KR20100041201A - Electrochemical method for water treatment - Google Patents
Electrochemical method for water treatment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20100041201A KR20100041201A KR1020080100260A KR20080100260A KR20100041201A KR 20100041201 A KR20100041201 A KR 20100041201A KR 1020080100260 A KR1020080100260 A KR 1020080100260A KR 20080100260 A KR20080100260 A KR 20080100260A KR 20100041201 A KR20100041201 A KR 20100041201A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- wastewater
- nacl
- electrolysis
- supply line
- nitrogen
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/46—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by electrochemical methods
- C02F1/461—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by electrochemical methods by electrolysis
- C02F1/467—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by electrochemical methods by electrolysis by electrochemical disinfection; by electrooxydation or by electroreduction
- C02F1/4672—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by electrochemical methods by electrolysis by electrochemical disinfection; by electrooxydation or by electroreduction by electrooxydation
- C02F1/4674—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by electrochemical methods by electrolysis by electrochemical disinfection; by electrooxydation or by electroreduction by electrooxydation with halogen or compound of halogens, e.g. chlorine, bromine
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F1/00—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage
- C02F1/66—Treatment of water, waste water, or sewage by neutralisation; pH adjustment
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F2201/00—Apparatus for treatment of water, waste water or sewage
- C02F2201/46—Apparatus for electrochemical processes
- C02F2201/461—Electrolysis apparatus
- C02F2201/46105—Details relating to the electrolytic devices
- C02F2201/4612—Controlling or monitoring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F2209/00—Controlling or monitoring parameters in water treatment
- C02F2209/06—Controlling or monitoring parameters in water treatment pH
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C02—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F—TREATMENT OF WATER, WASTE WATER, SEWAGE, OR SLUDGE
- C02F2209/00—Controlling or monitoring parameters in water treatment
- C02F2209/29—Chlorine compounds
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 전기분해를 이용한 수처리 방법에 관한 것으로, 자세하게는 폐수를 전기분해에 의해 생성된 차염소산나트륨을 사용하여 처리하되, 전기분해시 필요한 전해질의 효율적인 사용을 위해 NaCl 회수설비를 사용하고, 전기분해 장치의 규모를 줄이기 위해 바이패스(bypass)된 원폐수를 전기분해하여 산화제를 발생시켜 다시 원폐수로 투입하여 처리하는 폐수의 염소순환식 전해 수처리방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a water treatment method using electrolysis, and in detail, the wastewater is treated with sodium hypochlorite produced by electrolysis, but using NaCl recovery equipment for efficient use of the electrolyte required for electrolysis, The present invention relates to a chlorine-circulating electrolytic water treatment method of wastewater in which the bypassed wastewater is electrolyzed to reduce the size of the decomposition apparatus, generates an oxidizing agent, and then inputs the wastewater into the wastewater.
일반 생활하수나 산업폐수, 발전소 폐수 중의 유기물, 질소 등 영양 염류, 난분해성 물질은 자연 수중으로 유입될 경우 수중 오염부하가 높아지고 수계의 부영양화를 촉진하여 조류를 발생시키며, 이로 인하여 산소부족과 독성물질 배출 등의 영향으로 물고기가 폐사하고 생태계가 파괴되는 주원인이 된다.Nutrient salts such as organic sewage, industrial wastewater, power plant wastewater, nitrates, and non-decomposable substances, such as nitrogen, increase the pollutant load in the water and promote the eutrophication of the water, generating algae. It is the main cause of the death of fish and the destruction of ecosystems due to the discharge.
이에 각 산업공정에서 배출되는 배출수 중 오염물질의 관리 농도가 점점 강 화 되어 아래 표와 같이 배출 기준이 변경되어 2013년 이후로는 모든 폐수 배출 시설에서 BOD, COD, T-N 이 각각 10, 40, 20mg/L 이하로 강력히 규제된다.As the concentration of pollutants in the effluent discharged from each industrial process is gradually strengthened, the emission standard is changed as shown in the table below. Strongly regulated below / L
상기표에서 "( )"는 농공단지의 경우의 폐수종말처리시설의 방류수 수질기준In the above table, "()" is the standard of discharged water quality of wastewater treatment facilities in agricultural complex.
이하 폐수내 포함된 오염물질의 처리방법에 대해 살펴본다.The following describes how to treat the pollutants contained in the wastewater.
폐수내 유기물, 질소 물질을 처리하는 기존 처리 방법 중 대표적인 미생물 처리에 의한 방법은 미생물이 온도, 환경 등에 의한 영향을 받기 때문에 기존 처리장치에서는 여름 겨울 등에 처리효율이 떨어지며 폐수 오염 농도가 고농도로 갈수록 필요 부지가 늘어나므로 비교적 저농도의 경우에 사용 된다. 또한 폐수내 난분해성 물질이나 독성 물질이 포함 되어 있을 경우 사실상 생물학적 처리법으로는 처리할 수가 없다.Among the existing treatment methods for treating organic matter and nitrogenous substances in wastewater, the typical treatment method by microorganism is that the microorganisms are affected by temperature, environment, etc., so the treatment efficiency decreases in summer and winter in the existing treatment equipment, and the wastewater pollution concentration is increasingly required. As the site is increased, it is used in relatively low concentrations. In addition, if the waste water contains hardly decomposable substances or toxic substances, they cannot be treated by biological treatment.
생물처리법의 단점을 보완하고 적용하기 어려운 독성 및 난분해성 폐수 처리를 위하여 여러 가지 방법이 연구되고 있다. 예를 들자면 염소가스를 투입하는 방법, 차아염소산나트륨을 투입하는 방법 그리고 기존 특허에도 많이 설명되고 있는 전기분해를 이용한 처리법이 그 중 하나이다. Various methods have been studied for the treatment of toxic and hardly degradable wastewater, which are difficult to apply and to the disadvantages of biotreatment. For example, a method of adding chlorine gas, a method of adding sodium hypochlorite, and a treatment method using electrolysis, which are widely described in existing patents, are one of them.
먼저 염소가스를 투입하는 방법은 폐수에 염소 가스를 투입하여 반응시켜 처리하는 단순한 방법 중 하나이다. 장치 구성 역시 염소가스 탱크와 반응 탱크의 간단한 공정을 갖는 방법으로 초기 투자비가 적은 편이다.First, the method of adding chlorine gas is one of the simple methods of reacting and treating chlorine gas by adding it to wastewater. The device configuration also has a low initial investment by a simple process of a chlorine gas tank and a reaction tank.
그러나 이와 같은 방식은 염소 가스 자체의 독성으로 현장에서 염소가스를 취급하는데 매우 유의해야 하며 염소 가스 자체가 고가의 물질이라 처리비용이 상당히 비싼 방법이라는 단점이 있다. However, this method has to be very careful in handling chlorine gas in the field due to the toxicity of chlorine gas itself, and chlorine gas itself is an expensive material, and thus has a disadvantage that the treatment cost is quite expensive.
또한 폐수에 염소 가스 대신 10%의 고농도 차염소산나트륨이나 0.8~1%의 저농도 차염소산나트륨을 투입하는 방법으로 현장에서 고농도 또는 저농도 차염소산나트륨을 직접 만들어 투입하는 방식과 약품으로 사서 투입하는 방법이다. 고농도 차염인 10% 차염은 격막을 이용하여 만든 염소가스를 NaOH와 반응시켜 생산하여 벌크(bulk)로 공급하거나, 현장에서 제조장치를 직접 설치하여 투입하는 온-사이트(on-site) 방식이 있다. 그러나 이와 같은 방식은 고농도 차염을 만들기 위해 필요한 격막과 투입되는 전력량이 상당히 높은 비용이 필요하며, 이때 전해질도 고농도를 필요로 하여 생산비용이 올라간다는 단점이 있다. In addition, 10% high sodium hypochlorite or 0.8 ~ 1% low sodium hypochlorite instead of chlorine gas is injected into the waste water. . 10% flame, which is a high concentration flame, is produced by reacting chlorine gas produced by using diaphragm with NaOH and supplying it as a bulk or on-site method by directly installing a manufacturing equipment in the field. . However, such a method requires a high cost of the diaphragm and the amount of power input to make a high concentration flame, and the electrolyte also requires a high concentration has the disadvantage that the production cost increases.
또한 0.8~1%의 저농도 차염은 대부분 현장에서 제조하여 투입하는 방식을 사용하는데 고농도 차염생산과는 달리 격막 없이 무격막으로 제조하여 생산비용이 저렴한 편이다. 그러나 이와 같은 방식은 저농도 차염을 현장에서 만들어 투입할 경 우, 질소 농도에 따라 투입되는 외부 폐수량(저농도 차염수)이 증가하여 최종적으로 발생되는 폐수량이 증가하게 된다. 이는 처리 장치의 규모를 필요 이상으로 증가시키며 최종적으로 수처리비용을 증가시킨다는 단점이 있다. In addition, most of the low concentration of 0.8 ~ 1% of flame retardant is manufactured and put in the field. Unlike the production of high concentration of flame retardant, the production cost is low because it is manufactured without a diaphragm. However, in such a method, when the low concentration flame is made at the site, the amount of external waste water (low concentration salt water) is increased according to the nitrogen concentration, resulting in an increase in the amount of waste water finally generated. This has the disadvantage of increasing the size of the treatment apparatus more than necessary and finally increasing the water treatment cost.
또 다른 전기분해를 이용한 방법으로 폐수를 직접 전기분해 장치에 통과시켜 처리하는 방법이 있는데 폐수 내 유기물, 질소 성분 농도와 처리 효율에 따라 전기분해 장치 규모가 설계되고 폐수 내 전해물질이 부족한 경우 Cl 성분을 투입한다. 이 방법은 폐수에 전기분해 장치를 단일로 설치하여 장치에 폐수를 통과시키며 전기를 공급하여 유기물 및 질소성분을 분해시켜 처리하는 부수적인 장치가 필요 없는 간단한 구조이다. Another method using electrolysis is to treat wastewater by passing it directly through an electrolysis device. The size of the electrolysis device is designed according to the concentration of organic matter and nitrogen in the wastewater and the treatment efficiency. Input This method is a simple structure that installs a single electrolysis device in the waste water, passes the waste water through the device, and supplies electricity to decompose and process organic matter and nitrogen components.
그러나 폐수량이 많거나, 폐수 오염 부하가 높을 경우 전기분해 장치의 규모가 증가해야 하는데 전기분해 장치에 사용되는 전극은 비교적 고가이며, 장치의 규모가 일정이상 커지게 되면 이에 필요한 전기를 공급 하는 것에도 상당한 규모가 되어 장치를 설치하기 힘든 경우도 있다. 또한 폐수내 일정 전해물질이 포함되지 않았을 경우 전극의 수명이 줄어들고 처리 효율도 감소하게 되어 추가 약품 비용도 커지게 된다는 단점이 있다.However, if the amount of waste water is high or the load of waste water is high, the size of the electrolysis device should be increased. In some cases, it is quite difficult to install the device. In addition, when a certain electrolytic material is not included in the waste water, there is a disadvantage in that the lifetime of the electrode is reduced and the treatment efficiency is reduced, thereby increasing the cost of additional chemicals.
또한 도 3에 개략적으로 도시된 대한민국 특허 제 10-0687095호(질소 화합물의 역전전기투석-전기화학적 폐수처리공정)를 보면 그 구성이 기존 EDR + 전기분해 공정으로 이루어져 있음을 알 수 있는데, 이는 단순히 폐수중 질소를 농축하여 전 기분해 처리하는 것을 목적으로 하고 있다. 이 방법은 저농도의 질소계 폐수를 EDR을 이용하여 고농도로 농축하여 희석수는 재사용하고, 농축수는 전기분해에 의해 처리하는 방식을 채택한 것으로 EDR 농축법을 사용한 것 이외에는 일반적인 전기분해방법과 장단점이 거의 유사하다고 할 수 있다.In addition, the Republic of Korea Patent No. 10-0687095 (reverse electrodialysis-electrochemical wastewater treatment process of nitrogen compounds) shown schematically in Figure 3 can be seen that the configuration consists of the existing EDR + electrolysis process, which is simply It aims to concentrate the nitrogen in the waste water and treat it as it is. This method adopts the method of concentrating low concentration of nitrogen-based wastewater to high concentration using EDR, reusing dilute water, and treating the concentrated water by electrolysis. It is almost similar.
또 다른 기존 처리 방법중 도 4에 도시된 특허 제10-0670629호(복수탈염설비 재생폐수의 유기물질 및 질소를 제거하기위한 전기분해처리장치 및 처리방법)에서 내부 반송을 통해 처리효율을 증가시키는 공정이 있는데, 이는 폐수에 전해질을 투입하여 직접분해 한 후단에 반응탱크를 두고 폭기시켜는 단계와 이 반응탱크에서 일부를 전해질 투입 단계로 반송시켜 체류시간만 증기시키는 공정으로 일반적인 전기분해 공정과 별다른 차이점이 없다. 또한 전해질 공급을 바닷물이나 소금물을 10~30% 중량%로 주입하는데 이는 폐수 총량을 늘리는 결과를 가져와 최종적으로 장치가 커지게 되는 단점이 된다.In another existing treatment method, Patent No. 10-0670629 shown in Fig. 4 (electrolytic treatment apparatus and treatment method for removing organic substances and nitrogen from a plurality of demineralization facility regeneration wastewater) to increase the treatment efficiency through internal conveyance There is a process, in which an electrolyte is introduced into wastewater, which is directly decomposed, followed by aeration with a reaction tank, and a part of the reaction tank is returned to the electrolyte input step to steam only residence time, which is different from the general electrolysis process. There is no difference. In addition, 10-30% by weight of seawater or salt water is injected into the electrolyte supply, which results in an increase in the total amount of wastewater, resulting in a large device.
상기에서 살펴본 종래 기술중 직접 전기분해를 이용하여 유기물 및 질소함유 폐수를 처리하는 방법은 폐수량이나 오염물 부하 변화시 즉, 공급폐수의 공급량 또는 오염물 함유량 증가시 추가적인 별도의 전해질(염소이온) 투입 및 전기분해장치의 규모 증설과 이에 따른 추가적인 전기공급량이 필요하고, 폐수내 일정 농도의 전해질(염소이온)이 포함되지 않을 경우에는 전기분해장치를 구성하는 전극 수명이 줄어들고 처리효율도 감소한다는 단점으로 인해 다양한 폐수 공급조건에 따른 대응 이 떨어진다는 문제점이 있다.The conventional method of treating organic and nitrogen-containing wastewater by using direct electrolysis is to add an additional electrolyte (chlorine ion) and change electricity when the amount of wastewater or pollutant load is increased, that is, when the amount of feedwater or pollutant content is increased. Due to the drawbacks of the expansion of the cracking device and additional electricity supply, and the absence of a certain concentration of electrolyte (chlorine ion) in the wastewater, the electrode life of the electrolytic device is reduced and the treatment efficiency is reduced. There is a problem that the response to the waste water supply conditions is poor.
상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하기 위한 본 발명의 목적은 전기분해를 이용하여 폐수 처리시 필요한 전해질을 폐수 중에서 회수 후 재 순환시켜 저렴하게 고농도의 전해질 상태를 안정적으로 공급하여 전극의 수명을 연장토록 하고, 폐수원수 중 일부를 분기 후 전기분해하여 폐수내 오염물질을 제거하고, 전기분해시 생성된 차아염소산나트륨을 원폐수에 공급하여 산화방식으로 유기물 및 질소성분을 제거토록 하여 다중 방식으로 처리함으로써 장치의 크기를 소형화하고 전해질추가에 따른 손실을 방지하는 전해 처리방법을 제공하는 데 있다.An object of the present invention for solving the above problems is to recover the electrolyte required in the wastewater treatment using electrolysis in the wastewater and to recirculate it to supply a stable concentration of electrolyte at low cost to extend the life of the electrode, After branching some of the wastewater, it is electrolyzed to remove contaminants in the wastewater, and sodium hypochlorite generated during electrolysis is supplied to the raw wastewater to remove organic substances and nitrogen components by oxidation, and treated in a multiple manner. It is to provide an electrolytic treatment method for miniaturizing the size and preventing loss due to the addition of electrolyte.
상기한 바와 같은 목적을 달성하고 종래의 결점을 제거하기 위한 과제를 수행하는 본 발명은 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 포함한 원폐수를 분기시켜 일부를 전기분해조에서 유기물질 및 질소를 제거함과 동시에 산화제인 차아염소산나륨을 발생시키고, 이를 처리수조에서 원폐수와 혼합하여 원폐수 내 유기물질 및 질소를 제거시키고, 전기분해조에 사용되는 NaCl은 처리수조를 지난 혼합폐수를 NaCl회수설비에서 회수하여 재사용하는 염소순환식으로 전해 처리하는 방법을 특징으로 하는 전기분해를 이용한 수처리 방법을 제공함으로써 달성된다.The present invention, which achieves the object as described above and performs the task for eliminating the conventional drawbacks, is branching raw wastewater containing organic substances and nitrogen components to remove some organic substances and nitrogen from the electrolysis tank and simultaneously Generates sodium hypochlorite and mixes it with raw waste water in the treatment tank to remove organic substances and nitrogen in the waste water, and NaCl used in the electrolysis tank is chlorine that is recovered from the NaCl recovery facility and reused in the NaCl recovery facility. It is achieved by providing a water treatment method using electrolysis characterized by a method of electrolytic treatment in a cyclic manner.
상기 염소순환식으로 전해 처리하는 방법은,The electrolytic treatment by the chlorine circulation,
유기물질 및 질소 성분을 포함한 원폐수를 주공급라인과 분기공급라인으로 분기 공급하는 단계와;Quarterly supplying raw wastewater including organic substances and nitrogen components to the main supply line and the branch supply line;
주공급라인을 통해 유입된 원폐수와 분기공급라인을 거친 후 전기분해 처리되어 차아염소산나트륨을 함유한 폐수가 혼합된 혼합폐수로를 처리수조에서 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하는 단계와;Removing organic substances and nitrogen components from the treatment tank in a mixed wastewater passage in which the raw wastewater introduced through the main supply line and the branch supply line are electrolyzed and mixed with wastewater containing sodium hypochlorite;
NaCl회수설비에서 혼합폐수로부터 NaCl을 막접촉에 의해 회수시켜 분기공급라인을 통해 공급되는 원폐수쪽으로 NaCl을 공급하는 NaCl 회수 단계와;A NaCl recovery step of recovering NaCl from the mixed wastewater by the membrane contact in a NaCl recovery facility and supplying NaCl to the raw wastewater supplied through the branch supply line;
NaCl 회수 단계에서 NaCl을 공급받은 분기공급라인의 원폐수 농도가 낮을 경우 포화소금조에서 NaCl을 투입하여 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수로 만드는 NaCl 투입단계와;When the raw wastewater concentration of the branch feed line receiving NaCl in the NaCl recovery step is low, NaCl is introduced into a saturated salt bath to make NaCl-containing wastewater of high concentration;
고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수를 공급받은 전기분해조에서 전기분해하여 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하고, 동시에 생성된 차아염소산나트륨을 원폐수에 투입하는 전기분해단계;의 처리단계를 거치면서 염소순환식으로 전해 처리하는 방법을 특징으로 한다. Electrolysis in an electrolysis tank supplied with a high concentration of NaCl-containing wastewater to remove organic substances and nitrogen, and at the same time, an electrolysis step of introducing the generated sodium hypochlorite into the raw wastewater; It is characterized by the method of electrolytic treatment.
상기 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하는 단계와 NaCl회수단계 사이에 유기물질 및 질소 성분이 제거된 혼합폐수의 pH를 조정하는 중화단계와; 중화단계를 지난 혼합폐수 내 잔류 산화제를 제거하는 약품 처리 단계;를 더 포함하여 구성한 것을 특징으로 한다.A neutralization step of adjusting the pH of the mixed wastewater from which the organic material and the nitrogen component have been removed between the step of removing the organic material and the nitrogen component and the NaCl recovery step; The chemical treatment step of removing the residual oxidant in the mixed wastewater after the neutralization step; characterized in that it further comprises.
상기 저농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수는 3% 미만의 NaCl 농도인 것을 특징으로 한다.The low concentration of NaCl-containing wastewater is characterized in that the NaCl concentration of less than 3%.
상기 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수는 3% 이상의 NaCl 농도인 것을 특징으로 한다.The high concentration of NaCl-containing wastewater is characterized by a NaCl concentration of 3% or more.
상기 분기 공급하는 단계에서 주공급라인은 원폐수를 분기공급라인을 거친 후 전기분해 처리되어 차아염소산나트륨을 함유한 폐수와 혼합하여 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하는 처리수조 쪽으로 공급하는 단계이고, In the branch supplying step, the main supply line is a step of supplying raw wastewater to a treatment tank for removing organic matter and nitrogen by mixing with wastewater containing sodium hypochlorite after passing through the branch supply line.
분기공급라인은 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수를 공급받아 전기분해하여 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하고, 동시에 생성된 차아염소산나트륨을 생산하는 전기분해조 쪽으로 분기 공급하는 단계인 것을 특징으로 한다.The branch supply line is characterized in that the step of supplying a high concentration of NaCl-containing waste water to electrolysis to remove organic substances and nitrogen components, and at the same time branch feed to the electrolysis tank to produce the produced sodium hypochlorite.
상기 pH를 조정하는 중화단계는 처리수조를 통하면서 유기물 및 질소가 제거된 폐수의 낮아진 pH를 pH조정조에서 조정하여 전기분해하기 좋은 pH로 만드는 단계인 것을 특징으로 한다.The neutralization step of adjusting the pH is characterized in that the step of adjusting the lower pH of the waste water from which the organic matter and nitrogen is removed while adjusting the pH in the pH adjustment tank to a good pH for electrolysis.
상기 주공급라인과 분기공급라인으로 분기 공급하는 단계에서 분기 비율은 원폐수의 오염 부하에 따라 농도가 낮으면 주공급라인에 비해 분기라인의 공급비율을 낮게 선택적으로 나누는 것을 특징으로 한다.The branching ratio in the step of supplying to the main supply line and the branch supply line is characterized by selectively dividing the supply ratio of the branch line lower than the main supply line if the concentration is low according to the pollution load of the raw waste water.
상기 NaCl 회수 단계는 혼합폐수의 NaCl을 회수후, NaCl 농도가 낮아진 혼합폐수는 방류하는 단계인 것을 특징으로 한다.The NaCl recovery step is characterized in that after the recovery of NaCl of the mixed wastewater, the mixed wastewater NaCl concentration is discharged.
본 발명은 전기분해의 효율을 높이며 고가의 전극 수명을 늘리기 위한 전해질을 유입되는 저염분의 원폐수와 전기분해 처리된 고염분 폐수를 이용하여 NaCl 회수설비에서 Cl 이온을 회수후 전기분해장치에 재순환 공급함으로써 3% 농도의 NaCl을 유지하기 위해 투입되는 NaCl 투입량을 저감시킬수 있다는 장점과,The present invention recovers Cl ions from the NaCl recovery facility using the low salt raw wastewater and the electrolytically treated high salt wastewater into which the electrolyte is introduced to increase the efficiency of electrolysis and increase the life of the expensive electrode. By reducing the amount of NaCl added to maintain the NaCl concentration of 3%, and
NaCl 회수설비에 의한 Cl 이온의 재순환공정으로 인해 지속적으로 고농도 NaCl 산태를 유지함으로 인한 전극 수명 연장한다는 장점과 Due to the recycling process of Cl ions by NaCl recovery facility, the electrode life is extended by maintaining high concentration of NaCl continuously.
원폐수 일부를 분기후 전기분해하여 오염물질을 제거하는 공정과 전기분해시 생성된 산화제인 차아염소산나트륨을 원폐수에 투입하여 산화방식에 의해 원폐수 내 오염물질을 처리하는 공정으로 다중 제거함으로써 원폐수 전부를 전기분해장치에 투입하는 기존의 전기분해방식에 비하여 전기분해장치를 소형화 할 수 있다는 장점과,The process of removing some pollutants by electrolysis after dividing part of the waste water and the process of treating contaminants in the waste water by oxidizing method by adding sodium hypochlorite, an oxidant produced during electrolysis, to the waste water. Compared to the conventional electrolysis method in which all waste water is put into the electrolysis device, the electrolysis device can be miniaturized.
폐수를 일부 분기시키고 이를 전기분해하여 폐수처리하고 추가로 발생된 산화제를 원폐수와 혼합시켜 폐수 처리에 필요한 산화제량을 없거나 최소로 만드는 장점을 가진 유용한 발명으로 산업상 그 이용이 크게 기대되는 발명이다.This is a useful invention which has the advantage of branching the wastewater and electrolyzing it to treat the wastewater and mixing the generated oxidant with the original wastewater to reduce or minimize the amount of oxidant required for the wastewater treatment. .
이하 본 발명의 실시 예인 구성과 그 작용을 첨부도면에 연계시켜 상세히 설명하면 다음과 같다. 또한 본 발명을 설명함에 있어서, 관련된 공지기능 혹은 구성에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우 그 상세한 설명은 생략한다.Hereinafter, the configuration and the operation of the embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the following description of the present invention, a detailed description of known functions and configurations incorporated herein will be omitted when it may make the subject matter of the present invention rather unclear.
도 1은 본 발명의 한 실시예에 따른 염소 순환 처리 공정을 보인 폐수 처리공정도인데, 1 is a wastewater treatment process diagram showing a chlorine circulation treatment process according to an embodiment of the present invention,
도시된 바와 같이 본 발명 장치 구성은 원폐수를 주공급라인과 분기공급라인으로 분기후, 분기공급라인을 통해 공급된 원폐수를 전기분해하여 폐수처리함과 동시에 이때 발생된 차아염소산나트륨을 포함하는 유기물질 및 질소가 제거된 폐수를 원폐수와 혼합하여 차아염소산나트륨에 의해 유기물질과 질소 성분을 제거하는 처리수조와; 처리수조를 지난 혼합폐수를 중화하는 pH조정조와; pH조정조를 지난 혼합폐수 내 잔류 산화제를 제거하는 약품처리조와; NaCl 함유 혼합폐수를 분기공급라인으로 분기된 원폐수와 막접촉시켜 혼합폐수의 NaCl을 회수하여 분기공급라인으로 분기된 원폐수의 NaCl 농도를 높이고, NaCl 농도가 낮아진 혼합폐수는 방류시키는 NaCl회수설비와; NaCl회수설비를 거치면서 NaCl 농도가 높아진 분기공급라인의 폐수 농도에 따라 저농도일 경우 NaCl을 투입하여 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수로 만드는 전해질 보충용 포화소금조와; 고농도의 NaCl을 함유하는 분기공급라인의 폐수를 전기분해하여 유기물과 질소를 제거함과 동시에 차아염소산나트륨을 생성하여 처리수조에 공급하는 전기분해조;로 구성된다. As shown, the apparatus configuration of the present invention comprises branching the raw waste water into the main supply line and the branch supply line, and electrolytically decomposes the raw waste water supplied through the branch supply line to treat waste water and at the same time includes sodium hypochlorite generated at this time. A treatment tank for mixing organic wastewater from which organic matter and nitrogen have been removed with original wastewater to remove organic matter and nitrogen components by sodium hypochlorite; A pH adjusting tank for neutralizing the mixed wastewater passing through the treatment tank; a chemical treatment tank for removing residual oxidant in the mixed wastewater passing the pH adjusting tank; NaCl recovery facility that recovers NaCl of mixed wastewater by increasing the NaCl concentration of raw wastewater branched into branch supply line by membrane-contacting the mixed wastewater containing NaCl with branched supply line, and discharges the mixed wastewater with low NaCl concentration. Wow; Saturated salt tank for replenishing electrolyte to make NaCl-containing wastewater by adding NaCl when the concentration is low according to the wastewater concentration of the branch feed line where NaCl concentration is increased through NaCl recovery facility; It consists of an electrolysis tank that electrolyzes wastewater in a branch supply line containing a high concentration of NaCl to remove organic matter and nitrogen, and simultaneously generates sodium hypochlorite and supplies it to the treatment tank.
상기에서 고농도라 함은 3%이상의 NaCl 농도를 말하는 것이고, 저농도는 3%미만의 NaCl 농도를 말한다. In the above, high concentration refers to NaCl concentration of 3% or more, and low concentration refers to NaCl concentration of less than 3%.
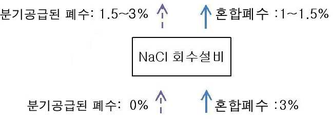
상기 NaCl회수설비를 거친 혼합폐수와 분기공급라인의 폐수농도를 도 2에 도시된 본 발명의 한 실시예에 따른 농도 변환 과정을 보면 분기된 폐수의 농도는 NaCl 회수설비를 거치게 되면 최초 0%에서 1.5~3%로 전환되고, 분기된 폐수와 막 접촉하여 NaCl이 회수되는 혼합폐수는 최초 3% 미만에서 1~1.5%로 전환된다. 물론 이와 같은 NaCl 농도는 한 실시예에 따른 예시적인 표현으로, 만약 폐수 오염 부하에 따라 주공급라인과 분기공급라인으로 공급되는 원폐수의 비율이 변하면 이러한 비율 역시 변동되게 된다. 즉, 회수되는 NaCl농도는 폐수의 오염 부하에 따라 장치를 설계하며 이에 따라 변경된다.In the concentration conversion process according to the embodiment of the present invention, the wastewater concentration of the mixed wastewater and the branch supply line which passed through the NaCl recovery system is shown in FIG. The mixed wastewater, where it is converted to 1.5 to 3% and the NaCl is recovered in membrane contact with the branched wastewater, is converted to less than 1% to 1% to 1.5%. Of course, such a NaCl concentration is an exemplary expression according to an embodiment, and if the ratio of the raw wastewater supplied to the main supply line and the branch supply line is changed according to the wastewater pollution load, the ratio is also changed. In other words, the NaCl concentration recovered is designed according to the pollutant load of the wastewater and is changed accordingly.
이하 본 발명을 구성하는 상기 각 구성요소를 보다 구체적으로 설명하면 다음과 같다.Hereinafter, the components of the present invention will be described in more detail.
유기물 및 질소 성분을 포함한 원폐수가 유입하면서 일부는 처리수조로 가는 주공급라인과 NaCl회수설비로 가는 분기공급라인으로 나누어진다. 두 라인의 비율은 원폐수의 오염 부하에 따라 선택적으로 변한다. As raw wastewater containing organic matter and nitrogen is introduced, some are divided into main feed line to the treatment tank and branch feed line to the NaCl recovery facility. The ratio of the two lines varies selectively depending on the pollutant load of the raw waste water.
즉, 상기 원폐수를 주공급라인과 분기공급라인으로 나누는 비율은 원폐수의 오염 부하에 따라 농도가 낮으면 주공급라인에 비해 분기라인의 공급비율을 낮게 선택적으로 나눈다.That is, the ratio of dividing the wastewater into the main supply line and the branch supply line selectively divides the supply ratio of the branch line lower than the main supply line when the concentration is low according to the pollution load of the original wastewater.
상기 처리수조는 전기분해조를 거친 폐수가 주공급라인의 원폐수와 혼합, 반응되는 곳으로 원폐수내의 유기물 및 질소 성분은 전기분해조에서 생성된 산화제인 차아염소산나륨에 의해 산화 되어 제거된다.The treatment tank is a place where the wastewater passed through the electrolysis tank is mixed with and reacted with the raw waste water of the main supply line. The organic matter and nitrogen components in the waste water are oxidized and removed by sodium hypochlorite, which is an oxidant produced in the electrolysis tank.
상기 pH조정조는 처리수조를 지난 폐수의 pH를 조정하는 곳이다. 전기분해조에서의 폐수내 질소 처리는 중성 내지 알카리성 pH에서 효율이 좋으며, NaOCl 등 산화제 발생시 pH가 증가된다. 이를 원폐수에 투입하는 처리수조 내의 화학 반응에 의하여 폐수 pH가 내려가게 된다. 따라서 후단의 NaCl회수장치에서 NaCl 회수시 pH도 같이 변하게 되므로 전기분해조에 공급되기 전에 내려간 pH를 다시 전기분해조에서 전기분해하기 알맞은 pH로 조정하는 곳이다.The pH adjusting tank is a place for adjusting the pH of the wastewater passing through the treatment tank. Nitrogen treatment in wastewater in the electrolysis bath is efficient at neutral to alkaline pH, and the pH is increased when oxidants such as NaOCl are generated. The pH of the wastewater is lowered by a chemical reaction in the treatment tank in which it is added to the wastewater. Therefore, the pH is also changed when NaCl is recovered in the NaCl recovery unit at the next stage, so that the pH lowered before being supplied to the electrolysis tank is adjusted to a suitable pH for electrolysis in the electrolysis tank.
상기 약품처리조는 처리수조를 지난 폐수 내 잔류 산화제를 제거하는 곳이다.The chemical treatment tank is a place for removing residual oxidant in the wastewater passing through the treatment tank.
상기 NaCl회수설비는 실시예로 EDR(전기투석) 장치를 이용할 수 있다. NaCl 회수설비로 유입된 분기공급라인을 통해 공급되는 원폐수는 처리수조를 통과한 혼합폐수와 교차하며 NaCl 회수설비의 원리 즉, 막접촉에 의한 투석 원리에 의해 혼합폐수 내의 Cl 이온이 분기공급라인으로 공급되는 원폐수 쪽으로 이동하게 된다. NaCl회수설비의 용량은 이동 하고자 하는 Cl 농도에 의해 조정되는데 투석되는 Cl 이온량이 많아질수록 NaCl 회수 설비의 용량이 커지게 되므로 공정의 효율과 설계 비용을 감안하여 결정한다. 이후 NaCl회수설비에서 NaCl 성분 일부가 회수된 혼합폐수는 배출되어 방류된다.The NaCl recovery facility may use an EDR (electrodialysis) device as an example. The raw waste water supplied through the branch supply line introduced into the NaCl recovery facility crosses the mixed wastewater that has passed through the treatment tank, and the Cl ions in the mixed waste water branch supply line according to the principle of NaCl recovery facility, that is, dialysis by membrane contact. It moves to the raw wastewater which is supplied to. The capacity of the NaCl recovery facility is adjusted by the Cl concentration to be moved. As the amount of Cl ion to be dialyzed increases, the capacity of NaCl recovery facility increases, so it is determined in consideration of the process efficiency and design cost. Afterwards, the mixed wastewater from which some of the NaCl components are recovered in the NaCl recovery facility is discharged and discharged.
상기 포화소금조는 NaCl회수설비를 지난 NaCl농도가 높아진 폐수의 NaCl 농도가 고농도에 미달할 경우 전기분해 효율이 높도록 NaCl을 투입하여 전해질인 NaCl의 농도를 고농도(3%이상)로 만드는 장치이다. 즉, 전기분해 반응에 있어 전극의 수명을 늘리고 전류 효율을 높게 유지하기 위하여 전해질인 NaCl 농도를 3% 이상으로 조정하는 것이 좋다. 따라서 NaCl 회수 설비에서 투석된 폐수 내 NaCl 농도가 3%에 미치지 못할 경우 NaCl을 투입 하는 장치이다.The saturated salt bath is a device that makes the concentration of NaCl as an electrolyte (higher than 3%) by adding NaCl so that the electrolysis efficiency is high when the NaCl concentration of the wastewater having increased NaCl concentration after passing the NaCl recovery facility is not high. In other words, in order to increase the life of the electrode in the electrolysis reaction and to maintain a high current efficiency, it is preferable to adjust the NaCl concentration of the electrolyte to 3% or more. Therefore, NaCl is added when NaCl concentration in wastewater dialyzed at NaCl recovery facility is less than 3%.
상기 전기분해조는 Ru, Ir, Pt 등의 귀금속류가 코팅된 DSA 전극(본 출원인의 선등록 특허 10-0407710에 따라 제작됨)을 양극으로 하고 양극과 동일한 DSA 또는 Ti 등의 코팅되지 않은 금속을 재료로 한 음극이 사용된다. 정류기를 통하여 양극과 음극에 +, - 전류가 공급되고 여러 가지 전기분해 반응에 의하여 분기공급라인을 통해 공급되는 폐수 내의 유기물질 및 질소 성분이 제거 된다. 유기물과 질소 제거시 초과 공급된 전류는 폐수 내에 NaOCl 등의 여러 가지 산화제를 발생 시키게 되고 다음 공정에서 산화제로 사용하게 된다. The electrolysis tank is a DSA electrode coated with noble metals such as Ru, Ir, Pt, etc. (manufactured according to the applicant's pre-registered patent 10-0407710) as an anode, and the same uncoated metal such as DSA or Ti as the anode is used. One cathode is used. + And-currents are supplied to the anode and cathode through the rectifier, and organic matter and nitrogen components in the wastewater supplied through the branch feed line are removed by various electrolysis reactions. When the excess of organics and nitrogen is removed, the excess current generates various oxidants such as NaOCl in the waste water and is used as oxidant in the next process.
상기와 같이 구성된 장치 구성에 의한 본 발명의 전해처리방법을 설명하면 다음과 같다.Referring to the electrolytic treatment method of the present invention by the device configuration configured as described above are as follows.
본 발명의 기본 수처리방법은 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 포함한 원폐수를 분기시켜 일부를 전기분해조에서 유기물질 및 질소를 제거함과 동시에 산화제인 차아염소산나륨을 발생시키고, 이를 처리수조에서 원폐수와 혼합하여 원폐수 내 유기물질 및 질소를 제거시키고, 전기분해조에 사용되는 NaCl은 처리수조를 지난 혼합폐수를 NaCl회수설비에서 회수하여 재사용하는 염소순환식으로 전해 처리하는 방법이다.In the basic water treatment method of the present invention, by branching the raw wastewater containing organic substances and nitrogen components, some of the organic substances and nitrogen are removed from the electrolysis tank and the generation of sodium hypochlorite, which is an oxidant, is mixed with the raw wastewater in the treatment tank. To remove organic substances and nitrogen in the raw waste water, and NaCl used in the electrolysis tank is a chlorine circulation electrolytic treatment in which the mixed wastewater passed through the treatment tank is recovered from the NaCl recovery facility and reused.
구체적으로 염소순환식으로 전해 처리하는 방법은 아래와 같이,Specifically, the electrolytic treatment by chlorine circulation is as follows,
유기물질 및 질소 성분을 포함한 원폐수를 주공급라인과 분기공급라인으로 분기 공급하는 단계와;Quarterly supplying raw wastewater including organic substances and nitrogen components to the main supply line and the branch supply line;
주공급라인을 통해 유입된 원폐수와 분기공급라인을 거친 후 전기분해 처리되어 차아염소산나트륨을 함유한 폐수와 혼합된 혼합폐수로부터 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하는 단계와;Removing organic substances and nitrogen components from the mixed wastewater mixed with the raw wastewater introduced through the main supply line and the branched supply line and then electrolyzed to treat the wastewater containing sodium hypochlorite;
유기물질 및 질소 성분이 제거된 혼합폐수의 pH를 조정하는 중화단계와;A neutralization step of adjusting the pH of the mixed wastewater from which organic substances and nitrogen components are removed;
중화단계를 지난 혼합폐수 내 잔류 산화제를 제거하는 약품 처리 단계와; A chemical treatment step of removing residual oxidant in the mixed wastewater after the neutralization step;
약품 처리단계를 거친 혼합폐수로부터 NaCl을 막접촉에 의해 회수시켜 분기공급라인을 통해 공급되는 원폐수쪽으로 NaCl을 공급하는 NaCl 회수 단계와;NaCl recovery step of recovering NaCl from the mixed wastewater subjected to the chemical treatment step by membrane contact and supplying NaCl to the raw wastewater supplied through the branch supply line;
NaCl 회수 단계에서 NaCl을 공급받은 분기공급라인의 원폐수 농도가 낮을 경우 NaCl을 투입하여 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수로 만드는 NaCl 투입단계와;NaCl input step of making a high concentration of NaCl containing waste water by adding NaCl when the raw waste water concentration of the branch supply line receiving NaCl in the NaCl recovery step is low;
고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수를 공급받아 전기분해하여 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하고, 동시에 생성된 차아염소산나트륨을 원폐수에 투입하는 전기분해단계;로 이루어진다. Electrolysis receives a high concentration of NaCl-containing wastewater to remove the organic matter and nitrogen components, and at the same time the electrolysis step of introducing the sodium hypochlorite to the original wastewater.
상기 분기 공급하는 단계에서 주공급라인은 원폐수를 분기공급라인을 거친 후 전기분해 처리되어 차아염소산나트륨을 함유한 폐수와 혼합하여 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하는 처리수조 쪽으로 공급하는 단계이고, 분기공급라인은 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수를 공급받아 전기분해하여 유기물질 및 질소 성분을 제거하고, 동시에 생성된 차아염소산나트륨을 생산하는 전기분해조 쪽으로 분기 공급하는 단계이다.In the branch supplying step, the main supply line is a step of supplying the raw wastewater to the treatment tank for removing organic matter and nitrogen by mixing with wastewater containing sodium hypochlorite after passing through the branch supply line. The supply line is a step of supplying a high concentration of NaCl-containing wastewater to electrolyze to remove organic substances and nitrogen components, and at the same time branch feed to the electrolysis tank to produce the produced sodium hypochlorite.
상기 유기물 및 질소제거단계에서 주공급라인은 처리수조와 연결되어 처리수조로 유입된 원폐수와 분기공급라인을 거친후 전기분해되어 오염물이 제거된 차아염소산나트륨을 함유한 폐수와 혼합하여 유기물 및 질소를 제거하는 단계이다.In the organic matter and nitrogen removal step, the main supply line is connected to the treatment tank and mixed with the wastewater containing sodium hypochlorite, which is electrolyzed by passing through the branched supply line with the raw wastewater introduced into the treatment tank, and the organic matter and nitrogen. Step to remove it.
상기 중화단계에서 pH 조정은 처리수조를 통해 유기물 및 질소가 제거된 폐수의 낮아진 pH를 pH조정조에서 pH를 조정하여 전기분해하기 좋은 pH로 만들기 위한 단계이다.The pH adjustment in the neutralization step is a step for making the pH lower in the organic matter and the waste water from which nitrogen is removed through the treatment tank to a pH suitable for electrolysis by adjusting the pH in the pH adjustment tank.
상기 약품 처리단계에서 약품은 처리수조에서 넘어온 잔류 산화제를 제거하는 단계이다.In the chemical treatment step, the chemical is a step of removing residual oxidant from the treatment tank.
상기 NaCl 회수단계는 약품 처리단계를 거친 혼합폐수를 NaCl회수설비에 의해 분기공급라인을 통해 공급된 원폐수와 막접촉시켜 혼합폐수로부터 NaCl을 회수하여 원폐수 쪽으로 공급하는 단계이다.The NaCl recovery step is a step of recovering NaCl from the mixed wastewater by supplying it to the raw wastewater by contacting the mixed wastewater subjected to the chemical treatment step with the raw wastewater supplied through the branch supply line by the NaCl recovery facility.
상기 NaCl 투입단계는 NaCl 회수단계를 지난 폐수의 NaCl 농도가 고농도(3%이상)가 아닐 경우 포화소금조의 NaCl을 투입하여 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수로 만드는 단계이다. 이와 같이 고농도상태를 만들어 다음 단계인 전기분해단계에서의 전기분해 효율을 높이게 된다.The NaCl input step is a step of making NaCl-containing wastewater of high concentration by adding NaCl in a saturated salt bath when the NaCl concentration of the wastewater after NaCl recovery is not high concentration (3% or more). By making a high concentration in this way, the electrolysis efficiency in the next step, the electrolysis step is increased.
상기 전기분해단계는 전기분해조에서 고농도의 NaCl 함유 폐수를 공급받아 전기분해하여 유기물 및 질소를 제거하고, 초과로 생성된 산화제인 차아염소산나트륨을 주공급라인의 처리수조로 투입하는 단계이다.In the electrolysis step, a high concentration of NaCl-containing wastewater is supplied from an electrolysis tank to electrolyze to remove organic matter and nitrogen, and sodium hypochlorite, which is an excess of an oxidant, is added to a treatment tank of a main supply line.
상기와 같은 본 발명 구성에 따라 원폐수 중 유기물 및 질소를 제거하는 메커니즘을 보다 구체적인 살펴보면 다음과 같다.Looking at the mechanism for removing the organic matter and nitrogen in the raw waste water according to the configuration of the present invention as described above in more detail.
전기분해에 의한 처리방법은 백금족의 금속을 티타늄 모재에 코팅 한 불용성 전극을 양극으로 하고 양극과 동일한 전극이나 코팅하지 않은 티타늄, 니켈 등의 금속판을 음극으로 하는 것을 한 유니트(unit)로 하여 양극, 음극에 전기를 공급하여 전기적인 방법에 의해 폐수 내 오염물질을 분해하는 기술이다.The electrolytic treatment is performed by using an insoluble electrode coated with a platinum group metal on a titanium base material as a positive electrode, and using the same electrode as an anode or an uncoated metal plate such as titanium or nickel as a negative electrode. It is a technology that decomposes pollutants in waste water by electric method by supplying electricity to cathode.
전기분해시 물 속에 Cl- 이온이 존재시에 아래와 같은 반응이 일어난다.In the presence of Cl - ions in water during electrolysis, the following reaction occurs.
양극 2Cl → Cl2 + 2e- Anode 2Cl → Cl 2 + 2e -
음극 2H2O + 2e- → 2OH- + H2 Anode 2H 2 O + 2e - → 2OH - + H 2
Cl2 + H2O → HOCl + H+ +Cl- Cl 2 + H 2 O → HOCl + H + + Cl -
HOCl → OCl- + H+ HOCl → OCl - + H +
물속에 전도도 및 처리율을 높이기 위해 NaCl을 투입할 경우 아래와 같은 반응으로 차아염소산 나트륨이 생성된다.In case NaCl is added to increase conductivity and throughput in water, sodium hypochlorite is produced by the following reaction.
NaCl + H2O + 2e- → NaOCl + H2 NaCl + H 2 O + 2e - → NaOCl + H 2
NaOCl → Na+ + OCl- NaOCl → Na + + OCl -
OCl- + H2O ↔ HOCl + OH- OCl - + H 2 O ↔ HOCl + OH -
물속의 유기물의 경우 전기분해시 양극에서 생성된 활성물질에 의해 산화되어 이산화탄소로 산화-연소되어 분해되거나, 위 식의 음극반응에 의해 생성된 차염 소산나트륨 등의 산화제에 의해 분해된다. In the case of organic matter in water, it is oxidized by the active material produced at the anode during electrolysis, oxidized and burned by carbon dioxide, or decomposed by an oxidizing agent such as sodium carbonate, which is produced by the above cathodic reaction.
R(유기물) + reacting agent → xCO2 + yH2O + zH2 R (organic) + reacting agent → xCO 2 + yH 2 O + zH 2
암모니아성 질소성분은 물속의 염소와 반응하여 염소 파괴법(Break point chlorination)과 같은 반응으로 처리된다. Ammoniacal nitrogen reacts with chlorine in water and is treated by reactions such as break point chlorination.
2NH+ + 3HOCl → N2 + 3H2O + 5H+ + 3Cl- 2NH + + 3HOCl → N 2 + 3H 2 O + 5H + + 3Cl -
2NH3 + Cl- → N2 + 6HCl + 6e- 2NH 3 + Cl - → N 2 + 6HCl + 6e -
질산성 질소나 아질산성 질소는 전기분해 장치 내 음극(-)에서 다음과 같은 반응에 따라 암모니아성으로 환원되거나 질소가스로 환원된다. Nitrate or nitrite nitrogen is reduced to ammonia or to nitrogen gas by the following reaction in the negative electrode (-) in the electrolysis device.
NO3 - + 6H2O + 8e- ⇒ NH3 + 9OH- NO 3 - + 6H 2 O + 8e - ⇒ NH 3 + 9OH -
NO3 - + 4H+ + 8e- ⇒ NH4+ + 3H2O NO 3 - + 4H + + 8e - ⇒ NH4 + + 3H 2 O
2NO3 - + 6H2O + 10e- ⇒ N2(g) + 12OH- 2NO 3 - + 6H 2 O + 10e - ⇒ N 2 (g) + 12OH -
NO2 - + 5H2O + 6e- ⇒ NH3 + 7OH- NO 2 - + 5H 2 O + 6e - ⇒ NH 3 + 7OH -
2NO2 - + 4H2O + 6e- ⇒ N2(g) + 8OH- 2NO 2 - + 4H 2 O + 6e - ⇒ N 2 (g) + 8OH -
환원된 NH3 는 양극에서 질소가스로 산화 되거나 물속에 생성된 산화제에 의해 산화되어 질소가스로 대기중으로 배출된다. The reduced NH 3 is oxidized to nitrogen gas at the anode or oxidized by oxidant generated in water and discharged to the atmosphere as nitrogen gas.
질소계 성분 중 에탄올아민에 대한 전기분해 반응은 다음과 같다. The electrolysis reaction for ethanolamine in the nitrogen-based component is as follows.
NH2CH2CH2OH + H2O ⇒ NH3 + 2HCHO + 2H+ + 2e- NH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH + H 2 O ⇒ NH 3 + 2HCHO + 2H + + 2e -
HCHO + 4OH- ⇒ CO2 + 3H2O + 4e- HCHO + 4OH - ⇒ CO 2 + 3H 2 O + 4e -
HCHO + 2OCl- ⇒ CO2 + 2Cl- + H2O HCHO + 2OCl - ⇒ CO 2 + 2Cl - + H 2 O
상기와 같은 구성 및 처리방법을 가진 본 발명에 따라 폐수를 처리하게 되면 방류되는 유기물 및 질소가 제거된 폐수 내 전해질 즉, NaCl의 농도를 NaCl 회수설비를 통해 다시 회수함으로써 전기분해에 사용되는 전해질 사용량을 줄이게 되어, 원폐수를 직접 전기분해시켜 산화제를 발생시키는 방법 사용시 소요되는 설계 금액 중 가장 큰 부분을 차지하는 전기분해조의 용량을 줄여 전체적인 설계비용을 줄이게 된다.When the wastewater is treated according to the present invention having the above-described configuration and treatment method, the amount of electrolyte used for electrolysis is recovered by recovering the concentration of electrolytes, ie, NaCl, discharged from the organic matter and nitrogen removed from the wastewater through the NaCl recovery facility. This reduces the overall design cost by reducing the capacity of the electrolysis tank, which accounts for the largest portion of the design cost when using the method of directly electrolyzing raw wastewater to generate oxidant.
본 발명은 상술한 특정의 바람직한 실시 예에 한정되지 아니하며, 청구범위에서 청구하는 본 발명의 요지를 벗어남이 없이 당해 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자라면 누구든지 다양한 변형실시가 가능한 것은 물론이고, 그 와 같은 변경은 청구범위 기재의 범위 내에 있게 된다. The present invention is not limited to the above-described specific preferred embodiments, and various modifications can be made by any person having ordinary skill in the art without departing from the gist of the present invention claimed in the claims. Of course, such changes will fall within the scope of the claims.
도 1은 본 발명의 한 실시예에 따른 염소 순환 처리 공정을 보인 전기분해 수처리 공정도이고,1 is an electrolytic water treatment process diagram showing a chlorine circulation treatment process according to an embodiment of the present invention,
도 2는 본 발명의 한 실시예에 따른 NaCl 회수설비 내 NaCl 회수 흐름도이고,2 is a flowchart of NaCl recovery in a NaCl recovery system according to an embodiment of the present invention,
도 3과 4는 기존 특허 내용 공정을 보인 개략도이다.3 and 4 is a schematic view showing a conventional patent content process.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020080100260A KR101046942B1 (en) | 2008-10-13 | 2008-10-13 | Water treatment method using electrolysis |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020080100260A KR101046942B1 (en) | 2008-10-13 | 2008-10-13 | Water treatment method using electrolysis |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20100041201A true KR20100041201A (en) | 2010-04-22 |
| KR101046942B1 KR101046942B1 (en) | 2011-07-06 |
Family
ID=42216981
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020080100260A KR101046942B1 (en) | 2008-10-13 | 2008-10-13 | Water treatment method using electrolysis |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101046942B1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101581810B1 (en) * | 2015-07-23 | 2015-12-31 | 코오롱이엔지니어링 주식회사 | Recycling system for oxidizer |
| KR20170122269A (en) * | 2015-04-17 | 2017-11-03 | 미츠비시 쥬코 칸쿄 카가쿠 엔지니어링 가부시키가이샤 | Hypochlorous acid supply device and boiler waste-water treatment method |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104230061B (en) * | 2014-09-09 | 2016-06-29 | 湖南康盟环保科技有限公司 | Ammonia nitrogen waste water treatment by catalytic oxidation |
| KR20230116611A (en) | 2022-01-28 | 2023-08-04 | (주)지티앤 | Electrolysis equipment for treatment of sewage |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008080236A (en) | 2006-09-27 | 2008-04-10 | Kobelco Eco-Solutions Co Ltd | Treatment method and treatment apparatus for ammoniacal nitrogen-containing wastewater |
| JP5188717B2 (en) | 2007-01-26 | 2013-04-24 | 壽化工機株式会社 | Electrolytic hypochlorite water production equipment |
| KR100874269B1 (en) * | 2007-04-19 | 2008-12-16 | (주) 테크윈 | High efficiency seawater electrolysis apparatus and electrolysis method including pretreatment process |
| KR20080050380A (en) * | 2008-05-16 | 2008-06-05 | 주식회사 태현수기 | Electrolitic sodium hypochlorite generating system |
-
2008
- 2008-10-13 KR KR1020080100260A patent/KR101046942B1/en active IP Right Grant
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20170122269A (en) * | 2015-04-17 | 2017-11-03 | 미츠비시 쥬코 칸쿄 카가쿠 엔지니어링 가부시키가이샤 | Hypochlorous acid supply device and boiler waste-water treatment method |
| KR101581810B1 (en) * | 2015-07-23 | 2015-12-31 | 코오롱이엔지니어링 주식회사 | Recycling system for oxidizer |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101046942B1 (en) | 2011-07-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7175765B2 (en) | Method for treating for-treatment water containing organic matter and nitrogen compound | |
| KR101026641B1 (en) | Non-degradable Waste Water Treatment Apparatus using Electrolysis and Photo-fenton Oxidation Process | |
| US7300592B2 (en) | Water treatment device | |
| WO2006112521A1 (en) | Method of electrolyzing wastewater containing ammonia nitrogen and apparatus therefor | |
| US20030052062A1 (en) | Nitrogen treating method and nitrogen treating system | |
| US7300591B2 (en) | Wastewater treating method and wastewater treating apparatus | |
| KR101046942B1 (en) | Water treatment method using electrolysis | |
| KR101866425B1 (en) | Apparatus for treatment of high concentration organic wastewater | |
| JP2008080236A (en) | Treatment method and treatment apparatus for ammoniacal nitrogen-containing wastewater | |
| KR20170099616A (en) | Electrodialysis coupled with electrochemical nitrogen removal Process for contaminated groundwater treatment, and Apparatus therefor | |
| KR100492471B1 (en) | A continuous electrical analytic oxidation reactor of waste water with high concentrated nitrogen compound | |
| JP2005218983A (en) | Wastewater treatment method and apparatus using electrolytic oxidation | |
| JPH07100466A (en) | Method for treating waste water | |
| KR100626842B1 (en) | Method of waste water treatment containing high concentration nitrogen combined electrolysis and biological process | |
| US20030150810A1 (en) | Water purification system and water purification method | |
| JPH08155463A (en) | Method and apparatus for decomposing ammoniacal nitrogen nitric-nitrogen and/or nitrous-nitrogen | |
| KR20060046358A (en) | The method for electrochemical wastewater treatment using boron doped diamond electrodes | |
| KR20170099615A (en) | Electrochemical Process for high concentration of nitrate containing wastewater treatment, and Apparatus therefor | |
| JP3788688B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for electrolytic treatment of oxidized nitrogen-containing water | |
| JP2006272060A (en) | Continuous treatment method and device for waste water containing nitrate nitrogen | |
| JP2009028629A (en) | Treatment method of waste water containing nitrate nitrogen and calcium ion | |
| KR102613581B1 (en) | An apparatus and method for treating waste water containing non-de gradable organic material | |
| CN111087049A (en) | Method for treating organic nitrogen wastewater | |
| KR200333663Y1 (en) | A continuous electrical analytic oxidation reactor of waste water with high concentrated nitrogen compound | |
| KR20040086096A (en) | Electrochemical process for wastewater containing nitric acid |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20140625 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20150622 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20160620 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20170609 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20180627 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20190603 Year of fee payment: 9 |