RU2158564C1 - Method for treating artificial denture - Google Patents
Method for treating artificial denture Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- RU2158564C1 RU2158564C1 RU2000101679A RU2000101679A RU2158564C1 RU 2158564 C1 RU2158564 C1 RU 2158564C1 RU 2000101679 A RU2000101679 A RU 2000101679A RU 2000101679 A RU2000101679 A RU 2000101679A RU 2158564 C1 RU2158564 C1 RU 2158564C1
- Authority
- RU
- Russia
- Prior art keywords
- citric acid
- water
- electrolyte
- composition
- potassium
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 17
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);zirconium(4+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Zr+4] RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 229910001928 zirconium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 36
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 20
- 229960003975 potassium Drugs 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000005282 brightening Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- MGFYIUFZLHCRTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrilotriacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O MGFYIUFZLHCRTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- KTVIXTQDYHMGHF-UHFFFAOYSA-L cobalt(2+) sulfate Chemical compound [Co+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O KTVIXTQDYHMGHF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910001020 Au alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000003353 gold alloy Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000001508 potassium citrate Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229960002635 potassium citrate Drugs 0.000 claims description 3
- QEEAPRPFLLJWCF-UHFFFAOYSA-K potassium citrate (anhydrous) Chemical class [K+].[K+].[K+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O QEEAPRPFLLJWCF-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000011082 potassium citrates Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- -1 potassium citric acid trisubstituted, zirconium oxide Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 229940044175 cobalt sulfate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910000361 cobalt sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- SDKPSXWGRWWLKR-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;9,10-dioxoanthracene-1-sulfonate Chemical compound [Na+].O=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=C1C=CC=C2S(=O)(=O)[O-] SDKPSXWGRWWLKR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 abstract description 11
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 abstract description 11
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 4
- WAIPAZQMEIHHTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Cr].[Co] Chemical class [Cr].[Co] WAIPAZQMEIHHTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanoic acid Natural products OC=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000000214 mouth Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000035807 sensation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000019615 sensations Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- NAVWVHRQSDHCHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid;potassium Chemical compound [K].OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O NAVWVHRQSDHCHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-(3-methoxyphenyl)aniline Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC(C=2C=CC(N)=CC=2)=C1 OSWFIVFLDKOXQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JAJIPIAHCFBEPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9,10-dioxoanthracene-1-sulfonic acid Chemical compound O=C1C2=CC=CC=C2C(=O)C2=C1C=CC=C2S(=O)(=O)O JAJIPIAHCFBEPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010006784 Burning sensation Diseases 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010020751 Hypersensitivity Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000005299 abrasion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000026935 allergic disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000007815 allergy Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N boric acid Chemical compound OB(O)O KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004327 boric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- GVPFVAHMJGGAJG-UHFFFAOYSA-L cobalt dichloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].[Co+2] GVPFVAHMJGGAJG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002537 cosmetic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005238 degreasing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000019253 formic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
- DITXJPASYXFQAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel;sulfamic acid Chemical compound [Ni].NS(O)(=O)=O DITXJPASYXFQAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 201000001245 periodontitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 231100000175 potential carcinogenicity Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052720 vanadium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000011179 visual inspection Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroplating And Plating Baths Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Изобретение относится к области медицины, а именно к стоматологии. The invention relates to medicine, namely to dentistry.
Известен способ обработки зубных протезов путем электрохимического нанесения покрытия на основе сплава золота на коррозионно-стойкий сплав, включающий ряд последовательных операций: обезжиривание, травление в 25% соляной кислоте, промывание в воде, электролитическую обработку протеза в растворе состава N 1 по режиму N 1, затем в растворе N 2 по режиму N 2, промывку и сушку. A known method of processing dentures by electrochemical coating based on a gold alloy on a corrosion-resistant alloy, which includes a number of sequential operations: degreasing, etching in 25% hydrochloric acid, rinsing in water, electrolytic treatment of the prosthesis in a solution of composition No. 1 according to mode No. 1, then in a solution of
Состав N 1 (мас.%)
Соль трехвалентного золота (например, K{Au(CN)4}-
Тетрацианоаурат калия - 0,25
Хлористый кобальт - 0,03
Лимонная кислота - 8,0
Амины (например, аминоалканы) - 0,2
Соляная кислота - Остальное, до pH < 1
Состав N 2 (мас.%)
Дицианоаурат калия - 0,5
Никель сульфаминовокислый - 0,4
Кислота нитрилотриуксусная - 1,7
Калий лимоннокислый - 6,0
Кислота муравьиная - 1,2
Кислота борная - 2,0
Блескообразующая добавка, например Лимеда - 0,1
Вода - Остальное
при этом время выдержки в электролите состава N 1 (режим N 1) составляет 3 - 6 мин при напряжении 4-5 В, а в электролите состава N 2 (режим N2)- 30 -50 мин при напряжении 2-4 В. Способ осуществляют при комнатной температуре. По окончании процесса протез промывают в воде и высушивают. Этот способ взят за прототип.Composition N 1 (wt.%)
Trivalent gold salt (for example, K {Au (CN) 4 } -
Potassium tetracyanoaurate - 0.25
Cobalt Chloride - 0.03
Citric Acid - 8.0
Amines (e.g. aminoalkanes) - 0.2
Hydrochloric acid - The rest, up to pH <1
Composition N 2 (wt.%)
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 0.5
Nickel sulfamic acid - 0.4
Nitrilotriacetic acid - 1.7
Potassium Citrate - 6.0
Formic acid - 1.2
Boric acid - 2.0
Brightening agent, for example Limeda - 0.1
Water - Else
while the exposure time in an electrolyte of composition No. 1 (mode No. 1) is 3-6 minutes at a voltage of 4-5 V, and in an electrolyte of composition No. 2 (mode N2) is 30-50 minutes at a voltage of 2-4 V. The method is carried out at room temperature. At the end of the process, the prosthesis is washed in water and dried. This method is taken as a prototype.
(Пат. N 2036622 РФ МПК6 A 61 C 31/02. Способ обработки зубных протезов. Копейкин В.Н., Сафарова Н.И., Сафарова К.Ю., Лебеденко И.Ю., Лебеденко А.И. / Сафарова Н.И. Бюл. 1995, N 16, с. 86).(Pat. N 2036622 RF IPC 6 A 61 C 31/02. Method of processing dentures. Kopeikin V.N., Safarova N.I., Safarova K.Yu., Lebedenko I.Yu., Lebedenko A.I. / Safarova N.I. Bull. 1995, N 16, p. 86).
Недостатком данного способа обработки зубных протезов является недостаточная износостойкость покрытия, его потенциальная канцерогенность и аллергичность из-за присутствия в нем никеля, а также трудоемкость выполнения из-за сложного состава электролита N 1. The disadvantage of this method of processing dentures is the lack of wear resistance of the coating, its potential carcinogenicity and allergy due to the presence of nickel in it, as well as the complexity of execution due to the complex composition of
Задачей изобретения является повышение износостойкости золотого покрытия, обеспечение его биосовместимости с организмом человека, упрощение способа обработки за счет изменения химического состава электролитов. The objective of the invention is to increase the wear resistance of the gold coating, ensuring its biocompatibility with the human body, simplifying the processing method by changing the chemical composition of electrolytes.
Повышение износостойкости покрытия зубного протеза достигается включением в состав электролита N 2 оксида циркония, исключение никеля из состава электролита N 2 обеспечивает его биосовместимость с организмом человека, упрощение способа происходит за счет изменения состава электролита N1, включающего дицианоаурат калия, лимонную кислоту и воду. An increase in the wear resistance of the denture coating is achieved by including zirconium oxide in the composition of
Способ осуществляется следующим образом. The method is as follows.
Металлическую поверхность зубного протеза, изготовленного из коррозионно-стойкого сплава, обезжиривают и протравливают в 25%-ном растворе соляной кислоты. После кратковременной промывки в воде протез помещают в электролит состава N 1, включающий дицианоаурат калия, лимонную кислоту, воду, мас.%:
Дицианоаурат калия - 0,15
Лимонная кислота - 8,0
Вода - остальное
pH 1-1,5
Время выдержки в электролите состава N 1 составляет 8 - 10 мин при плотности тока 0,3 -0,5 А/дм2, затем протез промывают в воде и погружают в электролит состава N 2, включающий дицианоаурат калия, кобальт сернокислый, трилон A, лимонную кислоту, калий лимоннокислый трехзамещенный, оксид циркония, блескообразующую добавку, поверхностно-активное вещество, воду, мас. %:
Дицианоаурат калия - 1,0
Кобальт сернокислый - 0,1
Трилон A - 0,25
Лимонная кислота - 3,0
Калий лимоннокислый трехзамещенный - 6,0
Оксид циркония - 0,5
Блескообразующая добавка - 0,008
Поверхностно-активное вещество - 0,008
Вода - Остальное
устанавливают величину тока, соответствующую плотности тока 0,8 - 1 А/дм2 и выдерживают в течение 2 - 2,5 часов для наращивания основного слоя золотого сплава.The metal surface of a denture made of a corrosion-resistant alloy is degreased and etched in a 25% hydrochloric acid solution. After a short wash in water, the prosthesis is placed in an electrolyte of
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 0.15
Citric Acid - 8.0
Water - the rest
pH 1-1.5
The exposure time in an electrolyte of
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 1.0
Cobalt Sulphate - 0.1
Trilon A - 0.25
Citric Acid - 3.0
Three-substituted potassium citrate - 6.0
Zirconium oxide - 0.5
Brightening Additive - 0.008
Surfactant - 0.008
Water - Else
set the current value corresponding to a current density of 0.8 - 1 A / DM 2 and incubated for 2 to 2.5 hours to build up the main layer of the gold alloy.
Весь способ осуществляют при комнатной температуре и постоянном перемешивании электролитов путем возвратно-поступательного движения штанги катода, на которой укрепляют протез, после чего протез извлекают из электролита, промывают в воде и высушивают. The whole method is carried out at room temperature and constantly stirring the electrolytes by reciprocating the cathode rod, on which the prosthesis is fixed, after which the prosthesis is removed from the electrolyte, washed in water and dried.
Пример: Больному Н., 55 лет, страдающему генерализованной формой пародонтита, осложненной вторичной частичной адентией нижней челюсти, показано изготовление цельнолитого шинирующего бюгельного протеза из высокопрочного кобальто- хромового сплава (КХС). Example: Patient N., 55 years old, suffering from a generalized form of periodontitis complicated by secondary partial adentia of the lower jaw, shows the manufacture of a cast cast splint arch prosthesis from a high-strength cobalt-chromium alloy (KHS).
Показанием к проведению обработки бюгельного протеза путем нанесения золотого покрытия на каркас протеза из кобальто-хромового сплава (КХС) явилось ощущение пациентом привкуса металла и жжение в полости рта. An indication for the treatment of the clasp prosthesis by applying a gold coating to the cobalt-chromium alloy prosthesis frame was the patient's sensation of a taste of metal and burning in the oral cavity.
Нанесение золотого покрытия проводили в электролитических ваннах. Протез тщательно обезжиривали, протравливали в 25% растворе соляной кислоты в течение 1 - 1,5 мин, промывали в воде и завешивали на медном контактном приспособлении в электролит состава 1, мас.%:
Дицианоаурат калия - 0,15
Лимонная кислота - 8,0
Вода - Остальное
pH 1-1,5
Процесс проводили при комнатной температуре. Устанавливали величину тока, соответствующую плотности тока 0,3 -0,5 А/дм2, время выдержки составляло 8 - 10 мин.The gold coating was carried out in electrolytic baths. The prosthesis was thoroughly degreased, etched in a 25% hydrochloric acid solution for 1 - 1.5 minutes, washed in water and hung on a copper contact fixture in an electrolyte of
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 0.15
Citric Acid - 8.0
Water - Else
pH 1-1.5
The process was carried out at room temperature. The current value was set corresponding to the current density of 0.3-0.5 A / dm 2 , the exposure time was 8 - 10 minutes.
По окончании процесса протез извлекали из электролита состава N 1, промывали водой и помещали в электролитическую ванну с составом N 2, мас.%:
Дицианоаурат калия - 1,0
Кобальт сернокислый - 0,1
Трилон A - 0,25
Лимонная кислота - 3,0
Калий лимоннокислый 3-х замещенный - 6,0
Оксид циркония - 0,5
Блескообразующая добавка - 0,008
Поверхностно-активное вещество - 0,008
Вода - Остальное
Процесс проводили при комнатной температуре. Устанавливали величину тока, соответствующую плотности тока 0,8-1 А/дм2. Время выдержки составляло 2-2,5 часа при постоянном перемешивании электролита за счет возвратно-поступательного движения катодной штанги.At the end of the process, the prosthesis was removed from the electrolyte of
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 1.0
Cobalt Sulphate - 0.1
Trilon A - 0.25
Citric Acid - 3.0
Potassium
Zirconium oxide - 0.5
Brightening Additive - 0.008
Surfactant - 0.008
Water - Else
The process was carried out at room temperature. Set the current value corresponding to a current density of 0.8-1 A / dm 2 . The exposure time was 2-2.5 hours with constant stirring of the electrolyte due to the reciprocating motion of the cathode rod.
После промывки в воде и высушивания протез накладывали в полости рта больного. Изменений пластмассовых частей протеза при визуальном осмотре не было выявлено. After washing in water and drying, the prosthesis was placed in the patient's oral cavity. Changes in the plastic parts of the prosthesis during visual inspection were not detected.
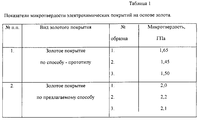
Субъективное ощущение больного хорошее. Больной доволен отсутствием привкуса металла, высоким косметическим эффектом протеза, а также блестящей поверхностью золотого покрытия. При контрольных осмотрах через 6 мес., 1 год и 1,5 года не было отмечено никаких жалоб больного на чувство жжения и привкус металла. Точечное истирание покрытия было выявлено после контрольного осмотра через 2,5 года после изготовления протеза. Было проведено восстановление золотого покрытия по описанному способу. Введение оксида циркония в состав золотого покрытия позволило увеличить износостойкость, а следовательно, срок службы золотого покрытия на 30% (за счет увеличения микротвердости), по сравнению со способом-прототипом (см. табл. 1). The subjective sensation of the patient is good. The patient is pleased with the absence of a taste of metal, the high cosmetic effect of the prosthesis, and the shiny surface of the gold coating. During follow-up examinations after 6 months, 1 year and 1.5 years, there were no complaints of the patient about a burning sensation and a taste of metal. Spot abrasion of the coating was revealed after a control inspection 2.5 years after the manufacture of the prosthesis. The gold plating was restored according to the described method. The introduction of zirconium oxide in the composition of the gold coating allowed to increase the wear resistance, and therefore, the service life of the gold coating by 30% (due to an increase in microhardness), compared with the prototype method (see table. 1).
Claims (1)
Дицианоаурат калия - 0,15
Лимонная кислота - 8,0
Вода - Остальное
pH - 1 - 1,5
при этом время выдержки в электролите состава N1 составляет 8 - 10 мин при плотности тока 0,3 - 0,5 А/дм2 и комнатной температуре, а в качестве электролита состава N2 используют раствор, содержащий соль одновалентного золота, сернокислый кобальт, Трилон А, лимонную кислоту, калий лимоннокислый трехзамещенный, оксид циркония, блескообразующую добавку, поверхностно-активное вещество, воду, взятые в следующих соотношениях, мас.%:
Дицианоаурат калия - 1,0
Кобальт сернокислый - 0,1
Трилон А - 0,25
Лимонная кислота - 3,0
Калий лимоннокислый трехзамещенный - 6,0
Оксид циркония - 0,5
Блескообразующая добавка - 0,008
Поверхностно-активное вещество - 0,008
Вода - Остальное
при этом время выдержки в электролите состава N2 составляет 2 - 2,5 ч при плотности тока 0,8 - 1 А/дм2 и комнатной температуре, при постоянном перемешивании его за счет возвратно-поступательного движения катодной штанги.A method of processing dentures by applying a gold alloy to a corrosion-resistant alloy, comprising sequentially immersing the prosthesis in electrolytes of two compositions, keeping them at a given current value and temperature and constant stirring, washing and drying, characterized in that they use N1 as an electrolyte a solution containing a salt of monovalent gold, citric acid, water, taken in the following proportions, wt.%:
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 0.15
Citric Acid - 8.0
Water - Else
pH - 1 - 1.5
the exposure time in an electrolyte of composition N1 is 8-10 minutes at a current density of 0.3 - 0.5 A / dm 2 and room temperature, and as an electrolyte of composition N2, a solution containing a monovalent gold salt, cobalt sulfate, Trilon A is used , citric acid, potassium citric acid trisubstituted, zirconium oxide, brightening additive, surfactant, water, taken in the following proportions, wt.%:
Potassium Dicyanoaurate - 1.0
Cobalt Sulphate - 0.1
Trilon A - 0.25
Citric Acid - 3.0
Three-substituted potassium citrate - 6.0
Zirconium oxide - 0.5
Brightening Additive - 0.008
Surfactant - 0.008
Water - Else
while the exposure time in an electrolyte of composition N2 is 2 - 2.5 hours at a current density of 0.8 - 1 A / dm 2 and room temperature, with constant stirring due to the reciprocating motion of the cathode rod.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2000101679A RU2158564C1 (en) | 2000-01-26 | 2000-01-26 | Method for treating artificial denture |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2000101679A RU2158564C1 (en) | 2000-01-26 | 2000-01-26 | Method for treating artificial denture |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| RU2158564C1 true RU2158564C1 (en) | 2000-11-10 |
Family
ID=20229714
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| RU2000101679A RU2158564C1 (en) | 2000-01-26 | 2000-01-26 | Method for treating artificial denture |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| RU (1) | RU2158564C1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2241410C2 (en) * | 2003-02-10 | 2004-12-10 | Якупов Рамиль Шамильевич | Method for treating dental prostheses |
| RU2469697C1 (en) * | 2011-05-23 | 2012-12-20 | Открытое акционерное общество "Научно-производственный комплекс "Суперметалл" имени Е.И. Рытвина" | Method of electroplating of removable dentures |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1456136A1 (en) * | 1985-02-25 | 1989-02-07 | Всесоюзный научно-исследовательский, проектно-конструкторский и технологический институт источников тока | Method of processing clasp dentures made of cobalt and chromium alloys |
| SU1655480A1 (en) * | 1988-10-03 | 1991-06-15 | Львовский государственный медицинский институт | Method for treating unit-cast stainless steel prosthesis |
| RU2036622C1 (en) * | 1993-07-14 | 1995-06-09 | Сафарова Надежда Ивановна | Method for finishing dental prostheses |
| RU2076661C1 (en) * | 1992-11-16 | 1997-04-10 | Владимир Биликович Рамзи | Method of production of dentures with two-layer composite coating |
-
2000
- 2000-01-26 RU RU2000101679A patent/RU2158564C1/en active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SU1456136A1 (en) * | 1985-02-25 | 1989-02-07 | Всесоюзный научно-исследовательский, проектно-конструкторский и технологический институт источников тока | Method of processing clasp dentures made of cobalt and chromium alloys |
| SU1655480A1 (en) * | 1988-10-03 | 1991-06-15 | Львовский государственный медицинский институт | Method for treating unit-cast stainless steel prosthesis |
| RU2076661C1 (en) * | 1992-11-16 | 1997-04-10 | Владимир Биликович Рамзи | Method of production of dentures with two-layer composite coating |
| RU2036622C1 (en) * | 1993-07-14 | 1995-06-09 | Сафарова Надежда Ивановна | Method for finishing dental prostheses |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RU2241410C2 (en) * | 2003-02-10 | 2004-12-10 | Якупов Рамиль Шамильевич | Method for treating dental prostheses |
| RU2469697C1 (en) * | 2011-05-23 | 2012-12-20 | Открытое акционерное общество "Научно-производственный комплекс "Суперметалл" имени Е.И. Рытвина" | Method of electroplating of removable dentures |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5287861B2 (en) | Method for producing metal with biocidal properties | |
| JP4460308B2 (en) | Metal implant | |
| US4038702A (en) | Electrochemical and chemical methods for production of non-thrombogenic metal heart valves | |
| JP5692729B2 (en) | Metal processing | |
| CN100392155C (en) | Plating solution for electrodepositing gold and gold alloy and its application | |
| US6852207B1 (en) | Method for producing prosthetic moulded parts for dental use | |
| RU2158564C1 (en) | Method for treating artificial denture | |
| JPS63203790A (en) | Cyanide-free bright copper-zinc alloy electroplating bath | |
| RU2036622C1 (en) | Method for finishing dental prostheses | |
| JPS62247100A (en) | Electropolishing solution | |
| RU2241410C2 (en) | Method for treating dental prostheses | |
| CN112368424A (en) | Electrolytic treatment method for coating stainless steel objects | |
| Smirnova et al. | Electrochemical Polishing of Silver in Acid Thiourea-Citrate Solutions in the Manufacture of Medical Instruments and Orthopedic Dental Structures | |
| RU2159596C1 (en) | Method for finishing dental prostheses | |
| SU1165394A1 (en) | Method of machining metal frames of dentures from cobalt-chromium alloy | |
| Zhu et al. | Corrosion characteristic of vitallium 2000 CoCrMo casting alloy in fluoride containing artificial saliva | |
| CN108560036B (en) | Surface-carried Zn2+Magnesium alloy material and preparation method and application thereof | |
| TW466109B (en) | Gold electroforming on the inner side of dental cast crowns | |
| SU1456154A1 (en) | Electrolyte for electric polishing of metal frames of dentures | |
| JP2002212018A (en) | Dental material | |
| UA19653U (en) | Method for galvanic gilding of basis of plastic removable denture | |
| JP4945743B2 (en) | Antibacterial medical prosthetic member and antibacterial treatment method for medical prosthetic member | |
| RU2469697C1 (en) | Method of electroplating of removable dentures | |
| TW201320970A (en) | Gold-plating process of titanium dental implant | |
| JPS58167795A (en) | Method for plating spectacle frame with noble metal |