RU2201166C2 - Method for fenestrated iliac wing - Google Patents
Method for fenestrated iliac wing Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2201166C2 RU2201166C2 RU98119131/14A RU98119131A RU2201166C2 RU 2201166 C2 RU2201166 C2 RU 2201166C2 RU 98119131/14 A RU98119131/14 A RU 98119131/14A RU 98119131 A RU98119131 A RU 98119131A RU 2201166 C2 RU2201166 C2 RU 2201166C2
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- wing
- autograft
- ilium
- fenestrated
- iliac
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 8
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000001356 surgical procedure Methods 0.000 abstract 1
- 210000003692 ilium Anatomy 0.000 description 11
- 210000000988 bone and bone Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 210000004872 soft tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000000399 orthopedic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 208000010392 Bone Fractures Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000017234 Bone cyst Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 206010017076 Fracture Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000027418 Wounds and injury Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 210000000459 calcaneus Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 210000000845 cartilage Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000002537 cosmetic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 2
- 208000028528 solitary bone cyst Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 230000003313 weakening effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 206010011732 Cyst Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010011985 Decubitus ulcer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010034156 Pathological fracture Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000006735 Periostitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000004210 Pressure Ulcer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000005250 Spontaneous Fractures Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 206010052428 Wound Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000009286 beneficial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036770 blood supply Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000031513 cyst Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006735 deficit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000000527 greater trochanter Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000000474 heel Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000001621 ilium bone Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000003049 pelvic bone Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000003460 periosteum Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002980 postoperative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002271 resection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004936 stimulating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002303 tibia Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 210000000689 upper leg Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Prostheses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к медицине, а именно к ортопедии и травматологии, т. е. к способам получения свободного кортикально-губчатого аутотрансплантата. The invention relates to medicine, namely to orthopedics and traumatology, i.e., to methods for producing a free cortical-spongy autograft.
Известно несколько аналогов получения кортикально-губчатых свободных аутотрансплантатов с заместительной, опорной и стимулирующей остеопарацию целью при лечении больных с ложными суставами и костными дефектами /Пирогов К. И. , 1853; Ollier, 1867; Руднев М.М., 1880; Радзимовский И.В., 1881; Лексер Э. , 1933; Петров Н.Н., 1913; Корнев П.Г., 1927; Немилов А.А., 1940; Новаченко Н.П., 1946; Бойчев Б., 1958; Мовшович И.А., 1994/. Наиболее широко используемым костно-пластическим материалом являются свободные аутотрансплантаты, взятые с гребня большеберцовой кости, большого вертела бедренной кости и крыла подвздошной кости. Общим недостатком известных способов получения костных аутотрансплантатов является образование ступенчатых западений, искажающих контуры и нарушающих каркасность донорского участка; вероятность выхождения линии остеотомии за пределы намеченного с ослаблением механической прочности донорского участка вплоть до наступления вторичного перелома; необходимость зачистки аутотрансплантатов от хрящевой ткани, препятствующей приживлению его к воспринимающему костному ложу. Several analogues of obtaining cortical-spongy free autografts with replacement, support and stimulating osteoparaction are known in the treatment of patients with false joints and bone defects / K. Pirogov, 1853; Ollier, 1867; Rudnev M.M., 1880; Radzimovsky I.V., 1881; Lexer E., 1933; Petrov N.N., 1913; Kornev P.G., 1927; Nemilov A.A., 1940; Novachenko N.P., 1946; Boychev B., 1958; Movshovich I.A., 1994 /. The most widely used osteoplastic material is free autografts, taken from the crest of the tibia, the greater trochanter of the femur and the wing of the ilium. A common disadvantage of the known methods for producing bone autografts is the formation of stepped depressions, distorting the contours and violating the frame of the donor site; the likelihood of the osteotomy line going beyond the limits indicated for the weakening of the mechanical strength of the donor site until the onset of a secondary fracture; the need to clean autografts from cartilage, which prevents its engraftment to the perceiving bone bed.
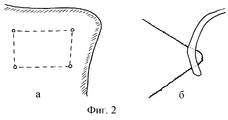
В качестве прототипа взят способ получения свободного аутотрансплантата с крыла подвздошной кости, преимуществами которого являются хорошая кровоснабжаемость /а значит, приживляемость к костному ложу/ спонгиозной ткани и возможность взятия большего ее количества с меньшей угрозой нарушения механической целостности и возникновения патологического перелома тазовой кости /Мовшович И. А., 1994/. Осуществляется способ-прототип следующим образом. По гребню подвздошной кости от ее передне-верхней ости делается разрез кожи и глубьлежащих мягких тканей длиной 12-14 см. Достигнув кости, скелетируют ее на нужном протяжении снаружи и снутри, освобождая от мягких тканей предназначенный для остеопластики донорский участок заданной формы и размеров. Затем намечают контуры последнего /фиг.1,а/ и долотом осуществляют его резекцию /фиг. 1,б/. После взятия аутотрансплантата мягкие ткани укладывают на свое место и послойно ушивают с оставлением, при необходимости, резинового дренажа. As a prototype, a method of obtaining a free autograft from the iliac wing was taken, the advantages of which are good blood supply / and, therefore, engraftment to the bone bed / spongy tissue and the possibility of taking more of it with less risk of impaired mechanical integrity and the occurrence of a pathological fracture of the pelvic bone / Movshovich I . A., 1994 /. A prototype method is implemented as follows. A cut of the skin and deep soft tissues 12-14 cm long is made along the iliac crest from its anteroposterior spine. Having reached the bone, they skeletonize it to the desired extent from the outside and inside, releasing the donor site of the given shape and size for soft tissue. Then outline the contours of the latter / Fig. 1, b /. After taking the autograft, soft tissues are laid in their place and sutured in layers, leaving, if necessary, rubber drainage.
Недостатками прототипа являются следующие:
1/ вероятность выхождения линии остеотомии за пределы намеченного с ослаблением механической прочности подвздошной кости вплоть до наступления вторичного перелома последней;
2/ необходимость в трудоемкой зачистке полученного трансплантата от хрящевой ткани, располагающейся по гребню подвздошной кости;
3/ функциональные неудобства при ношении одежды со стороны донорского участка, выражающиеся в давлении образованных костных краев от ступенчатых западений на мягкие ткани вплоть до развития внутренних пролежней;
4/ противоречие требованиям косметики, выражающееся в образовании ступенчатого западения на донорском участке, четко определяемого визуально, особенно у женщин и худощавых субъектов.The disadvantages of the prototype are the following:
1 / the likelihood of the osteotomy line exceeding the limits of the ilium planned with weakening of the mechanical strength of the ilium up to the onset of a secondary fracture of the ilium;
2 / the need for laborious cleaning of the obtained transplant from cartilage tissue located along the iliac crest;
3 / functional inconvenience when wearing clothes from the donor site, expressed in the pressure of the formed bone edges from step depressions on the soft tissues up to the development of internal pressure sores;
4 / a contradiction to the requirements of cosmetics, expressed in the formation of stepwise depressions on the donor site, clearly defined visually, especially in women and thin subjects.
Цель изобретения - уменьшение травматичности и длительности операции, повышение качества выполнения остеотомии с предупреждением вероятности образования косметически ущербного и функционально порочного ступенчатого западения на донорском участке с сохранением каркасности подвздошной кости. The purpose of the invention is to reduce the morbidity and duration of the operation, to improve the quality of osteotomy with the prevention of the likelihood of the formation of cosmetically flawed and functionally vicious step depressions on the donor site, while maintaining the frame of the ilium.
Поставленная цель достигается тем, что взятие аутотрансплантата выполняется путем окончатой остеотомии крыла подвздошной кости. This goal is achieved in that the autograft is taken by means of a graduated osteotomy of the ilium wing.
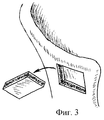
Изобретение осуществляется следующим образом. Производятся типичный разрез кожи и скелетирование крыла подвздошной кости на заданном протяжении. Затем намечаются контуры предполагаемого трансплантата, на углах которого дрелью со сверлом, диаметром 0,2-0,5 см, просверливаются отверстия /фиг.2, а/. Проволочная пила Джигли проводится в одно отверстие снаружи внутрь и выводится в обратном направлении через другое /соседнее/ отверстие /фиг.2,б/. Таким образом трансплантат последовательно выпиливается со всех /обычно - четырех/ сторон и извлекается /фиг.3/, мягкие ткани укладываются на свое место и послойно ушиваются. The invention is as follows. A typical skin incision and skeletonization of the ilium wing are performed for a given length. Then, the contours of the proposed transplant are outlined, at the corners of which a drill with a drill, 0.2-0.5 cm in diameter, holes are drilled (Fig. 2, a). The Jigley wire saw is held in one hole from the outside in and is output in the opposite direction through another / neighboring / hole / Fig.2, b /. Thus, the graft is sequentially sawn from all / usually four / sides and removed / Fig.3/, soft tissue is laid in its place and sutured in layers.
Преимуществами предлагаемого способа получения свободного кортикально-губчатого аутотрансплантата являются следующие:
1/ повышение качества выполнения остеотомии с исключением вероятности выхождения ее линии за пределы намеченного;
2/ устранение необходимости зачистки трансплантата от хрящевой ткани, имеющейся на гребне подвздошной кости и препятствующей приживлению аутотрансплантата к костному ложу;
3/ сохранение каркасности крыла подвздошной кости;
4/ предупреждение как функционального неудобства, так и косметической ущербности со стороны донорского участка, связанных с образованием ступенчатого западения.The advantages of the proposed method for producing a free cortical-spongy autograft are as follows:
1 / improving the quality of osteotomy with the exception of the likelihood of its line going beyond the intended range;
2 / elimination of the need to clean the graft from the cartilaginous tissue present on the iliac crest and preventing the autograft from engraftment to the bone bed;
3 / maintaining the frame of the ilium wing;
4 / prevention of both functional inconvenience and cosmetic impairment on the part of the donor site associated with the formation of stepwise deposition.
Примером получения кортикально-губчатого свободного аутотрансплантата путем выполнения окончатой остеотомии крыла подвздошной кости служит следующее наблюдение. An example of obtaining a cortical-spongy free autograft by performing a terminal osteotomy of the ilium wing is the following observation.
Больной Р., 22 лет, поступил в плановом порядке в ортопедическое отделение РОТЦ /история болезни 3-609/ 11.08.97 с жалобами на периодические умеренные ноющие боли в области левой пятки, впервые появившиеся после травмы 3 недели назад и усиливающиеся при осевой нагрузке. Рентгенологически была выявлена солитарная киста тела пяточной кости размерами 5,0 х 3,5 см, по поводу чего 19.08.97 в плановом порядке выполнена операция: удаление солитарной кисты левой пяточной кости с аутопластикой дефекта. Patient R., 22 years old, was admitted to the orthopedic department of the RTC / case history 3-609 / 11.08.97 with complaints of periodic moderate aching pain in the left heel area, which first appeared after the injury 3 weeks ago and intensified with axial load. X-ray revealed a solitary cyst of the calcaneus body with dimensions of 5.0 x 3.5 cm, about which the operation was performed as planned on 08/19/97: removal of a solitary cyst of the left calcaneus with autoplasty of the defect.
Взятие трансплантата осуществлялось следующим образом. От передне-верхней ости левой подвздошной кости по гребню последней произведен линейный разрез кожи и подлежащих мягких тканей длиной 12 см. Острым и тупым путем донорский участок подвздошной кости скелетирован с наружной и внутренней стороны. Намечены контуры предполагаемого трансплантата, на углах которого дрелью со сверлом, диаметром 0,3 см, просверлены 4 отверстия в теле подвздошной кости, 2 верхних из которых располагаются на 0,7-1,0 см ниже гребня последней. Через просверленные отверстия попарно снаружи внутрь и обратно проведена пила Джигли и осуществлена остеотомия со всех четырех сторон по периметру трансплантата. Таким образом получен аутотрансплантат размерами 6,0 х 4,0 см. Остающийся на донорском участке окончатый дефект снутри и снаружи прикрыт надкостницей и мышцами с оставлением трубчатого дренажа, удаленного на вторые сутки после операции. The graft was carried out as follows. From the anteroposterior spine of the left iliac bone along the crest of the latter, a linear incision was made of the skin and underlying soft tissues 12 cm long. In a sharp and blunt way, the donor site of the ilium is skeletonized from the outside and inside. The contours of the proposed transplant were outlined, at the corners of which a drill with a drill, 0.3 cm in diameter, 4 holes were drilled in the body of the ilium, the upper 2 of which are located 0.7-1.0 cm below the crest of the latter. Through the drilled holes, a Jigley saw was performed in pairs from the outside inward and back and an osteotomy was performed on all four sides around the graft. Thus, an autograft with dimensions of 6.0 x 4.0 cm was obtained. The window defect remaining on the donor site was covered inside and outside by the periosteum and muscles, leaving tubular drainage removed on the second day after the operation.
Полученный аутотрансплантат расщеплен на 2 части и плотно внедрен в образовавшийся после резекции солитарной кисты пяточной кости дефект. Послеоперационный период протекал гладко. Обе раны зажили первичным натяжением. Швы сняты на девятый день. Визуально контуры гребней подвздошной кости симметричны и неизменны. The obtained autograft is split into 2 parts and tightly embedded in the defect formed after resection of a solitary calcaneal cyst. The postoperative period was uneventful. Both wounds healed by primary intention. Sutures were removed on the ninth day. Visually, the contours of the iliac crests are symmetrical and unchanged.
Больной выписан 29.08.97 г. The patient was discharged 08/29/97
Таким образом, предлагаемый способ взятия свободного кортикально-губчатого аутотрансплантата с крыла подвздошной кости является надежным, выгодным и более оптимальным по сравнению с традиционным способом аутопластики, позволяет улучшить как непосредственные, так и отдаленные результаты лечения ортопедических больных, нуждающихся в свободной остеопластике, что позволяет рекомендовать его для широкого практического применения. Thus, the proposed method for taking a free cortical-spongy autograft from the iliac wing is reliable, beneficial and more optimal compared to the traditional method of autoplasty, it improves both immediate and long-term results of treatment of orthopedic patients requiring free osteoplasty, which allows us to recommend its for wide practical application.
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU98119131/14A RU2201166C2 (en) | 1998-10-21 | 1998-10-21 | Method for fenestrated iliac wing |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU98119131/14A RU2201166C2 (en) | 1998-10-21 | 1998-10-21 | Method for fenestrated iliac wing |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU98119131A RU98119131A (en) | 2000-08-20 |
| RU2201166C2 true RU2201166C2 (en) | 2003-03-27 |
Family
ID=20211515
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU98119131/14A RU2201166C2 (en) | 1998-10-21 | 1998-10-21 | Method for fenestrated iliac wing |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2201166C2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2476178C1 (en) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-02-27 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "СарНИИТО" Минздравсоцразвития России) | Method of sampling autotransplant from iliac crest |
-
1998
- 1998-10-21 RU RU98119131/14A patent/RU2201166C2/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| МОВШОВИЧ И.А. Оперативная ортопедия. - М.: Медицина, 1994. ОСТРОВЕРХОВ Г.Е. Курс оперативной хирургии. - М.: Медицина, 1964, с.362. Clin. Orthopaed. - 1986, 209, 224-226. * |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2476178C1 (en) * | 2011-12-19 | 2013-02-27 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение "Саратовский научно-исследовательский институт травматологии и ортопедии" Министерства здравоохранения и социального развития Российской Федерации (ФГБУ "СарНИИТО" Минздравсоцразвития России) | Method of sampling autotransplant from iliac crest |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Fernandez et al. | Non-union of the scaphoid. Revascularization of the proximal pole with implantation of a vascular bundle and bone-grafting. | |
| Kim et al. | Multiple congenital brachymetatarsia: a one-stage combined shortening and lengthening procedure without iliac bone graft | |
| RU2257174C1 (en) | Method for operative treatment of valgus deviation of the great toe of degree ii-iv and hammer-like deformation of the second toe | |
| RU2201166C2 (en) | Method for fenestrated iliac wing | |
| RU2164389C2 (en) | Method for making subtalar joint arthrodesis | |
| RU2432135C1 (en) | Method of plastic surgery on anterior cruciate ligament of knee joint and related graft for implementation thereof | |
| RU2210334C1 (en) | Method for combined plasty of thumb's stump | |
| RU2223058C2 (en) | Method for surgical treatment of customary brachial dislocation | |
| RU2737710C1 (en) | Method for treating arthrosis of first metatarsophalangeal articulation | |
| RU2147422C1 (en) | Method for treating the cases of osteochondritis dissecans | |
| RU2192188C2 (en) | Method for two-joint foot arthrodesis under arthroscopic control | |
| RU2283058C2 (en) | Method for carrying out osteoplastic knee joint arthrodesis in the cases of femoral distal metaepiphysis tumors | |
| RU2317035C2 (en) | Method for autoplasty of the lesions of lateral group of talocrural joint ligaments | |
| RU2475213C2 (en) | Endoprosthesis of long bone stump | |
| RU2236188C2 (en) | Method for treating chronic osteomyelitis of long bones | |
| RU2132657C1 (en) | Method for treating tumor-like bone disease | |
| RU2689183C1 (en) | Plasty method of tubular bone defect | |
| RU2166296C2 (en) | Method for taking autograft to make bone autoplastic repair | |
| RU2849937C1 (en) | Method of treating freiberg-köler disease | |
| RU2802152C1 (en) | Method of surgical treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint | |
| RU2180809C2 (en) | Surgical method for making dystrophic state correction in proximal infantine femur part | |
| RU2712005C1 (en) | Method for restoring the head of the metatarsal bone of the foot in keller ii-freiberg disease | |
| RU2332948C2 (en) | Method of revascularisation of large joints bone fragments | |
| RU2216292C1 (en) | Method for surgical treatment of luxation of acromial clavicular end | |
| RU2236189C2 (en) | Method for treating phalangeal enchondromas and those of wrist's metacarpal bones |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| MM4A | The patent is invalid due to non-payment of fees |
Effective date: 20011022 |