JP5857473B2 - Toroidal continuously variable transmission - Google Patents
Toroidal continuously variable transmission Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5857473B2 JP5857473B2 JP2011142932A JP2011142932A JP5857473B2 JP 5857473 B2 JP5857473 B2 JP 5857473B2 JP 2011142932 A JP2011142932 A JP 2011142932A JP 2011142932 A JP2011142932 A JP 2011142932A JP 5857473 B2 JP5857473 B2 JP 5857473B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- trunnion
- outer ring
- support beam
- disk
- beam portion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
この発明は、例えば車両(自動車)用の自動変速機、建設機械(建機)用の自動変速機、航空機(固定翼機、回転翼機、飛行船等)等で使用されるジェネレータ(発電機)用の自動変速機、ポンプ等の各種産業機械の運転速度を調節する為の自動変速機として利用する、ハーフトロイダル型のトロイダル型無段変速機の改良に関する。 The present invention relates to a generator (generator) used in, for example, an automatic transmission for a vehicle (automobile), an automatic transmission for a construction machine (construction machine), an aircraft (a fixed wing aircraft, a rotary wing aircraft, an airship, etc.), etc. The present invention relates to improvement of a half toroidal toroidal continuously variable transmission that is used as an automatic transmission for adjusting the operating speed of various industrial machines such as automatic transmissions and pumps.
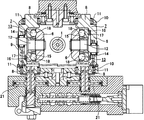
自動車用変速装置としてハーフトロイダル型のトロイダル型無段変速機を使用する事が、特許文献1〜4等の多くの刊行物に記載されると共に一部で実施されていて周知である。又、トロイダル型無段変速機と遊星歯車機構とを組み合わせて変速比の調整幅を広くする構造も、特許文献5等、やはり多くの刊行物に記載されて、従来から広く知られている。図7〜8は、これら各特許文献に記載されて従来から広く知られているトロイダル型無段変速機の第1例を示している。この従来構造の第1例の場合、入力回転軸1の両端寄り部分の周囲に1対の入力ディスク2、2を、それぞれがトロイド曲面である内側面同士を互いに対向させた状態で、前記入力回転軸1と同期した回転を自在に支持している。又、この入力回転軸1の中間部周囲に出力筒3を、この入力回転軸1に対する回転を自在に支持している。又、この出力筒3の外周面には、軸方向中央部に出力歯車4を固設すると共に、軸方向両端部に1対の出力ディスク5、5を、スプライン係合により、前記出力筒3と同期した回転を自在に支持している。又、この状態で、それぞれがトロイド曲面である、前記両出力ディスク5、5の内側面を、前記両入力ディスク2、2の内側面に対向させている。
The use of a half-toroidal toroidal continuously variable transmission as a transmission for an automobile is described in many publications such as
又、前記両入力ディスク2、2と前記両出力ディスク5、5との間に、それぞれの周面を球状凸面とした複数個のパワーローラ6、6を挟持している。これら各パワーローラ6、6は、それぞれトラニオン7、7に回転自在に支持されており、これら各トラニオン7、7は、それぞれ前記各ディスク2、5の中心軸に対し捩れの位置にある傾転軸8、8を中心とする揺動変位自在に支持されている。即ち、これら各トラニオン7、7は、それぞれの軸方向両端部に互いに同心に設けられた1対の傾転軸8、8と、これら各傾転軸8、8同士の間に存在する支持梁部9、9とを備えており、これら各傾転軸8、8が、支持板10、10に対し、ラジアルニードル軸受11、11を介して枢支されている。
Further, a plurality of
又、前記各パワーローラ6、6は、前記各トラニオン7、7を構成する支持梁部9、9の内側面に、基半部と先半部とが互いに偏心した支持軸12、12と、複数の転がり軸受とを介して、これら各支持軸12、12の先半部回りの回転、及び、これら各支持軸12、12の基半部を中心とする若干の揺動変位自在に支持されている。この様な各パワーローラ6、6の外側面と、前記各トラニオン7、7を構成する支持梁部9、9の内側面との間には、それぞれが前記複数の転がり軸受の一部である、スラスト玉軸受13、13と、スラストニードル軸受14、14とを、前記各パワーローラ6、6の側から順番に設けている。このうちのスラスト玉軸受13、13は、前記各パワーローラ6、6に加わるスラスト方向の荷重を支承しつつ、これら各パワーローラ6、6の回転を許容するものである。これら各スラスト玉軸受13、13は、前記各パワーローラ6、6の外側面に形成された内輪軌道15と、外輪16の内側面に形成された外輪軌道17との間に複数個の玉18、18を、転動自在に設けて成る。又、前記各スラストニードル軸受14、14は、前記各パワーローラ6、6から前記各スラスト玉軸受13、13を構成する外輪16、16に加わるスラスト荷重を支承しつつ、これら各外輪16、16及び前記各支持軸12、12の先半部が、これら各支持軸12、12の基半部を中心に揺動する事を許容するものである。
Each of the
上述の様なトロイダル型無段変速機の運転時には、駆動軸19により一方(図7の左方)の入力ディスク2を、押圧装置20を介して回転駆動する。この結果、前記入力回転軸1の両端部に支持された1対の入力ディスク2、2が、互いに近づく方向に押圧されつつ同期して回転する。そして、この回転が、前記各パワーローラ6、6を介して前記両出力ディスク5、5に伝わり、前記出力歯車4から取り出される。前記入力回転軸1と前記出力歯車4との間の変速比を変える場合は、油圧式のアクチュエータ21、21により前記各トラニオン7、7を前記各傾転軸8、8の軸方向に変位させる。この結果、前記各パワーローラ6、6の周面と前記各ディスク2、5の内側面との転がり接触部(トラクション部)に作用する、接線方向の力の向きが変化する(転がり接触部にサイドスリップが発生する)。そして、この力の向きの変化に伴って前記各トラニオン7、7が、自身の傾転軸8、8を中心に揺動し、前記各パワーローラ6、6の周面と前記各ディスク2、5の内側面との接触位置が変化する。これら各パワーローラ6、6の周面を、前記両入力ディスク2、2の内側面の径方向外寄り部分と、前記両出力ディスク5、5の内側面の径方向内寄り部分とに転がり接触させれば、前記入力回転軸1と前記出力歯車4との間の変速比が増速側になる。これに対して、前記各パワーローラ6、6の周面を、前記両入力ディスク2、2の内側面の径方向内寄り部分と、前記両出力ディスク5、5の内側面の径方向外寄り部分とに転がり接触させれば、前記入力回転軸1と前記出力歯車4との間の変速比が減速側になる。
During operation of the toroidal-type continuously variable transmission as described above, one input disk 2 (left side in FIG. 7) is rotationally driven by the
上述の様なトロイダル型無段変速機の運転時には、動力の伝達に供される各部材、即ち、前記入力、出力各ディスク2、5と前記各パワーローラ6、6とが、前記押圧装置20が発生する押圧力に基づいて弾性変形する。そして、この弾性変形に伴って、前記入力、出力各ディスク2、5が軸方向に変位する。又、前記押圧装置20が発生する押圧力は、前記トロイダル型無段変速機により伝達するトルクが大きくなる程大きくなり、それに伴って前記各部材2、5、6の弾性変形量も多くなる。従って、前記トルクの変動に拘らず、前記入力、出力各ディスク2、5の内側面と前記各パワーローラ6、6の周面との接触状態を適正に維持する為に、前記各トラニオン7、7に対して前記各パワーローラ6、6を、前記各ディスク2、5の軸方向に変位させる機構が必要になる。上述した従来構造の第1例の場合には、前記各パワーローラ6、6を支持した前記各支持軸12、12の先半部を、同じく基半部を中心として揺動変位させる事により、前記各パワーローラ6、6を前記軸方向に変位させる様にしている。
When the toroidal type continuously variable transmission as described above is operated, the members used for power transmission, that is, the input and
上述の様な従来構造の第1例の場合、前記各パワーローラ6、6を前記軸方向に変位させる為の構造が複雑で、部品製作、部品管理、組立作業が何れも面倒になり、コストが嵩む事が避けられない。この様な問題を解決する為の技術として前記特許文献3には、図9〜14に示す様な構造が記載されている。本発明は、この図9〜14に示した従来構造の第2例を改良するものであるから、次に、この従来構造の第2例に就いて説明する。この従来構造の第2例の特徴は、トラニオン7aに対してパワーローラ6aを、入力、出力各ディスク2、5(図7参照)の軸方向の変位を可能に支持する部分の構造にあり、トロイダル型無段変速機全体としての構造及び作用は、前述の図8〜9に示した従来構造の第1例と同様である。
In the case of the first example of the conventional structure as described above, the structure for displacing each of the
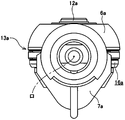
前記従来構造の第2例を構成するトラニオン7aは、両端部に互いに同心に設けられた1対の傾転軸8a、8bと、これら両傾転軸8a、8b同士の間に存在し、少なくとも入力、出力各ディスク2、5(図7参照)の径方向(図10、13〜14の上下方向)に関する内側(図10、13〜14の上側)の側面を円筒状凸面22とした、支持梁部23とを備える。前記両傾転軸8a、8bは、それぞれラジアルニードル軸受11a、11aを介して、支持板10、10(図8参照)に、揺動を可能に支持する。
The
又、前記円筒状凸面22の中心軸イは、図10、13に示す様に、前記両傾転軸8a、8bの中心軸ロと平行で、これら両傾転軸8a、8bの中心軸ロよりも、前記各ディスク2、5の径方向に関して外側(図10、13〜14の下側)に存在する。又、前記支持梁部23とパワーローラ6aの外側面との間に設けるスラスト玉軸受13aを構成する外輪16aの外側面に、部分円筒面状の凹部24を、この外側面を径方向に横切る状態で設けている。そして、この凹部24と、前記支持梁部23の円筒状凸面22とを係合させ、前記トラニオン7aに対して前記外輪16aを、前記各ディスク2、5の軸方向に関する揺動変位を可能に支持している。
Further, as shown in FIGS. 10 and 13, the center axis A of the
又、前記外輪16aの内側面中央部に支持軸12aを、この外輪16aと一体に固設して、前記パワーローラ6aをこの支持軸12aの周囲に、ラジアルニードル軸受25を介して、回転自在に支持している。更に、前記トラニオン7aの内側面のうち、前記支持梁部23の両端部と1対の傾転軸8a、8bとの連続部に、互いに対向する1対の段差面26、26を設けている。そして、これら両段差面26、26と、前記スラスト玉軸受13aを構成する外輪16aの外周面とを、当接若しくは近接対向させて、前記パワーローラ6aからこの外輪16aに加わるトラクション力を、何れかの段差面26、26で支承可能としている。
Further, a
上述の様に構成する従来構造の第2例のトロイダル型無段変速機によれば、前記パワーローラ6aを前記各ディスク2、5の軸方向に変位させて、構成各部材の弾性変形量の変化に拘らず、このパワーローラ6aの周面と前記各ディスク2、5との接触状態を適正に維持できる構造を、簡単で低コストに構成できる。
即ち、トロイダル型無段変速機の運転時に、入力、出力各ディスク2、5、各パワーローラ6a等の弾性変形に基づき、これら各パワーローラ6aをこれら各ディスク2、5の軸方向に変位させる必要が生じると、これら各パワーローラ6aを回転自在に支持している前記スラスト玉軸受13aの外輪16aが、外側面に設けた部分円筒面状の凹部24と支持梁部23の円筒状凸面22との当接面を滑らせつつ、この円筒状凸面22の中心軸イを中心として揺動変位する。この揺動変位に基づき、前記各パワーローラ6aの周面のうちで、前記各ディスク2、5の軸方向片側面と転がり接触する部分が、これら各ディスク2、5の軸方向に変位し、前記接触状態を適正に維持する。
According to the toroidal type continuously variable transmission of the second example of the conventional structure configured as described above, the
That is, during operation of the toroidal continuously variable transmission, the
前述した通り、前記円筒状凸面22の中心軸イは、変速動作の際に各トラニオン7aの揺動中心となる傾転軸8a、8bの中心軸ロよりも、前記各ディスク2、5の径方向に関して外側に存在する。従って、前記円筒状凸面22の中心軸イを中心とする揺動変位の半径は、前記変速動作の際の揺動半径よりも大きく、前記両入力ディスク2、2と前記両出力ディスク5、5との間の変速比の変動に及ぼす影響は少ない(無視できるか、容易に修正できる範囲に留まる)。
As described above, the central axis A of the cylindrical
図9〜14に示した従来構造の第2例の場合、図7〜8に示した同第1例に比べて、部品製作、部品管理、組立作業が何れも容易になり、コスト低廉化を図り易いが、変速動作を安定させる面からは、改良の余地がある。この理由は、前記各支持梁部23を中心とする前記各外輪16aの揺動変位を円滑に行わせる為、これら各支持梁部23の両端部分に1対ずつ設けた、前記各段差面26、26同士の間隔Dを、前記各外輪16aの外径dよりも少し大きく(D>d)する為である。これら各外輪16a、及び、この外輪16aと同心に支持された前記各パワーローラ6aは、前記間隔Dと前記外径dとの差(D−d)分だけ、前記各支持梁部23の軸方向に変位可能になる。
In the case of the second example of the conventional structure shown in FIGS. 9 to 14, parts manufacturing, parts management, and assembly work are all easier than the first example shown in FIGS. Although easy to achieve, there is room for improvement in terms of stabilizing the shifting operation. The reason for this is that each
一方、トロイダル型無段変速機を搭載した車両の運転時、前記各パワーローラ6aには前記各ディスク2、5から、加速時と減速時(エンジンブレーキの作動時)とで逆方向の力(トロイダル型無段変速機の技術分野で周知の「2Ft」)が加わる。そして、この力2Ftにより、前記各パワーローラ6aが、前記各外輪16aと共に、前記各支持梁部23の軸方向に変位する。この変位の方向は、前述した各アクチュエータ21、21による各トラニオン7、7(図8参照)の変位方向と同じであり、変位量が0.1mm程度であっても、変速動作が開始される可能性を生じる。そして、この様な原因で変速動作が開始された場合には、運転動作とは直接関連しない変速動作となり、何れ修正されるにしても、運転者に違和感を与える。特に、トロイダル型無段変速機が伝達するトルクが低い状態で、上述の様な、運転者が意図しない変速が行われると、運転者に与える違和感が大きくなり易い。
On the other hand, during operation of a vehicle equipped with a toroidal-type continuously variable transmission, each
上述の様にして生じる、運転動作とは直接関連しない変速動作の発生を抑える為には、前記間隔Dと前記外径dとの差(D−d)を僅少に(例えば数十μm程度に)抑える事が考えられる。但し、ハーフトロイダル型のトロイダル型無段変速機の運転時には、トラクション部から前記各パワーローラ6a、前記各外輪16aを介して前記各支持梁部23に加わるスラスト荷重により、前記各トラニオン7aが、図15に誇張して示す様に、前記各外輪16aを設置した側が凹となる方向に弾性変形する。そして、この弾性変形の結果、前記各トラニオン7a毎に1対ずつ設けた段差面26、26同士の間隔が縮まる。この様な状態でも、これら両段差面26、26同士の間隔Dが前記各外輪16aの外径d以下にならない様にする為には、通常状態(前記各トラニオン7aが弾性変形していない状態)での、前記間隔Dと前記外径dとの差を、図16(a)に示す様に、或る程度確保する必要があるが、加工精度等により、図16(b)に示す様なトラニオン7aによるパワーローラ6aの挟み込みが発生する可能性がある。
In order to suppress the occurrence of the speed change operation that is not directly related to the driving operation as described above, the difference (D−d) between the distance D and the outer diameter d is made small (for example, about several tens of μm). ) Can be suppressed. However, during the operation of the half-toroidal toroidal continuously variable transmission, each
本発明は、上述の様な事情に鑑み、コスト低廉化を図り易く、しかも変速動作を安定させられる構造を実現すべく発明したものである。 In view of the circumstances as described above, the present invention has been invented to realize a structure that can easily reduce the cost and stabilize the speed change operation.
本発明のトロイダル型無段変速機は、少なくとも1対のディスクと、複数のトラニオンと、これら各トラニオンと同数のパワーローラと、同じく同数のスラスト転がり軸受とを備える。
特に、本発明のトロイダル型無段変速機に於いては、前記トラニオンと前記外輪との間に、くさび型部材を設けている。そして、前記トラニオンが弾性変形しても、前記トラニオンが前記外輪を挟み込むことなく支承可能としている。
The toroidal-type continuously variable transmission of the present invention includes at least a pair of disks, a plurality of trunnions, the same number of power rollers as each trunnion, and the same number of thrust rolling bearings.
In particular, in the toroidal type continuously variable transmission of the present invention, a wedge-shaped member is provided between the trunnion and the outer ring. And even if the trunnion is elastically deformed, the trunnion can be supported without pinching the outer ring.
上述の様に構成する本発明のトロイダル型無段変速機によれば、コスト低廉化を図り易く、しかも変速動作を安定させられる構造を実現できる。
このうちのコスト低廉化は、前述の図9〜14に示した従来構造の第2例と同様の理由により、図り易い。
又、変速動作の安定化は、前記トラニオンと前記外輪との間に設けたくさび型部材により、前記トラニオンの弾性変形による前記外輪の挟み込みを防止する事により図れる。
According to the toroidal type continuously variable transmission of the present invention configured as described above, it is possible to realize a structure that can easily reduce the cost and stabilize the speed change operation.
Of these, cost reduction is easy to achieve for the same reason as in the second example of the conventional structure shown in FIGS.
Moreover, the speed change operation can be stabilized by preventing the outer ring from being caught by elastic deformation of the trunnion by a wedge-shaped member provided between the trunnion and the outer ring.
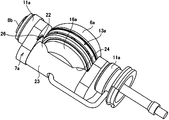
図1〜5は、本発明の実施の形態の1例を示している。尚、本例の特徴は、変速動作を安定させるべく、各トラニオン7bの支持梁部23に対し、スラスト玉軸受13a(図9〜14参照)を構成する外輪16bを、これら各支持梁部23に対する揺動変位を可能に支持しつつ、トラニオンが弾性変形しても、トラニオンが外輪を挟み込まない様にする為の構造にある。その他の部分の構造及び作用は、前述の図9〜14に示した従来構造の第2例と同様であるから、同等部分に関する図示並びに説明は、省略若しくは簡略にし、以下、本例の特徴部分を中心に説明する。
1 to 5 show an example of an embodiment of the present invention. The feature of this example is that the
本例の構造の場合、前記トラニオン7bと前記外輪16bとの間であって、支持梁部23の両端側に、1対のくさび部材27、27を設けている。また図5に示す様に、このくさび部材27、27には、前記トラニオン7bの支持梁部23の円筒状凸面22と係合する、外輪と同様の部分円筒面状の凹部28と、外輪16bの径方向端面に設けた傾斜面29と当接させる、前記トラニオン7bの支持梁部23の中心側からその両端側に向かうにつれて、支持梁部23から離れるように傾斜した傾斜面30と、前記トラニオン7bの段差面26aと当接する当接面31が設けられている。
In the case of the structure of this example, a pair of
このようにくさび部材27、27を設けることで、本例のトロイダル型無段変速機の運転時に、前述した図16に示す様にトラニオンが弾性変形したとしても、図6(b)に示す様にそれぞれのくさび部材27、27の当接面31、31が、前記トラニオン7bの段差面26a、26aに押されることにより、前記トラニオン7bの中心側にスライド移動し、外輪16bをパワーローラ6a側に押し出すので、前記トラニオン7bによる前記外輪16bの挟み込みを防止することができる。また、パワーローラ6aが押し出される移動量と、トラニオン7bが弾性変形による外輪16bの反対側への移動量とが、ある程度相殺されるため、パワーローラ6aとディスクとの接触部の移動量は、従来構造の第1例のトラニオンと比較して少なくなる。
By providing the
また、くさび型部材27の当接面30には、摩擦係数を低減させる表面処理を施してもよいし、くざび型部材を固体潤滑材により形成してもよい。
Further, the
また、くざび型部材27の凹部28は、ゴシックアーチ形状としてもよく、このようにすることで、この凹部28の内面とトラニオン7bの支持梁部23に設けた円筒状凸面22とが、これら両面の円周方向に関して2箇所位置で当接する為、これら両面の接触面積を確保して、これら両面の摩耗を抑える事ができる。
Further, the
また、トラニオン7bの支持梁部23と外輪16bとの間にパイプ部材32を設けている。パイプ部材32は長円形で、中心部に潤滑油を通過させる為の通孔33を形成している。そして、トラニオン7bの支持梁部23の一部で上流側給油路34の下流端開口部分に、上記パイプ部材32の一方の片半部を嵌合させる為の凹部35を形成しており、外輪16bの下流側給油路36の上流端開口部分に、上記パイプ部材32の他方の片半部を係合させる為の凹部37を形成している。この様なパイプ部材32の一方の片半部を上流側給油路34の下流端開口部分に形成した凹部35に嵌合させた状態で、他方の片半部を下流側給油路36の上流端開口部分に形成した凹部37に、ディスク2、5の弾性変形によりパワーローラ6aが揺動する範囲の変位を可能に、パイプ部材32と凹部37との間に隙間をもたせ係合させている。この様にして、上流側給油路34から下流側給油路36への潤滑供給をパイプ部材32の通孔33を通じて行う。
A
本発明は、トロイダル型無段変速機単独で実施できる他、特許文献5に記載されている様な、遊星歯車機構と組み合わせた無段変速装置として実施する事もできる。
The present invention can be implemented by a toroidal continuously variable transmission alone, or can be implemented as a continuously variable transmission in combination with a planetary gear mechanism as described in
1 入力回転軸
2 入力ディスク
3 出力筒
4 出力歯車
5 出力ディスク
6、6a パワーローラ
7、7a、7b トラニオン
8、8a、8b 傾転軸
9 支持梁部
10 支持板
11 ラジアルニードル軸受
12 支持軸
13 スラスト玉軸受
14 スラストニードル軸受
15 内輪軌道
16、16a、16b 外輪
17 外輪軌道
18 玉
19 駆動軸
20 押圧装置
21 アクチュエータ
22 円筒状凸面
23 支持梁部
24 凹部
25 ラジアルニードル軸受
26、26a 段差面
27 くさび部材
28 凹部
29 傾斜面
30 傾斜面
31 当接面
32 パイプ部材
33 通孔
34 上流側給油路
35 凹部
36 下流側給油路
37 凹部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011142932A JP5857473B2 (en) | 2011-06-28 | 2011-06-28 | Toroidal continuously variable transmission |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011142932A JP5857473B2 (en) | 2011-06-28 | 2011-06-28 | Toroidal continuously variable transmission |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013011287A JP2013011287A (en) | 2013-01-17 |
| JP2013011287A5 JP2013011287A5 (en) | 2014-08-07 |
| JP5857473B2 true JP5857473B2 (en) | 2016-02-10 |
Family
ID=47685331
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011142932A Expired - Fee Related JP5857473B2 (en) | 2011-06-28 | 2011-06-28 | Toroidal continuously variable transmission |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5857473B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5803584B2 (en) * | 2011-11-07 | 2015-11-04 | 日本精工株式会社 | Toroidal-type continuously variable transmission and processing method for parts thereof |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102005048074A1 (en) * | 2005-10-07 | 2007-04-12 | Daimlerchrysler Ag | Continuously adjustable variator for toroidal gear of motor vehicle, has bearing shell with direct contact to retention stirrup of variator |
| JP4905012B2 (en) * | 2006-06-02 | 2012-03-28 | 日本精工株式会社 | Toroidal continuously variable transmission |
| JP2010190379A (en) * | 2009-02-20 | 2010-09-02 | Nsk Ltd | Toroidal continuously variable transmission and continuously variable speed change device |
| JP5126206B2 (en) * | 2009-11-25 | 2013-01-23 | 日本精工株式会社 | Toroidal continuously variable transmission |
-
2011
- 2011-06-28 JP JP2011142932A patent/JP5857473B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013011287A (en) | 2013-01-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4905012B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| WO2012105663A1 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5088303B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5857473B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5990921B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5007600B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5126206B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5834525B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP6311451B2 (en) | Power roller unit for toroidal type continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5673205B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5862335B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP4706920B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP4807033B2 (en) | Half toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5742297B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP6508380B2 (en) | Power roller unit for toroidal type continuously variable transmission | |
| JP2013044412A (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5830999B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5803378B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5772026B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP6221754B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP6729105B2 (en) | Toroidal type continuously variable transmission | |
| JP4513391B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP5516859B2 (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission | |
| JP2006071028A (en) | Toroidal-type continuously variable transmission | |
| JP2012189199A (en) | Toroidal continuously variable transmission |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140619 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140619 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20140619 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140626 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150311 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150414 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150612 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20151117 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20151130 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5857473 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |