JP6833763B2 - Ethylene compound, UV absorber and resin composition - Google Patents
Ethylene compound, UV absorber and resin composition Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6833763B2 JP6833763B2 JP2018117942A JP2018117942A JP6833763B2 JP 6833763 B2 JP6833763 B2 JP 6833763B2 JP 2018117942 A JP2018117942 A JP 2018117942A JP 2018117942 A JP2018117942 A JP 2018117942A JP 6833763 B2 JP6833763 B2 JP 6833763B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- group
- resin composition
- resin
- compound
- ethylene compound
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C323/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups
- C07C323/23—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton
- C07C323/31—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton
- C07C323/32—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and nitrogen atoms, not being part of nitro or nitroso groups, bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton having at least one of the nitrogen atoms bound to an acyclic carbon atom of the carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C321/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides
- C07C321/24—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides having thio groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
- C07C321/28—Sulfides, hydropolysulfides, or polysulfides having thio groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C323/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups
- C07C323/50—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton
- C07C323/62—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atom of at least one of the thio groups bound to a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring of the carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D239/28—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with hetero atoms or with carbon atoms having three bonds to hetero atoms with at the most one bond to halogen, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D239/46—Two or more oxygen, sulphur or nitrogen atoms
- C07D239/60—Three or more oxygen or sulfur atoms
- C07D239/62—Barbituric acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/36—Sulfur-, selenium-, or tellurium-containing compounds
- C08K5/37—Thiols
- C08K5/372—Sulfides, e.g. R-(S)x-R'
- C08K5/3725—Sulfides, e.g. R-(S)x-R' containing nitrogen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/36—Sulfur-, selenium-, or tellurium-containing compounds
- C08K5/37—Thiols
- C08K5/375—Thiols containing six-membered aromatic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/36—Sulfur-, selenium-, or tellurium-containing compounds
- C08K5/37—Thiols
- C08K5/378—Thiols containing heterocyclic rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L101/00—Compositions of unspecified macromolecular compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09B—ORGANIC DYES OR CLOSELY-RELATED COMPOUNDS FOR PRODUCING DYES, e.g. PIGMENTS; MORDANTS; LAKES
- C09B57/00—Other synthetic dyes of known constitution
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K3/00—Materials not provided for elsewhere
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B5/00—Optical elements other than lenses
- G02B5/20—Filters
- G02B5/22—Absorbing filters
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02B—OPTICAL ELEMENTS, SYSTEMS OR APPARATUS
- G02B5/00—Optical elements other than lenses
- G02B5/20—Filters
- G02B5/22—Absorbing filters
- G02B5/223—Absorbing filters containing organic substances, e.g. dyes, inks or pigments
Description
本発明は、紫外〜紫色領域の光を吸収することができるエチレン化合物、これを含む樹脂組成物とその硬化物、および当該樹脂組成物を含む光学フィルターやセンサーに関するものである。 The present invention relates to an ethylene compound capable of absorbing light in the ultraviolet to purple region, a resin composition containing the ethylene compound and a cured product thereof, and an optical filter or sensor containing the resin composition.
従来、紫外〜紫色領域の光を吸収する様々な化合物が知られている。そのような化合物として、例えば、特許文献1にはベンゾフェノン系化合物が開示され、特許文献2にはメロシアニン系化合物が開示され、特許文献3にはトリアジン系化合物が開示されている。また、特許文献4、5には、トリアジン系紫外線吸収剤やベンゾトリアゾール系紫外線吸収剤やベンゾフェノン系紫外線吸収剤を含有する樹脂組成物や、当該樹脂組成物から形成された光学フィルムが開示されている。 Conventionally, various compounds that absorb light in the ultraviolet to purple region are known. As such compounds, for example, Patent Document 1 discloses a benzophenone-based compound, Patent Document 2 discloses a merocyanine-based compound, and Patent Document 3 discloses a triazine-based compound. Further, Patent Documents 4 and 5 disclose a resin composition containing a triazine-based ultraviolet absorber, a benzotriazole-based ultraviolet absorber, and a benzophenone-based ultraviolet absorber, and an optical film formed from the resin composition. There is.
紫外線吸収剤は樹脂に配合して樹脂組成物として用いられる場合があり、樹脂組成物は用途に応じて様々な形状に成形して用いられる。樹脂成形品の用途はますます広がっており、耐熱性が求められるような用途への使用も増えている。例えば透明樹脂から光学フィルターを形成する場合など、光学フィルターは樹脂組成物を透明基板上に塗膜して加熱することにより形成したり、半田リフローにより電子部品に実装したり、また蒸着により誘電体多層膜を形成したりすることがあるが、樹脂組成物中に紫外線吸収剤が含まれる場合は、これらのプロセスを経た後も所望の紫外線吸収性能が発揮されるように、紫外線吸収剤は十分な耐熱性を有することが求められる。 The ultraviolet absorber may be blended with a resin and used as a resin composition, and the resin composition is used by molding it into various shapes depending on the application. The applications of resin molded products are expanding more and more, and the applications where heat resistance is required are also increasing. For example, when forming an optical filter from a transparent resin, the optical filter is formed by coating a resin composition on a transparent substrate and heating it, mounting it on an electronic component by solder reflow, or a dielectric by vapor deposition. A multilayer film may be formed, but if the resin composition contains an ultraviolet absorber, the ultraviolet absorber is sufficient so that the desired ultraviolet absorbing performance is exhibited even after undergoing these processes. It is required to have excellent heat resistance.
本発明は、前記事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、紫外〜紫色領域に吸収ピークを示し、耐熱性に優れた化合物、および当該化合物を含む樹脂組成物や光学フィルターを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a compound showing an absorption peak in the ultraviolet to purple region and having excellent heat resistance, and a resin composition or an optical filter containing the compound. There is.
本発明は、以下の発明を含む。
[1]下記式(1)で表されることを特徴とするエチレン化合物。
[式(1)中、Lは2価以上の連結基を表し、aは2以上の整数を表し、Aはそれぞれ独立して下記式(2)で示される基を表す。]
[式(2)中、
R1はシアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基またはハロゲノアルキル基を表し、
R2は水素原子、シアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基、炭化水素基またはヘテロアリール基を表し、
R1とR2がともにアシル基、カルボン酸エステル基またはアミド基である場合、R1とR2は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよく、
R3は水素原子またはアルキル基を表し、
R4は水素原子、有機基または極性官能基を表し、複数のR4は互いに同一または異なっていてもよく、
Xは硫黄原子または酸素原子を表し、
*は式(1)の連結基Lとの結合部位を表す。]
[2]前記R2が水素原子、シアノ基、アシル基、カルボン酸エステル基またはアミド基を表す[1]に記載のエチレン化合物。
[3]トルエン中で測定した波長300nm〜600nmの範囲の吸収スペクトルにおいて、波長420nm以下に最大吸収ピークを有する[1]または[2]に記載のエチレン化合物。
[4][1]〜[3]のいずれかに記載のエチレン化合物を含有することを特徴とする紫外線吸収剤。
[5][1]〜[3]のいずれかに記載のエチレン化合物と樹脂成分とを含有することを特徴とする樹脂組成物。
[6]さらに近赤外線吸収色素および/または可視光吸収色素を含有する[5]に記載の樹脂組成物。
[7]さらにエポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤、その加水分解物、およびその加水分解縮合物よりなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1種を含有する[5]または[6]に記載の樹脂組成物。
[8][5]〜[7]のいずれかに記載の樹脂組成物を硬化した硬化物。
[9][5]〜[7]のいずれかに記載の樹脂組成物または[8]に記載の硬化物を含むことを特徴とする光学フィルター。
[10][9]に記載の光学フィルターを備えることを特徴とするセンサー。
The present invention includes the following inventions.
[1] An ethylene compound represented by the following formula (1).
[In the formula (1), L represents a linking group having a divalent value or more, a represents an integer of 2 or more, and A represents a group represented by the following formula (2) independently. ]
[In equation (2),
R 1 represents a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group, an amide group or a halogenoalkyl group.
R 2 represents a hydrogen atom, a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group, an amide group, a hydrocarbon group or a heteroaryl group.
When both R 1 and R 2 are acyl groups, carboxylic acid ester groups or amide groups, R 1 and R 2 may be linked to each other to form a ring.
R 3 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group
R 4 represents a hydrogen atom, an organic group or a polar functional group, and a plurality of R 4s may be the same or different from each other.
X represents a sulfur atom or an oxygen atom,
* Represents the binding site with the linking group L of the formula (1). ]
[2] The ethylene compound according to [1], wherein R 2 represents a hydrogen atom, a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group or an amide group.
[3] The ethylene compound according to [1] or [2], which has a maximum absorption peak at a wavelength of 420 nm or less in an absorption spectrum in the wavelength range of 300 nm to 600 nm measured in toluene.
[4] An ultraviolet absorber containing the ethylene compound according to any one of [1] to [3].
[5] A resin composition containing the ethylene compound according to any one of [1] to [3] and a resin component.
[6] The resin composition according to [5], which further contains a near-infrared absorbing dye and / or a visible light absorbing dye.
[7] The resin composition according to [5] or [6], which further contains at least one selected from the group consisting of an epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent, a hydrolyzate thereof, and a hydrolyzed condensate thereof.
[8] A cured product obtained by curing the resin composition according to any one of [5] to [7].
[9] An optical filter comprising the resin composition according to any one of [5] to [7] or the cured product according to [8].
[10] A sensor comprising the optical filter according to [9].
本発明のエチレン化合物は、紫外〜紫色領域に吸収ピークを示し、耐熱性に優れる。 The ethylene compound of the present invention shows an absorption peak in the ultraviolet to purple region and is excellent in heat resistance.
本発明のエチレン化合物は、下記式(1)で表されるものである。下記式(1)で表されるエチレン化合物は、紫外〜紫色領域にシャープな吸収ピークを示し、耐熱性に優れるものとなる。本発明のエチレン化合物は、紫外線吸収性エチレン化合物として機能させることができる。 The ethylene compound of the present invention is represented by the following formula (1). The ethylene compound represented by the following formula (1) shows a sharp absorption peak in the ultraviolet to purple region and has excellent heat resistance. The ethylene compound of the present invention can function as an ultraviolet-absorbing ethylene compound.
式(1)中、Lは2価以上の連結基を表し、aは2以上の整数を表し、Aはそれぞれ独立して下記式(2)で示される基を表す。 In the formula (1), L represents a linking group having a divalent value or more, a represents an integer of 2 or more, and A represents a group represented by the following formula (2) independently.
式(2)中、R1はシアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基またはハロゲノアルキル基を表し、R2は水素原子、シアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基、炭化水素基またはヘテロアリール基を表し、R1とR2がともにアシル基、カルボン酸エステル基またはアミド基である場合、R1とR2は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよく、R3は水素原子またはアルキル基を表し、R4は水素原子、有機基または極性官能基を表し、複数のR4は互いに同一または異なっていてもよく、Xは硫黄原子または酸素原子を表し、*は式(1)の連結基Lとの結合部位を表す。 In formula (2), R 1 represents a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group, an amide group or a halogenoalkyl group, and R 2 is a hydrogen atom, a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group or a carboxylic acid ester. Representing a group, amide group, hydrocarbon group or heteroaryl group, where R 1 and R 2 are both acyl groups, carboxylic acid ester groups or amide groups, R 1 and R 2 are linked to each other to form a ring. R 3 may represent a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group, R 4 may represent a hydrogen atom, an organic group or a polar functional group, a plurality of R 4s may be the same or different from each other, and X may be a sulfur atom or It represents an oxygen atom, and * represents a bonding site with the linking group L of the formula (1).
式(2)で表される基Aにおいて、R1とR2を含むエチレン構造部は発色団として機能する。式(2)では、R1とR2として、シアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基、ハロゲノアルキル基、炭化水素基またはヘテロアリール基が用いられる。式(2)中、R1(またはR2)はR3に対して、シス位にあってもよく、トランス位にあってもよい。 In the group A represented by the formula (2), the ethylene structural part containing R 1 and R 2 functions as a chromophore. In the formula (2), a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group, an amide group, a halogenoalkyl group, a hydrocarbon group or a heteroaryl group is used as R 1 and R 2. In equation (2), R 1 (or R 2 ) may be in the cis position or in the trans position with respect to R 3.
R1およびR2のアシル基(アルカノイル基)としては、メタノイル基、エタノイル基、プロパノイル基、ブタノイル基、ペンタノイル基、ヘキサノイル基、ヘプタノイル基、オクタノイル基、ノナノイル基、デカノイル基、ウンデカノイル基、ドデカノイル基、トリデカノイル基、テトラデカノイル基、ペンタデカノイル基、ヘキサデカノイル基、ヘプタデカノイル基、オクタデカノイル基、ノナデカノイル基、エイコサノイル基等が挙げられる。アシル基は、水素原子の一部が、アリール基、アルコキシ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基等で置換されていてもよい。前記アシル基中のアルキル基は、直鎖状であってもよく分岐状であってもよい。アシル基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は、2〜21が好ましく、より好ましくは2〜11であり、さらに好ましくは2〜6である。 The acyl groups (alkanoyl groups) of R 1 and R 2 include a methanoyl group, an etanoyl group, a propanoyl group, a butanoyl group, a pentanoyl group, a hexanoyl group, a heptanoil group, an octanoyl group, a nonanoyl group, a decanoyle group, an undecanoyl group, and a dodecanoyl group. , Tridecanoyl group, tetradecanoyl group, pentadecanoyl group, hexadecanoyl group, heptadecanoyl group, octadecanoyl group, nonadecanoyyl group, eikosanoyl group and the like. A part of the hydrogen atom of the acyl group may be substituted with an aryl group, an alkoxy group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group or the like. The alkyl group in the acyl group may be linear or branched. The number of carbon atoms of the acyl group (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 2 to 21, more preferably 2 to 11, and even more preferably 2 to 6.
R1およびR2のカルボン酸エステル基は、式:*−C(=O)−O−R11で表され、*は式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子への結合部位を表す。当該式中、R11は炭化水素基を表し、好ましくはアルキル基、アリール基またはアラルキル基を表す。 The carboxylic acid ester groups of R 1 and R 2 are represented by the formula: * -C (= O) -OR 11 , where * represents the binding site of the ethylene double bond of the formula (2) to the carbon atom. .. In the formula, R 11 represents a hydrocarbon group, preferably an alkyl group, an aryl group or an aralkyl group.
R11のアルキル基としては、メチル基、エチル基、プロピル基、イソプロピル基、n−ブチル基、イソブチル基、t−ブチル基、ペンチル基、ヘキシル基、2−エチルヘキシル基、ヘプチル基、オクチル基、ノニル基、デシル基、ウンデシル基、ドデシル基、トリデシル基、テトラデシル基、ペンタデシル基、ヘキサデシル基、ヘプタデシル基、オクタデシル基、ノナデシル基、イコシル基等の直鎖状または分岐状のアルキル基;シクロプロピル基、シクロブチル基、シクロペンチル基、シクロヘキシル基、シクロヘプチル基、シクロオクチル基、シクロノニル基、シクロデシル基等の環状(脂環式)アルキル基等が挙げられる。アルキル基は、水素原子の一部が、アルコキシ基、アリール基、シアノ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基等で置換されていてもよい。アルキル基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は1〜20が好ましく、具体的には、直鎖状または分岐状のアルキル基であれば炭素数1〜20が好ましく、より好ましくは1〜10であり、さらに好ましくは1〜5であり、環状のアルキル基であれば炭素数4〜10が好ましく、5〜8がより好ましい。 Alkyl groups of R 11 include methyl group, ethyl group, propyl group, isopropyl group, n-butyl group, isobutyl group, t-butyl group, pentyl group, hexyl group, 2-ethylhexyl group, heptyl group and octyl group. Linear or branched alkyl groups such as nonyl group, decyl group, undecyl group, dodecyl group, tridecyl group, tetradecyl group, pentadecyl group, hexadecyl group, heptadecyl group, octadecyl group, nonadecil group, icosyl group; cyclopropyl group , Cyclobutyl group, cyclopentyl group, cyclohexyl group, cycloheptyl group, cyclooctyl group, cyclononyl group, cyclodecyl group and other cyclic (aliphatic) alkyl groups. In the alkyl group, a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with an alkoxy group, an aryl group, a cyano group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group or the like. The number of carbon atoms of the alkyl group (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 1 to 20, and specifically, if it is a linear or branched alkyl group, the number of carbon atoms is preferably 1 to 20 and more preferably 1 to 20. It is 10, more preferably 1 to 5, and if it is a cyclic alkyl group, the number of carbon atoms is preferably 4 to 10, and more preferably 5 to 8.
R11のアリール基としては、フェニル基、ビフェニル基、ナフチル基、アントリル基、フェナントリル基、ピレニル基、インデニル基等が挙げられる。アリール基は、水素原子の一部が、アルキル基、アルコキシ基、シアノ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基等で置換されていてもよい。アリール基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は、6〜20が好ましく、より好ましくは6〜12である。 Examples of the aryl group of R 11 include a phenyl group, a biphenyl group, a naphthyl group, an anthryl group, a phenanthryl group, a pyrenyl group, an indenyl group and the like. A part of the hydrogen atom of the aryl group may be substituted with an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group or the like. The number of carbon atoms of the aryl group (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 6 to 20, and more preferably 6 to 12.
R11のアラルキル基としては、ベンジル基、フェネチル基、フェニルプロピル基、フェニルブチル基、フェニルペンチル基、ナフチルメチル基等が挙げられる。アラルキル基に含まれるアリール基は、水素原子の一部が、アルキル基、アルコキシ基、シアノ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基等で置換されていてもよい。アラルキル基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は、7〜25が好ましく、より好ましくは7〜15である。 Examples of the aralkyl group of R 11 include a benzyl group, a phenethyl group, a phenylpropyl group, a phenylbutyl group, a phenylpentyl group, a naphthylmethyl group and the like. In the aryl group contained in the aralkyl group, a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group or the like. The carbon number of the aralkyl group (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 7 to 25, and more preferably 7 to 15.
R1およびR2のアミド基は、式:*−C(=O)−NR12R13で表され、*は式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子への結合部位を表す。当該式中、R12は水素原子またはアルキル基を表す。R13は炭化水素基を表し、好ましくはアルキル基、アシル基、アリール基またはアラルキル基を表す。R12とR13のアルキル基、R13のアシル基とアリール基とアラルキル基の具体例は、上記のR11のアルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、およびR1とR2のアシル基の説明が参照される。 The amide groups of R 1 and R 2 are represented by the formula: * -C (= O) -NR 12 R 13 , where * represents the binding site of the ethylene double bond of the formula (2) to the carbon atom. In the formula, R 12 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group. R 13 represents a hydrocarbon group, preferably an alkyl group, an acyl group, an aryl group or an aralkyl group. Specific examples of the alkyl group of R 12 and R 13 , the acyl group of R 13 and the aryl group and the aralkyl group are described above for the alkyl group of R 11 , the aryl group, the aralkyl group, and the acyl group of R 1 and R 2. Is referenced.
R1とR2がともにアシル基である場合、R1とR2は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよく、この場合のR1とR2から形成される基としては、式:*−C(=O)−R14−C(=O)−*で表される基が示される。当該式中、R14は直鎖状または分岐状のアルキレン基を表し、*は式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子への結合部位を表す。アルキレン基は、水素原子の一部が、アリール基、アルコキシ基、シアノ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基等で置換されていてもよい。R14のアルキレン基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は、2〜10が好ましく、3〜8がより好ましい。R1とR2のアシル基が互いに連結することにより形成される基(環状基)としては、例えば下記式(3−1)に示される基が挙げられる。 When both R 1 and R 2 are acyl groups, R 1 and R 2 may be connected to each other to form a ring, and the group formed from R 1 and R 2 in this case is represented by the formula: The groups represented by * -C (= O) -R 14- C (= O)-* are shown. In the formula, R 14 represents a linear or branched alkylene group, and * represents the binding site of the ethylene double bond of the formula (2) to a carbon atom. In the alkylene group, a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with an aryl group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group or the like. The carbon number of the alkylene group of R 14 (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 2 to 10 and more preferably 3 to 8. Examples of the group (cyclic group) formed by linking the acyl groups of R 1 and R 2 to each other include the group represented by the following formula (3-1).
R1とR2がともにカルボン酸エステル基である場合、R1とR2は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよく、この場合のR1とR2から形成される基としては、式:*−C(=O)−O−R15−O−C(=O)−*で表される基が示される。当該式中、R15は直鎖状または分岐状のアルキレン基を表し、*は式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子への結合部位を表す。アルキレン基は、水素原子の一部が、アリール基、アルコキシ基、シアノ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基等で置換されていてもよい。R15のアルキレン基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は1〜8が好ましく、1〜6がより好ましい。R1とR2のカルボン酸エステル基が互いに連結することにより形成される基(環状基)としては、例えば下記式(3−2)に示される基が挙げられる。 When both R 1 and R 2 are carboxylic acid ester groups, R 1 and R 2 may be connected to each other to form a ring, and the group formed from R 1 and R 2 in this case is Formula: The group represented by * -C (= O) -OR 15- OC (= O)-* is shown. In the formula, R 15 represents a linear or branched alkylene group, and * represents the binding site of the ethylene double bond of the formula (2) to a carbon atom. In the alkylene group, a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with an aryl group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group or the like. The carbon number of the alkylene group of R 15 (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 1 to 8, and more preferably 1 to 6. Examples of the group (cyclic group) formed by linking the carboxylic acid ester groups of R 1 and R 2 to each other include the group represented by the following formula (3-2).
R1とR2がともにアミド基である場合、R1とR2は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよく、この場合のR1とR2から形成される基としては、式:*−C(=O)−NR16−R17−NR18−C(=O)−*で表される基が示される。当該式中、R16とR18は、水素原子または炭化水素基を表し、R17は直鎖状または分岐状のアルキレン基、またはカルボニル基を表し、*は式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子への結合部位を表す。R16とR18の炭化水素基としては、アルキル基、アリール基またはアラルキル基が好ましく挙げられる。R16とR18のアルキル基とアリール基とアラルキル基の具体例は、上記のR11のアルキル基、アリール基およびアラルキル基の説明が参照される。R17のアルキレン基は、水素原子の一部が、アリール基、アルコキシ基、シアノ基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基等で置換されていてもよい。R17のアルキレン基の炭素数(置換基を除く炭素数)は1〜8が好ましく、1〜6がより好ましい。R1とR2のアミド基が互いに連結することにより形成される基(環状基)としては、例えば下記式(3−3)と式(3−4)に示される基が挙げられる。 When both R 1 and R 2 are amide groups, R 1 and R 2 may be connected to each other to form a ring, and the group formed from R 1 and R 2 in this case is represented by the formula: The groups represented by * -C (= O) -NR 16- R 17- NR 18- C (= O)-* are shown. In the formula, R 16 and R 18 represent a hydrogen atom or a hydrocarbon group, R 17 represents a linear or branched alkylene group or a carbonyl group, and * represents an ethylene double bond of the formula (2). Represents the bond site of ethylene to a carbon atom. Preferred examples of the hydrocarbon group of R 16 and R 18 include an alkyl group, an aryl group or an aralkyl group. For specific examples of the alkyl group, aryl group and aralkyl group of R 16 and R 18 , the above description of the alkyl group, aryl group and aralkyl group of R 11 is referred to. In the alkylene group of R 17 , a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with an aryl group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group or the like. The carbon number of the alkylene group of R 17 (the number of carbon atoms excluding the substituent) is preferably 1 to 8, and more preferably 1 to 6. Examples of the group (cyclic group) formed by linking the amide groups of R 1 and R 2 to each other include groups represented by the following formulas (3-3) and (3-4).
R1のハロゲノアルキル基としては、上記に説明したR11のアルキル基の水素原子の一部または全部がハロゲン原子で置き換わったものが挙げられる。ハロゲン原子としては、フッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子、ヨウ素原子等が挙げられる。 Examples of the halogenoalkyl group of R 1 include those in which a part or all of the hydrogen atoms of the alkyl group of R 11 described above are replaced with halogen atoms. Examples of the halogen atom include a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom and an iodine atom.
R2の炭化水素基としては、脂肪族炭化水素基、芳香族炭化水素基(アリール基)が挙げられる。脂肪族炭化水素基は、飽和と不飽和のいずれであってもよく、また直鎖状、分岐状、環状のいずれであってもよい。脂肪族飽和炭化水素基の具体例は、上記のR11のアルキル基に関する説明が参照され、脂肪族不飽和炭化水素基の具体例は、上記に説明したR11のアルキル基の炭素−炭素単結合の一部が二重結合または三重結合に置き換わったものが挙げられる。芳香族炭化水素基(アリール基)の具体例は、上記のR11のアリール基に関する説明が参照される。R2の炭化水素基としては、アリール基が好ましい。 Examples of the hydrocarbon group of R 2 include an aliphatic hydrocarbon group and an aromatic hydrocarbon group (aryl group). The aliphatic hydrocarbon group may be saturated or unsaturated, and may be linear, branched, or cyclic. For a specific example of the aliphatic saturated hydrocarbon group, refer to the above description regarding the alkyl group of R 11 , and for a specific example of the aliphatic unsaturated hydrocarbon group, the carbon-carbon single carbon of the alkyl group of R 11 described above. Examples include those in which a part of the bond is replaced with a double bond or a triple bond. For specific examples of the aromatic hydrocarbon group (aryl group), the above description regarding the aryl group of R 11 is referred to. As the hydrocarbon group of R 2 , an aryl group is preferable.
R2のヘテロアリール基としては、チエニル基、チオピラニル基、イソチオクロメニル基、ピロリル基、イミダゾリル基、ピラゾリル基、ピリジル基、ピラリジニル基、ピリミジニル基、ピリダジニル基、チアゾリル基、イソチアゾリル基、フラニル基、ピラニル基等が挙げられる。なおヘテロアリール基は、炭素原子が式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子に結合していることが好ましく、ヘテロ原子に隣接する炭素原子が式(2)のエチレン二重結合の炭素原子に結合していることがより好ましく、これによりエチレン化合物の合成が容易になる。ヘテロアリール基の炭素数は、3〜18が好ましく、より好ましくは4〜12である。 The heteroaryl group of R 2 includes thienyl group, thiopyranyl group, isothiochromenyl group, pyrrolyl group, imidazolyl group, pyrazolyl group, pyridyl group, pyraridinyl group, pyrimidinyl group, pyridadinyl group, thiazolyl group, isothiazolyl group, furanyl group, Examples thereof include a pyranyl group. In the heteroaryl group, the carbon atom is preferably bonded to the carbon atom of the ethylene double bond of the formula (2), and the carbon atom adjacent to the hetero atom is the carbon atom of the ethylene double bond of the formula (2). It is more preferably bound to, which facilitates the synthesis of ethylene compounds. The heteroaryl group preferably has 3 to 18 carbon atoms, more preferably 4 to 12 carbon atoms.
式(2)において、R2は水素原子、シアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基またはアミド基であることが好ましく、これにより、紫外〜紫色領域の光を効果的に吸収しやすくなる。エチレン化合物の吸収ピークをより長波長側に設定したい場合など、例えば、完全な紫外領域ではなく、波長350nm〜420nmの領域の光を吸収させたいような場合などは、R2は水素原子ではないことが好ましい。 In the formula (2), R 2 is preferably a hydrogen atom, a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group or an amide group, which facilitates effective absorption of light in the ultraviolet to purple region. Become. When you want to set the absorption peak of an ethylene compound to a longer wavelength side, for example, when you want to absorb light in the wavelength region of 350 nm to 420 nm instead of the complete ultraviolet region, R 2 is not a hydrogen atom. Is preferable.
式(2)のR3は水素原子またはアルキル基を表し、アルキル基の具体例は、上記のR11のアルキル基に関する説明が参照される。R3のアルキル基は、好ましくは炭素数1〜3であり、より好ましくは炭素数1〜2である。R3としては水素原子が特に好ましい。 R 3 of the formula (2) represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group, and a specific example of the alkyl group is referred to in the above description of the alkyl group of R 11. The alkyl group of R 3 preferably has 1 to 3 carbon atoms, and more preferably 1 to 2 carbon atoms. A hydrogen atom is particularly preferable as R 3.
式(2)で表される基Aにおいて、エチレン構造部に結合したベンゼン環は、当該ベンゼン環に結合したX(硫黄原子または酸素原子)とともにエチレン構造部に電子を供与するように機能し、エチレン構造部の発色団の吸収波長を紫外〜紫色領域にくるように調整する。当該ベンゼン環に結合するR4は水素原子、有機基または極性官能基を表し、複数のR4は互いに同一または異なっていてもよい。 In the group A represented by the formula (2), the benzene ring bonded to the ethylene structure functions to donate an electron to the ethylene structure together with X (sulfur atom or oxygen atom) bonded to the benzene ring. Adjust the absorption wavelength of the chromophore of the ethylene structure so that it is in the ultraviolet to purple region. R 4 bonded to the benzene ring represents a hydrogen atom, an organic group or a polar functional group, and a plurality of R 4s may be the same or different from each other.
式(2)のR4の有機基としては、アルキル基、アルコキシ基、アルキルチオ基、アルコキシカルボニル基、アルキルスルホニル基、アルキルスルフィニル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、アリールオキシ基、アリールチオ基、アリールオキシカルボニル基、アリールスルホニル基、アリールスルフィニル基、ヘテロアリール基、アミノ基、アミド基、スルホンアミド基、カルボキシ基(カルボン酸基)、シアノ基等が挙げられる。R4の極性官能基としては、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、ニトロ基、スルホ基(スルホン酸基)等が挙げられる。 Examples of the organic group of R 4 of the formula (2) include an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an alkylthio group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, an alkylsulfonyl group, an alkylsulfinyl group, an aryl group, an aralkyl group, an aryloxy group, an arylthio group and an aryloxycarbonyl. Examples thereof include a group, an arylsulfonyl group, an arylsulfinyl group, a heteroaryl group, an amino group, an amide group, a sulfonamide group, a carboxy group (carboxylic acid group), a cyano group and the like. Examples of the polar functional group of R 4 include a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a nitro group, a sulfo group (sulfonic acid group) and the like.
R4のアルキル基の具体例は、上記のR11のアルキル基に関する説明が参照される。R4のアルキル基は置換基を有していてもよく、当該アルキル基が有する置換基としては、アリール基、ヘテロアリール基、ハロゲノ基、水酸基、カルボキシ基、アルコキシ基、シアノ基、ニトロ基、アミノ基、スルホ基等が挙げられる。 For specific examples of the alkyl group of R 4 , refer to the above description of the alkyl group of R 11. The alkyl group of R 4 may have a substituent, and the substituent of the alkyl group includes an aryl group, a heteroaryl group, a halogeno group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxy group, an alkoxy group, a cyano group and a nitro group. Examples include an amino group and a sulfo group.
R4のアルコキシ基、アルキルチオ基、アルコキシカルボニル基、アルキルスルホニル基、アルキルスルフィニル基に含まれるアルキル基の具体例は、R4のアルキル基に関する説明が参照される。 Specific examples of the alkyl group include an alkoxy group R 4, an alkylthio group, an alkoxycarbonyl group, an alkylsulfonyl group, the alkylsulfinyl group is described pertains to an alkyl group R 4 is referred to.
R4のアリール基とアラルキル基の具体例は、上記のR11のアリール基とアラルキル基に関する説明が参照される。R4のアリール基あるいはアラルキル基に含まれるアリール基は置換基を有していてもよく、当該置換基としては、アルキル基、アルコキシ基、ヘテロアリール基、ハロゲノ基、ハロゲノアルキル基、水酸基、シアノ基、ニトロ基、アミノ基、チオシアネート基、アシル基、アルコキシカルボニル基、アリールオキシカルボニル基、カルバモイル基、スルホ基、アルキルスルフィニル基、アリールスルフィニル基、アルキルスルホニル基、アリールスルホニル基、スルファモイル基等が挙げられる。 For specific examples of the aryl group and aralkyl group of R 4 , the above description of the aryl group and aralkyl group of R 11 is referred to. The aryl group contained in the aryl group or aralkyl group of R 4 may have a substituent, and the substituents include an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a heteroaryl group, a halogeno group, a halogenoalkyl group, a hydroxyl group and a cyano group. Group, nitro group, amino group, thiocyanate group, acyl group, alkoxycarbonyl group, aryloxycarbonyl group, carbamoyl group, sulfo group, alkylsulfinyl group, arylsulfinyl group, alkylsulfonyl group, arylsulfonyl group, sulfamoyl group and the like. Be done.
R4のアリールオキシ基、アリールチオ基、アリールオキシカルボニル基、アリールスルホニル基、アリールスルフィニル基に含まれるアリール基の具体例は、R4のアリール基に関する説明が参照される。 Aryloxy group R 4, an arylthio group, an aryloxycarbonyl group, specific examples of the arylsulfonyl group, the aryl group contained in arylsulfinyl group, description of aryl group R 4 is referred to.
R4のヘテロアリール基の具体例は、上記のR2のヘテロアリール基に関する説明が参照される。ヘテロアリール基は置換基を有していてもよく、ヘテロアリール基が有する置換基としては、アルキル基、アルコキシ基、アリール基、ハロゲノ基、ハロゲノアルキル基、水酸基、シアノ基、アミノ基、ニトロ基、チオシアネート基、アシル基、アルコキシカルボニル基、アリールオキシカルボニル基、カルバモイル基、スルホ基、アルキルスルフィニル基、アリールスルフィニル基、アルキルスルホニル基、アリールスルホニル基、スルファモイル基等が挙げられる。 For specific examples of the heteroaryl group of R 4 , refer to the above description of the heteroaryl group of R 2. The heteroaryl group may have a substituent, and the substituents of the heteroaryl group include an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an aryl group, a halogeno group, a halogenoalkyl group, a hydroxyl group, a cyano group, an amino group and a nitro group. , Thiocyanate group, acyl group, alkoxycarbonyl group, aryloxycarbonyl group, carbamoyl group, sulfo group, alkylsulfinyl group, arylsulfinyl group, alkylsulfonyl group, arylsulfonyl group, sulfamoyl group and the like.
R4のアミノ基としては、式:−NR21R22で表され、R21およびR22がそれぞれ独立して、水素原子、アルキル基、アルケニル基、アルキニル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、ヘテロアリール基であるもの等が挙げられる。アルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、ヘテロアリール基の具体例は上記の説明が参照され、アルケニル基とアルキニル基としては、上記に説明したアルキル基の炭素−炭素単結合の一部が二重結合または三重結合に置き換わった置換基が挙げられ、これらの置換基は水素原子の一部がハロゲン原子によって置換されていてもよい。また、R21とR22は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよい。 The amino group of R 4 is represented by the formula: -NR 21 R 22 , and R 21 and R 22 are independently hydrogen atom, alkyl group, alkenyl group, alkynyl group, aryl group, aralkyl group, heteroaryl. Examples include those that are the basis. Refer to the above description for specific examples of the alkyl group, aryl group, aralkyl group, and heteroaryl group, and as the alkenyl group and alkynyl group, a part of the carbon-carbon single bond of the alkyl group described above is double-bonded. Alternatively, substituents replaced with triple bonds may be mentioned, and these substituents may be partially substituted with halogen atoms. Further, R 21 and R 22 may be connected to each other to form a ring.
R4のアミド基としては、式:−NH−C(=O)−R23で表され、R23がアルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、ヘテロアリール基であるもの等が挙げられる。アルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、ヘテロアリール基の具体例は上記の説明が参照され、水素原子の一部がハロゲン原子によって置換されていてもよい。 Examples of the amide group of R 4 include those represented by the formula: -NH-C (= O) -R 23 , in which R 23 is an alkyl group, an aryl group, an aralkyl group, a heteroaryl group and the like. For specific examples of the alkyl group, aryl group, aralkyl group, and heteroaryl group, the above description is referred to, and a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with a halogen atom.
R4のスルホンアミド基としては、式:−NH−SO2−R24で表され、R24がアルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、ヘテロアリール基であるもの等が挙げられる。アルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、ヘテロアリール基の具体例は上記の説明が参照され、水素原子の一部がハロゲン原子によって置換されていてもよい。 Examples of the sulfonamide group of R 4 include those represented by the formula: -NH-SO 2- R 24 , in which R 24 is an alkyl group, an aryl group, an aralkyl group, a heteroaryl group and the like. For specific examples of the alkyl group, aryl group, aralkyl group, and heteroaryl group, the above description is referred to, and a part of the hydrogen atom may be substituted with a halogen atom.
R4のハロゲノ基としては、フルオロ基、クロロ基、ブロモ基、ヨード基等が挙げられる。 Examples of the halogeno group of R 4 include a fluoro group, a chloro group, a bromo group, an iodo group and the like.
R4としては、水素原子、アルキル基、アルコキシ基、アルキルチオ基、アラルキル基、アリールオキシ基およびアリールチオ基から選ばれる1種以上であることが好ましい。例えば、R4が含窒素置換基である場合は、置換基R4が加熱や反応によって分解したり他の構造に変化して、エチレン化合物が黄色などの着色を呈しやすくなるため、あまり好ましくない。エチレン化合物が安定して紫外〜紫色領域の光を吸収できるようにする観点からは、R4は水素原子またはアルキル基であることが好ましく、当該アルキル基は炭素数1〜4が好ましく、1〜3がより好ましい。なかでも、式(2)の基Aのベンゼン環に結合する4つのR4のうち、2以上が水素原子であることが好ましく、3以上が水素原子であることがより好ましく、4つ全部が水素原子であることが特に好ましい。 The R 4 is preferably one or more selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, an alkylthio group, an aralkyl group, an aryloxy group and an arylthio group. For example, when R 4 is a nitrogen-containing substituent, it is not so preferable because the substituent R 4 is decomposed by heating or reaction or changed to another structure, and the ethylene compound tends to be colored yellow or the like. .. From the viewpoint of enabling the ethylene compound to stably absorb light in the ultraviolet to purple region, R 4 is preferably a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group, and the alkyl group preferably has 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and 1 to 1 3 is more preferable. Among them, among the four R 4s bonded to the benzene ring of the group A of the formula (2), it is preferable that two or more are hydrogen atoms, more preferably three or more are hydrogen atoms, and all four are all. It is particularly preferably a hydrogen atom.
式(2)のXは硫黄原子または酸素原子を表し、これによりエチレン化合物が安定して紫外〜紫色領域の光を吸収しやすくなる。UV領域の光を効果的に吸収できるようにする観点からは、Xは硫黄原子であることが好ましい。 X in the formula (2) represents a sulfur atom or an oxygen atom, which makes it easier for the ethylene compound to stably absorb light in the ultraviolet to purple region. From the viewpoint of effectively absorbing light in the UV region, X is preferably a sulfur atom.
式(2)で表される基Aにおいて、Xはエチレン構造部に対してオルト位に結合していてもよく、メタ位に結合していてもよく、パラ位に結合していてもよい。なお、エチレン化合物の製造容易性の観点からは、Xはエチレン構造部に対してパラ位に結合していることが好ましい。 In the group A represented by the formula (2), X may be bonded to the ethylene structure portion at the ortho position, may be bonded to the meta position, or may be bonded to the para position. From the viewpoint of ease of production of the ethylene compound, it is preferable that X is bonded to the ethylene structure at the para position.
式(1)において、連結基Lには2以上の基Aが結合している。連結基Lに2以上の基Aが結合することにより、エチレン化合物の耐熱性を高めることができる。連結基Lに結合する2以上の基Aは、互いに同一であっても異なっていてもよい。式(1)の連結基Lに結合する基Aの数aは、8以下が好ましく、6以下がより好ましく、4以下がさらに好ましい。安定性の高いエチレン化合物を容易に製造できる点からは、aは3以下がより好ましく、2であることが特に好ましい。 In the formula (1), two or more groups A are bonded to the linking group L. By binding two or more groups A to the linking group L, the heat resistance of the ethylene compound can be enhanced. The two or more groups A attached to the linking group L may be the same or different from each other. The number a of the groups A bonded to the linking group L of the formula (1) is preferably 8 or less, more preferably 6 or less, still more preferably 4 or less. From the viewpoint that an ethylene compound having high stability can be easily produced, a is more preferably 3 or less, and particularly preferably 2.
連結基Lとしては、アルキレン基、アリーレン基、ヘテロアリーレン基、−O−、−CO−、−S−、−SO−、−SO2−、−NH−等の2価の連結基;アルキル基を有していてもよいメチン基(−C<)、−N<等の3価の連結基;>C<等の4価の連結基;およびこれらを組み合わせた連結基が挙げられる。アルキレン基は、直鎖状、分岐状、環状のいずれであってもよい。また、アルキレン基とアリーレン基は、水酸基および/またはチオール基を有していてもよい。 The linking group L is a divalent linking group such as an alkylene group, an arylene group, a heteroarylene group, -O-, -CO-, -S-, -SO-, -SO 2- , -NH-; an alkyl group. Examples thereof include a methine group (-C <), a trivalent linking group such as -N <; a tetravalent linking group such as> C <; and a linking group combining these groups. The alkylene group may be linear, branched or cyclic. Further, the alkylene group and the arylene group may have a hydroxyl group and / or a thiol group.
連結基Lとしては、例えば下記式(4−1)〜式(4−17)に示される基が挙げられる。式(4−1)〜式(4−17)において、*は基Aの結合部位を表す。式(4−1)〜式(4−9)の連結基Lには2つの基Aが結合し、式(4−10)〜式(4−13)の連結基Lには3つの基Aが結合し、式(4−14)〜式(4−15)の連結基Lには4つの基Aが結合し、式(4−16)には5つの基Aが結合し、式(4−17)には6つの基Aが結合する。 Examples of the linking group L include groups represented by the following formulas (4-1) to (4-17). In formulas (4-1) to (4-17), * represents the binding site of group A. Two groups A are bonded to the connecting groups L of the formulas (4-1) to (4-9), and three groups A are attached to the connecting groups L of the formulas (4-10) to (4-13). 4 groups A are bonded to the connecting group L of the formulas (4-14) to (4-15), and 5 groups A are bonded to the linking group L of the formula (4-16). Six groups A are attached to -17).
エチレン化合物の安定性を高める観点からは、連結基Lは、水素原子の一部が水酸基および/またはチオール基で置き換えられていてもよいアルキレン基、水素原子の一部が水酸基および/またはチオール基で置き換えられていてもよいアリーレン基、−O−、−S−、およびこれらの基を組み合わせた連結基が好ましい(ただし、エーテル結合およびチオエーテル結合は連続しない)。また、直鎖状または分岐状のアルキレン基の炭素数(連続する炭素数)は6以下が好ましく、4以下がより好ましく、3以下がさらに好ましい。環状のアルキレン基であれば、炭素数は4以上が好ましく、5以上がより好ましく、また10以下が好ましく、8以下がより好ましい。アリーレン基の炭素数は、5以上が好ましく、6以上がより好ましく、また10以下が好ましく、8以下がより好ましい。 From the viewpoint of enhancing the stability of the ethylene compound, the linking group L is an alkylene group in which a part of the hydrogen atom may be replaced with a hydroxyl group and / or a thiol group, and a part of the hydrogen atom is a hydroxyl group and / or a thiol group. An arylene group which may be replaced with, -O-, -S-, and a linking group in which these groups are combined are preferable (however, the ether bond and the thioether bond are not continuous). The carbon number (continuous carbon number) of the linear or branched alkylene group is preferably 6 or less, more preferably 4 or less, still more preferably 3 or less. If it is a cyclic alkylene group, the number of carbon atoms is preferably 4 or more, more preferably 5 or more, preferably 10 or less, and more preferably 8 or less. The number of carbon atoms of the arylene group is preferably 5 or more, more preferably 6 or more, preferably 10 or less, and more preferably 8 or less.
エチレン化合物としては、下記式(5)に示されるエチレン化合物が特に好ましく示される。このようなエチレン化合物は、例えば波長300nm〜420nmの範囲に吸収極大を有するピークを有し、紫外〜紫色領域の光を効果的に吸収できるとともに、安定性に優れるものとなり、製造が容易になる。下記式(5)において、R1aとR1bの説明は上記のR1の説明が参照され、R2aとR2bの説明は上記のR2の説明が参照され、R3aとR3bの説明は上記のR3の説明が参照され、XaとXbの説明は上記のXの説明が参照される。 As the ethylene compound, the ethylene compound represented by the following formula (5) is particularly preferably shown. Such an ethylene compound has, for example, a peak having an absorption maximum in the wavelength range of 300 nm to 420 nm, can effectively absorb light in the ultraviolet to violet region, has excellent stability, and is easy to manufacture. .. In the following equation (5), the description of R 1a and R 1b refers to the above description of R 1 , the description of R 2a and R 2b refers to the above description of R 2 , and the description of R 3a and R 3b . Refers to the description of R 3 above, and the description of X a and X b refers to the description of X above.
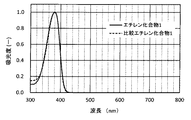
本発明のエチレン化合物は、トルエン中で測定した波長300nm〜600nmの範囲(より好ましくは300nm〜700nmの範囲であり、さらに好ましくは300nm〜800nmの範囲)の吸収スペクトルにおいて、波長420nm以下に最大吸収ピークを有することが好ましい。すなわちエチレン化合物は、トルエン中で吸収スペクトルを測定したとき、波長300nm〜420nmの範囲に吸収極大を有するピークを有し、かつ当該吸収ピークの吸収極大が波長300nm〜600nmの範囲で最大値をとることが好ましい。エチレン化合物がこのような吸収スペクトルを示すものであれば、紫外〜紫色領域の光を効果的に吸収できる。前記吸収ピークの極大波長は、310nm以上がより好ましく、315nm以上がさらに好ましく、また410nm以下がより好ましく、400nm以下がさらに好ましい。 The ethylene compound of the present invention has a maximum absorption at a wavelength of 420 nm or less in the absorption spectrum of a wavelength range of 300 nm to 600 nm (more preferably 300 nm to 700 nm, more preferably 300 nm to 800 nm) measured in toluene. It is preferable to have a peak. That is, the ethylene compound has a peak having an absorption maximum in the wavelength range of 300 nm to 420 nm when the absorption spectrum is measured in toluene, and the absorption maximum of the absorption peak has a maximum value in the wavelength range of 300 nm to 600 nm. Is preferable. If the ethylene compound exhibits such an absorption spectrum, it can effectively absorb light in the ultraviolet to violet region. The maximum wavelength of the absorption peak is more preferably 310 nm or more, further preferably 315 nm or more, further preferably 410 nm or less, and further preferably 400 nm or less.
エチレン化合物は、前記最大吸収ピークの極大波長における吸光度を1としたときに、当該吸収ピークの吸光度0.5におけるピーク幅が100nm以下であることが好ましく、80nm以下がより好ましく、70nm以下がさらに好ましい。エチレン化合物がこのような吸収スペクトルを示せば、紫外〜紫色領域の光を選択的に吸収できるものとなる。当該ピーク幅の下限値は特に限定されないが、例えば20nm以上であってもよく、30nm以上であってもよい。 When the absorbance of the maximum absorption peak at the maximum wavelength is 1, the ethylene compound preferably has a peak width of 100 nm or less at an absorbance of 0.5 of the absorption peak, more preferably 80 nm or less, and further 70 nm or less. preferable. If the ethylene compound shows such an absorption spectrum, it can selectively absorb light in the ultraviolet to violet region. The lower limit of the peak width is not particularly limited, but may be, for example, 20 nm or more, or 30 nm or more.
エチレン化合物は、前記最大吸収ピークの極大波長における吸光度を1としたときに、波長470nm〜600nmの範囲(好ましくは波長450nm〜700nmの範囲)の平均吸光度が0.03以下であることが好ましく、0.02以下がより好ましく、0.01以下がさらに好ましく、これにより可視光領域の広い範囲において、光線透過率を高めることができる。 The ethylene compound preferably has an average absorbance in the wavelength range of 470 nm to 600 nm (preferably in the wavelength range of 450 nm to 700 nm) of 0.03 or less, where 1 is the absorbance of the maximum absorption peak at the maximum wavelength. 0.02 or less is more preferable, and 0.01 or less is further preferable, which can increase the light transmittance in a wide range of the visible light region.
吸収スペクトルは、所定の波長範囲で測定ピッチ1nmごとに吸光度を測定することにより求める。測定ピッチ(1nm)未満における波長の吸光度の値は、1nmピッチの吸光度の測定値から線形補間することにより算出する。トルエン中のエチレン化合物の濃度は、最大吸収ピークの吸収極大における吸光度が1±0.003となるように調整する。波長470nm〜600nmの範囲の平均吸光度は、波長470nm〜600nmの範囲で1nmピッチで測定した131点の吸光度の値を平均することにより求める。 The absorption spectrum is obtained by measuring the absorbance in a predetermined wavelength range at every measurement pitch of 1 nm. The value of the absorbance at the wavelength below the measurement pitch (1 nm) is calculated by linear interpolation from the measured value of the absorbance at the measurement pitch of 1 nm. The concentration of the ethylene compound in toluene is adjusted so that the absorbance at the maximum absorption peak of the maximum absorption peak is 1 ± 0.003. The average absorbance in the wavelength range of 470 nm to 600 nm is determined by averaging the absorbance values of 131 points measured at a pitch of 1 nm in the wavelength range of 470 nm to 600 nm.
本発明のエチレン化合物は、紫外〜紫色領域の光を効果的に吸収できることから、紫外線吸収剤として好適に用いることができる。エチレン化合物は、任意の溶媒(例えば水や有機溶媒)に溶解または分散させて使用することができる。従って、紫外線吸収剤は溶媒を含有するものであってもよい。 Since the ethylene compound of the present invention can effectively absorb light in the ultraviolet to purple region, it can be suitably used as an ultraviolet absorber. The ethylene compound can be used by being dissolved or dispersed in any solvent (for example, water or an organic solvent). Therefore, the ultraviolet absorber may contain a solvent.
紫外線吸収剤に含まれるエチレン化合物は、1種のみであってもよいし、2種以上であってもよい。紫外線吸収剤は、本発明のエチレン化合物以外に公知の紫外線吸収剤(例えば、ベンゾトリアゾール系化合物、ベンゾフェノン系化合物、サリチル酸系化合物、ベンゾオキサジノン系化合物、シアノアクリレート系化合物、ベンゾオキサゾール系化合物、メロシアニン系化合物、トリアジン系化合物等)を含んでいてもよい。 The ethylene compound contained in the ultraviolet absorber may be only one kind or two or more kinds. The ultraviolet absorber is a known ultraviolet absorber other than the ethylene compound of the present invention (for example, benzotriazole compound, benzophenone compound, salicylic acid compound, benzoxazineone compound, cyanoacrylate compound, benzoxazole compound, merocyanine). It may contain a system compound, a triazine compound, etc.).
本発明のエチレン化合物は、例えば下記に示したスキームに従って製造することができる。下記のスキームにおいて、R1〜R3、X、Lは上記の式(1)における意味と同じであり、その好適態様も上記に説明した通りである。Yはハロゲン原子を表す。なお、下記において基R4は省略して示しており、また連結基Lとして2価の連結基を与える化合物を使用した例を示している。 The ethylene compound of the present invention can be produced, for example, according to the scheme shown below. In the following scheme, R 1 to R 3, X, L is the same meaning as in the formula (1), the preferred embodiments are also as described above. Y represents a halogen atom. In the following, the group R 4 is omitted, and an example in which a compound that gives a divalent linking group as the linking group L is used is shown.
まず、基Aの前駆体を与える式(6)の化合物と連結基Lを与える式(7)の化合物とを反応させることにより、連結基Lの両末端に基Aの前駆体が結合した式(8)の化合物が得られる。式(6)の化合物は、ハロゲノフェニルケトン化合物またはハロゲノフェニルアルデヒド化合物であり、式(6)の化合物は1種のみを用いてもよく、2種以上を用いてもよい。式(7)の化合物は、水酸基および/またはチオール基を有する化合物である。式(6)の化合物と式(7)の化合物とを反応させることにより、式(7)の化合物のX(硫黄原子または酸素原子)が式(6)の化合物のハロゲン原子が結合する炭素原子に求核的に作用し、連結基Lに基Aの前駆体が結合した式(8)の化合物が得られる。 First, by reacting the compound of the formula (6) that gives the precursor of the group A with the compound of the formula (7) that gives the linking group L, the precursor of the group A is bonded to both ends of the linking group L. The compound of (8) is obtained. The compound of the formula (6) is a halogenophenyl ketone compound or a halogenophenyl aldehyde compound, and the compound of the formula (6) may use only one kind or two or more kinds. The compound of formula (7) is a compound having a hydroxyl group and / or a thiol group. By reacting the compound of the formula (6) with the compound of the formula (7), the X (sulfur atom or oxygen atom) of the compound of the formula (7) is the carbon atom to which the halogen atom of the compound of the formula (6) is bonded. The compound of the formula (8) in which the precursor of the group A is bound to the linking group L is obtained.
化合物(7)としては、エチレングリコール、プロピレングリコール、ジエチレングリコール、トリエチレングリコール、1,2−エタンジチオール、1,2−プロパンジチオール、2−メルカプトエタノール、チオジグリコール、ビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテル、ビス(2−メルカプトエチル)スルフィド、1,3−ビス(2−メルカプトエチルチオ)プロパン、シクロヘキサンジオール、ベンゼンジオール、ビスフェノールA等の2価の連結基Lを与える化合物;グリセロール、ジメルカプロール、シクロヘキサントリール、ベンゼントリオール、トリメチロールプロパントリメルカプトアセテート、トリメチロールプロパントリス(3−メルカプトプロピオネート)、トリス−[(3−メルカプトプロピオニルオキシ)−エチル]−イソシアヌレート等の3価の連結基Lを与える化合物;エリトリトール、ペンタエリスリトールテトラキスメルカプトアセテート、ペンタエリスリトールテトラキス(3−メルカプトプロピオネート)等の4価の連結基Lを与える化合物;リビトール等の5価の連結基Lを与える化合物;ジペンタエリスリトールヘキサキスメルカプトアセテート、ジペンタエリスリトールヘキサキス(3−メルカプトプロピオネート)等の6価の連結基Lを与える化合物等を用いることができる。 Examples of the compound (7) include ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, 1,2-ethanedithiol, 1,2-propanedithiol, 2-mercaptoethanol, thiodiglycol, and bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether. , Bis (2-mercaptoethyl) sulfide, 1,3-bis (2-mercaptoethylthio) propane, cyclohexanediol, benzenediol, bisphenol A and other compounds that provide the divalent linking group L; glycerol, dimercaptols, Trivalent linking group L such as cyclohexanetril, benzenetriol, trimethylolpropanetrimercaptoaceto, trimethylolpropanetris (3-mercaptopropionate), tris-[(3-mercaptopropionyloxy) -ethyl] -isocyanurate. Compounds that give tetravalent linking group L such as erytritor, pentaerythritol tetrakis mercaptoaceto, pentaerythritol tetrakis (3-mercaptopropionate); compounds that give pentavalent linking group L such as ribitol; dipenta. Compounds and the like that provide a hexavalent linking group L, such as erythritol hexakis mercaptoaceto and dipentaerythritol hexakis (3-mercaptopropionate), can be used.
次いで、式(8)の化合物と式(9)の化合物とをKnoevenagel縮合反応させることにより、式(10)の本発明のエチレン化合物が得られる。式(9)の化合物は、R1とR2の間のメチレン基がシアノ基および/またはカルボニル基で挟まれていると、式(8)の化合物のカルボニル基との反応性が特に高まる。式(9)の化合物は1種のみを用いてもよく、2種以上を用いてもよい。 Then, the compound of the formula (8) and the compound of the formula (9) are subjected to a Knoevenagel condensation reaction to obtain the ethylene compound of the present invention of the formula (10). In the compound of formula (9), when the methylene group between R 1 and R 2 is sandwiched between a cyano group and / or a carbonyl group, the reactivity of the compound of formula (8) with the carbonyl group is particularly enhanced. Only one compound of the formula (9) may be used, or two or more compounds may be used.
化合物(9)としては、アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル、マロノニトリル、フェニル酢酸エステル、シアノ酢酸エステル、マロン酸ジエステル、2−シアノ−N,N−ジメチルアセトアミド、N−メチルアセトアセトアミド、アセトアセトアニリド、N,N,N’,N’−テトラメチルマロンアミド、1,3−シクロヘキサンジオン、ジメドン、メルドラム酸、バルビツール酸等を用いることができる。 Examples of compound (9) include acetonitrile, propionitrile, malononitrile, phenylacetic acid ester, cyanoacetic acid ester, malonic acid diester, 2-cyano-N, N-dimethylacetamide, N-methylacetamide, acetoacetanilide, N, N. , N', N'-tetramethylmalonamide, 1,3-cyclohexanedione, dimedone, meldrum acid, barbituric acid and the like can be used.
上記の反応は、溶媒存在下で行うことが好ましい。使用できる溶媒としては、例えば、クロロホルム、塩化メチレン等の塩素系炭化水素類;ベンゼン、トルエン、キシレン、トリメチルベンゼン等の芳香族炭化水素類;クロロトルエン、ジクロロベンゼン等の塩素系芳香族類;テトラヒドロフラン(THF)、ジオキサン、シクロペンチルメチルエーテル、ジイソプロピルエーテル、ジエチルエーテル等のエーテル類;アセトニトリル、プロピオニトリル、アクリロニトリル、ブチロニトリル等のニトリル類;メタノール、エタノール、プロパノール、ブタノール等のアルコール類;ギ酸、酢酸、プロピオン酸等の有機酸類;等が挙げられる。これらの溶媒は、1種のみを用いてもよく、2種以上を併用してもよい。 The above reaction is preferably carried out in the presence of a solvent. Examples of the solvent that can be used include chlorine-based hydrocarbons such as chloroform and methylene chloride; aromatic hydrocarbons such as benzene, toluene, xylene and trimethylbenzene; chlorine-based aromatics such as chlorotoluene and dichlorobenzene; tetrahydrofuran. Ethers such as (THF), dioxane, cyclopentylmethyl ether, diisopropyl ether, diethyl ether; nitriles such as acetonitrile, propionitrile, acrylonitrile, butyronitrile; alcohols such as methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol; formic acid, acetic acid, Organic acids such as propionic acid; and the like. Only one of these solvents may be used, or two or more of these solvents may be used in combination.
上記の反応において反応温度は適宜設定すればよく、例えば0℃以上が好ましく、5℃以上がより好ましく、10℃以上がさらに好ましく、また200℃以下が好ましく、150℃以下がより好ましい。当該反応は還流下で行ってもよい。反応時間は特に限定されず、反応の進行状況に応じて適宜設定すればよいが、例えば、0.5時間以上が好ましく、1時間以上がより好ましく、また48時間以下が好ましく、24時間以下がより好ましい。反応時の雰囲気は、式(8)の化合物の生成反応においては、不活性ガス(窒素、アルゴン等)雰囲気下で行うことが好ましい。 In the above reaction, the reaction temperature may be appropriately set, for example, 0 ° C. or higher is preferable, 5 ° C. or higher is more preferable, 10 ° C. or higher is further preferable, 200 ° C. or lower is preferable, and 150 ° C. or lower is more preferable. The reaction may be carried out under reflux. The reaction time is not particularly limited and may be appropriately set according to the progress of the reaction. For example, 0.5 hours or more is preferable, 1 hour or more is more preferable, 48 hours or less is preferable, and 24 hours or less is preferable. More preferred. The atmosphere at the time of the reaction is preferably an inert gas (nitrogen, argon, etc.) atmosphere in the reaction for producing the compound of the formula (8).
得られたエチレン化合物は、必要に応じて、ろ過、シリカゲルカラムクロマトグラフィー、アルミナカラムクロマトグラフィー、昇華、再結晶、晶析など公知の精製手段によって適宜精製することができる。 The obtained ethylene compound can be appropriately purified by a known purification means such as filtration, silica gel column chromatography, alumina column chromatography, sublimation, recrystallization, and crystallization, if necessary.
本発明のエチレン化合物は、樹脂成分と混合して、樹脂組成物とすることができる。本発明のエチレン化合物は耐熱性に優れることから、例えば熱可塑性樹脂に配合して、これを加熱成形した場合などでも、紫外線吸収効果を好適に発揮させることができる。また、本発明のエチレン化合物を含有する樹脂組成物は、紫外〜紫色領域の光に起因する劣化を抑制することができるとともに、これを硬化してフィルム等の樹脂成形体とすることで、紫外〜紫色領域の光をカットする光学フィルター等に適用することができる。さらに、樹脂組成物や樹脂成形体の保管の際や光学フィルターの製造・加工(例えば蒸着や実装など)の際に紫外光にさらされても、当該紫外光から樹脂成分や樹脂組成物中に含まれる他の成分(後述する近赤外線吸収色素など)を保護し、これらの成分の劣化を抑制することができる。 The ethylene compound of the present invention can be mixed with a resin component to form a resin composition. Since the ethylene compound of the present invention has excellent heat resistance, the ultraviolet absorbing effect can be suitably exhibited even when it is blended with a thermoplastic resin and heat-molded, for example. Further, the resin composition containing the ethylene compound of the present invention can suppress deterioration caused by light in the ultraviolet to purple region, and is cured to form a resin molded body such as a film to obtain ultraviolet rays. It can be applied to an optical filter or the like that cuts light in the purple region. Furthermore, even if the resin composition or resin molded body is exposed to ultraviolet light during storage or during manufacturing / processing of an optical filter (for example, vapor deposition or mounting), the ultraviolet light is transmitted into the resin component or resin composition. It is possible to protect other components contained (such as a near-infrared absorbing dye described later) and suppress deterioration of these components.
樹脂組成物は、本発明のエチレン化合物と樹脂成分とを少なくとも含むものである。樹脂組成物に含まれるエチレン化合物は、1種のみであってもよいし、2種以上であってもよい。樹脂組成物は、さらに他の紫外線吸収剤(例えば、ベンゾトリアゾール系化合物、ベンゾフェノン系化合物、サリチル酸系化合物、ベンゾオキサジノン系化合物、シアノアクリレート系化合物、ベンゾオキサゾール系化合物、メロシアニン系化合物、トリアジン系化合物等)を含有していてもよい。 The resin composition contains at least the ethylene compound of the present invention and a resin component. The ethylene compound contained in the resin composition may be only one kind or two or more kinds. The resin composition includes further ultraviolet absorbers (for example, benzotriazole-based compounds, benzophenone-based compounds, salicylic acid-based compounds, benzoxazine-based compounds, cyanoacrylate-based compounds, benzoxazole-based compounds, merocyanine-based compounds, and triazine-based compounds. Etc.) may be contained.
樹脂組成物中のエチレン化合物の含有量は、所望の性能を発現させる点から、樹脂組成物の固形分100質量%中、0.01質量%以上であることが好ましく、0.03質量%以上がより好ましく、0.1質量%以上がさらに好ましい。また、樹脂組成物の成形性や成膜性等を高める点から、樹脂組成物中のエチレン化合物の含有量は、樹脂組成物の固形分100質量%中、25質量%以下が好ましく、20質量%以下がより好ましく、15質量%以下がさらに好ましい。樹脂組成物が他の紫外線吸収剤をも含む場合は、これらの合計含有量が上記範囲にあることが好ましい。なお、他の紫外線吸収剤の含有量は、エチレン化合物100質量部に対し、100質量部以下が好ましく、60質量部以下がより好ましく、30質量部以下がさらに好ましい。樹脂組成物の固形分量とは、樹脂組成物が溶媒を含有する場合に、溶媒を除いた樹脂組成物の量を意味する。 The content of the ethylene compound in the resin composition is preferably 0.01% by mass or more, preferably 0.03% by mass or more, based on 100% by mass of the solid content of the resin composition, from the viewpoint of exhibiting desired performance. Is more preferable, and 0.1% by mass or more is further preferable. Further, from the viewpoint of improving the moldability and film forming property of the resin composition, the content of the ethylene compound in the resin composition is preferably 25% by mass or less, preferably 20% by mass, based on 100% by mass of the solid content of the resin composition. % Or less is more preferable, and 15% by mass or less is further preferable. When the resin composition also contains other UV absorbers, the total content of these is preferably in the above range. The content of the other ultraviolet absorber is preferably 100 parts by mass or less, more preferably 60 parts by mass or less, and further preferably 30 parts by mass or less with respect to 100 parts by mass of the ethylene compound. The solid content of the resin composition means the amount of the resin composition excluding the solvent when the resin composition contains a solvent.
樹脂組成物に含まれる樹脂成分は、公知の樹脂を用いることができる。樹脂成分としては、透明性が高く、本発明のエチレン化合物を溶解または分散できるものが好ましい。樹脂組成物が、後述するように近赤外線吸収色素や可視光吸収色素をも含有する場合は、樹脂成分は、当該色素も溶解または分散できるものが好ましい。このような樹脂成分を選択することにより、透過させたい波長域における高透過率と、遮断したい波長域における高吸収性を両立させることができる。 A known resin can be used as the resin component contained in the resin composition. As the resin component, one having high transparency and capable of dissolving or dispersing the ethylene compound of the present invention is preferable. When the resin composition also contains a near-infrared absorbing dye or a visible light absorbing dye as described later, the resin component is preferably one capable of dissolving or dispersing the dye. By selecting such a resin component, it is possible to achieve both high transmittance in the wavelength range to be transmitted and high absorption in the wavelength range to be blocked.
樹脂成分としては、重合が完結した樹脂のみならず、樹脂原料(樹脂の前駆体、当該前駆体の原料、樹脂を構成する単量体等を含む)であって、樹脂組成物を成形する際に重合反応または架橋反応して樹脂に組み込まれるものも用いることができる。本発明においては、いずれの樹脂も樹脂成分に含まれる。なお後者の場合は、重合反応で得られた反応液中に存在する、未反応物、反応性末端官能基、イオン性基、触媒、酸・塩基性基等により、エチレン化合物の構造の一部または全部が分解してしまうこともあり得る。従って、そのような懸念がある場合には、重合が完結した樹脂にエチレン化合物を配合して、樹脂組成物を形成することが望ましい。 The resin component is not only a resin whose polymerization has been completed, but also a resin raw material (including a resin precursor, a raw material of the precursor, a monomer constituting the resin, etc.), and when molding a resin composition. It is also possible to use a resin which is incorporated into a resin by a polymerization reaction or a cross-linking reaction. In the present invention, any resin is included in the resin component. In the latter case, a part of the structure of the ethylene compound is caused by the unreactant, the reactive terminal functional group, the ionic group, the catalyst, the acid / basic group, etc., which are present in the reaction solution obtained by the polymerization reaction. Or it is possible that everything will be disassembled. Therefore, when there is such a concern, it is desirable to add an ethylene compound to the polymerized resin to form a resin composition.
樹脂成分としては、透明性の高い樹脂を用いることが好ましく、これにより樹脂組成物に含まれるエチレン化合物の特性を好適に活用することができる。樹脂成分としては、例えば、(メタ)アクリル系樹脂、(メタ)アクリルウレタン系樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニル系樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニリデン樹脂、ポリオレフィン樹脂(例えば、ポリエチレン樹脂、ポリプロピレン樹脂)、シクロオレフィン系樹脂、メラミン樹脂、ウレタン樹脂、スチレン系樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル、ポリアミド樹脂(例えば、ナイロン)、アラミド樹脂、ポリイミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂、アルキド樹脂、フェノール樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂(例えば、ポリブチレンテレフタレート(PBT)樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)樹脂、ポリアリレート樹脂等)、ポリスルホン樹脂、ブチラール樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、ポリエーテル系樹脂、ABS樹脂(アクリロニトリルブタジエンスチレン樹脂)、AS樹脂(アクリロニトリル−スチレン共重合体)、シリコーン樹脂、変性シリコーン樹脂(例えば、(メタ)アクリルシリコーン系樹脂、アルキルポリシロキサン系樹脂、シリコーンウレタン樹脂、シリコーンポリエステル樹脂、シリコーンアクリル樹脂等)、フッ素系樹脂(例えば、フッ素化芳香族ポリマー、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)、パーフルオロアルコキシフッ素樹脂(PFA)、フッ素化ポリアリールエーテルケトン(FPEK)、フッ素化ポリイミド(FPI)、フッ素化ポリアミド酸(FPAA)、フッ素化ポリエーテルニトリル(FPEN)等)等が挙げられる。これらの中でも、透明性や耐熱性に優れる観点から、ポリイミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂、(メタ)アクリル系樹脂、シクロオレフィン系樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリアリレート樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、ポリスルホン樹脂、フッ素化芳香族ポリマーが好ましい。 As the resin component, it is preferable to use a highly transparent resin, whereby the characteristics of the ethylene compound contained in the resin composition can be suitably utilized. Examples of the resin component include (meth) acrylic resin, (meth) acrylic urethane resin, polyvinyl chloride resin, polyvinylidene chloride resin, polyolefin resin (for example, polyethylene resin and polypropylene resin), cycloolefin resin, and the like. Melamine resin, urethane resin, styrene resin, polyvinyl acetate, polyamide resin (eg nylon), aramid resin, polyimide resin, polyamideimide resin, alkyd resin, phenol resin, epoxy resin, polyester resin (eg polybutylene terephthalate (eg, polybutylene terephthalate) PBT) resin, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) resin, polyarylate resin, etc.), polysulfone resin, butyral resin, polycarbonate resin, polyether resin, ABS resin (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene resin), AS resin (acrylonitrile-styrene copolymer) , Silicone resin, modified silicone resin (eg, (meth) acrylic silicone resin, alkylpolysiloxane resin, silicone urethane resin, silicone polyester resin, silicone acrylic resin, etc.), fluororesin (eg, fluorinated aromatic polymer, etc.) Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), perfluoroalkoxyfluororesin (PFA), fluorinated polyaryl ether ketone (FPEK), fluorinated polyimide (FPI), fluorinated polyamic acid (FPAA), fluorinated polyether nitrile (FPEN) Etc.) etc. Among these, from the viewpoint of excellent transparency and heat resistance, polyimide resin, polyamideimide resin, (meth) acrylic resin, cycloolefin resin, epoxy resin, polyester resin, polyarylate resin, polyamide resin, polycarbonate resin, polysulfone. Resins and fluorinated aromatic polymers are preferable.
ポリイミド樹脂は、主鎖の繰り返し単位にイミド結合を含む重合体であり、例えば、テトラカルボン酸2無水物とジアミンとを縮重合させてポリアミド酸を得て、これを脱水・環化(イミド化)させることにより製造することができる。ポリイミド樹脂としては、芳香族環がイミド結合で連結された芳香族ポリイミドを用いることが好ましい。ポリイミド樹脂は、例えば、三菱ガス化学社製のネオプリム(登録商標)、デュポン社製のカプトン(登録商標)、三井化学社製のオーラム(登録商標)、サンゴバン社製のメルディン(登録商標)、東レプラスチック精工社製のTPS(登録商標)TI3000シリーズ等を用いることができる。 The polyimide resin is a polymer containing an imide bond in the repeating unit of the main chain. For example, polycondensation of tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride and diamine is carried out to obtain polyamic acid, which is dehydrated and cyclized (imidized). ) Can be manufactured. As the polyimide resin, it is preferable to use an aromatic polyimide in which aromatic rings are linked by an imide bond. Polyimide resins include, for example, Neoprim (registered trademark) manufactured by Mitsubishi Gas Chemicals, Kapton (registered trademark) manufactured by DuPont, Aurum (registered trademark) manufactured by Mitsui Chemicals, Meldin (registered trademark) manufactured by Coralvan, and Toray. TPS (registered trademark) TI3000 series manufactured by Plastic Seiko Co., Ltd. can be used.
ポリアミドイミド樹脂は、主鎖の繰り返し単位にアミド結合とイミド結合を含む重合体である。ポリアミドイミド樹脂は、例えば、ソルベイアドバンストポリマーズ社製のトーロン(登録商標)、東洋紡社製のバイロマックス(登録商標)、東レプラスチック精工社製のTPS(登録商標)TI5000シリーズ等を用いることができる。 The polyamide-imide resin is a polymer containing an amide bond and an imide bond in the repeating unit of the main chain. As the polyamide-imide resin, for example, Toron (registered trademark) manufactured by Solvay Advanced Polymers, Vilomax (registered trademark) manufactured by Toyobo, TPS (registered trademark) TI5000 series manufactured by Toray Plastics Precision Precision Co., Ltd., and the like can be used.
(メタ)アクリル系樹脂は、(メタ)アクリル酸またはその誘導体由来の繰り返し単位を有する重合体であり、例えば、ポリ(メタ)アクリル酸エステル樹脂等の(メタ)アクリル酸エステル由来の繰り返し単位を有する樹脂が好ましく用いられる。(メタ)アクリル系樹脂は主鎖に環構造を有するものも好ましく、例えば、ラクトン環構造、無水グルタル酸構造、グルタルイミド構造、無水マレイン酸構造、マレイミド環構造等のカルボニル基含有環構造;オキセタン環構造、アゼチジン環構造、テトラヒドロフラン環構造、ピロリジン環構造、テトラヒドロピラン環構造、ピペリジン環構造等のカルボニル基非含有環構造が挙げられる。なお、カルボニル基含有環構造には、イミド基などのカルボニル基誘導体基を含有する構造も含む。カルボニル基含有環構造を有する(メタ)アクリル系樹脂は、例えば、特開2004−168882号公報、特開2008−179677号公報、国際公開第2005/54311号、特開2007−31537号公報等に記載されたものを用いることができる。 The (meth) acrylic resin is a polymer having a repeating unit derived from (meth) acrylic acid or a derivative thereof, and for example, a repeating unit derived from a (meth) acrylic acid ester such as a poly (meth) acrylic acid ester resin. The resin to have is preferably used. The (meth) acrylic resin preferably has a ring structure in the main chain, for example, a carbonyl group-containing ring structure such as a lactone ring structure, a glutaric anhydride structure, a glutarimide structure, a maleic anhydride structure, and a maleimide ring structure; oxetane. Examples thereof include a carbonyl group-free ring structure such as a ring structure, an azetidine ring structure, a tetrahydrofuran ring structure, a pyrrolidine ring structure, a tetrahydropyran ring structure, and a piperidine ring structure. The carbonyl group-containing ring structure also includes a structure containing a carbonyl group derivative group such as an imide group. Examples of the (meth) acrylic resin having a carbonyl group-containing ring structure are described in JP-A-2004-168882, JP-A-2008-179677, International Publication No. 2005/54311, JP-A-2007-31537 and the like. The ones described can be used.
シクロオレフィン系樹脂は、モノマー成分の少なくとも一部としてシクロオレフィンを用い、これを重合して得られる重合体であり、主鎖の一部に脂環構造を有するものであれば特に限定されない。シクロオレフィン系樹脂としては、例えば、ポリプラスチック社製のトパス(登録商標)、三井化学社製のアペル(登録商標)、日本ゼオン社製のゼオネックス(登録商標)およびゼオノア(登録商標)、JSR社製のアートン(登録商標)等を用いることができる。 The cycloolefin-based resin is a polymer obtained by using cycloolefin as at least a part of the monomer component and polymerizing the cycloolefin, and is not particularly limited as long as it has an alicyclic structure in a part of the main chain. Examples of cycloolefin resins include Topas (registered trademark) manufactured by Polyplastics, Appel (registered trademark) manufactured by Mitsui Chemicals, Zeonex (registered trademark) and Zeonoa (registered trademark) manufactured by Zeon Corporation, and JSR Corporation. Arton (registered trademark) manufactured by ZEON Corporation can be used.
エポキシ樹脂は、エポキシ化合物(プレポリマー)を硬化剤や硬化触媒の存在下で架橋化することで硬化させることができる樹脂である。エポキシ化合物としては、芳香族エポキシ化合物、脂肪族エポキシ化合物、脂環式エポキシ化合物、水添エポキシ化合物等が挙げられ、例えば、大阪ガスケミカル社製のフルオレンエポキシ(オグソール(登録商標)PG−100)、三菱化学社製のビスフェノールA型エポキシ化合物(JER(登録商標)828EL)や水添ビスフェノールA型エポキシ化合物(JER(登録商標)YX8000)、ダイセル社製の脂環式エポキシ化合物(EHPE(登録商標)3150)や二官能脂環式エポキシ化合物(セロキサイド(登録商標)2021P)等を用いることができる。 Epoxy resin is a resin that can be cured by cross-linking an epoxy compound (prepolymer) in the presence of a curing agent or curing catalyst. Examples of the epoxy compound include aromatic epoxy compounds, aliphatic epoxy compounds, alicyclic epoxy compounds, hydrogenated epoxy compounds and the like. For example, fluorene epoxy manufactured by Osaka Gas Chemical Co., Ltd. (Ogsol (registered trademark) PG-100). , Mitsubishi Chemicals, Inc. bisphenol A type epoxy compound (JER® 828EL), hydrogenated bisphenol A type epoxy compound (JER®, registered trademark) YX8000), Daicel Co., Ltd. alicyclic epoxy compound (EHPE (registered trademark)) ) 3150), a bifunctional alicyclic epoxy compound (celloxide (registered trademark) 2021P) and the like can be used.
ポリエステル樹脂は、主鎖の繰り返し単位にエステル結合を含む重合体であり、例えば、多価カルボン酸(ジカルボン酸)とポリアルコール(ジオール)とを縮重合させることにより得ることができる。ポリエステル樹脂としては、ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリブチレンテレフタレート、ポリトリメチレンテレフタレート、ポリエチレンナフタレート、ポリブチレンナフタレート等が挙げられ、例えば、大阪ガス化学社製のOKPシリーズ、帝人社製のTRNシリーズ、テオネックス(登録商標)、デュポン社製のライナイト(登録商標)、三菱化学社製のノバペックス(登録商標)、三菱エンジニアリングプラスチックス社製のノバデュラン(登録商標)、東レ社製のルミラー(登録商標)、トレコン(登録商標)、ユニチカ社製のエリーテル(登録商標)等を用いることができる。 The polyester resin is a polymer containing an ester bond in the repeating unit of the main chain, and can be obtained, for example, by polycondensing a polyvalent carboxylic acid (dicarboxylic acid) and a polyalcohol (diol). Examples of the polyester resin include polyethylene terephthalate, polybutylene terephthalate, polytrimethylene terephthalate, polyethylene naphthalate, polybutylene naphthalate and the like. For example, OKP series manufactured by Osaka Gas Chemical Co., Ltd., TRN series manufactured by Teijin Co., Ltd., Theonex ( Registered trademark), Dupont's Rinite (registered trademark), Mitsubishi Chemical's Novapex (registered trademark), Mitsubishi Engineering Plastics' Novaduran (registered trademark), Toray's Lumirer (registered trademark), Trecon (registered trademark) Registered trademark), Elitel (registered trademark) manufactured by Unitica, etc. can be used.
ポリアリレート樹脂は、2価フェノール化合物と2塩基酸(例えば、フタル酸等の芳香族ジカルボン酸)とを縮重合して得られる重合体であり、主鎖の繰り返し単位に芳香族環とエステル結合とを含む繰り返し単位を有する。ポリアリレート樹脂は、例えば、クラレ社製のベクトラン(登録商標)、ユニチカ社製のUポリマー(登録商標)やユニファイナー(登録商標)等を用いることができる。 The polyarylate resin is a polymer obtained by polycondensing a dihydric phenol compound and a dibasic acid (for example, an aromatic dicarboxylic acid such as phthalic acid), and has an aromatic ring and an ester bond in the repeating unit of the main chain. It has a repeating unit including and. As the polyarylate resin, for example, Vectran (registered trademark) manufactured by Kuraray, U polymer (registered trademark) manufactured by Unitika Ltd., Unifier (registered trademark), and the like can be used.
ポリアミド樹脂は、主鎖の繰り返し単位にアミド結合を含む重合体であり、例えば、ジアミンとジカルボン酸とを縮重合させることにより得ることができる。ポリアミド樹脂は主鎖に脂肪族骨格を有するものであってもよく、このようなアミド樹脂として、例えばナイロンを用いることができる。ポリアミド樹脂は芳香族骨格を有するものであってもよく、このようなポリアミド樹脂としてアラミド樹脂が知られている。アラミド樹脂は、耐熱性に優れ、強い機械強度を有する点から好ましく用いられ、例えば、帝人社製のトワロン(登録商標)、コーネックス(登録商標)、デュポン社製のケブラー(登録商標)、ノーメックス(登録商標)等を用いることができる。 The polyamide resin is a polymer containing an amide bond in the repeating unit of the main chain, and can be obtained, for example, by polycondensing diamine and a dicarboxylic acid. The polyamide resin may have an aliphatic skeleton in the main chain, and as such an amide resin, for example, nylon can be used. The polyamide resin may have an aromatic skeleton, and an aramid resin is known as such a polyamide resin. Aramid resin is preferably used because it has excellent heat resistance and strong mechanical strength. For example, Twaron (registered trademark) and Cornex (registered trademark) manufactured by Teijin, Kevlar (registered trademark) manufactured by DuPont, and Nomex. (Registered trademark) and the like can be used.
ポリカーボネート樹脂は、主鎖の繰り返し単位にカーボネート基(−O−(C=O)−O−)を含む重合体である。ポリカーボネート樹脂としては、帝人社製のパンライト(登録商標)、三菱エンジニアリングプラスチック社製のユーピロン(登録商標)、ノバレックス(登録商標)、ザンター(登録商標)、住化スタイロンポリカーボネート社製のSDポリカ(登録商標)等を用いることができる。 The polycarbonate resin is a polymer containing a carbonate group (-O- (C = O) -O-) as a repeating unit of the main chain. Polycarbonate resins include Panlite (registered trademark) manufactured by Teijin, Upiron (registered trademark), Novarex (registered trademark), Zanter (registered trademark) manufactured by Mitsubishi Engineering Plastics, and SD Polyca manufactured by Sumika Stylon Polycarbonate. (Registered trademark) and the like can be used.
ポリスルホン樹脂は、芳香族環とスルホニル基(−SO2−)と酸素原子とを含む繰り返し単位を有する重合体である。ポリスルホン樹脂は、例えば、住友化学社製のスミカエクセル(登録商標)PES3600PやPES4100P、ソルベイスペシャルティポリマーズ社製のUDEL(登録商標)P−1700等を用いることができる。 The polysulfone resin is a polymer having a repeating unit containing an aromatic ring, a sulfonyl group (−SO 2−), and an oxygen atom. As the polysulfone resin, for example, Sumika Excel (registered trademark) PES3600P or PES4100P manufactured by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd., UDEL (registered trademark) P-1700 manufactured by Solvay Specialty Polymers, etc. can be used.
フッ素化芳香族ポリマーは、1以上のフッ素原子を有する芳香族環と、エーテル結合、ケトン結合、スルホン結合、アミド結合、イミド結合およびエステル結合よりなる群から選ばれる少なくとも1つの結合とを含む繰り返し単位を有する重合体であり、これらの中でも、1以上のフッ素原子を有する芳香族環とエーテル結合とを含む繰り返し単位を必須的に含む重合体であることが好ましい。フッ素化芳香族ポリマーは、例えば、特開2008−181121号公報に記載されたものを用いることができる。 The fluorinated aromatic polymer is a repeat containing an aromatic ring having one or more fluorine atoms and at least one bond selected from the group consisting of ether bonds, ketone bonds, sulfone bonds, amide bonds, imide bonds and ester bonds. It is a polymer having a unit, and among these, a polymer essentially containing a repeating unit containing an aromatic ring having one or more fluorine atoms and an ether bond is preferable. As the fluorinated aromatic polymer, for example, those described in JP-A-2008-181121 can be used.
樹脂成分は透明性が高いことが好ましく、これにより樹脂組成物を光学用途に好適に適用しやすくなる。樹脂成分は、例えば、厚さ0.1mmでの全光線透過率が75%以上であることが好ましく、80%以上がより好ましく、85%以上がさらに好ましい。樹脂成分の前記全光線透過率の上限は特に限定されず、全光線透過率は100%以下であればよいが、例えば95%以下であってもよい。全光線透過率は、JIS K 7105に基づき測定する。 The resin component preferably has high transparency, which facilitates suitable application of the resin composition to optical applications. As for the resin component, for example, the total light transmittance at a thickness of 0.1 mm is preferably 75% or more, more preferably 80% or more, still more preferably 85% or more. The upper limit of the total light transmittance of the resin component is not particularly limited, and the total light transmittance may be 100% or less, but may be, for example, 95% or less. Total light transmittance is measured based on JIS K 7105.
樹脂成分はガラス転移温度(Tg)が高いことが好ましく、これにより、樹脂組成物やこれから得られる各種成形体の耐熱性を高めることができる。樹脂成分のガラス転移温度は、例えば、110℃以上が好ましく、120℃以上がより好ましく、130℃以上がさらに好ましい。樹脂成分のガラス転移温度の上限は特に限定されないが、樹脂組成物の成形加工性を確保する点から、例えば380℃以下が好ましい。 The resin component preferably has a high glass transition temperature (Tg), which can enhance the heat resistance of the resin composition and various molded articles obtained from the resin composition. The glass transition temperature of the resin component is, for example, preferably 110 ° C. or higher, more preferably 120 ° C. or higher, and even more preferably 130 ° C. or higher. The upper limit of the glass transition temperature of the resin component is not particularly limited, but is preferably 380 ° C. or lower, for example, from the viewpoint of ensuring the molding processability of the resin composition.
樹脂組成物は近赤外線吸収色素および/または可視光吸収色素を含有していてもよい。樹脂組成物が、近赤外吸収色素および/または可視光吸収色素をさらに含有していれば、当該樹脂組成物から光選択透過性を有する光学フィルターを得ることができる。例えば、樹脂組成物が本発明のエチレン化合物と近赤外線吸収色素を含有していれば、紫外〜紫色領域および赤色〜近赤外領域の光の透過を抑え、可視光領域の光を優先的に透過させる光選択透過フィルター用の樹脂組成物として用いることができる。樹脂組成物が本発明のエチレン化合物と可視光吸収色素を含有する場合は、着色フィルターやブルーライト軽減フィルター用などの樹脂組成物とすることができる。 The resin composition may contain a near-infrared absorbing dye and / or a visible light absorbing dye. If the resin composition further contains a near-infrared absorbing dye and / or a visible light absorbing dye, an optical filter having light selective transmittance can be obtained from the resin composition. For example, if the resin composition contains the ethylene compound of the present invention and a near-infrared absorbing dye, the transmission of light in the ultraviolet to purple region and the red to near infrared region is suppressed, and the light in the visible light region is given priority. It can be used as a resin composition for a light selective transmission filter to be transmitted. When the resin composition contains the ethylene compound of the present invention and the visible light absorbing dye, it can be used as a resin composition for a coloring filter or a blue light reduction filter.
近赤外線吸収色素は、波長600nm〜1100nmの範囲に吸収極大を有するものが好ましい。近赤外領域色素は、より好ましくは、波長450nm〜1100nmの範囲における吸収スペクトルにおいて、波長600nm〜1100nmの範囲に吸収極大を有するピークを有し、かつ当該吸収ピークの吸収極大が波長450nm〜1100nmの範囲で最大値をとる。当該吸収極大波長は630nm以上がより好ましく、660nm以上がさらに好ましく、680nm以上がさらにより好ましく、また1000nm以下がより好ましく、900nm以下がさらに好ましく、800nm以下がさらにより好ましい。 The near-infrared absorbing dye preferably has an absorption maximum in the wavelength range of 600 nm to 1100 nm. The near-infrared region dye more preferably has a peak having an absorption maximum in the wavelength range of 600 nm to 1100 nm in an absorption spectrum in the wavelength range of 450 nm to 1100 nm, and the absorption maximum of the absorption peak has a wavelength of 450 nm to 1100 nm. Take the maximum value in the range of. The absorption maximum wavelength is more preferably 630 nm or more, further preferably 660 nm or more, further preferably 680 nm or more, still more preferably 1000 nm or less, further preferably 900 nm or less, still more preferably 800 nm or less.
可視光吸収色素としては、可視光領域(例えば、波長420nm超680nm未満の範囲)に極大吸収を有するものであれば特に制限なく用いることができる。なかでも、可視光吸収色素としては、視感度が高い波長500nm以上680nm未満の範囲に極大吸収を有するものを用いることが好ましい。 The visible light absorbing dye can be used without particular limitation as long as it has maximum absorption in the visible light region (for example, a wavelength range of more than 420 nm and less than 680 nm). Among them, as the visible light absorbing dye, it is preferable to use a dye having maximum absorption in a wavelength range of 500 nm or more and less than 680 nm, which has high luminosity factor.
近赤外吸収色素と可視光吸収色素は、有機色素であっても、無機色素であっても、有機無機複合色素(例えば、金属原子またはイオンが配位した有機化合物)であっても、特に限定されない。近赤外線吸収色素および可視光吸収色素としては、例えば、スクアリリウム系色素、クロコニウム系色素、中心金属イオンとして銅(例えば、Cu(II))や亜鉛(例えば、Zn(II))等を有していてもよい環状テトラピロール系色素(ポルフィリン類、クロリン類、フタロシアニン類、ナフタロシアニン類、コリン類等)、シアニン系色素、アゾ系色素、キノン系色素、キサンテン系色素、インドリン系色素、アリールメタン系色素、クアテリレン系色素、ジイモニウム系色素、ペリレン系色素、キナクドリン系色素、オキサジン系色素、ジピロメテン系色素、ニッケル錯体系色素、銅イオン系色素等が挙げられる。これらの色素は、1種のみを用いてもよく、2種以上を用いてもよい。なかでも、所望の波長光を効果的に吸収できる点から、近赤外吸収色素および可視光吸収色素として、シアニン系色素、スクアリリウム化合物、クロコニウム化合物、ジピロメテン系色素、およびフタロシアニン化合物から選ばれる少なくとも1種を用いることが好ましい。近赤外線吸収色素としては、近赤外領域の光を効果的に吸収し、可視光透過率を高めることが容易な点から、スクアリリウム化合物、クロコニウム化合物、およびフタロシアニン化合物から選ばれる少なくとも1種を用いることが好ましい。 The near-infrared absorbing dye and the visible light absorbing dye are particularly organic dyes, inorganic dyes, and organic-inorganic composite dyes (for example, organic compounds coordinated with metal atoms or ions). Not limited. Examples of the near-infrared absorbing dye and the visible light absorbing dye include a squarylium-based dye, a croconium-based dye, and copper (for example, Cu (II)) and zinc (for example, Zn (II)) as central metal ions. Cyclic tetrapyrrole pigments (porphyrins, chlorins, phthalocyanines, naphthalocyanines, cholines, etc.), cyanine pigments, azo pigments, quinone pigments, xanthene pigments, indolin pigments, arylmethane pigments, etc. Examples thereof include pigments, quaterylene-based pigments, diimonium-based pigments, perylene-based pigments, quinacdrine-based pigments, oxazine-based pigments, dipyrromethene-based pigments, nickel complex-based pigments, and copper ion-based pigments. Only one kind of these dyes may be used, or two or more kinds may be used. Among them, at least one selected from cyanine-based dyes, squarylium compounds, croconium compounds, dipyrromethene-based dyes, and phthalocyanine compounds as near-infrared absorbing dyes and visible light absorbing dyes from the viewpoint of being able to effectively absorb light of a desired wavelength. It is preferable to use seeds. As the near-infrared absorbing dye, at least one selected from a squarylium compound, a croconium compound, and a phthalocyanine compound is used because it can effectively absorb light in the near-infrared region and increase the visible light transmittance. Is preferable.
樹脂組成物中に近赤外線吸収色素および/または可視光吸収色素が含まれる場合、樹脂組成物中の近赤外線吸収色素と可視光吸収色素の含有量は、所望の性能を発現させる点から、樹脂組成物の固形分100質量%中、0.01質量%以上であることが好ましく、0.03質量%以上がより好ましく、0.1質量%以上がさらに好ましい。また、樹脂組成物の成形性や成膜性等を高める点から、樹脂組成物中の近赤外線吸収色素と可視光吸収色素の含有量は、樹脂組成物の固形分100質量%中、25質量%以下が好ましく、20質量%以下がより好ましく、15質量%以下がさらに好ましい。なお、エチレン化合物と近赤外線吸収色素と可視光吸収色素との合計含有量(あるいはさらに他の紫外線吸収剤を合わせた合計含有量)は、樹脂組成物の固形分100質量%中、30質量%以下となることが好ましく、25質量%以下がより好ましく、20質量%以下がさらに好ましい。 When the near-infrared absorbing dye and / or the visible light absorbing dye is contained in the resin composition, the content of the near-infrared absorbing dye and the visible light absorbing dye in the resin composition is a resin from the viewpoint of exhibiting desired performance. The solid content of the composition is preferably 0.01% by mass or more, more preferably 0.03% by mass or more, still more preferably 0.1% by mass or more, based on 100% by mass. Further, from the viewpoint of improving the moldability and film forming property of the resin composition, the content of the near-infrared absorbing dye and the visible light absorbing dye in the resin composition is 25% by mass in 100% by mass of the solid content of the resin composition. % Or less is preferable, 20% by mass or less is more preferable, and 15% by mass or less is further preferable. The total content of the ethylene compound, the near-infrared absorbing dye, and the visible light absorbing dye (or the total content including other ultraviolet absorbers) is 30% by mass based on 100% by mass of the solid content of the resin composition. It is preferably 25% by mass or less, more preferably 20% by mass or less.
樹脂組成物を、可視光領域の光を優先的に透過させる光選択透過フィルター用の樹脂組成物として用いるような場合は、近赤外線吸収色素として、例えば下記式(11)で表されるスクアリリウム化合物または下記式(12)で表されるクロコニウム化合物を用いることが好ましい。下記式(11)および式(12)において、R21〜R24はそれぞれ独立して、下記式(13)または式(14)で示される基を表す。 When the resin composition is used as a resin composition for a light selective transmission filter that preferentially transmits light in the visible light region, it is used as a near-infrared absorbing dye, for example, a squarylium compound represented by the following formula (11). Alternatively, it is preferable to use a croconium compound represented by the following formula (12). In the following formulas (11) and (12), R 21 to R 24 independently represent the groups represented by the following formulas (13) or (14).
式(13)中、環Pは、置換基を有していてもよい芳香族炭化水素環、芳香族複素環、またはこれらの環構造を含む縮合環を表し、R31〜R33はそれぞれ独立して、水素原子、有機基または極性官能基を表し、R32とR33は互いに連結して環を形成してもよい。式(14)中、R34〜R38はそれぞれ独立して、水素原子、有機基または極性官能基を表し、R34とR35、R35とR36、R36とR37、R37とR38はそれぞれ、互いに連結して環を形成していてもよい。*は、式(11)中の4員環または式(12)中の5員環との結合部位を表す。 In formula (13), ring P represents an aromatic hydrocarbon ring which may have a substituent, an aromatic heterocycle, or a fused ring containing these ring structures, and R 31 to R 33 are independent of each other. Thus, it represents a hydrogen atom, an organic group or a polar functional group, and R 32 and R 33 may be linked to each other to form a ring. In formula (14), R 34 to R 38 independently represent a hydrogen atom, an organic group or a polar functional group, and R 34 and R 35 , R 35 and R 36 , R 36 and R 37 , and R 37 . Each of R 38 may be connected to each other to form a ring. * Represents a binding site with a 4-membered ring in formula (11) or a 5-membered ring in formula (12).
R31〜R38の有機基と極性官能基の詳細は、上記のR4の有機基と極性官能基の説明が参照される。R31〜R38が独立した基である場合、R31〜R38はそれぞれ独立して、水素原子、アルキル基、アリール基、アラルキル基、アミノ基、アミド基またはヒドロキシ基であることが好ましい。これらの基の詳細は、上記のR4に関する説明が参照される。 For details of the organic groups and polar functional groups of R 31 to R 38 , refer to the above description of the organic groups and polar functional groups of R 4. When R 31 to R 38 are independent groups, it is preferable that R 31 to R 38 are independent hydrogen atoms, alkyl groups, aryl groups, aralkyl groups, amino groups, amide groups or hydroxy groups, respectively. Details of these groups are described for the above R 4 is referred to.
R32〜R38から形成される各環構造としては、炭化水素環や複素環が挙げられ、これらの環構造は芳香族性を有していても有していなくてもよいが、非芳香族炭化水素環または非芳香族複素環であることが好ましい。非芳香族炭化水素環としては、例えば、シクロペンタン、シクロヘキサン、シクロヘプタン等のシクロアルカン;シクロペンテン、シクロヘキセン、シクロヘキサジエン(例えば、1,3−シクロヘキサジエン)、シクロヘプテン、シクロヘプタジエン等のシクロアルケン等が挙げられる。非芳香族複素環としては、前記に説明したような炭化水素環の環を構成する炭素原子の1個以上が、N(窒素原子)、S(硫黄原子)およびO(酸素原子)から選ばれる少なくとも1種以上の原子に置き換わった環が挙げられる。非芳香族複素環としては、例えば、ピロリジン環、テトラヒドロフラン環、テトラヒドロチオフェン環、ピペリジン環、テトラヒドロピラン環、テトラヒドロチオピラン環、モルホリン環、ヘキサメチレンイミン環、ヘキサメチレンオキシド環、ヘキサメチレンスルフィド環、ヘプタメチレンイミン環等が挙げられる。 Examples of the ring structure formed from R 32 to R 38 include a hydrocarbon ring and a heterocycle, and these ring structures may or may not have aromaticity, but are non-aromatic. It is preferably a group hydrocarbon ring or a non-aromatic heterocycle. Examples of the non-aromatic hydrocarbon ring include cycloalkanes such as cyclopentane, cyclohexane and cycloheptane; cycloalkenes such as cyclopentene, cyclohexene and cyclohexadiene (for example, 1,3-cyclohexadiene), cycloheptene and cycloheptadiene. Can be mentioned. As the non-aromatic heterocycle, one or more carbon atoms constituting the ring of the hydrocarbon ring as described above are selected from N (nitrogen atom), S (sulfur atom) and O (oxygen atom). Examples include rings in which at least one or more atoms are replaced. Examples of the non-aromatic heterocycle include a pyrrolidine ring, a tetrahydrofuran ring, a tetrahydrothiophene ring, a piperidine ring, a tetrahydropyran ring, a tetrahydrothiopyran ring, a morpholine ring, a hexamethyleneimine ring, a hexamethylene oxide ring, and a hexamethylene sulfide ring. Examples include the heptamethyleneimine ring.
式(13)の基において、R32とR33が連結して形成される環構造としては、4〜9員の不飽和炭化水素環であることが好ましく、なかでもシクロペンテン、シクロヘキセン、シクロヘプテン、シクロオクテン等のシクロアルカンモノエンがより好ましい。このように式(13)の基が構成されていれば、赤色〜近赤外領域の吸収波形のショルダーピークが低減され、吸収ピークがシャープなものとなる。 In the group of formula (13), the ring structure formed by connecting R 32 and R 33 is preferably a 4- to 9-membered unsaturated hydrocarbon ring, among which cyclopentene, cyclohexene, cycloheptene, and cyclo. Cycloalkanemonoenes such as octene are more preferred. When the group of the formula (13) is configured in this way, the shoulder peak of the absorption waveform in the red to near infrared region is reduced, and the absorption peak becomes sharp.
式(13)の環Pの芳香族炭化水素環としては、ベンゼン環、ナフタレン環、フェナントレン環、アントラセン環、フルオランテン環、シクロテトラデカヘプタエン環等が挙げられる。芳香族炭化水素環は、環構造を1個のみ有するものであってもよく、2個以上の環構造が縮合したものであってもよい。環Pの芳香族複素環は、N(窒素原子)、O(酸素原子)およびS(硫黄原子)から選ばれる1種以上の原子を環構造に含み、芳香族性を有するものであり、例えば、フラン環、チオフェン環、ピロール環、ピラゾール環、オキサゾール環、チアゾール環、イミダゾール環、ピリジン環、ピリダジン環、ピリミジン環、ピラジン環、プリン環、プテリジン環等が挙げられる。芳香族複素環は、環構造を1個のみ有するものであってもよく、2個以上の環構造が縮合したものであってもよい。環Pのこれらの環構造を含む縮合環は、芳香族炭化水素環と芳香族複素環とが縮環した構造を有するものであり、例えば、インドール環、イソインドール環、ベンゾイミダゾール環、キノリン環、ベンゾピラン環、アクリジン環、キサンテン環、カルバゾール環等が挙げられる。環Pのπ共役系を適宜設定することにより、赤色〜近赤外領域の吸収波長を容易に調整することができる。 Examples of the aromatic hydrocarbon ring of the ring P of the formula (13) include a benzene ring, a naphthalene ring, a phenanthrene ring, an anthracene ring, a fluoranthene ring, a cyclotetradecaheptaene ring and the like. The aromatic hydrocarbon ring may have only one ring structure, or may be a condensation of two or more ring structures. The aromatic heterocycle of ring P contains one or more atoms selected from N (nitrogen atom), O (oxygen atom) and S (sulfur atom) in the ring structure and has aromaticity, for example. , Fran ring, thiophene ring, pyrol ring, pyrazole ring, oxazole ring, thiazole ring, imidazole ring, pyridine ring, pyridazine ring, pyrimidine ring, pyrazine ring, purine ring, pteridine ring and the like. The aromatic heterocycle may have only one ring structure or may be a condensed product of two or more ring structures. The fused ring containing these ring structures of ring P has a structure in which an aromatic hydrocarbon ring and an aromatic heterocycle are fused, and for example, an indole ring, an isoindole ring, a benzimidazole ring, and a quinoline ring. , Benzimidazole ring, acridine ring, xanthene ring, carbazole ring and the like. The absorption wavelength in the red to near infrared region can be easily adjusted by appropriately setting the π-conjugated system of the ring P.
環Pは置換基を有していてもよく、当該置換基としては上記に説明した有機基や極性官能基が挙げられる。環Pが置換基を有する場合、その数は1〜3が好ましく、1〜2がより好ましく、さらに好ましくは1である。環Pは置換基を有さなくてもよい。 Ring P may have a substituent, and examples of the substituent include the organic group and the polar functional group described above. When the ring P has a substituent, the number thereof is preferably 1 to 3, more preferably 1 to 2, and even more preferably 1. Ring P does not have to have a substituent.
式(13)の基を有するスクアリリウム化合物およびクロコニウム化合物の詳細は、特開2016−74649号公報の記載が参照される。 For details of the squarylium compound and the croconium compound having the group of the formula (13), refer to the description of JP-A-2016-74649.
式(14)で表される基においては、R35とR36が連結して環を形成していることが好ましく、さらにR36とR37が連結して環を形成していてもよい。この場合、少なくともR34とR38は独立した基となる。このように式(14)の基が構成されていれば、赤色〜近赤外領域の吸収ピークがシャープなものとなる。なお、R35とR36から形成される環構造やR36とR37から形成される環構造の環員数は5以上が好ましく、6以上がより好ましく、また12以下が好ましく、10以下がより好ましく、8以下がさらに好ましい。 In the group represented by the formula (14), it is preferable that R 35 and R 36 are connected to form a ring, and further, R 36 and R 37 may be connected to form a ring. In this case, at least R 34 and R 38 are independent groups. If the group of the formula (14) is configured in this way, the absorption peak in the red to near infrared region becomes sharp. The number of ring members of the ring structure formed of R 35 and R 36 and the ring structure formed of R 36 and R 37 is preferably 5 or more, more preferably 6 or more, preferably 12 or less, and more preferably 10 or less. It is preferable, and 8 or less is more preferable.
式(14)で表される基では、R36がアミノ基であるか、アミノ基であるR36がR35と連結して環を形成しているか、さらにR37とも連結して環を形成していることが好ましい。この場合、吸収極大波長が長波長側(例えば685nm以上)にシフトして、赤色領域の光の透過率を高めて、透過光の色味を実際のものに近付けることができる。 In the group represented by the formula (14), or R 36 is an amino group, or R 36 is an amino group forms a ring with R 35, form a ring further linked 37 both R It is preferable to do so. In this case, the absorption maximum wavelength can be shifted to the long wavelength side (for example, 685 nm or more) to increase the transmittance of light in the red region and bring the color of the transmitted light closer to the actual one.
式(14)で表される基を有するスクアリリウム化合物およびクロコニウム化合物は、スクアリリウム骨格またはクロコニウム骨格の両側のベンゼン環が連結基によって連結していてもよい。そのような化合物としては、例えば特開2015−176046号公報に開示されるスクアリリウム化合物が示される。 In the squarylium compound and the croconium compound having a group represented by the formula (14), the benzene rings on both sides of the squarylium skeleton or the croconium skeleton may be linked by a linking group. As such a compound, for example, a squarylium compound disclosed in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2015-176046 is shown.
樹脂組成物は、支持体(基板)上に樹脂層を形成した際の密着性を高める観点から、シランカップリング剤、シランカップリング剤の加水分解物、およびシランカップリング剤の加水分解縮合物から選ばれる少なくとも1種(以下、これらをまとめて「特定シラン化合物」と称する場合がある)を含有することが好ましい。ここで用いられるシランカップリング剤としては、エポキシ基、アミノ基、またはメルカプト基を含有するシランカップリング剤が好ましく、なかでもエポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤が好ましい。このようなシランカップリング剤を用いれば、樹脂組成物中にエチレン化合物が含まれることと相まって、樹脂層の支持体への密着性を高めることができる。 The resin composition is a silane coupling agent, a hydrolyzate of a silane coupling agent, and a hydrolyzed condensate of a silane coupling agent from the viewpoint of enhancing the adhesion when a resin layer is formed on a support (substrate). It is preferable to contain at least one selected from the above (hereinafter, these may be collectively referred to as "specific silane compound"). As the silane coupling agent used here, a silane coupling agent containing an epoxy group, an amino group, or a mercapto group is preferable, and an epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent is particularly preferable. When such a silane coupling agent is used, the adhesion of the resin layer to the support can be enhanced in combination with the inclusion of the ethylene compound in the resin composition.
エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤としては、エポキシ基とアルコキシシリル基を有する化合物を用いることができる。エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤には、エポキシ基が1つのみ含まれていてもよく、複数含まれていてもよく、またアルコキシシリル基が1つのみ含まれていてもよく、複数含まれていてもよい。 As the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent, a compound having an epoxy group and an alkoxysilyl group can be used. The epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent may contain only one epoxy group, may contain a plurality of epoxy groups, or may contain only one alkoxysilyl group, or may contain a plurality of epoxy silyl groups. You may.
エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤がアルコキシシリル基を1つのみ含むものである場合、当該シランカップリング剤としては、下記式(15)で表されるエポキシ基を有するアルコキシシランが好ましく用いられる。
SiR41 kR42 m(OR43)n(OH)4-k-m-n (15)
When the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent contains only one alkoxysilyl group, an alkoxysilane having an epoxy group represented by the following formula (15) is preferably used as the silane coupling agent.
SiR 41 k R 42 m (OR 43 ) n (OH) 4-kmn (15)
式(15)中、R41はエポキシ基含有基を表し、R42とR43はそれぞれ独立してアルキル基を表し、kは1〜3の整数を表し、mは0〜2の整数を表し、nは1〜3の整数を表す。kが2以上のとき、複数のR41は互いに同一であっても異なっていてもよく、mが2のとき、複数のR42は互いに同一であっても異なっていてもよく、nが2以上のとき、複数のOR43は互いに同一であっても異なっていてもよい。R41とR42とOR43とOHは、それぞれSiに直接結合する基である。 In formula (15), R 41 represents an epoxy group-containing group, R 42 and R 43 each independently represent an alkyl group, k represents an integer of 1-3, and m represents an integer of 0-2. , N represent an integer of 1-3. When k is 2 or more, the plurality of R 41s may be the same or different from each other, and when m is 2, the plurality of R 42s may be the same or different from each other, and n is 2. In the above case, the plurality of OR 43s may be the same or different from each other. R 41 , R 42 , OR 43, and OH are groups that directly bond to Si, respectively.
式(15)において、R41のエポキシ基含有基としては、エポキシ基を含むものであれば特に限定されず、グリシドキシ基含有基やシクロアルケンオキサイド(脂環式エポキシ基)含有基が挙げられる。グリシドキシ基やシクロアルケンオキサイドは、アルキレン基(好ましくは炭素数1〜10のアルキレン基)等の連結基を介してケイ素原子に結合していてもよい。R41にはエポキシ基が1つのみ含まれていることが好ましい。R41のエポキシ基含有基としては、グリシドキシ基、3−グリシドキシプロピル基、8−(グリシドキシ)−n−オクチル基、3,4−エポキシシクロヘキシル基、2−(3,4−エポキシシクロヘキシル)エチル基等が挙げられる。なお、樹脂層の支持体への密着性を高める観点から、R41に含まれるエポキシ基はケイ素原子との距離が離れすぎないことが好ましく、例えばグリシドキシ基やシクロアルケンオキサイドは、ケイ素原子に直接結合しているか、炭素数1〜6のアルキレン基を介してケイ素原子に結合していることが好ましい。 In the formula (15), the epoxy group-containing group of R 41 is not particularly limited as long as it contains an epoxy group, and examples thereof include a glycidoxy group-containing group and a cycloalkene oxide (alicyclic epoxy group) -containing group. The glycidoxy group and the cycloalkene oxide may be bonded to the silicon atom via a linking group such as an alkylene group (preferably an alkylene group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms). R 41 preferably contains only one epoxy group. Examples of the epoxy group-containing group of R 41 include a glycidoxy group, a 3-glycidoxypropyl group, an 8- (glycidoxy) -n-octyl group, a 3,4-epoxycyclohexyl group, and a 2- (3,4-epoxycyclohexyl) group. Examples include an ethyl group. From the viewpoint of enhancing the adhesion of the resin layer to the support, it is preferable that the epoxy group contained in R 41 is not too far from the silicon atom. For example, the glycidoxy group and the cycloalkene oxide are directly attached to the silicon atom. It is preferably bonded or bonded to a silicon atom via an alkylene group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
式(15)において、R42とR43のアルキル基は、炭素数1〜6が好ましく、より好ましくは1〜4であり、さらに好ましくは1〜3である。R42としては、メチル基、エチル基、n−プロピル基、イソプロピル基が好ましく挙げられる。OR43としては、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、n−プロポキシ基、イソプロポキシ基が好ましく挙げられる。 In the formula (15), the alkyl groups of R 42 and R 43 preferably have 1 to 6 carbon atoms, more preferably 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and further preferably 1 to 3 carbon atoms. Preferred examples of R 42 include a methyl group, an ethyl group, an n-propyl group and an isopropyl group. Preferred examples of OR 43 include a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, an n-propoxy group and an isopropoxy group.
式(15)において、kは1または2が好ましく、1がより好ましく、これにより樹脂層の支持体への密着性を高めやすくなる。また、mは0または1が好ましく、0がより好ましく、nは2または3が好ましい。 In the formula (15), k is preferably 1 or 2, more preferably 1, which makes it easier to improve the adhesion of the resin layer to the support. Further, m is preferably 0 or 1, more preferably 0, and n is preferably 2 or 3.
エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤がアルコキシシリル基を複数含むものである場合、当該シランカップリング剤としては、ポリマー型多官能エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤(以下、単に「ポリマー型シランカップリング剤」と称する場合がある)を用いることができる。ポリマー型シランカップリング剤は、有機ポリマー鎖にエポキシ基含有基とアルコキシシリル基含有基が結合した構造を有しており、1分子中にアルコキシシリル基を複数含むとともに、エポキシ基も複数含むことができる。なお、ポリマー型シランカップリング剤の有機鎖にはポリシロキサンは含まれない。ポリマー型シランカップリング剤は、このように1分子中にアルコキシシリル基とエポキシ基を複数有することができるため、樹脂や支持体との反応点が多く形成され、樹脂層の支持体への密着性を高めることができる。 When the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent contains a plurality of alkoxysilyl groups, the silane coupling agent is referred to as a polymer-type polyfunctional epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent (hereinafter, simply referred to as "polymer-type silane coupling agent"). In some cases) can be used. The polymer-type silane coupling agent has a structure in which an epoxy group-containing group and an alkoxysilyl group-containing group are bonded to an organic polymer chain, and contains a plurality of alkoxysilyl groups in one molecule and also contains a plurality of epoxy groups. Can be done. The organic chain of the polymer-type silane coupling agent does not contain polysiloxane. Since the polymer-type silane coupling agent can have a plurality of alkoxysilyl groups and epoxy groups in one molecule in this way, many reaction points with the resin and the support are formed, and the resin layer adheres to the support. It can enhance the sex.
エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解物は、当該シランカップリング剤に含まれるアルコキシシリル基を加水分解によりシラノール基に変換することで得ることができる。また、エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解縮合物は、当該シランカップリング剤の加水分解物に含まれるシラノール基を脱水縮合させてシロキサン結合(−Si−O−Si−)を形成することにより得ることができる。通常シランカップリング剤を加水分解させると、シランカップリング剤の加水分解物が得られるとともに、当該加水分解物に含まれるシラノール基の脱水縮合反応も起こることにより、シランカップリング剤の加水分解縮合物も容易に得られる。シランカップリング剤の加水分解縮合物は、同種のシランカップリング剤の加水分解物の脱水縮合物であってもよく、異種のシランカップリング剤の加水分解物の脱水縮合物であってもよい。 The hydrolyzate of the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent can be obtained by converting the alkoxysilyl group contained in the silane coupling agent into a silanol group by hydrolysis. Further, the hydrolyzate of the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent is formed by dehydrating and condensing the silanol groups contained in the hydrolyzate of the silane coupling agent to form a siloxane bond (-Si-O-Si-). Can be obtained by Usually, when a silane coupling agent is hydrolyzed, a hydrolyzate of the silane coupling agent is obtained, and a dehydration condensation reaction of silanol groups contained in the hydrolyzate also occurs, so that the hydrolysis condensation of the silane coupling agent occurs. Things can be easily obtained. The hydrolyzate of the silane coupling agent may be a dehydration condensate of the hydrolyzate of the same type of silane coupling agent, or may be a dehydration condensate of the hydrolyzate of a different type of silane coupling agent. ..
樹脂層の支持体への密着性を高める観点から、樹脂組成物は、少なくともエポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解物または加水分解縮合物を含有することが好ましい。より好ましくは、樹脂組成物中に、エポキシ基を有するアルコキシシラン(例えば、上記式(15)で表されるアルコキシシラン)の加水分解物または加水分解縮合物が含まれ、さらに好ましくは、エポキシ基を有するアルコキシシラン(例えば、上記式(15)で表されるアルコキシシラン)の加水分解縮合物が含まれる。この場合の脱水縮合物としては、例えば、樹脂組成物中に含まれる特定シラン化合物の重量平均分子量を測定したときに、五量体相当(ただし、アルコキシ基は全て水酸基になっているとする)の分子量以下となることが好ましく、四量体相当の分子量以下となることがより好ましい。当該重量平均分子量の具体的な値としては、例えば、300以上が好ましく、また1000以下が好ましく、800以下がより好ましく、600以下がさらに好ましい。また、特性シラン化合物100質量%中のエポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解物と加水分解縮合物の合計含有割合は、10質量%以上が好ましく、30質量%以上がより好ましく、50質量%以上がさらに好ましい。 From the viewpoint of enhancing the adhesion of the resin layer to the support, the resin composition preferably contains at least a hydrolyzate or a hydrolyzed condensate of an epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent. More preferably, the resin composition contains a hydrolyzate or a hydrolyzed condensate of an alkoxysilane having an epoxy group (for example, an alkoxysilane represented by the above formula (15)), and more preferably an epoxy group. A hydrolyzed condensate of an alkoxysilane having (for example, an alkoxysilane represented by the above formula (15)) is included. The dehydration condensate in this case is, for example, equivalent to a pentamer when the weight average molecular weight of the specific silane compound contained in the resin composition is measured (however, it is assumed that all the alkoxy groups are hydroxyl groups). The molecular weight is preferably less than or equal to the molecular weight of, and more preferably less than or equal to the molecular weight equivalent to the tetramer. As a specific value of the weight average molecular weight, for example, 300 or more is preferable, 1000 or less is preferable, 800 or less is more preferable, and 600 or less is further preferable. The total content of the hydrolyzate and the hydrolyzed condensate of the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent in 100% by mass of the characteristic silane compound is preferably 10% by mass or more, more preferably 30% by mass or more, and 50% by mass. The above is more preferable.
樹脂組成物中の特定シラン化合物の含有量は、樹脂組成物の固形分100質量%中、0.1質量%以上が好ましく、0.5質量%以上がより好ましく、1質量%以上がさらに好ましく、また20質量%以下が好ましく、10質量%以下がより好ましく、5質量%以下がさらに好ましい。 The content of the specific silane compound in the resin composition is preferably 0.1% by mass or more, more preferably 0.5% by mass or more, still more preferably 1% by mass or more, based on 100% by mass of the solid content of the resin composition. Further, 20% by mass or less is preferable, 10% by mass or less is more preferable, and 5% by mass or less is further preferable.
樹脂組成物中の特定シラン化合物の含有量は、ガスクロマトグラフィーや高速液体クロマトグラフィーにより求めることができる。ガスクロマトグラフィーや高速液体クロマトグラフィーにより樹脂組成物に含まれる特定シラン化合物を種類ごとに定量し、その総和から特定シラン化合物の含有量を求めることができる。シランカップリング剤の脱水縮合物(二量体や三量体等のオリゴマー)が含まれる場合は、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー分析などを組み合わせて、脱水縮合物の存在形態の判断材料とすることもできる。例えば、エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤を加水分解またはさらに脱水縮合する場合などは、初期に用いたシランカップリング剤の量から、加水分解またはさらに脱水縮合した後のその残存量を差し引くことで、その加水分解物と加水分解縮合物の含有量を求めることができる。 The content of the specific silane compound in the resin composition can be determined by gas chromatography or high performance liquid chromatography. The specific silane compound contained in the resin composition can be quantified for each type by gas chromatography or high performance liquid chromatography, and the content of the specific silane compound can be determined from the total. When a dehydrated condensate of a silane coupling agent (oligomer such as a dimer or a trimer) is contained, it may be used in combination with gel permeation chromatography analysis or the like to determine the existence form of the dehydrated condensate. it can. For example, in the case of hydrolyzing or further dehydrating and condensing an epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent, the residual amount after hydrolysis or further dehydration condensation is subtracted from the amount of the silane coupling agent used initially. The contents of the hydrolyzate and the hydrolyzed condensate can be determined.
樹脂組成物は、溶媒を含有するものであってもよい。例えば、樹脂組成物が塗料化された樹脂組成物である場合は、溶媒を含むことにより樹脂組成物の塗工が容易になる。塗料化された樹脂組成物は、例えば、エチレン化合物を樹脂成分を含む溶媒に溶解させたり、エチレン化合物を樹脂成分を含む溶媒(分散媒)に分散させることにより得ることができる。溶媒は、エチレン化合物の溶媒(溶剤)として機能するものであっても、分散媒として機能するものであってもよい。溶媒としては、例えば、メチルエチルケトン、メチルイソブチルケトン、シクロヘキサノン等のケトン類;PGMEA(2−アセトキシ−1−メトキシプロパン)、エチレングリコールモノブチルエーテル、エチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、エチレングリコールエチルエーテルアセテート等のグリコール誘導体類(エーテル化合物、エステル化合物、エーテルエステル化合物等);N,N−ジメチルアセトアミド等のアミド類;酢酸エチル、酢酸プロピル、酢酸ブチル等のエステル類;N−メチル−ピロリドン(具体的には、1−メチル−2−ピロリドン等)等のピロリドン類;トルエン、キシレン等の芳香族炭化水素類;シクロヘキサン、ヘプタン等の脂肪族炭化水素類;テトラヒドロフラン、ジオキサン、ジエチルエーテル、ジブチルエーテル等のエーテル類;メタノール、エタノール、プロパノール、ブタノール等のアルコール類;等が挙げられる。これらの溶媒は、1種のみを用いてもよく、2種以上を併用してもよい。 The resin composition may contain a solvent. For example, when the resin composition is a paint-based resin composition, the inclusion of a solvent facilitates coating of the resin composition. The paint-based resin composition can be obtained, for example, by dissolving the ethylene compound in a solvent containing a resin component or by dispersing the ethylene compound in a solvent (dispersion medium) containing a resin component. The solvent may function as a solvent (solvent) for the ethylene compound or as a dispersion medium. Examples of the solvent include ketones such as methyl ethyl ketone, methyl isobutyl ketone and cyclohexanone; glycol derivatives such as PGMEA (2-acetoxy-1-methoxypropane), ethylene glycol monobutyl ether, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether and ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate. Classes (ether compounds, ester compounds, ether ester compounds, etc.); amides such as N, N-dimethylacetamide; esters such as ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, butyl acetate; N-methyl-pyrrolidone (specifically, 1). Pyrrolidones such as −methyl-2-pyrrolidone); aromatic hydrocarbons such as toluene and xylene; aliphatic hydrocarbons such as cyclohexane and heptane; ethers such as tetrahydrofuran, dioxane, diethyl ether and dibutyl ether; methanol , Ethyls such as ethanol, propanol and butanol; and the like. Only one of these solvents may be used, or two or more of these solvents may be used in combination.
溶媒の含有量としては、樹脂組成物100質量%中、例えば50質量%以上であることが好ましく、70質量%以上がより好ましく、また100質量%未満が好ましく、95質量%以下がより好ましい。溶媒の含有量をこのような範囲内に調整することにより、エチレン化合物濃度の高い樹脂組成物を得ることが容易になる。 The content of the solvent is preferably, for example, 50% by mass or more, more preferably 70% by mass or more, more preferably less than 100% by mass, and more preferably 95% by mass or less in 100% by mass of the resin composition. By adjusting the content of the solvent within such a range, it becomes easy to obtain a resin composition having a high ethylene compound concentration.
樹脂組成物は表面調整剤を含んでいてもよく、これにより、樹脂組成物を硬化して樹脂層を形成した際に、樹脂層にストライエーションや凹み等の外観上の欠陥を生じることを抑制することができる。表面調整剤の種類は特に限定されず、シロキサン系界面活性剤、アセチレングリコール系界面活性剤、フッ素系界面活性剤、アクリル系レベリング剤などを用いることができる。表面調整剤としては、例えば、ビックケミー社製のBYK(登録商標)シリーズや信越化学工業社製のKFシリーズ等を用いることができる。 The resin composition may contain a surface conditioner, which suppresses appearance defects such as striations and dents in the resin layer when the resin composition is cured to form the resin layer. can do. The type of the surface conditioner is not particularly limited, and a siloxane-based surfactant, an acetylene glycol-based surfactant, a fluorine-based surfactant, an acrylic-based leveling agent, and the like can be used. As the surface conditioner, for example, BYK (registered trademark) series manufactured by Big Chemie, KF series manufactured by Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., and the like can be used.
樹脂組成物は分散剤を含んでいてもよく、これにより、樹脂組成物中でのエチレン化合物等の分散性を安定化し、再凝集を抑制することができる。分散剤の種類は特に限定されず、エフカアディティブズ社製のEFKAシリーズ、ビックケミー社製のBYK(登録商標)シリーズ、日本ルーブリゾール社製のソルスパース(登録商標)シリーズ、楠本化成社製のディスパロン(登録商標)シリーズ、味の素ファインテクノ社製のアジスパー(登録商標)シリーズ、信越化学工業社製のKPシリーズ、共栄社化学社製のポリフローシリーズ、ディーアイシー社製のメガファック(登録商標)シリーズ、サンノプコ社製のディスパーエイドシリーズ等を用いることができる。 The resin composition may contain a dispersant, which can stabilize the dispersibility of the ethylene compound and the like in the resin composition and suppress reaggregation. The type of dispersant is not particularly limited, and is EFKA series manufactured by Fuka Additives, BYK (registered trademark) series manufactured by Big Chemie, Solspers (registered trademark) series manufactured by Japan Lubrizol, and Disparon manufactured by Kusumoto Kasei. (Registered Trademark) Series, Ajinomoto Fine-Techno's Ajisper (Registered Trademark) Series, Shin-Etsu Chemical's KP Series, Kyoeisha Chemical's Polyflow Series, DIC's MegaFuck (Registered Trademark) Series, A Disper Aid series manufactured by San Nopco can be used.
樹脂組成物には、必要に応じて、可塑剤、界面活性剤、粘度調整剤、消泡剤、防腐剤、比抵抗調整剤、密着性向上剤等の各種添加剤が含まれていてもよい。 The resin composition may contain various additives such as a plasticizer, a surfactant, a viscosity modifier, a defoaming agent, a preservative, a resistivity adjuster, and an adhesion improver, if necessary. ..
樹脂組成物は、硬化することにより硬化物とすることができる。樹脂組成物は、樹脂成分の反応(例えば、重合反応や架橋反応)によって硬化するものであってもよく、樹脂組成物に含まれる溶媒が乾燥または加熱除去されることで硬化するものであってもよい。このような樹脂組成物としては、例えば、射出成形や押出成形等により成形することができる熱可塑性樹脂組成物や、スピンコート法、溶媒キャスト法、ロールコート法、スプレーコート法、バーコート法、ディップコート法、スクリーン印刷法、フレキソ印刷法、インクジェット法、スリットコート法等により塗工できるよう塗料化された樹脂組成物を用いることができる。なお本発明において、「硬化」とは、樹脂組成物の流動性が低下して実質的に流動性を有しない状態を意味する。「硬化」には、樹脂の反応(例えば、重合反応や架橋反応)によって樹脂組成物が固まる場合や、樹脂組成物に含まれる溶媒が除去されて樹脂組成物が固まる場合などが含まれる。 The resin composition can be made into a cured product by curing. The resin composition may be cured by a reaction of resin components (for example, a polymerization reaction or a cross-linking reaction), or may be cured by drying or heat-removing the solvent contained in the resin composition. May be good. Examples of such a resin composition include a thermoplastic resin composition that can be molded by injection molding, extrusion molding, or the like, a spin coating method, a solvent casting method, a roll coating method, a spray coating method, a bar coating method, and the like. A resin composition that has been made into a paint so that it can be coated by a dip coating method, a screen printing method, a flexographic printing method, an inkjet method, a slit coating method, or the like can be used. In the present invention, "curing" means a state in which the fluidity of the resin composition is reduced and the resin composition has substantially no fluidity. The "curing" includes a case where the resin composition is hardened by a reaction of the resin (for example, a polymerization reaction or a crosslinking reaction), a case where the solvent contained in the resin composition is removed, and the case where the resin composition is hardened.
樹脂組成物が熱可塑性樹脂組成物である場合は、当該樹脂組成物を、射出成形、押出成形、真空成形、圧縮成形、ブロー成形等をすることにより硬化物を得ることができる。この方法では、樹脂成分として熱可塑性樹脂を用い、当該熱可塑性樹脂にエチレン化合物を配合し、加熱成形することにより成形品が得られる。例えば、ベース樹脂の粉体またはペレットにエチレン化合物を添加し、150℃〜350℃程度に加熱し、溶解させた後、成形するとよい。成形品の形状は特に限定されるものではないが、板状、シート状、粒状、粉状、塊状、粒子凝集体状、球状、楕円球状、レンズ状、立方体状、柱状、棒状、錐形状、筒状、針状、繊維状、中空糸状、多孔質状等が挙げられる。また樹脂を混練する際に、可塑剤等の通常の樹脂成形に用いる添加剤を加えてもよい。 When the resin composition is a thermoplastic resin composition, a cured product can be obtained by subjecting the resin composition to injection molding, extrusion molding, vacuum molding, compression molding, blow molding, or the like. In this method, a molded product is obtained by using a thermoplastic resin as a resin component, blending an ethylene compound with the thermoplastic resin, and heat-molding. For example, it is preferable to add an ethylene compound to the powder or pellet of the base resin, heat it to about 150 ° C. to 350 ° C. to dissolve it, and then mold it. The shape of the molded product is not particularly limited, but plate-like, sheet-like, granular, powder-like, lump-like, particle-aggregate-like, spherical, elliptical-spherical, lenticular, cubic, columnar, rod-like, and conical, Examples include a tubular shape, a needle shape, a fibrous shape, a hollow thread shape, and a porous shape. Further, when kneading the resin, an additive used for ordinary resin molding such as a plasticizer may be added.
樹脂組成物が塗料化された樹脂組成物である場合は、エチレン化合物と樹脂成分を含む液状またはペースト状の樹脂組成物を、基材(例えば、樹脂板、フィルム、ガラス板等)上に塗工することで、厚さ200μm以下のフィルム状や、厚さ200μm超のシート状の硬化物を得ることができる。このようにして得られた硬化物は、基材から剥離してフィルムやシートとして取り扱うこともできるし、基材と一体化して取り扱うこともできる。 When the resin composition is a paint-based resin composition, a liquid or paste-like resin composition containing an ethylene compound and a resin component is applied onto a base material (for example, a resin plate, a film, a glass plate, etc.). By working, a cured product having a thickness of 200 μm or less or a sheet having a thickness of more than 200 μm can be obtained. The cured product thus obtained can be peeled off from the base material and handled as a film or sheet, or can be handled integrally with the base material.
樹脂組成物の硬化物は、単一の樹脂層(樹脂組成物が硬化して形成された層)から構成されていてもよく、複数の樹脂層から構成されていてもよい。硬化物が基材と一体化して取り扱われる場合は、硬化物は基材の一方面のみに形成されてもよく、両面に形成されてもよい。なお、硬化物と基材とが一体化したものは、樹脂組成物から形成された成形体を基材と熱圧着したり化学結合することによっても形成することができる。 The cured product of the resin composition may be composed of a single resin layer (a layer formed by curing the resin composition), or may be composed of a plurality of resin layers. When the cured product is handled integrally with the base material, the cured product may be formed on only one side of the base material or on both sides. The cured product and the base material integrated with each other can also be formed by thermocompression bonding or chemically bonding the molded product formed from the resin composition to the base material.
本発明のエチレン化合物は耐熱性に優れることから、熱可塑性樹脂に配合してこれを加熱成形した場合や熱圧着や化学結合により支持体と一体化させたりした場合でも、紫外線吸収効果を好適に発揮させることができる。また、高温での熱硬化反応が必要な樹脂(例えば、ポリイミド前駆体、エポキシ樹脂、アクリル樹脂等)や高温での乾燥が必要な樹脂(例えば、高沸点溶媒を含有する樹脂やガラス転移温度が高い樹脂)を用いて成形した場合でも、エチレン化合物の優れた耐熱性により、紫外線吸収効果を好適に発揮させることができる。 Since the ethylene compound of the present invention has excellent heat resistance, even when it is blended with a thermoplastic resin and heat-molded, or when it is integrated with a support by thermocompression bonding or chemical bonding, the ultraviolet absorption effect is suitable. It can be demonstrated. In addition, resins that require a thermal curing reaction at high temperatures (for example, polyimide precursors, epoxy resins, acrylic resins, etc.) and resins that require drying at high temperatures (for example, resins containing high boiling point solvents and glass transition temperatures) Even when molded using a high resin), the excellent heat resistance of the ethylene compound makes it possible to suitably exert the ultraviolet absorbing effect.
本発明のエチレン化合物を含有する紫外線吸収剤や樹脂組成物やその硬化物は、コートガラス、樹脂ガラス、内外装材等の建材、塗料、接着剤、自動車部品、食品、医薬品、化粧品、化学薬品等を入れるための容器、各種フィルム(保護フィルム、光学フィルム、位相差フィルム、包装用フィルム、農業用フィルム等)、各種レンズ(サングラス、ゴーグル、ブルーライトカット用眼鏡、医療用保護眼鏡等)、電線等において使用される電話線ケーブルシース材、紫外線を光源とする照射装置用部材、繊維、ディスプレイ部材、タッチパネル、光学フィルター部材、光学センサー部材、カバーガラスやカバーパネル等の表面保護部材、人体への有害光線を除去するフィルター部材、各種センサー部材(誤作動防止含む)、照明部材、太陽電池部材、看板、標識などに用いることができる。 The ultraviolet absorber or resin composition containing the ethylene compound of the present invention and its cured product are used for building materials such as coated glass, resin glass and interior / exterior materials, paints, adhesives, automobile parts, foods, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and chemicals. Containers for storing, various films (protective film, optical film, retardation film, packaging film, agricultural film, etc.), various lenses (sunglasses, goggles, blue light cut glasses, medical protective glasses, etc.), For telephone line cable sheath materials used in electric wires, etc., members for irradiation devices that use ultraviolet light as a light source, fibers, display members, touch panels, optical filter members, optical sensor members, surface protection members such as cover glass and cover panels, and human bodies. It can be used for filter members that remove harmful ultraviolet rays, various sensor members (including malfunction prevention), lighting members, solar cell members, signs, signs, and the like.
本発明の樹脂組成物は、オプトデバイス用途、表示デバイス用途、機械部品、電気・電子部品等の様々な用途で用いられるフィルター形成用の樹脂組成物として好ましく使用できる。樹脂組成物は、例えば、紫外線カットフィルターや可視光領域の光を優先的に透過させる光選択透過フィルター等の光学フィルターに適用することができる。 The resin composition of the present invention can be preferably used as a resin composition for forming a filter used in various applications such as opt device applications, display device applications, mechanical parts, and electrical / electronic parts. The resin composition can be applied to an optical filter such as an ultraviolet cut filter or a light selective transmission filter that preferentially transmits light in the visible light region.
携帯電話用カメラ、デジタルカメラ、車載用カメラ、ビデオカメラ、表示素子(LED等)等の撮像装置には、被写体の光を電気信号等に変換して出力する撮像素子が通常使用されているが、このような撮像素子は、例えばCCD(Charge Coupled Device)やCMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor)等の受光素子やレンズを備えるとともに、高性能化のため、画像処理等の妨げとなる光学ノイズ(例えばゴーストやフレア)を除去するための光選択透過フィルターが備えられる。このような光選択透過フィルターには、通常、高屈折率材料層と低屈折率材料層とを交互に積層した誘電体多層膜が設けられており、誘電体多層膜は、高屈折率材料層と低屈折率材料層の各層の厚みを調整することにより、所望の波長域の光の入射をカットすることができる。 Image sensors such as mobile phone cameras, digital cameras, in-vehicle cameras, video cameras, and display elements (LEDs, etc.) usually use image sensors that convert the light of the subject into electrical signals and output it. Such an image sensor is provided with a light receiving element or lens such as a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) or CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor), and optical noise (an optical noise that hinders image processing or the like) for high performance. For example, a light selective transmission filter for removing ghosts and flares) is provided. Such a light selective transmission filter is usually provided with a dielectric multilayer film in which high refractive index material layers and low refractive index material layers are alternately laminated, and the dielectric multilayer film is a high refractive index material layer. By adjusting the thickness of each layer of the low refractive index material layer, it is possible to cut the incident light in a desired wavelength range.
しかし、誘電体多層膜は入射角によってカット波長域あるいは透過波長域が変化するため、入射角が垂直方向から斜め方向に変化すると、カット波長域や透過波長域が短波長側にシフトする。そのため誘電体多層膜では、斜め方向の入射光に対しては、所望の波長域の光を十分にカットできなかったり、あるいは可視光領域の光線もカットして色味が変化する事態が生じうる。特に、撮像素子は近年、小型化とともに薄型化が強く求められており、これに伴いレンズと受光素子との距離が縮まることになるため、受光素子がより斜め方向からの入射光を受光する必要性が出てくる。この場合、カット波長域や透過波長域の入射角依存性がより強くなるため、従来はほとんど影響が出なかった短波長領域の光、すなわち紫外〜紫色領域の光の短波長側へのシフトが顕在化することとなる。 However, since the cut wavelength region or the transmission wavelength region of the dielectric multilayer film changes depending on the incident angle, when the incident angle changes from the vertical direction to the oblique direction, the cut wavelength region and the transmission wavelength region shift to the short wavelength side. Therefore, in the dielectric multilayer film, it may not be possible to sufficiently cut the light in the desired wavelength range with respect to the incident light in the oblique direction, or the light in the visible light region may also be cut to change the color. .. In particular, in recent years, there has been a strong demand for image pickup devices to be smaller and thinner, and the distance between the lens and the light receiving element is shortened accordingly. Therefore, the light receiving element needs to receive incident light from a more oblique direction. Sex comes out. In this case, since the incident angle dependence of the cut wavelength region and the transmission wavelength region becomes stronger, the light in the short wavelength region, that is, the light in the ultraviolet to purple region, which has hardly been affected in the past, is shifted to the short wavelength side. It will become apparent.
本発明の樹脂組成物は上記に説明したエチレン化合物を含有しており、このエチレン化合物は紫外〜紫色領域にシャープな吸収ピークを示すため、当該樹脂組成物から形成された光学フィルターは紫外〜紫色領域の光を選択的に吸収でき、可視光領域の短波長側における入射角依存性を低減できるものとなる。さらに、樹脂組成物がエチレン化合物とともに近赤外線吸収色素も含有していれば、当該樹脂組成物から形成された光学フィルターは、可視光領域の短波長側と長波長側の両方における入射角依存性を低減できるものとなる。しかも、光学フィルターに含まれるエチレン化合物は耐熱性に優れるため、樹脂組成物を加熱成形あるいは加熱硬化する際や、蒸着により誘電体多層膜を設けるような場合でも、エチレン化合物の分解や揮散が抑えられ、紫外〜紫色領域の光を効果的にカットできるものとなる。さらに、光学フィルターの保管や製造・加工(例えば蒸着や実装など)の際に紫外光にさらされても、当該紫外光に起因する樹脂成分や近赤外線吸収色素の劣化を抑制することができる。 The resin composition of the present invention contains the ethylene compound described above, and since this ethylene compound shows a sharp absorption peak in the ultraviolet to purple region, the optical filter formed from the resin composition is ultraviolet to purple. The light in the region can be selectively absorbed, and the dependence on the incident angle on the short wavelength side of the visible light region can be reduced. Further, if the resin composition contains a near-infrared absorbing dye as well as an ethylene compound, the optical filter formed from the resin composition has an incident angle dependence on both the short wavelength side and the long wavelength side of the visible light region. Can be reduced. Moreover, since the ethylene compound contained in the optical filter has excellent heat resistance, decomposition and volatilization of the ethylene compound are suppressed even when the resin composition is heat-molded or heat-cured, or when a dielectric multilayer film is provided by vapor deposition. Therefore, the light in the ultraviolet to purple region can be effectively cut. Further, even if the optical filter is exposed to ultraviolet light during storage, manufacturing, and processing (for example, vapor deposition or mounting), deterioration of the resin component and the near-infrared absorbing dye due to the ultraviolet light can be suppressed.
光学フィルターは、単一または複数の樹脂層から形成されてもよく、支持体と一体化されて形成されてもよい。支持体と一体化されたフィルターは、例えば、樹脂組成物を、支持体表面(または、支持体と樹脂層との間にバインダー層等の他の層を有する場合は、当該他の層の表面)にスピンコート法や溶媒キャスト法により塗布し、乾燥または硬化することにより形成することができる。また、支持体に対して、樹脂組成物から形成された面状成形体を熱圧着することによりフィルターを形成してもよい。 The optical filter may be formed from a single or a plurality of resin layers, or may be formed integrally with a support. The filter integrated with the support is, for example, when the resin composition has another layer such as a binder layer between the support surface (or the support and the resin layer, the surface of the other layer). ) Can be formed by applying it to) by a spin coating method or a solvent casting method, and drying or curing it. Further, the filter may be formed by thermocompression bonding a planar molded product formed from the resin composition to the support.
樹脂組成物から形成された樹脂層は、支持体の一方面のみに設けられてもよく、両面に設けられてもよい。樹脂層の厚さは特に限定されないが、所望の近赤外線カット性能を確保する点から、例えば0.5μm以上が好ましく、1μm以上がより好ましく、2μm以上がさらに好ましく、また1mm以下が好ましく、500μm以下がより好ましく、200μm以下がさらに好ましい。支持体上に塗料化された樹脂組成物を塗工するなどして樹脂層を形成する場合は、支持体によってフィルターの強度を確保することができるため、樹脂層の厚さをさらに薄くすることができる。支持体上に樹脂層を形成する場合の樹脂層の厚さは、例えば、50μm以下が好ましく、20μm以下がより好ましく、10μm以下がさらに好ましく、5μm以下が特に好ましい。 The resin layer formed from the resin composition may be provided on only one side of the support, or may be provided on both sides. The thickness of the resin layer is not particularly limited, but from the viewpoint of ensuring the desired near-infrared ray cutting performance, for example, 0.5 μm or more is preferable, 1 μm or more is more preferable, 2 μm or more is further preferable, and 1 mm or less is preferable, and 500 μm. The following is more preferable, and 200 μm or less is further preferable. When the resin layer is formed by applying a paint-based resin composition on the support, the strength of the filter can be ensured by the support, so that the thickness of the resin layer should be further reduced. Can be done. When the resin layer is formed on the support, the thickness of the resin layer is, for example, preferably 50 μm or less, more preferably 20 μm or less, further preferably 10 μm or less, and particularly preferably 5 μm or less.
支持体としては、樹脂板、樹脂フィルム、ガラス板等の透明基板を用いることが好ましい。支持体に用いられる樹脂板または樹脂フィルムは、例えば、上記に説明した樹脂成分から形成されたものが好ましく用いられる。光学フィルターの耐熱性を高める観点からは、支持体としてガラス基板を用いることが好ましく、このように形成された光学フィルターは、例えば、半田リフローにより電子部品に実装することが可能となる。またガラス基板は、高温にさらされても割れや反りが起こりにくいため、樹脂層との密着性を確保しやすくなる。支持体としてガラス基板を用いる場合は、支持体と樹脂層の間に、例えばシランカップリング剤から形成されたバインダー層を設けてもよく、これにより樹脂層とガラス基板との密着性を高めることができる。 As the support, it is preferable to use a transparent substrate such as a resin plate, a resin film, or a glass plate. As the resin plate or resin film used for the support, for example, those formed from the resin components described above are preferably used. From the viewpoint of increasing the heat resistance of the optical filter, it is preferable to use a glass substrate as the support, and the optical filter formed in this way can be mounted on an electronic component by, for example, solder reflow. Further, since the glass substrate is less likely to crack or warp even when exposed to a high temperature, it becomes easy to secure the adhesiveness with the resin layer. When a glass substrate is used as the support, a binder layer formed of, for example, a silane coupling agent may be provided between the support and the resin layer, thereby improving the adhesion between the resin layer and the glass substrate. Can be done.
支持体(基板)の厚みは、例えば、強度を確保する点から、0.05mm以上が好ましく、0.1mm以上がより好ましく、また薄型化の点から、0.4mm以下が好ましく、0.3mm以下がより好ましい。 The thickness of the support (board) is preferably 0.05 mm or more, more preferably 0.1 mm or more, and preferably 0.4 mm or less, preferably 0.3 mm, from the viewpoint of ensuring strength. The following is more preferable.
樹脂組成物から形成された樹脂層には、第2の樹脂層として、当該樹脂層と同一または異なる樹脂から構成された保護層を積層させてもよい。保護層を設けることにより、樹脂層に含まれるエチレン化合物の耐久性(耐分解性)を高めることができる。保護層は、樹脂層の一方面のみに設けられてもよく、両面に設けられてもよい。樹脂層が支持体上に設けられる場合は、保護層は、樹脂層の支持体とは反対側の面に設けられることが好ましい。 On the resin layer formed from the resin composition, a protective layer made of the same or different resin as the resin layer may be laminated as the second resin layer. By providing the protective layer, the durability (decomposition resistance) of the ethylene compound contained in the resin layer can be enhanced. The protective layer may be provided on only one side of the resin layer, or may be provided on both sides. When the resin layer is provided on the support, it is preferable that the protective layer is provided on the surface of the resin layer opposite to the support.
光学フィルターは、蛍光灯等の映り込みを低減する反射防止性や防眩性を有する層(反射防止膜)、傷付き防止性能を有する層、その他の機能を有する透明基材等を有していてもよい。光学フィルターは、樹脂層上に紫外線反射膜や近赤外線反射膜を有していてもよい。紫外線反射膜や近赤外線反射膜は、樹脂層よりも入光側に設けられていることが好ましい。光学フィルターに紫外線反射膜や近赤外線反射膜が設けられていれば、光学フィルターの透過光から紫外線や近赤外線をよりカットすることができる。紫外線反射膜と近赤外線反射膜は、1つで紫外線反射機能と近赤外線反射機能を有するものであってもよい。 The optical filter has a layer having antireflection and antiglare properties (antireflection film) to reduce reflection of fluorescent lamps, a layer having scratch prevention performance, a transparent base material having other functions, and the like. You may. The optical filter may have an ultraviolet reflective film or a near infrared reflective film on the resin layer. The ultraviolet reflective film and the near infrared reflective film are preferably provided on the light receiving side of the resin layer. If the optical filter is provided with an ultraviolet reflecting film or a near-infrared reflecting film, ultraviolet rays and near-infrared rays can be further cut from the transmitted light of the optical filter. The ultraviolet reflective film and the near-infrared reflecting film may have one ultraviolet reflecting function and one near infrared reflecting function.
紫外線反射膜、近赤外線反射膜、反射防止膜(可視光反射防止膜)は、高屈折率材料層と低屈折率材料層とを交互に積層した誘電体多層膜から構成することができる。従って、このような機能を光学フィルターに付与する場合は、光学フィルターは誘電体多層膜を有することが好ましい。高屈折率材料層を構成する材料としては、屈折率が1.7以上の材料を用いることができ、屈折率の範囲が通常1.7〜2.5の材料が選択される。高屈折率材料層を構成する材料としては、例えば、酸化チタン、酸化亜鉛、酸化ジルコニウム、酸化ランタン、酸化イットリウム、酸化インジウム、酸化ニオブ、酸化タンタル、酸化錫、酸化ビスマス等の酸化物;窒化ケイ素等の窒化物;前記酸化物や前記窒化物の混合物やそれらにアルミニウムや銅等の金属や炭素をドープしたもの(例えば、スズドープ酸化インジウム(ITO)、アンチモンドープ酸化スズ(ATO))等が挙げられる。低屈折率材料層を構成する材料としては、屈折率が1.6以下の材料を用いることができ、屈折率の範囲が通常1.2〜1.6の材料が選択される。低屈折率材料層を構成する材料としては、例えば、二酸化ケイ素(シリカ)、アルミナ、フッ化ランタン、フッ化マグネシウム、六フッ化アルミニウムナトリウム等が挙げられる。 The ultraviolet reflective film, the near infrared reflective film, and the antireflection film (visible light antireflection film) can be composed of a dielectric multilayer film in which high refractive index material layers and low refractive index material layers are alternately laminated. Therefore, when imparting such a function to the optical filter, it is preferable that the optical filter has a dielectric multilayer film. As a material constituting the high refractive index material layer, a material having a refractive index of 1.7 or more can be used, and a material having a refractive index in the range of 1.7 to 2.5 is usually selected. Examples of the material constituting the high refractive index material layer include oxides such as titanium oxide, zinc oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide, yttrium oxide, indium oxide, niobium oxide, tantalum oxide, tin oxide and bismuth oxide; silicon nitride. Nitridees such as; the oxides and mixtures of the nitrides, and those obtained by doping them with metals such as aluminum and copper and carbon (for example, tin-doped indium oxide (ITO), antimonated tin oxide (ATO)) and the like. Be done. As the material constituting the low refractive index material layer, a material having a refractive index of 1.6 or less can be used, and a material having a refractive index in the range of 1.2 to 1.6 is usually selected. Examples of the material constituting the low refractive index material layer include silicon dioxide (silica), alumina, lanthanum fluoride, magnesium fluoride, sodium hexafluoride, and the like.
光学フィルターはまた、アルミ蒸着膜、貴金属薄膜、酸化インジウムを主成分とし酸化スズを少量含有させた金属酸化物微粒子を分散させた樹脂膜等を有していてもよい。 The optical filter may also have an aluminum vapor deposition film, a noble metal thin film, a resin film in which metal oxide fine particles containing indium oxide as a main component and a small amount of tin oxide are dispersed.
光学フィルターの厚みは、例えば、1mm以下であることが好ましい。これにより、例えば、撮像素子の小型化への要請に十分に応えることができる。光学フィルターの厚みは、より好ましくは500μm以下、さらに好ましくは300μm以下、さらにより好ましくは150μm以下であり、また30μm以上が好ましく、50μm以上がさらに好ましい。 The thickness of the optical filter is preferably 1 mm or less, for example. Thereby, for example, it is possible to sufficiently meet the demand for miniaturization of the image sensor. The thickness of the optical filter is more preferably 500 μm or less, still more preferably 300 μm or less, even more preferably 150 μm or less, still more preferably 30 μm or more, still more preferably 50 μm or more.
光学フィルターは、イメージセンサー(撮像素子)、照度センサー、近接センサー等のセンサーの構成部材の一つとして用いることができる。例えばイメージセンサーは、被写体の光を電気信号等に変換して出力する電子部品として用いられ、CCD(Charge Coupled Device)やCMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor)等が挙げられる。イメージセンサーは、携帯電話用カメラ、デジタルカメラ、車載用カメラ、監視カメラ、表示素子(LED等)等に用いることができる。センサーは、上記の光学フィルターを1または2以上含み、必要に応じて、さらに他のフィルター(例えば、可視光線カットフィルター、赤外線カットフィルター、紫外線カットフィルター等)やレンズを有していてもよい。 The optical filter can be used as one of the constituent members of a sensor such as an image sensor (imaging element), an illuminance sensor, and a proximity sensor. For example, an image sensor is used as an electronic component that converts the light of a subject into an electric signal or the like and outputs it, and examples thereof include a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor). The image sensor can be used for a mobile phone camera, a digital camera, an in-vehicle camera, a surveillance camera, a display element (LED, etc.) and the like. The sensor includes one or more of the above optical filters, and may have other filters (for example, a visible light cut filter, an infrared cut filter, an ultraviolet cut filter, etc.) and a lens, if necessary.
以下、実施例を挙げて本発明をより具体的に説明するが、本発明は下記実施例によって制限を受けるものではなく、前・後記の趣旨に適合し得る範囲で適当に変更を加えて実施することも可能であり、それらはいずれも本発明の技術的範囲に包含される。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to Examples, but the present invention is not limited by the following Examples, and is carried out with appropriate modifications to the extent that it can be adapted to the gist of the above and the following. It is also possible, all of which are within the technical scope of the invention.
(1)化合物の合成
(1−1)合成例1:エチレン化合物1の合成
200mLの4口フラスコに、4−フルオロベンズアルデヒド4.98g(0.039mol)、ビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテル2.72g(0.020mol)、炭酸カリウム10.86g(0.079mol)、アセトニトリル74gを仕込み、窒素流通下(10mL/min)、撹拌羽を用いて撹拌しながら60℃で12時間反応させた。反応終了後、減圧ろ過によって不溶分をろ別した後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去した。得られた濃縮物を200mLの4口フラスコに入れ、そこにマロノニトリル5.19g(0.079mol)、ピペリジン3.32g(0.039mol)、メタノール68gを加え、還流条件下で4時間反応させた。反応終了後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去し、得られた濃縮物をカラムクロマトグラフィー(展開溶媒:クロロホルム)によって精製を行い、エチレン化合物1を6.2g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は71.3mol%であった。得られた化合物は、約5mgを分取して所定量の重水素化溶媒(重クロロホルムまたは重ジメチルスルホキシド)に希釈し、1H−NMR測定することにより、構造を特定した。
(1) Synthesis of compound (1-1) Synthesis example 1: Synthesis of ethylene compound 4.98 g (0.039 mol) of 4-fluorobenzaldehyde and bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether in a 200 mL 4-neck flask. 72 g (0.020 mol), 10.86 g (0.079 mol) of potassium carbonate, and 74 g of acetonitrile were charged and reacted at 60 ° C. for 12 hours while stirring with a stirring blade under nitrogen flow (10 mL / min). After completion of the reaction, the insoluble matter was filtered off by vacuum filtration, and then the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator. The obtained concentrate was placed in a 200 mL 4-neck flask, 5.19 g (0.079 mol) of malononitrile, 3.32 g (0.039 mol) of piperidine, and 68 g of methanol were added thereto, and the mixture was reacted under reflux conditions for 4 hours. .. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator, and the obtained concentrate was purified by column chromatography (developing solvent: chloroform) to obtain 6.2 g of ethylene compound 1. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 71.3 mol%. The structure of the obtained compound was specified by taking about 5 mg, diluting it in a predetermined amount of deuterated solvent (deuterated chloroform or deuterated dimethylsulfoxide), and measuring 1 H-NMR.
(1−2)合成例2:エチレン化合物2の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりにシアノ酢酸メチルを用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物2を15.9g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は87.4mol%であった。
(1-2) Synthesis Example 2: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 2 Ethylene compound 2 shown in Table 1 was prepared by the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that methyl cyanoacetate was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. 9.9 g was obtained. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 87.4 mol%.
(1−3)合成例3:エチレン化合物3の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりにマロン酸ジメチルを用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物3を3.4g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は35.7mol%であった。
(1-3) Synthesis Example 3: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 3 Ethylene compound 3 shown in Table 1 was prepared by the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that dimethyl malonate was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. I got 0.4g. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 35.7 mol%.
(1−4)合成例4:エチレン化合物4の合成
合成例3において、ピペリジンと等量モルの酢酸を追加して用いたこと以外、合成例3と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物4を6.1g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は80.0mol%であった。
(1-4) Synthesis Example 4: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 4 The ethylene compound 4 shown in Table 1 was subjected to the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 3 except that an equal volume of acetic acid was added to piperidine in Synthesis Example 3. Was obtained in an amount of 6.1 g. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 80.0 mol%.
(1−5)合成例5:エチレン化合物5の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりにシアノ酢酸ブチルを用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物5を1.3g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は14.8mol%であった。
(1-5) Synthesis Example 5: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 5 Ethylene compound 5 shown in Table 1 was prepared in the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that butyl cyanoacetate was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. 0.3 g was obtained. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 14.8 mol%.
(1−6)合成例6:エチレン化合物6の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりにシアノ酢酸イソブチルを用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物6を1.6g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は18.1mol%であった。
(1-6) Synthesis Example 6: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 6 Ethylene compound 6 shown in Table 1 was prepared by the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that isobutyl cyanoacetate was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. 1.6 g was obtained. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 18.1 mol%.
(1−7)合成例7:エチレン化合物7の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりにシアノ酢酸2−エチルヘキシルを用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物7を2.5g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は24.2mol%であった。
(1-7) Synthesis Example 7: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 7 The ethylene compound 7 shown in Table 1 was subjected to the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that 2-ethylhexyl cyanoacetic acid was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. Was obtained in an amount of 2.5 g. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 24.2 mol%.
(1−8)合成例8:エチレン化合物8の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりにメルドラム酸を用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表1に示すエチレン化合物8を5.8g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は49.1mol%であった。
(1-8) Synthesis Example 8: Synthesis of ethylene compound 8 Ethylene compound 8 shown in Table 1 was prepared in the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that meldrum's acid was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. I got 8g. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 49.1 mol%.
(1−9)合成例9:エチレン化合物9の合成
合成例1において、マロノニトリルの代わりに1,3−ジメチルバルビツール酸を用いたこと以外は、合成例1と同様の手順により表2に示すエチレン化合物9を7.3g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は58.9mol%であった。
(1-9) Synthesis Example 9: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 9 Table 2 shows the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 1 except that 1,3-dimethylbarbituric acid was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 1. 7.3 g of ethylene compound 9 was obtained. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 58.9 mol%.
(1−10)合成例10:エチレン化合物10の合成
合成例2において、ビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテルの代わりにエチレングリコールビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテルを用いたこと以外は、合成例2と同様の手順により表2に示すエチレン化合物10を3.8g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は75.6mol%であった。
(1-10) Synthesis Example 10: Synthesis of Ethylene Compound 10 Synthesis Example 2 except that ethylene glycol bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether was used instead of bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether in Synthesis Example 2. 3.8 g of ethylene compound 10 shown in Table 2 was obtained by the same procedure as above. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 75.6 mol%.
(1−11)合成例11:エチレン化合物11の合成
合成例3において、ビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテルの代わりにエチレングリコールビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテルを用いたこと以外は合成例3と同様の手順により表2に示すエチレン化合物11を1.1g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は25.2mol%であった。
(1-11) Synthesis Example 11: Synthesis of ethylene compound 11 In Synthesis Example 3, the same as Synthesis Example 3 except that ethylene glycol bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether was used instead of bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether. 1.1 g of ethylene compound 11 shown in Table 2 was obtained by the same procedure. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 25.2 mol%.
(1−12)合成例12:エチレン化合物12の合成
合成例6において、ビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテルの代わりにエチレングリコールビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテルを用いたこと以外は、合成例6と同様の手順により表2に示すエチレン化合物12を4.6g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は79.6mol%であった。
(1-12) Synthesis Example 12: Synthesis of ethylene compound 12 Synthesis Example 6 except that ethylene glycol bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether was used instead of bis (2-mercaptoethyl) ether in Synthesis Example 6. 4.6 g of ethylene compound 12 shown in Table 2 was obtained by the same procedure as above. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 79.6 mol%.
(1−13)合成例13:エチレン化合物13の合成
200mLの4口フラスコに、4−クロロベンズアルデヒド4.61g(0.0328mol)、エチレングリコールビス(2−メルカプトエチル)エーテル2.92g(0.016mol)、炭酸カリウム6.63g(0.048mol)、テトラブチルアンモニウムブロミド0.52g(0.0016mol)、アセトニトリル30.11gを仕込み、窒素流通下(10mL/min)、撹拌羽を用いて撹拌しながら75℃で6時間反応させた。反応終了後、減圧ろ過によって不溶分をろ別した後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去した。得られた濃縮物を200mLの4口フラスコに入れ、そこにマロン酸7.37g(0.071mol)、ピペリジン0.61g(0.007mol)、ピリジン15gを加え、還流条件下で2時間反応させた。反応終了後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去し、得られた濃縮物をカラムクロマトグラフィー(展開溶媒:クロロホルム)によって精製を行い、表2に示すエチレン化合物13を7.0g得た。4−クロロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は92.0mol%であった。得られた化合物は、約5mgを分取して所定量の重水素化溶媒(重クロロホルムまたは重ジメチルスルホキシド)に希釈し、1H−NMR測定することにより、構造を特定した。
(1-13) Synthesis Example 13: Synthesis of ethylene compound 13 In a 200 mL four-necked flask, 4.61 g (0.0328 mol) of 4-chlorobenzaldehyde and 2.92 g (0.22 g (0.23 mercaptoethyl) ether of ethylene glycol bis) are used. 016 mol), 0.63 g (0.048 mol) of potassium carbonate, 0.52 g (0.0016 mol) of tetrabutylammonium bromide, and 30.11 g of acetonitrile were charged and stirred under nitrogen flow (10 mL / min) using a stirring blade. The reaction was carried out at 75 ° C. for 6 hours. After completion of the reaction, the insoluble matter was filtered off by vacuum filtration, and then the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator. The obtained concentrate was placed in a 200 mL 4-neck flask, 7.37 g (0.071 mol) of malonic acid, 0.61 g (0.007 mol) of piperidine, and 15 g of pyridine were added thereto, and the mixture was reacted under reflux conditions for 2 hours. It was. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator, and the obtained concentrate was purified by column chromatography (developing solvent: chloroform) to obtain 7.0 g of ethylene compound 13 shown in Table 2. The yield with respect to 4-chlorobenzaldehyde was 92.0 mol%. The structure of the obtained compound was specified by taking about 5 mg, diluting it in a predetermined amount of deuterated solvent (deuterated chloroform or deuterated dimethylsulfoxide), and measuring 1 H-NMR.
(1−14)合成例14:エチレン化合物14の合成
200mLの4口フラスコに、合成例13で得られたエチレン化合物13を4.75g(0.010mol)、p−トルエンスルホン酸一水和物0.19g(0.001mol)、1−ブタノール80gを仕込み、窒素流通下(10mL/min)、撹拌羽を用いて撹拌しながら還流条件下で5時間反応させた。反応終了後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去し、得られた濃縮物をカラムクロマトグラフィー(展開溶媒:クロロホルム)によって精製を行い、表2に示すエチレン化合物14を4.9g得た。4−クロロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は83.5mol%であった。得られた化合物は、約5mgを分取して所定量の重水素化溶媒(重クロロホルムまたは重ジメチルスルホキシド)に希釈し、1H−NMR測定することにより、構造を特定した。
(1-14) Synthesis Example 14: Synthesis of ethylene compound 14. In a 200 mL four-necked flask, 4.75 g (0.010 mol) of the ethylene compound 13 obtained in Synthesis Example 13 and p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate 0.19 g (0.001 mol) and 80 g of 1-butanol were charged and reacted under reflux conditions under reflux conditions under nitrogen flow (10 mL / min) while stirring with a stirring blade. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator, and the obtained concentrate was purified by column chromatography (developing solvent: chloroform) to obtain 4.9 g of ethylene compound 14 shown in Table 2. The yield with respect to 4-chlorobenzaldehyde was 83.5 mol%. The structure of the obtained compound was specified by taking about 5 mg, diluting it in a predetermined amount of deuterated solvent (deuterated chloroform or deuterated dimethylsulfoxide), and measuring 1 H-NMR.
(1−15)合成例15:比較エチレン化合物1の合成
200mLの4口フラスコに、4−フルオロベンズアルデヒド3.85g(0.031mol)、4−クロロベンジルメルカプタン5.02g(0.031mol)、炭酸カリウム8.57g(0.062mol)、アセトニトリル36gを仕込み、窒素流通下(10mL/min)、撹拌羽を用いて撹拌しながら60℃で12時間反応させた。反応終了後、減圧ろ過によって不溶分をろ別した後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去した。得られた濃縮物を200mLの4口フラスコに入れ、そこにマロノニトリル4.10g(0.062mol)、ピペリジン2.64g(0.031mol)、メタノール41gを加え、還流条件下で4時間反応させた。反応終了後、エバポレーターを用いて溶媒を留去し、得られた濃縮物をカラムクロマトグラフィー(展開溶媒:クロロホルム)によって精製を行い、表2に示す比較エチレン化合物1を8.9g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は92.6mol%であった。
(1-15) Synthesis Example 15: Synthesis of Comparative Ethylene Compound 1 In a 200 mL 4-neck flask, 3.85 g (0.031 mol) of 4-fluorobenzaldehyde, 5.02 g (0.031 mol) of 4-chlorobenzyl mercaptan, and carbonate. 8.57 g (0.062 mol) of potassium and 36 g of acetonitrile were charged and reacted at 60 ° C. for 12 hours under nitrogen flow (10 mL / min) while stirring using a stirring blade. After completion of the reaction, the insoluble matter was filtered off by vacuum filtration, and then the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator. The obtained concentrate was placed in a 200 mL 4-neck flask, 4.10 g (0.062 mol) of malononitrile, 2.64 g (0.031 mol) of piperidine, and 41 g of methanol were added thereto, and the mixture was reacted under reflux conditions for 4 hours. .. After completion of the reaction, the solvent was distilled off using an evaporator, and the obtained concentrate was purified by column chromatography (developing solvent: chloroform) to obtain 8.9 g of Comparative Ethylene Compound 1 shown in Table 2. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 92.6 mol%.
(1−16)合成例16:比較エチレン化合物2の合成
合成例15において、マロノニトリルの代わりにシアノ酢酸メチルを用いたこと以外は、合成例15と同様の手順により表2に示す比較エチレン化合物2を1.7g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は29.9mol%であった。
(1-16) Synthesis Example 16: Synthesis of Comparative Ethylene Compound 2 Comparative ethylene compound 2 shown in Table 2 was subjected to the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 15 except that methyl cyanoacetate was used instead of malononitrile in Synthesis Example 15. 1.7 g was obtained. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 29.9 mol%.
(1−17)合成例17:比較エチレン化合物3の合成
合成例15において、4−クロロベンジルメルカプタンの代わりに4−イソプロピルベンゼンチオールを用いたこと以外は、合成例15と同様の手順により表2に示す比較エチレン化合物3を3.5g得た。4−フルオロベンズアルデヒドに対する収率は71.9mol%であった。
(1-17) Synthesis Example 17: Synthesis of Comparative Ethylene Compound 3 Table 2 follows the same procedure as in Synthesis Example 15 except that 4-isopropylbenzenethiol was used instead of 4-chlorobenzyl mercaptan in Synthesis Example 15. 3.5 g of the comparative ethylene compound 3 shown in the above was obtained. The yield with respect to 4-fluorobenzaldehyde was 71.9 mol%.
(2)エポキシ樹脂(EP樹脂)組成物の調製
(2−1)硬化触媒の調製
国際公開第1997/031924号に記載された合成法に従って、TPB(トリス(ペンタフルオロフェニル)ボラン)含有量7%の安藤パラケミー社製アイソパー(登録商標)E溶液255gを調製した。この溶液に水を60℃で滴下して白色結晶を析出させ、これを室温まで冷却した後、吸引ろ過し、n−ヘプタンで洗浄した。得られたケーキを60℃で減圧乾燥し、白色結晶であるTPB・水錯体(TPB含有粉末)を18.7g得た。この錯体は水分量9.2%(カールフィッシャー水分計)であり、TPB含有率は90.8%であった。乾燥後の錯体に対して19F−NMR分析とGC分析を実施したが、TPB以外のピークは検出されなかった。得られたTPB・水錯体2.0gとトルエンを1.1gとを配合し、室温で10分間混合した。その後、2mol/Lアンモニア・エタノール溶液を2.6g添加し、室温で60分間混合し、TPB触媒の均一溶液とした。これをカチオン硬化触媒とした。
(2) Preparation of Epoxy Resin (EP Resin) Composition (2-1) Preparation of Curing Catalyst TPB (tris (pentafluorophenyl) borane) content 7 according to the synthesis method described in International Publication No. 1997/031924. 25 g of Isopar® E solution manufactured by Ando Parachemy Co., Ltd. was prepared. Water was added dropwise to this solution at 60 ° C. to precipitate white crystals, which were cooled to room temperature, suction filtered, and washed with n-heptane. The obtained cake was dried under reduced pressure at 60 ° C. to obtain 18.7 g of a TPB / water complex (TPB-containing powder) as white crystals. This complex had a water content of 9.2% (Karl Fischer titer) and a TPB content of 90.8%. 19 F-NMR analysis and GC analysis were performed on the dried complex, but no peak other than TPB was detected. 2.0 g of the obtained TPB / water complex and 1.1 g of toluene were mixed and mixed at room temperature for 10 minutes. Then, 2.6 g of a 2 mol / L ammonia / ethanol solution was added and mixed at room temperature for 60 minutes to prepare a uniform solution of the TPB catalyst. This was used as a cationic curing catalyst.
(2−2)シラン加水分解物溶液の調製
3−グリシドキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン(東レ・ダウコーニング社製、OFS−6040)24.7質量部と2−プロパノール32.1質量部と蒸留水3.4質量部とを配合し、25℃で均一に混合した。そこに、ギ酸1.54質量部を加えて90分間混合し、3−グリシドキシプロピルトリメトキシシランの加水分解反応を進行させて、シラン加水分解物溶液を得た。
(2-2) Preparation of silane hydrolyzate solution 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (OFS-6040, manufactured by Toray Dow Corning) 24.7 parts by mass, 2-propanol 32.1 parts by mass and distilled water 3.4 parts by mass was blended and mixed uniformly at 25 ° C. To this, 1.54 parts by mass of formic acid was added and mixed for 90 minutes to proceed with the hydrolysis reaction of 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane to obtain a silane hydrolyzate solution.
(2−3)エポキシ樹脂組成物1の調製
エポキシ樹脂として2,2−ビス(ヒドロキシメチル)−1−ブタノールの1,2−エポキシ−4−(2−オキシラニル)シクロヘキサン付加物(ダイセル社製、EHPE3150)を100質量部、溶媒としてトルエン150質量部とo−キシレン75質量部、近赤外線吸収色素として下記に示すスクアリリウム化合物A(特開2016−74649号公報の実施例1−18に記載)を8.9質量部、合成例2で得られたエチレン化合物2を8.4質量部、表面調整剤としてビックケミー社製BYK−306(ポリエーテル変性ポリジメチルシロキサン)を0.3質量部配合し、40℃で均一に混合した。得られた混合物を25℃に降温後、上記で得られたカチオン硬化触媒2.5質量部とシラン加水分解物溶液10質量部を加えて均一に混合し、これを孔径0.45μmのフィルター(GLサイエンス社製、非水系13N)でろ過して異物を取り除き、エポキシ樹脂組成物1を得た。
(2-3) Preparation of Epoxy Resin Composition 1 As an epoxy resin, 1,2-epoxy-4- (2-oxylanyl) cyclohexane adduct of 2,2-bis (hydroxymethyl) -1-butanol (manufactured by Daicel Co., Ltd., 100 parts by mass of EHPE3150), 150 parts by mass of toluene and 75 parts by mass of o-xylene as a solvent, and the squarylium compound A shown below as a near-infrared absorbing dye (described in Example 1-18 of JP-A-2016-74649). 8.9 parts by mass, 8.4 parts by mass of the ethylene compound 2 obtained in Synthesis Example 2, and 0.3 parts by mass of BYK-306 (polyether-modified polydimethylsiloxane) manufactured by Big Chemie Co., Ltd. as a surface conditioner were blended. The mixture was uniformly mixed at 40 ° C. After lowering the temperature of the obtained mixture to 25 ° C., 2.5 parts by mass of the cation curing catalyst obtained above and 10 parts by mass of the silane hydrolyzate solution were added and mixed uniformly, and this was mixed with a filter having a pore size of 0.45 μm. Foreign matter was removed by filtration through a non-aqueous 13N) manufactured by GL Science Co., Ltd. to obtain an epoxy resin composition 1.
(2−4)エポキシ樹脂組成物2の調製
上記のエポキシ樹脂組成物1の調製例において、近赤外線吸収色素を用いなかったこと、またエチレン化合物2の代わりにエチレン化合物14を用いたこと以外は、同様の手順によりエポキシ樹脂組成物2を得た。
(2-4) Preparation of Epoxy Resin Composition 2 Except that the near-infrared absorbing dye was not used and the ethylene compound 14 was used instead of the ethylene compound 2 in the above preparation example of the epoxy resin composition 1. , An epoxy resin composition 2 was obtained by the same procedure.
(2−5)エポキシ樹脂組成物3の調製
上記のエポキシ樹脂組成物1の調製例において、エチレン化合物2の代わりに比較エチレン化合物1を用いたこと以外は、同様の手順によりエポキシ樹脂組成物3を得た。
(2-5) Preparation of Epoxy Resin Composition 3 The epoxy resin composition 3 is prepared by the same procedure except that the comparative ethylene compound 1 is used instead of the ethylene compound 2 in the above preparation example of the epoxy resin composition 1. Got
(2−6)エポキシ樹脂組成物4の調製
上記のエポキシ樹脂組成物1の調製例において、エチレン化合物2の代わりに比較エチレン化合物2を用いたこと以外は、同様の手順によりエポキシ樹脂組成物4を得た。
(2-6) Preparation of Epoxy Resin Composition 4 The epoxy resin composition 4 is prepared by the same procedure except that the comparative ethylene compound 2 is used instead of the ethylene compound 2 in the above preparation example of the epoxy resin composition 1. Got
(2−7)エポキシ樹脂組成物5の調製
上記のエポキシ樹脂組成物1の調製例において、エチレン化合物2の代わりに比較エチレン化合物3を用いたこと以外は、同様の手順によりエポキシ樹脂組成物5を得た。
(2-7) Preparation of Epoxy Resin Composition 5 The epoxy resin composition 5 is prepared by the same procedure except that the comparative ethylene compound 3 is used instead of the ethylene compound 2 in the above preparation example of the epoxy resin composition 1. Got
(3)シクロオレフィン系樹脂(COP樹脂)組成物の調製
(3−1)シクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物1の調製
シクロオレフィン系樹脂(ポリプラスチックス社製、TOPAS(登録商標)5013)126質量部をトルエン435質量部とo−キシレン439質量部の混合溶媒に加え、さらにそこに上記のスクアリリウム化合物Aを10質量部、合成例1で得られたエチレン化合物1を8.4質量部、表面調整剤としてビックケミー社製BYK−330(ポリエーテル変性ポリジメチルシロキサン)を0.52質量部加えて均一に混合し、シクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物1を得た。
(3) Preparation of Cycloolefin Resin (COP Resin) Composition (3-1) Preparation of Cycloolefin Resin Composition 1 Cycloolefin Resin (manufactured by Polyplastics, TOPAS® 5013) 126 parts by mass Was added to a mixed solvent of 435 parts by mass of toluene and 439 parts by mass of o-xylene, 10 parts by mass of the above squarylium compound A, and 8.4 parts by mass of the ethylene compound 1 obtained in Synthesis Example 1 for surface preparation. BYK-330 (polyether-modified polydimethylsiloxane) manufactured by Big Chemie Co., Ltd. was added as an agent by 0.52 parts by mass and mixed uniformly to obtain a cycloolefin resin composition 1.
(3−2)シクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物2の調製
上記のシクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物1の調製例において、エチレン化合物1の代わりに比較エチレン化合物1を用いたこと以外は、同様の手順によりシクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物2を得た。
(3-2) Preparation of Cycloolefin Resin Composition 2 Cyclo by the same procedure except that the comparative ethylene compound 1 was used instead of the ethylene compound 1 in the above preparation example of the cycloolefin resin composition 1. An olefin resin composition 2 was obtained.
(3−3)シクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物3の調製
上記のシクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物1の調製例において、エチレン化合物1の代わりに比較エチレン化合物3を用いたこと以外は、同様の手順によりシクロオレフィン系樹脂組成物3を得た。
(3-3) Preparation of Cycloolefin Resin Composition 3 Cyclo by the same procedure except that the comparative ethylene compound 3 was used instead of the ethylene compound 1 in the above preparation example of the cycloolefin resin composition 1. An olefin resin composition 3 was obtained.
(4)ポリアリレート樹脂(PAR樹脂)組成物の調製
(4−1)ポリアリレート樹脂の合成
撹拌翼を備えた容量2リットルの反応容器に、2,2’−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)プロパン10.01g(0.044mol)、水酸化ナトリウム3.59g(0.090mol)、イオン交換水300gを仕込み、溶解させた後、そこにトリエチルアミン0.89g(0.009mol)を加えて溶解させた。テレフタル酸ジクロリド3.57g(0.021mol)とイソフタル酸ジクロリド3.57g(0.021mol)を500gの塩化メチレンに溶解させた溶液を滴下漏斗に入れ、これを前記反応容器に取り付けた。反応容器中の溶液を20℃に保ちながら撹拌し、滴下漏斗から塩化メチレン溶液を60分間かけて滴下した。さらにそこに、塩化ベンゾイル0.71g(0.005mol)を10gの塩化メチレンに溶解させた溶液を添加し、60分間撹拌した。得られた反応液に酢酸水溶液を加えて中和して、水相のpHを7にしてから分液漏斗を用いて油相と水相を分離した。得られた油相を、撹拌下、メタノールに滴下してポリマーを再沈させ、沈殿をろ過により回収し、80℃オーブンで乾燥して白色固体のポリアリレート樹脂を得た。収量は11.5gであった。得られたポリアリレート樹脂の重量平均分子量(Mw)は33,780、数平均分子量(Mn)は8,130であった。ポリアリレート樹脂の重量平均分子量と数平均分子量は、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー測定により求めたポリスチレン換算の値である。
(4) Preparation of polyarylate resin (PAR resin) composition (4-1) Synthesis of polyarylate resin 2,2'-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propane in a reaction vessel having a capacity of 2 liters equipped with a stirring blade. 10.01 g (0.044 mol), 3.59 g (0.090 mol) of sodium hydroxide, and 300 g of ion-exchanged water were charged and dissolved, and then 0.89 g (0.009 mol) of triethylamine was added and dissolved. .. A solution prepared by dissolving 3.57 g (0.021 mol) of terephthalic acid dichloride and 3.57 g (0.021 mol) of isophthalic acid dichloride in 500 g of methylene chloride was placed in a dropping funnel, and this was attached to the reaction vessel. The solution in the reaction vessel was stirred while maintaining the temperature at 20 ° C., and the methylene chloride solution was added dropwise from the dropping funnel over 60 minutes. Further, a solution prepared by dissolving 0.71 g (0.005 mol) of benzoyl chloride in 10 g of methylene chloride was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred for 60 minutes. An aqueous acetic acid solution was added to the obtained reaction solution for neutralization to bring the pH of the aqueous phase to 7, and then the oil phase and the aqueous phase were separated using a separatory funnel. The obtained oil phase was added dropwise to methanol under stirring to reprecipitate the polymer, and the precipitate was recovered by filtration and dried in an oven at 80 ° C. to obtain a white solid polyarylate resin. The yield was 11.5 g. The weight average molecular weight (Mw) of the obtained polyarylate resin was 33,780, and the number average molecular weight (Mn) was 8,130. The weight average molecular weight and the number average molecular weight of the polyarylate resin are polystyrene-equivalent values obtained by gel permeation chromatography measurement.
(4−2)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物1の調製
上記で得られたポリアリレート樹脂100質量部をトルエン283質量部とo−キシレン283質量部の混合溶媒に加え、さらにそこに近赤外線吸収色素として上記のスクアリリウム化合物Aを3.3質量部と下記に示すスクアリリウム化合物Bを1.1質量部、合成例12で得られたエチレン化合物12を8質量部、表面調整剤としてビックケミー社製BYK−330(ポリエーテル変性ポリジメチルシロキサン)を0.52質量部加えて均一に混合し、ポリアリレート樹脂組成物1を得た。
(4-2) Preparation of Polyallylate Resin Composition 1 100 parts by mass of the polyallylate resin obtained above was added to a mixed solvent of 283 parts by mass of toluene and 283 parts by mass of o-xylene, and further added thereto as a near-infrared absorbing dye. 3.3 parts by mass of the above squarylium compound A and 1.1 parts by mass of the squarylium compound B shown below, 8 parts by mass of the ethylene compound 12 obtained in Synthesis Example 12, BYK-330 manufactured by Big Chemie as a surface conditioner. (Polyether-modified polydimethylsiloxane) was added in an amount of 0.52 parts by mass and mixed uniformly to obtain a polyarylate resin composition 1.
(4−3)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物2の調製
上記で得られたポリアリレート樹脂100質量部をトルエン283質量部とo−キシレン283質量部の混合溶媒に加え、さらにそこに上記のスクアリリウム化合物Aを3.3質量部、合成例13で得られた比較エチレン化合物1を8.4質量部、表面調整剤としてビックケミー社製BYK−330(ポリエーテル変性ポリジメチルシロキサン)を0.52質量部加えて均一に混合し、ポリアリレート樹脂組成物2を得た。
(4-3) Preparation of Polyallylate Resin Composition 2 100 parts by mass of the polyallylate resin obtained above is added to a mixed solvent of 283 parts by mass of toluene and 283 parts by mass of o-xylene, and the above squarylium compound A is further added thereto. 3.3 parts by mass, 8.4 parts by mass of the comparative ethylene compound 1 obtained in Synthesis Example 13, and 0.52 parts by mass of BYK-330 (polyether-modified polydimethylsiloxane) manufactured by Big Chemie as a surface conditioner. The mixture was uniformly mixed to obtain a polyarylate resin composition 2.
(4−4)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物3の調製
上記で得られたポリアリレート樹脂組成物1とエポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解溶液とを、前者:後者=99:1の質量比で25℃で均一に混合し、これを孔径0.1μmのフィルター(GLサイエンス社製、非水系13N)でろ過して異物を取り除くことで、ポリアリレート樹脂組成物3を得た。なお、エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解溶液は、3−グリシドキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン(東レ・ダウコーニング社製、OFS−6040)24.7質量部と2−プロパノール32.1質量部と蒸留水3.4質量部とを配合し、25℃で均一に混合した後、ギ酸1.54質量部を加えて90分間混合し、3−グリシドキシプロピルトリメトキシシランの加水分解反応を進行させることにより調製した。
(4-4) Preparation of Polyarylate Resin Composition 3 The polyarylate resin composition 1 obtained above and the hydrolyzed solution of the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent are mixed in a mass ratio of the former: the latter = 99: 1. The polyarylate resin composition 3 was obtained by uniformly mixing at 25 ° C. and filtering this with a filter having a pore size of 0.1 μm (manufactured by GL Science, non-aqueous 13N) to remove foreign substances. The hydrolyzed solution of the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent was 34.7 parts by mass of 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (OFS-6040 manufactured by Toray Dowcorning Co., Ltd.) and 32.1 parts by mass of 2-propanol. And 3.4 parts by mass of distilled water were mixed and mixed uniformly at 25 ° C., then 1.54 parts by mass of formic acid was added and mixed for 90 minutes to hydrolyze 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane. Prepared by advancing.
(4−5)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物4の調製
上記のポリアリレート樹脂組成物3の調製例において、スクアリリウム化合物Aおよびスクアリリウム化合物Bの代わりに可視光吸収色素として下記に示すスクアリリウム化合物C(Tetrahedron Letters, Vol.40, pp.4067-4068 (1999)の表1に開示されるProduct 3a)を用いたこと、またエチレン化合物12の代わりに合成例14で得られたエチレン化合物14を用いたこと以外は、ポリアリレート樹脂組成物3の調製例と同様の手順によりポリアリレート樹脂組成物4を得た。
(4-5) Preparation of Polyallylate Resin Composition 4 In the above preparation example of the polyallylate resin composition 3, the squarylium compound C (Tetrahedron Letters) shown below is used as a visible light absorbing dye instead of the squarylium compound A and the squarylium compound B. , Vol.40, pp.4067-4068 (1999) except that the product 3a) disclosed in Table 1 was used and the ethylene compound 14 obtained in Synthesis Example 14 was used instead of the ethylene compound 12. Obtained the polyallylate resin composition 4 by the same procedure as in the preparation example of the polyallylate resin composition 3.
(4−6)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物5の調製
ポリアリレート樹脂組成物3の調製例において、スクアリリウム化合物Aおよびスクアリリウム化合物Bを使用しなかったこと以外は、同様の手順によりポリアリレート樹脂組成物5を得た。
(4-6) Preparation of Polyallylate Resin Composition 5 The polyallylate resin composition 5 was prepared by the same procedure except that the squarylium compound A and the squarylium compound B were not used in the preparation example of the polyallylate resin composition 3. Got
(4−7)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物6の調製
ポリアリレート樹脂組成物5の調製例において、エポキシ基含有シランカップリング剤の加水分解溶液の代わりに、3−グリシドキシプロピルトリメトキシシラン(東レ・ダウコーニング社製、OFS−6040)24.7質量部と2−プロパノール32.1質量部と蒸留水3.4質量部とギ酸1.54質量部とを配合した混合溶液を用いた以外は、同様の手順によりポリアリレート樹脂組成物6を得た。
(4-7) Preparation of Polyarylate Resin Composition 6 In the preparation example of the polyarylate resin composition 5, instead of the hydrolyzed solution of the epoxy group-containing silane coupling agent, 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (Toray)・ Except for using a mixed solution containing 24.7 parts by mass of OFS-6040, manufactured by Dow Corning, 32.1 parts by mass of 2-propanol, 3.4 parts by mass of distilled water, and 1.54 parts by mass of formic acid. , Polyarylate resin composition 6 was obtained by the same procedure.
(4−8)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物7の調製
ポリアリレート樹脂組成物4の調製例において、スクアリリウム化合物Cを使用しなかったこと以外は、同様の手順によりポリアリレート樹脂組成物7を得た。
(4-8) Preparation of Polyarylate Resin Composition 7 A polyarylate resin composition 7 was obtained by the same procedure except that the squalylium compound C was not used in the preparation example of the polyarylate resin composition 4.
(4−9)ポリアリレート樹脂組成物8の調製
ポリアリレート樹脂組成物3の調製例において、エチレン化合物12を使用しなかったこと以外は、同様の手順によりポリアリレート樹脂組成物8を得た。
(4-9) Preparation of Polyarylate Resin Composition 8 A polyarylate resin composition 8 was obtained by the same procedure except that ethylene compound 12 was not used in the preparation example of the polyarylate resin composition 3.
(5)光学フィルターの作製
上記で得られた各樹脂組成物を、ガラス基板(Schott社製、D263Teco)上に2cc垂らした後、スピンコーター(ミカサ社製、1H−D7)を用い、0.2秒間かけて1600回転にし、20秒間その回転数で保持し、その後0.2秒間かけて0回転になるようにして、樹脂組成物をガラス基板上に成膜した。樹脂組成物を成膜したガラス基板を、精密恒温器(ヤマト科学社製、DH611)を用いて100℃で3分間初期乾燥した(キュア前)。その後、イナートオーブン(ヤマト科学社製、DN610I)を用いて50℃で30分間窒素置換した後、15分程度で190℃に昇温し、窒素雰囲気下で190℃で30分間乾燥することにより、ガラス基板上に樹脂層(吸収層)を形成した(キュア後)。ガラス基板上に形成した樹脂層の厚みは2μmであった。このようにガラス基板上に樹脂層を形成することにより光学フィルターを作製した。なお、樹脂層の厚みは、樹脂層を形成したガラス基板の厚みとガラス基板単独の厚みをそれぞれマイクロメーターにより測定し、両者の差から求めた。
(5) Preparation of Optical Filter After 2 cc of each of the resin compositions obtained above was dropped on a glass substrate (D263Teco manufactured by Schott), a spin coater (1HD7 manufactured by Mikasa) was used. The resin composition was formed on a glass substrate at 1600 rotations over 2 seconds, held at that rotation speed for 20 seconds, and then at 0 rotations over 0.2 seconds. The glass substrate on which the resin composition was formed was initially dried at 100 ° C. for 3 minutes using a precision thermostat (manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd., DH611) (before curing). Then, nitrogen was replaced at 50 ° C. for 30 minutes using an inert oven (manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd., DN610I), the temperature was raised to 190 ° C. in about 15 minutes, and the mixture was dried at 190 ° C. for 30 minutes in a nitrogen atmosphere. A resin layer (absorption layer) was formed on the glass substrate (after curing). The thickness of the resin layer formed on the glass substrate was 2 μm. An optical filter was produced by forming a resin layer on the glass substrate in this way. The thickness of the resin layer was determined by measuring the thickness of the glass substrate on which the resin layer was formed and the thickness of the glass substrate alone with a micrometer, and determining the difference between the two.
(6)エチレン化合物および光学フィルターの透過(吸収)スペクトル測定
(6−1)エチレン化合物の吸収スペクトル測定
分光光度計(島津製作所社製、UV−1800)を用いて、トルエン中の各エチレン化合物の吸収スペクトルを測定ピッチ1nmで測定し、波長300nm〜1100nmにおける光の透過率を求めた。波長300nm〜800nmの範囲における最大吸収ピークの極大波長λmaxを求め、その結果を表3にまとめた。また、エチレン化合物1および比較エチレン化合物1のトルエン中の吸収スペクトルを図1に示す。
(6) Measurement of transmission (absorption) spectrum of ethylene compound and optical filter (6-1) Measurement of absorption spectrum of ethylene compound Using a spectrophotometer (UV-1800, manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation), each ethylene compound in toluene The absorption spectrum was measured at a measurement pitch of 1 nm, and the light transmittance at a wavelength of 300 nm to 1100 nm was determined. The maximum wavelength λmax of the maximum absorption peak in the wavelength range of 300 nm to 800 nm was determined, and the results are summarized in Table 3. The absorption spectra of ethylene compound 1 and comparative ethylene compound 1 in toluene are shown in FIG.
(6−2)光学フィルターの透過スペクトル測定
ガラス基板上に樹脂層を形成した各光学フィルターについて、分光光度計(島津製作所社製、UV−1800)を用いて透過スペクトルを測定ピッチ1nmで測定し、波長300nm〜800nmにおける光の透過率を求めた。樹脂層のキュア前とキュア後の光学フィルターについて、透過スペクトルを測定した。結果を図2〜図12に示す。
(6-2) Measurement of transmission spectrum of optical filter For each optical filter having a resin layer formed on a glass substrate, the transmission spectrum was measured at a measurement pitch of 1 nm using a spectrophotometer (UV-1800, manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation). , The transmittance of light at a wavelength of 300 nm to 800 nm was determined. The transmission spectra of the optical filters before and after curing the resin layer were measured. The results are shown in FIGS. 2 to 12.
(6−3)結果
図1に示すように、エチレン化合物1と比較エチレン化合物1のトルエン中の吸収スペクトルは、いずれも波長約380nmに最大吸収ピークを示した。エチレン化合物あるいはさらにスクアリリウム化合物を含有する樹脂組成物から形成した光学フィルターの透過スペクトルは、図2、図3、図7、図10、図12に示すように、190℃のキュア前後で大きな変化は見られなかった。一方、比較エチレン化合物とスクアリリウム化合物を含有する樹脂組成物から形成した光学フィルターの透過スペクトルは、図4〜図6、図8、図9、図11に示すように、190℃のキュア後の紫外〜紫色領域の透過率が高くなった。これらの結果から、本発明のエチレン化合物は耐熱性に優れるものであることが分かる。
(6-3) Results As shown in FIG. 1, the absorption spectra of ethylene compound 1 and comparative ethylene compound 1 in toluene showed the maximum absorption peak at a wavelength of about 380 nm. As shown in FIGS. 2, 3, 7, 10, and 12, the transmission spectrum of the optical filter formed from the resin composition containing the ethylene compound or the squarylium compound does not change significantly before and after curing at 190 ° C. I couldn't see it. On the other hand, the transmission spectra of the optical filter formed from the resin composition containing the comparative ethylene compound and the squarylium compound are ultraviolet rays after curing at 190 ° C. as shown in FIGS. 4 to 6, 8, 9, and 11. ~ The transmittance in the purple area has increased. From these results, it can be seen that the ethylene compound of the present invention has excellent heat resistance.
(7)密着性評価
(7−1)初期耐剥離性試験
上記で得られた光学フィルターの樹脂層にカッター(エヌティー社製、A−300)で切り込みを入れ、縦列、横列にそれぞれ2mm間隔で10本のクロスカット線を設けることによって4mm2の四角を81マス作製し、評価用サンプル基板を作製した。このサンプル基板を、空気が入らないようにテープ(3M(スリーエム)社製、スコッチ(登録商標)透明粘着テープ透明美色(登録商標))を貼り付け、5秒間放置した。その後、サンプル基板からのテープの剥離を1秒以内に行い、下記基準で評価した。なお、いずれのマスにおいても剥離力が一定となるようにテープの剥離を行った。
A:作製した81マスの四角のうち、1マスも剥がれが発生しなかった
B:作製した81マスの四角のうち、1〜9マスに剥がれが発生した
C:作製した81マスの四角のうち、10〜81マスに剥がれが発生した
(7) Adhesion evaluation (7-1) Initial peeling resistance test Cut the resin layer of the optical filter obtained above with a cutter (manufactured by NT, A-300), and make cuts in columns and rows at 2 mm intervals. By providing 10 cross-cut lines, 81 squares of 4 mm 2 were prepared to prepare a sample substrate for evaluation. This sample substrate was attached with a tape (3M (3M), Scotch (registered trademark) transparent adhesive tape, transparent beauty color (registered trademark)) to prevent air from entering, and left for 5 seconds. Then, the tape was peeled off from the sample substrate within 1 second, and evaluated according to the following criteria. The tape was peeled off so that the peeling force was constant in all the cells.
A: No peeling occurred in any of the 81 squares prepared. B: Peeling occurred in 1 to 9 squares of the 81 squares prepared. C: Of the 81 squares prepared. , 10 to 81 squares were peeled off
(7−2)水煮沸後耐剥離性試験
上記で得られた光学フィルターの樹脂層にカッター(エヌティー社製、A−300)で切り込みを入れ、縦列、横列にそれぞれ2mm間隔で10本のクロスカット線を設けることによって4mm2の四角を81マス作製し、評価用サンプル基板を作製した。次に、このサンプル基板を、沸騰状態に加熱した超純水中に入れ、2時間煮沸した。続いて、室温にて、空気が入らないようにテープ(3M(スリーエム)社製、スコッチ(登録商標)透明粘着テープ透明美色(登録商標))を貼り付け、5秒間放置した。その後、サンプル基板からのテープの剥離を1秒以内に行い、下記基準で評価した。なお、いずれのマスにおいても剥離力が一定となるようにテープの剥離を行った。
A:作製した81マスの四角のうち、1マスも剥がれが発生しなかった
B:作製した81マスの四角のうち、1〜9マスに剥がれが発生した
C:作製した81マスの四角のうち、10〜81マスに剥がれが発生した
(7-2) Peeling resistance test after boiling in water The resin layer of the optical filter obtained above is cut with a cutter (A-300, manufactured by NT), and 10 cloths are made in columns and rows at 2 mm intervals. By providing a cut line, 81 squares of 4 mm 2 were prepared to prepare a sample substrate for evaluation. Next, this sample substrate was placed in ultrapure water heated to a boiling state and boiled for 2 hours. Subsequently, at room temperature, a tape (3M (3M), Scotch (registered trademark) transparent adhesive tape, transparent beauty color (registered trademark)) was attached to prevent air from entering, and the mixture was left for 5 seconds. Then, the tape was peeled off from the sample substrate within 1 second, and evaluated according to the following criteria. The tape was peeled off so that the peeling force was constant in all the cells.
A: No peeling occurred in any of the 81 squares prepared. B: Peeling occurred in 1 to 9 squares of the 81 squares prepared. C: Of the 81 squares prepared. , 10 to 81 squares were peeled off
(7−3)結果
ポリアリレート樹脂組成物1、3〜8を用いて作製した光学フィルターの初期耐剥離性試験および水煮沸後耐剥離性試験の結果を表4に示した。表4の結果から明らかなように、本発明のエチレン化合物とシランカップリング剤またはその加水分解(縮合)物を含有する樹脂組成物から形成した光学フィルターは、樹脂層とガラス基板との密着性に優れるものとなった。
(7-3) Results Table 4 shows the results of the initial peel resistance test and the peel resistance test after boiling of the optical filter prepared by using the polyarylate resin compositions 1, 3 to 8. As is clear from the results in Table 4, the optical filter formed from the resin composition containing the ethylene compound of the present invention and the silane coupling agent or a hydrolyzed product thereof has adhesion between the resin layer and the glass substrate. It became excellent.
本発明のエチレン化合物は、樹脂に配合してフィルム等に成形することにより、光学デバイス、表示デバイス、機械部品、電気・電子部品等の用途に有用な光選択透過フィルターなどに用いることができる。 The ethylene compound of the present invention can be used in an optical selective transmission filter or the like useful for applications such as optical devices, display devices, mechanical parts, electrical / electronic parts, etc. by blending it with a resin and molding it into a film or the like.
Claims (10)
[式(1)中、Lは、アルキレン基、−O−、−S−、−SO−、アルキル基を有していてもよいメチン基(−C<)、>C<の4価の連結基、またはこれらを組み合わせた連結基を表し、
aは2以上の整数を表し、
Aはそれぞれ独立して下記式(2)で示される基を表す。]
[式(2)中、
R1はシアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基またはハロゲノアルキル基を表し、
R2は水素原子、シアノ基、アシル基、カルボキシル基、カルボン酸エステル基、アミド基、炭化水素基またはヘテロアリール基を表し、
R1とR2がともにアシル基、カルボン酸エステル基またはアミド基である場合、R1とR2は互いに連結して環を形成していてもよく、
R3は水素原子またはアルキル基を表し、
R4は水素原子、有機基または極性官能基を表し、複数のR4は互いに同一または異なっていてもよく、
Xは硫黄原子を表し、
*は式(1)の連結基Lとの結合部位を表す。] An ethylene compound represented by the following formula (1).
[In formula (1), L, A alkylene group, - O-, - S -, - SO-, also methine group have A alkyl group (-C <),> C < 4 valent Represents a linking group of, or a linking group combining these
a represents an integer of 2 or more,
Each A independently represents a group represented by the following formula (2). ]
[In equation (2),
R 1 represents a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group, an amide group or a halogenoalkyl group.
R 2 represents a hydrogen atom, a cyano group, an acyl group, a carboxyl group, a carboxylic acid ester group, an amide group, a hydrocarbon group or a heteroaryl group.
When both R 1 and R 2 are acyl groups, carboxylic acid ester groups or amide groups, R 1 and R 2 may be linked to each other to form a ring.
R 3 represents a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group
R 4 represents a hydrogen atom, an organic group or a polar functional group, and a plurality of R 4s may be the same or different from each other.
X represents a sulfur atom
* Represents the binding site with the linking group L of the formula (1). ]
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017132977 | 2017-07-06 | ||
| JP2017132977 | 2017-07-06 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020087131A Division JP7027483B2 (en) | 2017-07-06 | 2020-05-19 | Ethylene compound manufacturing method, resin composition manufacturing method, cured product manufacturing method, optical filter manufacturing method, sensor manufacturing method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019014707A JP2019014707A (en) | 2019-01-31 |
| JP2019014707A5 JP2019014707A5 (en) | 2020-04-09 |
| JP6833763B2 true JP6833763B2 (en) | 2021-02-24 |
Family
ID=64949980
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018117942A Active JP6833763B2 (en) | 2017-07-06 | 2018-06-21 | Ethylene compound, UV absorber and resin composition |
| JP2020087131A Active JP7027483B2 (en) | 2017-07-06 | 2020-05-19 | Ethylene compound manufacturing method, resin composition manufacturing method, cured product manufacturing method, optical filter manufacturing method, sensor manufacturing method |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020087131A Active JP7027483B2 (en) | 2017-07-06 | 2020-05-19 | Ethylene compound manufacturing method, resin composition manufacturing method, cured product manufacturing method, optical filter manufacturing method, sensor manufacturing method |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP6833763B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102253364B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN110809573B (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI731248B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2019009093A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019151708A (en) * | 2018-03-01 | 2019-09-12 | 株式会社日本触媒 | Resin composition and optical filter |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7231430B2 (en) * | 2019-02-14 | 2023-03-01 | 株式会社日本触媒 | resin composition, ink and optical filter |
| WO2022168832A1 (en) * | 2021-02-03 | 2022-08-11 | 三井化学株式会社 | Optical material production method, polymerizable composition for optical material, and optical material |
| KR20240008309A (en) * | 2021-05-14 | 2024-01-18 | 니혼 이타가라스 가부시키가이샤 | Light-absorbing composition, light-absorbing film, method for producing light-absorbing film, and optical filter |
| WO2023218937A1 (en) * | 2022-05-13 | 2023-11-16 | Agc株式会社 | Optical filter and uv pigment |
| WO2024024442A1 (en) * | 2022-07-25 | 2024-02-01 | 株式会社日本触媒 | Resin composition |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1348142A (en) * | 1970-05-14 | 1974-03-13 | Sandoz Ltd | Derivatives of alpha-cyanacrylic acid their production and use as stabilizers for organic materials |
| US3850960A (en) * | 1971-05-04 | 1974-11-26 | Sandoz Ltd | Derivatives of alpha-cyanacrylic acid |
| US4591545A (en) * | 1983-05-10 | 1986-05-27 | Dainippon Ink And Chemicals, Inc. | Photosensitive image-forming material having a layer of photosensitive polyester modified with chain extender |
| JPH07100792B2 (en) * | 1986-05-13 | 1995-11-01 | 三菱化学株式会社 | Liquid crystal composition |
| US4749774A (en) * | 1986-12-29 | 1988-06-07 | Eastman Kodak Company | Condensation polymer containing the residue of a poly-methine compound and shaped articles produced therefrom |
| US4994512A (en) * | 1989-05-01 | 1991-02-19 | Eastman Kodak Company | Poly-methine compounds, condensation polymer having a poly-methine compound admixed therein and shaped articles produced therefrom |
| US5057594A (en) * | 1989-08-17 | 1991-10-15 | Eastman Kodak Company | Ultraviolet light-absorbing compounds and sunscreen formulations and polymeric materials containing such compounds or residues thereof |
| US6576797B1 (en) | 1994-03-31 | 2003-06-10 | Ciba Specialty Chemicals Corporation | Thioether substituted hydroxybenzophenones and stabilized compositions |
| JP2000136176A (en) | 1998-10-28 | 2000-05-16 | Chemiprokasei Kaisha Ltd | Polymethine compound and its production and use |
| JP4612219B2 (en) | 2000-04-20 | 2011-01-12 | 三井化学株式会社 | Process for producing substituted aromatic compounds |
| JP2003026942A (en) | 2001-05-11 | 2003-01-29 | Kanegafuchi Chem Ind Co Ltd | Resin composition |
| JP2003043259A (en) | 2001-08-01 | 2003-02-13 | Konica Corp | Optical film, polarizing plate and display device |
| KR100479405B1 (en) * | 2002-05-24 | 2005-03-30 | 주식회사 싸이제닉 | Cinnamic acid dimers, their preparation and the use thereof for treating neurodegenerative disease |
| BRPI0907987A2 (en) | 2008-03-13 | 2015-11-24 | Basf Se | use of benzylidene malonates, process for the preparation of compounds, cosmetic preparation, and compounds |
| JP2010059235A (en) * | 2008-09-01 | 2010-03-18 | Fujifilm Corp | Ultraviolet absorbent composition |
| JP2010100787A (en) | 2008-10-27 | 2010-05-06 | Fujifilm Corp | Ultraviolet absorber and polymeric material containing the same |
| WO2013047411A1 (en) | 2011-09-29 | 2013-04-04 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Novel triazine derivative and ultraviolet absorbent |
-
2018
- 2018-06-21 WO PCT/JP2018/023663 patent/WO2019009093A1/en active Application Filing
- 2018-06-21 JP JP2018117942A patent/JP6833763B2/en active Active
- 2018-06-21 KR KR1020197033137A patent/KR102253364B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2018-06-21 CN CN201880044437.1A patent/CN110809573B/en active Active
- 2018-06-28 TW TW107122248A patent/TWI731248B/en active
-
2020
- 2020-05-19 JP JP2020087131A patent/JP7027483B2/en active Active
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019151708A (en) * | 2018-03-01 | 2019-09-12 | 株式会社日本触媒 | Resin composition and optical filter |
| JP7128633B2 (en) | 2018-03-01 | 2022-08-31 | 株式会社日本触媒 | Resin composition and optical filter |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TWI731248B (en) | 2021-06-21 |
| TW201906813A (en) | 2019-02-16 |
| CN110809573B (en) | 2022-03-08 |
| JP2020154320A (en) | 2020-09-24 |
| JP7027483B2 (en) | 2022-03-01 |
| WO2019009093A1 (en) | 2019-01-10 |
| KR102253364B1 (en) | 2021-05-17 |
| KR20190132522A (en) | 2019-11-27 |
| JP2019014707A (en) | 2019-01-31 |
| CN110809573A (en) | 2020-02-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6833763B2 (en) | Ethylene compound, UV absorber and resin composition | |
| JP7015128B2 (en) | Optical selective transmission filter | |
| JP6256335B2 (en) | Optical filter for solid-state imaging device and use thereof | |
| WO2015056734A1 (en) | Optical filter, solid-state image pickup device, and camera module | |
| JP6334964B2 (en) | New cyanine compound, optical filter, and apparatus using optical filter | |
| JP6905317B2 (en) | Oxocarbon compounds, resin compositions, and light selective transmission filters | |
| JP2015040895A (en) | Optical filter, and apparatus using optical filter | |
| CN106397300A (en) | Cyanine compound, optical filter, apparatus using optical filter and resin composite | |
| JP6599192B2 (en) | Oxocarbon compounds | |
| JP6788444B2 (en) | Resin composition and optical filter | |
| JP7231430B2 (en) | resin composition, ink and optical filter | |
| JP7128633B2 (en) | Resin composition and optical filter | |
| JP6771880B2 (en) | Resin composition and laminate | |
| JP6959794B2 (en) | Squalilium compound | |
| JP6584913B2 (en) | Oxocarbon compounds | |
| JP2017179131A (en) | Squarylium compound | |
| JP2022173072A (en) | ethylene compound | |
| JP2022158995A (en) | ethylene compound | |
| JP6811602B2 (en) | Optical selective transmission filter | |
| JP2017151176A (en) | Light selective transmission filter | |
| JP6630161B2 (en) | Light selective transmission filter and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2017067871A (en) | Resin molding | |
| JP6885717B2 (en) | Oxocarbon compounds | |
| JP6920087B2 (en) | Squalilium compound | |
| WO2024024442A1 (en) | Resin composition |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20190712 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200228 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200228 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20200228 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20200316 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200324 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200519 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200707 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20200901 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20201105 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20210126 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210203 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6833763 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |