JP6198419B2 - Ink jet recording apparatus and ink amount detection method - Google Patents
Ink jet recording apparatus and ink amount detection method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6198419B2 JP6198419B2 JP2013052431A JP2013052431A JP6198419B2 JP 6198419 B2 JP6198419 B2 JP 6198419B2 JP 2013052431 A JP2013052431 A JP 2013052431A JP 2013052431 A JP2013052431 A JP 2013052431A JP 6198419 B2 JP6198419 B2 JP 6198419B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- ink
- tank
- interval
- sub
- recording
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Ink Jet (AREA)
Description
本発明は記録装置及びインク量検知方法に関する。本発明は、特に、例えば、インクを貯留するインクタンクとサブタンクとを備えたインクジェット記録装置及びそのサブタンクのインク量検知方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a recording apparatus and an ink amount detection method. The present invention particularly relates to, for example, an ink jet recording apparatus including an ink tank for storing ink and a sub tank, and an ink amount detection method for the sub tank.
近年、A1やA0といった大きなサイズの記録媒体への記録にインクジェット記録装置が用いられてきている。その用途は黒単色の線画から写真調の画像の記録に至るまで幅広い。中でも写真調の画像のような比較的高いデューティの画像を記録する場合、一枚の記録には多量のインクを消費する。その結果、インクタンクの交換は高い頻度になってしまう。インクタンク交換頻度が増加すると、記録動作中断に伴う時間のロスが増加するばかりでなく、記録動作中断による時間差によって生じる色ムラといった画像品質の劣化につながってしまうことがある。 In recent years, an ink jet recording apparatus has been used for recording on a recording medium having a large size such as A1 or A0. Its applications range from black line drawings to photographic image recording. In particular, when a relatively high duty image such as a photographic image is recorded, a large amount of ink is consumed for recording one sheet. As a result, ink tanks are frequently replaced. When the ink tank replacement frequency increases, not only the time loss due to the interruption of the recording operation increases, but also the image quality such as color unevenness caused by the time difference due to the interruption of the recording operation may be caused.
そこで、記録動作中断を伴うインクタンク交換を避けるために、例えば、特許文献1に開示されているように、インクタンクとは別のサブタンクを搭載するインクジェット記録装置が提案されている。特許文献1によるとインクタンクからサブタンクにインクを移動させ(以下、サブタンク充填)、サブタンクより記録ヘッドにインクを供給し記録動作を行っている。このような構成により、インクタンク内のインクを使いきった場合であってもサブタンク内のインクにより記録を継続することが可能となる。
Therefore, in order to avoid ink tank replacement accompanying interruption of the recording operation, for example, as disclosed in
サブタンク内のインクを消費して記録している間にインクタンクの交換を行えば、記録動作を中断することがないため、時間のロスや画像品質が劣化することを防ぐことができる。さらに、引用文献1によれば、サブタンクと記録ヘッドの間に流路を遮断する弁を兼ねた容積変化部材(ダイヤフラム弁)を設け、サブタンク内のインクの消費後には、サブタンク内を負圧にすることでインクタンクからサブタンクにインクを供給している。
If the ink tank is replaced while recording is performed while consuming ink in the sub tank, the recording operation is not interrupted, so that time loss and image quality deterioration can be prevented. Further, according to the cited
しかしながら、特許文献1に開示されたのとは別の構成のサブタンクを用いようとすると、インクタンクからサブタンクへのインク供給中にサブタンク内のインク量が正確に測定できない問題がある。具体的には、センサがサブタンク内がインクで満たされたと検知しても、実際にはサブタンク内がインクで満たされていないということが生じる。
However, if an attempt is made to use a sub-tank having a configuration different from that disclosed in
つまり、特許文献1に開示された構成では、サブタンクの選択に自由度がなく、その形状や構成が異なる構成のサブタンクを用いることができないと問題がある。
In other words, the configuration disclosed in
本発明は上記従来例に鑑みてなされたもので、別の構成のサブタンクを用いる場合にもインク供給中にサブタンク内のインク量を正確に測定可能なインクジェット記録装置及びインク量検知方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described conventional example, and provides an ink jet recording apparatus and an ink amount detecting method capable of accurately measuring the ink amount in the sub tank even when the sub tank having another configuration is used. For the purpose.
上記目的を達成するために本発明のインクジェット記録装置は、次のような構成からなる。 In order to achieve the above object, an ink jet recording apparatus of the present invention has the following configuration.
即ち、インクを貯留するインクタンクと、前記インクタンクから供給されたインクを貯留するサブタンクと、前記サブタンクから供給されたインクを吐出し記録媒体に記録を行う記録ヘッドと、前記サブタンクと前記記録ヘッドとの間に配され、容積を変化させることにより前記インクタンクから前記サブタンクに第1の間隔で所定量のインクを供給する供給動作を行う供給手段と、前記サブタンクの上部に設けられた一対の電極と、前記一対の電極に定電流を流した際の電圧値或いは定電圧を印加した際に流れる電流値を検知する検知動作を第2の間隔で行う検知手段と、を備え、前記検知手段の検知結果に基づいて前記供給動作を停止し、前記第1の間隔より前記第2の間隔が長く、前記第2の間隔は前記第1の間隔の整数倍とは異なることを特徴とする。 That is, the i Nkutanku for storing ink, a sub tank for storing ink supplied from the ink tank, a recording head for recording on a recording medium by discharging an ink supplied from the sub tank, before Symbol sub-tank and the recording disposed between the head, a supply means for supplying operation of supplying a predetermined amount of ink in the first interval to the sub tank from the ink tank by changing the volume pair which is provided in an upper portion of the sub-tank comprising of the electrode, and a detection means for performing the second distance detection operation for detecting a current flowing upon application of a voltage value or the constant voltage of which was obtained by applying a constant current to the pair of electrodes, the detection the supply operation is stopped on the basis of the means of detection result, wherein the second interval than the first interval is long, the second distance is different from an integral multiple of the first interval And wherein the door.
また本発明を別の側面から見れば、インクを貯留するインクタンクと、前記インクタンクから供給されたインクを貯留するサブタンクと、前記サブタンクから供給されたインクを吐出し記録媒体に記録を行う記録ヘッドと、前記サブタンクと前記記録ヘッドとの間に配され、容積を変化させることにより前記インクタンクから前記サブタンクに第1の間隔で所定量のインクを供給する供給動作を行う供給手段と、前記サブタンクの上部に設けられた一対の電極とを備えたインクジェット記録装置におけるインク量検知方法であって、前記一対の電極に定電流を流した際の電圧値或いは定電圧を印加した際に流れる電流値を検知する検知動作を第2の間隔で行い、前記検知動作の検知結果に基づいて前記供給動作を停止し、前記第1の間隔より前記第2の間隔が長く、前記第2の間隔は前記第1の間隔の整数倍とは異なることを特徴とするインク量検知方法を備える。 Also, look at the present invention from another aspect, the recording performed and Lee Nkutanku for storing ink, a sub tank for storing ink supplied from the ink tank, a recording medium by discharging an ink supplied from the sub tank a head, disposed between said recording head and the sub tank, a supply means for supplying operation of supplying a predetermined amount of ink in the first interval to the sub tank from the ink tank by changing the volume, the an ink amount detecting method in the ink jet recording apparatus having a pair of electrodes provided on the upper portion of the sub tank, a current flowing upon application of a voltage value or the constant voltage of which was obtained by applying a constant current to said pair of electrodes performs a detection operation for detecting the value in the second interval, the feed operation is stopped based on the detection result of the previous SL detection operation, than the first distance Serial second distance is long, the second interval comprises an ink amount detecting method of being different from an integral multiple of the first interval.
従って本発明によれば、サブタンクへのインク供給とサブタンクのインク量検知の実行タイミングを異ならせることで正確にサブタンク内のインク量を測定することができるという効果がある。 Therefore, according to the present invention, there is an effect that the ink amount in the sub tank can be accurately measured by changing the execution timing of the ink supply to the sub tank and the ink amount detection of the sub tank.
以下添付図面を参照して本発明の好適な実施例について、さらに具体的かつ詳細に説明する。なお、既に説明した部分には同一符号を付し重複説明を省略する。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described more specifically and in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. In addition, the same code | symbol is attached | subjected to the already demonstrated part and duplication description is abbreviate | omitted.
なお、この明細書において、「記録」(「プリント」という場合もある)とは、文字、図形等有意の情報を形成する場合のみならず、有意無意を問わない。また人間が視覚で知覚し得るように顕在化したものであるか否かを問わず、広く記録媒体上に画像、模様、パターン等を形成する、または媒体の加工を行う場合も表すものとする。 In this specification, “recording” (sometimes referred to as “printing”) is not limited to the case of forming significant information such as characters and graphics, but may be significant. It also represents the case where an image, a pattern, a pattern, etc. are widely formed on a recording medium, or the medium is processed, regardless of whether it is manifested so that humans can perceive it visually. .
また、「記録媒体」とは、一般的な記録装置で用いられる紙のみならず、広く、布、プラスチック・フィルム、金属板、ガラス、セラミックス、木材、皮革等、インクを受容可能なものも表すものとする。 “Recording medium” refers not only to paper used in general recording apparatuses but also widely to cloth, plastic film, metal plate, glass, ceramics, wood, leather, and the like that can accept ink. Shall.
さらに、「インク」(「液体」と言う場合もある)とは、上記「記録(プリント)」の定義と同様広く解釈されるべきものである。従って、記録媒体上に付与されることによって、画像、模様、パターン等の形成または記録媒体の加工、或いはインクの処理(例えば記録媒体に付与されるインク中の色剤の凝固または不溶化)に供され得る液体を表すものとする。 Further, “ink” (sometimes referred to as “liquid”) should be interpreted widely as in the definition of “recording (printing)”. Therefore, by being applied on the recording medium, it is used for formation of images, patterns, patterns, etc., processing of the recording medium, or ink processing (for example, solidification or insolubilization of the colorant in the ink applied to the recording medium). It shall represent a liquid that can be made.
またさらに、「ノズル」とは、特にことわらない限り吐出口ないしこれに連通する液路およびインク吐出に利用されるエネルギーを発生する素子を総括して言うものとする。 Furthermore, unless otherwise specified, the “nozzle” collectively refers to an ejection port or a liquid channel communicating with the ejection port and an element that generates energy used for ink ejection.
以下に用いる記録ヘッド用基板(ヘッド基板)とは、シリコン半導体からなる単なる基体を指し示すものではなく、各素子や配線等が設けられた構成を差し示すものである。 The recording head substrate (head substrate) used below does not indicate a simple substrate made of a silicon semiconductor but indicates a configuration in which each element, wiring, and the like are provided.
さらに、基板上とは、単に素子基板の上を指し示すだけでなく、素子基板の表面、表面近傍の素子基板内部側をも示すものである。また、本発明でいう「作り込み(built-in)」とは、別体の各素子を単に基体表面上に別体として配置することを指し示している言葉ではなく、各素子を半導体回路の製造工程等によって素子板上に一体的に形成、製造することを示すものである。 Further, the term “on the substrate” means not only the element substrate but also the surface of the element substrate and the inside of the element substrate near the surface. In addition, the term “built-in” as used in the present invention is not a term indicating that each individual element is simply arranged separately on the surface of the substrate, but each element is manufactured in a semiconductor circuit. It shows that it is integrally formed and manufactured on an element plate by a process or the like.
次に、インクジェット記録装置の実施例について説明する。この記録装置は、ロール状に巻かれた連続シート(記録媒体)を使用し、そのシートにB0やA0サイズの画像を記録する大判プリントを行う装置である。なお、使用する記録媒体にカット紙を用いても良いことは言うまでもない。 Next, examples of the ink jet recording apparatus will be described. This recording apparatus uses a continuous sheet (recording medium) wound in a roll shape, and performs large format printing in which an image of B0 or A0 size is recorded on the sheet. Needless to say, a cut sheet may be used as the recording medium to be used.
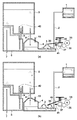
図1は、本発明の代表的な実施例であるインクジェット記録装置の構成概略を示す部分破断斜視図である。 FIG. 1 is a partially broken perspective view showing a schematic configuration of an ink jet recording apparatus which is a typical embodiment of the present invention.
図1に示すように、インクジェット記録装置(以下、記録装置)50は互いに向き合った2つの脚部55の上端部に跨るように固定されている。キャリッジ60には、記録ヘッド1が搭載されている。記録時は搬送ロールホルダユニット52にセットされた記録媒体を記録位置まで給紙し、キャリッジ60がキャリッジモータ(不図示)及びベルト62より矢印Bで示す方向(主走査方向)に往復移動しながら、記録ヘッド1の各ノズルからインク滴が吐出される。キャリッジ60が記録媒体の一端まで移動すると、搬送ローラ51が所定量だけ記録媒体を矢印Aで示す方向(副走査方向)へ搬送する。このように記録動作と搬送動作とを交互に繰り返すことにより記録媒体全体に画像を形成する。画像形成後は、カッタ(不図示)によって記録媒体をカットし、カットされた記録媒体はスタッカ53に積載されていく。
As shown in FIG. 1, an ink jet recording apparatus (hereinafter referred to as a recording apparatus) 50 is fixed so as to straddle the upper ends of two
インク供給ユニット63には、黒、シアン、マゼンタ、イエロなどといったインク色ごとに分かれた(装置に脱着可能な)インクタンク5が備えられており、インクタンク5は供給チューブ2に接続されている。また、供給チューブ2はキャリッジ60の往復運動の際に暴れることのないように、チューブガイド61によって束ねられている。
The
記録ヘッド1の記録媒体に対向した面には主走査方向と略直交した方向に複数のノズル列(不図示)を持ち、ノズル列単位で供給チューブ2と接続している。
A surface of the
さらに回復ユニット70が主走査方向に記録媒体範囲外で、かつ記録ヘッド1のノズル面に対向する位置に設けられている。回復ユニット70は、必要に応じて記録ヘッド1のノズル面からインク又は空気を吸い出すノズルのクリーニングや記録ヘッド内部に溜まった空気を強制的に吸い出す吸引動作を実行する。
Further, a
記録装置50の右側には操作パネル54が設けられており、インクタンク5内のインクが空になった際に警告メッセージを表示してユーザにその旨を通知し、インクタンク5の交換を促すことができる。
An
図2に図1に示した記録装置のインク供給系の構成を示す図である。前述のように、記録装置50は複数の色のインクを使用するがインク供給系の構成は、複数のインクにわたって共通な構成なので、ここでは一色のインクの供給系について示す。
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of an ink supply system of the recording apparatus illustrated in FIG. 1. As described above, the
図2に示すように、記録装置に脱着可能な容積一定のインクタンク5は底部に2か所のジョイント部を有しており、そのジョイント部が装置の第1の中空管8及び第2の中空管9と連結している。第1の中空管8及び第2の中空管9は中空の金属針で構成されている。インクタンク5内の第2の中空管9の周囲にインクタンク底面から立ち壁42が形成されている。この構造により、第1の中空管と第2の中空管との間に微小電流(定電流)を流した場合、立ち壁42よりも貯留したインク残量の高さが低くなっていると、インクを介した電流の流れが妨げられ、2つの中空管の間の抵抗値が増加する。これによって、インクタンク5内のインク切れが近いことを検出可能にしている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the fixed-
また、インクタンク5が記録装置から外された場合にも、2つの中空管の間の抵抗値が増加し、新たなインクタンク5と交換された後には、2つの中空管の間の抵抗値が低下するので、このような抵抗値の変化からもインクタンクの脱着を検出可能である。
Further, when the
第2の中空管9は大気連通室6に連通しており、大気連通室6内の大気連通路7を介して、インクタンク5は大気と連通する。また、インクタンク5の底面45と容積一定のサブタンク4の天面46とを第1の中空管8で連通し、サブタンク4と記録ヘッド1は供給チューブ2を介して連通している。サブタンク4は天面の略全域を垂直方向下側にいくほど断面積が広がる傾斜面49で構成し、最も高い位置(即ち、天面46)で第1の中空管8と接続している。そして、サブタンク4内の上部には、金属によって構成された電極部(中実管)10が設けてある。第1の中空管8と電極部10との間に微小電流(定電流)を流した際、これらの間の抵抗値により、サブタンク内のインクが満タンかどうかを検知している。
The second
サブタンク4からのインク流出口は側面47の最も低い位置48に設けている。サブタンク4と供給チューブ2との間には供給流路を開放/閉塞することが可能な容積変化可能な可撓性部材によって構成された開閉弁3が設けてある。開閉弁3は圧縮バネ38で常時開放方向に付勢されており、カム37によってレバー39が押され、中心軸40を中心に回転することで閉塞する。カム37はフォトセンサ41によって位置出し可能に構成しており、駆動源であるDCモータ35によりギア36を介して回転制御している。なお、ここでは開閉弁3がサブタンク4に具え付けられている構成を示しているが、サブタンク4と記録ヘッド1との間のインク供給チューブ2に開閉弁3を設けてもよい。
The ink outlet from the sub tank 4 is provided at the
図3は図1に示す記録装置の制御構成を示すブロック図である。 FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing a control configuration of the recording apparatus shown in FIG.
図3に示すように、記録装置50には装置全体を制御するCPU11、ユーザが操作するキーや情報を表示する操作パネルを含むユーザインタフェース12、制御ソフトウエアを内蔵するROM13を備える。さらに、記録装置50は制御ソフトウエアを動作させる際に一時的に使用するRAM14、制御信号やセンサ信号や記録信号などを入出力するI/Oポート15、図1で言及したような駆動部16、インクタンクの残量を検出するインク残量センサ17を備える。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
インク残量センサ17は、上述した第1の中空管8と第2の中空管9との間に微小電流を流したときの、これらの間の抵抗値を監視し、インク切れが近いことを検出する。インクタンク5の脱着を検出するインクタンク装着センサ18は、インクタンク5に備えられたEEPROM20から読込値で、その脱着を判断している。また、インクタンク装着センサ18を介してEEPROM20の内容は書き換えられる。
The ink remaining
図4はインクタンク5内のインクを使い切り、サブタンク4内のインクを使用して記録動作を実行している(ストップレス記録)状況でのインク供給系の状態を示す図である。なお、図4において、図2を参照して既に説明した構成要素には同じ参照番号を付し、その説明は省略する。
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a state of the ink supply system in a state where the ink in the
図5はストップレス記録の制御シーケンスを示す図である。 FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a control sequence of stopless recording.
記録装置50はインクタンク5内のインクを使い切った際は、サブタンク4内のインクを用いて画像形成を継続可能であり、サブタンク4内のインクを消費すると、大気連通路7からインクタンク5を経由して空気がサブタンク4に導入される。図4に示すように、導入された空気はサブタンク4の上方に溜まる。このような状態でされたにサブタンク4内のインクをさらに消費すると、サブタンク4内のインク面が低下し、第1の中空管8と電極部10とがインクを介して電気的に接続されなくなる。その結果、これらの間に電流が流れにくくなる。
When the
従って、ステップS201では、第1の中空管8と電極部10との間に微小電流を流し、これらの間の電圧値を測定することで、サブタンク4内のインクが消費されている(即ち、サブタンクが満タンではない)ことを検知することができる。ここで、サブタンク4内のインクを消費されていると判断されることは、インクタンク5が空になったことを示しており、処理はステップS202に進み、ユーザにインクタンク5が空であることを操作パネルを通じて通知し、インクタンクの交換を促す。
Accordingly, in step S201, the ink in the sub tank 4 is consumed by passing a minute current between the first
インクタンク5が交換されるまでの間、サブタンク4内のインク使用許容量までは画像形成を許容し、続行する。この実施例では、その許容量は約11mlであり、記録装置50では記録可能な最大サイズの用紙に100%の濃度で記録した場合に最低1枚は記録可能なインク量に相当する。インク使用許容量を使用しきったかどうかは次の方法で判定する。即ち、サブタンク4内のインク使用許容量を予め記録装置に記憶させておき、記録ヘッド1からのインク液滴吐出数をカウントすることでインク消費量を計算する。次に、その消費量と許容量を比較して、消費量が許容量以下であれば、記録を許容し、許容量を超えた場合は、画像形成を停止させて、インクタンク5が空であることを通知しながらインクタンク5の交換を待つ。ここでは、サブタンク4のインク残量をその検知手段を設けずに、インクの吐出量に換算する方法を用いたが、サブタンク4内にインク残量検知手段を設けても良い。
Until the
ステップS203では、サブタンク4内のインク使用許容量を消費しきる前にインクタンクを交換したかどうかを調べ、交換がなされたと判断した場合、処理はステップS204に進み、画像形成中であるかどうかを調べる。そして、画像形成中であると判断された場合には、その画像形成の終了を待ち合わせる。そして、画像形成の停止を確認して、処理はステップS205に進み、次の画像形成の開始前にサブタンク4内にインクを充填する。なお、サブタンクへのインク充填制御の詳細については後述する。充填後に次の画像形成を開始する。このようにして、画像形成の間(例えば、あるページとその次のページの記録の間など)に、サブタンクへのインク充填を行う。 In step S203, it is checked whether or not the ink tank has been replaced before the ink use allowable amount in the sub tank 4 has been consumed. If it is determined that the ink tank has been replaced, the process proceeds to step S204 to determine whether or not image formation is in progress. Investigate. If it is determined that the image is being formed, the end of the image formation is awaited. After confirming that image formation has stopped, the process proceeds to step S205, and ink is filled into the sub tank 4 before the start of the next image formation. Details of the ink filling control to the sub tank will be described later. After the filling, the next image formation is started. In this way, ink is filled into the sub tank during image formation (for example, during recording of a certain page and the next page).
これに対して、ステップS203において、インクタンク5の交換がまだなされていないと判断された場合、処理はステップS207に進み、さらにサブタンク4内のインク使用許容量を消化しきったかどうかを調べる。ここで、その許容量を消化したと判断された場合、処理はステップS207に進み、直ちに記録動作を停止する。これは、記録を停止しないと、サブタンク4からインク供給流路を経由して記録ヘッド1へ空気が混入し、結果、インク吐出不良が発生し、記録画像の品位が低下するためである。そして、ステップS208では、インクタンク5の交換を促すメッセージを表示する。
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S203 that the
図6はインクタンク5を交換後のインク供給系の状態を示す図である。
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a state of the ink supply system after the
図6において、(a)は開閉弁3を閉塞から開放にした状態を示し、(b)は開閉弁3を開放から閉塞にした状態を示している。この実施例では、開閉弁3の容積をV1、第1の中空管の容積をV2とした際に、V1>V2の関係が成り立つようにしている。この実施例では、V1=約0.45ml、V2=約0.09mlである。従って、図6(a)に示すように、開閉弁3を閉塞状態から開放状態にすると、容積V1―V2(約0.36ml)分のインクをインクタンク5からサブタンク4へ引き込むことができる(インクの流入)。この容積をV3(=V1−V2)とする。その際、インクタンク5へは大気連通室6から空気が容積V3分引き込まれる(空気の流出)。
6A shows a state where the on-off
その後、図6(b)に示すように、DCモータ35によってカム37を回転させてレバー39により開閉弁3を押圧させ、開放状態から閉塞状態にすることで、サブタンク4内の空気が容積V3分だけサブタンク4からインクタンク5へ押し出される。この際、インクタンク5から容積V3分のインクが大気連通室6へ押し出される。この時、開閉弁3から記録ヘッド1までのインク供給流路の圧損が開閉弁3からインクタンク5までの圧損に比べてはるかに大きいため、インクは記録ヘッド1側には殆ど流れない。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 6 (b), the
その後、再び図6(a)に示すように、DCモータ35によってカム37を回転させて、圧縮バネ38でレバー39を付勢すると、開閉弁3は閉塞状態から開放状態になる。その際、大気連通室6からインクをV3分インクタンク5へ引き込むと当時にインクタンク5からサブタンク4へV3分インクを引き込む。その後、再びDCモータ35を回転させて図6(b)に示すように開閉弁3を開放状態から閉塞状態にする。即ち、1回の開閉弁3の開閉動作により所定量のインクがインクタンク5からサブタンク4に充填される。
Thereafter, as shown in FIG. 6A again, when the
図7はストップレス記録制御中に必要となるサブタンク充填制御の詳細な処理シーケンスを示すフローチャートである。 FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing a detailed processing sequence of sub tank filling control required during stopless recording control.
この実施例では、ステップS301において、開閉弁3の開閉動作(充填用)を繰り返し制御する。そして、ステップS302ではその開閉動作毎にサブタンク4がインクで満たされたかどうかを確認する。これは、上述のように第1の中空管8とサブタンク4に設けた電極部10との間に微小電流を流し、その結果得られる、第1の中空管8と電極部10との間の電圧値を測定することによって確認することができる。
In this embodiment, in step S301, the opening / closing operation (for filling) of the opening /
ここで、インクで満たされていないと判断された場合、処理はステップS303に進み、インクタンク5内にインクがあるかどうかを確認する。ここで、インクがあると判断された場合は、処理はステップS301に戻り、開閉弁3の開閉動作(充填用)を繰り返す。これに対して、インクタンク5内にインクがないと判断された場合、処理はステップS304に進み、インクタンク5の交換を促し、ステップS305においてインクタンクの交換完了を待ち合わせる。そして、インクタンク5の交換が確認されたなら、処理はステップS301に戻り、再び開閉弁3の開閉動作(充填用)を繰り返す。
If it is determined that the ink is not filled, the process advances to step S303 to check whether there is ink in the
なお、インクタンク5内にインクがあるかどうかは、第1の中空管8と第2の中空管9との間に微小電流を流した際にこれらの間の電圧値を測定することによってインク切れが近いことを判断する。また、インク切れが近く、残量がゼロにちかい(ニアエンド)場合の判断は、インクタンク5のEEPROM20に格納されている残量の情報に基づいて行う。即ち、開閉弁3の一回の開閉動作によりV3の容量(約0.36ml)をインクタンク5からサブタンク4へ導入可能なので、EEPROM20に格納されている残量を示す情報から計算することで判断する。
Whether ink is present in the
さて、ステップS302により、サブタンク4がインクで満たされたことが確認されると、処理は終了する。 When it is confirmed in step S302 that the sub tank 4 is filled with ink, the process ends.
なお、この実施例では、インク供給のためにインク溜まりとしても機能する開閉弁を用いるとしたが、そのインク供給手段と開閉弁を分けてもよい。その場合は、そのインク供給手段をサブタンクと開閉弁の間に設けた方が望ましい。また、インク供給手段は蛇腹形態でもダイアフラム形態でも良く、容積変化可能な可撓性部材で形成された物でよい。 In this embodiment, an on-off valve that also functions as an ink reservoir for supplying ink is used. However, the ink supply means and the on-off valve may be separated. In that case, it is desirable to provide the ink supply means between the sub tank and the on-off valve. The ink supply means may be in the form of a bellows or a diaphragm, and may be formed of a flexible member whose volume can be changed.
さて、図7に示すサブタンク充填制御において、この実施例では、サブタンク4にインクを充填する開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔に対して、サブタンク4内のインク量を検知する検知間隔は別に制御する。即ち、サブタンク充填制御が開始されると開閉弁3の開閉動作とサブタンク4内のインク量検知をそれぞれの間隔で連続的に実行する。
In the sub-tank filling control shown in FIG. 7, in this embodiment, the detection interval for detecting the ink amount in the sub-tank 4 is controlled separately from the execution interval of the opening / closing operation of the on-off
図8はサブタンク内のインク量検知の測定電圧とサブタンク充填時間との関係を示す図である。 FIG. 8 is a diagram showing the relationship between the measurement voltage for detecting the ink amount in the sub tank and the sub tank filling time.
図8において、(a)はサブタンク充填制御を実行した際に、サブタンク4内のインク量検知の測定結果(中空管8と電極部(中実管)10の間に微弱な電流を流した際の電圧値の測定結果)の時間変化を示している。図8(a)において、検知電圧の時間変化は3つの領域に分けられる。即ち、領域1はサブタンク充填動作開始からの電圧が高い値から電圧が下がり始めるまでの領域、領域2は電圧が変動しながら低下している領域、領域3は電圧が低下して安定している領域である。
In FIG. 8, (a) shows the measurement result of the ink amount detection in the sub tank 4 (a weak current was passed between the
図9は、図8(a)に示す3つの領域それぞれに対応するサブタンク4内のインク量の変化を示す図である。各領域におけるサブタンク4内のインクの状態は、次のように説明できる。 FIG. 9 is a diagram showing a change in the ink amount in the sub tank 4 corresponding to each of the three regions shown in FIG. The state of the ink in the sub tank 4 in each region can be explained as follows.
即ち、領域1は図9(a)に示すように中実管10の高さまでインクが供給されていない状態である。領域2は図9(b)に示すように中実管10の高さまでインクが供給されて開閉弁3の開閉動作の度にインクが矢印のように流れて中空管8と中実管10との間の電圧値が変動している状態である。そして、領域3は図9(b)に示すようにサブタンク4内がインクで満たされている状態である。
That is, the
このように図2に示すようなインク流路構成の場合、サブタンク充填中の中空管8と中実管10との間の電圧値の挙動から、サブタンク4内がインクで満たされた領域3を検出する条件が設定される。
Thus, in the case of the ink flow path configuration as shown in FIG. 2, the
図10は設定条件を説明する図である。即ち、図10に示すように、条件1として領域1での検知電圧が所定の電圧以下(この実施例では2.1V以下)の値であることを設定する。また、条件2として前回測定電圧との差の絶対値が所定の閾値以下(この実施例では0.1V以下)であることを所定回数(この実施例では5回)連続で検出することを設定する。そして、これら2つの条件の両方が満たされた場合にサブタンク4内がインクで満たされたと判定する。
FIG. 10 is a diagram for explaining setting conditions. That is, as shown in FIG. 10, the
図8(b)は、図8(a)に示した電圧変化の挙動に対して図10に示した2つの条件を用いて判定した結果を示す図である。図8(b)によれば、領域1では図10に示す条件1を満たさず、領域2では図10に示す条件2を満たさないが、領域3では条件1、2の両方を満たすため矢印Cの時点でサブタンク4内がインクで満たされたと判定される。
FIG. 8B is a diagram illustrating a result of determination using the two conditions illustrated in FIG. 10 with respect to the behavior of the voltage change illustrated in FIG. According to FIG. 8B, the
しかしながら、発明者は、実際にはサブタンク内がインクで満たされていないにもかかわらず、インクが満たされたと判定されてしまう場合があることを発見した。 However, the inventor has found that there is a case where it is determined that the ink is filled even though the sub tank is not actually filled with ink.
図11はその具体例を示す電圧の時間変化を示す図である。 FIG. 11 is a diagram showing a change with time of voltage showing a specific example.
図11に示すように、図10に示す2つの条件を用いて判定を行ってもサブタンク4内がインクで満たされたとの判定が不正確になっている。図11に示す領域2では、今回の測定電圧値と前回の測定電圧値との差が小さいため、条件2を矢印Dの時点で満たしてしまう。しかしながら、実際にサブタンク内がインクで満たされるのは矢印Eで示す時点のため、矢印Dのタイミングではサブタンク4内がインクで満たされていない。
As shown in FIG. 11, even if the determination is made using the two conditions shown in FIG. 10, the determination that the sub tank 4 is filled with ink is inaccurate. In
ここで、サブタンク4内のインク量検知を実行したタイミングにおける開閉弁3の開閉状態をフォトセンサ41で検出したところ、開閉弁3は同じ状態を繰り返していた。
Here, when the opening / closing state of the opening /
図12はインク供給動作及びインク量検知動作とサブタンク充填時間との関係を示す図とサブタンク内のインク量検知による測定電圧とサブタンク充填時間との関係を示す図である。 FIG. 12 is a diagram showing the relationship between the ink supply operation, the ink amount detection operation, and the sub tank filling time, and the relationship between the measurement voltage by the ink amount detection in the sub tank and the sub tank filling time.
図12において、(a)は図11に示す測定を行った時のインク量検知動作の検知間隔とインク供給動作の実行間隔を示している。図12(a)に示す場合、フォトセンサ41の結果(即ち、インク供給のタイミング)とインク量検知タイミングとは、矢印と●との位置が示唆するように揃っている。これは、サブタンク内がインクで満たされていないにも係らず、サブタンク内のインクの流れ等を介して中空管8と中実管10との間で電流が流れてしまったことによると考えられる。さらに全てのインク量検知動作のタイミングが、開閉弁3の開閉状態が同じ状態となるタイミングで実行しているため、中空管8と中実管10との間のインクの流れ方が毎回類似する。このため、毎回ほぼ同じ量の電流が流れてしまうため、電圧値の変動が小さくなったと考えられる。
12A shows the detection interval of the ink amount detection operation and the execution interval of the ink supply operation when the measurement shown in FIG. 11 is performed. In the case shown in FIG. 12A, the result of the photosensor 41 (that is, the ink supply timing) and the ink amount detection timing are aligned as indicated by the positions of the arrows and ●. This is considered to be due to the fact that a current flows between the
発明者らはこの点について考察し、サブタンク4内のインク量検知動作を実行したタイミングにおける開閉弁3の開閉状態を毎回異なる状態となるように制御することで、回避できることを見出した。
The inventors have considered this point, and have found that this can be avoided by controlling the open / close state of the on-off
具体的には、図7に示したサブタンク充填制御において、サブタンク4にインクを充填する開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔に対して、サブタンク4内のインク量検知動作の検知間隔は別に制御する。そして、インク量検知動作の検知間隔が開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔の整数倍と異なるように制御することで、サブタンク4内のインク量検知動作を実行したタイミングにおける開閉弁3の開閉状態を異ならせる。
Specifically, in the sub tank filling control shown in FIG. 7, the detection interval of the ink amount detection operation in the sub tank 4 is controlled separately from the execution interval of the opening / closing operation of the on / off
例えば、図12(b)に示すように、インク量検知動作の検知間隔(Tp)を2.31秒、インク供給動作の実行間隔(Ts)を0.32秒に設定することにより、TpはTsの7.2倍で整数倍とならないように設定する。これにより、インク量検知のタイミング毎に開閉弁3の開閉状態が異なるようになる。従って、サブタンク内にインクの流れ等があり、たとえ中空管8と中実管10との間に電流が流れたとしても、毎回同じ量の電流が流れることを回避することができ、電圧値に変動を生じさせることができる。
For example, as shown in FIG. 12B, by setting the detection interval (Tp) of the ink amount detection operation to 2.31 seconds and the execution interval (Ts) of the ink supply operation to 0.32 seconds, Tp is Set so that 7.2 times Ts does not become an integer multiple. As a result, the open / close state of the open /
図12(c)は、図12(b)に示すように、インク量検知動作とインク供給動作の実行間隔をそれぞれ制御した場合のインク量検知により測定される電圧変化を示している。図12(c)に示されるように、領域2においても電圧が0.1Vより大きく変動しているため条件2は満たされず、領域3の矢印Fのタイミングで図10に示した2つの条件が満たされたと判定される。つまり、サブタンク4内にインクは満たされた時点で正しく判定がなされるのである。
FIG. 12C shows a voltage change measured by ink amount detection when the execution intervals of the ink amount detection operation and the ink supply operation are controlled as shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 12C,
さて、以上説明した実施例では、サブタンク4内のインク量検知を1色のインクに対してのみ実行する例を用いて説明したが、本発明はこれによって限定されるものではない。例えば、インク量検知動作の検知間隔の間に、検知対象とするインクを切り替えて測定を行ったり、インクタンクとサブタンクを切り替えて測定を行ってもよい。 In the above-described embodiment, the ink amount detection in the sub-tank 4 has been described using only one color ink. However, the present invention is not limited to this. For example, during the detection interval of the ink amount detection operation, measurement may be performed by switching the ink to be detected, or measurement may be performed by switching between the ink tank and the sub tank.
このように、この実施例では図7に示すサブタンク充填制御中に図10に示す条件でサブタンク4内がインクで満たされているかを判定する場合に、インク量検知動作の検知間隔が開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔の整数倍とは異なるように制御している。この結果、図10に示す条件で判定を行った際に、サブタンク充填中におけるサブタンク内のインク量の測定を正確に行うことが可能になる。 Thus, in this embodiment, when it is determined whether the sub tank 4 is filled with ink under the conditions shown in FIG. 10 during the sub tank filling control shown in FIG. Is controlled so as to be different from an integral multiple of the execution interval of the opening / closing operation. As a result, when the determination is made under the conditions shown in FIG. 10, it is possible to accurately measure the ink amount in the sub tank during filling of the sub tank.
次に、サブタンク4内のインク量検知動作の検知間隔が開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔の整数倍と異なるように制御する場合に、其々の間隔の設定方法について説明する。
Next, a method for setting each interval when the detection interval of the ink amount detection operation in the sub tank 4 is controlled to be different from an integral multiple of the execution interval of the opening / closing operation of the on-off
それぞれの間隔の設定により、インク量検知タイミングにおける開閉弁3の開閉状態を異ならせることができる。この開閉状態の変動により、インク量検知タイミングでの電圧値が変動する。そこで、この実施例では其々の間隔の設定範囲を規定することにより、開閉状態の変動を最大にすることでサブタンク内のインク量測定をより正確にする。
The open / close state of the open /
インク量検知動作の検知間隔が開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔よりも長い場合、インク量検知タイミング毎に開閉弁3の開閉状態が異なるようにするために、インク量検知間隔(Tp)が開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔(Ts)の整数(N)倍でない必要がある。
When the detection interval of the ink amount detection operation is longer than the execution interval of the opening / closing operation of the opening /
即ち、
Tp≠(Ts×N)……(1)
の関係を満たす必要がある。ここで、NはTp割るTsの整商である。
That is,
Tp ≠ (Ts × N) (1)
It is necessary to satisfy the relationship. Here, N is the quotient of Ts divided by Tp.
図13はインク供給動作のタイミングとインク量検知のタイミングを異ならせる様子を示す図である。図13において、インク量検知するタイミング毎における開閉弁3の開閉状態の違いは●と矢印の位置(タイミング)の差であり、(Tp−Ts×N)の分だけ開閉状態が遅れている。この遅延時間(Tp−Ts×N)によってサブタンク4内の中空管8と中実管10間のインクの流れ方が変わり、測定値の変動度合いが変わってくる。
FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating a state in which the timing of the ink supply operation is different from the timing of detecting the ink amount. In FIG. 13, the difference in the open / close state of the open /
サブタンク4内のインクが満たされた判定は図10に示した条件を用いるので、インク量検知を連続的にCr回、実行する間の開閉弁3の開閉状態の遅れ時間の合計は(Tp−Ts×N)×Crになる。この合計(Tp−Ts×N)×Crが式(2)が示す条件のように開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔(Ts)以上になると、開閉弁3の開閉状態の遅延時間が開閉弁3の開閉動作の1周期以上となる。つまり、サブタンク4内の中空管8と中実管10との間のインクの流れ方の変動が最大となる開閉弁3の開状態と閉状態がCr回のインク量検知測定中に含まれることになる。式(2)が示す条件とは以下の通りである。即ち、
(Tp−Ts×N)×Cr≧Ts ……(2)
である。
Since the determination shown in FIG. 10 is used for the determination that the ink in the sub tank 4 is filled, the total delay time of the on / off state of the on-off
(Tp−Ts × N) × Cr ≧ Ts (2)
It is.
サブタンク4内がインクで満たされていなければ、Cr回のインク量検知測定中に電圧値が変動して図10に示した条件が満足されず、サブタンク充填制御が継続される。 If the sub tank 4 is not filled with ink, the voltage value fluctuates during the ink amount detection measurement of Cr times and the condition shown in FIG. 10 is not satisfied, and the sub tank filling control is continued.
さて、式(2)の両辺をCrで割ると式(3)が得られる。即ち、
(Tp−Ts×N)≧(Ts/Cr) ……(3)
である。式(3)は、インク量検知タイミング毎に生じる開閉弁3の開閉状態の遅延時間(Tp−Ts×N)は開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔を連続測定回数のCrで割った値(Ts/Cr)以上になることが望ましいことを示している。
Now, when both sides of the formula (2) are divided by Cr, the formula (3) is obtained. That is,
(Tp−Ts × N) ≧ (Ts / Cr) (3)
It is. Formula (3) is the delay time (Tp−Ts × N) of the open / close state of the open /
これを考慮し、この実施例では、開閉弁3の開閉動作の実行間隔(Ts)がTs=0.32秒、連続測定回数(Cr)が5回、N=7の場合、式(3)よりサブタンク4内のインク量検知の検知間隔(Tp)を2.304秒以上に設定した。
Considering this, in this embodiment, when the execution interval (Ts) of the opening / closing operation of the opening /
なお、インク供給動作の実行間隔(Ts)が式(2)が示唆するように、ある範囲の装置ばらつきを持っている場合、インク量を検知する検知間隔(Tp)はTsのばらつき上限値(Ts1)よりも大きな値に設定することが望ましい。なお、式(2)に示す装置ばらつきは、モータ等の影響によるものであるため、検知間隔が最大となる構成を意図的に作り出して測定することで、ばらつき上限値(Ts1)を求めることができる。 In addition, when the execution interval (Ts) of the ink supply operation has a certain range of apparatus variation as suggested by the equation (2), the detection interval (Tp) for detecting the ink amount is the upper limit of the variation in Ts ( It is desirable to set a value larger than Ts1). Note that the device variation shown in Equation (2) is due to the influence of a motor or the like, and therefore the variation upper limit value (Ts1) can be obtained by intentionally creating and measuring a configuration that maximizes the detection interval. it can.
以上説明したように、インク量検知動作の検知間隔が開閉弁の開閉動作の実行間隔の整数倍と異なるように制御する場合に、その検知間隔(Tp)と実行間隔(Ts)が連続測定回数(Cr)と整数(N)を用いて、式(3)の関係になるよう制御している。なお、連続測定回数(Cr)は10以下の方が測定時間の短縮のためにも望ましい。 As described above, when the detection interval of the ink amount detection operation is controlled to be different from an integral multiple of the execution interval of the opening / closing operation of the on-off valve, the detection interval (Tp) and the execution interval (Ts) are the number of continuous measurements. Using (Cr) and an integer (N), control is performed so as to satisfy the relationship of Expression (3). Note that the number of continuous measurements (Cr) is preferably 10 or less in order to shorten the measurement time.
従って以上説明した実施例に従えば、Cr回のインク量検知タイミングにおいて、開閉弁3の開閉動作の1周期以上で測定を行え、測定電圧の変動を最大することができるため、サブタンク内のインク量測定を正確に行うことができる。
Therefore, according to the embodiment described above, since the measurement can be performed in one cycle or more of the opening / closing operation of the opening /
なお、この実施例では第1の中空間8と電極部10との間に微小電流(定電流)を流したときの電圧値を検知し、検知された電圧値の変化からインクを介した通電を検知してインク量を判断している。しかしながら、本発明はこれによって限定されるものではない。例えば、第1の中空間8と電極部10との間に一定電圧を印加した時に流れる電流値を検知し、検知された電流値の変化からインク量を判断してもよい。この場合には、検知された電流値が予め定められた電流以上であり、かつ、連続して2つの電流値の差の絶対値が予め定められた電流値以下であることが予め定められた回数、連続して検出された場合にサブタンクがインクで満たされたと判断することができる。
In this embodiment, a voltage value when a minute current (constant current) is passed between the first
Claims (11)
前記インクタンクから供給されたインクを貯留するサブタンクと、
前記サブタンクから供給されたインクを吐出し記録媒体に記録を行う記録ヘッドと、
前記サブタンクと前記記録ヘッドとの間に配され、容積を変化させることにより前記インクタンクから前記サブタンクに第1の間隔で所定量のインクを供給する供給動作を行う供給手段と、
前記サブタンクの上部に設けられた一対の電極と、
前記一対の電極に定電流を流した際の電圧値を検知する検知動作を第2の間隔で行う検知手段と、を備え、
前記検知手段の検知結果に基づいて前記供給動作を停止し、
前記第1の間隔より前記第2の間隔が長く、前記第2の間隔は前記第1の間隔の整数倍とは異なることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 And stomach Nkutanku for storing ink,
A sub tank for storing ink supplied from the ink tank ;
A recording head that discharges ink supplied from the sub-tank and performs recording on a recording medium;
Disposed between the front Symbol subtank the recording head, a supply means for supplying operation of supplying a predetermined amount of ink in the first interval to the sub tank from the ink tank by changing the volume,
A pair of electrodes provided on the upper portion of the sub-tank,
Detecting means for detecting a voltage value when a constant current is passed through the pair of electrodes at a second interval ;
Stop the supply operation based on the detection result of the detection means,
The inkjet recording apparatus , wherein the second interval is longer than the first interval, and the second interval is different from an integer multiple of the first interval .
前記第1の間隔をTsとし、
前記予め定められた回数をCrとし、
前記Tpを前記Tsで割った際の整商を、Nとした場合に、
(Tp−Ts×N)≧(Ts/Cr)
となる関係があることを特徴とする請求項2に記載のインクジェット記録装置。 The second interval is Tp,
The first interval is Ts,
The predetermined number of times is Cr,
The integral quotient when divided by the Tp in the Ts, in case of a N,
(Tp−Ts × N) ≧ (Ts / Cr)
The inkjet recording apparatus according to claim 2 , wherein:
前記インクタンクから供給されたインクを貯留するサブタンクと、
前記サブタンクから供給されたインクを吐出して記録媒体に記録を行う記録ヘッドと、
前記サブタンクと前記記録ヘッドとの間に配され、容積を変化させることにより前記インクタンクから前記サブタンクに第1の間隔で所定量のインクを供給する供給動作を行う供給手段と、
前記サブタンクの上部に設けられた一対の電極と、
前記一対の電極に定電圧を印加した際に流れる電流値を検知する検知動作を第2の間隔で行う検知手段と、を備え、
前記検知手段の検知結果に基づいて前記供給動作を停止し、
前記第1の間隔より前記第2の間隔が長く、前記第2の間隔は前記第1の間隔の整数倍とは異なることを特徴とするインクジェット記録装置。 And stomach Nkutanku for storing ink,
A sub tank for storing ink supplied from the ink tank ;
A recording head for recording on a recording medium by discharging ink supplied from the sub tank;
Disposed between the front Symbol subtank the recording head, a supply means for supplying operation of supplying a predetermined amount of ink in the first interval to the sub tank from the ink tank by changing the volume,
A pair of electrodes provided on the upper portion of the sub-tank,
And a detection means for performing a detection operation for detecting a current flowing upon application of a constant voltage to the pair of electrodes in the second interval,
Stop the supply operation based on the detection result of the detection means,
The inkjet recording apparatus , wherein the second interval is longer than the first interval, and the second interval is different from an integer multiple of the first interval .
前記第1の間隔をTsとし、
前記予め定められた回数をCrとし、
前記Tpを前記Tsで割った際の整商を、Nとした場合に、
(Tp−Ts×N)≧(Ts/Cr)
となる関係があることを特徴とする請求項5に記載のインクジェット記録装置。 The second interval is Tp,
The first interval is Ts,
The predetermined number of times is Cr,
The integral quotient when divided by the Tp in the Ts, in case of a N,
(Tp−Ts × N) ≧ (Ts / Cr)
The inkjet recording apparatus according to claim 5 , wherein:
前記一対の電極に定電流を流した際の電圧値を検知する検知動作を第2の間隔で行い、
前記検知動作の検知結果に基づいて前記供給動作を停止し、
前記第1の間隔より前記第2の間隔が長く、前記第2の間隔は前記第1の間隔の整数倍とは異なることを特徴とするインク量検知方法。 And b Nkutanku for storing ink, a sub tank for storing ink supplied from the ink tank, a recording head for recording on a recording medium by discharging an ink supplied from the sub-tank, and the recording head and the sub-tank arranged between a supply unit for supplying operation of supplying a predetermined amount of ink in the first interval to the sub tank from the ink tank by changing the volume, and a pair of electrodes provided on the upper portion of the sub-tank an ink amount detecting method in the inkjet recording apparatus provided with,
A detection operation for detecting a voltage value when a constant current is passed through the pair of electrodes is performed at a second interval ,
The supply operation is stopped based on the detection result of the previous SL detecting operation,
2. The ink amount detection method according to claim 1, wherein the second interval is longer than the first interval, and the second interval is different from an integral multiple of the first interval .
前記一対の電極に定電圧を印加した際に流れる電流値を検知する検知動作を第2の間隔で行い、
前記検知動作の検知結果に基づいて前記供給動作を停止し、
前記第1の間隔より前記第2の間隔が長く、前記第2の間隔は前記第1の間隔の整数倍とは異なることを特徴とするインク量検知方法。 And b Nkutanku for storing ink, a sub tank for storing ink supplied from the ink tank, a recording head for recording on a recording medium by discharging an ink supplied from the sub-tank, and the recording head and the sub-tank arranged between a supply unit for supplying operation of supplying a predetermined amount of ink in the first interval to the sub tank from the ink tank by changing the volume, and a pair of electrodes provided on the upper portion of the sub-tank an ink amount detecting method in the inkjet recording apparatus provided with,
A detection operation for detecting a current value flowing when a constant voltage is applied to the pair of electrodes is performed at a second interval ,
The supply operation is stopped based on the detection result of the previous SL detecting operation,
2. The ink amount detection method according to claim 1, wherein the second interval is longer than the first interval, and the second interval is different from an integral multiple of the first interval .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013052431A JP6198419B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2013-03-14 | Ink jet recording apparatus and ink amount detection method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013052431A JP6198419B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2013-03-14 | Ink jet recording apparatus and ink amount detection method |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014177033A JP2014177033A (en) | 2014-09-25 |
| JP2014177033A5 JP2014177033A5 (en) | 2016-04-28 |
| JP6198419B2 true JP6198419B2 (en) | 2017-09-20 |
Family
ID=51697475
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013052431A Active JP6198419B2 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2013-03-14 | Ink jet recording apparatus and ink amount detection method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6198419B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6463206B2 (en) * | 2015-04-02 | 2019-01-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Inkjet recording device |
| JP6478811B2 (en) * | 2015-05-27 | 2019-03-06 | キヤノン株式会社 | Inkjet recording device |
| JP6498098B2 (en) | 2015-10-30 | 2019-04-10 | キヤノン株式会社 | Recording apparatus and liquid storage member |
| JP6900168B2 (en) * | 2016-10-27 | 2021-07-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | Recording device and its control method |
| JP7218528B2 (en) * | 2018-09-28 | 2023-02-07 | ブラザー工業株式会社 | liquid consumption device |
| JP6666052B2 (en) * | 2019-03-14 | 2020-03-13 | キヤノン株式会社 | Recording device |
| JP7225336B2 (en) | 2020-02-20 | 2023-02-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | recording device |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003305862A (en) * | 2002-04-11 | 2003-10-28 | Canon Inc | Device for detecting ink remaining amount |
| JP2003312000A (en) * | 2002-04-25 | 2003-11-06 | Canon Inc | Liquid jet recorder and method of supplying recording liquid therefor |
| JP2006123365A (en) * | 2004-10-29 | 2006-05-18 | Canon Finetech Inc | Inkjet recording device |
| JP5058828B2 (en) * | 2008-01-09 | 2012-10-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Inkjet recording device |
| JP5483909B2 (en) * | 2009-03-10 | 2014-05-07 | キヤノン株式会社 | Inkjet recording device |
| JP2011104932A (en) * | 2009-11-20 | 2011-06-02 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Image forming apparatus |
-
2013
- 2013-03-14 JP JP2013052431A patent/JP6198419B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014177033A (en) | 2014-09-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6198419B2 (en) | Ink jet recording apparatus and ink amount detection method | |
| US9597888B2 (en) | Printing apparatus and ink amount control method for ink tank | |
| JP6564341B2 (en) | Inkjet recording apparatus and ink remaining amount detection method | |
| US9517628B2 (en) | Printing apparatus, method, and non-transitory storage medium | |
| CN102770274B (en) | System for determining the autonomy in consumable fluids of a continuous ink jet printer | |
| JP5979917B2 (en) | Inkjet recording device | |
| US10569560B2 (en) | Inkjet printing apparatus and ink filling method for the same | |
| US8246151B2 (en) | Liquid supply devices | |
| JP6478607B2 (en) | Ink supply apparatus and inkjet recording apparatus | |
| US9272522B1 (en) | Printing apparatus and ink amount detection method | |
| JP2016159620A (en) | Inkjet recording device | |
| JP2015044379A (en) | Liquid discharge device and control method of the same | |
| JP2017170751A (en) | Ink jet recording device | |
| JP2012096363A (en) | Inkjet recording apparatus | |
| JP4599878B2 (en) | Inkjet printer | |
| JP5990085B2 (en) | Ink jet recording apparatus and ink filling method thereof | |
| JP6322946B2 (en) | Image recording apparatus and liquid cartridge | |
| US9604465B2 (en) | Ink-jet recording apparatus | |
| JP6651809B2 (en) | Liquid ejection device | |
| JP2014079973A (en) | Ink jet recorder | |
| JP2007230041A (en) | Liquid ejecting apparatus and auxiliary storage means | |
| JP2019177566A (en) | Liquid discharge device | |
| JP7350506B2 (en) | Recording device, its control method, and program | |
| WO2022071151A1 (en) | Liquid discharging apparatus | |
| JP7013156B2 (en) | Liquid discharge device, liquid remaining amount management method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160309 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160309 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20161213 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20161222 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170215 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170724 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170822 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6198419 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |