JP6217612B2 - Vehicle vibration control device - Google Patents
Vehicle vibration control device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6217612B2 JP6217612B2 JP2014244298A JP2014244298A JP6217612B2 JP 6217612 B2 JP6217612 B2 JP 6217612B2 JP 2014244298 A JP2014244298 A JP 2014244298A JP 2014244298 A JP2014244298 A JP 2014244298A JP 6217612 B2 JP6217612 B2 JP 6217612B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- motor
- torque
- power
- damper
- spring constant
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 36
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/62—Hybrid vehicles
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/72—Electric energy management in electromobility
Landscapes
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (AREA)
- Control Of Driving Devices And Active Controlling Of Vehicle (AREA)
- Electric Propulsion And Braking For Vehicles (AREA)
Description
この発明は、車両の振動を低減する制御装置に関し、特にハイブリッド車の走行中に振動を低減するように駆動力源のトルクを制御する装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a control device that reduces vibration of a vehicle, and more particularly to a device that controls torque of a driving force source so as to reduce vibration during traveling of a hybrid vehicle.
車両が走行する場合には、不可避的に振動が生じる。特許文献1には、エンジンを備えたハイブリッド車(HV車)において、エンジンが要因になる振動を低減するように構成された装置が記載されている。この特許文献1に記載された装置は、エンジンの出力軸にモータがクラッチを介して連結され、これらエンジンとモータとが出力するトルクを、変速機を介して駆動輪に伝達するように構成されたハイブリッド車の異常振動を防止するように構成された装置であり、そのクラッチには剛性変曲点のあるダンパが備えられている。そして、駆動系の共振点では、エンジンのトルクとモータとのトルクを合算した総駆動トルクが変化しないようにそれぞれのトルクを変化させて、ダンパの変曲点を回避するように構成されている。
When the vehicle travels, vibration inevitably occurs.
ハイブリッド車が走行している状態では、タイヤの回転アンバランスが強制力となって振動が生じることがある。特許文献1に記載された装置は、エンジンのトルク変動が強制力となる振動を低減もしくは防止するように構成されている装置であるから、ハイブリッド車がエンジンを停止してモータの駆動力で走行している状態ではハイブリッド車の共振を推定し、また共振を抑制もしくは防止することができない。また、特許文献1に記載された装置は、ダンパの剛性変曲点を回避できるとしても、タイヤの回転アンバランスに起因する共振の振動数を予め知り得ないので、特許文献1に記載された発明では、このような不特定の周波数での共振を抑制もしくは防止することは困難である。
When the hybrid vehicle is running, vibrations may occur due to the rotational unbalance of the tires acting as a force. The device described in
この発明は上記の技術的課題に着目してなされたものであって、ハイブリッド車がモータ走行している状態での共振あるいは過大な振動を抑制もしくは防止することのできる車両の振動制御装置を提供することを目的とするものである。 The present invention has been made paying attention to the above technical problem, and provides a vehicle vibration control device capable of suppressing or preventing resonance or excessive vibration when the hybrid vehicle is running on a motor. It is intended to do.
上記の目的を達成するために、この発明は、エンジンが出力した動力を発電機能のある第1モータ側と駆動輪側とに分割する動力分割機構と、前記エンジンの出力軸の所定方向の回転を止めるブレーキ機構と、前記ブレーキ機構と前記動力分割機構との間に設けられ捻り角度によってばね定数が変化するダンパと、前記駆動輪に伝達されるトルクを加減する発電機能のある第2モータとを備え、前記出力軸の前記所定方向の回転を前記ブレーキ機構によって止めた状態で前記第1モータおよび前記第2モータの動力で走行可能な車両の振動制御装置において、前記第1モータおよび前記第2モータのうち少なくとも第2モータの動力で走行している状態で前記第1モータの出力トルクに基づいて前記ダンパのばね定数を推定し、推定された前記ばね定数で走行している状態での共振点を含む所定の周波数域である共振帯に入る振動を生じる車速か否かを判断し、前記共振帯に入る振動を生じる車速であることが判断された場合に前記ダンパに掛かる前記第1モータのトルクを変更して前記ばね定数を変化させるように構成されていることを特徴とするものである。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a power split mechanism that splits power output from an engine into a first motor side having a power generation function and a drive wheel side, and rotation of the output shaft of the engine in a predetermined direction. A brake mechanism that stops the engine, a damper that is provided between the brake mechanism and the power split mechanism and has a spring constant that changes depending on a twist angle, and a second motor that has a power generation function that adjusts torque transmitted to the drive wheels A vibration control apparatus for a vehicle capable of running with the power of the first motor and the second motor in a state where the rotation of the output shaft in the predetermined direction is stopped by the brake mechanism. The spring constant of the damper is estimated based on the output torque of the first motor in a state where the motor is running with the power of at least the second motor of the two motors. It is determined whether or not the vehicle speed causes a vibration that enters a resonance band that is a predetermined frequency range including a resonance point in a state of traveling at a spring constant, and is determined to be a vehicle speed that causes a vibration that enters the resonance band. In this case, the spring constant is changed by changing the torque of the first motor applied to the damper.
この発明においては、共振帯に入る振動が生じることが判断されると、ダンパのばね定数が変更される。共振帯はダンパのばね定数に応じた周波数域であるから、ばね定数が変更されると共振帯が変化する。その結果、その時点の車速で走行しても過大な振動が生じることを抑制もしくは防止することができる。 In the present invention, when it is determined that vibration that enters the resonance band occurs, the spring constant of the damper is changed. Since the resonance band is a frequency range corresponding to the spring constant of the damper, the resonance band changes when the spring constant is changed. As a result, it is possible to suppress or prevent the occurrence of excessive vibration even when traveling at the vehicle speed at that time.
この発明は、エンジンと発電機能のあるモータとを動力源とし、かつモータの動力のみによって走行するEV走行を選択できるハイブリッド車の振動を制御する装置である。そのハイブリッド車の駆動系統の一例を簡単に説明すると、図4はいわゆる2モータタイプのハイブリッド車を模式的に示している。エンジン1が出力した動力を第1モータ(MG1)2側と駆動輪3側とに分割する動力分割機構4が設けられている。動力分割機構4は、要は、3つの回転要素を備えた差動機構によって構成され、より具体的には、遊星歯車機構によって構成され、例えばサンギヤに第1モータが連結され、キャリヤにエンジン1のトルクが入力され、リングギヤから駆動輪3に向けてトルクを出力するように構成することができる。
The present invention is an apparatus for controlling vibration of a hybrid vehicle that uses an engine and a motor having a power generation function as a power source and can select EV traveling that travels only by the power of the motor. An example of the drive system of the hybrid vehicle will be briefly described. FIG. 4 schematically shows a so-called two-motor type hybrid vehicle. A power split mechanism 4 is provided that splits the power output from the
EV走行を可能にし、またEV走行時にエンジン1を引き摺ることによる動力損失を低減するために、エンジン1の出力軸(クランクシャフト)5の回転を止めるブレーキ機構6が設けられている。動力分割機構4が遊星歯車機構などの差動機構によって構成されている場合、第1モータ2が走行のためのトルクを出力すると、エンジン1の出力軸5には負回転方向(エンジン1の本来の回転方向とは反対方向)のトルクが作用する。このトルクをブレーキ機構6によって受けて出力軸5の負方向の回転を止めるように構成されている。したがって、ブレーキ機構6は摩擦ブレーキやドグクラッチなどの正逆両方向の回転を止める構成であってもよく、あるいは一方向クラッチであってもよい。
A brake mechanism 6 that stops the rotation of the output shaft (crankshaft) 5 of the
ブレーキ機構6と前記動力分割機構4との間に、エンジントルクの振動を抑制するダンパ7が設けられている。ダンパ7は、例えば前述した特許文献1に記載されているようなバネダンパであって、駆動側のプレートと従動側のプレートとの間にコイルバネが配置され、これらのプレートにトルクが作用して各プレートが相対的にねじれることによりコイルバネが圧縮されて振動を低減するように構成されている。また、そのコイルバネとして長さやばね定数が異なる複数種類のコイルバネが設けられており、したがってダンパ7は捻り角とトルクとの関係すなわちねじれ特性が一定でなく変化するように構成されている。その例を図5に示してあり、ここに示す例は、ばね定数が3段階(K1 <K2 <K3 )に変化する例である。なお、ここで説明している具体例では、前述したように、第1モータ2が出力する走行のためのトルクが前記出力軸5もしくはブレーキ機構6に掛かるから、第1モータ2が出力したトルクは、ダンパ7に対して捻り角を増大させるトルクもしくは減少させるトルクとして作用する。したがって、第1モータ2のトルクによってダンパ7の捻り角を変化させてダンパ7のねじれ特性を変更することができる。図5には第1モータ2のトルクによる捻り角の変化の方向を併記してある。なお、図5において、第1モータ2のトルク(MG1トルク)の負領域とは、第1モータ2が前記負回転方向に回転して出力するトルクの領域であり、正領域とは、第1モータ2が正回転方向に回転して出力するトルクの領域である。
A
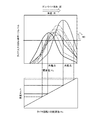
上記のダンパ7には、ブレーキ機構6によってエンジン1の出力軸5の回転を止めている状態では、駆動輪(タイヤ)3側からの振動が入力される。その振動は駆動輪3の回転アンバランスや路面の凹凸などに起因する振動である。ダンパ7は、上述したようにねじれ特性が変化するので、ダンパ7あるいは駆動系統の全体の共振点がダンパ7のばね定数に応じて変化する。図6は、駆動輪3側から入力される振動の周波数をタイヤ回転数周波数で表し、ばね定数を多様に変化させた場合における、そのタイヤ回転数周波数と、駆動輪3側から所定のトルクを入力した場合のサージレベル(振動加速度)との関係を示した図である。なお、ばね定数は捻り角の単位角度当たりのトルクに置き換えることができる。図6に示すように、上述したダンパ7を使用した駆動系統では、ダンパ7のばね定数が大きくなるのに従って共振点が高周波数側に変化する。
When the rotation of the output shaft 5 of the
図4に示すハイブリッド車は、更に、第2モータ8を備えている。第2モータ8は、前述した第1モータ2と同様に発電機能のあるモータであって、上記の動力分割機構4から駆動輪3にトルクを伝達する経路の所定箇所に連結されている。すなわち、第2モータ8は駆動輪3に伝達されるトルクを増加あるいは減少させるように構成されている。前述した第1モータ2およびこの第2モータ8とは、図示しないインバータを介してバッテリなどの蓄電装置に接続されている。これら各モータ2,8は相互に電力を授受できるように構成されており、第1モータ2で発電した電力を第2モータ8に供給して第2モータ8がモータとして機能し、また反対に第2モータ8で発電した電力を第1モータ2に供給して第1モータ2をモータとして機能させるように構成されている。また、各モータ2,8に蓄電装置から給電してこれらがモータとして機能し、EV走行するように構成されている。なお、図4における符号9は終減速機となっているデファレンシャルギヤを示す。
The hybrid vehicle shown in FIG. 4 further includes a
上述したブレーキ機構6の係合や解放の制御、各モータ2,8のトルクなどの動作状態を電気的に制御する電子制御装置(ECU)10が設けられている。ECU10はマイクロコンピュータを主体にして構成され、入力されたデータや予め格納されているデータなどを使用して、予め記憶しているプログラムに従って演算を行い、演算の結果を制御指令信号としてブレーキ機構6や各モータ2,8もしくは前記インバータに出力するように構成されている。その入力信号は、EV走行の実行や不実行の状態、第1モータ2の出力トルク、アクセル開度もしくはスロットル開度、アクセルペダルやブレーキペダルの操作量、車速、駆動輪3の回転数などである。
An electronic control unit (ECU) 10 is provided for electrically controlling the operation state such as the engagement and release of the brake mechanism 6 and the torques of the
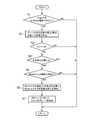
EV走行状態では、エンジン1が停止しているので、ダンパ7は駆動輪3側から伝達される振動(トルク変動)を吸収するように動作する。したがって、そのばね定数(ねじれ特性)に応じて共振点が決まる。この発明の一例である振動制御装置は、このようなEV走行時の振動を低減し、あるいは共振などによる過度な振動を抑制するように、ダンパ7のばね定数(ねじれ特性)を制御するように構成されている。その制御は、具体的には上記のECU10によって行われる。その制御の一例を図1にフローチャートで示してある。図1に示すルーチンは、ハイブリッド車が走行している際に繰り返し実行され、先ず、EV走行中か否かが判断される(ステップS1)。EV走行は、二つのモータ2,8が走行のための動力を出力している状態、もしくは第2モータ8が走行のための動力を出力している状態であり、したがってこれらのモータ2,8の制御状態に基づいて判断することができる。またEV走行は車速やアクセル開度などに応じて設定されるから、ステップS1の判断は車速やアクセル開度に基づいて行うことができる。また、ステップS1では、前記出力軸5の回転をブレーキ機構6によって止めることができるか否かの判断に置き換えてもよく、あるいはそれら二つの判断を同時に行ってもよい。
In the EV traveling state, since the
ステップS1で否定的に判断された場合には、特に制御を行うことなくリターンする。これに対してステップS1で肯定的に判断された場合には、その時点で設定されるばね定数、および共振が生じる車速が求められる(ステップS2)。EV走行しているので、振動は駆動輪3側から伝達されるトルクの変動が要因となる。その場合、ダンパ7は第1モータ2のトルクによってねじれるから、前述した図5および図6に示す関係があることにより、ダンパ7の捻り角およびそれに伴うばね定数は第1モータ2のトルクに基づいて推定あるいは求めることができる。そして、推定もしくは算出されたばね定数での共振点は図6に示す関係に基づいて求めることができる。また一方、駆動輪3が回転することに伴う回転1次周波数と車速との関係は、使用している駆動輪3の外径などに基づいて予め求めておくことができる。その例を図2に示してある。なお、図2には前述した図6と同様の図を併記してある。したがって、ばね定数に基づく共振点が求められると、共振が生じる車速や、サージレベル(すなわち振動)が設計上予め定めた許容値を超える(NGとなる)共振点を含む所定の周波数範囲である共振帯の車速を図2に基づいて求めることができる。
If a negative determination is made in step S1, the process returns without performing any particular control. On the other hand, if a positive determination is made in step S1, the spring constant set at that time and the vehicle speed at which resonance occurs are obtained (step S2). Since the vehicle is traveling in the EV mode, the vibration is caused by the fluctuation of the torque transmitted from the
このように求められた共振帯の下限車速Aと上限車速Bとを定め、現時点の車速Vがそれらの車速範囲に入っているか否か(A<V<Bか否か)が判断される(ステップS3)。この判断は、現時点の車速で共振が生じるか否か、あるいは振動が許容範囲を超えるか否かの判断に相当する。このステップS3で否定的に判断された場合には、振動低減のための制御を新たに行う必要がないので、リターンする。 The lower limit vehicle speed A and the upper limit vehicle speed B of the resonance band thus determined are determined, and it is determined whether or not the current vehicle speed V is in the vehicle speed range (whether A <V <B). Step S3). This determination corresponds to a determination as to whether resonance occurs at the current vehicle speed or whether the vibration exceeds an allowable range. If a negative determination is made in step S3, there is no need to newly perform control for vibration reduction, and the routine returns.
これに対してステップS3で肯定的に判断された場合には、車速の変化が速いか否かの判断を行う。具体的には、スロットル開度が全開でないか否か(WOTでないか否か)、アクセル開度の変化が緩やかか否か、ブレーキ操作量の変化もしくは操作速度が緩やかか否かなどが判断される(ステップS4)。これらの判断は、しきい値を実験やシミュレーションなどによって予め定めておき、検出された操作量などとしきい値とを比較して行えばよい。車速の変化が設計上想定されている以上であることによりステップS4で否定的に判断された場合には、実際の車速が上記の共振帯の車速を速やかに通過し、振動低減のための制御を新たに行う必要がないと考えられるので、特に制御を行うことなくリターンする。 On the other hand, when a positive determination is made in step S3, it is determined whether or not the vehicle speed changes rapidly. Specifically, it is determined whether the throttle opening is not fully open (whether it is not WOT), whether the change in accelerator opening is gradual, whether the brake operation amount is changed, or whether the operation speed is gradual. (Step S4). These determinations may be made by predetermining a threshold value through experiments, simulations, or the like, and comparing the detected operation amount with the threshold value. If a negative change is determined in step S4 because the change in the vehicle speed is more than assumed in the design, the actual vehicle speed quickly passes the vehicle speed in the resonance band, and control for vibration reduction is performed. Therefore, it is considered that there is no need to perform a new operation.
ステップS4で肯定的に判断された場合には、ダンパ7のばね定数を変更するために第1モータ2のトルクを制御するとした場合に、そのトルク制御に伴う駆動トルクの変動を抑制するように第2モータ8のトルクを変化させることができるか否かが判断される(ステップS5)。前述した動力分割機構4が遊星歯車機構によって構成されている場合、ダンパ7の正回転方向のばね定数を増大させるように第1モータ2のトルクを負回転方向に増大させると、エンジン1の出力軸5がブレーキ機構6によって固定されていることにより、動力分割機構4から出力されるトルクが増大する。また反対に、ダンパ7の負回転方向のばね定数を増大させるように第1モータ2のトルクを正回転方向に増大させると、動力分割機構4から出力されるトルクが低下する。このような駆動トルクの変動を抑制するために第2モータ8のトルクが増大もしくは減少させられる。その場合、蓄電装置から電力を出力し、あるいは出力量を減少させ、もしくは充電を行うことになる。これに対して、蓄電装置の充電残量(SOC)によっては放電あるいは充電が制限され、それに伴って第2モータ8のトルク制御が制限される。ステップS5ではこのような第2モータ8についての制御が制限されているか否かが判断される。したがって、第2モータ8のトルク制御を行う余力がないことによりステップS5で否定的に判断された場合には、特に制御を行うことなくリターンする。
If the determination in step S4 is affirmative, when the torque of the
一方、第2モータ8のトルク制御が可能であってステップS5で肯定的に判断された場合には、ダンパ7のばね定数を変更し、それに伴って共振点あるいは共振帯を高周波数側もしくは低周波数側に変更する(ステップS6)。例えば、第1モータ2が負回転方向のトルクを出力し、かつ第2モータ8が正回転方向のトルクを出力するいわゆる両駆動モードでEV走行し、その車速がある程度高車速であれば、第1モータ2の出力トルクが大きいことにより共振点が高車速側になっている。この状態で実際の車速が共振帯の車速に入らないように共振点を低下させるとすれば、第1モータ2の出力トルク(負回転方向のトルク)を低下させる。その状態を図3に示してある。前述したように、第1モータ2のトルクを正回転方向に増大するように(負回転方向のトルクを低減するように)変化させると、動力分割機構4から駆動輪3に向けて出力されるトルクが低下する。このようなトルクの低下を補うように第2モータ8の出力トルクを増大させる。その制御量は、第1モータ2の電流値や動力分割機構4におけるギヤ比などに基づいて求めることができる。
On the other hand, if the torque control of the
共振点を変化させるための第1モータ2のトルクを低下させることがあり、その場合、第1モータ2のトルクに応じてトルクの低下勾配(トルクレート)を設定する(ステップS7)。具体的には、第1モータ2のトルクの絶対値を「0」程度の予め定めた小さいトルクに低下させる場合には、トルクレートを予め定めた小さい値に設定し、これとは反対に第1モータ2のトルクを前記予め定めた小さいトルクにまで低下させない場合には、トルクレートの低下制御を実行しない。このようなトルクレートの制御は、いわゆるガタ音を防止するためである。すなわち、第1モータ2のトルクを低下させることにより、ダンパ7においてコイルスプリングを挟み付ける力が小さくなり、その挟み付ける力よりも、正負に変化する加振力が大きくなると、急激にねじれが解放されてガタ音が発生する可能性がある。このような事態を回避もしくは抑制するために、トルクレートを緩やかにする。
The torque of the
以上、この発明の具体例を説明したが、この発明は上述した具体例に限定されないのであって、この発明では、特許請求の範囲に記載されている構成を逸脱しない種々の構成を採用してよい。 Although specific examples of the present invention have been described above, the present invention is not limited to the specific examples described above, and the present invention adopts various configurations that do not deviate from the configurations described in the claims. Good.
1…エンジン(ENG)、 2…第1モータ(MG1)、 3…駆動輪、 4…動力分割機構、 5…出力軸(クランクシャフト)、 6…ブレーキ機構、 7…ダンパ、 8…第2モータ、 9…終減速機、 10…電子制御装置(ECU)。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
前記第1モータおよび前記第2モータの動力で走行している状態で前記第1モータの出力トルクに基づいて前記ダンパのばね定数を推定し、
推定された前記ばね定数で走行している状態での共振点を含む所定の周波数域である共振帯に入る振動を生じる車速か否かを判断し、
前記共振帯に入る振動を生じる車速であることが判断された場合に前記ダンパに掛かる前記第1モータのトルクを変更して前記ばね定数を変化させる
ように構成されていることを特徴とする車両の振動制御装置。 A power split mechanism that splits the power output by the engine into a first motor side having a power generation function and a drive wheel side; a brake mechanism that stops rotation of the output shaft of the engine in a predetermined direction; the brake mechanism and the power split And a second motor having a power generation function that adjusts the torque transmitted to the drive wheel, and that rotates the output shaft in the predetermined direction. In a vehicle vibration control device capable of traveling with the power of at least the second motor of the first motor and the second motor while stopped by the brake mechanism,
Estimating the spring constant of the damper based on the output torque of the first motor in a state of running with the power of the first motor and the second motor;
Determining whether the vehicle speed causes a vibration to enter a resonance band that is a predetermined frequency range including a resonance point in a state of traveling with the estimated spring constant;
The vehicle is configured to change the spring constant by changing the torque of the first motor applied to the damper when it is determined that the vehicle speed causes vibrations entering the resonance band. Vibration control device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014244298A JP6217612B2 (en) | 2014-12-02 | 2014-12-02 | Vehicle vibration control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014244298A JP6217612B2 (en) | 2014-12-02 | 2014-12-02 | Vehicle vibration control device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016107673A JP2016107673A (en) | 2016-06-20 |
| JP6217612B2 true JP6217612B2 (en) | 2017-10-25 |
Family
ID=56122894
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014244298A Expired - Fee Related JP6217612B2 (en) | 2014-12-02 | 2014-12-02 | Vehicle vibration control device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6217612B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6492045B2 (en) * | 2016-11-07 | 2019-03-27 | 株式会社Subaru | Vehicle control device |
| JP6536543B2 (en) * | 2016-11-17 | 2019-07-03 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| JP6900908B2 (en) | 2018-01-09 | 2021-07-07 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| JP6911775B2 (en) * | 2018-01-12 | 2021-07-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| JP7027920B2 (en) | 2018-02-01 | 2022-03-02 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Hybrid vehicle control device |
| WO2023070309A1 (en) * | 2021-10-26 | 2023-05-04 | 罗伯特•博世有限公司 | Detection method and detection apparatus for detecting unevenness of road surface, and program product |
| CN118107556B (en) * | 2024-04-28 | 2024-10-18 | 中国第一汽车股份有限公司 | Control method, device and computer equipment of hybrid power system |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4949918B2 (en) * | 2007-04-23 | 2012-06-13 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Vehicle and control method thereof |
| US7996145B2 (en) * | 2007-05-03 | 2011-08-09 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | Method and apparatus to control engine restart for a hybrid powertrain system |
| JP5109929B2 (en) * | 2008-10-23 | 2012-12-26 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Internal combustion engine start control device |
| JP2012035692A (en) * | 2010-08-05 | 2012-02-23 | Toyota Motor Corp | Engine start control device for vehicle |
| CN103987605A (en) * | 2011-12-12 | 2014-08-13 | 丰田自动车株式会社 | Drive control device for hybrid vehicle |
| KR101394703B1 (en) * | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-15 | 현대자동차주식회사 | Method for prevention abnormal vibration of hybrid vehicle |
| JP5413547B1 (en) * | 2013-02-06 | 2014-02-12 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Control device for hybrid vehicle |
-
2014
- 2014-12-02 JP JP2014244298A patent/JP6217612B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2016107673A (en) | 2016-06-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6217612B2 (en) | Vehicle vibration control device | |
| KR101628545B1 (en) | The regenerative braking control method of the hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5472904B2 (en) | Hybrid vehicle backlash vibration reduction method | |
| US20120083950A1 (en) | Enhanced stability control for an electric powertrain | |
| WO2011118254A1 (en) | Hybrid vehicle control device | |
| KR102139512B1 (en) | Hybrid vehicle control method and control device | |
| CN104105629A (en) | Control device of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP7006532B2 (en) | Torque control device | |
| KR101588751B1 (en) | Control method for clutch of hybrid electirc vehicle | |
| JP5834927B2 (en) | Vehicle drive device | |
| JP7027920B2 (en) | Hybrid vehicle control device | |
| CN108082173A (en) | Control device for vehicle and the control method for vehicle | |
| JP6114631B2 (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| JP5772921B2 (en) | Vehicle shift control device and shift control method | |
| JP5476732B2 (en) | Vehicle shift control device and shift control method | |
| US9643597B2 (en) | Control apparatus for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5115323B2 (en) | Vehicle sprung mass damping control device | |
| WO2015019399A1 (en) | Vehicle vibration suppression control device | |
| JP5867109B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP6658170B2 (en) | Engine stop control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP7188368B2 (en) | Vehicle driving force control device | |
| JP2012091584A (en) | Hybrid vehicle control device | |
| JP6493016B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5853800B2 (en) | Motor generator for vehicle | |
| KR101013870B1 (en) | Transmission reverse rotation prevention method of hybrid vehicle using clutch slip |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170113 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170817 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170829 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170911 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6217612 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |