WO2011039823A1 - Plant diagnostic equipment - Google Patents
Plant diagnostic equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011039823A1 WO2011039823A1 PCT/JP2009/005123 JP2009005123W WO2011039823A1 WO 2011039823 A1 WO2011039823 A1 WO 2011039823A1 JP 2009005123 W JP2009005123 W JP 2009005123W WO 2011039823 A1 WO2011039823 A1 WO 2011039823A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- plant
- database
- category
- data
- data item
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G05—CONTROLLING; REGULATING
- G05B—CONTROL OR REGULATING SYSTEMS IN GENERAL; FUNCTIONAL ELEMENTS OF SUCH SYSTEMS; MONITORING OR TESTING ARRANGEMENTS FOR SUCH SYSTEMS OR ELEMENTS
- G05B23/00—Testing or monitoring of control systems or parts thereof
- G05B23/02—Electric testing or monitoring
- G05B23/0205—Electric testing or monitoring by means of a monitoring system capable of detecting and responding to faults
- G05B23/0218—Electric testing or monitoring by means of a monitoring system capable of detecting and responding to faults characterised by the fault detection method dealing with either existing or incipient faults
- G05B23/0221—Preprocessing measurements, e.g. data collection rate adjustment; Standardization of measurements; Time series or signal analysis, e.g. frequency analysis or wavelets; Trustworthiness of measurements; Indexes therefor; Measurements using easily measured parameters to estimate parameters difficult to measure; Virtual sensor creation; De-noising; Sensor fusion; Unconventional preprocessing inherently present in specific fault detection methods like PCA-based methods
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a plant diagnostic apparatus for detecting a plant abnormality.
- the plant diagnostic device detects the occurrence of an abnormality or accident based on the measurement data from the plant when an abnormal transient or accident occurs in the plant.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a diagnostic apparatus using adaptive resonance theory (ART).
- ART has a function of classifying multidimensional data into categories according to their similarity.
- measurement data at normal time is classified into a plurality of categories using ART.
- current measurement data is classified into categories by ART, and when this category is different from a plurality of categories generated at normal time, an abnormality is diagnosed.
- an object of the present invention is to provide a plant diagnostic apparatus that can appropriately select data items to be used for diagnosis in advance and can further suppress the occurrence of an alarm in a normal state. is there.
- the diagnostic device of the present invention has the following features.
- the plant diagnostic device includes a measurement signal database for storing plant measurement signals, an operation history database for storing operation signals when the operator performs operations using the external input device, and an operator when an abnormality occurs in the plant.
- Learning means for extracting data items to be used for plant diagnosis from display information displayed on the image display device by an operation performed using the external input device.
- the learning means of the plant diagnosis device is a method for weighting display information displayed on the screen from the display time of the display screen displayed on the image display device when a plant abnormality occurs, and data used for plant diagnosis. You may provide the process data item determination part which extracts an item.
- the plant diagnosis device may display the extracted data item on the image display device and may be used for determination to add to the monitoring item of the plant diagnosis.
- the plant diagnosis apparatus includes a control logic database that stores plant control logic and a design information database that stores design information, and the storage information of these databases may be displayed as display information on the image display device. .
- a measurement signal database that stores plant measurement signals
- a processing data extraction unit that extracts a diagnostic signal used to diagnose the state of the plant from the measurement signal database, and a diagnosis extracted by the processing data extraction unit
- a reference signal database for storing signals
- a classification means for classifying data stored in the reference signal database into categories
- a classification result database for storing results classified by the classification means, and the latest data extracted by the processing data extraction means
- the diagnostic signal does not belong to the category stored in the classification result database
- a diagnostic means for generating and classifying a new category
- a diagnostic result database for storing the classification result of the diagnostic means, a diagnostic result database, and a classification result Using category information stored in the database
- a plant diagnosis device equipped with an alarm generating means for generating an alarm when the frequency of generation of a new category within a certain period exceeds a certain value (threshold)
- an external input signal from an external input device consisting of a mouse and a keyboard is received.
- a learning means having an operation
- a measurement signal database for storing the measurement signal of the plant, a processing data extraction means for extracting a reference signal used for diagnosing the state of the plant from the measurement signal database, and a reference extracted by the processing data extraction means
- a reference signal database for storing signals, a classification means for classifying data stored in the reference signal database into categories, a classification result database for storing results classified by the classification means, and the latest data extracted by the processing data extraction means
- the diagnostic signal does not belong to the category stored in the classification result database
- a diagnostic unit that generates and classifies a new category
- a diagnostic result database that stores the classification result of the diagnostic unit, the diagnostic result database, and the classification Correct category attributes stored in results database
- the category attribute database that defines whether the category attribute is stored and the category attribute database and the information stored in the diagnosis result database, the classification result database, and the category attribute database, the category of the abnormal attribute is generated within a certain period of time.
- An operation history database for storing an external input signal from an external input device composed of a mouse and a keyboard, and an operation history in a plant diagnostic apparatus having an alarm generation means for generating an alarm when the frequency exceeds a certain value (threshold)
- a processing data item determining unit that determines a data item to be extracted by the processing data extracting unit
- a category attribute determining unit that determines whether the category attribute is normal or abnormal based on operation history information stored in the database
- the plant diagnosis apparatus also includes a control logic database in which control logic information for controlling the plant is stored, and a design information database in which plant design information is stored.
- the learning means stores the control logic database in the control logic database. The control logic information that is stored and the design information stored in the design information database may be processed together.
- the plant diagnostic apparatus has an image display device that displays information stored in a database in the diagnostic device, and the operation history database displays at least the time when the operation was performed and the image display device. The screen relationship should be saved.
- the plant diagnosis apparatus calculates the importance of the data item based on at least the data item related to the screen displayed on the image display device and the period during which the screen is displayed in the processing data item determination unit. It is preferable that the processing data extraction unit extracts the data item having a high importance extracted by the processing data item determination unit from the measurement signal database.
- the plant diagnosis apparatus calculates the importance of the data item based on at least the data item related to the screen displayed on the image display device and the period during which the screen is displayed in the processing data item determination unit. It has a function to extract high data items, displays the data items of high importance extracted by the processing data item determination means on the image display device, and adds and deletes data items by operation from the external input device Then, the data item may be determined, and the processing data extraction unit may extract data of the data item determined by the operation from the external input device from the measurement signal database.
- the category attribute determination unit holds the data of the ratio of the period during which the screen is displayed for each category, and determines the attribute of the category based on the similarity of the data of the ratio of the displayed period. It is preferable that the alarm generating means has a function of changing from abnormal to normal, and the alarm generation means generates an alarm when the generation ratio of the category having the abnormality attribute exceeds a certain value.
- the category attribute determination unit holds data for the ratio of the period for which the screen was displayed for each category, and abnormal category attributes based on the similarity of the data for the ratio of the displayed period It is preferable to have a function of changing normally from the above and a function of correcting the attribute of the category displayed on the image display device based on the external input signal input from the external input device.
- Data items used for diagnosis can be set appropriately in advance, improving diagnosis performance. In addition, unnecessary alarms can be suppressed.
- FIG. It is a block diagram which shows the diagnostic apparatus of this invention. It is a flowchart figure explaining the basic operation
- FIG. It is a figure explaining an example of the classification result in FIG. It is a figure explaining the aspect of the data preserve
- FIG. 6 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the learning means 800. It is a figure which shows the example of the screen which the operator of the plant 100 displays on the image display apparatus 950. It is a figure which shows time and a screen display timing as an aspect of the data preserve
- FIG. It is a figure which shows the operation result of the process data item determination part 810.
- FIG. It is a figure which shows the example of the data item addition screen displayed on the image display apparatus 950 by step S1220. It is a figure explaining the classification
- FIG. It is a figure explaining the example of the data aspect preserve
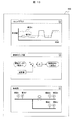
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a plant diagnostic apparatus according to the present invention, in which a plant 100 is diagnosed by a plant diagnostic apparatus 200.
- the diagnostic device 200 includes processing data extraction means 400, classification means 500, diagnostic means 600, alarm generation means 700, and learning means 800 as arithmetic devices.
- the diagnostic apparatus 200 includes a measurement signal database 310, a reference signal database 320, a classification result database 330, a diagnosis result database 340, an operation history database 350, a control logic database 360, a design information database 370, and a category attribute database 380 as databases. I have.
- an operation history database 350 is provided in order to “appropriately set data items used for diagnosis in advance”.
- the actions of the operator when the abnormality occurs (various operations using the keyboard 910 and the mouse 920 performed toward the image display device 950) reflect the long-time knowledge of the operator. ing. Accordingly, the operation history at this time is stored in the operation history database 350 and analyzed to obtain a data item used for diagnosis.
- the diagnostic apparatus 200 includes an external input interface 210 and an external output interface 220 as interfaces with the outside.
- the diagnostic device 200 is created by operating the measurement signal 1 from the plant 100 and measuring the various state quantities of the plant through the external input interface 210 and operating the external input device 900 including the keyboard 910 and the mouse 920.
- the external input signal 2 to be input is input.
- the image display data 14 is output from the diagnostic apparatus 200 to the image display apparatus 950 via the external output interface 220.
- the measurement signal 3 input via the external input interface 210 is stored in the measurement signal database 310.
- the processing data extraction unit 400 extracts the diagnostic signal 6 used for diagnosis from the measurement signal 5 stored in the measurement signal database 310 and stores it in the reference signal database 320.
- the classification unit 500 classifies the reference signal 7 into categories.
- the classification result 8 is stored in the classification result database 330.
- the processing content of the classification means 500 will be described later with reference to FIG.
- diagnosis unit 600 when the latest diagnosis signal 6 extracted by the processing data extraction unit 400 belongs to the classification result database 330, the diagnosis signal 6 is classified into the category. On the other hand, if the latest diagnostic signal 6 extracted by the processing data extraction unit 400 does not belong to the category stored in the classification result database 330, a new category is generated and the diagnostic signal 6 is classified.
- the diagnosis result 10 that is the classification result created by the diagnosis unit 600 is stored in the diagnosis result database 340. The processing contents of the diagnosis unit 600 will be described later with reference to FIG.
- the category attribute database 380 stores category attributes stored in the classification result database 330 and the diagnosis result database 340.
- the category attributes are normal and abnormal.
- the category attributes stored in the classification result database 330 are normal.
- the initial attribute of the new category generated by the diagnosis unit 600 is abnormal.
- the attributes of these categories can be modified using the learning means 800. This correction method in the learning means 800 will be described later with reference to FIG.
- the diagnosis result 11 stored in the diagnosis result database 340, the classification result 12 stored in the classification result database 330, the category attribute information 25 stored in the category attribute database 380, and the measurement signal database Whether or not to generate an alarm is determined using the latest measurement signal 4 stored in 310.
- the alarm generation means 700 has a criterion for generating the following three types of alarms, and determines whether to generate an alarm by arbitrarily combining them. (For example, an alarm is generated when both condition 1 and condition 2 are satisfied, an alarm is generated when either condition 1 or condition 2 is satisfied, etc.)
- Condition 1 The measurement signal 4 at the latest time deviates from a predetermined range (threshold value).
- Condition 2 The frequency of generating a new category within a certain period exceeds a certain value (threshold value).
- Condition 3 The frequency of generation of abnormal attribute categories within a certain period exceeds a certain value (threshold).
- the alarm generation unit 700 transmits the alarm signal 13 to the external output interface 220.
- the alarm signal 13 is converted into image display information 14 by the external output interface 220 and displayed on the image display device 950.
- the external input signal 20 is stored in the operation history database 350.
- the learning unit 800 includes a processing data item determination unit 810 and a category attribute determination unit 820.
- the learning means 800 includes two of the processing data item determination unit 810 and the category attribute determination unit 820. However, only one of them may be included.
- the processing data item determination unit 810 determines a data item to be extracted by the processing data extraction unit 400 using at least information stored in the operation history database 350.
- the processing data item information 24 is transmitted to the processing data extraction unit 400.
- the category attribute determination unit 820 determines the category attribute as normal or abnormal using at least information stored in the operation history database 350.
- the category attribute information 30 is stored in the category attribute database 380.
- the processing data item determination unit 810 and the category attribute determination unit 820 include a control logic database 360 in which the control logic of the plant 100 is stored as needed, and a design information database in which design information of the plant 100 is stored. Information of the classification result database 330 and the diagnosis result database 340 can also be used.
- the diagnostic device information 50 stored in the measurement signal database 310, the reference signal database 320, the classification result database 330, the diagnosis result database 340, the operation history database 350, the control logic database 360, and the design information database 370 is an image display device. 950 can be displayed. These pieces of information can be corrected using the external input device 900 as necessary.
- the operation history database 350, the control logic database 360, the design information database 370, and the category attribute database 380 are all inside the diagnostic apparatus 200, but some of them are arranged outside the diagnostic apparatus 200 so that only the data is communicated. It may be.
- the diagnostic apparatus 200 there is one plant to be diagnosed, but a plurality of plants can be diagnosed by the diagnostic apparatus 200.
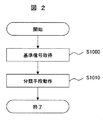
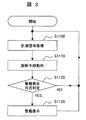
- FIG. 2 and 3 are flowcharts for explaining the basic operation of the diagnostic apparatus 200.
- FIG. The diagnostic apparatus 200 has two basic operations: a normal state learning mode for classifying normal data into categories based on information stored in the reference signal database 320, and a diagnostic mode for diagnosing the state of the plant 100.
- the normal state learning mode and the diagnostic mode are operated independently for each measurement signal sampling period or each period preset by the operator.
- 2 is a flowchart for explaining the operation in the normal state learning mode
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart for explaining the operation in the diagnosis mode.
- steps S1000 and S1010 are executed in combination as shown in FIG.
- the processing data extraction unit 400 is operated to extract the diagnostic signal 6 from the measurement signal 5 in the measurement signal database 310.
- the diagnostic signal 6 is stored in the reference signal database 320.
- the data stored in the reference signal database 320 is data for a period during which the operator determines that the operation state of the plant is normal.
- step S1010 the classification means 500 is operated to classify the reference signal 7 stored in the reference signal database 320, and the classification result 8 is stored in the classification result database 330.
- steps S1100, S1110, S1120, and S1130 are executed in combination as shown in FIG.
- step S1000 the measurement signal 1 from the plant 100 is taken into the diagnostic device 200 via the external input interface 210, and the measurement signal 3 is stored in the measurement signal database 310.
- the processing data extraction unit 400 is operated, the measurement signal 5 is extracted from the measurement signal database 310, and the diagnostic signal 6 with the latest time is transmitted to the diagnostic unit 600.
- step S1010 the diagnosis unit 600 is operated and the diagnosis result 10 is transmitted to the diagnosis result database 340.
- step S1020 the alarm generation means 700 is operated to determine whether an alarm can be generated. If it is determined in step S1020 that an alarm can be generated, the process proceeds to step S1030. If the alarm is not generated, the process returns to step S1000.
- step S1030 the alarm signal 13 output from the alarm generation means 700 is converted into the image display information 14 by the external output interface 220 and output to the image display device 950. This notifies the plant operator of an alarm.
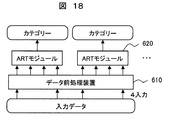
- FIG. 4 is a block diagram for explaining an embodiment of the classification means 500 and the diagnosis means 600.
- ART adaptive resonance theory
- other clustering methods such as vector quantization
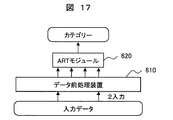
- the classification unit 500 and the diagnosis unit 600 respectively execute a flowchart composed of the data preprocessing device 610 and the ART module 620 shown in FIG.
- the data preprocessing device 610 converts the operation data into input data for the ART module 620. The steps will be described below.
- the normalization method will be described by taking the plant process quantity xi as an example.
- the number of data of xi is N and the nth measurement value is xi (n). Further, if the maximum value and the minimum value in the N pieces of data are Max_i and Min_i, respectively, normalized data Nxi (n) is obtained by Expression (1).
- Nxi (n) ⁇ + (1 ⁇ ) ⁇ (xi (n) ⁇ Min_i) / (Max_i ⁇ Min_i) (1)
- it is a constant of ⁇ (0 ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ 0.5)
- the data is normalized to the range of [ ⁇ , 1 ⁇ ] by the equation (1).
- the complement of the normalized data is calculated and added to the input data.
- CNxi (n) 1 ⁇ Nxi (n) (2)
- data consisting of data Nxi (n) and CNxi (n) is input to the ART module 620 as input data.
- the above is the input data conversion processing of the operation data to the ART module 620 in the data preprocessing device 610.
- the ART module 620 classifies input data into a plurality of categories.
- the ART module 620 includes an F0 layer 621, an F1 layer 622, an F2 layer 623, a memory 624, and a selection subsystem 625, which are coupled to each other.
- the F1 layer 622 and the F2 layer 623 are coupled via a weighting factor, and the weighting factor represents a prototype (prototype) of a category into which input data is classified.
- Process 1 The input vector is normalized by the F0 layer 621, and noise is removed.
- a suitable category candidate is selected by comparing the input data input to the F1 layer 622 with a weighting factor.
- Process 3 The validity of the category selected by the selection subsystem 625 is evaluated by the ratio with the parameter ⁇ . If it is determined to be valid, the input data is classified into the category, and the process proceeds to process 4. If it is not judged to be valid, the category is reset, and an appropriate category candidate is selected from the other categories (the process 2 is repeated). Increasing the value of parameter ⁇ makes the category classification finer, and decreasing ⁇ makes the classification coarser. This parameter ⁇ is referred to as a vigilance parameter.
- Process 4 When all existing categories are reset in Process 2, it is determined as a new category, and a new weighting factor representing a prototype of the new category is generated.
- the characteristic of the data classification algorithm of the ART module 620 is the process 4.
- the stored pattern is not changed and a new pattern can be stored. For this reason, it is possible to store a new pattern while storing patterns learned in the past.
- the ART module 620 learns the given pattern. Therefore, when new input data is input to the learned ART module 620, it is possible to determine which pattern is near by the above algorithm. If the pattern has never been experienced before, it is classified into a new category.
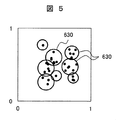
- FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining an example of the classification result.
- two items of measurement data are displayed and represented by a two-dimensional graph.
- the measurement data is divided into a plurality of categories 630 (circles in FIG. 5) by the ART module 620.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining a mode of data stored in the measurement signal database 310, the reference signal database 320, and the classification result database 330. 6 may be considered as a display screen when displayed on the image display device 950 of FIG. Therefore, for example, in the measurement signal database 310 of FIG. 6, a wider range of data can be scroll-displayed by the scroll 301 on the vertical and horizontal screens. Further, by selecting the reference tab 302 in the reference signal database 320, only items classified into the reference can be displayed together. The data stored in the diagnosis result database 340 and the classification result database 330 are the same. Further, the data of these databases are processed into various forms as shown in FIG. 6 and further shown in FIGS. 13, 14, 15, 16, and 20 to be converted into display information. Is displayed.
- the upper part of FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining the mode of data stored in the measurement signal database 310.
- values of a plurality of data items (items A, B, C, etc.) measured by the plant 100 are stored for each sampling period (vertical time). .
- the middle part of FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining the mode of data stored in the reference signal database 320.
- the processing data extraction unit 400 in FIG. 1 extracts a data group used for diagnosis of the plant 100 from the measurement signal database 310 in the upper part of FIG.
- a data group used for diagnosis of the plant 100 from the measurement signal database 310 in the upper part of FIG.
- the measurement values of all the data items are stored in time series as one data group, whereas the reference signal database 320 is selected according to the reference and limited. Measurement values of data items are stored in a time series as a plurality of data groups.
- the lower part of FIG. 6 is a diagram for explaining the mode of data stored in the classification result database 330.
- the classification result database 330 stores the time, the relationship between the category numbers in which the data at that time is classified (lower left in FIG. 6), and the relationship between the category number and the weighting factor (lower right in FIG. 6).
- the classification result database 330 stores the classification results for each data group stored in the reference signal database 320.
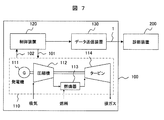
- FIG. 7 shows a thermal power plant as a plant to which the present invention is applied.
- the thermal power plant 100 includes a gas turbine generator 110, a control device 120, and a data transmission device 130.
- the gas turbine generator 110 includes a generator 111, a compressor 112, a combustor 113, and a turbine 114.
- the compressed air generated by the compressor 112 is sent to the combustor 113, mixed with fuel, and burned by the combustor 113.
- the turbine 114 is rotated by the high-pressure gas generated by the combustion, and the generator 111 generates power.
- the control device 120 controls the output of the gas turbine generator 110 according to the power demand. Further, the control device 110 inputs operation data 102 measured by a sensor (not shown) installed in the gas turbine generator 110.
- the operation data 102 is a state quantity such as an intake air temperature, a fuel input amount, a turbine exhaust gas temperature, a turbine rotational speed, a generator power generation amount, a turbine shaft vibration, and the like, and is measured every sampling period. It also measures weather information such as atmospheric temperature.
- the control device 120 calculates a control signal 101 for controlling the gas turbine generator 110 using these operation data 102.
- the signal data transmission device 130 transmits the measurement signal 1 including the operation data 102 measured by the control device 120 and the control signal 101 calculated by the control device 120 to the diagnosis device 200.
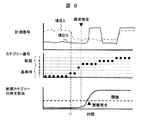
- FIG. 8 shows an example when the measurement signal obtained from the plant of FIG. As shown in FIG. 8, for example, a generator output as item A and an atmospheric temperature measurement signal as item B are input to the diagnostic unit 600 in the diagnostic apparatus 200.
- the initial items A and B are stable at a substantially constant value, but then the item A decreases at time t1, then decreases after the item B increases, and finally both items increase. It is assumed that it has changed.
- the measurement signal 4 belongs to any one of the category numbers 1 to 4 in the time zone before the occurrence of the abnormality in FIG. It belongs to a category (new categories 5, 6, and 7) that is not sometimes present.
- the occurrence rate of new categories calculated by the moving average of the number of new categories occurring in a certain period increases after the occurrence of an abnormality.
- the alarm generation means 700 generates an alarm when the new category generation ratio exceeds a preset threshold value.
- the alarm can be notified to the operator.
- the categories before the occurrence of the abnormality are classified into the categories at the reference time, no alarm is generated in the normal state in this example.
- the example shown in FIG. 9 is that no alarm is generated at the time of abnormality
- the example shown in FIG. 10 is that the alarm is generated at the time of abnormality
- the normal state shown in FIG. There are cases where alarms sometimes occur.
- the learning apparatus 800 is mounted in the diagnostic apparatus 200 of the present invention in order to prevent an alarm from being generated when an abnormality occurs and an alarm from occurring when the apparatus is normal. The operation of the learning unit 800 will be described later with reference to FIG.
- FIG. 9 shows the results when the data of items A and B are diagnosed
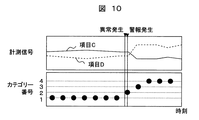
- FIG. 10 shows the results when the data of items C and D input at the same time as in FIG. 9 are diagnosed.
- FIG. 9 shows the results when the data of items A and B are diagnosed
- FIG. 10 shows the results when the data of items C and D input at the same time as in FIG. 9 are diagnosed.
- the measured values of both item A and item B do not change even after an abnormality occurs. Therefore, even if the diagnostic value is classified by the diagnostic unit 600, the categories classified before and after the occurrence of the abnormality are the same. In this case, the alarm generation means 700 does not generate an alarm.
- FIG. 10 shows the result of diagnosing the measured values of item C and item D in the same time zone as FIG.
- the measured values of item C and item D have changed greatly after the occurrence of abnormality, a new category (category numbers 2 to 4) is generated, and an alarm is also generated.
- the processing data item determination unit 810 in the learning unit 800 of the present invention has a function of selecting data items to be used for diagnosis from data items stored in the measurement signal database 310.
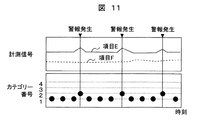
- FIG. 11 is a diagram for explaining a case where an alarm is generated in a normal state.
- the normal category number is 1 and the plant state is normal.
- the data of the item E changed slightly, and as a result of classifying the measurement values by the diagnostic unit 600, a new category (category number 2) was generated. As a result, an alarm is generated even in a normal state.
- the category attribute determination unit 820 of the present invention has a function of normally distinguishing category attributes from abnormalities.
- the operation content of the learning unit 800 including the processing data item determination unit 810 and the category attribute determination unit 820 will be described.
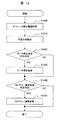
- FIG. 12 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the learning means 800. As shown in FIG. 12, this flowchart is executed by combining steps S1200, S1210, S1220, S1230, S1240, and S1250.
- the operation history database 350 in FIG. 1 includes the result of the operation of the plant 100 operator using the external input device 900 (for example, information on the screen displayed on the image display device 950, control parameter Adjustments, etc.) are saved.
- step S1200 the learning unit 800 acquires the operation history information 21 from the operation history database 350.
- step S1210 the processing data item determination unit 810 and the category attribute determination unit 820 of FIG.
- the processing data item determination unit 810 determines a data item to be extracted by the processing data extraction unit 400.
- the category attribute determining unit 820 determines the category attribute.
- step S1220 the data item determined by the processing data item determination unit 810 is displayed on the image display device 950.
- the operator of the plant 100 checks the displayed data item and decides whether to add the data item. When adding a data item, it progresses to step S1230 and adds the data item extracted by the process data extraction means 400. FIG. If no data item is added, the process advances to step S1240.
- step S1240 the category attribute determined by the category attribute determining unit 820 is displayed on the image display device 950.
- the operator of the plant 100 checks the displayed category attribute and decides whether to change the category attribute stored in the category attribute database 380. If the category attribute is to be changed, the process proceeds to step S1240, and the category attribute is changed. If the category attribute is not changed, the process ends.
- steps S1220 and S1240 the operator is inquired whether the data item can be added and whether the category attribute can be changed. However, this is omitted, and the data item is automatically added and the category attribute is changed. May be executed. Also, any one of steps S1220 and S1230 or steps S1240 and S1250 may be excluded from this flowchart, and only one of the processing data item determination unit 810 and the category attribute determination unit 820 may be operated.
- FIG. 13 shows an example of a screen displayed by the operator of the plant 100 on the image display device 950
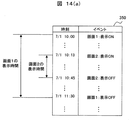
- FIG. 14 shows the mode of data stored in the operation history database 350
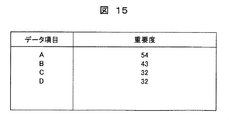
- FIG. 15 shows the operation of the processing data item determination unit 810
- step S1220 shows an example of a data item addition screen displayed on the image display device 950.
- FIG. 17 to FIG. 19 show changes in the classification means 500 and the diagnosis means 600 when a data item is added in step S1230.
- An example of data stored in 830 and an example of a category attribute correction screen displayed on the image display device in step S1240 will be described with reference to FIG.
- FIG. 13 is an example of a screen displayed on the image display device 950 by the operator of the plant 100.
- the upper part of FIG. 13 shows display information on the image display device 950 using information stored in the measurement signal database 310 of FIG. It is an example of a screen when being displayed as.
- the measurement signal database 310 stores the relationship between the time and the measurement value of the data item as described in the upper part of FIG. In this example, this information is displayed as a trend graph with the horizontal axis as the time axis as shown in the upper items A and B of FIG. From this screen, the change with time of each measurement signal can be visually confirmed.
- FIG. 13 is an example of a screen when information stored in the control logic database 360 of FIG. 1 is displayed as display information on the image display device 950.
- the control logic database 360 stores a logic diagram for calculating the control signal 101 from the operation data 102 in the control device 120 of FIG.
- the middle part of FIG. 13 shows an example of a logic diagram of proportional / integral control widely used for plant control.
- the item C is taken as the operation data 1, and the relationship between the operation data and the control signal can be visually confirmed as the control signal 1 (item D) obtained by proportional-integral calculation of the error from the set value.
- the lower part of FIG. 13 is an example of a screen when information stored in the design information database 370 of FIG. 1 is displayed as display information on the image display device 950.
- the design information database 370 stores design information of the gas turbine generator 110 shown in FIG. 7. For example, a system diagram showing a relationship between a fluid path and a sensor arrangement position (T: temperature sensor, P: pressure sensor). Is saved.
- the information shown in FIG. 13 is displayed on the image display device 950 of FIG. 1, and the operation state of the plant 100 is constantly monitored.
- the operator specifies the cause of the abnormality, and furthermore, in order to converge and stabilize the abnormality, a trend graph, a control logic diagram, a system diagram, etc. that are considered to be related to the abnormality are displayed on the keyboard 910 and mouse 920. The user should have made an appropriate selection using and displayed the response.
- the operation of the image display device 950 by the operator at this time should be based on the knowledge under the operator's consciousness. If it is an abnormal state that is being developed in front of you, you should have been checking the relationship with other process quantities that the operator is interested in based on experience. It is highly likely that these items include “data items used for diagnosis” that are not yet clearly recognized.
- the processing data item determination unit 810 determines data items related to the abnormality based on information displayed on the image display device 950 by the operator. Further, the operation history database 350 stores information on the screen displayed on the image display device 950 by the operator at the time of normality and abnormality. The category attribute determination unit determines whether the category attribute is normal or abnormal based on this information.
- FIG. 14 is a diagram for explaining a mode of data stored in the operation history database 350.
- the operation history database 350 of FIG. 1 stores the time and screen display timing (display ON) and erased timing (display OFF) information in association with each other. Yes.
- the screen 1 was displayed from 10:00 on July 1 to 11:30 on the same day.
- Screen 2 was displayed from 10:13 to 10:45 on the same day.
- the display time and the data item information related to the displayed screen are stored for each screen.
- the display time can be obtained by subtracting the display ON time from the display OFF time.
- a and B were displayed as related data items for 1 hour and 30 minutes.
- C and D were displayed for 32 minutes as related data items.
- the related data items are data items displayed on the drawing shown in FIG.
- the related data items displayed on the screen 950 in FIG. 13 are items A and B in the trend graph on the upper screen
- the data items related to the control logic in the middle in FIG. 13 are items C and D
- the data items related to the figure are items E, F, G, H, I, and J.
- the timing at which the screen is displayed and the timing at which the screen is deleted are stored in the operation history database 350.
- the number of times the mouse is clicked, the number of times the set value is confirmed, etc. All information related to operations using 900 may be stored.
- an ID may be assigned to each operator, and the operation contents for each operator may be stored in the operation history database 350.
- FIG. 15 is a diagram for explaining the operation result of the processing data item determination unit 810.
- the processing data item determination unit calculates the importance of the data item for a certain period using the information stored in the operation history database 350.
- the importance of the data item is calculated by the following equation (4), for example.
- S ⁇ ⁇ T (4)
- S is the importance of the data item
- ⁇ is the weighting factor
- T is the display time of the screen related to the data item.
- S ⁇ ⁇ T + ⁇ ⁇ C (5)
- ⁇ is a weighting factor
- C is the number of times the mouse is clicked on the screen related to the data item.
- the data item determination unit 810 determines that “a data item having a high importance is an effective data item for detecting the occurrence of an abnormality”, and extracts a certain number (for example, 10) of data items in descending order of importance. To do.
- FIG. 16 is a diagram for explaining an example of the data item addition screen displayed on the image display device 950 in step S1220.
- the data items extracted by the processing data item determination unit 810 are displayed in descending order of importance, and it is confirmed to the operator whether to add to the data used for diagnosis.
- zone Z1 on screen 950 a message indicating that the report is related to a pump abnormality at 0:00 on July 1, 2009 is displayed in zone Z1 on screen 950, and the purpose of “in order to detect an abnormality similar to the above abnormality” is described in zone 2. It is recommended to add the following data item. " In zone 3, the data item is displayed together with its name, and the importance of the data item calculated by the processing data item determination unit 810 is also described. The operator confirms the check mark in the check box 1223 and clicks the “Add” button 1221 when adding the data while viewing the displayed data, and clicks the “Cancel” button 1222 when not adding the data.
- the data item extracted by the processing data item determination unit 810 can be deleted, and the data item can be added.
- the data item can be added.
- an arbitrary data item stored in the measurement signal database 310 can be added by clicking a button 1224.
- the lower part of FIG. 16 is a screen for manually setting all data items used for diagnosis without using the processing data item determination unit 810.
- the number of data items measured from the plant 100 varies depending on the scale of the plant, but there are thousands of data items for a large-scale plant. From these data items, it takes a lot of time to select the data items used for diagnosis one by one.
- the processing data item determination unit 810 of the present invention it is possible to shorten the time for selecting a data item to be used for diagnosis.
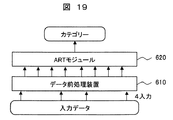
- FIG. 17 to 19 are diagrams for explaining changes in the classification means 500 and the diagnosis means 600 when a data item is added in step S1230 of FIG.
- FIG. 17 is a diagram for explaining the classification unit 500 and the diagnosis unit 600 before the data item is added.
- the number of input data is two.
- changes in the classification unit 500 and the diagnosis unit 600 when two data items are added in step S1230 and the number of input data becomes four will be described.
- one ART module is added, and two input data added to this ART module are input to create a category.
- the data item input to one ART module is changed from 2 to 4.
- a method of adding an ART module to add data items used for diagnosis or a method of adding data items to be used for diagnosis by increasing the number of data items input to one ART module. Is used.
- FIG. 20 is a diagram for explaining the mode of data stored in the category attribute database 830 and an example of the category attribute correction screen displayed on the image display device in step S1240.
- the category attribute database 830 stores the relationship between the category number (1 to 6), the category attribute (normal, abnormal), and the screen display time ratio (%) together with the data items A, B, and C. Has been.
- the category attribute determination unit 820 has a function of changing a category having an abnormal category attribute to a normal category based on the information on the screen display time ratio.
- the category attribute determination unit 820 calculates the similarity between the normal category and the abnormal category using the following equation (6). If the similarity is less than or equal to the threshold, the category attribute is corrected from abnormal to normal.
- SI (TA1-TA2) 2 + (TB1-TB2) 2 + (TC1-TC2) 2 (6)
- SI is the similarity
- TA1 is the display time of screen 1 when a normal category is occurring
- TA2 is the display time of screen 1 when an abnormal category is occurring
- TB1 is a normal category is occurring
- TB2 is the display time of screen 2 when an abnormal category is occurring
- TC1 is the display time of screen 3 when a normal category is occurring
- TC2 is an abnormal category It is the display time of the screen 3 when
- the operation state of the plant may be normal.
- the operator does not determine that there is an abnormality even if an alarm is generated, so the screen displayed on the image display device 950 is the same as when the category attribute is normal. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of unnecessary alarms by correcting the category attributes normally from abnormalities.
- step S1240 is a diagram for explaining an example of the category attribute correction screen displayed on the image display device in step S1240.
- the desired item “Add the following category to the normal category? Are you sure?” Is displayed on this screen, and the category number at this time is displayed together with the measurement signal in FIG.
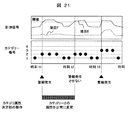
- FIG. 21 is a diagram for explaining an example of operation as a result of correcting the category attribute.
- a new category (category number 2) occurred and an alarm occurred.
- the category attribute determination unit 820 was operated, and the attribute of category number 2 was changed normally.
- no alarm is generated at time t2.
- the alarm generation means 700 has a function of generating an alarm when the measured value exceeds a threshold in addition to the function of generating an alarm based on the category information.
- a function for generating an alarm when a measured value exceeds a threshold value and a function for generating an alarm based on category information can be linked so that no alarm is generated at time t2.
- the learning unit 800 of the present invention automatically performs selection of data items used for diagnosis and determination of conditions for generating an alarm based on the operation history information of the operator. Thereby, it becomes possible to improve diagnostic accuracy and exclude unnecessary alarms.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Testing And Monitoring For Control Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
条件1:最新の時刻の計測信号4が、定められた範囲(閾値)を逸脱する。
条件2:ある一定期間内における新規カテゴリーの生成頻度が、一定値(閾値)を超える。
条件3:ある一定期間内における異常属性のカテゴリーの生成頻度が、一定値(閾値)を超える。 The alarm generation means 700 has a criterion for generating the following three types of alarms, and determines whether to generate an alarm by arbitrarily combining them. (For example, an alarm is generated when both
Condition 1: The
Condition 2: The frequency of generating a new category within a certain period exceeds a certain value (threshold value).
Condition 3: The frequency of generation of abnormal attribute categories within a certain period exceeds a certain value (threshold).
Nxi(n)=α+(1-α)×(xi(n)-Min_i)/(Max_i-Min_i) …(1)
ここで、α(0≦α<0.5)の定数であり、(1)式によりデータは[α、1-α]の範囲に正規化される。次に、正規化したデータの補数を計算し、入力データに加える。 The normalization method will be described by taking the plant process quantity xi as an example. The number of data of xi is N and the nth measurement value is xi (n). Further, if the maximum value and the minimum value in the N pieces of data are Max_i and Min_i, respectively, normalized data Nxi (n) is obtained by Expression (1).
Nxi (n) = α + (1−α) × (xi (n) −Min_i) / (Max_i−Min_i) (1)
Here, it is a constant of α (0 ≦ α <0.5), and the data is normalized to the range of [α, 1−α] by the equation (1). Next, the complement of the normalized data is calculated and added to the input data.
CNxi(n)=1-Nxi(n) …(2)
次に、データNxi(n)及びCNxi(n)からなるデータを入力データとしてARTモジュール620に入力する。以上が、データ前処理装置610における運転データのARTモジュール620への入力データ変換処理である。 The complement CNxi (n) of the normalized data Nxi (n) is calculated by equation (2).
CNxi (n) = 1−Nxi (n) (2)
Next, data consisting of data Nxi (n) and CNxi (n) is input to the
WJ(new)=Kw・p+(1-Kw)・WJ(old) …(3)
ここで、Kwは学習率パラメータであり、入力ベクトルを新しい重み係数に反映させる度合いを決定する。 Process 5: When the input data is classified into the category J, the weighting factor WJ (new) corresponding to the category J is derived from the past weighting factor WJ (old) and the input data p (or data derived from the input data) ( 3) Update with equation.
WJ (new) = Kw.p + (1-Kw) .WJ (old) (3)
Here, Kw is a learning rate parameter and determines the degree to which the input vector is reflected in the new weighting factor.
S = α×T …(4)
ここで、Sはデータ項目の重要度、αは重み係数、Tはデータ項目に関係する画面の表示時間である。また、次の(5)式を用いてデータ項目の重要度を計算してもよい。
S = α×T+β×C …(5)
ここで、βは重み係数、Cはデータ項目に関係する画面でマウスがクリックされた回数である。 The importance of the data item is calculated by the following equation (4), for example.
S = α × T (4)
Here, S is the importance of the data item, α is the weighting factor, and T is the display time of the screen related to the data item. Moreover, you may calculate the importance of a data item using following (5) Formula.
S = α × T + β × C (5)
Here, β is a weighting factor, and C is the number of times the mouse is clicked on the screen related to the data item.
SI=(TA1-TA2)2+(TB1-TB2)2+(TC1-TC2)2 …(6)
ここで、SIは類似度、TA1は正常カテゴリーが発生している時における画面1の表示時間、TA2は異常カテゴリーが発生している時における画面1の表示時間、TB1は正常カテゴリーが発生している時における画面2の表示時間、TB2は異常カテゴリーが発生している時における画面2の表示時間、TC1は正常カテゴリーが発生している時における画面3の表示時間、TC2は異常カテゴリーが発生している時における画面3の表示時間である。 As described above, the initial attribute of the new category generated when the
SI = (TA1-TA2) 2 + (TB1-TB2) 2 + (TC1-TC2) 2 (6)
Here, SI is the similarity, TA1 is the display time of
以上述べたように、本発明の学習手段800は、オペレータの操作履歴情報に基づいて、診断に使用するデータ項目の選定、及び警報発生の条件決定を自動的に実施する。これにより、診断精度の向上、及び不要な警報を除外することが可能となる。 The alarm generation means 700 has a function of generating an alarm when the measured value exceeds a threshold in addition to the function of generating an alarm based on the category information. A function for generating an alarm when a measured value exceeds a threshold value and a function for generating an alarm based on category information can be linked so that no alarm is generated at time t2.
As described above, the
200 診断装置
210 外部入力インターフェイス
220 外部出力インターフェイス
310 計測信号データベース
320 基準信号データベース
330 分類結果データベース
340 診断結果データベース
350 操作履歴データベース
360 制御ロジックデータベース
370 設計情報データベース
380 カテゴリー属性データベース
400 処理データ抽出手段
500 分類手段
600 診断手段
700 警報発生手段
800 学習手段
810 処理データ項目決定部
820 カテゴリー属性決定部
900 外部入力装置
910 キーボード
920 マウス
950 画像表示装置 100
Claims (12)
- プラントの計測信号と、オペレータが外部入力装置を用いて操作を行なったときの操作信号とを入力し、画像表示装置にプラントの状態を表示情報として表示するプラント診断装置において、
プラント診断装置は、前記プラントの計測信号を保存する計測信号データベースと、
オペレータが前記外部入力装置を用いて操作を行なったときの操作信号を記憶する操作履歴データベースと、
前記プラントの異常発生時に、オペレータが前記外部入力装置を用いて行なった操作により前記画像表示装置に表示された表示情報の中から、プラントの診断に使用するデータ項目を抽出する学習手段と、
を有することを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic device for inputting a plant measurement signal and an operation signal when the operator performs an operation using an external input device, and displaying the state of the plant as display information on the image display device,
The plant diagnostic apparatus includes a measurement signal database that stores measurement signals of the plant, and
An operation history database for storing operation signals when an operator performs an operation using the external input device;
Learning means for extracting data items used for diagnosis of the plant from display information displayed on the image display device by an operation performed by the operator using the external input device when the plant abnormality occurs,
A plant diagnostic apparatus comprising: - 第1項記載のプラント診断装置において、
前記学習手段は、前記プラントの異常発生時に、前記画像表示装置に表示された表示画面の表示時間から、当該画面に表示されている表示情報の重み付けを行ないプラントの診断に使用するデータ項目を抽出する処理データ項目決定部を備えることを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to item 1,
The learning means weights display information displayed on the screen and extracts data items used for diagnosis of the plant from the display time of the display screen displayed on the image display device when an abnormality occurs in the plant. A plant diagnostic apparatus comprising a processing data item determining unit for performing the processing. - 第1項あるいは第2項記載のプラント診断装置において、
前記抽出されたデータ項目を前記画像表示装置に表示し、プラント診断の監視項目に追加することの判別に供することを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to item 1 or 2,
A plant diagnostic apparatus characterized in that the extracted data item is displayed on the image display device and used for determination to be added to a monitoring item for plant diagnosis. - 第1項乃至第3項のいずれかに記載のプラント診断装置において、
プラント診断装置は、前記プラントの制御ロジックを保存する制御ロジックデータベースと、設計情報を保存する設計情報データベースを備えており、これらのデータベースの保存情報が前記画像表示装置に表示情報として表示されることを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to any one of Items 1 to 3,
The plant diagnosis apparatus includes a control logic database that stores the control logic of the plant and a design information database that stores design information, and the storage information of these databases is displayed as display information on the image display apparatus. A plant diagnostic apparatus characterized by - プラントの計測信号を保存する計測信号データベースと、
該計測信号データベースからプラントの状態を診断するのに使用する診断信号を抽出する処理データ抽出手段と、該処理データ抽出手段で抽出した診断信号を保存する基準信号データベースと、該基準信号データベースに保存されているデータをカテゴリーに分類する分類手段と、該分類手段で分類した結果を保存する分類結果データベースと、前記処理データ抽出手段で抽出した最新の診断信号が、前記分類結果データベースに保存されているカテゴリーに属さない場合に新しいカテゴリーを発生させて分類する診断手段と、該診断手段での分類結果を保存する診断結果データベースと、該診断結果データベースと前記分類結果データベースに保存されているカテゴリーの情報を用いて、ある一定期間内における新規カテゴリーの生成頻度が、一定値(閾値)を超えた時に警報を発生させる警報発生手段を備えたプラント診断装置において、
マウス、キーボードから成る外部入力装置からの外部入力信号を保存する操作履歴データベースと、該操作履歴データベースに保存されている操作履歴情報に基づいて、前記処理データ抽出手段で抽出するデータ項目を決定する処理データ項目決定部を有する学習手段を備えたことを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 A measurement signal database for storing plant measurement signals;
Processing data extracting means for extracting a diagnostic signal used for diagnosing the state of the plant from the measurement signal database, a reference signal database for storing the diagnostic signal extracted by the processing data extracting means, and saving in the reference signal database A classification means for classifying the collected data into categories, a classification result database for storing results classified by the classification means, and the latest diagnostic signal extracted by the processing data extraction means are stored in the classification result database. A diagnostic means for generating and classifying a new category when it does not belong to a category, a diagnostic result database for storing a classification result in the diagnostic means, a category of the categories stored in the diagnostic result database and the classification result database Use information to generate new categories within a certain period , In the plant diagnosis system including an alarm generating means for generating an alarm when it exceeds a certain value (threshold value),
Based on an operation history database for storing an external input signal from an external input device such as a mouse and a keyboard, and an operation history information stored in the operation history database, a data item to be extracted by the processing data extraction unit is determined. A plant diagnosis apparatus comprising learning means having a processing data item determination unit. - プラントの計測信号を保存する計測信号データベースと、該計測信号データベースからプラントの状態を診断するのに使用する基準信号を抽出する処理データ抽出手段と、該処理データ抽出手段で抽出した基準信号を保存する基準信号データベースと、該基準信号データベースに保存されているデータをカテゴリーに分類する分類手段と、該分類手段で分類した結果を保存する分類結果データベースと、前記処理データ抽出手段で抽出した最新の診断信号が、前記分類結果データベースに保存されているカテゴリーに属さない場合に新しいカテゴリーを発生させて分類する診断手段と、該診断手段での分類結果を保存する診断結果データベースと、該診断結果データベースと前記分類結果データベースに保存されているカテゴリーの属性を正常か異常かに定義し、前記カテゴリーの属性を保存するカテゴリー属性データベースと、前記診断結果データベース、前記分類結果データベース、前記カテゴリー属性データベースに保存されている情報を用いて、ある一定期間内における異常属性のカテゴリーの生成頻度が、一定値(閾値)を超えた時に警報を発生させる警報発生手段を備えたプラント診断装置において、
マウス、キーボードから成る外部入力装置からの外部入力信号を保存する操作履歴データベースと、該操作履歴データベースに保存されている操作履歴情報に基づいて、前記処理データ抽出手段で抽出するデータ項目を決定する処理データ項目決定部と、カテゴリーの属性を正常か異常に決定するカテゴリー属性決定部の少なくとも1つの決定部を有する学習手段を備えたことを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 A measurement signal database for storing plant measurement signals, a processing data extraction means for extracting a reference signal used for diagnosing the state of the plant from the measurement signal database, and a reference signal extracted by the processing data extraction means A reference signal database, a classification means for classifying data stored in the reference signal database into categories, a classification result database for storing results classified by the classification means, and the latest extracted by the processing data extraction means A diagnostic means for generating and classifying a new category when a diagnostic signal does not belong to a category stored in the classification result database, a diagnostic result database for storing a classification result in the diagnostic means, and the diagnostic result database And the category attributes stored in the classification result database A category attribute database that defines whether the category attribute is stored and the category attribute database that stores the attribute of the category, and information stored in the diagnosis result database, the classification result database, and the category attribute database. In the plant diagnostic apparatus provided with an alarm generating means for generating an alarm when the generation frequency of the category exceeds a certain value (threshold),
Based on an operation history database for storing an external input signal from an external input device such as a mouse and a keyboard, and an operation history information stored in the operation history database, a data item to be extracted by the processing data extraction unit is determined. A plant diagnostic apparatus comprising: a learning means having a processing data item determining unit and at least one determining unit of a category attribute determining unit that determines whether a category attribute is normal or abnormal. - 請求項5あるいは請求項6に記載されたプラント診断装置において、
前記プラントを制御するための制御ロジック情報が保存されている制御ロジックデータベースと、前記プラントの設計情報が保存されている設計情報データベースを備え、前記学習手段では前記制御ロジックデータベースに保存されている制御ロジック情報と、前記設計情報データベースに保存されている設計情報も合わせて処理することを特徴とするプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to claim 5 or 6,
A control logic database in which control logic information for controlling the plant is stored; and a design information database in which design information of the plant is stored. The learning unit performs control stored in the control logic database. A plant diagnosis apparatus characterized in that logic information and design information stored in the design information database are also processed. - 請求項5あるいは請求項6に記載されたプラント診断装置において、
前記診断装置内のデータベースに保存されている情報を表示する画像表示装置を有し、前記操作履歴データベースには、少なくとも操作を実施した時刻と、前記画像表示装置に表示されている画面の関係が保存されていることを特徴としたプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to claim 5 or 6,
An image display device that displays information stored in a database in the diagnostic device, and the operation history database includes a relationship between at least an operation time and a screen displayed on the image display device; Plant diagnostic equipment characterized by being stored. - 請求項7に記載されたプラント診断装置において、
前記処理データ項目決定部では、少なくとも前記画像表示装置に表示された画面に関係するデータ項目と画面が表示されていた期間に基づいて、データ項目の重要度を計算し、重要度が高いデータ項目を抽出する機能を有し、前記処理データ抽出手段では、処理データ項目決定手段で抽出した重要度が高いデータ項目のデータを計測信号データベースから抽出することを特徴としたプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to claim 7,
The processing data item determination unit calculates the importance of the data item based on at least the data item related to the screen displayed on the image display device and the period during which the screen is displayed, and the data item having a high importance A plant diagnostic apparatus characterized in that the processing data extraction means extracts data items of data items with high importance extracted by the processing data item determination means from the measurement signal database. - 請求項7に記載されたプラント診断装置において、
前記処理データ項目決定部では、少なくとも前記画像表示装置に表示された画面に関係するデータ項目と画面が表示されていた期間に基づいて、データ項目の重要度を計算し、重要度が高いデータ項目を抽出する機能を有し、前記処理データ項目決定手段で抽出した重要度が高いデータ項目のデータを画像表示装置上に表示し、前記外部入力装置からの操作でデータ項目を追加、削除してデータ項目を決定し、前記処理データ抽出手段では、前記外部入力装置からの操作で決定したデータ項目のデータを計測信号データベースから抽出することを特徴としたプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to claim 7,
The processing data item determination unit calculates the importance of the data item based on at least the data item related to the screen displayed on the image display device and the period during which the screen is displayed, and the data item having a high importance The data item data having a high degree of importance extracted by the processing data item determining means is displayed on the image display device, and the data item is added or deleted by an operation from the external input device. A plant diagnosis apparatus characterized in that a data item is determined, and the processing data extraction means extracts data item data determined by an operation from the external input device from a measurement signal database. - 請求項7に記載されたプラント診断装置において、
前記カテゴリー属性決定部では、カテゴリー毎に画面が表示されていた期間の割合のデータを保持し、表示されていた期間の割合のデータの類似性に基づいて、カテゴリーの属性を異常から正常に変更する機能を有し、前記警報発生手段では異常の属性を持つカテゴリーの発生割合が一定値を超えた時に警報を発生させることを特徴としたプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to claim 7,
The category attribute determination unit holds data for the ratio of the period for which the screen was displayed for each category, and changed the category attribute from abnormal to normal based on the similarity of the data for the ratio of the displayed period A plant diagnostic apparatus characterized in that the alarm generating means generates an alarm when an occurrence ratio of a category having an abnormal attribute exceeds a certain value. - 請求項7に記載されたプラント診断装置において、
前記カテゴリー属性決定部ではカテゴリー毎に画面が表示されていた期間の割合のデータを保持し、表示されていた期間の割合のデータの類似性に基づいて、カテゴリーの属性を異常から正常に変更する機能と、画像表示装置上に表示されたカテゴリーの属性を前記外部入力装置からの入力された外部入力信号に基づいて修正する機能を持つことを特徴としたプラント診断装置。 In the plant diagnostic apparatus according to claim 7,
The category attribute determination unit holds data of the ratio of the period during which the screen was displayed for each category, and changes the attribute of the category from abnormal to normal based on the similarity of the data of the ratio of the displayed period A plant diagnostic apparatus having a function and a function of correcting an attribute of a category displayed on an image display device based on an external input signal input from the external input device.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200980161696.3A CN102576227B (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2009-10-02 | Plant diagnostic equipment |
| PCT/JP2009/005123 WO2011039823A1 (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2009-10-02 | Plant diagnostic equipment |
| JP2011533967A JP5199478B2 (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2009-10-02 | Plant diagnostic equipment |
| IN2779DEN2012 IN2012DN02779A (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2009-10-02 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/005123 WO2011039823A1 (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2009-10-02 | Plant diagnostic equipment |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011039823A1 true WO2011039823A1 (en) | 2011-04-07 |
Family
ID=43825680
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/005123 WO2011039823A1 (en) | 2009-10-02 | 2009-10-02 | Plant diagnostic equipment |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5199478B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN102576227B (en) |
| IN (1) | IN2012DN02779A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2011039823A1 (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103454515A (en) * | 2012-05-31 | 2013-12-18 | Ge医疗系统环球技术有限公司 | Imaging self-diagnosing system and method |
| JP2017117034A (en) * | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-29 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Diagnosis device and diagnostic method |
| WO2018003192A1 (en) * | 2016-06-29 | 2018-01-04 | 株式会社日立製作所 | System and method for assisting in establishing operation and maintenance knowledge information |
| CN109597366A (en) * | 2017-10-02 | 2019-04-09 | 费希尔-罗斯蒙特系统公司 | System and method for the multi-site performance monitoring to Process Control System |
| CN110023862A (en) * | 2016-12-28 | 2019-07-16 | 三菱日立电力系统株式会社 | Diagnostic device, diagnostic method and program |
| JP2019121257A (en) * | 2018-01-10 | 2019-07-22 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Monitor control assistance device |
| JP2019153018A (en) * | 2018-03-01 | 2019-09-12 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Diagnostic device and diagnostic method |
| WO2020027207A1 (en) * | 2018-08-03 | 2020-02-06 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Abnormality detecting method, information processing device, and abnormality detecting system |
| US20200210144A1 (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-07-02 | Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems, Ltd. | Data sorting device and method, and monitoring and diagnosis device |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6078019B2 (en) * | 2014-04-02 | 2017-02-08 | 三菱電機ビルテクノサービス株式会社 | Equipment monitoring apparatus and program |
| JP6620056B2 (en) * | 2016-03-31 | 2019-12-11 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Device abnormality diagnosis method and device abnormality diagnosis device |
| JP2018106432A (en) * | 2016-12-27 | 2018-07-05 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Online monitoring apparatus and online monitoring method |
| CN110785717B (en) * | 2017-06-19 | 2022-12-09 | 杰富意钢铁株式会社 | Abnormal state diagnostic device and abnormal state diagnostic method for process |
| US11433539B2 (en) | 2018-07-31 | 2022-09-06 | Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. | Abnormality determination device and abnormality determination method |
| CN109885951A (en) * | 2019-02-28 | 2019-06-14 | 中科云创(厦门)科技有限公司 | Equipment fault diagnosis method and device |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004206583A (en) * | 2002-12-26 | 2004-07-22 | Nisshin Flour Milling Inc | Learning type abnormality notification device and its method |
| JP2005258649A (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2005-09-22 | Hitachi Ltd | Data sorting method and device |
| JP2007123007A (en) * | 2005-10-27 | 2007-05-17 | Hitachi Ltd | Method and equipment for diagnosing fuel cell system |
| JP2009042997A (en) * | 2007-08-08 | 2009-02-26 | Hitachi Ltd | Data sorting method and apparatus |
-
2009
- 2009-10-02 IN IN2779DEN2012 patent/IN2012DN02779A/en unknown
- 2009-10-02 WO PCT/JP2009/005123 patent/WO2011039823A1/en active Application Filing
- 2009-10-02 CN CN200980161696.3A patent/CN102576227B/en active Active
- 2009-10-02 JP JP2011533967A patent/JP5199478B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004206583A (en) * | 2002-12-26 | 2004-07-22 | Nisshin Flour Milling Inc | Learning type abnormality notification device and its method |
| JP2005258649A (en) * | 2004-03-10 | 2005-09-22 | Hitachi Ltd | Data sorting method and device |
| JP2007123007A (en) * | 2005-10-27 | 2007-05-17 | Hitachi Ltd | Method and equipment for diagnosing fuel cell system |
| JP2009042997A (en) * | 2007-08-08 | 2009-02-26 | Hitachi Ltd | Data sorting method and apparatus |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103454515A (en) * | 2012-05-31 | 2013-12-18 | Ge医疗系统环球技术有限公司 | Imaging self-diagnosing system and method |
| JP2017117034A (en) * | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-29 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Diagnosis device and diagnostic method |
| WO2018003192A1 (en) * | 2016-06-29 | 2018-01-04 | 株式会社日立製作所 | System and method for assisting in establishing operation and maintenance knowledge information |
| JP2018005392A (en) * | 2016-06-29 | 2018-01-11 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Formulation support system and formulation support method for operation maintenance knowledge information |
| CN110023862A (en) * | 2016-12-28 | 2019-07-16 | 三菱日立电力系统株式会社 | Diagnostic device, diagnostic method and program |
| CN110023862B (en) * | 2016-12-28 | 2022-01-14 | 三菱动力株式会社 | Diagnostic device, diagnostic method, and computer-readable recording medium |
| JP2019091425A (en) * | 2017-10-02 | 2019-06-13 | フィッシャー−ローズマウント システムズ,インコーポレイテッド | System and method for multi-site performance monitoring of process control system |
| CN109597366A (en) * | 2017-10-02 | 2019-04-09 | 费希尔-罗斯蒙特系统公司 | System and method for the multi-site performance monitoring to Process Control System |
| JP7287740B2 (en) | 2017-10-02 | 2023-06-06 | フィッシャー-ローズマウント システムズ,インコーポレイテッド | System and method for multi-site performance monitoring of process control systems |
| JP2019121257A (en) * | 2018-01-10 | 2019-07-22 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Monitor control assistance device |
| JP2019153018A (en) * | 2018-03-01 | 2019-09-12 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Diagnostic device and diagnostic method |
| JP7180985B2 (en) | 2018-03-01 | 2022-11-30 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Diagnostic device and diagnostic method |
| WO2020027207A1 (en) * | 2018-08-03 | 2020-02-06 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Abnormality detecting method, information processing device, and abnormality detecting system |
| US20200210144A1 (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2020-07-02 | Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems, Ltd. | Data sorting device and method, and monitoring and diagnosis device |
| US11886831B2 (en) * | 2018-12-27 | 2024-01-30 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | Data sorting device and method, and monitoring and diagnosis device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5199478B2 (en) | 2013-05-15 |
| JPWO2011039823A1 (en) | 2013-02-21 |
| CN102576227B (en) | 2014-06-25 |
| CN102576227A (en) | 2012-07-11 |
| IN2012DN02779A (en) | 2015-09-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5199478B2 (en) | Plant diagnostic equipment | |
| JP5544418B2 (en) | Plant diagnostic device, diagnostic method, and diagnostic program | |
| JP5292477B2 (en) | Diagnostic device and diagnostic method | |
| JP5097739B2 (en) | Plant abnormality diagnosis apparatus and abnormality diagnosis method | |
| CN102999038B (en) | The diagnostic device of generating set and the diagnostic method of generating set | |
| EP3191797B1 (en) | Gas turbine sensor failure detection utilizing a sparse coding methodology | |
| JP5129725B2 (en) | Device abnormality diagnosis method and system | |
| US6408259B1 (en) | Alert generation for trend performance analysis | |
| CN104756029B (en) | A kind of system of the parts group of monitoring device | |
| US8250017B2 (en) | System and method for prediction of gas turbine trips due to gas control valve failures | |
| JP5150590B2 (en) | Abnormality diagnosis apparatus and abnormality diagnosis method | |
| WO2012073289A1 (en) | Plant diagnostic device and plant diagnostic method | |
| US20110178963A1 (en) | system for the detection of rare data situations in processes | |
| US20190130294A1 (en) | System fault isolation and ambiguity resolution | |
| CN107710089B (en) | Plant equipment diagnosis device and plant equipment diagnosis method | |
| JP7469991B2 (en) | Diagnosis device and parameter adjustment method | |
| JP4430384B2 (en) | Equipment diagnostic apparatus and diagnostic method | |
| JPWO2018051568A1 (en) | Plant abnormality diagnosis device and plant abnormality diagnosis system | |
| JP6830414B2 (en) | Diagnostic device and diagnostic method | |
| CN109308484A (en) | Aero-engine multiclass failure minimum risk diagnostic method and device | |
| JP6685124B2 (en) | Diagnostic device and diagnostic method | |
| King et al. | Probabilistic approach to the condition monitoring of aerospace engines | |
| CN117009791B (en) | Method and system for identifying faults of aeroengine | |
| WO2023156074A1 (en) | Enhanced performance model matching, augmentation and prediction |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980161696.3 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09850014 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2011533967 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2779/DELNP/2012 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 09850014 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |