JP6688498B2 - Degradation method and degradation product of proteoglycan - Google Patents
Degradation method and degradation product of proteoglycan Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6688498B2 JP6688498B2 JP2015201754A JP2015201754A JP6688498B2 JP 6688498 B2 JP6688498 B2 JP 6688498B2 JP 2015201754 A JP2015201754 A JP 2015201754A JP 2015201754 A JP2015201754 A JP 2015201754A JP 6688498 B2 JP6688498 B2 JP 6688498B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- proteoglycan
- molecular weight
- degradation product
- raw material
- aqueous solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000007857 degradation product Substances 0.000 title claims description 79
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title description 33
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 title description 6
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 title description 6
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 claims description 58
- NWUYHJFMYQTDRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-bis(ethenyl)benzene;1-ethenyl-2-ethylbenzene;styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1.CCC1=CC=CC=C1C=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1C=C NWUYHJFMYQTDRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 23
- 239000003729 cation exchange resin Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 22
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 102000016611 Proteoglycans Human genes 0.000 description 201
- 108010067787 Proteoglycans Proteins 0.000 description 201
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 63
- 241000972773 Aulopiformes Species 0.000 description 49
- 235000019515 salmon Nutrition 0.000 description 49
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 47
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 47
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 45
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 42
- 238000001641 gel filtration chromatography Methods 0.000 description 40
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 30
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 29
- 239000008367 deionised water Substances 0.000 description 29
- 229910021641 deionized water Inorganic materials 0.000 description 29
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 29
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 29
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 28
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 28
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 24
- 238000002835 absorbance Methods 0.000 description 20
- 238000000354 decomposition reaction Methods 0.000 description 20
- FNEHAOQZWPHONV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9h-carbazole;sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O.C1=CC=C2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=C1 FNEHAOQZWPHONV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 229920002307 Dextran Polymers 0.000 description 17
- 238000010828 elution Methods 0.000 description 17
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 16
- 229960004106 citric acid Drugs 0.000 description 15
- 238000000862 absorption spectrum Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000011088 calibration curve Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000004737 colorimetric analysis Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 12
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 9
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000002537 cosmetic Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000003480 eluent Substances 0.000 description 8
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000000502 dialysis Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000006386 neutralization reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000012506 Sephacryl® Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000013361 beverage Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 108091003079 Bovine Serum Albumin Proteins 0.000 description 2
- IAJILQKETJEXLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Galacturonsaeure Natural products O=CC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)=O IAJILQKETJEXLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002683 Glycosaminoglycan Polymers 0.000 description 2
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Chemical compound C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010306 acid treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- IAJILQKETJEXLJ-QTBDOELSSA-N aldehydo-D-glucuronic acid Chemical compound O=C[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)C(O)=O IAJILQKETJEXLJ-QTBDOELSSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229940098773 bovine serum albumin Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 210000000845 cartilage Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229940097043 glucuronic acid Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 150000002337 glycosamines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000005342 ion exchange Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000006210 lotion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000003491 skin Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 235000000346 sugar Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- KIUKXJAPPMFGSW-DNGZLQJQSA-N (2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3-Acetamido-2-[(2S,3S,4R,5R,6R)-6-[(2R,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3-acetamido-2,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-4-yl]oxy-2-carboxy-4,5-dihydroxyoxan-3-yl]oxy-5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-4-yl]oxy-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CC(=O)N[C@H]1[C@H](O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O3)C(O)=O)O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)NC(C)=O)[C@@H](C(O)=O)O1 KIUKXJAPPMFGSW-DNGZLQJQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylamide Chemical compound NC(=O)C=C HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000251468 Actinopterygii Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920000936 Agarose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 241000271566 Aves Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000283690 Bos taurus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000283153 Cetacea Species 0.000 description 1
- YASYEJJMZJALEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Citric acid monohydrate Chemical compound O.OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O YASYEJJMZJALEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000008186 Collagen Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010035532 Collagen Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000251729 Elasmobranchii Species 0.000 description 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000010834 Extracellular Matrix Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010037362 Extracellular Matrix Proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000287828 Gallus gallus Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000003886 Glycoproteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000288 Glycoproteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 1
- GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitric acid Chemical compound O[N+]([O-])=O GRYLNZFGIOXLOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000001188 articular cartilage Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000013040 bath agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003796 beauty Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000004556 brain Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000001768 cations Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- PBAYDYUZOSNJGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N chelidonic acid Natural products OC(=O)C1=CC(=O)C=C(C(O)=O)O1 PBAYDYUZOSNJGU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000013330 chicken meat Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960002303 citric acid monohydrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229920001436 collagen Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000593 degrading effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008556 epithelial cell proliferation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002744 extracellular matrix Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 235000019688 fish Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004108 freeze drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004676 glycans Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960000789 guanidine hydrochloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- PJJJBBJSCAKJQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N guanidinium chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].NC(N)=[NH2+] PJJJBBJSCAKJQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002674 hyaluronan Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960003160 hyaluronic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- GPRLSGONYQIRFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydron Chemical compound [H+] GPRLSGONYQIRFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003472 neutralizing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910017604 nitric acid Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002952 polymeric resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001282 polysaccharide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005017 polysaccharide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 description 1
- -1 rinse Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002453 shampoo Substances 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon dioxide Inorganic materials O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001694 spray drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000008163 sugars Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000000542 sulfonic acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000009772 tissue formation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000017423 tissue regeneration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000108 ultra-filtration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000870 ultraviolet spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003176 water-insoluble polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Polysaccharides And Polysaccharide Derivatives (AREA)
Description
本発明は、化粧料や医薬品、飲食品、日用品などで使用されるプロテオグリカンの分解物及びその製造方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a decomposed product of proteoglycan used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, foods and drinks, daily necessities, etc., and a method for producing the same.
プロテオグリカンは天然の高分子化合物であり、アミノ糖やウロン酸から構成されるグリコサミノグリカンを主成分とする多糖類とタンパク質との共有結合物の総称である。プロテオグリカンは、一般の糖タンパク質と比較して、全成分中のグリコサミノグリカン含量が極めて多いことを特徴とする。プロテオグリカンは、起源となる原料の種類や抽出・製造条件により、分子量や含まれるアミノ酸や糖(中性糖、ウロン酸、アミノ糖など)の種類や量、比率も異なり、千差万別である。 Proteoglycan is a naturally occurring high molecular compound, and is a generic term for covalently bonded proteins and polysaccharides composed mainly of glycosaminoglycans composed of amino sugars and uronic acids. Proteoglycans are characterized by an extremely high content of glycosaminoglycans in all components, as compared with general glycoproteins. Proteoglycans vary in molecular weight and in the type, amount, and ratio of amino acids and sugars (neutral sugar, uronic acid, amino sugars, etc.) that they contain, depending on the type of raw material that is the source and the extraction and production conditions. .
プロテオグリカンは、生体成分として多様な機能性を持つ重要な天然成分である。主要な各種臓器、脳、皮膚をはじめとした体全体の組織中の細胞外マトリックスや細胞表面に存在するほか、関節軟骨の主成分としても存在している。プロテオグリカンは、コラーゲンやヒアルロン酸と複合体を作ることで身体組織や皮膚組織を維持しており、組織形成や伝達物質としての役割などを有し、組織修復にも関係する成分である。 Proteoglycan is an important natural component having various functions as a biological component. In addition to being present on the extracellular matrix and cell surface in tissues of the entire body including various major organs, brain and skin, it is also present as the main component of articular cartilage. Proteoglycan maintains body tissues and skin tissues by forming a complex with collagen and hyaluronic acid, has a role as a tissue formation and a transmitter, and is a component related to tissue repair.
プロテオグリカンは、保水性や上皮細胞増殖作用などの様々な機能を有することが明らかになってきており、化粧品や食品など様々な分野において用いられている。しかし、プロテオグリカンは高分子のため、水に溶解すると高い粘性を有し、濃度が高くなると水に溶解しにくかったり、添加対象の化粧品や食品などの粘性へ影響を与えたりするなど、取扱いに難点がある。そのため、粘度の低いプロテオグリカンが求められている。一般的に、粘度は物質の分子量と相関があり、分子量が小さくなる程、その物質を溶解した溶液の粘度も低くなる。 Proteoglycans have been revealed to have various functions such as water retention and epithelial cell proliferation action, and are used in various fields such as cosmetics and foods. However, since proteoglycan is a polymer, it has a high viscosity when dissolved in water, and it becomes difficult to dissolve it in water when the concentration is high, or it affects the viscosity of cosmetics or foods to which it is added. There is. Therefore, proteoglycans with low viscosity are required. Generally, viscosity has a correlation with the molecular weight of a substance, and the lower the molecular weight, the lower the viscosity of the solution in which the substance is dissolved.
プロテオグリカンを分解する技術として、酵素を用いた方法が報告されている(特許文献1〜5)。しかし、これら酵素を用いた方法では、プロテオグリカンを分解する酵素自体が高価であり、また、分解して得た低分子プロテオグリカンと酵素とを分離しなければならないなど、コスト面および工程面で欠点があった。 As a technique for degrading proteoglycan, a method using an enzyme has been reported (Patent Documents 1 to 5). However, in the method using these enzymes, the enzyme itself that decomposes proteoglycan is expensive, and the low molecular weight proteoglycan obtained by decomposition must be separated from the enzyme. there were.
上記課題を鑑み、本発明は、より低コストでかつ簡易な方法でプロテオグリカン分解物を提供することを目的とする。 In view of the above problems, it is an object of the present invention to provide a proteoglycan degradation product at a lower cost and with a simple method.
上記課題を解決するために、本発明の一つの態様は、原料のプロテオグリカンをプロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂、もしくは強酸やクエン酸の少なくとも一つにて処理し、次に加温することを要旨とする。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problems, one embodiment of the present invention is to treat the raw material proteoglycan with at least one of a proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin, or a strong acid or citric acid, and then heating. Use as a summary.
本発明の他の態様は、分子量が40kDa以下であり、純水に対する相対粘度が26.5℃で1.5以下であり、1w/v%水溶液の270nmの吸光度が2以上であるプロテオグリカン分解物であることを要旨とする。 Another aspect of the present invention is a proteoglycan degradation product having a molecular weight of 40 kDa or less, a relative viscosity with respect to pure water of 1.5 or less at 26.5 ° C., and an absorbance of a 1 w / v% aqueous solution at 270 nm of 2 or more. The main point is.
本発明により、低コストでかつ簡易な方法でプロテオグリカン分解物が提供される。 According to the present invention, a proteoglycan degradation product is provided at a low cost and by a simple method.
以下、実施の形態をより具体的に説明する。 Hereinafter, the embodiment will be described more specifically.
プロテオグリカンの原料由来としては、牛、鶏、鯨などの哺乳類や鳥類の軟骨や、鮭、鮫、エイなどの魚類の軟骨であり、その種類を問わない。また、プロテオグリカンの抽出薬剤についても、酢酸などの有機酸などの酸、アルカリ、グアニジン塩酸、水、温熱水など様々あるが、本発明では抽出薬剤や温度や時間などの抽出・製造の条件も限定しないものである。 The source of proteoglycan is cartilage of mammals and birds such as cows, chickens and whales, and cartilage of fish such as salmon, sharks and rays, regardless of the type. There are various proteoglycan extraction agents such as acids such as acetic acid and organic acids, alkali, guanidine hydrochloride, water, hot water, etc., but the present invention also limits extraction and production conditions such as temperature and time. It does not.
本発明のプロテオグリカンの分解方法としては、その一つは最初に原料のプロテオグリカンを含む水溶液をプロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂にて処理することである。プロトンとは水素イオンのことであり、プロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂とは、樹脂のイオン交換基と結合している陽イオンがプロトンである強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂のことである。強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂は、担体にスルホン酸基のイオン交換基が導入された水不溶性の高分子樹脂である。担体としてはスチレン系やフェノール系、ビニル系、アクリルアミド系などの合成樹脂やセルロース系、アガロース系、デキストラン系などがある。樹脂を使用する前には、常法により酸やアルカリなどで予備洗浄し、酸によりプロトン型に活性化する必要がある。 One of the methods for decomposing the proteoglycan of the present invention is to first treat an aqueous solution containing the raw material proteoglycan with a proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin. A proton is a hydrogen ion, and a proton type strong acidic cation exchange resin is a strong acidic cation exchange resin in which the cation bonded to the ion exchange group of the resin is a proton. The strongly acidic cation exchange resin is a water-insoluble polymer resin in which an ion exchange group of a sulfonic acid group is introduced into a carrier. Examples of the carrier include styrene type, phenol type, vinyl type, acrylamide type synthetic resins, cellulose type, agarose type, dextran type and the like. Before using the resin, it is necessary to perform pre-washing with an acid or alkali by a conventional method and activate the proton type with an acid.
原料のプロテオグリカンを含む水溶液をプロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂に接触させる際、原料のプロテオグリカンを含む水溶液には、原料のプロテオグリカン以外の物質、特にイオン物質は入っていないほうが好ましい。イオン物質が共存するときは、イオン強度は低いほうが望ましい。 When the aqueous solution containing the raw material proteoglycan is brought into contact with the proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin, it is preferable that the aqueous solution containing the raw material proteoglycan does not contain a substance other than the raw material proteoglycan, particularly an ionic substance. When ionic substances coexist, lower ionic strength is desirable.
プロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂の接触方法としては、カラムなどに樹脂を充填し、原料のプロテオグリカンを含む水溶液をカラムに通過させる方式や、バッチ式などがある。接触時間は数分以上必要である。使用するプロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂の量は、樹脂の種類により異なるが、出発原料となる元のプロテオグリカンに対して、その樹脂の交換容量に安全率を乗じた以上の樹脂量は必要である。次に、プロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂と接触させたプロテオグリカンを、ろ過などの方法により、樹脂から分離して回収する。ろ過後のプロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂を水で洗浄し、樹脂に付着しているプロテオグリカンの残留分を回収する。 As a method of contacting the proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin, there is a method in which a resin is packed in a column or the like and an aqueous solution containing a raw material proteoglycan is passed through the column, or a batch method. The contact time should be several minutes or longer. The amount of proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin used depends on the type of resin, but it is necessary to have a resin amount that is greater than the exchange capacity of the original proteoglycan used as the starting material multiplied by the safety factor. is there. Next, the proteoglycan brought into contact with the proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin is separated from the resin and collected by a method such as filtration. The proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin after filtration is washed with water, and the residue of proteoglycan attached to the resin is recovered.
原料のプロテオグリカンを強酸で処理するとき、強酸としては塩酸、硫酸、硝酸などの無機酸やトリフルオロ酢酸などが挙げられる。また、原料のプロテオグリカンはクエン酸で処理してもよいし、強酸とクエン酸の混合物で処理してもよい。原料のプロテオグリカンと強酸、クエン酸の接触方法は、強酸やクエン酸の溶液に原料のプロテオグリカンを溶解してもよいし、原料のプロテオグリカンの水溶液に強酸やクエン酸を添加してもよい。強酸やクエン酸の濃度は原料のプロテオグリカンの種類や濃度にもよるが、原料のプロテオグリカン水溶液中の強酸の濃度はおおよそ5mM以上、クエン酸濃度はおおよそ0.1%以上が好ましい。また、接触時間は、強酸、クエン酸共に1時間以上、好ましくは10時間以上必要である。接触後、添加した強酸やクエン酸は除去したほうがよい。除去方法は限外ろ過でもよいし、透析、その他通常用いられている方法でよい。 When the raw material proteoglycan is treated with a strong acid, examples of the strong acid include inorganic acids such as hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid, and trifluoroacetic acid. The raw material proteoglycan may be treated with citric acid or a mixture of strong acid and citric acid. As a method of contacting the raw material proteoglycan with the strong acid or citric acid, the raw material proteoglycan may be dissolved in a solution of the strong acid or citric acid, or the strong acid or citric acid may be added to the aqueous solution of the raw material proteoglycan. The concentration of strong acid or citric acid depends on the kind and concentration of the proteoglycan as the raw material, but the concentration of strong acid in the aqueous solution of proteoglycan as the raw material is preferably about 5 mM or more, and the concentration of citric acid is preferably about 0.1% or more. The contact time is required to be 1 hour or more, preferably 10 hours or more for both strong acid and citric acid. After the contact, it is better to remove the added strong acid or citric acid. The removal method may be ultrafiltration, dialysis, or any other commonly used method.
次に、プロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂、または強酸やクエン酸で処理して得たプロテオグリカンを含む水溶液を加温する。加温の温度と時間は、原料のプロテオグリカンの種類や量にもよるが、加温の温度が70℃以上の場合は、加温時間は24時間以上必要である。加温の温度が50℃や60℃の場合は、より長時間必要である。 Next, the proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin or an aqueous solution containing proteoglycan obtained by treating with a strong acid or citric acid is heated. The heating temperature and time depend on the type and amount of the raw material proteoglycan, but when the heating temperature is 70 ° C. or higher, the heating time needs to be 24 hours or longer. When the heating temperature is 50 ° C. or 60 ° C., longer time is required.
得られた水溶液はプロテオグリカン分解物を含む水溶液であり、そのまま使用することもできるが、噴霧乾燥や凍結乾燥などにより粉末化してもよいし、アルコールやアセトンなどの有機溶剤により沈殿、風乾して、粉末化してもよい。また、中和してプロテオグリカン分解物の金属塩水溶液とした後に同様の処理を行うと、酸性であるプロテオグリカン分解物が中性になり、様々な製品の原料としての扱いが容易になる。 The obtained aqueous solution is an aqueous solution containing a proteoglycan degradation product, and can be used as it is, but may be powdered by spray drying, freeze drying, or the like, or precipitated by an organic solvent such as alcohol or acetone, and air dried, It may be powdered. Further, when the same treatment is performed after neutralizing the aqueous solution of the proteoglycan decomposition product to give a metal salt, the proteoglycan decomposition product which is acidic becomes neutral and can be easily handled as a raw material for various products.
また、プロトン型強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂、または強酸やクエン酸で処理して得たプロテオグリカンを含む水溶液を、加温しながら濃縮、粉末化することでもプロテオグリカンを分解することができる。 The proteoglycan can also be decomposed by concentrating and powdering an aqueous solution containing a proton-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin or a proteoglycan obtained by treating with a strong acid or citric acid while heating.
本発明の物質は、ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法で測定した分子量が40kDa以下であり、オストワルド式による純水に対する相対粘度が26.5℃で1.5以下であり、1w/v%水溶液の270nmの吸光度が光路長1cmで、2以上であるプロテオグリカン分解物である。 The substance of the present invention has a molecular weight of 40 kDa or less measured by gel filtration chromatography, a relative viscosity to pure water according to Ostwald's equation of 1.5 or less at 26.5 ° C., and a 270 nm of 1 w / v% aqueous solution. It is a proteoglycan degradation product having an optical path length of 1 cm and 2 or more.
本発明のプロテオグリカン分解物は、化粧料や飲料・食品などの原料として用いても、元の化粧料や飲料・食品などの粘性をほとんど変化させないという特徴がある。化粧料としては、化粧水や美容液、乳液、クリ−ム、リップ類などの化粧品や、シャンプー、リンス、入浴剤、石鹸などのトイレタリー用品が挙げられる。また、飲料にも容易に添加が可能であり、食品にも同様に適用できる。 The proteoglycan degradation product of the present invention is characterized in that it hardly changes the viscosity of the original cosmetics, beverages, foods, etc. even when used as a raw material for cosmetics, beverages, foods, etc. Examples of the cosmetics include cosmetics such as lotion, beauty essence, milky lotion, cream and lips, and toiletry products such as shampoo, rinse, bath agent and soap. Further, it can be easily added to beverages and can be similarly applied to foods.
以下に実施例を示して本発明を具体的に説明するが、これは単に例示の目的で述べるものであり、本発明はこれらの実施例に限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail with reference to Examples, but the present invention is described for the purpose of illustration only, and the present invention is not limited to these Examples.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造1:強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂処理)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂(商品名:AG 50W−X8 resin、バイオラッド社製)をガラス製カラムに充填し(内径2.5cm、高さ8.2cm)、1M塩酸100mLを流下して樹脂を洗浄・活性化した後、脱イオン水200mLを流下して過剰の塩酸を除去した。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.6gを脱イオン水45mLに溶解した溶液を、室温でカラム上方から添加・流下した。その後、樹脂に脱イオン水を110mL流下し、溶出液150mLを得た。
(Production of proteoglycan degradation product 1: strong acid cation exchange resin treatment)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. A strongly acidic cation exchange resin (trade name: AG 50W-X8 resin, manufactured by Bio-Rad) was packed in a glass column (inner diameter 2.5 cm, height 8.2 cm) and 100 mL of 1M hydrochloric acid was flowed down to remove the resin. After washing and activating, 200 mL of deionized water was flown down to remove excess hydrochloric acid. A solution prepared by dissolving 0.6 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material in 45 mL of deionized water was added and flowed down from above the column at room temperature. Then, 110 mL of deionized water was made to flow through the resin to obtain 150 mL of an eluate.
この強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂の溶出液10mLをバイアル瓶に入れ、蓋を閉め、70℃に加温した定温乾燥器(Drying Oven DX31、ヤマト科学(株)製)内へ静置した。24時間後、定温乾燥器よりバイアル瓶を取り出し、自然に冷却した。蓋を開け、50mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液1mL、5mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液9mLを反応液に加えて中和をし、プロテオグリカン分解物水溶液20mLを得た。 10 mL of the eluate of this strongly acidic cation exchange resin was placed in a vial, the lid was closed, and the mixture was left standing in a constant temperature dryer (Drying Oven DX31, manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd.) heated to 70 ° C. After 24 hours, the vial was taken out from the constant temperature dryer and naturally cooled. The lid was opened, and 1 mL of 50 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 5 mL of 5 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution were added to the reaction solution for neutralization to obtain 20 mL of proteoglycan degradation product aqueous solution.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の分子量測定)
実施例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量を、ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はトヨパール HW55F(内径2.7cm、高さ116cm、東ソー(株)製)、ポンプはLKB・PumpP−1(ファルマシア社製)、フラクションコレクターはLKB・FRAC−100(ファルマシア社製)を用いた。実施例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解物水溶液5mLを、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、4mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量75,000、38,500;和光純薬工業(株)製、150,000、10,000;シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。
(Measurement of molecular weight of proteoglycan degradation product)
The molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 1 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. Resin for gel filtration chromatography is Toyopearl HW55F (inner diameter 2.7 cm, height 116 cm, manufactured by Tosoh Corp.), pump is LKB Pump P-1 (Pharmacia), fraction collector is LKB FRAC-100 (Pharmacia). Manufactured) was used. 5 mL of the proteoglycan degradation product aqueous solution according to Example 1 was added from above the column. The eluent was a 1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. With respect to the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak, dextran (average molecular weight 75,000, 38,500; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 150,000, 10,000; Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.) was used as a molecular weight standard substance. The molecular weight was determined from the calibration curve using
図1は、実施例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図1中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、実施例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量は10kDa以下と算出された。 FIG. 1 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 1, where the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the carbazole sulfate of the gel filtration chromatography eluate fraction. The absorbance of the color developing solution at 535 nm is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 1 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 1 was calculated to be 10 kDa or less.
なお、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量をゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はSephacryl S−500 HR(内径2.8cm、高さ120cm、GEヘルスケア社製)、ポンプはAC−2120ペリスタ・バイオミニポンプ(アトー(株)製)、フラクションコレクターはADVANTEC FRC−2120 Fraction Collector(アドバンテック東洋(株)製)を用いた。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン10mgを0.1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液5mLに溶解した溶液を、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は0.1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、5.5mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量1,400,000、670,000、410,000、150,000、シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。 The molecular weight of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material was measured by gel filtration chromatography. The resin for gel filtration chromatography is Sephacryl S-500 HR (internal diameter 2.8 cm, height 120 cm, manufactured by GE Healthcare), the pump is AC-2120 Perista Biomini Pump (manufactured by Ato Corporation), and the fraction collector is ADVANTEC. FRC-2120 Fraction Collector (manufactured by Advantech Toyo Corp.) was used. A solution prepared by dissolving 10 mg of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material in 5 mL of 0.1 M sodium chloride aqueous solution was added from above the column. The eluent was 0.1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. Calibration curve using dextran (average molecular weight of 1,400,000, 670,000, 410,000, 150,000, manufactured by Sigma-Aldrich) as a molecular weight standard for the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak The molecular weight was calculated from
図2は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンのゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図2中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量は、1,400kDa以上と確認された。 FIG. 2 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material, where the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the color fraction of the eluate fraction of gel filtration chromatography by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method. The absorbance of the liquid at 535 nm is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 2 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, it was confirmed that the salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material had a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more.
実施例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解物と原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量の比較より、実施例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解物は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンが約140分の1の大きさに分解されたものであることがわかった。 From the comparison of the molecular weights of the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 1 and the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material, the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 1 was obtained by decomposing the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material to a size of about 1/140. I knew it was.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造条件の検討:加温温度)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂(商品名:AG 50W−X8 resin、バイオラッド社製)をガラス製カラムに充填し(内径2.5cm、高さ8.2cm)、1M塩酸100mLを流下して樹脂を洗浄・活性化した後、脱イオン水200mLを流下して過剰の塩酸を除去した。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.6gを脱イオン水45mLに溶解した溶液を、室温でカラム上方から添加・流下した。その後、樹脂に脱イオン水を110mL流下し、溶出液150mLを得た。
(Examination of production conditions of proteoglycan degradation products: heating temperature)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. A strongly acidic cation exchange resin (trade name: AG 50W-X8 resin, manufactured by Bio-Rad) was packed in a glass column (inner diameter 2.5 cm, height 8.2 cm) and 100 mL of 1M hydrochloric acid was flowed down to remove the resin. After washing and activating, 200 mL of deionized water was flown down to remove excess hydrochloric acid. A solution prepared by dissolving 0.6 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material in 45 mL of deionized water was added and flowed down from above the column at room temperature. Then, 110 mL of deionized water was made to flow through the resin to obtain 150 mL of an eluate.
この強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂の溶出液10mLをバイアル瓶に入れ、蓋を閉め、47℃に加温した定温乾燥器(Drying Oven DX31、ヤマト科学(株)製)内へ静置した。24時間後、定温乾燥器よりバイアル瓶を取り出し、自然に冷却した。蓋を開け、50mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液1mL、5mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液9mLを反応液に加えて中和をし、プロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプル水溶液20mLを得た。 10 mL of the eluate of this strongly acidic cation exchange resin was placed in a vial, the lid was closed, and the mixture was allowed to stand still in a constant temperature dryer (Drying Oven DX31, manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd.) heated to 47 ° C. After 24 hours, the vial was taken out from the constant temperature dryer and naturally cooled. The lid was opened, and 1 mL of a 50 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 5 mL of a 5 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution were added to the reaction solution for neutralization to obtain 20 mL of a proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample aqueous solution.
比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプル水溶液10mLを、透析用セルロースチューブ(外周9cm×長さ15cm、エーディア(株)製)に入れ、上下の口を封じ、4℃の低温室で、外液を脱イオン水にして3日間透析した。外液の脱イオン水は1日に3回交換した。その後セルロースチューブ内液を回収し、凍結乾燥し(凍結乾燥機 EYELA FDU−1200、東京理科器械(株)製)、15.9mgの白色綿状固体である比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルを得た。 The proteoglycan decomposition condition examination sample aqueous solution 10mL which concerns on the comparative example 1 was put into the cellulose tube for dialysis (perimeter 9cm x length 15cm, Adia Co., Ltd. make), the upper and lower mouths were sealed, and a 4 degreeC low-temperature room used external liquid Was deionized water and dialyzed for 3 days. The deionized water of the external solution was changed three times a day. Then, the liquid in the cellulose tube was collected, freeze-dried (freeze dryer EYELA FDU-1200, manufactured by Tokyo Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.), and 15.9 mg of a white flocculent solid, a proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1. Got
比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの分子量を、ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はSephacryl S−500 HR(内径2.8cm、高さ120cm、GEヘルスケア社製)、ポンプはAC−2120ペリスタ・バイオミニポンプ(アトー(株)製)、フラクションコレクターはADVANTEC FRC−2120 Fraction Collector(アドバンテック東洋(株)製)を用いた。比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプル水溶液5mLをカラム上方から添加した。溶離液は0.1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、5.5mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量1,400,000、670,000、410,000、150,000、シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。 The molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. The resin for gel filtration chromatography is Sephacryl S-500 HR (internal diameter 2.8 cm, height 120 cm, manufactured by GE Healthcare), the pump is AC-2120 Perista Biomini Pump (manufactured by Ato Corporation), and the fraction collector is ADVANTEC. FRC-2120 Fraction Collector (manufactured by Advantech Toyo Corp.) was used. The proteoglycan decomposition condition examination sample aqueous solution 5 mL which concerns on the comparative example 1 was added from the column upper part. The eluent was 0.1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. Calibration curve using dextran (average molecular weight of 1,400,000, 670,000, 410,000, 150,000, manufactured by Sigma-Aldrich) as a molecular weight standard for the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak The molecular weight was calculated from
図3は、比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルのゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図3中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの分子量は1,400kDa以上と確認された。 FIG. 3 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1, where the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the fraction of gel elution chromatography. The absorbance at 535 nm of the carbazole-sulfuric acid color development liquid is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 3 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, it was confirmed that the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1 was 1,400 kDa or more.
実施例2に記載したとおり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量が1,400kDa以上であることより、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンは分解されておらず、比較例1の方法ではプロテオグリカン分解物を製造することはできないことがわかった。 As described in Example 2, since the raw material salmon-derived proteoglycan has a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more, the raw salmon-derived proteoglycan is not decomposed, and the proteoglycan degradation product is produced by the method of Comparative Example 1. I found that I could not.
比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの紫外可視吸収スペクトルを測定した。比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの1w/v%水溶液をセル長1cmの石英セルに入れ、紫外可視分光光度計(U−3010型分光光度計、(株)日立製作所製)で測定した。測定条件については、測定波長範囲は190〜800nm、スキャンスピードは60nm/分、サンプリング間隔は0.2nm、対照溶液として純水を用意し、ダブルビーム方式で実施した。なお、比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの1w/v%水溶液の800nmの吸光度をゼロとして、各波長での吸光度を測定した。 The UV-visible absorption spectrum of the proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1 was measured. A 1 w / v% aqueous solution of a proteoglycan decomposition condition examination sample according to Comparative Example 1 was placed in a quartz cell having a cell length of 1 cm, and measured with an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (U-3010 spectrophotometer, manufactured by Hitachi Ltd.). . Regarding measurement conditions, the measurement wavelength range was 190 to 800 nm, the scan speed was 60 nm / min, the sampling interval was 0.2 nm, pure water was prepared as a control solution, and the measurement was carried out by the double beam method. The absorbance at each wavelength was measured by setting the absorbance at 800 nm of the 1 w / v% aqueous solution of the proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1 to zero.
図4は比較例1に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの1w/v%水溶液の190〜800nmの紫外可視吸収スペクトルを表す図であり、横軸は測定波長(nm)、縦軸は吸光度を表す。図4の測定結果より、270nmの吸光度は0.803であった。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンについても、同様の条件で測定を行った。図5は原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの1w/v%水溶液の190〜800nmの紫外可視吸収スペクトルを表す図であり、横軸は測定波長(nm)、縦軸は吸光度を表す。図5の測定結果より、270nmの吸光度は0.542であった。 FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum at 190 to 800 nm of a 1 w / v% aqueous solution of a proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 1, in which the horizontal axis represents the measurement wavelength (nm) and the vertical axis represents the absorbance. From the measurement result of FIG. 4, the absorbance at 270 nm was 0.803. The salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material was also measured under the same conditions. FIG. 5 is a diagram showing an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum at 190 to 800 nm of a 1 w / v% aqueous solution of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material, the horizontal axis represents the measurement wavelength (nm), and the vertical axis represents the absorbance. From the measurement result of FIG. 5, the absorbance at 270 nm was 0.542.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造2:強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂処理)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂(商品名:AG 50W−X8 resin、バイオラッド社製)をガラス製カラムに充填し(内径2.5cm、高さ8.2cm)、1M塩酸60mLを流下して樹脂を洗浄・活性化した後、脱イオン水150mLを流下して過剰の塩酸を除去した。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.4gを脱イオン水30mLに溶解した溶液を、室温でカラム上方から添加・流下した。その後、樹脂に脱イオン水を270mL流下し、溶出液約300mLを得た。得られた溶出液をウォーターバスで47℃に加温しながら、約10mLになるまで45分間濃縮した(エバポレーター;EYELA ROTARY VACUUM EVAPORATOR Nシリーズ、東京理科器械(株)製、恒温水循環装置;Neo Cool Circulator CF600(アスピレーター付)、ヤマト科学(株)製)。得られた濃縮液を凍結乾燥し(凍結乾燥機 EYELA FDU−1200、東京理科器械(株)製)、0.32gの白色綿状固体であるプロテオグリカン分解物を得た。
(Production of proteoglycan degradation product 2: treatment with strongly acidic cation exchange resin)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. A strongly acidic cation exchange resin (trade name: AG 50W-X8 resin, manufactured by Bio-Rad) was packed in a glass column (inner diameter 2.5 cm, height 8.2 cm), and 1 M hydrochloric acid 60 mL was flowed down to remove the resin. After washing and activating, 150 mL of deionized water was flowed down to remove excess hydrochloric acid. A solution prepared by dissolving 0.4 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material in 30 mL of deionized water was added and flowed down from above the column at room temperature. Then, 270 mL of deionized water was made to flow through the resin to obtain about 300 mL of the eluate. The obtained eluate was heated to 47 ° C. in a water bath and concentrated to about 10 mL for 45 minutes (evaporator; EYELA ROTARY VACUM EVAPOTORATOR N series, manufactured by Tokyo Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., constant temperature water circulation device; Neo Cool). Circulator CF600 (with aspirator), manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd. The obtained concentrated liquid was freeze-dried (freeze dryer EYELA FDU-1200, manufactured by Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Ltd.) to obtain 0.32 g of a proteoglycan degradation product which was a white cotton-like solid.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の分析)
実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のタンパク質含量を、比色法であるローリー法にて、牛血清アルブミン(アクロス社)を標準物質とした検量線から求めたところ、6.3重量%であった。ウロン酸含量を、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にて、グルクロン酸(シグマ社)を標準物質とした検量線から求めたところ、38.3重量%であった。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンについて同様に分析したところ、タンパク質含量は6.5重量%、ウロン酸含量は34.6重量%であった。これらの結果から、実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のタンパク質とウロン酸含量は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンとほとんど変化がないことが明らかとなった。
(Analysis of proteoglycan degradation products)
The protein content of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was found to be 6.3% by weight by a Lowry method, which is a colorimetric method, from a calibration curve using bovine serum albumin (Across) as a standard substance. . The uronic acid content was determined by a carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method, from a calibration curve using glucuronic acid (Sigma) as a standard substance, and was found to be 38.3% by weight. When the salmon-derived proteoglycan as the raw material was analyzed in the same manner, the protein content was 6.5% by weight and the uronic acid content was 34.6% by weight. From these results, it was revealed that the protein and uronic acid content of the proteoglycan hydrolyzate according to Example 3 were almost the same as those of the salmon-derived proteoglycan as the raw material.
実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物0.2w/v%の水溶液のpHは2.5であり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.2w/v%の水溶液のpHは6.2であった。 The pH of the aqueous solution of proteoglycan degradation product 0.2 w / v% according to Example 3 was 2.5, and the pH of the raw material salmon-derived proteoglycan 0.2 w / v% aqueous solution was 6.2.
実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の相対粘度をオストワルド式で測定した。測定器具にはオストワルド相対粘度計No.1(柴田科学(株)製)を用い、溶媒は脱イオン水とし、実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の5mg/mL水溶液の粘度を26.5℃の水浴中で測定した。結果、実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物5mg/mL水溶液の相対粘度は1.1であった。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン5mg/mL水溶液を同様の条件で測定したところ、相対粘度は3.7であった。 The relative viscosity of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was measured by the Ostwald method. Ostwald relative viscometer No. 1 (manufactured by Shibata Kagaku Co., Ltd.), deionized water was used as the solvent, and the viscosity of a 5 mg / mL aqueous solution of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was measured in a water bath at 26.5 ° C. As a result, the relative viscosity of the 5 mg / mL aqueous solution of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was 1.1. When a 5 mg / mL aqueous solution of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material was measured under the same conditions, the relative viscosity was 3.7.
実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量をゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はトヨパール HW55F(内径2.7cm、高さ116cm、東ソー(株)製)、ポンプはLKB・PumpP−1(ファルマシア社製)、フラクションコレクターはLKB・FRAC−100(ファルマシア社製)を用いた。実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物10mgを1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液5mLに溶解し、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、4mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量75,000、38,500;和光純薬工業(株)製、150,000、10,000;シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。 The molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. Resin for gel filtration chromatography is Toyopearl HW55F (inner diameter 2.7 cm, height 116 cm, manufactured by Tosoh Corp.), pump is LKB Pump P-1 (Pharmacia), fraction collector is LKB FRAC-100 (Pharmacia). Manufactured) was used. 10 mg of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was dissolved in 5 mL of a 1 M sodium chloride aqueous solution and added from above the column. The eluent was a 1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. With respect to the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak, dextran (average molecular weight 75,000, 38,500; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 150,000, 10,000; Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.) was used as a molecular weight standard substance. The molecular weight was determined from the calibration curve using
図6は、実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図6中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量は32kDaと算出された。 FIG. 6 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3, where the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the carbazole sulfate of the gel filtration chromatography eluate fraction. The absorbance of the color developing solution at 535 nm is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 6 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was calculated to be 32 kDa.
実施例2に記載したとおり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量は、1,400kDa以上であった。実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物と原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量の比較より、実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンが約44分の1の大きさに分解されたものであることがわかった。 As described in Example 2, the salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material had a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more. From the comparison of the molecular weights of the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 3 and the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material, the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 3 was obtained by decomposing the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material to a size of about 1/44. I knew it was.
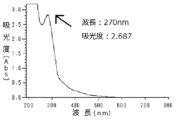
実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の紫外可視吸収スペクトルについて、比較例1と同様の条件で測定を行った。図7は実施例3に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の1w/v%水溶液の190〜800nmの紫外可視吸収スペクトルを表す図であり、横軸は測定波長(nm)、縦軸は吸光度を表す。図7の測定結果より、270nmの吸光度は2.650であった。 The UV-visible absorption spectrum of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 3 was measured under the same conditions as in Comparative Example 1. 7: is a figure showing the ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum of 190-800 nm of 1 w / v% aqueous solution of the proteoglycan degradation product which concerns on Example 3, a horizontal axis | shaft shows a measurement wavelength (nm) and a vertical axis | shaft represents light absorbency. From the measurement result of FIG. 7, the absorbance at 270 nm was 2.650.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造条件の検討:中和工程の導入)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂(商品名:AG 50W−X8 resin、バイオラッド社製)をガラス製カラムに充填し(内径2.5cm、高さ8.2cm)、3M塩酸100mLを流下して樹脂を洗浄・活性化した後、脱イオン水200mLを流下して過剰の塩酸を除去した。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.4gを脱イオン水30mLに溶解した溶液を、室温でカラム上方から添加・流下した。その後、樹脂に脱イオン水を300mL流下し、溶出液約300mLを得た。得られた溶出液を撹拌しながら、1M水酸化ナトリウム水溶液および50mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液を滴下して中和をした。次に、ウォーターバスで47℃に加温しながら、約40mLになるまで40分間濃縮した(エバポレーター;EYELA ROTARY VACUUM EVAPORATOR Nシリーズ、東京理科器械(株)製、恒温水循環装置;Neo Cool Circulator CF600(アスピレーター付)、ヤマト科学(株)製)。この濃縮液を透析用セルロースチューブ(外周9cm×長さ35cm、エーディア(株)製)に入れ、外液を脱イオン水にして3日間透析した。外液の脱イオン水は1日に3回交換した。その後セルロースチューブ内液を回収し、ウォーターバスで47℃に加温しながら、約10mLになるまで30分間濃縮した(エバポレーター;EYELA ROTARY VACUUM EVAPORATOR Nシリーズ、東京理科器械(株)製、恒温水循環装置;Neo Cool Circulator CF600(アスピレーター付)、ヤマト科学(株)製)。得られた濃縮液を凍結乾燥し(凍結乾燥機 EYELA FDU−1200、東京理科器械(株)製)、0.36gの白色綿状固体であるプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルを得た。
(Examination of production conditions of proteoglycan degradation products: introduction of neutralization process)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. A strongly acidic cation exchange resin (trade name: AG 50W-X8 resin, manufactured by Bio-Rad) was packed in a glass column (inner diameter 2.5 cm, height 8.2 cm) and 100 mL of 3M hydrochloric acid was flowed down to remove the resin. After washing and activating, 200 mL of deionized water was flown down to remove excess hydrochloric acid. A solution prepared by dissolving 0.4 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material in 30 mL of deionized water was added and flowed down from above the column at room temperature. Then, 300 mL of deionized water was made to flow through the resin to obtain about 300 mL of the eluate. While stirring the obtained eluate, 1 M aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and 50 mM aqueous sodium hydroxide solution were added dropwise to neutralize. Next, while heating at 47 ° C. in a water bath, the mixture was concentrated for 40 minutes until it reached about 40 mL (evaporator; EYELA ROTARY VACUM EVAPOORATOR N series, manufactured by Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Ltd., constant temperature water circulation device; Neo Cool Circulator CF600 ( With aspirator), Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd.). The concentrated solution was put into a dialysis cellulose tube (outer circumference 9 cm × length 35 cm, manufactured by Adia Co., Ltd.), and the outer solution was deionized water and dialyzed for 3 days. The deionized water of the external solution was changed three times a day. After that, the liquid in the cellulose tube was collected and concentrated for 30 minutes while heating to 47 ° C. in a water bath until it reached about 10 mL (evaporator; EYELA ROTARY VACUM EVAPOORATOR N series, manufactured by Tokyo Rika Kikai Co., Ltd., constant temperature water circulation device. Neo Cool Circulator CF600 (with aspirator, manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd.). The obtained concentrated solution was freeze-dried (freeze dryer EYELA FDU-1200, manufactured by Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Ltd.) to obtain 0.36 g of a white flocculent solid proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample.
比較例2に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの分子量を、ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はSephacryl S−500 HR(内径2.8cm、高さ120cm、GEヘルスケア社製)、ポンプはAC−2120ペリスタ・バイオミニポンプ(アトー(株)製)、フラクションコレクターはADVANTEC FRC−2120 Fraction Collector(アドバンテック東洋(株)製)を用いた。比較例2に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプル10mgを0.1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液5mLに溶解し、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は0.1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、5.5mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量1,400,000、670,000、410,000、150,000、シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。 The molecular weight of the proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 2 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. The resin for gel filtration chromatography is Sephacryl S-500 HR (internal diameter 2.8 cm, height 120 cm, manufactured by GE Healthcare), the pump is AC-2120 Perista Biomini Pump (manufactured by Ato Co., Ltd.), and the fraction collector is ADVANTEC. FRC-2120 Fraction Collector (manufactured by Advantech Toyo Corp.) was used. A proteoglycan decomposition condition examination sample 10 mg according to Comparative Example 2 was dissolved in 0.1 M sodium chloride aqueous solution 5 mL and added from above the column. The eluent was 0.1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. Calibration curve using dextran (average molecular weight of 1,400,000, 670,000, 410,000, 150,000, manufactured by Sigma-Aldrich) as a molecular weight standard for the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak The molecular weight was calculated from
図8は、比較例2に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルのゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図8中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、比較例2に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの分子量は1,400kDa以上と確認された。 FIG. 8 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 2, where the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the eluate fraction of gel filtration chromatography. The absorbance at 535 nm of the carbazole-sulfuric acid color development liquid is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 8 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation condition study sample according to Comparative Example 2 was confirmed to be 1,400 kDa or more.
実施例2に記載したとおり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量が1,400kDa以上であることより、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンは分解されておらず、比較例2の方法ではプロテオグリカン分解物を製造することはできないことがわかった。 As described in Example 2, since the raw material salmon-derived proteoglycan has a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more, the raw salmon-derived proteoglycan is not decomposed, and the proteoglycan degradation product is produced by the method of Comparative Example 2. I found that I could not.
比較例2に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの紫外可視吸収スペクトルについて、比較例1と同様の条件で測定を行った。図9は比較例2に係るプロテオグリカン分解条件検討サンプルの1w/v%水溶液の190〜800nmの紫外可視吸収スペクトルを表す図であり、横軸は測定波長(nm)、縦軸は吸光度を表す。図9の測定結果より、270nmの吸光度は0.526であった。 The UV-visible absorption spectrum of the proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 2 was measured under the same conditions as in Comparative Example 1. FIG. 9 is a diagram showing an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum of a 1 w / v% aqueous solution of a proteoglycan decomposition condition study sample according to Comparative Example 2 at 190 to 800 nm, in which the horizontal axis represents the measurement wavelength (nm) and the vertical axis represents the absorbance. From the measurement result of FIG. 9, the absorbance at 270 nm was 0.526.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造3:強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂処理)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。強酸性陽イオン交換樹脂(商品名:ダイヤイオンSK1B、三菱化学(株)製)をガラス製カラムに充填し(内径2cm、高さ8cm)、1M塩酸100mLを流下して樹脂を洗浄・活性化した後、脱イオン水200mLを流下して過剰の塩酸を除去した。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.4gを脱イオン水30mLに溶解した溶液を、室温でカラム上方から添加・流下した。その後、樹脂に脱イオン水を100mL流下し、溶出液約125mLを得た。得られた溶出液をウォーターバスで47℃に加温しながら、約10mLになるまで30分間濃縮した(エバポレーター;EYELA ROTARY VACUUM EVAPORATOR Nシリーズ、東京理科器械(株)製、恒温水循環装置;Neo Cool Circulator CF600(アスピレーター付)、ヤマト科学(株)製)。得られた濃縮液を凍結乾燥し(凍結乾燥機 EYELA FDU−1200、東京理科器械(株)製)、0.35gの白色綿状固体であるプロテオグリカン分解物を得た。
(Production of proteoglycan degradation product 3: treatment with strongly acidic cation exchange resin)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. A strong acid cation exchange resin (trade name: Diaion SK1B, manufactured by Mitsubishi Chemical Co., Ltd.) is packed in a glass column (inner diameter 2 cm, height 8 cm), and 100 mL of 1M hydrochloric acid is flowed down to wash and activate the resin. After that, 200 mL of deionized water was flowed down to remove excess hydrochloric acid. A solution prepared by dissolving 0.4 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material in 30 mL of deionized water was added and flowed down from above the column at room temperature. Then, 100 mL of deionized water was made to flow through the resin to obtain about 125 mL of the eluate. The obtained eluate was heated to 47 ° C. in a water bath and concentrated for 30 minutes until it became about 10 mL (evaporator; EYELA ROTARY VACUM EVAPOTORATOR N series, manufactured by Tokyo Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., constant temperature water circulation device; Neo Cool). Circulator CF600 (with aspirator), manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd. The obtained concentrated liquid was freeze-dried (freeze dryer EYELA FDU-1200, manufactured by Tokyo Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd.) to obtain 0.35 g of a white cotton-like solid proteoglycan degradation product.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の分析)
実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のタンパク質含量を、比色法であるローリー法にて、牛血清アルブミン(アクロス社製)を標準物質とした検量線から求めたところ、6.3重量%であった。ウロン酸含量を、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にて、グルクロン酸(シグマ社製)を標準物質とした検量線から求めたところ、37.2重量%であった。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンについて同様に分析したところ、タンパク質含量は6.5重量%、ウロン酸含量は34.6重量%であった。これらの結果から、実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のタンパク質とウロン酸含量は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンとほとんど変化がないことが明らかとなった。
(Analysis of proteoglycan degradation products)
The protein content of the proteoglycan hydrolyzate according to Example 5 was found to be 6.3% by weight by the Lowry method, which is a colorimetric method, from a calibration curve using bovine serum albumin (manufactured by ACROS Co., Ltd.) as a standard substance. It was The uronic acid content was determined by a carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method, from a calibration curve using glucuronic acid (manufactured by Sigma) as a standard substance and found to be 37.2% by weight. When the salmon-derived proteoglycan as the raw material was analyzed in the same manner, the protein content was 6.5% by weight and the uronic acid content was 34.6% by weight. From these results, it was revealed that the protein and uronic acid content of the proteoglycan hydrolyzate according to Example 5 were almost the same as those of the salmon-derived proteoglycan as the raw material.
実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物0.2w/v%の水溶液のpHは2.6であり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.2w/v%の水溶液のpHは6.2であった。 The pH of the aqueous solution of proteoglycan degradation product 0.2 w / v% according to Example 5 was 2.6, and the pH of the raw material salmon-derived proteoglycan 0.2 w / v% aqueous solution was 6.2.
実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の相対粘度をオストワルド式で測定した。測定器具にはオストワルド相対粘度計No.1(柴田科学(株)製)を用い、溶媒は脱イオン水とし、実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の5mg/mL水溶液の粘度を26.5℃の水浴中で測定した。結果、実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物5mg/mL水溶液の相対粘度は1.2であった。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン5mg/mL水溶液を同様の条件で測定したところ、相対粘度は3.7であった。 The relative viscosity of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was measured by the Ostwald method. Ostwald relative viscometer No. 1 (manufactured by Shibata Scientific Co., Ltd.) was used, the solvent was deionized water, and the viscosity of a 5 mg / mL aqueous solution of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was measured in a water bath at 26.5 ° C. As a result, the relative viscosity of the 5 mg / mL aqueous solution of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was 1.2. When a 5 mg / mL aqueous solution of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material was measured under the same conditions, the relative viscosity was 3.7.
実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量をゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はトヨパール HW55F(内径2.7cm、高さ116cm、東ソー(株)製)、ポンプはLKB・PumpP−1(ファルマシア社製)、フラクションコレクターはLKB・FRAC−100(ファルマシア社製)を用いた。実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物10mgを1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液5mLに溶解し、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、4mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量75,000、38,500;和光純薬工業(株)製、150,000、10,000;シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。 The molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. Resin for gel filtration chromatography is Toyopearl HW55F (inner diameter 2.7 cm, height 116 cm, manufactured by Tosoh Corp.), pump is LKB Pump P-1 (Pharmacia), fraction collector is LKB FRAC-100 (Pharmacia). Manufactured) was used. 10 mg of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was dissolved in 5 mL of a 1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the solution was added from above the column. The eluent was a 1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. For the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak, dextran (average molecular weight 75,000, 38,500; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 150,000, 10,000; Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.) was used as a molecular weight standard substance. The molecular weight was determined from the calibration curve using
図10は、実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図10中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量は12kDaと算出された。 FIG. 10 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5, in which the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the carbazole sulfate of the gel filtration chromatography eluate fraction. The absorbance of the color developing solution at 535 nm is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 10 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was calculated to be 12 kDa.
実施例2に記載したとおり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量は、1,400kDa以上であった。実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物と原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量の比較より、実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンが約120分の1の大きさに分解されたものであることがわかった。 As described in Example 2, the salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material had a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more. From the comparison of the molecular weights of the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 5 and the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material, the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 5 was obtained by decomposing the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material to a size of about 1/120. I knew it was.
実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の紫外可視吸収スペクトルについて、比較例1と同様の条件で測定を行った。図11は実施例5に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の1w/v%水溶液の190〜800nmの紫外可視吸収スペクトルを表す図であり、横軸は測定波長(nm)、縦軸は吸光度を表す。図11の測定結果より、270nmの吸光度は2.687であった。 The ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5 was measured under the same conditions as in Comparative Example 1. FIG. 11 is a diagram showing an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum at 190 to 800 nm of a 1 w / v% aqueous solution of a proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 5, in which the horizontal axis represents the measurement wavelength (nm) and the vertical axis represents the absorbance. From the measurement result of FIG. 11, the absorbance at 270 nm was 2.687.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造4:強酸処理)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.1gを脱イオン水40mLに溶解し、撹拌しながら、塩酸の終濃度が0.05Mになるように1M塩酸を2.1mL滴下した。4℃で3時間撹拌した後、反応液を透析用セルロースチューブ(外周9cm×長さ35cm、エーディア(株)製)に入れ、外液を25mM塩酸にし、4℃で一晩透析した。その後、外液を脱イオン水に変え、3日間透析した。外液の脱イオン水は1日3回交換した。セルロースチューブ内液をメスシリンダーに移し、全量100mLとなるよう、脱イオン水を加えた。溶液のうち30mLをバイアル瓶に入れ、蓋を閉め、70℃に加温した定温乾燥器(Drying Oven DX31、ヤマト科学(株)製)内へ静置した。24時間後、定温乾燥器よりバイアル瓶を取り出し、自然に冷却した。蓋を開け、50mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液1mL、5mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液4mLを反応液に加えて中和をし、プロテオグリカン分解物水溶液35mLを得た。
(Production of proteoglycan degradation product 4: strong acid treatment)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. 0.1 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material was dissolved in 40 mL of deionized water, and 2.1 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid was added dropwise so that the final concentration of hydrochloric acid was 0.05 M while stirring. After stirring at 4 ° C. for 3 hours, the reaction solution was put into a dialysis cellulose tube (outer circumference 9 cm × length 35 cm, manufactured by Adia Co., Ltd.), and the external solution was made into 25 mM hydrochloric acid and dialyzed at 4 ° C. overnight. Then, the external solution was changed to deionized water and dialyzed for 3 days. The deionized water of the external solution was changed three times a day. The liquid in the cellulose tube was transferred to a graduated cylinder, and deionized water was added so that the total amount was 100 mL. 30 mL of the solution was placed in a vial, the lid was closed, and the solution was allowed to stand still in a constant temperature dryer (Drying Oven DX31, manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd.) heated to 70 ° C. After 24 hours, the vial was taken out from the constant temperature dryer and naturally cooled. The lid was opened, and 1 mL of 50 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 4 mL of 5 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution were added to the reaction solution for neutralization to obtain 35 mL of proteoglycan degradation product aqueous solution.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の分子量測定)
実施例7に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量を、ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はトヨパール HW55F(内径2.7cm、高さ116cm、東ソー(株)製)、ポンプはLKB・PumpP−1(ファルマシア社製)、フラクションコレクターはLKB・FRAC−100(ファルマシア社製)を用いた。実施例7に係るプロテオグリカン分解物水溶液5mLを、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、4mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量75,000、38,500;和光純薬工業(株)製、150,000、10,000;シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。
(Measurement of molecular weight of proteoglycan degradation product)
The molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 7 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. Resin for gel filtration chromatography is Toyopearl HW55F (inner diameter 2.7 cm, height 116 cm, manufactured by Tosoh Corp.), pump is LKB Pump P-1 (Pharmacia), fraction collector is LKB FRAC-100 (Pharmacia). Manufactured) was used. 5 mL of the proteoglycan degradation product aqueous solution according to Example 7 was added from above the column. The eluent was a 1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. Each of the obtained eluate fractions was analyzed for uronic acid content by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. With respect to the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak, dextran (average molecular weight 75,000, 38,500; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 150,000, 10,000; Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.) was used as a molecular weight standard substance. The molecular weight was determined from the calibration curve using
図12は、実施例7に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図12中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、実施例7に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量は17kDaと算出された。 FIG. 12 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 7, in which the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the carbazole sulfate of the gel filtration chromatography eluate fraction. The absorbance of the color developing solution at 535 nm is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 12 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 7 was calculated to be 17 kDa.
実施例2に記載したとおり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量は、1,400kDa以上であった。実施例7に係るプロテオグリカン分解物と原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量の比較より、実施例7に係るプロテオグリカン分解物は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンが約82分の1の大きさに分解されたものであることがわかった。 As described in Example 2, the salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material had a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more. From the comparison of the molecular weights of the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 7 and the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material, the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 7 was obtained by decomposing the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material to a size of about 1/82. I knew it was.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の製造5:クエン酸処理)
原料のプロテオグリカンは、市販の鮭由来プロテオグリカン((株)角弘プロテオグリカン研究所)を購入して用いた。原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカン0.1gを脱イオン水40mLに溶解し、撹拌しながら、クエン酸の終濃度が1.8%になるようにクエン酸一水和物を0.8g加えた。4℃で3時間撹拌した後、反応液を透析用セルロースチューブ(外周9cm×長さ35cm、エーディア(株)製)に入れ、外液を1%クエン酸水溶液にし、4℃で一晩透析した。その後、外液を脱イオン水に変え、3日間透析した。外液の脱イオン水は1日3回交換した。セルロースチューブ内液をメスシリンダーに移し、全量100mLとなるよう、脱イオン水を加えた。溶液のうち30mLをバイアル瓶に入れ、蓋を閉め、70℃に加温した定温乾燥器(Drying Oven DX31、ヤマト科学(株)製)内へ静置した。24時間後、定温乾燥器よりバイアル瓶を取り出し、自然に冷却した。蓋を開け、50mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液1mL、5mM水酸化ナトリウム水溶液4mLを反応液に加えて中和をし、プロテオグリカン分解物水溶液35mLを得た。
(Production of proteoglycan degradation product 5: citric acid treatment)
As the raw material proteoglycan, commercially available salmon-derived proteoglycan (Kadohiro Proteoglycan Research Institute Co., Ltd.) was purchased and used. 0.1 g of salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material was dissolved in 40 mL of deionized water, and 0.8 g of citric acid monohydrate was added with stirring so that the final concentration of citric acid was 1.8%. After stirring at 4 ° C for 3 hours, the reaction solution was placed in a dialysis cellulose tube (outer circumference 9 cm x length 35 cm, manufactured by Adia Co., Ltd.), and the external solution was made into a 1% citric acid aqueous solution and dialyzed at 4 ° C overnight. . Then, the external solution was changed to deionized water and dialyzed for 3 days. The deionized water of the external solution was changed three times a day. The liquid in the cellulose tube was transferred to a graduated cylinder, and deionized water was added so that the total amount was 100 mL. 30 mL of the solution was placed in a vial, the lid was closed, and the solution was allowed to stand still in a constant temperature dryer (Drying Oven DX31, manufactured by Yamato Scientific Co., Ltd.) heated to 70 ° C. After 24 hours, the vial was taken out from the constant temperature dryer and naturally cooled. The lid was opened, and 1 mL of 50 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 4 mL of 5 mM sodium hydroxide aqueous solution were added to the reaction solution for neutralization to obtain 35 mL of proteoglycan degradation product aqueous solution.
(プロテオグリカン分解物の分子量測定)
実施例9に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量を、ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー法により測定した。ゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー用樹脂はトヨパール HW55F(内径2.7cm、高さ116cm、東ソー(株)製)、ポンプはLKB・PumpP−1(ファルマシア社製)、フラクションコレクターはLKB・FRAC−100(ファルマシア社製)を用いた。実施例9に係るプロテオグリカン分解物水溶液5mLを、カラム上方から添加した。溶離液は1M塩化ナトリウム水溶液、流速0.5mL/分で、4mLずつ溶出液を分取した。得られた各溶出液画分に対して、比色法であるカルバゾール硫酸法にてウロン酸含量を分析した。得られたウロン酸含量ピークの溶出体積に対して、分子量標準物質としてデキストラン(平均分子量75,000、38,500;和光純薬工業(株)製、150,000、10,000;シグマアルドリッチ社製)を用いた検量線から分子量を求めた。
(Measurement of molecular weight of proteoglycan degradation product)
The molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 9 was measured by gel filtration chromatography. Resin for gel filtration chromatography is Toyopearl HW55F (inner diameter 2.7 cm, height 116 cm, manufactured by Tosoh Corp.), pump is LKB Pump P-1 (Pharmacia), fraction collector is LKB FRAC-100 (Pharmacia). Manufactured) was used. 5 mL of the proteoglycan degradation product aqueous solution according to Example 9 was added from above the column. The eluent was a 1 M aqueous sodium chloride solution, and the flow rate was 0.5 mL / min. The uronic acid content of each obtained eluate fraction was analyzed by the carbazole-sulfuric acid method, which is a colorimetric method. With respect to the elution volume of the obtained uronic acid content peak, dextran (average molecular weight 75,000, 38,500; manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd., 150,000, 10,000; Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ltd.) was used as a molecular weight standard substance. The molecular weight was determined from the calibration curve using
図13は、実施例9に係るプロテオグリカン分解物のゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの結果を示すものであり、横軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィーの溶出体積、縦軸はゲルろ過クロマトグラフィー溶出液画分のカルバゾール硫酸法呈色液の535nmでの吸光度を示す。図13中の数字(kDa表記)は、分子量標準物質であるデキストランの平均分子量を示す。この結果から、実施例9に係るプロテオグリカン分解物の分子量は17kDaと算出された。 FIG. 13 shows the results of gel filtration chromatography of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 9, in which the horizontal axis represents the elution volume of gel filtration chromatography and the vertical axis represents the carbazole sulfate of the gel filtration chromatography eluate fraction. The absorbance of the color developing solution at 535 nm is shown. The numbers (kDa notation) in FIG. 13 indicate the average molecular weight of dextran, which is a molecular weight standard substance. From this result, the molecular weight of the proteoglycan degradation product according to Example 9 was calculated to be 17 kDa.
実施例2に記載したとおり、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量は、1,400kDa以上であった。実施例9に係るプロテオグリカン分解物と原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンの分子量の比較より、実施例9に係るプロテオグリカン分解物は、原料の鮭由来プロテオグリカンが約82分の1の大きさに分解されたものであることがわかった。 As described in Example 2, the salmon-derived proteoglycan as a raw material had a molecular weight of 1,400 kDa or more. From the comparison of the molecular weights of the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 9 and the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material, the proteoglycan degradation product of Example 9 was obtained by decomposing the salmon-derived proteoglycan of the raw material to a size of about 1/82. I knew it was.
本発明により、プロテオグリカン分解物が低コストで製造され、安価に提供されることになり、化粧料産業や食品産業に広く利用されることが可能となる。 INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY According to the present invention, a proteoglycan degradation product can be produced at low cost and provided at low cost, and can be widely used in the cosmetics industry and the food industry.
Claims (1)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014211702 | 2014-10-16 | ||
| JP2014211702 | 2014-10-16 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016079402A JP2016079402A (en) | 2016-05-16 |
| JP2016079402A5 JP2016079402A5 (en) | 2018-11-15 |
| JP6688498B2 true JP6688498B2 (en) | 2020-04-28 |
Family
ID=55955889
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015201754A Expired - Fee Related JP6688498B2 (en) | 2014-10-16 | 2015-10-13 | Degradation method and degradation product of proteoglycan |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6688498B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6701588B2 (en) * | 2015-07-27 | 2020-05-27 | 地方独立行政法人青森県産業技術センター | Magnesium supplier |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS582301A (en) * | 1981-06-30 | 1983-01-07 | Dai Ichi Seiyaku Co Ltd | Polysaccharide and its preparation |
| FR2659351B1 (en) * | 1990-03-08 | 1994-12-02 | Pf Medicament | DELIPID POLYSACCHARIDE COMPOUND, PREPARATION METHOD, COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING SAME. |
| JP3731150B2 (en) * | 2000-08-22 | 2006-01-05 | 株式会社角弘 | Purification method of cartilage-type proteoglycan |
| JP5470612B2 (en) * | 2008-05-22 | 2014-04-16 | 国立大学法人弘前大学 | Sugar chain modification method and sugar chain modification apparatus |
| JP5749067B2 (en) * | 2011-05-09 | 2015-07-15 | 株式会社グライコスモ研究所 | Proteoglycan production method |
| JP6253047B2 (en) * | 2013-01-24 | 2017-12-27 | 地方独立行政法人青森県産業技術センター | Proteoglycan and cosmetics |
-
2015
- 2015-10-13 JP JP2015201754A patent/JP6688498B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016079402A (en) | 2016-05-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Zhu et al. | Structural characterization and in vitro antioxidant activities of chondroitin sulfate purified from Andrias davidianus cartilage | |
| Abdallah et al. | Hyaluronic acid and Chondroitin sulfate from marine and terrestrial sources: Extraction and purification methods | |
| Peniche et al. | Chitin and chitosan: major sources, properties and applications | |
| Zou et al. | Preparation of chondroitin sulfates with different molecular weights from bovine nasal cartilage and their antioxidant activities | |
| Liu et al. | Compositional analysis and structural elucidation of glycosaminoglycans in chicken eggs | |
| EP1270599B1 (en) | Salmon-origin chondroitin sulfate | |
| JP6253047B2 (en) | Proteoglycan and cosmetics | |
| CN106519074A (en) | Preparation method and application of water-soluble carboxymethyl chitosan with controllable molecular weight | |
| JP6464485B2 (en) | High water retention proteoglycan, cosmetics and method for producing high water retention proteoglycan | |
| CN108484796B (en) | Preparation process of low-molecular sodium hyaluronate | |
| Sandeep et al. | A brief overview on chitosan applications | |
| AU2018276567A1 (en) | Moisturizing topical preparation | |
| CN103882083A (en) | Method for preparing antioxidant collagen peptide | |
| CN102304193A (en) | Preparation method and application of oligomeric hyaluronic acid | |
| Rýglová et al. | The proportion of the key components analysed in collagen-based isolates from fish and mammalian tissues processed by different protocols | |
| Zhang et al. | Isolation and structural characterization of glycosaminoglycans from heads of red salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) | |
| JP6688498B2 (en) | Degradation method and degradation product of proteoglycan | |
| Ibram et al. | Comparison of extraction methods of chitin and chitosan from different sources | |
| Danarto et al. | Optimizing deacetylation process for chitosan production from green mussel (perna viridis) shell | |
| JP2017125164A (en) | High water holding modified proteoglycan | |
| EP3119814B1 (en) | Chondroitin sulphate purification method | |
| JP2016079126A (en) | Effective water retention agent | |
| JP6757016B2 (en) | Polysulfated proteoglycan | |
| HUE030096T2 (en) | Shark-like chondroitin sulphate and process for the preparation thereof | |
| JP4719878B2 (en) | Chondroitin sulfate from heron |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20181005 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20181005 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20191008 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20191118 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200317 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200330 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6688498 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |