KR20140079795A - Prestressed glass roll - Google Patents
Prestressed glass roll Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20140079795A KR20140079795A KR1020147011170A KR20147011170A KR20140079795A KR 20140079795 A KR20140079795 A KR 20140079795A KR 1020147011170 A KR1020147011170 A KR 1020147011170A KR 20147011170 A KR20147011170 A KR 20147011170A KR 20140079795 A KR20140079795 A KR 20140079795A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- glass
- intermediate material
- layers
- glass film
- roll
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B7/00—Layered products characterised by the relation between layers; Layered products characterised by the relative orientation of features between layers, or by the relative values of a measurable parameter between layers, i.e. products comprising layers having different physical, chemical or physicochemical properties; Layered products characterised by the interconnection of layers
- B32B7/04—Interconnection of layers
- B32B7/06—Interconnection of layers permitting easy separation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B17/00—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres
- B32B17/06—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material
- B32B17/065—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of paper or cardboard
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B17/00—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres
- B32B17/06—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material
- B32B17/066—Layered products essentially comprising sheet glass, or glass, slag, or like fibres comprising glass as the main or only constituent of a layer, next to another layer of a specific material of foam
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B3/00—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form
- B32B3/26—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form characterised by a particular shape of the outline of the cross-section of a continuous layer; characterised by a layer with cavities or internal voids ; characterised by an apertured layer
- B32B3/263—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form characterised by a particular shape of the outline of the cross-section of a continuous layer; characterised by a layer with cavities or internal voids ; characterised by an apertured layer characterised by a layer having non-uniform thickness
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B3/00—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form
- B32B3/26—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form characterised by a particular shape of the outline of the cross-section of a continuous layer; characterised by a layer with cavities or internal voids ; characterised by an apertured layer
- B32B3/28—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form characterised by a particular shape of the outline of the cross-section of a continuous layer; characterised by a layer with cavities or internal voids ; characterised by an apertured layer characterised by a layer comprising a deformed thin sheet, i.e. the layer having its entire thickness deformed out of the plane, e.g. corrugated, crumpled
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B3/00—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form
- B32B3/26—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form characterised by a particular shape of the outline of the cross-section of a continuous layer; characterised by a layer with cavities or internal voids ; characterised by an apertured layer
- B32B3/30—Layered products comprising a layer with external or internal discontinuities or unevennesses, or a layer of non-planar form; Layered products having particular features of form characterised by a particular shape of the outline of the cross-section of a continuous layer; characterised by a layer with cavities or internal voids ; characterised by an apertured layer characterised by a layer formed with recesses or projections, e.g. hollows, grooves, protuberances, ribs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B2266/00—Composition of foam
- B32B2266/02—Organic
- B32B2266/0214—Materials belonging to B32B27/00
- B32B2266/025—Polyolefin
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24355—Continuous and nonuniform or irregular surface on layer or component [e.g., roofing, etc.]
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24479—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.] including variation in thickness
- Y10T428/24612—Composite web or sheet
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24628—Nonplanar uniform thickness material
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24752—Laterally noncoextensive components
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T428/00—Stock material or miscellaneous articles
- Y10T428/24—Structurally defined web or sheet [e.g., overall dimension, etc.]
- Y10T428/24752—Laterally noncoextensive components
- Y10T428/24769—Cellulosic
Abstract
유리 롤은 적어도 하나의 유리 필름 및 중간 재료를 포함하고, 이들은 와인딩 코어 상에 적어도 2개의 층으로 포개어 감기고, 유리 필름 층들은 중간 재료 층들에 의해 유리 롤에 고정된다. 유리 롤은 다음 단계를 포함하는 방법에 의해 제조된다: 유리 필름, 와인딩 코어 및 압축 가능한 중간 재료를 제공하는 단계, 와인딩 코어 상에 중간 재료의 적어도 하나의 내부 층을 감는 단계, 유리 필름이 중간 재료와 교대로 층층이 와인딩 코어 상에 놓이고 중간 재료 및/또는 유리 필름이 중간 재료를 압축하기에 적합한 인장 응력으로 감기도록, 유리 필름과 중간 재료를 와인딩 코어 상에 감는 단계, 및 유리 필름의 단부를 유리 롤에 고정하는 단계.The glass roll comprises at least one glass film and an intermediate material which are superposed on at least two layers on the winding core and the glass film layers are fixed to the glass roll by the intermediate material layers. The glass roll is produced by a method comprising the steps of: providing a glass film, a winding core and a compressible intermediate material; winding at least one inner layer of the intermediate material on the winding core; Winding a glass film and an intermediate material onto the winding core such that the layer is alternately placed on the winding core and the intermediate material and / or the glass film are wound with a tensile stress suitable for compressing the intermediate material, Securing to a glass roll.
Description
본 발명은 와인딩 코어 상에 감긴 유리 필름과 개별 유리 필름 층들 사이의 중간 재료로 이루어진 유리 롤에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a glass roll comprising an intermediate material between a glass film wound on a winding core and individual glass film layers.
다양한 용도를 위해, 예를 들면 가전 제품의 분야에서 예를 들면 반도체 모듈용, 유기 LED 광원용 또는 얇은 또는 휘어진 디스플레이 장치용 커버 유리로서 또는 회생 에너지 또는 에너지 기술 분야에서, 예를 들면 태양 전지용으로, 얇은 유리가 점차 더 사용된다. 이에 대한 예들은 터치 패널, 커패시터, 박막 배터리, 가요성 인쇄 회로 기판, 가요성 OLED, 가요성 광 전지 모듈 또는 e-페이퍼이다. 얇은 유리는 많은 용도에서 그 탁월한 특성, 예를 들면 내화학약품성, 내온도변동성, 내열성, 가스 불투과성, 높은 전기 절연력, 조절된 팽창 계수, 가요성, 높은 광학 품질 및 광 투과성 또는 2개의 얇은 유리면의 파이어폴리시된 표면(fire-polished surface)으로 인한 매우 낮은 조도를 가진 높은 표면 품질로 인해 점점 더 중요해지고 있다. 여기서, 얇은 유리는 약 1.2 ㎜ 미만의 두께 내지 15 ㎛ 이하의 두께를 가진 유리 필름을 말한다. 유리 필름으로서 얇은 유리는 그 가요성으로 인해 제조 후에 롤업되어 유리 롤로서 저장되거나 또는 제작 또는 후속 가공을 위해 이송되는 것이 증가하는 추세이다. 롤투롤(roll to roll) 공정에서, 유리 필름은 중간 처리, 예를 들면 표면의 코팅 또는 제작 후에 다시 롤업되어 후속 사용에 공급될 수 있다. 유리를 감는 것은 평면 재료의 저장 및 이송에 비해 더 경제적이고 컴팩트한 저장, 이송 및 후속 가공에서의 취급의 장점을 갖는다.For various applications, for example in the field of consumer electronics, for example for semiconductor modules, for organic LED light sources or for cover glass for thin or curved display devices, or in the field of regenerative energy or energy technology, Thin glass is increasingly used. Examples of such are touch panels, capacitors, thin film batteries, flexible printed circuit boards, flexible OLEDs, flexible photovoltaic modules or e-papers. Thin glass can be used for many applications, such as chemical resistance, resistance to temperature, heat resistance, gas impermeability, high electrical insulation, controlled expansion coefficient, flexibility, high optical quality and light transmittance, or two thin Are becoming increasingly important due to their high surface quality with very low roughness due to the fire-polished surface of the glass surface. Here, the thin glass refers to a glass film having a thickness of less than about 1.2 mm and a thickness of not more than 15 m. The thin glass as the glass film is in a tendency to be rolled up after manufacture due to its flexibility and stored as a glass roll or transferred for fabrication or subsequent processing. In a roll to roll process, the glass film may be re-rolled up after intermediate processing, such as coating or making the surface, and supplied for subsequent use. Winding glass has the advantages of more economical and compact storage, transport and handling in subsequent machining compared to the storage and transfer of flat materials.
유리는 상기 탁월한 특성들과 더불어 취성 재료로서 낮은 파괴 강도를 갖는데, 그 이유는 인장 응력에 대한 낮은 저항성을 갖기 때문이다. 유리가 휘어질 때, 휘어진 유리의 외부 표면에 인장 응력이 생긴다. 유리 롤의 파손 없는 저장을 위해 그리고 파손 없는 이송을 위해, 먼저 롤업된 유리 필름 내에 균열 및 파손의 생성을 막는 에지의 품질 및 무결성이 중요하다. 아주 작은 균열, 예를 들면 미세 균열과 같은 에지에서의 손상은 유리 필름에서 더 큰 균열 또는 파손에 대한 원인이 될 수 있다. 또한, 감긴 유리 필름의 상부면 상의 인장 응력으로 인해, 롤업된 유리 필름에 균열 또는 파손의 생성을 방지하기 위해서는 표면의 무결성 및 무스크래치 또는 무결함이 중요하다. 또한, 롤업된 유리 필름에 균열 또는 파손의 생성을 방지하기 위해, 제조로 인한 유리 내의 내압도 가능한 작거나 또는 없어야 한다. 통상의 제조에서 3개의 팩터가 제한적으로만 최적화될 수 있기 때문에, 이러한 롤업된 유리의 파괴 감도가 그 재료 특성의 기존 한계로 높아진다. 따라서, 유리 필름을 감기 위해 그리고 유리 롤의 저장 및 이송을 위해, 유리의 손상을 방지하기 위한 특별한 조치 및 조건이 중요하다.Glass has a low fracture strength as a brittle material with these excellent properties, because it has low resistance to tensile stress. When the glass is bent, a tensile stress is generated on the outer surface of the curved glass. For storage without breakage of glass rolls and for breakage-free transport, the quality and integrity of the edges that prevent the creation of cracks and breaks in the roll-up glass film first is important. Very small cracks, for example, damage at the edge, such as microcracks, can cause greater cracking or breakage in the glass film. In addition, due to the tensile stress on the top surface of the wound glass film, the integrity of the surface and scratches or non-scratches are important in order to prevent cracking or breakage in the roll-up glass film. Further, in order to prevent the generation of cracks or breakage in the rolled-up glass film, the withstand pressure in the glass due to manufacture should be as small as possible or not. Because the three factors in normal manufacture can only be optimized in a limited manner, the destructive sensitivity of these rolled-up glasses increases to the existing limits of their material properties. Therefore, for winding the glass film and for storing and transporting the glass roll, special measures and conditions are necessary to prevent damage to the glass.
여기서 한편으로는 유리 롤 상의 개별 또는 모든 유리 필름 층들의 진동이 문제이다. 다른 한편으로는 와인딩 코어 상에 롤업된 유리의 축 방향 이동이 손상을 야기할 수 있다. 또한, 개별 또는 모든 유리 필름 층들 간의, 즉 유리 필름 층들의 상대적인, 측면으로 향한 축 방향 이동은 매우 임계적이다. 유리 필름 층들은 계단형으로 포개어 놓이므로, 파손에 매우 민감한 돌출 에지 영역이 생긴다. 이러한 효과는 유리 필름 층 또는 유리 롤의 신축 자재에 의해 나타난다. 이 경우, 특히 다른 유리 필름 층에 대해 돌출한 하나 또는 다수의 다른 유리 필름 층의 영역이 파손 또는 균열될 수 있고, 이는 외부로부터 충격 또는 접촉에 의해 또는 진동에 의해 지원될 수 있다. 즉, 유리 필름의 돌출 영역들은 이 상태에서 유리 롤 결합체 내에서 보호되지 않는다.Here, on the one hand, the vibration of individual or all glass film layers on the glass roll is a problem. On the other hand, the axial movement of the glass rolled up on the winding cores can cause damage. In addition, the relative, sideward axial movement between individual or all glass film layers, i.e., the glass film layers, is very critical. Since the glass film layers are stacked in a stepped manner, there is a protruding edge area very sensitive to breakage. This effect is manifested by the stretching material of the glass film layer or the glass roll. In this case, the area of one or more other glass film layers, which protrude particularly for the other glass film layers, can be broken or cracked, which can be supported by impact or contact from the outside or by vibration. That is, the protruding regions of the glass film are not protected in this state in the glass roll combination.
또한, 유리 필름 층들 사이의 입자형 내포물이 손상을 일으키는 것이 방지되어야 한다. 한편으로는 내포물이 표면을 긁을 수 있고, 이는 특히 유리 필름 층들 간의 이동 또는 유리 필름 층들의 상대 이동에 의해 지원되거나, 또는 내포물이 점 형태의 압축 하중의 야기에 의해 균열 또는 파손을 일으킨다.In addition, the granular inclusions between the glass film layers must be prevented from causing damage. On the one hand, the inclusions can scratch the surface, which is particularly supported by the movement between the glass film layers or by the relative movement of the glass film layers, or the inclusion causes cracking or breakage due to the generation of a point-like compressive load.
유리 표면들 사이의 오염 입자에 의한 얇은 유리의 파손을 방지하기 위해, WO 87/06626은 유리 롤을 사용해서 롤투롤 공정에서 얇은 유리를 코팅하기 위한 방법을 제시하고, 유리 층들 사이에 유리에 대해 비마모성인 재료의 하나 또는 다수의 층, 예를 들면 플라스틱 필름이 제공된다. 플라스틱 필름은 폴리에스터 또는 폴리에틸렌과 같은 폴리머일 수 있고, 유리 상의 금속 코팅 또는 금속 산화물 코팅을 보호하기 위해 엠보싱된 패턴을 포함한다. 여기서는 유리 필름 층들의 측면 이동 또는 진동의 문제에 대한 해결책은 제공되지 않는다. 유리 표면 또는 코팅 표면과 중간 층 재료 사이의 상호 작용의 문제와 관련해서도 해결책이 제공되지 않는다.In order to prevent breakage of thin glass by contaminating particles between glass surfaces, WO 87/06626 proposes a method for coating a thin glass in a roll-to-roll process using a glass roll, One or more layers of non-abrasive material, for example a plastic film, are provided. The plastic film may be a polymer such as polyester or polyethylene and includes an embossed pattern to protect the metal coating or metal oxide coating on the glass. No solution is provided here for the problem of lateral movement or vibration of the glass film layers. No solution is provided in terms of the problem of the interaction between the glass surface or the coating surface and the intermediate layer material.
US 3,622,298은 유리 필름의 제조 및 롤업과 관련해서, 유리 필름 층들 사이의 중간 층으로서 크래프트지의 사용을 개시하며, 예를 들어 이송시 유리 필름 층의 이동 또는 진동의 문제를 인식하지 않았다.US 3,622,298 discloses the use of kraft paper as an intermediate layer between glass film layers in connection with the manufacture and roll-up of glass films, and has not recognized the problem of movement or vibration of the glass film layer, for example during transport.
US 3,089,801은 크래프트지 또는 알루미늄 필름의 사용을 개시한다. 여기서, 종이는 보강재로서 얇은 유리 상에 분리 가능하게 접착된다. 이로 인해, 유리는 벤딩 및 핸들링시 더 큰 강도를 얻기 때문에, 롤업 시에도 파손으로부터 보호된다. 그러나, 이 조치는 예를 들어 유리 롤의 이송시 유리 필름 층들의 이동 또는 진동에 의해 생기는 바와 같은, 유리 롤 상의 유리 필름의 가능한 파손의 원인을 방지하지 않는다. 또한, 접착된 종이 층이 파편이 분리되어 떨어지는 것을 방지하지만, 균열 또는 파손의 생성을 방지하지는 않는다.US 3,089,801 discloses the use of kraft paper or aluminum film. Here, the paper is detachably adhered on a thin glass as a reinforcing material. Because of this, the glass is protected from breakage even during roll-up, as it gains greater strength in bending and handling. However, this measure does not prevent the possible causes of breakage of the glass film on the glass roll, for example, as caused by movement or vibration of the glass film layers during transport of the glass roll. In addition, the layer of bonded paper prevents the debris from falling off separately, but does not prevent the creation of cracks or breakage.
US 2011/0171417은 얇은 유리의 에지들을 보호하기 위해, 롤업하여 유리 롤을 형성하기 전에 2개의 플라스틱 층들 사이에 얇은 유리의 적층을 개시한다. 얇은 유리의 한 면 상에 접착된 지지체 층이 제공되고, 상기 지지체 층은 얇은 유리의 가장자리를 지나 돌출한다. 얇은 유리의 다른 면 상에서 전체 면에 또는 에지의 영역에서만 그리고 에지를 지나 돌출하여 커버 층이 분리 가능하게 접착되므로, 에지들이 2개의 플라스틱 층들 사이에 적층되어 주어진 다음, 얇은 유리가 롤업된다. US 3,089,801에도 유리 롤 상의 유리 필름의 가능한 파손의 원인을 방지하기 위한 해결책이 제공되지 않는다. 접착 중간 층들의 분리시 유리 필름의 파손 위험도 문제이다. 또한, 접착제의 접착성 잔류물 또는 접착제에 의한 유리 표면의 영향이 상기 해결책의 단점이다.US 2011/0171417 discloses the lamination of thin glass between two plastic layers before rolling up to form a glass roll to protect the edges of the thin glass. A layer of a glued support is provided on one side of the thin glass, which protrudes past the edge of the thin glass. Since the cover layer is detachably adhered to the entire surface or only in the region of the edge and beyond the edge on the other side of the thin glass, the edges are laminated between the two plastic layers and then the thin glass is rolled up. US 3,089,801 does not provide a solution to prevent the possible causes of breakage of the glass film on the glass roll. The risk of breakage of the glass film in the separation of the adhesive interlayers is also a problem. The disadvantage of the above solution is the influence of the glass surface on the adhesive residue or adhesive of the adhesive.
WO 2010/038760은 상기 문제를 인식했고, 해결책으로서 유리 필름 층들 사이에 버퍼 아치의 측면 돌출을 제시한다. 유리 롤은 롤업된 유리에 대해 이격된 플랜지를 가진 와인딩 코어를 포함한다. 측면으로 돌출한 버퍼 아치 재료는 와인딩 코어 상에서 전체 유리 롤의 측면 이동시 또는 개별 유리 필름 층의 측면 이동시 또는 유리 필름 층들 간의 신축 자재시, 롤업된 유리 필름의 에지들이 플랜지에 충돌하여 파손되는 것을 방지한다. 여기서도 와인딩 코어 상에서 유리 필름 층 또는 유리의 측면 이동을 방지할 해결책이 제시되지 않는 것이 단점이다. 그 결과, 유리 롤이 예를 들어 신축 자재하거나 또는 유리 필름 층들이 공진 진동 상태인 경우 돌출한 버퍼 층 또는 중간 층에도 불구하고 유리의 파손이 나타날 수 있다. 이동시 에지들이 플랜지로부터 이격되는 해결책만이 제공된다. 또한, 유리 롤을 풀 때 돌출한 중간 층들이 서로 걸릴 수 있어서 유리 에지가 허용되지 않는 하중을 받아 파손되는 단점이 있다.WO 2010/038760 recognizes this problem and presents a lateral protrusion of the buffer arch between the glass film layers as a solution. The glass roll includes a winding core having flanges spaced apart from the roll-up glass. The laterally protruding buffer arch material prevents the edges of the rolled-up glass film from colliding with the flange to break when the entire glass roll is laterally moved on the winding core or when the side of the individual glass film layer is stretched or stretched between the glass film layers . Again, it is a disadvantage that no solution is proposed to prevent lateral movement of the glass film layer or glass on the winding core. As a result, breakage of the glass may occur despite the protruding buffer layer or intermediate layer when the glass roll is for example stretchable or the glass film layers are in a resonant oscillation state. Only a solution is provided in which the edges are separated from the flange upon movement. Further, the intermediate layers protruded when the glass roll is unwound can be caught by each other, and the glass edge is damaged by an unacceptable load.
US 2011/0200812는 유리 시트 또는 유리 필름을 롤업하여 슬리브를 형성하는 것을 개시하며, 여기서는 유리 필름의 2개의 층들 사이에 중간 층이 삽입되어 유리 필름 슬리브 내에 균열 발생을 방지한다. 중간 층은 US 2011/0200812에서 유리 필름의 손상을 방지하기 위해 그리고 유리 롤에 가해지는 극단의 압력을 흡수하기 위해 사용된다.US 2011/0200812 discloses forming a sleeve by rolling up a glass sheet or a glass film wherein an intermediate layer is inserted between the two layers of the glass film to prevent cracking in the glass film sleeve. The intermediate layer is used in US 2011/0200812 to prevent damage to the glass film and to absorb extreme pressure applied to the glass roll.
또한, WO 2010/038760 A1은 중간 층이 개별 유리 층들 사이로 삽입되므로 파손 위험이 줄어든 유리 롤을 개시한다. 이 공보도 손상을 피하기 위한 중간 층의 삽입만을 개시한다.WO 2010/038760 A1 also discloses a glass roll in which the risk of breakage is reduced because the intermediate layer is inserted between individual glass layers. This publication also only initiates insertion of the intermediate layer to avoid damage.
WO 87/06626은 유리 롤 내에서 인접한 유리 층의 표면을 분리하기 위해 코팅 방법인 스퍼터링에 의해 개별 유리 층에 코팅을 제공한 유리 롤을 개시한다. 상기 공보도 슬리브 내의 인접한 유리 층들의 면 접촉 및 에지 접촉을 방지하기 위한 중간 층의 삽입만을 개시한다. 감김이 느슨한 경우 유리 층들은 서로 측면으로 이동되거나 또는 진동할 수 있다.WO 87/06626 discloses a glass roll provided with coatings on individual glass layers by sputtering which is a coating method to separate the surfaces of adjacent glass layers in a glass roll. The publication also discloses only the insertion of the intermediate layer to prevent surface contact and edge contact of adjacent glass layers in the sleeve. If the winding is loose, the glass layers may move laterally or oscillate with respect to each other.
본 발명의 과제는 전술한 단점을 없애고 롤업된 유리에 대한 큰 보호와 더불어 유리 롤의 이동 또는 진동을 방지하는 유리 롤을 제공하는 것이다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION It is an object of the present invention to provide a glass roll which eliminates the aforementioned disadvantages and prevents movement or vibration of the glass roll together with a great protection against roll-up glass.
상기 과제는 청구항 제 1 항 및 제 17 항 및 청구항 제 41 항 및 제 43 항의 특징에 의해 달성된다. 바람직한 실시예들은 종속 청구항 제 2 항 내지 제 16 항, 제 18 항 내지 제 40 항 및 제 42 항에 제시된다.This object is achieved by the features of claims 1 and 17 and claims 41 and 43. Preferred embodiments are given in
유리 롤은 적어도 하나의 유리 필름 및 중간 재료를 포함하고, 상기 유리 필름 및 중간 재료는 와인딩 코어 상에 적어도 2개의 층으로 포개어 감기고, 유리 필름 층들은 중간 재료 층에 의해 고정된다. 본 명세서에서 고정은, 유리 롤 내에서 감긴 유리 층들 사이에, 감긴 방향에 대해 실질적으로 횡으로 힘의 작용시 슬리브의 가능한 곧게 감긴 측면이 가급적 유지되며 유리 롤의 신축 자재가 가급적 방지되게 하는 힘이 작용하는 것을 말한다.The glass roll comprises at least one glass film and an intermediate material, wherein the glass film and the intermediate material are superposed on at least two layers on the winding core, and the glass film layers are fixed by the intermediate material layer. The fixation herein refers to a force between the glass layers wound in the glass rolls such that the possibly straightened wound side of the sleeve when the force acts substantially transversely with respect to the winding direction is maintained as much as possible and the elastic material of the glass roll is preferably prevented .
발명자는 유리 시트의 예비 응력에 따라 롤 내부의 마찰이 영향을 받을 수 있기 때문에 유리 층들 간의 이동, 즉 유리 롤의 신축 자재가 방지될 수 있다는 것을 알았다.The inventors have found that the movement between the glass layers, that is, the stretching of the glass roll, can be prevented because the friction inside the roll can be affected by the pre-stress of the glass sheet.
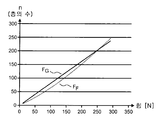
n개의 감긴 층을 가진 슬리브에서 층들 사이에 정지 마찰 계수 μ가 나타나고 방사방향력 FR이 작용하면, 감긴 재료와 코어 사이의 마찰 FF은 다음과 같다:In a sleeve with n winding layers, a static friction coefficient μ appears between the layers and, when the radial force FR acts, the friction FF between the wound material and the core is:
방사방향력 FR은 감을 때 예를 들면 중간 재료에 세팅될 수 있는 예비 응력 FV에 상응한다. 즉, FR = FV.The radial direction force FR corresponds to a pre-stress FV that can be set, for example, on the intermediate material when it is rolled. That is, FR = FV.
슬리브가 신축 자재하지 않도록 하기 위해, 마찰이 슬리브에 작용하는 중량보다 커야 한다. 즉, FF > FG. 마찰 대 총 질량의 비가 가장 내부의 유리 필름 층에서 가장 바람직하지 않기 때문에, 슬리브가 대개 가장 내부의 층에서 파손된다. 슬리브에 작용하는 중량은 다음 식으로 표시된다:In order to prevent the sleeve from stretching, the friction must be greater than the weight acting on the sleeve. That is, FF> FG. Since the ratio of friction to total mass is the least desirable in the innermost glass film layer, the sleeve is usually broken in the innermost layer. The weight acting on the sleeve is expressed by the following equation:
상기 식에서, In this formula,
FV 예비 응력FV pre-stress
FG 중량FG weight
FR 방사방향력FR Radial Direction
FF 마찰(감긴 재료와 코어 사이의)FF friction (between wound material and core)
n 감긴 층의 수n Number of wound layers
b 유리 재료 폭b Glass material width
r 롤 반경(코어)r Roll radius (core)
t1 유리 두께t1 Glass thickness
t2 중간 층 두께t2 intermediate layer thickness
μ 정지 마찰 계수μ static friction coefficient
PF 표면 압력PF surface pressure
AF 작용면AF working face
m 감긴 재료의 총 질량m Total mass of wound material
ρ 유리 밀도ρ glass density
g = 9.81 m/s2 g-힘, g-가속도g = 9.81 m / s 2 g-force, g-acceleration
식에 나타나는 바와 같이, 롤의 신축 자재를 방지하기 위해 상대적으로 적은 예비 응력 FV = FR이 필요하다.As shown in the equation, a relatively small preliminary stress FV = FR is required in order to prevent the stretching material of the roll.
발명자의 공로에 의해, 상기 식에 따라 각각의 유리 시트에 대해By virtue of the inventors, according to the above formula, for each glass sheet,
b 유리 재료 폭b Glass material width
r 롤 반경(코어)r Roll radius (core)
t1 유리 두께t1 Glass thickness
t2 중간 층 두께t2 intermediate layer thickness
μ 정지 마찰 계수μ static friction coefficient
ρ 유리 밀도ρ glass density
과 같은 공지된 특성 및 미리 정해진, 감긴 층의 수 n에서, n 개의 감긴 층을 가진 유리 슬리브의 신축 자재를 방지하기 위해 필요한 예비 응력 FV가 결정될 수 있다., The preliminary stress FV required to prevent the stretching material of the glass sleeve having n winding layers can be determined at the number n of predetermined winding layers.
와인딩 코어는 통상 200 내지 600 ㎜의 직경을 갖고, 나무, 플라스틱, 판지, 금속 또는 복합 재료와 같은 안정한 재료로 이루어질 수 있다. 와인딩 코어는 표면에 적합한 미끄럼 방지 및 경우에 따라 압축 가능한 코팅을 갖거나 또는 구조화된 표면을 가질 수 있다.The winding cores typically have a diameter of 200 to 600 mm and may be made of a stable material such as wood, plastic, cardboard, metal or composite material. The winding core may have a slip resistant and optionally compressible coating suitable for the surface or may have a structured surface.
유리 필름은 특정 길이를 가진 연속하는 긴 시트이고, 하나의 유리 롤에서 유리 필름들은 단일 길이를 가질 수 있거나 또는 다수의 짧은 길이로 하나의 롤에 감긴다. 통상, 이러한 유리 필름은 300 내지 800 ㎜ 범위의 폭 및 200 내지 1000 m의 길이를 갖는다. 이러한 유리 필름들은 공지된 방식으로 다운-드로우 방법 또는 오버플로-다운-드로우-퓨전 방법에 의해 제조된다(예를 들면 다운-드로우 방법에 대해 WO 02/051757 A2 및 오버플로-다운-드로우-퓨전 방법에 대해 WO 03/051783 A1 참고). 성형되고 드로잉된 무한 시트가 하나의 유리 롤 상에 감기고 명세에 따라 길이 절단된다.The glass film is a continuous long sheet having a specific length, and in one glass roll, the glass films can have a single length or are wound on one roll in a plurality of short lengths. Typically, such glass films have a width in the range of 300 to 800 mm and a length of 200 to 1000 m. Such glass films are produced by the down-draw method or the over-flow-down-draw-fusion method in a known manner (see, for example, WO 02/051757 A2 for over- See WO 03/051783 A1). The formed and drawn infinite sheet is wound on one glass roll and lengthwise cut according to the specification.
유리 필름은 이 경우 적합한 종류의 유리, 특히 붕소실리케이트 유리 또는 알루미노붕소실리케이트 유리로 이루어질 수 있다. 롤업시 파손 위험 및 균열 생성을 줄이기 위해, 표면은 파이어폴리시되어 매우 매끄러울 수 있다. 이로 인해, 유리 필름은 휘어진 유리의 외부면에서 더 큰 인장 응력을 흡수할 수 있고 더 작은 반경으로 휘어질 수 있다. 표면 조도에 따라 각각의 유리에 있어 표면에 임계 응력이 주어지고, 상기 임계 응력에서는 표면 조도의 크기 범위에 있는 깊이를 가진 기존 초기 균열이 독자적으로 계속 이동하여 유리를 파괴한다(취성 파괴). 유리가 얇을수록, 주어진 휨 반경에 의해 표면에 생기는 응력이 더 작아진다. 따라서, 예를 들면 레이저 스크라이빙된 에지를 가진 100 ㎛ 두께의 유리 필름이 파손 없이 50 ㎜의 반경 둘레로, 30 ㎛ 두께의 유리 필름이 파손 없이 24 ㎜의 반경 둘레로, 또는 15 ㎛ 두께의 유리 필름이 파손 없이 12 ㎜의 반경 둘레로 감겨질 수 있다. 또한, 50 ㎛ 두께의 유리 필름이 파손 없이 5 ㎜ 반경 둘레로 감겨질 수 있고 2 ㎜의 반경도 가능하다. 특히 저-알칼리 유리의 얇은 드로잉에 의해 바람직하게는 15-30 ㎛의 두께 범위에서 특히 매끄러운 표면이 형성되는 것으로 나타났다.The glass film may in this case consist of a suitable kind of glass, in particular borosilicate glass or aluminoborosilicate glass. To reduce risk of breakage and cracking during roll-up, the surface may be fire-polished and very smooth. As a result, the glass film can absorb larger tensile stress on the outer surface of the curved glass and can be bent to a smaller radius. According to the surface roughness, critical stress is given to the surface of each glass, and at the critical stress, the existing initial crack having a depth in the range of the surface roughness continuously moves independently to destroy the glass (brittle fracture). The thinner the glass, the smaller the stress on the surface due to the given bending radius. Thus, for example, a 100 micron thick glass film with a laser scribed edge may be formed around a radius of 50 millimeters without breakage, a 30 micron thick glass film around a 24 millimeter radius without breakage, The glass film can be wound around a radius of 12 mm without breakage. Further, a glass film having a thickness of 50 占 퐉 can be wound around a radius of 5 mm without breakage, and a radius of 2 mm is also possible. In particular, the thin drawing of the low-alkali glass has been shown to produce a particularly smooth surface, preferably in the thickness range of 15-30 [mu] m.
얇은 유리의 파손 없는 감김을 보장하기 위해, 예를 들면 파이어폴리시와 같은 적합한 조치에 의해 미세 균열을 거의 갖지 않으며 낮은 조도를 갖는 에지가 제공되므로, 낮은 파손 확률을 가진 유리 시트의 감김이 제공된다.The winding of the glass sheet with a low breakage probability is provided in order to ensure the breakage-free winding of the thin glass, by means of suitable measures such as, for example, fire-protection, with few microcracks and low edge roughness.
특정 직경을 가진 유리 슬리브를 제조할 수 있는 가능성은 파손 확률로 표시된다. 즉, 유리 시트 또는 1000 m의 길이 및 5 ㎛ 내지 350 ㎛, 특히 15 ㎛ 내지 200 ㎛ 범위의 두께를 가진 다수의 유리 필름의 고려시 유리 필름이 50 ㎜ 내지 1000 ㎜, 특히 150 ㎜ 내지 650 ㎜ 범위의 직경을 가진 롤로 감길 때 깨질 확률은 1% 미만이다.The possibility of manufacturing a glass sleeve with a specific diameter is indicated by the breakage probability. That is, considering the glass sheet or a number of glass films having a length of 1000 m and a thickness in the range from 5 탆 to 350 탆, particularly from 15 탆 to 200 탆, the glass film has a thickness in the range of 50 mm to 1000 mm, Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > 1%. ≪ / RTI >
표 1에는 상이한 유리 필름들에 대해, 롤 반경으로 유리 필름의 롤업에 의해 생긴 에지 강도, 즉 응력이 MPa로 표시된다.Table 1 shows the edge strength, or stress, in MPa, caused by the roll-up of the glass film in roll radius, for different glass films.
유리는 마인츠에 소재하는 Schott AG의 유리 AF32eco, D263Teco 및 MEMpax 이다. 응력 σ(MPa)은 유리 두께 d(㎛) 및 감긴 유리 롤의 직경 D(㎜)에 따라 제시된다. 에지 강도 즉, 유리 시트의 외부면 상의 응력을 결정하기 위한 식은 다음과 같다:The glass is Schott AG's glass AF32eco, D263Teco and MEMpax from Mainz. The stress? (MPa) is given according to the glass thickness d (占 퐉) and the diameter D (mm) of the wound glass roll. The equation for determining the edge strength, i. E. The stress on the outer surface of the glass sheet, is as follows:
σ= E·y/r σ = E · y / r
상기 식에서, E는 탄성 계수이고, y는 롤업될 유리 시트의 유리 두께 절반 d/2 이며, r 은 롤업된 유리 시트의 롤업 반경이다.Where y is the glass thickness of the glass sheet to be rolled up to d / 2 and r is the roll-up radius of the rolled up glass sheet.
분석할 다수의 샘플에 대한 파괴 확률을 알면, 표 1의 σ에 대한 값에 의해, 특정 길이 및 롤 반경을 가진 유리 시트의 파손 또는 파손 확률(P)이 결정될 수 있다. 파손 확률은 와이불 분포를 형성하고, 상기 분포의 폭은 와이불-파라미터에 의해 특성화된다.Knowing the probability of failure for a number of samples to be analyzed, the value for σ in Table 1 can determine the breakage or failure probability P of a glass sheet having a specific length and roll radius. The breakage probability forms a wobble distribution, and the width of the distribution is characterized by a wobble-parameter.
WIKIPEDIA-백과 사전에 따르면, 와이불 분포는 유리와 같은 취성 재료의 수명 및 파손 빈도를 나타내기 위해 사용되는 포지티브 실수의 집합에 대한 연속 확률 분포이다. 와이불 분포는 기술적 시스템의 고장률을 나타내기 위해 사용될 수 있다. 와이불 분포는 분포의 폭, 소위 와이불 계수에 의해 특성화된다. 일반적으로 계수가 커질수록 분포가 좁아진다.According to the WIKIPEDIA-Encyclopedia, the quadratic distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a set of positive real numbers used to indicate the lifetime and frequency of breakage of brittle materials such as glass. And blanket distribution can be used to indicate the failure rate of the technical system. And blanket distributions are characterized by the width of the distribution, the so-called blanket coefficients. Generally, the larger the coefficient, the narrower the distribution.
50 ㎜의 샘플 길이로 2점 휨 측정을 실시하면, 와이불 계수를 아는 경우 길이 L을 가진 유리 시트의 파손 확률은 다음과 같이 결정된다:When two-point bending measurements are made with a sample length of 50 mm, the probability of breakage of a glass sheet with length L is determined as follows:
상기 식에서, In this formula,
P는 롤 반경 r에서 길이 L의 유리 시트의 파손 확률이고,P is the breakage probability of the glass sheet of length L in roll radius r,
L은 파손 확률이 결정되는 유리 시트 길이이고,L is the glass sheet length at which the breakage probability is determined,
l은 2점 테스트에서 사용되는 관련 샘플 길이이고, 바람직하게는 l = 50 ㎜,l is the relevant sample length used in a two point test, preferably l = 50 mm,
σ(r)은 롤 반경 r으로 롤업에 의해 생긴 응력이고, μ는 2점-휨에 의해 결정된 응력이며, β는 분포의 폭 및 그에 따라 작은 강도로의 연장을 나타내는 와이불 계수이다.σ (r) is the stress caused by the roll-up at roll radius r, μ is the stress determined by the two-point bending, and β is the bending modulus indicating the width of the distribution and hence the extension to small strength.
파손 확률의 허용은, 두께 d의 유리 시트를 반경 r으로 감고자 하고 1000 m의 롤업 길이에서 1%의(또는 더 작은) 파손 확률을 달성하고자 하며 2점 측정의 관련 샘플 길이가 50 ㎜인 경우 하기 조건식을 세우는 것을 가능하게 한다:Allowance of breakage probability is to achieve a breakage probability of 1% (or smaller) at a roll-up length of 1000 m with a radius r of a glass sheet of thickness d and to achieve a breakage probability of 50% It makes it possible to establish the following conditional expression:
σ(r)에 대해 표 1의 응력이 주어지면, 시스템을 특성화하고 "성능 지수"라고도 하는 파라미터로서 하기 식이 주어진다:Given the stresses in Table 1 for [sigma] (r), the system is characterized and given the following equation as a parameter called "figure of merit &
바람직하게는 파이어폴리시와 같은 조치에 의한 에지 강도의 상승에 의해, α의 값이 예를 들면 12로부터 14.5로 상승한다.Preferably, the value of alpha rises from, for example, 12 to 14.5 due to an increase in edge strength by a measure such as fire policy.
본 발명에 따라 감긴 유리 필름은 통상 최대 350 ㎛, 바람직하게는 최대 100 ㎛, 더욱 바람직하게는 최대 50 ㎛, 특히 바람직하게는 최대 30 ㎛ 그리고 적어도 5 ㎛, 바람직하게는 적어도 10 ㎛, 특히 바람직하게는 적어도 15 ㎛의 두께를 갖는다. 여기서는 바람직하게 이러한 얇은 유리 필름이 그 탄성으로 인해 문제없이 작은 반경으로 휘어지고 감길 수 있다.The wound glass film according to the invention is usually at most 350 μm, preferably at most 100 μm, more preferably at most 50 μm, particularly preferably at most 30 μm and at least 5 μm, preferably at least 10 μm, Has a thickness of at least 15 [mu] m. Here, such a thin glass film is preferably bent and wound to a small radius without problems due to its elasticity.
바람직한 유리 필름 두께들은 15, 25, 30, 35, 50, 55, 80, 100, 130, 160, 190, 280 ㎛ 이다.Preferred glass film thicknesses are 15, 25, 30, 35, 50, 55, 80, 100, 130, 160, 190, 280 탆.
본 발명에 따라 감긴 유리 필름은 그 양 측면의 적어도 하나의 표면에, 바람직하게는 양 측면의 표면에, 그리고 경우에 따라 적어도 2개의 마주 놓인 에지에, 특히 전술한 파손 확률을 제공하기 위해 파이어폴리시된 표면을 갖는다.The wound glass film according to the present invention may be applied to at least one surface of both sides thereof, preferably on both sides of the surface, and in some cases at least two opposing edges, Lt; / RTI >
2차 평균 조도(RMS) Rq는 그 양 측면 중 적어도 하나의 측면의 표면에서 최대 1 나노미터, 바람직하게는 최대 0.8 나노미터, 더욱 바람직하게는 최대 0.5 나노미터이다. 평균 표면 조도 Ra는 그 양 측면 중 적어도 하나의 측면의 표면에서, 670 ㎛ 의 측정 길이에 대해 최대 2 나노미터, 바람직하게는 최대 1.5 나노미터, 특히 바람직하게는 최대 1 나노미터이다. 바람직한 실시예에서, 유리 필름의 양 측면의 표면이 상기 조도 값을 갖는다. 특히, 휠 때 인장 응력을 받는 유리 필름의 측면이 상기 조도 값을 특징으로 한다.The secondary average roughness (RMS) Rq is at most 1 nanometer, preferably at most 0.8 nanometer, more preferably at most 0.5 nanometer at the surface of at least one side of both sides thereof. The average surface roughness Ra is at most 2 nanometers, preferably at most 1.5 nanometers, particularly preferably at most 1 nanometer, for a measurement length of 670 mu m, at the surface of at least one side surface of both sides thereof. In a preferred embodiment, the surfaces on both sides of the glass film have the above illuminance values. In particular, the side surface of the glass film subjected to tensile stress at the wheel is characterized by the roughness value.
상기 매끄러운 표면은 유리 표면에서 인장 응력으로 인한 파손 위험 없이 유리 필름의 휨 및 롤업을 용이하게 하지만, 이는 유리 롤 내의 유리 필름 층들 간의 측면 이동 또는 유리 필름 층들의 상대 측면 이동을 촉진하고, 다소 뚜렷하게 유리 필름 층들의 신축 자재 또는 와인딩 코어 상에 롤업된 유리의 측면 이동을 촉진하는데, 그 이유는 유리 표면의 마찰 계수가 매우 작기 때문이다.The smooth surface facilitates bending and roll-up of the glass film without risk of breakage due to tensile stress on the glass surface, but this facilitates lateral movement of the glass film layers in the glass roll or relative side movement of the glass film layers, Promotes lateral movement of the rolled up glass on the stretching material or winding core of the film layers, because the coefficient of friction of the glass surface is very small.
본 발명에 따라 이는 유리 필름 층들이 중간 재료에 의해 유리 롤 상에 고정됨으로써 방지된다. 중간 재료는 유리 롤의 롤업된 상태에서 각각의 유리 필름 층을 양면에서 적어도 부분적으로, 바람직하게는 전체 면에서 커버한다. 이 경우, 먼저 적어도 하나의 중간 재료 층이 와인딩 코어 상에 감기고, 그 위에 제 1 유리 필름 층이 놓인 다음 중간 재료와 유리 필름이 교대로 롤업된다. 전체 유리 필름 길이가 감기면, 마지막 유리 필름 층을 고정하기 위해 하나 또는 다수의 중간 재료 층들이 외부에서 유리 롤 둘레로 감긴다. 가장 하부의 또는 내부의 중간 재료 층, 즉 와인딩 코어와 제 1 유리 필름 층 사이의 접촉 층이 대안으로서 다른 재료로 형성될 수 있거나 또는 와인딩 코어가 고정 재료로 코팅된다. 마지막 가장 상부의 또는 외부의 중간 재료 층 또는 다수의 중간 재료 층은 대안으로서 또는 추가로 예를 들면 특별한 외부 보호 필름 또는 종이 및/또는 접착 시트 또는 고정 시트와 같은 다른 재료로 이루어진 층으로 형성될 수 있다. 여기서는, 내부 중간 층들의 압력을 유지하기 위해, 가장 상부의 유리 필름 층이 확실하게 고정되는 것이 중요하다.According to the invention this is prevented by the glass film layers being fixed on the glass roll by the intermediate material. The intermediate material covers each glass film layer at least partially, preferably entirely, on both sides in a roll-up state of the glass roll. In this case, at least one intermediate material layer is first wound on the winding core, on which the first glass film layer is placed, and then the intermediate material and the glass film are alternately rolled up. If the entire glass film length is wound, one or more layers of intermediate material are wound from the outside around the glass roll to fix the last glass film layer. The innermost or inner intermediate material layer, i.e. the contact layer between the winding core and the first glass film layer, can alternatively be formed of different materials or the winding core is coated with a fixing material. The last topmost or outer intermediate material layer or multiple layers of intermediate material may alternatively or additionally be formed of a layer made of, for example, a special outer protective film or paper and / or other material such as an adhesive sheet or a fixing sheet have. Here, in order to maintain the pressure of the inner intermediate layers, it is important that the uppermost glass film layer is securely fixed.
중간 재료는 본 발명에 따라 중간 재료가 필요에 따라 압축되거나 또는 압축 하중을 받거나 또는 신장될 정도의 크기인 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력으로 감긴다. 롤투롤 공정에서도 유리 필름은 감길 때, 중간 재료가 필요에 따라 압축되거나 또는 압축 하중을 받는 정도의 크기인 특정 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력으로 감긴다. 통상, 중간 재료의 약한 압축으로 충분하다. 압축에 의해, 일반적으로 유리 필름 층들이 충분히 고정되기에 충분한, 유리 필름과 중간 재료의 긴밀하고 컴팩트한 슬리브 유닛이 형성된다. 유리 필름 층들은 압축된 중간 재료에 의해 고정된다.The intermediate material is wound in accordance with the present invention with a pre- or tensile stress of a magnitude to such an extent that the intermediate material is compressed, or subjected to a compressive load or stretched as required. In the roll-to-roll process, the glass film is wound with a specific pre-stress or tensile stress, which is of the order of magnitude to the extent that the intermediate material is compressed as required or subjected to a compressive load when rolled. Usually, a weak compression of the intermediate material is sufficient. By compression, a tight and compact sleeve unit of a glass film and an intermediate material is formed, which is generally sufficient for the glass film layers to be sufficiently fixed. The glass film layers are fixed by a compressed intermediate material.
본 발명의 바람직한 실시예에서, 중간 재료는 탄성력을 갖고, 압축된 상태에서 인접한 유리 필름 표면에 대해 상응하는 이완력을 가진 복원 압력을 가한다. 이로 인해, 유리 필름 층들의 특히 확실한 고정이 이루어진다. 여기서, 유리 필름 층들은 압축된 중간 재료에 의해 고정되고, 상기 중간 재료는 복원 압력을 유리 필름 층들에 대해 가한다.In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the intermediate material has an elastic force and exerts a restoring pressure with a corresponding relaxing force against the adjacent glass film surface in the compressed state. This results in a particularly secure fixation of the glass film layers. Here, the glass film layers are fixed by a compressed intermediate material, which applies a restoring pressure to the glass film layers.
중간 재료는 유리 표면과 상호 작용해서 특정 정지 마찰을 갖고, 상기 정지 마찰은 이동에 대한 유리 필름 층들의 고정 정도를 나타낸다. 상기 정지 마찰은 유리 필름 표면에 대한 중간 재료의 복원 압력 또는 표면 장력에 의해 또는 중간 재료에 대한 유리 필름의 복원 압력 또는 표면 장력에 의해 높아진다. 중간 재료 및 예비 응력에 따라 중간 재료 층에 의해 가해진 복원 압력은 1 내지 200 kPa(킬로파스칼)이다. 유리 롤 내의 유리 필름들의 고정에 대한 제 3 팩터는 매우 매끄러운 유리 표면에 대한 중간 재료의 접착이다. 상기 접착은 유리 필름 표면에 대한 중간 재료의 압력에 의해 또는 중간 재료에 대한 유리 필름의 압력에 의해 커진다.The intermediate material interacts with the glass surface to have a certain static friction, which represents the degree of fixation of the glass film layers to movement. The static friction is increased by the restoring pressure or the surface tension of the intermediate material with respect to the glass film surface or by the restoring pressure or the surface tension of the glass film with respect to the intermediate material. The restoration pressure applied by the intermediate material and the intermediate material layer in accordance with the pre-stress is 1 to 200 kPa (kilopascals). A third factor for the fixing of the glass films in the glass roll is the adhesion of the intermediate material to a very smooth glass surface. The adhesion is increased by the pressure of the intermediate material against the glass film surface or by the pressure of the glass film against the intermediate material.
중간 재료는 유리 롤 내의 유리 필름과 함께 정지 마찰에 의한 압력 끼워맞춤 결합을 형성하기 때문에, 유리 필름은 유리 롤 내에 고정된다.Since the intermediate material forms a pressure-fit bond by static friction with the glass film in the glass roll, the glass film is fixed in the glass roll.
감길 때 중간 재료 및/또는 유리 필름의 인장 응력이 클수록, 더 적은 공기가 함께 감기고, 이는 유리 필름 결합체에서 유리 롤 내의 유리 필름 층들의 진동을 저지한다. 중간 재료 및/또는 유리 필름이 감기는 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력에 따라 규정된 와인딩 타이트니스(winding tightness)가 달성된다. 와인딩 타이트니스가 클수록 유리 필름이 유리 롤 내에 더 양호하게 고정된다.The greater the tensile stress of the intermediate material and / or the glass film upon winding, the less air is wound together as it cools, which prevents the vibration of the glass film layers in the glass roll in the glass film combination. A prescribed winding tightness is achieved in accordance with the pre-stress or tensile stress at which the intermediate material and / or the glass film is wound. The larger the winding tightness, the better the glass film is fixed within the glass roll.
또한, 유리 필름 내의 평탄하지 않음은 압축 가능한 중간 재료에 의해 보상된다. 이로 인해, 유리 필름의 파손을 일으키는 응력 증가가 방지될 수 있다. 상기 평탄하지 않음은 상이한 두께 프로파일로 인한 예를 들면 "워프(warp)"(응력에 의해 동결된 더 큰 파형) 및 "웨이브니스(waviness)"(표면의 미세 파형)이다.Also, the unevenness in the glass film is compensated by the compressible intermediate material. As a result, an increase in stress causing breakage of the glass film can be prevented. The non-planar is for example "warp" (a larger waveform frozen by stress) and "waviness" (microfine of the surface) due to different thickness profiles.
또한, 유리 필름 층들 사이의 오염의 입자형 내포물이 압축 가능한 중간 재료에 의해 흡수되기 때문에, 입자와 유리 필름 사이의 응력 피크가 보상되고 유리 필름의 손상이 방지될 수 있다. 상기 입자는 유리 필름의 롤업 전에 이미 유리 필름의 표면에 또는 중간 재료의 표면에 존재했던 입자이다.In addition, since the particulate inclusion of the contamination between the glass film layers is absorbed by the compressible intermediate material, the stress peaks between the particles and the glass film can be compensated and damage to the glass film can be prevented. The particles are particles which have already existed on the surface of the glass film or on the surface of the intermediate material before the roll-up of the glass film.
본 발명에 따른 유리 롤은 또한, 높은 와인딩 타이트니스 및 중간 재료에 의해 유리 필름 상으로 가해진 복원 압력에 의한 유리 필름 층들의 고정으로 인해, 유리 필름의 개별 층들 사이로 오염물의 침투에 대한 유리 롤의 확실한 측면 밀봉이 달성될 수 있다는 장점을 갖는다.The glass roll according to the present invention is also characterized by the fact that due to the fixing of the glass film layers by the restoring pressure exerted on the glass film by the high winding tightness and the intermediate material the clearness of the glass roll against the penetration of contaminants between the individual layers of the glass film Side sealing can be achieved.
일 실시예에서, 중간 재료 층들은 유리 필름 에지를 충돌로부터 보호하기 위해 측면으로 유리 필름 에지를 지나 돌출할 수 있다. 이 경우, 돌출은 유리 롤을 감을 때 중간 재료 층들이 걸리지 않도록 제한된다.In one embodiment, the intermediate material layers may project laterally beyond the glass film edge to protect the glass film edge from impact. In this case, the protrusion is restricted so that the intermediate material layers do not get caught when winding the glass roll.
본 발명의 다른 실시예에서, 슬리브의 폭에 걸쳐 연장되거나 또는 그것을 지나 연장되는 중간 층 대신에, 전술한 바와 같이, 더 좁은 하나의 중간 층 또는 다수의 중간 층 또는 중간 층 시트들이 제공되고, 이 경우 개별 중간 층 시트들의 폭은 감긴 유리 시트의 폭보다 훨씬 더 작다. 이는 청구항 제 17항의 대상이다. 청구항 제 17 항에 따라, 유리 필름이 제 1 폭을, 중간 재료 시트들 각각은 제 2 폭을 갖고, 상기 제 2 폭 B2가 제 1 폭 B1보다 훨씬 더 좁은 것이 요구된다.In another embodiment of the present invention, instead of the intermediate layer extending over or beyond the width of the sleeve, a narrower intermediate layer or multiple intermediate or intermediate layer sheets are provided, as described above, The width of the individual intermediate layer sheets is much smaller than the width of the rolled glass sheet. This is the subject of claim 17. According to claim 17, it is required that the glass film has a first width, each of the intermediate material sheets has a second width, and the second width B2 is much narrower than the first width B1.
중간 층 시트들의 폭은 실제로 마찰에 영향을 주지 않는다. 중간 층 시트들의 폭이 줄어들면, 자동으로 표면 장력이 커진다. 표면 장력은 작용 면과 곱해져서 방사방향력을 제공하고, 상기 방사방향력은 정지 마찰 계수와 함께 마찰을 제공한다. 또한, 다수의 유리 시트들을 사용함으로써, 기하학적 불균일성, 예를 들면 웨이브니스, 워프가 매우 쉽게 보상될 수 있다. 이와는 달리, 중간 층의 전체 면의 불균일성은 중간 층 재료의 압축률에 의해서만 흡수될 수 있다. 이를 위해, 중간 층 재료에 따라 부분적으로 매우 큰 힘이 필요하며, 이 힘은 유리 시트로 전달되지 않고 유리 두께 및 그로 인해 없어진 강성으로 인해 중간 층 재료에도 가해질 수 없다. 상기 힘이 항상 평형 상태에 있기 때문에, 중간 층 재료의 경도에 따라 응력이 상응하는 크기로 유리 롤 내에 형성된다. 따라서, 압축 불가능한 중간 층 재료, 예를 들면 클린룸 필름의 경우, 전체 응력이 유리 시트에 의해 흡수되어야 한다.The width of the interlayer sheets does not actually affect friction. As the width of the intermediate layer sheets decreases, the surface tension automatically increases. The surface tension is multiplied by the working surface to provide a radial force, which provides friction with a static coefficient of friction. Further, by using a plurality of glass sheets, the geometric non-uniformity, e.g., wave and warp, can be compensated very easily. Alternatively, the non-uniformity of the entire surface of the intermediate layer can be absorbed only by the compressibility of the intermediate layer material. To this end, a very large force is required in part depending on the intermediate layer material, which force is not transmitted to the glass sheet and can not be applied to the intermediate layer material due to the glass thickness and hence the stiffness lost. Since the force is always in equilibrium, the stress is formed in the glass roll at a corresponding magnitude according to the hardness of the intermediate layer material. Thus, in the case of an uncompressible intermediate layer material, such as a clean room film, the total stress must be absorbed by the glass sheet.
또한, 좁은 중간 층 시트들을 사용할 수 있는 가능성이 있다. 이는 유리 시트가 하나의 유리 층으로부터 다음 유리 층으로 이격된다는 장점을 갖지만, 다수의 좁은 중간 층 시트들의 사용시 좁은 중간 층 시트의 좌우에서 또는 사이 공간 내에서 기하학적 불규칙성이 연장될 수 있다.In addition, there is a possibility that narrow intermediate layer sheets can be used. This has the advantage that the glass sheet is spaced from one glass layer to the next glass layer, but geometric irregularities can be prolonged in the use of a number of narrower intermediate layer sheets, right or left of the narrower intermediate layer sheet or in the interspace.
유리 시트의 일면의 특정한 곡률도 가능하다. 이러한 유리 시트에서는 중성 선이 규정된다. 상기 중성 선은, 유리 시트를 감긴 층마다 유리 시트 에지들의 동일한 간격으로 정확히 감는 경우 압축력 및 인장력이 없는, 유리 시트를 따른 선이다. 곡률을 가진 유리 시트가 다른 시트형의 감길 수 있는 재료에 비해 팽창 및 압축될 수 없기 때문에, 이러한 유리 시트를 감을 때 유리 층들 간의 원추형 간격 또는 깔대기형 슬리브가 주어지고, 깔대기형 슬리브의 내부면은 슬리브의 전체 압축 하중을 흡수해야 하며, 이는 일반적으로 에지의 손상 및 파손을 야기한다.A specific curvature of one side of the glass sheet is also possible. In such a glass sheet, a neutral line is defined. The neutral line is a line along the glass sheet that is free of compressive and tensile forces when the glass sheet is wound exactly at the same spacing of glass sheet edges per wound layer. Since the glass sheet with curvature can not be expanded and compressed compared to other sheet-type windable materials, conical spacing or funnel-shaped sleeves between the glass layers are provided when winding such glass sheet, and the inner surface of the funnel- Of the total compressive load of the edge, which generally causes damage and breakage of the edge.
이 문제를 해결하기 위해, 적어도 하나의 중간 층 시트가 중성 선을 따라 유리 시트의 중앙에 놓이므로, 중간 층의 폭에 걸쳐 중성 선이 그 좌우에 다소 컴팩트하게 감겨질 수 있다. 유리 시트의 폭 중앙에 좁은 중간 층 시트를 상기 방식으로 배치하는 것이 특히 바람직한데, 그 이유는 유리 시트들이 예를 들면 다운-드로우 시스템의 드로잉 공정으로부터 나오면 유리 시트들은 종종 평행한 가장자리를 갖는 것이 아니라, 예를 들면 일 킬로미터의 반경을 가진 특정 곡률을 갖는다. 이러한 유리 시트들이 감겨서 롤을 형성하면, 시트들이 깔대기 형태로 롤업되는 문제가 생긴다. 시트의 일 면, 즉 휘어진 시트의 외부 면을 향한 면이 느슨하게 감기고, 다른 면, 즉 내부 면을 향한 면은 긴밀하게 감긴다. 이로 인해, 유리 롤의 전체 압력이 내부 에지에 가해지고, 이는 유리 에지의 파손 또는 손상을 일으킬 수 있다. 이를 방지하기 위해, 단일 또는 다수의 스트립으로서 형성될 수 있는 단 하나의 좁은 스트립이 중간 층으로서 제공되고, 상기 스트립은 바람직하게 중앙에 배치되므로, 감긴 개별 유리 층 면들 또는 유리 층 가장자리들 간의 상이한 간격이 자유로이 형성될 수 있고 압력은 중간 재료 층의 중앙에 가해진다. 유리 롤의 신축 자재를 방지하는 지지력은 유리 롤의 중앙에 제공되며 에지에는 제공되지 않는다. 그렇지 않으면 에지에서 균열 또는 파손이 쉽게 나타날 수 있다. 중간 층을 중앙에 삽입함으로써, 특히 평행하지 않은 에지들을 가진 유리 시트에서 유리 롤 또는 유리 슬리브가 충분한 안정성 및 파괴 강도를 갖는다.To solve this problem, since at least one intermediate layer sheet is placed in the center of the glass sheet along the neutral line, the neutral line can be wound somewhat compactly on its left and right over the width of the intermediate layer. It is particularly preferred to arrange the narrow intermediate sheet in the middle of the width of the glass sheet in this manner because the glass sheets often do not have parallel edges when the glass sheets come out of the drawing process of the down- , For example a radius of one kilometer. When these glass sheets are rolled to form rolls, there is a problem that the sheets roll up in funnel form. The surface of the sheet, that is, the surface facing the outer surface of the curved sheet is loosely wound, and the other surface, that is, the surface facing the inner surface, is tightly wound. As a result, the total pressure of the glass roll is applied to the inner edge, which can cause breakage or damage of the glass edge. To prevent this, only one narrow strip, which can be formed as a single or multiple strips, is provided as an intermediate layer and the strips are preferably centrally located, so that different spacing Can be formed freely and the pressure is applied to the center of the intermediate material layer. The holding force to prevent the stretching material of the glass roll is provided at the center of the glass roll and not at the edge. Otherwise, cracking or breakage can easily occur at the edge. By inserting the middle layer in the middle, glass rolls or glass sleeves have sufficient stability and breaking strength, especially in glass sheets with edges that are not parallel.
중간 층의 폭은 유리 층 또는 유리 시트의 폭보다 훨씬 더 작고, 유리 시트의 폭의 10 내지 70%, 바람직하게는 유리 시트의 폭의 30 내지 50%이다.The width of the intermediate layer is much smaller than the width of the glass layer or glass sheet and is 10 to 70% of the width of the glass sheet, preferably 30 to 50% of the width of the glass sheet.
좁은 중간 층 재료의 사용을 위해, 단일 층에도 사용될 수 있는 다음에 언급한 모든 재료들이 사용된다. 이들은 모든 폭으로, 예를 들면 2 ㎜ 내지 600 ㎜ 범위의 폭으로 그리고 임의의 수로, 예를 들면 2 내지 300 피스로 사용될 수 있다. 개별 중간 층의 폭은 예를 들면 유리 층의 전체 폭의 0.1 % 내지 10 % 일 수 있다. 줄, 실, 분말 및 과립도 가능하다. 또한, 중간 층이 중간 층 시트로서 형성되면, 중간 층 시트의 폭이 시트의 연장에 따라 변할 수 있다. 즉 감소하거나 증가할 수 있다. 중간 층 시트의 폭은 전체 시트 길이에 걸쳐 동일할 필요는 없다.For use of the narrow intermediate layer material, all of the following materials which can also be used for a single layer are used. They can be used in all widths, for example in the range from 2 mm to 600 mm, and in any number, for example from 2 to 300 pieces. The width of the individual intermediate layer may be, for example, 0.1% to 10% of the total width of the glass layer. Ropes, yarns, powders and granules are also possible. Further, if the intermediate layer is formed as an intermediate layer sheet, the width of the intermediate layer sheet may vary according to the extension of the sheet. That is, it can be reduced or increased. The width of the intermediate layer sheet need not be the same throughout the entire sheet length.
중간 재료는 중간 재료로서 적합한 모든 압축 가능한 재료이다. 특히, 두께는 유리 롤의 제조를 위한 경제적인 적용에 상응해야 한다. 특히 가요성 포옴(foam) 재료, 예를 들면 포옴 필름과 같은 재료(구조 재료)의 밀도보다 낮은 겉보기 밀도를 가진 다공성 재료가 바람직하다. 이는 횡단면에 걸쳐 거의 일정한 겉보기 밀도를 가진 균일한 포옴 재료일 수 있거나 또는 인테그랄 포옴 재료일 수 있다. 이러한 인테그랄 포옴 재료는 횡단면에 걸쳐 상이한 겉보기 밀도 분포를 갖는다. 겉보기 밀도는 횡단면 중앙을 향해 줄어든다. 이러한 포옴 재료의 중간 재료 층은 바람직한 휨 거동 및 거의 다공 없는 표면에 대한 양호한 접착성을 갖는다.The intermediate material is any compressible material suitable as an intermediate material. In particular, the thickness must correspond to an economical application for the production of glass rolls. Particularly preferred is a porous material having an apparent density lower than the density of a flexible foam material, such as a foam film (a structural material). It can be a uniform foam material with a nearly constant apparent density across the cross-section, or it can be an integral foam material. Such integral foam materials have different bulk density distributions across the cross-section. The apparent density decreases toward the center of the cross section. The intermediate material layer of such a foam material has the desired flexural behavior and good adhesion to a nearly porous surface.
중간 재료로서, 분말, 조각 또는 입자로서 느슨한 형태로 또는 트랙 형태로 포옴 재료, 엠보싱된 또는 달리 구조화된 종이, 판지, 플라스틱 필름 또는 금속 필름과 같은 압축 가능한 재료가 적합하다. 바람직하게는 재료로서 압축 가능한 판지 또는 예를 들면 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료, 특히 교차 결합된 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료로 이루어진 포옴 필름, 또는 폴리에틸렌 또는 폴리우레탄으로 이루어진 포옴 필름이 사용된다. 포옴 재료는 바람직하게 밀폐 기포이다. 또한, 화물 자동차 플레인 또는 합성 가죽과 같은 압축 가능한 재료가 적합하다. As intermediate materials, compressible materials such as foam materials, embossed or otherwise structured paper, paperboard, plastic film or metal film in loose form or in track form as powder, flakes or particles are suitable. Preferably the material is a compressible paperboard or a foam film made of, for example, a polyolefin foam material, in particular a foam film made of a cross-linked polyolefin foam material, or a foam film made of polyethylene or polyurethane. The foam material is preferably a closed cell. Also suitable are compressible materials such as cargo planes or synthetic leather.
또한, 느슨하게 또는 고정 결합된 다층 중간재료가 적합하고, 이 경우 바람직하게는 유리 필름과 접촉한 재료가 결합체의 표면에 주어지며 압축 가능한 재료가 결합체의 코어 내에 주어진다. 코어 재료는 다수의 층으로도 구성될 수 있다. 유리 필름 접촉 재료는 중간 재료의 하나의 표면에만 배치될 수 있다. 표면의 재료는 유리 필름 표면과의 접촉에 맞게 조정된다. 이 경우, 특히 양호한 화학적 적합성이 고려되므로, 중간 재료, 예컨대 실리콘의 잔류물이 유리 표면에 남지 않거나 또는 이온 확산이 이루어지지 않는다. 또한, 면에 걸쳐 유리 필름 표면의 에이징 프로세스의 변화가 상이하게 일어나는 것이 방지되어야 하며, 이는 특히 후속 코팅 프로세스에 바람직하지 않고, 예를 들면 구조화된 그리고 심하게 다공성인 중간 재료에 의해 야기될 수 있다. 중간 재료 결합체의 코어 내의 재료는 양호한 압축 작용 및 바람직하게는 추가로 양호한 복원력의 작용과 관련해서 선택된다.Also loosely or fixedly bonded multilayer intermediate materials are suitable, in which case preferably the material in contact with the glass film is given to the surface of the assembly and a compressible material is given in the core of the assembly. The core material may also be composed of multiple layers. The glass film contact material may be disposed only on one surface of the intermediate material. The material of the surface is adjusted to the contact with the glass film surface. In this case, particularly good chemical suitability is taken into account, so that a residue of intermediate material such as silicon does not remain on the glass surface or ion diffusion does not occur. Also, the change in the aging process of the glass film surface across the surface must be prevented from occurring differently, which may be caused by an intermediate material which is not particularly favorable for subsequent coating processes, for example structured and heavily porous. The material in the core of the intermediate material combination is selected with respect to the action of good compression action and preferably further good restoring force.
중간 재료의 두께는 바람직하게는 2 ㎜보다 작거나 같고, 더욱 바람직하게는 1 ㎜보다 작거나 같으며, 특히 바람직하게는 0.5 ㎜보다 작거나 같다. 유리 시트가 측면 에지, 즉 가장자리 영역 내의 두꺼운 부분을 갖는 실시예에서, 중간 재료는 더 두껍고 8 ㎜ 까지의 두께를 가질 수 있다. 폭에 걸쳐 더 얇은 유리 필름에 대한 더 두꺼운 가장자리 영역의 필요한 보상을 위해, 다수의 중간 재료 층들이 포개어 롤업될 수 있다. 제 1 중간 재료 층은 유리 필름의 전체 폭에 걸쳐, 그리고 그 위에 및/또는 그 아래 하나 또는 다수의 더 좁은 중간 재료 층은 얇은 유리 필름 횡단면의 폭 내에서 유리 필름 층들 사이에 배치될 수 있다.The thickness of the intermediate material is preferably less than or equal to 2 mm, more preferably less than or equal to 1 mm, and particularly preferably less than or equal to 0.5 mm. In embodiments where the glass sheet has a thick edge in the side edge, i. E. The edge area, the intermediate material may be thicker and up to 8 mm thick. To compensate for the need for a thicker edge region for a thinner glass film across the width, multiple layers of intermediate material can be rolled up. The first intermediate material layer may be disposed between the glass film layers within the width of the thin glass film transverse section over and over the entire width of the glass film and / or one or more of the narrower intermediate material layers below it.
파이어폴리시된 유리 표면과 상호 작용해서 0.15 내지 10 N, 바람직하게는 1 내지 10 N 범위의 정지 마찰(Fs)을 갖는 중간 재료가 바람직하다. 정지 마찰은 극복해야 할 힘의 피크를 말하므로, 중간 재료가 유리 표면에 대해 이동된다.Intermediate materials having static friction (F s ) in the range of 0.15 to 10 N, preferably 1 to 10 N, in cooperation with the fire-polished glass surface are preferred. The static friction refers to the peak of the force to be overcome, so that the intermediate material is moved relative to the glass surface.
또한, 파이어폴리시된 유리 표면과 상호 작용해서 0.15 내지 5 N, 바람직하게는 0.2 내지 2.5 N, 특히 바람직하게는 1 내지 2.5 N 범위의 마찰력(FD)을 갖는 중간 재료가 바람직하다. 마찰력은 정지 마찰의 극복 후에 테스트 거리에 걸쳐 평균화된 힘을 말하며, 상기 힘은 중간 재료와 유리 표면 간의 상대 이동을 위해 필요하다.Also preferred is an intermediate material having a frictional force (F D ) in the range of 0.15 to 5 N, preferably 0.2 to 2.5 N, particularly preferably 1 to 2.5 N in interaction with the fire-polished glass surface. The frictional force refers to the force averaged over the test distance after overcoming traction, which force is needed for relative movement between the intermediate material and the glass surface.
정지 마찰(Fs) 및 마찰력(FD)에 대한 값은 각각 1.96 N의 수직력으로 DIN 50 014에 따른 23℃ 및 50% 상대 대기 습도의 표준 대기에서 Schenk-Trebel 사의 전기 기계식 유니버셜 테스트 기계에서 DIN EN ISO 8295에 따라 측정한 것이다.The values for static friction (F s ) and frictional force (F D ) were measured on a Schenk-Trebel electromechanical universal testing machine at 23 ° C and 50% relative atmospheric humidity according to
다른 본 발명에 따른 실시예에서, 유리 필름의 측면들 중 적어도 하나가 플라스틱 층, 특히 폴리머 층으로 코팅된다.In another embodiment according to the invention, at least one of the sides of the glass film is coated with a plastic layer, in particular a polymer layer.
특별한 실시예에서, 상기 플라스틱 층은 중간 재료를 형성한다. 이는 롤업 및 풀기가 현저히 간단해진다는 특별한 장점을 갖는데, 그 이유는 유리 필름으로부터 분리된 재료가 다른 롤에 제공될 필요가 없거나 또는 풀 때 롤로부터 분리되어 수용될 필요가 없기 때문이다.In a particular embodiment, the plastic layer forms an intermediate material. This has the particular advantage that the roll-up and unwinding becomes significantly simpler, because the material separated from the glass film need not be provided to the other rolls or it does not need to be received separately from the rolls when released.
본 발명은 또한 유리 필름, 와인딩 코어 및 압축 가능한 중간 재료를 제공하는 단계, 와인딩 코어 상에 중간 재료의 적어도 하나의 내부 층을 감는 단계, 상기 유리 필름이 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 중간 재료와 교대로 층층이 감기도록 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 유리 필름 및 상기 중간 재료를 감는 단계로서, 상기 중간 재료 및/또는 상기 유리 필름은 길이 방향으로 작용하는 인장 응력으로 감기고, 상기 인장 응력은 중간 재료의 압축을 야기하는, 감는 단계, 및 유리 필름 단부를 유리 롤에 고정하는 단계를 포함하는 유리 롤의 제조 방법을 포함한다.The present invention also relates to a method of manufacturing a winding core comprising the steps of providing a glass film, a winding core and a compressible intermediate material, winding at least one inner layer of the intermediate material on the winding core, Winding the glass film and the intermediate material on the winding core so that the layer is wound, wherein the intermediate material and / or the glass film are wound with tensile stress acting in the longitudinal direction, the tensile stress causing the compression of the intermediate material And a step of fixing the glass film end to the glass roll.
와인딩 코어는 충분한 휨 강성 및 압축 강도를 가진 모든 안정한 재료로 이루어질 수 있다. 중간 재료는 바람직하게 롤에 감겨서 제공된다. 유리 필름은 다운-드로우 방법 또는 오버플로-다운-드로우-퓨전 방법과 같은 제조 방법으로부터 무한 시트로서 제공되거나 또는 롤업되어 유리 롤로서 제공된다.The winding cores can be made of any stable material with sufficient flexural stiffness and compressive strength. The intermediate material is preferably provided by being wound on a roll. The glass film is provided as an infinite sheet from a manufacturing method such as a down-draw method or an overflow-down-draw-fusion method, or is provided as a glass roll by being rolled up.
먼저, 중간 재료의 하나 또는 다수의 층이 와인딩 코어 상에 감김으로써, 도착하는 중간 재료와 이미 롤업된 중간 재료 사이에 스팬드렐(spandrel)이 생긴다. 롤업될 유리 필름 시트의 길이의 시작 부분이 상기 스팬드렐 내로 도입되고, 중간 재료와 교대로 층층이 롤업된다. 따라서, 유리 필름은 2개의 표면에서 바람직하게는 전체 면에서 중간 재료에 의해 커버된다. 이 경우, 중간 재료는 그 길이 방향으로 작용하는 특정 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력으로 유리 롤 상에 감기도록 공급되고, 중간 재료 공급 롤의 푸는 속도와 유리 롤을 롤업하는 속도가 서로 비례해서 제어됨으로써 롤업된다. 중간 재료 공급 롤은 각각 상응하게 제동된다. 인장 응력은 각각 센서에 의해 측정되고 상응하게 제어된다. 유리 필름이 롤로부터 분리되면, 유리 필름이 그 길이 방향으로 작용하는 특정 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력으로 유리 롤 상에 감기도록 공급되어 롤업될 수 있다. 이 경우, 둘 다, 즉 중간 재료 및 유리 필름이 그들의 길이 방향으로 작용하는 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력으로 유리 롤 상에 감기도록 공급되어 롤업될 수 있다. 각각의 경우, 인장 응력은 소정 와인딩 타이트니스가 달성되고 중간 재료가 압축되도록 세팅된다.First, one or more layers of intermediate material are wound on the winding cores to create a spandrel between the arriving intermediate material and the already rolled intermediate material. The beginning of the length of the glass film sheet to be rolled up is introduced into the span drel, and the layer is rolled up alternately with the intermediate material. Thus, the glass film is covered by the intermediate material on two surfaces, preferably on the entire surface. In this case, the intermediate material is fed so as to be wound on the glass roll with a specific preliminary stress or tensile stress acting in the longitudinal direction thereof, and rolled up by controlling the speed of unwinding the intermediate material supply roll and the speed of rolling up the glass roll in proportion to each other . The intermediate material feed rolls are each braked accordingly. The tensile stresses are measured and correspondingly controlled by sensors, respectively. When the glass film is separated from the roll, the glass film may be fed and rolled up to be wound on the glass roll with a specific pre-stress or tensile stress acting in its longitudinal direction. In this case, both can be supplied and rolled up to wind on the glass roll with both pre-stress or tensile stress acting in their longitudinal direction, i.e., the intermediate material and the glass film. In each case, the tensile stress is set such that a given winding tightness is achieved and the intermediate material is compressed.
롤업될 유리 필름 시트의 길이의 끝부분이 놓이면, 바람직하게는 중간 재료의 하나 또는 다수의 층이 외부 유리 필름 층 및 유리 필름 단부의 고정을 위해 유리 롤 둘레로 감긴다. 추가로 또는 대안으로서, 다른 재료, 예를 들면 패딩된 외부 보호 필름, 종이 또는 접착 시트 또는 고정 시트에 의한 유리 롤의 외부 커버링이 이루어질 수 있다. 여기서는 유리 필름 층들의 느슨해짐을 방지하고 중간 층들의 복원 압력을 유지하기 위해, 최상부의 유리 필름 층이 확실히 고정되는 것이 중요하다.If the end of the length of the glass film sheet to be rolled up lies, preferably one or more layers of the intermediate material are wound around the glass roll for fixing of the outer glass film layer and the glass film end. Additionally or alternatively, outer covering of the glass roll with other materials, such as padded outer protective film, paper or adhesive sheet or fixing sheet, can be made. It is important here that the topmost glass film layer is securely fixed in order to prevent loosening of the glass film layers and to maintain the restoring pressure of the intermediate layers.
본 발명은 또한 유리 롤 내의 유리 필름 사이의 중간 재료로서 압축 가능한 재료, 특히 포옴 재료 필름의 용도를 포함하고, 상기 중간 재료는 유리 필름과 교대로 포개어 적어도 각각 2개의 층으로 와인딩 코어 상에 감길 수 있으며, 중간 재료 층들은 유리 필름 층들을 고정할 수 있다. 특히, 이러한 포옴 재료 필름은 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료, 특히 교차 결합된 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료 또는 폴리에틸렌 또는 폴리우레탄으로 이루어진다. The invention also encompasses the use of a compressible material, in particular a foam material film, as an intermediate material between glass films in a glass roll, said intermediate material being wrapped alternately with the glass film and wound on the winding core in at least two respective layers And the intermediate material layers can fix the glass film layers. In particular, such a foam material film is comprised of a polyolefin foam material, particularly a cross-linked polyolefin foam material or polyethylene or polyurethane.
본 발명은 와인딩 코어 상의 유리 롤이 자체 지지되며 안정하기 때문에, 측면 플랜지 및 그 밖의 다른 장치 및 패키징 재료가 생략될 수 있고, 롤업된 유리 필름에 대한 큰 보호가 이루어지는 간단하고 컴팩트한 유리 롤을 제공한다. 특히, 본 발명에 따른 유리 롤은 수직의 또는 경사진 축을 가진 수직의 또는 경사진 이송을 허용하고, 이는 유리 롤의 핸들링 동안 큰 자유도를 가능하게 한다. 통상, 이러한 유리 롤은 300 내지 1500 ㎜의 폭 및 300 내지 1000 ㎜의 외경을 갖는다. 이러한 롤의 중량은 약 30 내지 200 kg이다.The present invention provides a simple and compact glass roll with lateral flanges and other devices and packaging materials that can be omitted and with great protection against roll-up glass films, because the glass roll on the winding core is self-supporting and stable do. In particular, the glass roll according to the invention permits vertical or inclined transport with a vertical or inclined axis, which allows a great degree of freedom during handling of the glass roll. Typically, such glass rolls have a width of 300 to 1500 mm and an outer diameter of 300 to 1000 mm. The weight of these rolls is about 30 to 200 kg.
더 오랜 이송 또는 저장을 위해, 유리 롤은 이송 필요에 따라 전체적으로 적합한 패키징의 보호 케이싱 내에 패키징될 수 있다.For longer transport or storage, the glass rolls can be packaged in a protective casing of the overall packaging as required for transport.
본 발명에 의해, 선행 기술의 단점을 갖지 않고 롤업된 유리에 대한 큰 보호와 더불어 유리 롤의 이동 또는 진동을 방지하는 유리 롤이 제공된다.The present invention provides a glass roll that does not have the disadvantages of the prior art and prevents movement or vibration of the glass roll with great protection against roll-up glass.
이하의 상세한 실시예는 본 발명을 상세히 설명한다.
도 1은 본 발명에 따른 유리 롤의 횡단면도.
도 2는 본 발명에 따른 유리 롤의 제조를 위한 롤업 장치의 예시.
도 3은 본 발명에 따른 유리 롤의 제조를 위한, 도 2에 대한 대안적 롤업 장치의 예시.
도 4a 및 도 4b는 감긴 유리 롤의 종단면도.
도 5는 일 실시예에서 감긴 층의 수에 따른 중량 및 마찰을 나타낸 그래프.
도 6a는 에지의 곡률을 가진, 하나의 평면에서 설계된 유리 시트의 평면도.
도 6b는 유리 롤의 폭보다 작은 폭을 가진 롤업된 중간 층을 가진 유리 롤의 단면도이며, 유리 시트는 상기 평면에서 도 6a에서와 같이 곡률을 가질 수 있다.The following detailed examples illustrate the present invention in detail.
1 is a cross-sectional view of a glass roll according to the present invention.
Figure 2 is an illustration of a roll-up device for the production of a glass roll according to the present invention.
Fig. 3 is an illustration of an alternative roll-up device for Fig. 2 for the production of a glass roll according to the present invention. Fig.
4A and 4B are longitudinal cross-sectional views of a wound glass roll.
5 is a graph showing weight and friction as a function of the number of layers wound in one embodiment.
6a is a plan view of a glass sheet designed in one plane, with curvature of the edge.
Figure 6b is a cross-sectional view of a glass roll with a rolled up intermediate layer having a width less than the width of the glass roll, and the glass sheet may have a curvature as in Figure 6a in that plane.
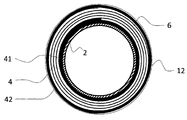
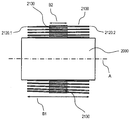
도 1에 도시된 바와 같은 예시적인 유리 롤(1)에서 와인딩 코어(2) 상에 3개의 중간 재료 층들이 롤업되어, 내부 중간 재료 층(41)을 형성한다. 후속해서, 유리 필름과 중간 재료가 층층이 교대로 롤업되므로, n 개의 유리 층(6) 및 n 개의 중간 재료 층(4)이 유리 롤(1) 상에 놓인다. 외부 중간 재료 층(42)은 추가의 중간 재료 층에 의해 보강되어 형성된다. 독자적인 풀림에 대해 외부의 중간 재료 층(42)을 고정하기 위해, 외부에서 유리 롤(1) 둘레로 하나 또는 다수의 고정 시트(12)가 장착된다. 중간 재료 층들(4)은 압축되고 50 내지 100 kPa의 복원 압력으로 유리 필름 층(6)에 대해 작용하므로, 유리 롤(1)은 컴팩트하고 예비 응력을 받으며, 유리 필름 층들(6)은 유리 롤 내에 고정된다. The three intermediate material layers are rolled up on the winding
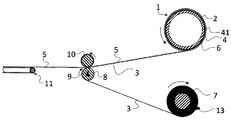
도 1에 따른 유리 롤(1)의 제조를 위해, 예를 들면 도 2에 따른 롤업 메커니즘이 적용된다. 도시되지 않은 다운-드로우 시스템에서 500 ㎜의 폭 및 50 ㎛의 두께를 가진 무한 유리 필름 시트(5)가 성형되어 드로잉된다. 상기 유리 필름 시트는 벨트 컨베이어(11)에 의해 방향 전환 롤러 쌍(8 및 10)으로 안내되고, 상기 롤러 쌍으로부터 감길 유리 롤(1)에 공급된다. 도시되지 않은 구동 샤프트 상에 400 ㎜의 코어 직경을 가진 판지로 이루어진 와인딩 코어(2)가 장착되고, 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 먼저 내부 중간 재료 층(41)을 형성하는, 중간 재료(3)의 3개의 층이 롤업된다. 중간 재료(3)는 1 ㎜의 두께를 가진 교차 결합된 밀폐 기포의 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료로 이루어진 포옴 재료 필름, 예를 들면 Luzern에 소재하는 Sekisui Alveo AG의 Alveolit TA 1001로 판매되는 포옴 재료 필름이다. 중간 재료(3)는 중간 재료 공급 롤(7)로부터 풀려진다. 중간 재료는 중간 재료 방향 전환 롤러(8) 둘레로 안내되어 와인딩 코어(2) 상에 감기고, 상기 와인딩 코어는 중간 재료 공급 롤(7)과 반대 방향으로 회전한다.For the production of the glass roll 1 according to Fig. 1, for example, a roll-up mechanism according to Fig. 2 is applied. In the unillustrated down-draw system, an endless glass film sheet 5 having a width of 500 mm and a thickness of 50 탆 is molded and drawn. The glass film sheet is guided by the
3개의 내부 중간 재료 층(41)의 롤업 후에, 중간 재료 층들(41)과 도착하는 중간 재료(3)로 형성된 스팬드렐(spandrel) 내로 유리 필름(5)의 시트의 시작 부분이 도입되므로, 유리 필름이 유리 롤(1) 또는 구동되는 와인딩 코어에 동반되어 중간 재료(3)의 층들 사이로 매립된다. 유리 필름(5) 및 중간 재료(3)가 이제 교대하는 층으로서, 1000 m의 전체 유리 필름 길이가 유리 롤(1) 상에 롤업될 때까지 각각 n 개의 층으로 롤업된다.Since the beginning of the sheet of the glass film 5 is introduced into the spandrel formed of the
후속해서, 유리 필름의 길이가 절단된다. 이를 위해, 기계적인 스크라이빙 및/또는 레이저를 이용한 분리 방법, 예를 들면 레이저 스크라이빙 방법이 적용된다. 후자의 경우, 번들링된 레이저 빔, 통상 CO2-레이저 빔에 의해 유리가 정확히 규정된 선을 따라 가열되고 바로 후속하는 압축 공기 또는 공기 액체 혼합물의 차가운 제트에 의해, 유리가 미리 정해진 에지를 따라 크랙될 정도의 열 응력이 유리 내에 생긴다. 후속해서, 다수의, 적어도 2개의 2층 중간 재료(3)가 외부 중간 재료 층(42)을 형성하기 위해 유리 롤 둘레로 감긴다. 외부의 중간 재료 층들(42)의 자동 롤업과는 달리, 이들은 3개의 고정 시트(12)에 의해 고정된다. 이들은 전체 유리 롤(1)의 압축 해제를 방지하므로, 전체 유리 롤은 단단히 고정된 유리 필름 층들(6)과 함께 안전하게 저장되고 이송될 수 있다. 유리 롤은 약 650 ㎜의 외경 및 약 110 kg의 중량을 갖는다.Subsequently, the length of the glass film is cut. For this purpose, mechanical scribing and / or separation using a laser, for example a laser scribing method, is applied. In the latter case, the bundle of laser beams, usually the CO 2 laser beam, is heated along a line exactly defined by the glass, and the cold jet of the immediately following compressed air or air liquid mixture causes the glass to crack along a predetermined edge A thermal stress is generated in the glass. Subsequently, a plurality of, at least two two-layer
중간 재료(3)는 길이 방향으로 작용하는 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력 하에서 와인딩 코어(2) 또는 유리 필름 층(6) 상에 감기므로, 상기 중간 재료는 압축된 중간 재료 층(4, 41, 42)으로서 개별 유리 필름 층(6)의 하부에 및/또는 상부에 놓인다. 상기 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력을 제어하기 위해, 중간 재료 방향 전환 롤러(8)에 센서(9)가 접속되고, 상기 센서는 구동되는 유리 롤(1) 또는 와인딩 코어와 제동된 중간 재료 공급 롤(7) 사이의 중간 재료(3)의 인장력을 측정한다. 예를 들면, 센서(9)는 제동 장치(13)의 제동 작용에 따라 롤(8) 둘레에 중간 재료의 휘감김에 의해 주어지는 압력을 측정하는 인장 감지 롤러이다. 미리 정해진 설정값에 따라 중간 재료 공급 롤(7)은 제동 장치(13)에 의해, 필요한 인장력을 세팅하기 위해 필요한 정도로 제동된다. 상기 길이 방향을 향한 인장력은 중간 재료(3)를 감을 때 마지막으로 롤업된 유리 필름 층에 작용하는 예비 응력을 야기한다. 중간 재료는 다시 펴지려고 하는 동안 유리 롤(1) 내에서 복원 압력을 유리 필름 층들(6)에 가하기 때문에, 상기 유리 필름 층들이 유리 롤 내에 고정된다. 동시에, 중간 재료(3)는 인장력에 의해 당겨진다. 길이가 다시 수축되려고 하는 동안 중간 재료는 유리 롤(1) 내에서 추가의 힘을 유리 필름 층들(6)에 가함으로써, 상기 유리 필름 층들이 유리 롤 내에 고정된다.The intermediate material is wound on the winding
본 발명에 따른 다른 실시예에서, 유리 필름은 유리 필름 공급 롤로부터 제공되고, 방향 전환 롤러 쌍(8 및 10)을 통해 감길 유리 롤(1)에 공급된다. 여기서도 와인딩 코어(2) 또는 감길 유리 롤(1)은 구동되는 장치 상에 장착된다. 상기 장치는 이 실시예에서 중간 재료 공급 롤(7)로부터 중간 재료(3)를 당길 뿐만 아니라, 유리 필름 공급 롤로부터 유리 필름(3)을 당긴다. 이 실시예에서, 유리 필름(3)은 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력을 가지고 유리 롤(1)에 감기고, 이를 위해 유리 필름 공급 롤용 풀기 장치 내에 제동 장치가 그리고 유리 필름 방향 전환 롤러 내에 센서가 제공된다. 센서는 유리 필름의 인장력을 측정한다. 제어 장치에 의해 유리 필름 공급 롤용 풀기 장치는 필요한 인장력이 세팅될 정도로 제동된다. 이로 인해, 유리 롤(1) 내의 중간 재료(3)의 압축 및 규정된 와인딩 타이트니스가 확실하게 세팅됨으로써, 유리 필름 층들(6)이 유리 롤(1) 내에 확실하게 고정된다.In another embodiment according to the present invention, a glass film is provided from a glass film supply roll and supplied to the glass roll 1 to be wound through a pair of
도 3은 본 발명에 따른 유리 롤의 제조를 위한, 도 2에 대한 대안적 롤업 장치를 도시한다. 여기서는 유리 롤의 다른 방향 롤업 장치가 바람직하며, 이는 조건에 따라 유리 필름의 제공시 바람직하다. 이 실시예에서는 내부 중간 재료 층(41)의 제공 후에 유리 필름의 도입을 위한 스팬드렐을 제공하기 위해, 추가의 중간 재료 공급 롤(71)이 제공된다. 2개의 공급 롤(7 및 71)의 중간 재료가 중간 재료 층(41)을 형성하기 위해 와인딩 코어(2) 상에 감긴다. 2개의 중간 재료 웨브 사이에 생긴 스팬드렐 내로 유리 필름(5)의 시트의 시작 부분이 도입되므로, 유리 필름이 유리 롤(1) 또는 구동되는 와인딩 코어에 동반되어 중간 재료(3, 31)의 층들 사이로 매립된다. 적은 수의 층들이 감긴 후에, 중간 재료(31)가 분리되므로, 후속해서 중간 재료(3)는 유리 필름(5)과 교대하는 층으로서, 1000 m의 전체 유리 필름 길이가 유리 롤(1) 상에 롤업될 때까지, n 개의 층으로 롤업된다.Fig. 3 shows an alternative roll-up device for Fig. 2 for the production of a glass roll according to the invention. Here, a roll-up device in the other direction of the glass roll is preferable, which is preferable in the provision of the glass film according to the conditions. In this embodiment, an additional intermediate
후속해서, 유리 필름의 길이가 절단된다. 다수의, 적어도 2개의 2층 중간 재료(3)가 외부 중간 재료 층(42)의 형성을 위해 유리 롤 둘레에 감긴다. 외부 중간 재료 층들(42)의 독자적인 롤업과는 달리, 이들은 고정 접착 시트와 함께 감긴다. 이들은 전체 유리 롤(1)의 압축 해제를 방지하므로, 전체 유리 롤은 단단히 고정된 유리 필름 층들(6)과 함께 안전하게 저장되고 이송될 수 있다. 유리 롤은 약 650 ㎜의 외경 및 약 110 kg의 중량을 갖는다.Subsequently, the length of the glass film is cut. A plurality of, at least two two-layer intermediate materials (3) are wound around the glass roll for the formation of the outer intermediate material layer (42). Unlike the original roll-up of the outer intermediate material layers 42, they are wound with a fixed adhesive sheet. These prevent the decompression of the entire glass roll 1, so that the entire glass roll can be safely stored and transported together with the firmly fixed glass film layers 6. [ The glass roll has an outer diameter of about 650 mm and a weight of about 110 kg.
중간 재료(3 및 31)는 길이 방향으로 작용하는 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력 하에 와인딩 코어(2) 또는 유리 필름 층(6)에 감기므로, 중간 재료는 압축된 중간 재료 층들(4, 41, 42)로서 개별 유리 필름 층(6) 하부에 및/또는 상부에 놓인다. 상기 예비 응력 또는 인장 응력을 제어하기 위해, 중간 재료 방향 전환 롤러(8)에 센서(9)가 접속되고, 상기 센서는 구동되는 유리 롤(1) 또는 와인딩 코어와 제동된 중간 재료 공급 롤(7) 사이의 중간 재료(3)의 인장력을 측정한다. 미리 정해진 설정값에 따라 중간 재료 공급 롤(7)은 제동 장치(13)에 의해, 필요한 인장력을 세팅하기 위해 필요한 정도로 제동된다. 중간 재료(31)의 인장력은 중간 재료 공급 롤(71)에 작용하는 제동 장치(131)에 의해 와인딩 코어(2)의 회전 속도에 따라 세팅된다. 상기 길이 방향을 향한 인장력은 중간 재료(3, 31)를 감을 때 마지막으로 롤업된 유리 필름 층에 작용하는 예비 응력을 야기한다. 다시 팽창되려는 시도 중에, 상기 시도는 유리 롤(1) 내에서 복원 압력을 유리 필름 층들(6)에 가하기 때문에, 상기 유리 필름 층들이 유리 롤 내에 고정된다. 동시에, 중간 재료(3, 31)는 인장력에 의해 당겨진다. 길이가 다시 수축되려는 시도 중에 상기 시도는 유리 롤(1)에서 추가의 힘을 유리 필름 층들(6)에 가함으로써, 상기 유리 필름 층들은 유리 롤 내에 고정된다.The intermediate material is wound around the winding
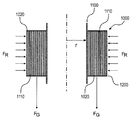
도 4a 및 도 4b에는 유리 시트가 중간 층들과 함께 반경 r을 가진 와인딩 코어로서 드럼(1100) 상에 롤업된 슬리브(1000)가 도시된다. 이 경우, 도 4a는 수직으로 세운 슬리브(1000)를 그리고 도 4b는 슬리브(1000)의 종단면도를 도시한다. 슬리브(1000)는 중간 층(1020)에 의해 각각 인접한 층으로부터 분리된 다수의 유리 층들(1110)로 이루어진다. 유리 층의 두께는 일 실시예에서 0.05 ㎜ 이고, 중간 층의 두께는 0.5 ㎜ 이다.4A and 4B show a
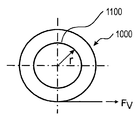
롤에 작용하는 방사방향력은 FR로 표시되고, 롤의 중량은 FG로 표시된다. 방사방향력의 크기는 실질적으로 중간 층에 의해 제공되는 예비 응력(FV)에 의해 결정되고, 상기 예비 응력으로 유리 슬리브가 감긴다. 슬리브의 측벽(1200)이 축에 대해 평행하게 또는 축 방향으로 이동됨으로써 슬리브 또는 롤(1000)이 신축 자재한 것을 방지하기 위해, 감긴 층의 수(n) 및 정지 마찰 계수(μ)와 더불어 감긴 재료와 코어 사이의 마찰(FF)을 결정하는 방사방향력(FR)이 중량(FG) 보다 커야 한다.The radial direction force acting on the roll is denoted by FR, and the weight of the roll is denoted by FG. The magnitude of the radial force is substantially determined by the pre-stress (FV) provided by the intermediate layer, and the pre-stress causes the glass sleeve to be wound. The number n of wound layers and the static friction coefficient mu, as well as the number of turns of the winding 1000, in order to prevent the
정지 마찰 계수에 대한 파라미터(μ)와 층의 수(n)를 알면, 감긴 재료와 와인딩 코어 사이의 마찰(FF)은 다음 식으로 나타난다:Knowing the parameter (μ) and the number of layers (n) for the coefficient of static friction, the friction (FF) between the wound material and the winding core is given by:
상기 실시예에서 중량에 대해서는 다음 식이 주어진다:For the weight in the above example, the following equation is given:
상기 식에서, t1은 유리 두께이고, n은 감긴 층의 수이며, t2는 중간 층의 두께이고, ρ는 유리 비중이며 g는 g-가속도이다. 마찰(FF)이 슬리브의 중량보다 커야 하면, FV=FR 이기 때문에 예비 응력은 감긴 층의 수(n)가 미리 정해진 경우 매우 간단히 결정될 수 있다.Where t1 is the glass thickness, n is the number of wound layers, t2 is the thickness of the intermediate layer, p is the glass specific gravity and g is the g-acceleration. If the friction FF has to be larger than the weight of the sleeve, since FV = FR, the preliminary stress can be determined very simply when the number n of wound layers is predetermined.
도 4b에는 슬리브의 종단면도가 도시되며, 여기서 와인딩 코어의 롤 반경은 r로 표시되고, 슬리브가 롤업되는 예비 응력은 FV로 표시되며, 상기 예비 응력은 슬리브 내의 방사방향력을 결정한다. 본 발명에 따라 예비 응력은 바람직하게 중간 층 내로 도입된다.Figure 4b shows a longitudinal section of the sleeve, in which the roll radius of the winding core is denoted by r, the pre-stress at which the sleeve is rolled up is denoted by FV, and the pre-stress determines the radial directional force in the sleeve. The pre-stress according to the invention is preferably introduced into the intermediate layer.
도 5에는, 예비 응력 FV = 0.7 뉴튼, ρ = 2.3 kg/dm3, 유리 층 두께 t1 = 0.05 ㎜ 및 중간 층 두께 t2 = 0.5 ㎜를 가진 실시예에 대해 상기 식에 의해 주어지는 힘(FR)이 뉴튼으로 그리고 FG가 뉴튼으로 제시된다. 이 경우, 정지 마찰 계수 μ= 1.1 였고, 롤 반경 r = 200 ㎜ 였다. 유리 재료 폭 b = 400 ㎜로 선택되었다.5, the pre-stress FV = 0.7 Newton, ρ = 2.3 kg / dm 3 , the force (FR) given by the formula for an embodiment with a glass layer thickness t1 = 0.05 ㎜ and an intermediate layer thickness t2 = 0.5 ㎜ the Newton and FG are presented as Newton. In this case, the static friction coefficient mu = 1.1 and the roll radius r = 200 mm. Glass material width b = 400 mm.
도 5에 나타나는 바와 같이, 중량은 선택된 파라미터(FG)에서 항상 방사방향력(FR)으로부터 주어지는 마찰(FF)보다 작다. 방사방향력은 예비 응력에 의해 세팅된다.As shown in Fig. 5, the weight is always smaller than the friction FF given from the radial direction force FR in the selected parameter FG. The radial force is set by preliminary stress.
도 5에 도시된 실시예에서, 약 180 내지 190 개의 층 수에서나 FG 곡선과 마찰 FF의 곡선이 만나므로, 200 개를 초과하는 층에서 층들 사이의 정지 마찰은 중량을 보상하며 따라서 유리 슬리브의 신축 자재가 나타나지 않는 것을 보장하기에 불충분하다.In the embodiment shown in Fig. 5, the friction between the FG curve and the friction FF is matched at about 180 to 190 layers, so that the static friction between the layers in more than 200 layers compensates for the weight, It is insufficient to ensure that the material does not appear.
여기에 제시된 실시예가 특별한 유리 -Schott AG의 AF32 eco- 및 예시적인 예비 응력 FV = 0.7 뉴튼에 대해 주어졌기는 하지만, 전술한 식에 의해 각각의 유리 종류 및 예비 응력에 대해 어떤 수의 유리 층부터 유리 슬리브의 신축 자재가 나타나는지 또는 미리 정해진 유리 층의 수에서 신축 자재를 방지하기 위해 어떤 예비 응력이 필요한지를 결정하는 것이 가능하다.Although the embodiments presented herein are given for a particular glass-Schott AG AF32 eco- and for an exemplary pre-stress FV = 0.7 Newton, it is possible to obtain from the above formula any number of glass layers for each glass type and pre- It is possible to determine what preliminary stress is needed to prevent the elastic material from appearing in the stretching material of the glass sleeve or from the predetermined number of glass layers.
알칼리 없는 유리 AF32 eco는 하기 조성을 중량%로 갖는다.Alkali-free glass AF32 eco has the following composition in weight percent.
SiO2 61SiO 2 61
Al2O3 18Al 2 O 3 18
B2O3 10B 2 O 3 10
CaO 5CaO 5
BaO 3
MgO 3
유리의 변태 온도(Tg)는 717℃이다. 그 밀도는 2.43 g/㎤이다. 유리 필름의 상부면 및 하부면의 2차 평균 조도(Rq)는 0.4 내지 0.5 nm 이다. 즉, 표면은 매우 매끄럽다.The transformation temperature (Tg) of the glass is 717 캜. Its density is 2.43 g / cm < 3 >. The secondary average roughness (Rq) of the upper and lower surfaces of the glass film is 0.4 to 0.5 nm. That is, the surface is very smooth.
도 6a 및 도 6b에는 다수의 유리 층들(2100)이 축(A)을 중심으로 와인딩 코어(2000) 상에 감긴 실시예가 도시된다. 개별 유리 층들(2100) 사이의 중간 층들(2130)은 유리 슬리브의 전체 폭(B)에 걸쳐 연장되는 것이 아니라, 중간 재료 또는 중간 층(2130)의 폭(B2)은 유리 층들의 폭(B1)보다 훨씬 더 짧다.6A and 6B show an embodiment in which a plurality of
슬리브의 구성은 도 6b에 나타난다. 도 6a에는 와인딩 코어(2000) 상에 감길 때 다수의 유리 층(2100)을 형성하는 풀린 유리 시트(2110)의 평면도가 도시된다. 도 6a에 나타나는 바와 같이, 유리 시트(2110)의 에지들(2120.1, 2120.2)이 평행하지 않고, 일정한 곡률을 갖는다. 내부 에지(2120.1)는 예를 들면 곡률 반경(RB1)으로 표시될 수 있고, 외부면은 곡률 반경(RB2)으로 표시될 수 있다. 곡률 반경(RB1, RB2)은 매우 크고 예를 들면 1 내지 수 킬로미터의 범위에 놓인다. 일반적으로 내부 에지(2120.1)의 곡률 반경(RB1)은 외부 에지(2120.2)의 곡률 반경(RB2)보다 작다. 도 6b에 도시된 바와 같은 유리 시트가 감겨서 도 6a에 도시된 바와 같은 슬리브를 형성하면, 외부 에지(2120.2)에서 보상 중간 층 없이 개별 유리 층들의 간격은 일반적으로 내부 에지(2120.1)에서보다 더 크다. 즉, 슬리브 내의 압력이 내부 에지(2120.1)에서 최대이다. 유리 시트(2100)의 중앙에 유리 층의 폭보다 훨씬 더 작은 폭을 가진 중간 층(2130)이 있는, 도 6a에 도시된 실시예에 의해, 상기 효과가 보상될 수 있고, 외부 에지(2120.2) 및 내부 에지(2120.1)에서 중간 층의 좌측 및 우측에 개별 유리 층의 실질적인 자유 이격 및 그에 따라 응력 없는 감김을 가능하게 하는 슬리브가 얻어진다.The configuration of the sleeve is shown in Figure 6B. 6A shows a top plan view of a unrolled
도 6b에는 단일 중간 층 시트가 중간 층으로서 도시되지만, 유리의 전체 폭(B1)을 커버하기 위해 다수의 상기 중간 층이 제공될 수 있다. 물론, 휘어진 유리 시트들을 보상하기 위해, 단일 중간 층이 중앙에 제공될 수 있다.Although a single intermediate layer sheet is shown as an intermediate layer in Figure 6b, a number of said intermediate layers may be provided to cover the entire width B1 of the glass. Of course, in order to compensate for warped glass sheets, a single intermediate layer can be provided at the center.
전술한 바와 같이, 전체 유리 층의 폭(B1)의 일부에 걸쳐서만 연장되는 중간 층에 의해 유리 표면의 기하학적 불규칙성, 예를 들면 웨이브니스 및 워프가 쉽게 보상될 수 있고, 이 경우 중간 층의 각각의 재료 내로 힘 도입이 점 형태로 또는 부분적으로 과도하게 상승하지 않는다.As described above, the geometrical irregularities of the glass surface, e.g., wave and warp, can be easily compensated for by the intermediate layer extending only over a portion of the entire glass layer width B1, Lt; RTI ID = 0.0 > partially < / RTI >
본 발명은 전술한 특징들의 조합에 제한되지 않으며, 당업자는 본 발명의 범주를 벗어나지 않으면서 본 발명의 전체 특징을 바람직하다면 임의로 조합하거나 또는 단독으로 사용할 수 있다.The present invention is not limited to the combination of the above-mentioned features, and a person skilled in the art can use the entire features of the present invention, if desired, in any combination or alone without departing from the scope of the present invention.
1 유리 롤
2 와인딩 코어
3, 31 중간 재료
4 중간 재료 층
41 내부 중간 재료 층
42 외부 중간 재료 층
5 유리 필름
6 유리 필름 층
7, 71 중간 재료 공급 롤
8 중간 재료 방향 전환 롤러
9 센서
10 유리 필름 방향 전환 롤러
11 벨트 컨베이어
12 고정 시트
13, 131 제동 장치
1000 슬리브
1020 중간 층
1110 유리 층
1200 측벽
2000 와인딩 코어
2100 유리 층
2110 유리 시트
2120.1, 2120.2 내부 에지/외부 에지
2130 중간 층
본 발명은 하기 문장에 설명되는 양상을 포함하고, 상기 양상은 상세한 설명의 부분이지만 청구범위는 아니다.
문장
1. 적어도 하나의 유리 필름 및 중간 재료를 포함하고, 이들은 와인딩 코어 상에 적어도 2개의 층으로 포개어 감기는, 유리 롤에 있어서,
상기 유리 필름 층들이 중간 재료 층들에 의해 고정된 것을 특징으로 하는 유리 롤.
2. 문장 1에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름 층들이 압축된 중간 재료에 의해 고정된, 유리 롤.
3. 문장 2에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름 층들이 압축된 중간 재료에 의해 고정되고, 상기 중간 재료는 상기 유리 필름 층들에 대해 복원 압력을 가하는, 유리 롤.
4. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료는 포옴 재료 필름인, 유리 롤.
5. 문장 4에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료는 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료, 특히 교차 결합된 폴리올레핀 포옴 재료인, 유리 롤.
6. 문장 1 내지 3 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료는 엠보싱된 또는 달리 구조화된 종이 또는 판지인, 유리 롤.
7. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름은 최대 350 ㎛, 바람직하게는 최대 100 ㎛, 더욱 바람직하게는 최대 50 ㎛, 특히 바람직하게는 최대 30 ㎛의 두께를 갖는, 유리 롤.
8. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름은 적어도 5 ㎛, 바람직하게는 적어도 10 ㎛, 특히 바람직하게는 적어도 15 ㎛의 두께를 갖는, 유리 롤.
9. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름은 그 양 측면의 적어도 하나의 표면에 파이어폴리시된 표면을 갖는, 유리 롤.
10. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름은 그 양 측면의 적어도 하나의 표면에 최대 1 나노미터, 바람직하게는 최대 0.8 나노미터, 특히 바람직하게는 최대 0.5 나노미터의 2차 평균 조도(RMS) Rq를 갖는, 유리 롤.
11. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름은 그 양 측면의 적어도 하나의 표면에 최대 2 나노미터, 바람직하게는 최대 1.5 나노미터, 특히 바람직하게는 최대 1 나노미터의 평균 표면 조도 Ra를 갖는, 유리 롤.
12. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름의 측면들 중 적어도 하나가 플라스틱 층, 특히 폴리머 층으로 코팅된, 유리 롤.
13. 문장 12에 있어서, 상기 플라스틱 층이 중간 재료를 형성하는, 유리 롤.
14. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료가 다수의 중간 재료 층들로 형성된, 유리 롤.
15. 문장 14에 있어서, 상기 다수의 중간 재료 층은 상이한 폭을 갖는, 유리 롤.
16. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료 층들은 측면으로 상기 유리 필름 층을 지나 돌출한, 유리 롤.
17. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료 층에 의한 상기 유리 필름 층의 고정은 상기 유리 필름 층과 상기 중간 재료 층 사이에 작용하는 0.15 내지 10 N, 바람직하게는 1 내지 10 N 범위의 정지 마찰 Fs 에 의해 이루어지는, 유리 롤.
18. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 있어서, 상기 중간 재료 층에 의한 상기 유리 필름 층의 고정은 상기 유리 필름 층과 상기 중간 재료층 사이에 작용하는 0.15 내지 5 N, 바람직하게는 0.2 내지 2.5 N, 특히 바람직하게는 1 내지 2.5 N 범위의 마찰력 FD 에 의해 이루어지는, 유리 롤.
19. 상기 문장들 중 어느 하나에 따른 유리 롤의 제조 방법에 있어서,
a) 유리 필름, 와인딩 코어 및 압축 가능한 중간 재료를 제공하는 단계,
b) 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 중간 재료의 적어도 하나의 내부 층을 감는 단계,
c) 상기 유리 필름이 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 중간 재료와 교대로 층층이 감기도록 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 유리 필름 및 상기 중간 재료를 감는 단계로서, 상기 중간 재료 및/또는 상기 유리 필름은 길이 방향으로 작용하는 인장 응력으로 감기고, 상기 인장 응력은 중간 재료의 압축을 야기하는, 감는 단계,
d) 상기 유리 롤 상에 유리 필름 단부를 고정하는 단계를 포함하는, 유리 롤의 제조 방법.
20. 문장 17에 있어서, 상기 유리 필름 단부의 고정은 상기 중간 재료의 적어도 하나의 외부 층에 의해 이루어지는, 유리 롤의 제조 방법.
21. 중간 재료가 상기 유리 필름과 교대로 포개어 적어도 2개의 층으로 와인딩 코어 상에 감길 수 있고, 유리 필름 층들은 중간 재료 층에 의해 고정될 수 있는, 유리 롤 내의 유리 필름들 사이의 중간 재료로서 압축 가능한 재료, 특히 포옴 재료 필름의 용도.1 glass roll
2 winding core
3, 31 intermediate material
4 intermediate material layer
41 Inner intermediate material layer
42 outer intermediate material layer
5 glass film
6 glass film layer
7, 71 intermediate material supply roll
8 Middle Material Orientation Roller
9 sensor
10 Glass Film Orientation Roller
11 Belt conveyor
12 fixed seat
13, 131 Brake device
1000 sleeves
1020 intermediate layer
1110 glass layer
1200 side wall
2000 winding core
2100 glass layer
2110 glass sheet
2120.1, 2120.2 internal edge / external edge
2130 intermediate layer
The present invention includes aspects described in the following sentence, which aspects are part of the detailed description, but are not intended to be limiting.
sentence
1. A glass roll comprising at least one glass film and an intermediate material, which are rolled up into at least two layers on a winding core,
Characterized in that the glass film layers are fixed by intermediate material layers.
2. The glass roll according to statement 1, wherein said glass film layers are fixed by a compressed intermediate material.
3. The glass roll of
4. A glass roll according to any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the intermediate material is a foam material film.
5. The glass roll of
6. A glass roll according to any one of statements 1 to 3, wherein said intermediate material is an embossed or otherwise structured paper or cardboard.
7. The glass roll according to any of the preceding sentences, wherein the glass film has a thickness of at most 350 μm, preferably at most 100 μm, more preferably at most 50 μm, particularly preferably at most 30 μm.
8. The glass roll according to any of the preceding sentences, wherein the glass film has a thickness of at least 5 mu m, preferably at least 10 mu m, particularly preferably at least 15 mu m.
9. The glass roll according to any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the glass film has a fire-polished surface on at least one surface of both sides thereof.
10. The glass film according to any one of the preceding sentences, wherein at least one surface of both sides of the glass film has a secondary average roughness of at most 1 nanometer, preferably at most 0.8 nanometer, particularly preferably at most 0.5 nanometer (RMS) Rq.
11. The glass film according to any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the glass film has an average surface roughness Ra of at most 2 nanometers, preferably at most 1.5 nanometers, particularly preferably at most 1 nanometer, on at least one surface of both sides thereof ≪ / RTI >
12. The glass roll according to any one of the preceding sentences, wherein at least one of the sides of the glass film is coated with a plastic layer, in particular a polymer layer.
13. The glass roll of
14. A glass roll as in any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the intermediate material is formed from a plurality of layers of intermediate material.
15. The glass roll of statement 14, wherein said plurality of intermediate material layers have different widths.
16. The glass roll of any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the intermediate material layers project laterally past the glass film layer.
17. The method of any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the fixation of the glass film layer by the intermediate material layer is performed in a range of 0.15 to 10 N, preferably 1 to 10 N, which acts between the glass film layer and the intermediate material layer Is made by the static friction F s of the glass roll.
18. The method of any one of the preceding sentences, wherein the fixation of the glass film layer by the intermediate material layer is performed at a temperature of from 0.15 to 5 N, preferably from 0.2 to 2.5 N, particularly preferably formed by a friction force F D in the range of 1 to 2.5 N, a glass roll.
19. A method of making a glass roll according to any one of the preceding sentences,
a) providing a glass film, a winding core and a compressible intermediate material,
b) winding at least one inner layer of intermediate material on the winding core,
c) winding the glass film and the intermediate material on the winding core such that the glass film is wound on the winding core alternately with the intermediate material, wherein the intermediate material and / or the glass film are oriented in the longitudinal direction Winding, said tensile stress causing compression of the intermediate material,
d) fixing the glass film end on the glass roll.
20. The method of claim 17, wherein the fixing of the glass film end is by at least one outer layer of the intermediate material.
21. An intermediate material between glass films in a glass roll, wherein the intermediate material is alternately superimposed with the glass film and can be wound on the winding core in at least two layers, and the glass film layers can be fixed by an intermediate material layer Use of a compressible material, especially a foam material film.
Claims (43)
상기 유리 필름은 그 양 측면의 적어도 하나의 표면에 파이어폴리시된 표면(fire-polished surface)을 포함하고, 상기 유리 필름은, 그 양 측면의 적어도 하나의 표면에서 최대 1 nm, 바람직하게는 최대 0.8 nm, 특히 바람직하게는 최대 0.5 nm의 2차 평균 조도 (RMS) Rq를 갖는 것을 특징으로 하는 유리 롤.A glass roll, comprising at least one glass film and an intermediate material, wherein the glass film and the intermediate material are superposed on at least two layers on a winding core, wherein the glass film layers are fixed to the intermediate material layer,
Wherein the glass film comprises a fire-polished surface on at least one surface of both sides thereof, the glass film having a maximum of at least 1 nm, preferably at most 0.8 (RMS) Rq of at most 0.5 nm, most preferably at most 0.5 nm.
b 유리 재료 폭
r 롤 반경(코어)
t1 유리 두께
t2 중간 층 두께
μ 정지 마찰 계수
ρ 유리 밀도
및 미리 알려진, 감긴 층의 수 n에서, 예비 응력 FV는 마찰 FF가 슬리브의 중량 FG보다 더 크도록 선택되는 것을 특징으로 하는 유리 롤.16. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 15,
b Glass material width
r Roll radius (core)
t1 Glass thickness
t2 intermediate layer thickness
μ static friction coefficient
ρ glass density
And in the previously known number of winding layers n, the pre-stress FV is selected such that the friction FF is greater than the weight FG of the sleeve.
상기 중간 재료는 중간 재료 층으로서 적어도 하나의 중간 층 시트 또는 중간 층을 포함하고, 상기 유리 필름은 제 1 폭(B1)을 가지며 상기 중간 층 시트는 제 2 폭(B2)을 갖고, 상기 제 2 폭(B2)은 상기 제 1 폭(B1)보다 훨씬 더 좁은 것을 특징으로 하는 유리 롤.At least one glass film and an intermediate material, wherein the glass film and the intermediate material are superposed on at least two layers on a winding core, wherein the glass film layers are fixed to the intermediate material,
Wherein the intermediate material comprises at least one intermediate layer sheet or intermediate layer as an intermediate material layer, the glass film having a first width (B1) and the intermediate layer sheet having a second width (B2) And the width (B2) is much narrower than the first width (B1).
b 유리 재료 폭
r 롤 반경(코어)
t1 유리 두께
t2 중간 층 두께
μ 정지 마찰 계수
ρ 유리 밀도
및 미리 알려진, 감긴 층의 수 n에서, 예비 응력 FV은 마찰 FF가 슬리브의 중량 FG보다 더 크도록 선택되는 것을 특징으로 하는 유리 롤.40. The process according to any one of claims 1 to 39,
b Glass material width
r Roll radius (core)
t1 Glass thickness
t2 intermediate layer thickness
μ static friction coefficient
ρ glass density
And in the previously known number of winding layers n, the pre-stress FV is chosen such that the friction FF is greater than the weight FG of the sleeve.
a) 유리 필름, 와인딩 코어 및 압축 가능한 중간 재료를 제공하는 단계,
b) 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 중간 재료의 적어도 하나의 내부 층을 감는 단계,
c) 상기 유리 필름이 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 중간 재료와 교대로 층층이 감기도록 상기 와인딩 코어 상에 상기 유리 필름 및 상기 중간 재료를 감는 단계로서, 상기 중간 재료 및/또는 상기 유리 필름은 길이 방향으로 작용하는 인장 응력으로 감기고, 상기 인장 응력은 상기 중간 재료의 압축을 야기하는, 감는 단계, 및
d) 유리 필름 단부를 상기 유리 롤에 고정하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 유리 롤의 제조 방법.40. A method of producing a glass roll according to any one of claims 1 to 40,
a) providing a glass film, a winding core and a compressible intermediate material,
b) winding at least one inner layer of the intermediate material on the winding core,
c) winding the glass film and the intermediate material on the winding core such that the glass film is wound on the winding core alternately with the intermediate material, wherein the intermediate material and / or the glass film are oriented in the longitudinal direction Wherein said tensile stress causes compression of said intermediate material, and
d) fixing the end of the glass film to the glass roll.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011084132A DE102011084132A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2011-10-07 | glass role |
| DE102011084132.6 | 2011-10-07 | ||
| PCT/EP2012/004169 WO2013050163A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2012-10-05 | Prestressed glass roll |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20140079795A true KR20140079795A (en) | 2014-06-27 |
Family
ID=47073400
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020147011170A KR20140079795A (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2012-10-05 | Prestressed glass roll |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20140220300A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP6173322B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20140079795A (en) |
| CN (2) | CN103857523A (en) |
| DE (2) | DE102011084132A1 (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI488795B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2013050163A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20210141763A (en) * | 2014-01-29 | 2021-11-23 | 코닝 인코포레이티드 | Stack assembly |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103787119B (en) * | 2012-10-29 | 2016-12-28 | 财团法人工业技术研究院 | Transmission device |
| DE102013110803A1 (en) * | 2013-09-30 | 2015-04-02 | Schott Ag | Process for the further processing of thin glass and according to the method produced thin glass |
| DE102014113149A1 (en) * | 2014-09-12 | 2016-03-17 | Schott Ag | Thin glass roll and process for its production |
| WO2016123000A1 (en) * | 2015-01-29 | 2016-08-04 | Corning Incorporated | Methods and apparatus for conveying glass ribbon |
| DE102016116259A1 (en) * | 2015-09-11 | 2017-03-16 | Schott Ag | Apparatus and method for stabilizing disks of a brittle-hard material |
| DE102016218176A1 (en) * | 2015-10-02 | 2017-04-06 | Schott Ag | Long-term flexible glass material, as well as method for producing a long-term flexible glass material |
| JP6162281B1 (en) * | 2016-03-16 | 2017-07-12 | 住友化学株式会社 | Method for controlling film winding apparatus, film winding body, film winding apparatus, and method for manufacturing film winding body |
| WO2021124913A1 (en) * | 2019-12-16 | 2021-06-24 | 旭化成株式会社 | Glass cloth, prepreg, and printed wiring board |
| CN113529238B (en) * | 2020-03-30 | 2022-12-30 | 旭化成株式会社 | Roll-shaped long glass cloth, prepreg, and printed wiring board |
| KR20220010366A (en) * | 2020-07-17 | 2022-01-25 | 코닝 인코포레이티드 | A glass roll |
Family Cites Families (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3089801A (en) | 1957-05-27 | 1963-05-14 | Minnesota Mining & Mfg | Ultra-thin glass sheet |
| US3622298A (en) | 1969-08-13 | 1971-11-23 | Owens Corning Fiberglass Corp | Method and apparatus for manufacturing glass films |
| EP0265512A1 (en) | 1986-05-02 | 1988-05-04 | MSC Specialty Films, Inc. | Sputter-coated thin glass sheeting in roll form and method for continuous production thereof |
| DE10015823A1 (en) * | 2000-03-30 | 2001-10-18 | Epcos Ag | Enclosed layered stack, eg for batteries, consists of intermediate layers which are sepd from each other, with a wound strip between them. |
| DE10064977C1 (en) | 2000-12-23 | 2002-10-02 | Schott Glas | Device for the production of thin glass panes |
| WO2003051783A1 (en) | 2001-12-14 | 2003-06-26 | Corning Incorporated | Apparatus and method for making sheet glass by the overflow downdraw fusion process |
| US20080047940A1 (en) * | 2006-08-28 | 2008-02-28 | Xinghua Li | Article with multiple surface depressions and method for making the same |
| JP2008107510A (en) | 2006-10-25 | 2008-05-08 | Nitto Denko Corp | Substrate for display element and its manufacturing method |
| JP5532506B2 (en) * | 2008-10-01 | 2014-06-25 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Glass roll |
| JP5532507B2 (en) * | 2008-10-01 | 2014-06-25 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Glass roll and glass roll processing method |
| JP5788134B2 (en) * | 2008-10-01 | 2015-09-30 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | GLASS ROLL AND GLASS ROLL MANUFACTURING METHOD |
| DE102009008292B4 (en) | 2009-02-10 | 2014-09-25 | Schott Ag | Capacitor and method for producing such |
| KR100927157B1 (en) * | 2009-02-26 | 2009-11-18 | (주)기가레인 | Probe block |
| US8980382B2 (en) | 2009-12-02 | 2015-03-17 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Oxygen-doping for non-carbon radical-component CVD films |
| US20110023548A1 (en) * | 2009-07-29 | 2011-02-03 | Garner Sean M | Glass substrate comprising an edge web portion |
| EP2460779B1 (en) * | 2009-07-30 | 2019-03-06 | Nippon Electric Glass Co., Ltd. | Glass roll and process for production thereof |
| JP5403487B2 (en) * | 2009-08-19 | 2014-01-29 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Glass roll |
| JP2011121320A (en) | 2009-12-11 | 2011-06-23 | Nippon Electric Glass Co Ltd | Glass film laminate, glass roll thereof, and method for manufacturing glass roll |
| JP5720885B2 (en) * | 2010-03-03 | 2015-05-20 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Glass roll and method for producing glass roll |
| JP2011190132A (en) | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Nippon Electric Glass Co Ltd | Glass roll and method for producing the same |
| TWI591029B (en) * | 2010-05-28 | 2017-07-11 | 康寧公司 | Method of winding glass ribbon |
| TWI565646B (en) * | 2010-11-30 | 2017-01-11 | 康寧公司 | Winding glass ribbon by tensioning interleaving material |
| DE102011084129A1 (en) | 2011-10-07 | 2013-04-11 | Schott Ag | Glass foil with specially designed edge |
| DE102013102848B3 (en) | 2013-03-20 | 2014-02-06 | Schott Ag | Thin glass used as substrate for layered composite for organic light-emitting diode, contains specified amount of silica, boric oxide, zinc oxide and barium oxide, and has preset value of refraction index |
-
2011
- 2011-10-07 DE DE102011084132A patent/DE102011084132A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2012
- 2012-10-05 CN CN201280049433.5A patent/CN103857523A/en active Pending
- 2012-10-05 KR KR1020147011170A patent/KR20140079795A/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2012-10-05 JP JP2014533797A patent/JP6173322B2/en active Active
- 2012-10-05 WO PCT/EP2012/004169 patent/WO2013050163A1/en active Application Filing
- 2012-10-05 CN CN201811331051.7A patent/CN109397800A/en active Pending
- 2012-10-05 DE DE112012004186.0T patent/DE112012004186A5/en active Pending
- 2012-10-05 TW TW101136834A patent/TWI488795B/en active
-
2014
- 2014-04-07 US US14/246,800 patent/US20140220300A1/en not_active Abandoned
-
2018
- 2018-05-14 US US15/978,814 patent/US11090905B2/en active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20210141763A (en) * | 2014-01-29 | 2021-11-23 | 코닝 인코포레이티드 | Stack assembly |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103857523A (en) | 2014-06-11 |
| TWI488795B (en) | 2015-06-21 |
| WO2013050163A1 (en) | 2013-04-11 |
| US20140220300A1 (en) | 2014-08-07 |
| US11090905B2 (en) | 2021-08-17 |
| TW201323307A (en) | 2013-06-16 |
| DE112012004186A5 (en) | 2014-07-10 |
| JP2015505742A (en) | 2015-02-26 |
| US20180257337A1 (en) | 2018-09-13 |
| CN109397800A (en) | 2019-03-01 |
| JP6173322B2 (en) | 2017-08-02 |
| DE102011084132A1 (en) | 2013-04-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR20140079795A (en) | Prestressed glass roll | |
| KR101554198B1 (en) | Glass roll | |
| US8806894B2 (en) | Process for producing glass roll with a separable protective sheet | |
| US8241751B2 (en) | Glass roll and process for producing glass roll | |
| US20110177325A1 (en) | Glass roll, device for producing glass roll, and process for producing glass roll | |
| KR101886885B1 (en) | Roll of flexible glass and method for rolling | |
| JP6024659B2 (en) | Thin glass winder and storage device | |
| US10953629B2 (en) | Rolled graphite sheet | |
| WO2023027891A1 (en) | Roll-to-roll glass lamination system and method of laminating glass |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WITN | Application deemed withdrawn, e.g. because no request for examination was filed or no examination fee was paid |