JP6278859B2 - Elevator maintenance method and elevator system - Google Patents
Elevator maintenance method and elevator system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6278859B2 JP6278859B2 JP2014146644A JP2014146644A JP6278859B2 JP 6278859 B2 JP6278859 B2 JP 6278859B2 JP 2014146644 A JP2014146644 A JP 2014146644A JP 2014146644 A JP2014146644 A JP 2014146644A JP 6278859 B2 JP6278859 B2 JP 6278859B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- elevator
- car
- sheave
- floor
- floor height
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、エレベーターの保守方法及びエレベーターシステムに係り、特に、階高測定運転を行うエレベーターの保守方法及びエレベーターシステムに関する。 The present invention relates to an elevator maintenance method and an elevator system, and more particularly to an elevator maintenance method and an elevator system that perform floor height measurement operation.
エレベーターは、通常、据付時に各階の位置データを制御装置に取り込む階高測定運転を実施する。この階高測定運転は、かごを最下階から最上階まで運転させて行う。そして、階高測定運転では、巻上機の電動機に設置されたパルス発生器が出力するパルスをカウントし、かごに設置されたかご位置検出器が各階床に設置されるドア開閉可能ゾーンを示す遮へい板を横切ったときに動作して、このかご位置検出器が動作(遮へい板を検出)した際のパルスのカウント値を各階の位置データとして制御装置に記憶する。ここで記憶した各階の位置データに基づき、エレベーターの制御装置は、かごの位置に応じて、加速・減速といった電動機の速度制御を行なう。 The elevator normally performs a floor height measurement operation in which the position data of each floor is taken into the control device at the time of installation. This floor height measurement operation is performed by driving the car from the lowest floor to the top floor. In the floor height measurement operation, the pulse output from the pulse generator installed in the motor of the hoisting machine is counted, and the car position detector installed in the car indicates the door openable / closable zone installed in each floor. It operates when crossing the shielding plate, and the count value of the pulse when this car position detector operates (detects the shielding plate) is stored in the control device as position data of each floor. Based on the stored position data of each floor, the elevator control device performs motor speed control such as acceleration / deceleration according to the position of the car.
巻上機のシーブは、主ロープと常に接触しており経年的に磨耗する。磨耗が進むと、階高測定運転時に記憶した各階の位置データと実際の運転におけるかご位置の関係がずれる。そのため、階高測定運転は、定期的にある期間毎に実施するのが一般的である。例えば、特開平9−221284号公報(特許文献1)には、時間条件が成立したことによりシーブ摩耗確認運転を行わせ、シーブの摩耗値が所定値以内に収まっているか否かをチェックし、シーブの摩耗値が所定値以上である場合に、階床位置のパルスデータを再設定することが記載されている。また、特許文献1のシーブ摩耗確認運転では、エレベーターはいずれかの終端階に帰着し、パルスデータが初期化され、その後、エレベーターは反対側の終端階へ向かって走行する。そして、着床した後、走行開始時から走行終了時までに実際に変化したパルスデータ値(A)、および記憶装置内に格納されている両終端階位置のパルスデータの差(B)を算出する。そして、記憶装置に、これらのデータA、B及び「A−B」を記憶し、シーブ磨耗度を判断している。
The sheave of the hoist is always in contact with the main rope and wears over time. As wear progresses, the relationship between the position data stored at the time of floor height measurement operation and the car position in actual operation shifts. Therefore, the floor height measurement operation is generally performed periodically at certain intervals. For example, in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 9-212284 (Patent Document 1), when the time condition is satisfied, the sheave wear confirmation operation is performed, and it is checked whether or not the sheave wear value is within a predetermined value. It is described that the pulse data of the floor position is reset when the sheave wear value is equal to or greater than a predetermined value. In the sheave wear confirmation operation of
しかしながら、特許文献1におけるデータA、Bには、シーブ磨耗量のほかに、主ロープのクリープ量や終端階検出の検出誤差等が含まれて、必ずしも正確にシーブ磨耗量を検出しているとは言えない。また、特許文献1では、シーブ磨耗確認運転を実施してシーブ磨耗量を算出したうえで階高測定運転の要否を判定する必要があり、通常のサービス運転とは異なる特有の運転をさせなければならない。
However, the data A and B in
本発明の目的は、通常のサービス運転とは異なるエレベーターの運転を実施することなく、階高測定運転の要否を判定することが可能なエレベーターの保守方法及びエレベーターシステムを提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide an elevator maintenance method and an elevator system capable of determining whether or not a floor height measurement operation is necessary without performing an elevator operation different from a normal service operation.
本発明は、定期検査等の際にシーブ摩耗量を実測し、この実測したシーブ摩耗量とエレベーターの制御パラメータに基づき、シーブ摩耗による階と階の間のかご移動距離の偏差を求めて、このかご移動距離の偏差に基づき階高測定運転の要否判断を行うようにしたことを特徴とする。 The present invention measures the sheave wear amount during periodic inspections, etc., and obtains the deviation of the car movement distance between floors due to sheave wear based on the measured sheave wear amount and the control parameters of the elevator. The necessity of floor height measurement operation is determined based on the deviation of the car movement distance.
本発明によれば、通常のサービス運転とは異なるエレベーターの運転を実施することなく、階高測定運転の要否を判定することが可能となる。
上記した以外の課題、構成及び効果は、以下の実施形態の説明により明らかにされる。
According to the present invention, it is possible to determine whether or not a floor height measurement operation is necessary without performing an elevator operation different from a normal service operation.
Problems, configurations, and effects other than those described above will be clarified by the following description of embodiments.
以下、図面を用いて本発明の一実施例を詳細に説明する。
図1は、本発明の一実施例のエレベーターシステムの概略構成を示す図である。図1において、1はかご、2は巻上機の負荷を軽減するための釣合い錘、3はシーブ4に巻掛けられた主ロープであり、主ロープ3の一端にはかご1が、他端には釣合い錘2が結合されている。5はかご1に取り付けられたかご位置検出器であり、各階乗場7とかご1の段差が無い位置関係で各階に設置される遮へい板6に対向するように設けられている。かご位置検出器5は、発信部と受信部からなり、遮へい板6を横切ったときに動作(位置検出)する。8はシーブ4を駆動する電動機、9は電動機8の回転に応じてパルス信号を発するパルス発生器、11はパルス発生器9から出力されるパルス信号やその他各種データを取り込んでエレベーターを制御する制御装置、12は三相交流電源、10は三相交流をエレベーターの動作に適する電力に変換する電力変換装置である。制御装置11から電力変換器10に指令信号を与えることにより、電動機8の回転数を適宜制御する。また、パルス発生器9から出力されるパルス信号を制御装置11に取り込むことで、かご1の動きを制御装置11が適宜監視することが可能である。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of an elevator system according to an embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1, 1 is a cage, 2 is a counterweight for reducing the load of the hoisting machine, 3 is a main rope wound around the
図2は、本発明の実施例による階高測定運転判定を行うブロック構成図である。このブロック構成は、図1に示したエレベーターシステムの概略構成図における制御装置11に含まれるものである。
図2において、9は電動機8の回転に応じてパルス信号を発するパルス発生器、13はアナログ−ディジタル(A/D)変換器、14は階高測定運転を始めとする全体的な動作の制御を行う運転制御用マイコンでありマイクロコンピュータ(CPU)と称す。15はCPU14の動作プログラム、制御パラメータおよびかご位置データなどを格納したプログラム格納用メモリ(ROM)、16は処理したデータを一時的に書き込む処理データ書き込み用メモリ(RAM)、17はエレベーターの運転を操作する操作器、18は外部回路との間でデータ入出力を行う入出力インターフェース、19は共通制御バス、20は外部接続された外部操作器、21は階高測定運転要否判定を含むエレベーターの各種情報を外部に発報する外部発報器である。そして、パルス発生器9はA/D変換器13の入力に接続され、A/D変換器13の出力は共通制御バス19に統合される。同様に、ROM15は共通制御バス19に統合され、RAM16も共通制御バス19に統合される。同じく、CPU14の制御端子も共通制御バス19に統合される。また、入出力インターフェース18には外部操作器20と外部発報器21が接続される。操作器17は、例えば、定期検査などのときにエレベーターの運転を操作するために用いられ(階高測定運転指示を含む)、また、エレベーターを制御するための各種パラメータをROM15に記憶させるなどの際にも用いられる。外部操作器20は、操作器17が設けられていない又は操作できない場合に用いられる。また、外部操作器20は、機械室内はもとより操作しやすい場所であれば任意の場所に接続して構わない。また、例えば、機械室を設けていないエレベーターにおいて特に有効に用いられる。外部発報器21は、階高測定運転要否を初めとしたエレベーターの各種情報を外部に発報する機器であり、例えば、ディスプレイなどである。外部発報器21も外部操作器20と同様に機械室内はもとより操作しやすい場所であれば任意の場所に接続して構わない。また、図示を省略するが、階高測定運転要否を初めとしたエレベーターの各種情報は、入出力インターフェース18に接続した回線を介してサービスセンタ(遠隔監視装置)などのエレベーター設置場所から離れた場所に伝送するようにしても良い。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a floor height measurement operation determination according to the embodiment of the present invention. This block configuration is included in the control device 11 in the schematic configuration diagram of the elevator system shown in FIG.
In FIG. 2, 9 is a pulse generator that generates a pulse signal according to the rotation of the
次に、図3A〜図5を用いて本発明の実施例における階高測定運転の要否判定を行う方法について説明する。
エレベーターは、据付時に各階の位置データを制御装置11内のROM15に記憶させる階高測定運転を実施する。この階高測定運転は操作器17または外部操作器20を作業者が操作することにより実施する。階高測定運転は、かご1を最下階から最上階まで運転させ、その際に電動機8に設置されたパルス発生器9が出力するパルスをCPU14がカウントし、かご位置検出器5が各階の遮へい板6を通過して検出する毎にその際のカウント値をROM15が記憶し、各階の位置データとするものである。ここで記憶した各階の位置データに基づき、CPU14は、かご1の位置に応じて、加速・減速といった電動機8の速度制御を行なう。
Next, a method for determining necessity of floor height measurement operation in the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 3A to 5.
The elevator performs a floor height measurement operation in which position data of each floor is stored in the
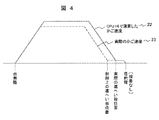
一方で、エレベーターのシーブ4は、主ロープ3と常に接触しており、経年的に磨耗することは周知である。磨耗が進むと、階高測定運転時にROM15に記憶した各階の位置データと実際の運転におけるかご位置の関係がずれる。これを図4により説明する。
図4は、シーブ摩耗した場合の実際のかご速度と運転制御用マイコン上のかご速度の関係を示す図であり、シーブ4の磨耗が進んだ場合の通常運転における、実際のかご速度とCPU14で演算されるかご速度の比較を示す。シーブ4の磨耗が進むと、CPU14で演算されるかご速度22よりも実際のかご速度23は遅い状態となる。図4に示すように、CPU14で演算されるかご位置は、シーブの摩耗が考慮されていないため、実際のかご位置よりも先を行ってしまう。実際のかご速度23はシーブが摩耗しているため、同じ回転数(同じパルス)でもかご速度が遅くなり、また、CPU14が出発階から目的階の遮へい板位置まで所要パルスをカウントしても実際の遮へい板位置まで到達しないことになる。これは、CPU14上、実際の遮へい板位置よりも前に遮へい板が位置していると見てしまい、着床間際の減速位置が早まることを意味する(制御上の遮へい板位置が実際の遮へい板位置よりも前にある)。したがって、減速位置が早まって着床間際の微速走行時間が長くなってしまう。また、実際のかご位置よりもCPU14で算出した仮想のかご位置が先行しており、仮想のかご位置がこれ以上走行禁止の距離に到達した時点で非常停止となり、停止ショックが発生する可能性がある。すなわち、CPU14が出発階から目的階(段差なし)までの所要パルスを超えてカウントした場合、CPU14上、かご1が目的階よりも行き過ぎてしまったと判断して非常停止するような異常を発生してしまう可能性がある。
On the other hand, it is well known that the
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing the relationship between the actual car speed when sheave wear occurs and the car speed on the microcomputer for operation control. In the normal operation when the wear of the
このような事情により、階高測定運転は、定期的にある期間毎に実施するのが一般的である。階高測定運転は、シーブが摩耗していない場合は実施する必要がない。本実施例では、階高測定運転の要否判定を、例えば、1年に1回の定期検査において、シーブ4の磨耗量を実際に測定し、その摩耗量をかご位置のずれ量(かご移動距離の偏差)に換算して、階高測定運転の要否を自動的に判定することができるようにしている。
Under such circumstances, the floor height measurement operation is generally performed periodically at certain intervals. The floor height measurement operation is not necessary when the sheave is not worn. In this embodiment, whether or not the floor height measurement operation is necessary is determined by, for example, actually measuring the wear amount of the
図3A,図3Bは、本発明の実施例において、実測したシーブの摩耗量からかごの移動距離の偏差を算出するための各種パラメータを説明する図である。図3Aは機械室ありのエレベーターを示し、図3Bは機械室なしのエレベーターを図示している。Dはシーブ4の直径(mm)であり、nはシーブ4の回転数(回転/秒)、Vはかご1の昇降速度(m/min)、Kはローピングであり、図3AではローピングKは1(ローピング比1:1)であり、図3BではローピングKは2(ローピング比2:1)である。 3A and 3B are diagrams for explaining various parameters for calculating the deviation of the moving distance of the car from the measured sheave wear amount in the embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3A illustrates an elevator with a machine room, and FIG. 3B illustrates an elevator without a machine room. D is the diameter of the sheave 4 (mm), n is the number of rotations of the sheave 4 (rotation / second), V is the raising / lowering speed of the car 1 (m / min), K is roping, and in FIG. 1 (the roping ratio is 1: 1), and in FIG. 3B, the roping K is 2 (the roping ratio is 2: 1).
図3A,図3Bに示すとおり、シーブ4の直径をD(mm)、ローピングをK、シーブ4の回転数をn(回転/秒)とした場合、かご1の移動距離L(mm)は、(1)式で与えられる。
L=(π×D×n)/K (mm/秒)・・・(1)
そして、シーブ1回転(n=1)あたりのかご1の移動距離L1(mm)は、(2)式で与えられる。
L1=(π×D)/K (mm/回転)・・・(2)
シーブ4の磨耗量をΔD(mm)とした場合、シーブ1回転(n=1)あたりのかご1の移動距離の差分ΔL1(mm)は、(3)式で与えられる。
ΔL1=(π×ΔD)/K (mm/回転)・・・(3)
階と階の間の距離をA(m)とした場合、A(m)運転した場合のシーブ4の回転数N1(回転)は、(4)式で与えられる。
N1=(A×1000)/L1 (回転)・・・(4)
シーブがΔD摩耗した場合の階と階の間のかご1の移動距離の差分(偏差)ΔL2(mm)は、(5)式で与えられる。
ΔL2=ΔL1×N1 (mm)・・・(5)
着床間際の微速走行速度をB(m/min)、微速走行時間をC(秒)とすると、その間のかご1の移動距離L3(mm)は、(6)式で与えられる。
L3=(B×C)×1000/60 (mm)・・・(6)
(5)式と(6)式の関係は、L3>ΔL2でなければならない。これは、階と階の間のかご1の移動距離の差分ΔL2が大きくなり、L3≦ΔL2となった場合、次のような問題が発生するためである。
一つは、上述したように、着床間際の微速走行時間が大きくなり、エレベーターの運転効率が悪くなることである。また、ΔL2だけ実際のかご位置よりもCPU14で算出した仮想のかご位置が先行しており、上述したように、仮想のかご位置がこれ以上走行禁止の距離に到達した時点で非常停止となり、停止ショックが発生する可能性があるためである。したがって、L3はエレベーターの着床運転が異常にならない判定値であり、階高測定運転の要否判定値である。
3A and 3B, when the diameter of the
L = (π × D × n) / K (mm / second) (1)
The travel distance L 1 (mm) of the
L 1 = (π × D) / K (mm / rotation) (2)
When the amount of wear of the
ΔL 1 = (π × ΔD) / K (mm / rotation) (3)
When the distance between the floors is A (m), the rotational speed N 1 (rotation) of the
N 1 = (A × 1000) / L 1 (rotation) (4)
The difference (deviation) ΔL 2 (mm) of the moving distance of the
ΔL 2 = ΔL 1 × N 1 (mm) (5)
If the slow traveling speed just before landing is B (m / min) and the slow traveling time is C (seconds), the moving distance L 3 (mm) of the
L 3 = (B × C) × 1000/60 (mm) (6)
The relation between the expressions (5) and (6) must be L 3 > ΔL 2 . This is because the following problem occurs when the difference ΔL 2 of the movement distance of the
One is that, as described above, the slow traveling time immediately before landing increases, and the operation efficiency of the elevator deteriorates. Further, the virtual car position calculated by the
そして、このような異常動作を未然に防止するために、本実施例では、シーブ4の磨耗量を実際に測定して、シーブ摩耗によるかご1の移動量の偏差が、エレベーターが異常動作に至らない範囲であるか否かを判断して、階高測定運転の実施要否の判定を行い、その判定結果を、外部発報器21を用いて表示するものである。
In order to prevent such an abnormal operation, in this embodiment, the amount of wear of the
なお、(1)式〜(6)式に記載されているパラメータ、すなわち、シーブ4の直径D(mm)、ローピングK、階と階の間の距離A(m)、着床間際の微速走行速度B(m/min)および微速走行時間C(秒)などは、ROM15、外部操作器20または遠隔監視装置に格納されている制御パラメータである。
It should be noted that the parameters described in the equations (1) to (6), that is, the diameter D (mm) of the
作業者は、1年に1回の定期検査時などエレベーターの運転が乗客に提供されない期間で、エレベーターが停止しているタイミングで、シーブ4の直径を実際に測定する。そして、前回の検査時におけるシーブの直径(ROM15に格納されているD)との差分であるシーブ4の磨耗量ΔDが求められる。または、定期検査等でエレベーターが停止している間にシーブ4の磨耗量ΔDを実際に測定する。実際に測定したシーブ4の直径またはシーブ4の摩耗量(シーブの直径は摩耗した状態を反映するものであるので、便宜上、両者を本願明細書ではシーブ摩耗量と称する)は、操作器17または外部操作器20を用いてCPU14に入力する。CPU14では、ROMに格納されたパラメータを用いて、前述の(2)式〜(6)式を自動的に算出し、階高測定運転の要否を外部発報器21に表示して、作業者に知らせるものである。そして、階高測定運転の要の場合に、階高測定運転を実施し、摩耗したシーブに対応した各階の位置データ(かご位置検出器5が各階の遮へい板6を通過して検出する際のカウント値)を更新する。
The worker actually measures the diameter of the
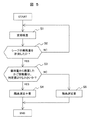
図5に、以上の階高測定運転の要否判定フローを示す。
定期検査時(S1)にエレベーターのシーブ4の磨耗量を実際に測定し(S2)、CPU14で磨耗量から換算したかご移動量が判定値よりも小さいか否か判断する(S3)。判定値以上の場合、階高測定運転要と判断し(S4)、判定値よりも小さければ階高測定運転不要と判断し(S5)、その判定結果を外部発報器21に表示する。
FIG. 5 shows a flow for determining whether or not the above floor height measurement operation is necessary.
During the regular inspection (S1), the amount of wear of the
このようにエレベーターシステムを構成し、保守を行うことにより、階高測定運転の要否を判定するための通常のサービス運転とは異なる特有の運転を実施する必要はない。また、特別な装置を追加することなく、階高測定運転の要否判定を簡易に行うことができる。
また、シーブ磨耗量を直接測定するため、主ロープのクリープ量や終端階検出の検出誤差といった従来技術におけるシーブ磨耗量測定の誤差要因も排除できる。
また、元々エレベーターの運転制御用マイコン、外部操作器または遠隔監視装置に登録されている制御パラメータと実際に測定したシーブ磨耗量から階高測定運転の要否を判定しているので、異なる仕様のエレベーターにおいても汎用的に適用できる。すなわち、ROM15、外部操作器20または遠隔監視装置に各種エレベーターの制御パラメータを記憶させておけば、制御パラメータを切替えることで異なる仕様のエレベーターにおいても汎用的に階高測定運転の要否が判定できる。
By configuring the elevator system in this way and performing maintenance, it is not necessary to perform a specific operation different from a normal service operation for determining whether or not the floor height measurement operation is necessary. In addition, it is possible to easily determine whether or not the floor height measurement operation is necessary without adding a special device.
Further, since the sheave wear amount is directly measured, it is possible to eliminate the error factors of the sheave wear amount measurement in the prior art such as the main rope creep amount and the detection error of the end floor detection.
In addition, the necessity of floor height measurement operation is determined from the control parameters registered in the elevator operation control microcomputer, external controller or remote monitoring device and the actually measured sheave wear amount. It can be applied to elevators for general purposes. In other words, if the control parameters of various elevators are stored in the
なお、本実施例では、現地で測定したシーブ磨耗量を、操作器17または外部操作器20を用いてCPU14にセットし、エレベーターの制御装置11に実装されたROM15に格納した制御パラメータを用いてかご1の移動量の偏差量を算出する処理について説明したが、予め外部操作器20に現地エレベーターのパラメータを格納しておき、現地で測定したシーブ径を外部操作器20のCPUにセットし、外部操作器20側で上記(2)〜(6)式を演算して階高測定運転の要否を判定するようにしても良い。また、制御パラメータを変更することで別のエレベーターに適用するも可能である。
In this embodiment, the sheave wear amount measured in the field is set in the
また、制御パラメータを遠隔監視装置側で格納しておき、測定したシーブ径を、外部操作器20を用いて遠隔監視装置のCPUにセットすることで、遠隔監視装置側で上記(2)〜(6)式を演算して階高測定運転要否の判定を行い、判定結果を遠隔装置側で表示するようにしても良い。この場合、遠隔監視装置側で監視対象の全てのエレベーターの状態を把握することが可能となる。
Further, the control parameters are stored on the remote monitoring device side, and the measured sheave diameter is set in the CPU of the remote monitoring device using the
なお、本発明は上記した実施例に限定されるものではなく、様々な変形例が含まれる。例えば、上記した実施例は本発明を分かりやすく説明するために詳細に説明したものであり、必ずしも説明した全ての構成を備えるものに限定されるものではない。また、ある実施例の構成の一部を他の実施例の構成に置き換えることが可能であり、また、ある実施例の構成に他の実施例の構成を加えることも可能である。また、各実施例の構成の一部について、他の構成の追加、削除、置換をすることが可能である。 In addition, this invention is not limited to an above-described Example, Various modifications are included. For example, the above-described embodiments have been described in detail for easy understanding of the present invention, and are not necessarily limited to those having all the configurations described. Further, a part of the configuration of one embodiment can be replaced with the configuration of another embodiment, and the configuration of another embodiment can be added to the configuration of one embodiment. Further, it is possible to add, delete, and replace other configurations for a part of the configuration of each embodiment.
1・・・かご
2・・・釣合い錘
3・・・主ロープ
4・・・シーブ
5・・・かご位置検出器
6・・・遮へい板
7・・・各階乗場
8・・・電動機
9・・・パルス発生器
10・・・電力変換装置
11・・・エレベーターの制御装置
12・・・三相交流電源
13・・・A/D変換器
14・・・制御用マイコン(CPU)
15・・・プログラム格納用メモリ(ROM)
16・・・データ書き込み用メモリ(RAM)
17・・・操作器
18・・・入出力インターフェース
19・・・共通制御バス
20・・・外部操作器
21・・・外部発報器
DESCRIPTION OF
15 ... Program storage memory (ROM)
16: Data writing memory (RAM)
17 ...
Claims (8)
エレベーターの運転が乗客に提供されない期間でエレベーターが停止している状態で巻上機のシーブのシーブ摩耗量ΔDを実測し、
前記実測したシーブ摩耗量ΔDとエレベーターの制御パラメータに基づき、シーブ摩耗による階と階の間のかご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を求め、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 に基づき階高測定運転の要否判定を行い、
前記エレベーターの制御パラメータは、前記シーブの直径D、ローピングK、階と階との間の距離A、着床間際の微速走行速度B、及び着床間際の微速走行時間Cを含み、
前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を、微速走行時間Cを微速走行速度Bで走行した場合のかご移動距離である階高測定運転の要否判定値L 3 と比較して、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 が前記要否判定値L 3 以上の場合に階高測定運転が要と判定することを特徴とするエレベーターの保守方法。 In the elevator maintenance method that determines whether or not elevator floor height measurement operation is necessary and performs elevator floor height measurement operation,
Measure the sheave wear amount ΔD of the sheave of the hoisting machine in a state where the elevator is stopped in a period when the operation of the elevator is not provided to the passenger,
Wherein based on the control parameters of the actually measured sheave wear amount ΔD and elevator, a deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance between the floor and the floor due to the sheave wear, the car travel distance needed for based floor high measurement operation on the deviation [Delta] L 2 of Make a negative decision,
The control parameters of the elevator include the diameter D of the sheave, the roping K, the distance A between floors, the slow traveling speed B just before landing, and the slow traveling time C just before landing,
The deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance, compared to the necessity determination value L 3 of the floor height measurement operation is car travel distance in the case of traveling the slow-speed travel time C at a very low speed running speed B, the car travel distance Elevator method of maintenance floor height measuring operation if the deviation [Delta] L 2 is equal to or greater than the necessity determination value L 3, characterized in that the determination as needed.
前記実測したシーブ摩耗量ΔDと、前記シーブの直径D、前記ローピングK、前記階と階との間の距離Aに基づいて前記シーブ摩耗による階と階の間のかご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を求めることを特徴とするエレベーターの保守方法。 In the elevator maintenance method according to claim 1 ,
Before Symbol actually measured sheave wear amount [Delta] D, the diameter D of the sheave, the roping K, the floor and the deviation of the car travel distance between the floor and the floor by the sheave wear based on the distance A between the floor [Delta] L 2 Elevator way of maintenance, characterized by asking you to.
前記制御装置は、前記パルス発生器に接続されたアナログ−ディジタル変換器と、運転制御用のマイクロコンピュータと、前記マイクロコンピュータの動作プログラムや制御パラメータおよびかご位置データを格納するメモリと、外部回路との間でデータ入出力を行う入出力インターフェースとを備え、
前記制御装置内のメモリに、エレベーター据付時に、前記制御装置内に設けられたエレベーターの運転を操作する操作器または前記入出力インターフェースに接続されエレベーターの運転を操作する外部操作器を操作して実施した階高測定運転に基づく各階の位置データを記憶するようにしたエレベーターシステムにおいて、
前記操作器または前記外部操作器は、前記制御装置にエレベーターの検査の際に実測したシーブ摩耗量を入力できるように構成され、
前記マイクロコンピュータは、前記実測したシーブ摩耗量ΔDと前記メモリに格納されている制御パラメータに基づき、シーブの摩耗による階と階の間のかご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を求め、階高測定運転の要否を判定するものであり、
前記制御パラメータは、前記シーブの直径D、ローピングK、階と階との間の距離A、着床間際の微速走行速度B、及び着床間際の微速走行時間Cを含み、
前記マイクロコンピュータは、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を、微速走行時間Cを微速走行速度Bで走行した場合のかご移動距離である階高測定運転の要否判定値L 3 と比較して、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 が前記要否判定値L 3 以上の場合に階高測定運転が要と判定することを特徴とするエレベーターシステム。 A car, a counterweight, a main rope to which the car is coupled at one end and the counterweight is coupled to the other end, a sheave around which the main rope is wound, an electric motor for driving the sheave, and the electric motor A pulse generator that generates a pulse signal according to the rotation of the motor, a control device that takes in various data including the pulse signal output from the pulse generator and controls the elevator, and the motor based on a command from the control device An elevator system comprising a power conversion device that supplies power, a shielding plate installed on each floor, and a car position detector that is attached to the car and operates by passing through the shielding plate,
The control device includes an analog-digital converter connected to the pulse generator, a microcomputer for operation control, a memory for storing operation programs, control parameters, and car position data of the microcomputer, an external circuit, With an input / output interface for data input / output between
When the elevator is installed in the memory in the control device, it is operated by operating an operation device that operates the elevator provided in the control device or an external operation device that is connected to the input / output interface and operates the operation of the elevator. In the elevator system that stores the position data of each floor based on the measured floor height measurement operation,
The operating device or the external operating device is configured to be able to input a sheave wear amount actually measured during an elevator inspection to the control device,
The microcomputer obtains a deviation ΔL 2 of the car movement distance between floors due to sheave wear based on the actually measured sheave wear amount ΔD and the control parameter stored in the memory, and performs the floor height measurement operation. To determine whether it is necessary ,
The control parameters include the diameter D of the sheave, the roping K, the distance A between floors, the slow running speed B just before landing, and the slow running time C just before landing,
The microcomputer deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance, compared to the necessity determination value L 3 of the floor height measurement operation is car travel distance in the case of traveling the slow-speed travel time C at a very low speed running speed B, Elevator system deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance is equal to or floor height measurement operation determines that essential in the case of more than the necessity determination value L 3.
前記入出力インターフェースに前記階高測定運転の要否判定を外部に発報する外部発報器が接続可能になっていることを特徴とするエレベーターシステム。 In the elevator system according to claim 3 ,
An elevator system capable of connecting to the input / output interface an external alarm device that issues a determination as to whether or not the floor height measurement operation is necessary.
前記制御装置は、前記パルス発生器に接続されたアナログ−ディジタル変換器と、運転制御用のマイクロコンピュータと、前記マイクロコンピュータの動作プログラムや制御パラメータおよびかご位置データを格納するメモリと、外部回路との間でデータ入出力を行う入出力インターフェースとを備え、
前記制御装置内のメモリに、エレベーター据付時に、前記制御装置内に設けられたエレベーターの運転を操作する操作器または前記入出力インターフェースに接続されエレベーターの運転を操作する外部操作器を操作して実施した階高測定運転に基づく各階の位置データを記憶するようにしたエレベーターシステムにおいて、
前記外部操作器は、エレベーターの制御パラメータを格納しており、エレベーターの検査の際に実測したシーブの摩耗量ΔDと前記格納されている制御パラメータに基づき、シーブの摩耗による階と階の間のかご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を求め、階高測定運転の要否を判定するものであり、
前記制御パラメータは、前記シーブの直径D、ローピングK、階と階との間の距離A、着床間際の微速走行速度B、及び着床間際の微速走行時間Cを含み、
前記外部操作器は、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を、微速走行時間Cを微速走行速度Bで走行した場合のかご移動距離である階高測定運転の要否判定値L 3 と比較して、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 が前記要否判定値L 3 以上の場合に階高測定運転が要と判定することを特徴とするエレベーターシステム。 A car, a counterweight, a main rope to which the car is coupled at one end and the counterweight is coupled to the other end, a sheave around which the main rope is wound, an electric motor for driving the sheave, and the electric motor A pulse generator that generates a pulse signal according to the rotation of the motor, a control device that takes in various data including the pulse signal output from the pulse generator and controls the elevator, and the motor based on a command from the control device An elevator system comprising a power conversion device that supplies power, a shielding plate installed on each floor, and a car position detector that is attached to the car and operates by passing through the shielding plate,
The control device includes an analog-digital converter connected to the pulse generator, a microcomputer for operation control, a memory for storing operation programs, control parameters, and car position data of the microcomputer, an external circuit, With an input / output interface for data input / output between
When the elevator is installed in the memory in the control device, it is operated by operating an operation device that operates the elevator provided in the control device or an external operation device that is connected to the input / output interface and operates the operation of the elevator. In the elevator system that stores the position data of each floor based on the measured floor height measurement operation,
The external controller stores elevator control parameters. Based on the sheave wear amount ΔD measured at the time of inspection of the elevator and the stored control parameters, the level between floors due to sheave wear is determined. The deviation ΔL 2 of the car movement distance is obtained to determine whether or not the floor height measurement operation is necessary .
The control parameters include the diameter D of the sheave, the roping K, the distance A between floors, the slow running speed B just before landing, and the slow running time C just before landing,
The external operating device is a deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance, compared to the necessity determination value L 3 of the floor height measurement operation is car travel distance in the case of traveling the slow-speed travel time C at a very low speed running speed B Elevator system floor height measuring operation if the deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance is equal to or greater than the necessity determination value L 3 is equal to or determined as needed.
前記外部操作器は、複数機種のエレベーターの制御パラメータを格納しており、制御パラメータを切換えることにより複数機種のエレベーターの階高測定運転の要否を判定することができるように構成されていることを特徴とするエレベーターシステム。 In the elevator system according to claim 5 ,
The external controller stores control parameters for multiple types of elevators, and is configured to be able to determine the necessity of floor height measurement operation for multiple types of elevators by switching the control parameters. Elevator system characterized by
前記制御装置は、前記パルス発生器に接続されたアナログ−ディジタル変換器と、運転制御用のマイクロコンピュータと、前記マイクロコンピュータの動作プログラムや制御パラメータおよびかご位置データを格納するメモリと、外部回路との間でデータ入出力を行う入出力インターフェースとを備え、
前記制御装置内のメモリに、エレベーター据付時に、前記制御装置内に設けられたエレベーターの運転を操作する操作器または前記入出力インターフェースに接続されエレベーターの運転を操作する外部操作器を操作して実施した階高測定運転に基づく各階の位置データを記憶するようにしたエレベーターシステムにおいて、
前記入出力インターフェースには遠隔監視装置が接続され、
前記遠隔監視装置は、エレベーターの制御パラメータを格納しており、エレベーターの検査の際に実測したシーブの摩耗量ΔDと前記格納されている制御パラメータに基づき、シーブの摩耗による階と階の間のかご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を求め、階高測定運転の要否を判定するものであり、
前記制御パラメータは、前記シーブの直径D、ローピングK、階と階との間の距離A、着床間際の微速走行速度B、及び着床間際の微速走行時間Cを含み、
前記遠隔監視装置は、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 を、微速走行時間Cを微速走行速度Bで走行した場合のかご移動距離である階高測定運転の要否判定値L 3 と比較して、前記かご移動距離の偏差ΔL 2 が前記要否判定値L 3 以上の場合に階高測定運転が要と判定することを特徴とするエレベーターシステム。 A car, a counterweight, a main rope to which the car is coupled at one end and the counterweight is coupled to the other end, a sheave around which the main rope is wound, an electric motor for driving the sheave, and the electric motor A pulse generator that generates a pulse signal according to the rotation of the motor, a control device that takes in various data including the pulse signal output from the pulse generator and controls the elevator, and the motor based on a command from the control device An elevator system comprising a power conversion device that supplies power, a shielding plate installed on each floor, and a car position detector that is attached to the car and operates by passing through the shielding plate,
The control device includes an analog-digital converter connected to the pulse generator, a microcomputer for operation control, a memory for storing operation programs, control parameters, and car position data of the microcomputer, an external circuit, With an input / output interface for data input / output between
When the elevator is installed in the memory in the control device, it is operated by operating an operation device that operates the elevator provided in the control device or an external operation device that is connected to the input / output interface and operates the operation of the elevator. In the elevator system that stores the position data of each floor based on the measured floor height measurement operation,
A remote monitoring device is connected to the input / output interface,
The remote monitoring device stores elevator control parameters. Based on the sheave wear amount ΔD actually measured during the elevator inspection and the stored control parameters, the distance between floors due to sheave wear is determined. The deviation ΔL 2 of the car movement distance is obtained to determine whether or not the floor height measurement operation is necessary .
The control parameters include the diameter D of the sheave, the roping K, the distance A between floors, the slow running speed B just before landing, and the slow running time C just before landing,
The remote monitoring device, the deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance, compared to the necessity determination value L 3 of the floor height measurement operation is car travel distance in the case of traveling the slow-speed travel time C at a very low speed running speed B Elevator system floor height measuring operation if the deviation [Delta] L 2 of the car travel distance is equal to or greater than the necessity determination value L 3 is equal to or determined as needed.
前記遠隔監視装置は、複数機種のエレベーターの制御パラメータを格納しており、制御パラメータを切換えることにより複数機種のエレベーターの階高測定運転の要否を判定することができるように構成されていることを特徴とするエレベーターシステム。 In the elevator system according to claim 7 ,
The remote monitoring device stores control parameters for multiple types of elevators, and is configured to be able to determine the necessity of floor height measurement operation for multiple types of elevators by switching the control parameters. Elevator system characterized by
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014146644A JP6278859B2 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2014-07-17 | Elevator maintenance method and elevator system |
| CN201510423714.8A CN105314487B (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2015-07-17 | The maintenance method of elevator and elevator device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014146644A JP6278859B2 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2014-07-17 | Elevator maintenance method and elevator system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016023015A JP2016023015A (en) | 2016-02-08 |
| JP2016023015A5 JP2016023015A5 (en) | 2017-01-12 |
| JP6278859B2 true JP6278859B2 (en) | 2018-02-14 |
Family
ID=55242946
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014146644A Active JP6278859B2 (en) | 2014-07-17 | 2014-07-17 | Elevator maintenance method and elevator system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6278859B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN105314487B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113830631B (en) * | 2021-10-13 | 2023-04-11 | 无锡新马赫动力控制有限公司 | Novel operation control system and control method of intelligent elevator |
| CN114715752B (en) * | 2022-06-08 | 2022-08-23 | 凯尔菱电(山东)电梯有限公司 | Abnormity detection method and system for elevator |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63277185A (en) * | 1987-05-07 | 1988-11-15 | 株式会社東芝 | Controller for elevator |
| JPH01235801A (en) * | 1988-03-17 | 1989-09-20 | Toshiba Corp | Measuring instrument for rope groove of elevator sheave |
| JPH09221284A (en) * | 1996-02-19 | 1997-08-26 | Toshiba Corp | Elevator control device |
| JPH10197237A (en) * | 1997-01-09 | 1998-07-31 | Hitachi Building Syst Co Ltd | Device for measuring groove wear-amount of sheave |
| JPH1137703A (en) * | 1997-07-22 | 1999-02-12 | Hitachi Building Syst Co Ltd | Method for measuring rope groove of elevator sheave |
| JP4828041B2 (en) * | 2001-05-15 | 2011-11-30 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Measuring method and jig for measuring the groove of elevator sheave |
| JP2012025556A (en) * | 2010-07-26 | 2012-02-09 | Toshiba Elevator Co Ltd | Elevator |
| JP5602613B2 (en) * | 2010-12-27 | 2014-10-08 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Elevator equipment |
| CN102992128B (en) * | 2011-09-15 | 2015-07-22 | 日立电梯(中国)有限公司 | Validation method for absolute floor of elevator |
| CN103204416B (en) * | 2012-01-12 | 2015-06-24 | 上海三菱电梯有限公司 | Wear detection device for elevator driving rope sheave |
| CN103204417B (en) * | 2012-01-12 | 2015-08-19 | 上海三菱电梯有限公司 | Elevator drive rope sheave wear detector and method of inspection |
-
2014
- 2014-07-17 JP JP2014146644A patent/JP6278859B2/en active Active
-
2015
- 2015-07-17 CN CN201510423714.8A patent/CN105314487B/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105314487A (en) | 2016-02-10 |
| JP2016023015A (en) | 2016-02-08 |
| CN105314487B (en) | 2017-12-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2918536B1 (en) | Condition monitoring of vertical transport equipment | |
| JP6049902B2 (en) | Elevator diagnostic equipment | |
| EP3366626B1 (en) | Elevator safety system and method of monitoring an elevator system | |
| JP2011042480A (en) | Elevator device | |
| KR102065518B1 (en) | Elevator device | |
| JP5704700B2 (en) | Elevator control device and sensor | |
| SG192362A1 (en) | Electric safety elevator | |
| JP2009215057A (en) | Compulsory deceleration control system of elevator | |
| WO2016190281A1 (en) | Elevator device, control method therefor, and remote determination device for elevator state | |
| JP5947094B2 (en) | elevator | |
| JP6304443B2 (en) | Elevator diagnostic equipment | |
| CN101674996A (en) | Elevator | |
| JP6278859B2 (en) | Elevator maintenance method and elevator system | |
| JP2013001474A (en) | Safety operation system and safety operation method of elevator | |
| JPH11199153A (en) | Diagnostic device for elevator | |
| JP2011143982A (en) | Device and method for controlling brake of elevator | |
| JP2013049568A (en) | Brake holding torque adjusting device for hoisting machine and brake holding torque adjusting method for the same | |
| JP2008290845A (en) | Elevator system | |
| WO2018016061A1 (en) | Elevator | |
| JP6280838B2 (en) | Moving device, hoisting machine, crane device, and wheel life estimation method used therefor | |
| JP4486104B2 (en) | Elevator diagnostic operation apparatus and diagnostic operation method | |
| JP2014108834A (en) | Rope strand rupture detection device for elevator, and method of detecting rope strand rupture | |
| JP2013241247A (en) | Elevator sheave diagnosis device | |
| JP2007204263A (en) | Main rope deterioration diagnostic system of elevator | |
| JP2014162621A (en) | Main rope inspection device of elevator |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20161124 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20161124 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170928 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20171003 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20171113 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180109 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20180116 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6278859 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |