; acid amides such as DMF and N P; and mixtures thereof.
The amount of Compound (17) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of copper iodide to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (18) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting
the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (18) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0076]
(Production method 15)
Compound (20) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms can be produced by reacting Compound (13) with boronic acid compound (19) in the presence of a palladium compound:
(13) (19) (20)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, A1, A2, A3, and V1 are as defined above, and RAr represents a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
The reaction can be performed in the presence of a base and /or a phase transfer catalyst as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include inorganic salts such as sodium acetate, potassium acetate, potassium carbonate, tripotassium phosphate, and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Examples of the phase transfer catalyst to be used in the reaction include quaternary ammonium salts such as tetrabutylammonium bromide and benzyltriethylammonium bromide .
The reaction can be performed in the presence of a ligand as necessary.
Examples of the ligand to be used in the reaction include 2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2 ' , 6' -dimethoxybiphenyl .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; acid amides such as DMF and N P; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the palladium compound to be used in the reaction include palladium acetate, tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium, {1,1'- bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene } dichloropalladium-methylene
chloride complex, and bis ( triphenylphosphine ) palladium dichloride, and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium (0).
The amount of boronic acid compound (19) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of the palladium compound to be used in the reaction is usually 0.01 to 0.5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (20) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (20) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0077]
(Production method 16) (Step (E-4) )
Compound (23) of the formula (1) wherein n is 0 can be produced by reacting Compound (21) with Compound (22) in the presence of a base:
(21) (22) (23)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3, and V2 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include water; ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal hydrides such as sodium hydride.
The amount of Compound (22) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (21) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (21) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 150 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (23) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (23) can be further purified by chromatography,
recrystallization, and the like.
[0078]
(Production method 17) (Step (F-2))
Compound (23) of the formula (1) wherein n is 0 can be produced by reacting Compound (24) with Compound (25) in the presence of a base:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3, and L are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrides of alkali metal or alkali earth metal such as sodium hydride, potassium hydride, and calcium hydride; inorganic bases such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; and organic bases such as triethylamine .
The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (24) . The amount of Compound (25) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (24) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (23) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (23) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0079]
(Production method 18)
Compound (26) of the formula (1) wherein n is 1 can be produced by oxidizing Compound (23) :
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, and A3 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acetic acid; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include sodium periodate or m-chloroperbenzoic acid .
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (23) . Preferably, the amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is 1 to 1.2 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (23) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 80 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 12 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (26) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by washing the organic layer with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium sulfite, thiosodium sulfate) and an aqueous solution of a base (e.g. sodium hydrogen carbonate) as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (26) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0080]
(Production method 19)
Compound (27) of the formula (1) wherein n is 2 can be produced by reacting Compound (23) in the presence of an oxidizing agent:
(23) (27)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, and A3 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acetic acid; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include m-chloroperbenzoic acid or an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide.
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 2 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (23) . Preferably, the amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is 2 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (23) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 120 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 12 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (27) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by washing the organic layer with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium sulfite, thiosodium sulfate) and an aqueous solution of a base (e.g. sodium hydrogen carbonate) as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound
(27) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0081]
(Production method 20)
Compound (27) of the formula (1) wherein n is 2 can be produced by reacting Compound (26) in the presence of an oxidizing agent:
(26) (27)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, and A3 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a
solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acetic acid; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include m-chloroperbenzoic acid or an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide.
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 4 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (26) . Preferably, the amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is 1 to 2 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (26) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 120 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 12 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (27) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by washing the organic layer with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium sulfite, thiosodium sulfate) and an aqueous solution of a base (e.g. sodium hydrogen carbonate) as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (27) can be further purified by chromatography,
recrystallization, and the like.
[0082]
(Production method 21) (Step (A-3), Step (B-3) )
Compound (12) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting Compound (35) in the presence of an acid:
(35) (12) wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, and chlorobenzene; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the acid include sulfonic acids such as p- toluenesulfonic acid, and polyphosphoric acid.
The amount of the acid to be used in the reaction is usually 0.1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (35) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (12) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (12) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0083]
(Production method 22)
Compound (34-a) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is SH, Compound (34-b) which is a disulfide form of Compound (34- a) , Compound (36) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is SR6x, and Compound (37) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is S(0)mR6x can be produced, for example, by the following method:
L are as defined above.
Step (22-1)
Compound (34-a) and / or Compound (34-b) can be produced by reacting Compound (13) with a thiolating agent in the presence of a catalyst.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; acid amides such as DMF and N P; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the thiolating agent to be used in the reaction include sodium sulfide, sodium sulfide nonahydrate, and thiourea.
Examples of the catalyst to be used in the reaction include copper (I) chloride, copper (I) bromide, and copper (I) iodide.
The reaction can be performed in the presence of a base as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, tripotassium phosphate, and triethylamine .
The amount of the thiolating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of the catalyst to be used in the reaction is usually 0.1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (13) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 50 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (34-a) and / or Compound (34-b) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (34-a) and / or Compound (34-b) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0084]
Step (22-2)
Compound (36) can be produced by reacting Compound (34-a) and / or Compound (34-b) with Compound (38-1) in the presence of a base.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane, diethyl ether, THF, and tert-butyl methyl ether; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, 1, 2-dichloroethane, and chlorobenzene; hydrocarbons such as toluene, benzene, and xylene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate;
nitriles such as acetonitrile; aprotic polar solvents such as DMF, N P, 1, 3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone, and dimethylsulfoxide; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds such as pyridine, picoline, 2 , 6-lutidine, DBU, and 1,5- diazabicyclo [ 4.3.0 ] -5-nonen; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and N-ethyldiisopropylamine; and inorganic bases such as tripotassium phosphate, potassium carbonate, sodium hydride, sodium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide.
The amount of Compound (38-1) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (34-a) and / or Compound (34-b) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (34-a) and / or Compound (34-b) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 120 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (36) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (36) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0085]
Step (22-3)
Compound (37) wherein m is 1 or 2 can be produced by oxidizing Compound (36) .
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acetic acid; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include m-chloroperbenzoic acid and an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide.
The reaction can be performed in the presence of a catalyst as necessary,
Examples of the catalyst to be used in the reaction include sodium tungstate.
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (36) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 120 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 12 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (37) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting
the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by washing the organic layer with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium sulfite, thiosodium sulfate) and an aqueous solution of a base (e.g. sodium hydrogen carbonate) as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (37) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0086]
(Production method 23)
Compound (39) of the formula (1) wherein R6 is NH2, Compound (40) of the formula (1) wherein R5 is NHR10, and Compound (41) of the formula (1) wherein R5 is NR10R11 can be produced, for example, by the following method:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R10, R11, R7, A1, A2, A3, n, V1, and L are as defined above.
Step (23-1)
Compound (39) can be produced by aminating Compound
(13) .
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include water; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane, diethyl ether, and THF; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and 1, 2-dichloroethane; nitriles such as acetonitrile; aprotic polar solvents such as DMF, NMP, and dimethylsulfoxide; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the aminating agent to be used in the reaction include ammonia, ammonia water, and lithium amide.
Examples of the copper compound to be used in the reaction include copper, copper (I) iodide, copper (I) oxide, copper (II) oxide, copper (II) acetylacetone, copper (II) acetate, and copper (II) sulfate.
A ligand can be added to the reaction as necessary. Examples of the ligand to be used in the reaction include acetylacetone, salen, and phenanthroline .
A base can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds such as pyridine, picoline, 2 , 6-lutidine, DBU, and 1,5-
diazabicyclo [ 4.3.0] -5-nonen; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and N-ethyldiisopropylamine; and inorganic bases such as tripotassium phosphate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, and sodium hydroxide.
The amount of the aminating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of the copper compound to be used in the reaction is usually 0.02 to 0.5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of the ligand to be used in the reaction is 0.02 to 2 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) as necessary. The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) as necessary.
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (39) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (39) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0087]
Step (23-2)
Compound (40) can be produced by reacting Compound (39) with Compound (38-1) in the presence of a base.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, -dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrides of alkali metal or alkali earth metal such as sodium hydride, potassium hydride, and calcium hydride; inorganic bases such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; and organic bases such as triethylamine .
The amount of Compound (38-1) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (40) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (40) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (40) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the
organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (40) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0088]
Step (23-3)
Compound (41) can be produced by reacting Compound (40) with Compound (38-2) in the presence of a base.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as D F and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrides of alkali metal or alkali earth metal such as sodium hydride, potassium hydride, and calcium hydride; inorganic bases such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; and organic bases such as triethylamine .
The amount of Compound (38-2) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (40) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (40) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (41) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (41) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0089]
(Production method 24)
Compound (43) of the formula (1) wherein R
6 is OR
11 can be roduced, for example, by the following method:
(13) (43)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, R11, A1, A2, A3, V1, and n are as defined above.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides
such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrides of alkali metal or alkali earth metal such as sodium hydride, potassium hydride, and calcium hydride; inorganic bases such as sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate, and cesium carbonate; and organic bases such as triethylamine .
A copper compound can be added to the reaction as necessary .
Examples of the copper compound to be used in the reaction include copper, copper (I) iodide, copper (I) bromide, and copper (I) chloride.
The amount of Compound (42) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (13) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 20 to 250 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 48 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (43) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by
filtration. The isolated Compound (43) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like [0090]
(Production method 25) (Step (A-l))
Compound (12) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting Compound (11) with Compound (5) :
(11) (5) (12)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
Compound (12) can be produced according to the method described in Production method 2 using Compound (11) instead of Compound (2) .
[0091]
(Production method 26) (Production method D)
Compound (12) of the formula (1) wherein A1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting Compound (IK) with a sulfating agent:
(1 K) (12)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is performed in the presence or absence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as 1,4-dioxane, diethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, tert-butyl methyl ether, and Diglyme; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, 1 , 2-dichloroethane, and chlorobenzene; hydrocarbons such as toluene, benzene, and xylene; nitrile such as acetonitrile; pyridines such as pyridine, picoline, and lutidine; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the sulfating agent to be used in the reaction include phosphorus pentasulfide and Lawesson's reagent (2, 4-bis- ( -methoxyphenyl ) -1, 3-dithia-2, 4- diphosphetane 2 , 4-disulfide) .
The amount of the sulfating agent to be used in the reaction is usually one or more moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( IK) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (12) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the
organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (12) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0092]
The intermediates of the present invention can be produced, for example, by the following method.
(Production method of intermediate 1)
Compound (2) can be produced by the following method:
(Ml) (M2) (2)
wherein, R6, R7, R8, A2, and A3 are as defined above.
(Step 1)
Compound (M2) can be produced by reacting Compound (Ml) in the presence of a nitrating agent.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform, acetic acid, concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid, water and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the nitrating agent to be used in the reaction include concentrated nitric acid.
The amount of the nitrating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (Ml) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -10 to 100 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M2) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring the reaction mixture into water and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (M2) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0093]
(Step 2)
Compound (2) can be produced by reacting Compound (M2) with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenating catalyst.
The reaction is usually performed under 1 to 100 atms of hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1 , 4-dioxane; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the hydrogenating catalyst to be used in
the reaction include transition metal compounds such as palladium-carbon, palladium hydroxide, Raney® nickel, and platinum oxide.
The amount of hydrogen to be used in the reaction is usually 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (Ml) . The amount of the hydrogenating catalyst to be used in the reaction is usually 0.001 to 0.5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (Ml) .
An acid (or base, and the like) can be added to the reaction as necessary.
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (2) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, filtrating the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (2) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0094]
(Production method of intermediate 2) (Step (A-2))
Compound (6) can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound (5) in the presence of a dehydration- condensing agent:
(2) (5)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile ; acid amides such as D F and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as WSC and 1, 3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and BOP reagent.
The amount of Compound (5) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) .
The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (2) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 140 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (6) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (6) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0095]
(Production method of intermediate 3) (Step (B-2))
Compound (6) can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound ( 3) in the presence of a base:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base include alkali metal carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4-dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound (M3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (6) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (6) can be further purified by chromatography,
recrystallization, and the like.
[0096]
(Production method of intermediate 4)
Compound (7) can be produced by the following method:
( 4) (MS) (7)
wherein, R6, R7, A2, and A3 are as defined above.
(Step 1)
Compound (M5) can be produced by reacting Compound (M4) in the presence of a nitrating agent.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as chloroform, acetic acid, concentrated sulfuric acid, concentrated nitric acid, water, and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the nitrating agent to be used in the reaction include concentrated nitric acid.
The amount of the nitrating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M4) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -10 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M5) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring the reaction mixture into water and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound ( 5) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0097]
(Step 2)
Compound (7) can be produced by reacting Compound (M5) with hydrogen in the presence of a hydrogenating catalyst.
The reaction is usually performed under 1 to 100 atms of hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the hydrogenating catalyst to be used in the reaction include transition metal compounds such as palladium-carbon, palladium hydroxide, Raney® nickel, and platinum oxide.
The amount of hydrogen to be used in the reaction is usually 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M5) . The amount of the hydrogenating catalyst to be used in the
reaction is usually 0.001 to 0.5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M5) .
An acid (or base, and the like) can be added to the reaction as necessary.
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (7) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, filtrating the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (7) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0098]
(Production method of intermediate 5) (Step (C-2))
Compound (9) can be produced by reacting Compound (7) with Compound (3) :
(7) (3)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a
solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; and mixtures thereof.
The amount of Compound (3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) .
An acid or base can be added to the reaction as necessary .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 150 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (9) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (9) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0099]
(Production method of intermediate 6) (Step (A-2))
Compound (10) can be produced by reacting Compound (7) with Compound (5) in the presence of a dehydration- condensing agent:
wherein, R
1, R
2, R
3, R
4, R
5, R
6, R
7, A
2, A
3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene ; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as WSC and 1, 3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and BOP reagent.
The amount of Compound (5) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) . The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (7 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 140 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (10) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (10) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0100]
(Production method of intermediate 7) (Step ( B-2))
Compound (10) cab be produced by reacting Compound with Compound (M3) in the presence of a base:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen- containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4- dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound (M3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (7) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (10) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound
(10) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0101]
(Production method of intermediate 8)
Compound (11) can be produced by the following method:
( 6) (M7) (11)
wherein, R6, R7, A2, and A3 are as defined above.
(Step 1)
Compound (M7) can be produced by reacting Compound ( 6) with thiourea in the presence of a base.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
The amount of thiourea to be used in the reaction is usually 0.5 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M6) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M6) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually
within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M7) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring an acid into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound ( 7) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0102]
(Step 2)
Compound (11) can be produced by reducing Compound
( 7) .
The reduction reaction can be performed, for example, in the presence of a reducing agent such as iron powder and zinc powder; acids such as hydrochloric acid and acetic acid; and water.
The reaction can be usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acid amides such as D F and NMP; and mixtures thereof.
The amount of the reducing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 3 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M7) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (11) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, adding water to the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (11) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0103]
(Production method of intermediate 9)
Compound (28) of Compound (21) wherein A1 is -NR8- can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound (M8) in the resence of a base:
defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include hydrogen carbonates such as sodium hydrogen carbonate and potassium hydrogen carbonate; carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; sulfites such as sodium sulfite and potassium sulfite; and mixtures thereof .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene ; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile ; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
The amount of Compound (M8) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (28) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring
water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (28) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0104]
(Production method of intermediate 10) (Step (E-l) )
Compound (28) of Compound (21) wherein A1 is -NR8- can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound (M9) in the resence of a dehydration-condensing agent:
defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, tert-butyl methyl ether, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO;
nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as WSC and 1, 3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and BOP reagent.
A catalyst can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the catalyst to be used in the reaction include 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (hereinafter referred to as HOBt) .
The amount of Compound (M9) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the catalyst to be used in the reaction is usually 0.01 to 0.1 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (28) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (28) can be further purified by chromatography,
recrystallization, and the like.
[0105]
(Production method of intermediate 11) (Step (E-3) )
Compound (28) of Compound (21) wherein A1 is -NR8 - can be produced by dehydration-condensing Compound (M10):
(M10)
wherein, R2 , R3 , R4 , R5 , R6 , R7 , R8, A2, A3, and V2 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as. THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile ; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, and pentanol; and mixtures thereof.
In the reaction, an acid or a dehydrating agent can be used as necessary. Examples of the acid to be used in the
reaction include sulfonic acids such as p-toluenesulfonic acid, and carboxylic acids such as acetic acid. Examples of the dehydrating agent to be used in the reaction include phosphorous oxychloride, acetic anhydride, and trifluoroacetic anhydride.
The amount of the acid or dehydrating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 10) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (28) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (28) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0106]
(Production method of intermediate 12) (Step (E-3) )
Compound (28) of Compound (21) wherein A
1 is -NR
8- can be produced by reacting Compound (M10) in the presence of a base :
(M10) (28)
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and V2 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile ; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol, tert-butanol, and pentanol; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include tripotassium phosphate.
The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M10) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (28) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (28) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0107]
(Production method of intermediate 13) (Step (E-2))
Compound (M10) can be produced by reacting Compound (2) with Compound (M9) in the presence of a dehydration- condensing agent:
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and V2 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl
acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as WSC and 1, 3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and BOP reagent.
The amount of Compound ( 9) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) . The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 140 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M10) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (M10) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0108]
(Production method of intermediate 14)
Compound (M10) can be produced by reacting Compound
with Compound ( 12) in the presence of a base
(2) (Ml 2) (M i o)
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2, A3, and V2 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base include alkali metal carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4-dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound (M12) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (2) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (2 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M10) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (M10) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0109]
(Production method of intermediate 15)
Compound (29) of Compound (3) wherein n is 0 can be produced by the following method:
wherein, R
1, R
2, R
3, R
4, R
5, and V
2 are as defined above.
(Step 115-1)
Compound (M14) can be produced by reacting Compound
(M13) with Compound (22) in the presence of a base.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile ; acid amides such as DMF and N P; sulfoxides such as D SO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal hydrides such as sodium hydride.
The amount of Compound (22) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 13) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M13) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 150 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M14) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound ( 14) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0110]
(Step 115-2)
Compound (29) can be produced by reducing Compound (M14) .
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1 , 4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the reducing agent to be used in the reaction include diisobutylaluminium hydrate.
The amount of the reducing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 2 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (Ml4 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (29) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (29) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0111]
(Production method of intermediate 16)
Compound (29) of Compound (3) wherein n is 0 can be produced by reacting Compound (M8) with Compound (22) in the presence of a base:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and V2 are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal hydrides such as sodium hydride.
The amount of Compound (22) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M15) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M8) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually
within a range of 0 to 150 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.5 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (29) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (29) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0112]
(Production method of intermediate 17)
Compound (30) of Compound (5) wherein n is 0 can be produced by hydrolyzing Compound (M14) in the presence of a base, and Compound ( 23) of Compound (5) wherein n is 1 or 2 can be produced by the following method:
(M14) (30)
Step (11 7 -2) Step(I1 7 -4)
(M22) ( 23) wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are as defined above, and r
represents 1 or 2.
[0113]
(Step 117-1)
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M14) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 120 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (30) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, acidifying the reaction mixture and than extracting with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (30) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0114]
(Step 117-2)
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acetic acid; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include m-chloroperbenzoic acid and an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide.
The reaction can be performed in the presence of a catalyst as necessary.
Examples of the catalyst to be used in the reaction include sodium tungstate.
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (Ml4 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 120 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 12 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M22) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by washing the organic layer with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium sulfite, thiosodium sulfate) and an aqueous solution of a base (e.g. sodium hydrogen
carbonate) as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound
( 22) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0115]
(Step 117-3)
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide.
The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 22) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 120 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound ( 23) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, acidifying the reaction mixture and than extracting with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound ( 23) can be further purified
by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0116]
(Step 117-4)
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acetic acid; water; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction include m-chloroperbenzoic acid and an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide.
The reaction can be performed in the presence of a catalyst as necessary.
Examples of the catalyst to be used in the reaction include sodium tungstate.
The amount of the oxidizing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 30 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 120 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 12 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M23) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by
washing the organic layer with an aqueous solution of a reducing agent (e.g. sodium sulfite, thiosodium sulfate) and an aqueous solution of a base (e.g. sodium hydrogen carbonate) as necessary, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (M23) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0117]
(Production method of intermediate 18)
Compound (30) of Compound (5) wherein n is 0 can be produced by hydrolyzing Compound (M14) in the presence of an acid:
(M14) (3°)
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are as defined above.
In the reaction, usually, an aqueous solution of the acid is used as a solvent.
Examples of the acid to be used in the reaction include mineral acids such as hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, phosphoric acid, and sulfuric acid, and carboxylic acids such as acetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid.
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the
reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (30) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, extracting the reaction mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (30) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0118]
(Production method of intermediate 19)
Compound (M3) can be produced by chlorinating Compound (5) in the presence of a chlorinating agent:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane and chloroform; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the chlorinating agent to be used in the
reaction include thionyl chloride and oxalyl dichloride.
The amount of the chlorinating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 5 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M3) can be isolated by evaporating the solvent.
[0119]
(Production method of intermediate 20)
Compound (M21) of Compound (2) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom can be produced, for example, by the following method:
wherein, R6, R7, R8, and A2 are as defined above, and X9 represents a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom.
(Step 120-1)
Compound (Ml 9) can be produced by reacting Compound (M17) with Compound (M18) .
The reaction is performed in the presence or absence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include water, alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane, diethyl ether, and THF; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and 1 , 2-dichloroethane ; nitriles such as acetonitrile; aprotic polar solvents such as DMF, N P, and dimethylsulfoxide; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
A base can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds such as pyridine, picoline, 2 , 6-lutidine, diazabicycloundecene (hereinafter referred to as DBU) , and 1,5- diazabicyclo [4.3.0] -5-nonen; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and N-ethyldiisopropylamine; and inorganic bases such as potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, and sodium hydroxide.
The amount of Compound (M18) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M17 ) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M19)
can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (M19) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0120]
(Step 120-2)
Compound (M20) can be produced by reacting Compound
(M19) with a halogenating agent.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include water; acetic acid; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane, diethyl ether, and THF; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; halogenated hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and 1,2- dichloroethane; nitriles such as acetonitrile; aprotic polar solvents such as D F and N P; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the halogenating agent to be used in the reaction include a chlorinating agent such as N- chlorosuccinimide and chlorine; a brominating agent such as N-bromosuccinimide and bromine; and an iodinating agent such as N-iodosuccinimide and iodine.
The amount of the halogenating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (Ml 9) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -10 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M20) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (M20) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0121]
(Step 120-3)
Compound (M21) can be produced by reacting Compound (M20) with an aminating agent in the presence of a copper compound .
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent .
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include water; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; ethers such as 1,4-dioxane, diethyl ether, and THF; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; halogenated
hydrocarbons such as dichloromethane, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, and 1 , 2-dichloroethane; nitriles such as acetonitrile; aprotic polar solvents such as DMF, NMP, and dimethylsulfoxide; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the aminating agent to be used in the reaction include ammonia, ammonia water, and lithium amide.
Examples of the copper compound to be used in the reaction include copper, copper (I) iodide, copper (I) oxide, copper (II) oxide, copper (II) acetylacetone, copper (II) acetate, and copper (II) sulfate.
A ligand can be added to the reaction as necessary. Examples of the ligand to be used in the reaction include acetylacetone, salen, and phenanthroline .
A base can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the base to be used in the reaction include nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compounds such as pyridine, picoline, 2 , 6-lutidine , DBU, and 1,5- diazabicyclo [ 4.3.0 ] -5-nonen; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and N-ethyldiisopropylamine; and inorganic bases such as tripotassium phosphate, potassium carbonate, cesium carbonate, and sodium hydroxide.
The amount of the aminating agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound ( 20) . The amount of the copper compound to be
used in the reaction is usually 0.02 to 0.5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M20) . The amount of the ligand to be used in the reaction is 0.02 to 2 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M20) as necessary. The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M20) as necessary.
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 30 to 200 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 48 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M21) can be isolated by pouring the reaction mixture into water, extracting with an organic solvent, and concentrating the organic layer; pouring the reaction mixture into water, and collecting the generated solids by filtration; or collecting the solids generated in the reaction mixture by filtration. The isolated Compound (M21) can be further purified by recrystallization, chromatography, and the like.
[0122]
(Production method of intermediate 21) (Step (A-2) )
Compound (35) can be produced by reacting Compound
(11) with Compound (5) in the presence of a dehydration- condensing agent:
wherein, R
1, R
2, R
3, R
4, R
5, R
6, R
7, A
2, A
3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1 , 4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as DMF and N P; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as WSC and 1 , 3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and BOP reagent.
The amount of Compound (5) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound ( 11) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 140 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (35) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (35) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0123]
(Production method of intermediate 22) (Step (B-2))
Compound (35) can be produced by reacting Compound (11) with Compound (M3) in the presence of a base:
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
The reaction is usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether,
tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1, 4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as D F and NMP; sulfoxides such as D SO; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the base include alkali metal carbonates such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4-dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound (M3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (11) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of -20 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (35) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (35) can be further purified by chromatography,
recrystallization, and the like.
[0124]
(Production method of intermediate 23) (Step (E-l) )
Compound (M24) of Compound (21) wherein A1 is oxygen atom can be produced by reacting Compound (7) Compound (M9) :
(7) (M9) (M24)
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, n, and V2 are as defined above.
Compound ( 24) can be produced according to the method described in (Production method 6) using Compound ( 9) instead of Compound (5) .
[0125]
(Production method of intermediate 24) (Step (E-2))
Compound (M25) of Compound (IE) wherein A
1 is an oxygen atom can be produced by reacting Compound (7) with Compound (M9) . Additionally, Compound ( 26) of Compound (IE) wherein A
1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by reacting Compound (11) with Compound (M9) :
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, n, and V2 are as defined above.
Compound (M25) can be produced according to the method described in Production method of intermediate 6 using Compound (M9) instead of Compound (5) .
Compound (M26) can be produced according to the method described in Production method of intermediate 21 using Compound (11) instead of Compound (5).
[0126]
(Production method of intermediate 25) (Step (E-3))
Compound (M27) of Compound (21) wherein A
1 is an oxygen atom can be produced by cyclizing Compound ( 25) . Additionally, Compound ( 28) of Compound (21) wherein A
1 is a sulfur atom can be produced by cyclizing Compound (M26) :
(M26) (M28)
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, n, and V2 are as defined above.
Compound ( 27) can be produced according to the method described in Production method 8 or Production method 9 using Compound ( 25) instead of Compound (10) .
Compound (M28) can be produced according to the method described in Production method 21 using Compound ( 26) instead of Compound (35) .
[0127]
(Production method of intermediate 26) (Step (F-l) )
Compound (24) can be produced by reacting Compound (21) with sodium sulfide, sodium hydrogen sulfide, or hydrogen sulfide:
(21) (24)
wherein, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3, n, and V2 are as
defined above.
Compound (24) can be produced according to the method described in Production method 16 using sodium sulfide, sodium hydrogen sulfide, or hydrogen sulfide instead of Compound (22) .
When sodium sulfide or sodium hydrogen sulfide is used, a reaction is usually performed without a base.
[0128]
(Production method of intermediate 27) (Production method D)
Compound (IK) can be produced by reacting Compound (M30) with Compound (5) :
(M29) (M30) (1K) wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above.
[0129]
(Step 127-1)
Compound (M30) can be produced by reducing Compound (M29) .
The reduction reaction can be performed in the presence of a reducing agent such as iron powder and zinc powder; acids such as hydrochloric acid and acetic acid; and water.
The reaction can be usually performed in the presence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; alcohols such as methanol and ethanol; acid amides such as DMF and N P; and mixtures thereof .
The amount of the reducing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 3 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M29) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 100 °C . The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (M30) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, adding water to the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (M30) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
[0130]
(Step 127-2)
The reaction is usually performed in the presence or absence of a solvent.
Examples of the solvent to be used in the reaction include ethers such as THF, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, tert-butyl methyl ether, and 1,4-dioxane; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as hexane, heptane, and octane; aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; halogenated hydrocarbons such as chlorobenzene; esters such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate; nitriles such as acetonitrile; acid amides such as D F and NMP; sulfoxides such as DMSO; nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and quinoline; and mixtures thereof.
Examples of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction include carbodiimides such as SC and
1, 3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and BOP reagent.
The amount of Compound (5) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M30) . The amount of the dehydration-condensing agent to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 5 moles based on 1 mole of
Compound (M30) .
The reaction temperature of the reaction is usually within a range of 0 to 140 °C. The reaction time of the reaction is usually within a range of 0.1 to 24 hours.
After the completion of the reaction, Compound (IK) can be isolated by post-treatments, for example, pouring water into the reaction mixture and then extracting the mixture with an organic solvent, followed by drying and concentrating the organic layer. The isolated Compound (IK) can be further purified by chromatography, recrystallization, and the like.
Alternatively, Compound (IK) can be produced according to the above method using Compound (M3) instead of Compound (5) .
When Compound (M3) is used, the reaction is usually performed without a dehydration-condensing agent
A base can be added to the reaction as necessary.
Examples of the base include carbonates of alkali metal such as sodium carbonate and potassium carbonate; tertiary amines such as triethylamine and diisopropylethylamine; and nitrogen-containing aromatic compounds such as pyridine and 4-dimethylaminopyridine .
The amount of Compound ( 3) to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 3 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M30) . The amount of the base to be used in the reaction is usually 1 to 10 moles based on 1 mole of Compound (M30) .
[0131]
(Production method of intermediate 28)
Compound (F) can be produced by reacting Compound (G)
with an aminating agent:
wherein, Xg, R6, R7, A1, A2, and A3 are as defined the above.
Compound (F) can be produced according to the method described in Step (120-3) of Production method of intermediate 20 using Compound (G) instead of Compound (M20) .
[0132]
Examples of Compound (B) include the following compounds :
[0133]
An amide compound of the formula (6):
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2,
defined above (referred to as Compound (6))
[0134]
An amide compound of the formula (10) :
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above (referred to as Compound (10) ) ;
[0135]
An amide compound of the formula (35) :
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2, A3, and n are as defined above (referred to as Compound (35) ) ;
[0136]
An amide compound of the formula (IB) :
wherein :
Alb represents -NR8b-, an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom;
A2b represents a nitrogen atom or =CR9b-;
A3b represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10b-;
Rlb represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group
optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
R2b, R3 , R4b, and R5b are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllb, -S(0)mRllb, -SF5, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom: provided that at least two of R2b, R3b, Rb, and R5b represent a hydrogen atom;
R6b represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllb,
-S(0)mRllb, -SF5, a cyano group, a nitro group, or a halogen atom;
R7b represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllb, -S (0) mRllb, -SF5, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R8b represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group, a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
R9b and R10b are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -0Rllb, -S(0)mRllb, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
Rllb and R12b are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom; and
m represents 0, 1, or 2, and n represents 0, 1, or 2; provided that: in -S(0)mRllb, when m is 1 or 2, Rllb is not a hydrogen atom; and when Alb is an oxygen atom, and A2b is a methine group, any one of R2b, R3b, R , and R5b are a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllb, -S(0)mRllb, a cyano group, a nitro group, or a halogen atom (hereinafter, referred to as Compound (IB) ) ;
[0137]
And examples of Compound (IB) include the following compounds :
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is -
NR8b-;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b-, and R8b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A is - NR8b-, and R8b is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8-, and R8b is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is -
NR8- , and R8b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b-, and R8b is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is -
NR8b- , and R8b is an ethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Al is - NR8b- , and R8b is a propyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b-, and R8b is an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b-, and R8b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Al is - NR8b- , and R8b is a methoxymethyl group or an ethoxymethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , and R8b is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Al is -
NR -, and R is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a cyclopentyl group, or a cyclohexyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , and R8b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is an oxygen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8 - or a sulfur atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, and R8b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, and R8b is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is =CR9b-, and A3b is =CR10b-;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is =CR9b-, A3b is =CR10b-, and R9b and R10b are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is =CR9b-, A3b is =CR10b-, and R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is a nitrogen atom, and A3b is =CR10 -;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is =CR9b-, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is =CR9b-, R9b is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is =CR9b-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein A2b is a nitrogen atom, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is -
NR8 - , A2b is =CR9b-, and A3b is =CR10b-;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , A2b is =CRb-, A3b is =CR10b-, and R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is an oxygen atom, A2 is =CR9b-, and A3b is =CR10b-;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom, A2b is =CR9b-, and A3 is =CR10b-;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom, A2b is =CR9b-, A3b is =CR10b-, and R9b and R10 are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , A2b is =CR9b-, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , A2b is =CRb-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, and A3b is a
nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is an oxygen atom, A2b is =CR9b-, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom, A2 is =CR9b-, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom, A2b is =CR9b-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2b is =CR9b-, A3b is =CR10b-, and R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, R8 is a methyl group, A2b is =CR9-, A3b is =CR10b-, and R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, R8b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group or an isopropyl group, A2b is =CR9b-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, R8b is a methyl group, A2b is =CR9-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, and A3b is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rl is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2, 2-trifluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is an ethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a propyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R is an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rl is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a
2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rl is a
C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, or a cyclopentyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3b,
Rb, and R5 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3b, R4b, and Rb are same or different and are independently a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic
group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2 , R3b, R4b, and R5b are same or different and are independently - ORllb or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3b, R4b, and R5b are same or different and are independently - S(0)mRllb or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3 ,
R4b, and R5b are same or different and are independently a cyano group, a nitro group, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3b, R4b, and R5b are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2-pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, or a 3- chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a 2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a 2-pyrimidyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R , R , and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2 , R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2 , R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R , R , and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is an ethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a propyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2 , Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a pentafluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a heptafluoropropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rb, R4b, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a fluorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2 , R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is -SF5;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R3b, R4b, and R5b are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R , R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R , R , and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2-pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, a 3-chloro- 5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a
C1-C6 alkyl group, R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Rlb is a C1-C6 alkyl group, R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, and R3b is a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a
C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a
C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a pentafluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a heptafluoropropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6 is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more
halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R is -
ORlib .
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a C1-C6 alkoxy group having one ore more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a trifluoromethoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is - S (0)mRllb;
An amide compound of the formula (IB,) wherein R6b is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a
trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a cyano group or a nitro group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is -
SF5;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R is a
C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine
atoms, or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a pentafluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a
heptafluoropropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is -
ORllb;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C6 alkoxy group having one ore more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is - S(0)mRllb;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine
atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7 is a cyano group or a nitro group;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7 is a
bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is -
SF5;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R7b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms,
a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein R6b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein m is 0;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein m is 1;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein m is 2;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein n is 0;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein n is 1;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein n is 2;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - or a sulfur atom , R 8b is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2b is
" r A3b is =CR10b-, R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom, Rlb is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6b is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group
having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- or a sulfur atom, R8 is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2b is =CR9b-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, A3b is a nitrogen atom, Rlb is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, R2 , Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6b is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is - NR8b- , R8b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2b is =CR9b-, A3b is =CR10b-, R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom, Rlb is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2b, R4b, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a
heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom, A2b is =CR9b-, A3b is =CR10b-, R9b and R10b are a hydrogen atom, Rlb is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group or a 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2b, Rb, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, R6b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is -
NR - , R is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2b is =CR9b-, R9b is a hydrogen atom, A3 is a nitrogen atom, Rlb is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, R6b is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (IB) wherein Alb is a sulfur atom, A2b is =CR9 -, R9b is a hydrogen atom, A3b is a nitrogen atom, Rlb is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, or a 2, 2, 2-trifluoroethyl group, R2b, R4b, and R5b are a hydrogen atom, R3b is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine
atom or a bromine atom, R is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7b is a hydrogen atom;
[0138]
And examples of Compound (6) include the following compounds:
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is
=CH-;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A3 is
=CH-;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A3 is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is
=CH-, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is
=CH-, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is =CH-, A3 is =CR10-, and R10 is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a
C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more atoms or groups selected from Group X;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more
halogen atoms, -OR11, -NR11R12, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom, R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R is a trifluoromethoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4,
and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, an iodine atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a methyl group, and R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more
halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is an ethyl group, and R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is
a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a chlorine atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R1 is a propyl group, and R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mR13-, -NR1:LR12, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRi:L, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mR , or a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more halogen atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is - OR11, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is - S(0)mRi:L, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRi:L, or a halogen atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl
group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a cyclopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a methoxymethyl group, or an ethoxymethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein R8 is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is =CH-, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a hydrogen atom, R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R1 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a hydrogen atom or a halogen atom, R3 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom, and R6 and R7 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mR1:L, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A is =CH-, A3 is a nitrogen atom, R8 is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group or propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, R6 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7 is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (6) wherein A2 is =CH-, A3 is a nitrogen atom or =CR10-, R10 is a hydrogen atom, R8 is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom, R1 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, or propyl group, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7 is a hydrogen atom.
[0139]
Examples of Compound (C) include
compounds :
[0140]
An amide compound of the formula ( 10)
wherein, V2, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, A2 and A3 are as defined above (referred to as Compound ( 10) ) ;
[0141]
An amide compound of the formula (M25) :
wherein, V2, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2 and A3 are as defined above (referred to as Compound (M25) ) ;
[0142]
An amide compound of the formula (M26) :
wherein, V2, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A2 and A3 are as defined
above (referred to as Compound (M26) ) ;
[0143]
A compound of the formula (1C) :
wherein,
represents a fluorine atom or a chlorine atom;
represents -NR8c-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom;
A2c represents a nitrogen atom or =CR9c-;
A3c represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10c-;
R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllc, S(0)mRllc, -SF5, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom: provided that at least one of R2c, R3c, and
R5c represent a hydrogen atom;
R4c represents a hydrogen atom;
R6c represents a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or -SF5;
R7c represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllc, -S (0) mRllc, -SF5, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R8c represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group, a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
R9c and R10c are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally
having one or more halogen atoms, -0Rllc, -S(0)mRllc, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
Rllc and R12c are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom; and m represents 0, 1, or 2;
provided that: in -S(0)mRllc, when m is 1 or 2, Rllc is not a hydrogen atom; and when Alc is -NR8c-, and A2c and A3c are a methine group, R8c is a hydrogen atom or a methyl group (hereinafter, referred to as Compound (1C));
[0144]
And examples of Compound (1C) include the following compounds :
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Xc is a fluorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Xc is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is -
NR8c-;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is -
NR8c-, and R8c is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is -
NR8c-, and R8c is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is an ethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a propyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is -
NR8c-, and R8c is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a methoxymethyl group or an ethoxymethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8 is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a
cyclopentyl group, or a cyclohexyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, and R8c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is an oxygen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is a sulfur atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is -
NR8c- or a sulfur atom, and R8c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, and R8c is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is =CRc-, and A3c is =CR10c-;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, and R9c and R10c are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, and R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is a nitrogen atom, and A3c is =CR10c-;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is
=CR9c-, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is =CR9c-, Rc is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is
=CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A2c is a nitrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, A2c is =CR9c-, and A3c is =CR10c-;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, and R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is an oxygen atom, A2c is =CR9c-, and A3c is =CR10c-;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is a sulfur atom, A2c is =CR9c-, and A3c is =CR10c-;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is a sulfur atom, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, and R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, A2c is =CR9c-, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, Ac is =CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A c is an oxygen atom, A2c is =CR9c-, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is a sulfur atom, A2c is =CR9c-, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is a sulfur atom, A2c is =CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, R8c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group or an isopropyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, and R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, R8c is a methyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, and R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, R8c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group or an isopropyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, R8c is a methyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, and A3c is a nitrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Rc, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently -ORllc or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently - S(0)mRllc or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently a cyano group, a nitro group, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and
R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, or a 3-chloro- 5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and Rc are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 2-pyrimidyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms ;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and
R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and
R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a methyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and
R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is an ethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a propyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is an isopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a pentafluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a heptafluoropropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a heptafluoroisopropyl
group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a fluorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is -SF5;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c, R3c, and R5c are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C6 chain
hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R2c and
R5c are a hydrogen atom, and R3c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R c is a trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a pentafluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a heptafluoropropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is -
SF5;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a
C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a
C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a
C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a
trifluoromethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a pentafluoroethyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a heptafluoropropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is -
ORllc;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a C1-C6 alkoxy group having one ore more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethoxy group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is -
S(0)mRllc;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a cyano group or a nitro group;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a
chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a chlorine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a bromine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is -
SF5;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a
C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R7c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a
C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein m is 0 An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein m is 1 An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein m is 2 An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, R8c is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom, R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, R3c is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6c is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7c is a hydrogen
atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c- or a sulfur atom, R8c is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, Rc is a hydrogen atom, A3c is a nitrogen atom, R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, R3c is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6c is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is - NR8c-, R8c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom, R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, R3c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein Alc is a sulfur atom, A2c is =CR9c-, A3c is =CR10c-, R9c and R10c are a hydrogen atom, R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, R3c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula wherein Alc is -NR8c-, R8c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2c is =CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, A3c is a nitrogen atom, R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, R3c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7c is a hydrogen atom;
An amide compound of the formula (1C) wherein A ° is a sulfur atom, A2c is =CR9c-, R9c is a hydrogen atom, A3c is a nitrogen atom, R2c and R5c are a hydrogen atom, R3c is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, R6c is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7c is a hydrogen atom.
[0145]
Examples of Compound (24) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (ID) :
wherein :
Ald represents -NR8d-, an oxygen atom, or a sulfur atom;
A2d represents a nitrogen atom or =CRd-;
A3d represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10d-;
R2d, R3d, Rd, and R5d are same ore different and
represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlld, -S(0)mRlld, -SF5, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom: provided that at least two of R2d, R3d, R4d, and R5d represent a hydrogen atom;
R6 represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORll , -S(0)mRlld, -SF5, a cyano group, a nitro group, or a halogen atom;
R7d represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group
optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -0Rlld, -S(0)mRlld, -SF5, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R8d represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group, a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
R9d and R10d are same ore different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR11, -S(0)mRn, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
Rll and R12d are same ore different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom; and m represents 0, 1, or 2 :
provided that in -S(0)mRlld, Rlld is not a hydrogen atom (hereinafter, referred to as Compound (ID) ) ;
[0146]
And examples of Compound (ID) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-; A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a C1-C6 alkyl' group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8 -, and R8d is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- , and R8d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- , and R8d is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6
alkoxy group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a methoxymethyl group or an ethoxymethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R8d is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a cyclopentyl group, or a cyclohexyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, and R is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is an oxygen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Al is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, and R8d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, and R8d is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is =CRd-, and A3d is =CR10d-;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A is =CR -, A3d is =CR10d-, and R9d and R10d are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is =CR9d-,
, 3d is =CR10d-, and R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is a nitrogen atom, and A3d is =CR10d-;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is =CR9d-, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is =CR9d-,
R9d is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a hydrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A2d is a nitrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- , A2d is =CR9d-, and A3d is =CR10d-;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, A2d is =CR9d-, A3d is =CR10d-, and R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is an oxygen atom, A2d is =CR9d-, and A3d is =CR10d-;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is a sulfur atom, A2d is =CR9d-, and A3d is =CR10d-;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein A is a sulfur atom, A2d is =CR9d-, A3d is =CR10d-, and R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, A2d is =CR9d-, and A3 is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Al is -NR8d-, A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a hydrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is an oxygen atom, A is =CR -, and A is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is a sulfur atom, A2d is =CR9d-, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Al is a sulfur atom, A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a hydrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, R8d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group or an isopropyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, A3d is =CR10d-, and R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, R8d is a methyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, A3d is =CR10d-, and R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, R8d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a
hydrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, R8d is a methyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a hydrogen atom, and A3d is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, Rd, and R5d are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, R4d, and R5d are same or different and are independently a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, Rd, and R5d are same or different and are independently -ORlld or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, Rd, and R5d are same or different and are independently S(0)mRlld or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, Rd,
and R are same or different and are independently a cyano group, a nitro group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, R4d, and R5d are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R3d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, or a 3-chloro- 5-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, Rd, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 2-pyrimidyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, Rd, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R , R , and R are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, Rd, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ra, R4a, and are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R , R4a, and are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula ID) wherein R^a, Rqa, and are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R , R¾a, and are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R , R , and are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R , R , and are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R , R , and R are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, Rd, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, Rd, and Rd are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R^a, Rja, R4a, and R5d are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3
alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R2d, Rd, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, and R3d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more
halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6 is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl
groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is -ORlld;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C6 alkoxy group having one ore more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is S(0)mRlld;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a cyano group or a nitro group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a
trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R is a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is -ORlld;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C6 alkoxy group having one ore more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is S(0)mRlld;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms,
or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a cyano group or a nitro group;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R7d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein R6d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a
trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein m is 0;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein m is 1;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein m is 2;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, R8d is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, A3d is =CR10d-, R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom, R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, R3d is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- or a sulfur atom, R8d is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a hydrogen atom, A3d is a nitrogen atom, R2d, R4d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, R3d is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6d is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a Cl- C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a
C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d-, R8d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, A3d is =CR10d-, R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom, R2d, R4 , and R5d are a hydrogen atom, R3d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is a sulfur atom, A2d is =CR9d-, A3 is =CR10d-, R9d and R10d are a hydrogen atom, R , R , and R are a hydrogen atom, R is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine
atom, or a bromine atom, R6d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is -NR8d- , R8d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2d is =CR9d-, R d is a hydrogen atom, A3d is a nitrogen atom, R2d, R d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, R3d is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (ID) wherein Ald is a sulfur atom, A2d is =CR9d-, R9d is a hydrogen atom, A3d is a nitrogen atom, R2d, R d, and R5d are a hydrogen atom, R3d is
a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6d is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom, and R7d is a hydrogen atom [0147]
Examples of Compound (21) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (IE) :
wherein:
Xe represents a fluorine atom or a chlorine atom;
Ale represents -NR8e- , an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom;
A2e represents a nitrogen atom or =CR9e-;
A3e represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10e-;
R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally
having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlle, S(0)mRlle, -SF5, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom: provided that at least one of R2e, R3e, and R5e represent a hydrogen atom;
R4e represents a hydrogen atom;
R6e represents a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or -SF5;
R7e represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlle, S(0)mRlle, -SF5, a cyano group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R8e represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group, a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
R and R are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlle, -S(0)mRlle, a cyano group, a nitro group, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
Rlle and R12e are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom; and m represents 0, 1, or 2 :
provided that; in -S(0)mRlle, when m is 1 or 2, Rlle is not a hydrogen atom; when Ale is an oxygen atom, and A2e and A3e are a methine group, one of R2e, R3e, and R5e are a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORlle, -S(0)mRlle, a cyano group, a nitro group, or a halogen atom, and two others are a hydrogen atom; and when Ale is -NR8e-, and A2e is a methine group, R8e is a methyl group (hereinafter, referred to as Compound ( IE ) ) ;
[0148]
Examples of Compound (IE) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Xe is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Xe is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-; A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- , and R8e is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- , and R8e is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- , and R8e is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- , and R8e is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group having one C1-C6 alkoxy group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a methoxymethyl group or an ethoxymethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a C3-C6 alicyclic hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, and R8e is a cyclopropyl group, a cyclobutyl group, a cyclopentyl group, or a cyclohexyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- , and R8e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is an oxygen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, and R8e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or
a sulfur atom, and R8e is a methoxymethyl group, an ethoxymethyl group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is =CRe-, and A3e is =CR10e-;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is =CR9e-,
A3e is =CR10e-, and R9e and R10e are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, and R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is a nitrogen atom, and A3e is =CR10e-;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein A2e is a nitrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is =CR10e-;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, and R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein is an oxygen atom, A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is =CR10e-;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom, A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is =CR10e-;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, and R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- ,
A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is an oxygen atom, A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom, A2e is =CR9e-, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom, A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, R8e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, and R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, R8e is a methyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is
=CR10e-, and R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, R8e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, R8e is a methyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, and A3e is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and are independently a phenyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 5- membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and are independently -0Rlle or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R , R , and R are same or different and are independently -S(0)mRlle or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and are independently a cyano group, a nitro group, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2-pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, or a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a 2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a 2-pyrimidyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a 3-chloro-5-trifluoromethyl-2- pyridyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are
a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C6 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a- hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e, R3e, and R5e are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a 6-membered heterocyclic group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or C1-C3 alkyl groups optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a 2-pyridyl group, a 2- pyrimidyl group, a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, a 3-chloro-5- trifluoromethyl-2-pyridyl group, a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, and R3e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R7e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a
heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkoxy group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein m is 0;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein m is 1;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein m is 2;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, R8e is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom, R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6e is a Cl- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3
alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e- or a sulfur atom, R8e is a C1-C6 alkyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, A3e is a nitrogen atom, R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms or a halogen atom, R6e is a Cl- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-, R8e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom, R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group,
a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom, A2e is =CR9e-, A3e is =CR10e-, R9e and R10e are a hydrogen atom, R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is -NR8e-,
R8e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group, A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, A3e is a nitrogen atom, R2e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group,
a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7e is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein Ale is a sulfur atom, A2e is =CR9e-, R9e is a hydrogen atom, A3e is a nitrogen atom, R2e, R4e and R5e are a hydrogen atom, R3e is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom, R6e is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7e is a hydrogen atom.
[0149]
Examples of Compound (F) include the following compounds :
[0150]
A compound of the formula (M21) :
wherein, R6, R7, R8 and A2 are as defined above (referred to as Compound ( 21) ) ;
[0151]
A compound of the formula (IF) :
wherein :
A2f represents a nitrogen atom or =CR9f-;
A3f represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10f-;
R6f represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllf, S(0)mRllf, -SF5, or a halogen atom;
R7f represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllf, S(0)mRllf, -SF5, hydrogen atom, or a halogen atom;
R8f represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
R9f and R10f are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
Rllf and R12f are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
m represents 0, 1, or 2:
provided that in -S(0)mRllf, when m is 1 or 2, Rllf is not a hydrogen atom (hereinafter, referred to as Compound
(IF) ) ;
[0152]
And examples of Compound (IF) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, and A3f is =CR10f-;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is a nitrogen atom, and A3f is =CR10f-;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, and A3f is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is a nitrogen atom, and A3f is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, and A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-,
R9f is a hydrogen atom, and A3f is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a C1-C3
alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R6f is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R7f is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R8f is a C1-C3
alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R8f is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R8f is a propyl group;
p
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein R8f is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a C2- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a C2- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen
atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a Cl- C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group or an iodine atom, R is a hydrogen atom, and R is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom: provided that when R6f is an iodine atom, R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-,
R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is an iodine atom, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, R9f is a hydrogen atom, A3f is a nitrogen atom, R6f is an iodine atom, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a C2- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-,
A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a C2- C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-,
A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a Cl- C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-, A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A is =CR -, A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7f is a hydrogen atom, and R8f is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (IF) wherein A2f is =CR9f-,
A3f is =CR10f-, R9f and R10f are a hydrogen atom, R6f is -SF5, R is a hydrogen atom, and R is a methyl group;
[0153]
And examples of Compound (M21) include the following compounds:
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-; A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is nitrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or hydrogen;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R8 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or hydrogen;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R8 is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R8 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R6 is a bromine atom or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein R6 is a
trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms ;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6
is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, or a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group or pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (M21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 21) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group.
[0154]
Examples of Compound (G) include the following compounds :
[0155]
A compound of the formula (M20) :
wherein, Xg, R6, R7, R8 and A2 are as defined above (referred to as Compound ( 20) ) ;
[0156]
A compound of the formula (1G) :
wherein :
X9 represents a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A2g represents a nitrogen atom or =CR9g-;
A3g represents a nitrogen atom or =CR10g-;
R6g represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllg, S(0)mRllg, -SF5, or a halogen atom;
R7g represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllg, S(0)mRllg, -SF5, or a halogen atom;
R8g represents a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group
optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
R9g and R10g are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
Rllg and R129 are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
m represents 0, 1, or 2 :
provided that in -S(0)mR119, when m is 1 or 2, Rllg is not a hydrogen atom (hereinafter, referred to as Compound (1G) ) ;
[0157]
And examples of Compound (1G) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is =CR9g-, and A3g is =CR10g-;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is a
nitrogen atom, and AJg is =CRiUg-;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is =CR9g-, and A3g is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is a nitrogen atom, and A3g is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g-, and R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, and A3g is a nitrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl
group, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R6g is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R7g is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein R8g is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CRg-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms
or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CRg-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, or an iodine atom, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom: provided that when R6g is an iodine atom, R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, Rg is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a
trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R 9 is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CRg-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is an iodine atom, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, R9g is a hydrogen atom, A3g is a nitrogen atom, R6g is an iodine atom, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g-, R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a
chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g- Rg and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a C2-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g- R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group having one or more fluorine atoms or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group having one or more fluorine atoms, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a C1-C3 alkyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g- R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g- R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g-
R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CRg-, A3g is =CR10g- R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom or a bromine atom, A2g is =CR9g-, A3g is =CR10g- R9g and R10g are a hydrogen atom, R6g is -SF5, R7g is a hydrogen atom, and R8g is a methyl group;
[0158]
And examples of Compound (M20) include the following compounds:
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein Xg is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein X9 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein Xg is an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein A2 is =CH-; A compound of the formula (M20) wherein A2 is nitrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is a C1-C6
chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R8 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a bromine atom, or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 alkoxy group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a C1-C6 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, a C1-C6 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, or a C1-C6 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a bromine atom or an iodine atom;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein R6 is a
trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, and R7 is hydrogen;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein X9 is a bromine atom, A2 is =CH-, R6 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group, a difluoromethyl group, a fluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, or a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, or an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a trifluoromethyl group or a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6
is a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula ( 20) wherein A2 is =CH-, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (M20) wherein Xg is a bromine atom, A2 is =CH-, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, a trifluoromethoxy group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is hydrogen, and R8 is a methyl group.
[0159]
Examples of Compound (3), Compound (5), and Compound ( 3) include the following compounds:
A compound of the formula (IH) :
wherein:
Rlh represents a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
R13 represents a hydrogen atom, hydroxy group, or a chlorine atom;
R2h, R3h, Rh, and R5h are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllh, S(0)mRllh, -SF5, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
Rllh and R12h are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom; and n represents 0, 1, or 2 (hereinafter, referred to as
Compound ( 1H) ) ;
[0160]
And examples of Compound (1H) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R13 is a
hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R13 is hydroxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R13 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R13 is a hydrogen atom or hydroxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R3h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R3h, Rh, and R5h are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R3h, R4h, and R5h are same or different and are independently -ORllh or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R3h, R4h, and R5h are same or different and are independently - S(0)mRllh or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R3h, R4h, and R5h are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllh, -
S(0)mRllh or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4 , and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4 , and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h
are a hydrogen atom, and R is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is -ORllh;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is -S(0)mRllh;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4 , and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and Rh are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a
trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or -SF5;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein n is 0;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein n is 1;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein n is 2;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3h a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllh, -S(0)mRllh, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rl is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more
fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl
group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a methyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3h a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllh, -S(0)mRnh, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl
group, R , R , and R are a hydrogen atom, and R is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a methyl group, and R13 is hydroxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a methyl group, and R13 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a methyl group, and R13 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, Rh, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a trifluoromethyl group, and R13 is hydroxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a
trifluoromethyl group, and R13 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a trifluoromethyl group, and R13 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2 , Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a chlorine atom, and R13 is hydroxy group;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a chlorine atom, and R13 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a chlorine atom, and R13 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a bromine atom, and R13 is hydroxy group;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a bromine atom, and R13 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, R3h is a bromine atom, and R13 is a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is an ethyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R3h a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -ORllh, -S(0)mRllh, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, and R3h is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (IH) wherein Rlh is a propyl
group, and R is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, Rh, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and Rh are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a
chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (1H) wherein Rlh is a propyl group, R2h, R4h, and R5h are a hydrogen atom, and R3h is -SF5.
[0161]
Examples of Compound (M22) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (II) :
wherein :
R11 represents a C1-C6 alkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
R21, R31, R41, and R51 are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR111, S(0)mR11:L, -SF5, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
R111 and R121 are same or different and represent independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom; and r represents 1 or 2 (hereinafter, referred to as Compound ( II ) ) ;
[0162]
And examples of Compound (II) include the following compounds :
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more halogen atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R31, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R31, R41, and R51 are same or different and are independently a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R2i, R31, R41, and R51 are same or different and are independently -OR111 or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formulad (II) wherein R21, R31, R41, and R51 are same or different and are independently - S(0)mR11:L or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R , R , R , and R51 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR111, - S(0)mR1:Ll, or a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkyl group having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, or a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51
are a hydrogen atom, and R is a propyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is an isopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a pentafluoroethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a heptafluoropropyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a heptafluoroisopropyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R3i is -OR111;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R2i, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is -S (0) mRl ;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine
atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R3x is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, or a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R , R , and R are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R2i, Ri, and R5i are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R2i, Ri, and R5i are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R2i, R4i, and R5i are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, or a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and RSl
are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a methyl group, an ethyl group, a propyl group, an isopropyl group, a trifluoromethyl group, a pentafluoroethyl group, a heptafluoropropyl group, a heptafluoroisopropyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, or -SF5;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein r is 1;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein r is 2;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R31 a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR111, -S (0) mR11:L, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a
C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a
fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a methyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R31 a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR111, -S(0)mR1:Ll, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a
C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is an ethyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is -SF5;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are same or different and are independently a halogen atom or a hydrogen atom, and R31 a C1-C6 chain hydrocarbon group optionally having one or more halogen atoms, -OR111, -S(0)mRni, a halogen atom, or a hydrogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkoxy group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms ;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a C1-C3 alkylsulfanyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, a C1-C3 alkylsulfinyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms, or a C1-C3 alkylsulfonyl group optionally having one or more fluorine atoms;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a halogen atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a methyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is an ethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethyl group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a trifluoromethoxy group;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a fluorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R is a propyl group, R21, R41, and R51 are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a chlorine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl group, R21, R41, and RSl are a hydrogen atom, and R31 is a bromine atom;
A compound of the formula (II) wherein R11 is a propyl
group, R , R , and R are a hydrogen atom, and R 1 is -SF5.
[0163]
Examples of the present compound are shown bellow.
A compound of the formula (A) :
wherein R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19:
[0164]
Table 1
R1 A1 A3 n
Me — NM e— = N- 0
Me — NM e— = N- 1
Me — NM e— = N- 2
E t — NM e— = N- 0
E t — NM e— = N- 1
E t — NM e— = N- 2
P r — NM e— = N- 0
P r — NM e— = N- 1
P r — NM e— = N- 2 i P r — NM e— = N- 0 i P r — NM e— = N- 1 i P r — NM e— = N- 2 t B u — NM e— = N- 0 t B u — NM e— = N- 1 t B u — NM e— = N- 2
CF3 — NM e— = N- 0
CF3 — NM e— = N- 1
CF3 — NM e— = N- 2
CH2C F3 — NM e— = N- 0
CH2CF3 — NM e— = N- 1
— NM e— = N- 2
CH=CH2 — NM e— = N- 0
CH=CHZ — NM e— = N- 1
CH=CH2 — NM e— = N- 2
[0165]
Table 2
[0166]
Table 3
R1 A1 A3 n t B u — NM e— = CH- 0 t B u — NM e— = CH- 1 t B u — NM e— = CH- 2
CF3 — NM e— = CH- 0
CF3 — NM e— = CH- 1
CF3 — NM e— = CH- 2
CH2C F3 — NM e— = CH- 0
CH2C F3 — NM e— = CH- 1
CH2C F 3 — NM e— = CH- 2
CH=CH2 — NM e— = CH- 0
CH=CH2 — NM e— = CH- 1
CH=CH2 — NM e— = CH- 2
CH 2 C H— CH 2 — NM e— = CH- 0
CH2CH = CH — NM e— = CH- 1
CH2CH— CH2 — NM e— = CH- 2
C≡CH — NM e— = CH- 0
C≡CH — NM e— = CH- 1
C≡CH — NM e— = CH- 2
CH2C≡CH — NM e— = CH- 0
CH2C≡CH — NM e— = CH- 1
CH2C≡CH — NM e— = CH- 2
C y P r — NM e— = CH- 0
C y P r — NM e— = CH- 1
C y P r — NM e— = CH- 2
[0167]
Table 4
R 1 A1 A3 n
Me -NMe - = CB r - 0
Me — NM e— = CB r - 1
Me -NMe - = CB r - 2
E t — NM e— = CB r - 0
E t -NMe - = CB r - 1
E t -NMe - = CB r - 2
P r -NMe - = CB r - 0
P r -NMe - = CB r - 1
P r -NMe - = CB r - 2 i P r -NMe - = CB r - 0 i P r -NMe - = CB r - 1 i P r -NMe - = CB r - 2 t B u -NMe - = CB r - 0 t B u -NMe - = CB r - 1 t B u -NMe - = CB r - 2
CF3 -NMe - = CB r - 0
CF3 -NMe - = CB r - 1
CF3 -NMe - = CB r - 2
CH2C F3 -NMe - = CB r - 0
CH2C P 3 -NMe - = CB r - 1
CH2C F g -NMe - = CB r - 2
CH=CH2 -NMe - = CB r - 0
CH=CH2 -NMe - = CB r - 1
CH=CH2 -NMe - = CB r - 2
[0168]
Table 5
R1 A1 A3 n
CH2CH = CH2 — NM e— = CB r - 0
CH2CH=CH2 — NMe - = CB r - 1
CHgCH = CH2 — NMe - = CB r - 2
C≡CH -NMe - = CB r - 0
C≡CH -NMe - = CB r - 1
C≡CH -NMe - = CB r - 2
CH2C≡CH -NMe - = CB r - 0
CH2C≡CH — NMe— = CB r - 1
CH2C≡CH -NMe - = CB r - 2
C y P r -NMe - = CB r - 0
C y P r -NMe - = CB r - 1
C y P r -NMe - = CB r - 2
Me -N (CHjOMe) - = N- 0
Me -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
Me -N (CHjOMe) - = N- 2
E t -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
E t -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
E t -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
P r -N (CHjOMe) - = N- 1
P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2 i P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0 i P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1 i P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
[0169]
Table 6
R 1 A1 A3 n t B u -N (CHjOMe) - = N- 0 t B u -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1 t B u — N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
CF3 -N (CHjOMe) - = N- 1
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
-N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
— N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
C O 2 C -F -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
CH2CH = CHg -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
CH2CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
CH2CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
C≡CH — N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
CH2C≡CH — N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
CH2C≡CH — N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
CH2C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 0
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 1
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = N- 2
[0170]
Table 7
R 1 A1 A3 n
Me -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
Me — N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
Me -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
E t — N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
E t -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
E t -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
P r -N (CHjOMe) - = CH- 1
P r — N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2 i P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0 i P r -N (CHjOMe) - = CH- 1 i P r -N (CHjOMe) - = CH- 2 t B u -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0 t B u -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1 t B u -N (CHjOMe) - = CH- 2
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
CHjC F -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
C H C F -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
C H C F -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
CH=CH2 — N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
[0171]
Table 8
R 1 A 1 A3 n
CH2CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
CH2CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
CH2CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
CH2C≡CH — N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
CH2C≡CH — N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
CH2C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 0
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 1
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CH- 2
Me -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
Me -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
Me -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
E t — N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
E t — N (CH2OMe) - = C B r - 1
E t -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
P r — N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2 i P r — N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0 i P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1 i P r — N (CH2OMe) - = C B r - 2
[0172]
Table 9
R1 A1 A3 n t B u -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0 t B u -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1 t B u -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB t - 1
CF3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
CH2C F 3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
CH C F 3 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
CHgC F g -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
CH2CH = CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
C H 2 C H = C H 2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
CH2CH=CH2 -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
C≡CH -N (CHjOMe) - = CB r - 1
C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
CH2C≡CH -N (CHjOMe) - = CB r - 0
CH2C≡CH -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
CH2C≡CH -N (CHjOMe) - = CB r - 2
CyP r -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 0
CyP r -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 1
C y P r -N (CH2OMe) - = CB r - 2
[0173]
Table 10
R 1 A1 A3 n.
Me O = N- 0
Me O = N- 1
Me O = N- 2
E t O = N- 0
E t O = N- 1
E t O = N- 2
P r O = N- 0
P r O = N- 1
P r O = N- 2 i P r O = N- 0 i P r O = N- 1 i P r O = N- 2 t B u O = N- 0 t B u O = N- 1 t B u O = N- 2
CF3 O = N- 0
CF3 O = N- 1
CF3 O = N- 2
CH2C F3 O = N- 0
CH2C F 3 O = N- 1
CH2C F 3 O = N- 2
CH=CH2 O = N- 0
CH=CH2 O = N- 1
CH=CH2 O = N- 2
[0174]
Table 11
R1 A1 A3 n
CH2C H = CH2 O = N- 0
CH2CH = CH2 O = N- 1 o = N- 2
C≡CH o = N- 0
C≡CH o = N- 1
C≡CH o = N- 2
CH2C≡CH o = N- 0
CH2C≡CH o = N- 1
CH2C≡CH o = N- 2
C y P r o = N- 0
C y P r o = N- 1
C y P r o = N- 2
Me o = CH- 0
Me o = CH- 1
Me o = CH- 2
E t o = CH- 0
E t o = CH- 1
E t o = CH- 2
P r o = CH- 0
P r o = CH- 1
P r o = CH- 2 i P r o = CH- 0 i P r o = CH- 1 i P r o = CH- 2
[0175]
Table 12
[0176]
Table 13
[0177] Table 14
R 1 A1 A3 n
CH2CH = CH O = CB r - 0
CH2CH = CH2 O = CB r - 1
CH2CH = CH2 o = CB r - 2
C≡CH o = CB r - 0
C≡CH o = CB r - 1
C≡CH o = CB r - 2
CH2C≡CH o = CB r - 0
CH2C≡CH o = CB r - 1
CHjC≡CH o = CB r - 2
Cy P r o = CB r - 0
C y P r o = CB r - 1
Cy P r o = CB r - 2
[0178]
Table 15
R1 A1 A3 n.
Me S = N- 0
Me s = N- 1
Me s = N- 2
E t s = N- 0
E t s = N- 1
E t s = N- 2
P r s = N- 0
P r s = N- 1
P r s = N- 2 i P r s = N- 0 i P r s = N- 1 i P r s = N- 2 t B u s = N- 0 t B u s = N- 1 t B u s = N- 2
CF3 s = N- 0
CF3 s = N- 1
CF3 s = N- 2
CH2C F3 s = N- 0
C ΡΪ 2 C F 3 s = N- 1
CH2C P 3 s = N- 2
CH=CH2 s = N- 0
CH=CH2 s = N- 1
CH=CH2 s = N- 2
[0179]
Table 16
R1 A1 A3 n
CH2CH = CH2 S = N- 0
CH2 H = CH2 s = N- 1
CHgCH = CH2 s = N- 2
C≡CH s = N- 0
C≡CH s = N- 1
C≡CH s = N- 2
CH2C≡CH s = N- 0
CH2C≡CH s = N- 1
CH2C≡CH s = N- 2
C y P r s = N- 0
C y P r s = N- 1
C y P r s = N- 2
Me s = CH- 0
Me s = CH- 1
Me s = CH- 2
E t s = CH- 0
E t s = CH- 1
E t s = CH- 2
P r s = CH- 0
P r s = CH- 1
P r s = CH- 2 i P r s = CH- 0 i P r s = CH- 1 i P r s = CH- 2
[0180]
Table 17
R1 A1 A3 n t B u S = CH- 0 t B u S = CH- 1 t B u s = CH- 2
CF3 s = CH- 0
CF3 s = CH- 1
CF3 s = CH- 2
CH2C F3 s = CH- 0
CH2C F 3 s = CH- 1
C Hg C F 3 s = CH- 2
CH=CH2 s = CH- 0
CH=CH2 s = CH- 1
CH=CH2 s = CH- 2
CH 2 C H = C O 2 s = CH- 0
CHgCH = CH2 s = CH- 1
CH2CH = CH2 s = CH- 2
C≡CH s = CH- 0
C≡CH s = CH- 1
C≡CH s = CH- 2
CH2C≡CH s = CH- 0
CH2C≡CH s = CH- 1
CH2C≡CH s = CH- 2
C y P r s = CH- 0
C y P r s = CH- 1
Cy P r s = CH- 2
[0181]
Table 18
Rl A1 A3 n
Me S = CB r - 0
Me S = CB r - 1
Me S = CB r - 2
E t S = CB r - 0
E t S = CB r - 1
E t s = CB r - 2
P r s = CB r - 0
P r s = CB r - 1
P r s = CB r - 2 i P r s = CB r - 0 i P r s = CB r - 1 i P r s = CB r - 2 t B u s = CB r - 0 t B u s = CB r - 1 t B u s = CB r - 2
CF3 s = CB r - 0
CF3 s = CB r - 1
CF3 s = CB r - 2
C H C F 3 s = CB r - 0
CH2C P 3 s = CB r - 1
CH2C F 3 s = CB r - 2
CH=CH2 s = CB r - 0
CH=CH2 s = CB r - 1
CH=CH2 s = CB r - 2
[0182]
Table 19
R 1 A1 A3 n
S = CB r - 0
CH2CH=CH s = CB r - 1
CHjCH = CH2 s = CB r - 2
C≡CH s = CB r - 0
C≡CH s = CB r - 1
C≡CH s = CB r - 2
CH2C≡CH s = CB r - 0
CH2C≡CH s = CB r - 1
CH2C≡CH s = CB r - 2
C y P r s = CB r - 0
C y P r s = CB r - 1
Cy P r s = CB r - 2
[0183]
In the above Tables 1 to 19, Me represents a methyl group, Et represents an ethyl group, Pr represents a propyl group, iPr represents an isopropyl group, tBu represents a tert-butyl group, and CyPr represents a cyclopropyl group.
[0184]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a fluorine atom, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0185]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0186]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5
are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a fluorine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0187]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R4 are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a fluorine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0188]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a chlorine atom, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0189]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0190]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a chlorine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0191]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R4 are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a chlorine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0192]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a methyl group, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3,
and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0193]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0194]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a methyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0195]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R4 are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a methyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0196]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a trifluoromethyl group, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0197]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0198]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a trifluoromethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0199]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R4 are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a trifluoromethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0200]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a bromine atom, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0201]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0202]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a bromine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0203]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3 and R4 are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a bromine atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0204]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19 [0205]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0206]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a pentafluoroethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0207]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3 and R4 are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a pentafluoroethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0208]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0209]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0210]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R4 is a trifluoromethoxy group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0211]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R3, and R4
are a hydrogen atom, R5 is a trifluoromethoxy group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0212]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a 2-pyridyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0213]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a 3-chloro-2-pyridyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0214]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a 2-pyrimidyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0215]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is -SF5, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0216]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a hydrogen atom, R7 is a trifluoromethyl group, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0217]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0218]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a heptafluoroisopropyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0219]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0220]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH- , R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0221]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0222]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4 , and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0223]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0224]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0225]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0226]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a difluoromethyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a
combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0227]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0228]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0229]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0230]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH- , R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0231]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH- , R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1,
A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0232]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0233]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0234]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0235]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0236]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0237]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0238]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0239]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH- , R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0240]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0241]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0242]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfanyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0243]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0244]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0245]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is
a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0246]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0247]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0248]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH- , R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0249]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0250]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfinyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0251]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0252]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0253]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0254]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH- , R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0255]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0256]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0257]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0258]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is a trifluoromethylsulfonyl group, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0259]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0260]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0261]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0262]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0263]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0264]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0265]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0266]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is a bromine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0267]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0268]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0269]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0270]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0271]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0272]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0273]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0274]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is an iodine atom, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0275]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R3, R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0276]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a fluorine atom, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0277]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a chlorine atom, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0278]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a bromine atom, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0279]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a methyl group, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0280]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethyl group, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0281]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a pentafluoroethyl group, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0282]
A compound of the formula (A) wherein A2 is =CH-, R2,
R4, and R5 are a hydrogen atom, R3 is a trifluoromethoxy group, R6 is -SF5, R7 is a hydrogen atom, and R1, A1, A3, and n are a combination shown in Tables 1-19.
[0283]
Examples of pests against which the present compound has an activity include noxious arthropods such as noxious insects and noxious acarines, and nematodes. In particular, examples of the pests include the following.
[0284]
Hemiptera: Delphacidae such as Laodelphax striatellus,
Nilaparvata lugens, and Sogatella furcifera;
Deltocephalidae such as Nephotettix cincticeps, Nephotettix virescens, and Empoasca onukii; Aphididae such as Aphis gossypii, Myzus persicae, Brevicoryne brassicae, Aphis spiraecola, Macrosiphum euphorbiae, Aulacorthum solani, Rhopalosiphum padi, Toxoptera citricidus, and Hyalopterus pruni; Pentatomidae such as Nezara antennata, Riptortus clavetus, Leptocorisa chinensis, Eysarcoris parvus, and Halyomorpha mista; Aleyrodidae such as Trialeurodes vaporariorum, Bemisia tabaci, Dialeurodes citri, and Aleurocanthus spiniferus; Coccidae such as Aonidiella aurantii, Comstockaspis perniciosa, Unaspis citri, Ceroplastes rubens, Icerya purchasi, Planococcus kraunhiae, Pseudococcus longispinis, and Pseudaulacaspis pentagona; Tingidae; Cimices such as Cimex lectularius; and Psyllidae.
[0285]
Lepidoptera: Pyralidae such as Chilo suppressalis , Tryporyza incertulas, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis, Notarcha derogata, Plodia interpunctella, Ostrinia furnacalis, Hellula undalis, and Pediasia teterrellus; Noctuidae such as Spodoptera litura, Spodoptera exigua, Pseudaletia separata, Mamestra brassicae, Agrotis ipsilon, Plusia nigrisigna, Thoricoplusia spp., Heliothis spp . , and Helicoverpa spp.; Pieridae such as Pieris rapae; Tortricidae such as Adoxophyes spp., Grapholita molesta,
Leguminivora glycinivorella, Matsumuraeses azukivora, Adoxophyes orana fasciata, Adoxophyes honmai . , Homona magnanima, Archips fuscocupreanus, and Cydia pomonella; Gracillariidae such as Caloptilia theivora and Phyllonorycter ringoneella; Carposinidae such as Carposina niponensis; Lyonetiidae such as Lyonetia spp . ; Lymantriidae such as Lymantria spp. and Euproctis spp; Yponomeutidae such as Plutella xylostella; Gelechiidae such as Pectinophora gossypiella and Phthorimaea operculella; Arctiidae such as Hyphantria cunea; and Tineidae such as Tinea translucens and Tineola bisselliella .
[0286]
Thysanoptera : Thripidae such as Frankliniella occidentalis , Thrips palmi, Scirtothrips dorsalis, Thrips tabaci, and Frankliniella intonsa.
[0287]
Diptera : Culices such as Culex pipiens pallens, Culex tritaeniorhynchus, and Culex qu nquefasciatus ; Aedes spp. such as Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus; Anopheles spp. such as Anopheles sinensis; Chironomidae; Muscidae such as Musca domestica and uscina stabulans; Calliphoridae; Sarcophagidae; Fanniidae; Anthomyiidae such as Delia platura and Delia antiqua; Agromyzidae such as Agromyza oryzae, Hydrellia griseola, Liriomyza sativae, Liriomyza trifolii, and Chromatomyia horticol; Chloropidae such as
Chlorops oryzae; Tephritidae such as Dacus cucurbitae and Ceratitis capitata; Drosophilidae ; Phoridae such as Megaselia spiracularis ; Psychodidae such as Clogmia albipunctata; Simuliidae; Tabanidae such as Tabanus trigonus; and stable flies.
[0288]
Coleoptera: Diabrotica spp. such as Diabrotica virgifera virgifera and Diabrotica undecimpunctata howardi; Scarabaeidae such as Anomala cuprea, Anomala rufocuprea, and Popillia japonica; weevils such as Sitophilus zeamais, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus, Callosobruchuys chienensis, Echinocnemus squameus, Anthonomus grandis, and Sphenophorus venatus; Tenebrionidae such as Tenebrio molitor and Tribolium castaneum; Chrysomelidae such as Oulema oryzae, Aulacophora femoralis, Phyllotreta striolata, and Leptinotarsa decemlineata; Dermestidae such as Anthrenus verbasci and Dermestes maculates; Anobiidae such as Lasioderma serricorne; Epilachna such as Epilachna vigintioctopunctata; Scolytidae such as Lyctus brunneus and Tomicus piniperda; Bostrychidae; Ptinidae; Cerambycidae such as Anoplophora malasiaca; Agriotes spp., and Paederus fuscipes .
[0289]
Orthoptera: Locusta migratoria, Gryllotalpa africana, Oxya yezoensis, Oxya japonica, and Gryllidae.
[0290]
Hymenoptera : Formicidae such as onomorium pharaosis, Formica fusca japonica, Ochetellus glaber, Pristomyrmex pungens, Pheidole noda, Acromyrmex spp . , and Solenopsis spp.; Vespidae; Betylidae; and Tenthredinidae such as Athalia rosae and Athalia japonica.
[0291]
Nematoda: Aphelenchoides besseyi, Nothotylenchus acris, Meloidogyne incognita, Meloidogyne hapla, Meloidogyne javanica, Heterodera glycines, Globodera rostochiensis , Pratylenchus coffeae, and Pratylenchus neglectus.
[0292]
Blattodea: Blattella germanica, Periplaneta fuliginosa, Periplaneta americana, Periplaneta brunnea, and Blatta orientalis.
[0293]
Acarina: Tetranychidae such as Tetranychus urticae, Tetranychus kanzawai, Panonychus citri, Panonychus ulmi, and Oligonychus spp.; Eriophyidae such as Aculops pelekassi, Phyllocoptruta citri, Aculops lycopersici, Calacarus carinatus, Acaphylla theavagrans, Eriophyes chibaensis, and Aculus schlechtendali; Tarsonemidae such as
Polyphagotarsonemus latus; Tenuipalpidae such as Brevipalpus phoenicis; Tuckerellidae; Ixodidae such as Haemaphysalis longxcornis, Haemaphysalis flava, Dermacentor
taiwanicus, Ixodes ovatus, Ixodes persulcatus, Ixodes scapularis, Boophilus microplus, and Rhipicephalus sanguineus; Acaridae such as Tyrophagus putrescentiae and Tyrophagus similis; Pyroglyphidae such as Dermatophagoides farinae and Dermatophagoides ptrenyssnus ; Cheyletidae such as Cheyletus eruditus, Cheyletus malaccensis, and Cheyletus moorei; Dermanyssidae such as Ornithonyssus bacoti, Ornithonyssus sylvairum, and Dermanyssus gallinae; Trombiculidae such as Leptotrombidium akamushi; and Araneae such as Chiracanthium japonicum and Latrodectus hasseltii.
[0294]
The pest controlling agent of the present invention contains the present compound and an inert carrier. Generally, the pest controlling agent of the present invention is a formulation such as an emulsion, an oil solution, a powder, a granule, a wettable powder, a flowable formulation, a microcapsule, an aerosol, a smoking agent, a poison bait, and a resin formulation which are obtained by mixing the present compound and an inert carrier such as a solid carrier, a liquid carrier and a gaseous carrier, and further adding a surfactant and other adjuvant for formulation, if necessary.
The pest controlling agent of the present invention usually contains the present compound in an amount of 0.01 % to 95 % by weight.
[0295]
Examples of the solid carrier to be used for formulation include a fine power and a granule of clays
(such as kaolin clay, diatomite, bentonite, Fubasami clay, and acid clay) , synthetic hydrated silicon oxide, talc, ceramic, other inorganic minerals (such as sericite, quartz, sulfur, activated carbon, calcium carbonate, and hydrated silica), and chemical fertilizers (such as ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate, ammonium nitrate, urea, and ammonium chloride) as well as synthetic resins (such as polypropylene, polyacrylonitrile, polyester resins such as methyl polymethacrylate and polyethylene terephthalate , nylon resins such as nylon-6, nylon-11, and nylon-66, polyamide resins, polyvinyl chloride, polyvinylidene chloride, and vinyl chloride-propylene copolymer) .
[0296]
Examples of the liquid carrier include water, alcohols (such as methanol, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, butanol, hexanol, benzyl alcohol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and phenoxyethanol ) , ketones (such as acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, and cyclohexanone ) , aromatic hydrocarbons (such as toluene, xylene, ethylbenzene, dodecylbenzene, phenylxylylethane, and methylnaphthalene ) , aliphatic hydrocarbons (such as hexane, cyclohexane, kerosine, and light oil), esters (such as ethyl acetate, butyl acetate,
isopropyl mylistate, ethyl oleate, diisopropyl adipate, diisobutyl adipate, and propyleneglycol monomethyl ether acetate) , nitriles (such as acetonitrile and isobutyronitrile) , ethers (such as diisopropyl ether, 1,4- dioxane, ethylene glycol dimethyl ether, diethylene glycol dimethyl ether, diethylene glycol monomethyl ether, propylene glycol monomethyl ether, dipropylene glycol monomethyl ether, and 3-methoxy-3-methyl-l-butanol ) , acid amides (such as N, -dimethylformamide and N,N- dimethylacetamide) , halogenated hydrocarbons (such as dichloromethane, trichloroethane, and tetrachlorocarbon) , sulfoxides (such as dimethylsulfoxide) , propylene carbonate, and vegetable oils (such as soy bean oil and cotton seed oil) .
[0297]
Examples of the gaseous carrier include fluorocarbons , butane gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) , dimethyl ether, and carbon dioxide.
[0298]
Examples of the surfactant include nonionic surfactant such as polyoxyethylene alkyl ether, polyoxyethylene alkylaryl ether, and polyethyleneglycol fatty acid ester; and anionic surfactant such as alkylsulfonic acid salts, alkylbenzenesulfonic acid salts, and alkylsurfic acid salts.
[0299]
Examples of the other adjuvant for formulation include binders, dispersants, colorants and stabilizers, and particularly for example, casein, gelatin, polysaccharides (such as starch, gum arabic, cellulose derivatives, and alginic acid) , lignin derivatives, synthetic water-soluble polymers (such as polyvinyl alcohol, polyvinylpyrrolidone, and polyacrylic acid) , PAP (acidic isopropyl phosphate) , BHT (2, 6-di-t-butyl-4-methylphenol) , and BHA (a mixture of 2-t-butyl-4-methoxyphenol and 3-t-butyl-4-methoxyphenol ) .
[0300]
The method for controlling pests of the present invention is applying an effective amount of the present compound to pests directly and/or habitats of pests (such as plant, soil, indoor, and in-body of animals) . The present compound is usually used as the pest controlling agent of the present invention in the method for controlling pests of the present invention.
[0301]
When the pest controlling agent of the present invention is used for a control of pests in agriculture, the application amount is usually 1 to 10, 000 g as the present compound per 10, 000 m2. When the pest controlling agent of the present invention is a formulation of emulsions, wettable powders or flowables, they are usually applied after a dilution with water to have an active
ingredient concentration of 0.01 to 10, 000 ppm. When the pest controlling agent of the present invention is a formulation of granules or powders, they are usually applied as such.
[0302]
The formulations and the dilute aqueous solutions of the formulation may be sprayed directly to the plant to be protected from pests, or may be applied to the soil to control the pests living in a soil.
[0303]
Furthermore, the resin formulations of sheets or strip form can be applied by a method such as winding around plants, stretching in the vicinity of plants, and laying on the soil surface at the plant bottom.
[0304]
When the pest controlling agent of the present invention is used for a control of pests in indoor, the application amount is usually 0.01 to 1, 000 mg as the present compound per 1 m2 in case of application for plane surface, and 0.01 to 500 mg as the present compound per 1 m3 in case of application for space. When the pest controlling agent of the present invention is a formulation of emulsions, wettable powders or flowables, they are usually applied after a dilution with water to have an active ingredient concentration of 0.1 to 1,000 ppm. When
the pest controlling agent of the present invention is a formulation of oil solutions, aerosols, smoking agents and poison baits, they are usually applied as such.
[0305]
The pest controlling agent of the present invention could be used in farmlands on which "crops" shown below are cultivated .
Agricultural crops: corn, rice, wheat, barley, rye, oat, sorghum, cotton, soybean, peanut, sarrazin, sugar beet, rapeseed, sunflower, sugar cane, and tobacco;
Vegetables: Solanaceae vegetables (such as eggplant, tomato, green pepper, hot pepper, and potato) , Cucurbitaceae vegetables (such as cucumber, pumpkin, zucchini, watermelon, and melon) , Cruciferae vegetables (such as Japanese radish, turnip, horseradish, kohlrabi, Chinese cabbage, cabbage, brown mustard, broccoli, and cauliflower) , Compositae vegetables (such as burdock, garland chrysanthemum, artichoke, and lettuce) , Liliaceae vegetables (such as Welsh onion, onion, garlic, and asparagus), Umbelliferae vegetables (such as carrot, parsley, celery, and parsnip) , Chenopodiaceae vegetables (such as spinach, and Swiss chard) , Labiatae vegetables (such as Japanese basil, mint, and basil), strawberry, sweat potato, yam, and aroid;
Fruit trees: pomaceous fruits (such as apple, common
pear, Japanese pear, Chinese quince, and quince) , stone fleshy fruits (such as peach, plum, nectarine, Japanese plum, cherry, apricot, and prune) , citrus plants (such as Satsuma mandarin, orange, lemon, lime, and grapefruit) , nuts (such as chestnut, walnut, hazel nut, almond, pistachio, cashew nut, and macadamia nut) , berry fruits (such as blueberry, cranberry, blackberry, and raspberry) , grape, persimmon, olive, loquat, banana, coffee, date, coconut palm, and oil palm;
Trees other fruit trees: tea, mulberry, flowering trees (such as azalea, japonica, hydrangea, sasanqua, lllicium anisatum, cherry tree, tulip poplar, crepe myetle, and orange osmanthus), street trees (such as ash tree, birch, dogwood, eucalyptus, ginkgo, lilac, maple tree, oak, poplar, cercis, Chinese sweet gum, plane tree, zelkova, Japanese arborvitae, fir tree, Japanese hemlock, needle juniper, pine, spruce, yew, elm, and horse-chestnut), sweet viburnum, Podocarpus macrophyllus, Japanese cedar, Japanese cypress, croton, spindle tree, and Chainese howthorn.
Lawn: zoysia (such as Japanese lawn grass and mascarene grass), Bermuda grass (such as Cynodon dactylon), bent grass (such as creeping bent grass, Agrostis stolonifera, and Agrostis tenuis) , bluegrass (such as Kentucky bluegrass and rough bluegrass) , fescue (such as tall fescue, chewing fescue, and creeping fescue) , ryegrass
(such as darnel and perennial ryegrass), cocksfoot, and timothy grass;
Others: flowers (such as rose, carnation, chrysanthemum, Eustoma grandiflorum Shinners, gypsophila, gerbera, pot marigold, salvia, petunia, verbena, tulip, aster, gentian, lily, pansy, cyclamen, orchid, lily of the valley, lavender, stock, ornamental kale, primula, poinsttia, gladiolus, cattleya, daisy, cymbidium, and begonia) , biofuel plants (such as Jatropha, curcas, safflower, Camelina alyssum, switchgrass, miscanthus, reed canary grass, Arundo donax, kenaf, cassava, willow, and algae), and foliage plant.
[0306]
The "crops" include genetically modified crops.
[0307]
The pest controlling agent of the present invention can be used as a mixture with or together with other insecticides, acaricides, nematocides, fungicides, plant growth regulators, herbicides, and synergists. Examples of active ingredients of the insecticide, the acaricide, the nematocide, the fungicide, the herbicide, and the synergist are shown below.
[0308]
Active ingredients of insecticides:
(1) Organic phosphorus compounds:
Acephate, Aluminium phosphide, butathiofos, cadusafos, chlorethoxyfos , chlorfenvinphos , chlorpyrifos , chlorpyrifos-methyl, cyanophos : CYAP, DCIP (diazinon, dichlorodiisopropyl ether), dichlofenthion : ECP, dichlorvos: DDVP, dimethoate, dimethylvinphos , disulfoton, EPN, ethion, ethoprophos, etrimfos, fenthion: MPP, fenitrothion : MEP, fosthiazate, formothion, Hydrogen phosphide, isofenphos, isoxathion, malathion, mesulfenfos, methidathion : DMTP, monocrotophos , naled: BRP, oxydeprofos : ESP, parathion, phosalone, phosmet: P P, pirimiphos-methyl, pyridafenthion, quinalphos, phenthoate : PAP, profenofos, propaphos, prothiofos, pyraclorfos, salithion, sulprofos, tebupirimfos , temephos, tetrachlorvinphos , terbufos, thiometon, trichlorphon : DEP, vamidothion, phorate, and cadusafos.
(2) Carbamate compounds:
Alanycarb, bendiocarb, benfuracarb, BPMC, carbaryl, carbofuran, carbosulfan, cloethocarb, ethiofencarb, fenobucarb, fenothiocarb, fenoxycarb, furathiocarb, isoprocarb: MIPC, metolcarb, methomyl, methiocarb, NAC, oxamyl, pirimicarb, propoxur: PHC, XMC, thiodicarb, xylylcarb, and aldicarb.
(3) Pyrethroid compounds:
Acrinathrin, allethrin, benfluthrin, beta-cyfluthrin, bifenthrin, cycloprothrin, cyfluthrin, cyhalothrin,
cypermethrin, deltamethrin, esfenvalerate, ethofenprox, fenpropathrin, fenvalerate, flucythrinate, flufenoprox, flumethrin, fluvalinate, halfenprox, imiprothrin, permethrin, prallethrin, pyrethrins, resmethrin, sigma- cypermethrin, silafluofen, tefluthrin, tralomethrin, transfluthrin, tetramethrin, phenothrin, cyphenothrin, alpha-cypermethrin, zeta-cypermethrin, lambda-cyhalothrin, gamma-cyhalothrin, furamethrin, tau-fluvalinate, metofluthrin, profluthrin, dimefluthrin, 2,3,5,6- tetrafluoro-4- (methoxymethyl ) benzyl (EZ) - (IRS, 3RS; IRS, 3SR) - 2, 2-dimethyl-3-prop-l-enylcyclopropanecarboxylate, 2,3,5,6- tetrafluoro-4-methylbenzyl (EZ) - (IRS, 3RS; IRS, 3SR) -2,2- dimethyl-3-prop-l-enylcyclopropanecarboxylate, and 2,3,5,6- tetrafluoro-4- (methoxymethyl ) benzyl (IRS, 3RS; IRS, 3SR) -2,2- dimethyl-3- ( 2-methyl-l-propenyl ) cyclopropanecarboxylate .
(4) Nereistoxin compounds:
Cartap, bensultap, thiocyclam, monosultap, and bisultap .
(5) Neonicotinoid compounds:
Imidacloprid, nitenpyram, acetamiprid, thiamethoxam, thiacloprid, dinotefuran, and clothianidin .
(6) Benzoylurea compounds:
Chlorfluazuron, bistrifluron, diafenthiuron, diflubenzuron, fluazuron, flucycloxuron, flufenoxuron, hexaflumuron, lufenuron, novaluron, noviflumuron,
teflubenzuron, triflumuron, and triazuron.
(7) Phenylpyrazole compounds:
Acetoprole, ethiprole, fipronil, vaniliprole, pyriprole, and pyrafluprole .
(8) Bt toxines :
Live spores derived from and crystal toxins produced from Bacillus thurxngiesis and a mixture thereof;
(9) Hydrazine compounds:
Chromafenozide, halofenozide, methoxyfenozide , and tebufenozide .
(10) Organic chlorine compounds:
Aaldrin, dieldrin, dienochlor, endosulfan, and methoxychlor .
(11) Other insecticidal active ingredients:
Mmachine oil, nicotine-sulfate; avermectin-B, bromopropylate , buprofezin, chlorphenapyr, cyantraniliprole cyromazine, D-D ( 1 , 3-Dichloropropene ) , emamectin-benzoate, fenazaquin, flupyrazofos , hydroprene, methoprene, indoxacarb, metoxadiazone, milbemycin-A, pymetrozine, pyridalyl, pyriproxyfen, spinosad, sulfluramid, tolfenpyrad triazamate, flubendiamide, lepimectin, arsenic acid, benclothiaz, calcium cyanamide, calcium polysulfide, chlordane, DDT, DSP, flufenerim, flonicamid, flurimfen, formetanate, metarn-ammonium, metam-sodium, Methyl bromide, Potassium oleate, protrifenbute, spiromesifen, sulfoxaflor,
sulfur, metaflumizone, spirotetramat, pyrifluquinazone, spinetoram, chlorantraniliprole , tralopyril, cyantraniliprole, a compound of the following formula (K) :
wherein :
R100 is chlorine, bromine, or a trifluoromethyl group,
R200 is chlorine, bromine, or a methyl group, and
R300 is chlorine, bromine, or a cyano group,
and a compound of the following formula (L) :
wherein :
Riooo s chlorine bromine, or iodine.
[0309]
Active ingredients of acardides:
Acequinocyl, amitraz, benzoximate, bifenaate, bromopropylate, chinomethionat, chlorobenzilate, CPCBS (chlorfenson) , clofentezine, cyflumetofen, Kelthane
(dicofol) , etoxazole, fenbutatin oxide, fenothiocarb, fenpyroximate, fluacrypyrim, fluproxyfen, hexythiazox, propargite: BPPS, polynactins, pyridaben, Pyrimidifen, tebufenpyrad, tetradifon, spirodiclofen, spiromesifen, spirotetramat , amidoflumet , and cyenopyrafen .
[0310]
Active ingredients of nematocides:
DCIP, fosthiazate, levamisole hydrochloride
(levamisole) , methyisothiocyanate, morantel tartarate, and imicyafos .
[0311]
Active ingredients of fungicides:
Azole fungicidal compounds such as propiconazole, prothioconazole, triadimenol, prochloraz, penconazole, tebuconazole, flusilazole, diniconazole, bromuconazole , epoxiconazole, difenoconazole, cyproconazole, metconazole, triflumizole, tetraconazole, myclobutanil , fenbuconazole , hexaconazole, fluquinconazole, triticonazole, bitertanol, imazalil, and flutriafol;
Cyclic amine fungicidal compouds such as fenpropimorph, tridemorph, and fenpropidin;
Benzimidazole fungicidal compounds such as carbendezim, benomyl, thiabendazole, and thiophanate-methyl ;
Procymidone; cyprodinil; pyrimethanil ; diethofencarb; thiuram; fluazinam; mancozeb; iprodione; vinclozolin;
chlorothalonil ; captan; mepanipyrim; fenpiclonil; fludioxonil; dichlofluanid; folpet; kresoxim-methyl ; azoxystrobin; trifloxystrobin; fluoxastrobin; picoxystrobin; pyraclostrobin; dimoxystrobin; pyribencarb; spiroxamine; quinoxyfen; fenhexamid; famoxadone; fenamidone; zoxamide; ethaboxam; amisulbrom; iprovalicarb; benthiavalicarb; cyazofamid; mandipropamid; boscalid; penthiopyrad; metrafenone; fluopiran; bixafen; cyflufenamid; proquinazid; isotianil, and tiadinil.
[0312]
Active ingredients of herbicides:
(1) Phenoxyfatty acid herbicidal compounds:
2,4-PA, MCP, MCPB, phenothiol, mecoprop, fluroxypyr, triclopyr, clomeprop, and naproanilide .
(2) Benzoic acid herbicidal compounds:
2,3,6-TBA, dicamba, clopyralid, picloram, aminopyralid, quinclorac, and quinmerac.
(3) Urea herbicidal compounds:
Diuron, linuron, chlortoluron, isoproturon, fluometuron, isouron, tebuthiuron, methabenzthiazuron, cumyluron, daimuron, and methyl-daimuron .
(4) Triazine herbicidal compounds:
Atrazine, ametoryn, cyanazine, simazine, propazine, simetryn, dimethametryn, prometryn, metribuzin, triaziflam, and indaziflam.
(5) Bipyridinium herbicidal compounds:
Paraquat and diquat.
(6) Hydroxybenzonitrile herbicidal compounds:
Bromoxynil and ioxynil.
(7) Dinitroaniline herbicidal compounds:
Pendimethalin, prodiamine, and trifluralin.
(8) Organic phosphorus herbicidal compounds:
Amiprofos-methyl, butamifos, bensulide, piperophos, anilofos, glyphosate, glufosinate, glufosinate-P, and bialaphos.
(9) Carbamate herbicidal compounds:
Di-allate, tri-allate, EPTC, butylate, benthiocarb, esprocarb, molinate, dimepiperate, s ep, chlorpropham, phenmedipham, phenisopham, pyributicarb, and asulam.
(10) Acid amide herbicidal compounds:
Propanil, propyzamide, bromobutide, and etobenzanid.
(11) Chloroacetanilide herbicidal compounds:
Acetochlor, alachlor, butachlor, dimethenamid, propachlor, metazachlor, metolachlor, pretilachlor, thenylchlor, and pethoxamid.
(12) Diphenylether herbicidal compounds:
Acifluorfen-sodium, bifenox, oxyfluorfen, lactofen, fomesafen, chlomethoxynil , and aclonifen.
(13) Cyclic imide herbicidal compounds:
Oxadiazon, cinidon-ethyl , carfentrazone-ethyl ,
surfentrazone, flumiclorac-pentyl , flumioxazin, pyraflufen- ethyl, oxadiargyl, pentoxazone, fluthiacet-methyl , butafenacil, benzfendizone, bencarbazone, and saflufenacil .
(14) Pyrazole herbicidal compounds:
Benzofenap, pyrazolate, pyrazoxyfen, topramezone, and pyrasulfotole .
(15) Triketone herbicidal compounds:
Isoxaflutole, benzobicyclon, sulcotrione, mesotrione, tembotrione, and tefuryltrione .
(16) Aryloxyphenoxypropionic acid herbicidal compounds:
Clodinafop-propargyl, cyhalofop-butyl , diclofop-methyl, fenoxaprop-ethyl, fluazifop-butyl , haloxyfop-methyl , quizalofop-ethyl , and metamifop.
(17) Trioneoxime herbicidal compounds:
Alloxydim-sodium, sethoxydim, butroxydim, clethodim, cloproxydim, cycloxydim, tepraloxydim, tralkoxydim, and profoxydim.
(18) Sulfonylurea herbicidal compounds:
Chlorsulfuron, sulfometuron-methyl , metsulfuron-methyl , chlorimuron-ethyl, tribenuron-methyl , triasulfuron, bensulfuron-methyl, thifensulfuron-methyl , pyrazosulfuron- ethyl, primisulfuron-methyl, nicosulfuron, amidosulfuron, cinosulfuron, imazosulfuron, rimsulfuron, halosulfuron- methyl, prosulfuron, ethametsulfuron-methyl, triflusulfuron-methyl, flazasulfuron, cyclosulfamuron,
flupyrsulfuron, sulfosulfuron, azimsulfuron, ethoxysulfuron, oxasulfuron, iodosulfuron-methyl-sodium, foramsulfuron, mesosulfuron-methyl, trifloxysulfuron, tritosulfuron, orthosulfamuron, flucetosulfuron, and propyrisulfuron .
(19) Imidazolinone herbicidal compounds:
Imazamethabenz-methyl , imazamethapyr, imazamox, imazapyr, imazaquin, and imazethapyr.
(20) Sulfonamide herbicidal compounds:
Flumetsulam, metosulam, diclosulam, florasulam, cloransulam-methyl, penoxsulam, and pyroxsulam.
(21) Pyrimidinyloxybenzoic acid herbicidal compounds:
Pyrithiobac-sodium, bispyribac-sodium, pyriminobac- methyl, pyribenzoxim, pyriftalid, and pyrimisulfan .
(22) Other herbicidal compounds:
Bentazon, bromacil, terbacil, chlorthiamid, isoxaben, dinoseb, amitrole, cinmethylin, tridiphane, dalapon, diflufenzopyr-sodium, dithiopyr, thiazopyr, flucarbazone- sodium, propoxycarbazone-sodium, mefenacet, flufenacet, fentrazamide, cafenstrole, indanofan, oxaziclomefone, benfuresate, ACN, pyridate, chloridazon, norflurazon, flurtamone, diflufenican, picolinafen, beflubutamid, clomazone, amicarbazone, pinoxaden, pyraclonil, pyroxasulfone, thiencarbazone-methyl , aminocyclopyrachlor, ipfencarbazone , and methiozolin.
[0313]
Active ingredients of synergists:
Piperonyl butoxide, sesamex, sulfoxide, N-(2- ethylhexyl) -8, 9, 10-trinorborn-5-ene-2 , 3-dicarboxyimide ( GK 264), N-declyimidazole, WARF-antiresistant , TBPT, TPP, IBP, PSCP, methyl iodide (CH3I) , t-phenylbutenone, diethylmaleate, DMC, FD C, ETP, and ET .
Examples
[0314]
The present invention is described in more detail by
Production Examples, Formulation Examples, and Test Examples, but the present invention is not limited to these Examples.
[0315]
First, Production Examples of the present compound are shown below.
[0316]
Production Example 1
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (1.34 g) , 2-methylsulfanylbenzaldehyde (1.28 g) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (2.19 g) , and DMF(14 ml) was stirred with heating at 80 °C for 1 hour, and then heated to 120 °C, and stirred with heating for further 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured,
and extracted with ethyl acetate 3 times. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.74 g of 3-methyl-2- (2-methylsulfanylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 1) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.72-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.32 (lH,m), 7.58- 7.53 (lH,m), 7.45-7.42 (2H,m), 7.36-7.31 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.44 (3H,s)
[0317]
Production Example 2
To a mixture of 3-methyl-2- (2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.32 g) , methanol (4 ml) and water (6 ml), sodium periodate (0.42 g) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour, and then heated to 40 °C, and stirred with heating for further 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and
extracted with chloroform 2 times. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.32 g of 2- (2- methylsulfinylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 2 ) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.38-8.35 (lH,m), 8.33- 8.32 (lH,m), 7.89-7.84 (lH,m), 7.73-7.69 (lH,m), 7.62-7.59 (lH,m), 3.92 (3H,s), 3.03 (3H,s)
[0318]
Production Example 3
To a mixture of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.30 g) and chloroform (9 ml), 69 % of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (0.70 g) was added under ice-cooling, and then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 2 hours. Then, into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform 2 times. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate,
and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.32 g of 2- ( 2-methylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 3) .
1H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.31-8.27 (2H,m), 7.88- 7.80 (2H,m), 7.59-7.55 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.29 (3H,s)
[0319]
Production Example 4-1
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (1.0 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzaldehyde (0.96 g) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (1.80 g) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (1.80 g) and D F (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 160 °C for 5 hours. The reaction mixture was ice-cooled, and water was added thereto. The precipitated crystal was collected by filtration, and washed with water, then hexane . The obtained crystal was dried under reduced pressure to give 1.09 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 4).
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.56- 7.49 (2H,m), 7.47-7.43 (lH,m), 7.39-7.34 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0320]
Alternatively, Present Compound 4 can be synthesized by the following method.
[0321]
Production Example 4-2
To a mixture of N- ( 2-methylamino-5- trifluoromethylpyridine-3-yl ) -2-ethylsulfanyl-benzamide (6.0 g) and xylene (170 ml), p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (5.47 g) was added, and stirred under reflux for 9 hours. After the reaction mixture was allowed to stand to cool to room temperature, the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, and then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 5.17 g of Present Compound 4.
[0322]
Production Example 5
A mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.25 g) , sodium periodate (0.24 g) , methanol (6 ml), water (2 ml), and THF (0.8 ml) was stirred at room temperature for 20 minutes, and then heated to 50 °C, and stirred with heating for further 1.5 hours. To the ice-cooled reaction mixture, water was added. The precipitated crystal was collected by filtration. The obtained crystal was dissolved in ethyl acetate, and washed with saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, then saturated brine, sequentially. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was washed with hexane to give 0.20 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 5) .
Present Compound 5
^-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 8.27- 8.24 (lH,m), 7.86-7.81 (lH,m), 7.72-7.68 (lH,m), 7.62-7.59 (lH,m), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.42-3.31 (lH,m), 3.02-2.92 (lH,m),
1.31 (3H,t)
[0323]
Production Example 6
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.25 g) and chloroform (3 ml), 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %, 0.43 g) was added under ice-cooling, and then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour. To the reaction mixture, chloroform was added under ice- cooling, and then saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, then saturated brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The obtained crystal was washed with hexane, then methyl-tert-butyl ether to give 0.27 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methy1-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 6) .
Present Compound 6
-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m) , 8.25- 21 (lH,m), 7.87-7.79 (2H,m) , 7.58-7.55 (lH,m), 3.72
(3H,s), 3.42 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t)
[0324]
Production Example 7
A mixture of N-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (0.96 g) , 2-propylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.08 g) , SC (0.78 g) , and pyridine (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 120 °C for 1.5 hours. To the reaction mixture, HOBt (0.74 g) was added, and stirred with heating for 1.5 hours. WSC (0.38 g) was added thereto, and stirred with heating for further 2 hours . Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.23 g of 3-methyl-2- ( 2- propylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 7). Present Compound 7
""■H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.72-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.53- 7.51 (2H,m), 7.46-7.43 (lH,m), 7.38-7.33 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.81 (2H,t), 1.65-1.54 (2H,m) , 0.93 (3H,t)
[0325]
Production Example 8
A mixture of 3-methyl-2- (2-propylsulfanylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.22 g) , sodium periodate (0.27 g) , methanol (2 ml), and water (4 ml) was stirred with heating at 40 °C for 1.5 hours. To the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were added, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.17 g of 3-methyl-2- (2- propylsulfinylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 8). Present Compound 8
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.77-8.74 (lH,m), 8.31-8.27 (2H,m), 7.86- 7.80 (lH,m), 7.72-7.66 (lH,m), 7.63-7.59 (lH,m), 3.90 (3H,s), 3.44-3.36 (lH,m), 2.94-2.85 (lH,m), 2.02-1.87 (lH,m), 1.85-1.72 (lH,m), 1.06 (3H,t)
[0326]
Production Example 9
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-propylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.22 g) and chloroform (3 ml) , 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %, 0.33 g) was added under ice-cooling, and then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.24 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 9) .
Present Compound 9
^"H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 8.24- 8.21 (lH,m), 7.86-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.58-7.54 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.41-3.33 (2H,m) , 1.76-1.65 (2H,m), 1.00 (3H,t)
[0327]
Production Example 10
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (0.96 g) , 2-allylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.46 g) , WSC (1.06 g) , and xylene (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 145 °C for 3 hours. After the mixture was evaporated to remove xylene, acetic acid (10 ml) was added thereto, and stirred with heating at 120 °C for further 1 hour. To the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, 5 mol/1 of aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added to neutralize, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.83 g of 2- (2- allylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 10) .
Present Compound 10
1H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.34-8.32 (lH,m), 7.55- 7.49 (2H,m), 7.48-7.45 (lH,m), 7.42-7.36 (lH,m), 5.81-5.70 (lH,m), 5.15-5.04 (2H,m) , 3.77 (3H,s), 3.49-3.45 (2H,m)
[0328]
Production Example 11
The procedure was performed according to the metho described in Production Example 9 using 2- (2 allylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- (2 propylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b]pyridine to give 2- (2-allylsulfonylphenyl) -3-methyl-6 trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafte referred to as Present Compound 11) .
Present Compound 11
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.31-8.29 (lH,m), 8.17- 8.14 (lH,m), 7.86-7.76 (2H,m), 7.58-7.55 (lH,m), 5.81-5.69
(lH,m), 5.37-5.28 (2H,m) , 4.21-4.14 (2H,m) , 3.72 (3H,s)
[0329]
Production Example 12
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (0.96 g) , 2-isopropylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.47 g) , WSC (1.06 g) , and pyridine (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 120 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
A mixture of the resulting residue and acetic acid (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 118 °C for 1.5 hours, and then acetic anhydride (10 ml) was poured thereinto, and stirred with heating at 118 °C for 1.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with tert-butyl methyl ether. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.05 g of 2- (2-isopropylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 12).
Present Compound 12
1H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.72-8.71 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 7.61- 7.58 (lH,m), 7.56-7.51 (lH,m), 7.49-7.46 (lH,m), 7.43-7.38 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.38-3.27 (lH,m), 1.18 (6H,d)
[0330]
Production Example 13
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 8 using 2- (2- isopropylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methy1-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-
propylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine to give 2- (2-isopropylsulfinylphenyl) -3-methyl- 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 13) .
Present Com ound 13
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.75 (lH,m), 8.31-8.30 (lH,m), 8.18- 8.15 (lH,m), 7.84-7.80 (lH,m), 7.72-7.67 (lH,m), 7.62-7.59 (lH,m), 3.87 (3H,s), 3.50-3.39 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,d), 1.09 (3H,d)
[0331]
Production Example 14
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 9 using 2- (2- isopropylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- (2- propylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine to give 2- ( 2-isopropylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methyl- 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 14) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.75-8.74 (lH,m), 8.28-8.27 (lH,m), 8.22- 8.19 (lH,m), 7.86-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.57-7.54 (lH,m), 3.85-3.74 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 1.24 (6H,d)
[0332]
Production Example 15
To a mixture of tert-butylthiol (0.67 g) and D F (12 ml), sodium hydride (60 % in oil) was added under ice- cooling. The mixture was stirred under ice-cooling for 10 minutes, and then 2- (2-fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (1.09 g) was added. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, and then stirred with heating at 60 °C for 1.5 hours, then at 80 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.19 g of 2- (2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl- 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 15) .
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.70 (lH,m), 8.31-8.29 (lH,m), 7.78- 7.75 (lH,m), 7.62-7.52 (3H,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 1.12 (9H,s)
[0333]
Production Examples 16 and 17
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.87 g) and chloroform (12 ml), 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %) (0.95 g) was added under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.33 g of 2- (2-tert-butylsulfinylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 16) and 0.52 g of 2- (2- tert-butylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 17 ) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m) , 8.19- 8.15 (lH,m), 7.85-7.80 (lH,m), 7.75-7.70 (lH,m), 7.63-7.59 (lH,m), 3.84 (3H,s), 1.05 (9H,s)
Present Compound 17
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ : 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.28-8.26 (lH,m), 8.17- 8.12 (lH,m), 7.86-7.80 (2H,m) , 7.57-7.53 (lH,m), 3.66 (3H,s), 1.31 (9H,s)
[0334]
Production Example 18
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (0.86 g) , 2-trifluoromethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.00 g) , WSC (0.76 g) , and pyridine (9 ml) was stirred with heating at 120 °C for 3.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure .
A mixture of the resulting residue, tripotassium phosphate (2.87 g) , and 1-pentanol (9 ml) was stirred with
heating at 135 °C for 3.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.98 g of 3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-2- ( 2-trifluoromethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3H- imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 18 ) .
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m), 7.98-
7.93 (lH,m), 7.71-7.59 (3H,m), 3.77 (3H,s)
[0335]
Production Example 19
To a mixture of 3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2- (2- trifluoromethylsulfanylphenyl) -3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.80 g) and chloroform (7 ml), 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %) (0.49 g) was added under ice- cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, stirred for 20 minutes, and then heated to 62 °C, and stirred under reflux for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium
hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.44 g of 3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-2- ( 2-trifluoromethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 19) .
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ : 8.77-8.74 (lH,m), 8.46-8.41 (lH,m), 8.36-
8.33 (lH,m), 7.92-7.83 (3H,m) , 4.04 (3H,s)
[0336]
Production Example 20
A mixture of 3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2- (2- trifluoromethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.25 g) and acetic acid (7 ml) was heated to 80 °C, and 30 % of an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide (3 ml) was added dropwise thereto. The mixture was heated to 100 °C, and then stirred with heating for 5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer
was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 76 mg of 3-methyl- 6-trifluoromethyl-2- ( 2-trifluoromethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 20) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.35-8.32 (2H,m) , 8.05- 8.01 (lH,m), 7.97-7.93 (lH,m), 7.72-7.70 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s)
[0337]
Production Example 21
To a mixture of N2-ethyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (700 mg) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (690 mg) , and pyridine (20 ml) , WSC (720 mg) was added at room temperature, and heated to 95 °C, and then stirred with heating for 10 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
The resulting residue was dissolved in xylene (20 ml),
and p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (1.6 g) was added thereto. The mixture was heated to 170 °C, and stirred with heating for 9.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 295 mg of 3-ethyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 21) .
Present Compound 21
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.70 (lH,s), 8.32 (lH,s), 7.60-7.30 (4H,m), 4.25 (2H,q), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.35-1.30 (3H,m) , 1.27- 1.21 (3H,m)
[0338]
Production Examples 22 and 23
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 3-ethyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine instead of 2- (2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give
140 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-ethyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 22) and 60 mg of 2-(2- ethylsulfonylphenyl) -3-ethyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 23 ) .
Present Compound 22
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.31 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,dd),
7.84 (lH,dt), 7.70 (lH,dt), 7.58 (lH,dd), 4.35 (2H,q),
3.43-3.30 (lH,m), 3.06-2.94 (lH,m), 1.41 (3H,t), 1.30 (3H,t)
Present Compound 23
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.71 (lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d), 7.56-7.47
(2H,m), 7.43 (lH,dd), 7.39-7.31 (lH,m), 4.25 (2H,q), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.32 (3H,t), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0339]
Production Example 24
A mixture of 2-ethylsulfanyl-N- ( 2-propylamino-5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-3-yl ) -benzamide (710 mg) , p-
toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (1.1 g) , and xylene (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 160 °C for 10 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 522 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-propyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 24 ) .
Present Compound 24
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.31 (lH,d), 7.56-7.32 (4H,m), 4.18 (2H,t), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.78-1.73 (2H,m) , 1.28- 1.21 (3H,m), 0.79 (3H,t)
[0340]
Production Examples 25 and 26
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-propyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2- (2-tert-
butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 100 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-propyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 25) and 42 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3- propyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 26) .
Present Compound 25
^-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.74 (1H, d) , 8.31 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,dd), 7.84 (lH,td), 7.70 (lH,td), 7.58 (lH,dd), 4.33-4.24 (2H,m) , 3.40-3.35 (lH,m), 3.03-2.98 (lH,m), 1.84-1.71 (2H,m) , 1.29 (3H,t), 0.81 (3H,t)
Present Compound 26
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.65 (lH,s), 8.21-8.13 (2H,m) , 7.79-7.70
(2H,m), 7.52-7.49 (lH,m), 4.12-3.92 (2H,m) , 3.50-3.30
(2H,m), 1.81-1.70 (2H,m) , 1.22-1.16 (3H,m) , 0.84-0.76 (3H,m)
[0341]
Production Example 27
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 21 using N2-isopropyl-5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2, 3-diamine instead of N2-ethyl-5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2 , 3-diamine to give 130 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-isopropyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 21) .
Present Compound 27
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.28 (lH,d), 7.55-7.47 (2H,m), 7.39-7.31 (2H,m) , 4.40-4.33 (lH,m), 2.91 (2H,q), 1.77-1.66 (6H,m), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0342]
Production Examples 28 and 29
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-isopropy1-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 60 mg of 2- (2-
ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-isopropyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 28) and 55 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3- isopropyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 29) .
Present Compound 28
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73 (1H, d) , 8.28 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,dd), 7.83 (lH,td), 7.69 (lH,td), 7.50 (lH,dd), 4.60-4.48 (lH,m), 3.38-3.26 (lH,m), 3.05-2.95 (lH,m), 1.77-1.71 (6H,m), 1.27 (3H,t)
Present Compound 29
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.71 (lH,d), 8.24-8.22 (2H,m) , 7.85-7.78 (2H,m), 7.55-7.52 (lH,m), 4.33-4.26 (lH,m), 3.72-3.62 (lH,m), 3.44-3.34 (lH,m), 1.77-1.69 (6H,m), 1.28 (3H,t)
[0343]
Production Example 30
The procedure was performed according to the method
described in Production Example 21 using N2-cyclopropyl-5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2 , 3-diamine instead of N2-ethyl-5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2 , 3-diamine to give 280 mg of 3- cyclopropyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 30) .
Present Compound 30
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.74 (lH,s), 8.31 (lH,s), 7.53-7.47 (3H,m), 7.39-7.31 (lH,m), 3.55-3.49 (lH,m) , 2.90 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t), 1.01-0.94 (2H,m) , 0.93-0.86 (2H,m)
[0344]
Production Examples 31 and 32
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 3- cyclopropyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 114 mg of 3-cyclopropyl-2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 31) and 109 mg of 3-cyclopropyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6-
trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 32).
Present Compound 31
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.29-8.26 (2H,m) , 7.85-7.79 (2H,m), 7.72-7.67 (lH,m), 3.57-3.51 (lH,m), 3.49-3.39 (lH,m), 3.09-2.95 (lH,m), 1.34 (3H,t), 1.29-1.16 (lH,m), 1.09-0.92 (2H,m), 0.80-0.65 (lH,m)
Present Compound 32
^- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (lH,s), 8.27-8.22 (2H,m) , 7.87-7.78 (2H,m), 7.65 (lH,dd), 3.60 (2H,brs), 3.39-3.33 (lH,m), 1.29 (3H,t), 1.11-1.11 (2H,m), 0.93 (2H,brs).
[0345]
Production Examples 33 and 34
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (270 mg) and DMF (10 ml) , 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil) (80 mg) and chloromethyl ethyl ether (118 μΐ) were sequentially added
under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 5 hours. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 180 mg of 3-ethoxymethyl-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 33) and 70 mg of 1- ethoxymethyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl- lH-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 34) ) .
Present Compound 33
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.73 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,d), 7.58-7.47
(3H,m), 7.35 (lH,td), 5.60 (2H,s), 3.50 (2H,q), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t), 1.10 (3H,t)
Present Compound 34
1H-NMR (CDCI
3) δ: 8.90 (lH,d), 8.19 (lH,d), 7.56-7.50 (3H,m), 7.40-7.36 (lH,m) , 5.45 (2H,s), 3.25 (2H,q), 2.85 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t), 1.04 (3H,t)
[0346]
Production Examples 35 and 36
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 3- ethoxymethyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 86 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-ethoxymethyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 35) and 96 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3- ethoxymethyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 36) .
Present Compound 35
■""H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,dd), 8.04 (lH,dd), 7.82 (lH,td), 7.70 (lH,td), 5.83 (lH,d), 5.47 (lH,d), 3.80-3.70 (2H,m) , 3.61-3.49 (lH,m), 3.10-3.01 (lH,m), 1.40 (3H,t), 1.25 (3H,t)
Present Compound 36
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.75 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,dd), 7.86-7.78 (2H,m), 7.72 (lH,dd), 5.51 (2H,brs), 3.64 (2H,q), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t), 1.17 (3H,t)
[0347]
Production Example 37
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (98 mg) and DMF (6 ml), 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil) (29 mg) and chloromethyl methyl ether (25 μΐ) were sequentially added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated room temperature, and stirred for 4 hours. Then, water was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 72 mg of 3-methoxymethyl-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 37). Present Compound 37
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74 (lH,d), 8.36 (lH,d), 7.58-7.47 (3H,m), 7.35 (lH,td), 5.55 (2H,s), 3.31 (3H,s), 2.90 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0348]
Production Example 38
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 37 using 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine instead of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 79 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methoxymethyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 38).
Present Compound 38
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (lH,d), 8.31 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,dd), 7.87-7.78 (2H,m), 7.72 (lH,dd), 5.48 (2H,brs), 3.50 (2H,q), 3.43 (3H,s), 1.28 (3H,t)
[0349]
Production Example 39
A mixture of 2-ethylsulfanyl-N- (5-methyl-2- methylaminopyridin-3-yl ) -benzamide (1.40 g) , tripotassium phosphate (1.97 g) , and tert-butanol ( 10 ml) was stirred under reflux at 82 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.27 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3, 6-dimethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 39) .
Present Compound 39
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.28-8.26 (lH,m), 7.89-7.88 (lH,m), 7.50- 7.43 (3H,m), 7.35-7.30 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 2.51 (3H,s), 1.22 (3H,t)
[0350]
Production Examples 40 and 41
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3 , 6-dimethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
instead of 2- (2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl) -3, 6-dimethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 40) and 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl) -3, 6-dimethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 41) .
Present Com ound 40
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.32-8.31 (lH,m), 8.24-8.21 (lH,m), 7.88- 7.86 (lH,m), 7.81-7.77 (lH,m), 7.69-7.64 (lH,m), 7.60-7.57 (lH,m), 3.83 (3H,s), 3.38-3.28 (lH,m), 2.97-2.87 (lH,m), 2.52 (3H,s), 1.27 (3H,t)
Present Compound 41
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.31-8.29 (lH,m), 8.23-8.20 (lH,m), 7.84- 7.75 (3H,m), 7.57-7.54 (lH,m), 3.66 (3H,s), 3.45 (2H,q) , 2.51 (3H,s), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0351]
Production Example 42
A mixture of 5-bromo-N2-methylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine (0.70 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (0.66 g) , SC (0.80
g) , HOBt (23 mg) , and pyridine (20 ml) was stirred under reflux at 120 °C for 30 minutes. After the reaction mixture was allowed to stand overnight, the mixture was stirred under reflux at 120 °C for 9.5 hours again. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured under ice-cooling, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. A mixture of the resulting residue and acetic anhydride (7 ml) was stirred under reflux at 140 °C for 1 hour. Aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was added to the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature to neutralize, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.60 g of 6-bromo-2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 42) .
Present Compound 42
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.47 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,d), 7.54-7 (2H,m), 7.45-7.42 (lH,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,
2.86 (2H, q ) , 1.23 (3H,t)
[0352]
Production Example 43
A mixture of 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.20 g) , sodium periodate (0.18 g), methanol (3 ml), water (1 ml), and THF (0.4 ml) was stirred at room temperature for 3.5 hours. Water was poured thereinto under ice-cooling, and then the precipitated solid was collected by filtration. The obtained solid was washed with water and hexane, and dried to give 0.19 g of 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 43) .
Present Compound 43
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.52-8.51 (lH,m), 8.26-8.22 (lH,m), 8.21- 8.20 (lH,m), 7.84-7.78 (lH,m), 7.71-7.65 (lH,m), 7.60-7.57 (lH,m), 3.83 (3H,s), 3.39-3.28 (lH,m), 2.99-2.88 (lH,m) , 1.29 (3H,t)
[0353]
Production Example 44
To a mixture of 6-bromo-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.20 g) arid chloroform (3
ml), 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %) (0.34 g) was added under ice-cooling, and then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 3.5 hours. Chloroform and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured thereinto under ice-cooling, and stirred, and then, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting solid was washed with hexane, and dried to give 0.20 g of 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 44 ) .
Present Compound 44
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.50 (lH,d), 8.23-8.20 (lH,m), 8.17 (lH,d), 7.86-7.77 (2H,m) , 7.57-7.54 (lH,m), 3.66 (3H,s),
3.42 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0354]
Production Example 45
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 21 using 5-iodo-N2-methyl- pyridin-2 , 3-diamine instead of N2-ethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-
pyridin-2 , 3-diamine to give 435 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6-iodo-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b]pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 45). Present Com ound 45
■""H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.60 (lH,d), 8.39 (lH,d), 7.54-7.41 (3H,m), 7.38-7.31 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t)
[0355]
Production Examples 46 and 47
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6-iodo-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine instead of 2- (2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 136 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -6-iodo-3-methyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 46) and 107 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6- iodo-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 47) .
""■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.63 (lH,d), 8.38 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,dd), 7.81 (lH,td), 7.68 (lH,td), 7.59 (lH,dd), 3.83 (3H,s), 3.39-3.29 (lH,m), 2.99-2.88 (lH,m), 1.29 (3H,t)
Present Com ound 47
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.63 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,dd), 7.85-7.77 (2H,m), 7.56 (lH,dd), 3.65 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0356]
Production Example 48
A mixture of zinc cyanide (0.47 g) , tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium ( 0.12 g) , 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.70 g) , and N-methylpyrrolidone (hereinafter referred to as NMP) (4 ml) was stirred at 90 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel
column chromatography to give 0.59 g of 6-cyano-2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 48).
Present Compound 48
!H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,d), 7.49-7.58 (2H,m), 7.42-7.47 (lH,m), 7.34-7.40 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s),
2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0357]
Production Example 49
To a mixture of 6-cyano-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.40 g) and chloroform (5 ml), 70 % of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (0.35 g) was added under ice-cooling, and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. To the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was added, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give 0.40 g of 6-cyano-2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 49) .
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,d), 7.84 (lH,t), 7.71 (lH,t), 7.56-7.64 (lH,m), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.28-3.41 (lH,m), 2.91-3.04 (lH,m), 1.26-1.35 (3H,m)
[0358]
Production Example 50
To a mixture of 6-cyano-2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.25 g) and chloroform (5 ml), 70 % of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (0.35 g) was added, and stirred at 50 °C for 2 hours. To the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and sodium sulfite were added, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.27 g of 6-cyano-2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 50 ) .
Present Com ound 50
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73 (lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d), 8.20-8.26
(lH,m), 7.80-7.89 (2H,m) , 7.54-7.60 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s),
3.33-3.45 (2H,m), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0359]
Production Example 51
To a mixture of 6-bromo-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (2 g) and THF (60 ml), n- butyllithium (1.6 M in hexane) (4.3 ml) was added dropwise with cooling in dry-ice-acetone bath. The mixture was stirred for 30 minutes, and then DMF (2.2 ml) was poured. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and then saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 189 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridin-6- carbaldehyde (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 51) .
Present Compound 51
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 10.20 (lH,s), 8.96 (lH,d), 8.55 (lH,d), 7.56-7.24 (4H,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.90-2.83 (2H,m) , 1.25-1.21 (3H,m)
[0360]
Production Example 52
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridin-6-carbaldehyde (122 mg) and chloroform (3 ml), bis ( 2-methoxyethyl ) aminosulfur trifluoride (700 μΐ) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with chloroform and ethyl acetate, sequentially. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 49 mg of 6- difluoromethyl-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine .
Present Compound 52
""■H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.59 (lH,s), 8.23 (lH,s), 7.56-7.43 (3H,m), 7.38-7.33 (lH,m), 6.88 (lH,t), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t)
[0361]
Production Examples 53 and 54
The procedure was performed according to the method
described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 6- difluoromethyl-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2- (2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 110 mg of 6-difluoromethyl- 2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b]pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 53) and 101 mg of 6-difluoromethyl-2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 54) .
Present Compound 53
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.62 (lH,s), 8.26-8.23 (2H,m) , 7.83 (lH,td), 7.70 (lH,td), 7.62 (lH,dd), 6.90 (lH,t), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.42-3.32 (lH,m), 3.02-2.92 (lH,m), 1.30 (3H,t) Present Compound 54
""■H-N R (CDCI3) δ : 8.61 (lH,s), 8.24-8.19 (2H,m) , 7.87-7.78 (2H,m), 7.58 (lH,dd), 6.89 (lH,t), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0362]
Production Example 55
A mixture of 6-bromo-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (500 mg) , NMP (24 ml), xylene (10 ml), copper iodide (1.1 g) , and sodium pentafluoropropionate (1.1 g) was heated to 170 °C, and stirred with heating for 3 days. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with tert-butyl methyl ether. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 43 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) - 3-methyl-6-pentafluoroethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 55) .
Present Compound 55
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.66 (lH,d), 8.30 (lH,d), 7.56-7.49 (2H,m), 7.47-7.43 (lH,m), 7.38-7.34 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0363]
Production Example 56
A mixture of 6-bromo-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.35 g) , tripotassium
phosphate (0.42 g) , phenylboronic acid (0.13 g) , 2- dicyclohexylphosphino-2' , 6' -dimethoxybiphenyl (0.03 g) , tris (dibenzylideneacetone) dipalladium ( 0 ) (0.01 g) , and 1,4- dioxane (3 ml) was stirred with heating at 70 °C for 2 hours, and then heated to 90 °C, and stirred with heating for further 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.37 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-phenyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 56) .
Present Compound 56
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.67 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,d), 7.63-7.69 (2H,m), 7.45-7.54 (5H,m), 7.38-7.43 (lH,m), 7.32-7.37 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0364]
Production Example 57
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 2- (2-
ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-phenyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -
6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.04 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-phenyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 57 ) .
Present Compound 57
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.22-8.25 (lH,m), 8.20 (lH,d), 7.77-7.86 (2H,m) , 7.64-7.68 (2H,m) , 7.57-7.60 (lH,m), 7.48-7.54 (2H,m) , 7.38-7.44 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s),
3.40-3.53 (2H,m), 1.23-1.29 (3H,m)
[0365]
Production Example 58
To a mixture of 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (350 mg) and 1,4-dioxane (5 ml), 2-fluorophenylboronic acid (150 mg) , tripotassium phosphate (600 mg) , 2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2 ' , 6' - dimethoxybiphenyl (25 mg) , and tris (dibenzylideneacetone) palladium(O) (14 mg) were sequentially added, heated to 80 °C, and stirred with heating for 8 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then water was poured into the
reaction mixture, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 349 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- ( 2-fluorophenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 58) .
Present Compound 58
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.63-8.61 (lH,m), 8.27-8.25 (lH,m), 7.54- 7.46 (4H,m), 7.41-7.18 (4H,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.28-1.22 (3H,m)
[0366]
Production Examples 59 and 60
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- ( 2-fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 150 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -6- ( 2-fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 59) and 140 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6- (2-
fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 60) .
Present Compound 59
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.67-8.65 (lH,m), 8.27-8.23 (2H,m) , 7.81 (lH,td), 7.69 (lH,t), 7.62 (lH,dd), 7.53 (lH,td), 7.43-7.37 (lH,m), 7.31-7.21 (2H,m) , 3.89 (3H,s), 3.42-3.32 (lH,m), 3.02-2.92 (lH,m), 1.29 (3H,t)
Present Com ound 60
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.64 (lH,d), 8.24-8.20 (2H,m) , 7.84-7.76 (2H,m), 7.60-7.57 (lH,m), 7.55-7.49 (lH,m), 7.40-7.33 (lH,m), 7.29-7.18 (2H,m) , 3.72 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q), 1.28-
1.22 (3H,m)
[0367]
Production Example 61
To a mixture of 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (350 mg) and 1,4-dioxane (5 ml) , 3-fluorophenylboronic acid (150 mg) , sodium carbonate (320 mg) , and dichloro [ 1 , 1' - bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] palladium ( II ) (22 mg) were
sequentially added. The mixture was heated to 80 °C, and stirred with heating for 8 hours. Into the mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 240 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) - 6- (3-fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 61) .
Present Com ound 61
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.65 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 7.55-7.41 (5H,m), 7.38-7.32 (2H,m) , 7.15-7.05 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0368]
Production Examples 62 and 63
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- ( 3-fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 120 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl) -6- ( 3-fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-
imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 62) and 34 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6- ( 3- fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 63) .
Present Com ound 62
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.69 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd), 8.22 (lH,d), 7.82 (lH,td), 7.69 (lH,td), 7.62 (lH,dd), 7.51-7.42 (2H,m) , 7.39-7.34 (lH,m), 7.15-7.08 (lH,m), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.43-3.33 (lH,m), 3.02-2.92 (lH,m), 1.30 (3H,t)
Present Com ound 63
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.60 (lH,d), 8.16 (lH,dd), 8.11 (lH,d), 7.78-7.71 (2H,m), 7.51 (lH,dd), 7.42-7.34- (2H,m) , 7.28 (lH,dd), 7.06-6.99 (lH,m), 3.65 (3H,s), 3.40 (2H,q), 1.19 (3H,t)
[0369]
Production Example 64
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 61 using 4- fluorophenylboronic acid instead of 3-fluorophenylboronic
acid to give 140 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- (4- fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 64).
Present Compound 64
""■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.61 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,d), 7.63-7.57 (2H,m), 7.54-7.45 (3H,m) , 7.38-7.33 (lH,m), 7.23-7.16 (2H,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0370]
Production Example 65
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- (4-fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2- methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine to give 58 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6- ( 4- fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 65) .
Present Com ound 65
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.64 (lH,d), 8.24-8.22 (lH,m), 8.15
(lH,d), 7.86-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.62-7.58 (3H,m) , 7.22-7.18
(2H,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.47 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t)
[0371]
Production Example 66
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 21 using N3-methyl-5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2 , 3-diamine instead of N2-ethyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine to give 67 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -l-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-lH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 66) .
Present Compound 66
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.87 (lH,d), 7.99 (lH,d), 7.54-7.48 (3H,m), 7.41-7.34 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 2.84 (2H,q), 1.21 (3H,t)
[0372]
Production Example 67
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 1 using N1-methyl-4- trifluoromethylbenzene-1 , 2-diamine instead of N2-methyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine to give 0.28 g of 1- methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethyl-lH-
benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 67) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.12 (lH,brs), 7.62-7.58 (lH,m), 7.55- 7.48 (2H,m), 7.45-7.39 (2H,m) , 7.34-7.29 (lH,m), 3.70 (3H,s), 2.41 (3H,s)
[0373]
Production Example 68
A mixture of 2-ethylsulfanyl-N- ( 2-methylamino-5- trifluoromethylphenyl ) -benzamide (1.64 g) , p- toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (1.76 g) , and xylene (50 ml) was stirred under reflux at 150 °C for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.40 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -l-methyl-5- trifluoromethyl-lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 68).
Present Com ound 68
■"■H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.12-8.10 (lH,m), 7.61-7.58 (lH,m), 7.53- 7.44 (4H,m), 7.38-7.32 (lH,m), 3.69 (3H,s), 2.84 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t)
[0374]
Production Example 69
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 2 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole instead of 3-methyl-2- (2- methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine to give 0.30 g of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -1- methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 69) .
Present Com ound 69
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 8.10-8.07 (lH,m), 7.83- 7.78 (lH,m), 7.70-7.62 (2H,m) , 7.57-7.51 (2H,m) , 3.79 (3H,s), 3.36-3.26 (lH,m), 2.98-2.88 (lH,m), 1.26 (3H,t)
[0375]
Production Example 70
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole instead of 3-methyl-2- (2- methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine to give 0.24 g of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -1- methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 70) .
Present Compound 70
!fi-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 8.07-8.05 (lH,m), 7.84- 7.77 (2H,m), 7.64-7.61 (lH,m), 7.57-7.54 (lH,m), 7.53-7.49 (lH,m), 3.63 (3H,s), 3.46-3.34 (2H,m) , 1.23 (3H,t)
[0376]
Production Example 71
To a mixture of 3-chloro-N2-methyl-5- trifluoromethylbenzene-1 , 2-diamine (1.12 g) and THF (5 ml), 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid hydrochloride (1.00 g) was added under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour. Sodium hydrogen carbonate (0.46 g) was added thereto, and then the reaction mixture was allowed to stand overnight. The reaction mixture was heated to 66 °C,
and stirred under reflux for 1.5 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid hydrochloride (0.5 g) was added at room temperature. After the reaction mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature overnight, sodium hydrogen carbonate (1.00 g) was added, and stirred. The reaction mixture was ice-cooled, and then water was added under ice-cooling, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated brine, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.48 g of 7-chloro-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -l-methyl-5- trifluoromethyl-lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 71) .
Present Com ound 71
!H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.99-7.98 (lH,m), 7.54-7.48 (3H,m), 7.44- 7.41 (lH,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 3.94 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0377]
Production Example 72
The procedure was performed according to the method
described in Production Example 2 using 7-chloro-2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -1-methy1-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2- methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine to give 0.13 g of 7-chloro-2- ( 2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethy1-lH- benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 72) .
Present Com ound 72
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.23-8.20 (lH,m), 7.97-7.95 (lH,m), 7.85- 7.80 (lH,m), 7.71-7.66 (lH,m), 7.58-7.51 (2H,m) , 4.04
(3H,s), 3.32-3.21 (lH,m), 2.96-2.87 (lH,m), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0378]
Production Example 73
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 7-chloro-2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole instead of 3-methyl-2- (2- methylsulfanylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b]pyridine to give 0.16 g of 7-chloro-2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound
73) .
Present Com ound 73
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 7.94-7.92 (lH,m), 7.86- 7.78 (2H,m), 7.58-7.52 (2H,m) , 3.90 (3H,s), 3.60-3.16 (2H,m), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0379]
Production Example 74
A mixture of 3-bromo-N2-methyl-5- trifluoromethylbenzene-1 , 2-diamine (2.22 g) , 2- ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.80 g) , WSC (1.40 g) , and pyridine (10 ml) was stirred under reflux at 115 °C for 6 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.48 g of 7-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5- trifluoromethyl-lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 74).
^- MR (CDC13) δ: 8.03-8.02 (lH,m), 7.71-7.70 (lH,m), 7.54- 7.47 (2H,m), 7.44-7.41 (lH,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 3.95 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0380]
Production Examples 75 and 76
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 7-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole instead of 2- (2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 7-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5- trifluoromethyl-lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 75) and 7-bromo-2- ( 2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- benzimidazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 76) .
Present Com ound 75
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 8.03-7.99 (lH,m), 7.86- 7.80 (lH,m), 7.77-7.75 (lH,m), 7.72-7.66 (lH,m), 7.56-7.52
(lH,m), 4.05 (3H,s), 3.33-3.23 (lH,m), 2.98-2.88 (lH,m),
1.26 (3H,t)
Present Com ound 76
XH-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 7.99-7.96 (lH,m), 7.86- 7.78 (2H,m), 7.75-7.73 (lH,m), 7.57-7.53 (lH,m), 3.90 (3H,s), 3.58-3.19 (2H,m) , 1.25 (3H,t)
[0381]
Production Example 77
To a mixture of N- ( 2-hydroxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -
2-methylsulfanylbenzamide (0.33 g) , triphenylphosphine (0.34 g) , and THF (7 ml), diethyl azodicarboxylate (40 % in toluene) (0.57 g) was added dropwise, and stirred at room temperature for 1.5 hours. Triphenylphosphine (79 mg) and diethyl azodicarboxylate (40 % in toluene, 0.13 g) were added to the mixture, and stirred for further 1 hour. The mixture was heated to 50 °C, and stirred for 1.5 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then the mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.28 g of 2- (2- methylsulfanylphenyl) -5-trifluoromethylbenzoxazole
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 77).
Present Compound 77
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.22-8.19 (lH,m), 8.17-8.15 (lH,m), 7.71- 7.67 (lH,m), 7.66-7.63 (lH,m), 7.55-7.50 (lH,m), 7.41-7.37
(lH,m), 7.32-7.27 (lH,m), 2.57 (3H,s)
[0382]
Production Example 78
A mixture of 2-amino-4-trifluoromethyl-phenol (0.97 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.10 g) , WSC (1.27 g) , HOBt (37 mg) , and pyridine (5 ml) was stirred under reflux at 115 °C for 2.5 hours. After the mixture was allowed to stand overnight, the mixture was stirred under reflux at 115 °C for 6 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, and saturated brine, sequentially, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
A mixture of the resulting residue, p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (2.09 g) , and xylene (50 ml) was stirred under reflux at 153 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and
extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, water, 10 % aqueous citric acid solution, water, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, and saturated brine, sequentially, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.98 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -5- trifluoromethylbenzoxazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 78).
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.19-8.15 (2H,m) , 7.71-7.67 (lH,m), 7.66- 7.63 (lH,m), 7.52-7.47 (lH,m), 7.45-7.42 (lH,m), 7.31-7.27 (lH,m), 3.06 (2H,q), 1.44 (3H,t)
[0383]
Production Example 79
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 2 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzoxazole instead of 3-methyl-2- (2-methylsulfanylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.27 g of 2-(2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzoxazole
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 79) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.35-8.30 (2H,m) , 8.12-8.10 (lH,m), 7.85- 7.79 (lH,m), 7.75-7.66 (3H,m) , 3.48-3.38 (lH,m), 3.00-2.90 (lH,m), 1.41 (3H,t)
[0384]
Production Example 80
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzoxazole instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.24 g of 2-(2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzoxazole
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 80) .
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.28-8.24 (lH,m), 8.11-8.09 (lH,m), 7.99-
7.95 (lH,m), 7.85-7.77 (2H,m), 7.72-7.70 (2H,m) , 3.82 (2H,q), 1.40 (3H,t)
[0385]
Production Example 81
A mixture of 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl-N- ( 2-hydroxy-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl ) -benzamide (0.92 g) and phosphorous oxychloride (5 ml) was heated to 120 °C, and stirred under reflux. The reaction mixture cooled to room temperature was allowed to stand overnight. The mixture was heated to 120 °C again, and stirred under reflux for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and then the precipitated solid was collected by filtration, washed with water and hexane, and dried to give 0.53 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethyloxazolo [ 5 , 4-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 81) .
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.67 (lH,s), 8.40 (lH,s), 8.25 (lH,d), 7.53 (lH,t), 7.45 (lH,d), 7.32 (lH,t), 3.08 (2H,q), 1.45
(3H,t)
[0386]
Production Example 82
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 2 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyloxazolo [5,4-
b] pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) - 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.17 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyloxazolo [5,4- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 82) Present Compound 82
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.41-8.38 (2H,m) , 8.36- 8.33 (lH,m), 7.90-7.84 (lH,m), 7.74-7.69 (lH,m), 3.45-3.35 (lH,m), 3.00-2.90 (lH,m), 1.40 (3H,t)
[0387]
Production Example 83
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyloxazolo [5, 4- b]pyridine instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) - 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.19 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyloxazolo [5, 4- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 83) Present Compound 83
^"H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.40-8.37 (lH,m), 8.29-
8.26 (lH,m), 8.05-8.02 (lH,m), 7.89-7.81 (2H,m) , 3.81
(2H,q), 1.43 (3H,t)
[0388]
Production Example 84
A mixture of 2-amino-4-trifluoromethylbenzenethiol hydrochloride (0.50 g) , 2-methylsulfanylbenzaldehyde (0.33 g) , diisopropylethylamine (0.28 g) , and DMSO (4 ml) was heated to 170-180 °C, and stirred with heating for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.42 g of 2- (2- methylsulfanylphenyl) -5-trifluoromethylbenzothiazole
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 84).
^-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.42-8.40 (lH,m), 8.05-8.02 (lH,m), 7.92- 7.89 (lH,m), 7.66-7.63 (lH,m), 7.50-7.42 (2H,m), 7.32-7.27 (lH,m), 2.51 (3H,s)
[0389]
Production Example 85
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 71 using 2-amino-4- trifluoromethylbenzenethiol hydrochloride instead of 3- chloro-N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylbenzene-1 , 2-diamine to give 0.50 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -5- trifluoromethylbenzothiazole (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 85).
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.41-8.39 (lH,m), 8.06-8.00 (2H,m) , 7.66- 7.62 (lH,m), 7.55-7.51 (lH,m), 7.48-7.42 (lH,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 2.96 (2H,q), 1.33 (3H,t)
[0390]
Production Example 86
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 2 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzothiazole instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.25 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzothiazole
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 86).
!H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.36-8.32 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 8.08- 8.05 (lH,m), 7.97-7.94 (lH,m), 7.80-7.75 (lH,m), 7.71-7.68 (lH,m), 7.66-7.61 (lH,m), 3.56-3.45 (lH,m), 3.02-2.93 (lH,m), 1.46 (3H,t)
[0391]
Production Example 87
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 3 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzothiazole instead of 3-methyl-2- ( 2-methylsulfanylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.30 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -5-trifluoromethylbenzothiazole
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 87) .
H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 8.26-8.23 (lH,m), 8.10- 8.06 (lH,m), 7.81-7.69 (4Hfm) , 3.75 (2H,q), 1.36 (3H,t)
[0392]
Production Example 88
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-
diamine (1.14 g) , 3-chloro-2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.56 g) , SC (1.02 g) , and pyridine (12 ml) was stirred under reflux at 115 °C for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
To the resulting residue, tripotassium phosphate (3.82 g) and pyridine (12 ml) were added, and stirred under reflux at 115 °C for 2.5 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then the solvent was evaporated. Tripotassium phosphate (3.82 g) and DMSO (12 ml) were added to the resulting residue, and stirred with heating at 150 °C for 1 hour. The mixture was heated to 165 °C, and stirred with heating for further 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water and saturated brine, dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.96 g of 2- ( 3-chloro-2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 88 ) .
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 7.71 (lH,dd), 7.48-7.42 (2H,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 2.73 (2H,q), 1.05 (3H,t)
[0393]
Production Example 89
To a mixture of 2- ( 3-chloro-2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.72 g) and chloroform (10 ml), 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: 69-75 %, 0.66 g) was added under ice-cooling, and then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 20 minutes. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform 2 times. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.67 g of 2- ( 3-chloro-2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 89) .
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.69 (lH,d), 8.25 (lH,d), 7.64 (lH,dd), 7.58 (lH,t), 7.39 (lH,dd), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.60-3.49 (lH,m), 3.33-3.23 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t)
[0394]
Production Example 90
A mixture of 2- ( 3-chloro-2-ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.48 g) and acetic acid (12 ml) was stirred with heating at 80 °C, and then 30 % of an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide (6 ml) was added dropwise. The mixture was heated to 100 °C, and stirred with heating for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.21 g of 2- (3- chloro-2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 90) .
^-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.25 (lH,d), 7.85-7.81 (lH,m), 7.71 (lH,t), 7.46-7.43 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.59-
3.41 (2H,m), 1.33 (3H,t)
[0395]
Production Examples 91 and 92
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfany1-phenyl ) -3-methyl-6-pentafluoroethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 27 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfinyl- phenyl ) -3-methyl-6-pentafluoroethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 112) and 31 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -3-methyl-6- pentafluoroethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 113) .
Present Compound 112
-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 8.27 (1H
7.84 (lH,t), 7.71 (lH,t), 7.60 (lH,d), 3.90 (3H,s), 3.43- 3.33 (lH,m), 3.04-2.94 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t)
Present Compound 113
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.69 (lH,s), 8.25 (lH,s), 8.23-8.22 ( lH,m), 7.88-7.79 (2H,m) , 7.59-7.52 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t)
[0396]
Production Example 93
A mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (1.14 g) , 2-ethylsulfanyl-4-fluorobenzoic acid (1.44 g) , WSC (1.02 g) , and pyridine (12 ml) was stirred with heating at 120 °C for 1.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure .
To the resulting residue, p-toluenesulfonic acid (3.42 g) , xylene (10 ml) and NMP (2 ml) were added, and stirred under reflux at 150 °C for 4.5 hours with removing water with Dean-Stark apparatus. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with
ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.05 g of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-4- fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 116) .
Present Compound 116
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.70-8.68 (lH,m), 8.31-8.28 (lH,m), 7.43- 7.38 (lH,m), 7.17-7.13 (lH,m), 7.04-6.98 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t)
[0397]
Production Examples 94 and 95
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-fluorophenyl ) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.85 g) and chloroform (12 ml) , 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %, 0.81) was added under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred for 30 minutes. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with
chloroform. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.33 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfinyl-4- fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 117) and 0.52 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl4-fluorophenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 118) .
Present Compound 117
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.75 (lH,m), 8.31-8.30 (lH,m), 8. 7.98 (lH,m), 7.65-7.61 (lH,m) , 7.41-7.36 (lH,m) , 3 (3H,s), 3.47-3.37 (lH,m), 3.04-2.94 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t) Present Compound 118
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m) , 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 7.97- 7.94 (lH,m), 7.60-7.51 (2H,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t)
[0398]
Production Example 96
To a pressure-resistant reaction container, 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (1.74 g) , copper (II) acetylacetone (0.26 g) , acetylacetone (0.50 g) , cesium carbonate (3.25 g) , N P (9 ml), and 28 % of aqueous ammonia (4 ml) were added, and stirred at 120 °C for 6 hours. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.20 g of 6-amino- 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 125) .
Present Compound 125
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.99 (lH,d), 7.40-7.49 (4H,m), 7.28-7.34 (lH,m), 3.61-3.70 (5H,m) , 2.85 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t)
[0399]
Production Example 97
A mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -6-iodo-3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (311 mg) , copper iodide (1.5 g) , sodium heptafluorobutyrate (1.8 g) , NMP (5 ml), and xylene (25 ml) was stirred with heating at 150 °C for 12 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and 28 % aqueous ammonia were poured, and extracted with tert-butyl methyl ether. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 118 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -6-heptafluoropropyl-3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 128).
Present Compound 128
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ : 8.65 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 7.56-7.51 (2H,m), 7.48-7.43 (lH,m), 7.38-7.34 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0400]
Production Examples 98 and 99
The procedure was performed according to the method
described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -6-heptafluoropropyl-3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 2- ( 2-ethylsulfinyl-phenyl ) - 6-heptafluoropropyl-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 129) and 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6-heptafluoropropyl-3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 130) .
Present Compound 129
^-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.29-8.24 (2H,m) , 7.87-7.81 (lH,m), 7.74-7.68 (lH,m), 7.61 (lH,dd), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.43- 3.32 (lH,m), 3.05-2.94 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t)
Present Compound 130
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.67 (lH,d), 8.26-8.22 (2H,m) , 7.87-7.81 (2H,m), 7.59-7.55 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.26
(3H, t) .
[0401]
Production Example 100
To a mixture of 2- ( 4-chloro-2-fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl- 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.83 g) and DMF (5 ml), a suspension of sodium ethylmercaptide (80 %, 0.26 g) was added dropwise in DMF under ice-cooling, and stirred for 1 hour under ice-cooling. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured under ice-cooling, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography. 0.20 g of the resulting product was subjected to recycle preparation liquid chromatography to give 0.12 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-chlorophenyl) -3-methyl- 6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 133) .
Present Compound 133
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.44 (lH,d), 7.38 (lH,d), 7.34-7.30 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.91
(2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t)
[0402]
Production Examples 101 and 102
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanyl-4-chlorophenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl- SH-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine to give 0.34 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfinyl-4-chlorophenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 134) and 0.17 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4- chlorophenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 135) .
Present Compound 134
■"■H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.76-8.75 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 8.25 (lH,d), 7.68-7.65 (lH,m), 7.56 (lH,d), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.49- 3.39 (lH,m), 3.05-2.95 (lH,m), 1.35 (3H,t)
Present Compound 135
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 8.23- 8.21 (lH,m), 7.83-7.80 (lH,m), 7.51 (lH,d), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.45 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t)
[0403]
Production Example 103
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -6-iodo-3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (430 mg) , copper iodide (229 mg) , and DMF (3 ml), sodium sulfide nonahydrate (721 mg) was added at room temperature. The mixture was stirred with heating at 110 °C for 6 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride water solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 85 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) - 3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridin-6-thiol (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 145) :
■""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.41 (lH,d), 8.11 (lH,d), 7.53-7.47 (2H,m), 7.46-7.42 (lH,m), 7.37-7.31 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.56 (lH,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t); and
and 98 mg of a compound of the following formula (hereinafter referred to as Compound (145A).
Compound (145A)
■""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.48 (2H,d), 8.25 (2H,d), 7.53-7.47 (4H,m), 7.47-7.43 (2H,m) , 7.36-7.32 (2H,m) , 3.73 (6H,s),
2.86 (4H,q), 1.23 (6H,t)
[0404]
Production Example 104
To a mixture of 6-bromo-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (348 mg) , [1,1- bis (diphenylphosphino) ferrocene] palladium ( II ) dichloride dichloromethane adduct (41 mg) , and THF (5 mL) , diisopropyl zinc (1 M in toluene, 2 mL) was added at room temperature. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours,
washed with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 290 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -6-isopropyl-3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 147 ) .
Present Compound 147
1H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.35 (lH,s), 7.97 (lH,s), 7.51-7.42 (3H,m), 7.32-7.26 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.15-3.08 (lH,m), 2.83 (2H, q ) , 1.35 (6H,d), 1.20 (3H,t).
[0405]
Production Example 105
To a mixture of copper cyanide (514 mg) and THF (20 ml) , tert-butylmagnesium chloride (1 in THF) was added with cooling at -78 °C, and stirred at the temperature for 2 hours. To the mixture, a mixture of 6-bromo-2- (2- ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine ( 1 g) and THF (10 ml) was added dropwise with cooling at -78 °C.
The reaction mixture was stirred for 16 hours with
warming to room temperature gradually, and then saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to 111 mg of 6-tert-butyl-2- ( 2- ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 150).
Present Compound 150
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.53 (lH,d), 8.11 (lH,d), 7.51-7.46 (2H,m), 7.45-7.40 (lH,m), 7.36-7.29 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s),
2.86 (2H,q), 1.45 (9H,s), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0406]
Production Example 106
A mixture of N2-methyl-6-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (0.96 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.01 g) , WSC (1.06 g) , and pyridine (5 ml) was stirred under reflux for 3 hours . Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. To the resulting
residue, a mixture of tripotassium phosphate (2.65 g) and 1-propanol (10 ml) was added, and stirred under reflux for 4 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.98 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-5- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 151).
Present Compound 151
""■H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.20 (lH,d), 7.67 (lH,d), 7.56-7.48 (2H,m), 7.47-7.42 (lH,m), 7.40-7.33 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0407]
Production Examples 107 and 108
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-
imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.23 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -3-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 159) and 0.42 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3- methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 160) .
Present Compound 159
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.26 (lH,dd), 8.19 (lH,dd), 7.86-7.80 (lH,m), 7.74-7.67 (2H,m) , 7.60 (lH,dd), 3.90 (3H,s), 3.41- 3.27 (lH,m), 3.02-2.89 (lH,m), 1.31-1.26 (3H,m)
Present Compound 160
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.25-8.21 (lH,m), 8.15 (lH,d), 7.88-7.78 (2H,m), 7.69 (lH,d), 7.59-7.54 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t)
[0408]
Production Example 109
A mixture of Compound (145A) (3.3 g) and DMF (60m) was
cooled to -50 °C, and bubbled with trifluoroiodomethane (17 g) . The mixture was kept at -50 °C, and tetrakis (dimethylamino) ethylene (3.8 ml) was added dropwise. The reaction mixture was stirred for 5 hours with warming gradually. The mixture was diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 3.2 g of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl- phenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethylsulfanyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 161) .
Present Compound 161
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.66 (lH,d), 8.39 (lH,d), 7.57-7.49 (2H,m), 7.48-7.42 (lH,m), 7.39-7.33 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0409]
Production Example 110-a
To a mixture of 6-bromo-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (1 g) and THF (20 ml), n- butyllithium (1.5 M in hexane, 2.1 ml) was added dropwise
at -78 °C. The mixture was stirred at -78 °C for 30 minutes, and then methyl trifluoroacetate (577 μΐ) was added dropwise. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and then saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give 778 mg of crude 1- [2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b] pyridin-6-yl] -2,2, 2-trifluoro-ethanone (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 91) .
Present Compound 91
[0410]
Production Example 110-b
To a mixture of the crude 1- [ 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl- phenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridin-6-yl] -2,2,2- trifluoro-ethanone from Production Example 110-a (778 mg) , methanol (5 ml), and THF (20 ml), sodium borohydride (109 mg) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 hours, and then IN aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium
sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 170 mg of 1- [2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -3-methyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridin-6-yl ] -2,2, 2-trifluoro-ethanol (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 265).
Present Compound 265
^- MR (CDC13) δ: 8.56 (lH,s), 8.25 (lH,s), 7.58-7.35 (4H,m), 5.24 (lH,brs), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.90 (2H,q), 1.27-1.19 (3H,m)
[0411]
Production Example 110-c
To a mixture of 1- [2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridin-6-yl] -2,2, 2-trifluoro- ethanol (98 mg) , toluene (10 ml), and pyridine (50 μΐ) , thionyl chloride (1 ml) was added. The mixture was stirred with heating at 50 °C for 5 hours, and then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 66 mg of 6- ( l-chloro-2 , 2 , 2-
trifluoro-ethyl) -2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 266) .
Present Compound 266
XH-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.52 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 7.52-7.49 (2H,m), 7.44 (lH,dd), 7.37-7.33 (lH,m), 5.36 (lH,q), 3.75 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0412]
Production Example 110-d
To a mixture of 6- ( l-chloro-2 , 2 , 2-trifluoro-ethyl ) -2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (61 mg) and methanol (5 ml), sodium borohydride (20 mg) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3 hours, and then IN aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 40 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-6- (2,2, 2-trifluoro-ethyl) -3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 165) .
Present Compound 165
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.53 (lH,s), 8.45-8.37 (lH,m), 7.78-7.31 (4H,m), 3.84 (3H,s), 3.60-3.50 (2H,m), 2.91-2.82 (2H,m) , 1.23-1.16 (3H,m)
[0413]
Production Example 111
A mixture of N3-methyl-6-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (0.38 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (0.40 g) , WSC (0.42 g) , and pyridine (3 ml) was stirred under reflux for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. To the resulting residue, tripotassium phosphate (1.06 g) and 1-propanol (4 ml) were added, and stirred under reflux for 4 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.33 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH-
imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 166) .
Present Compound 166
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.85 (lH,d), 7.68 (lH,d), 7.58-7.47 (3H,m), 7.43-7.33 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 2.83 (2H,q), 1.20 (3H,t)
[0414]
Production Examples 112 and 113
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.23 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfinylphenyl ) -l-methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 167) and 0.42 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -1- methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-lH-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 168).
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.25 (lH,dd), 7.91 (lH,d), 7.83 (lH,td),
7.74 (lH,d), 7.69 (lH,td), 7.56 (lH,dd), 3.83 (3H,s), 3.53- 3.37 (lH,m), 3.18-3.05 (lH,m), 1.30 (3H,t)
Present Compound 168
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.26-8.19 (lH,m), 7.90-7.86 (lH,m), 7.85- 7.80 (2H,m), 7.72 (lH,d), 7.59-7.53 (lH,m), 3.66 (3H,s), 3.60-3.30 (2H,m), 1.24 (3H,t)
[0415]
Production Example 114
To a mixture of ethylmercaptide (80 %, 0.35 g) and DMF (9 ml), a solution of 2- (2-fluoro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl) - 3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (1.0 g) in DMF was added dropwise under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. To the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium
sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.10 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4- trifluoromethylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 174 ) .
Present Compound 174
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m), 7.70- 7.68 (lH,m), 7.62-7.56 (2H,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.95 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t)
[0416]
Production Examples 115 and 116
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl) -3-methy1-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2- (2- tert-butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 0.51 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfinyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 175) and 0.26 g of 2- (2-
ethylsulfonyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 176) .
Present Compound 175
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.79-8.78 (lH,m), 8.57-8.55 (lH,m), 8.35- 8.34 (lH,m), 7.97-7.94 (lH,m), 7.77 (lH,d), 3.94 (3H,s), 3.53-3.43 (lH,m), 3.07-2.98 (lH,m), 1.36 (3H,t)
Present Compound 176
■""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.51-8.49 (lH,m), 8.31- 8.30 (lH,m), 8.12-8.09 (lH,m) , 7.74 (lH,d), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q), 1.29 (3H,t)
[0417]
Production Example 117
A mixture of 3-amino-5- ( trifluoromethyl ) pyridin-2- thiol0.56g, 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (0.52 g) , WSC (0.80 g) , HOBt (39 mg) , and pyridine (6 ml) was stirred at 60 °C for 2 hours. After the reaction mixture was allowed to
stand to cool, water was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
A mixture of the resulting residue, p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (0.65 g) , and N-methylpyrrolidinone (5 ml) was stirred with heating at 150 °C for 2 hours. After the reaction mixture was allowed to cool, water was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.38 g of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl ) - 6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5, 4-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 183) .
Present Compound 183
""■H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.86 (lH,d), 8.57 (lH,d), 8.03 (lH,dd), 7.55 (lH,dd), 7.48 (lH,td), 7.36 (lH,td), 2.98 (2H,q), 1.34 (3H, t) .
[0418]
Production Examples 118 and 119
The procedure was performed according to the method
described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl ) -6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5,4- b] pyridine instead of 2- ( 2-tert-butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give
0.13 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -6-
(trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5, 4-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 184) and 0.14 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5, 4- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound
185) .
^"H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.90 (lH,d), 8.49 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,dd), 7.99 (lH,dd), 7.81 (lH,td), 7.67 (lH,td), 3.52-3.42 (lH,m), 3.01-2.92 (lH,m), 1.45 (3H,t).
Present Compound 185
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.92 (lH,d), 8.52 (lH,d), 8.25 (lH,dd),
7.84-7.71 (3H,m), 3.73 (2H,q), 1.37 (3H,t).
[0419]
Production Example 120-1
A mixture of 2- (2-fluorophenyl) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (7.83 g) , sodium sulfide (6.20 g) , and NMP (27 ml) was stirred with heating at 150 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water and 12N hydrochloric acid were poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.74 g of a compound of the following formula:
(hereinafter referred to as Compound (186A) ) .
^- MR (CDC13) δ: 8.73-8.71 (2H,m), 8.31-8.29 (2H,m) , 7.77-
7.73 (2H,m), 7.47-7.37 (6H,m), 3.77 (6H,s)
[0420]
Production Example 120-2
To a solution of sodium hydride (60 % in oil, 0.12 g) in DMF, Compound (186A) (0.80 g) of the following formula:
was added under ice-cooling, and stirred for 10 minutes under ice-cooling. To the mixture, 2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethyl iodide (0.65 g) was added under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred for 15 minutes. Then, the mixture was heated to 60 °C, and stirred with heating for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.23 g of 3- methyl-2- [2- (2 , 2 , 2-trifluoroethylsulfanylphenyl ) ] -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 186) .
Present Compound 186
-NMR (CDCI3) δ : 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.34-8.32 (lH,m), 7. 74 (lH,m), 7.61-7.48 (3H,m) , 3.75 (3H,s), 3.37 (2H,q)
[0421]
Production Examples 121 and 122
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 3-methyl- 2- [2- (2, 2, 2-trifluoroethylsulfanylphenyl) ] -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2- tert-butylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methy1-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 73 mg of 3-methyl-2- [2- (2,2, 2-trifluoroethylsulfinylphenyl ) ] -6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 187) and 68 mg of 3-methyl-2- [2- (2, 2, 2- trifluoroethylsulfanylphenyl ) ] -6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 188).
Present Compound 187
XH-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.47-8.44 (lH,m), 8.29- 8.26 (lH,m), 7.91-7.87 (lH,m), 7.80-7.74 (2H,m), 4.85-4.73 (lH,m), 4.03 (3H,s), 3.55-3.43 (lH,m)
Present Compound 187
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.35-8.31 (2H,m) , 7.95- 7.84 (2H,m), 7.63-7.60 (lH,m), 4.61-4.47 (2H,m) , 3.75 (3H,s)
[0422]
Production Examples 123 and 124
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoroitiethylsulfanyl- 3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2- (2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethylsulfanyl-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 209) and 2- (2- ethylsulfinyl-phenyl) -6-trifluoromethylsulfanyl-3-methyl-
3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 210).
Present Compound 209
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.36 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,dd),
7.87-7.77 (2H,m), 7.59 (lH,dd), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t)
Present Compound 210
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.69 (lH,d), 8.38 (lH,d), 8.25 (lH,dd), 7.86-7.80 (lH,m), 7.72-7.67 (lH,m), 7.60 (lH,dd), 3.88 (3H,s), 3.43-3.31 (lH,m), 3.03-2.92 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t)
[0423]
Production Examples 125 and 126
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Examples 16 and 17 using 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6-trifluoromethylsulfanyl-3-methyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2-(2-tert- butylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine to give 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -6- trifluoromethylsulfinyl-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 214) and 2-(2- ethylsulfonylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethylsulfonyl3-methy1-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 215 ) .
Present Compound 214
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.55 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,dd),
7.90-7.83 (2H,m), 7.61 (lH,dd), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t)
Present Compound 215
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.05 (lH,d), 8.65 (lH,d), 8.26-8.23 (lH,m), 7.90-7.85 (2H,m) , 7.61-7.57 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s),
3.41 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t)
[0424]
Production Example 127
To a mixture of 2- [2-fluoro-4-
(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] -6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5,4- b]pyridine (0.18 g) and DMF (2 ml), sodium thiomethoxide
(63 mg) was added under ice-cooling, and stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The
resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.11 g of 2- [2-ethylsulfanyl-4- (trifluoromethyl) phenyl] -6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5, 4- b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 267).
■"Ή-ΝΜΡΝ. (CDC13) δ: 8.90 (lH,d), 8.61 (lH,d), 8.14 (lH,d), 7.75 (lH,s), 7.58 (lH,d), 3.04 (2H,q), 1.38 (3H,t).
[0425]
Production Example 128
To a mixture of 2- [2-ethylsulfanyl-4-
(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] -6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5,4- b]pyridine (0.11 g) and chloroform (3 ml), 3- chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %) (0.13 g) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 12 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with chloroform, washed with 10 % aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution and saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, sequentially, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.11 g of 2- [2- ethylsulfonyl4- ( trifluoromethyl ) phenyl] -6-
(trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [5, 4-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 251) .
Present Compound 251
XH-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.95 (lH,s), 8.55 (lH,s), 8.52 (lH,s), 8.07 (lH,d), 7.88 (lH,d), 3.77 (2H,q), 1.40 (3H,t).
[0426]
Production Example 129
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl- 3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridin-6-thiol (535 mg) , iodomethane (166 μΐ) , and ethanol (5 ml), potassium hydroxide (200 mg) was added at room temperature, and stirred for 5 hours. To the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was added, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 515 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-6-methylsulfanyl- 3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 253) .
Present Compound 253
1H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.46 (lH,d), 8.10 (lH,d), 7.52-7.42 (3H,m), 7.37-7.26 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 2.54 (3H,s), 1.22 (3H,t)
[0427]
Production Example 130
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -3-methyl-6- methylsulfanyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (363 mg) and chloroform (5 ml), 69-75 % of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (1.13 g) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 5 hours, and then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 356 mg of 2- (2- ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -6-methylsulfony13-methy1-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Present Compound 254) .
Present Compound 254
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.02 (lH,d), 8.58 (lH,d), 8.23 (lH,dd), 7.90-7.81 (2H,m), 7.59 (lH,dd), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.42 (2H,q), 3.19 (3H,s), 1.26 (3H,t).
[0428]
Production Example 131-1
A mixture of 6-bromo-2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (1.02 mg) , copper iodide (280 mg) , 1 , 10-phenanthroline (268 mg) , benzyl alcohol (456 μΐι) , cesium carbonate (1.9 g) , NMP (4 mL) , and xylene (20 mL) was stirred with heating at 150 °C for 8 hours. After the mixture was allowed to stand to cool to room temperature, into the mixture, 28 % of aqueous ammonia and saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution were poured, extracted with tert-butyl methyl ether. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 402 mg of 6-benzyloxy-2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter referred to as Compound 268A) .
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.27 (lH,d), 7.67 (lH,d), 7.45-7.33 (9H,m), 5.16 (2H,s), 3.70 (3H,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t).
[0429]
Production Example 131-2
To a mixture of 6-benzyloxy-2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl- phenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine262mg, and chloroform (3 mL) , boron tribromide (1 in dichloromethane ) (698 μΐ.) was added under ice-cooling, and stirred for 3 hours. Into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with chloroform then ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 168 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl- phenyl) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine-6-0I
(hereinafter, Present Compound 268).
Present Compound 268
S )
^-NMR (D SO-D6) δ : 9.58 (lH,brs), 8.02 (lH,d), 7.60-7.54 (2H,m), 7.47 (lH,d), 7.41 (lH,d), 7.38-7.33 (lH,m), 3.54 (3H,s), 2.94 (2H,q), 1.16 (3H,t).
[0430]
Production Example 132
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl- 3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine-6-ol (579 mg) , chloroform (20 mL) , and acetonitrile (6 mL) , 69 % of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (1.05 g) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, stirred for 3 hours, and filtered. The resulting filtered substance was washed with chloroform to give 566 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-phenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine-6-ol (hereinafter, Present Compound 269) .
Present Compound 269
[0431]
Production Example 133-1
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-phenyl) -3-methyl- 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridine-6-ol (566 mg) and DMF (5 mL) , 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil, 129 mg) was added, and stirred with heating at 50 °C for 1 hour. After the mixture
was allowed to stand to cool to room temperature, to the mixture, carbon disulfide (1.08 mL) was added, and stirred at room temperature (2.5 hours). To a mixture, iodomethane
(446 L) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 1.5 hours. Into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 681 mg of S-methyl 0- [2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-phenyl) -3- methyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine-6-yl] dithiocarboxylate
(hereinafter referred to as Compound 270A) .
Compound 27 OA
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.30-8.25 (lH,m), 8.24-8.18 (lH,m), 7.85- 7.76 (3H,m), 7.58-7.53 (lH,m), 3.69 (3H,brs), 3.44 (2H,q), 2.71 (3H,brs), 1.26-1.22 (3H,m) .
[0432]
Production Example 133-2
To a mixture of S-methyl 0- [ 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonyl- phenyl ) -3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine-6- yl] dithiocarboxylate (371 mg) and chloroform (3 mL) , HF-
pyridine complex (1.25 mL) and 1 , 3-dibromo-5 , 5- dimethylhydantoin (1.58 g) were added with cooling at -55 °C. The mixture was stirred for 7 hours with heating to room temperature gradually, and then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was washed with aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to reversed-phase silica gel column chromatography to give 29 mg of 6- (bromo-difluoro- methoxy) -2- ( 2-ethylsulfonyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 270) and 76 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfonyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethoxy-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 271) .
Present Compound 270
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.43 (lH,d), 8.26-8.21 (lH,m), 7.97-7.97 (lH,m), 7.87-7.80 (2H,m) , 7.56 (lH,dd), 3.70 (3H,s), 3.45 (2H,q) , 1.26 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 271
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.42 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,dd), 7.94-7.94 (lH,m), 7.87-7.79 (2H,m) , 7.56 (lH,dd), 3.70 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
[0433]
Production Example 134
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Production Example 103 using 2- (2- ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl) -6-iodo-3-methyl-3H- imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine instead of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl- phenyl ) -6-iodo-3-methyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine to give Compound 301A.
A mixture of Compound 301A (0.94 g) and DMF (13 ml) was cooled to -50 °C, and bubbled with excessive amounts of CF3I gas to dissolve the compound in DMF. To the mixture, tetrakis (dimethylamino) ethylenediamine (1.2 ml) was added dropwise at a rate that the internal temperature did not exceed -40 °C . Then, the mixture was heated to -10 °C over 1 hour, and stirred at -10 °C for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, heated to room temperature, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under
reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected silica gel column chromatography to give 0.68 g of 2- ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethylsulfanyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter, Present Compound 301) .
Present Compound 301
"""H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.66 (lH,d)8.39 (lH,d), 7.67-7.64 (lH,m), 7.59-7.52 (2H,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 2.94 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t).
[0434]
Production Example 135
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-4- trifluoromethylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethylsulfanyl- 3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine and chloroform (5 ml), 69 % of 3- chloroperbenzoic acid (1.05 g) was added under ice-cooling, and then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1.5 hours. Then, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution was poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give
0.20 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethylsulfanyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 306) .
Present Compound 306
^-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.71-8.70 (lH,m), 8.50-8.49 (lH,m), 8.38- 8.36 (lH,m), 8.12-8.08 (lH,m), 7.74-7.71 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.29 (3H,t).
[0435]
Production Example 136
A mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-4- trifluoromethylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethylsulfinyl- 3H-imidazo [ , 5-b] pyridine (0.26 g) , sodium tungstate dihydrate (36 mg) , 30 % of aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution (1 ml) and acetonitrile (5 ml) was stirred under reflux for 4.5 hours. The mixture was cooled to room temperature. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.24 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfonyl-4-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-
trifluoromethylsulfonyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter, Present Compound 302) .
Present Compound 302
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 9.08-9.07 (lH,m), 8.68-8.66 (lH,m), 8.52- 8.50 (lH,m), 8.16-8.12 (lH,m), 7.76-7.73 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 3.46 (2H,q), 1.30 (3H,t)
[0436]
Production Example 137-1
To a mixture of 4- ( 1 , 2 , 2 , 2-tetrafluoro-1- trifluoromethyl-ethyl ) -benzene-1 , 2-diamine (552 mg) , 2- ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (401 mg) , and pyridine (27 mL) , l-ethyl-3- ( 3-dimethylaminopropyl ) carbodiimide hydrochloride (422 mg) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (27 mg) were added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 hours, diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was dissolved in a mixed solution of DMF (7.5 mL) and toluene (30 mL) , and then p- toluenesulfonic acid (837 mg) was added at room temperature. The mixture was stirred with heating at 130 °C for 8 hours,
and allowed to stand to cool to room temperature. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 97 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -5- ( 1 , 2 , 2 , 2- tetrafluoro-l-trifluoromethyl-ethyl ) -ΙΗ-benzimidazole
(hereinafter, Present Compound 346).
Present Com ound 346
aH-NMR (CDC13) δ: 12.08-11.87 (lH,m), 8.31 (lH,s), 8.12- 7.44 (4H,m), 7.42-7.30 (2H,m), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t).
[0437]
Production Example 137-2
To a mixture of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -5- ( 1 , 2 , 2 , 2- tetrafluoro-l-trifluoromethyl-ethyl ) -lH-benzimidazole (97 mg) and DMF (10 mL) , sodium hydride (11 mg) and iodomethane (16 μΐ,) were added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 5 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 35 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) - l-methyl-6- (1,2,2, 2-tetrafluoro-l-trifluoromethyl-ethyl ) - lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter, Present Compound 304) and 80 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl) -l-methyl-5- (1, 2, 2, 2- tetrafluoro-l-trifluoromethyl-ethyl ) -ΙΗ-benzimidazole
(hereinafter, Present Compound 305) .
Present Compound 304
XH-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.93 (lH,d), 7.68 (lH,s), 7.55-7.44 (4H,m), 7.37-7.29 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 305
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.12 (lH,s), 7.61-7.41 (5H,m), 7.36-7.30 (lH,m), 3.68 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t).
[0438]
Production Example 138-1
To a mixture of 2-nitro-4- (pentafluorosulphur) -
phenylamine (2.0 g) and DMF (15 mL) , sodium hydride (313 mg) and iodomethane (447 L) were added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 5 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with water, and then the precipitated powder was collected by filtration. The resulting powder was washed with hexane to give 2.0 g of methyl- (2-nitro-4- (pentafluorosulphur) -phenyl) -amine . methyl- [2-nitro-4- (pentafluorosulphur) -phenyl] -amine
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.60 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,brs), 7.78 (lH,dd),
6.89 (lH,d) , 3.10 (3H,d) .
[0439]
Production Example 138-2
To a mixture of methyl- [2-nitro-4-
(pentafluorosulphur) -phenyl] -amine (2.0 g) , acetic acid (1.9 mL) , ethanol (80 mL) , and water (20 mL) , iron powder (1.5 g) was added with stirring with heating at 80 °C . The reaction mixture was stirred with heating at 80 °C for 6 hours, and filtered through Celite
®. The resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and diluted with IN aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. The mixed solution was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under
reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.6 g of N
1-methyl-4- (pentafluorosulphur ) -benzene-1 , 2-diamine (Compound (lF)-35) . N
1-methyl-4- (pentafluorosulphur ) -benzene-1, 2-diamine
[0440]
Production Example 138-3
To a mixture of N1-methyl-4- (pentafluorosulphur ) - benzene-1 , 2-diamine (575 mg) , 2-fluoro-4 trifluoromethyl- benzaldehyde (348 ]iL) , and DMF (5 mL) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (290 mg) was added at room temperature. The mixture was heated to 100 °C, and stirred with heating for 10 hours. After the mixture was allowed to stand to cool to room temperature, the mixture was diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in DMF, and then and sodium ethanethiolate (175 mg) was added at room temperature thereto. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 8 hours, and then into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and
concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 537 mg of 2- ( 2-ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl ) -1- methyl-5- (pentafluorosulphur) -lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter, Present Compound 314).
Present Compound 314
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.28 (lH,d), 7.79 (lH,dd), 7.67 (lH,s), 7.57 (2H,s), 7.46 (lH,d), 3.70 (3H,s), 2.93 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H, t) .
[0441]
Production Example 139
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethyl- phenyl) -l-methyl-5- (pentafluorosulphur) -lH-benzimidazole (370 mg) and chloroform (10 mL) , 69-75 % of 3- chloroperbenzoic acid (335 mg) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 0.5 hours. Into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 115 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfinyl-4- trifluoromethyl-phenyl ) -l-methyl-5- (pentafluorosulphur) -1H- benzimidazole (hereinafter, Present Compound 315) and 244 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl ) -l-methyl-5- (pentafluorosulphur) -lH-benzimidazole (hereinafter, Present Compound 316) .
Present Compound 315
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.54-8.49 (lH,m), 8.26-8.21 (lH,m), 7.95- 7.89 (lH,m), 7.85-7.80 (lH,m), 7.74-7.68 (lH,m), 7.52-7.47 (lH,m), 3.82 (3H,s), 3.48-3.36 (lH,m), 3.06-2.94 (lH,m), 1.35-1.27 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 316
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.50-8.41 (lH,m), 8.24-8.16 (lH,m), 8.09- 8.02 (lH,m), 7.83-7.65 (2H,m), 7.50-7.39 (lH,m), 3.64 (3H,s), 3.49-3.37 (2H,m) , 1.30-1.24 (3H,m).
[0442]
Production Example 140
A mixture of 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.0 g) , oxalyl chloride (0.7 ml), DMF (1 drop) and chloroform (4 ml) was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
A mixture of the resulting residue, 2-amino-3-chloro- 5-trifluoromethylpyridine (1.08 g) and N- ethyldiisopropylamine (0.85 g) was stirred at 140 °C for 2 hours . After the reaction mixture was allowed to stand to cool, into the mixture, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
A mixture of the resulting residue, Lawesson's reagent (2.1 g) , and chlorobenzene (10 ml) was refluxed for 3 hours. After the reaction mixture was allowed to stand to cool, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.14 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6- (trifluoromethyl) thiazolo [4,5- bjpyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 328).
Present Compound 328
S )
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.02 (lH,d), 8.55 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,dd), 7.60 (lH,dd) ,■ 7.49 (lH,td), 7.40 (lH,td), 2.99 (2H,q), 1.33 (3H,t) .
[0443]
Production Example 141
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6- (trifluoromethyl ) thiazolo [4, 5-b] pyridine (0.14 g) and chloroform (3 ml) , 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %, 0.21 g) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 12 hours. The reaction mixture was diluted with chloroform, washed with 10 % of aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 57 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfonylphenyl) -6- (trifluoromethyl ) thiazolo [4, 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 329) .
Present Com ound 329
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 9.04 (lH,d), 8.62 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd), 7.84-7.77 (2H,m), 7.71 (lH,dd), 3.81 (2H,q), 1.36 (3H,t).
[0444]
Production Example 142
To a mixture of sodium ethyl mercaptide ( 80 %, 0.63 g) and DMF (10 ml), a solution of 2- ( 4-bromo-2-fluorophenyl ) - 3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b] pyridine (2.08 g) in DMF was added dropwise under ice-cooling, then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 30 minutes. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.57 g of 2- (4-bromo-2- ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 238). Present Compound 238
[0445]
Production Example 143
To a mixture of 2- (4-bromo-2-ethylsulfanylphenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.40 g) and chloroform (5 ml) , 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %, 0.29 g) was added under ice-cooling, then
heated to room temperature, and stirred for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.26g of 2- (4-bromo-2-ethylsulfinylphenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter, Present Compound 239) and 0.17 g of 2- (4- bromo-2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 240). Present Compound 239
Present Compound 240
[0446]
Production Example 144
A mixture of 2- ( 4-bromo-2-ethylsulfonylphenyl ) -3-
methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.20 g) , 2-tributylstannylpyrimidine (0.17 g) , tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (27 mg) and toluene (5 ml) was heated at reflux under nitrogen atmosphere for 5.5 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, to the mixture, 2-tributylstannylpyrimidine (0.17 g) and tetrakis (triphenylphosphine) palladium (27 mg) were added, and stirred under reflux for further 8 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, water was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.20 g of 2- [2-ethylsulfonyl-4- (pyrimidine-2-yl) -phenyl) -3- methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter, Present Compound 333) .
Present Compound 333
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.77-8.74 (lH,m), 8.38-8.36 (lH,m), 8.30- 8.27 (lH,m), 8.00-7.95 (lH,m), 7.63-7.55 (lH,m), 7.43
(lH,d), 7.41-7.30 (2H,m) , 3.72 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t) .
[0447]
Production Example 145-1
To a mixture of 2-chloro-l , 3-dinitro-5- trifluoromethyl-benzene (20 g) and DMF (30 mL) , 40 % of aqueous methylamine solution (15 mL) was added dropwise under ice-cooling. The mixture was stirred for 6 hours under ice-cooling, and then the reaction mixture was added to iced water. The precipitated powder was collected by filtration, and washed with water to give 20 g of (2,6- dinitro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl) -methyl-amine .
(2, 6-dinitro-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl) -methyl-amine
[0448]
Production Example 145-2
To a mixture of (2, 6-dinitro-4-trifluoromethyl- phenyl ) -methyl-amine (5.0 g) , acetic acid (11 mL) , ethanol (100 mL) , and ice (20 g) , iron powder (6.4 g) was added under ice-cooling. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 3.5 hours, and filtered through Celite®. The resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure, and diluted with IN aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. The solution was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and
concentrated under reduced pressure to give 3.1 g of N'- methy1-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene-l , 2 , 3-triamine .
N ' -methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene-l , 2 , 3-triamine
[0449]
Production Example 145-3
To a mixture of ' -methyl-5-trifluoromethyl-benzene- 1 , 2 , 3-triamine (1.3 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1.3 g) , and pyridine (12 mL) , l-ethyl-3- ( 3- dimethylaminopropyl ) carbodiimide hydrochloride (1.4 g) and l-hydroxybenzotriazole (86 mg) were added at room temperature. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 hours, then heated to 110 °C, and stirred with heating for 8 hours. After the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, the reaction mixture was diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 339 mg of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-phenyl ) -3-methyl-6- trifluoromethyl-3H-benzimidazole-4-ylamine (hereinafter, Present Compound 336) .
Present Compound 336
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 7.55 (lH,s), 7.50-7.36 (3H,m), 7.33-7.28 (lH,m), 6.77 (lH,d), 4.04 (2H,brs), 3.91 (3H,s), 2.83 (2H,q) , 1.21 (3H,t) .
[0450]
Production Example 146
To a mixture of sodium ethyl mercaptide (80 %, 0.33 g) and DMF (4 ml), a solution of 2- (2-fluoro-4- (pentafluorosulphur ) phenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (1.19 g) in DMF was added dropwise under ice-cooling, then heated to room temperature, and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.21 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-
(pentafluorosulphur ) phenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 341). Present Compound 341
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.74 (lH,m), 8.36-8.34 (lH,m), 7.81 (lH,d), 7.73 (lH,dd), 7.58-7.54 (lH,m), 3.80 (3H,s), 2.95 (2H,q) , 1.29 (3H,t) .
[0451]
Production Example 147
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-
(pentafluorosulphur) phenyl) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (0.90 g) and chloroform (6 ml), 3- chloroperbenzoic acid (purity: not less than 65 %, 0.68 g) was added under ice-cooling, then heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.45 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfinyl-4- (pentafluorosulphur) phenyl) - 3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4, 5-b]pyridine
(hereinafter, Present Compound 342) and 0.44 g of 2- (2- ethylsulfonyl-4- (pentafluorosulphur) phenyl) -3-methyl-6-
trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter,
Present Compound 343) .
Present Compound 342
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.80-8.78 (lH,m), 8.65 (lH,d), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 8.07 (lH,dd), 7.78-7.75 (lH,m), 3.95 (3H,s), 3.55- 3.45 (lH,m), 3.10-3.00 (lH,m), 1.36 (3H,t).
Present Compound 343
■"Ή -Ν ΡΝ. (CDC13) δ: 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.61 (lH,d), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 8.22 (lH,dd), 7.74-7.70 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.50 (2H,q) , 1.30 (3H, t) .
[0452]
Production Example 148-1
To a mixture of 5-trifluoromethyl-pyridine-2-ylamine (65 g) and chloroform (100 mL) , N-bromosuccinimide (71 g) was added in 5 parts under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour, then heated to 80 °C, and stirred with heating for 30 minutes.
After the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution and saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over■ sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 96 g of 3-bromo-5-trifluoromethyl-pyridine-2-ylamine .
3-bromo-5-trifluoromethyl-pyridine-2-ylamine
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.27 (lH,d), 7.86 (lH,d), 5.38 (2H,brs).
[0453]
Production Example 148-2
To an autoclave reactor, 3-bromo-5-trifluoromethyl- pyridine-2-ylamine (40 g) , acetylacetone copper (II) (2.2 g) , acetylacetone (6.6 g) , cesium carbonate (59 g) , and NMP (105 mL) were added, and then 28 % of aqueous ammonia solution (25 mL) was added under ice-cooling. After the reactor was sealed, the mixture heated to 110 °C, and stirred with heating for 12 hours. The mixture was ice- cooled to room temperature, then diluted with water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel
column chromatography to give 15g 5-trifluoromethyl- pyridine-2 , 3-diamine (Compound (lF)-22).
5-trifluoromethyl-pyridine-2 , 3-diamine
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.93 (lH,d), 7.04 (lH,d), 4.71 (2H,brs), 3.46 (2H,brs) .
[0454]
Production Example 148-3
To a mixture of 5-trifluoromethyl-pyridine-2 , 3-diamine (8.6 g) , 2-formyl-5-trifluoromethylphenylethylsulfide (11 g) , and DMF (67 mL) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (6.1 g) was added at room temperature. After the mixture was stirred with heating at 100 °C for 3 hours, to the mixture, copper (II) chloride dihydrate (1 g) was added, and stirred at 100 °C for further 1 hour. After the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, the reaction mixture was added to water, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give a yellow powdered solid. The solid was washed with hot hexane to give 12 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethyl- phenyl) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine
(hereinafter, Present Compound 344).
resent Compound 344
■""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 12.79 (lH,brs), 8.72 (lH,brs), 8.49-8.34 (2H,m), 7.79 (lH,s), 7.64 (lH,d), 3.00 (2H,q), 1.31 (3H,t).
[0455]
Production Example 149
To a mixture of 2- (2-ethylsulfanyl-4-trifluoromethyl- phenyl ) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] pyridine (12 g) and chloroform (111 mL) , 69-75 % of 3-chloroperbenzoic acid (8.0 g) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 0.5 hours. Into the mixture, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution were poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 9.1 g of 2- (2-ethylsulfonyl-4-trifluoromethyl-phenyl) -6- trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4 , 5-b] pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 345) .
1H-N R (D SO-Dg) δ: 14.15 (lH,brs), 8.83 (lH,s), 8.58 (lH,s), 8.41 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,s), 8.19 (lH,d), 3.97 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t) .
[0456]
Production Example 150
A mixture of N- ( 2-amino-5-trifluoromethylpyridine-3- yl ) -2-ethylsulfanyl-benzamide (200 mg) , tert-butylalcohol (1 ml), and THF (9 ml) was stirred with heating at 80 °C, then 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil, 56 mg) was added thereto. The mixture was stirred with heating at 80 °C for 2 hours, and then 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil, 56 mg) was added. The mixture was further stirred with heating at the same temperature for 2 hours, and then to the mixture, 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil, 56 mg) was added, and stirred with heating at the same temperature for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and evaporated to remove the solvent, and then to the mixture, saturated ammonium chloride solution was added, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 132 mg of 2- (2-
ethylsulfanylphenyl) -6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b]pyridine (hereinafter, Present Compound 351).
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.67 (lH,d), 8.51-8.48 (lH,m), 8.33 (lH,d), 7.66-7.61 (lH,m), 7.51-7.46 (2H,m), 2.93 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t)
[0457]
The above present compounds and present compounds produced by a similar production method to those of the above present compounds are shown in the following tables.
[0458]
The com ound of the formula (1-2):
wherein, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, A1, A2, A3, and represent a combination shown in Tables 20-34.
[0459]
Table 20
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
1 Me H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
2 Me H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
3 Me H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
4 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
5 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
6 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
7 Pr H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
8 Pr H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
9 Pr H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
10 CH2=CHCH2 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
11 CH2=CHCH2 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
12 iPr H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
13 iPr H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
14 iPr H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
15 tBu H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
16 tBu H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
17 tBu H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
18 CF3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
19 CF3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
20 CF3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
21 Et H H H H CF3 H NEt CH N 0
22 Et H H H H CF3 H NEt CH N 1
23 Et H H H H CF3 H NEt CH N 2
24 Et H H H H CF3 H NPr CH N 0
25 Et H H H H CF3 H NPr CH N 1
[0460]
Table 21
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
26 Et H H H H CF3 H NPr CH N 2
27 Et H H H H CF3 H NiPr CH N 0
28 Et H H H H CF3 H NiPr CH N 1
29 Et H H H H CF3 H NiPr CH N 2
30 Et H H H H CF3 H NCycPr CH N 0
31 Et H H H H CF3 H NCycPr CH N 1
32 Et H H H H CF3 H NCycPr CH N 2
33 Et H H H H CF3 H NCH2OEt CH N 0
34 Et H H H H H CF3 NCH2OEt N CH 0
35 Et H H H H CF3 H NCH2OEt CH N 1
36 Et H H H H CF3 H NCH2OEt CH N 2
37 Et H H H H CF3 H NCH2OMe CH N 0
38 Et H H H H CF3 H NCH2OMe CH N 2
39 Et H H H H Me H NMe CH N 0
40 Et H H H H Me H NMe CH N 1
41 Et H H H H Me H NMe CH N 2
42 Et H H H H Br H NMe CH N 0
43 Et H H H H Br H NMe CH N 1
44 Et H H H H Br H NMe CH N 2
45 Et H H H H I H NMe CH N 0
46 Et H H H H I H NMe CH N 1
47 Et H H H H I H NMe CH N 2
48 Et H H H H CN H NMe CH N 0
49 Et H H H H CN H NMe CH N 1
50 Et H H H H CN H NMe CH N 2
[0461]
Table 22
[0462]
Table 23
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
76 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe CH CBr 2
77 Me H H H H CF3 H O CH CH 0
78 Et H H H H CF3 H O CH CH 0
79 Et H H H H CF3 H O CH CH 1
80 Et H H H H CF3 H O CH CH 2
81 Et H H H H CF3 H O CH N 0
82 Et H H H H CF3 H O CH N 1
83 Et H H H H CF3 H O CH N 2
84 Me H H H H CF3 H S CH CH 0
85 Et H H H H CF3 H S CH CH 0
86 Et H H H H CF3 H S CH CH 1
87 Et H H H H CF3 H S CH CH 2
88 Et CI H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
89 Et CI H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
90 Et CI H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
91 Et H H H H C (0) CF3 H NMe CH N 0
92 Me H H H SMe CF3 H NMe CH N 0
93 Me H H H SOMe CF3 H NMe CH N 1
S02M
94 Me H H H e CF3 H NMe CH N 2
95 Et H H H SEt CF3 H NMe CH N 0
96 Et H H H SOEt CF3 H NMe CH N 1
S02E
97 Et H H H t CF3 H NMe CH N 2
98 Et H H H H CI H NMe CH N 0
99 Et H H H H CI H NMe CH N 1
100 Et H H H H CI H NMe CH N 2
[0463]
Table 24
[0464]
Table 25
[0465]
Table 26
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
151 Et H H H H H CF3 NMe CH N 0
152 Et H H H OMe CF3 H NMe CH N 0
153 Et H H H OMe CF3 H NMe CH N 1
154 Et H H H OMe CF3 H NMe CH N 2
155 Et H H H OH CF3 H NMe CH N 0
156 Et F H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
157 Et F H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
158 Et F H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
159 Et H H H H H CF3 NMe CH N 1
160 Et H H H H H CF3 NMe CH N 2
161 Et H H H H SCF3 H NMe CH N 0
162 Et H H H H NMe2 H NMe CH N 0 pyrrolidin-
163 Et H H H H 1-yl H NMe CH N 0
164 Et H H H H NHCOMe H NMe CH N 0
165 Et H H H H CH2CF3 H NMe CH N 0
166 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe N CH 0
167 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe N CH 1
168 Et H H H H CF3 H NMe N CH 2
169 Et H H H F CF3 H NMe CH N 0
170 Et H H H F CF3 H NMe CH N 1
171 Et H H H F CF3 H NMe CH N 2
172 Et H H H H N (Me) COMe H NMe CH N 0
173 Et H H H H NH2 H NMe CH N 1
114 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
175 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
[0466]
Table 27
[0467]
Table 28
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
201 Et H H CF3 H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
202 Et H H CF3 H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
203 Et H H CF3 H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
204 Et H H H H 2-Cl-Ph H NMe CH N 0
205 Et H H H H 3-Cl-Ph H NMe CH N 0
206 Et H H H H 4-Cl-Ph H NMe CH N 0
[0468]
Table 29
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
4-C1-
226 Et H H H H Pyrazole H NMe CH N 2
3-C1-
227 Et H H H H triazole H NMe CH N 0
4-CF3-
228 Et H H H H imidazole H NMe CH N 0
229 Et H H H H 2-N02-Ph H NMe CH N 0
230 Et H H H H 3-N02-Ph H NMe CH N 0
231 Et H H H H 2-CN-Ph H NMe CH N 0
232 Et H H H H 3-CN-Ph H NMe CH N 0
233 Et H H H H 4-CN-Ph H NMe CH N 0
3-CF3-
234 Et H H H H triazole H NMe CH N 0
3-CF3-5-Me-
235 Et H H H H triazole H NMe CH N 0
3-C1-
236 Et H H H H triazole H NMe CH N 2
4-CF3-
237 Et H H H H imidazole H NMe CH N 1
238 Et H Br H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
239 Et H Br H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
240 Et H Br H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
241 Et H CN H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
242 Et H CN H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
243 Et H CN H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
246 Et H C2F5 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
247 Et H C2F5 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
248 Et H C2F5 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
249 Et H CHO H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
250 Et H Ph H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
[0469]
Table 30
[0470]
Table 31
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
276 Et H H H H SC(CH3)3 H NMe CH N 0
277 Et H H H H S02C(CH3)3 H NMe CH N 2
278 Et H CF3 H H Br H NMe CH N 0
279 Et H CF3 H H Br H NMe CH N 1
280 Et H CF3 H H Br H NMe CH N 2
281 Et H H H H SCH=C=CH2 H NMe CH N 0
282 Et H H H H S02CH=C=CH2 H NMe CH N 2
283 Et H H H H S02CH2CH=CH2 H NMe CH N 2
284 Et H H H H NHS02CH3 H NMe CH N 2
285 Et H N02 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
286 Et H N02 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
287 Et H N02 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
289 Et H H H H NHS02CF3 H NMe CH N 2
290 Et H H H H NCH3S02CF3 H NMe CH N 2
291 Et H H H H NCH3S02CH3 H NMe CH N 2
292 Et H CF3 H H CF2CF3 H NMe CH N 0
293 Et H CI H H CF3 H S CH N 0
294 Et H CI H H CF3 H S CH N 2
295 Et H H H H C(OH) (CF3)2 H NMe CH N 0
296 Et H H H H C(C1) (CF3)2 H NMe CH N 0
297 Et H H H H C(C1) (CF3)2 H NMe CH N 1
298 Et H H H H C(C1) (CF3)2 H NMe CH N 2
299 Et H CF3 H H CF2CF3 H NMe CH N 2
300 Et H CF3 H H I H NMe CH N 0
[0471]
Table 32
[0472]
Table 33
[0473]
Table 34
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
351 Et H H H H CF3 H NH CH N 0
352 Et H H H H CF3 H NH CH N 1
353 Et H H H H CF3 H NH CH N 2
354 Et H H H H CF3 H NH CH CH 0
355 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NEt CH N 2
356 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2CH=CH2 CH N 2
357 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2CCH CH N 2
358 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2CN CH N 2
359 Et H CF3 H H H CF3 NCH2CN N CH 2
360 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2OEt CH N 2
361 Et H CF3 H H H CF3 NCH2OEt N CH 2
362 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2SMe CH N 2
363 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NPr CH N 2
364 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H N(CH2)3CH3 CH N 2
365 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2C02Me CH N 2
366 Et H CF3 H H H CF3 NCH2C02Me N CH 2
367 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCH2CH=CC12 CH N 2
368 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NC02tBu CH N 2
369 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH CH 0
370 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH CH 1
371 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH CH 2
372 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NC02Me CH N 2
373 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NCOMe CH N 2
374 Et H OCF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
375 Et H OCF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 1
[0474]
Table 35
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
376 Et H OCF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CF2CF2C
377 Et H F2CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
2- pyridy
378 Et H 1 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
379 Et H NH2 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
380 Et H NHCOCF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
381 Et H iPr H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
382 Et H CHO H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CH2CH2C
383 H2CH3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
CH2C02C
384 H3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
CH2CH=C
385 ci2 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
CH2CCCH
386 3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
387 CH2CN H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
CH2C (CH
388 3 ) 3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
CH2CH2C
389 N H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
390 CH2CyBu H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
391 CF2Br H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 0
392 Et H CF2H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
393 Et H CH2OH H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
(CH2)3C
394 H3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CH2C02C
395 H3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CH2CH=C
396 Cl2 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CH2CCCH
397 3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
398 CH2CN H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CH2C (CH
399 3 ) 3 H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
CH2CH2C
400 N H H H H CF3 H NMe CH N 2
[0475]
Table 36
[0476]
Table 37
Present
Compound R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 R7 A1 A2 A3 n
426 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH CBr 0
427 Et H CF3 H H CF3 H NMe CH CSCH2CH3 0
[0477]
In the above Tables 20-37, Me represents a methyl group, Et represents an ethyl group, Pr represents a propyl group, iPr represents an isopropyl group, tBu represents a tert-butyl group, CyPr represents a cyclopropyl group, CyBu represents a cyclobutyl group, 2-F-Ph represents a 2- fluorophenyl group, 3-F-Ph represents a 3-fluorophenyl group, 4-F-Ph represents a 4-fluorophenyl group, 2-CF3-Ph represents a 2-trifluoromethylphenyl group, 3-CF3-Ph represents a 3-trifluoromethylphenyl group, 4-CF3-Ph represents a 4-trifluoromethylphenyl group, 2-Cl-Ph represents a 2-chlorophenyl group, 3-Cl-Ph represents a 3- chlorophenyl group, 4-Cl-Ph represents a 4 -chlorophenyl group, 2-N02-Ph represents a 2-nitrophenyl group, 3-N02-Ph represents a 3-nitrophenyl group, 2-CN-Ph represents a 2- cyanophenyl group, 3-CN-Ph represents a 3-cyanophenyl group, 4-CN-Ph represents a 4-cyanophenyl group, 3-Py represents a pyridin-3-yl group, 4-Py represents a pyridin-4-yl group, 6-Cl-3-Py represents a 6-chloropyridin-3-yl group, 5-F-3-Py represents a 6-fluoropyridin-3-yl group, 4-Cl-pyrazole represents a 4-chloropyrazol-l-yl group, 3-Cl-triazole represents a 3-chloro- (lH-1, 2, 4-triazol) -1-yl group, 3-CF3- triazole represents a 3-trifluoromethyl- ( lH-1 , 2 , 4-triazol ) -
1-yl group, 3-CF3-5-Me-triazole represents a 3- trifluoromethyl-5-methyl- (lH-1, 2, 4-triazol) -1-yl group, and 4-CF3-imidazole represents a 4-trifluoromethylimidazol-l-yl group .
[0478]
The """H-NMR data of the present compounds listed in Tables 20-37 are shown below.
[0479]
Present Compound 92
^-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.36-8.35 (lH,m), 7.49 (lH,t), 7.17 (2H,d), 3.70 (3H,s), 2.41 (6H,s).
Present Compound 94
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.80-8.78 (lH,m), 8.60 (2H,d), 8.30-8.28
(lH,m), 8.08 (lH,t), 3.70 (3H,s), 3.09 (6H,s).
Present Compound 95
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 7.47-
7.43 (lH,m), 7.28-7.25 (2H,m), 3.69 (3H,s), 2.97-2.79
(4H,m) , 1.24 (6H, t) .
Present Compound 96
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.85-8.75 (lH,m), 8.38-7.96 (4H,m), 3.81-
3.71 (3H,m), 3.15-2.65 (4H,m), 1.22-1.03 (6H,m).
Present Compound 97
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.79 (lH,d), 8.54 (2H,d), 8.27 (lH,d), 8.06 (lH,t), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.32-3.07 (4H,m), 1.19 (6H,t). Present Compound 98
!fi-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.39 (lH,d), 8.07 (lH,d), 7.54-7.48 (2H,m), 7.45-7.43 (lH,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s),
2.86 (2H,q) , 1.23 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 99
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.43 (lH,d), 8.26-8.22 (lH,m), 8.06 (lH,d), 7.84-7.79 (lH,m), 7.71-7.65 (lH,m), 7.60-7.57 (lH,m), 3.84 (3H,s), 3.39-3.29 (lH,m), 2.99-2.89 (lH,m),
1.29 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 100
1H-N R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.42 (lH,d), 8.23-8.20 (lH,m), 8.02 (lH,d), 7.86-7.77 (2H,m) , 7.57-7.54 (lH,m), 3.67 (3H,s),
3.42 (2H,q) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 101
1H-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 10.83 (lH,s), 8.63 (lH,s), 7.55-7.43 (3H,m), 7.38-7.32 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 102
^"H-NMR ( C DC I 3 ) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.47- 7.42 (2H,m), 7.39-7.38 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.97 (2H,q), 2.82 (2H,q), 1.34 (3H,t), 1.21 (3H,t).
Present Compound 103
1H-N R ( C DCI3 ) δ: 8.12 (lH,s), 7.69 (lH,d), 7.62-7.57 (lH,m), 7.53-7.45 (3H,m), 7.36-7.31 (lH,m), 5.43 (2H,s), 3.26 (2H,q), 2.84 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t), 1.04 (3H,t).
Present Compound 104
1H-NMR ( CDCI 3 ) δ: 7.94-7.88 (2H,m) , 7.61-7.56 (lH,m), 7.54-
7.44 (3H,m), 7.37-7.30 (lH,m), 5.44 (2H,s), 3.27 (2H,q), 2.84 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t), 1.05 (3H,t).
Present Compound 107
1H-NMR ( C DC I 3 ) δ: 8.72-8.69 (lH,m), 8.33-8.30 (lH,m), 7.55-
7.45 (3H,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 4.40 (2H,t), 3.65 (2H,t), 3.14 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 108
1H-N R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.65 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,d), 7.50-7.39 (3H,m), 7.33-7.26 (lH,m), 5.23 (2H,s), 2.81 (2H,q), 1.98 (3H,s) , 1.17 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 109
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d), 7.56-7.46 (3H,m), 7.39-7.33 (lH,m), 4.40 (2H,t), 2.92-2.80 (4H,m), 1.85 (3H,s) , 1.24 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 110
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.71 (lH,d), 8.31 (lH,d), 7.55-7.47 (2H,m), 7.45-7.41 (lH,m), 7.38-7.32 (lH,m), 4.21 (2H,t), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.75-1.63 (2H,m) , 1.28-1.11 (5H,m), 0.78 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 111
■"■fi-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.84-8.81 (lH,m), 8.65-8.61 (lH,m), 7.48- 7.37 (3H,m), 7.35-7.27 (lH,m), 2.74-2.64 (2H,m) , 1.26 (9H, s) , 1.10-1.04 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 114
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.59-8.52 (ΙΗ,πι), 8.31-8.17 (lH,m), 7.61- 7.32 (4H,m), 5.24 (lH,brs), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.97-2.82 (2H,m), 1.31-1.15 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 115
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.51 (lH,s), 8.22 (lH,s), 7.55-7.50 (2H,m), 7.47-7.43 (lH,m), 7.38-7.32 (lH,m), 5.81 (lH,dq), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 119
^- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.71-8.70 (lH,m), 8.31-8.29 (lH,m), 7.49- 7.45 (lH,m), 7.14-7.09 (2H,m) , 4.00 (3H,s), 3.71 (3H,s), 2.74 (2H,q) , 1.04 (3H,t) .
[0480]
Present Compound 121
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.68-8.66 (lH,m), 8.28-8.27 (lH,m), 7.35 (lH,d), 6.99 (lH,d), 6.86-6.83 (lH,m), 3.88 (3H,s), 3.74 (3H,s), 2.84 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t).
Present Compound 122
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 7.77 (lH,d), 7.53 (lH,d), 7.19-7.15 (lH,m), 4.00 (3H,s), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.46-3.36 (lH,m), 3.00-2.90 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t). Present Compound 123
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.27-8.25 (lH,m), 7.71 (lH,d), 7.46 (lH,d), 7.32-7.28 (lH,m), 3.99 (3H,s), 3.70 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 124
!fi-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.12 (lH,brs), 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.33- 8.30 (lH,m), 7.15 (lH,d), 6.88 (lH,d), 6.63-6.60 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.77 (2H,q), 1.19 (3H,t).
Present Compound 126
""Ή-Ν ΡΧ. (CDC13) δ: 8.55 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,d), 7.83 (lH,t), 7.69 (lH,t), 7.60 (lH,d), 5.84 (lH,dq), 3.88 (3H,s), 3.42-3.30 (lH,m), 3.03-2.91 (lH,m), 1.33-1.25 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 127
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.53 (lH,s), 8.26-8.16 (2H,m) , 7.88-7.78 (2H,m), 7.59-7.53 (lH,m), 5.82 (lH,dq), 3.70 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 131
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 7.74-7.68 (lH,m), 7.49-7.40 (2H,m) , 3.73 (3H,s), 2.74 (2H,q), 1.06 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 132
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.64 (lH,s), 8.24 (lH,s), 7.65 (lH,d), 7.58 (lH,t), 7.39 (lH,d), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.63-3.47 (lH,m), 3.37-3.22 (lH,m), 1.38-1.30 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 136
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.32 (lH,m), 7.52- 7.49 (lH,m), 7.47-7.43 (2H,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 137
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 8.20 (lH,d), 7.81-7.78 (lH,m), 7.60 (lH,d), 3.93 (3H,s), 3.42- 3.32 (lH,m), 3.02-2.92 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t).
Present Compound 138
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.75 (lH,m), 8.29-8.28 (lH,m), 8.16 (lH,d), 7.80-7.77 (lH,m), 7.57 (lH,d), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.40 (2H,q) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 139
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.37-8.35 (lHfm) , 7.48- 7.44 (lH,m), 7.38-7.34 (2H,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.00-2.83 (2H,m) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 140
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.80-8.78 (lH,m), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 8.11- 8.08 (lH,m), 7.79 (lH,t), 7.73-7.71 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 3.37-3.27 (lH,m), 3.09-2.99 (lH,m), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 141
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.76 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 8.16- 8.13 (lH,m), 7.89-7.87 (lH,m), 7.77 (lH,t), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.61-3.49 (lH,m), 3.34-3.24 (lH,m), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 142
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.71 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 7.54 (lH,d), 7.10-7.06 (lH,m), 7.03 (lH,d), 3.85 (3H,s), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.68 (2H,q), 1.12 (3H,t).
Present Compound 143
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.31-8.30 (lH,m), 8.14
(lH,d), 7.34-7.30 (lH,m), 7.08 (lH,d), 3.93 (3H,s), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.29-3.19 (lH,m), 2.97-2.86 (lH,m), 1.26 (3H,t). Present Compound 144
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.74-8.73 (lH,m), 8.28-8.27 (lH,m), 8.13 (lH,d), 7.25-7.21 (lH,m), 7.03 (lH,d), 3.94 (3H,s), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.34 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 146
""Ή-ΝΜΡΝ. (CDC13) δ: 8.30 (lH,s), 7.93 (lH,s), 7.49-7.42 (3H,m), 7.33-7.27 (lH,m), 3.72 (3H,s), 2.89-2.78 (4H,m), 1.33 (3H, t) , 1.22 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 148
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 7.94 (lH,d), 7.48-7.39 (3H,m) , 7.34-7.25 (2H,m), 3.67 (3H,s), 3.26-3.16 (2H,m) , 2.89-2.80 (2H,m) ,
1.34-1.27 (3H,m), 1.26-1.19 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 149
XH-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.09 (lH,d), 7.50-7.41 (4H,m), 7.34-7.27 (lH,m), 3.68 (3H,s), 3.38 (4H,q), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t),
1.17 (6H,t).
[0481]
Present Compound 152
"""H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.71-8.69 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.47
(lH,t), 7.06 (lH,d), 6.86 (lH,d), 3.76 (3H,s), 3.69 (3H,s),
2.98-2.82 (2H,m), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 153
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.30-8.29 (lH,m), 7.79-
7.76 (2H,m), 7.22-7.18 (lH,m), 3.86 (3H,s), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.42-3.30 (lH,m), 3.09-2.97 (lH,m), 1.29 (3H,t).
Present Compound 154
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.27-8.25 (lH,m), 7.82- 7.73 (2H,m), 7.37-7.34 (lH,m), 3.83 (3H,s), 3.68 (3H,s), 3.67-3.56 (lH,m), 3.36-3.26 (lH,m), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 155
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 7.93 (lH,brs), 7.36 (lH,t), 7.09-7.06 (lH,m), 6.95-6.92 (lH,m), 3.85 (3H,s), 2.87-2.78 (2H,m) , 1.21 (3H,t).
Present Compound 156
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.51-
7.45 (lH,m), 7.36-7.31 (2H,m) , 3.75 (3H,s), 2.78 (2H,q),
1.10 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 157
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 7.70-
7.64 (lH,m), 7.44-7.38 (lH,m), 7.33 (lH,d), 3.81 (3H,s),
3.53-3.43 (lH,m), 3.42-3.31 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t).
Present Compound 158
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.28-8.26 (lH,m), 7.84-
7.78 (lH,m), 7.55-7.49 (lH,m), 7.38-7.35 (lH,m), 3,77
(3H,s), 3.50-3.34 (2H,m) , 1.34 (3H,t).
Present Compound 162
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.14 (lH,d), 7.51-7.40 (4H,m), 7.35-7.27 (lH,m), 3.69 (3H,s), 3.00 (6H,s), 2.90-2.81 (2H,m) , 1.26-
1.19 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 163
■""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.92 (lH,d), 7.48-7.43 (3H,m) , 7.34-7.28 (lH,m), 7.26 (lH,d), 3.68 (3H,s), 3.40-3.32 (4H,m), 2.84 (2H,q), 2.08-2.05 (4H,m), 1.22 (3H,t).
Present Compound 164
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.72 (lH,s), 8.41 (lH,d), 8.23 (lH,d), 7.37-7.28 (3H,m), 7.18-7.13 (lH,m), 3.58 (3H,s), 2.74
(2H,q), 2.02 (3H,s), 1.09 (3H,t).
Present Compound 169
!H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.37-8.35 (lH,m), 7.54- 7.48 (lH,m), 7.27-7.24 (lH,m), 7.09-7.03 (lH,m), 3.77
(3H,d), 2.93 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 170
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.79-8.76 (lH,m), 8.35-8.32 (lH,m) , 8.03
(lH,d), 7.87-7.80 (lH,m), 7.43 (lH,t), 3.84 (3H,d), 3.51- 3.40 (lH,m), 3.13-3.02 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t).
Present Compound 171
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m), 8.07- 8.04 (lH,m), 7.86-7.80 (lH,m), 7.62-7.57 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 3.69-3.58 (lHfm), 3.41-3.31 (lH,m), 1.29 (3H,t).
Present Compound 172
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.32 (lH,d), 7.94 (lH,d), 7.57-7.48 (2H,m), 7.47-7.43 (lH,m), 7.39-7.33 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 3.36 (3H,s), 2.91 (2H,q), 1.93 (3H,s), 1.27 (3H,t).
Present Compound 173
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.21 (lH,dd), 8.03 (lH,d), 7.77 (lH,td), 7.65 (lH,td), 7.57 (lH,dd), 7.37 (lH,d), 3.78 (3H,s), 3.36- 3.24 (lH,m), 2.96-2.83 (lH,m), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 177
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.55 (lH,d), 8.39 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,brs), 7.55-7.42 (3H,m), 7.38-7.31 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H, q) , 1.23 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 178
1H-N R ( D SO-Dg) δ: 11.57 (lH,brs), 8.68-8.64 (lH,m), 8.45- 8.42 (lH,m), 8.10 (lH,d), 7.90 (2H,dd), 7.78 (lH,t), 3.83 (3H,s), 3.41-3.30 (lH,m), 2.94-2.81 (lH,m), 1.16 (3H,t). Present Compound 179
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.18 (lH,brs), 8.52-8.48 (lH,m), 8.38- 8.34 (lH,m), 8.25-8.17 (lH,m), 7.87-7.76 (2H,m) , 7.59-7.52 (lH,m), 3.65 (3H,s), 3.47 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 180
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.40 (lH,d), 8.06 (lH,d), 7.82 (lH,d), 7.66-7.59 (lH,m), 7.58-7.46 (4H,m), 7.44-7.39 (lH,m) , 7.38- 7.31 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.90 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
[0482]
Present Compound 181
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.65 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,d), 7.89 (lH,s), 7.83 (lH,d), 7.69-7.60 (2H,m), 7.53-7.46 (3H,m) , 7.38-7.33 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 182
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.67 (lH,d), 8.27 (lH,d), 7.78-7.75 (4H,m), 7.56-7.44 (3H,m), 7.39-7.32 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 189
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.30-8.28 (lH,m), 7.50- 7.47 (lH,m), 7.40 (lH,t), 7.35-7.32 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 2.64 (3H,s), 2.53 (2H,q), 1.00 (3H,t).
Present Compound 190
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.71-8.70 (lH,m), 8.26-8.24 (lH,m), 7.53 (lH,t), 7.47-7.44 (lH,m), 7.31-7.28 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.54-3.43 (lH,m), 3.27-3.17 (lH,m), 2.66 (3H,s), 1.29 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 191
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.24-8.22 (lH,m), 7.65 (lH,t), 7.60-7.56 (lH,m), 7.34-7.31 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.52-3.32 (2H,m), 2.85 (3H,s), 1.32 (3H,t).
Present Compound 192
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.71-8.69 (lH,m), 8.31-8.30 (lH,m), 7.35- 7.31 (2H,m), 7.19-7.15 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 2.46 (3H,s) , 1.22 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 193
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.73 (lH,m), 8.30-8.28 (lH,m), 8.06- 8.05 (lH,m), 7.49-7.48 (2H,m) , 3.88 (3H,s), 3.42-3.32 (lH,m), 3.00-2.90 (lH,m), 2.58 (3H,s), 1.32 (3H,t).
Present Compound 194
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.27-8.26 (lH,m), 8.03-
8.02 (lH,m), 7.64-7.61 (lH,m), 7.44 (lH,d), 3.70 (3H,s),
3.41 (2H,q), 2.59 (3H,s), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 195
^-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.45 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,d), 8.05 (lH,d),
7.85-7.78 (2H,m), 7.73-7.61 (3H,m), 7.56 (lH,t), 7.44 (lH,d), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.46-3.32 (lH,m), 3.03-2.91 (lH,m),
1.29 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 196
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.43 (lH,d), 8.28-8.20 (lH,m), 8.06-8.00
(lH,m), 7.90-7.75 (3H,m) , 7.67-7.59 (2H,m) , 7.54 (lH,t),
7.44 (lH,d), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 197
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.29-8.23 (2H,m), 7.92-7.78
(3H,m), 7.74-7.60 (4H,m), 3.90 (3H,s), 3.47-3.33 (lH,m),
3.06-2.93 (lH,m), 1.32 (3H,t).
Present Compound 198
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.69 (lH,d), 8.26-8.19 (2H,m) , 7.92-7.89 (lH,m), 7.87-7.76 (3H,m) , 7.69-7.57 (3H,m) , 3.73 (3H,s), 3.50 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t).
Present Compound 199
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.71 (lH,d), 8.29-8.23 (2H,m) , 7.85-7.79 (lH,m), 7.78-7.75 (4H,m) , 7.70 (lH,td), 7.63 (lH,dd), 3.90 (3H,s), 3.44-3.32 (lH,m), 3.05-2.92 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t).
Present Compound 200
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.70 (lH,d), 8.27-8.19 (2H,m), 7.87-7.78 (2H,m), 7.77-7.75 (4H,m), 7.62-7.57 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,d) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 201
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.74 (lH,m), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 7.78- 7.74 (lH,m), 7.71-7.69 (lH,m), 7.54 (lH,d), 3.80 (3H,s), 2.98 (2H,q) , 1.31 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 202
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.79-8.78 (lH,m), 8.44-8.41 (lH,m), 8.35- 8.33 (lH,m), 8.10-8.06 (lH,m), 7.89-7.87 (lH,m), 3.94 (3H,s), 3.50-3.40 (lH,m), 3.07-2.97 (lH,m), 1.34 (3H,t). Present Compound 203
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.77 (lH,m), 8.40-8.37 (lH,m) , 8.31- 8.30 (lH,m), 8.10-8.06 (lH,m), 7.86-7.84 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.45 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 204
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.53 (lH,d), 8.19 (lH,d), 7.56-7.26 (8H,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 205
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.63 (lH,d), 8.23 (lH,d), 7.65-7.29 (8H,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t).
Present Compound 206
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.62 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,d), 7.59-7.53 (2H,m), 7.51-7.40 (5H,m) , 7.36-7.29 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s),
2.87 (2H,q) , 1.23 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 207
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.62 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,d), 7.93 (lH,dd), 7.56-7.42 (4H,m), 7.40-7.34 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present . Compound 208
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.74 (lH,m), 8.67-8.64 (lH,m), 8.52 (lH,d), 8.27 (lH,d), 7.73-7.65 (lH,m), 7.57-7.46 (3H,m) , 7.41-7.34 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
[0483]
Present Compound 211
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.93 (lH,d), 8.69-8.62 (2H,m) , 8.27 (lH,d), 8.00-7.92 (lH,m), 7.55-7.31 (5H,m) , 3.79 (3H,s),
2.89 (2H, q) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 212
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.69 (3H,m) , 8.33 (lH,d), 7.63-7.57 (2H,m), 7.56-7.44 (3H,m), 7.40-7.32 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s),
2.89 (2H,q) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 213
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.79 (lH,d), 8.28 (lH,d), 7.97 (lH,s),
7.70 (lH,s), 7.55-7.43 (3H,m), 7.40-7.30 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t).
Present Compound 216
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.56 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd), 8.16 (lH,d), 7.84-7.78 (lH,m), 7.69 (lH,td), 7.62 (lH,dd), 7.56-7.52
(ΙΗ,πι), 7.46-7.43 (lH,m), 7.42-7.33 (2H,m) , 3.90 (3H,s), 3.44-3.31 (lH,m), 3.03-2.91 (lH,m), 1.30 (3H,t).
Present Compound 217
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.55 (lH,d), 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 8.14 (lH,d), 7.85-7.76 (2H,m) , 7.59 (lH,dd), 7.53 (lH,dd), 7.44 (lH,dd), 7.40-7.29 (2H,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 218
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.68-8.64 (lH,m), 8.28-8.23 (lH,m), 8.22- 8.19 (lH,m), 7.84-7.78 (lH,m), 7.71-7.66 (lH,m), 7.65-7.59
(2H,m), 7.56-7.49 (lH,m), 7.46-7.41 (lH,m), 7.40-7.34
(lH,m), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.45-3.33 (lH,m) , 3.04-2.92 (lH,m),
1.31 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 219
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.65 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,dd), 8.18 (lH,d),
7.86-7.76 (2H,m), 7.64-7.62 (lH,m), 7.59 (lH,dd), 7.52
(lH,dt), 7.42 (lH,t), 7.36 (lH,dt), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.48
(2H,q) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound220
"'"H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.66-8.62 (lH,m), 8.24-8.20 (lH,m), 8.19-
8.17 (lH,m), 7.86-7.75 (2H,m) , 7.62-7.54 (3H,m), 7.48-7.42
(2H,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.56-3.41 (2H,m) , 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 221
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (lH,d), 8.74 (2H,dd), 8.30 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd), 7.83 (lH,td), 7.71 (lH,td), 7.65-7.59 (3H,m),
3.91 (3H,s), 3.44-3.32 (lH,m), 3.05-2.93 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 222
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 9.07-8.56 (3H,m) , 8.28 (lH,d), 8.25-8.20 (lH,m), 7.89-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.66-7.56 (3H,m), 3.73 (3H,s),
3.47 (2H,q) , 1.26 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 223
■"■H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.64 (lH,d), 8.26-8.21 (lH,m), 8.18 (lH,d), 7.92 (lH,dd), 7.89-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.60 (lH,dd), 7.47 (lH,d), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.52-3.41 (2H,m) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 224
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.74 (lH,m), 8.69 (lH,d), 8.53 (lH,d), 8.29-8.23 (2H,m), 7.87-7.80 (lH,m), 7.74-7.67 (2H,m), 7.66-7.61 (lH,m), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.45-3.31 (lH,m), 3.05-2.93 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t).
Present Compound 225
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.74 (lH,m), 8.67 (lH,d), 8.53 (lH,d), 8.26-8.23 (lH,m), 8.22-8.20 (lH,m), 7.89-7.79 (2H,m), 7.71-7.66 (lH,m), 7.64-7.59 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s),
3.48 (2H,q) , 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 226
1H-NMR ( DMSO-D6) δ: 8.96 (lH,d), 8.89 (lH,s), 8.54 (lH,d), 8.14 (lH,dd), 8.02-7.87 (4H,m), 3.60 (3H,s), 3.55 (2H,q), 1.12 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 227
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.74 (lH,d), 8.48 (lH,s), 8.28 (lH,d), 7.57-7.50 (2H,m), 7.49-7.45 (lH,m), 7.40-7.34 (lH,m), 3.79
(3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 228
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.51 (lH,d), 8.10 (lH,d), 7.89 (lH,s), 7.66-7.63 (lH,m), 7.58-7.43 (3H,m) , 7.41-7.33 (lH,m), 3.80
(3H,s), 2.90 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 229
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.38 (lH,d), 8.05 (lH,d), 7.98 (lH,dd), 7.70 (lH,td), 7.60-7.43 (5H,m), 7.39-7.31 (lH,m), 3.78
(3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 230
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.69 (lH,d), 8.54-8.51 (lH,m), 8.31-8.29 (lH,m), 8.27 (lH,dd), 7.98 (lH,d), 7.69 (lH,t), 7.57-7.46 (3H,m), 7.40-7.34 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 231
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.62 (lH,d), 8.25 (lH,d), 7.83 (lH,dd), 7.71 (lH,td), 7.59 (lH,dd), 7.55-7.46 (4H,m), 7.39-7.32 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 232
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.63 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,d), 7.93 (lH,s), 7.89 (lH,d), 7.74-7.58 (2H,m) , 7.56-7.45 (3H,m), 7.40-7.33 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t).
Present Compound 233
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.66 (lH,d), 8.27 (lH,d), 7.83-7.73 (4H,m), 7.56-7.45 (3H,m) , 7.40-7.32 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q) , 1.25 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 234
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.78 (lH,d), 8.68 (lH,s), 8.34 (lH,d), 7.54-7.26 (4H,m), 3.80 (3H,s), 2.93-2.82 (2H,m) , 1.28-1.19 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 235
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.55 (lH,d), 8.17 (lH,d), 7.57-7.24 (4H,m), 3.81 (3H,s), 2.93-2.86 (2H,m), 2.60 (3H,s), 1.28- 1.23 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 236
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.49 (lH,s), 8.27 (lH,d), 8.25-8.22 (lH,m), 7.89-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.63-7.57 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 237
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.57 (lH,d), 8.27 (lH,d), 8.11 (lH,d), 7.92 (lH,s), 7.88-7.82 (lH,m), 7.75-7.68 (2H,m) , 7.65 (lH,d), 3.93 (3H,s), 3.46-3.32 (lH,m), 3.06-2.94 (lH,m), 1.32 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 238
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.32 (lH,m), 7.59 (lH,d), 7.50-7.47 (lH,m), 7.30 (lH,d), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.91 (2H, q) , 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 239
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.39 (lH,d), 8.32-8.31 (lH,m), 7.84-7.81 (lH,m), 7.49 (lH,d), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.50- 3.40 (lH,m), 3.06-2.96 (lH,m), 1.35 (3H,t).
Present Compound 240
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.37 (lH,d), 8.31-8.29 (lH,m), 7.99-7.96 (lH,m), 7.44 (lH,d), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
[0484]
Present Compound 241
!fi-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 7.70-
7.69 (lH,m), 7.63-7.60 (lH,m), 7.57-7.54 (lH,m), 3.79
(3H,s), 2.95 (2H,q), 1.30 (3H,t).
Present Compound 242
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.80-8.78 (lH,m), 8.59-8.57 (lH,m), 8.36-
8.34 (lH,m), 7.99-7.96 (lH,m), 7.78 (lH,d), 3.96 (3H,s),
3.57-3.46 (lH,m), 3.10-3.00 (lH,m), 1.37 (3H,t).
Present Compound 243
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.79-8.77 (lH,m), 8.53-8.51 (lH,m), 8.32- 8.30 (lH,m), 8.14-8.10 (lH,m), 7.74-7.71 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.29 (3H,t).
Present Compound 246
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.74 (lH,m), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 7.66- 7.65 (lH,m), 7.61-7.55 (2H,m) , 3.80 (3H,s), 2.95 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 247
^-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.80-8.78 (lH,m), 8.54-8.53 (lH,m), 8.35- 8.34 (lH,m), 7.95-7.91 (lH,m), 7.79 (lH,d), 3.95 (3H,s), 3.52-3.41 (lH,m), 3.09-2.99 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t).
Present Compound 248
^"H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.47-8.46 (lH,m), 8.31- 8.30 (lH,m), 8.10-8.07 (lH,m), 7.76 (lH,d), 3.76 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 249
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 10.12 (lH,s), 8.75-8.74 (lH,m), 8.36-8.34 (lH,m), 7.97-7.96 (lH,m), 7.83-7.81 (lH,m), 7.64 (lH,d), 3.80 (3H,s), 3.00 (2H,q), 1.30 (3H,t).
Present Compound 250
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.71 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m), 7.72- 7.64 (3H,m), 7.59-7.42 (5H,m) , 3.83 (3H,s), 2.92 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 255
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.51 (lH,d), 8.19 (lH,d), 7.53-7.42 (3H,m), 7.38-7.29 (lH,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 2.97-2.83 (4H,m), 1.33-1.19 (6H,m) .
Present Compound 256
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.96 (lH,d), 8.54 (lH,d), 8.28-8.18 (lH,m), 7.91-7.80 (2H,m) , 7.63-7.55 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 3.24 (2H,q), 1.38 (3H,t), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 257
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.53 (lH,d), 8.23 (lH,d), 7.54-7.42 (3H,m), 7.38-7.29 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.33-3.22 (lH,m), 2.87 (2H,q), 1.30 (6H,d), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 258
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.92 (lH,d), 8.51 (lH,d), 8.22 (lH,dd), 7.92-7.81 (2H,m), 7.62 (lH,dd), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 3.36-3.26 (lH,m), 1.38 (6H,d), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 259
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.64-8.58 (lH,m), 8.33-8.29 (lH,m), 7.53- 7.30 (4H,m), 3.75-3.73 (3H,m) , 3.45-3.38 (2H,m) , 2.89-2.82 (2H,m) , 1.27-1.21 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 260
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.01 (lH,d), 8.59 (lH,d), 8.25-8.21 (lH,m), 7.91-7.82 (2H,m) , 7.63-7.58 (lH,m), 4.07 (2H,q), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 261
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.48 (lH,d), 8.18 (lH,d), 7.53-7.41 (3H,m), 7.38-7.28 (lH,m), 5.95-5.81 (lH,m), 5.06-4.92 (2H,m), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.51 (2H,d), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t). Present Compound 262
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.65-8.60 (lH,m), 8.40-8.35 (lH,m), 7.55- 7.48 (2H,m), 7.47-7.41 (ΐΗ,πι), 7.37-7.31 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.92-2.83 (2H,m) , 1.27-1.18 (3H,m).
Present Compound 263
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.64 (lH,d), 8.39 (lH,d), 7.56-7.49
(2H,m), 7.47-7.43 (lH,m), 7.38-7.32 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q) , 1.24 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 264
XH-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.63 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,d), 7.56-7.42 (3H,m), 7.38-7.32 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 272
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.67 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd), 7.83 (lH,td), 7.70 (lH,td), 7.61 (lH,dd), 3.88 (3H,s), 3.40-3.35 (lH,m), 3.01-2.95 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t).
Present Compound 273
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.66 (lH,d), 8.34 (lH,d), 8.24-8.22
(lH,m), 7.89-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.59-7.56 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s),
3.43 (2H,q) , 1.25 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 274
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd),
7.83 (lH,td), 7.70 (lH,td), 7.61 (lH,dd), 3.89 (3H,s),
3.43-3.32 (lH,m), 3.04-2.93 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t).
Present Compound 275
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.67 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,d), 8.23 (lH,dd),
7.89-7.77 (2H,m), 7.57 (lH,dd), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q),
1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 276
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.56 (lH,d), 8.27 (lH,d), 7.53-7.41 (3H,m), 7.39-7.25 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.33
(9H, s) , 1.24 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 277
^-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.92 (lH,d), 8.52 (lH,d), 8.25-8.20 (lH,m), 7.89-7.84 (2H,m) , 7.63-7.58 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,q), 1.43 (9H,s), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 278
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.50 (lH,d), 8.24 (lH,d), 7.68-7.66 (lH,m), 7.60-7.54 (2H,m) , 3.73 (3H,s), 2.94 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 279
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.56-8.54 (2H,m) , 8.23 (lH,d), 7.95-7.91
(lH,m), 7.77-7.74 (lH,m), 3.88 (3H,s), 3.50-3.40 (lH,m),
3.04-2.94 (lH,m), 1.34 (3H,t).
Present Compound 280
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.53 (lH,d), 8.49-8.48 (lH,m), 8.19
(lH,d), 8.10-8.07 (lH,m), 7.74-7.71 (lH,m) , 3.68 (3H,s),
3.48 (2H,q) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 281
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.50 (lH,d), 8.20 (lH,d), 7.51-7.48 (2H,m), 7.46-7.43 (lH,m), 7.37-7.31 (lH,m), 5.96 (lH,t), 4.97 (2H,d), 3.73 (3H,s), 2.90-2.83 (2H,m) , 1.23 (3H,t).
Present Compound 282
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.99 (lH,d), 8.54 (lH,d), 8.26-8.20 (lH,m), 7.88-7.80 (2H,m) , 7.58-7.11 (lH,m), 6.36 (lH,t), 5.53 (2H,d), 3.76-3.68 (3H,m) , 3.46-3.35 (2H,m) , 1.30-1.21
(3H,m) .
Present Compound 283
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.93 (lH,d), 8.51 (lH,d), 8.25-8.22 (lH,m), 7.88-7.81 (2H,m), 7.59-7.57 (lH,m), 5.95-5.84 (lH,m), 5.42 (lH,d), 5.23 (lH,dd), 3.93 (2H,d), 3.73 (3H,s), 3.42 (2H, q) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 284
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.26-8.15 (lH,m), 8.05-7.97 (lH,m), 7.87- 7.74 (2H,m), 7.62-7.55 (lH,m), 7.40-7.32 (lH,m), 3.70-3.57 (6H,m), 3.54-3.42 (2H,m) , 1.30-1.19 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 285
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.37-8.35 (lH,m), 8.28-
8.27 (lH,m), 8.18-8.14 (lH,m), 7.65-7.62 (lH,m), 3.81
(3H,s), 3.04 (2H,q), 1.34 (3H,t).
Present Compound 286
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.13-9.11 (lH,m), 8.81-8.79 (lH,m) , 8.54-
8.51 (lH,m), 8.37-8.34 (lH,m), 7.87 (lH,d), 3.98 (3H,s),
3.60-3.49 (lH,m), 3.13-3.02 (lH,m), 1.40 (3H,t).
Present Compound 287
:H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.08-9.05 (lH,m), 8.80-8.77 (lH,m), 8.68
(lH,dd), 8.34-8.31 (lH,m), 7.81 (lH,d), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.52
(2H, q) , 1.32 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 289
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.19 (lH,dd), 8.01 (lH,d), 7.83-7.73 (2H,m), 7.55 (lH,dd), 7.35 (lH,d), 3.61 (3H,s), 3.46 (2H,q),
1.23 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 290
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.51 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,dd), 8.07 (lH,d), 7.90-7.81 (2H,m), 7.59 (lH,dd), 3.69 (3H,s), 3.50-3.42 (5H,m) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 291
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.21 (lH,dd), 8.16 (lH,d), 7.83-7.72
(2H,m), 7.55 (lH,dd), 7.40 (lH,d), 3.63 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q),
3.01 (6H,s) , 1.24 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 292
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.69-8.68 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.70-
7.68 (lH,m), 7.62-7.55 (2H,m) , 3.79 (3H,s), 2.97 (2H,q),
1.29 (3H,t).
Present Compound 293
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.86 (lH,d), 8.56 (lH,d), 7.96 (lH,d),
7.48 (lH,d), 7.32 (lH,dd), 3.02 (2H,t), 1.37 (3H,d).
Present Compound 294
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.93 (lH,d), 8.52 (lH,d), 8.25 (lH,d), 7.78 (lH,dd), 7.67 (lH,d), 3.76 (2H,q), 1.40 (3H,t).
Present Compound 295
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74 (lH,s), 8.59 (lH,d), 7.56-7.49 (2H,m), 7.41 (lH,dd), 7.37-7.31 (lH,m)f 6.84 (lH,brs), 3.75 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t).
Present Compound 296
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.89 (lH,d), 8.56 (lH,d), 7.56-7.42
(3H,m), 7.39-7.33 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.89 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 297
■"■H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.93 (lH,d), 8.53 (lH,d), 8.26 (lH,dd), 7.84 (lH,td), 7.71 (lH,td), 7.60 (lH,dd), 3.89 (3H,s), 3.42-3.32 (lH,m), 3.05-2.96 (lH,m), 1.31 (3H,t).
Present Compound 298
1H-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.91 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,d), 8.23 (lH,dd), 7.87-7.80 (2H,m), 7.56 (lH,dd), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.45 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 299
1H-N R ( C DCI 3 ) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.51-8.49 (lH,m), 8.29- 8.27 (lH,m), 8.13-8.09 (lH,m), 7.74-7.71 (lH,m), 3.74
(3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.29 (3H t) .
Present Compound 300
1H-N R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.60 (lH,d), 8.39 (lH,d), 7.65-7.64
(lH,m), 7.58-7.51 (2H,m) , 3.70 (3H,s), 2.91 (2H,q), 1.25
(3H, t) .
Present Compound 303
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.09 (lH,s), 7.52 (lH,d), 7.46-7.35 (3H,m), 7.25 (lH,t), 7.12 (lH,d), 3.56 (3H,s), 2.78 (2H,q), 1.17 (3H,t).
Present Compound 307
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.65 (lH,d), 8.49-8.47 (lH,m), 8.37 (lH,d), 8.10-8.06 (lH,m), 7.74-7.71 (lH,m), 3.67 (3H,s),
3.47 (2H,q) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 308
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.09 (lH,s), 7.59-7.42 (5H,m), 7.37-7.31 (lH,m), 3.69 (3H,s), 2.85 (2H,q), 1.23 (3H,t).
Present Compound 309
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.22 (lH,d), 8.07 (lH,s), 7.80 (lH,t), 7.67 (lH,t), 7.62-7.52 (3H,m) , 3.79 (3H,s), 3.37-3.26 (lH,m), 3.01-2.89 (lH,m), 1.27 (3H,t).
Present Compound 310
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.20-8.18 (lH,m), 8.06 (lH,s), 7.82-7.74 (2H,m), 7.59-7.52 (3H,m) , 3.61 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,brs), 1.22 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 311
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 7.83 (lH,d), 7.69 (lH,d), 7.60 (lH,dd), 7.54-7.49 (lH,m), 7.48-7.42 (lH,m), 7.41-7.35 (lH,m), 6.69 (lH,d), 3.00 (2H,q), 2.93 (3H,s), 1.32 (3H,t).
Present Compound 312
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.25-8.19 (2H,m) , 7.83-7.78 (2H,m) , 7.68 (lH,t), 7.55 (lH,d), 7.47 (lH,d), 3.79 (3H,s), 3.36-3.26 (lH,m), 3.00-2.90 (lH,m) , 1.27 (3H,t).
Present Compound 313
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.23-8.20 (2H,m) , 7.85-7.76 (3H,m) , 7.57- 7.53 (lH,m), 7.46 (lH,d), 3.62 (3H,s), 3.39 (2H,brs), 1.24 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 317
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.65-8.64 (lH,m), 8.29-8.28 (lH,m), 7.35- 7.31 (2H,m), 7.18-7.15 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 2.46 (3H,s) , 1.23 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 318
^Ή -ΝΜΡΝ (CDC13) δ: 8.69-8.68 (lH,m), 8.28-8.26 (lH,m), 8.07- 8.05 (lH,m), 7.50-7.48 (2H,m) , 3.89 (3H,s), 3.44-3.33 (lH,m), 3.01-2.92 (lH,m), 2.58 (3H,s), 1.32 (3H,t).
Present Compound 319
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.68-8.66 (lH,m), 8.25-8.23 (lH,m), 8.04- 8.02 (lH,m), 7.65-7.61 (lH,m), 7.45-7.42 (lH,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.47-3.38 (2H,m) , 2.59 (3H,s), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 320
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.68 (lH,d), 8.00-7.94 (lH,m), 7.55-7.51 (lH,m), 7.48-7.43 (lH,m), 7.36-7.31 (lH,m), 2.97 (2H,q), 1.33 (3H,t).
Present Compound 321
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.81 (lH,d), 8.71 (lH,d), 8.08 (lH,d), 7.72 (lH,s), 7.56 (lH,d), 3.03 (2H,q), 1.37 (3H,t).
Present Compound 322
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.81 (lH,d), 8.55 (lH,d), 8.07-8.00
(lH,m), 7.59-7.53 (lH,m), 7.52-7.45 (lH,m), 7.41-7.33
(lH,m), 2.99 (2H,q), 1.35 (3H,t).
Present Compound 323
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.85 (lH,d), 8.59 (lH,d), 8.15 (lH,d), 7.75 (lH,s), 7.59 (lH,d), 3.05 (2H,q), 1.38 (3H,t).
Present Compound 324
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.87 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,d), 8.28-8.22 (lH,m), 7.85-7.76 (2H,m) , 7.74-7.70 (lH,m), 3.74 (2H,q), 1.37 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 325
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.90 (lH,s), 8.57-8.49 (2H,m) , 8.07 (lH,d), 7.88 (lH,d), 3.77 (2H,q), 1.40 (3H,t).
Present Compound 326
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.93 (lH,d), 8.61 (lH,d), 7.45-7.34 (3H,m), 2.91 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t).
Present Compound 327
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.95 (lH,d), 8.55 (lH,d), 8.14 (lH,dd), 7.86 (lH,dd), 7.73 (lH,t), 3.40 (2H,q), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 330
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.73 (lH,m), 8.28-8.27 (lH,m), 8.22 (lH,d), 7.82 (lH,dd), 7.51 (lH,d), 6.86 (lH,dd), 6.03 (lH,d), 5.58 (lH,d), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.44 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H,t). Present Compound 331
^-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.28-8.26 (lH,m), 8.05- 8.03 (lH,m), 7.67-7.64 (lH,m), 7.46 (lH,d), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,q), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.37 (3H,t), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 332
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.46-8.44 (lH,m), 8.31- 8.30 (lH,m), 8.09-8.05 (lH,m), 7.76 (lH,d), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q) , 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 334
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.89 (lH,d), 8.46 (lH,d), 8.27 (lH,dd), 7.85 (lH,td), 7.71 (lH,td), 7.62 (lH,dd), 3.92 (3H,s), 3.45-3.34 (lH,m), 3.04-2.94 (lH,m), 2.18 (6H,s), 1.32 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 335
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.87 (lH,d), 8.44 (lH,d), 8.26-8.19
(lH,m), 7.93-7.81 (2H,m) , 7.64-7.60 (lH,m), 3.74 (3H,s),
3.43 (2H,q), 2.80 (6H,s), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 337
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.26 (lH,s), 7.80 (lH,s), 7.43-7.36
(lH,m), 7.34-7.30 (lH,m), 7.27-7.21 (2H,m), 7.17 (lH,td),
3.66 (3H,s), 2.77 (2H,q), 2.12 (3H,s), 1.15 (3H,t).
Present Compound 338
^-N R (CDCI3) δ: 7.82-7.80 (lH,m), 7.50-7.43 (3H,m), 7.37-
7.30 (lH,m), 7.19 (lH,s), 3.93 (3H,s), 2.87-2.82 (8H,m),
1.22 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 339
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 7.65 (lH,s), 7.60-7.53 (3H,m), 6.82 (lH,s), 4.01 (2H,brs), 3.94 (3H,s), 2.92 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 340
"""H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 7.82 (lH,s), 7.67 (lH,s), 7.61-7.53 (2H,m), 7.23 (lH,s), 3.96 (3H,s), 2.93 (2H,q), 2.86 (6H,s), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 347
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.58 (lH,s), 7.56-7.29 (5H,m) , 3.73 (3H,s), 2.88 (2H,q), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 348
^- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.61 (lH,s), 8.28 (lH,dd), 7.81 (lH,td), 7.68 (lH,td), 7.62 (lH,dd), 7.27 (lH,t), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.68- 3.58 (lH,m), 3.12-3.02 (lH,m), 1.37 (3H,t).
Present Compound 349
■""H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.59 (lH,s), 8.21 (lH,dd), 7.86-7.77 (2H,m), 7.60 (lH,dd), 7.27 (lH,t), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.54 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 350
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.46 (lH,s), 7.51-7.32 (4H,m), 3.86-3.71 (lH,m), 3.68 (3H,s), 2.86 (2H,q), 1.61 (3H,s), 1.59 (3H,s), 1.22 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 352
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.69 (lH,s), 8.33 (lH,s), 8.25 (lH,dd),
8.21 (lH,dd), 7.73-7.58 (2H,m) , 3.47-3.36 (lH,m), 3.13-3.01
(lH,m) , 1.57-0.71 (3H,m) .
Present Compound 355
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (lH,d), 8.51 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d),
8.10 (lH,dd), 7.74 (lH,d), 4.22 (2H,q), 3.55 (2H,q), 1.42
(3H, t) , 1.30 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 356
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.48 (lH,s), 8.31 (lH,d),
8.05 (lH,d),7.73 (lH,d), 6.02-5.90 (lH,m), 5.19 (lH,d), 4.96 (lH,d), 4.79 (2H,s), 3.51 (2H,q), 1.29 (3H,t).
Present Compound 357
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.81 (lH,d), 8.49 (lH,s), 8.33 (lH,d), 8.11 (lH,d),7.94 (lH,d), 4.95 (2H,brs), 3.46 (2H,q), 2.34- 2.31 (lH,m) , 1.29 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 358
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.83 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,d), 8.37 (lH,d), 8.18 (lH,dd), 7.93 (lH,d), 5.10 (2H,brs), 3.35 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 359
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.98 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,d), 8.21-8.17 (2H,m), 7.89 (lH,d), 4.97 (lH,brs), 4.85 (lH,brs), 3.47 (lH,brs), 3.34 (lH,brs), 1.28-1.20 (3H,m).
Present Compound 360
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.47 ( lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d),
8.08 (lH,dd), 7.90 (lH,d), 5.53 (2H,s), 3.67 (2H,q), 3.58 (2H,q), 1.31 (3H,t), 1.18 (3H,t).
Present Compound 361
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.91 (lH,d), 8.48 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,d),
8.09 (lH,dd), 7.81 (lH,d), 5.36 (2H,s), 3.60-3.49 (4H,m), 1.28 (3H,t) , 1.19 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 362
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (lH,d), 8.47 (lH,d), 8.31 (lH,d), 8.10 (lH,dd), 7.98 (lH,d), 5.23 (2H,brs), 3.45 (2H,q), 2.26
(3H,s) , 1.28 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 363
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 8.09 (lH,dd), 7.74 (lH,d), 4.12 (2H,q), 3.53 (2H,q), 1.89- 1.79 (2H,m), 1.29 (3H,t), 0.90 (3H,t).
Present Compound 364
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.51 (lH,d), 8.29 (lH,d), 8.09 (lH,dd), 7.74 (lH,d), 4.17-4.10 (2H,m) , 3.53 (2H,q), 1.82-1.75 (2H,m), 1.34-1.24 (5H,m), 0.86 (3H,t).
Present Compound 365
""■H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.46 (lH,d), 8.33( lH,d), 8.05 (lH,dd), 7.87 (lH,d), 4.91 (2H,brs), 3.77 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,q) , 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 366
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.92 (lH,d), 8.47 (lH,d), 8.07 (lH,dd), 7.96 (lH,d), 7.83 (lH,d), 4.82 (lH,brs), 4.69 (lH,brs), 3.81 (3H,s), 3.54 (lH,brs), 3.40 (lH,brs), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 367
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d), 8.11 (lH,dd), 7.73 (lH,d), 6.12 (lH,t), 4.92 (2H,d), 3.48 (2H,q) , 1.29 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 368
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (lH,d), 8.42 (lH,d), 8.21 (lH,d), 7.99 (lH,dd), 7.67 (lH,d), 3.60-3.50 (lH,m), 3.40-3.30 (lH,m), 1.70 (9H,s), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 369
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.13 (lH,s), 7.67 (lH,s), 7.62 ( lH,d), 7.59-7.57 (2H,m), 7.52 (lH,d), 3.70 (3H,s), 2.92 (2H,q), 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 370
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.53 (lH,s), 8.10 (lH,s), 7.93 (lH,d), 7.75 (lH,d),7.65 (lH,d), 7.57 (lH,d), 3.85 (3H,s), 3.52- 3.41 (lH,m), 3.05-2.95 (lH,m), 1.32 (3H,t).
Present Compound 371
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.48 (lH,s), 8.10-8.05 (2H,m) , 7.74 (lH,d), 7.62 (lH,d), 7.53 (lH,d), 3.63 (3H,s), 3.47 (2H,q), 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 372
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77 (lH,d), 8.50 <lH,d), 8.30 (lH,d), 8.10 (lH,dd), 7.73( lH,d), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q), 1.29 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 373
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.83 (lH,d), 8.37-8.34 (2H,m) , 8.04 (lH,dd), 7.72 (lH,d), 3.30-3.11 (2H,brm), 3.04 (3H,s), 1.24 (3H,t).
Present Compound 374
1 H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.32 (lH,m), 7.48 (lH,d), 7.29-7.27 (1H, m) , 7.21-7.17 (lH,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.92 (2H,q) , 1.29 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 375
1 H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 8.14- 8.12 (lH,m), 7.68 (lH,d), 7.54-7.50 (lH,m), 3.93 (3H,s), 3.49-3.39 (lH,m), 3.06-2.96 (lH,m), 1.33 (3H,t).
Present Compound 376
1 H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.30-8.28 (lH,m), 8.09- 8.07 (lH,m), 7.70-7.66 (lH,m), 7.63 (lH,d), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.46 (2H,q) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 377
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.77 (lH,m), 8.47-8.45 (lH,m), 8.32- 8.30 (lH,m), 8.09-8.06 (lH,m), 7.76 (lH,d), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.48 (2H,q) , 1.27 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 378
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.83-8.74 (3H,m), 8.54 (lH,dd), 8.31- 8.29( lH,m) ,7.95-7.86 (2H,m) , 7.68 (lH,d), 7.41-7.37 (lH,m), 3.75 (3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q), 1.30 (3H,t).
Present Compound 379
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.27-8.25 (lH,m), 7.43 (lH,d), 7.29 (lH,d), 6.99 (lH,dd), 4.28 (2H,brs), 3.70 (3H,s), 3.40 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 380
1H-NMR (DMSO-D6) δ: 11.94 (lH,brs), 8.86-8.84 (lH,m), 8.62- 8.60 (lH,m), 8.53 (lH,d), 8.28 (lH,dd), 7.95 (lH,d), 3.64 (3H,s), 3.56 (2H,q), 1.14 (3H,t).
Present Compound 381
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.28-8.25 (lH,m), 8.07-
8.05 (lH,m), 7.69-7.66 (lH,m), 7.47 (lH,d), 3.72 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,q), 3.18-3.10 (lH,m), 1.37 (6H,d), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 382
^•H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 10.23 (lH,s), 8.78-8.76 (lH,m), 8.71 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,dd), 8.31 (lH,d), 7.77 (lH,d), 3.74 (3H,s), 3.49 (2H,q) , 1.30 (3H,t) .
Present Compound 383
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.32-8.31 (lH,m), 7.55- 7.49 (2H,m), 7.46-7.43 (lH,m), 7.38-7.33 (lH,m), 3.77 (3H,s), 2.84 (2H,t), 1.58-1.50 (2H,m) , 1.39-1.29 (2H,m) , 0.85 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 384
!H-NMR ( C DCI3 ) δ: 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.66- 7.63 (lH,m), 7.58-7.53 (lH,m), 7.49-7.41 (2H,m) , 3.79 (3H,s), 3.66 (3H,s), 3.60 (2H,s).
Present Compound 385
1H-NMR ( C DCI3 ) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.34-8.32 (lH,m), 7.61- 7.55 (2H,m), 7.52-7.44 (2H,m) , 5.85 (lH,t), 3.77 (3H,s), 3.54 (2H,d) .
Present Compound 386
■"■H-NMR ( C DCI3 ) δ: 8.72-8.71 (lH,m), 8.32-8.31 (lH,m), 7.68- 7.65 (lH,m), 7.59-7.54 (lH,m), 7.47 (lH,dd), 7.44-7.39 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 3.55 (2H,q), 1.75 (3H,t).
Present Compound 387
1H-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.87-
7.84 (lH,m), 7.70-7.64 (lH,m), 7.63-7.58 (lH,m), 7.56 (lH,dd), 3.78 (3H,s), 3.61 (2H,s).
Present Compound 388
""■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.72-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.57- 7.48 (2H,m), 7.45-7.42 (lH,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H,s), 2.82 (2H,s), 0.91 (9H,s).
Present Compound 389
1H-NMR ( C DCI3 ) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.71-
7.68 (lH,m), 7.63-7.58 (lH,m), 7.55-7.51 (2H,m) , 3.76 (3H,s), 2.97 (2H,t), 2.52 (2H,t).
Present Compound 390
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.70 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.53-
7.49 (2H,m), 7.46-7.42 (lH,m), 7.39-7.33 (lH,m), 3.76 (3H,s), 2.90 (2H,d), 2.50-2.37 (lH,m), 2.06-1.96 (2H,m) , 1.87-1.71 (2H,m), 1.67-1.56 (2H,m) .
Present Compound 391
^"H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.35-8.34 (lH,m), 7.98-
7.94 (lH,m), 7.71-7.67 (2H,m) , 7.63-7.60 (lH,m), 3.78 (3H, s) .
Present Compound 392
^- MR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.38-8.36 (lH,m), 8.31-
8.29 (lH,m), 8.02-7.99 (lH,m), 7.69 (lH,d), 6.85 (lH,t),
3.73 (3H,s), 3.54-3.33 (2H,m), 1.28 (3H,t).
Present Compound 393
1H-NMR ( C DCI 3 ) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.29-8.27 (lH,m), 8.21-
8.19 (lH,m), 7.88-7.84 (lH,m), 7.56 (lH,d), 4.97-4.93 (2H,m), 3.71 (3H,s), 3.43 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Present Compound 394
^- MR (CDC13) δ: 8.75-8.73 (1H, m) , 8.28-8.26 (1H, m) , 8.25-8.22 (1H, m) , 7.87-7.79 (2H, m) , 7.58-7.55 (1H, m) , 3.72 (3H, s), 3.43-3.37 (2H, m) , 1.70-1.60 (2H, m) , 1.45- 1.35 (2H, m) , 0.90 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 395
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (1H, m) , 8.33-8.29 (2H, m) , 7.91-7.81 (2H, m) , 7.60-7.57 (1H, m) , 4.68 (2H, br s), 3.74 (3H, s) , 3.72 (3H, s) .
Present Compound 396
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.74 (1H, m) , 8.29-8.27 (1H, m) , 8.22-8.20 (1H, m) , 7.92-7.82 (2H, m) , 7.61-7.58 (1H, m) , 5.92 (1H, t), 4.40 (2H, d) , 3.73 (3H, s) .
Present Compound 397
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (1H, m) , 8.32-8.28 (2H, m) , 7.89-7.80 (2H, m) , 7.60-7.57 (1H, m) , 4.35 (2H, br s), 3.73 (3H, s) , 1.78 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 398
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.78-8.76 (1H, m) , 8.43-8.40 (1H, m) , 8.30-8.29 (1H, m) , 8.00-7.95 (1H, m) , 7.94-7.89 (1H, m) , 7.68-7.65 (1H, m) , 4.83 (2H, br s), 3.78 (3H, s).
Present Compound 399
'''H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.74 (1H, m) , 8.27-8.24 (2H, m) ,
7.83-7.80 (2H, m) , 7.55-7.52 (1H, m) , 3.71 (3H, s) , 3.45 (2H, br s) , 1.06 (9H, s) .
Present Compound 400
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.77-8.75 (1H, m) , 8.33-8.32 (1H, m) , 8.29-8.26 (1H, m) , 7.95-7.90 (1H, m) , 7.89-7.84 (1H, m) ,
7.64-7.61 (1H, m) , 3.87 (2H, t) , 3.73 (3H, s) , 2.78 (2H, t) . Present Compound 401
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (1H, m) , 8.32-8.30 (1H, m) , 8.22-8.19 (1H, m) , 7.86-7.78 (2H, m) , 7.57-7.54 (1H, m) , 3.70 (3H, s), 3.51 (2H, d) , 2.75-2.63 (1H, m) , 2.06-1.96 (2H, m) , 1.94-1.70 (4H, m) .
Present Compound 402
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (1H, m) , 8.33-8.30 (2H, m) , 8.03-7.98 (1H, m) , 7.95-7.90 (1H, m) , 7.70-7.68 (1H, m) , 3.70 (3H, s) .
Present Compound 403
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (1H, m) , 8.29-8.28 (1H, m) , 8.21-8.19 (1H, m) , 7.87-7.84 (1H, m) , 7.63-7.60 (1H, m) , 5.61 (2H, d) , 3.72 (3H, s), 3.54-3.32 (2H, m) , 1.27 (3H, t). Present Compound 404
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.71 (1H, m) , 8.33-8.31 (1H, m) ,
7.61-7.50 (3H, m) , 7.47-7.42 (1H, m) , 6.42 (1H, dd) , 5.37 (1H, d) , 5.35 (1H, d) , 3.79 (3H, s).
Present Compound 405
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.75 (1H, m) , 8.35-8.33 (1H, m) ,
8.17-8.14 (1H, m) , 7.82-7.77 (1H, m) , 7.69-7.61 (2H, m) , 7.42 (1H, dd) , 6.17 (1H, d) , 5.86 (1H, d) , 3.97 (3H, . s) .
Present Compound 406
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.74 (1H, m) , 8.30-8.29 (1H, m) , 8.25-8.22 (1H, m) , 7.84-7.80 (2H, m) , 7.57-7.54 (1H, m) , 7.10 (1H, dd) , 6.31 (1H, d) , 6.03 (1H, d) , 3.74 (3H, s).
Present Compound 407
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.47 (1H, d) , 8.04 (1H, dd) , 7.84 (1H, d) , 7.56 (1H, dd) , 7.48 (1H, td) , 7.37 (1H, td) , 2.98 (2H, q) , 1.34 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 408
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.44 (1H, d) , 8.25 (1H, dd) , 7.89 (1H, d) , 7.84-7.71 (3H, m) , 3.72 (2H, q) , 1.37 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 409
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.68-8.66 (1H, m) , 8.31-8.30 (1H, m) ,
7.48 (1H, d) , 7.29-7.26 (1H, m) , 7.21-7.17 (1H, m) , 3.80 (3H, s), 2.93 (2H, q) , 1.29 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 410
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.71 (1H, m) , 8.30-8.29 (1H, m) , 8.14-8.12 (1H, m) , 7.68 (1H, d) , 7.55-7.51 (1H, m) , 3.93
(3H, s), 3.50-3.40 (1H, m) , 3.08-2.98 (1H, m) , 1.33 (3H, t) . Present Compound 411
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.71-8.69 (1H, m) , 8.27-8.26 (1H, m) , 8.09-8.07 (1H, m) , 7.70-7.66 (1H, m) , 7.62 (1H, d) , 3.74 (3H, s), 3.47 (2H, q) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 412
^"H-NMR (DMSO-D6) δ: 7.88 (1H, s) , 7.81 (1H, s), 7.73 (1H, d) , 7.69 (1H, d) , 7.39 (1H, s) , 3.84 (3H, s), 3.09 (2H, q) , 2.84 (3H, s) , 1.19 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 413
1H-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.50 (1H, s), 7.94-7.89 (2H, m) , 7.69 (1H, d) , 7.35 (1H, s), 3.99 (3H, s), 3.42-3.32 (1H, m) , 3.01- 2.90 (1H, m) , 2.85 (3H, s) , 1.28 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 414
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.48 (1H, d) , 8.07 (1H, dd) , 7.88 (1H, s), 7.72 (1H, d) , 7.32 (1H, s), 3.82 (3H, s) , 3.45 (2H, br s), 2.82 (3H, s) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 415
XH-NMR (DMSO-D6) δ: 8.13 (1H, d) , 7.96 (1H, d) , 7.82 (1H, s), 7.77-7.71 (2H, m) , 3.65 (3H, s), 3.09 (2H, q) , 1.18 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 416
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.52 (1H, d) , 8.06 (1H, d) , 7.93 (1H, dd) , 7.72 (1H, d) , 7.28 (1H, d) , 3.80 (3H, s), 3.49-3.39 (1H, m) , 3.05-2.95 (1H, m) , 1.33 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 417
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.48 (1H, d) , 8.09 (1H, dd) , 8.02 (1H, d) , 7.74 (1H, d) , 7.25 (1H, d) , 3.60 (3H, s) , 3.45 (2H, q) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 418
XH-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.11 (1H, s) , 7.67 (1H, s), 7.61-7.56 (3H, m) , 7.53 (1H, d) , 3.70 (3H, s), 2.93 (2H, q) , 1.28 (3H, t) . Present Compound 419
XH-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.53 (1H, d) , 8.09 (1H, s), 7.93 (1H, dd) , 7.74 (1H, d) , 7.64 (1H, d) , 7.59 (1H, d) , 3.85 (3H, s), 3.51-3.40 (1H, m) , 3.06-2.97 (1H, m) , 1.32 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 420
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.49 (1H, d) , 8.10-8.04 (2H, m) , 7.73 (1H, d) , 7.60 (1H, d) , 7.55 (1H, d) , 3.64 (3H, s), 3.47 (2H, q) , 1.25 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 421
1H-NM (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.71 (1H, m) , 8.32-8.31 (1H, m) , 7.57-7.49 (2H, m) , 7.47-7.44 (1H, m) , 7.39-7.34 (1H, m) , 3.78 (3H, s), 2.78 (2H, d) , 0.99-0.89 (1H, m) , 0.54-0.48 (2H, m) , 0.18-0.14 (2H, m) .
Present Compound 422
"""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.75 (1H, m) , 8.34-8.31 (1H, m) , 8.28-8.26 (1H, m) , 7.85-7.80 (1H, m) , 7.71-7.67 (1H, m) , 7.61-7.58 (1H, m) , 3.91 (3H, s) , 3.27 (1H, dd) , 3.04 (1H, dd) , 1.33-1.22 (1H, m) , 0.71-0.62 (2H, m) , 0.43-0.31 (2H, m) .
Present Compound 423
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (1H, m) , 8.31-8.26 (2H, m) , 7.88-7.79 (2H, m) , 7.57-7.54 (1H, m) , 3.72 (3H, s), 3.34 (2H, d) , 1.05-0.94 (1H, m) , 0.57-0.50 (2H, m) , 0.26-0.20
(2H, m) .
Present Compound 424
""Ή-ΝΜΡΝ. (CDC13) δ: 8.30 (1H, d) , 8.20 (1H, s), 7.78-7.67 (2H, m) , 7.63 (1H, s) , 7.52 (1H, d) , 3.11 (2H, q) , 1.47 (3H, t) . Present Compound 425
1H-NM (CDC13) δ: 8.53 (1H, s) , 8.18-8.12 (2H, m) , 8.08 (1H, d) , 7.77-7.72 (2H, m) , 3.91 (2H, q) , 1.44 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 426
!H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.12 (1H, s), 7.66 (1H, s), 7.62 (1H, dd) , 7.57 (1H, br s), 7.52 (1H, d) , 3.70 (3H, s) , 2.92 (2H, q) , 1.26 (3H, t) .
Present Compound 427
■""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 7.95 (1H, d) , 7.64 (1H, s) , 7.57-7.51 (3H, m) , 4.03 (3H, s), 3.04 (2H, q) , 2.93 (2H, q) , 1.37 (3H, t) , 1.29-1.20 (3H, m) .
[0485]
The productions of the intermediates of the present compound are shown in the following Reference Production Examples .
[0486]
Reference Production Example 1
A mixture of N
2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (1.91 g) , 2-fluorobenzaldehyde (1.86 g) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (1.56 g) , and DMF (10 ml) was stirred with heating under reflux at 153 °C for 3 hours. Into the
reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.89 g of 2- (2- fluorophenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-3H-imidazo [4,5- b]pyridine (Compound (IE)—Fl).
^-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.73-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.32 (lH,m), 7.76- 7.72 (lH,m), 7.64-7.58 (lH,m), 7.41-7.36 (lH,m), 7.32-7.27
(lH,m), 3.89 (3H,d)
[0487]
Reference Production Example 2-a
To a mixture of 2-chloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridxne (18.2) and N-methylpyrrolidone (100 ml), 40 % of aqueous methylamine solution (23.3 g) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. Water was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate 3 times. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 17.3 g of N-methyl- ( 5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2-yl ) -amine.
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.34(s,lH), 7.60(dd,lH), 6.40(d,lH),
4.89 (brs, 1H) , 2.97(d,3H)
[0488]
Reference Production Example 2-b
To a mixture of N-methyl- ( 5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2- yl) -amine (17.3 g) and sulfuric acid (100 ml), nitric acid (12.3 g) was added dropwise, and stirred with heating at 80 °C for 2 hours. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then the reaction mixture was poured into water. The precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with water, and dried under reduced pressure to give 18.8 g of N- 5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2-yl ) -amine .
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.66-8.64 (m, 2H) , 8.43 (brs , 1H) , 3.23(d,3H) [0489]
Reference Production Example 2-c
A mixture of N-methyl- ( 3-nitro-5-trifluoromethyl- pyridin-2-yl) -amine (6.93 g) , 5 % of palladium-carbon (0.69 g) , and ethanol was stirred under about 1 atm of hydrogen at room temperature for 10 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered through Celite
®, and then the filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give 5.02 g of N
2-
methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine (Compound (1F)-
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.04(s,lH), 6.98(d,lH), 4.56 (brs , 1H) , 3.25 (brs,2H) , 3.06(d,3H)
[0490]
The compound of Reference Production Example 2-c can also be produced by the following production method.
[0491]
Reference Production Example 2-d
To a mixture of N-methyl- ( 5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2- yl) -amine (3.48 g) and D F (20 ml), N-bromosuccinimide (4.27 g) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 4.8 g of N-methyl- ( 3-bromo-5-trifluoromethyl- pyridin-2-yl ) -amine.
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 3.08 (3H,d), 5.40 (lH,brs), 7.78 (1H, 8.34 (1H, s) .
[0492]
Reference Production Example 2-e
To a pressure-resistant reaction container, N-methyl- ( 3-bromo-5-trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2-yl ) -amine (0.51 g) , copper (II) acetylacetone (0.11 g) , acetylacetone (0.20 g) , cesium carbonate (1.30 g) , NMP (2 ml), and 28 % of aqueous ammonia (1 ml) were added, and stirred at 120 °C for 7 hours, then at 130 °C for 3 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, and then saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.28 g of N2-methyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamin .
[0493]
Reference Production Example 3-a
A mixture of 2-chloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridxne (12 g) , 70 % of aqueous ethylamine solution (16 ml), and NMP (7 ml) was stirred with heating at 70 °C for 1 day. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and then the precipitated solid was collected by filtration. The obtained solid was washed with water, and dried to give 6.3 g of N-ethyl- ( 5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2- yl ) -amine .
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.25 (lH,s), 7.51 (lH,d), 6.31 (lH,d),
4.84 (lH,brs), 3.32-3.25 (2H,m) , 1.27-1.11 (3H,m)
[0494]
Reference Production Example 3-b
A mixture of N-methyl- ( 5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl ) - amine (1.0 g) and sulfuric acid (7 ml) was stirred with heating at 95 °C, and then a mixture of fuming nitric acid (0.45 ml) and sulfuric acid (3 ml) were added thereto, and stirred with heating for 1 hour. The reaction mixture cooling to room temperature was poured into ice, and then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel chromatography to give 600 mg of N-ethyl-(3- nitro-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl ) -amine .
[0495]
Reference Production Example 3-c
A mixture of iron powder (700 mg) , acetic acid (60 μΐ) ,
ethanol (5 ml), and water (3 ml) was stirred with heating at 70 °C, and then a mixture of N-ethyl- (3-nitro-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl ) -amine (490 mg) and ethanol (10 ml) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred with heating at 70 °C for 3 hours. The reaction mixture cooled to room temperature was filtered through Celite
®, and the resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was diluted with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.29 g of N
2-ethyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine (Compound (lF)-8).
^"H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.01 (lH,d), 6.97 (lH,d), 3.51 (2H,q),
1.27 (3H,t)
[0496]
Reference Production Example 4-a
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Reference Production Example 3-a using n- propylamine instead of 70 % of aqueous ethylamine solution to give 10 g of N-propyl- ( 5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl ) -
amine .
H
[0497]
Reference Production Example 4-b
A mixture of N-propyl- ( 5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl ) - amine (3.0 g) and sulfuric acid (20 ml) was stirred with heating at 95 °C, and then a mixture of fuming nitric acid (1.3 ml) and sulfuric acid (10 ml) was added dropwise, and stirred with heating for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was poured into ice, and then saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
To a mixture of the resulting residue, ethanol (12 ml) and water (8 ml), iron powder (2.5 g) and acetic acid (0.5 ml) were added, heated to 70 °C, and stirred with heating for 2 hours. The reaction mixture cooled to room temperature was filtered through Celite
®, and then the resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.5 g of N
2-propyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine .
[0498]
Reference Production Example 4-c
A mixture of N-propyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (770 mg) , 2-ethylsulfanyl-benzoic acid (700 mg) , WSC (740 mg) , and pyridine (20 ml) was stirred with heating at 95 °C for 7 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 422 mg of 2-ethylsulfanyl-N- ( 2-propylamino-5- trifluorometh lpyridin-3-yl) -benzamide (Compound (IB) -513).
[0499]
Reference Production Example 5-a
The procedure was performed according to the metho described in Reference Production Example 3-b using 5 trifluoromethylpyridin-2-ol instead of N-methyl- ( 5 trifluoromethylpyridin-2-yl ) -amine to give 3.3 g of 3
nitro-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-ol .
^-NMR (DMSO-de) δ: 13.54 (lH,brs), 8.67 (lH,d), 8.46 (lH,d)
[0500]
Reference Production Example 5-b
To a mixture of 3-nitro-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-ol (3.2 g) and DMF (1 drop), phosphorous oxychloride (8.2 ml) was added at room temperature. The mixture was heated to 105 °C, and stirred with heating for 2 days. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, and then the reaction mixture was poured into ice, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give 2.5 g of 2-chloro-3-nitro-5-trifluoromethylpyridxne .
[0501]
Reference Production Example 5-c
To a mixture of 2-chloro-3-nitro-5- trifluoromethylpyridine (1.5 g) and ethanol (15 ml), isopropylamine (1.8 ml) was added under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred with heating for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture, 2 mol/1 of aqueous solution of
hydrochloric acid was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure.
To the resulting residue, ethanol (30 ml), water (20 ml), ammonium chloride (0.7 g) , iron powder (445 mg) , and ammonium chloride (0.7 g) were sequentially added at room temperature. The mixture was heated to 70 °C, and stirred with heating for 1 day. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure to give 970 mg of N
2-isopropyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine (Compound (IF) -15).
[0502]
Reference Production Example 6
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Reference Production Example 5-c using cyclopropylamine instead of isopropylamine to give 750 mg of N
2-cyclopropyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine .
H
[0503]
Reference Production Example 7
The procedure was performed according to the method described in Reference Production Example 3-c using 5- trifluoromethyl-pyridin-2 , 3-diamine instead of N
2-propyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine to give 4.7 g of N-(2- amino-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl ) -2-ethylsulfanyl- benzamide (Compound (1B)-512).
1H-N R ( DMSO-De) δ: 9.75 (lH,s), 8.17 (lH,s), 8.09 (lH,s), 7.64 (lH,d), 7.53-7.45 (2H,m), 7.34-7.28 (lH,m), 6.71 (2H,s), 2.97 (2H,q), 1.22 (3H,t)
[0504]
Reference Production Example 8
A mixture of 5 , N2-dimethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine (1.13 g) ,
2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (1,79 g) , WSC (1.38 g) , and pyridine (20 ml) was stirred with heating under reflux at 120 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.58 g of 2-ethylsulfanylphenyl-N-
(5-methyl-2-methylaminopyridin-3-yl) -benzamide (Compound -514) .
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.18 (lH,brs), 7.97-7.93 (lH,m), 7.85- 7.80 (lH,m), 7.54-7.42 (3H,m), 7.39-7.33 (lH,m), 3.03-2.93 (5H,m), 1.32 (3H,t)
[0505]
Reference Production Example 9
To a mixture of 5-iodo-3-nitropyridin-2-ylamine (1.0 g) and DMF (20 ml), 60 % of sodium hydride (in oil, 180 mg) and methyl iodide (240 μΐ) were sequentially added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, and then the precipitated solid was collected by filtration, and dried.
The obtained solid was dissolved in THF. The solution was added dropwise to a mixture of iron powder (633 mg) , acetic acid (1 ml), ethanol (30 ml), and water (20 ml) with heating at 70 °C . The mixture was stirred with heating at 70 °C for 3.5 hours. The reaction mixture cooled to room temperature was filtered through Celite
®. The resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column
chromatography to give 980 mg of 5-iodo-N
2-methylpyridin- 2, 3-diamine (Compound (lF)-6).
[0506]
Reference Production Example 10-a
To a mixture of 5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine (1.2 g) and pyridine (20 ml), methyl chloroformate (0.63 ml) was added under ice-cooling. The mixture was heated to room temperature, stirred for 8 hours, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 628 mg of methyl ( 2-amino-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl ) -carbamate.
1H-N R (CDC13) δ : 8.65 (lH,brs), 8.18-7.99 (2H,m), 5.75 (2H,brs), 3.79 (3H,s)
[0507]
Reference Production Example 10-b
To a mixture of methyl (2-amino-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl) -carbamate (100 mg) and THF (15 ml) , lithium aluminum hydride (26 mg) was added under ice- cooling. The mixture was stirred for 15 minutes under ice-
cooling, heated to 90 °C, and stirred with heating for 1.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, aqueous sodium hydroxide solution was poured, and extracted with tert-butyl methyl ether. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 77 mg of N
3-methyl-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-2, 3-diamine .
[0508]
Reference Production Example 11-a
To a mixture of methyl- (2-nitro-4- trifluoromethylphenyl) -amine (4.40 g) and DMF (20 ml), N- chlorosuccinimide (3.67 g) was added under ice-cooling, and stirred for 3 hours. The mixture was heated to room temperature, and allowed to stand. Water was poured thereinto under ice-cooling, and then the precipitated solid was collected by filtration. The obtained solid was washed with water, and dried to give 3.96 g of (2-chloro-6- nitro-4-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -methylamine .
1H-N R (CDCI
3) δ: 8.19 (lH,d), 7.68 (lH,d), 7.17 (lH,brs),
3.19 (3H,d)
[0509]
Reference Production Example 11-b
To a mixture of (2-chloro-6-nitro-4- trifluoromethylphenyl) -methylamine (3.70 g) and ethanol (60 ml), Raney
® nickel (slurry in water, 0.5 ml) was added, and stirred under about 1 atm of hydrogen at room temperature for 1.5 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 2.95 g of 3-chloro-N
2-methyl-5- trifluoromethylbenzene-1 , 2-diamine .
1H-N R (CDCI
3) δ: 7.02 (lH,d), 6.82 (lH,d), 4.09 (2H,brs), 3.49 (lH,brs), 2.74 (3H,d)
[0510]
Reference Production Example 12
A mixture of 2-amino-4-trifluoromethylphenol (1.00 g) , 2-methylsulfanylbenzoic acid (0.95 g) , SC (1.41 g) , and pyridine (10 ml) was stirred with heating at 80 °C for 2.5 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, 1 mol/1 of hydrochloric acid was poured, and extracted with
ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, water, and saturated brine, sequentially, dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.33 g of N- ( 2-hydroxy-5-trifluoromethylphenyl ) -2- methylsulfanyl-benzamide (Compound (IB) -515).
1H-N R (DMSO-De) δ : 9.50 (lH,brs), 8.24 (lH,s), 7.61 (lH,d), 7.50 (lH,t), 7.42 (lH,d), 7.37 (lH,dd), 7.27 (lH,t), 7.06 (lH,d), 2.45 (3H,s)
[0511]
Reference Production Example 13
To a mixture of 3-amino-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2-ol (0.75 g) and THF (5 ml), 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid hydrochloride (0.93 g) was added under ice-cooling, heated to room temperature, and stirred for 2 hours. After the mixture was allowed to stand overnight, the mixture was heated to 50 °C, and stirred with heating for 6 hours. To the mixture, sodium hydrogen carbonate (0.35 g) was added, and stirred with heating for further 2.5 hours. After the mixture was allowed to stand, water was poured thereinto, and the precipitated solid was collected by filtration. The
obtained solid was washed with water, and dried to give 1.37 g of 2-ethylsulfanyl-N- ( 2-hydroxy-5- trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl) -benzamide (Compound (IB) -506).
1H-NMR (CDC1
3) δ: 11.68 (lH,brs), 9.35 (lH,brs), 8.87 (lH,d), 7.75-7.71 (lH,m), 7.49-7.43 (3H,m), 7.33-7.29 (lH,m), 2.99 (2H,q), 1.34 (3H,t)
[0512]
Reference Production Example 14
To a mixture of 3-chloroanthranilic acid (3.43 g) and
1 mol/1 of hydrochloric acid (20 ml), sodium nitrite (1.38 g) was added portionwise at room temperature, and stirred for 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was added dropwise to a mixture of potassium butylxanthogenate (5.65 g) and water (20 ml) at room temperature, and stirred for 1 hour. 3N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (20 ml) and diethylsulfuric acid (2.9 ml) were added thereto, heated to 100 °C, and stirred under reflux for 1 hour. To the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, 12 mol/1 of hydrochloric acid was added dropwise under ice-cooling until the reaction mixture reached pH 1-2. The precipitated solid was collected by filtration, and dried under reduced pressure .
To the obtained solid, 3N aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (10 ml), ethanol (10 ml), and ethyl iodide (6.86 g) were added, heated to 80 °C, and stirred under reflux for 2 hours. To the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, 12 mol/1 of hydrochloric acid was added dropwise under ice-cooling until the reaction mixture reached pH 1-2, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give chloro-2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid.

1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.10-8.05 (lH,m), 7.68 (lH,dd), 7.43 (lH,t), 3.00 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t)
[0513]
Reference Production Example 15
To a pressure-resistant reaction container, 3-amino-2- chloro-5-trifluoromethylpyridine (5 g) , copper (II) acetylacetone (1.31 g) , acetylacetone (2.50 g) , cesium carbonate (16.25 g) , N P (20 ml), and 40 % of aqueous methylamine solution (15 ml) were added, and stirred at 100 °C for 3 hours, at 120 °C for 3 hours, then at 140 °C for 5 hours. After the mixture was allowed to cool to room
temperature, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 2.09 g of N
2-methyl-6-trifluoromethylpyridin-2, 3-diamine .
!fi-NMR (CDC13) δ: 3.04 (3H,s), 3.41 (2H,brs), 4.22 (lH,brs), 6.84 (lH,d), 6.91 (lH,d).
[0514]
Reference Production Example 16-a
To a mixture of 3-amino-2-chloro-6- trifluoromethylpyridine (3.93 g) and chloroform (30 ml), pivaloyl chloride (2.65 g) and triethylamine (4.04 g) were added under ice-cooling, and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, then at 60 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 6.59 g of N- (2-chloro-6- trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl ) -2 , 2-dimethylpropionamide .
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 1.36 (9H,s), 7.65 (lH,d), 8.17 (lH,brs), 8.97 (lH,d) .
[0515]
Reference Production Example 16-b
To a mixture of N- (2-chloro-6-trifluoromethylpyridin- 3-yl) -2, 2-dimethylpropionamide (6.59 g) and THF (30 ml), sodium hydride (60 % in oily, 1 g) was added under ice- cooling, and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. The reaction mixture was ice-cooled, and then methyl iodide (10 g) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 4 hours. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. To the resulting residue, acetonitrile (40 ml), concentrated hydrochloric acid (40 ml) , and isopropanol (40 ml) were added, and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours, at 60 °C for 2 hours, then at 80 °C for 2 hours. Into the reaction mixture cooled to room temperature, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel
column chromatography to give 2.60 g of (2-chloro-6- trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl ) -methylamine .

H
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.49 (lH,d), 6.89 (lH,d), 4.82 (lH,brs),
2.96 (3H,d) .
[0516]
Reference Production Example 16-c
To a pressure-resistant reaction container, (2-chloro- 6-trifluoromethylpyridin-3-yl) -methylamine (2.60 g) , copper (II) acetylacetone (0.64 g) , acetylacetone (1.23 g) , cesium carbonate (7.99 g) , NMP (10 ml), and 28 % of aqueous ammonia (7 ml) were added, and stirred at 140 °C for 8 hours. After the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was poured thereinto, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give
3-methyl-6-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3-diamine .
-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 2.89 (3H,d), 3.56 (lH,brs), 4.29 (2H,brs) 77 (lH,d) , 7.13 (lH,d) .
[0517]
Reference Production Example 17
A mixture of 3-amino-5- (trifluoromethyl) pyridine- thiol (0.20 g) , 2-ethylsulfanylbenzaldehyde (0.20 g) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (0.13 g) , copper (II) chloride
(0.41 g), and DMF (2.5 ml) was stirred at 120 °C for 8 hours. After the reaction mixture was allowed to cool, water was added thereto, and ethyl acetate was poured. The mixture was filtered, and the resulting filtrate was extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was washed with water, dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 0.18 g of 2- [2-fluoro-4- (trifluoromethyl ) phenyl] -6- zolo [5, 4-b] pyridine ( (IE) -F57 ) .
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 7.58 (lH,d), 7.64 (lH,d), 8.57-8.63
(2H,m) , 8.92 (1H, s) .
[0518]
Reference Production Example 18
A mixture of N
2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridin-2 , 3- diamine (5,37 g) , 2-fluoro-4-trifluorobenzaldehyde (6.92 g) , sodium hydrogen sulfite (3.75 g) , and DMF (30 ml) was stirred at 150 °C for 3 hours. Into the reaction mixture
cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 7.83 g of 2- (2-fluoro-4- trifluoromethylphenyl ) -3-methyl-6-trifluoromethyl-SH- imidazo [ 4 , 5-b] yridine ( (1E)-F6) .
■""H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.75 (lH,d), 8.35 (lH,d), 7.91 (lH,t), 7.67 (lH,d), 7.59 (lH,d), 3.92 (3H,d).
[0519]
Reference Production Example 19-a
To a mixture of 2-chloro-5-iodppyridine (7.2 g) , N P (75 mL) , and xylene (75 mL) , pentafluorosodium propionate (28 g) and copper iodide (14 g) were added at room temperature, heated to 150 °C, and stirred with heating for 5.5 hours. After the mixture was cooled to 80 °C, to the mixture, 40 % of aqueous methylamine solution (180 mL) was added in parts 4 every 2 hours, and stirred with heating for 8.5 hours. The mixture was ice-cooled to 0 °C, and then 28 % of aqueous ammonia and saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution were poured thereinto, and extracted with TBE . The combined organic layer was dried
over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 4.6 g of methyl- ( 5-pentafluoroethyl- pyridine-2-yl ) -amine.
meth l- ( 5-pentafluoroethyl-pyridine-2-yl ) -amine
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.28 (lH,d), 7.56 (lH,dd), 6.41 (lH,d),
5.74 (lH,brs) , 2.95 (3H,d) .
[0520]
Reference Production Example 19-b
To a mixture of methyl- ( 5-pentafluoroethyl-pyridine-2- yl) -amine (4.6 g) and acetonitrile (70 mL) , N- bromosuccinimide (5.0 g) was added under ice-cooling, and stirred at room temperature for 8 hours. Into a mixture, saturated aqueous sodium thiosulfate solution and aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution were poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 6.3 g of (3-bromo-5- pentafluoroethyl-pyridine-2-yl ) -methyl-amine .
( 3-bromo-5- entafluoroethyl-pyridine-2-yl ) -methyl-amine
^-NMR (CDCI
3) δ: 8.29 (lH,d), 7.74 (lH,d), 5.45 (lH,brs),
3.09 (3H,d) .
[0521]
Reference Production Example 19-c
To an autoclave reactor, ( 3-bromo-5-pentafluoroethyl- pyridine-2-yl) -methyl-amine (2.0 g) , acetylacetone copper (II) (86 mg) , acetylacetone (263 mg) , cesium carbonate (3.2 g) , and NMP (13 mL) were added, and then 28 % of aqueous ammonia (5 mL) was added under ice-cooling. After the reactor was sealed, the mixture was heated to 110 °C, and stirred with heating for 15 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was diluted with water, and extracted with MTBE . The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 623 mg of N2-methyl-5-pentafluoroethyl-2 , 3-diamine (Compound (lF)-2) .
N
2-meth l-5-pentafluoroethyl-2 , 3-diamine
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 7.99 (lH,d), 6.94 (lH,d), 4.64 (lH,brs),
3.30 (2H,brs) , 3.06 (3H,d) .
[0522]
Reference Production Example 20-a
A mixture of 2-chloro-5-iodppyridine (23.9 g) , thiobenzoic acid (14 ml), copper iodide (1.90 g) , 1,10- phenanthroline (3.60 g) , diisopropylethylamine (35 ml), and toluene (200 ml) was stirred at 110 °C for 4 hours. After the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, water was poured thereinto. The insoluble material was filtered through Celite®, and then the filtered material was washed with ethyl acetate, and the filtrate was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 21.2 g of S- ( 6-chloropyridine-3-yl ) thiobenzoate .
- ( 6-chloropyridine-3-yl ) thiobenzoate
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ : 8.43-8.42 (lH,m), 8.01-7.98 (2H,m) , 7.79- 7.76 (lH,m), 7.66-7.61 (lH,m), 7.52-7.47 (2H,m) , 7.44-7.41
(lH,m) .
[0523]
Reference Production Example 20-b
A mixture of S- ( 6-chloropyridine-3-yl ) thiobenzoate (21.2 g) , potassium carbonate (17.6 g) , and methanol (170 ml) was stirred at room temperature for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered, and then the filtered
material was washed with methanol, and filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure. To the resulting crude, IN aqueous sodium hydroxide solution (170 ml) was added, and then an aqueous solution of potassium ferricyanide (56.0 g) was added dropwise, and stirred at room temperature for 2 hours . The reaction mixture was extracted with methyl-tert-butyl ether. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 11.5 g of a compound of the following formula:
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.41 (2H,d), 7.74 (2H,dd), 7.29 (2H,d).
[0524]
Reference Production Example 20-c
A mixture of a compound (11.5 g) of the following formula :
DMF (133 ml) was cooled to -50 °C, and bubbled with excessive amounts of CF3I gas to dissolve the compound in DMF. To the mixture, tetrakis (dimethylamino) ethylenediamine (37.0 ml) was added dropwise at a rate that the internal temperature did not exceed -40 °C. Then, the mixture was
heated to -10 °C over 1 hour, and stirred at -10 °C for 2 hour. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, heated to room temperature, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 7.25 g of 2-chloro-5- trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine .
2-chloro-5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.62 (lH,d), 7.93 (lH,dd), 7.43 (lH,d).
[0525]
Reference Production Example 20-d
To a mixture of 2-chloro-5- trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine (1.71 g) and NMP (16 ml), 40 % of aqueous methylamine solution (1.86 g) was added dropwise, and then the mixture was heated to 60 °C, and stirred with heating for 2 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, potassium carbonate (1.66 g) was added thereto, and 40 % of aqueous methylamine solution (1.86 g) was added dropwise. The mixture was heated to 60 °C, and stirred with heating for further 2 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, water was poured, and extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic
layer was dried over magnesium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.52 g of methyl- ( 5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2-yl ) -amine, methyl- ( 5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2-yl ) -amine
"""H-NMR (CDC13) δ : 8.28 (lH,d), 7.63 (lH,dd), 6.41-6.38 (lH,m), 4.90 (lH,brs), 2.96 (3H,d,).
[0526]
Reference Production Example 20-e
To a mixture of methyl- ( 5- trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2-yl ) -amine (1.52 g) and chloroform (24 mL) , N-bromosuccinimide (1.43 g) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. Into the reaction mixture, water was poured, and extracted with chloroform. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.96 g of (3-bromo-5- trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2-yl ) -methylamine .
( 3-bromo-5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2-yl ) - methylamine
1H-NMR (CDC1
3) δ: 8.28 (lH,d), 7.83 (lH,d), 5.40 (lH,brs), 3.07 (3H,d) .
[0527]
Reference Production Example 20-f
To a pressure-resistant reaction container, (3-bromo- 5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2-yl ) -methylamine (1.96 g) , acetylacetone copper (II) (89 mg) , acetylacetone (0.27 g) , cesium carbonate (2.34 g) , and N P (7 ml), 28 % of aqueous ammonia (5 ml) was added, and stirred at 110 °C for 8.5 hours. After the mixture was cooled to room temperature, into the reaction mixture, water was poured. The insoluble material was filtered through Celite®, and then the filtered material was washed with ethyl acetate, and filtrate was extracted with ethyl acetate. The combined organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to silica gel column chromatography to give 1.18 g of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2 , 3- diamine (Compound (IF) -3).
N
2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylsulfanylpyridine-2 , 3-diamine
1H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.01-7.99 (lH,m), 7.07-7.05 (lH,m), 4.60 (lH,brs), 3.22 (2H,brs), 3.05 (3H,d).
[0528]
Reference Production Example 21-a
To a mixture of 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid (9.11 g) , chloroform (100 ml), and oxalyl chloride (9.72 g) , DMF (2 drops) was added, and stirred at room temperature for 6 hours. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give 10.03 g of 2-ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid chloride (Compound (1H)-241).
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.31 (lH,dd), 7.57-7.50 (lH,m), 7.42-7.32 (lH,m), 7.28-7.21 (lH,m), 3.00 (2H,q), 1.41 (3H,t).
[0529]
Reference Production Example 21-b
To a mixture of N2-methyl-5-trifluoromethylpyridine- 2,3-diamine (3.82 g) and THF (40 ml), 2- ethylsulfanylbenzoic acid chloride (4.42 g) was added, stirred at 50 °C for 2 hours, then stirred under reflux for 2 hours. After the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, sodium hydrogen carbonate (1.85 g) was added thereto, and stirred at 50 °C for 2 hours. After the mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, water was poured thereinto, and then the precipitated solid was collected by the filtration. The resulting solid was washed with water and hexane, and dried to give 7.15 g of N-(2-
methylamino-5-trifluoromethylpyridine-3-yl) -2- ethylsulfanyl-benzamide (Compound ((IB) -19).
1H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.36 (1H,S), 8.26 (1H,S), 7.85 (lH,d), 7.76 (1H,S), 7.53 (lH,d), 7.47 (lH,t), 7.39 (lH,t), 5.55 (lH,brs), 3.08 (3H,d), 3.01 (2H,q), 1.32 (3H,t).
[0530]
The above intermediate, Compounds (IB) -(IE) are shown in the following tables.
[0531]
A compound of the formula (IB) :
wherein, A represents =CH-, R , R , R , R represents a hydrogen atom, andR , R , R , A , A , and n represent a combination of Rlx, R3x, R6x, Alx, A3x, and n, respectively, shown in Tables 38-58 (Compounds ( ( IB) -1 ) - ( ( IB) -504 ) ) .
[0532]
A compound of the formula (1C) :
wherein, Xc represents a fluorine atom, A20 represents =CH-, R2C, RC, R5C, R7C represents a hydrogen atom, and R3C, R6C, Alc, and A3C represent a combination of R3x, R6x, Alx, and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 38-52 (Compound (1C)-F1 to Compound (1C)-F9, Compound (1C)-F37 to Compound (1C)-F45, Compound (1C)-F55 to Compound (1C)-F63, Compound (1C)-F73 to Compound (1C)-F81, Compound (1C)-F109 to Compound (1C)- F117, Compound (1C)-F127 to Compound (1C)-F135, Compound (1C)-F145 to Compound (1C)-F153, Compound (1C)-F181 to Compound (1C)-F189, Compound (1C)-F199 to Compound (1C)- F207, Compound (1C)-F217 to Compound (1C)-F225, Compound (1C)-F253 to Compound (1C)-F261, Compound (1C)-F271 to Compound (1C)-F279, Compound (1C)-F289 to Compound (1C)- F297, Compound (1C)-F325 to Compound (1C)-F333, and Compound (1C)-F343 to Compound (IC) -F351) .
[0533]
A compound of the formula (IC) wherein Xc is a chlorine atom, A2C is =CH-, R2C, R4C, R5C, R7C is a hydrogen atom, R3C, R6C, Alc and A3C, represent a combination of R3x, R6x, Alx and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 38-52 (Compound (1C)-C1 to Compound (1C)-C9, Compound (1C)-C37 to
Compound (1C)-C45, Compound (1C)-C55 to Compound (1C)-C63, Compound (1C)-C73 to Compound (1C)-C81, Compound (1C)-C109 to Compound (1C)-C117, Compound (1C)-C127 to Compound (1C)- C135, Compound (1C)-C145 to Compound (1C)-C153, Compound (1C)-C181 to Compound (1C)-C189, Compound (1C)-C199 to Compound (1C)-C207, Compound (1C)-C217 to Compound (1C)- C225, Compound (1C)-C253 to Compound (1C)-C261, Compound (1C)-C271 to Compound (1C)-C279, Compound (1C)-C289 to Compound (1C)-C297, Compound (1C)-C325 to Compound (1C)- C333, and Compound (1C)-C343 to Compound (1C)-C351).
[0534]
A compound of the formula (ID) :
wherein, A represents =CH-, R , R , R , R/a represents a hydrogen atom, and R3d, R6d, Ald and A3d, represent a combination of R3x, R6x, Alx and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 38-58 (Compound (1D)-1 to Compound (ID) -9, Compound (ID) -37 to Compound (ID) -45, Compound (ID) -55 to Compound (ID) -63, Compound (ID) -73 to Compound (ID) -81, Compound (ID) -109 to Compound (ID) -117, Compound (ID) -127 to Compound (ID) -135, Compound (ID) -145 to Compound (ID) -153, Compound (ID) -181 to Compound (ID) -189, Compound (ID) -199 to Compound (ID) -207, Compound (ID) -217 to Compound (1D)-
225, Compound (ID) -253 to Compound (ID) -261, Compound (1D)- 271 to Compound (ID) -279, Compound (ID) -289 to Compound (ID) -297, Compound (ID) -325 to Compound (ID) -333, Compound (ID) -343 to Compound (ID) -351, Compound (ID) -361 to Compound (ID) -369, Compound (ID) -397 to Compound (ID) -405, Compound (ID) -415 to Compound (ID) -423, Compound (ID) -433 to Compound (ID) -441, Compound (ID) -469 to Compound (1D)- 477, and Compound (ID) -487 to Compound (ID) -495).
[0535]
A compound of the formula (IE) :
wherein, X6 represents a fluorine atom, A e represents =CH-, R2e, Re, R5e, R7e represents a hydrogen atom, R3e, R6e, Ale, and A3e represent a combination of R3x, R6x, Alx, and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 38-52 (Compound (1E)-F1 to Compound (1E)-F9, Compound (1E)-F37 to Compound (1E)-F45, Compound (1E)-F55 to Compound (1E)-F63, Compound (1E)-F73 to Compound (1E)-F81, Compound (1E)-F109 to Compound (1E)- F117, Compound (1E)-F127 to Compound (1E)-F135, Compound (1E)-F145 to Compound (1E)-F153, Compound (1E)-F181 to Compound (1E)-F189, Compound (1E)-F199 to Compound (1E)- F207, Compound (1E)-F217 to Compound (1E)-F225, Compound (1E)-F253 to Compound (1E)-F261, Compound (1EJ-F271 to
Compound (1E)-F279, Compound (1E)-F289 to Compound (1E)- F297, Compound (1E)-F325 to Compound (1E)-F333, and Compound (1EJ-F343 to Compound (1E)-F351).
[0536]
A compound of the formula (IE) wherein, Xe represents a chlorine atom, A2e represents =CH-, R2e, R4e, R5e, R7e represents a hydrogen atom, R3e, R6e, Ale, and A3e represent a combination of R3x, R6x, Alx, and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 38-52 (Compound (IE) -CI to Compound (1E)-C9, Compound (1E)-C37 to Compound (1E)-C45, Compound (1E)-C55 to Compound (1E)-C63, Compound (1E)-C73 to Compound (1E)- C81, Compound (1E)-C109 to Compound (1E)-C117, Compound (1E)-C127 to Compound (1E)-C135, Compound (1E)-C145 to Compound (1E)-C153, Compound (1E)-C181 to Compound (1E)- C189, Compound (1E)-C199 to Compound (1E)-C207, Compound (1E)-C217 to Compound (1E)-C225, Compound (1E)-C253 to Compound (1E)-C261, Compound (1EJ-C271 to Compound (1E)- C279, Compound (1E)-C289 to Compound (1E)-C297, Compound (1E)-C325 to Compound (1E)-C333, and Compound (1E)-C343 to Compound (1E)-C351).
[0537]
Table 38
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Alx A3x n
1 Me H CF3 NMe N 0
2 Me F CF3 NMe N 0
3 Me CI CF3 NMe N 0
4 Me Br CF3 NMe N 0
5 Me Me CF3 NMe N 0
6 Me CF3 CF3 NMe N 0
7 Me OCF3 CF3 NMe N 0
8 Me C2 F5 CF3 NMe N 0
9 Me SF5 CF3 NMe N 0
10 Me H CF3 NMe N 2
11 Me F CF3 NMe N 2
12 Me CI CF3 NMe N 2
13 Me Br CF3 NMe N 2
14 Me Me CF3 NMe N 2
15 Me CF3 CF3 NMe N 2
16 Me OCF3 CF3 NMe N 2
17 Me C2 F5 CF3 NMe N 2
18 Me SF5 CF3 NMe N 2
19 Et H CF3 NMe N 0
20 Et F CF3 NMe N 0
21 Et CI CF3 NMe N 0
22 Et Br CF3 NMe N 0
23 Et Me CF3 NMe N 0
24 Et CF3 CF3 NMe N 0
25 Et OCF3 CF3 NMe N 0
[0538]
Table 39
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Alx A3x n
26 Et C2 F5 CF3 NMe N 0
27 Et SF5 CF3 NMe N 0
28 Et H CF3 NMe N 2
29 Et F CF3 NMe N 2
30 Et CI CF3 NMe N 2
31 Et Br CF3 NMe N 2
32 Et Me CF3 NMe N 2
33 Et CF3 CF3 NMe N 2
34 Et OCF3 CF3 NMe N 2
35 Et C2F5 CF3 NMe N 2
36 Et SF5 CF3 NMe N 2
37 Et H CF3 NMe CH 0
38 Et F CF3 NMe CH 0
39 Et CI CF3 NMe CH 0
40 Et Br CF3 NMe CH 0
41 Et Me CF3 Me CH 0
42 Et CF3 CF3 Me CH 0
43 Et OCF3 CF3 NMe CH 0
44 Et C2F5 CF3 NMe CH 0
45 Et SF5 CF3 NMe CH 0
46 Et H CF3 NMe CH 2
47 Et F CF3 NMe CH 2
48 Et CI CF3 NMe CH 2
49 Et Br CF3 NMe CH 2
50 Et Me CF3 NMe CH 2
[0539]
Table 40
[0540]
Table 41
[0541]
Table 42
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Aix A3x n
101 Et F CF2CF3 NMe N 2
102 Et CI CF2CF3 NMe N 2
103 Et Br CF2CF3 NMe N 2
104 Et Me CF2CF3 NMe N 2
105 Et CF3 CF2CF3 NMe N 2
106 Et OCF3 CF2CF3 NMe N 2
107 Et C2F5 CF2CF3 NMe N 2
108 Et SF5 CF2CF3 NMe N 2
109 Et H CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
110 Et F CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
111 Et CI CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
112 Et Br CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
113 Et Me CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
114 Et CF3 CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
115 Et OCF3 CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
116 Et C2F5 CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
117 Et SF5 CF2CF3 NMe CH 0
118 Et H CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
119 Et F CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
120 Et CI CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
121 Et Br CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
122 Et Me CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
123 Et CF3 CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
124 Et OCF3 CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
125 Et C2F5 CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
[0542]
Table 43
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Aix A3x n
126 Et SF5 CF2CF3 NMe CH 2
127 Et H CF2CF3 S N 0
128 Et F CF2CF3 S N 0
129 Et CI CF2CF3 S N 0
130 Et Br CF2CF3 S N 0
131 Et Me CF2CF3 S N 0
132 Et CF3 CF2CF3 S N 0
133 Et OCF3 CF2CF3 S N 0
134 Et C2F5 CF2CF3 S N 0
135 Et SF5 CF2CF3 S N 0
136 Et H CF2CF3 S N 2
137 Et F CF2CF3 S N 2
138 Et CI CF2CF3 S N 2
139 Et Br CF2CF3 S N 2
140 Et Me CF2CF3 S N 2
141 Et CF3 CF2CF3 S N 2
142 Et OCF3 CF2CF3 S N 2
143 Et C2F5 CF2CF3 S N 2
144 Et SF5 CF2CF3 S N 2
145 Me H SCF3 NMe N 0
146 Me F SCF3 NMe N 0
147 Me CI SCF3 NMe N 0
148 Me Br SCF3 NMe N 0
149 Me Me SCF3 NMe N 0
150 Me CF3 SCF3 NMe N 0
[0543]
Table 44
[0544]
Table 45
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Aix A3x n
176 Et Me SCF3 NMe N 2
177 Et CF3 SCF3 NMe N 2
178 Et OCF3 SCF3 NMe N 2
179 Et C2F5 SCF3 Me N 2
180 Et SF5 SCF3 Me N 2
181 Et H SCF3 NMe CH 0
182 Et F SCF3 NMe CH 0
183 Et CI SCF3 NMe CH 0
184 Et Br SCF3 NMe CH 0
185 Et Me SCF3 NMe CH 0
186 Et CF3 SCF3 NMe CH 0
187 Et OCF3 SCF3 NMe CH 0
188 Et C2F5 SCF3 NMe CH 0
189 Et SF5 SCF3 NMe CH 0
190 Et H SCF3 NMe CH 2
191 Et F SCF3 NMe CH 2
192 Et CI SCF3 NMe CH 2
193 Et Br SCF3 NMe CH 2
194 Et Me SCF3 NMe CH 2
195 Et CF3 SCF3 NMe CH 2
196 Et OCF3 SCF3 NMe CH 2
197 Et C2F5 SCF3 NMe CH 2
198 Et SF5 SCF3 NMe CH 2
199 Et H SCF3 S N 0
200 Et F SCF3 S N 0
[0545]
Table 46
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Alx A3x n
201 Et CI SCF3 S N 0
202 Et Br SCF3 S N 0
203 Et Me SCF3 S N 0
204 Et CF3 SCF3 S N 0
205 Et OCF3 SCF3 S N 0
206 Et C2F5 SCF3 S N 0
207 Et SF5 SCF3 S N 0
208 Et H SCF3 S N 2
209 Et F SCF3 S N 2
210 Et CI SCF3 S N 2
211 Et Br SCF3 s N 2
212 Et Me SCF3 s N 2
213 Et CF3 SCF3 s N 2
214 Et OCF3 SCF3 s N 2
215 Et C2F5 SCF3 s N 2
216 Et SF5 SCF3 S N 2
217 Me H SOCF3 Me N 0
218 Me F SOCF3 NMe N 0
219 Me CI SOCF3 NMe N 0
220 Me Br SOCF3 NMe N 0
221 Me Me SOCF3 NMe N 0
222 Me CF3 SOCF3 NMe N 0
223 Me OCF3 SOCF3 NMe N 0
224 Me C2F5 SOCF3 NMe N 0
225 Me SF5 SOCF3 NMe N 0
[0546]
Table 47
[0547]
able 48
[0548]
Table 49
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Alx A3x n
276 Et CF3 SOCF3 S N 0
277 Et OCF3 SOCF3 S N 0
278 Et C2F5 SOCF3 S N 0
279 Et SF5 SOCF3 S N 0
280 Et H SOCF3 S N 2
281 Et F SOCF3 S N 2
282 Et CI SOCF3 S N 2
283 Et Br SOCF3 S N 2
284 Et Me SOCF3 S N 2
[0549]
Table 50
[0550]
Table 51
[0551]
Table 52
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Aix A3X n
351 Et SF5 S02CF3 S N 0
352 Et H S02CF3 S N 2
353 Et F S02CF3 S N 2
354 Et CI S02CF3 S N 2
355 Et Br S02CF3 S N 2
356 Et Me S02CF3 S N 2
357 Et CF3 S02CF3 S N 2
358 Et OCF3 S02CF3 S N 2
359 Et C2F5 S02CF3 S N 2
360 Et SF5 SO2CF3 S N 2
[0552]
Table 53
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6X Aix A3X n
361 Me H Br Me N 0
362 Me F Br Me N 0
363 Me CI Br NMe N 0
364 Me Br Br NMe N 0
365 Me Me Br NMe N 0
366 Me CF3 Br NMe N 0
367 Me OCF3 Br NMe N 0
368 Me C2F5 Br NMe N 0
369 Me SF5 Br NMe N 0
370 Me H Br NMe N 2
371 Me F Br NMe N 2
372 Me CI Br NMe N 2
373 Me Br Br NMe N 2
374 Me Me Br NMe N 2
375 Me CF3 Br NMe N 2
376 Me OCF3 Br NMe N 2
377 Me C2F5 Br NMe N 2
378 Me SF5 Br NMe N 2
379 Et H Br NMe N 0
380 Et F Br NMe N 0
381 Et CI Br NMe N 0
382 Et Br Br NMe N 0
383 Et Me Br NMe N 0
384 Et CF3 Br NMe N 0
385 Et OCF3 Br NMe N 0
[0553]
Table 54
Intermediate Rlx R3x R6x Aix A3x n
386 Et C2F5 Br Me N 0
387 Et SF5 Br Me N 0
388 Et H Br NMe N 2
389 Et F Br NMe N 2
390 Et CI Br NMe N 2
391 Et Br Br NMe N 2
392 Et Me Br NMe N 2
393 Et CF3 Br NMe N 2
394 Et OCF3 Br NMe N 2
395 Et C2F5 Br NMe N 2
396 Et SF5 Br NMe N 2
397 Et H Br NMe CH 0
398 Et F Br NMe CH 0
399 Et CI Br NMe CH 0
400 Et Br Br NMe CH 0
401 Et Me Br NMe CH 0
402 Et CF3 Br NMe CH 0
403 Et OCF3 Br NMe CH 0
404 Et C2F5 Br NMe CH 0
405 Et SF5 Br NMe CH 0
406 Et H Br NMe CH 2
407 Et F Br NMe CH 2
408 Et CI Br NMe CH 2
409 Et Br Br NMe CH 2
410 Et Me Br NMe CH 2
[0554]
Table 55
424 Et H Br s N 2
425 Et F Br s N 2
426 Et CI Br s N 2
427 Et Br Br s N 2
428 Et Me Br s N 2
429 Et CF3 Br s N 2
430 Et OCF3 Br s N 2
431 Et C2F5 Br s N 2
432 Et SF5 Br s N 2
433 Me H I NMe N 0
434 Me F I Me N 0
435 Me CI I NMe N 0
[0555]
Table 56
Intermediate Rlx R3X R6x Alx A3x n
436 Me Br I NMe N 0
437 Me Me I NMe N 0
438 Me CF3 I NMe N 0
439 Me OCF3 I NMe N 0
440 Me C2F5 I NMe N 0
441 Me SF5 I NMe N 0
442 Me H I NMe N 2
443 Me F I NMe N 2
444 Me CI I NMe N 2
445 Me Br I NMe N 2
446 Me Me I NMe N 2
447 Me CF3 I NMe N 2
448 Me OCF3 I NMe N 2
449 Me C2F5 I NMe N 2
450 Me SF5 I NMe N 2
451 Et H I NMe N 0
452 Et F I NMe N 0
453 Et CI I NMe N 0
454 Et Br I NMe N 0
455 Et Me I NMe N 0
456 Et CF3 I NMe N 0
457 Et OCF3 I NMe N 0
458 Et C2F5 I NMe N 0
459 Et SF5 I NMe N 0
460 Et H I NMe N 2
[0556]
Table 57
Intermediate Rlx R3x RGx Alx A3x n
461 Et F I NMe N 2
462 Et CI I NMe N 2
463 Et Br I NMe N 2
464 Et Me I NMe N 2
465 Et CF3 I NMe N 2
466 Et OCF3 I NMe N 2
467 Et C2F5 I NMe N 2
468 Et SF5 I NMe N 2
469 Et H I NMe CH 0
470 Et F I NMe CH 0
471 Et CI I NMe CH 0
472 Et Br I NMe CH 0
473 Et Me I NMe CH 0
474 Et CF3 I NMe CH 0
475 Et OCF3 I NMe CH 0
476 Et C2F5 I NMe CH 0
477 Et SF5 I NMe CH 0
478 Et H I NMe CH 2
479 Et F I NMe CH 2
480 Et CI I NMe CH 2
481 Et Br I NMe CH 2
482 Et Me I NMe CH 2
483 Et CF3 I NMe CH 2
484 Et OCF3 I NMe CH 2
485 Et C2F5 I NMe CH 2
[0557]
Table 58
Intermediate Rlx R3x RGx Alx A3x n
486 Et SF5 I NMe CH 2
487 Et H I S N 0
488 Et F I S N 0
489 Et CI I S N 0
490 Et Br I S N 0
491 Et Me I S N 0
492 Et CF3 I S N 0
493 Et OCF3 I S N 0
494 Et C2F5 I s N 0
495 Et SF5 I s N 0
496 Et H I s N 2
497 Et F I s N 2
498 Et CI I s N 2
499 Et Br I s N 2
500 Et Me I s N 2
501 Et CF3 I s N 2
502 Et OCF3 I s N 2
503 Et C2F5 I s N 2
504 Et SF5 I s N 2
[0558]
In the above Tables 38-58, Me represents a methyl group, and Et represents an ethyl group.
[0559]
The 1H-NMR data of Compound (IB) are shown below.
Compound (IB) -505
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76 (1H,S), 8.33 (lH,s), 8.04 (1H,S), 7.88-7.76 (2H,m), 7.78-7.60 (2H,m) , 6.30 (lH,brs), 3.30- 3.20 (lH,m), 3.10 (3H,d), 3.10-2.98 (lH,m), 1.26 (3H,t). Compound (IB) -28
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.39 (1H,S), 8.08 (lH,d), 7.85-7.55 (4H,m), 7.26-7.20 (lH,m), 6.29 (lH,brs), 3.51 (2H,q), 3.05 (3H,d) , 1.33 (3H, t) .
Compound (IB) -379
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.28 (lH,brs), 8.14 (lH,d), 7.90-7.75 (2H,m), 7.58-7.35 (3H,m), 5.06 (lH,brs), 3.20-2.96 (5H,m), 1.32 (3H,q) .
Compound (IB) -507
""■H- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.39-8.38 (lH,m), 7.80 (lH,brs), 7.70- 7.68 (lH,m) , 7.67-7.61 (2H,m), 7.44-7.39 (lH,m), 5.80 (lH,brs), 3.10-3.07 (3H,m), 3.00 (2H,q), 1.26 (3H,t).
Compound (IB) -508
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.41-8.38 (lH,m), 8.29-8.26 (lH,m), 8.16- 8.12 (lH,m), 7.93-7.89 (lH,m) , 7.86 (lH,brs), 7.76-7.73 (lH,m), 5.39-5.33 (lH,brm), 3.14 (2H,q), 3.08 (3H,d), 1.42 (3H, t) .
Compound (IB) -24
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.39 (lH,brs), 7.96 (lH,brs), 7.92 (lH,d), 7.77-7.71 (2H,m), 7.62 (lH,d), 5.42 (lH,brs), 3.12-3.03 (5H,m) , 1.37 (3H, t) .
Compound ( IB) - 509
^- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.38 (lH,brs), 7.89 (lH,d), 7.80 (lH,d),
7.57-7.51 (lH,m), 7.50-7.44 (lH,m), 7.43-7.36 (lH,m), 7.05-
6.99 (lH,m) , 5.22 (lH,brs) , 3.06 (3H,s), 3.00 (2H,q), 1.32 (3H,t) .
Compound (IB) -451
■""H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.26 (lH,brs), 7.87 (lH,s), 7.84 (lH,d), 7.52 (lH,d), 7.49-7.42 (lH,m), 7.41-7.35 (lH,m), 7.20-7.15 (lH,m), 5.12 (lH,brs), 3.02-2.97 (5H,m); 1.32 (3H,t).
Compound (IB) -511
^- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.30 (lH,s), 8.10 (lH,brs), 7.76-7.76 (2H,m), 7.50 (lH,d), 7.45 (lH,t), 7.36 (lH,t), 5.41 (lH,d), 4.37-4.27 (lH,m), 2.99 (2H,q), 1.30-1.28 (9H,m).
Compound (IB) -37
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.18 (lH,brs), 7.84 (lH,d), 7.60-7.30 (5H,m) , 6.77 (lH,d), 4.85 (lH,brs), 3.01 (2H,q), 2.93 (3H,d) , 1.32 (3H, t) .
Compound (IB) -33
""■H-NMR (Acetone-d6) δ: 9.56 (lH,brs), 8.36-8.35 (lH,m), 8.30-8.23 (3H,m), 7.87-7.85 (lH,m), 6.44 (lH,brs), 3.65 (2H,q), 3.03 (3H,d), 1.31 (3H,t).
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 9.35 (lH,s), 8.92 (lH,s), 8.03 (lH,d), 7.74 (1H,S) ,7.62 (lH,d), 7.57 (lH,s), 7.44( lH,d), 7.14 (lH,d), 3.05 (2H,q), 1.36 (3H,t).
[0560]
The 1H-NMR data of Compound (1C) are shown below.
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.40 (lH,s), 7.73-7.71 (lH,m), 7.29-7.24 (3H,m), 4.99 (lH,brs), 3.08 (3H,d).
Compound (1C)-F3
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.40 (lH,s), 8.14 (lH,dd), 7.93 (lH,d),
7.72 (lH,s), 7.36 (lH,d), 7.32-7.27 (lH,m), 4.99 (lH,brs), 3.08 (3H,d) .
Compound (1C)-F4
^-N R (CDC13) δ: 8.39 (lH,s), 8.06 (lH,dd), 7.93 (lH,d), 7.72 (1H,S) , 7.51 (lH,d), 7.44 (lH,d), 4.99 (lH,brs), 3.07 (3H,d) .
Compound (1C)-F5
■"■H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.38(1H,S) , 8.15-7.94 (2H,m), 7.73 (lH,s), 7.15 (lH,d), 7.03 (lH,d), 5.06 (lH,brs), 3.07 (3H,d), 2.45 (3H, s) .
Compound (1C)-F6
XH- R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.41 (lH,brs), 8.33 (lH,t), 7.99 (lH,d), 7.75 (lH,d), 7.64 (lH,d), 7.53 (lH,d), 4.97 (lH,brs), 3.08
(3H,d) .
Compound (1C) -F37
""■H- R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.25-8.06 (2H,m), 7.64-7.53 (2H,m), 7.47
(lH,d)f 7.34 (lH,t), 7.24-7.15 (lHfm), 6.80 (lH,d), 4.38
(lH,brs) , 2.93 (3H,d) .
Compound (1C)-C37
1H- R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 7.85 (lH,d), 7.64 (lH,brs), 7.56 (lH,s), 7.52-7.38 (4H,m) , 6.80 (lH,d), 4.49 (lH,brs), 2.93 (3H,s). Compound (1C)-F42
""■H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.33 (lH,t), 8.10 (lH,d), 7.66-7.57 (2H,m), 7.55-7.45 (2H,m) , 6.82 (lH,d), 4.29 (lHfbrs), 2.93 (3H,d) .
Compound (1C)-F145
■"■H-NMR (CDC13) δ: 8.35 (lH,s), 8.19 (lH,t), 8.02 (lH,d), 7.76 (1H,S) ,7.64-7.54 (lH,m), 7.36 (lH,t), 7.25-7.20 (lH,m), 5.06 (lH,brs), 3.07 (3H,d).
Compound (1C)-C145
1H- MR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.35 (lH,brs), 7.86 (lH,d), 7.77-7.71 (lH,m), 7.63-7.39 (4H,m) , 5.19 (lH,brs), 3.08( 3H,d).
Compound (1C)-F150
XH-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.40-8.28 (2H,m), 7.98 (lH,d), 7.77 (lH,s), 7.64 (lH,d), 7.53 (lH,d), 4.98 (lH,brs), 3.08 (3H,d) .
Compound (1C) -F73
^- MR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.34 (lH,brs), 8.24-8.15 (lH,m) , 8.05 (lH,d), 7.68(lH,s), 7.65-7.54 (lH,m), 7.40-7.32 (lH,m), 7.25-7.18 (lH,m), 5.09 (lH,brs), 3.09 (3H,d).
Compound (1C)-C73
""■H-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.35 (lH,s), 7.87 (lH,d), 7.65 (lH,s), 7.62 (lH,brs), 7.54-7.40 (3H,m), 5.21 (lH,brs), 3.09 (3H,d). Compound (1C)-F78
1H- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.40-8.29 (2H,m), 8.01 (lH,d), 7.69 (lH,s), 7.64 (lH,d), 7.53 (lH,d), 5.00 (lH,brs), 3.09 (3H,d) .
Compound (1C) -Fl
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.39 (lH,s), 8.19 (lH,t), 8.03 (lH,d), 7.74 (1H,S) ,7.66-7.55 (lH,m), 7.36 (lH,t), 7.25-7.19 (lH,m),
5.05 (lH,brs), 3.08 (3H,d).
Compound (1C)-C1
^-NMR (CDC1
3) δ: 8.40 (lH,s), 7.86 (lH,d), 7.72 (lH,s), 7.59 (lH,brs), 7.54-7.40 (3H,m) , 5.15 (lH,brs), 3.08 (3H,d). Compound (1C)-F506
""■H-NMR (DMSO-Dg) δ: 9.59 (lH,d), 8.50 (lH,s), 7.91 (lH,t),
7.70-7.60 (lH,m) , 7.45-7.33 (4H,m), 7.07 (lH,d).
[0561]
The 1H-NMR data of Compound (ID) are shown below.
Compound ( ID) -1
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.72 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m), 7.55- 7.51 (lH,m), 7.47-7.41 (2H,m), 7.37-7.32 (lH,m), 4.12 (lH,brs) , 3.84 (3H, s) .
[0562]
The H-NMR data of Compound (IE) are shown below.
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.29 (lH,d), 7.90 (lH,t), 7.81
7.66 (lH,d), 7.57 (lH,d), 7.48 (lH,d), 3.82 (3H,d).
Compound (1E)-F9
■"Ή-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.37-8.35 (ΙΗ,πι) , 7.93- 7.87 (lH,m), 7.80 (lH,dd), 7.74 (lH,dd), 3.92 (3H,d).
Compound (1E)-F7
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.75-8.73 (lH,m), 8.34-8.32 (lH,m), 7.81 (lH,t), 7.29-7.25 (lH,m), 7.22-7.18 (lH,m), 3.91 (3H,d). Compound (1E)-F42
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.13 (lH,s), 7.91 (lH,t), 7.67-7.61 (2H,m) , 7.58-7.51 (2H,m) , 3.82 (3H,d).
Compound (IE) -CI
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73 (lH,dd), 8.33 (lH,dd), 7.61-7.51 (3H,m) , 7.51-7.45 (lH,m), 3.81 (3H,s)
Compound (1E)-F1
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72 (lH,d), 8.32 (lH,d), 7.79-7.65 (lH,m) , 7.63-7.58 (lH,m), 7.42-7.36 (lH,m), 7.33-7.25 (lH,m), 3.89 (3H,d)
XH-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.37-8.35 (lH,m), 7.63- 7.55 (lH,m), 7.15 (2H,t), 3.86 (3H,s).
Compound (IE) -F507
^-NMR (CDC1
3) δ: 8.76-8.73 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (ΙΗ,τη), 7.53- 7.40 (2H,m), 7.37-7.30 (lH,m), 3.92 (3H,d).
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (1H,
7.18 (3H,m), 3.99 (3H,s), 3.89 (3H,d).
1H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.70-8.69 (lH,m), 8.30-8.28 (lH,m), 7.66 (lH,t), 6.91 (lH,dd), 6.81 (lH,dd), 3.91 (3H,s), 3.88 (3H,d) .
Compound (1E)-F3
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.70
(lH,t), 7.39 (lH,dd), 7.34 (lH,dd), 3.89 (3H,d).
■"■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.38-8.36 (lH,m), 7.58- 7.51 (lH,m), 7.43 (lH,d), 7.23 (lH,t), 3.80 (3H,s).
""
■H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.72-8.70 (ΙΗ,τη), 8.33-8.31 (lH,m), 7.56- 7.49 (lH,m), 6.93-6.86 (2H,m) , 3.84 (3H,s), 3.77 (3H,s). Compound ( IE) -F511
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 10.78 (lH,brs), 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.33- 8.31 (lH,m), 7.46-7.39 (ΙΗ,τη), 6.98 (lH,d), 6.84-6.78 (lH,m) , 3.96 (3H,d) .
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.79-8.77 (lH,m), 8.48 (lH,d), 8.38-8.36 (lH,m), 8.34 (lH,dd), 7.82 (lH,d), 3.84 (3H,s).
XH- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.71 (lH,m), 8.33-8.31 (ΙΗ,τη), 7.48- 7.43 (2H,m), 7.32 (lH,dd), 3.81 (3H,s), 3.06 (2H,q), 1.41 (3H, t) .
Compound (1E)-F512
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.73-8.70 (ΙΗ,τη), 8.32-8.30 (lH,m) , 7.55- 7.49 (lH,m) , 7.47-7.41 (lH,m), 7.31-7.22 (lH,m) , 3.88 (3H,d) , 2.40 (3H,d) .
Compound (1E)-F5
1H- R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.71-8.69 (lH,m), 8.31-8.30 (lH,m), 7.61 (lH,t), 7.18 (lH,d), 7.10 (lH,d), 3.88 (3H,d), 2.48 (3H,s). Compound (IE) -F4
XH-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.33-8.32 (lH,m), 7.63 (lH,t), 7.56-7.48 (2H,m), 3.88 (3H,d).
1H- R ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.70-8.68 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m), 7.64- 7.55 (lH,m), 7.18-7.12 (2H,m), 3.86 (3H,s).
""
■H-NMR (CDCI
3) δ: 8.77-8.75 (lH,m), 8.40-8.38 (lH,m), 6.96- 6.90 (2H,m), 6.75 (lH,t), 3.86-3.85 (3H,m).
Compound (1E)-F515
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.74 (lH,m), 8.37-8.35 (lH,m), 7.38- 7.33 (2H,m) , 3.85 (3H, s) .
Hi-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.74-8.73 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m) , 7.81 (lH,t), 7.69-7.65 (2H,m), 7.63-7.60 (lH,m), 7.55-7.49 (3H,m), 7.48-7.43 (lH,m), 3.94 (3H,d).
!H-N R (CDCI3) δ: 8.79-8.77 (ΙΗ,τη), 8.40-8.38 (lH,m), 7.47- 7.42 (2H,m) , 3.87 (3H, s) .
1H- R (CDCI3) δ: 7.90 (lH,t), 7.63 (lH,dd), 7.59 (lH,d), 7.54 (lH,d), 6.84 (lH,d), 4.05 (3H,d), 4.02 (2H,brs).
Compound (1E)-C508
1H-NMR (CDCI
3) δ: 8.74-8.72 (lH,m), 8.35-8.33 (lH,m), 7.50- 7.47 (lH,m), 7.41-7.34 (2H,m), 3.79 (3H,s), 2.50 (3H,s). Compound (IE) -F519
""■H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.76-8.75 (lH,m), 8.36-8.34 (lH,m), 7.99- 7.94 (lH,m), 7.91-7.86 (lH,m), 7.54-7.49 (lH,m) , 3.92
(3H,d) .
Compound (1E)-F78
^-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.71-8.69 (lH,m), 8.34-8.33 (lH,m), 7.93- 7.88 (lH,m), 7.69-7.66 (lH,m), 7.61-7.57 (lH,m), 3.92
(3H,d) .
Compound (1E)-F77
^-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.65 (lH,s), 8.29 (lH,s), 7.64-7.58 (lH,m), 7.20-7.17 (lH,m), 7.13-7.08 (lH,m), 3.90-3.87 (3H,m) , 2.49 (3H, s) .
Compound (1E)-F149
'''H-NMR ( CDCI3 ) δ: 8.66-8.64 (lH,m), 8.39-8.37 (lH,m), 7.60 (lH,t), 7.20-7.16 (lH,m), 7.12-7.08 (lH,m), 3.86 (3H,d), 2.48 (3H, s) .
Compound (1E)-F73
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.67 (lH,d), 8.30 (lH,d), 7.74 (lH,td), 7.66-7.57 (lH,m) , 7.39 (lH,td), 7.34-7.27 (lH,m) , 3.90 (3H,d) .
Compound (IE) -C73
■"■H- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.68 (lH,d), 8.31 (lH,d), 7.62-7.53 (3H,m), 7.48 (lH,td), 3.81 (3H,s).
Compound (1E)-F79
""■H- R (CDCI3) δ: 8.70-8.68 (1H, m) , 8.33-8.30 (1H, m) , 7.81 (1H, t) , 7.30-7.25 (1H, m) , 7.22-7.18 (1H, m) , 3.91 (3H, d) .
[0563]
The above intermediate, Compounds (1F)-(1G) are shown in the following tables.
[0564]
A compound of the formula (IF) :
wherein A2f represents =CH-, R7f represents a hydrogen atom, and R6£, R8f, and A3f represent a combination of R6x, R8x, and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 59-61 (Compounds ( (IF) -1) - ( (IF) -56) ) .
[0565]
A compound of the formula (1G) :
wherein X
9 represents a chlorine atom, A
29 represents =CH-, R
7g represents a hydrogen atom, and R
69, R
8g, and A
3g represent a combination of R
6x, R
8x, and A
3x, respectively, shown in Tables 59-61 (Compounds ( (1G) -CI) - ( (1G) -C56) ) .
A compound of the formula (1G) wherein X9 represents a bromine atom, A2g represents =CH- , R7g represents a hydrogen atom, and R6g, R89, and A3g represent a combination of R6x, R8x, and A3x, respectively, shown in Tables 59-61 (Compounds ( (1G) -Bl) - ( (1G) -B56) ) .
[0566]
Table 59
Intermediate R6x R8x A3x
1 CF3 CH3 N
2 CF2CF3 CH3 N
3 SCF3 CH3 N
4 SOCF3 CH3 N
5 S02CF3 CH3 N
6 I CH3 N
7 SF5 CH3 N
8 CF3 CH2CH3 N
9 CF2CF3 CH2CH3 N
10 SCF3 CH2CH3 N
11 SOCF3 CH2CH3 N
12 SO2CF3 CH2CH3 N
13 I CH2CH3 N
14 SF5 CH2CH3 N
15 CF3 CH(CH3)2 N
16 CF2CF3 CH(CH3)2 N
17 SCF3 CH(CH3)2 N
18 SOCF3 CH(CH3)2 N
19 S02CF3 CH(CH3)2 N
20 I CH(CH3)2 N
21 SF5 CH(CH3)2 N
22 CF3 H N
23 CF2CF3 H N
24 SCF3 H N
25 SOCF3 H N
[0567]
Table 60
[0568]
Table 61
Intermediate R6X R8x A3x
51 CF2CF3 H CH
52 SCF3 H CH
53 SOCF3 H CH
54 S02CF3 H CH
55 I H CH
56 SF5 H CH
[0569]
The above intermediate, Compounds (1H)-(1I) are shown in the following tables.
[0570]
A compound of the formula (1H) :
wherein, R , R , R , R , R5h, R13h, and n represent a combination of Rlx, R2x, R3x, R4x, R5x, R13x, and n , respectively, shown in Tables 62-75 (Compounds ((1H)-1)- ( (1H) -288) .
[0571]
A com ound of the formula (II) :
wherein, R11, R21, R31, R4i, R5i, and r represent a combination of Rlx, R2x, R3x, R4x, R5x, and n, respectively, shown in Tables 63, 64, 66, and 67 (Compounds ((II) -17)- ((II) -48) and Compounds ( (II) -65) - ( (II) -96) .
[0572]
Table 62
Intermediate n
1 Me H H H H H 0
2 Me H F H H H 0
3 Me H CI H H H 0
4 Me H Br H H H 0
5 Me H Me H H H 0
6 Me H Et H H H 0
7 Me H Pr H H H 0
8 Me H CF3 H H H 0
9 Me H C2F5 H H H 0
10 Me H SF5 H H H 0
11 Me H OCH3 H H H 0
12 Me H OC2H5 H H H 0
13 Me H OCF3 H H H 0
14 Me H SCF3 H H H 0
15 Me H SOCF3 H H H 0
16 Me H S02CF3 H H H 0
[0573]
Table 63
[0574]
Table 64
Intermediate n
26 Me H SFs H H H 1
27 Me H OCH3 H H H 1
28 Me H OC2H5 H H H 1
29 Me H OCF3 H H H 1
30 Me H SCF3 H H H 1
31 Me H SOCF3 H H H 1
32 Me H S02CF3 H H H 1
33 Me H H H H H 2
34 Me H F H H H 2
35 Me H CI H H H 2
36 Me H Br H H H 2
37 Me H Me H H H 2
38 Me H Et H H H 2
39 Me H Pr H H H 2
40 Me H CF3 H H H 2
41 Me H C2F5 H H H 2
42 Me H SF5 H H H 2
43 Me H OCH3 H H H 2
44 Me H OC2H5 H H H 2
45 Me H OCF3 H H H 2
46 Me H SCF3 H H H 2
47 Me H SOCF3 H H H 2
48 Me H S02CF3 H H H 2
[0575]
Table 65
[0576]
Table 66
Intermediate n
65 Et H H H H H 1
66 Et H F H H H 1
67 Et H CI H H H 1
68 Et H Br H H H 1
69 Et H Me H H H 1
70 Et H Et H H H 1
71 Et H Pr H H H 1
72 Et H CF3 H H H 1
73 Et H C2F5 H H H 1
74 Et H SF5 H H H 1
75 Et H OCH3 H H H 1
76 Et H OC2H5 H H H 1
77 Et H OCF3 H H H 1
78 Et H SCF3 H H H 1
79 Et H SOCF3 H H H 1
80 Et H S02CF3 H H H 1
81 Et H H H H H 2
82 Et H F H H H 2
83 Et H CI H H H 2
84 Et H Br H H H 2
85 Et H Me H H H 2
86 Et H Et H H H 2
87 Et H Pr H H H 2
88 Et H CF3 H H H 2
89 Et H C2F5 H H H 2
[0577]
Table 67
[0578]
Table 68
Intermediate Rlx R3x n
97 Me H H H H OH 0
98 Me H F H H OH 0
99 Me H CI H H OH 0
100 Me H Br H H OH 0
101 Me H Me H H OH 0
102 Me H Et H H OH 0
103 Me H Pr H H OH 0
104 Me H CF3 H H OH 0
105 Me H C2F5 H H OH 0
106 Me H SF5 H H OH 0
107 Me H OCH3 H H OH 0
108 Me H OC2H5 H H OH 0
109 Me H OCF3 H H OH 0
110 Me H SCF3 H H OH 0
111 Me H SOCF3 H H OH 0
112 Me H S02CF3 H H OH 0
113 Me H H H H OH 1
114 Me H F H H OH 1
115 Me H CI H H OH 1
116 Me H Br H H OH 1
117 Me H Me H H OH 1
118 Me H Et H H OH 1
119 Me H Pr H H OH 1
120 Me H CF3 H H OH 1
[0579]
Table 69
Intermediate Rlx R13x n
121 Me H C2F5 H H OH 1
122 Me H SF5 H H OH 1
123 Me H OCH3 H H OH 1
124 Me H OC2H5 H H OH 1
125 Me H OCF3 H H OH 1
126 Me H SCF3 H H OH 1
127 Me H SOCF3 H H OH 1
128 Me H S02CF3 H H OH 1
129 Me H H H H OH 2
130 Me H F H H OH 2
131 Me H CI H H OH 2
132 Me H Br H H OH 2
133 Me H Me H H OH 2
134 Me H Et H H OH 2
135 Me H Pr H H OH 2
136 Me H CF3 H H OH 2
137 Me H C2F5 H H OH 2
138 Me H SF5 H H OH 2
139 Me H OCH3 H H OH 2
140 Me H OC2H5 H H OH 2
141 Me H OCF3 H H OH 2
142 Me H SCF3 H H OH 2
143 Me H SOCF3 H H OH 2
144 Me H S02CF3 H H OH 2
145 Et H H H H OH 0
[0580]
Table 70
Intermediate n
146 Et H F H H OH 0
147 Et H CI H H OH 0
148 Et H Br H H OH 0
149 Et H Me H H OH 0
150 Et H Et H H OH 0
151 Et H Pr H H OH 0
152 Et H CF3 H H OH 0
153 Et H C2F5 H H OH 0
154 Et H SFs H H OH 0
155 Et H OCH3 H H OH 0
156 Et H OC2H5 H H OH 0
157 Et H OCF3 H H OH 0
158 Et H SCF3 H H OH 0
159 Et H SOCF3 H H OH 0
160 Et H S02CF3 H H OH 0
161 Et H H H H OH 1
162 Et H F H H OH 1
163 Et H CI H H OH 1
164 Et H Br H H OH 1
165 Et H Me H H OH 1
166 Et H Et H H OH 1
167 Et H Pr H H OH 1
168 Et H CF3 H H OH 1
169 Et H C2F5 H H OH 1
170 Et H SF5 H H OH 1
[0581] Table 71
Intermediate Rlx R2X R3x R4X R5X R13X n
171 Et H OCH3 H H OH 1
172 Et H OC2H5 H H OH 1
173 Et H OCF3 H H OH 1
174 Et H SCF3 H H OH 1
175 Et H SOCF3 H H OH 1
176 Et H S02CF3 H H OH 1
177 Et H H H H OH 2
178 Et H F H H OH 2
179 Et H CI H H OH 2
180 Et H Br H H OH 2
181 Et H Me H H OH 2
182 Et H Et H H OH 2
183 Et H Pr H H OH 2
184 Et H CF3 H H OH 2
185 Et H C2F5 H H OH 2
186 Et H SF5 H H OH 2
187 Et H OCH3 H H OH 2
188 Et H OC2H5 H H OH 2
189 Et H OCF3 H H OH 2
190 Et H SCF3 H H OH 2
191 Et H SOCF3 H H OH 2
192 Et H S02CF3 H H OH 2
193 Me H H H H CI 0
194 Me H F H H CI 0
195 Me H CI H H CI 0
[0582] Table 72
Intermediate R1X R2x R3x R4X R5X R13X n
196 Me H Br H H CI 0
197 Me H Me H H CI 0
198 Me H Et H H CI 0
199 Me H Pr H H CI 0
200 Me H CF3 H H CI 0
201 Me H C2F5 H H CI 0
202 Me H SF5 H H CI 0
203 Me H OCH3 H H CI 0
204 Me H OC2H5 H H CI 0
205 Me H OCF3 H H CI 0
206 Me H SCF3 H H CI 0
207 Me H SOCF3 H H CI 0
208 Me H S02CF3 H H CI 0
209 Me H H H H CI 1
210 Me H F H H CI 1
211 Me H CI H H CI 1
212 Me H Br H H CI 1
213 Me H Me H H CI 1
214 Me H Et H H CI 1
215 Me H Pr H H CI 1
216 Me H CF3 H H CI 1
217 Me H C2F5 H H CI 1
218 Me H SF5 H H CI 1
219 Me H OCH3 H H CI 1
220 Me H OC2H5 H H CI 1
[0583]
Table 73
Intermediate n
221 Me H OCF3 H H CI 1
222 Me H SCF3 H H CI 1
223 Me H SOCF3 H H CI 1
224 Me H S02CF3 H H CI 1
225 Me H H H H CI 2
226 Me H F H H CI 2
227 Me H CI H H CI 2
228 Me H Br H H CI 2
229 Me H Me H H CI 2
230 Me H Et H H CI 2
231 Me H Pr H H CI 2
232 Me H CF3 H H CI 2
233 Me H C2F5 H H CI 2
234 Me H SF5 H H CI 2
235 Me H OCH3 H H CI 2
236 Me H OC2H5 H H CI 2
237 Me H OCF3 H H CI 2
238 Me H SCF3 H H CI 2
239 Me H SOCF3 H H CI 2
240 Me H S02CF3 H H CI 2
241 Et H H H H CI 0
242 Et H F H H CI 0
243 Et H CI H H CI 0
244 Et H Br H H CI 0
245 Et H Me H H CI 0
[0584]
Table 74
[0585]
271 Et H SOCF
3 H H CI 1
272 Et H S02CF3 H H CI 1
273 Et H H H H CI 2
274 Et H F H H CI 2
275 Et H CI H H CI 2
276 Et H Br H H CI 2
277 Et H Me H H CI 2
278 Et H Et H H CI 2
279 Et H Pr H H CI 2
280 Et H CF3 H H CI 2
281 Et H C2F5 H H CI 2
282 Et H SF5 H H CI 2
283 Et H OCH3 H H CI 2
284 Et H OC2H5 H H CI 2
285 Et H OCF3 H H CI 2
286 Et H SCF3 H H CI 2
287 Et H SOCF3 H H CI 2
288 Et H S02CF3 H H CI 2
[0586]
In the above Tables 62-75, Me represents a methyl group, and Et represents an ethyl group.
[0587]
The 1H-NMR data of Compound (1H) are shown below.
Compound (1H)-184
1H- MR (CDCI3) δ: 9.23 (lH,brs), 8.37 (lH,brs), 8.03-7.98 (2H,m), 3.63 (2H,q) , 1.39 (3H,t) Compound ( 1H) -280
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.33 (lH,brs) , 8.09-7.98 (2H,m) , 3.43 (2H,q) , 1.38 (3H,t) Compound (1H) -177
■""H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.12 (lH,dd), 7.87 (lH,dd), 7.77-7.68 (2H,m) , 3.59(2H,q), 1.35 (3H,t) .
Compound (1Η)-248
^-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.22 (lH,d), 7.55 (lH,s), 7.43 (lH,d), 3.02 (2H,q) ,1.43(3H,t) .
[0588]
The 1H- MR data of Compound (II) are shown below.
Compound (II) -88
!H-NMR (CDCI3) δ: 8.43-8.42 (lH,m), 8.10-8.03 (2H,m), 3.45 (2H,q), 1.38 (3H,t)
[0589]
Formulation Example 1
Any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (10 parts) is dissolved in a mixture of xylene (35 parts) and N,N- dimethylformamide (35 parts) , and to the mixture is added polyoxyethylene styryl phenyl ether (14 parts) and calcium dodecylbenzenesulfonate (6 parts) , and stirred to give emulsions of each compound.
[0590]
Formulation Example 2
Sodium lauryl sulfate (4 parts) , calcium lignin sulfonate (2 parts) , synthetic hydrated silicone oxide powder (20 parts) and diatomite (54 parts) are mixed, then to the mixture is added any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (20 parts) , and mixed to give wettable powders of each compound .
[0591]
Formulation Example 3
To any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (2 parts) is added synthetic hydrated silicone oxide powder (1 part) , calcium lignin sulfonate (2 parts) , bentonite (30 parts) , and kaolin clay (65 parts) , and mixed. Then, to the mixture is added an appropriate amount of water, further stirred, granulated with a granulator, and draft-dried to give granules of each compound.
[0592]
Formulation Example 4
Any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (1 part) is dissolved in an appropriate amount of acetone. To the mixture is added synthetic hydrated silicone oxide powder (5 parts), PAP (0.3 parts), and Fubasami clay (93.7 parts), and well stirred. Then, acetone is removed by evaporation to give powders of each compound.
[0593]
Formulation Example 5
A mixture (ratio by weight = 1:1) of polyoxyethylene alkyl ether sulfate ammonium salt and white carbon (35 parts) , any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (10 parts) , and water (55 parts) are mixed, pulverized by a wet grinding method to give formulations of each compounds.
[0594]
Formulation Example 6
Any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (0.1 parts) is dissolved in xylene (5 parts) and trichloroethane (5 parts) , and mixed with deodorized kerosine (89.9 parts) to give oil solutions of each compounds.
[0595]
Formulation Example 7
Any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (10 mg) is dissolved in acetone (0.5 ml). The mixture is added to animal powdered solid feed (powdered solid feed for breeding, CE-2, from CLEA Japan, Inc.), (5 g) and mixed uniformly. Then, acetone is removed by evaporation to give poison baits of each compound.
[0596]
Formulation Example 8
Any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (0.1 parts) and
Neothiosol (Chuo Kasei Co. Ltd.) (49.9 parts) are charged into an aerosol container. After an aerosol valve is attached to the container, dimethyl ether (25 parts) and LPG (25 parts) are charged into the container. The container is vibrated, and attaching an actuator to give oily aerosols of each compound.
[0597]
Formulation Example 9
Any one of Present Compounds 1-427 (0.6 parts), BHT (2 , 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) (0.01 parts), xylene (5
parts), deodorized kerosine (3.39 parts), and an emulsifier (Atmos 300 (a registered trade name for Atmos Chemical
Ltd.)) (1 part) are mixed and dissolved. The mixture and distilled water (50 parts) are charged into an aerosol container, and attaching a valve. Then, propellant (LPG) (40 parts) is pressure-charged into the container through the valve to give aqueous aerosols of each compound.
[0598]
The effects of the present compounds to control pests are shown in Test Examples.
[0599]
Test Example 1
The test spray solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds 1-7, 10-14, 18-23, 33-38, 46, 53, 55, 66, 68-70, 72, 75, 81-83, 88-90, 98-99, 102-104, 112-113, 115-118, 121-123, 126-142, 144, 151, 156- 159, 161, 167-171, 174-176, 183, 185-186, 188, 192-194, 209-210, 214-215, 235, 238-243, 246-256, 259, 262, 264, 270-273, 279-280, 285, 291-292, 294, 297-299, 301-302, 306- 313, 316-319, 324-325, 327, 330-331, 333, 343, 345, 353, 357-361, 371 and 374-379 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration .
On the other hand, on a cucumber seedling (the first true leaf stage) planted in a plastic cup was inoculated
with about 30 Aphis gossypii, and leaving it for a day. Twenty ml of each of the above test spray solutions was sprayed on this seedling.
Six days after spraying, the number of the surviving Aphis gossypii parasitized on the leaves of the cucumber was examined, and a control value was calculated according to the following equation:
Control value (%) = {1 - (Cb x Tai)/(Cai x Tb) ) x 100 wherein symbols represent as follows:
Cb: the number of insects in a non-treated section before treatment,
Cai: the number of insects in a non-treated section in observation,
Tb: the number of insects in a treated-section before treatment ,
Tai: the number of insects in a treated-section in observation;
wherein the non-treated section represents a section where the test spray solution prepared by diluting the formulation without the present compound in Formulation Example 5 with the same amount of water as in the treated- section was sprayed. As a result, in the treated-section of the test spray
solution of each of Present Compounds 1-7, 10-14, 18-23, 33-38, 46, 53, 55, 66, 68-70, 72, 75, 81-83, 88-90, 98-99, 102-104, 112-113, 115-118, 121-123, 126-142, 144, 151, 156- 159, 161, 167-171, 174-176, 183, 185-186, 188, 192-194, 209-210, 214-215, 235, 238-243, 246-256, 259, 262, 264, 270-273, 279-280, 285, 291-292, 294, 297-299, 301-302, 306- 313, 316-319, 324-325, 327, 330-331, 333, 343, 345, 353, 357-361, 371 and 374-379, the control value of 90 % or more was shown.
[0600]
Test Example 2
The test diluted solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds 1-6, 13, 14, 16, 21-23, 33, 34, 36, 43, 46, 48-50, 53, 55, 66, 69, 70, 82, 83, 88, 89, 98-100, 116-118, 122-123, 133-135, 137, 139-140, 142-143, 156-159, 167, 169, 171, 175-176, 192-194, 224, 237-239, 241-243, 247, 254, 256, 280, 299, 306, 317- 319, 330-331, 333, 353, 376 and 379 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration.
A root part of a cucumber seedling (the first true leaf stage) from which soil had been washed off was immersed in 5 ml of each of the diluted solutions, and one day after treatment, on the cucumber leaf surface was inoculated with 30 Aphis gossypii (whole stage) . After
further seven days, the number of insect of living Aphis gossypii parasitized on the leaves of the cucumber was examined, and a control value was calculated according to the following equation:
Control value (%) = {1 - (Cb x Tai)/(Cai x Tb) ) x 100 wherein symbols represent as follows:
Cb: the number of insects in a non-treated section before treatment,
Cai: the number of insects in a non-treated section in observation,
Tb: the number of insects in a treated-section before treatment,
Tai: the number of insects in a treated-section in observation;
wherein the non-treated section represents a section where the test diluted solution prepared by diluting the formulation without the present compound in Formulation Example 5 with the same amount of water as in the treated- section was used.
As a result, in the treated-section of the test diluted solution of each of Present Compounds 1-6, 13, 14, 16, 21-23, 33, 34, 36, 43, 46, 48-50, 53, 55, 66, 69, 70, 82, 83, 88, 89, 98-100, 116-118, 122-123, 133-135, 137,
139-140, 142-143, 156-159, 167, 169, 171, 175-176, 192-194, 224, 237-239, 241-243, 247, 247, 254, 256, 280, 299, 306, 317-319, 330-331, 333, 353, 376 and 379, the control value of 90 % or more was shown.
[0601]
Test Example 3
The test diluted solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds 2-6, 35-38, 50, 55, 89, 90, 112-113, 116-118, 123, 130, 132, 134-135, 157-158, 169-171, 175-176, 194, 209-210, 214-215, 239-240, 242-243, 248, 254, 270-273, 280, 299, 302, 306, 309, 318- 319, 330-331, 333, 345, 359, 361 and 375-376 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration.
On the other hand, a cucumber seedling (the second true leaf stage) planted in a plastic cup was drenched at its foot with 5 ml of each of the diluted solutions, and kept in a greenhouse of 25 °C for 7 days. On the cucumber leaf surface was inoculated with 30 Aphis gossypii (whole stage) , and further kept in the greenhouse for 6 days, then the number of insect of living Aphis gossypii parasitized on the leaves of this cucumber was examined, and a control value was calculated according to the following equation: Control value (%) = {1 - (Cb x Tai) / (Cai x Tb) ) x 100
wherein symbols represent as follows:
Cb: the number of insects in a non-treated section before treatment,
Cai: the number of insects in a non-treated section in observation,
Tb: the number of insects in a treated-section before treatment,
Tai: the number of insects in a treated-section in observation;
wherein the non-treated section represents a section where the test diluted solution prepared by diluting the formulation without the present compound in Formulation Example 5 with the same amount of water as in the treated- section was used.
As a result, in the treated-section of the test diluted solution of each of Present Compounds 2-6, 35-38, 50, 55, 89, 90, 112-113, 116-118, 123, 130, 132, 134-135, 157-158, 169-171, 175-176, 194, 209-210, 214-215, 239-240, 242-243, 248, 254, 270-273, 280, 299, 302, 306, 309, 318- 319, 330-331, 333, 345, 359, 361 and 375-376, the control value of 90 % or more was shown.
[0602]
Test Example 4
The test spray solutions were prepared by diluting the
formulations of each of Present Compounds 1, 3-7, 12, 14, 21, 33-38, 46, 55, 68, 69, 83, 84, 88-90, 102, 112-113, 116-118, 128, 130-133, 136-139, 142-143, 152, 156-158, 161, 169-171, 174-176, 183-186, 188, 201, 209-210, 214-215, 238, 246, 248, 251, 262, 292, 298-299, 301-302, 306, 308-309, 314, 324-325, 327, 343, 353, 360, 374 and 376 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration.
On the other hand, a rice seedling (the second leaf stage) planted in a polyethylene cup was sprayed with 10 ml of each of the above test spray solutions. After air-drying, 20 third-fourth instar larvae of Nilaparvata lugens were released, and kept in the greenhouse of 25 °C . After 6 days, the number of insect of living Nilaparvata lugens parasitized on the rice was examined, and a control value was calculated according to the following equation:
Control value (%) = {1 - (Cb x Tai)/(Cai x Tb) ) x 100 wherein symbols represent as follows:
Cb: the number of insects in a non-treated section before treatment,
Cai: the number of insects in a non-treated section in observation,
Tb : the number of insects in a treated-section before treatment,
Tai: the number of insects in a treated-section in observation;
wherein the non-treated section represents a section where the test spray solution prepared by diluting the formulation without the present compound in Formulation Example 5 with the same amount of water as in the treated- section was sprayed.
As a result, in the treated-section of the test spray solution of each of Present Compounds 1, 3-7, 12, 14, 21, 33-38, 46, 55, 68, 69, 83, 84, 88-90, 102, 112-113, 116-118, 128, 130-133, 136-139, 142-143, 152, 156-158, 161, 169-171, 174-176, 183-186, 188, 201, 209-210, 214-215, 238, 246, 248, 251, 262, 292, 298-299, 301-302, 306, 308-309, 314, 324-325, 327, 343, 353, 360, 374 and 376, the control value of 90 % or more was shown.
[0603]
Test Example 5
The test diluted solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds 4-6, 33-36, 38, 55, 89, 90, 112-113, 117-118, 123, 130, 132, 137-138, 143, 156-158, 169-171, 174-176, 185, 214, 248, 251, 272, 292, 294, 297-299, 301-302, 306, 324, 327, 343, 345, 353, 357, 359-361 amd 374-376 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient
concentration .
On the other hand, a rice seedling (2 weeks after sowing, the second leaf stage) planted in a plastic cup was drenched at its foot with 5 ml of each of the diluted solutions, and kept in a greenhouse of 25 °C for 7 days. Twenty third-fourth instar larvae of Nilaparvata lugens were released, and further kept in the greenhouse for 6 days, then the number of insect of living Nilaparvata lugens parasitized on the rice was examined, and a control value was calculated according to the following equation:
Control value (%) = {1 - (Cb x Tai)/(Cai x Tb) ) x 100 wherein symbols represent as follows:
Cb: the number of insects in a non-treated section before treatment,
Cai : the number of insects in a non-treated section in observation,
Tb: the number of insects in a treated-section before treatment,
Tai : the number of insects in a treated-section in observation;
wherein the non-treated section represents a section where the test diluted solution prepared by diluting the formulation without the present compound in Formulation Example 5 with the same amount of water as in the treated-
section was used.
As a result, in the treated-section of the test diluted solution of each of Present Compounds 4-6, 33-36, 38, 55, 89, 90, 112-113, 117-118, 123, 130, 132, 137-138, 143, 156-158, 169-171, 174-176, 185, 214, 248, 251, 272, 292, 294, 297-299, 301-302, 306, 324, 327, 343, 345, 353, 357, 359-361 and 374-376, the control value of 90 % or more was shown.
[0604]
Test Example 6
The test spray solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds 4-6, 21, 22, 49, 50, 55, 75, 88, 112-113, 116-118, 128-132, 161, 169-171, 174-176, 188, 209-210, 214-215, 238-240, 247-248, 255, 259, 262, 270-273, 280, 291-292, 296-299, 301-302, 306-311, 317, 319, 331, 333, 343, 345, 357, 360, 374 and 376 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration.
On the other hand, Bemisia tabaci adult was released on a tomato seedling (the third true leaf stage) planted in a polyethylene cup, and made to lay eggs for about 72 hours. The tomato seedling was kept in a greenhouse for 8 days. When instar larvae hatched from the eggs, the above test spray solution was sprayed in the amount of 20 ml/cup. The
cup was kept in a greenhouse at 25 °C . After the keeping for 7 days, the number of surviving instar larvae on the tomato leaves was examined, and a control value was calculated according to the following equation:
Control value (%) = {1 - (Cb x Tai)/(Cai x Tb) ) x 100 wherein symbols represent as follows:
Cb: the number of insects in a non-treated section before treatment,
Cai: the number of insects in a non-treated section in observation,
Tb: the number of insects in a treated-section before treatment,
Tai : the number of insects in a treated-section in observation;
wherein the non-treated section represents a section where the test spray solution prepared by diluting the formulation without the present compound in Formulation Example 5 with the same amount of water as in the treated- section was sprayed.
As a result, in the treated-section of the test spray solution of each of Present Compounds 4-6, 21, 22, 49, 50, 55, 75, 88, 112-113, 116-118, 128-132, 161, 169-171, 174- 176, 188, 209-210, 214-215, 238-240, 247-248, 255, 259, 262,
270-273, 280, 291-292, 296-299, 301-302, 306-311, 317, 319, 331, 333, 343, 345, 357, 360, 374 and 376, the control value of 90 % or more was shown.
[0605]
Test Example 7
The test spray solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds 1-14, 16-23, 25, 28-36, 42-47, 49, 50, 53-55, 59, 64, 66, 68-76, 80, 81-83, 85-90, 97-98, 100, 116-118, 123, 133-142, 144, 151-154, 156-160, 169-171, 174-176, 181, 183-188, 190-191, 193-194, 197-198, 201-203, 209-210, 214-215, 230, 238-243, 246-248, 262-264,278-281, 285-287, 292, 294, 299-303, 306-307, 311, 313-316, 318-319, 327, 330-333, 335, 341-343, 345, 348-349, 353, 358, 360, 365, 369-371 and 374-378 obtained in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration.
On the other hand, Cabbage (the third leaf stage) planted in a polyethylene cup was sprayed with 20 mL/cup of each of the test spray solution. After the test solution was dried, the aerial part was cut off, and then placed in a 50 mL volume cup. Five second instar larvae of Plutella xylostella were released into the cup, and the cup was sealed with a lid. After the cup was kept at 25 °C for 5 days, the number of living insects was counted. A death rate was calculated according to the following equation:
Death rate (%) = (Number of dead insects/Number of tested insects) x 100 As a result, in the treated-section of the test spray solution of each of Present Compounds 1-14, 16-23, 25, 28- 36, 42-47, 49, 50, 53-55, 59, 64, 66, 68-76, 80-83, 85-90, 97-98, 100, 116-118, 123, 133-142, 144, 151-154, 156-160, 169-171, 174-176, 181, 183-188, 190-191, 193-194, 197-198, 201-203, 209-210, 214-215, 230, 238-243, 246-248, 262-264, 278-281, 285-287, 292, 294, 299-303, 306-307, 311, 313-316, 318-319, 327, 330-333, 335, 341-343, 345, 348-349, 353, 358, 360, 365, 369-371 and 374-378, the death rate of 80 % or more was shown.
[0606]
Test Example 8
The test spray solutions were prepared by diluting the formulations of each of Present Compounds2-9 , 11, 13, 14, 17-20, 22, 23, 28, 29, 31, 35-37, 43-47,54-55, 68-83, 86-90, 106, 112-113, 117-118, 128-129, 131-138, 140-142, 157-158, 161, 164, 169-171, 174-176, 183-185, 187-188, 191, 194, 201-203, 209-210, 214-215, 230, 238-240, 242-243, 246-248, 251, 262-263, 270-275, 278-281, 285-287, 290, 292, 294, 296-302, 305-316, 318-319, 324-325, 327, 329-333, 335, 341- 343, 345, 349, 355-357, 360, 369-371 and 374-378 obtained
in Formulation Example 5 with water so as to give 500 ppm of an active ingredient concentration.
On the other hand, an apple tree was planted in a plastic cup, and grown until the seventh-eighth leaf was spread. The apple tree was sprayed with 20 mL/cup of each of the test spray solution. After the test solution was dried, 60 first-instar Adoxophyes orana fasciata were released, and the cup was covered with a plastic cup upside-down which the bottom was cut off and a filter paper was put thereon. After 7 days, the number of living insects was counted, and a death rate was calculated according to the following equation:
Death rate (%) = (Number of dead insects/Number of tested insects) x 100
As a result, in the treated-section of the test spray solution of each of Present Compounds 2-9, 11, 13, 14, 17- 20, 22, 23, 28, 29, 31, 35-37, 43-47, 54-55, 68-83, 86-90, 106, 112-113, 117-118, 128-129, 131-138, 140-142, 157-158, 161, 164, 169-171, 174-176, 183-185, 187-188, 191, 194, 201-203, 209-210, 214-215, 230, 238-240, 242-243, 246-248, 251, 262-263, 270-275, 278-281, 285-287, 290, 292, 294, 296-302, 305-316, 318-319, 324-325, 327, 329-333, 335, 341- 343, 345, 349, 355-357, 360, 369-371 and 374-378, the death
rate of 90 % or more was shown.
Industrial Applicability
[0607]
The present compound has an activity of controlling pests and is useful as an active ingredient of a pest controlling agent.