WO2005087007A1 - Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide - Google Patents
Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2005087007A1 WO2005087007A1 PCT/US2005/008029 US2005008029W WO2005087007A1 WO 2005087007 A1 WO2005087007 A1 WO 2005087007A1 US 2005008029 W US2005008029 W US 2005008029W WO 2005087007 A1 WO2005087007 A1 WO 2005087007A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- carbon atoms
- composition
- glyphosate
- hydrocarbyl
- linear
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 CC1*=CC*1 Chemical compound CC1*=CC*1 0.000 description 3
- JAPMJSVZDUYFKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1C2C1CCC2 Chemical compound C1C2C1CCC2 JAPMJSVZDUYFKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GDOPTJXRTPNYNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1CCCC1 Chemical compound CC1CCCC1 GDOPTJXRTPNYNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FZYAWKAFHZVPGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCCCC(C)C1CC(C)CC1 Chemical compound CCCCC(C)C1CC(C)CC1 FZYAWKAFHZVPGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N57/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds
- A01N57/18—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds having phosphorus-to-carbon bonds
- A01N57/20—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic phosphorus compounds having phosphorus-to-carbon bonds containing acyclic or cycloaliphatic radicals
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N25/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests
- A01N25/30—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators, characterised by their forms, or by their non-active ingredients or by their methods of application, e.g. seed treatment or sequential application; Substances for reducing the noxious effect of the active ingredients to organisms other than pests characterised by the surfactants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N37/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids
- A01N37/36—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and a singly bound oxygen or sulfur atom attached to the same carbon skeleton, this oxygen or sulfur atom not being a member of a carboxylic group or of a thio analogue, or of a derivative thereof, e.g. hydroxy-carboxylic acids
- A01N37/38—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and a singly bound oxygen or sulfur atom attached to the same carbon skeleton, this oxygen or sulfur atom not being a member of a carboxylic group or of a thio analogue, or of a derivative thereof, e.g. hydroxy-carboxylic acids having at least one oxygen or sulfur atom attached to an aromatic ring system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N37/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids
- A01N37/36—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and a singly bound oxygen or sulfur atom attached to the same carbon skeleton, this oxygen or sulfur atom not being a member of a carboxylic group or of a thio analogue, or of a derivative thereof, e.g. hydroxy-carboxylic acids
- A01N37/38—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and a singly bound oxygen or sulfur atom attached to the same carbon skeleton, this oxygen or sulfur atom not being a member of a carboxylic group or of a thio analogue, or of a derivative thereof, e.g. hydroxy-carboxylic acids having at least one oxygen or sulfur atom attached to an aromatic ring system
- A01N37/40—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing organic compounds containing a carbon atom having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most two bonds to halogen, e.g. carboxylic acids containing at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and a singly bound oxygen or sulfur atom attached to the same carbon skeleton, this oxygen or sulfur atom not being a member of a carboxylic group or of a thio analogue, or of a derivative thereof, e.g. hydroxy-carboxylic acids having at least one oxygen or sulfur atom attached to an aromatic ring system having at least one carboxylic group or a thio analogue, or a derivative thereof, and one oxygen or sulfur atom attached to the same aromatic ring system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01N—PRESERVATION OF BODIES OF HUMANS OR ANIMALS OR PLANTS OR PARTS THEREOF; BIOCIDES, e.g. AS DISINFECTANTS, AS PESTICIDES OR AS HERBICIDES; PEST REPELLANTS OR ATTRACTANTS; PLANT GROWTH REGULATORS
- A01N39/00—Biocides, pest repellants or attractants, or plant growth regulators containing aryloxy- or arylthio-aliphatic or cycloaliphatic compounds, containing the group or, e.g. phenoxyethylamine, phenylthio-acetonitrile, phenoxyacetone
- A01N39/02—Aryloxy-carboxylic acids; Derivatives thereof
- A01N39/04—Aryloxy-acetic acids; Derivatives thereof
Definitions
- the present invention relates generally to herbicidal compositions or formulations, and to methods of using such compositions to kill or control the growth and proliferation of unwanted plants.
- the present invention relates to herbicidal compositions, as well as their methods of use, which comprise N-phosphonomethylglycine (glyphosate), or a herbicidal derivative thereof, and an auxin herbicide, or a herbicidal derivative thereof, optionally with one or more suitable surfactants.
- Such compositions cause early visual symptoms of treatment and/or enhanced effectiveness or control when applied to the foliage of plants.
- Glyphosate is well known in the art as an effective post-emergent foliar-applied herbicide. In its acid form, glyphosate has a structure represented by the formula:
- Glyphosate potassium salt has a molecular weight of 207.
- This salt is disclosed, for example, by Franz in U.S. Patent No. 4,405,531 , as one of the "alkali metal" salts of glyphosate useful as herbicides, with potassium being specifically disclosed as one of the alkali metals, along with lithium, sodium, cesium and rubidium.
- Example C discloses the preparation of the monopotassium salt by reacting the specified amounts of glyphosate acid and potassium carbonate in an aqueous medium.
- Herbicidal compositions comprising the herbicide N-phosphonomethyl-glycine or derivatives thereof ("glyphosate"), are useful for suppressing the growth of, or killing, unwanted plants such as grasses, weeds and the like.
- Glyphosate typically is applied to the foliage of the target plant. After application the glyphosate is absorbed by the foliar tissue of the plant and translocated throughout the plant. Glyphosate noncompetitively blocks an important biochemical pathway which is common to virtually all plants, but which is absent in animals.
- glyphosate is very effective in killing or controlling the growth of unwanted plants, the uptake (i.e., absorption) of glyphosate by the plant foliar tissue and translocation of glyphosate throughout the plant is relatively slow. Visual symptoms that a plant has been treated with glyphosate may not appear until one week or more after treatment.
- compositions which exhibit long-term control of unwanted plants and exhibit early visual symptoms of treatment. These compositions would be well suited to applications in cooler temperatures wherein the early visual symptoms may be readily seen while the long-term control would improve as temperatures increase.
- the present invention provides herbicidal compositions comprising glyphosate or a herbicidal derivative thereof, an auxin herbicide or a herbicidal derivative thereof, and at least one surfactant.
- the present invention also provides methods for killing or controlling the growth of plants by contacting the foliage of the plants with the diluted concentrate composition.
- One embodiment of the present invention is directed to an aqueous herbicidal concentrate composition
- glyphosate or a herbicidal derivative thereof an auxin comprising one or more auxin herbicides selected from the group consisting of 2,4-D, 2,4-DB, dichlorprop, MCPA, MCPB, mecoprop, dicamba, picloram, quniclorac and agriculturally acceptable salts or esters thereof and a surfactant component in solution or stable suspension, emulsion or dispersion, comprising one or more surfactants.
- the glyphosate (acid equivalent basis) and the auxin herbicide (acid equivalent basis) are present in a weight ratio of at least 32:1 and the composition has a cloud point of at least about 50°C and a crystallization point not higher than about 0°C.
- Another embodiment of the present invention is directed to an aqueous herbicidal concentrate composition
- glyphosate predominantly in the form of the potassium salt thereof in a concentration of at least 65 grams acid equivalent per liter
- an auxin herbicide comprising one or more auxin herbicides selected from the group consisting of 2,4-D, 2,4-DB, dichlorprop, MCPA, MCPB, mecoprop, dicamba, picloram, quniclorac and agriculturally acceptable salts or esters thereof.
- the herbicidal concentrate composition further comprises a first surfactant component in solution or stable suspension, emulsion or dispersion comprising one or more surfactants selected from the group consisting of secondary or tertiary amines, dialkoxylated quaternary ammonium salts, monoalkoxylated quaternary ammonium salts, quaternary ammonium salts, ether amines, amine oxides, dialkoxylated amines, aminated alkoxylated alcohols, alkyl alkoxylated phosphates and alkylpolyglycosides.
- a first surfactant component in solution or stable suspension, emulsion or dispersion comprising one or more surfactants selected from the group consisting of secondary or tertiary amines, dialkoxylated quaternary ammonium salts, monoalkoxylated quaternary ammonium salts, quaternary ammonium salts, ether amines, amine oxides, dial
- Yet another embodiment of the present invention is directed to an aqueous herbicidal concentrate composition
- glyphosate predominantly in the form of the isopropylammonium salt thereof in a concentration of greater than 360 grams acid equivalent per liter
- an auxin herbicide component comprising one or more auxin herbicides selected from the group consisting of 2,4-D, 2,4-DB, dichlorprop, MCPA, MCPB, mecoprop, dicamba, picloram, quniclorac and agriculturally acceptable salts or esters thereof
- a surfactant component in solution or stable suspension, emulsion or dispersion, comprising one or more surfactants.
- the glyphosate (acid equivalent basis) and the auxin herbicide component (acid equivalent basis) are present in a weight ratio of at least 9.5:1 and the composition has a cloud point of at least about 50°C and a crystallization point not higher than about 0°C.
- Another embodiment of the present invention is directed to a method of killing or controlling weeds or unwanted plants comprising diluting an aqueous herbicidal concentrate composition in an amount of water to form an application mixture and applying a herbicidally effective amount of the application mixture to foliage of the weeds or unwanted plants, wherein the weeds or unwanted plants comprise Commelina and the aqueous herbicidal concentrate composition comprises glyphosate or a herbicidal derivative thereof, an auxin herbicide component comprising one or more auxin herbicides selected from the group consisting of 2,4-D, 2,4-DB, dichlorprop, MCPA, MCPB, mecoprop, dicamba, picloram, quniclorac and agriculturally acceptable salts or esters thereof, and a surfactant component in solution or stable suspension, emulsion or dispersion, comprising one or more surfactants.
- herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate or a derivative thereof, an auxin herbicide or a derivative thereof, and a suitable surfactant are provided that are advantageous for a number of reasons, including early visual symptoms of plant treatment, rapid uptake by the target plant, and control of a broad spectrum of plant species, as well as enhanced, more consistent control of unwanted plants. Although use of reduced application rates is not preferred, in at least some embodiments, lower application rates may be used without a significant loss of effectiveness of plant control.
- an aqueous herbicidal composition of N-phosphonomethyl glycine (glyphosate) predominantly in the form of the potassium salt thereof, and an auxin herbicide.
- the word "predominantly” in the above context means that at least about 50%, preferably at least about 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90 or about 95%, by weight of the glyphosate, expressed as a.e., is present as the potassium salt.
- Other salts of glyphosate which can make up the balance of the glyphosate component are agriculturally acceptable salts including the isopropylamine, di- ammonium, ammonium, sodium, monoethanolamine, n-propylamine, methylamine, ethylamine, hexamethylenediamine, dimethylamine or trimethylsulfonium salts.
- the second salt ion should be chosen so as not to adversely affect the viscosity, cloud point, non-crystallization and other stability properties of the composition.
- Another aspect of the present invention is an aqueous herbicidal composition of N-phosphonomethyl glycine (glyphosate), predominantly in the form of the isopropylamine salt thereof, and an auxin herbicide.
- Other salts of glyphosate which can make up the balance of the glyphosate component are agriculturally acceptable salts including the di-ammonium, ammonium, sodium, potassium, monoethanolamine, n-propylamine, methylamine, ethylamine, hexamethylenediamine, dimethylamine or trimethylsulfonium salts.
- the auxin herbicide is selected from the group consisting of 2,4- dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), 4-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)butanoic acid (2,4- DB), dichloroprop, (4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)acetic acid (MCPA), 4-(4-chloro-2- methylphenoxy)butanoic acid (MCPB), mecoprop, dicamba, picloram, quinclorac, agriculturally acceptable salts or esters of any of these herbicides, and mixtures thereof.
- the auxin herbicide is selected from the group consisting of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), dicamba, salts or esters thereof, and mixtures thereof.
- 2,4-D is thought to acidify the cell wall by stimulating the activity of a membrane-bound ATPase-driven proton pump. The reduction in apoplasmic pH induces cell elongation by increasing the activity of certain enzymes responsible for cell wall loosening. Low concentrations of 2,4-D are reported to stimulate RNA polymerase, resulting in subsequent increases in RNA, DNA, and protein biosynthesis.
- the auxin herbicide is at least 1 % soluble by weight in water at pH 6.
- the auxin herbicide can be present in the composition in the form of its acid, an agriculturally acceptable salt (e.g., isopropylamine, di-ammonium, ammonium, sodium, monoethanolamine, n- propylamine, methylamine, ethylamine, hexamethylenediamine, dimethylamine or trimethylsulfonium), or an agriculturally acceptable ester (e.g., methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, octyl, ethoxyethyl, butoxyethyl or methoxypropyl).
- the salt or ester ion of the auxin herbicide should be chosen to not affect the viscosity, cloud point, non-crystallization and other stability properties of the composition.
- the glyphosate and auxin herbicide compositions may contain 5 g a.e./L (grams acid equivalent per liter) to 600 g glyphosate a.e./L, preferably from 65 to about 600, from about 75 to about 600, from about 100 to about 600, from about 150 to about 600, from about 200 to about 600, from about 250 to about 600, from about 300 to about 600, from about 350 to about 600, from about 400 to about 600, from about 450 to about 600, or from about 480 to about 600 g glyphosate a.e./L.
- 5 g a.e./L grams acid equivalent per liter
- 600 g glyphosate a.e./L preferably from 65 to about 600, from about 75 to about 600, from about 100 to about 600, from about 150 to about 600, from about 200 to about 600, from about 250 to about 600, from about 300 to about 600, from about 350 to about 600, from about 400 to about 600, from about 450 to about 600,
- the weight ratio of the glyphosate (acid equivalent basis) to the auxin herbicide (acid equivalent basis) varies depending on the activity of the auxin herbicide which is generally determined using the standard use rates. A person skilled in the art would know that a higher standard use rate indicates a lower activity and thus more of the auxin herbicide should be used to achieve acceptable results.
- the weight ratio of glyphosate to 2,4-D, 2,4-DB, MCPA, or MCPB is about 10:1 to about 100:1.
- the weight ratio of glyphosate to mecoprop is about 10:1 to about 50:1.
- the weight ratio of glyphosate to dicamba, or picloram is about 20:1 to about 200:1.
- the weight ratio of glyphosate to 2,4-D is about 20:1 to about 100:1 ; more preferably, about 20:1 to about 50:1 ; particularly, about 25:1 to about 50:1.
- the weight ratio of glyphosate to dicamba is about 40:1 to about 200:1; more preferably, about 40:1 to about 100:1 ; particularly, about 50:1 to about 100:1.
- the glyphosate in the glyphosate and auxin herbicide compositions is present in an amount of at least about 75, 100, 125, 150, 175, 200, 225, 250, 275, 300, 325, 350, 375, 400, 425, 450, 475, 480, 500, 525, 550, 575, 580 or 600 g a.e./L.
- the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e. basis) are present in compositions of the invention in a weight ratio of at least 33:1 , 34:1 , 35:1 , 36:1 , 37:1 , 38:1 , 39:1 , 40:1 , 45:1 , 50:1 , 55:1 , 60:1 , 65:1 , 70:1 , 75:1 , 80:1 , 85:1 , 90:1 , 95:1 , 100:1 , 110:1 , 120:1 , 130:1 , 140:1 , 150:1 , 160:1 , 170:1 , 180:1 , 190:1 or 200:1.
- the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e. basis) are present in a weight ratio of from about 40:1 to about 200:1 , from about 50:1 to about 200: 1 , from about 60: 1 to about 200: 1 , from about 50: 1 to about 150: 1 , from about 50:1 to about 100:1 or from 32:1 to about 50:1.
- the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e. basis) are present in compositions of the invention in a weight ratio of at least about 5:1 , 6:1 , 7:1 , 8:1 , 9:1 , 10:1 , 15:1 , 20:1 , 25:1 , 30:1 , 35:1 , 40:1 , 45:1 , 50:1 , 55:1 , 60:1 , 65:1 , 70:1 , 75:1 , 80:1 , 85:1 , 90:1 , 95:1 , 100:1 , 110:1 , 120:1 , 130:1 , 140:1 , 150:1 , 160:1 , 170:1 , 180:1 , 190:1 or 200:1.
- the glyphosate is present in an amount of at least 65 g a.e./L.
- the glyphosate concentration is between 360 and 445 g a.e./L, and the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e. basis) are present in a weight ratio of about 5:1 to about 50:1 , about 5:1 to about 40:1 , or about 8:1 to about 36:1.
- the glyphosate concentration is between 445 and 480 g a.e./L, and the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e.
- the glyphosate concentration is between 360 and 525 g a.e./L, and the glyphosate (a.e.
- auxin herbicide component a.e. basis
- the glyphosate concentration is at least 480 g a.e./L
- the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e. basis) are present in a weight ratio of about 25:1 to about 80:1 , about 50:1 to about 80:1 , about 63:1 to about 80:1 , or about 25:1 to about 52:1.
- the potassium glyphosate and auxin herbicide composition of the present invention is useful in controlling a variety of broadleaf weeds.
- These weeds include Velvetleaf, Redroot Pigweed, Pigweed Species, Tall Waterhemp, Giant Ragweed, Indian Mustard, Sicklepod, Lambsquarters, Wild Poinsettia, Common Mallow, Hemp Sesbania, Prickly Sida, Wild Mustard, Momingglory (Brazil), Momingglory, Ivyleaf Mominglory, Pitted Momingglory, Buckwheat, Cutleaf Evening Primrose, Curly Dock, Common Chickweed, Common Dayflower and Tropical Spiderwort.
- Also provided by the present invention is a method of killing or controlling weeds or unwanted vegetation comprising diluting with a suitable volume of water a herbicidally effective amount of a composition as provided herein to form an application mixture, and applying the application mixture to foliage of the weeds or unwanted vegetation.
- the user can mix one or more adjuvants with a composition of the invention and the water of dilution when preparing the application composition.
- adjuvants can include additional surfactant and/or an inorganic salt such as ammonium sulfate with the aim of further enhancing herbicidal efficacy.
- an inorganic salt such as ammonium sulfate
- the composition in a particular contemplated method of use of a composition of the invention, is applied to foliage of crop plants genetically transformed or selected to tolerate glyphosate, and simultaneously to foliage of weeds or undesired plants growing in close proximity to such crop plants.
- This method of use results in control of the weeds or undesired plants while leaving the crop plants substantially unharmed.
- Crop plants genetically transformed or selected to tolerate glyphosate include those whose seeds are sold by Monsanto Company or under license from Monsanto Company bearing the Roundup Ready® trademark. These include varieties of wheat, turfgrass, and corn.
- Plant treatment compositions can be prepared simply by diluting a concentrate composition of the invention in water. Application of plant treatment compositions to foliage is preferably accomplished by spraying, using any conventional means for spraying liquids, such as spray nozzles, atomizers or the like.
- Compositions of the invention can be used in precision farming techniques, in which apparatus is employed to vary the amount of pesticide applied to different parts of a field, depending on variables such as the particular plant species present, soil composition, etc. In one embodiment of such techniques, a global positioning system operated with the spraying apparatus can be used to apply the desired amount of the composition to different parts of a field.
- a plant treatment composition is preferably dilute enough to be readily sprayed using standard agricultural spray equipment.
- Useful spray volumes for the present invention can range from about 10 to about 1000 liters per hectare (l/ha) or higher, by spray application.
- the glyphosate and auxin herbicide compositions may contain about 300 to about 600 g a.e./L of glyphosate, predominantly in the form of the potassium salt thereof.
- the balance of the glyphosate component is made up of agriculturally acceptable salts including the isopropylamine, monoethanolamine, n-propylamine, methylamine, ethylamine, ammonium, diammonium, hexamethylenediamine, dimethylamine or trimethylsulfonium salts.
- the glyphosate and auxin herbicide compositions may contain about 450 to about 600 g a.e./L of glyphosate, predominantly in the form of the potassium salt thereof.
- concentration of glyphosate may be increased in the composition, the concentration of the auxin herbicide may be decreased to achieve acceptable weed control.
- the weight ratio of the glyphosate to the auxin herbicide is about 25:1 to about 100:1.
- the weight ratio of the glyphosate to 2,4-D is about 25:1 to about 50:1.
- the glyphosate and auxin herbicide compositions may contain about 360 to about 600 g a.e./L of glyphosate, predominantly in the form of the isopropylamine salt thereof.
- the balance of the glyphosate component is made up of agriculturally acceptable salts including the monoethanolamine, n-propylamine, methylamine, ethylamine, ammonium, diammonium, potassium, hexamethylenediamine, dimethylamine or trimethylsulfonium salts.
- the glyphosate and auxin herbicide compositions may contain about 360 to about 450 g a.e./L of glyphosate, predominantly in the form of the isopropylamine salt thereof.
- concentration of glyphosate may be increased in the composition, the concentration of the auxin herbicide may be decreased to achieve acceptable weed control.
- the weight ratio of the glyphosate to the auxin herbicide is about 10:1 to about 20:1.
- the glyphosate is present in an amount of at least about 370, 380, 390, 400, 410, 420, 430, 440, 450, 475, 480, 500, 525, 550, 575, 580 or 600 g a.e./L, and the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e. basis) are present in a weight ratio of at least 9.5:1, 9.6:1, 9.7:1 , 9.8:1, 9.9:1 , 10:1 , 11 :1 , 12:1, 13:1, 14:1 , 15:1 , 16:1 , 17:1 , 18:1 , 19:1 , or 20:1.
- the glyphosate is present in an amount of from about 400 to about 600, from about 420 to about 600, from about 430 to about 600, from about 440 to about 600, from about 450 to about 600, or from about 480 to about 600 g a.e./L, and the glyphosate (a.e. basis) and auxin herbicide component (a.e.
- Surfactants and cosurfactants effective in formulating glyphosate, such as potassium or isopropylamine glyphosate, with auxin herbicides include cationic, nonionic, anionic, and amphoteric surfactants and cosurfactants as described below and mixtures thereof, wherein the surfactant component is present in an amount of at least about 5 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
- Cationic surfactants and cosurfactants effective in such glyphosate formulations include:
- R 1 is hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 2 and R 3 are hydrogen or hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms.
- preferred R 1 , R 2 , and R 3 hydrocarbyl groups are linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl groups.
- R 1 is a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from about 8 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 2 and R 3 are independently hydrogen or a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms.
- R 1 is a linear or branched alkyl or alkenyl group having from about 12 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 2 and R 3 are independently hydrogen, methyl or ethyl.
- R 1 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 12 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 2 and R 3 are independently linear or branched hydroxyalkyl groups having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms.
- R 11 is hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 12 in each of the x (R 12 O) and y (R 12 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 13 is hydrogen, or a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 4 carbon atoms
- x and y are independently an average number from 1 to about 40
- X " is an agriculturally acceptable anion.
- R 11 and R 14 hydrocarbyl groups are linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl groups.
- R 11 and R 14 are independently a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from 1 to about 25 carbon atoms
- R 12 in each of the x (R 12 O) and y (R 12 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 13 is hydrogen, methyl or ethyl
- the sum of x and y is an average number from about 2 to about 30.
- R 11 and R 14 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 12 in each of the x (R 12 O) and y (R 12 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 13 is hydrogen or methyl
- the sum of x and y is an average number from about 2 to about 20.
- R 11 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms and R 14 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 12 in each of the x (R 12 O) and y (R 12 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 13 is hydrogen or methyl
- x is an average number from about 2 to about 20.
- R 11 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms and R 14 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms
- R 2 in each of the x (R 12 O) and y (R 12 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 13 is hydrogen or methyl
- x is an average number from about 2 to about 15, or
- R 11 and R 14 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 12 in each of the x (R 12 O) and y (R 12 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 13 is hydrogen or methyl
- x is an average number from about 5 to about 15.
- Preferred dialkoxylated quaternary ammonium surfactants include EthoquadTM C12 (a PEG 2 coco methyl ammonium chloride from Akzo Nobel), PEG 5 coco methyl ammonium chloride, PEG 5 tallow methyl ammonium chloride, PEG 5 ditallow ammonium bromide, and PEG 10 ditallow ammonium bromide.
- EthoquadTM C12 a PEG 2 coco methyl ammonium chloride from Akzo Nobel
- PEG 5 coco methyl ammonium chloride PEG 5 tallow methyl ammonium chloride
- PEG 5 ditallow ammonium bromide PEG 5 ditallow ammonium bromide
- PEG 10 ditallow ammonium bromide PEG 10 ditallow ammonium bromide.
- R 21 , R 24 , and R 25 hydrocarbyl groups are linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl groups.
- R 21 , R 24 and R 25 are independently a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from 1 to about 25 carbon atoms
- R 22 in each of the x 2 (R 22 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 23 is hydrogen, methyl or ethyl
- x 2 is an average number from 1 to about 40.
- R 21 , R 24 and R 25 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 22 in each of the x 2 (R 22 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 23 is hydrogen or methyl
- x 2 is an average number from 1 to about 30.
- R 21 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 22 in each of the x 2 (R 22 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 23 is hydrogen or methyl
- R 24 and R 25 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 22 carbon atoms
- x 2 is an average number from 1 to about 30.
- R 21 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 22 in each of the x 2 (R 22 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 23 is hydrogen or methyl
- R 24 and R 25 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms
- x 2 is an average number from about 5 to about 25.
- R 21 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 16 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 22 in each of the x 2 (R 22 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 23 is hydrogen or methyl
- R 24 and R 25 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 3 carbon atoms
- x 2 is an average number from about 5 to about 25.
- Preferred monoalkoxylated quaternary ammonium surfactants include PEG 7 C 18 dimethyl ammonium chloride and PEG 22 C 18 dimethyl ammonium chloride, (d) quaternary ammonium salts having the formula:
- R 31 , R 33 and R 34 are independently hydrogen or hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 32 is hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- X " is an agriculturally acceptable anion.
- preferred R 31 , R 32 , R 33 , and R 34 hydrocarbyl groups are linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl groups.
- R 3i is a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from about 8 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 32 ', R 33 and R 34 are independently a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 31 is a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 32 ', R 33 and R 34 are independently a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms.
- R 31 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 16 carbon atoms
- R 32 -, R 33 and R 34 are independently a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms.
- R 31 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 14 carbon atoms
- R 32 , R 33 and R 34 are methyl.
- Preferred commercially available quaternary ammonium surfactants include ArquadTM C-50 (a dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride from Akzo Nobel) and ArquadTM T-50 (a tallow trimethyl ammonium chloride from Akzo Nobel).
- R 41 is hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 42 is hydrocarbylene or substituted hydrocarbylene having from 2 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 43 and R 44 are independently hydrogen, hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms, or -(R 45 O) x 4 R 46 , R 45 in each of the x 4 (R 45 -O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene, R 46 is hydrogen, or a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 4 carbon atoms, and x 4 is an average number from 1 to about 50.
- preferred R 41 , R 42 , R 43 , and R 44 hydrocarbyl (hydrocarbylene) groups are linear or branched alkyl (alkylene), linear or branched alkenyl (alkenylene), linear or branched alkynyl (alkynylene), aryl (arylene), or aralkyl (aralkylene) groups.
- R 41 is a linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, ar l, or aralkyl group having from 8 to about 25 carbon atoms
- R 42 is a linear or branched alkylene or alkenylene group having from 2 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 43 and R 44 are independently hydrogen, a linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl group having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms, or -(R 45 O) x R 46 , R 45 in each of the x 4 (R 45 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 46 is hydrogen, methyl or ethyl
- x 4 is an average number from 1 to about 30.
- R 41 is a linear or branched alkyl or alkenyl group having from 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 42 is a linear or branched alkylene or alkenylene group having from 2 to about 6 carbon atoms
- R 43 and R 44 are independently hydrogen, a linear or branched alkyl or alkenyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms, or -(R 45 O) x 4 R 46 , R 45 in each of the x 4 (R 45 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 46 is hydrogen or methyl
- x 4 is an average number from 1 to about 15.
- R 41 is a linear or branched alkyl or alkenyl group having from 8 to about 18 carbon atoms
- R 42 is ethylene or propylene
- R 3 and R 4 are independently hydrogen, methyl, or -(R 45 O) x 4 R 46
- R 45 in each of the x 4 (R 45 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 46 is hydrogen
- x 4 is an average number from 1 to about 5.
- R 51 , R 52 and R 53 are independently hydrogen, hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl, -(R 54 O) x 5 R 55 , or -R 56 (OR 54 ) x 5 OR 55
- R 54 in each of the x 5 (R 54 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 55 is hydrogen, or a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 56 is hydrocarbylene or substituted hydrocarbylene having from 2 to about 6 carbon atoms
- x 5 is an average number from 1 to about 50
- the total number of carbon atoms in R 51 , R 52 and R 53 is at least 8.
- preferred R 51 , R 52 , R 53 , and R 56 hydrocarbyl (hydrocarbylene) groups are linear or branched alkyl (alkylene), linear or branched alkenyl (alkenylene), linear or branched alkynyl (alkynylene), aryl (arylene), or aralkyl (aralkylene) groups.
- R 51 and R 52 are independently hydrogen, a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms, or -(R 54 O) x 5 R 55 ,
- R 53 is a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from about 8 to about 30 carbon atoms,
- R 54 in each of the x 5 (R 54 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene;
- R 55 is hydrogen, methyl or ethyl, and x 5 is an average number from 1 to about 30.
- R 51 and R 52 are independently hydrogen, or a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms, and R 53 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms; or R 51 and R 52 are independently -(R 54 O) x 5 R 55 , R 53 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms, R 54 in each of the x 5 (R 54 O) groups is ethylene or propylene, R 55 is hydrogen or methyl, and x 5 is an average number from 1 to about 10.
- R 51 and R 52 are independently methyl, and R 53 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 18 carbon atoms; or R 51 and R 52 are independently - (R 54 O) x 5 R 55 , R 53 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 18 carbon atoms, R 54 in each of the x 5 (R 54 O) groups is ethylene or propylene, R 55 is hydrogen, and x 5 is an average number from 1 to about 5.
- amine oxide surfactants include Chemoxide L70. (g) dialkoxylated amines having the formula:
- R 61 is a linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl group having from about 6 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 62 in each of the x 6 (R 62 O) and the y 6 (R 62 O) groups is independently C 2 - C 4 alkylene
- R 63 is hydrogen, or a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 4 carbon atoms and x 6 and y 6 are independently an average number from 1 to about 40.
- R 61 is a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from about 8 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 62 in each of the x 6 (R 62 O) and the y 6 (R 62 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 63 is hydrogen, methyl or ethyl
- x 6 and y 6 are independently an average number from 1 to about 20.
- R 61 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 25 carbon atoms
- R 62 in each of the x 6 (R 62 O) and the y 6 (R 62 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 63 is hydrogen or methyl
- x and y are independently an average number from 1 to about 10.
- R 6 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 8 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 62 in each of the x 6 (R 62 O) and the y 6 (R 62 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 63 is hydrogen or methyl
- x 6 and y 6 are independently an average number from 1 to about 5.
- Preferred commercially available dialkoxylated amines include TrymeenTM 6617 (from Cognis), EthomeenTM C/12, C/15, C/20, C/25, T/12, T/15, T/20 and T/25 (from Akzo Nobel), and GenaminTM T-200 DG and T-200 NF (from Clariant).
- R 71 is hydrogen or hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 72 in each of the x 7 (R 72 O) and y 7 (R 72 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 73 is hydrocarbylene or substituted hydrocarbylene having from 2 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 74 and R 75 are each independently hydrogen, hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms, -(R 76 ) n 7 -(R 72 O) y 7 R 77 , or R 74 and R 75 , together with the nitrogen atom to which they are attached, form a cyclic or heterocyclic ring
- R 7 ⁇ is hydrocarbylene or substituted hydrocarbylene having from 1 to about 30 carbon atoms
- R 77 is hydrogen or a linear or branched alkyl group having 1 to about 4 carbon atoms, n 7 is 0 or 1 , x 7
- preferred R 71 , R 73 , R 74 , R 75 , and R 76 hydrocarbyl (hydrocarbylene) groups are linear or branched alkyl (alkylene), linear or branched alkenyl (alkenylene), linear or branched alkynyl (alkynylene), aryl (arylene), or aralkyl (aralkylene) groups.
- R 71 is a linear or branched alkyl or linear or branched alkenyl group having from about 8 to about 25 carbon atoms
- R 72 in each of the x 7 (R 72 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 73 is a linear or branched alkylene group having from 2 to about 20 carbon atoms
- R 74 and R 75 are each independently hydrogen or a linear or branched alkyl group having from 1 to about 6 carbon atoms
- x 7 is an average number from 1 to about 30.
- R 71 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 12 to about 22 carbon atoms
- R 72 in each of the x 7 (R 72 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 73 is a linear or branched alkylene group having from 2 to about 6 carbon atoms
- R 74 and R 75 are each independently hydrogen, methyl, or tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl
- x 7 is an average number from about 2 to about 30.
- R 71 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 12 to about 18 carbon atoms
- R 72 in each of the x 7 (R 72 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 73 is ethylene or propylene
- R 74 and R 75 are each independently hydrogen, methyl or tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl
- x 7 is an average number from about 4 to about 20.
- R 71 is a linear or branched alkyl group having from about 12 to about 18 carbon atoms
- R 72 in each of the x 7 (R 72 O) groups is independently ethylene or propylene
- R 73 is ethylene
- R 74 and R7 5 are methyl
- x 7 is an average number from about 4 to about 20.
- Preferred monoalkoxylated amines include PEG 13 or 18 C 14 . 15 ether propylamines and PEG 7, 10, 15 or 20 C 16 . 18 ether propylamines (from Tomah) and PEG 13 or 18 C 14 . 15 ether dimethyl propylamines and PEG 10, 15 or 20 or 25 C 16 . 18 ether dimethyl propylamines (from Tomah) and SurfonicTM AGM-550 from Huntsman.
- Preferred anionic surfactants effective in forming potassium glyphosate formulations include:
- R 81 and R 83 are independently a linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl group having from about 4 to about 30 carbon atoms;
- R 82 in each of the m (R 82 O) and the n (R 82 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene; and m and n are independently from 1 to about 30.
- R 91 is a linear or branched alkyl, linear or branched alkenyl, linear or branched alkynyl, aryl, or aralkyl group having from about 8 to about 30 carbon atoms;
- R 92 in each of the a (R 92 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene; and a is from 1 to about 30.
- Representative alkyl alkoxylated phosphates include oleth-10 phosphate, oleth-20 phosphate and oleth-25 phosphate.
- nonionic surfactants or cosurfactants effective in such glyphosate formulations include:
- R 101 is hydrogen or C.,_ 18 hydrocarbyl
- R 104 is hydrogen or C,. 4 hydrocarbyl
- q is 0 or 1
- sug is (i) an open or cyclic structure derived from sugars, such as, for example, glucose or sucrose (referred to herein as a sugar unit), or (ii) a hydroxyalkyl, polyhydroxyalkyl or poly(hydroxyalkyl)alkyl group, u is an average number from 1 to about 2, and v is an integer from 1 to 3.
- This group includes several commercial surfactants collectively known in the art or referred to herein as "alkyl polyglucosides" or "APGs". Suitable examples are sold by Henkel as AgrimulTM PG-2069, AgrimulTM PG-2076 and AgrimulTM PG-2067.
- polysiloxane surfactants having the formula:
- R 1 is -C ⁇ H 2n O(CH 2 CH 2 O) m (CH 2 CH(CH 3 )O) q X
- n is 0 to 6
- a is 0 to about 100
- b is 0 to about 10
- m is 0 to about 30
- q is 0 to about 30
- X is hydrogen or a C.,. 20 hydrocarbyl or C 2 . 6 acyl group
- R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R 9 , R 10 groups are independently substituted or unsubstituted C ⁇ o hydrocarbyl or nitrogen containing groups.
- n is 0 to 6
- a is 1 to about 30
- b is 0 to about 10
- m is 0 to about 30
- q is 0 to about 3
- X is hydrogen or a C,. 6 hydrocarbyl or C 2 . 6 acyl group
- R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R g , R 10 groups are independently substituted or unsubstituted C, ⁇ hydrocarbyl or nitrogen containing groups.
- the polysiloxane is a polyoxyethylene heptamethyl trisiloxane wherein R ⁇ is - C n H 2 ⁇ O(CH 2 CH 2 O) m (CH 2 CH(CH 3 )O) q X, n is 3 or 4, a is 1 , b is 0, m is 1 to about 30, q is 0, X is hydrogen or a methyl, ethyl or acetyl group, and R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R g , R 10 groups are independently substituted or unsubstituted C ⁇ hydrocarbyl or nitrogen containing groups.
- a is 1 to 5, b is 0 to 10, n is 3 or 4, m is 1 to about 30, q is 0, X is hydrogen or a methyl, ethyl or acetyl group, and R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R 9 , and R 10 are methyl groups.
- a is 1 to 5, b is 0 to 10, n is 3 or 4, m is 4 to 12, q is 0, X is hydrogen or a methyl or acetyl group, R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R 9 , and R 10 are methyl groups.
- a is 1 , b is 0, n is 3 or 4, m is 1 to about 30, b is 0, X is hydrogen or a methyl, ethyl or acetyl group, and R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R 9 , and R 10 are methyl groups.
- a is 1 , b is 0, n is 3, m is 8, b is 0, X is methyl and R 2 , R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 6 , R 7 , R 8 , R 9 , and R 10 are methyl groups.
- Trisiloxanes of the above formula are generally described in product literature of Crompton Corporation and in U.S. Patent No. 3,505,377.
- Several of such trisiloxanes are ethoxylated organosilicone wetting agents available from Crompton Corporation as Silwet® silicone glycol copolymers. Both liquid organosilicones and dry organosilicones can be used in the surfactant composition; both are included within the scope of the invention.
- More preferred trisiloxanes are those sold commercially in the United States or elsewhere by Crompton Corporation as Silwet® L-77, Silwet® 408 and Silwet® 800, by Dow- Corning as Sylgard® 309, by Exacto, Inc., as Qwikwet® 100, and by Goldschmidt as Breakthru S-240.
- R 2 is hydrogen.
- glyphosate salts e.g., potassium or isopropylamine
- Suitable alkyl or aryl amine compounds may also contain 0 to about 5 EO groups.
- Preferred alkylamine compounds include C 6 to C 12 alkylamines having 0 to 2 EO groups.
- etheramine compounds having 4 to 12 carbons and 0 to about 5 EO groups also enhance the compatibility of such formulations.
- the compounds which enhance the compatibility of such surfactants include:
- R 111 is linear or branched alkyl or aryl having from about 4 to about 16 carbon atoms
- R 112 is hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, or -(CH 2 CH 2 O) d H
- R 113 is hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, or -(CH 2 CH 2 O) e H wherein the sum of d and e is not more than about 5
- R 114 is hydrogen or methyl
- R 116 in each of the c (R 116 O) groups is independently C 2 -C 4 alkylene
- R 115 is hydrocarbylene or substituted hydrocarbylene having from 2 to about 6 carbon atoms
- A- is an agriculturally acceptable anion.
- the ratio (by weight) of the glyphosate a.e. to the surfactant is typically in the range of from about 1 :1 to about 20:1 , preferably from about 2:1 to about 10:1 , more preferably from about 2:1 to about 8:1 , still more preferably from about 2:1 to about 6:1 , still more preferably from about 3:1 to about 6:1 , and still more preferably about 4.5:1 to 6:1.
- the surfactant of the compositions of the invention comprises a first surfactant component which includes one or more surfactants selected from the group consisting of:
- the surfactant of the compositions of the invention comprises a first surfactant component as described in detail above and additionally a second surfactant component which includes one or more surfactant(s) selected from the group consisting of:
- the second surfactant component is selected from the group consisting of:
- the density of the formulation of the invention is preferably at least 1.210 grams/liter, more preferably at least about 1.215, 1.220, 1.225, 1.230, 1.235, 1.240, 1.245, 1.250, 1.255, 1.260, 1.265, 1.270, 1.275, 1.280, 1.285, 1.290, 1.295, 1.300, 1.305, 1.310, 1.315, 1.320, 1.325, 1.330, 1.335, 1.340, 1.345, 1.350, 1.355, 1.360, 1.365, 1.370, 1.375, 1.380, 1.385, 1.390, 1.395, 1.400, 1.405, 1.410, 1.415, 1.420, 1.425, 1.430, 1.435, 1.440, 1.445, or 1.450 grams/liter.
- a solubilizer also commonly referred to as a cloud point enhancer or stabilizer
- a cloud point enhancer or stabilizer can significantly improve the properties of the formulations of the present invention.
- Suitable solubilizers for use with the novel formulations of the present invention include, for example, cocoamine (Armeen C), dimethylcocoamine (Arquad DMCD), cocoammonium chloride (Arquad C), PEG 2 cocoamine (Ethomeen C12), PEG 5 tallowamine (Ethomeen T15), and PEG 5 cocoamine (Ethomeen C15), all of which are manufactured by Akzo Nobel (California).
- Additional excipient ingredients may include conventional formulation additives such as dyes, thickeners, crystallization inhibitors, antifreeze agents (e.g., glycols, such as ethylene glycol, or polyethylene glycols such as polyethylene glycol 200, 400, 600, 1500, 4000 or 6000), foam moderating agents (e.g., AntifoamTM or Y-14088 AntifoamTM, both available from Crompton Corporation), antidrift agents, compatibilizing agents, antioxidants (e.g., ascorbic acid and sodium sulfite, in order for example to prevent the formation of a nitrosamine), other co-solvents (e.g., N-methylpyrrolidone, DMSO, DMF, propylene carbonate, or ethylene glycol), or some other agent added to lessen or overcome antagonism associated with hard water (e.g., ammonium sulfate, EDTA or a polymeric water conditioner, such as a polyacrylic acid).
- antifreeze agents
- additives such as solvents and organic acids may be added to enhance concentrate stability.
- These additives generally function to increase solubility or dispersability of the surfactants in the aqueous carrier thus enabling the formulation of robust concentrates exhibiting enhanced thermal and pH stability, reduced viscosity, and high glyphosate loading.
- water soluble solvents include acetates, C,.. 6 alkanols, C ⁇ diols, C,. 6 alkyl ethers of alkylene glycols and polyalkylene glycols, and mixtures thereof.
- the alkanol can be selected from methanol, ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol, the various positional isomers of butanol, pentanol, and hexanol, and mixtures thereof. It may also be possible to utilize in addition to, or in place of, said alkanols, the diols such as methylene, ethylene, diethylene, propylene, dipropylene, and butylene glycols, and mixtures thereof, and including polyalkylene glycols. These components are generally employed in dispersion- effective or solubilizing effective amounts.
- Suitable organic acids include, among others, acetic, dichloroacetic, citric, malic, oxalic, salicylic and tartaric. Effective concentrations of organic acids are generally between about 0.1 wt% and 5 wt%.
- herbicides can be included in the compositions of the invention other than the glyphosate and auxin herbicides, it is preferred that the glyphosate and the auxin herbicides are the only herbicides in the composition.
- hydrocarbon and “hydrocarbyl” as used herein describe organic compounds or radicals consisting exclusively of the elements carbon and hydrogen. These moieties include alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, and aryl moieties. These moieties also include alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, and aryl moieties substituted with other aliphatic or cyclic hydrocarbon groups, such as alkaryl, alkenaryl and alkynaryl. Unless otherwise indicated, these moieties preferably comprise 1 to 30 carbon atoms.
- hydrocarbylene as used herein describes radicals joined at two ends thereof to other radicals in an organic compound, and which consist exclusively of the elements carbon and hydrogen.
- moieties include alkylene, alkenylene, alkynylene, and arylene moieties. These moieties also include alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, and aryl moieties substituted with other aliphatic or cyclic hydrocarbon groups, such as alkaryl, alkenaryl and alkynaryl. Unless otherwise indicated, these moieties preferably comprise 1 to 30 carbon atoms.
- substituted hydrocarbyl moieties described herein are hydrocarbyl moieties which are substituted with at least one atom other than carbon, including moieties in which a carbon chain atom is substituted with a hetero atom such as nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, phosphorous, boron, sulfur, or a halogen atom.
- substituents include halogen, heterocyclo, alkoxy, alkenoxy, alkynoxy, aryloxy, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, ketal, acyl, acyloxy, nitro, amino, amido, cyano, thiol, acetal, sulfoxide, ester, thioester, ether, thioether, hydroxyalkyl, urea, guanidine, amidine, phosphate, amine oxide, and quaternary ammonium salt.
- substituted hydrocarbylene moieties described herein are hydrocarbylene moieties which are substituted with at least one atom other than carbon, including moieties in which a carbon chain atom is substituted with a hetero atom such as nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, phosphorous, boron, sulfur, or a halogen atom.
- substituents include halogen, heterocyclo, alkoxy, alkenoxy, alkynoxy, aryloxy, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, ketal, acyl, acyloxy, nitro, amino, amido, cyano, thiol, acetal, sulfoxide, ester, thioester, ether, thioether, hydroxyalkyl, urea, guanidine, amidine, phosphate, amine oxide, and quaternary ammonium salt.
- the alkyl groups described herein are preferably lower alkyl containing from one to 18 carbon atoms in the principal chain and up to 30 carbon atoms. They may be straight or branched chain or cyclic and include methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, isobutyl, hexyl, 2- ethylhexyl, and the like.
- alkenyl groups described herein are preferably lower alkenyl containing from two to 18 carbon atoms in the principal chain and up to 30 carbon atoms. They may be straight or branched chain or cyclic and include ethenyl, propenyl, isopropenyl, butenyl, isobutenyl, hexenyl, and the like.
- alkynyl groups described herein are preferably lower alkynyl containing from two to 18 carbon atoms in the principal chain and up to 30 carbon atoms. They may be straight or branched chain and include ethynyl, propynyl, butynyl, isobutynyl, hexynyl, and the like.
- aryl as used herein alone or as part of another group denote optionally substituted homocyclic aromatic groups, preferably monocyclic or bicyclic groups containing from 6 to 12 carbons in the ring portion, such as phenyl, biphenyl, naphthyl, substituted phenyl, substituted biphenyl or substituted naphthyl. Phenyl and substituted phenyl are the more preferred aryl.
- aralkyl denotes a group containing both alkyl and aryl structures such as benzyl.
- the alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl and aralkyl groups can be substituted with at least one atom other than carbon, including moieties in which a carbon chain atom is substituted with a hetero atom such as nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, phosphorous, boron, sulfur, or a halogen atom.
- substituents include hydroxy, nitro, amino, amido, nitro, cyano, sulfoxide, thiol, thioester, thioether, ester and ether, or any other substituent which can increase the compatibility of the surfactant and/or its efficacy enhancement in the potassium glyphosate formulation without adversely affecting the storage stability of the formulation.
- halogen or halo as used herein alone or as part of another group refer to chlorine, bromine, fluorine, and iodine. Fluorine substituents are often preferred in surfactant compounds.
- hydroxyalkyl includes alkyl groups substituted with at least one hydroxy group, and includes bis(hydroxyalkyl)alkyl, tris(hydroxyalkyl)alkyl and poly(hydroxyalkyl)alkyl groups.
- Preferred hydroxyalkyl groups include hydroxymethyl (-CH 2 OH), and hydroxyethyl (-C 2 H 4 OH), bis(hydroxymethyl)methyl (-CH(CH 2 OH) 2 ), and tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl (-C(CH 2 OH) 3 ).
- cyclic as used herein alone or as part of another group denotes a group having at least one closed ring, and includes alicyclic, aromatic (arene) and heterocyclic groups.
- heterocyclo or “heterocyclic” as used herein alone or as part of another group denote optionally substituted, fully saturated or unsaturated, monocyclic or bicyclic, aromatic or nonaromatic groups having at least one heteroatom in at least one ring, and preferably 5 or 6 atoms in each ring.
- the heterocyclo group preferably has 1 or 2 oxygen atoms, 1 or 2 sulfur atoms, and/or 1 to 4 nitrogen atoms in the ring, and may be bonded to the remainder of the molecule through a carbon or heteroatom.
- exemplary heterocyclo include heteroaromatics such as furyl, thienyl, pyridyl, oxazolyl, pyrrolyl, indolyl, quinolinyl, or isoquinolinyl and the like, and non-aromatic heterocyclics such as tetrahydrofuryl, tetrahydrothienyl, piperidinyl, pyrrolidino, etc.
- substituents include one or more of the following groups: hydrocarbyl, substituted hydrocarbyl, keto, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, acyl, acyloxy, alkoxy, alkenoxy, alkynoxy, aryloxy, halogen, amido, amino, nitro, cyano, thiol, thioester, thioether, ketal, acetal, ester and ether.
- heteroaromatic as used herein alone or as part of another group denote optionally substituted aromatic groups having at least one heteroatom in at least one ring, and preferably 5 or 6 atoms in each ring.
- the heteroaromatic group preferably has 1 or 2 oxygen atoms, 1 or 2 sulfur atoms, and/or 1 to 4 nitrogen atoms in the ring, and may be bonded to the remainder of the molecule through a carbon or heteroatom.
- Exemplary heteroaromatics include furyl, thienyl, pyridyl, oxazolyl, pyrrolyl, indolyl, quinolinyl, or isoquinolinyl and the like.
- substituents include one or more of the following groups: hydrocarbyl, substituted hydrocarbyl, keto, hydroxy, protected hydroxy, acyl, acyloxy, alkoxy, alkenoxy, alkynoxy, aryloxy, halogen, amido, amino, nitro, cyano, thiol, thioether, thioester, ketal, acetal, ester and ether.
- acyl denotes the moiety formed by removal of the hydroxyl group from the group - COOH of an organic carboxylic acid, e.g., RC(O)-, wherein R is R 1 , R 1 O-, R 1 R 2 N- , or R 1 S-, R 1 is hydrocarbyl, heterosubstituted hydrocarbyl, or heterocyclo and R 2 is hydrogen, hydrocarbyl or substituted hydrocarbyl.
- acyloxy denotes an acyl group as described above bonded through an oxygen linkage (--O-), e.g., RC(O)O- wherein R is as defined in connection with the term "acyl.”
- pesticide includes chemicals and microbial agents used as active ingredients of products for control of crop and lawn pests and diseases, animal ectoparasites, and other pests in public health.
- the term also includes plant growth regulators, pest repellants, synergists, herbicide safeners (which reduce the phytotoxicity of herbicides to crop plants) and preservatives, the delivery of which to the target may expose dermal and especially ocular tissue to the pesticide. Such exposure can arise by drift of the pesticide from the delivery means to the person performing the application of the pesticide or being present in the vicinity of an application.
- aqueous concentrate composition of glyphosate salt further containing a surfactant and auxin herbicide is meant not exhibiting phase separation on exposure to temperatures up to about 50 °C, and preferably not forming crystals of glyphosate or salt thereof on exposure to a temperature of about 0 °C for a period of up to about 7 days (i.e., the composition must have a crystallization point of 0 °C or lower).
- high temperature storage stability is often indicated by a cloud point of about 50 °C or more.
- Cloud point of a composition is normally determined by heating the composition until the solution becomes cloudy, and then allowing the composition to cool, with agitation, while its temperature is continuously monitored. A temperature reading taken when the solution clears is a measure of cloud point. A cloud point of 50 °C or more is normally considered acceptable for most commercial purposes for a glyphosate SL formulation.
- the cloud point should be 60 °C or more, and the composition should withstand temperatures as low as about -10 °C, preferably as low as about -20 °C, more preferably as low as about -30°C, for up to about 7 days without phase separation (i.e., without separation of frozen water or solid insoluble surfactant from the composition) and without crystal growth(even in the presence of seed crystals of the glyphosate salt).
- Herbicidal effectiveness is one of the biological effects that can be enhanced through this invention.
- Herbicidal effectiveness refers to any observable measure of control of plant growth, which can include one or more of the actions of (1) killing, (2) inhibiting growth, reproduction or proliferation, and (3) removing, destroying, or otherwise diminishing the occurrence and activity of plants.
- the herbicidal effectiveness data set forth herein report "control” as a percentage following a standard procedure in the art which reflects a visual assessment of plant mortality and growth reduction by comparison with untreated plants, made by technicians specially trained to make and record such observations. In all cases, a single technician makes all assessments of percent control within any one experiment or trial. Such measurements are relied upon and regularly reported by Monsanto Company in the course of its herbicide business.
- the spray compositions of the following examples contain an exogenous chemical, such as glyphosate salt as indicated, in addition to the excipient ingredients listed.
- the amount of exogenous chemical was selected to provide the desired rate in grams per hectare (g/ha) when applied in a spray volume of 93 l/ha.
- Several exogenous chemical rates were applied for each composition.
- the concentration of exogenous chemical varied in direct proportion to exogenous chemical rate, but the concentration of excipient ingredients was held constant across different exogenous chemical rates.
- STD1 725 g/l of glyphosate potassium salt in aqueous solution with no added surfactant.
- STD2 50% by weight of glyphosate IPA salt in aqueous solution together with a surfactant. This formulation is sold by Monsanto Company under the ROUNDUP ULTRAMAX ® trademark.
- STD3 570 g/l of glyphosate IPA salt in an aqueous solution with no added surfactant.
- compositions of the examples were used in compositions of the examples. They may be identified as follows.
- Seeds of the plant species indicated were planted in 88 mm square pots in a soil mix which was previously sterilized and prefertilized with a 14-14-14 NPK slow release fertilizer at a rate of 3.6 kg/m 3 .
- the pots were placed in a greenhouse with sub-irrigation. About one week after emergence, seedlings were thinned as needed, including removal of any unhealthy or abnormal plants, to create a uniform series of test pots.
- Pots were assigned to different treatments in a fully randomized experimental design with 6 replications. A set of pots was left untreated as a reference against which the effects of a treatment could later be evaluated.
- Treatments were made using dilute aqueous compositions. These could be prepared as spray compositions directly from their ingredients, or by dilution with water of preformulated concentrate compositions.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, reported in g a.e./liter, and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 1a.
- the 806D0T, 806E7S, 806F4Q and 806G3B formulations contained 62 grams acid equivalent per liter.
- Formulations 806A2D, 806B9H, 806C5Z, 806F4Q and 806G3B contained the IPA salt of 2,4-D measured in grams acid equivalent per liter. Table 1a
- compositions of Table 1a and comparative compositions STD1 and STD2 were applied to velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti, ABUTH) plants. Results, averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 1 b.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, reported in g a.e./liter, and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 2a.
- the 820A9T, 820C1Z, 820D6Q, 820E3F, 820F0G and 820H7D formulations contained 62 grams acid equivalent per liter.
- Formulation 820B4H contained the IPA salt of 2,4-D measured in grams acid equivalent per liter.
- compositions of Table 2a and comparative compositions STD1 and STD2 were applied to velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti, ABUTH) plants. Results at 4 days after treatment (4DAT) and 14 days after treatment (14DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 2b.
- compositions of Table 3a and comparative compositions STD1, STD2, RT MasterTM and Field MasterTM were applied to velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti, ABUTH) and Japanese millet (Echinochloa crus-galli var. frumentae, ECHCF) plants. Results at 5 days after treatment (5DAT) and 16 days after treatment (16DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 3b.
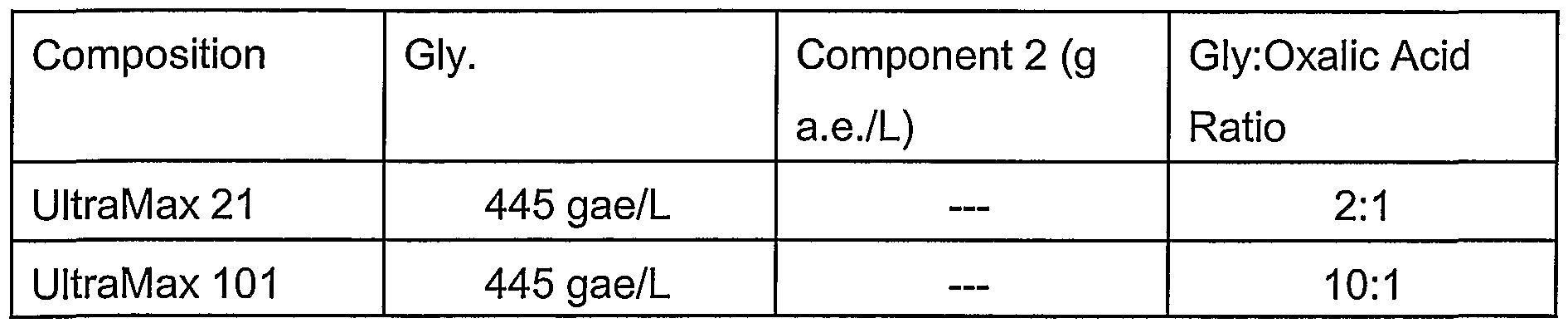
- the order of efficacy averaged across application rates for the ABUTH %inhibition was UltraMax 21 > Field Master 21 > UltraMax 101 > RT Master 21 > UltraMax 301 > RT Master 101 > Field Master 101 > RT Master 301 > STD2 > Field Master 301 > RT Master > Field Master > STD1.
- the order of efficacy averaged across application rates for ECHF %inhibition was RT Master 21 > RT Master 101 > UltraMax 101 > UltraMax 21 > RT Master 301 > UltraMax 301 > STD 3 > RT Master > Field Master 21 > Field Master 101 > Field Master > Field Master 301 > STD1.
- compositions of Table 4a and comparative compositions Roundup® RTU, Fallow Master®, STD1 and STD2 were applied to velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti, ABUTH) and Japanese millet (Echinochloa crus-galli var. frumentae, ECHCF) plants. Results at 14 days after treatment (14DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 4b. Table 4b.
- the order of efficacy averaged across application rates for the ABUTH %inhibition was FallowMaster 21 > FallowMaster 101 > FallowMaster 301 > UltraMax 21 > UltraMax 101 > FallowMaster > UltraMax 301 > STD2 > RTU 21 > Roundup RTU > RTU 101 > STU 301 > STD1.
- the order of efficacy averaged across application rates for ECHF %inhibition was FallowMaster 301 > FallowMaster 101 > FallowMaster 21 > FallowMaster > UltraMax 21 > UltraMax 101 > STD 3 > UltraMax 301 > STD1 > Roundup RTU > RTU 301 > RTU 21 > RTU 101.
- compositions of Table 5a and comparative composition RT MasterTM were applied to pitted momingglory (IPOLA) and cocklebur (XANST) plants. Results at 10 days after treatment (10DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 5b.
- compositions of Table 6a and comparative compositions RT MasterTM and STD2 were applied to pitted momingglory (IPOLA). Results at 5 days after treatment (5DAT) and 12 days after treatment (12DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 6b.
- compositions of Table 7a and comparative composition 128A5X were applied to Zebrina pendula (ZEBPE). Results at 29 days after treatment (29DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 7b. Table 7b.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in g a.e./L and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 8a.
- compositions of Table 8a and comparative composition 128A5X were applied to Zebrina pendula (ZEBPE). Results at 28 days after treatment (28DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 8b.
- the most active composition was 128A5X.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 9a.
- compositions of Table 9a and comparative composition 128A5X were applied to Zebrina pendula (ZEBPE). Results at 27 days after treatment (27DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 9b. Table 9b.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 10a.
- compositions of Table 10a and comparative composition T28A5X were applied to commelina (COMBE). Results at 33 days after treatment (33DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 10b. Table 10b.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 11a.
- compositions of Table 11a and comparative composition 128A5X were applied to commelina (COMBE). Results at 20 days after treatment (20DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 11b. Table 11 b.
- the most active composition was 128A5X.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 12a.
- Formulation 553I3Z was the most effective composition for commelina.
- compositions of Table 13a and RT Master were applied to commelina (COMBE). Results at 20 days after treatment (20DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 13b. Table 13b.
- compositions in this example were RT Master and 481Z7Y. These results indicate that a second active ingredient (2,4-D or carfentrazone) increases the activity of the composition against commelina.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 14a, as well as those shown in Table 13a.
- compositions of Tables 13a and 14a and RT Master were applied to commelina (COMBE). Results at 10 days after treatment (10DAT), 24 days after treatment (24DAT) and 41 days after treatment (41 DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 14b. Table 14b.
- compositions that were most effective, particularly against commelina regrowth were 822B9T, 822C6U and RT Master, which all contain 2,4-D as a second active ingredient.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 15a.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 16a.
- compositions of Table 16a, Assure II and RT Master were applied to commelina (COMBE). Results at 7 days after treatment (7DAT) and 31 days after treatment (31 DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 16b.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 17a.
- RT Master was the most effective composition for controlling momingglory at 7 and 15 days after treatment.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing the listed amount of glyphosate salt in wt% and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 18a. Table 18a.
- compositions of Table 18a, Pursuit and RT Master were applied to momingglory (IPOSS). Results at 14 days after treatment (14DAT), averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 18b. Table 18b.
- RT Master was the most efficacious composition at the application levels of the experiment.
- Aqueous compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, IPA 2,4-D salt and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 19a.
- the formulations were prepared by mixing the 40.5% w/w a.e. aqueous solution of IPA 2,4-D to a concentration in w/w% as indicated by [2,4-D] in Table 19a, surfactant(s), glycol followed by addition of 47.8 (47.4)% w/w a.e. aqueous solution of potassium glyphosate to a concentration in w/w% as indicated by [gly] in Table 19a and then taking the total volume to 100% with water.
- Formulations were tested for cloud point and for density. Table 19a.
- aqueous compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, 2,4-D acid and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 19b.
- the formulations were prepared by mixing the 98% w/w a.e. aqueous solution of 2,4-D acid to a concentration in w/w% as indicated by [2,4- D] in Table 19b, surfactant(s), glycol followed by addition of 47.8 (47.4)% w/w a.e. aqueous solution of potassium glyphosate to a concentration in w/w% as indicated by [gly] in Table 19b and then taking the total volume to 100% with water.
- Formulations were tested for cloud point and for density.
- aqueous compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, octyl amine 2,4-D salt and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 19c.
- the formulations were prepared by mixing an aqueous solution of 2,4-D octyl amine salt to a concentration in w/w% as indicated by [2,4-D] in Table 19b, surfactant(s), glycol followed by addition of 47.8 (47.4)% w/w a.e. aqueous solution of potassium glyphosate to a concentration in w/w% as indicated by [gly] in Table 19b and then taking the total volume to 100% with water.
- Formulations were tested for cloud point and for density. Table 19c.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, reported in wt.% a.e. and excipient ingredients as shown for the formulations in Table 19a above.
- the formulations were compared to RT Master® and Roundup Weathermax®.
- the compositions comparative compositions RT Master® and Roundup Weathermax®, were applied to velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti, ABUTH) plants. Results, averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 21a. Table 21a.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, reported in wt.% a.e. and excipient ingredients as shown for formulations in Table 22a.
- the formulations were compared to RT Master® and Roundup Weathermax®.
- the 681 C4J composition in Table 19a, compositions in Table 22a and comparative compositions RT Master® and Roundup Weathermax®, were applied to velvetleaf (Abutilon theophrasti, ABUTH) plants. Results, averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 22b. Table 22a.
- Aqueous concentrate compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, reported in wt.% a.e. and excipient ingredients as shown for formulations in Tables 22a. The formulations were compared to RT Master® and Roundup Weathermax®.
- Example 24 The experiment in Example 24 was repeated using an TT nozzle to apply the formulations to the Roundup ready soybean plants. Results, averaged for all replicates of each treatment, are shown in Table 25a.
- Aqueous compositions were prepared containing potassium glyphosate salt, dicamba and excipient ingredients as shown in Table 26a. Formulations were tested for cloud point and for density. Table 26a.
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Pest Control & Pesticides (AREA)
- Agronomy & Crop Science (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL05725288T PL1722634T3 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| BRPI0508542-0A BRPI0508542B1 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | HERBICIDE CONCENTRATE COMPOSITIONS UNDERSTANDING GLYPHOSATE AND AUXINE HERBICIDE |
| AT05725288T ATE517548T1 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | HERBICIDAL COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING N-PHOSPHONOMETHYLGLYCINE AND AN AUXIN HERBICIDE |
| BR122014007725A BR122014007725B1 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | method of killing or controlling weeds or unwanted plants comprising applying glyphosate aqueous herbicide concentrate composition |
| EP05725288.4A EP1722634B2 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| ES05725288T ES2368721T5 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethylglycine and an auxin herbicide |
| CA2558642A CA2558642C (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| AU2005221166A AU2005221166C1 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US55206504P | 2004-03-10 | 2004-03-10 | |
| US60/552,065 | 2004-03-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2005087007A1 true WO2005087007A1 (en) | 2005-09-22 |
Family
ID=34962570
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2005/008029 WO2005087007A1 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2005-03-10 | Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (5) | US20060019828A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1722634B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1960634A (en) |
| AT (1) | ATE517548T1 (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2005221166C1 (en) |
| BR (2) | BR122014007725B1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2558642C (en) |
| ES (1) | ES2368721T5 (en) |
| PL (1) | PL1722634T3 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2005087007A1 (en) |
| ZA (1) | ZA200607467B (en) |
Cited By (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2006127501A2 (en) | 2005-05-24 | 2006-11-30 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| WO2007147208A1 (en) * | 2006-06-23 | 2007-12-27 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Phenoxy alkanoate herbicidal composition and method of preparation and use |
| WO2009006169A2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2009-01-08 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| US20090305896A1 (en) * | 2006-12-06 | 2009-12-10 | Akzo Nobel N.V. | Compatibility agents for herbicidal formulations comprising 2,4-(Dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid salts |
| US8293683B2 (en) | 2006-12-06 | 2012-10-23 | Akzo Nobel N.V. | Alkylamidopropyl dialkylamine surfactants as adjuvants |
| DE102012002272A1 (en) | 2012-02-04 | 2013-08-08 | Clariant International Ltd. | Pesticidal compositions |
| WO2013149999A1 (en) * | 2012-04-05 | 2013-10-10 | Basf Se | Soluble liquid formulations of quinclorac ammonium salts |
| WO2011140020A3 (en) * | 2010-05-04 | 2013-11-14 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a dicamba derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| US20140080706A1 (en) * | 2011-06-01 | 2014-03-20 | Basf Se | Method of preparing an aqueous tank mix comprising a base |
| US20140171319A1 (en) * | 2011-08-02 | 2014-06-19 | Basf Se | Aqueous Composition Comprising a Pesticide and a Base Selected from an Alkali Salt of Hydrogencarbonate |
| EP2744347A1 (en) * | 2011-08-16 | 2014-06-25 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Complexes of herbicidal carboxylic acids and amine-containing polymers or oligomers |
| WO2014154603A1 (en) * | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-02 | Akzo Nobel Chemicals International B.V. | Concentrated agricultural composition |
| AU2013203311B2 (en) * | 2005-05-24 | 2014-11-06 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicidal compatability improvement |
| AU2013201552B2 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2015-01-15 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| EP2934122A4 (en) * | 2012-11-05 | 2016-07-13 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Auxin herbicidal mixtures |
| RU2658989C2 (en) * | 2013-10-22 | 2018-06-26 | Акцо Нобель Кемикалз Интернэшнл Б.В. | Simple polysaccharides ethers highly concentrated liquid forms |
| US10285404B2 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2019-05-14 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Glyphosate composition for dicamba tank mixtures with improved volatility |
| US10334849B2 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2019-07-02 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Salts of carboxylic acid herbicides |
| US10455837B2 (en) | 2015-08-26 | 2019-10-29 | Dow Argosciences Llc | Complexes of cloquintocet and amine-containing polymers or oligomers |
| US10499646B2 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2019-12-10 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| US10736322B2 (en) | 2012-06-04 | 2020-08-11 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Aqueous concentrated herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate salts and dicamba salts |
| US11503826B2 (en) | 2009-08-10 | 2022-11-22 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Low volatility auxin herbicide formulations |
Families Citing this family (35)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2006096617A2 (en) | 2005-03-04 | 2006-09-14 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Mitigating necrosis in transgenic glyphosate-tolerant cotton plants treated with herbicidal glyphosate formulations |
| US7855326B2 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2010-12-21 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Methods for weed control using plants having dicamba-degrading enzymatic activity |
| BRPI0712484B1 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2017-06-06 | Monsanto Technology Llc | method for selecting transformed cells |
| US7838729B2 (en) | 2007-02-26 | 2010-11-23 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of DMO and uses thereof |
| BRPI0914226B1 (en) * | 2008-06-18 | 2021-01-19 | Stepan Company | concentrate containing ultra high load glyphosate salt, method for making it and method for controlling unwanted vegetation |
| BRPI0910494A2 (en) * | 2008-07-08 | 2015-07-28 | Akzo Nobel Nv | Solubilization method of an active plant growth regulator |
| AR074976A1 (en) * | 2008-09-29 | 2011-03-02 | Monsanto Technology Llc | FORMULATIONS OF GLYPHOSPHATE CONTAINING TENSIOACTIVE AGENTS OF AMIDO ALKYLAMINES |
| CA2758727C (en) | 2009-04-22 | 2017-09-19 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | High-strength, herbicidal compositions of glyphosate and 2,4-d salts |
| CA2765888C (en) * | 2009-06-25 | 2017-11-21 | Hong Zhang | Herbicidal concentrate compositions containing glyphosate and dicamba salts |
| CN102027911B (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2013-06-19 | 南京华洲药业有限公司 | Herbicidal composition containing dithiopyr and 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid and application thereof |
| CN102027912B (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2013-01-23 | 南京华洲药业有限公司 | Herbicide composition containing dithiopyr and clopyralid and application thereof |
| CN102027923B (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2013-01-23 | 南京华洲药业有限公司 | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing picloram and pendimethalin and application thereof |
| CN102027924B (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2013-01-23 | 南京华洲药业有限公司 | Herbicidal composition containing picloram and dicamba |
| CN102027960B (en) * | 2009-09-28 | 2013-01-23 | 南京华洲药业有限公司 | Herbicidal composition containing picloram and isoproturon and application thereof |
| US8618179B2 (en) * | 2010-01-18 | 2013-12-31 | Basf Se | Composition comprising a pesticide and an alkoxylate of 2-propylheptylamine |
| PE20121692A1 (en) * | 2010-01-18 | 2012-11-30 | Basf Se | COMPOSITION INCLUDING A PESTICIDE AND A 2-PROPYLHEPTILAMINE ALCOXYLATE |
| US20110201497A1 (en) * | 2010-02-16 | 2011-08-18 | Basf Se | Composition Comprising A Pesticide and an Alkoxylate of Iso-Heptadecylamine |
| EP2384625A1 (en) * | 2010-05-06 | 2011-11-09 | Akzo Nobel Chemicals International B.V. | Surfactant blends for auxin activity herbicides |
| US9258996B2 (en) * | 2010-03-17 | 2016-02-16 | Basf Se | Composition comprising a pesticide and an alkoxylate of iso-nonylamine |
| JP5931875B2 (en) * | 2010-08-24 | 2016-06-08 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | Compositions and methods for improving the compatibility of water-soluble herbicide salts |
| GB201101743D0 (en) * | 2011-02-01 | 2011-03-16 | Syngenta Ltd | Herbicidal compositions |
| EP2680692B1 (en) | 2011-02-28 | 2017-04-12 | Basf Se | Composition comprising a pesticide, an alkoxylate of 2-propylheptylamine and a further surfactant |
| CN102907422A (en) * | 2012-10-16 | 2013-02-06 | 江苏钟山化工有限公司 | Water-borne thickener composition and preparation method as well as application thereof |
| AU2013337293B2 (en) | 2012-11-05 | 2017-06-15 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Low volatility herbicidal compositions |
| NZ736753A (en) * | 2013-10-11 | 2018-11-30 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Aqueous herbicidal concentrates |
| CN104381296A (en) * | 2014-11-25 | 2015-03-04 | 广东中迅农科股份有限公司 | Weeding composition containing picloram and glyphosate |
| CN105145622B (en) * | 2015-09-25 | 2017-07-28 | 山东潍坊润丰化工股份有限公司 | The Herbicidal combinations and its compounding method and application of a kind of glyphosate salt and 2,4 D esters |
| CN109310095A (en) | 2016-05-11 | 2019-02-05 | 孟山都技术公司 | The glyphosate formulation of amide-containing alkylamine surfactant |
| CN106962394A (en) * | 2017-03-12 | 2017-07-21 | 安徽省益农化工有限公司 | A kind of high-efficiency ammonia chloropyridines weeds herbicide |
| CA3065526A1 (en) * | 2017-06-13 | 2018-12-20 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Auxin herbicidal compositions containing an ammonium compound |
| IT201700095717A1 (en) * | 2017-08-24 | 2019-02-24 | Lamberti Spa | HERBICIDE COMPOSITION |
| UY38029A (en) | 2017-12-22 | 2019-07-31 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Aqueous HERBICIDE COMPOSITIONS THAT INCLUDE A GLUFOSINATE COMPONENT AND A AUXINE HERBICIDE COMPONENT |
| US12052993B2 (en) * | 2018-05-25 | 2024-08-06 | Upl Ltd | Aqueous herbicidal intermixtures |
| US20220338474A1 (en) * | 2019-09-20 | 2022-10-27 | Rhodia Operations | Stable herbicidal compositions comprising amine oxide and tertiary amine |
| CN112471171B (en) * | 2020-12-11 | 2022-03-29 | 黑龙江恒元汉麻科技有限公司 | Application of hemp stem field standing degumming agent for fibers and degumming process method |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002096199A2 (en) | 2001-05-21 | 2002-12-05 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Stable liquid pesticide compositions |
Family Cites Families (184)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US303A (en) * | 1837-07-29 | Cooking-stove | ||
| US2505059A (en) | 1946-08-16 | 1950-04-25 | Baker Chem Co J T | 2, 4-d salt and composition containing the same |
| GB851008A (en) | 1958-03-28 | 1960-10-12 | Amchem Prod | New amine salts of aromatic acids, their use in herbicidal compositions and processes for their production |
| US3013054A (en) | 1958-08-04 | 1961-12-12 | Velsicol Chemical Corp | 2-methoxy-3, 6-dichlorobenzoates |
| US3276856A (en) | 1965-03-22 | 1966-10-04 | Amchem Prod | Herbicidal compositions |
| US3852340A (en) | 1966-09-26 | 1974-12-03 | Akzona Inc | Plant hormone carboxylic acid salts of aliphatic polyamines |
| DE1913049C3 (en) | 1968-03-21 | 1979-10-31 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Co., Saint Paul, Minn. (V.St.A.) | Pesticides for combating plants in water |
| US3594151A (en) | 1968-11-12 | 1971-07-20 | Diamond Shamrock Corp | Herbicidally active spray composition |
| US3600407A (en) | 1969-04-04 | 1971-08-17 | Velsicol Chemical Corp | Furfuryl-2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoate |
| US3751239A (en) | 1969-05-29 | 1973-08-07 | Rohm & Haas | Herbicidal compositions containing n-(1,1-dialkyl-3-chloroacetonyl) benzamides |
| US3799758A (en) | 1971-08-09 | 1974-03-26 | Monsanto Co | N-phosphonomethyl-glycine phytotoxicant compositions |
| US3713404A (en) | 1971-04-16 | 1973-01-30 | Gen Foods Corp | Plant husbandry |
| US3870732A (en) | 1973-08-21 | 1975-03-11 | Velsicol Chemical Corp | Mixed salts of aluminum |
| US4022610A (en) | 1973-10-15 | 1977-05-10 | Velsicol Chemical Corporation | Herbicidal mixed salts of magnesium |
| US3910974A (en) | 1973-10-15 | 1975-10-07 | Velsicol Chemical Corp | Mixed salts of magnesium of 2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoic acid and a carboxylic acid |
| US3923849A (en) | 1973-10-29 | 1975-12-02 | Velsicol Chemical Corp | Aluminum salts of 2-methoxy-3,6-dichlorobenzoic acid |
| US4405531A (en) | 1975-11-10 | 1983-09-20 | Monsanto Company | Salts of N-phosphonomethylglycine |
| HU182980B (en) * | 1979-12-28 | 1984-03-28 | Nitrokemia Ipartelepek | Concentrates and spray solutions containing n-bracket-phosphono-methyl-bracket closed-glycine |
| US4936900A (en) | 1983-04-04 | 1990-06-26 | E. I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Stabilized aqueous formulations of sulfonylurea salts |
| US4692184A (en) | 1984-04-24 | 1987-09-08 | Monsanto Company | 2,6-substituted pyridine compounds |
| US4534783A (en) | 1984-01-03 | 1985-08-13 | Monsanto Co. | High concentration encapsulation of water soluble-materials |
| US4546196A (en) | 1984-06-11 | 1985-10-08 | Velsicol Chemical Corporation | 3-Chlorobenzyl-3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzoate |
| CA1242748A (en) | 1984-11-26 | 1988-10-04 | Rita S. Jones | Salt of dicamba |
| USH224H (en) * | 1985-05-30 | 1987-03-03 | A. E. Staley Manufacturing Company | Glycoside-containing agricultural treatment composition |
| GB8528856D0 (en) * | 1985-11-22 | 1985-12-24 | Ici Plc | Herbicidal compounds |
| US5188958A (en) | 1986-05-29 | 1993-02-23 | Calgene, Inc. | Transformation and foreign gene expression in brassica species |
| US4936901A (en) | 1986-07-09 | 1990-06-26 | Monsanto Company | Formulations of water-dispersible granules and process for preparation thereof |
| US4729781A (en) | 1986-08-04 | 1988-03-08 | Sandoz Ltd. | 3,6-dichloro-2-methoxybenzohydroxamic acid derivatives and use as herbicidal agents |
| US6312679B1 (en) | 1986-08-18 | 2001-11-06 | The Dow Chemical Company | Dense star polymer conjugates as dyes |
| US5004863B2 (en) | 1986-12-03 | 2000-10-17 | Agracetus | Genetic engineering of cotton plants and lines |
| US5015580A (en) | 1987-07-29 | 1991-05-14 | Agracetus | Particle-mediated transformation of soybean plants and lines |
| EP0270496B1 (en) | 1986-12-05 | 1993-03-17 | Ciba-Geigy Ag | Method for the transformation of plant protoplasts |
| CA1293974C (en) | 1986-12-29 | 1992-01-07 | Richard G. Hebbourn | Preparation of alkanolamine salts of carboxylic acid herbicides |
| US5668085A (en) * | 1987-04-29 | 1997-09-16 | Monsanto Company | Glyphosate formulations comprising alkoxylated amine surfactants |
| EP0290416B2 (en) | 1987-04-29 | 2005-03-16 | Monsanto Europe S.A. | Improved glyphosate formulations |
| DE3719264A1 (en) * | 1987-06-10 | 1988-12-29 | Hoechst Ag | LIQUID PESTICIDAL MIXTURE |
| US5250500A (en) | 1988-02-08 | 1993-10-05 | Floratine Products Group | Herbicidal compositions containing tetrapotassium pyrophosphate as spray adjuvant |
| US5416011A (en) | 1988-07-22 | 1995-05-16 | Monsanto Company | Method for soybean transformation and regeneration |
| NZ230497A (en) | 1988-09-02 | 1992-05-26 | Du Pont | Layered, granular water-soluble or water-dispersible pesticide |
| US5035738A (en) | 1988-12-23 | 1991-07-30 | Sandoz Ltd. | Aminopropylmorpholine salts, compositions and uses thereof |
| NZ231897A (en) | 1988-12-30 | 1992-09-25 | Monsanto Co | Dry water-soluble granular composition comprising glyphosate and a liquid surfactant |
| US5550318A (en) | 1990-04-17 | 1996-08-27 | Dekalb Genetics Corporation | Methods and compositions for the production of stably transformed, fertile monocot plants and cells thereof |
| US7705215B1 (en) | 1990-04-17 | 2010-04-27 | Dekalb Genetics Corporation | Methods and compositions for the production of stably transformed, fertile monocot plants and cells thereof |
| WO1991010725A1 (en) | 1990-01-22 | 1991-07-25 | Dekalb Plant Genetics | Fertile transgenic corn plants |
| US5484956A (en) | 1990-01-22 | 1996-01-16 | Dekalb Genetics Corporation | Fertile transgenic Zea mays plant comprising heterologous DNA encoding Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxin |
| US5834006A (en) | 1990-04-05 | 1998-11-10 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Latex-based agricultural compositions |
| US5703015A (en) * | 1990-08-09 | 1997-12-30 | Monsanto Company | Pesticidal compositions of polyoxyalkylene alkylamine surfactants having reduced eye irritation |
| US6403865B1 (en) | 1990-08-24 | 2002-06-11 | Syngenta Investment Corp. | Method of producing transgenic maize using direct transformation of commercially important genotypes |
| DE4030687A1 (en) | 1990-09-28 | 1991-05-16 | Kast Walter Klaus Dr Sc Agr | Weed control in viniculture and fruit growing - using dil natural or synthetic acetic acid, opt. with surfactant |
| AU658150B2 (en) | 1990-10-04 | 1995-04-06 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Improved formulations |
| US5384253A (en) | 1990-12-28 | 1995-01-24 | Dekalb Genetics Corporation | Genetic transformation of maize cells by electroporation of cells pretreated with pectin degrading enzymes |
| ATE150254T1 (en) | 1991-01-24 | 1997-04-15 | Monsanto Co | FORMULATIONS OF GLYPHOSATES |
| FR2675014B1 (en) | 1991-04-09 | 1993-06-25 | Rhone Poulenc Chimie | AQUEOUS COMPOSITIONS OF PHYTOSANITARY ACTIVE MATERIALS COMPRISING SUCROGLYCERIDES. |
| US5883046A (en) | 1991-06-05 | 1999-03-16 | Sandoz Ltd. | Microencapsulated agricultural chemicals |
| US5733848A (en) | 1991-06-05 | 1998-03-31 | Sandoz Ltd. | Process for making microparticulate agricultural chemicals |
| US5221319A (en) | 1991-08-16 | 1993-06-22 | Pbi-Gordon Corporation | Dry, water-soluble, substituted phenoxy and/or benzoic acid herbicidal compositions and method of preparing same |
| US5518908A (en) | 1991-09-23 | 1996-05-21 | Monsanto Company | Method of controlling insects |
| US5266553A (en) | 1991-10-21 | 1993-11-30 | Riverdale Chemical Company | Method of manufacturing a dry water-soluble herbicidal salt composition |
| US5229355A (en) | 1992-02-28 | 1993-07-20 | Isp Investments Inc. | Leaching inhibition of crop treating chemicals with polymers |
| US5231070A (en) | 1992-02-28 | 1993-07-27 | Isp Investments Inc. | Leaching inhibition of crop treating chemicals with lactam containing polymers |
| US5283228A (en) | 1992-07-27 | 1994-02-01 | Isp Investments, Inc. | Leaching inhibition of crop treating chemicals with amino containing polymers |
| US5229354A (en) | 1992-02-28 | 1993-07-20 | Isp Investments Inc. | Leaching inhibition of crop treating chemicals with nitrogen containing polymers |
| GB2267825B (en) | 1992-05-26 | 1995-08-30 | Dowelanco | Herbicidal aqueous-based microemulsion compositions |
| EP0604662B1 (en) | 1992-07-07 | 2008-06-18 | Japan Tobacco Inc. | Method of transforming monocotyledon |
| US5317003A (en) * | 1992-07-16 | 1994-05-31 | Monsanto Company | Herbicidal compositions comprising glyphosate salts and alkoxylated quaternary amine surfactants |
| JP3345930B2 (en) | 1993-01-06 | 2002-11-18 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Active control device |
| US5565409A (en) | 1993-04-02 | 1996-10-15 | Monsanto Company | Liquid concentrated herbicidal microemulsion compositions comprising glyphosate and either oxyfluorfen or acifluorfen |
| US5374603A (en) | 1993-04-23 | 1994-12-20 | Dowelanco | Agricultural formulations comprising fluroxypyr esters which are liquid at 25° C. |
| NZ277191A (en) | 1993-12-17 | 1998-05-27 | Monsanto Co | Enhanced rain-fastness biocides comprising secondary or tertiary alcohol surfactants, glyphosates, and tertiary alkylamine surfactants |
| US5631152A (en) | 1994-10-26 | 1997-05-20 | Monsanto Company | Rapid and efficient regeneration of transgenic plants |
| DE4444708A1 (en) | 1994-12-15 | 1996-06-20 | Basf Ag | Use of auxin-type herbicides for the treatment of transgenic crop plants |
| US5643853A (en) | 1995-02-28 | 1997-07-01 | Purdue Research Foundation | Thiol activation of cytotoxic and auxin-herbicidal agents and root formation stimulation |
| US5965487A (en) | 1995-03-15 | 1999-10-12 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Mixed herbicidal compositions |
| US5698210A (en) * | 1995-03-17 | 1997-12-16 | Lee County Mosquito Control District | Controlled delivery compositions and processes for treating organisms in a column of water or on land |
| US5750468A (en) * | 1995-04-10 | 1998-05-12 | Monsanto Company | Glyphosate formulations containing etheramine surfactants |
| PT820231E (en) † | 1995-04-10 | 2000-05-31 | Monsanto Co | GLYPHOSATE FORMULATIONS CONTAINING ETERAMINE SURFACTANTS |
| PL328095A1 (en) | 1995-10-25 | 1999-01-04 | Du Pont | Herbicidal sulphonamides |
| AR004705A1 (en) | 1995-11-07 | 1999-03-10 | Sabba Da Silva Lima Michele | LIQUID AGROCHEMICAL COMPOSITION, METHOD TO CONVERT IT INTO A STABLE LIQUID AND ADJUVANT COMPOSITION FOR THE PREPARATION OF THE SAME. |
| DE19607633A1 (en) | 1996-02-29 | 1997-09-04 | Bayer Ag | Herbicidal agents based on N-phosphonomethyl-glycine esters |
| EP0808569A1 (en) | 1996-05-24 | 1997-11-26 | Monsanto Europe S.A./N.V. | New herbicidal compositions and use thereof |
| US6586367B2 (en) * | 1996-09-05 | 2003-07-01 | Syngenta Crop Protection, Inc. | Process for the control of weeds |
| US6107249A (en) | 1996-10-07 | 2000-08-22 | Zeneca Limited | Glyphosate formulations |
| US6245713B1 (en) | 1996-10-25 | 2001-06-12 | Monsanto Company | Plant treatment compositions having enhanced biological effectiveness |
| US5981840A (en) | 1997-01-24 | 1999-11-09 | Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. | Methods for agrobacterium-mediated transformation |
| CZ299866B6 (en) | 1997-06-30 | 2008-12-17 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Fungicide controlled-release particles, composition, seeds, method of delivering agricultural chemical to a plant, and method of producing the composition |
| NZ502397A (en) | 1997-07-22 | 2002-04-26 | Monsanto Co | Storage stable high-loaded ammonium glyphosate and surfactant formulations |
| NZ502499A (en) | 1997-07-30 | 2001-11-30 | Monsanto Co | Herbicide consisting of glyphosate composition and polyamine derivatives |
| US5877112A (en) | 1997-08-27 | 1999-03-02 | Helena Chemical Company | Agricultural formulation |
| DE19815820A1 (en) * | 1998-04-08 | 1999-10-14 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Synergistic herbicidal agents based on leaf herbicides containing phosphorus, imidazolinones and growth herbicides |
| PL198545B1 (en) | 1998-07-29 | 2008-06-30 | Syngenta Ltd | Base-triggered release microcapsules |
| MY117587A (en) | 1998-07-30 | 2004-07-31 | Syngenta Ltd | Acid-triggered release microcapsules |
| DE19836737A1 (en) | 1998-08-13 | 2000-02-17 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Use of a synergistic herbicide combination including a glufosinate- or glyphosate-type, imidazolinone, protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitory azole or cyclohexanedione herbicide to control weeds in maize |
| DE19836660A1 (en) | 1998-08-13 | 2000-02-17 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Use of a synergistic herbicide combination including a glufosinate- or glyphosate-type, imidazolinone or protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitory azole herbicide to control weeds in soya |
| DE19836726A1 (en) | 1998-08-13 | 2000-02-17 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Use of a synergistic herbicide combination including glufosinate- or glyphosate-type, imidazolinone or protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitory azole herbicide to control weeds in oil seed rape |
| DE19836700A1 (en) | 1998-08-13 | 2000-02-17 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Use of a synergistic herbicide combination including a glufosinate- or glyphosate-type, imidazolinone or protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitory azole herbicide to control weeds in cereals |
| DE19836684A1 (en) | 1998-08-13 | 2000-02-17 | Hoechst Schering Agrevo Gmbh | Use of a synergistic herbicidal combination including a glufosinate- or glyphosate-type, imidazolinone or protoporphyrinogen oxidase to control weeds in rice |
| ES2405266T3 (en) * | 1998-08-13 | 2013-05-30 | Bayer Cropscience Ag | Herbicidal agents for tolerant or resistant corn crops |
| GB9819693D0 (en) | 1998-09-10 | 1998-11-04 | Zeneca Ltd | Glyphosate formulation |
| DE69920035T2 (en) | 1998-11-23 | 2005-09-15 | Monsanto Technology Llc. | HIGHLY CONCENTRATED AQUEOUS GLYPHOSATE COMPOSITIONS |
| NZ511853A (en) * | 1998-11-23 | 2003-12-19 | Monsanto Co | Compact storage and shipping system for glyphosate herbicide |
| EP1135024B1 (en) | 1998-11-30 | 2004-12-29 | Flamel Technologies | Promoting biological effectiveness of exogenous chemical substances in plants |
| WO2000042207A2 (en) | 1999-01-14 | 2000-07-20 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Soybean transformation method |
| US6432878B1 (en) | 1999-01-15 | 2002-08-13 | Cognis Corporation | Adjuvant composition |
| ATE282311T1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2004-12-15 | Basf Ag | AQUEOUS SUSPENSION CONCENTRATE |
| UA72761C2 (en) | 1999-04-23 | 2005-04-15 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Compositions and method of eliminating plant growth or controlling thereof |
| AUPQ017699A0 (en) | 1999-05-05 | 1999-05-27 | Victorian Chemicals International Pty Ltd | Agrochemical composition |
| US6774087B1 (en) | 1999-06-22 | 2004-08-10 | Fmc Corporation | Liquid herbicide composition |
| US6713433B2 (en) | 1999-08-11 | 2004-03-30 | Monsanto Technology, Llc | Coformulation of an oil-soluble herbicide and a water-soluble herbicide |
| US6908882B1 (en) | 1999-09-09 | 2005-06-21 | Monsanto Company | Enhanced method of killing weeds with glyphosate herbicide |
| JP5433120B2 (en) | 1999-09-30 | 2014-03-05 | モンサント テクノロジー エルエルシー | Packaged mix pesticide composition with improved stability |
| CN1192707C (en) * | 1999-10-26 | 2005-03-16 | 陶氏益农有限责任公司 | Thick suspending agent of herbicide |
| HUP0301968A3 (en) | 1999-11-17 | 2004-06-28 | Bayer Ag | Selective and synergistic herbicide compositions containing 2,6-disubstituted pyridine derivatives, preparation and use thereof |
| US6939555B2 (en) | 2000-01-21 | 2005-09-06 | Helena Holding Company | Manufacture and use of an deposition aid |
| US6992045B2 (en) | 2000-05-19 | 2006-01-31 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Pesticide compositions containing oxalic acid |
| MY158895A (en) † | 2000-05-19 | 2016-11-30 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Potassium glyphosate formulations |
| US6300323B1 (en) * | 2000-08-08 | 2001-10-09 | Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Ltd. | (Poly)ethereal ammonium salts of herbicides bearing acidic moieties and their use as herbicides |
| US7008904B2 (en) | 2000-09-13 | 2006-03-07 | Monsanto Technology, Llc | Herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate and bipyridilium |
| US6410783B1 (en) | 2000-10-19 | 2002-06-25 | Basf Corporation | Method of producing carboxylic acid salts |
| US8232230B2 (en) | 2000-12-01 | 2012-07-31 | Helena Holding Company | Manufacture and use of a herbicide formulation |
| US6992047B2 (en) | 2001-04-11 | 2006-01-31 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Method of microencapsulating an agricultural active having a high melting point and uses for such materials |
| DE60236428D1 (en) * | 2001-05-21 | 2010-07-01 | Monsanto Technology Llc | ETHERAMIN-TENSIDE-CONTAINING PESTICIDE CONCENTRATES |
| AUPR682201A0 (en) | 2001-08-03 | 2001-08-30 | Nufarm Limited | Glyphosate composition |
| WO2003024218A1 (en) | 2001-09-14 | 2003-03-27 | Professor Sigge & Martin Ab | Method of inhibiting plant growth or sprouting of tubers |
| BR0212870A (en) | 2001-09-26 | 2004-10-13 | Platte Chemical Co | Herbicidal composition, suspension concentrate and methods of exterminating or controlling unwanted growth and vegetation and of preparing a herbicidal composition and suspension concentrate |
| US6579831B1 (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2003-06-17 | Nufarms Americas Inc | Liquid herbicidal compositions and use thereof in a granular herbicide |
| RU2208930C1 (en) | 2002-02-13 | 2003-07-27 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Экстерн" | Herbicide composition for control of weed |
| US20040138176A1 (en) | 2002-05-31 | 2004-07-15 | Cjb Industries, Inc. | Adjuvant for pesticides |
| WO2003101197A1 (en) | 2002-05-31 | 2003-12-11 | Cjb Industries, Inc. | Adjuvant for pesticides |
| WO2004019684A2 (en) | 2002-08-31 | 2004-03-11 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Process for the preparation of a dry pesticidal composition containing a dicarbodylate component |
| CN1513326A (en) | 2002-12-31 | 2004-07-21 | 中山市除害消毒管理站 | High effective hygienic pesticide for controlling mosquito and flies and accelerating growth of plants |
| US20050026781A1 (en) | 2003-04-22 | 2005-02-03 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate and a pyridine analog |
| EP2712503A3 (en) | 2003-04-22 | 2016-03-23 | Monsanto Technology LLC | Herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate and a pyridine analog |
| US9668471B2 (en) | 2003-05-28 | 2017-06-06 | AgQuam LLC | Manufacture and use of agricultural spray adjuvants for hard water conditions |
| US20070149409A1 (en) | 2003-12-29 | 2007-06-28 | Hi-Cap Formulations Ltd. | Pesticide formulations with substituted biopolymers and organic polymers for improving residual activity, droplet size, adherence and rainfastness on leaves and reduction in soil leaching |
| CN1960634A (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2007-05-09 | 孟山都技术公司 | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| EP2308977B2 (en) | 2004-04-30 | 2017-04-26 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Novel herbicide resistance gene |
| WO2005115144A1 (en) | 2004-05-25 | 2005-12-08 | William Stringfellow | Pesticide composition |
| US20060040828A1 (en) | 2004-08-18 | 2006-02-23 | Jianhua Mao | Biologically active formulation containing polyethyleneimine and its derivatives |
| CA2598184A1 (en) | 2005-02-21 | 2006-08-24 | Basf Aktiengesellschaft | Active substance composition comprising at least one nitrogen atom-containing, hyperbranched polymer |
| US7223718B2 (en) | 2005-03-07 | 2007-05-29 | Falcon Lab Llc | Enhanced glyphosate herbicidal concentrates |
| DE102005014293A1 (en) | 2005-03-24 | 2006-09-28 | Basf Ag | Thickener based on polymers containing amine groups |
| PL1893016T3 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2018-02-28 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | Water-in-oil suspoemulsions |
| WO2006127501A2 (en) | 2005-05-24 | 2006-11-30 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| US7431845B2 (en) | 2005-06-23 | 2008-10-07 | Nalco Company | Method of clarifying oily waste water |
| EP1931760A4 (en) | 2005-10-07 | 2010-10-20 | Univ Alabama | Multi-functional ionic liquid compositions |
| US8883689B2 (en) | 2005-12-06 | 2014-11-11 | Bayer Cropscience Lp | Stabilized herbicidal compositions |
| US20070184980A1 (en) | 2006-01-25 | 2007-08-09 | Helena Holding Company | Manufacture and use of herbicide chlorinated phenoxy formulation |
| KR101424829B1 (en) | 2006-03-24 | 2014-08-01 | 바스프 에스이 | Agrochemical formulations |
| JP5122841B2 (en) | 2006-03-24 | 2013-01-16 | 石原産業株式会社 | Herbicidal composition |
| US7855326B2 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2010-12-21 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Methods for weed control using plants having dicamba-degrading enzymatic activity |
| CA2662492C (en) | 2006-09-06 | 2014-12-16 | Jeffrey Fowler | Pickering emulsion formulations |
| GB0703394D0 (en) | 2007-02-22 | 2007-03-28 | Ciba Sc Holding Ag | Process for Preparing and Applying Pesticide or Herbicide Formulation |
| CA2677979A1 (en) | 2007-02-26 | 2008-09-04 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Ionic liquids derived from herbicidal carboxylic acids and certain trialkylamines or heteroarylamines |
| MX2009008934A (en) | 2007-02-26 | 2009-08-28 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Process for the preparation of certain substituted sulfilimines. |
| RU2366176C2 (en) | 2007-03-13 | 2009-09-10 | Закрытое акционерное общество промышленная группа "Алсико" | Gerbicide composition and method of weed elimination |
| EP2308309B1 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2013-07-31 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| AU2008296737B2 (en) | 2007-08-30 | 2014-01-09 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Stable emulsion formulation hindering interaction across the water-oil interface |
| CN101932236A (en) | 2007-11-07 | 2010-12-29 | 罗地亚管理公司 | Herbicidal composition comprising an aminophosphate or aminophosphonate salt and a viscosity reducing agent |
| US7695541B1 (en) | 2008-03-24 | 2010-04-13 | Frizzell Raymond B | Non-acidic, high calcium load aqueous fertilizer |
| PL2337452T3 (en) | 2008-07-03 | 2015-05-29 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Combinations of derivatized saccharide surfactants and etheramine oxide surfactants as herbicide adjuvants |
| AR074976A1 (en) | 2008-09-29 | 2011-03-02 | Monsanto Technology Llc | FORMULATIONS OF GLYPHOSPHATE CONTAINING TENSIOACTIVE AGENTS OF AMIDO ALKYLAMINES |
| WO2010046422A2 (en) | 2008-10-22 | 2010-04-29 | Basf Se | Use of auxin type herbicides on cultivated plants |
| ES2458348T3 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2014-05-05 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Herbicidal composition based on auxins |
| AU2010202620B2 (en) | 2008-12-23 | 2013-10-31 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Dicamba herbicide composition |
| RU2384064C1 (en) | 2008-12-29 | 2010-03-20 | Государственное учреждение "Научно-исследовательский технологический институт гербицидов и регуляторов роста растений с опытно-экспериментальным производством Академии наук Республики Башкортостан" | Herbicide agent |
| RU2395203C1 (en) | 2009-01-21 | 2010-07-27 | Государственное учреждение "Научно-исследовательский технологический институт гербицидов и регуляторов роста растений с опытно-экспериментальным производством Академии наук Республики Башкортостан" | Herbicide composition |
| BRPI1016228B1 (en) | 2009-03-06 | 2021-02-09 | Syngenta Participations Ag | compatibilized aqueous pesticide formulation, method of inhibiting at least one pest in a harvest area and method of forming said aqueous formulation |
| CA2758727C (en) | 2009-04-22 | 2017-09-19 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | High-strength, herbicidal compositions of glyphosate and 2,4-d salts |
| US20120142533A1 (en) | 2009-06-15 | 2012-06-07 | Accuform Technologies, Llc | Reduced vaporization compositions and methods |
| US20110019652A1 (en) | 2009-06-16 | 2011-01-27 | Powerwave Cognition, Inc. | MOBILE SPECTRUM SHARING WITH INTEGRATED WiFi |
| CA2765888C (en) | 2009-06-25 | 2017-11-21 | Hong Zhang | Herbicidal concentrate compositions containing glyphosate and dicamba salts |
| US20120142532A1 (en) | 2009-08-10 | 2012-06-07 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Low volatility auxin herbicide formulations |
| SG10201710398WA (en) | 2009-09-02 | 2018-01-30 | Akzo Nobel Chemicals Int Bv | Nitrogen- containing surfactants for agricultural use |
| UA108623C2 (en) | 2009-09-30 | 2015-05-25 | LOWER-CELL AMIN ANTI-PESTICIDE SALTS | |
| RU2408188C1 (en) | 2009-11-17 | 2011-01-10 | Государственное учреждение "Научно-исследовательский технологический институт гербицидов и регуляторов роста растений с опытно-экспериментальным производством Академии наук Республики Башкортостан" | Herbicide agent |
| WO2011082161A1 (en) | 2009-12-28 | 2011-07-07 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Alabama For And On Behalf Of The University Of Alabama | Fabrication method for diamond film coating of drill bit |
| CA2785654C (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2018-02-27 | Syngenta Participations Ag | Pesticidal composition |
| EP2566324B2 (en) | 2010-05-04 | 2019-08-28 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Method of controlling undesirable vegetation with a composition comprising a dicamba salt and a glyphosate salt |
| BR112013007821B1 (en) | 2010-10-01 | 2018-05-08 | Nufarm Australia Ltd | Method for the preparation of an aqueous glyphosate concentrate composition having mixture of amine salts |
| GB201101743D0 (en) | 2011-02-01 | 2011-03-16 | Syngenta Ltd | Herbicidal compositions |
| WO2012163824A1 (en) | 2011-06-01 | 2012-12-06 | Basf Se | Method of preparing an aqueous tank mix comprising a base |
| UY34416A (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2013-01-03 | Monsanto Technology Llc | ? CARBOXYL ACID HERBICID SALTS? |
| AR091268A1 (en) | 2012-06-04 | 2015-01-21 | Monsanto Technology Llc | WATER CONCENTRATED HERBICIDE COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING GLYPHOSATE SALTS AND DICAMBA SALTS |
| DK2961276T3 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2018-11-19 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Glyphosate and dicamba tank mixtures with improved volatility |
-
2005
- 2005-03-10 CN CNA200580014758XA patent/CN1960634A/en active Pending
- 2005-03-10 AT AT05725288T patent/ATE517548T1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2005-03-10 PL PL05725288T patent/PL1722634T3/en unknown
- 2005-03-10 US US11/077,279 patent/US20060019828A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2005-03-10 CA CA2558642A patent/CA2558642C/en active Active
- 2005-03-10 BR BR122014007725A patent/BR122014007725B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2005-03-10 BR BRPI0508542-0A patent/BRPI0508542B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2005-03-10 AU AU2005221166A patent/AU2005221166C1/en active Active
- 2005-03-10 EP EP05725288.4A patent/EP1722634B2/en active Active
- 2005-03-10 ES ES05725288T patent/ES2368721T5/en active Active
- 2005-03-10 WO PCT/US2005/008029 patent/WO2005087007A1/en active Application Filing
-
2006
- 2006-09-06 ZA ZA200607467A patent/ZA200607467B/en unknown
-
2010
- 2010-06-04 US US12/802,395 patent/US20110034332A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2014
- 2014-05-08 US US14/273,025 patent/US10499646B2/en active Active
-
2019
- 2019-11-12 US US16/680,994 patent/US11864558B2/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-05-11 US US16/871,148 patent/US20200267988A1/en active Pending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2002096199A2 (en) | 2001-05-21 | 2002-12-05 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Stable liquid pesticide compositions |
Cited By (49)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11864558B2 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2024-01-09 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| US10499646B2 (en) | 2004-03-10 | 2019-12-10 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
| AU2006251766B2 (en) * | 2005-05-24 | 2013-05-30 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| WO2006127501A3 (en) * | 2005-05-24 | 2007-06-28 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| US11154062B2 (en) | 2005-05-24 | 2021-10-26 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| WO2006127501A2 (en) | 2005-05-24 | 2006-11-30 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| US8492309B2 (en) | 2005-05-24 | 2013-07-23 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| US8236731B2 (en) | 2005-05-24 | 2012-08-07 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicide compatibility improvement |
| AU2013203311B2 (en) * | 2005-05-24 | 2014-11-06 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Herbicidal compatability improvement |
| WO2007147208A1 (en) * | 2006-06-23 | 2007-12-27 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Phenoxy alkanoate herbicidal composition and method of preparation and use |
| EP2040551A1 (en) * | 2006-06-23 | 2009-04-01 | Nufarm Australia Limited | Phenoxy alkanoate herbicidal composition and method of preparation and use |
| EP2040551A4 (en) * | 2006-06-23 | 2010-02-17 | Nufarm Australia Ltd | Phenoxy alkanoate herbicidal composition and method of preparation and use |
| US20090305896A1 (en) * | 2006-12-06 | 2009-12-10 | Akzo Nobel N.V. | Compatibility agents for herbicidal formulations comprising 2,4-(Dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid salts |
| US8293683B2 (en) | 2006-12-06 | 2012-10-23 | Akzo Nobel N.V. | Alkylamidopropyl dialkylamine surfactants as adjuvants |
| US9012365B2 (en) | 2006-12-06 | 2015-04-21 | Akzo Nobel N.V. | Compatibility agents for herbicidal formulations comprising 2,4-(Dichlorophenoxy) acetic acid salts |
| AU2008270684B2 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2014-10-02 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| WO2009006169A2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2009-01-08 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| JP2010532371A (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2010-10-07 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | Synergistic herbicidal compositions containing substituted phenoxyalkanoic acid derivatives and glyphosate derivatives |
| WO2009006169A3 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2009-08-06 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| EP2308309A1 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2011-04-13 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| AU2013203187B2 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2015-01-22 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| AU2013201552B2 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2015-01-15 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| EP2505062A1 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2012-10-03 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a substituted phenoxy alkanoic acid derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| US11503826B2 (en) | 2009-08-10 | 2022-11-22 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Low volatility auxin herbicide formulations |
| AU2011248389B2 (en) * | 2010-05-04 | 2014-05-29 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a dicamba derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| JP2013542172A (en) * | 2010-05-04 | 2013-11-21 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing dicamba derivative and glyphosate derivative |
| WO2011140020A3 (en) * | 2010-05-04 | 2013-11-14 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Synergistic herbicidal composition containing a dicamba derivative and a glyphosate derivative |
| JP2016006073A (en) * | 2010-05-04 | 2016-01-14 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | Synergistic herbicide composition containing dicamba derivative and glyphosate derivative |
| US20140080706A1 (en) * | 2011-06-01 | 2014-03-20 | Basf Se | Method of preparing an aqueous tank mix comprising a base |
| US20140171319A1 (en) * | 2011-08-02 | 2014-06-19 | Basf Se | Aqueous Composition Comprising a Pesticide and a Base Selected from an Alkali Salt of Hydrogencarbonate |
| EP2744347A4 (en) * | 2011-08-16 | 2015-04-15 | Dow Agrosciences Llc | Complexes of herbicidal carboxylic acids and amine-containing polymers or oligomers |
| EP2744347A1 (en) * | 2011-08-16 | 2014-06-25 | Dow AgroSciences LLC | Complexes of herbicidal carboxylic acids and amine-containing polymers or oligomers |
| US10334849B2 (en) | 2011-10-26 | 2019-07-02 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Salts of carboxylic acid herbicides |
| WO2013113498A1 (en) | 2012-02-04 | 2013-08-08 | Clariant International Ltd | Pesticide compositions |
| DE102012002272A1 (en) | 2012-02-04 | 2013-08-08 | Clariant International Ltd. | Pesticidal compositions |
| AU2013245040B2 (en) * | 2012-04-05 | 2016-09-29 | Basf Se | Soluble liquid formulations of quinclorac ammonium salts |
| RU2633618C2 (en) * | 2012-04-05 | 2017-10-16 | Басф Се | Soluble liquid compositions of quinclorac ammonium salts |
| WO2013149999A1 (en) * | 2012-04-05 | 2013-10-10 | Basf Se | Soluble liquid formulations of quinclorac ammonium salts |
| US10736322B2 (en) | 2012-06-04 | 2020-08-11 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Aqueous concentrated herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate salts and dicamba salts |
| EP2934122A4 (en) * | 2012-11-05 | 2016-07-13 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Auxin herbicidal mixtures |
| US10485232B2 (en) | 2012-11-05 | 2019-11-26 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Auxin herbicidal mixtures |
| US9743662B2 (en) | 2012-11-05 | 2017-08-29 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Auxin herbicidal mixtures |
| US11452290B2 (en) | 2012-11-05 | 2022-09-27 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Auxin herbicidal mixtures |
| US10285404B2 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2019-05-14 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Glyphosate composition for dicamba tank mixtures with improved volatility |
| US11399544B2 (en) | 2013-02-27 | 2022-08-02 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Glyphosate composition for dicamba tank mixtures with improved volatility |
| RU2619989C2 (en) * | 2013-03-26 | 2017-05-22 | Акцо Нобель Кемикалз Интернэшнл Б.В. | Concentrated agricultural composition |
| WO2014154603A1 (en) * | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-02 | Akzo Nobel Chemicals International B.V. | Concentrated agricultural composition |
| RU2658989C2 (en) * | 2013-10-22 | 2018-06-26 | Акцо Нобель Кемикалз Интернэшнл Б.В. | Simple polysaccharides ethers highly concentrated liquid forms |
| US10455837B2 (en) | 2015-08-26 | 2019-10-29 | Dow Argosciences Llc | Complexes of cloquintocet and amine-containing polymers or oligomers |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| BRPI0508542A (en) | 2007-08-14 |
| US20110034332A1 (en) | 2011-02-10 |
| CN1960634A (en) | 2007-05-09 |
| EP1722634B1 (en) | 2011-07-27 |
| US20200267988A1 (en) | 2020-08-27 |
| CA2558642A1 (en) | 2005-09-22 |
| AU2005221166B2 (en) | 2011-07-14 |
| ATE517548T1 (en) | 2011-08-15 |
| AU2005221166A1 (en) | 2005-09-22 |
| CA2558642C (en) | 2017-08-08 |
| AU2005221166C1 (en) | 2015-07-02 |
| ES2368721T3 (en) | 2011-11-21 |
| US20060019828A1 (en) | 2006-01-26 |
| US11864558B2 (en) | 2024-01-09 |
| ES2368721T5 (en) | 2021-05-06 |
| US20200253212A1 (en) | 2020-08-13 |
| BR122014007725B1 (en) | 2016-10-11 |
| EP1722634A1 (en) | 2006-11-22 |
| US20140364313A1 (en) | 2014-12-11 |
| BRPI0508542B1 (en) | 2014-09-16 |
| US10499646B2 (en) | 2019-12-10 |
| ZA200607467B (en) | 2008-08-27 |
| PL1722634T3 (en) | 2011-12-30 |
| EP1722634B2 (en) | 2020-09-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11864558B2 (en) | Herbicidal compositions containing N-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide | |
| ES2425050T3 (en) | Foam-poor preparations for plant protection | |
| RU2297143C2 (en) | Aqueous herbicide composition (versions) and herbicide method (versions) | |
| AU691425B2 (en) | Glyphosate formulations containing etheramine surfactants | |
| EP1791431B1 (en) | Glyphosate formulations with early burndown symptoms | |
| US20020123430A1 (en) | Pesticide compositions containing oxalic acid | |
| ES2334111T3 (en) | PESTICIDE COMPOSITIONS CONTAINING OXALIC ACID. | |
| NZ517124A (en) | Enhanced method of killing weeds with glyphosate herbicide | |
| US10736322B2 (en) | Aqueous concentrated herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate salts and dicamba salts | |
| AU2002245592A1 (en) | Pesticide compositions containing oxalic acid | |
| WO2004093546A1 (en) | Herbicidal compositions containing glyphosate and a pyridine analog | |
| AU2017330321B2 (en) | Fast symptom herbicidal compositions containing an organophosphorus herbicide, bipyridilium and alkoxylated alcohol surfactant | |
| MXPA06010398A (en) | Herbicidal compositions containing n-phosphonomethyl glycine and an auxin herbicide |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AE AG AL AM AT AU AZ BA BB BG BR BW BY BZ CA CH CN CO CR CU CZ DE DK DM DZ EC EE EG ES FI GB GD GE GH GM HR HU ID IL IN IS JP KE KG KP KR KZ LC LK LR LS LT LU LV MA MD MG MK MN MW MX MZ NA NI NO NZ OM PG PH PL PT RO RU SC SD SE SG SK SL SM SY TJ TM TN TR TT TZ UA UG US UZ VC VN YU ZA ZM ZW |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): GM KE LS MW MZ NA SD SL SZ TZ UG ZM ZW AM AZ BY KG KZ MD RU TJ TM AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR BF BJ CF CG CI CM GA GN GQ GW ML MR NE SN TD TG |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2005221166 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2005725288 Country of ref document: EP Ref document number: 200607467 Country of ref document: ZA Ref document number: 2558642 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 5147/DELNP/2006 Country of ref document: IN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: PA/a/2006/010398 Country of ref document: MX Ref document number: 06090956 Country of ref document: CO |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2005221166 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20050310 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 2005221166 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200580014758.X Country of ref document: CN |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 2005725288 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: PI0508542 Country of ref document: BR |