JP6300676B2 - Analysis method and automatic analyzer - Google Patents
Analysis method and automatic analyzer Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6300676B2 JP6300676B2 JP2014154847A JP2014154847A JP6300676B2 JP 6300676 B2 JP6300676 B2 JP 6300676B2 JP 2014154847 A JP2014154847 A JP 2014154847A JP 2014154847 A JP2014154847 A JP 2014154847A JP 6300676 B2 JP6300676 B2 JP 6300676B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- reaction
- reagent
- solid phase
- labeled
- measurement
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、血液や血清、血漿などを試料あるいは検体とし、抗原抗体反応を利用して分析を行う分析方法及び自動分析装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an analysis method and an automatic analyzer that perform analysis using an antigen-antibody reaction using blood, serum, plasma, or the like as a sample or specimen.
血液、血清、血漿、或いは体液等を試料或いは検体とする分析方法には、抗原抗体反応に基づく結合を利用して、試料中のホルモン、腫瘍マーカ、感染症病原体マーカ、感染抗体等の微量物質を定性的或いは定量的に検出する方法が知られている。しかしながら、抗原抗体反応を利用した分析方法では、試料中に分析対象の物質が高濃度に含まれる場合には、分析結果の数値が実際の値よりも低くなってしまう現象(ゾーン現象やフック現象などと呼ばれる現象)が生じる場合がある。 For analysis methods using blood, serum, plasma, or body fluid as a sample or specimen, a trace substance such as a hormone, tumor marker, infectious disease pathogen marker, or infectious antibody in a sample is utilized using binding based on an antigen-antibody reaction. A method for detecting qualitatively or quantitatively is known. However, in the analysis method using the antigen-antibody reaction, when the sample contains a high concentration of the substance to be analyzed, the numerical value of the analysis result becomes lower than the actual value (zone phenomenon or hook phenomenon) May occur).
このようなゾーン現象に関し、例えば、特許文献1(特表2010−520461号公報)には、プロゾーン現象などのイムノアッセイ定量妨害の影響を低減することにより検体濃度の正確且つ簡単な改良型定量的測定を可能にすることを目的として、試験試料中に存在する該当検体を捕捉抗体により捕捉し、捕捉抗体と検体と第1の抗体コンジュゲートの複合体を形成し、混合物から未結合検体の除去後に該当検体と結合する第2の抗体コンジュゲートを加えることにより検体を抗体コンジュゲートにより検出するイムノアッセイに関する技術が開示されている。 With regard to such a zone phenomenon, for example, Patent Document 1 (Japanese Patent Publication No. 2010-520461) discloses an improved and accurate quantitative analysis of the analyte concentration by reducing the influence of immunoassay interference such as the prozone phenomenon. For the purpose of enabling measurement, the target sample present in the test sample is captured by the capture antibody, a complex of the capture antibody, the sample and the first antibody conjugate is formed, and the unbound sample is removed from the mixture. A technique relating to an immunoassay in which an analyte is detected by an antibody conjugate by adding a second antibody conjugate that binds to the analyte later is disclosed.
ところで、ゾーン現象やフック現象などの回避を目的の一つとした方法としては、いわゆる抗原抗体法の2ステップ反応(2ステップ法)が知られている。一般的に、2ステップ反応では、固相と捕捉抗体や捕捉抗原と試料とを混合し、分析対象物と捕捉抗体との結合物を形成させた後に洗浄を行い、未結合の試料成分および分析対象物を除去し(bound/free分離)、さらに標識抗体を加えて捕捉抗体―分析対象物―標識抗体のサンドイッチを形成させた後に洗浄を行って標識抗体に由来する発光等を検出し分析対象物量あるいは濃度を計測する。この2ステップ反応では、1回目の洗浄により未結合の分析対象物が除去されるので、標識抗体の結合の阻害が抑制され、したがって、ゾーン現象が起こりにくいとされている。 By the way, a so-called antigen-antibody method two-step reaction (two-step method) is known as a method aimed at avoiding the zone phenomenon and the hook phenomenon. In general, in a two-step reaction, a solid phase and a capture antibody or a capture antigen and a sample are mixed, and after forming a conjugate of an analyte and a capture antibody, washing is performed, and unbound sample components and analysis are performed. After removing the target (bound / free separation) and adding a labeled antibody to form a capture antibody-analyte-labeled antibody sandwich, washing is performed to detect luminescence, etc. derived from the labeled antibody, and to be analyzed Measure quantity or concentration. In this two-step reaction, the unbound analyte is removed by the first washing, so that inhibition of the binding of the labeled antibody is suppressed, and therefore the zone phenomenon is unlikely to occur.
また、分析時間やオペレータの手間などの抑制を目的の一つとした方法としては、固相と捕捉抗体や捕捉抗原、標識抗体や標識抗原と試料とを、試料分注後かつ標識抗体分注前の洗浄を行うことなく混合反応させ、その後洗浄を行って固相に未結合の試薬および試料成分を除去し、分析対象物の計測を行う1ステップ反応(1ステップ法)が知られている。しかしながら、1ステップ反応においては、ゾーン現象が計測結果に大きく影響してしまう。1ステップ法において、試料中に分析対象物が高濃度に含まれる場合、あるいはそれが予想される場合には、試料をあらかじめ希釈し、ゾーン現象が起こらないと予想される濃度にまで試料を希釈し、計測に供することもあるが、その場合には、1試料につき、試料希釈を伴わない測定と、伴う測定との2回の計測を行う必要が生じることも多い。 In addition, as a method for suppressing the analysis time and the labor of the operator, the solid phase, the capture antibody, the capture antigen, the labeled antibody, the labeled antigen and the sample are dispensed after the sample is dispensed and before the labeled antibody is dispensed. There is known a one-step reaction (one-step method) in which a mixing reaction is performed without performing washing, and then washing is performed to remove unbound reagents and sample components on the solid phase and measurement of an analysis object is performed. However, in the one-step reaction, the zone phenomenon greatly affects the measurement result. In the one-step method, if an analyte is contained in a high concentration in the sample, or if it is expected, the sample is diluted in advance, and the sample is diluted to a concentration at which the zone phenomenon is not expected to occur. However, in this case, it is often necessary to perform two measurements for each sample: measurement without sample dilution and measurement with the sample.
本発明は上記に鑑みてなされたものであり、ゾーン現象による測定結果の正確性の低下を抑制することができる分析方法及び自動分析装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above, and an object of the present invention is to provide an analysis method and an automatic analyzer that can suppress a decrease in accuracy of measurement results due to a zone phenomenon.
上記目的を達成するために、本発明は、分析対象の試料が収容された反応容器に捕捉体を含む捕捉抗体試薬または捕捉抗原試薬を添加する1回目の捕捉体添加処理を行う手順と、前記反応容器に標識体を含む標識抗原試薬または標識抗体試薬を添加する1回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、前記反応容器に反応固相を含む反応固相試薬を添加する1回目の反応固相添加処理を行う手順と、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した成分以外の成分を除去するために前記反応固相を洗浄する1回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、前記反応容器から少なくとも一部の前記反応固相を取り出し、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した標識体に係る物理量を測定する1回目の測定処理を行う手順と、前記1回目の測定処理後の前記反応容器に2回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、前記2回目の標識体添加処理後に2回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、前記2回目の反応固相洗浄処理の後に2回目の測定処理を行う手順と、前記2回目の測定処理の結果に基づいて、1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する手順とを有するものとする。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention includes a procedure for performing a first capturing body addition process of adding a capturing antibody reagent or a capturing antigen reagent containing a capturing body to a reaction container in which a sample to be analyzed is stored, A procedure for performing a first labeled body addition process in which a labeled antigen reagent or labeled antibody reagent containing a labeled body is added to a reaction container, and a first reaction solid phase in which a reaction solid phase reagent including a reaction solid phase is added to the reaction container. A procedure for performing a phase addition treatment, a procedure for performing a first reaction solid phase washing treatment for washing the reaction solid phase in order to remove components other than the components that form bonds including the reaction solid phase, and the reaction Removing at least a part of the reaction solid phase from the container, and performing a first measurement process for measuring a physical quantity related to the labeled body including the reaction solid phase to form a bond; and after the first measurement process Second time in the reaction vessel A procedure for performing a label addition process, a procedure for performing a second reaction solid phase washing process after the second label addition process, and a procedure for performing a second measurement process after the second reaction solid phase washing process And a procedure for selectively determining one measurement result from a plurality of measurement result candidate values obtained by the first measurement process based on the result of the second measurement process.
ゾーン現象による測定結果の正確性の低下を抑制することができる。 A decrease in the accuracy of the measurement result due to the zone phenomenon can be suppressed.
以下、本発明の一実施の形態を図1〜図6を参照しつつ説明する。 Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
(1)全体構成
図1は、本実施の形態に係る自動分析装置の全体構成を概略的に示す図である。
(1) Overall Configuration FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing an overall configuration of an automatic analyzer according to the present embodiment.
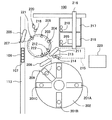
図1において、自動分析装置100は、分析対象の試料や検体(以下、単に試料と称する)を収容する試料容器108と、試料容器108を搭載したラック107を搬送するラック搬送ライン113と、試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する標識抗原または標識抗体を含む標識試薬を収容する標識試薬容器201Aと、試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する捕捉抗原または捕捉抗体を含む捕捉試薬を収容する捕捉試薬容器201Bと、試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する反応固相を含む反応固相試薬を収容する反応固相試薬容器201Cと、試薬容器201A,201B,201Cを搭載する試薬ディスク202と、試料、標識試薬および反応固相試薬を分注して反応させる反応容器205と、反応容器205を搭載する反応ディスク203と、試料容器108から反応容器205に試料を分注する試料分注機構206と、標識試薬容器201A、捕捉試薬容器201B、及び反応固相試薬容器201Cから標識試薬、捕捉試薬及び反応固相試薬を反応容器205に分注する試薬分注機構208と、反応ディスク203の反応液吸引位置212において、反応容器205中の反応液を吸引し、反応液中の各種標識物質(標識体)に係る物理量に基づいて分析対象成分の定性・定量分析を行う検出ユニット215(分析機構)と、反応容器205に分注された試料、標識試薬および反応固相試薬の混合液中の反応固相を反応容器の内壁に集合させる反応固相集合機構402と、未使用の反応容器205や分注チップ210を移送する移送機構216と、試料の分析に係る分析処理等の各処理(後述)を行うとともに自動分析装置100全体の動作を制御する制御部223とから概略構成されている。
In FIG. 1, an
(1−1)ラック搬送ライン113
試料容器108は、ラック107に複数搭載された状態でラック搬送ライン113に沿って搬送される。試料容器108には、血清や血漿、体液などの分析対象の生体試料(以下、単に試料と称する)が収容されている。ラック搬送ライン113上には、試料吸引位置207が配置されている。
(1-1)
A plurality of
(1−2)試薬ディスク202
試薬ディスク202には、分析処理に用いる各種試薬が収容された複数の試薬容器201A,201B,201Cが周方向に並べて配置されている。試薬ディスク202は、図示しない回転駆動装置によって周方向に回転駆動されることにより、試薬容器201A,201B,201Cを周方向に搬送する。試薬ディスク202における試薬容器201A,201B,201Cの搬送経路上には、試薬吸引位置209が配置されている。
(1-2)
On the
試薬ディスク202に配置される試薬容器としては、例えば、標識試薬容器201Aや捕捉試薬容器201B、反応固相試薬容器201Cなどがある。標識試薬容器201Aには、試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する抗体や抗原を各種標識物質で標識した標識抗体や標識抗原を含む標識試薬(標識抗体試薬や標識抗原試薬)が収容されており、捕捉試薬容器201Bには、試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する捕捉体(捕捉抗体や標識抗原)を含む捕捉試薬(捕捉抗原試薬や捕捉抗体試薬)が収容されており、反応固相試薬容器201Cには、反応固相を含む反応固相試薬が収容されている。
Examples of the reagent container disposed on the
なお、試薬ディスク202に配置される試薬容器の他の様態としては、標識試薬、捕捉試薬、反応固相試薬のうち2種類の試薬の機能を同時に有する試薬(例えば、2種類の試薬が混合された試薬)を収容した試薬容器と残りの1種類の試薬の機能を有する試薬を収容した試薬容器とを配置する場合、或いは、3種類の試薬の機能を同時に有する試薬(例えば、3種類の試薬が混合された試薬)を収容した試薬容器を配置する場合があっても良い。
As another aspect of the reagent container disposed on the
本実施の形態に係る自動分析装置においては、血液、血清、血漿あるいは体液を試料とし、ホルモン、腫瘍マーカ、感染症病原体マーカ、感染抗体等の微量物質の計測分析を行うとき、分析対象のタンパク質の分析項目ごとに、抗原抗体反応に基づく結合により、試料中のタンパク質等を定性的あるいは定量的に検出する。抗原抗体反応の場となる反応固相面はプラスチック、ガラス材の平板あるいは粒子、酸化鉄を内封する磁性粒子等が用いられる。このような固相において分析対象のタンパク質に結合する抗体あるいは抗原は、捕捉抗体、捕捉抗原、キャプチャー抗体あるいはキャプチャー抗原と称される。また、放射性同位元素、蛍光色素、発光色素、酵素、希土類錯体、金属イオン等を結合され、分析対象のタンパク質に結合する抗体あるいは抗原は標識抗原、標識抗体、ラベル抗原、コンジュゲートあるいはトレーサー等と称される。 In the automatic analyzer according to the present embodiment, when measuring analysis of trace substances such as hormones, tumor markers, infectious disease pathogen markers, and infectious antibodies using blood, serum, plasma or body fluid as a sample, the protein to be analyzed For each analysis item, protein or the like in the sample is detected qualitatively or quantitatively by binding based on the antigen-antibody reaction. As the reaction solid phase surface for the antigen-antibody reaction, plastic, glass plate or particles, magnetic particles containing iron oxide, or the like are used. Such an antibody or antigen that binds to the protein to be analyzed in the solid phase is referred to as a capture antibody, a capture antigen, a capture antibody, or a capture antigen. In addition, antibodies or antigens that bind radioisotopes, fluorescent dyes, luminescent dyes, enzymes, rare earth complexes, metal ions, etc., and bind to proteins to be analyzed are labeled antigens, labeled antibodies, labeled antigens, conjugates, tracers, etc. Called.
(1−3)反応ディスク203
反応ディスク203には、試料と各種試薬の混合液(反応液)が収容される複数の反応容器205が周方向に並べて配置されており、恒温で保持されている。反応ディスク203は、図示しない回転駆動装置によって周方向に回転駆動されることにより、反応容器205を周方向に搬送する。反応ディスク203における反応容器205の搬送経路上には、反応容器設置位置204、試料吐出位置221、試薬添加位置222、反応液吸引位置212などが配置されている。また、反応ディスク203には、反応容器205中の混合液(反応液)中の反応固相を反応容器205の内壁に集合させる反応固相集合機構402(後の図2等参照)が設けられている。
(1-3)
On the
(1−3.1)反応固相集合機構402
反応固相集合機構402は、制御部223による各種処理の実行に応じて反応固相の集合及び解放を行うものであり、反応容器205に収容された混合液(反応液)中の反応固相を反応容器205の内壁に集合させて固定するものである。反応固相が反応容器205の内壁に固定された状態で、反応容器205に純水や緩衝液、専用の洗浄液などを添加および除去することにより、反応固相を流出させることなく反応固相の洗浄(後述の反応固相洗浄処理)を行うことができる。反応固相集合機構402の具体的構成としては、例えば、反応固相が磁性体を含む場合には、磁石等の磁気によって反応固相を反応容器205の内壁に引き付けて集合させ、固定する。
(1-3.1) Reaction solid
The reaction solid
(1−4)試料分注機構206
図2は、試料分注機構206を周辺構成とともに抜き出して示す図である。
(1-4)
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing the
試料分注機構206は、水平方向への回動及び上下移動可能に構成されており、試料吸引位置207においてプローブ401の先端を試料容器108内の試料に接液させて所定量の吸引を行い、試料吐出位置221において反応容器205に吐出する。試料分注機構206のプローブ401が移動する軌道上には、分注に用いる未使用の分注チップ210をプローブ401に結合する結合位置218や、使用済みの分注チップを破棄するチップ破棄位置220が配置されている。分注後のプローブ401は、プローブ洗浄機403にて試料成分の洗浄を行う。プローブ洗浄機403では、送水弁408を通して洗浄カップ407に供給される洗浄水により、洗浄カップ407内に挿入されたプローブ401の外面を洗浄するとともに、プローブ401によって洗浄カップ407内の洗浄水を吸い上げ、廃棄ボトル404に移動して吐出することでプローブ401の洗浄を行う。
The
(1−5)試薬分注機構208
試薬分注機構208は、試料分注機構206と同様の構成を有している。すなわち、試薬分注機構208は、水平方向への回動及び上下移動可能に構成されており、試薬吸引位置209においてプローブの先端を試薬容器201A,201B,201C内の試薬に接液させて所定量の吸引を行い、試薬添加位置222において反応容器205に吐出する。分注後のプローブは、試料分注機構206におけるプローブ洗浄機403と同様の構成を有するプローブ洗浄機にて試薬成分の洗浄を行う。すなわち、試薬分注機構208のプローブ洗浄機では、送水弁を通して洗浄カップに供給される洗浄水により、洗浄カップ内に挿入されたプローブの外面を洗浄するとともに、プローブによって洗浄カップ内の洗浄水を吸い上げ、廃棄ボトルに移動して吐出することでプローブの洗浄を行う。
(1-5)
The
(1−6)移送機構216
自動分析装置100には、未使用の反応容器205を保管する反応容器保管部219、及び未使用の分注チップ210を保管する分注チップ保管部217が設けられており、反応容器205及び分注チップ210は移送機構216により移送される。移送機構216は、X軸,Y軸,Z軸の3方向に移動可能に構成されており、反応容器保管部219から反応ディスク203の反応容器設置位置204への反応容器205の搬送や、分注チップ保管部217からチップ結合位置218への分注チップ210の移送を行う。
(1-6)
The
(1−7)検出ユニット215
検出ユニット215は、反応ディスク203の反応液吸引位置212において、反応容器205中の反応液を吸引し、検出ユニット内部に配置されたフローセル(図示せず)に送る反応液吸引機構211が設けられており、反応液をフローセルに通すことによって、反応液中の標識抗原または標識抗体に関する物理量、すなわち、標識体に関する物理量を測定する。測定する物理量としては、例えば、標識体に蛍光色素や発光色素を用いた場合には光量を測定し、標識体に放射性同位体を用いた場合には放射線を測定する。
(1-7)
The
反応液吸引機構211は、水平方向への回動及び上下動可能に構成されており、反応液吸引機構211のプローブが移動する軌道上には、分析に用いる緩衝液(後述)を吸引する緩衝液吸引位置213や、吸引した反応液の流路の洗浄に用いる洗浄液を吸引する洗浄液吸引位置214が配置されている。反応液吸引機構211において、反応液や緩衝液の吸引後のプローブは、図示しないプローブ洗浄機によって外壁の洗浄を行う。
The reaction
(1−8)制御部223
制御部223は、自動分析装置100の全体の動作を制御するとともに、試料の分析に係る処理として、標識体添加処理、捕捉体添加処理、反応固相添加処理、反応固相洗浄処理、測定処理などを実施する分析処理制御装置としての機能を有している。
(1-8)
The
(1−8.1)標識体添加処理
標識体添加処理は、標識試薬容器201Aに収容された標識試薬(標識抗体試薬や標識抗原試薬)を試薬分注機構208によって反応容器205に分注する処理であり、分析対象成分により、標識抗体試薬か標識抗原試薬の何れかが選択されて用いられる。
(1-8.1) Labeled body addition process In the labeled body addition process, the labeled reagent (labeled antibody reagent or labeled antigen reagent) accommodated in the labeled
(1−8.2)捕捉体添加処理
捕捉体添加処理は、捕捉試薬容器201Bに収容された捕捉試薬(捕捉抗体試薬や捕捉抗原試薬)を試薬分注機構208によって反応容器205に分注する処理であり、分析対象成分により、捕捉抗体試薬か捕捉抗原試薬の何れかが選択されて用いられる。
(1-8.2) Capturing body addition process In the capturing body addition process, the capture reagent (capture antibody reagent or capture antigen reagent) accommodated in the
(1−8.3)反応固相添加処理
反応固相添加処理は、反応固相試薬容器201Cに収容された反応固相試薬を試薬分注機構208によって反応容器205に分注する処理である。
(1-8.3) Reaction Solid Phase Addition Process The reaction solid phase addition process is a process of dispensing the reaction solid phase reagent accommodated in the reaction solid phase reagent container 201C into the
なお、標識体添加処理、捕捉体添加処理、及び反応固相添加処理については、試薬ディスク202に配置される試薬容器の様態に応じて、実質的に同時に実施される場合がある。例えば、標識試薬、捕捉試薬、反応固相試薬のうち2種類の試薬の機能を同時に有する試薬を収容した試薬容器と残りの1種類の試薬の機能を有する試薬を収容した試薬容器とが試薬ディスク202に配置されている場合には、3つの処理のうち2つが同時に実施されることとなり、また、3種類の試薬の機能を同時に有する試薬を収容した試薬容器が試薬ディスク202に配置されている場合には、3つの処理が同時に実施される。
The labeling body addition process, the capturing body addition process, and the reaction solid phase addition process may be performed substantially simultaneously depending on the state of the reagent container disposed on the
(1−8.4)反応固相洗浄処理
反応固相洗浄処理は、反応容器205に収容された反応液中の反応固相を反応固相集合機構402によって反応容器205の内壁に集合させ固定した状態で、試料分注機構206や試薬分注機構208、或いは、図示しない専用の添加機構により、純水や緩衝液、或いは専用の洗浄液などを添加および除去することにより、反応固相の洗浄を行う処理である。この反応固相洗浄処理により、反応固相を含んで結合を形成した成分以外の成分(試料成分、試薬成分、標識抗体、捕捉抗体)は、破棄される。
(1-8.4) Reaction solid phase cleaning treatment In the reaction solid phase washing treatment, the reaction solid phase in the reaction solution contained in the
(1−8.5)測定処理
測定処理は、反応容器205内の反応液を反応液吸引機構211によって吸引し、検出ユニット215の内部に設置されたフローセルによって、反応液中の標識抗原または標識抗体に関する物理量、すなわち、標識体に関する物理量を測定する処理である。測定する物理量としては、例えば、標識体に蛍光色素や発光色素を用いた場合には光量を測定し、標識体に放射性同位体を用いた場合には放射線を測定する。なお、標識体の種類により、ラジオイムノアッセイ、エンザイムイムノアッセイ、蛍光イムノアッセイ、化学発光イムノアッセイ、電気化学発光イムノアッセイなどが知られている。
(1-8.5) Measurement Process In the measurement process, the reaction liquid in the
(2)分析処理
本実施の形態の制御部(分析処理制御装置)による分析処理について図3〜図6を参照しつつ説明する。
(2) Analysis process The analysis process by the control part (analysis process control apparatus) of this Embodiment is demonstrated, referring FIGS. 3-6.
図3は、本実施の形態における分析処理の流れを概略的に示す図である。 FIG. 3 is a diagram schematically showing the flow of analysis processing in the present embodiment.
分析処理では、まず、分析対象の試料が収容された反応容器205に捕捉抗体試薬または捕捉抗原試薬を添加する1回目の捕捉体添加処理と、反応容器に標識抗原試薬または標識抗体試薬を添加する1回目の標識体添加処理と、反応容器に反応固相試薬を添加する1回目の反応固相添加処理とを行い、攪拌・インキュベートを行う(図3の工程1)。
In the analysis process, first, a capture body addition process in which a capture antibody reagent or a capture antigen reagent is added to a
次に、反応固相を含んで結合を形成した成分以外の成分の除去(すなわち、バウンド・フリー分離)を行う反応固相洗浄処理(1回目)を行う(図3の工程2)。
Next, a reaction solid phase cleaning process (first time) is performed in which components other than the components including the reaction solid phase that have formed a bond are removed (that is, bounce-free separation) (
次に、反応容器205中の標識体に係る物理量を測定する測定処理(1回目)を行う(図3の工程3)。
Next, a measurement process (first time) for measuring a physical quantity related to the label in the
次に、測定処理(1回目)後に残った反応液に少量の標識体添加処理(2回目)を行う(図3の工程4)。なお、工程の標識体添加処理における標識試薬の添加量(少量)とは、工程1において添加した標識体の量と比較して、1/2〜1/1000の標識体が添加されるような量である。
Next, a small amount of labeled substance addition treatment (second time) is performed on the reaction solution remaining after the measurement treatment (first time) (step 4 in FIG. 3). Note that the amount of labeling reagent added (small amount) in the labeling process in the step is such that 1/2 to 1/1000 of the labeling substance is added compared to the amount of the labeling substance added in
次に、標識体添加処理(2回目)を行った反応液に攪拌・インキュベートを行う(図3の工程5)。 Next, the reaction solution subjected to the labeling treatment (second time) is stirred and incubated (step 5 in FIG. 3).
次に、標識体添加処理(2回目)後に反応固相洗浄処理(2回目)を行う(図3の工程6)。
Next, a reaction solid phase washing process (second time) is performed after the labeling substance addition process (second time) (
次に、反応固相洗浄処理(2回目)の後に測定処理(2回目)を行い(図3の工程7)、その測定結果に基づいて、測定処理(1回目)により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する。 Next, a measurement process (second time) is performed after the reaction solid phase cleaning process (second time) (step 7 in FIG. 3), and a plurality of measurements obtained by the measurement process (first time) based on the measurement result One measurement result is selectively determined from the result candidate values.
図4は、図3の工程3の測定処理(1回目)において得られる検量線の一例におけるシグナル値と分析対象物の濃度の関係を示す図である。 FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the relationship between the signal value and the concentration of the analyte in an example of a calibration curve obtained in the measurement process (first time) of step 3 in FIG.
図4において、検量線40は、試料中の分析対象物濃度が上昇するに従いシグナル値が上昇し、緩やかなS字を描きシグナルの最高値(ピーク値)に達する。また、分析対象物濃度がさらに高い場合、シグナル値は一転して濃度の上昇に従い緩やかに下降する。ピーク値からの下降のある場合、ゾーン現象があることがわかる。未知の試料の計測を行う場合、分析対象物濃度は予想できないため、ゾーン現象を示す濃度であるかどうかは不明であり、従って、測定結果がシグナル値S0をとった場合に、検量線240上の濃度値VA(状態A)、或いは、ゾーン現象が発生して検量線240が下降する範囲での濃度値VB(状態B)の何れかの値をとる。
In FIG. 4, the calibration curve 40 increases in signal value as the analyte concentration in the sample increases, draws a gentle S-shape, and reaches the maximum value (peak value) of the signal. Further, when the analyte concentration is higher, the signal value changes and gradually decreases as the concentration increases. When there is a drop from the peak value, it can be seen that there is a zone phenomenon. When an unknown sample is measured, the analyte concentration cannot be predicted, so it is unknown whether the concentration is indicative of a zone phenomenon. Therefore, when the measurement result takes the signal value S0, it is on the
図5は、図3の工程7の測定処理(2回目)において得られるシグナル値の一例を示す図である。 FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of signal values obtained in the measurement process (second time) of step 7 in FIG. 3.
図5において、試料中の分析対象物濃度が比較的低い状態(すなわち、状態A)の場合には、図3の工程4における標識試薬添加処理(少量)の後(T2)においてもシグナル値(S1)は、工程3の測定処理(1回目)のシグナル値(S1,T1)と比較して大きな上昇はない。一方、試料中の分析対象物濃度が比較的高い状態(すなわち、状態B)の場合には、図3の工程3の測定処理(1回目)時(T1)において反応固相の表面には捕捉体と分析対象物との結合物が多く残留しており、したがって、図3の工程4における標識試薬添加処理(少量)の後(T2)において、捕捉体−抗原(抗体)−標識体のサンドイッチが形成され、標識体が多く観察されることからシグナル値(S2)は上昇する。すなわち、測定処理(2回目)において、高いシグナル値(S2)が得られる場合、図4においては状態Bであり、したがって、濃度値VBを測定結果として選択決定する。状態の判定は、図5において予め基準値(Sth)を設定し、測定処理(2回目)の測定結果と比較することによって、分析対象物濃度が状態Aの値(VA)であるか状態Bの値(VB)であるかを判定できる。なお、この基準値(Sth)は、図3の工程4において標識体添加処理後のシグナル値の上昇の有無を判断するためのものであるため、測定処理(1回目)でのシグナル値に基づいて基準値(Sth)そのものが上下することとなる。 In FIG. 5, in the case where the concentration of the analyte in the sample is relatively low (that is, state A), the signal value (T2) after the labeling reagent addition process (small amount) in step 4 of FIG. S1) does not increase significantly compared to the signal value (S1, T1) of the measurement process (first time) in step 3. On the other hand, when the concentration of the analyte in the sample is relatively high (ie, state B), it is captured on the surface of the reaction solid phase at the time of the measurement process (first time) (T1) in step 3 of FIG. Many binding substances remain between the body and the analyte, and therefore, after the labeling reagent addition process (small amount) in step 4 of FIG. 3 (T2), the sandwich of the capture body-antigen (antibody) -labeled body And the signal value (S2) rises because a large number of labeled bodies are observed. That is, when a high signal value (S2) is obtained in the measurement process (second time), it is in state B in FIG. 4, and therefore the concentration value VB is selected and determined as the measurement result. The determination of the state is performed by setting a reference value (Sth) in FIG. 5 in advance and comparing it with the measurement result of the measurement process (second time) to determine whether the analyte concentration is the value of state A (VA) or state B. It is possible to determine whether the value is VB. This reference value (Sth) is for determining whether or not there is an increase in the signal value after the labeling agent addition process in Step 4 of FIG. 3, and is therefore based on the signal value in the measurement process (first time). Thus, the reference value (Sth) itself goes up and down.
図6は、分析処理の処理内容を示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing the processing contents of the analysis processing.
図6において、分析制御装置としての制御部223は、まず、反応容器205に分析対象の試料を分注し(ステップS100)、次に、標識試薬や捕捉試薬、反応固相試薬を添加する試薬添加処理を行う(ステップS110)。続いて、反応容器205の混合液(反応液)を攪拌してインキュベータに搭載して反応させ(ステップS120)、反応が終了した後、試料及び残余の試薬を含む反応液の除去と反応固相の洗浄を行う反応固相洗浄処理を行う(ステップS130)。次に、反応固相を溶液に懸濁して固相上に抗原抗体結合を介して保持されている標識体に係る物理量の計測(測定処理(1回目))を行う(ステップS140)。そして、測定処理(1回目)の測定結果に基づいて、測定結果候補値(VA)を算出し(ステップS141)、また、測定結果候補値(VB)を算出する(ステップS142)。また、ステップS140の測定処理(1回目)と並行して(或いは、ステップS141、S142が終了すると)、反応容器205に収容されている測定処理(1回目)の残分の反応液に標識試薬を少量添加する標識試薬添加処理(少量)を行う(ステップS150)。続いて、反応容器205の混合液(反応液)を攪拌してインキュベータに搭載して反応させ(ステップS155)、そして、インキュベータに搭載して反応が終了した後、反応固相洗浄処理(2回目)を行い(ステップS160)、続いて、測定処理(2回目)を行う(ステップS170)。ここで、ステップS170での測定結果(シグナル値)が基準値(Sth)以上であるかどうかを判定し(ステップS180)、判定結果がNOの場合には、ゾーン現象無しであると判定して、測定結果候補値(VA)を測定結果として選択決定し(ステップS181)、処理を数量する。また、ステップS180での判定結果がYESの場合には、ゾーン現象有りであると判定して、測定結果候補(VB)を測定結果として選択決定し(ステップS182)、処理を終了する。
In FIG. 6, a
以上のように構成した本実施の形態の効果を説明する。 The effect of the present embodiment configured as described above will be described.
血液、血清、血漿、或いは体液等を試料或いは検体とする分析方法には、抗原抗体反応に基づく結合を利用して、試料中のホルモン、腫瘍マーカ、感染症病原体マーカ、感染抗体等の微量物質を定性的或いは定量的に検出する方法が知られている。しかしながら、抗原抗体反応を利用した分析方法では、試料中に分析対象の物質が高濃度に含まれる場合には、分析結果の数値が実際の値よりも低くなってしまう現象(ゾーン現象やフック現象などと呼ばれる現象)が生じる場合がある。 For analysis methods using blood, serum, plasma, or body fluid as a sample or specimen, a trace substance such as a hormone, tumor marker, infectious disease pathogen marker, or infectious antibody in a sample is utilized using binding based on an antigen-antibody reaction. A method for detecting qualitatively or quantitatively is known. However, in the analysis method using the antigen-antibody reaction, when the sample contains a high concentration of the substance to be analyzed, the numerical value of the analysis result becomes lower than the actual value (zone phenomenon or hook phenomenon) May occur).
これに対して、本実施の形態においては、分析対象の試料が収容された反応容器に捕捉体を含む捕捉抗体試薬または捕捉抗原試薬を添加する1回目の捕捉体添加処理を行う手順と、前記反応容器に標識体を含む標識抗原試薬または標識抗体試薬を添加する1回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、前記反応容器に反応固相を含む反応固相試薬を添加する1回目の反応固相添加処理を行う手順と、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した成分以外の成分を除去するために前記反応固相を洗浄する1回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、前記反応容器中の標識体に係る物理量を測定する1回目の測定処理を行う手順と、前記1回目の測定処理後に2回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、前記2回目の標識体添加処理後に2回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、前記2回目の反応固相洗浄処理の後に2回目の測定処理を行う手順と、前記2回目の測定処理の結果に基づいて、1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する手順とを有するように構成したので、ゾーン現象による測定結果の正確性の低下を抑制することができる。 On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the procedure for performing the first capture body addition process of adding the capture antibody reagent or capture antigen reagent containing the capture body to the reaction container containing the sample to be analyzed, A procedure for performing a first labeled body addition process in which a labeled antigen reagent or labeled antibody reagent containing a labeled body is added to a reaction container, and a first reaction solid phase in which a reaction solid phase reagent including a reaction solid phase is added to the reaction container. A procedure for performing a phase addition treatment, a procedure for performing a first reaction solid phase washing treatment for washing the reaction solid phase in order to remove components other than the components that form bonds including the reaction solid phase, and the reaction A procedure for performing a first measurement process for measuring a physical quantity related to a label in a container, a procedure for performing a second label addition process after the first measurement process, and a procedure for performing a second label addition process after the second measurement process. The second reaction solid phase cleaning process And a plurality of measurement results obtained by the first measurement process based on the result of the second measurement process and the procedure of performing the second measurement process after the second reaction solid phase cleaning process. And a procedure for selectively determining one measurement result from the candidate value, it is possible to suppress a decrease in accuracy of the measurement result due to the zone phenomenon.
すなわち、蛍光測定法あるいは発光測定法による分析法あるいは装置において試料の抗原抗体反応に基づく分析測定を行う時、ゾーン現象によってシグナル値が低下し、計測値の正確性を損なう要因があることから、これに対処し試料中の分析対象物量と濃度とを正しく計測することができる。 That is, when performing an analytical measurement based on an antigen-antibody reaction of a sample in an analysis method or apparatus based on a fluorescence measurement method or a luminescence measurement method, there is a factor that decreases the signal value due to the zone phenomenon and impairs the accuracy of the measurement value. In response to this, the amount and concentration of the analyte in the sample can be correctly measured.
さらには、試料中測定対象物がゾーン現象を起こす高濃度であっても、真値を正しく計測できる。また同様に、陰性値である場合は正しく陰性であることを判断できる。 Furthermore, the true value can be measured correctly even if the measurement object in the sample has a high concentration that causes the zone phenomenon. Similarly, if it is a negative value, it can be determined that the negative value is correct.
また、試料を希釈して再測定を伴う場合、通常測定の2倍の試薬量が必要となるが、本実施の形態においては、標識試薬が1/2〜1/1000程度あればよく、効果的に試料中の分析対象物量と濃度とを正しく計測することができる。また、本測定と希釈測定の2つのテストを繰り返す必要がなく、したがって、測定に要する時間を短縮することができる。 In addition, when the sample is diluted and remeasurement is required, the reagent amount twice as large as that in the normal measurement is required. However, in this embodiment, it is sufficient that the labeling reagent is about 1/2 to 1/1000. In particular, the amount and concentration of the analyte in the sample can be measured correctly. Further, it is not necessary to repeat the two tests of the main measurement and the dilution measurement, and therefore the time required for the measurement can be shortened.
さらに、1ステップ法はゾーン現象が計測結果に大きく影響してしまうという問題点があるが、本実施の形態においては、その弱点をカバーしつつ、測定レンジ桁数を2倍とすることができる。例えば、10^4の測定レンジを有する場合には、10^8のレンジまでを有効に測定することができ、感染症項目を最小試薬使用量でカバーすることができる。 Furthermore, although the one-step method has a problem that the zone phenomenon greatly affects the measurement result, in the present embodiment, the number of measurement range digits can be doubled while covering the weak points. . For example, in the case of having a measurement range of 10 ^ 4, it is possible to effectively measure up to a range of 10 ^ 8, and infectious disease items can be covered with the minimum reagent usage.
なお、本実施の形態においては、測定処理(1回目)の測定結果に基づいて基準値を設定し、測定処理(2回目)の測定結果と基準値との比較により、測定処理(1回目)の測定結果(がゾーン現象の影響を受けない値なのか、受けた値なのか)を選択的に確定した(図5等参照)がこれに限られない。すなわち、例えば、測定処理(2回目)における標識試薬の添加直後と、標識試薬の添加から予め定めた時間が経過した後との少なくとも2回の測定を行い、その測定結果の差分に基づいて、1回目の測定結果を選択的に確定するように構成してもよい。この場合においても、本実施の形態と同様の効果を得ることができる。 In the present embodiment, the reference value is set based on the measurement result of the measurement process (first time), and the measurement process (first time) is compared with the measurement result of the measurement process (second time) and the reference value. However, the measurement result (see FIG. 5 and the like) is selectively limited (see FIG. 5 and the like). That is, for example, at least two measurements are performed immediately after the addition of the labeling reagent in the measurement process (second time) and after a predetermined time has elapsed since the addition of the labeling reagent, and based on the difference between the measurement results, The first measurement result may be selectively determined. Even in this case, the same effect as the present embodiment can be obtained.
また、本実施の形態においては、反応固相洗浄処理(2回目)を行うように構成したがこれに限られず、標識体添加処理(2回目)の後に測定処理(2回目)を行うように、構成しても良い。 In the present embodiment, the reaction solid phase cleaning process (second time) is performed. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the measurement process (second time) is performed after the label addition process (second time). , May be configured.
100 自動分析装置
107 ラック
108 試料容器
113 ラック搬送ライン
201A 標識試薬容器
201B 捕捉試薬容器
201C 反応固相試薬容器
203 反応ディスク
204 反応容器設置位置
205 反応容器
206 試料分注機構
207 試料吸引位置
208 試薬分注機構
209 試薬吸引位置
210 分注チップ
211 反応液吸引機構
212 反応液吸引位置
213 緩衝液吸引位置
214 洗浄液吸引位置
215 検出ユニット
216 反応容器移送機構
217 分注チップ保管部
218 チップ結合位置
219 反応容器保管部
220 チップ破棄位置
221 試料吐出位置
222 試薬添加位置
223 制御部
240 検量線
402 反応固相集合機構
100
Claims (6)
前記反応容器に標識体を含む標識抗原試薬または標識抗体試薬を添加する1回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、
前記反応容器に反応固相を含む反応固相試薬を添加する1回目の反応固相添加処理を行う手順と、
前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した成分以外の成分を除去するために前記反応固相を洗浄する1回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、
前記反応容器から少なくとも一部の前記反応固相を取り出し、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した標識体に係る物理量を測定する1回目の測定処理を行う手順と、
前記1回目の測定処理後の前記反応容器に2回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の標識体添加処理後に2回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の反応固相洗浄処理の後に2回目の測定処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の測定処理の結果に基づいて、1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する手順と
を有することを特徴とする分析方法。 A procedure for performing a first capture body addition process of adding a capture antibody reagent or capture antigen reagent containing a capture body to a reaction container containing a sample to be analyzed;
A procedure for performing a first labeled body addition process of adding a labeled antigen reagent or labeled antibody reagent containing a labeled body to the reaction container;
A procedure for performing a first reaction solid phase addition treatment in which a reaction solid phase reagent containing a reaction solid phase is added to the reaction vessel;
A procedure for performing a first reaction solid phase washing treatment for washing the reaction solid phase in order to remove components other than the component that forms a bond including the reaction solid phase;
Removing at least a part of the reaction solid phase from the reaction vessel, and performing a first measurement process for measuring a physical quantity related to the labeled body including the reaction solid phase to form a bond;
A procedure for performing a second labeled body addition treatment on the reaction vessel after the first measurement treatment;
A procedure for performing a second reaction solid phase washing treatment after the second labeling agent addition treatment;
A procedure for performing a second measurement process after the second reaction solid phase washing process;
And a procedure for selectively determining one measurement result from a plurality of measurement result candidate values obtained by the first measurement process based on the result of the second measurement process.
前記反応容器に標識体を含む標識抗原試薬または標識抗体試薬を添加する1回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、
前記反応容器に反応固相を含む反応固相試薬を添加する1回目の反応固相添加処理を行う手順と、
前記反応容器から少なくとも一部の前記反応固相を取り出し、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した標識体に係る物理量を測定する1回目の測定処理を行う手順と、
前記1回目の測定処理後の前記反応容器に2回目の標識体添加処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の標識体添加処理後に2回目の測定処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の測定処理の結果に基づいて、1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する手順と
を有することを特徴とする分析方法。 A procedure for performing a first capture body addition process of adding a capture antibody reagent or capture antigen reagent containing a capture body to a reaction container containing a sample to be analyzed;
A procedure for performing a first labeled body addition process of adding a labeled antigen reagent or labeled antibody reagent containing a labeled body to the reaction container;
A procedure for performing a first reaction solid phase addition treatment in which a reaction solid phase reagent containing a reaction solid phase is added to the reaction vessel;
Removing at least a part of the reaction solid phase from the reaction vessel, and performing a first measurement process for measuring a physical quantity related to the labeled body including the reaction solid phase to form a bond;
A procedure for performing a second labeled body addition treatment on the reaction vessel after the first measurement treatment;
A procedure for performing a second measurement process after the second labeled body addition process;
And a procedure for selectively determining one measurement result from a plurality of measurement result candidate values obtained by the first measurement process based on the result of the second measurement process.
前記2回目の標識体添加処理では、前記1回目の標識体添加処理において添加した標識体の量の1/2〜1/1000の量の標識体が添加されるように前記標識抗体試薬を添加することを特徴とする分析方法。 The analysis method according to claim 1 or 2,
The labeled antibody reagent to said at second labels addition treatment, the label of an amount of 1 / 2-1 / 1000 of the amount of added label in labeled form addition treatment of the first is added The analysis method characterized by adding.
前記2回目の測定処理は、
前記2回目の標識体添加処理の直後に前記標識体に係る物理量を測定する第1測定と、
前記2回目の標識体添加処理の後に予め定めた時間が経過した時に前記標識体に係る物理量を測定する第2測定とを有し、
前記第1測定の結果と前記第2測定の結果の差分に基づいて、前記1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定することを特徴とする分析方法。 The analysis method according to claim 1 or 2,
The second measurement process includes:
A first measurement for measuring a physical quantity related to the label immediately after the second label addition process;
And a second measurement for measuring a physical quantity relating to the label when the predetermined time after the second label addition treatment has elapsed,
One measurement result is selectively determined from a plurality of measurement result candidate values obtained by the first measurement process based on a difference between the first measurement result and the second measurement result. Analysis method to do.
捕捉体を含む捕捉抗体または捕捉抗原、標識体を含む標識抗原または標識抗体、反応固相のうち、前記第1の試薬に含有されていないものを含有する第2の試薬を添加する2回目の添加処理を行う手順と、
前記反応容器から少なくとも一部の前記反応固相を取り出し、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した標識体に係る物理量を測定する1回目の測定処理を行う手順と、
前記1回目の測定処理後の前記反応容器に標識体を含む標識抗原または標識抗体を含有する試薬を添加する添加処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の標識体添加処理後に2回目の反応固相洗浄処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の反応固相洗浄処理の後に2回目の測定処理を行う手順と、
前記2回目の測定処理の結果に基づいて、1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する手順と
を有することを特徴とする分析方法。 The first time when a capture antibody or capture antigen containing a capture body, a labeled antigen or label antibody containing a label, and a first reagent containing a plurality of reaction solid phases are added to a reaction container containing a sample to be analyzed A procedure for performing the addition process of
Second time of adding a second reagent containing a capture antibody or capture antigen containing a capture body, a labeled antigen or labeled antibody containing a label, and a reaction solid phase not contained in the first reagent A procedure for performing the addition process;
Removing at least a part of the reaction solid phase from the reaction vessel, and performing a first measurement process for measuring a physical quantity related to the labeled body including the reaction solid phase to form a bond;
A procedure for performing an addition process of adding a reagent containing a labeled antigen or labeled antibody containing a labeled body to the reaction container after the first measurement process;
A procedure for performing a second reaction solid phase washing treatment after the second labeling agent addition treatment;
A procedure for performing a second measurement process after the second reaction solid phase washing process;
And a procedure for selectively determining one measurement result from a plurality of measurement result candidate values obtained by the first measurement process based on the result of the second measurement process.
前記試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する標識抗原または標識抗体を含む標識試薬を収容する標識試薬容器と、
前記試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する捕捉抗原または捕捉抗体を含む捕捉試薬を収容する捕捉試薬容器と、
前記試料中の分析対象成分と特異的な抗原抗体結合を形成する場となる反応固相を含む反応固相試薬を収容する反応固相試薬容器と、
前記試料および前記標識試薬、捕捉試薬、固相試薬を分注して反応させる反応固相を収容する反応容器と、
前記試料容器から前記反応容器に前記試料を分注する試料分注機構と、
前記標識試薬容器、捕捉試薬容器、および反応固相試薬容器から前記標識試薬、補足試薬、および固相試薬をそれぞれ前記反応容器に分注する試薬分注機構と、
前記反応容器中の標識体に係る物理量に基づいて前記分析対象成分の定性・定量分析を行う分析機構と、
前記反応容器中の標識体に係る物理量を測定する測定処理を行う測定機構と、
前記試料が収容された前記反応容器に前記捕捉試薬を添加する1回目の捕捉体添加処理と、前記反応容器に標識試薬を添加する1回目の標識体添加処理と、前記反応容器に反応固相試薬を添加する1回目の固相添加処理と、前記反応固相を含んで抗原抗体結合を形成した成分以外を除去するために前記反応固相を洗浄する1回目の反応固相洗浄処理と、前記反応容器から少なくとも一部の前記反応固相を取り出し、前記反応固相を含んで結合を形成した標識体に係る物理量を測定する1回目の測定処理と、前記1回目の測定処理後の前記反応容器への2回目の標識体添加処理と、前記2回目の標識体添加処理後に2回目の反応固相洗浄処理と、前記2回目の反応固相洗浄処理の後に2回目の測定処理とを行い、前記2回目の測定処理の結果に基づいて、1回目の測定処理により得られた複数の測定結果候補値から1つの測定結果を選択的に確定する分析処理制御装置と
を備えたことを特徴とする自動分析装置。 A sample container for storing a sample to be analyzed;
A labeled reagent container containing a labeled antigen that forms a specific antigen-antibody bond with a component to be analyzed in the sample or a labeled reagent containing a labeled antibody;
A capture reagent container containing a capture antigen that forms a specific antigen-antibody bond with a component to be analyzed in the sample or a capture reagent containing the capture antibody;
A reaction solid phase reagent container that contains a reaction solid phase reagent including a reaction solid phase that forms a specific antigen-antibody bond with a component to be analyzed in the sample;
A reaction container containing a reaction solid phase for dispensing and reacting the sample and the labeling reagent, the capture reagent, and the solid phase reagent;
A sample dispensing mechanism for dispensing the sample from the sample container to the reaction container;
A reagent dispensing mechanism for dispensing the labeling reagent, the supplementary reagent, and the solid phase reagent from the labeling reagent container , the capture reagent container, and the reaction solid phase reagent container , respectively, to the reaction container;
An analysis mechanism for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of the component to be analyzed based on a physical quantity relating to a label in the reaction container;
A measurement mechanism for performing a measurement process for measuring a physical quantity related to the labeled body in the reaction container;
First capture body addition process for adding the capture reagent to the reaction container containing the sample, first label addition process for adding a labeling reagent to the reaction container, and a reaction solid phase in the reaction container A first solid phase addition treatment for adding a reagent, a first reaction solid phase washing treatment for washing the reaction solid phase in order to remove components other than the components that have formed the antigen-antibody bond including the reaction solid phase, Taking out at least a part of the reaction solid phase from the reaction vessel, and measuring the physical quantity of the labeled body including the reaction solid phase to form a bond, and the measurement process after the first measurement process A second labeling treatment process to the reaction vessel, a second reaction solid phase washing process after the second labeling substance addition process, and a second measurement process after the second reaction solid phase washing process. To the result of the second measurement process Zui, the automatic analyzer characterized by comprising an analysis processor control system for selectively placing one measurement results from a plurality of measurements candidate value obtained by the first measurement process.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014154847A JP6300676B2 (en) | 2014-07-30 | 2014-07-30 | Analysis method and automatic analyzer |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014154847A JP6300676B2 (en) | 2014-07-30 | 2014-07-30 | Analysis method and automatic analyzer |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016031334A JP2016031334A (en) | 2016-03-07 |
| JP2016031334A5 JP2016031334A5 (en) | 2017-08-10 |
| JP6300676B2 true JP6300676B2 (en) | 2018-03-28 |
Family
ID=55441792
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014154847A Active JP6300676B2 (en) | 2014-07-30 | 2014-07-30 | Analysis method and automatic analyzer |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6300676B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018142944A1 (en) * | 2017-02-06 | 2018-08-09 | 株式会社 日立ハイテクノロジーズ | Automated analyzer |
| WO2019049395A1 (en) * | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | アルフレッサファーマ株式会社 | Analysis device and analysis method |
| CN110456073B (en) * | 2019-08-21 | 2023-09-22 | 广东菲鹏生物有限公司 | Method and kit for detecting antibody by double antigen sandwiches |
| CN113049800A (en) * | 2019-12-28 | 2021-06-29 | 深圳市帝迈生物技术有限公司 | Immunoassay analyzer, detection method thereof and computer readable storage medium |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62293163A (en) * | 1986-06-13 | 1987-12-19 | Toshiba Corp | Immunological analysis |
| DE3633497A1 (en) * | 1986-10-02 | 1988-04-14 | Hoechst Ag | IMMUNOMETRIC DETERMINATION PROCEDURE |
| JPH06213893A (en) * | 1993-01-20 | 1994-08-05 | Hitachi Ltd | Prozone check method |
| JPH10282099A (en) * | 1997-04-10 | 1998-10-23 | Hitachi Ltd | Automatic analyzer |
| DE60117699T2 (en) * | 2000-12-26 | 2006-10-19 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Kadoma | ANALYSIS PROCEDURE BY SPECIFIC BINDING AND DEVICE THAT USES THE PROCESS |
| JP3654591B2 (en) * | 2001-09-14 | 2005-06-02 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Specific binding analysis method and specific binding analysis device |
| US20030119203A1 (en) * | 2001-12-24 | 2003-06-26 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Lateral flow assay devices and methods for conducting assays |
| US20080057528A1 (en) * | 2006-08-30 | 2008-03-06 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Detection of hydrogen peroxide released by enzyme-catalyzed oxidation of an analyte |
| JP5553615B2 (en) * | 2007-03-01 | 2014-07-16 | アボット・ラボラトリーズ | Immunoassay showing reduced prozone phenomenon |
| JP2009098080A (en) * | 2007-10-19 | 2009-05-07 | Panasonic Corp | Immunochromatographic measurement apparatus |
| JP2010175355A (en) * | 2009-01-29 | 2010-08-12 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Automatic analyzer |
| JP2013205374A (en) * | 2012-03-29 | 2013-10-07 | Chugoku Electric Power Co Inc:The | Quantitative method of antigen sample |
-
2014
- 2014-07-30 JP JP2014154847A patent/JP6300676B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016031334A (en) | 2016-03-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5364064B2 (en) | Reaction cuvettes for complex automated analyzers of biological samples | |
| CN108254584B (en) | Analysis method and analysis device | |
| JP6300676B2 (en) | Analysis method and automatic analyzer | |
| JP5005511B2 (en) | Immunodiagnostics with reduced non-specific reactions | |
| JP6313977B2 (en) | Sample analyzer and sample analysis method | |
| US20200256868A1 (en) | Immunoassay apparatus | |
| JP6389248B2 (en) | Electrochemiluminescence method and analytical system for detecting analytes in liquid samples | |
| US20170059562A1 (en) | Immune measuring apparatus and immune measuring method | |
| JP5852334B2 (en) | Automatic analysis method | |
| JP2010032215A (en) | Autoanalyzer | |
| JP3661605B2 (en) | Immunoassay apparatus and immunoassay method | |
| JPH11242032A (en) | Sample analysis device and method | |
| CN102301238A (en) | Automatic Analyzer | |
| JP2001091519A (en) | Autoanalyzer | |
| CN107966563A (en) | A kind of antimyeloperoxidase antibody IgG chemiluminescence immunoassay kits and preparation method thereof | |
| JP3739547B2 (en) | Automatic analyzer | |
| JP5286299B2 (en) | Analysis equipment | |
| JP2013152247A (en) | Nonspecific interaction inhibitor and application of the same to diagnostic measuring system | |
| JPH0829424A (en) | Immunological analyzing method and its device | |
| JP7161851B2 (en) | Method for confirming state of immunoassay device and immunoassay device | |
| JP2010164432A (en) | Automatic analysis apparatus and abnormal stop recovery method for the same | |
| JP2014228318A (en) | Automatic analyzer and automatic analysis method | |
| JP2015055552A (en) | Automatic analyzer and analytic method | |
| WO2020166611A1 (en) | Analysis device | |
| WO2023233914A1 (en) | Inspection device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170626 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170626 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20180131 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180213 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20180227 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6300676 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |