JP7166811B2 - image forming device - Google Patents
image forming device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7166811B2 JP7166811B2 JP2018126700A JP2018126700A JP7166811B2 JP 7166811 B2 JP7166811 B2 JP 7166811B2 JP 2018126700 A JP2018126700 A JP 2018126700A JP 2018126700 A JP2018126700 A JP 2018126700A JP 7166811 B2 JP7166811 B2 JP 7166811B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cartridge
- image
- intermediate transfer
- toner
- developing means
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、レーザープリンタ、複写機等の電子写真方式を用いる画像形成装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an electrophotographic image forming apparatus such as a laser printer and a copying machine.
電子写真方式を用いた画像形成装置は、一般的に、像担持体としてのドラム状の感光体(以下、感光ドラムと称する)や、画像に対応したトナー像を感光ドラムに形成するためのプロセス手段を有している。また、従来からこのような画像形成装置においては、感光ドラム及びトナー像を形成するためのプロセス手段を一体的にカートリッジ化して、画像形成装置に対して着脱可能とするプロセスカートリッジ方式が採用されている。 An electrophotographic image forming apparatus generally includes a drum-shaped photoreceptor (hereinafter referred to as a photoreceptor drum) as an image carrier and a process for forming a toner image corresponding to an image on the photoreceptor drum. have the means. Conventionally, such an image forming apparatus employs a process cartridge system in which a photosensitive drum and a process means for forming a toner image are integrated into a cartridge and detachable from the image forming apparatus. there is
通常、プロセスカートリッジ方式を採用した画像形成装置においては、新品のプロセスカートリッジ(以下、単にカートリッジと称する)を画像形成装置に装着した場合に、画像形成を行うための準備動作が実行される。この準備動作としては、例えば、トナーの漏れ防止を目的として現像手段に設けられる封止部材(シール部材)を除去する動作などがあげられる。特許文献1には、新品のカートリッジが画像形成装置本体に挿入された際に、該当カートリッジを駆動する駆動源からの駆動力を受けて回転する回転部材によって、現像手段に設けられたシール部材を除去する構成が開示されている。
Generally, in an image forming apparatus adopting the process cartridge system, a preparatory operation for forming an image is executed when a new process cartridge (hereinafter simply referred to as cartridge) is installed in the image forming apparatus. The preparatory operation includes, for example, an operation of removing a sealing member (sealing member) provided in the developing means for the purpose of preventing toner leakage. In
また、近年、各色の感光ドラムから中間転写体に順次トナー像を転写し、さらに中間転写体から紙やOHPシート等転写材に一括してトナー像を転写する中間転写方式を用いたカラーの画像形成装置においても、プロセスカートリッジ方式が採用されている。特許文献2には、カートリッジの一部の部材を駆動させる駆動源と、中間転写体を駆動させる駆動源とを共通化させた中間転写方式の画像形成装置の構成が開示されている。 In recent years, color images have been produced using an intermediate transfer system in which toner images are sequentially transferred from photosensitive drums of each color to an intermediate transfer body, and then the toner images are collectively transferred from the intermediate transfer body to a transfer material such as paper or an OHP sheet. The forming apparatus also adopts the process cartridge system. Japanese Unexamined Patent Application Publication No. 2002-100000 discloses a configuration of an intermediate transfer type image forming apparatus in which a drive source for driving some members of a cartridge and a drive source for driving an intermediate transfer body are shared.
ここで、中間転写方式の画像形成装置では、中間転写体から転写材にトナー像を二次転写した後に中間転写体に残留したトナー(以下、転写残トナーと称する)を除去する必要がある。転写残トナーを除去するクリーニング方式としては、中間転写ベルトに当接する当接部材としてのクリーニングブレードによって転写残トナーを掻き取ってクリーニング容器に回収する、所謂ブレードクリーニング方式が広く用いられている。 Here, in the intermediate transfer type image forming apparatus, it is necessary to remove toner remaining on the intermediate transfer body after the toner image is secondarily transferred from the intermediate transfer body to the transfer material (hereinafter referred to as transfer residual toner). As a cleaning method for removing the transfer residual toner, a so-called blade cleaning method is widely used in which the transfer residual toner is scraped off by a cleaning blade as a contact member that contacts the intermediate transfer belt and collected in a cleaning container.
特許文献2の構成においては、中間転写体と駆動源が共通であるカートリッジを交換した場合に、カートリッジの準備動作の実行に伴って中間転写体も回転駆動されてしまう。この時、準備動作が完了するまでは、中間転写体とクリーニングブレードとが当接する位置にトナーなどの潤滑剤が供給されない状態で中間転写体が回転し続ける。すると、中間転写体とクリーニングブレードとが当接する位置において大きな摩擦力が生じ、その結果、クリーニングブレードの先端が変形してしまうおそれがある。 In the configuration disclosed in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2002-200000, when the cartridge sharing the drive source with the intermediate transfer member is replaced, the intermediate transfer member is also rotationally driven as the preparatory operation of the cartridge is performed. At this time, until the preparatory operation is completed, the intermediate transfer body continues to rotate in a state in which lubricant such as toner is not supplied to the position where the intermediate transfer body and the cleaning blade abut. Then, a large frictional force is generated at the position where the intermediate transfer member and the cleaning blade contact each other, and as a result, the tip of the cleaning blade may be deformed.
そこで、本発明は、カートリッジの一部の部材を駆動させる駆動源と、中間転写体を駆動させる駆動源とを共通化させた画像形成装置において、中間転写体に当接する当接部材の先端の変形を抑制することを目的とする。 Accordingly, the present invention provides an image forming apparatus in which a drive source for driving some members of a cartridge and a drive source for driving an intermediate transfer body are shared, and the tip of the contact member that contacts the intermediate transfer body is The purpose is to suppress deformation.
本発明は、装置本体と、第1の像担持体にトナー像を形成するための第1の現像手段を有する第1のカートリッジと、前記第1の像担持体とは異なる色のトナー像を担持する第2の像担持体にトナー像を形成するための第2の現像手段を有する第2のカートリッジと、前記第1の像担持体及び前記第2の像担持体と当接可能な中間転写体と、前記中間転写体に当接して当接部を形成し、前記中間転写体に残留したトナーを回収する当接部材と、
前記中間転写体を回転駆動させる第1駆動源と、前記第1駆動源とは異なる第2駆動源であって、前記第2のカートリッジに駆動力を伝達する前記第2駆動源と、前記第1駆動源によって前記中間転写体を回転させ、前記第2駆動源から前記第2のカートリッジに駆動力を伝達することにより、前記第2の像担持体を介して前記第2の現像手段から前記当接部にトナーを供給するための供給動作を実行可能に制御する制御部と、を有し、前記第1のカートリッジが前記装置本体に対して着脱可能な画像形成装置において、前記制御部は、新品の前記第1のカートリッジを前記装置本体に挿入した場合に、前記第2の像担持体を前記中間転写体に当接させた状態で前記供給動作を実行するように制御することを特徴とする。
The present invention comprises an apparatus main body, a first cartridge having a first developing means for forming a toner image on a first image carrier, and a toner image of a color different from that of the first image carrier. a second cartridge having a second developing means for forming a toner image on a second image carrier; and an intermediate contactable with the first image carrier and the second image carrier. a transfer member; a contact member that contacts the intermediate transfer member to form a contact portion and collects toner remaining on the intermediate transfer member;
a first driving source for rotationally driving the intermediate transfer member; a second driving source different from the first driving source, the second driving source for transmitting a driving force to the second cartridge; 1 driving source rotates the intermediate transfer member, and the second driving source transmits the driving force to the second cartridge, thereby transferring the image from the second developing means through the second image bearing member to the and a controller for controlling a supply operation for supplying toner to a contact portion, wherein the first cartridge is attachable to and detachable from the apparatus main body, wherein the controller comprises: wherein, when a new first cartridge is inserted into the apparatus main body, the supply operation is performed while the second image bearing member is in contact with the intermediate transfer member. and
本発明によれば、カートリッジの一部の部材を駆動させる駆動源と、中間転写体を駆動させる駆動源とを共通化させた画像形成装置において、中間転写体に当接する当接部材の先端の変形を抑制することができる。 According to the present invention, in an image forming apparatus in which a drive source for driving a part of the members of the cartridge and a drive source for driving the intermediate transfer body are shared, the leading edge of the contact member that contacts the intermediate transfer body is Deformation can be suppressed.
以下、図面を参照して、本発明の好適な実施例を例示的に詳しく説明する。ただし、以下の実施例に記載されている構成部品の寸法、材質、形状、それらの相対配置などは、本発明が適用される装置の構成や各種条件により適宜変更されるべきものである。従って、特に特定的な記載がない限りは、本発明の範囲を限定する趣旨のものではない。 Preferred embodiments of the present invention will be exemplarily described in detail below with reference to the drawings. However, the dimensions, materials, shapes, and relative positions of components described in the following examples should be appropriately changed according to the configuration of the apparatus to which the present invention is applied and various conditions. Accordingly, it is not intended to limit the scope of the invention unless specifically stated.
(実施例1)
[画像形成装置の構成]
図1は、本実施例に係る画像形成装置100の概略構成を示す模式的な断面図である。本実施例の画像形成装置100は、電子写真方式を用いてフルカラー画像の形成が可能な中間転写方式を採用した、タンデム型のレーザービームプリンターである。
(Example 1)
[Configuration of Image Forming Apparatus]
FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view showing a schematic configuration of an
画像形成装置100は、一列に配置された4つの画像形成部a、b、c、dを有し、各画像形成部a~dは、それぞれイエロー(Y)マゼンタ(M)、シアン(C)、ブラック(Bk)の各色の画像を形成する。
The
画像形成部aは、像担持体としてドラム型(円筒形)の感光体(以下、感光ドラム1aと称する)、帯電手段としての帯電ローラ2a、感光ドラム1aに残留したトナーを回収するドラムクリーニング手段3a、及び現像手段4a、を有する。本実施例の画像形成装置100において、これらの1a~4aの各手段は一体型のプロセスカートリッジ9a(以下、カートリッジ9aと称する)を構成し、画像形成装置100の本体に対して着脱可能である。
The image forming portion a includes a drum-shaped (cylindrical) photosensitive member (hereinafter referred to as a
現像手段4aは、現像剤担持体としての現像ローラ41aと、現像剤としての非磁性一成分トナーを収容する現像容器42aと、現像ローラ41aにトナーを供給する供給ローラ43aと、現像剤規制手段としての現像ブレード44aと、を有する。図1に示す露光手段12aは、レーザー光を多面鏡によって走査させるスキャナユニットで構成され、画像信号に基づいて変調された走査ビームを感光ドラム1aに照射することで、感光ドラム1aに静電潜像を形成する。
The developing
なお、以下の説明において、各画像形成部a~dの構成及び動作は、使用するトナーの色が異なることを除けば、実質的に同じである。したがって、以下、特に区別を要しない場合は、いずれかの色用の要素であることを示す符号の末尾a、b、c、dは省略して、当該要素について統括的に説明する。 In the following description, the configurations and operations of the image forming units a to d are substantially the same except that the colors of toners used are different. Therefore, hereinafter, the elements will be generally described by omitting the suffixes a, b, c, and d indicating that they are elements for one of the colors unless they are particularly distinguished.
各画像形成部a~dと対向する位置には、各感光ドラム1a、1b、1c、1dの全てと当接可能であって、移動可能な中間転写体としての無端状ベルトで構成された中間転写ベルト13が配置されている。中間転写ベルト13は、二次転写対向ローラ24(以下、単に対向ローラ24と称する)、駆動ローラ14、張架ローラ15の3本のローラにより張架されている。そして、駆動ローラ14が回転駆動されることによって、中間転写ベルト13は、図中矢印R2方向で示されるベルト搬送方向に移動(回転)する。なお、中間転写ベルト13の幅方向とは、図示矢印R2方向で示される中間転写ベルト13の移動方向と直交する方向であり、図1における奥行き方向のことである。
At a position facing the image forming units a to d, an intermediate belt composed of an endless belt serving as a movable intermediate transfer member that can contact all of the
中間転写ベルト13を介して、感光ドラム1と対向する位置には、一次転写部材としての一次転写ローラ10が配置されている。一次転写ローラ10は、中間転写ベルト13を介して感光ドラム1に対して所定の圧力で付勢されており、中間転写ベルト13と感光ドラム1とが接触する一次転写部(一次転写ニップ)N1を形成している。感光ドラム1に対する一次転写ローラ10の付勢状態を解除することにより、中間転写ベルト13と感光ドラム1とを離間させて一次転写部N1を解消することが可能である。本実施例の画像形成装置100においては、画像形成を行わない非画像形成時に一次転写ローラ10の付勢状態を解除することによって、中間転写ベルト13と感光ドラム1とを離間させている。
A
また、本実施例の画像形成装置100は、画像形成部a~dの全てを用いて画像形成を行うフルカラーモードと、黒色(Bk)のトナー像を形成することが可能な画像形成部のみを用いて画像形成を行うモノカラーモードと、を選択して実行することが可能である。フルカラーモードを実行する場合、全ての一次転写ローラ10を感光ドラム1に向けて付勢することによって、感光ドラム1a、1b、1c、1dの全てを中間転写ベルト13に当接させる。一方で、モノカラーモードを実行する場合は、一次転写ローラ10a、10b、10cの付勢力を解除し、一次転写ローラ10dのみを感光ドラム1dに向けて付勢する。即ち、モノカラーモードを実行する場合においては、黒色のトナー像を担持する感光ドラム1dのみを中間転写ベルト13に当接させて画像形成を行う。
Further, the
中間転写ベルト13の外周面側において、対向ローラ24と対向する位置には、二次転写部材としての二次転写ローラ25が配置されている。二次転写ローラ25は、中間転写ベルト13を介して対向ローラ24に対して所定の圧力で付勢されており、中間転写ベルト13と二次転写ローラ25とが接触する二次転写部(二次転写ニップ)N2を形成している。
A
なお、本実施例では、一次転写ローラ10a~10dは、外径5mmのニッケルメッキ鋼棒の芯金に、外径14mmとなるよう発泡性弾性体を被覆して構成されており、106Ωの抵抗を有するものを用いた。本実施例の画像形成装置100の構成において良好な画像形成を行うためには、一次転写ローラ10の抵抗は、103~107Ωの範囲に設定されていることが望ましい。
In this embodiment, the
また、本実施例では、二次転写ローラ25は、外径8mmのニッケルメッキ鋼棒の芯金に、外径16mmとなるよう発泡性弾性体を被覆して構成されており、108Ωの抵抗を有するものを用いた。本実施例の画像形成装置100の構成において良好な画像形成を行うためには、二次転写ローラ25の抵抗は、107~109Ωの範囲に設定されていることが好ましい。
Further, in this embodiment, the
駆動ローラ14は、アルミニウム芯金にカーボンを導電剤として分散した抵抗105Ω、肉厚0.085mmのシリコーンゴムを被覆した外径26.3mmのものを用いた。張架ローラ15は、外径24mmのアルミニウムの金属棒を用いており、片側の端部を49Nずつ付勢されることで、総圧98Nのテンションを中間転写ベルト13に付与している。二次転写ローラ25の対向に位置する対向ローラ24は、アルミニウム芯金にカーボンを導電剤として分散した抵抗105Ω、肉厚1.0mmのEPDMゴムを被覆した外径18mmのものを用いた。
The driving
中間転写ベルト13は、厚さ73μm、体積抵抗率1010Ω・cmのポリイミドを基材として構成されたものを用いた。本実施例における中間転写ベルト13の体積抵抗率は、Hiresta・UP MCP-HT450(三菱化学社製)を用いて、室温25℃、湿度50%の環境下において、印加電圧50Vで測定した場合に、1010Ω・cmであった。なお、本実施例の画像形成装置100の構成において良好な画像形成を行うためには、中間転写ベルト13の体積抵抗率は、109~1012Ω・cmの範囲に設定されていることが好ましい。
The
[画像形成動作]
図1に示される制御基板101は、画像形成装置100の制御を行うための電気回路が搭載された制御基板であり、制御手段としてのCPU102が搭載されている。制御基板101は、ホスト機器(不図示)などから送信された信号を受信することで、予めプログラムされた動作を行うことが可能であり、CPU102が各種手段を制御することで画像形成動作が実行される。本実施例におけるCPU102は、転写材Pの搬送に関する駆動源や中間転写ベルト13、及びカートリッジ9a~9dの駆動源等の制御、画像形成に関する制御、更には故障検知に関する制御など、画像形成装置の動作を一括して制御している。
[Image forming operation]
A
画像形成動作が開始されると、各感光ドラム1、中間転写ベルト13は、所定のプロセススピードで、それぞれ図中矢印R1、R2方向に回転を始める。回転する感光ドラム1の表面は、帯電ローラ2により所定の極性(本実施例では負極性)に略一様に帯電させられる。このとき帯電ローラ2には、不図示の帯電電源から所定の帯電電圧が印加される。その後、感光ドラム1は、各画像形成部に対応した画像情報に応じて露光手段12によって露光されることにより、感光ドラム1の表面に、画像情報に従った静電潜像が形成される。
When the image forming operation is started, the
現像ローラ41は、供給ローラ43によって供給されたトナーであって現像剤塗布ブレード42によってトナーの正規の帯電極性(本実施例においては負極性)に帯電されたトナーを担持し、不図示の現像電源から所定の現像電圧を印加される。これにより、感光ドラム1に形成された潜像が、感光ドラム1と現像ローラ41との対向部(現像部)において負極性のトナーによって可視化され、感光ドラム1にトナー像が形成される。
The developing
次に、感光ドラム1に形成されたトナー像は、一次転写部N1において、一次転写ローラ10の作用により、回転駆動されている中間転写ベルト13に転写(一次転写)される。このとき、一次転写ローラ10には、一次転写電源22から、トナーの正規の帯電極性とは逆極性(本実施例では正極性)の一次転写電圧が印加される。例えば、フルカラー画像の形成時には、各画像形成部Sにおいて各感光ドラム1に静電潜像が形成され、これが現像されて各色のトナー像となる。そして、各画像形成部Sの各感光ドラム1に形成された各色のトナー像が、各一次転写部N1a、N1b、N1c、N1dにおいて中間転写ベルト13に順次に重ね合わせるように転写され、中間転写ベルト13に4色のトナー像が形成される。
Next, the toner image formed on the
また、収容部としての給紙カセット50に積載されている記録用紙などの転写材Pは、不図示の供給ローラ、及び、不図示の搬送ローラによりレジストローラ51まで搬送される。転写材Pは、レジストローラ51によって、中間転写ベルト13上のトナー像に同期し、中間転写ベルト13と二次転写ローラ25とで形成される二次転写部N2へ搬送される。そして、中間転写ベルト13上に担持された4色の多重トナー像が、二次転写部N2において、二次転写ローラ25の作用により、転写材Pに一括して転写される。このとき、二次転写ローラ25には、二次転写電源26からトナーの正規の帯電極性とは逆極性(本実施例では正極性)の二次転写電圧が印加される。
A transfer material P such as recording paper stacked in a
その後、トナー像が転写された転写材Pは、定着手段19に搬送される。転写材Pに二次転写されたトナー像は、定着手段19の定着ローラと加圧ローラとで挟持されて搬送される過程で加圧及び加熱されることで転写材Pに定着され、その後、排紙ローラ対52によって画像形成装置100の装置本体の外部に排出される。
Thereafter, the transfer material P onto which the toner image has been transferred is conveyed to fixing
なお、一次転写後に感光ドラム1に残留したトナーは、ドラムクリーニング手段3に設けられ、感光ドラム1に当接するクリーニングブレード31によって感光ドラム1の表面から除去される。また、二次転写部N2を通過した後に中間転写ベルト13に残った転写残トナーは、中間転写ベルト13を介して張架ローラ15に対向して設けられたベルトクリーニング手段20によって、中間転写ベルト13の表面から除去される。後に詳細に説明するが、中間転写ベルト13の移動方向に関して二次転写部N2よりも下流側に配置されるベルトクリーニング手段20は、張架ローラ15に対向する位置で中間転写ベルト13の外周面に当接するクリーニングブレード29(当接部材)を有する。
Toner remaining on the
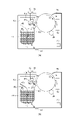
[ベルトクリーニング手段20]
図2(a)は、後述するクリーニングブレード29が弾性変形していない場合のクリーニングブレード29の取り付け位置を説明した仮想断面図であり、図2(b)は、ベルトクリーニング手段20の構成を説明する概略断面図である。
[Belt cleaning means 20]
FIG. 2(a) is a virtual cross-sectional view for explaining the mounting position of the
ベルトクリーニング手段20は、クリーニング容器27と、クリーニング容器27内に設けられたクリーニング作用部28と、を有する。クリーニング容器27は、中間転写ベルト13等を有する中間転写ユニット(不図示)の枠体の一部として構成されている。クリーニング作用部28は、クリーニング部材(当接部材)としてのクリーニングブレード29と、クリーニングブレード29を支持する支持部材30と、を有する。クリーニングブレード29は、弾性材料であるウレタンゴム(ポリウレタン)から構成される弾性ブレードであり、亜鉛メッキ鋼板を材料とする板金で形成された支持部材30に接着された状態で支持されている。
The belt cleaning means 20 has a cleaning
クリーニングブレード29は、中間転写ベルト13の移動方向(以下、ベルト搬送方向と称する)と交差する中間転写ベルト13の幅方向(クリーニングブレード29の長手方向)に関して長い板状部材である。また、クリーニングブレード29は、短手方向に関して、自由端側の端部29aを中間転写ベルト13に対して当接されており、固定端側の端部29bを支持部材30に対して接着された状態で固定されている。このクリーニングブレード29の長手方向の長さは240mmであり、厚さは2.0mmであり、クリーニングブレード29の硬度はJIS K 6253規格で77°である。
The
クリーニング作用部28は、中間転写ベルト13の表面に対して揺動可能に構成されている。すなわち、支持部材30は、クリーニング容器27に固定された揺動軸32を介して、中間転写ベルト13の表面に対して揺動可能に支持されている。クリーニング容器27内に設けられた付勢手段として加圧バネ34によって支持部材30が加圧されることで、揺動軸32を中心としてクリーニング作用部28が可動し、クリーニングブレード29が中間転写ベルト13に付勢(押圧)される。
The cleaning
クリーニングブレード29に対向して、中間転写ベルト13の内周側には、張架ローラ15が配置されている。クリーニングブレード29は、張架ローラ15に対向する位置で、ベルト搬送方向に対してカウンター方向で中間転写ベルト13の表面に当接されている。すなわち、クリーニングブレード29は、その短手方向における自由端側の端部29aがベルト搬送方向に関する上流側を向くようにして、中間転写ベルト13の表面に当接されている。これにより、図2(b)に示すように、クリーニングブレード29と中間転写ベルト13との間にブレードニップ部33(当接部)が形成されている。クリーニングブレード29は、ブレードニップ部33において、移動する中間転写ベルト13の表面から転写残トナーを掻き取り、クリーニング容器27に回収する。
A
本実施例では、クリーニングブレード29の取り付け位置は、次のように設定されている。図2(a)に示すように、設定角θが22°、侵入量δが1.45mm、当接圧が5.5N/mmである。ここで、設定角θは、中間転写ベルト13とクリーニングブレード29(より詳細にはその自由端側の端面)との交点における張架ローラ15の接線と、クリーニングブレード29(より詳細にはその厚さ方向に略直交する一方の表面)とがなす角度である。また、侵入量δは、クリーニングブレード29が張架ローラ15に対して重なる厚さ方向の長さである。また、当接圧は、ブレードニップ部33におけるクリーニングブレード29からの押圧力(長手方向における線圧)で定義され、フィルム式加圧力測定システム(商品名:PINCH,ニッタ社製)を用いて測定される。このように設定することで、高温高湿環境(室温30℃、湿度80%)でのクリーニングブレード29の捲れやスリップ音を抑制でき、良好なクリーニング性能を得ることができる。また、このように設定することで、低温低湿環境(室温15℃、湿度10%)でのクリーニング不良を抑制して、良好なクリーニング性能を得ることができる。
In this embodiment, the mounting position of the
また、中間転写ベルト13及びクリーニングブレード29が新品時の場合、ブレードニップ部33にはトナーが存在しておらず摩擦抵抗が大きくなる傾向にある。この摩擦抵抗が大きくなると、カウンター方向で中間転写ベルト13に対して当接しているクリーニングブレード29が、ベルト搬送方向に沿って当接した状態になってしまう現象(捲れ)や、スリップ音などの異音が発生するおそれがある。捲れが発生した場合、クリーニングブレード29によって中間転写ベルト13に残留したトナーをせき止めることが困難になることで、クリーニング不良が発生してしまうおそれがある。
Further, when the
そこで、本実施例の画像形成装置100は、画像形成を行う前の新品のクリーニングブレード29の端部29aに初期潤滑剤としてフッ化黒鉛(セフボンCMA:セントラル硝子社製)を塗布する構成としている。即ち、中間転写ベルト13及びクリーニングブレード29が新品の時は、フッ化黒鉛が潤滑剤としての機能を果たし、画像形成が開始された後においては、各現像手段4から供給されたトナーが潤滑剤としての機能を果たす。これにより、ブレードニップ部33において摩擦抵抗が大きくなることを抑制し、クリーニングブレード29の捲れや異音の発生を抑制できる。
Therefore, the
なお、中間転写ベルト13の材料などに応じて適宜選定されるものであるが、クリーニングブレード29のゴム硬度は、JIS K 6253規格で70°以上、且つ80°以下の範囲が好ましい。ゴム硬度が上記範囲よりも低いと、使用によるクリーニングブレード29の端部29aの摩耗量が増加して、耐久性が低下することがあり、上記範囲よりも高いと弾性力が減少して、中間転写ベルト13との摩擦により欠けなどが発生することがある。
The rubber hardness of the
また、中間転写ベルト13の材料などに応じて適宜選定されるものであるが、クリーニングブレード29の当接圧は、4.0N/mm以上、7.0N/mm以下の範囲が好ましい。当接圧が上記範囲よりも小さいと、良好なクリーニング性能が得られないことがあり、上記範囲よりも大きいと中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動するための負荷が大きくなりすぎることがある。
The contact pressure of the
[画像形成装置の駆動構成]
図3は、本実施例における、各感光ドラム1及び中間転写ベルト13の駆動構成を説明する模式図である。図3に示すように、本実施例においては、第1駆動源としてのモータM1によって、カートリッジ9dに駆動力を伝達して感光ドラム1dを回転駆動させ、且つ、中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動させている。また、第2駆動源としてのモータM2によって、各カートリッジ9a~9cに駆動力を伝達して感光ドラム1a~1cを回転駆動させている。この構成により、感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とをそれぞれ別々のモータで駆動する構成に比べて、モータの個数を5個から2個に削減することが可能となる。
[Driving Configuration of Image Forming Apparatus]
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram for explaining the drive configuration of each
また、本実施例においては、感光ドラム1dの回転軸に固定された不図示のギアと、現像ローラ41dの回転軸に固定された不図示のギアと、を連結することにより、モータM1からの駆動力を現像手段4dに伝達する構成としている。即ち、感光ドラム1dが回転駆動されることで、現像手段4dにおいて、現像ローラ41d、供給ローラ43d、そして後に説明する撹拌部材11dがそれぞれ回転する。
Further, in this embodiment, by connecting a gear (not shown) fixed to the rotation shaft of the
[カートリッジ9]
次に、本実施例におけるカートリッジ9a~9dの構成について、カートリッジ9aを用いて説明する。図4(a)は、カートリッジ9dを長手方向(回転軸線方向)から見た概略断面図である。図4(b)は、カートリッジ9aの新品時における、長手方向(回転軸線方向)から見た概略断面図である。
[Cartridge 9]
Next, the configuration of the
図4(a)に示すように、現像手段4aは、現像ローラ41a、供給ローラ43a、現像ブレード44a、開口45a、トナーを収容する収容室46a、トナー収容室の上部に設けられ、現像ローラ41aと供給ローラ43aを格納する現像室47a、を有する。本実施例においては、トナーは、正規の極性として負極性に帯電し、粒径が7μmである非磁性球形トナーを用いた。またトナーの表面には、トナー外添剤として粒径20nmのシリカ粒子(外添粒子)が添加されている。
As shown in FIG. 4A, the developing
現像ブレード44aは現像ローラ41aの回転方向(図示矢印R4方向)に対してカウンター方向に当接しており、供給ローラ43aによって供給されたトナーのコート量規制及び電荷付与を行っている。現像ブレード44aは薄い板状部材からなり、薄板のバネ弾性を利用して当接圧力を形成し、その表面がトナー及び現像ローラ41aに接触当接される。本実施例では、現像ブレード44aとして、厚さ0.1mmの板バネ状のSUS製の薄板に半導電性樹脂をコーティングしたものを用いた。また、現像ブレード44aは、薄板のバネ弾性を利用して当接圧力を形成することで、現像ブレード44aの表面を現像ローラ41aに担持されたトナーに接触させる構成とした。
The developing
現像ブレード44aには、現像ブレード電源81から所定の電圧が印加される。これにより、トナーは現像ブレード44aと現像ローラ41a間の放電、及び現像ブレード44aと現像ローラ41aとの摺擦による摩擦帯電によって、マイナス電荷を付与されると同時に層厚を規制される。なお、本実施例においては、画像形成中では現像ローラ41aの電位に対する現像ブレード44aの電位差がΔV=-100Vとなるように、現像ブレード電源81から出力する電圧を制御している。
A predetermined voltage is applied from a developing
なお、現像ローラ41aは新品時に初期潤滑剤として、粒径が2μmのシリコーン粒子(トスパール120:モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアル社製)が塗布されている。これにより、新品時に現像ローラ41aと現像ブレード44aとの間に発生する摩擦力を低減させて、現像ブレード44aの変形(捲れ)の発生を抑制することができる。画像形成が実行された以降においては、現像ローラ41aと現像ブレード44aとの間にトナーが介在することで摩擦力を一定以下に保つことができる。したがって、新品時に現像ローラ41aに塗布されたシリコーン粒子は、新品のカートリッジ9aが画像形成装置100の装置本体に装着されたあとに実行される、画像形成の準備動作時に現像ローラ41aから除去される。なお、本実施例においては、初期塗布剤としてシリコーン粒子を用いたが、これに限らず、潤滑性、耐環境性を有するものであれば、新品時に現像ローラ41aにトナーを塗布する構成としてもよい。
When the developing
供給ローラ43aは、現像ローラ41aの周面上に所定のニップ部を形成して配設されており、図示矢印R5方向に回転する。供給ローラ43aは導電性芯金の外周に発泡体を形成した弾性スポンジローラである。供給ローラ43aと現像ローラ41aは所定の侵入量を持って接触し、接触部Ndを形成している。本実施例においては、現像ローラ41a、供給ローラ43aは、共に外径φ20であり、供給ローラ43aの現像ローラ41aへの侵入量を1.5mmに設定した。
The
また、供給ローラ43aと現像ローラ41aは接触部Ndにおいて互いに逆方向に移動するよう回転している。この動作により、供給ローラ43aによる現像ローラ41aへのトナー供給及び現像残として残った現像ローラ41a上のトナーの剥ぎ取りを行っている。この時、供給ローラ43aに対して現像ローラ41aとの電位差を調整することにより、現像ローラ41aへのトナー供給量を調整することが出来る。本実施例では、供給ローラ43aの電位に対して現像ローラ41aの電位がΔV=+50Vとなるように、供給ローラ電源82から供給ローラ43aに対して印加する電圧(直流電圧)の値を設定している。
Further, the
収容室46a内には撹拌部材11a(除去部材)が設けられている。撹拌部材11aは、収容室46a内に収納されたトナーを攪拌すると共に、供給ローラ43aの上部に向けて、開口45aから図中矢印G方向にトナーを搬送する。
A stirring
現像ローラ41aと感光ドラム1aとが当接する位置(以下、現像部Ngと称する)において、現像ローラ41aと感光ドラム1aは、互いの表面が同一方向に移動するように、それぞれ回転駆動される。画像形成時においては、現像ローラ電源80から現像ローラ41aに感光ドラム1aの帯電極性(本実施例では負極性)と同極性の直流電圧が印加される。これにより、現像部Ngにおいて、現像ローラ41aに担持された負極性に帯電したトナーが感光ドラム1aの静電潜像部に移動し、静電潜像を現像してトナー像を形成する。
At a position where the developing
<封止部材の開封動作>
図4(b)に示すように、カートリッジ9aが新品の時においては、現像ローラ41aと供給ローラ43aが設けられた現像室47aと、トナーを収容する収容室46aと、が封止部材48aにより区分されている。これは、ユーザーがカートリッジの使用を開始するまでの間に、収容室46aからトナーが漏れることを抑制するためである。
<Opening operation of sealing member>
As shown in FIG. 4B, when the
図4(b)に示すように、封止部材48aの一端部は開口45aを封止するように、開口45aの周縁部に剥離可能に固定される。他端部は、撹拌部材11aの一端に固定される。ユーザーが新品のカートリッジ9aの使用を開始すると、モータM2からの駆動力を受けることで、収容室46aに設けられる撹拌部材11aが図4中における時計方向に回転する。この撹拌部材11aの回転により、封止部材48aは開口45aの周縁部から剥離され、開口45aが開封される。そして、時計方向に回転する撹拌部材11aにより収容室46aから現像室47aへトナーを搬送することが可能となる。なお、封止部材48aの固定方法は、本実施例ではヒートシール方式を用いたが、これに限らず、他に、超音波溶着や両面テープ等の固定方法を用いても良い。
As shown in FIG. 4B, one end of the sealing
[カートリッジの準備動作]
本実施例では、画像形成装置100の装置本体に装着されたカートリッジが新品か否かを、各カートリッジ9に具備された不揮発性の記憶手段(以下、メモリと称す)の検知結果から判断する。図1に示すように、各カートリッジ9には、メモリと、メモリへの情報の読み書きを制御するための伝達部とが一体化された基板91が設けられている。また、画像形成装置100の本体には、各カートリッジ9の伝達部からの情報をCPU102に設けられる記憶部に伝達する伝達部(不図示)が設けられている。
[Cartridge preparation operation]
In this embodiment, whether or not the cartridges mounted in the main body of the
本実施例においては、カートリッジが画像形成装置100に装着されると、各カートリッジ9側の基板91と画像形成装置100側の伝達部とが対面して接触した状態になる。これにより、制御基板101に設けられるCPU102と、各カートリッジ9のメモリが電気的に接続された状態となり、CPU102によって、メモリに記録された情報の読み込みやメモリに対する情報の書込みを実行することが可能となる。
In this embodiment, when the cartridges are attached to the
なお、メモリとしては、通常の半導体による電子的なメモリが特に制限なく使用することができる。また、本実施例においては、カートリッジが画像形成装置100に装着された場合に、各カートリッジ9側の基板91と画像形成装置100側の伝達部とが対面して接触した状態になる構成について説明した。しかし、これに限らず、カートリッジが画像形成装置100に装着された場合に、各カートリッジ9側の基板91と画像形成装置100側の伝達部とを接触させず、近距離通信などを用いてCPU102によるメモリへの情報の読み書きを実行してもよい。
As the memory, an electronic memory made of ordinary semiconductors can be used without particular limitation. Also, in this embodiment, when the cartridges are installed in the
本実施例の画像形成装置100においては、装置本体に新品のカートリッジが装着された場合に、新品のカートリッジの現像手段4における封止部材48の除去動作を含む画像形成動作を行うための準備動作が実行される。図5は、画像形成装置100の装置本体に新品のカートリッジが装着された場合に実行される制御を説明するフローチャートである。
In the
図5に示すように、まず、制御手段としてのCPU102は、各カートリッジ9のメモリの情報を読み込み、中間転写ベルト13と共通の駆動源であるモータM1によって駆動されるカートリッジ9dが新品か否かを検知する(ステップS1)。カートリッジ9dが新品であると検知された場合は、次にモータM2によって駆動されるカートリッジ9a~9cのうちいずれかのカートリッジが新品か否かを検知する(ステップS2)。なお、ステップS1でカートリッジ9dが新品でないと検知された場合であっても、ステップS2と同様の検知をステップS3で行う。
As shown in FIG. 5, first, the
ステップS2でカートリッジ9a~9cのうちいずれかのカートリッジが新品であると検知された場合は、第1の準備動作を実行する(ステップS4)。一方、ステップS2でカートリッジ9a~9cのいずれのカートリッジも新品ではないと検知された場合は、第2の準備動作を実行する(ステップS5)。また、ステップS3でカートリッジ9a~9cのうちいずれかのカートリッジが新品であると検知された場合は、第3の準備動作を実行する(ステップS6)。そして、各ステップS4~S6における準備動作が実行された後に、CPU102は、画像形成装置100が画像形成可能な状態であると判断する(ステップS8)。
If any one of the
なお、ステップS3でカートリッジ9a~9cのいずれのカートリッジも新品ではないと検知された場合は、CPU102は、全てのカートリッジ9a~9dが新品でないと判断する。そして、画像形成を行うための前述の第1~第3のいずれの準備動作も実行せず、ステップ8へと進む。図5に示すように、本実施例においては、いずれのカートリッジ9が装着されたかで、CPU102によって実行される準備動作が異なる。以下、図6(a)~(c)を用いて、第1~第3の準備動作について詳細に述べる。
If none of the
<第1の準備動作>
図6(a)は、第1の準備動作のフローを説明するフローチャートである。第1の準備動作は、カートリッジ9dが新品で、かつ、カートリッジ9a~9cのうち少なくとも1つ以上のカートリッジが新品であることをCPU102が検知した場合に実行される準備動作である。
<First preparation operation>
FIG. 6A is a flowchart for explaining the flow of the first preparatory operation. The first preparatory operation is executed when the
図6(a)に示すように、まず、CPU102は、ステップS101において、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材に駆動を伝達するモータM2の駆動を開始する。この時、各感光ドラム1a~1dは中間転写ベルト13に対して離間させている。そして、ステップS102において、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2c、現像ローラ41a~41c、供給ローラ43a~43c、現像ブレード44a~44c)への電圧印加を開始する。本実施例では、帯電ローラ2a~2cに-1000V、現像ローラ41a~41cに-300V、供給ローラ43a~43cに-350V、現像ブレード44a~44cに-450Vの所定の電圧をそれぞれ印加した。
As shown in FIG. 6A, first, in step S101, the
その後、ステップS103において、新品のカートリッジにおける画像形成を行う準備動作が完了するまでの間、前述の所定の電圧を印加した状態で、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材を回転駆動させる。ここで、新品のカートリッジにおける画像形成を行う準備動作とは、封止部材48の剥離と、現像室47へのトナーの供給と、供給ローラ43から現像ローラ41へのトナーの供給の動作を指す。
After that, in step S103, various members of the
ステップ104においては、現像ローラ41a~41cから感光ドラム1a~1cに設けられたクリーニングブレード31a~31cに対して、潤滑剤としてのトナーを供給する。トナーの供給を行う場合、CPU102は、まず、露光手段12a~12cからの走査ビームにより、帯電ローラ2a~2cによって帯電された感光ドラム1a~1cの表面に静電潜像を形成する。この時、感光ドラム1の回転方向(図1における矢印R1方向)に関して現像ローラ41の1周分の長さであって、感光ドラム1の長手方向に関して画像を形成可能な最大幅の静電潜像を形成する。その後、この静電潜像を現像ローラ41a~41cに担持されたトナーによって現像し、感光ドラム1a~1cにドラム供給用トナー像を形成する。なお、本実施例におけるクリーニングブレード31a~31cへのトナーの供給動作では、前述のドラム供給用トナー像を一定間隔ごとに計40回形成する。これらのドラム供給用トナー像は、感光ドラム1の回転に伴ってクリーニングブレード31に到達し、クリーニングブレード31と感光ドラム1とが当接する位置において潤滑剤として機能する。
In step 104, toner as a lubricant is supplied from the developing
続いて、ステップS105において、感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とを当接させ、ステップS106において、カートリッジ9dの各種部材及び中間転写ベルト13に駆動を伝達するモータM1の駆動を開始する。
Subsequently, in step S105, the
そして、ステップS107において、カートリッジ9dの各種部材(帯電ローラ2d、現像ローラ41d、供給ローラ43d、現像ブレード44d)への電圧印加を開始する。本実施例では、帯電ローラ2dに-1000V、現像ローラ41dに-300V、供給ローラ43dに-350V、現像ブレード44dに-450Vの所定の電圧をそれぞれ印加した。
Then, in step S107, voltage application to various members of the
その後、ステップS108において、新品のカートリッジ9dにおける画像形成を行う準備動作が完了するまでの間、前述の所定の電圧を印加した状態で、カートリッジ9dの各種部材を回転駆動させる。ここで、新品のカートリッジ9dにおける画像形成を行う準備動作とは、封止部材48dの剥離と、現像室47dへのトナーの供給と、供給ローラ43dから現像ローラ41dへのトナーの供給の動作を指す。なお、ステップS108においては、カートリッジ9dにおける前述の準備動作の実行とともに、カートリッジ9a~9cから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給する。
After that, in step S108, various members of the
カートリッジ9a~9cから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給する動作は、以下のようにして行われる。まず、各感光ドラム1a~1cに、感光ドラム1の回転方向(図1における矢印R1方向)に関して現像ローラ41の2周分の長さであって、感光ドラム1の長手方向に関して画像を形成可能な最大幅のハーフトーン画像の静電潜像を形成する。その後、この静電潜像を、現像手段4a~4cの現像ローラ41a~41cに担持されたトナーによって現像し、感光ドラム1a~1cにベルト供給用トナー像を形成する。そして、各感光ドラム1a~1cに形成されたベルト供給用トナー像を各一次転写部N1a~N1cにおいて中間転写ベルト13に転写する。これらのベルト供給用トナー像は、中間転写ベルト13の移動に伴ってベルトクリーニング手段20に到達し、中間転写ベルト13とクリーニングブレード29とが当接するブレードニップ部33に供給され、潤滑剤として機能する。
The operation of supplying toner from the
その後、ステップS109において、感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とを離間させた後に、ステップS110において、感光ドラム1dのクリーニングブレード31dにトナーを供給する。クリーニングブレード31dへのトナーの供給動作は、ステップS104でカートリッジ9a~9cにおいて実施したのと同様に、感光ドラム1dにドラム供給用トナー像を形成することによって実行される。これらのドラム供給用トナー像は、感光ドラム1dの回転に伴ってクリーニングブレード31dに到達し、クリーニングブレード31dと感光ドラム1dとが当接する位置において潤滑剤として機能する。
After that, in step S109, after the
そして、ステップS110において、カートリッジ9a~9dの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2d、現像ローラ41a~41d、供給ローラ43a~43d、現像ブレード44a~44d)への電圧印加を停止する。その後、ステップS112において、モータM1とモータM2の駆動を停止し、第1の準備動作が完了する。
Then, in step S110, voltage application to various members of the
なお、本実施例においては、ステップS103とステップS104でカートリッジ9a~9cすべてに関して各種動作を実行する構成について説明したが、これらの動作は、新品のカートリッジのみで実行されても良い。例えば、CPU102によって、カートリッジ9aのみが新品であると判断された場合、ステップS103及びステップS104の動作をカートリッジ9aのみにおいて実行する構成としても良く、カートリッジ9a~9cを連動させて実行する構成としても良い。
In the present embodiment, steps S103 and S104 have been described with respect to all the
また、本実施例においては、ステップS108において、カートリッジ9a~9cすべてに関してベルト供給用トナー像を形成する構成について説明したが、これに限らない。ブレードニップ部33に所定のトナーを供給することが可能であれば、カートリッジ9a~9cのいずれか1つ若しくは2つにおいて、ベルト供給用トナー像を形成する構成としても良い。
Further, in this embodiment, in step S108, the configuration for forming the belt-supply toner image for all the
<第2の準備動作>
図6(b)は、第2の準備動作のフローを説明するフローチャートである。第2の準備動作は、カートリッジ9dは新品だが、カートリッジ9a~9cは新品ではないことをCPU102が検知した場合に実行される準備動作である。
<Second preparatory operation>
FIG. 6B is a flowchart for explaining the flow of the second preparatory operation. The second preparatory operation is executed when the
図6(b)に示すように、まず、CPU102は、ステップS201において感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とを当接させる。そして、ステップS202において、カートリッジ9dの各種部材及び中間転写ベルト13に駆動を伝達するモータM1と、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材に駆動を伝達するモータM2の駆動を開始する。
As shown in FIG. 6B, first, the
続いて、ステップS203において、カートリッジ9a~9dの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2d、現像ローラ41a~41d、供給ローラ43a~43d、現像ブレード44a~44d)への電圧印加を開始する。本実施例では、帯電ローラ2a~2dに-1000V、現像ローラ41a~41dに-300V、供給ローラ43a~43dに-350V、現像ブレード44a~44dに-450Vの所定の電圧をそれぞれ印加した。
Subsequently, in step S203, voltage application to various members of the
その後、ステップS204において、新品のカートリッジ9dにおける画像形成を行う準備動作が完了するまでの間、前述の所定の電圧を印加した状態で、カートリッジ9dの各種部材を回転駆動させる。ここで、新品のカートリッジ9dにおける画像形成を行う準備動作とは、封止部材48dの剥離と、現像室47dへのトナーの供給と、供給ローラ43dから現像ローラ41dへのトナーの供給の動作を指す。なお、ステップS204においては、カートリッジ9dにおける前述の準備動作の実行とともに、カートリッジ9a~9cから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給する。
After that, in step S204, various members of the
カートリッジ9a~9cから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給する動作は、以下のようにして行われる。まず、各感光ドラム1a~1cに、感光ドラム1の回転方向(図1における矢印R1方向)に関して現像ローラ41の2周分の長さであって、感光ドラム1の長手方向に関して画像を形成可能な最大幅のハーフトーン画像の静電潜像を形成する。その後、この静電潜像を、現像手段4a~4cの現像ローラ41a~41cに担持されたトナーによって現像し、感光ドラム1a~1cにベルト供給用トナー像を形成する。そして、各感光ドラム1a~1cに形成されたベルト供給用トナー像を各一次転写部N1a~N1cにおいて中間転写ベルト13に転写する。これらのベルト供給用トナー像は、中間転写ベルト13の移動に伴ってベルトクリーニング手段20に到達し、中間転写ベルト13とクリーニングブレード29とが当接するブレードニップ部33に供給され、潤滑剤として機能する。
The operation of supplying toner from the
その後、ステップS205において、感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とを離間させた後に、ステップS206において、感光ドラム1dのクリーニングブレード31dにトナーを供給する。クリーニングブレード31dへのトナーの供給動作を実行する場合、CPU102は、まず、露光手段12dからの走査ビームにより、帯電ローラ2dによって帯電された感光ドラム1dの表面に静電潜像を形成する。この時、感光ドラム1dの回転方向(図1における矢印R1方向)に関して現像ローラ41dの1周分の長さであって、感光ドラム1dの長手方向に関して画像を形成可能な最大幅の静電潜像を形成する。その後、この静電潜像を現像ローラ41dに担持されたトナーによって現像し、感光ドラム1dにドラム供給用トナー像を形成する。なお、本実施例におけるクリーニングブレード31dへのトナーの供給動作では、前述のドラム供給用トナー像を一定間隔ごとに計40回形成する。これらのドラム供給用トナー像は、感光ドラム1の回転に伴ってクリーニングブレード31dに到達し、クリーニングブレード31dと感光ドラム1とが当接する位置において潤滑剤として機能する。
After that, in step S205, the
そして、ステップS207において、カートリッジ9a~9dの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2d、現像ローラ41a~41d、供給ローラ43a~43d、現像ブレード44a~44d)への電圧印加を停止する。その後、ステップS208において、モータM1とモータM2の駆動を停止し、第2の準備動作を終了する。
Then, in step S207, voltage application to various members of the
なお、本実施例においては、ステップS204において、カートリッジ9a~9cすべてに関してベルト供給用トナー像を形成する構成について説明したが、これに限らない。ブレードニップ部33に所定のトナーを供給することが可能であれば、カートリッジ9a~9cのいずれか1つ若しくは2つにおいて、ベルト供給用トナー像を形成する構成としても良い。
In this embodiment, in step S204, the configuration for forming the belt-supply toner image for all the
<第3の準備動作>
図6(c)は、第3の準備動作のフローを説明するフローチャートである。第3の準備動作は、カートリッジ9dは新品ではないが、カートリッジ9a~9cのうち少なくとも1つ以上のカートリッジが新品であることをCPU102が検知した場合に実行される準備動作である。
<Third preparatory operation>
FIG. 6(c) is a flowchart for explaining the flow of the third preparatory operation. The third preparatory operation is performed when the
図6(c)に示すように、まず、CPU102は、ステップS301において、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材に駆動を伝達するモータM2の駆動を開始する。この時、各感光ドラム1a~1dは中間転写ベルト13に対して離間させている。そして、ステップS302において、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2c、現像ローラ41a~41c、供給ローラ43a~43c、現像ブレード44a~44c)への電圧印加を開始する。本実施例では、帯電ローラ2a~2cに-1000V、現像ローラ41a~41cに-300V、供給ローラ43a~43cに-350V、現像ブレード44a~44cに-450Vの所定の電圧をそれぞれ印加した。
As shown in FIG. 6(c), first, in step S301, the
その後、ステップS303において、新品のカートリッジにおける画像形成を行う準備動作が完了するまでの間、前述の所定の電圧を印加した状態で、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材を回転駆動させる。ここで、新品のカートリッジにおける画像形成を行う準備動作とは、封止部材48の剥離と、現像室47へのトナーの供給と、供給ローラ43から現像ローラ41へのトナーの供給の動作を指す。
After that, in step S303, various members of the
ステップ304においては、現像ローラ41a~41cから感光ドラム1a~1cに設けられたクリーニングブレード31a~31cに対して、潤滑剤としてのトナーを供給する。トナーの供給を行う場合、CPU102は、まず、露光手段12a~12cからの走査ビームにより、帯電ローラ2a~2cによって帯電された感光ドラム1a~1cの表面に静電潜像を形成する。この時、感光ドラム1の回転方向(図1における矢印R1方向)に関して現像ローラ41の1周分の長さであって、感光ドラム1の長手方向に関して画像を形成可能な最大幅の静電潜像を形成する。その後、この静電潜像を現像ローラ41a~41cに担持されたトナーによって現像し、感光ドラム1a~1cにドラム供給用トナー像を形成する。なお、本実施例におけるクリーニングブレード31a~31cへのトナーの供給動作では、前述のドラム供給用トナー像を一定間隔ごとに計40回形成する。これらのドラム供給用トナー像は、感光ドラム1の回転に伴ってクリーニングブレード31に到達し、クリーニングブレード31と感光ドラム1とが当接する位置において潤滑剤として機能する。
In step 304, toner as a lubricant is supplied from the developing
そして、ステップS305において、カートリッジ9a~9cの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2c、現像ローラ41a~41c、供給ローラ43a~43c、現像ブレード44a~44c)への電圧印加を停止する。その後、ステップS306において、モータM2の駆動を停止し、第3の準備動作を終了する。
Then, in step S305, voltage application to various members of the
なお、本実施例においては、ステップS303とステップS304でカートリッジ9a~9cすべてに関して各種動作を実行する構成について説明したが、これらの動作は、新品のカートリッジのみで実行されても良い。例えば、CPU102によって、カートリッジ9aのみが新品であると判断された場合、ステップS303及びステップS304の動作をカートリッジ9aのみにおいて実行する構成としても良く、カートリッジ9a~9cを連動させて実行する構成としても良い。
In this embodiment, steps S303 and S304 have explained the configuration in which various operations are performed with respect to all the
[クリーニングブレード29の変形の抑制]
図7は、本実施例の第1の準備動作における、各ステップに要する時間を説明するタイミングチャートである。
[Suppression of Deformation of Cleaning Blade 29]
FIG. 7 is a timing chart explaining the time required for each step in the first preparatory operation of this embodiment.
図7に示すように、最も時間が長いステップはステップS104、およびステップS110の感光ドラム1に当接されたクリーニングブレード31にトナーを供給する動作である。これは、本実施例においては、先に説明したドラム供給用トナー像を一定間隔ごとに計40回形成し、現像手段4からドラムクリーニング手段3にトナーを供給しているためである。以下、ステップS104、およびステップS110において、このような動作を実行する理由について説明する。
As shown in FIG. 7, the step that takes the longest time is the operation of supplying toner to the cleaning blade 31 in contact with the
本実施例においては、現像ローラ41は新品時に初期潤滑剤として、粒径が2μmのシリコーン粒子(トスパール120:モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアル社製)が塗布されている。初期塗布剤が現像ローラ41に残存し続けると、現像ローラ41のトナーの保持量や帯電量が不安定になるおそれがある。このため、本実施例においては、感光ドラム1のクリーニングブレード31にトナーを供給する動作を実行する際に、ドラム供給用トナー像の形成とともに現像ローラ41に塗布された初期塗布剤の吐出しを実行している。
In this embodiment, the developing
また、本実施例の第1の準備動作のステップS104及びステップS110においては、更に、現像ローラ41に担持されるトナーの保持量と帯電量を安定化させるために、一定量のトナー吐出しを行っている。新品のカートリッジ9において、初期に収容室46から現像ローラ41に供給されるトナーは、小粒径で高帯電量の静電的に移動しやすいトナーであることが多い。これらのトナーが現像ローラ41上に存在すると、現像ローラ41に担持されたトナーは、粒径や帯電量のばらつきが大きくなることで一次転写性、二次転写性が不安的になるおそれがある。そのため、本実施例においては、現像ローラ41に供給される初期のトナーを、一定量感光ドラム1へ吐き出す動作を実行している。
Further, in steps S104 and S110 of the first preparation operation of the present embodiment, a constant amount of toner is discharged in order to stabilize the amount of toner held and the amount of charge carried by the developing
ステップS104およびS110に次いで時間が長いステップはステップS103である。これは封止部材48を剥離した後に、トナーを収容室46から現像室47へ所定量搬送する必要があり、撹拌部材11を一定回数以上、回転させる必要があるためである。本実施例では、ステップS104およびステップS110の所要時間は60秒(s)、ステップS103の所要時間は9秒(s)である。
Step S103 takes the second longest time after steps S104 and S110. This is because it is necessary to convey a predetermined amount of toner from the storage chamber 46 to the developing chamber 47 after the sealing member 48 is peeled off, and it is necessary to rotate the stirring
画像形成装置100に新品のカートリッジ9dが装着され、カートリッジ9dにおいて画像形成を行うための準備動作を実行する必要がある場合、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが存在しない状態で中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動させる状態が生じる可能性がある。これは、モータM1によってカートリッジ9dにおいて各種部材を回転駆動させた場合、中間転写ベルト13も回転駆動されるためである。この時、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが存在しない状態で中間転写ベルト13が長時間回転駆動されると、ブレードニップ部33にトナーなどの潤滑剤が供給されない状態で中間転写ベルト13が長時間回転し続けることになる。その結果、ブレードニップ部33において大きな摩擦力が生じ、クリーニングブレード29の先端の変形(捲れ)が発生してしまうおそれがある。
When a
図7に示す時間t1は、本実施例の第1の準備動作時における、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが供給されていない状態で、中間転写ベルト13が回転駆動される時間である。ここで、図7に示すように、時間t1は、ステップS106の所要時間と、ステップS107の所要時間と、ステップS108における感光ドラム1a~1cから中間転写ベルト13にベルト供給用トナー像が供給されるまでの所要時間と、の和である。本実施例における時間t1は、約4.4秒(s)である。
A time t1 shown in FIG. 7 is a time during which the
図8は、本実施例の比較例における、カートリッジ9dが新品で、かつ、カートリッジ9a~9cのうち少なくとも1つ以上のカートリッジが新品であることをCPU102が検知した場合に実行される準備動作のフローを説明するフローチャートである。本実施例の比較例は、準備動作のフローが異なる点を除いて、画像形成装置の構成などは本実施例と実質同一である。したがって、以下の説明においては、本実施例と共通する部分に関しては同一の符号を付して比較例の説明を行う。
FIG. 8 shows the preparatory operation executed when the
図8に示すように、比較例の構成において、まず、CPU102は、ステップS401でモータM1とモータM2の駆動を開始する。この時、各感光ドラム1a~1dは中間転写ベルト13に対して離間させている。そして、ステップS202において、カートリッジ9a~9dの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2d、現像ローラ41a~41d、供給ローラ43a~43d、現像ブレード44a~44d)への電圧印加を開始する。ここで、各種部材に印加する電圧の値は本実施例と同一である。
As shown in FIG. 8, in the configuration of the comparative example, first, the
その後、ステップS403において、新品のカートリッジにおける画像形成を行う準備動作が完了するまでの間、前述の所定の電圧を印加した状態で、カートリッジ9a~9dの各種部材を回転駆動させる。ステップ404においては、現像ローラ41a~41dから感光ドラム1a~1dに設けられたクリーニングブレード31a~31dに対して、潤滑剤としてのトナーを供給する。新品のカートリッジにおける画像形成を行う準備動作、およびトナーの供給動作に関しては、本実施例と同一であるため説明を省略する。
After that, in step S403, various members of the
続いて、ステップS405において、感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とを当接させ、ステップS406において、カートリッジ9a~9dから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給する。カートリッジ9a~9dから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給する動作は、実質本実施例と同一であり、まずは、各感光ドラム1a~1dにおいてベルト供給用トナー像を形成する。そして、これらのベルト供給用トナー像を中間転写ベルト13に転写することで中間転写ベルト13とクリーニングブレード29とが当接するブレードニップ部33にトナーを供給する。中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給した後に、ステップS407において、感光ドラム1a~1dと中間転写ベルト13とを離間させる。
Subsequently, in step S405, the
そして、ステップS408において、カートリッジ9a~9dの各種部材(帯電ローラ2a~2d、現像ローラ41a~41d、供給ローラ43a~43d、現像ブレード44a~44d)への電圧印加を停止する。その後、ステップS112において、モータM1とモータM2の駆動を停止し、比較例における準備動作が完了する。
Then, in step S408, voltage application to various members of the
このように、比較例においては、全てのカートリッジ9a~9dにおいて、同時に回転駆動を開始して各種準備動作を実行する。したがって、比較例の構成においては、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが存在しない状態で中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動する時間が、本実施例よりも長くなる。図7に対応させると、ステップS106mS107を除くステップS101からステップS108の間(実質、時間t2に対応)、比較例の構成においては、ブレードニップ部33にトナーが供給されない状態で中間転写ベルト13が駆動される。この時間は、約73.4秒となる。
In this way, in the comparative example, all the
<評価結果>
次に、図6(a)のフローチャートで示した本実施例の第1の準備動作と、図8のフローチャートで示した比較例の準備動作に関して、ブレードニップ部33における、クリーニングブレード29の捲れ、及び異音の発生の有無の評価を行った。この評価は、新品の中間転写ベルト13を用い、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが無い状態で画像形成装置100に新品のカートリッジ9a~9dを装着し、本実施例及び比較例の準備動作を実行する際の捲れ及び異音の発生を確認することで行った。なお、クリーニングブレード29の先端部に、潤滑剤としてのフッ化黒鉛(セフボンCMA:セントラル硝子社製)があらかじめ塗布された状態で評価を実施した。また、この評価は、室温30℃、湿度80%の高温高湿環境、室温23℃、湿度50%の標準環境、室温15℃湿度10%の低温低湿環境において、それぞれ実施した。表1に評価結果を示した。
<Evaluation results>
Next, regarding the first preparatory operation of the present embodiment shown in the flowchart of FIG. 6A and the preparatory operation of the comparative example shown in the flowchart of FIG. And the presence or absence of abnormal noise was evaluated. In this evaluation, a new
表1に示すように、本実施例の構成においては、ブレードニップ部33において、クリーニングブレード29の捲れや、異音は発生しなかった。一方、比較例1においては、標準環境では捲れや異音の発生はなかったが、高温高湿環境下で、準備動作中にクリーニングブレード29の捲れが発生し、低温低湿環境下では異音が発生した。これは、トナーが無い状態での中間転写ベルト13の回転駆動時間が長いことで、ブレードニップ部33における摩擦力が高くなったためである。より詳細には、高温高湿環境下においては、クリーニングブレード29が柔らかくなるため、比較例の構成においてブレードニップ部33における摩擦力が高くなることで、クリーニングブレード29の先端の捲れが発生した。また、低温低湿環境下においては、クリーニングブレード29が固くなるため、比較例の構成においてブレードニップ部33における摩擦力が高くなることで、クリーニングブレード29と中間転写ベルト13との間における振動によって異音が発生した。
As shown in Table 1, in the configuration of this example, the
次に、中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給しない状態で中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動(以下、空回転と称する)させたときの、回転時間に対する中間転写ベルト13の駆動トルクを測定した。図9は、画像形成装置100から全てのカートリッジを取り外し、クリーニングブレード29を新品の中間転写ベルト13に当接させた状態で、中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動させた際の、モータM1のトルクの測定結果である。なお、クリーニングブレードには初期潤滑剤としてセフボンを塗布している。図9の測定は、室温30℃、湿度80%の高温高湿環境下で行った。
Next, the driving torque of the
図9に示すように、中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動させるモータM1は、中間転写ベルト13を回転させる時間が長くなるほど、トルクが上昇する傾向を示した。これは、回転駆動開始直後からクリーニングブレード29に塗布されたセフボンが脱離し、ブレードニップ部33にトナーなどの潤滑剤が存在しなくなることで、ブレードニップ部33において摩擦力が上昇するためである。図9に示す測定結果より、中間転写ベルト13を48秒間回転駆動させると、モータM1の駆動トルクが3.5kgf・cmに達した。そして、本実施例の画像形成装置100の構成においては、この時点で、クリーニングブレード29の捲れが生じた。即ち、図9に示される測定結果から、本実施例の画像形成装置100においてクリーニングブレード29の捲れの発生を防止するためには、モータM1によって中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動させるときの駆動トルクが3.5kgf・cm以下である必要がある。
As shown in FIG. 9, the torque of the motor M1 that rotates the
本実施例において第1の準備動作を実行する場合、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが存在しない状態で中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動する時間t1は4.4秒であった。この時間は、クリーニングブレード29において捲れが発生する時間(48秒)に対して十分小さい。一方、比較例の構成において準備動作を実行する場合、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが存在しない状態で中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動する時間t2は約73.4秒であり、この時間は、クリーニングブレード29において捲れが発生する時間より長い。
In the present embodiment, when the first preparatory operation is executed, the time t1 for rotating the
以上説明したように、本実施例によれば、中間転写ベルト13と、カートリッジ9の少なくとも1つ以上が同一駆動源である構成において、新品のカートリッジ9を装着した場合に、クリーニングブレード29の先端の変形を抑制することが可能である。より詳細には、新品のカートリッジ9dを装着したときに実行される準備動作において、中間転写ベルト13と共通の駆動源ではないカートリッジ9a~9cから中間転写ベルト13にトナーを供給しつつ、カートリッジ9dにおいて準備動作を行っている。これにより、ブレードニップ部33にトナーなどの潤滑剤がない状態で中間転写ベルト13を回転駆動させる時間が短くなることで、クリーニングブレード29の先端の変形を抑制することが可能である。
As described above, according to this embodiment, in a configuration in which the
なお、本実施例では、中間転写ベルト13とカートリッジ9d(Bk)とを第1駆動源であるモータM1によって駆動する構成としたが、これに限定されるものではない。中間転写ベルト13と駆動源が共通のカートリッジ9は、カートリッジ9a~9dの何れでも良く、また、駆動源が共通のカートリッジは1~3個のいずれでも良い。なお、中間転写ベルト13にトナーが供給されるまでの時間を最短化するには、中間転写ベルト13の移動方向に関して、ベルトクリーニング手段20に最も近い位置に配置されるカートリッジからトナー供給を行うことが好ましい。本実施例では、中間転写ベルト13とは異なる駆動源から駆動され、且つ、ベルトクリーニング手段20に最も近い位置に配置されているのは、カートリッジ9cである。
In this embodiment, the
また、本実施例の第1および第2準備動作は、中間転写ベルト13やベルトクリーニング手段20を有する中間転写ユニットの使用状況に応じて、実行可否を判断してもよい。例えば、中間転写ユニットが新品の時はブレードニップ部33にトナーが存在しない。一方で、中間転写ユニットがある程度使用された以降は、ベルトクリーニング手段20によって二次転写後に中間転写ベルト13に残留したトナーを回収する動作を実行済みであることから、ブレードニップ部33にトナーが存在する可能性がある。したがって、中間転写ユニットが新品の場合であって、新品のカートリッジが画像形成装置本体に挿入された場合に、クリーニングブレード29の捲れの発生を抑制するために、CPU102によって前述の第1および第2の準備動作を実行する構成としても良い。このように、中間転写ユニットが新品時、あるいは新品時から所定期間(所定枚数)使用された場合等、中間転写ユニットの使用状況に応じて、第1および第2準備動作の実行可否を判断してもよい。
Further, whether or not the first and second preparatory operations of this embodiment can be executed may be determined according to the usage status of the
図10は本実施例の変形例の画像形成装置の構成を示す概略断面図である。本実施例では、感光ドラム1、帯電ローラ2、ドラムクリーニング手段3、および現像手段4を有する一体型のカートリッジ9に関して説明したが、これに限定されるものではない。例えば、図10に示すように、感光ドラム1、帯電ローラ2、およびドラムクリーニング手段3を有する感光ドラムユニットと、現像ローラ41、トナー、供給ローラ43、現像ブレード44、を有する現像手段4と、が別体の二体型カートリッジであっても良い。図10に示す二体型カートリッジにおいては、感光ドラムユニットと現像手段4は、画像形成装置の装置本体に対してそれぞれ着脱が可能である。
FIG. 10 is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the configuration of an image forming apparatus according to a modification of this embodiment. In this embodiment, the integrated cartridge 9 having the
また、本実施例においては、現像方式として1成分接触現像方式を採用しているが、現像方式としては非接触(ジャンピング)現像方式を用いたり、2成分現像方式を用いたりしても、同様の効果を得ることができる。2成分現像方式を用いた構成では、例えばトナー初期化シーケンス時に、前記第1および第2準備動作を行えばよい。 Further, in this embodiment, the one-component contact developing system is adopted as the developing system, but a non-contact (jumping) developing system or a two-component developing system may be used as the developing system. effect can be obtained. In the configuration using the two-component development method, the first and second preparatory operations may be performed, for example, during the toner initialization sequence.
(実施例2)
実施例1においては、第2駆動源としてのモータM2によって、各カートリッジ9a~9cに駆動力を伝達して感光ドラム1a~1cを回転駆動させる構成について説明した。これに対し、実施例2においては、図11に示すように、現像手段4a~4cを、第2駆動源としてのモータM2ではなく、第3駆動源としてのモータM3によって駆動し、カートリッジ9dの現像手段4dは第1駆動源としてのモータM1によって駆動する。なお、実施例2は、現像手段4a~4cを駆動する駆動源がモータM3であることを除いて、実施例1と実質同一の構成を有する。したがって、以下の説明においては、実施例1と共通する部分に関しては、同一の符号を付して説明を省略する。
(Example 2)
In the first embodiment, the motor M2 as the second drive source transmits a driving force to each of the
図11は、本実施例における、各感光ドラム1及び中間転写ベルト13の駆動構成を説明する模式図である。本実施例の画像形成装置は、カートリッジ9dの各種部材と中間転写ベルト13とを駆動するモータM1(第1駆動源)と、感光ドラム1a~1cを駆動するモータM2(第2駆動源)と、現像手段4a~4cを駆動するモータM3(第3駆動源)と、を有する。また、本実施例の画像形成装置は、各現像ローラ41a~41dを、対応する各感光ドラム1a~1dに対して当接又は離間させることが可能である。具体的には、CPU102によって画像形成装置に設けられた現像当接離間モータ(不図示)を制御することによって、現像ローラ41を感光ドラム1に対して、当接、又は離間させることが可能である。
FIG. 11 is a schematic diagram for explaining the driving configuration of each
本実施例におけるカートリッジ9a~9cの駆動構成について述べる。供給ローラ43a~43cの回転軸に固定された不図示のギアと、撹拌部材11a~11cに固定された不図示のギアと、が連結されている。また、現像ローラ41a~41cの回転軸に固定された不図示のギアと、供給ローラ43a~43cの回転軸に固定された不図示のギアと、が連結されている。そして、供給ローラの回転軸にはモータM3からの回転駆動力が伝達される。
The driving structure of the
本実施例のように、現像手段4a~4cに駆動を伝達する駆動源を別途設け、且つ、現像ローラ41を感光ドラム1に対して当接又は離間可能な構成とすることにより、実施例1の効果だけでなく、以下のような効果が得られる。即ち、現像手段4a~4cと、感光ドラム1a~1cと、を個別に回転駆動させることが可能であるため、各部材の回転駆動の必要可否に応じて個別に駆動の制御を行うことが可能となるので、各部材同士の摺擦などによる耐久劣化を低減することができる。
As in the present embodiment, by separately providing a driving source for transmitting the driving force to the developing means 4a to 4c and by configuring the developing
例えば、図6(a)のフローチャートにおけるステップS103に示されるような封止部材48の除去時には、感光ドラム1a~1cを回転駆動させる必要がない。より具体的には、現像ローラ41a~41cを感光ドラム1a~1cから離間させた状態で、モータM3によって現像手段4a~4cを駆動することで封止部材48の除去を行うことができる。そして、封止部材48の除去後に、モータM2を駆動開始し、現像ローラ41a~41cを感光ドラム1a~1cに当接させて次のステップS104を実行すれば良い。即ち、撹拌部材11a~11cの除去時に感光ドラム1a~1cを回転させないことにより、感光ドラム1a~1cと、クリーニングブレード31a~31cや帯電ローラ2a~2cとの間で発生する摩耗や摺擦を抑制することが可能である。この結果、感光ドラム1a~1cの耐久劣化を低下させることが可能である。
For example, when removing the sealing member 48 as shown in step S103 in the flowchart of FIG. 6A, it is not necessary to rotate the
なお、本実施例では、モータM3から供給ローラ43a~43cに駆動を伝達し、供給ローラ43a~43cの回転軸に固定されたギアなどを介して現像手段4a~4cにおけるその他の部材に駆動を伝達する構成としたが、これに限らない。例えば、モータM3から現像ローラ41a~41cに駆動を伝達した後に、ギアなどを介して現像手段4a~4cにおけるその他の部材に駆動を伝達する構成としても良い。
In this embodiment, the drive is transmitted from the motor M3 to the
1 感光体ドラム
4 現像手段
9 カートリッジ
13 中間転写ベルト
29 クリーニングブレード
M1 モータ
M2 モータ
1
Claims (12)
第1の像担持体にトナー像を形成するための第1の現像手段を有する第1のカートリッジと、前記第1の像担持体とは異なる色のトナー像を担持する第2の像担持体にトナー像を形成するための第2の現像手段を有する第2のカートリッジと、
前記第1の像担持体及び前記第2の像担持体と当接可能な中間転写体と、
前記中間転写体に当接して当接部を形成し、前記中間転写体に残留したトナーを回収する当接部材と、
前記中間転写体を回転駆動させる第1駆動源と、
前記第1駆動源とは異なる第2駆動源であって、前記第2の像担持体に駆動力を伝達する前記第2駆動源と、
前記第2の現像手段に駆動力を伝達する第3駆動源と、
前記第1駆動源によって前記中間転写体を回転させ、前記第2駆動源から前記第2の像担持体に駆動力を伝達し、前記第3駆動源によって前記第2の現像手段に駆動力を伝達することにより、前記第2の像担持体を介して前記第2の現像手段から前記当接部にトナーを供給するための供給動作と、画像形成するための準備動作と、を実行可能に制御する制御部と、を有し、
前記第1のカートリッジおよび前記第2のカートリッジが前記装置本体に対して着脱可能な画像形成装置において、
前記制御部は、新品の前記第1のカートリッジを前記装置本体に挿入した場合に、前記第2の像担持体を前記中間転写体に当接させた状態で前記供給動作を実行するように制御し、
新品の前記第2のカートリッジを前記装置本体に挿入した場合に、前記第2の像担持体と前記中間転写体を離間させた状態で、前記第2駆動源からの駆動力によって前記第2のカートリッジにおいて前記準備動作を実行し、
前記第2の現像手段を前記第2の像担持体に対して当接又は離間させることが可能であることを特徴とする画像形成装置。 a device body;
A first cartridge having a first developing means for forming a toner image on a first image carrier, and a second image carrier carrying a toner image of a color different from that of the first image carrier. a second cartridge having a second developing means for forming a toner image on the
an intermediate transfer member contactable with the first image carrier and the second image carrier;
a contact member that contacts the intermediate transfer body to form a contact portion and collects toner remaining on the intermediate transfer body;
a first drive source for rotationally driving the intermediate transfer member;
a second drive source that is different from the first drive source and that transmits a drive force to the second image carrier;
a third driving source that transmits a driving force to the second developing means;
The intermediate transfer member is rotated by the first drive source, the drive force is transmitted from the second drive source to the second image bearing member , and the drive force is applied to the second developing means by the third drive source. By transmitting the toner, a supply operation for supplying toner from the second developing means to the contact portion via the second image bearing member and a preparatory operation for image formation can be executed. and a control unit for controlling,
In an image forming apparatus in which the first cartridge and the second cartridge are detachable with respect to the apparatus main body,
The control unit performs control so that when the new first cartridge is inserted into the apparatus main body, the supply operation is performed while the second image bearing member is in contact with the intermediate transfer member. death,
When a new second cartridge is inserted into the apparatus main body, the second image bearing member and the intermediate transfer member are separated from each other by the driving force from the second driving source. performing the preparatory operation on the cartridge;
An image forming apparatus , wherein said second developing means can be brought into contact with or separated from said second image bearing member .
前記制御部が前記準備動作を実行することによって、前記除去部材が前記封止部材を除去するように構成されることを特徴とする請求項1に記載の画像形成装置。 The new first cartridge includes a sealing member for suppressing leakage of toner accommodated in the first developing means, and a toner supply from the first developing means to the first image bearing member. a removing member for removing the sealing member by receiving a driving force from the first driving source,
2. The image forming apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the removing member removes the sealing member when the control section executes the preparatory operation.
前記制御部は、前記封止部材が除去された後に、前記第1の像担持体と前記当接部材とが当接する位置に向けて前記第1の現像手段からトナーを供給することを特徴とする請求項2に記載の画像形成装置。 a contact member that contacts the first image carrier and collects toner remaining on the first image carrier;
After the sealing member is removed, the control section supplies toner from the first developing device toward a position where the first image bearing member and the contact member are in contact with each other. 3. The image forming apparatus according to claim 2.
第1の像担持体にトナー像を形成するための第1の現像手段を有する第1のカートリッジと、前記第1の像担持体とは異なる色のトナー像を担持する第2の像担持体にトナー像を形成するための第2の現像手段を有する第2のカートリッジと、
前記第1の像担持体及び前記第2の像担持体と当接可能な中間転写体と、
前記中間転写体に当接して当接部を形成し、前記中間転写体に残留したトナーを回収する当接部材と、
前記中間転写体を回転駆動させる第1駆動源と、
前記第1駆動源とは異なる第2駆動源であって、前記第2の像担持体に駆動力を伝達する前記第2駆動源と、
前記第2の現像手段に駆動を伝達する第3駆動源と、
前記第1駆動源によって前記中間転写体を回転させ、前記第2駆動源から前記第2の像担持体に駆動力を伝達し、前記第3駆動源によって前記第2の現像手段に駆動力を伝達することにより、前記第2の像担持体を介して前記第2の現像手段から前記当接部にトナーを供給するための供給動作と、画像形成するための準備動作と、を実行可能に制御する制御部と、を有し、
前記第1のカートリッジおよび前記第2のカートリッジが前記装置本体に対して着脱可能な画像形成装置において、
前記制御部は、新品の前記第1のカートリッジを前記装置本体に挿入した場合に、前記第2の像担持体を前記中間転写体に当接させた状態で前記第1のカートリッジにおける前記準備動作および前記供給動作を実行し、
新品の前記第1のカートリッジと、新品の前記第2のカートリッジを前記装置本体に挿入した場合に、前記第2の像担持体と前記中間転写体を離間させた状態で、前記第2駆動源からの駆動力によって前記第2のカートリッジにおける前記準備動作を実行した後に、前記第2駆動源から前記第2のカートリッジに駆動力を伝達しつつ、前記第2の像担持体を前記中間転写体に当接させた状態で前記第1駆動源からの駆動力によって前記中間転写体を回転させることにより前記供給動作を実行し、
前記第2の現像手段を前記第2の像担持体に対して当接又は離間させることが可能であることを特徴とする画像形成装置。 a device body;
A first cartridge having a first developing means for forming a toner image on a first image carrier, and a second image carrier carrying a toner image of a color different from that of the first image carrier. a second cartridge having a second developing means for forming a toner image on the
an intermediate transfer member contactable with the first image carrier and the second image carrier;
a contact member that contacts the intermediate transfer body to form a contact portion and collects toner remaining on the intermediate transfer body;
a first drive source for rotationally driving the intermediate transfer member;
a second drive source that is different from the first drive source and that transmits a drive force to the second image carrier;
a third drive source that transmits drive to the second developing means;
The intermediate transfer member is rotated by the first drive source, the drive force is transmitted from the second drive source to the second image bearing member, and the drive force is applied to the second developing means by the third drive source. By transmitting the toner, a supply operation for supplying toner from the second developing means to the contact portion via the second image bearing member and a preparatory operation for image formation can be executed. and a control unit for controlling,
In an image forming apparatus in which the first cartridge and the second cartridge are detachable with respect to the apparatus main body,
When a new first cartridge is inserted into the apparatus main body, the control unit performs the preparatory operation in the first cartridge while the second image bearing member is in contact with the intermediate transfer member. and performing the supply operation;
When the new first cartridge and the new second cartridge are inserted into the apparatus main body, the second driving is performed while the second image bearing member and the intermediate transfer member are separated from each other. After executing the preparatory operation in the second cartridge by the driving force from the source, while transmitting the driving force from the second driving source to the second cartridge, the second image carrier is subjected to the intermediate transfer. executing the supply operation by rotating the intermediate transfer member by a driving force from the first drive source while being in contact with the body ;
An image forming apparatus , wherein said second developing means can be brought into contact with or separated from said second image bearing member .
前記制御部が前記第2のカートリッジにおける前記準備動作を実行することによって、前記除去部材が前記封止部材を除去するように構成されることを特徴とする請求項3又は4に記載の画像形成装置。 The new second cartridge includes a sealing member for suppressing leakage of toner accommodated in the second developing means, and a toner supply from the second developing means to the second image carrier. a removing member for removing the sealing member by receiving a driving force from the second driving source, and
5. The image forming method according to claim 3 , wherein the removal member removes the sealing member by the control section executing the preparatory operation in the second cartridge. Device.
前記制御部が前記第2の現像手段を前記第2の像担持体に対して離間させた状態で前記第2のカートリッジにおける前記準備動作を実行することによって、前記封止部材を除去するように構成されることを特徴とする請求項1乃至4のいずれか1項に記載の画像形成装置。 The new second cartridge includes a sealing member for suppressing leakage of toner accommodated in the second developing means, and a toner supply from the second developing means to the second image carrier. a removing member for removing the sealing member by receiving a driving force from the third driving source,
The control unit removes the sealing member by executing the preparatory operation in the second cartridge while the second developing means is separated from the second image bearing member. 5. The image forming apparatus according to claim 1 , wherein the image forming apparatus comprises:
前記制御部は、前記封止部材が除去された後に、前記第2の像担持体と前記当接部材とが当接する位置に向けて前記第2の現像手段からトナーを供給することを特徴とする請求項7に記載の画像形成装置。 a contact member that contacts the second image carrier and collects toner remaining on the second image carrier;
After the sealing member is removed, the control section supplies toner from the second developing device toward a position where the second image bearing member and the contact member are in contact with each other. 8. The image forming apparatus according to claim 7 .
前記制御部は、前記記憶手段に記録された情報を読み取ることで、前記第1のカートリッジ、又は前記第2のカートリッジが新品であるかを検知することを特徴とする請求項1乃至9のいずれか1項に記載の画像形成装置。 wherein the second cartridge is detachable from the apparatus main body, the first cartridge and the second cartridge each have a non-volatile storage means,
10. The control unit detects whether the first cartridge or the second cartridge is new by reading information recorded in the storage unit. 1. The image forming apparatus according to item 1 or 1.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018126700A JP7166811B2 (en) | 2018-07-03 | 2018-07-03 | image forming device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018126700A JP7166811B2 (en) | 2018-07-03 | 2018-07-03 | image forming device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020008613A JP2020008613A (en) | 2020-01-16 |
| JP2020008613A5 JP2020008613A5 (en) | 2021-07-29 |
| JP7166811B2 true JP7166811B2 (en) | 2022-11-08 |
Family
ID=69151307
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018126700A Active JP7166811B2 (en) | 2018-07-03 | 2018-07-03 | image forming device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7166811B2 (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006184546A (en) | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Canon Inc | Image forming apparatus |
| JP2009175411A (en) | 2008-01-24 | 2009-08-06 | Canon Inc | Image forming device |
| JP2015022189A (en) | 2013-07-19 | 2015-02-02 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image forming apparatus |
| JP2016184143A (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2016-10-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | Developer container, developing device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus |
| JP2018072423A (en) | 2016-10-25 | 2018-05-10 | 株式会社リコー | Image formation apparatus |
-
2018
- 2018-07-03 JP JP2018126700A patent/JP7166811B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006184546A (en) | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Canon Inc | Image forming apparatus |
| JP2009175411A (en) | 2008-01-24 | 2009-08-06 | Canon Inc | Image forming device |
| JP2015022189A (en) | 2013-07-19 | 2015-02-02 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image forming apparatus |
| JP2016184143A (en) | 2015-03-27 | 2016-10-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | Developer container, developing device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus |
| JP2018072423A (en) | 2016-10-25 | 2018-05-10 | 株式会社リコー | Image formation apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020008613A (en) | 2020-01-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4208513B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| US9116459B2 (en) | Electrophotographic image forming apparatus | |
| US9098062B2 (en) | Process cartridge and image forming apparatus | |
| JP6598483B2 (en) | Cleaning device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus | |
| US9703232B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus that performs a contacting operation for contacting a developing member with an image bearing member | |
| JP7166811B2 (en) | image forming device | |
| JP2014112266A (en) | Electrophotographic image forming apparatus | |
| JP4656091B2 (en) | Developer and image forming apparatus | |
| JP4707175B2 (en) | Developing device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2006349760A (en) | Developing apparatus and image forming apparatus provided with it | |
| JP4354348B2 (en) | Charging device, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2006184796A (en) | Belt conveyance apparatus | |
| JP6679255B2 (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP2013097099A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2001228709A (en) | Toner developing device, process cartridge and electrophotographic recorder | |
| JP4882901B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus, image forming system, and image forming method | |
| JP5530964B2 (en) | Developing device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2023075866A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2021117241A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2005275022A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2023075865A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2003330267A (en) | Developing device and image forming apparatus | |
| CN111722508A (en) | Image forming apparatus with a toner supply device | |
| JP2021076808A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2006038132A (en) | Driving force transmission device and image forming device using this device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210621 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210621 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220531 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20220531 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220725 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20220927 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20221026 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 7166811 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |