JP6970871B2 - Motor drive device and refrigerator using it - Google Patents
Motor drive device and refrigerator using it Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6970871B2 JP6970871B2 JP2017208351A JP2017208351A JP6970871B2 JP 6970871 B2 JP6970871 B2 JP 6970871B2 JP 2017208351 A JP2017208351 A JP 2017208351A JP 2017208351 A JP2017208351 A JP 2017208351A JP 6970871 B2 JP6970871 B2 JP 6970871B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- motor
- brushless
- voltage
- switching element
- timing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25D—REFRIGERATORS; COLD ROOMS; ICE-BOXES; COOLING OR FREEZING APPARATUS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F25D11/00—Self-contained movable devices, e.g. domestic refrigerators
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P27/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage
- H02P27/04—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage
- H02P27/06—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters
- H02P27/08—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters with pulse width modulation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Control Of Motors That Do Not Use Commutators (AREA)
- Devices That Are Associated With Refrigeration Equipment (AREA)
Description
本発明はインバータ制御によりブラシレスDCモータを駆動するモータ駆動装置および、これを用いた冷蔵庫に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a motor drive device that drives a brushless DC motor by inverter control, and a refrigerator using the motor drive device.
従来この種のモータ駆動装置は、PWM(Pulse Width Modulation)制御の矩形波120度通電を基本としてブラシレスDCモータを駆動し、PWM制御のオンデューティが100%となったとき通電区間を120度以上に広げることで、高速・高負荷駆動領域を拡張している(例えば特許文献1参照)。 Conventionally, this type of motor drive device drives a brushless DC motor based on PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controlled square wave 120 degree energization, and when the on-duty of PWM control reaches 100%, the energized section is 120 degrees or more. By expanding to, the high-speed and high-load drive region is expanded (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
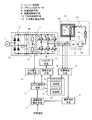
図9は特許文献1に記載されたモータ駆動装置を示すものである。図9に示すように、インバータ回路3を構成する、各スイッチング素子3aから3fが、オフからオンに移行する際、オンタイミング制御手段103により進角制御を行い、オンからオフに移行する際は、オフタイミング制御手段104で進角制御を行わないことで、オーバーラップ通電を行う。
FIG. 9 shows the motor drive device described in Patent Document 1. As shown in FIG. 9, when each of the
またモータ駆動電力が目標電力値となるように導通角と進み角およびインバータ入力直流電圧を制御して高出力、高回転を可能としつつ低損失化している(例えば特許文献2参照)。図10は特許文献2に記載されたモータ駆動装置を示すものである。図10に示すようにブラシレスDCモータの駆動制御手段201は、駆動電力を検出する電力検出手段202と、インバータの駆動信号パターンの生成とインバータ入力電圧を設定する通電パルス信号生成制御手段203を有し、駆動電力が目標設定電力値に一致するように、インバータ入力電圧値と通電角および進角を制御する。
Further, the conduction angle, the lead angle, and the inverter input DC voltage are controlled so that the motor drive power becomes the target power value to enable high output and high rotation, while reducing the loss (see, for example, Patent Document 2). FIG. 10 shows the motor drive device described in
しかしながら上記特許文献1の構成では、スイッチング素子のターンオンを早くしてブラシレスDCモータへの電力供給区間を120度以上に広げることで高負荷・高速駆動領域を拡張することは可能であるが、PWM制御を行うためスイッチング素子のオン/オフに伴う損失が発生する。さらにPWM制御による高周波スイッチングはモータ鉄損の増加が伴うという課題を有していた。 However, in the configuration of Patent Document 1, it is possible to expand the high load / high speed drive region by accelerating the turn-on of the switching element and expanding the power supply section to the brushless DC motor to 120 degrees or more, but PWM. Since the control is performed, a loss occurs due to the on / off of the switching element. Further, high frequency switching by PWM control has a problem that the motor iron loss is increased.
また、上記特許文献2に記載の構成では、ブラシレスDCモータの通電角増減により速度制御を行うため、速度制御が可能なタイミングは通電角を変更する転流時(例えば4極モータの場合1回転中に12回)に限られる。従って、外乱により急激にインバータ入力電圧が変動(特に上昇)した場合、応答性が遅れ、電圧の過剰印加による大幅な遅れ位相状態によるブラシレスDCモータの脱調停止や、脱調時における大電流の発生で、回転子の永久磁石の減磁破損といった信頼性上の課題を有していた。
Further, in the configuration described in
本発明は前記従来の課題を解決するものであり、モータ駆動装置の低損失化による機器の高効率化と、信頼性の向上を図ることを目的とする。 The present invention solves the above-mentioned conventional problems, and an object of the present invention is to improve the efficiency and reliability of a device by reducing the loss of a motor drive device.
前記従来の課題を解決するために、本発明のモータ駆動装置は、ブラシレスDCモータと、前記ブラシレスDCモータに電力を供給する6個のスイッチング素子で構成されるインバータと、前記ブラシレスDCモータの回転子の回転位置を検出する位置検出手段と、前記インバータの出力電圧を前記インバータのスイッチング素子を高周波数でオン/オフを行うことで前記ブラシレスDCモータ供給する電圧を調整するPWM制御手段と、PWM制御による前記インバータのスイッチング素子のオン時間の時比率が最大となるように前記ブラシレスDCモータの3相巻線の通電相を決める通電相制御手段と、前記インバータの入力電圧を検出する入力電圧検出手段と、交流電圧を直流電圧に変換する整流回路と、前記整流回路の出力を直流電圧にする平滑回路と、前記整流回路の整流方式を全波整流と倍電圧整流に切り替える切換え手段を有し、前記切換え手段により前記整流回路の整流方式が全波整流から倍電圧整流に切り替えたとき、前記PWM制御手段は、前記スイッチング素子のオン時間の時比率を下げるようにしている。 In order to solve the above-mentioned conventional problems, the motor drive device of the present invention includes a brushless DC motor, an inverter composed of six switching elements for supplying power to the brushless DC motor, and rotation of the brushless DC motor. Position detecting means for detecting the rotation position of the child, PWM control means for adjusting the voltage supplied by the brushless DC motor by turning on / off the switching element of the inverter at a high frequency, and PWM. An energizing phase control means that determines the energizing phase of the three-phase winding of the brushless DC motor so that the time ratio of the on-time of the switching element of the inverter by control is maximized, and an input voltage detection that detects the input voltage of the inverter. It has a means , a rectifier circuit that converts an AC voltage into a DC voltage, a smoothing circuit that converts the output of the rectifier circuit to a DC voltage, and a switching means for switching the rectification method of the rectifier circuit between full-wave rectification and double-voltage rectification. When the rectification method of the rectifier circuit is switched from full-wave rectification to double-voltage rectification by the switching means, the PWM control means reduces the time ratio of the on-time of the switching element .
これにより安定した駆動状態ではPWM制御のオン時間の時比率は100%となりインバータのスイッチング損失が大幅に低減できる。さらにPWM制御による高周波電流も大幅に抑制でき、モータ鉄損も低減できる。また入力電圧が大きく上昇した場合、PWM制御のオン時間の時比率を下げることで、モータ印加電圧の急激な上昇を抑え、過剰な電圧印加による脱調および大電流の発生を抑制することができる。
また、ブラシレスDCモータの低速・低負荷での駆動では全波整流入力でインバータ損失を抑制した高効率駆動、高速・高負荷時は倍電圧入力による高出力駆動と、駆動状態に応じた最適な駆動が可能となる。更に、全波整流から倍電圧整流への切り替えに伴う急峻な入力電圧の上昇に対しても、ブラシレスDCモータの脱調停止、過電流による減磁、あるいは急激なブラシレスDCモータの速度変動を抑制でき、信頼性の高いモータ駆動装置を提供することができる。
As a result, in a stable drive state, the time ratio of the PWM control on time becomes 100%, and the switching loss of the inverter can be significantly reduced. Furthermore, high-frequency current due to PWM control can be significantly suppressed, and motor iron loss can be reduced. Further, when the input voltage rises significantly, by lowering the time ratio of the on-time of the PWM control, it is possible to suppress a sudden rise in the motor applied voltage, and to suppress step-out and generation of a large current due to excessive voltage application. ..
In addition, when driving a brushless DC motor at low speed and low load, high efficiency drive that suppresses inverter loss with full-wave rectification input, and high output drive with double voltage input at high speed and high load, are optimal according to the drive state. It can be driven. Furthermore, even if the input voltage rises sharply due to the switch from full-wave rectification to voltage doubler rectification, detuning of the brushless DC motor, demagnetization due to overcurrent, or sudden speed fluctuation of the brushless DC motor is suppressed. It is possible to provide a highly reliable motor drive device.
本発明のモータ駆動装置は、インバータとブラスレスDCモータの損失低減で高効率化を図るとともに、入力電圧の変動時も安定した駆動ができ高い信頼性を確保するものである。 The motor drive device of the present invention aims to improve efficiency by reducing the loss of the inverter and the brassless DC motor, and can stably drive the motor even when the input voltage fluctuates to ensure high reliability.
第1の発明は、ブラシレスDCモータと、前記ブラシレスDCモータに電力を供給する6個のスイッチング素子で構成されるインバータと、前記ブラシレスDCモータの回転子の回転位置を検出する位置検出手段と、前記インバータの出力電圧を前記インバータのスイッチング素子を高周波数でオン/オフを行うことで前記ブラシレスDCモータ供給する電圧を調整するPWM制御手段と、PWM制御による前記インバータのスイッチング素子のオン時間の時比率が最大となるように前記ブラシレスDCモータの3相巻線の通電相を決める通電相制御手段と、前記インバータの入力電圧を検出する入力電圧検出手段と、交流電圧を直流電圧に変換する整流回路と、前記整流回路の出力を直流電圧にする平滑回路と、前記整流回路の整流方式を全波整流と倍電圧整流に切り替える切換え手段を有し、前記切換え手段により前記整流回路の整流方式が全波整流から倍電圧整流に切り替えたとき、前記PWM制御手段は、前記スイッチング素子のオン時間の時比率を下げるようにしている。
これにより安定した駆動状態ではスイッチング素子の高周波でのオン/オフ動作が行われないので、インバータのスイッチング損失とモータの鉄損が大幅に低減でき、さらに入力電圧が大きく上昇した時、PWM制御のオン時間の時比率を下げることで、モータ印加電圧の急激な上昇を抑え、過剰な電圧印加による脱調および大電流の発生を抑制できるので、高効率で高信頼性のモータ駆動装置を提供できる。
また、ブラシレスDCモータの低速・低負荷での駆動では全波整流入力でインバータ損失を抑制した高効率駆動、高速・高負荷時は倍電圧入力による高出力駆動と、駆動状態に応じた最適な駆動が可能となる。更に、全波整流から倍電圧整流への切り替えに伴う急峻な入力電圧の上昇に対しても、ブラシレスDCモータの脱調停止、過電流による減磁、あるいは急激なブラシレスDCモータの速度変動を抑制でき、信頼性の高いモータ駆動装置を提供することができる。
The first invention comprises a brushless DC motor, an inverter composed of six switching elements for supplying power to the brushless DC motor, and a position detecting means for detecting the rotational position of the rotor of the brushless DC motor. When the PWM control means for adjusting the output voltage of the inverter by turning on / off the switching element of the inverter at a high frequency to adjust the voltage supplied by the brushless DC motor and the ON time of the switching element of the inverter by PWM control. An energizing phase control means that determines the energizing phase of the three-phase winding of the brushless DC motor so that the ratio becomes maximum, an input voltage detecting means that detects the input voltage of the inverter, and rectification that converts an AC voltage into a DC voltage. It has a circuit, a smoothing circuit that makes the output of the rectifier circuit a DC voltage, and a switching means for switching the rectification method of the rectifier circuit between full-wave rectification and double-voltage rectification. When switching from full-wave rectification to double-voltage rectification, the PWM control means reduces the time ratio of the on-time of the switching element.
As a result, the switching element is not turned on / off at high frequencies in a stable drive state, so the switching loss of the inverter and the iron loss of the motor can be significantly reduced, and when the input voltage rises significantly, PWM control is performed. By lowering the time ratio of the on-time, it is possible to suppress a sudden rise in the motor applied voltage and suppress step-out and large current generation due to excessive voltage application, so it is possible to provide a highly efficient and highly reliable motor drive device. ..
In addition, when driving a brushless DC motor at low speed and low load, high efficiency drive that suppresses inverter loss with full-wave rectification input, and high output drive with double voltage input at high speed and high load, are optimal according to the drive state. It can be driven. Furthermore, even if the input voltage rises sharply due to the switch from full-wave rectification to voltage doubler rectification, detuning of the brushless DC motor, demagnetization due to overcurrent, or sudden speed fluctuation of the brushless DC motor is suppressed. It is possible to provide a highly reliable motor drive device.
第2の発明は、第1の発明のモータ駆動装置により駆動されるブラシレスDCモータが、冷凍サイクルの圧縮機を駆動するものである。これにより本発明のモータ駆動装置によって圧縮機のCOPを向上することが出来、高効率かつ高信頼性の冷凍サイクルを提供できる。 In the second invention, the brushless DC motor driven by the motor drive device of the first invention drives the compressor of the refrigeration cycle. Thereby, the COP of the compressor can be improved by the motor drive device of the present invention, and a highly efficient and highly reliable refrigeration cycle can be provided.
第3の発明は、第1または第2の発明のモータ駆動装置により駆動される圧縮機を有する冷蔵庫である。これにより高効率高信頼性の冷凍サイクルにより、低消費電力で信頼性の高い冷蔵庫が提供できる。更に高周波スイッチングに伴う高周波数帯域の騒音が抑制され冷蔵庫の静音化が可能となる。 The third invention is a refrigerator having a compressor driven by the motor drive device of the first or second invention. As a result, a highly efficient and highly reliable refrigerating cycle can provide a highly reliable refrigerator with low power consumption. Furthermore, noise in the high frequency band associated with high frequency switching is suppressed, and the refrigerator can be made quieter.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。なお、本実施の形態によって本発明が限定されるわけではない。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. The present invention is not limited to the present embodiment.
(実施の形態1)
図1は本発明の実施の形態1におけるモータ駆動装置のブロック図を示すものである。
(Embodiment 1)
FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of a motor drive device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
図1において、交流電源1は一般的な商用電源であり、日本国内の場合実効値100V50Hzまたは60Hzである。コンバータ回路2は交流電源1を直流電圧に変換する。図1におけるコンバータ回路2は4個のダイオードをブリッジ接続した整流回路2aとコンデンサによる平滑回路2b、出力電圧を切換えるスイッチ部2cで構成することで、出力電圧を倍電圧整流と全波整流の2段階に切り替える構成としている。
In FIG. 1, the AC power supply 1 is a general commercial power supply, and in the case of Japan, the effective value is 100 V 50 Hz or 60 Hz. The
インバータ回路3は6個のスイッチング素子3a〜3fで構成され、本実施の形態1ではMOSFETを用いる。そして、各スイッチング素子を3相ブリッジ接続し、任意のスイッチング素子のオン/オフを切り替えることで、入力直流電圧を3相交流電圧に変換する。
The
ブラシレスDCモータ4は3相巻線を有する固定子と永久磁石を有する回転子により構成され、インバータ回路3からの3相交流電力により駆動される。
The
位置検出手段5はブラシレスDCモータ4の磁極位置を検出するものであり、本実施の形態1ではモータ端子電圧から、回転子の回転により固定子巻線に発生する誘起電圧の位相(ゼロクロスポイント)を検出する方式としている。ただし、ホールIC等の位置センサを用いる方法や、電流センサ等による電流検出方法等でも構わない。
The position detecting means 5 detects the magnetic pole position of the
速度検出手段6は位置検出手段5の出力信号からブラシレスDCモータ4の駆動速度を検出するものであり、本実施の形態1ではブラシレスDCモータ4の回転子の回転により固定子巻線に生じる誘起電圧のゼロクロス周期を基に算出する。
The
速度誤差検出手段7は、速度検出手段6により得たブラシレスDCモータ4の駆動速度と目標速度との差を検出する。
The speed
通電相制御手段8は位置検出手段5からの信号を基に、前記ブラシレスDCモータ4の固定子巻線に電気角90度以上150度以下の通電角範囲で電力を供給する相を設定する。また通電相制御手段8はスイッチング素子3a〜3fをターンオンおよびターンオフするタイミングを設定するオンタイミング制御部9と、オフタイミング制御部10とを有しているため、インバータ回路3のスイッチング素子のオン、オフのそれぞれのタイミングを個別に設定することができる。
The energizing phase control means 8 sets a phase for supplying electric power to the stator winding of the
PWM制御手段11は、インバータ回路3の3相交流出力をPWM制御で調節し、ブラシレスDCモータ4が目標速度で駆動するように制御する。ここで『ブラシレスDCモータ巻線への電力を供給する電気角最小値の2倍から電気角120度を引いた値』を『電気角120度』で除した値より大きいPWMオン時間時比率で駆動している場合、PWM制御手段11はオン時間の時比率が最大値(100%)となるようにオフタイミング制御部10はスイッチング素子のターンオフタイミングを早く行っていく。具体的には、各スイッチング素子のオン区間の最小値が90度の場合、(90度×2−120)÷120=50[%]となり、PWMオン時間比率が50%以上で駆動している場合、オン時間比率100%となるように、スイッチング素子のオフタイミングを早く行うようにしていく。
The PWM control means 11 adjusts the three-phase AC output of the
ターンオフタイミングの変更は、ブラシレスDCモータ4の動作状態への急激な変化を防ぐため、徐々に早めて行くことが望ましいが、1度の制御周期で行っても特に問題ない。尚、PWM制御手段11によるオン時間時比率調整でのブラシレスDCモータ4の速度制御は、先述したPWM制御のオン時間時比率以下で駆動している場合に限られるため、起動時や、低速駆動時、低負荷駆動時、および倍電圧入力時における、比較的低負荷、低速駆動時に行われる。それ以外の安定した駆動状態では、PWM制御手段11はオン時間時比率が100%となるように、通電相制御手段8によるスイッチング素子のオフタイミングを調整してブラシレスDCモータ4の速度制御を行う。
It is desirable to gradually change the turn-off timing in order to prevent a sudden change to the operating state of the
波形合成手段12はPWM制御手段11により生成したPWM信号と通電相制御手段8により生成した信号を合成し、合成した信号を基にドライブ手段13によりインバータ回路3の各スイッチング素子3a〜3fをオンまたはオフ状態にして、生成した任意の3相交流電圧をブラシレスDCモータ4に供給し駆動する。
The waveform synthesis means 12 synthesizes the PWM signal generated by the PWM control means 11 and the signal generated by the energization phase control means 8, and the drive means 13 turns on the
電圧検出回路14は、直列に接続した複数の抵抗を平滑回路の出力部に接続し、任意の抵抗の両端電圧を取り出すようにしている。入力電圧検出手段15は電圧検出回路14から取り出した電圧からインバータ回路3の入力電圧を検出し、PWM制御手段11に入力する。
The
PWM制御手段11は入力電圧が急峻に変動(特に上昇)したことを検出したとき、その電圧の上昇率に応じて、PWM制御によるインバータ回路3のスイッチング素子のオン時間の時比率を設定(電圧上昇時は時比率を下げる)し、波形合成手段12に出力する。すなわち、インバータ入力電圧が急激に上昇したとき、ブラシレスDCモータの入力電圧が大きく変化しないように、PWM制御のオン時間時比率が瞬時に下げられ、任意の通電角でPWM制御により駆動が行われる。以降、通電相制御手段8のオフタイミング制御部10により、PWM制御のオン時間時比率が100%となるように、スイッチング素子のオフタイミングが進めていく。
When the PWM control means 11 detects that the input voltage fluctuates sharply (particularly rises), the PWM control means 11 sets the time ratio of the on-time of the switching element of the
なお、インバータ回路3への入力電圧が急激に低下した場合、PWM制御を行っているときは入力電圧の低下度合いに応じて、PWM制御のオン時間時比率を増加して、ブラシレスDCモータ4の入力電圧の変化を抑制することも可能であるが、時比率100%で駆動している場合は対応することはできない。しかしながら、瞬時停電等で入力電圧が急激に低下した場合は、平滑回路2bに蓄積された電荷からブラシレスDCモータ4に電力が供給されるため、急激な電圧低下は回避される。したがって、電圧の急激な低下によるブラシレスDCモータ4の脱調は発生しにくく、入力電圧変化を抑制することは特に必要でない。
When the input voltage to the
圧縮要素16は、ブラシレスDCモータ4の回転子の軸に接続され、冷媒ガスを吸入し、圧縮して吐出する。このブラシレスDCモータ4と圧縮要素16とを同一の密閉容器に収納し、圧縮機17を構成する。圧縮機17で圧縮された吐出ガスは、凝縮器18、減圧器19、蒸発器20を通って圧縮機17の吸い込みに戻るような冷凍空調システムを構成し、凝縮器18では放熱、蒸発器20では吸熱を行うので、加熱や吸熱を行うことができる。尚、必要に応じて凝縮器18や蒸発器20に送風機などを使い、熱交換をさらに促進することもある。また本実施の形態1では、冷凍空調システムは冷蔵庫21の冷凍サイクルとして用い、蒸発器20は断熱壁22で囲われた食品貯蔵室23内を冷却するために用いる。
The
以上のように構成されたモータ駆動装置について以下その動作と作用を説明する。 The operation and operation of the motor drive device configured as described above will be described below.
図2は本実施の形態1におけるモータ駆動装置のタイミングチャート図である。図2(a)は一般的な120度通電での駆動波形およびタイミング図であり、(b)はオフタイミング制御部10によりスイッチング素子のオフタイミングを調整してブラシレスDCモータ4を駆動したときの波形とタイミングを示している。ブラシレスDCモータ4の回転により発生する誘起電圧をE、端子電圧をVuとして示している。両波形ともU相のみを示しているが、V相およびW相波形はそれぞれ位相が120度ずれた同形状の波形となっている。高圧側に接続したスイッチング素子3a、3b、3cの駆動信号をU+、V+、W+として示し、低圧側接続のスイッチング素子3d、3e、3fの駆動信号はそれぞれの高圧側SW素子の駆動信号から180度位相がずれた波形となる。
FIG. 2 is a timing chart of the motor drive device according to the first embodiment. FIG. 2A is a general drive waveform and timing diagram when energized at 120 degrees, and FIG. 2B is a case where the off-timing of the switching element is adjusted by the off-
固定子巻線の通電相の切換えタイミング(図示せず)を図るために、回転子磁極相対位置検出に誘起電圧のゼロクロスポイントを位置信号として検出する。ゼロクロスポイントの検出は当該相巻線への電圧印加がされていない(図2に示すU相では、スイッチング素子3a、3dの両方がオフとなる)区間(C1、C2、C3、C4)に現れる誘起電圧とインバータ入力電圧Vdcの1/2との大小関係が反転するポイント(P1、P2)を検出する。よって電気角1周期あたり各相2回、3相合計で6回、電気角60度毎に位置信号が発生する。
In order to determine the switching timing (not shown) of the energized phase of the stator winding, the zero cross point of the induced voltage is detected as a position signal in the rotor magnetic pole relative position detection. The detection of the zero cross point appears in the section (C1, C2, C3, C4) in which the voltage is not applied to the phase winding (in the U phase shown in FIG. 2, both the
図2(a)に示す120度通電におけるスイッチング素子(高圧側接続の3a、3b、3c)の通電パターン(U+、V+、W+)を見ると、位置検出後(P1)電気角30度後にW+のオフと同時にU+(スイッチング素子3a)をオンすることで、電気角360度全範囲で常に3相いずれかの巻線が通電される。一方、図2(b)では位置検出(P1)後、電気角30度経過する前にW+(スイッチング素子3c)をオフにしたのち、電気角30度後にU+をオンするようにしている。
Looking at the energization patterns (U +, V +, W +) of the switching element (3a, 3b, 3c connected on the high voltage side) at 120 degree energization shown in FIG. By turning on U + (switching
C1〜C4区間で誘起電圧が現れるのは他相のスイッチング素子がオンしている、即ちPWM制御のオン期間のみである。従って、スイッチング素子のターンオフは、ターンオンより早く行い、ブラシレスDCモータ4への電力供給区間を短くしている。これにより固定子巻線の電力供給区間が短くなり、PWM制御によるオン・オフ回数が少なくなるので、インバータ回路3の損失が抑制できる。更に、電力供給区間を短くすることで、PWM制御のオン時間が長くなり、位置検出信号の取得可能期間が長くなるので、位置検出精度が向上することになる。
The induced voltage appears in the C1 to C4 sections only when the switching element of the other phase is on, that is, only during the on period of the PWM control. Therefore, the turn-off of the switching element is performed earlier than the turn-on, and the power supply section to the
さらに、スイッチング素子をオフするタイミングは位置検出直後から、位置検出後電気角30度経過(位置検出P1に対して区間A1の範囲)後までとして、当該位置検出(P1)で確実に転流可能な範囲且つ、誘起電圧に対して進み位相となるようにして、遅れ位相によるトルク低下が発生しないように考慮している。 Further, the timing of turning off the switching element is from immediately after the position detection to after the electric angle of 30 degrees has elapsed after the position detection (the range of the section A1 with respect to the position detection P1), and the commutation can be reliably performed by the position detection (P1). Consideration is given so that the torque does not decrease due to the delayed phase by setting the lead phase with respect to the induced voltage in a wide range.
このようにスイッチング素子(3a〜3f)のオフタイミングを位置検出直後から30度以内とすることで、3相巻線への電力供給区間を90度以上120度以下に調節して、電力供給休止区間(A1、A2、A3)が短いほど大きな進角B(電力無供給区間の電気角の1/2)が自動的に付加されるようになる。これにより、モータトルクが増加し電力無供給区間があるにもかかわらず脱調等の無い安定した駆動が可能となる。 By setting the off timing of the switching element (3a to 3f) within 30 degrees immediately after the position is detected in this way, the power supply section to the three-phase winding is adjusted to 90 degrees or more and 120 degrees or less, and the power supply is suspended. The shorter the section (A1, A2, A3), the larger the advance angle B (1/2 of the electric angle of the non-power supply section) is automatically added. As a result, the motor torque increases and stable driving without step-out or the like is possible even though there is a non-power supply section.
負荷の増加等によりスイッチング素子のオフタイミングが位置検出後30度となったときが、120度通電で駆動可能な最大負荷である。この時オフタイミングを位置検出後30度の位置に固定し、PWM制御のオン時間時比率を100%とした状態で、オンタイミングを最大30度まで進める(即ち位置検出信号取得と同時に転流)ことで150度まで通電角を広げることができる。このときブラシレスDCモータ4の入力電流は最大17%程度増加し、駆動領域の拡張が可能となる。
When the off timing of the switching element reaches 30 degrees after the position is detected due to an increase in the load or the like, the maximum load that can be driven by energizing 120 degrees is the maximum load. At this time, the off-timing is fixed at the position of 30 degrees after the position is detected, and the on-timing is advanced up to 30 degrees with the on-time ratio of PWM control set to 100% (that is, commutation at the same time as the position detection signal is acquired). This makes it possible to widen the energization angle up to 150 degrees. At this time, the input current of the
次にスイッチング素子のオフタイミング調整動作について、フローチャートを用い、その動作を説明する。 Next, the operation of the off-timing adjustment of the switching element will be described using a flowchart.
図3はスイッチング素子のオフタイミング制御の開始を判断するフローチャート図である。図3において、まずS11において、PWM制御手段11で生成したスイッチング素子のオン時間時比率が所定値より大きくなっているかを確認し、所定値より大きい場合はS12に進みオフタイミング調整制御を開始し、所定値より小さい場合はPWM制御を行うようにする。オン時間時比率の所定値の設定は、本実施の形態1では各スイッチング素子の最低オン区間を電気角90度としているため、{(90度×2)−120度}/120度から50%としているが、用途により適正な任意の値を選定する。 FIG. 3 is a flowchart for determining the start of off-timing control of the switching element. In FIG. 3, first, in S11, it is confirmed whether the on-time ratio of the switching element generated by the PWM control means 11 is larger than the predetermined value, and if it is larger than the predetermined value, the process proceeds to S12 and the off-timing adjustment control is started. If it is smaller than a predetermined value, PWM control is performed. In the first embodiment, the minimum on section of each switching element is set to an electric angle of 90 degrees, so that the setting of the predetermined value of the on-time ratio is from {(90 degrees × 2) −120 degrees} / 120 degrees to 50%. However, select an appropriate value depending on the application.
このようにスイッチング素子のオフタイミング調整制御の開始を所定のPWMオン時間時比率以上の時としてPWM制御と併用することで、起動時等の極端に駆動速度が低い場合や、低速駆動時で非常に負荷が低い場合、倍電圧入力時で比較的負荷が軽い時や低速時などで、巻線への電力供給区間が極端に短くなることによる起動の失敗や不安定な運転状態、あるいは極端なトルク低下等を防止し、あらゆる負荷条件でも安定した駆動ができるようにしている。 By using the start of the off-timing adjustment control of the switching element together with the PWM control when the predetermined PWM on-time ratio or more is used in this way, it is extremely low when the drive speed is extremely low such as at startup or when the drive is at low speed. When the load is low, when the load is relatively light at the time of voltage doubler input, or when the load is low, the power supply section to the winding becomes extremely short, resulting in startup failure, unstable operating conditions, or extreme. It prevents torque reduction, etc., and enables stable driving under all load conditions.
図4はPWM制御からオフタイミング調整への移行を示すフローチャート図である。図3に示したフローにより、オフタイミング調整制御の開始を決定したとき、S21においてスイッチング素子のオフタイミングを任意の時間早く行い、S22でPWM制御により速度制御を行う。オフタイミングを早くすることで、ブラシレスDCモータ4への電力供給区間が短くなっていくため、PWM制御によるオン時間の時比率は増加することになる。S23でPWM制御によるオン時間時比率が100未満であるときS21に戻りその動作を続ける。S23でオン時間時比率が100%に到達した時、S24に進みオン時間時比率を100%の状態を保持して、以降はS25でスイッチング素子のオフタイミングの調整でブラシレスDCモータ4が目標速度で駆動するように速度制御を行う。さらに、スイッチング素子のオフタイミングが位置検出後30度(即ち120度通電状態)となったときは、オンタイミングを位置検出直後から位置検出後30度までの間で調整を行うオンタイミング制御を行い、ブラシレスDCモータの駆動可能領域を拡張し、目標速度で駆動する。
FIG. 4 is a flowchart showing the transition from PWM control to off-timing adjustment. When the start of the off-timing adjustment control is determined by the flow shown in FIG. 3, the off-timing of the switching element is performed earlier in S21 by an arbitrary time, and the speed is controlled by PWM control in S22. By advancing the off timing, the power supply section to the
ここでインバータ回路3への入力電圧が急激に上昇した場合の動作について説明する。これは商用電源に瞬時停電が生じたことでインバータ回路3の入力電圧低下状態からの復帰時や、コンバータ回路2の整流方式が全波整流から倍電圧整流に切り替わった瞬間を想定している。
Here, the operation when the input voltage to the
図5は本発明の実施の形態1におけるインバータ回路3への入力電圧が大きく上昇した場合の動作フローチャートであり、図1と合わせてその動作を説明する。
FIG. 5 is an operation flowchart when the input voltage to the
まずS31において入力電圧検出手段15は電圧検出回路14から取得した電圧からインバータ回路3の入力電圧を検出する。次にS32においてPWM制御手段11は、インバータ回路3の入力電圧が前回検出値より規定値以上上昇していないかを確認し、規定値以上の上昇が無い場合はS35で今回の検出値を前回値として格納し処理を抜ける。
First, in S31, the input
一方S32で電圧上昇が大きいと判断した場合S33において、検出した入力電圧に応じたPWM制御のオン時間時比率を計算する。本発明の実施の形態1でのオン時間時比率計算は、電圧変動が生じる前後でブラシレスDCモータ4の印加電圧を等しくするように、「オン時間時比率[%]=(前回検出電圧[V]/今回検出電圧[V])×100」として算出し、PWM制御手段11は、S34で算出したオン時間時比率でPWM波形を出力したあと、S35で今回の検出値を前回値として格納する。
On the other hand, when it is determined in S32 that the voltage rise is large, in S33, the on-time ratio of the PWM control according to the detected input voltage is calculated. In the calculation of the on-time ratio in the first embodiment of the present invention, "on-time ratio [%] = (previous detection voltage [V]" so that the applied voltage of the
このようにインバータ回路3への入力電圧が急激に上昇した時、インバータ回路3への入力電圧の変化前後でのブラシレスDCモータ4への入力電圧が同等となるようなPWM制御のオン時間時比率を瞬時に計算し出力することで、ブラシレスDCモータへの入力電圧の急激な変化を抑制し、脱調および回転子永久磁石の減磁の原因となる過電流の発生を防止している。
When the input voltage to the
また、インバータ回路3への入力電圧を全波整流から、倍電圧整流に変更して、ブラシレスDCモータ4の出力範囲を拡張する際においても、ブラシレスDCモータ4を一旦停止することなく切換えることが出来るので、非常に使い勝手の良いモータ駆動装置を提供できる。
Further, even when the input voltage to the
なお、入力電圧の検出周期は、電圧変動に対する応答性を良くするために、PWMタイマ周期で行うことが一番好ましいが、使用するプロセッサの計算能力やA/D変換速度などを考慮して設定する。 The input voltage detection cycle is most preferably set by the PWM timer cycle in order to improve the responsiveness to voltage fluctuations, but it is set in consideration of the computing power of the processor to be used and the A / D conversion speed. do.
次にスイッチング素子のオフタイミング調整制御への移行後のブラシレスDCモータの速度制御について図1および図6を用いてその動作を説明する。 Next, the operation of the speed control of the brushless DC motor after the shift to the off-timing adjustment control of the switching element will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 and 6.
図6は本実施の形態1のスイッチング素子のオフタイミング調整制御の動作フローチャート図である。図6においてまずS41において、速度検出手段6で検出したブラシレスDCモータ4の駆動速度と目標速度との偏差を速度誤差検出手段7で検出し、目標速度より早い場合はS42に進む。S42では、PWM制御手段11でのオン時間時比率100%を保持して、オフタイミング制御部10によりオフタイミングを早くすることが可能か否かを判断し、可能であればスイッチング素子のオフ時間を早めることで巻線への電力供給区間を減じてブラシレスDCモータ4の速度が低下するように速度制御を行い(S43)、不可能であればPWM制御手段11におけるPWM制御を併用する(S44)。本実施の形態1において、オフタイミングを早くすることが可能か否かの判断は、スイッチング素子のオフタイミングが位置検出後すぐである場合はこれ以上タイミングを早めることが出来ないと判断する。本実施の形態1では進角を0度としているので固定子巻線への最低電力供給区間は電気角90度となる。
FIG. 6 is an operation flowchart of the off-timing adjustment control of the switching element of the first embodiment. In FIG. 6, first, in S41, the speed
ブラシレスDCモータ4の駆動速度が目標速度より遅いと判断(S45)した時S46に進み、スイッチング素子のオフが位置検出から電気角30度経過するまでに行われているかを判断する。オフタイミングが電気角30度経過より前に行われている場合S47に進みスイッチング素子のオフタイミングを遅らせて、ブラシレスDCモータの巻線への電力供給区間を増やし、駆動速度が上昇するように速度制御を行う。S46でオフスイッチング素子のオフタイミングが電気角30度経過位置である場合はS48に進む。S48ではこれ以上スイッチング素子のオフタイミングを遅らせた場合、誘起電圧に対して印加電圧位相が遅れ位相となり、モータトルクの低下およびこれに伴う脱調等の可能性があるため、オンタイミングを早めることで巻線への電力供給区間を増やしてブラシレスDCモータの駆動速度が上昇するように速度制御を行う。
When it is determined (S45) that the drive speed of the
本実施の形態1では、オンタイミングを早める上限は位置検出直後までとして、このときの巻線への最大電力供給区間は電気角150度となり、このときブラシレスDCモータの電流は約17%増加し、出力範囲も拡張することができる。 In the first embodiment, the upper limit for accelerating the on-timing is immediately after the position is detected, and the maximum power supply section to the winding at this time is an electric angle of 150 degrees, at which time the current of the brushless DC motor increases by about 17%. , The output range can also be expanded.
なお、駆動速度が目標速度と等しい場合はS45にて制御を抜けることになる。 If the drive speed is equal to the target speed, the control is exited in S45.
また、本実施の形態1では進角を0度としているため、電気角120度通電でスイッチング素子のオフタイミングとオンタイミングが位置検出後30度のタイミングで一致して行われることになる。固定子内部に永久磁石が埋め込まれたIPMモータでは、最適な駆動実現のためには最適な進角を設ける必要がある。従ってIPMモータ等、あらゆるモータを最適に駆動出来るように、スイッチング素子のオフタイミング調整範囲は、位置検出直後から、位置検出タイミングから「(電気角30度)−(進角)」まで経過した位置。スイッチング素子のオンタイミングは、位置検出タイミングから「(電気角30度)−(進角)」だけ経過したタイミング(例えば進角10度の場合、ターンオフは位置検出から電気角20度経過までの範囲で調整し、ターンオンは位置検出後電気角20度後)で行い、かつ位置検出からターンオフまでの電気角と、位置検出からターンオンまでの電気角の和を60度以下として、ターンオフをターンオンより電気角0度から30度までの任意の範囲で調整できるようにして、位置検出から電気角30度までの間で進角とオン・オフのタイミングを自由に設定可能としている。 Further, since the advance angle is set to 0 degrees in the first embodiment, the off timing and the on timing of the switching element are coincidently performed at the timing of 30 degrees after the position is detected by energizing the electric angle of 120 degrees. In an IPM motor in which a permanent magnet is embedded inside the stator, it is necessary to provide an optimum advance angle in order to realize an optimum drive. Therefore, the off-timing adjustment range of the switching element is the position where "(electric angle 30 degrees)-(advance angle)" has passed from the position detection timing immediately after the position detection so that all motors such as IPM motors can be driven optimally. .. The on-timing of the switching element is the timing when only "(electric angle 30 degrees)-(advance angle)" has elapsed from the position detection timing (for example, in the case of an advance angle of 10 degrees, the turn-off is in the range from the position detection to the elapse of 20 degrees electric angle. Turn-on is performed after 20 degrees of electric angle after position detection), and the sum of the electric angle from position detection to turn-off and the electric angle from position detection to turn-on is 60 degrees or less, and turn-off is electric from turn-on. The angle can be adjusted in an arbitrary range from 0 degrees to 30 degrees, and the advance angle and on / off timing can be freely set from the position detection to the electric angle of 30 degrees.
尚、進角を付加したときの各スイッチング素子のオン区間は電気角で「90度+進角」から120度の範囲で調整されることになる。 The on section of each switching element when the advance angle is added is adjusted in the range of "90 degrees + advance angle" to 120 degrees in terms of the electric angle.
さらにブラシレスDCモータ4を高速・高負荷で駆動する場合は、ターンオフタイミングを位置検出から「(電気角30度)−(進角)」経過したタイミングとして、ターンオンタイミングを位置検出直後から、位置検出から「電気角30度−進角」だけ経過したタイミングの範囲で調整することで各スイッチング素子のオン区間を電気角120度から「電気角150−進角」の範囲で調整できる。
Furthermore, when driving the
従って、スイッチング素子のターンオン、ターンオフタイミングの調整により電気角90度から150度までの範囲(進角0度の時)でブラシレスDCモータへの電力供給区間を調整できることになり、低速・低負荷の駆動から高速・高負荷の駆動まで幅広い負荷・速度状態での駆動に対応可能である。 Therefore, by adjusting the turn-on and turn-off timings of the switching element, the power supply section to the brushless DC motor can be adjusted in the range of the electric angle of 90 degrees to 150 degrees (when the advance angle is 0 degrees), and the power supply section to the brushless DC motor can be adjusted at low speed and low load. It can handle a wide range of loads and speeds, from driving to high-speed and high-load driving.
次に本実施の形態1におけるブラシレスDCモータの端子電圧について図6を用いて説明する。図7(a)および(b)は図2(a)における区間C1、F1を示し、図7(c)および(d)は図2(b)における区間C3,F2を示している。 Next, the terminal voltage of the brushless DC motor according to the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIG. 7 (a) and 7 (b) show sections C1 and F1 in FIG. 2 (a), and FIGS. 7 (c) and 7 (d) show sections C3 and F2 in FIG. 2 (b).
図7(a)、(b)に示すように120度通電のPWM制御での波形を示す図2(a)は高周波のPWMキャリア周波数成分(周期f)が重畳されている。また図7(a)に示すようにC1区間では、PWM制御がオンした瞬間にモータ巻線や浮遊容量等の影響によるリンギングノイズ成分も重畳する。C1区間はブラシレスDCモータの端子電圧Vuとインバータ入力電圧の1/2を比較して、その大小関係が反転するポイントをブラシレスDCモータの誘起電圧のゼロクロス点(P点)として検出するが、リンギングノイズ成分によりPx点と誤検出してしまう。この位置検出ズレは、ブラシレスDCモータの駆動速度の脈動や振動、騒音の増大、駆動効率の低下などの原因となる。 As shown in FIGS. 7 (a) and 7 (b), FIG. 2 (a) showing a waveform under PWM control of 120-degree energization is superimposed with a high-frequency PWM carrier frequency component (period f). Further, as shown in FIG. 7A, in the C1 section, a ringing noise component due to the influence of the motor winding, stray capacitance, etc. is superimposed at the moment when the PWM control is turned on. In the C1 section, the terminal voltage Vu of the brushless DC motor is compared with 1/2 of the inverter input voltage, and the point where the magnitude relationship is reversed is detected as the zero crossing point (point P) of the induced voltage of the brushless DC motor, but ringing. It is erroneously detected as a Px point due to the noise component. This position detection deviation causes pulsation and vibration of the drive speed of the brushless DC motor, an increase in noise, a decrease in drive efficiency, and the like.
一方で図7(c)に示すように、PWM制御のオン時間時比率を100%とした場合、端子電圧Vuには誘起電圧波形が現れ、正確なゼロクロスポイント(P点)での位置検出が可能であり、低騒音、低振動、低損失な安定した駆動が実現できる。 On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 7 (c), when the on-time ratio of PWM control is 100%, an induced voltage waveform appears at the terminal voltage Vu, and the position can be detected accurately at the zero cross point (point P). It is possible, and stable drive with low noise, low vibration, and low loss can be realized.
また区間F1区間では、図7(b)に示すようにPWM制御による高周波でのスイッチング素子のオン・オフに伴うスイッチング損失が発生するが、図7(d)に示すようにオン時間時比率100%の駆動ではスイッチング動作は行われないためスイッチング損失は発生せず、回路損失の低減による高効率化が実現できる。 Further, in the section F1, as shown in FIG. 7 (b), a switching loss occurs due to the on / off of the switching element at high frequency by PWM control, but as shown in FIG. 7 (d), the on-time ratio is 100. Since the switching operation is not performed in the% drive, no switching loss occurs, and high efficiency can be realized by reducing the circuit loss.
さらにブラシレスDCモータに流れる電流を図8に示す。図8(a)は120度通電によるPWM制御での波形であり、PWM制御でのスイッチング素子のオン・オフに伴う高周波電流成分が重畳していることが分かる。この高周波電流成分はモータ鉄損の原因となる一方、図8(b)に示すPWM制御のオン時間時比率100%での運転では高周波電流成分の発生はないため、モータ損失の低減によるモータ駆動装置の高効率化が図れる。 Further, the current flowing through the brushless DC motor is shown in FIG. FIG. 8A is a waveform in the PWM control by energizing 120 degrees, and it can be seen that the high frequency current component accompanying the on / off of the switching element in the PWM control is superimposed. While this high-frequency current component causes motor iron loss, the high-frequency current component does not occur during operation at the on-time ratio of 100% for PWM control shown in FIG. 8 (b), so that the motor is driven by reducing the motor loss. The efficiency of the device can be improved.
以上のように構成したモータ駆動装置で圧縮機を駆動する冷却システムを持つ冷蔵庫について説明する。 A refrigerator having a cooling system for driving a compressor with a motor drive device configured as described above will be described.
近年の冷蔵庫は、真空断熱材の採用など断熱技術の向上により、外部からの熱侵入が非常に少なくなっている。このため扉開閉が頻繁に行われる朝夕の家事時間帯を除けば、1日の大半で冷蔵庫内は安定した冷却状態にあり、圧縮機は冷凍能力を下げた低速・低負荷での駆動が行われている。従って、冷蔵庫の消費電力を削減するためには、圧縮機すなわちブラシレスDCモータの低速・低出力時の駆動効率を上げることが非常に有効である。 In recent years, refrigerators have very little heat intrusion from the outside due to improvements in heat insulation technology such as the adoption of vacuum heat insulating materials. For this reason, except for the morning and evening housework hours when doors are frequently opened and closed, the refrigerator is in a stable cooling state for most of the day, and the compressor is driven at low speed and low load with reduced refrigerating capacity. It has been. Therefore, in order to reduce the power consumption of the refrigerator, it is very effective to increase the driving efficiency of the compressor, that is, the brushless DC motor at low speed and low output.
本発明の実施の形態1では、ブラシレスDCモータが低速・低負荷で駆動している状態において、PWM制御による高周波のオン・オフ制御を行わず、PWMオン時間時比率を100%となるように、スイッチング素子のオンまたはオフタイミングを調整しながらブラシレスDCモータの駆動速度制御を行う。これによりインバータ回路3はPWM制御によるスイッチングロスの発生が無くインバータの回路効率を大幅に向上することが出来る。
In the first embodiment of the present invention, when the brushless DC motor is driven at a low speed and a low load, the high frequency on / off control by the PWM control is not performed, and the PWM on time ratio is 100%. , The drive speed of the brushless DC motor is controlled while adjusting the on or off timing of the switching element. As a result, the
本実施の形態1では、インバータ回路3のスイッチング素子にはMOSFETを用いている。MOSFETはその構造的特徴から、オン時の出力電流の経路にPN接合を持たないため、特に低電流出力時におけるオン時の損失は、IGBT等の他のパワーデバイスと比較して非常に低くなる。
In the first embodiment, a MOSFET is used as the switching element of the
先述したように冷蔵庫は1日の大半で低速・低負荷での駆動がされているためブラシレスDCモータに流れる電流が低い。従って、本発明のモータ駆動装置を冷蔵庫の圧縮機に用いるとき、インバータ回路3のスイッチング素子にMOSFETを用いることは、冷蔵庫の消費電力の低減に非常に有効となる。
As mentioned above, since the refrigerator is driven at low speed and low load for most of the day, the current flowing through the brushless DC motor is low. Therefore, when the motor drive device of the present invention is used for the compressor of the refrigerator, using the MOSFET for the switching element of the
また、PWM制御によるオン・オフ制御を行わないことでブラシレスDCモータの巻線電流には高周波電流成分が無く、モータ鉄損を大幅に抑制できモータ効率の向上が図れる。 Further, by not performing on / off control by PWM control, the winding current of the brushless DC motor does not have a high frequency current component, the motor iron loss can be significantly suppressed, and the motor efficiency can be improved.
さらにPWM制御は一般的に1kHから20kHz程度のPWM周波数でのスイッチング動作が行われ、この周波数成分が騒音として発生する。冷蔵庫は昼夜にかかわらず1日中運転しているため、静音設計は非常に重要である。本実施の形態1のモータ駆動装置は、オン時間の時比率が100%であり、PWM制御に起因する騒音の発生が無いため、冷蔵庫の静音設計に非常に有効である。また、冷蔵庫は圧縮機が一旦停止した場合、圧縮機の機械部の信頼性の観点から、低圧側と高圧側の圧力差が平衡するまで再起動を遅延する必要があるが、ブラシレスDCモータの入力電圧が急上昇したときも、停止することなく安定した駆動を継続できるので、圧縮機停止による庫内温度の上昇もなく、安定した冷却状態を保つことができる。 Further, in PWM control, a switching operation is generally performed at a PWM frequency of about 1 kHz to 20 kHz, and this frequency component is generated as noise. Quiet design is very important because the refrigerator runs all day, day and night. The motor drive device of the first embodiment has an on-time time ratio of 100% and does not generate noise due to PWM control, so that it is very effective for a quiet design of a refrigerator. In addition, once the compressor is stopped, it is necessary to delay the restart of the refrigerator until the pressure difference between the low pressure side and the high pressure side is balanced from the viewpoint of the reliability of the mechanical part of the compressor. Even when the input voltage suddenly rises, stable driving can be continued without stopping, so a stable cooling state can be maintained without the rise in the refrigerator temperature due to the compressor stopping.
さらに冷蔵庫の負荷増大に伴い、高速駆動により冷凍能力を上げた運転を行いたい場合も、ブラシレスDCモータの入力電圧を、圧縮機の停止による庫内冷却のロス無く、切換えることが出来る。 Further, as the load on the refrigerator increases, the input voltage of the brushless DC motor can be switched without the loss of cooling inside the refrigerator due to the stop of the compressor even when it is desired to perform the operation with the refrigerating capacity increased by high-speed driving.
以上のように本発明にかかるモータ駆動装置は、モータ駆動装置の回路損失の低減およびモータ効率の向上、高信頼性、駆動騒音と振動の低減が可能となるため、冷蔵庫、エアコン、洗濯機、ポンプ、扇風機、ファン、電気掃除機など、ブラシレスDCモータを用いたあらゆる機器にも適用できる。 As described above, the motor drive device according to the present invention can reduce the circuit loss of the motor drive device, improve the motor efficiency, have high reliability, and reduce the drive noise and vibration. Therefore, the refrigerator, the air conditioner, the washing machine, and the like. It can be applied to all devices using brushless DC motors such as pumps, electric fans, fans, and vacuum cleaners.
3 インバータ
4 ブラシレスDCモータ
5 位置検出手段
8 通電相制御手段
11 PWM制御手段
17 圧縮機
21 冷蔵庫
3
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017208351A JP6970871B2 (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2017-10-27 | Motor drive device and refrigerator using it |
| PCT/JP2018/038387 WO2019082718A1 (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2018-10-16 | Motor drive device and refrigerator using this |
| CN201880051912.8A CN111034026A (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2018-10-16 | Motor driving device and refrigerator using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017208351A JP6970871B2 (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2017-10-27 | Motor drive device and refrigerator using it |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019083595A JP2019083595A (en) | 2019-05-30 |
| JP2019083595A5 JP2019083595A5 (en) | 2020-12-03 |
| JP6970871B2 true JP6970871B2 (en) | 2021-11-24 |
Family
ID=66246448
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017208351A Active JP6970871B2 (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2017-10-27 | Motor drive device and refrigerator using it |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6970871B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN111034026A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019082718A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024209901A1 (en) * | 2023-04-05 | 2024-10-10 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Motor drive control device |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06165519A (en) * | 1992-11-27 | 1994-06-10 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | Method for driving electric motor |
| JP4277762B2 (en) * | 2004-08-05 | 2009-06-10 | パナソニック株式会社 | Refrigerator control device |
| JP2009261212A (en) * | 2008-03-17 | 2009-11-05 | Toshiba Corp | Inverter apparatus and inverter system |
| JP5259303B2 (en) * | 2008-08-26 | 2013-08-07 | 株式会社東芝 | Inverter device |
| TWI460970B (en) * | 2010-04-02 | 2014-11-11 | Leadtrend Tech Corp | Adaptive slope-compensation module and method thereof |
| JP6533950B2 (en) * | 2015-08-28 | 2019-06-26 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Motor drive device, compressor drive device using the same, refrigeration apparatus and refrigerator |
| CN106828181B (en) * | 2017-04-13 | 2023-09-15 | 安费诺汽车连接系统(常州)有限公司 | Charging control device of electric automobile |
-
2017
- 2017-10-27 JP JP2017208351A patent/JP6970871B2/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-10-16 WO PCT/JP2018/038387 patent/WO2019082718A1/en active Application Filing
- 2018-10-16 CN CN201880051912.8A patent/CN111034026A/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2019082718A1 (en) | 2019-05-02 |
| JP2019083595A (en) | 2019-05-30 |
| CN111034026A (en) | 2020-04-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5195444B2 (en) | Brushless DC motor driving apparatus, refrigerator and air conditioner using the same | |
| JP6134905B2 (en) | MOTOR DRIVE DEVICE AND ELECTRIC DEVICE USING THE SAME | |
| WO2017208873A1 (en) | Motor drive apparatus, and electric device having compressor using same | |
| JP2012222842A (en) | Motor drive device and electric appliance using the same | |
| JP2008289310A (en) | Motor drive and refrigerator using the same | |
| JP3672637B2 (en) | Compressor motor control device | |
| JP5402310B2 (en) | Motor drive device, compressor and refrigerator | |
| JP2001263256A (en) | Control device for compressor | |
| JP2010233415A (en) | Motor driving device and refrigerator using the same | |
| JP6970871B2 (en) | Motor drive device and refrigerator using it | |
| JP2010252406A (en) | Motor drive and refrigerator using the same | |
| JP3776102B2 (en) | Brushless motor control device | |
| JP5387396B2 (en) | Motor drive device, compressor and refrigerator | |
| JP5521405B2 (en) | Motor drive device and electric apparatus using the same | |
| JP2008172880A (en) | Method and device for driving brushless dc motor | |
| JP6979568B2 (en) | Motor drive device and refrigerator using it | |
| JP2002112588A (en) | Freezing system controller | |
| JP6706757B2 (en) | MOTOR DRIVE DEVICE AND ELECTRIC DEVICE HAVING COMPRESSOR USING THE SAME | |
| JP2012186876A (en) | Compressor drive unit and refrigerator using the same | |
| JP5747145B2 (en) | Motor drive device and electric apparatus using the same | |
| JP2001309692A (en) | Control device of refrigerating system | |
| JP6706756B2 (en) | MOTOR DRIVE DEVICE AND ELECTRIC DEVICE HAVING COMPRESSOR USING THE SAME | |
| JP6450939B2 (en) | Motor drive device, compressor drive device using the same, refrigeration device, and refrigerator | |
| JP5407790B2 (en) | Motor drive device and compressor and refrigerator using the same | |
| JP2019092353A (en) | Motor drive device and refrigerator using the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20190121 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20201022 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20201022 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20210914 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210927 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6970871 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |