JP5772397B2 - Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode - Google Patents
Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5772397B2 JP5772397B2 JP2011186750A JP2011186750A JP5772397B2 JP 5772397 B2 JP5772397 B2 JP 5772397B2 JP 2011186750 A JP2011186750 A JP 2011186750A JP 2011186750 A JP2011186750 A JP 2011186750A JP 5772397 B2 JP5772397 B2 JP 5772397B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- active material
- material layer
- layer
- foil
- positive electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Battery Electrode And Active Subsutance (AREA)
Description
本発明は、導電性を有する箔状電極板上において、前記箔状電極板の表面を露出させる未塗工部が形成されるように、導電体層と活物質層とを順次に重ねて積層させて、電池の電極を作製する電池用電極の製造方法、及び、電池用電極に関する。
In the present invention, a conductive layer and an active material layer are sequentially stacked on a conductive foil-shaped electrode plate so that an uncoated portion that exposes the surface of the foil-shaped electrode plate is formed. The present invention relates to a battery electrode manufacturing method for producing a battery electrode, and a battery electrode.
かかる電池用電極は、電池の主要部分である発電要素を構成するものであり、発電要素においては、正極側及び負極側の夫々について箔状電極板の上に活物質層を積層して電極とし、正極側の電極と負極側の電極とを、セパレータを挟んだ状態で、交互に重ねた構成とする場合が多い。
この電池用の電極においては、箔状電極板に活物質を積層する際、箔状電極板と活物質との材料の選択によっては、両者の密着性を必ずしも十分には確保できない場合もある。
このような場合、下記特許文献1に記載のように、箔状電極板と活物質層との間に、両者の密着性を改善して、接触抵抗を低減するための導電体層(いわゆる、アンダーコート層)を配置する構成とすることが考えられている。
箔状電極板と活物質層との間に導電体層を配置することで、活物質層の接着強度が向上し、電池容量や寿命特性を向上させることができる。
Such a battery electrode constitutes a power generation element that is a main part of the battery. In the power generation element, an active material layer is laminated on a foil electrode plate for each of the positive electrode side and the negative electrode side to form an electrode. In many cases, the positive electrode and the negative electrode are alternately stacked with a separator interposed therebetween.
In this battery electrode, when the active material is laminated on the foil electrode plate, the adhesion between the foil electrode plate and the active material may not always be sufficiently ensured depending on the selection of the material.
In such a case, as described in
By disposing the conductor layer between the foil electrode plate and the active material layer, the adhesive strength of the active material layer can be improved, and the battery capacity and life characteristics can be improved.
しかしながら、箔状電極板と活物質層との間に、密着性向上のための導電体層を配置する場合、電極の製造工程において弊害が発生する場合がある。
すなわち、箔状電極板への導電体層の形成態様としては、導電体層の形成目的を考慮して、上層側の活物質層の形成領域には確実に導電体層が存在するように設定され、通常、導電体層の形成領域を活物質層の形成領域よりも広くして、導電体層の形成領域に活物質層の形成領域が完全に含まれるように設定している。
従って、箔状電極板上において、活物質層を形成していない未塗工部と、活物質層の形成領域との境界部においては、下層側の導電体部分が露出している領域が存在することになる。
However, when a conductor layer for improving adhesion is disposed between the foil-like electrode plate and the active material layer, a negative effect may occur in the electrode manufacturing process.
In other words, the conductive layer is formed on the foil electrode plate in consideration of the purpose of forming the conductive layer so that the conductive layer is surely present in the upper active material layer formation region. In general, the region for forming the conductor layer is made wider than the region for forming the active material layer so that the region for forming the conductor layer completely includes the region for forming the active material layer.
Therefore, on the foil electrode plate, there is a region where the lower conductor portion is exposed at the boundary between the uncoated portion where the active material layer is not formed and the active material layer formation region. Will do.
電極の製造工程においては、活物質層の形成位置を検出して、その検出位置情報に基づいて何らかの処理を施す工程があり、活物質層の形成位置の検出には、活物質層の端縁位置を光学的位置検出手段にて検出する場合が多い。
光学的位置検出手段にて活物質層の端縁位置を検出しようとするとき、正確に位置検出するためには、活物質層の端縁位置の両側で反射光の状態が明確に変化する必要がある。
一般に、基材となる箔状電極板と活物質層とでは、それらからの反射光の状態に明確な差異があるが、活物質層と導電体層とでは、通常、それらは同系色となる場合が多く、それらからの反射光の状態が類似して、明確な区別がつきにくいものとなる。
このため、上述のように、箔状電極板上において、活物質層を形成していない未塗工部と、活物質層の形成領域との境界部においては、下層側の導電体部分が露出している領域が存在すると、活物質層の形成領域と導電体部分の露出領域との境界位置は、上記のような光学的位置検出手段によっては、正確な位置の特定が困難となり、検出結果に誤差を含んでしまうことになる。
この活物質層の端縁位置の検出誤差は、その位置情報を利用した工程において、処理精度の低下をもたらし、ひいては電池性能の低下を招くことになってしまう。
本発明は、かかる実情に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的は、電池の電極において、箔状電極板と活物質層との間に導電体層を配置する場合においても、活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出できるようにする点にある。
In the manufacturing process of the electrode, there is a step of detecting the formation position of the active material layer and performing some processing based on the detected position information. The detection of the formation position of the active material layer includes the edge of the active material layer. In many cases, the position is detected by an optical position detection means.
When detecting the edge position of the active material layer with the optical position detection means, the state of the reflected light needs to change clearly on both sides of the edge position of the active material layer in order to accurately detect the position. There is.
In general, there is a clear difference in the state of reflected light from the foil-like electrode plate and the active material layer as the base material, but they are usually similar in color between the active material layer and the conductor layer. In many cases, the states of the reflected light from them are similar, making it difficult to distinguish clearly.
For this reason, as described above, on the foil electrode plate, the conductor portion on the lower layer side is exposed at the boundary between the uncoated portion where the active material layer is not formed and the active material layer forming region. If there is an active region, the boundary position between the formation region of the active material layer and the exposed region of the conductor portion is difficult to specify accurately depending on the optical position detection means as described above. Will contain errors.
This detection error of the edge position of the active material layer results in a decrease in processing accuracy and a decrease in battery performance in a process using the position information.
The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and the object thereof is to provide an active material layer even when a conductor layer is disposed between a foil electrode plate and an active material layer in a battery electrode. It is in the point that the edge position of can be detected with high accuracy.
本出願の第1の発明は、導電性を有する箔状電極板上における、前記箔状電極板の表面を露出させる未塗工部の形成位置以外の領域に、導電体層と活物質層とを順次に重ねて積層させて、電池の電極を作製する電池用電極の製造方法において、前記活物質層の形成領域における前記未塗工部の存在側の端縁部の少なくとも一部において、上層側の前記活物質層の端縁が、下層側の前記導電体層の端縁よりも前記未塗工部側に位置する活物質層はみ出し部を形成する工程と、前記活物質層はみ出し部において、光学的位置検出手段にて前記活物質層の存在位置を特定する工程とを有する。 1st invention of this application is a conductor layer, an active material layer, and the area | region other than the formation position of the uncoated part which exposes the surface of the said foil-like electrode board on the foil-like electrode board which has electroconductivity. In the method for manufacturing a battery electrode in which a battery electrode is manufactured by sequentially stacking and laminating, an upper layer is formed on at least a part of an edge portion on the side where the uncoated part is present in the active material layer forming region. A step of forming an active material layer protruding portion in which an edge of the active material layer on the side is located on the uncoated portion side with respect to an edge of the conductor layer on the lower layer side, and in the protruding portion of the active material layer And a step of specifying the position of the active material layer by an optical position detecting means.
すなわち、箔状電極板上での、導電体層と活物質層との積層形態として、上層側の活物質層の端縁が、下層側の導電体層の端縁よりも未塗工部側に位置して、活物質層が導電体層よりも未塗工部側にはみ出す状態で積層する。
これによって、上記のように活物質層等を配置した領域では、下層側の導電体層が露出していないので、光学的位置検出手段による導電体層と活物質層との弁別が困難な状況であっても、活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出できる。
活物質層における導電体層の形成領域からはみ出した部分には、箔状電極板との間に導電体層が存在しないのであるが、導電体層が存在しないからと言って、その部分が電池動作に全く寄与しない訳ではなく、多少電池容量等を低下させるに留まる。
しかも、活物質層における導電体層の形成領域からのはみ出し部分は、大面積にする必要はなく、必要最小限の面積で良いので、活物質層全体から見た電池容量の低下はわずかなものである。
That is, as a laminated form of the conductor layer and the active material layer on the foil electrode plate, the edge of the upper active material layer is closer to the uncoated part side than the edge of the lower conductor layer The active material layer is laminated in a state where the active material layer protrudes to the uncoated part side of the conductor layer.
As a result, in the region where the active material layer or the like is arranged as described above, the lower conductive layer is not exposed, and therefore it is difficult to discriminate between the conductive layer and the active material layer by the optical position detection means. Even so, the edge position of the active material layer can be detected with high accuracy.
In the portion of the active material layer that protrudes from the region where the conductor layer is formed, the conductor layer does not exist between the foil-like electrode plate, but the portion does not exist because the conductor layer does not exist. It does not contribute to the operation at all, but only slightly reduces the battery capacity.
Moreover, the portion of the active material layer that protrudes from the region where the conductor layer is formed need not be a large area, and may be the minimum necessary area, so that the battery capacity seen from the entire active material layer is only slightly reduced. It is.
又、本出願の第2の発明は、上記第1の発明の構成に加えて、前記活物質層はみ出し部において、前記活物質層の端縁と前記導電体層の端縁との距離が2mm以下に設定されている。
すなわち、導電体層からの活物質層のはみ出し幅を、2mm以下に設定することで、活物質層と箔状電極板との接着強度の低下を十分に抑制できることを実験により確認できた。
According to a second invention of the present application, in addition to the configuration of the first invention, a distance between an edge of the active material layer and an edge of the conductor layer is 2 mm at the protruding portion of the active material layer. It is set as follows.
That is, it was confirmed by experiments that the decrease in the adhesive strength between the active material layer and the foil electrode plate can be sufficiently suppressed by setting the protruding width of the active material layer from the conductor layer to 2 mm or less.
又、本出願の第3の発明は、上記第1又は第2の発明の構成に加えて、正極側の前記箔状電極板に形成した前記活物質層はみ出し部における前記活物質層の端縁位置を前記光学的位置検出手段にて検出し、その検出した位置情報に基づいて、正極側の前記箔状電極板上における前記活物質層と前記未塗工部との境界部分の上に、前記箔状電極板よりも電気抵抗の大きい短絡防止層を形成する。
すなわち、正極側電極と負極側電極とを対向配置して発電要素を構成する場合、通常、負極側の活物質層の形成領域を、正極側の活物質層の形成領域よりも大面積として、高価な正極活物質が有効に電池動作に寄与できるように設計する。又、リチウムイオン電池の場合では、負極側の活物質層の形成領域を、正極側の活物質層の形成領域よりも大面積とすることで、充電時に負極側の活物質層の形成されていない箇所にLi電析が発生してしまうのを防止できる。
これは、正極側電極において正極活物質層が形成されていない部分が負極側電極と対向していることを意味している。
このような状態で、異物の侵入等によって、正極活物質層が形成されていない部分と負極側部分とが接触してしまうと、その接触部分の電気抵抗の低さによって大きな短絡電流が流れてしまうことになる。
そこで、正極側の箔状電極板において、正極活物質層が形成されていない部分のうちの負極側電極と対向する部分に電気抵抗の大きい短絡防止層を形成して、大電流が流れる短絡事故を防止する。
この短絡防止層は、正極活物質層の端縁に沿って精度良く配置する必要があり、上述のように、正極活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出し、その検出情報を利用して、短絡防止層を形成することが特に有効となる。
In addition to the structure of the first or second invention, the third invention of the present application is an edge of the active material layer at the protruding portion of the active material layer formed on the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side. On the boundary portion between the active material layer and the uncoated portion on the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side based on the detected position information, the position is detected by the optical position detection means, A short-circuit prevention layer having an electric resistance larger than that of the foil electrode plate is formed.
That is, when the power generation element is configured by arranging the positive electrode and the negative electrode to face each other, the negative electrode side active material layer formation region is usually larger than the positive electrode side active material layer formation region, It is designed so that an expensive positive electrode active material can effectively contribute to battery operation. In the case of a lithium ion battery, the active material layer on the negative electrode side is formed to have a larger area than the formation region of the active material layer on the positive electrode side, so that the active material layer on the negative electrode side is formed during charging. It is possible to prevent Li electrodeposition from occurring at a location where there is not.
This means that the portion of the positive electrode on which the positive electrode active material layer is not formed faces the negative electrode.
In such a state, when the portion where the positive electrode active material layer is not formed and the negative electrode side portion come into contact with each other due to the intrusion of foreign matter, a large short-circuit current flows due to the low electrical resistance of the contact portion. Will end up.
Therefore, in the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side, a short-circuit accident in which a large current flows by forming a short-circuit prevention layer having a large electrical resistance in a portion of the portion where the positive electrode active material layer is not formed and facing the negative electrode-side electrode To prevent.
This short-circuit prevention layer needs to be accurately arranged along the edge of the positive electrode active material layer. As described above, the edge position of the positive electrode active material layer is accurately detected, and the detection information is used. It is particularly effective to form a short-circuit prevention layer.
又、本出願の第4の発明は、上記第1〜第3のいずれか発明の構成に加えて、前記活物質層はみ出し部における前記活物質層の端縁位置を前記光学的位置検出手段にて検出し、その検出した位置情報に基づいて、前記導電体層及び前記活物質層を積層した状態の前記箔状電極板の切断位置を設定する。
すなわち、電極の製造工程においては、箔状電極板に活物質層等を積層した後に、複数に切断分離することで、複数の電極をまとめて作製することがよく行われている。
このような製造工程を採用する場合、切断分離する際の活物質層の面積が精度良く設定されている必要があり、この切断によって活物質層の面積がばらつくと、電池容量のばらつきを招くことになる。
このような場合に、活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出し、その検出情報を利用して、切断位置を設定することが特に有効となる。
According to a fourth invention of the present application, in addition to the configuration of any one of the first to third inventions, an edge position of the active material layer in the protruding portion of the active material layer is used as the optical position detection means. Based on the detected position information, a cutting position of the foil electrode plate in a state where the conductor layer and the active material layer are laminated is set.
That is, in an electrode manufacturing process, after laminating an active material layer or the like on a foil-like electrode plate, a plurality of electrodes are often manufactured together by cutting and separating into a plurality.
When adopting such a manufacturing process, it is necessary that the area of the active material layer at the time of cutting and separation be set with high accuracy. If the area of the active material layer varies due to this cutting, battery capacity variation may be caused. become.
In such a case, it is particularly effective to accurately detect the edge position of the active material layer and set the cutting position using the detection information.
又、本出願の第5の発明は、上記第1〜第4のいずれかの発明の構成に加えて、前記箔状電極板は長尺帯状に形成され、前記導電体層及び前記活物質層は、前記箔状電極板の幅方向端部に前記未塗工部が位置する状態で、前記箔状電極板の長手方向に延びる帯状に形成され、前記活物質層と前記未塗工部との境界部分の略全長に亘る範囲が前記活物質層はみ出し部として設定されている。 According to a fifth invention of the present application, in addition to the configuration of any one of the first to fourth inventions, the foil electrode plate is formed in a long band shape, and the conductor layer and the active material layer Is formed in a strip shape extending in the longitudinal direction of the foil electrode plate in a state where the uncoated part is located at the widthwise end of the foil electrode plate, and the active material layer and the uncoated part, A range extending substantially over the entire length of the boundary portion is set as the protruding portion of the active material layer.
すなわち、長尺帯状の箔状電極板上に、それの長手方向に延びる状態で導電体層及び活物質層を帯状に形成する場合において、箔状電極板の長手方向に延びる活物質層と未塗工部との境界部分の略全長に亘って、活物質層の端縁を精度良く検出できる。
これによって、長尺帯状の電極に対する各種の処理を精度良く行うことが可能となる。
That is, when a conductor layer and an active material layer are formed in a strip shape on a long strip-like foil electrode plate in a state extending in the longitudinal direction, the active material layer extending in the longitudinal direction of the foil electrode plate The edge of the active material layer can be detected with high accuracy over substantially the entire length of the boundary with the coating portion.
This makes it possible to accurately perform various types of processing on the long strip electrode.
又、本出願の第6の発明は、導電性を有する箔状電極板上における、前記箔状電極板の表面を露出させる未塗工部の形成位置以外の領域に、導電体層と活物質層とが順次に重ねて積層された電池用電極において、前記活物質層の形成領域における前記未塗工部の存在側の端縁部の少なくとも一部において、上層側の前記活物質層の端縁が、下層側の前記導電体層の端縁よりも前記未塗工部側に位置する活物質層はみ出し部が形成されている。 In addition, the sixth invention of the present application provides a conductive layer and an active material in a region other than a formation position of an uncoated portion that exposes the surface of the foil-shaped electrode plate on the conductive foil-shaped electrode plate. In the battery electrode in which the layers are sequentially stacked and stacked, at least a part of the edge portion on the existing side of the uncoated portion in the active material layer forming region, the end of the active material layer on the upper layer side An active material layer protruding portion whose edge is located closer to the uncoated portion than the edge of the conductor layer on the lower layer side is formed.
すなわち、箔状電極板上での、導電体層と活物質層との積層形態として、上層側の活物質層の端縁が、下層側の導電体層の端縁よりも未塗工部側に位置して、活物質層が導電体層よりも未塗工部側にはみ出す状態で積層する。
これによって、上記のように活物質層等を配置した領域では、下層側の導電体層が露出していないので、光学的位置検出手段にて活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出できる。
That is, as a laminated form of the conductor layer and the active material layer on the foil electrode plate, the edge of the upper active material layer is closer to the uncoated part side than the edge of the lower conductor layer The active material layer is laminated in a state where the active material layer protrudes to the uncoated part side of the conductor layer.
As a result, in the region where the active material layer or the like is arranged as described above, the lower conductor layer is not exposed, so that the edge position of the active material layer can be detected with high accuracy by the optical position detecting means.
又、本出願の第7の発明は、上記第6の発明の構成に加えて、前記活物質層はみ出し部において、前記活物質層の端縁と前記導電体層の端縁との距離が2mm以下に設定されている。
すなわち、導電体層からの活物質層のはみ出し幅を、2mm以下に設定することで、正極活物質層と箔状正極板との接着強度の低下を十分に抑制することができる。
According to a seventh aspect of the present application, in addition to the structure of the sixth aspect, a distance between an edge of the active material layer and an edge of the conductor layer is 2 mm at the protruding portion of the active material layer. It is set as follows.
That is, by setting the protruding width of the active material layer from the conductor layer to 2 mm or less, it is possible to sufficiently suppress the decrease in the adhesive strength between the positive electrode active material layer and the foil-like positive electrode plate.
又、本出願の第8の発明は、上記第6又は第7の発明に構成に加えて、正極側の前記箔状電極板における前記活物質層と前記未塗工部との境界部分の上に、前記箔状電極板よりも電気抵抗の大きい短絡防止層が形成されている。
正極側の箔状電極板において活物質層と未塗工部との境界部分の上に、正極側の箔状電極板よりも電気抵抗の大きい短絡防止層を備えることで、異物等の侵入によって正極側電極と負極側電極とが接触したときに、大きな短絡電流が流れるのを防止する構成とする場合において、正極活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出し、その検出情報を利用して、精度良く短絡防止層を形成することができる。
In addition to the configuration of the sixth or seventh invention described above, the eighth invention of the present application is provided on the boundary portion between the active material layer and the uncoated portion of the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side. Further, a short-circuit prevention layer having a larger electric resistance than that of the foil electrode plate is formed.
By providing a short-circuit prevention layer having a higher electrical resistance than the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side on the boundary portion between the active material layer and the uncoated part in the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side, When configured to prevent a large short circuit current from flowing when the positive electrode side electrode and the negative electrode side electrode are in contact, the edge position of the positive electrode active material layer is accurately detected, and the detection information is used. The short-circuit prevention layer can be formed with high accuracy.
上記第1の発明によれば、電池の電極において、箔状電極板と活物質層との間に導電体層を配置する場合においても、上層側の活物質層の端縁が、下層側の導電体層の端縁よりも未塗工部側に位置して、活物質層が導電体層よりも未塗工部側にはみ出す状態で積層することで、活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出できるものとなる。
又、上記第2の発明によれば、導電体層から活物質層がはみ出す構成とした場合でも、活物質層と箔状電極板との接着強度の低下を十分に抑制できる。
又、上記第3の発明によれば、正極活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出して、短絡防止層を精度良く形成することができる。
又、上記第4の発明によれば、活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出し、その検出情報を利用して、電極を切断することで、電池容量のばらつきを抑制することができる。
又、上記第5の発明によれば、箔状電極板の長手方向の略全長に亘って活物質層の端縁を精度良く検出できるので、長尺帯状の電極に対する各種の処理を精度良く行うことが可能となる。
According to the first invention, in the battery electrode, even when the conductor layer is disposed between the foil electrode plate and the active material layer, the edge of the upper active material layer is located on the lower layer side. Accurate positioning of the edge of the active material layer by placing the active material layer on the uncoated part side of the conductor layer and protruding from the conductor layer to the uncoated part side It can be detected well.
Further, according to the second aspect, even when the active material layer protrudes from the conductor layer, it is possible to sufficiently suppress a decrease in the adhesive strength between the active material layer and the foil electrode plate.
According to the third aspect, the edge position of the positive electrode active material layer can be detected with high accuracy, and the short-circuit prevention layer can be formed with high accuracy.
According to the fourth aspect of the invention, variation in battery capacity can be suppressed by accurately detecting the edge position of the active material layer and cutting the electrode using the detected information.
Further, according to the fifth aspect, since the edge of the active material layer can be detected with high accuracy over substantially the entire length in the longitudinal direction of the foil-like electrode plate, various treatments for the long band-like electrode are performed with high accuracy. It becomes possible.
又、本出願の第6の発明によれば、箔状電極板と活物質層との間に導電体層を配置する場合においても、活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出できるものとなる。
又、本出願の第7の発明によれば、活物質層が導電体層よりも未塗工部側にはみ出す状態で積層する場合でも、活物質層と箔状電極板との接着強度の低下を十分に抑制することができる。
又、本出願の第8の発明によれば、正極活物質層の端縁位置を精度良く検出して、短絡防止層を精度良く形成することができる。
Further, according to the sixth invention of the present application, the edge position of the active material layer can be accurately detected even when the conductor layer is disposed between the foil electrode plate and the active material layer. .
Further, according to the seventh invention of the present application, even when the active material layer is laminated in a state of protruding to the uncoated part side from the conductor layer, the adhesive strength between the active material layer and the foil electrode plate is reduced. Can be sufficiently suppressed.
According to the eighth invention of the present application, the edge position of the positive electrode active material layer can be detected with high accuracy, and the short-circuit prevention layer can be formed with high accuracy.
以下、本発明の電池用正極側電極の製造方法の実施の形態を図面に基づいて説明する。
本実施の形態では、電池として二次電池の1例である非水電解液二次電池(より具体的にはリチウムイオン電池)を例示して、その製造方法を説明する。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of a method for producing a positive electrode for a battery according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
In the present embodiment, a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery (more specifically, a lithium ion battery), which is an example of a secondary battery, is illustrated as a battery, and a manufacturing method thereof will be described.
〔非水電解液二次電池RBの構成〕
図12の斜視図に示すように、本実施の形態の非水電解液二次電池RBは、有底筒状(より具体的には有底矩形筒状)の缶体1の開放面に蓋部2を被せて溶接して構成した電池筐体BC(以下において、単に「筐体BC」と称する)を有している。蓋部2は、短冊状の長方形の板材にて形成され、それの筐体BC外方側となる面に正極の電極端子である端子ボルト5と負極の電極端子である端子ボルト7とが取り付けられている。
缶体1は蓋部2の形状に合わせて扁平形状の直方体であり、従って、筐体BC全体としても扁平な略直方体形状を有している。
[Configuration of Nonaqueous Electrolyte Secondary Battery RB]
As shown in the perspective view of FIG. 12, the non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery RB of the present embodiment has a lid on the open surface of a bottomed tubular body (more specifically, a bottomed rectangular tubular body). It has a battery casing BC (hereinafter simply referred to as “casing BC”) formed by covering and welding the portion 2. The lid portion 2 is formed of a strip-shaped rectangular plate material, and a
The
筐体BCの内方側には、図11において2点鎖線で示す発電要素3と集電体4,6とが電解液に浸される状態で収納配置されている。図11は、缶体1を除いた状態で、下方側から見上げた斜視図として、筐体BCの内方側を示している。
集電体4,6は、発電要素3と端子ボルト5,7とを電気的に接続するための部材であり、何れも導電体にて形成されている。
集電体4と集電体6とは、略同一形状のものが対称に配置される関係となっているが、材質が異なる。正極側の集電体4はアルミニウムにて形成され、負極側の集電体6は銅にて形成されている。
On the inner side of the casing BC, the
The current collectors 4 and 6 are members for electrically connecting the
The current collector 4 and the current collector 6 have a relationship in which substantially the same shape is arranged symmetrically, but the materials are different. The positive electrode side current collector 4 is made of aluminum, and the negative electrode side current collector 6 is made of copper.
集電体4,6は、上記の金属材料からなる幅狭の略矩形板状部材を、所定の形状に屈曲形成して構成しており、端子ボルト5,7の配置面である蓋部2の表面に沿って延びる形状の部分と、蓋部2の長手方向端部付近で下方側(端子ボルト5,7の存在側と反対側)へ90度屈曲して、蓋部2の筐体BC内方側の面の法線方向に延びる部分とが連なる略L字状の屈曲形状を有している。集電体4,6の縦姿勢部分において、更に発電要素3側に屈曲させて、発電要素3と接続するための接続部4a,6aが形成されている。
略L字状の集電体4,6は、蓋部2と、その蓋部2の長手方向の端部に直交姿勢で連なる缶体1の幅狭の側面とに沿う姿勢で配置されている。
The current collectors 4 and 6 are formed by bending and forming a narrow, substantially rectangular plate member made of the above metal material into a predetermined shape, and the lid portion 2 which is a surface on which the
The substantially L-shaped current collectors 4, 6 are arranged in a posture along the lid portion 2 and the narrow side surface of the
発電要素3は、詳しくは後述するが、何れも導電性を有する材料で長尺帯状の形状に形成された正極側の箔状電極板(以下において、「箔状正極板」と称する)及び負極側の箔状電極板(以下において、「箔状負極板」と称する)の夫々に活物質を塗布して正極側電極及び負極側電極を作製し、それらを同じく長尺のセパレータを挟んで積層状態で巻回した、いわゆる巻回型の発電要素として構成されている。
発電要素3は、上記のように巻回した状態で、正極側電極の未塗工部3a(正極活物質が塗布されずに箔状正極板が露出している部分)が側方(箔状正極板の長手方向と直交する方向)に突出し、負極側電極の未塗工部3b(負極活物質が塗布されずに箔状負極板が露出している部分)が反対側の側方(箔状負極板の長手方向と直交する方向)に突出している。
本実施の形態の発電要素3は、扁平形状に正極側電極及び負極側電極等を巻回して、扁平形状の筐体BCに適合させている。
発電要素3の缶体1内での配置姿勢は、正極側電極等の巻回軸心が蓋部2の長手方向と平行となる姿勢としており、図11に概略的に示すように、正極側電極の未塗工部3aの位置に集電体4の接続部4aが入り込み、負極側電極の未塗工部3bの位置に集電体6の接続部6aが入り込む位置関係としている。
正極側電極の未塗工部3aは束ねられた状態で集電体4の接続部4aに溶接され、負極側電極の未塗工部3bは束ねられた状態で集電体6の接続部6aに溶接され、集電体4,6で発電要素3を支持している。
As will be described in detail later, the
In the state where the
The
The
The uncoated portion 3a of the positive electrode is welded to the connecting
上述のように金属製(具体的には、アルミニウム製)の蓋部2に取り付けられている正極側の端子ボルト5は正極側の集電体4に電気的に接続され、負極側の端子ボルト7は負極側の集電体6に電気的に接続されている。
正極側の集電体4は、端子ボルト5の頭部側に一体形成されているリベット8を経て端子ボルト5に電気的に接続され、リベット8は、集電体4,集電体4及びリベット8と蓋部2との間の電気的絶縁のための下部ガスケット12,蓋部2,リベット8を含む端子ボルト5と蓋部2との間の電気的絶縁のための上部ガスケット11を貫通した状態で、筐体BC内方側端部でかしめられ、これによって集電体4を蓋部2に固定している。
負極側も同様の構成であり、負極側の集電体6は、端子ボルト7の頭部側に一体形成されているリベット15を経て端子ボルト7に電気的に接続され、リベット15は、集電体6,集電体6及びリベット15と蓋部2との間の電気的絶縁のための下部ガスケット18,蓋部2,リベット15を含む端子ボルト7と蓋部2との間の電気的絶縁のための上部ガスケット17を貫通した状態で、筐体BC内方側端部でかしめられ、これによって集電体6を蓋部2に固定している。
上部ガスケット11,17及び下部ガスケット12,18は、蓋部2と蓋部2を貫通するリベット8,15との間の気密シールの機能も果たしている。
As described above, the
The current collector 4 on the positive electrode side is electrically connected to the
The negative electrode side has the same configuration, and the negative electrode side current collector 6 is electrically connected to the
The
〔非水電解液二次電池RBの製造工程〕
次に、上記構成の二次電池RBの製造工程を、発電要素3の電極板の製造工程を主体に説明する。
〔正極側電極の製造工程〕
先ず、発電要素3の正極側電極の製造工程について説明する。
正極側電極は、上述のように、箔状正極板に正極活物質を塗布して作製しており、本実施の形態では、耐酸化性に優れるアルミニウム箔を箔状正極板として用いる。本実施の形態では、このアルミニウム箔は、幅が160mmの長尺帯状に形成しており、アルミニウム箔の厚さは12μm〜25μmで良いが、15μmの厚さとすることが好適である。アルミニウム箔以外では、チタン,ステンレス鋼,ニッケル及び導電性高分子等を箔状に形成して箔状正極板として用いることができる。
上記の箔状正極板に塗布する正極活物質は、本実施の形態では、リン酸鉄リチウム(LiFePO4)を使用しており、それとの関係で、箔状正極板と正極活物質層との間に、正極活物質層の付着強度を向上させて接触抵抗の低減等を図るための導電体層(いわゆる、「アンダーコート層」)を塗布しており、導電体層と正極活物質層とを順次に重ねて積層させている。
本実施の形態では、この導電体層を形成するための塗布剤として、アセチレンブラック10重量%,グリセル化キトサン4.5重量%,ピロリメット酸4.5重量%及びNMP(N−メチル−2−ピロリドン)81重量%を混合してスラリー状としたものを使用しており、この塗布剤を箔状正極板の表裏両面に塗布する。
[Manufacturing process of non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery RB]
Next, the manufacturing process of the secondary battery RB having the above configuration will be described mainly with respect to the manufacturing process of the electrode plate of the
[Production process of positive electrode]
First, the manufacturing process of the positive electrode of the
As described above, the positive electrode is prepared by applying a positive electrode active material to a foil-shaped positive plate. In this embodiment, an aluminum foil having excellent oxidation resistance is used as the foil-shaped positive plate. In the present embodiment, the aluminum foil is formed in a long band shape having a width of 160 mm, and the thickness of the aluminum foil may be 12 μm to 25 μm, but is preferably 15 μm. Other than aluminum foil, titanium, stainless steel, nickel, conductive polymer, etc. can be formed into a foil shape and used as a foil-like positive electrode plate.
In the present embodiment, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO 4 ) is used as the positive electrode active material applied to the foil-shaped positive electrode plate, and the relation between the foil-shaped positive electrode plate and the positive electrode active material layer is related thereto. A conductor layer (so-called “undercoat layer”) for improving the adhesion strength of the positive electrode active material layer to reduce contact resistance is applied between the conductor layer and the positive electrode active material layer. Are stacked one after another.
In the present embodiment, as a coating agent for forming this conductor layer, acetylene black 10% by weight, glycerated chitosan 4.5% by weight, pyrrolimetic acid 4.5% by weight and NMP (N-methyl-2- (Pyrrolidone) 81% by weight is used as a slurry, and this coating agent is applied to both the front and back surfaces of the foil-like positive electrode plate.
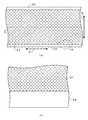
図2(a)に、箔状正極板であるアルミニウム箔22の表面に導電体層21を形成した状態を、平面視で示す。
図2(a)において、矢印Bは長尺帯状のアルミニウム箔22の幅方向を示しており、その幅方向両端部に上記の未塗工部3aとなるエリアが設定されている。導電体層21は、その未塗工部3aの形成位置以外の幅方向中央領域において、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向(図2(a)において、矢印Aで示す方向)に延びる帯状に形成されている。幅方向両端部の導電体層21が形成されない部分の幅(アルミニウム箔22の幅方向での長さ)は、本実施の形態では、夫々10mmに設定している。
尚、図2(b)は、後工程での処理状態との対比のために、図2(a)において2点鎖線Dで囲んで概略的な位置を示す部分の拡大図を示すものである。
アルミニウム箔22は長尺帯状であり、ロール状に巻き取られた状態のアルミニウム箔22を、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向(図2(a)において、矢印Aで示す方向)に送り搬送して、搬送されるアルミニウム箔22上に、グラビアコートにより導電体層21を塗布する。導電体層21の塗布厚は、本実施の形態では、乾燥後に導電体層21の厚さが1μm〜2μmとなるように設定している。
本実施の形態では、2条分の正極側電極を同時処理で作製する。すなわち、アルミニウム箔22は、幅方向(図2(a)において、矢印Bで示す方向)の長さが、正極側電極の幅の2倍の幅であり、正極側電極の製造工程の最終工程で、図2において1点鎖線Cで示す幅方向中央位置で切断して、2条分の正極側電極に分離する。
導電体層21の塗布位置は、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向(矢印Bで示す方向)端縁位置を光学的に検出して、その位置情報に基づいて、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向中央位置と、導電体層21の塗布幅の中央位置とが一致するように、高精度に制御されている。
導電体層21は、塗布後に乾燥処理される。
以上の導電体層21の塗布工程を、アルミニウム箔22の反対側の面でも繰り返す。
FIG. 2A shows a state in which the
In FIG. 2A, an arrow B indicates the width direction of the long strip-shaped
Note that FIG. 2B shows an enlarged view of a portion showing a schematic position surrounded by a two-dot chain line D in FIG. 2A for comparison with a processing state in a subsequent process. .
The
In the present embodiment, two strips of the positive electrode are produced by simultaneous processing. That is, the length of the
The position where the
The
The above coating process of the
導電体層21が塗布され、更に、乾燥された後、次に、導電体層21の上に塗り重ねる状態で活物質層と短絡防止層とを塗布する。
本実施の形態では、上述のように、正極活物質としてリン酸鉄リチウム(LiFePO4)を使用している。
短絡防止層は、発電要素3として組み立てたときに、正極側電極において、正極活物質が塗布されていない部分のうち、負極側電極の負極活物質層と対向する部分に塗布形成することで、正極側電極の未塗工部3aと負極側電極とが対向してしまうことのないようにするためのものである。短絡防止層を備えることによって、異物等の侵入によってセパレータが破られたような場合でも、負極活物質層と箔状正極板とが接触して発熱等の事象が発生してしまことを防止できる。
この短絡防止層は正極活物質層の塗布後に塗布するのであるが、正極活物質層の塗布と短絡防止層の塗布とを一連に行い、正極活物質層が乾燥していない状態で短絡防止層を塗布している。このようにすることで、短絡防止層の剥離強度を高めることができる。
After the
In the present embodiment, as described above, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO 4 ) is used as the positive electrode active material.
When the short-circuit prevention layer is assembled as the
This short-circuit prevention layer is applied after the application of the positive electrode active material layer, but the application of the positive electrode active material layer and the application of the short-circuit prevention layer are performed in series, and the short-circuit prevention layer is in a state where the positive electrode active material layer is not dried. Is applied. By doing in this way, the peeling strength of a short circuit prevention layer can be raised.
先ず、正極活物質層の塗布について説明する。
正極活物質層は、マイクロサイズ粒子のLiFePO4の粉体87重量%と、導電助剤であるアセチレンブラック5重量%と、結着剤であるポリフッ化ビリニデン(PVDF)8重量%との混合物に、NMP(N−メチル−2−ピロリドン)を加えてペースト状とした正極合剤ペーストを、導電体層21が塗布されたアルミニウム箔22の表裏両面に塗布して、導電体層21とアルミニウム箔22の積層構造を形成する。
尚、上記のマイクロサイズ粒子のLiFePO4は、D50(メディアン径)が20μmのものを使用しており、全てのLiFePO4粒子は、層厚が約1nmのカーボンコート層で被覆されている。LiFePO4粒子の粒子径には、このカーボンコート層も含めている。
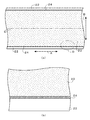
塗布の工程は、導電体層21の塗布工程と同様であり、導電体層21を形成したアルミニウム箔22を、それの長手方向に送り搬送して、搬送されるアルミニウム箔22の導電体層21の上に上記のペーストをダイコートにより塗布することで、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向に延びる帯状の正極活物質層23を形成し、図3(a)に示す状態とする。
正極活物質層23は、図3(a)に示すように、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向(図3(a)において、矢印Aで示す方向)に延びる帯状に塗布している。正極活物質層23の塗布厚は、40μm〜130μmで良く、本実施の形態では130μmとしている。
正極活物質層23の塗布位置は、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向(図3(a)において、矢印Bで示す方向)端縁位置あるいは導電体層21の幅方向端縁位置を光学的に検出して、その位置情報に基づいて、アルミニウム箔22や導電体層21の幅方向中央位置と、正極活物質層23の塗布幅の中央位置とが一致するように高精度に制御されている。
First, application of the positive electrode active material layer will be described.
The positive electrode active material layer is a mixture of 87% by weight of micro-sized particles of LiFePO 4 powder, 5% by weight of acetylene black as a conductive aid, and 8% by weight of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) as a binder. , NMP (N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone) was added to form a positive electrode mixture paste on both the front and back surfaces of the
Note that the micro-sized particles of LiFePO 4 having a D50 (median diameter) of 20 μm are used, and all the LiFePO 4 particles are covered with a carbon coat layer having a layer thickness of about 1 nm. This carbon coat layer is included in the particle diameter of the LiFePO 4 particles.
The coating process is the same as the coating process of the
As shown in FIG. 3A, the positive electrode
The positive electrode
正極活物質層23の塗布幅(図3(a)において、矢印Bで示す方向での塗布幅)は、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向両端部に未塗工部3aとなるアルミニウム箔22の露出領域が位置する状態で、導電体層21を完全に覆う塗布幅に設定している。
図3(a)における2点鎖線Dで囲む領域付近を拡大したものを、図2(b)と対応させて、図3(b)に示している。
図2(b)における導電体層21の端縁を、図3(b)において破線Eで示しており、上層側の正極活物質層23の幅方向(矢印Bで示す方向)の端縁は、破線Eで示す下層側の導電体層21の端縁よりも、未塗工部3aとなるアルミニウム箔22が露出する領域側に位置して、正極活物質層23が導電体層21からはみ出している。
説明の便宜上、この正極活物質層23が導電体層21の形成位置からアルミニウム箔22の露出領域側へはみ出している部分を「活物質層はみ出し部」と称する場合がある。
本実施の形態では、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向において、導電体層21及び正極活物質層23の塗布範囲の全長に亘って、正極活物質層23が導電体層21からはみ出しており、正極活物質層と未塗工部との境界部分の略全長に亘る範囲が前記活物質層はみ出し部として設定されている。
アルミニウム箔22の幅方向(矢印Bで示す方向)における、正極活物質層23の端縁位置と導電体層21の端縁位置(破線Eで示す位置)との距離W(図3(b)参照)は、2mm以下となるように、正極活物質層23の塗布幅を設定している。
The coating width of the positive electrode active material layer 23 (the coating width in the direction indicated by the arrow B in FIG. 3A) is the exposed region of the
FIG. 3B shows an enlarged view of the region surrounded by the two-dot chain line D in FIG. 3A, corresponding to FIG. 2B.
The edge of the
For convenience of explanation, a portion where the positive electrode
In the present embodiment, in the longitudinal direction of the
A distance W between the edge position of the positive electrode
正極活物質層23の塗布後、同一の搬送経路において、引き続いて短絡防止層の塗布を行う。
短絡防止層は、電気的絶縁部材の微粒子を結着剤と混合し、更に、それを適宜の液体と混合してペースト状として、正極活物質層23が塗布されたアルミニウム箔22の表裏両面に塗布する。
上記の電気的絶縁部材の微粒子としては、Al2O3,SiO2,ZrO2,TiO2,MgO等の無機粒子の他、ポリイミド粉末等の有機粒子を用いることができる。これらのうち、安定性や取り扱いの容易さ等から、Al2O3を使用するのが好ましく、特に、箔状正極板との密着性や接合強度等の観点からγ型アルミナ粒子が好ましい。
上記微粒子の粒径は、一次粒径の中央値で1nm〜2000nmのものが使用できるが、箔状正極板と密着性や接合強度の観点からは、1nm〜200nmのものを使用するのが好ましく、1nm〜20nmであることが更に好ましい。
電気的絶縁部材の微粒子と混合する結着剤としては、ポリフッ化ビリニデン(PVDF),ポリイミド,ポリアミドイミド等を用いることができるが、箔状正極板との密着性や接合強度の観点からは、PVDFを用いることが好ましい。
本実施の形態では、粒径5nm,比表面積96m2/g,タップ密度0.04g/cm3のγ型アルミナ粒子2.1kgを、結着剤であるPVDFを12%含有したNMP溶液21.39g(PVDF量として2.567kg)をNMP6.0kgに溶解した液に混合し、均一に分散させて、スラリー状の短絡防止剤ペーストとした。
短絡防止層24の構成材料としては、上述のような電気的絶縁部材である必要は必ずしもないが、十分に電気抵抗が高いことが必要であり、少なくともアルミニウム箔22よりも電気抵抗の大きくなければ意味がない。
After the application of the positive electrode
The short-circuit prevention layer is obtained by mixing the fine particles of the electrically insulating member with a binder and further mixing it with an appropriate liquid to form a paste on both front and back surfaces of the
As the fine particles of the electrical insulating member, organic particles such as polyimide powder can be used in addition to inorganic particles such as Al 2 O 3 , SiO 2 , ZrO 2 , TiO 2 and MgO. Of these, Al 2 O 3 is preferably used from the viewpoints of stability and ease of handling, and γ-type alumina particles are particularly preferable from the viewpoint of adhesion to the foil-like positive electrode plate and bonding strength.
The particle diameter of the fine particles can be 1 nm to 2000 nm as the median of the primary particle diameter, but it is preferable to use 1 nm to 200 nm from the viewpoint of adhesion to the foil-like positive electrode plate and bonding strength. More preferably, it is 1 nm-20 nm.
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), polyimide, polyamideimide, etc. can be used as the binder to be mixed with the fine particles of the electrically insulating member, but from the viewpoint of adhesion and foil strength with the foil-like positive electrode plate, It is preferable to use PVDF.
In this embodiment, 2.1 kg of NMP solution containing 2.1 kg of γ-type alumina particles having a particle size of 5 nm, a specific surface area of 96 m 2 / g, and a tap density of 0.04 g /
The constituent material of the short-
塗布の工程は、正極活物質層23等の塗布工程と同様であり、正極活物質層23等が塗布された状態で送り搬送されているアルミニウム箔22に対して、ダイコートにより短絡防止層24を塗布し、図4(a)に示す状態とする。
図4(b)は、図2(b)及び図3(b)と対応させて、図4(a)において2点鎖線Dで示す領域付近を拡大して示している。
短絡防止層24の塗布位置は、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向(図4(a)において、矢印Bで示す方向)における正極活物質層23の両端位置において、正極活物質層23の端縁に重なると共に、正極活物質層23の端縁からアルミニウム箔22の露出部分側へ設定幅の範囲に亘る状態で、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向(図4(a)において、矢印Aで示す方向)に延びる帯状に塗布している。
The coating process is the same as the coating process of the positive electrode
FIG. 4B is an enlarged view of the vicinity of the region indicated by a two-dot chain line D in FIG. 4A in correspondence with FIGS. 2B and 3B.
The application position of the short-
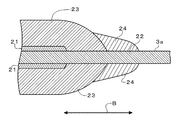
正極活物質層23と短絡防止層24との境界付近を、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向視の拡大断面図として示す図1に示すように、短絡防止層24は、正極活物質層23と未塗工部3aとの境界部分の上に形成し、正極活物質層23の端縁付近の傾斜部分と重なる位置から、アルミニウム箔22の露出領域に拡がる状態で塗布されている。又、短絡防止層24の塗布厚さは、3μm〜15μmとしており、短絡防止層24が正極活物質層23の塗布部分よりも高くならないようにしている。
このように、短絡防止層24を、正極活物質層23の端縁付近における傾斜部分から塗布しているのは、正極活物質層23と短絡防止層24との接合強度を強くするためであり、又、短絡防止層24の高さを、正極活物質層23の高さよりも低くしているのは、短絡防止層24では、金属酸化物の微粒子を確実に結着させるために結着材の使用量が多めになっており、正極活物質層23の上に乗った状態で塗布されると、後述のプレス加工処理において、プレス用のロールから離れにくくなるからである。尚、図1においては、正極活物質層23及び短絡防止層24をアルミニウム箔22の表裏両面に塗布した状態で示しており、又、各層の厚さは、必ずしも正確な比率で描いたものではない。
As shown in FIG. 1 showing the vicinity of the boundary between the positive electrode
Thus, the reason why the short-
アルミニウム箔22の幅方向(図1等において、矢印Bで示す方向)での短絡防止層24の塗布幅は、正極側電極と負極側電極とを巻回したときに、正極側電極において、負極側電極の負極活物質層の塗布部分と対向する領域のうちの正極活物質層23が塗布されていない領域を覆う幅に設定されている。
すなわち、負極側電極の負極活物質層の塗布幅は、上述の正極活物質層23よりも若干幅広に設定されており、正極活物質層23の塗布幅と負極活物質層の塗布幅の差の部分を上記短絡防止層24で埋める関係としている。
短絡防止層24の塗布位置は、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向における正極活物質層23の端縁位置を、撮像装置等の光学センサを用いた光学的位置検出手段にて検出して、その検出情報に基づいて正極活物質層23の存在位置を特定し、短絡防止層24の端縁が、正極活物質層23の端縁の傾斜部分に重なるように(図1参照)、高精度に制御されている。
The coating width of the short-
That is, the application width of the negative electrode active material layer of the negative electrode is set to be slightly wider than the positive electrode
As for the application position of the short-
この光学的位置検出手段としては、例えば、撮像装置にて正極活物質層23の端縁位置付近を撮像し、その撮像画像における、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向での色変化情報から正極活物質層23の端縁位置を特定すれば良い。
このようにして検出した正極活物質層23の端縁位置の検出情報に基づいて、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向での、短絡防止層24の塗布位置あるいはアルミニウム箔22の搬送位置を制御することで、短絡防止層24を精度良く塗布することができる。
このように短絡防止層24の形成位置を制御する関係で、光学的位置検出手段は、正極活物質層23の端縁位置を、短絡防止層24の塗布の全長に亘って連続的に検出しており、上述のように、正極活物質層23と未塗工部3aとの境界部分の略全長に亘る範囲を上記活物質層はみ出し部として設定している。
アルミニウム箔22に正極活物質層23及び短絡防止層24が塗布された後、乾燥処理され、更に、アルミニウム箔22の反対側の面にも、上記工程により正極活物質層23及び短絡防止層24が塗布され、乾燥処理される。
As this optical position detection means, for example, the vicinity of the edge position of the positive electrode
By controlling the application position of the short-
Thus, the optical position detection means continuously detects the edge position of the positive electrode
After the positive electrode
以上の工程によって、アルミニウム箔22の表裏両面に、導電体層21,正極活物質層23及び短絡防止層24が形成された後、プレス加工処理を行う。
このプレス加工処理には、正極側電極の湾曲抑制のためのプレス加工と、正極活物質層23の高密度化等のためのプレス加工とがあり、送り搬送されるアルミニウム箔22(正極活物質層23等が塗布されたもの)に対して、順次に加工処理される。
プレス加工処理は、図6に概略的に示すプレス加工装置PMにて行う。
プレス加工装置PMは、正極活物質層23等を塗布したアルミニウム箔22のロール31からアルミニウム箔22を引き出し、所定のテンションを付加して搬送駆動する搬送系32と、正極活物質層23等を塗布したアルミニウム箔22のうち、幅方向両端部のアルミニウム箔22が露出している部分を延伸するための間欠ロールプレス装置33と、正極活物質層23の塗布領域全体を延伸するための主ロールプレス装置34とが備えられて構成されている。
After the
The press processing includes press processing for suppressing the bending of the positive electrode, and press processing for increasing the density of the positive electrode
The press processing is performed by a press processing apparatus PM schematically shown in FIG.
The press working apparatus PM pulls out the
間欠ロールプレス装置33は、図7の斜視図に概略的に示すように、アルミニウム箔22の搬送経路を挟んで、一対の圧着ローラ35,36が備えられ、図示を省略するモータによって一対の圧着ローラ35,36が回転駆動されている。
一対の圧着ローラ35,36のうちの一方の圧着ローラ35には、それの周面の幅方向両端部において、低い段差を有して台地状に突出する凸部35aが、設定間隔をおいて周方向に並ぶ状態で形成されている。
凸部35aの形状は、圧着ローラ35の周面の法線方向視で略矩形形状に形成しており、より具体的には、内方側の角部を丸めた長方形形状としている。
圧着ローラ35における凸部35aの形成位置は、正極活物質層23等が塗布形成されたアルミニウム箔22における幅方向両端部に対応する位置に設定され、凸部35aは、幅方向両端部のアルミニウム箔22の露出部分のみを押圧する。
正極活物質層23の未塗布部分を、圧着ローラ35の凸部35aで押圧し、予め延伸しておくことで、正極側電極の湾曲を抑制するのであるが、詳しくは後述する。
As schematically shown in the perspective view of FIG. 7, the intermittent
One pressure roller 35 of the pair of
The shape of the
The positions where the
The uncoated portion of the positive electrode
間欠ロールプレス装置33における各部の具体的な大きさとしては、圧着ローラ35は、直径が118mmの円柱形状のローラに高さが1mmの凸部35aが形成されている。
圧着ローラ35における、周方向での凸部35aの並び間隔(ピッチ)は、15mm〜50mmに設定すれば、所望の延伸効果が得られ、30mm程度に設定することで特に良好な結果が得られた。
一対の圧着ローラ35,36は、挟持搬送物に対して所定の圧力をかけてプレス加工するのであるが、本実施の形態では、100kgf/cm2以上の線圧をかけるように設定している。
As a specific size of each part in the intermittent
If the interval (pitch) of the
The pair of
主ロールプレス装置34は、本実施の形態では、直径が300mmのプレス用ローラを使用し、正極活物質層23の塗布形成部分に対して、200kgf/cm2の線圧をかけて押圧する。
間欠ロールプレス装置33による線圧と主ロールプレス装置34による線圧との関係は、間欠ロールプレス装置33による線圧が、主ロールプレス装置34による線圧の少なくとも30%以上となるように設定することで、湾曲が発生しないことを確認できた。
本実施の形態では、上記搬送系32,間欠ロールプレス装置33及び主ロールプレス装置34は、正極活物質層23等を塗布形成したアルミニウム箔22を、分速20m以上の速度で搬送駆動している。
搬送系32によって、アルミニウム箔22にかけられるテンションは、10N〜60N程度で良いが、20N〜30Nとすることが好ましい。
In the present embodiment, the main
The relationship between the linear pressure by the intermittent
In the present embodiment, the
The tension applied to the
正極活物質層23等を塗布形成したアルミニウム箔22は、ロール31から引き出されて、間欠ロールプレス装置33及び主ロールプレス装置34を通過してプレス加工処理されることで、図5において平面視で示すように、圧着ローラ35の凸部35aに対応する加圧痕25が形成される。本実施の形態では、上記のプレス加工処理によって、130μmの厚さであった正極活物質層23は片側80μmの厚さまで圧縮され、又、正極活物質層23の未塗布部分において間欠ロールプレス装置33でプレス加工された部分には、元の厚さの95%まで圧延された加圧痕25が形成される。
間欠ロールプレス装置33でのプレス加工処理無しに、主ロールプレス装置34にてアルミニウム箔22における正極活物質層23の塗布形成部分をプレス加工すると、強い圧力がかかる正極活物質層23の塗布形成部分は長手方向に延びるが、アルミニウム箔22の露出部分はそれほど強い圧力は作用せず、長手方向での延びが小さくなる。
具体例としては、正極活物質層23の塗布形成部分におけるプレス加工前後の長手方向での伸び率が0.346%のときに、アルミニウム箔22の露出部分におけるプレス加工前後の長手方向での伸び率が0.031%となり、伸び率で10倍以上の開きがある。
この延びの差に対してなにも対策を施さず、正極活物質層23等を塗布形成したアルミニウム箔22を上記のプレス加工処理後に、図5において1点鎖線Cで示す位置で切断すると、正極活物質層23の塗布側が凸となる姿勢で弓なりに湾曲してしまうことになる。
これに対して、上述のように、間欠ロールプレス装置33にてアルミニウム箔22の露出部分をプレス処理して延伸させることで、正極活物質層23の塗布形成部分における長手方向の延びと、アルミニウム箔22の露出部分における長手方向の延びとがバランスし、図5において1点鎖線Cで示す位置で切断したときの湾曲が十分に抑制される。
The
If the application forming portion of the positive electrode
As a specific example, when the elongation ratio in the longitudinal direction before and after the press working in the coating formation portion of the positive electrode
No measures are taken against the difference in elongation, and the
On the other hand, as described above, the exposed portion of the
上記のようにして、プレス加工処理が完了すると、次に、正極活物質層23を塗布したアルミニウム箔22を、長手方向に切断処理する。
切断位置は、図5において1点鎖線Cで示す位置であり、1点鎖線Cで示す位置で切断することによって、全く同一形状の2条分の正極側電極を得る。
この切断処理は、図6で示す装置と同様にして、プレス加工処理後のアルミニウム箔22(正極活物質層23等を塗布したもの)を送り搬送しながら、1点鎖線Cで示す位置に例えばカッタの刃等をあてて切断する。
1点鎖線Cの位置は、幅方向での正極活物質層23の塗布範囲の中央であり、カッタ等による切断位置の設定は、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向での正極活物質層23の幅方向両端の端縁位置を、撮像装置等の光学センサを用いた光学的位置検出手段にて検出し、両端縁位置の中心を切断するように制御する。
この光学的位置検出手段としては、短絡防止層24の塗布の場合と同様に、例えば、撮像装置にて正極活物質層23の端縁位置付近を撮像し、その撮像画像における、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向での色変化情報から正極活物質層23の端縁位置を特定すれば良い。
このようにして検出した正極活物質層23の端縁位置の検出情報に基づいて、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向での、カッタ等の位置あるいはアルミニウム箔22の搬送位置を制御することで、正極活物質層23を塗布したアルミニウム箔22を精度良く切断することができる。もちろん、正極活物質層23の幅方向両端の端縁位置のうち一方のみを光学的に検出し、その検出位置から正極活物質層23の塗布幅の1/2だけ離れた位置を切断位置として特定するようにしても良い。
以上のようにアルミニウム箔22の切断位置を制御する関係で、光学的位置検出手段は、正極活物質層23の端縁位置を、アルミニウム箔22の全長に亘って連続的に検出しており、上述のように、正極活物質層23と未塗工部3aとの境界部分の略全長に亘る範囲を上記活物質層はみ出し部として設定している。
When the press working process is completed as described above, the
The cutting position is a position indicated by a one-dot chain line C in FIG. 5. By cutting at the position indicated by the one-dot chain line C, two strips of positive electrode on the same shape are obtained.
This cutting process is performed in the same manner as the apparatus shown in FIG. 6, for example, at a position indicated by an alternate long and short dash line C while feeding and transporting the
The position of the one-dot chain line C is the center of the coating range of the positive electrode
As this optical position detection means, as in the case of the application of the short-
Based on the detection information of the edge position of the positive electrode
As described above, the optical position detection means continuously detects the edge position of the positive electrode
〔負極側電極の製造工程〕
次に、発電要素3の負極側電極の製造工程について説明する。
負極側電極についても、正極側電極の場合と同様に2条分の負極側電極を同時処理で作製し、負極側電極の製造工程の最終工程として、幅方向に2条分が連なったものを幅方向中央位置で切断して、2条の負極側電極に分離する。
負極側電極は、上述のように、箔状負極板に負極活物質を塗布して作製しており、本実施の形態では、還元場において安定で導電性に優れた銅箔を箔状負極板として用いる。この銅箔は、幅が170mmの長尺帯状に形成されたものであり、厚さは7μm〜15μmで良いが、本実施の形態では10μmの厚さとしている。銅箔以外では、ニッケル,鉄,ステンレス鋼,チタン,アルミニウム,焼成炭素,導電性高分子,導電性ガラス及びAl−Cd合金等や、接着性,導電性及び耐酸化性の向上のために銅等の表面をカーボン,ニッケル,チタンあるいは銀等で処理したものを箔状に形成して箔状正極板として用いることができる。これらのうちでは、ニッケル箔,鉄箔及びこれらを一部に含む合金箔も、還元場において安定で導電性に優れている。
上記の箔状負極板に塗布する負極活物質は、本実施の形態では、グラファイトを使用しているが、グラファイト以外にも、Liイオンを吸蔵及び放出する各種の材料を用いることができる。例えば、スピネル型結晶構造を有するチタン酸リチウム,リチウム金属,リチウム含有合金(例えば、リチウム−アルミニウム,リチウム−鉛,リチウム−スズ,リチウム−アルミニウム−スズ及びリチウム−ガリウム等),ウッド合金,無定型炭素,繊維状炭素,石油ピッチ系炭素及び石炭コークス系炭素等を用いることができる。
更に、炭素材料にはスズ酸化物やケイ素酸化物等の金属酸化物の他、リンやホウ素を添加して改質を行うことも可能である。又、グラファイトとリチウム金属あるいはリチウム含有合金等とを併用することや、電気化学的に還元することによって炭素材料に予めリチウムを挿入するようにしても良い。
[Negative electrode manufacturing process]
Next, the manufacturing process of the negative electrode of the
Similarly to the case of the positive electrode, the negative electrode on the negative electrode was prepared by simultaneous processing, and as a final step in the manufacturing process of the negative electrode, the two continuous electrodes were formed in the width direction. It cut | disconnects in the width direction center position, and isolate | separates into two negative electrode side electrodes.
As described above, the negative electrode is prepared by applying a negative electrode active material to a foil-like negative electrode plate. In this embodiment, a copper foil that is stable in a reduction field and excellent in conductivity is made of a foil-like negative electrode plate. Used as This copper foil is formed in the shape of a long strip having a width of 170 mm, and the thickness may be 7 μm to 15 μm, but in this embodiment, the thickness is 10 μm. Other than copper foil, nickel, iron, stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, calcined carbon, conductive polymer, conductive glass, Al-Cd alloy, etc., and copper for improving adhesion, conductivity and oxidation resistance. Such a surface treated with carbon, nickel, titanium, silver or the like can be formed into a foil shape and used as a foil-like positive electrode plate. Among these, nickel foil, iron foil, and alloy foil including them in part are also stable in a reduction field and excellent in conductivity.
In the present embodiment, graphite is used as the negative electrode active material applied to the foil-like negative electrode plate, but various materials that occlude and release Li ions can be used in addition to graphite. For example, lithium titanate having a spinel crystal structure, lithium metal, lithium-containing alloy (for example, lithium-aluminum, lithium-lead, lithium-tin, lithium-aluminum-tin and lithium-gallium), wood alloy, amorphous Carbon, fibrous carbon, petroleum pitch carbon, coal coke carbon, and the like can be used.
Further, the carbon material can be modified by adding phosphorus or boron in addition to metal oxides such as tin oxide and silicon oxide. Alternatively, lithium may be inserted into the carbon material in advance by using graphite and lithium metal or a lithium-containing alloy together or by electrochemical reduction.
上記の負極活物質については、グラファイト94重量%と結着剤であるPVDF6重量%とからなる混合物にNMPを加えてペースト状として負極合剤ペーストとし、銅箔の表裏両面に塗布する。
本実施の形態の負極側電極では、正極側電極における導電体層21及び短絡防止層24に相当する層の塗布形成は行わないが、上記負極活物質のペーストの塗布方法自体は正極活物質の塗布工程と同様であり、長手方向に送り搬送される銅箔上に、上記の負極活物質のペーストをダイコートにより塗布する。
負極活物質層は、40μm〜60μmの層厚で、銅箔の長手方向に延びる帯状に塗布している。又、正極と負極の容量は、正極の容量を100としたときの負極の容量が140となるように調整した。
負極活物質層の塗布位置は、銅箔の幅方向端縁位置を光学的に検出して、その位置情報に基づいて、銅箔の幅方向中央位置と、負極活物質層の塗布幅の中央位置とが一致するように高精度に制御されている。
負極活物質層の塗布領域の両側に位置する幅(銅箔の幅方向での長さ)が10mmの領域は、未塗工部3bとなる。
銅箔に負極活物質層が塗布された後、乾燥処理され、更に、銅箔の反対側の面にも、上記工程により負極活物質層が塗布され、乾燥処理される。
About said negative electrode active material, NMP is added to the mixture which consists of 94 weight% of graphite, and PVDF6 weight% which is a binder, it is set as a paste at the negative mix paste, and is apply | coated to both front and back surfaces of copper foil.
In the negative electrode of the present embodiment, the layers corresponding to the
The negative electrode active material layer has a layer thickness of 40 μm to 60 μm and is applied in a strip shape extending in the longitudinal direction of the copper foil. Moreover, the capacity | capacitance of a positive electrode and a negative electrode was adjusted so that the capacity | capacitance of a negative electrode might be 140 when the capacity | capacitance of a positive electrode was set to 100.
The application position of the negative electrode active material layer is obtained by optically detecting the width direction edge position of the copper foil, and based on the position information, the center position of the copper foil in the width direction and the center of the application width of the negative electrode active material layer It is controlled with high accuracy so that the position matches.
A region having a width (length in the width direction of the copper foil) of 10 mm located on both sides of the application region of the negative electrode active material layer is an
After the negative electrode active material layer is applied to the copper foil, it is subjected to a drying treatment. Further, the negative electrode active material layer is also applied to the opposite surface of the copper foil by the above-described process, followed by a drying treatment.
以上の工程によって、銅箔の表裏両面に負極活物質層が形成された後、正極側電極の場合と同様に、プレス加工処理を行う。
負極側電極についてのプレス加工処理も、正極側電極の場合のプレス加工処理と同様であり、負極側電極の湾曲抑制のためのプレス加工と、負極活物質層の高密度化等のためのプレス加工とがある。
プレス加工処理に使用する装置も正極側電極の場合と同様であり、図6に概略的に示すプレス加工装置PMにて、一連に送り搬送される負極活物質層を塗布形成した銅箔に対して、負極側電極の湾曲抑制のためのプレス加工と、負極活物質層の高密度化等のためのプレス加工とを順次に行う。
After the negative electrode active material layers are formed on both the front and back surfaces of the copper foil by the above steps, a pressing process is performed as in the case of the positive electrode.
The press processing for the negative electrode is also the same as the press processing for the positive electrode, the press for suppressing the bending of the negative electrode, the press for increasing the density of the negative active material layer, etc. There is processing.
The apparatus used for the press processing is the same as that of the positive electrode, and the press working apparatus PM schematically shown in FIG. Then, the press working for suppressing the bending of the negative electrode and the press working for increasing the density of the negative electrode active material layer are sequentially performed.
負極側電極のプレス加工処理では、間欠ロールプレス装置33において、例えば10μmの銅箔に対しては、0.03μmの加圧痕を形成するように設定し、主ロールプレス装置34では、40μm〜60μmの負極活物質層を24μm〜37μmの厚さに圧縮するように設定している。
負極側電極においても、間欠ロールプレス装置33にて銅箔の露出部分をプレス処理して延伸させることで、主ロールプレス装置34の押圧による負極活物質層の塗布形成部分における長手方向の延びと、銅箔の露出部分における長手方向の延びとがバランスし、負極側電極の湾曲が十分に抑制される。
In the press processing of the negative electrode, the intermittent
Also in the negative electrode side electrode, the exposed portion of the copper foil is pressed and stretched by the intermittent
上記のようにして、プレス加工処理が完了すると、次に、負極活物質層を塗布形成した銅箔を、長手方向に切断処理する。
この工程も正極側電極と同様であり、銅箔(負極活物質層を塗布したもの)を送り搬送しながら、負極活物質層の塗布範囲の幅方向中央位置で切断する。
この切断は、負極活物質層の幅方向両端の端縁位置を光学的に検出し、両端縁位置の中心を、カッタ等によって切断すれば良い。
When the press processing is completed as described above, the copper foil coated with the negative electrode active material layer is then cut in the longitudinal direction.
This process is also the same as that of the positive electrode, and is cut at the center position in the width direction of the application range of the negative electrode active material layer while feeding and conveying the copper foil (the negative electrode active material layer applied).
This cutting may be performed by optically detecting the edge positions at both ends in the width direction of the negative electrode active material layer and cutting the centers of the both edge positions with a cutter or the like.
〔発電要素3の組立〕
発電要素3は、上述のようにして作製した正極側電極41と負極側電極42とを、セパレータ43を挟んだ状態で、扁平な板状の巻回軸周りに所定の長さ分を巻回し、図8に概略的に示す状態とする。図8は、巻回後に取り外される上記巻回軸を除いた状態で示している。
セパレータ43としては、ポリオレフィン系,ポリエステル系,ポリアクリロニトリル系,ポリフェニレンサルファイド系,ポリイミド系あるいはフッ素樹脂系等の微孔膜や不織布を用いることができる。セパレータ43の濡れ性が悪い場合には、界面活性剤等による処理を施しても良い。
[Assembly of power generation element 3]
The
As the
〔二次電池RBの組立〕
上記のようにして組み立てた発電要素3は、蓋部2側の組品に溶接により組み付ける。
蓋部2側の組品は、正極側では、端子ボルト5の頭部側のリベット8を、上部ガスケット11,蓋部2,下部ガスケット12及び集電体4を貫通させて蓋部2に組み付け、リベット8の筐体BC内方側の端部をかしめて固定する。
負極側でも、端子ボルト7の頭部側のリベット15を、上部ガスケット17,蓋部2,下部ガスケット18及び集電体6を貫通させて蓋部2に組み付け、リベット15の筐体BC内方側の端部をかしめて固定する。
発電要素3は、正極側電極41の未塗工部3a(アルミニウム箔が露出している部分)を集電体4の接続部4aと超音波溶接等によって溶接し、負極側電極42の未塗工部3b(銅箔が露出している部分)を集電体6の接続部6aと超音波溶接等によって溶接する。
発電要素3を組み付けると、この蓋部2側の組品を缶体1に挿入して、蓋部2の端縁と缶体1の開口端とをレーザ溶接にて溶接する。
その後、電解液の注液や初期充電等の工程を経て二次電池RBが完成する。電解液としては、本実施の形態では、エチレンカーボネイト(EC)とジメチルカーボネイト(DMC)とメチルエチルカーボネイト(MEC)との体積比30:40:30の混合溶媒にLiPF6(六フッ化リン酸リチウム)を1mol/L(リットル)の割合で溶解したものを用いた。
尚、上述した正極側電極及び負極側電極の作製から電池組み立てに至る全ての工程は、露点−50℃以下のドライルームで行っている。
[Assembly of secondary battery RB]
The
As for the assembly on the lid 2 side, on the positive electrode side, the rivet 8 on the head side of the
Even on the negative electrode side, the rivet 15 on the head side of the
The
When the
Then, secondary battery RB is completed through processes, such as electrolyte injection and initial charge. As an electrolytic solution, in this embodiment, LiPF 6 (hexafluorophosphoric acid) is used in a mixed solvent of ethylene carbonate (EC), dimethyl carbonate (DMC), and methyl ethyl carbonate (MEC) in a volume ratio of 30:40:30. What melt | dissolved lithium in the ratio of 1 mol / L (liter) was used.
In addition, all the processes from preparation of the positive electrode side electrode and negative electrode side electrode described above to battery assembly are performed in a dry room having a dew point of −50 ° C. or less.
〔二次電池RBの評価〕
次に、上記工程における作製条件を変化させて製作した二次電池RBの評価について説明する。
ここでの二次電池RBの評価としては、二次電池RB間の電池容量のばらつきと、正極側電極における正極活物質層23の剥離強度との2項目について評価している。
先ず、二次電池RB間の電池容量のばらつきについて説明する。
上記工程では、箔状正極板であるアルミニウム箔22上において、導電体層21の上に正極活物質層23を塗布する際、図3(b)に示すように、正極活物質層23の幅方向(矢印Bで示す方向)の端縁は、破線Eで示す導電体層21の端縁から、アルミニウム箔22が露出する領域へ、距離「W」で示す分だけはみ出している。
これは、導電体層21を露出させないためのものであり、導電体層21を露出させてしまうと、二次電池RBの電池容量のばらつきの原因となる。
上述のような2条分の正極側電極を一体に作製する二次電池RBの製造工程においては、2条分が連なった状態の正極側電極を各条に切断分離する際に、切断後の正極活物質層23の塗布幅を各条で極力一致させて、容量ばらつきを十分に抑制する必要がある。
正極側電極の切断作業において、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向(図5等において、矢印Bにて示す方向)の端縁位置を検出して、その検出情報に基づいて切断位置を設定したのでは、アルミニウム箔22上への正極活物質層23の塗布位置の誤差(上記幅方向での誤差)が、二次電池RBの電池容量のばらつきの要因となってしまう。
[Evaluation of secondary battery RB]
Next, evaluation of the secondary battery RB manufactured by changing the manufacturing conditions in the above process will be described.
As the evaluation of the secondary battery RB here, two items of the battery capacity variation between the secondary batteries RB and the peel strength of the positive electrode
First, the variation in battery capacity between the secondary batteries RB will be described.
In the above process, when the positive electrode
This is for preventing the
In the manufacturing process of the secondary battery RB in which the positive electrodes on the two strips as described above are integrally manufactured, when the positive electrode on the two strips are connected to each strip, It is necessary to make the application width of the positive electrode
In the cutting operation of the positive electrode, the edge position in the width direction of aluminum foil 22 (the direction indicated by arrow B in FIG. 5 and the like) is detected, and the cutting position is set based on the detection information. An error in the application position of the positive electrode
このため、上記の二次電池RBの製造工程では、切断位置の設定の基準を、アルミニウム箔22の幅方向端縁位置ではなく、正極活物質層23の幅方向端縁位置としている。
尚、正極活物質層23の幅方向端縁位置には、短絡防止層24が塗布されているが、この短絡防止層24は実質的に透明とみなすことができ、正極活物質層23の幅方向端縁位置の検出にはほとんど影響を与えない。
このように正極活物質層23の幅方向端縁位置を基準とする場合において、導電体層21と正極活物質層23とは同系色であることがほとんどであり、両者を光学的に精度良く弁別することは困難である。
このため、導電体層21が露出していると、導電体層21の幅方向端縁位置を正極活物質層23の端縁位置であると誤検出する等して、正極活物質層23の幅方向端縁位置を精度良く検出することができず、正極側電極を各条に切断分離した際の、各条における正極活物質層23の面積のばらつきが大となって、二次電池RBの電池容量をばらつかせてしまう。
このような、正極側電極における導電体層21の端縁と正極活物質層23の端縁との位置関係が、二次電池RBの電池容量のばらつき度合いに与える影響を実験によって評価した。
その評価実験の結果を表1に示す。
表1に実験結果を示す二次電池RBは、正極活物質層23の塗布幅を90mmとして、5Ahの容量の二次電池RBとして作製したものである。
For this reason, in the manufacturing process of the secondary battery RB, the reference for setting the cutting position is not the width direction edge position of the
In addition, although the short
As described above, when the position of the edge in the width direction of the positive electrode
For this reason, if the
The influence of the positional relationship between the edge of the
The results of the evaluation experiment are shown in Table 1.
The secondary battery RB whose experimental results are shown in Table 1 was manufactured as a secondary battery RB having a capacity of 5 Ah with the coating width of the positive electrode
表1において「はみ出し量」としているものは、図3(b)における距離「W」の値であり、「はみ出し量」を負の値で示しているものは、正極活物質層23の幅方向端縁位置が、導電体層21の幅方向端縁位置よりも引退し、導電体層21が露出している幅の値であることを示している。
表1において「容量ばらつき」として示す値が、各「はみ出し量」に対する二次電池RBの容量ばらつきを示すものであり、図5において1点鎖線Cで示す位置で切断分離して生成された2条の正極側電極の夫々で二次電池RBを作製し、両者の電池容量の差をとったものである。この電池容量は、5Aで定電流充電を行った後、4.2Vで定電圧充電を1.5時間行い、その後、2.5Vに達するまで5Aで定電流放電を行って、その時の積算電流値から求めた。
表1における「はみ出し量」と「容量ばらつき」との関係をグラフ化したものが、図9である。
図9のグラフから明らかなように、「はみ出し量」が負の値、すなわち、導電体層21が露出している状態では、容量ばらつきが大きくなっているのに比べて、「はみ出し量」が「0」より大きい領域、すなわち、導電体層21が正極活物質層23によって完全に覆われている状態では、容量ばらつきが小さい値で一定となっている。
In Table 1, “extruding amount” is the value of the distance “W” in FIG. 3B, and “extruding amount” is a negative value, which is the width direction of the positive electrode
The value shown as “capacity variation” in Table 1 indicates the capacity variation of the secondary battery RB with respect to each “extension amount”, and is generated by cutting and separating at the position indicated by the one-dot chain line C in FIG. A secondary battery RB was produced with each of the positive electrodes on the strip, and the difference in battery capacity between them was taken. This battery capacity is constant current charge at 5A, followed by constant voltage charge at 4.2V for 1.5 hours, and then constant current discharge at 5A until 2.5V is reached. It was calculated from the value.
FIG. 9 is a graph showing the relationship between “amount of protrusion” and “capacity variation” in Table 1.
As is apparent from the graph of FIG. 9, when “the amount of protrusion” is a negative value, that is, in the state where the
次に、正極活物質層23の剥離強度の評価について説明する。
上述のように、正極活物質層23が導電体層21を完全に覆うことで、二次電池RBの電池容量のばらつきを抑制できるのであるが、その反面、導電体層21の塗布領域からはみ出した正極活物質層23は、アルミニウム箔22との間に導電体層21が存在しないために、アルミニウム箔22との密着性が問題となる。
そこで、正極活物質層23のアルミニウム箔22との密着性を、正極活物質層23の剥離強度として評価し、上記の「はみ出し量」に対して、正極活物質層23の剥離強度がどのように変化するかを測定した。
Next, the evaluation of the peel strength of the positive electrode
As described above, the positive electrode
Therefore, the adhesion of the positive electrode
上記の剥離強度は、完成した正極側電極を5.0cm×3.5cm程度の寸法に裁断し、幅18mmのテープを、正極側電極とテープとの接着部分の長さが3cm程度になるように、短絡防止層24付近の上に張り付けた後、その貼り付けたテープを引きはがして、引きはがしに要する力をフォースゲージにて測定した。貼り付けたテープの引きはがし方は、図14に示すように、正極側電極41に貼り付けたテープ51の先端51a側を折り返して、その先端51aをフォースゲージの先端部分で挟んで矢印Fの方向に引っ張り、剥離強度を得た。
この剥離強度の測定結果を、表1の「剥離強度」欄に、各「はみ出し量」に対する値として示している。
The above peel strength is such that the finished positive electrode is cut into a size of about 5.0 cm × 3.5 cm, and a tape having a width of 18 mm is formed so that the length of the bonded portion between the positive electrode and the tape is about 3 cm. Further, after pasting on the vicinity of the short-
The measurement results of the peel strength are shown in the “Peel strength” column of Table 1 as values for each “extrusion amount”.
表1の「はみ出し量」と「剥離強度」との関係をグラフ化したものを、図10に示す。
対応する「はみ出し量」が「0」以下の値となっている領域での「剥離強度」のデータは、導電体層21の上に乗っている正極活物質層23の端縁部に短絡防止層24を形成し、その短絡防止層24を引きはがすことによる剥離強度を測定しているので、測定した剥離強度は、十分に大きな値で一定となっている。
これに対して、対応する「はみ出し量」が「0」より大きな値となっている領域での「剥離強度」のデータは、「はみ出し量」が1.0mm以下では、正極活物質層23が導電体層21の上に乗っているのと同等の値を示し、「はみ出し量」が1.0mmを超えると「剥離強度」が徐々に低下して、「はみ出し量」が2.0mm以下の範囲までは、ある程度の「剥離強度」を確保していることを示している。
「はみ出し量」が2.0mmを超える領域では「剥離強度」は一定の値となり、実際の正極活物質層23の剥離強度が、測定のバックグラウンド(正極活物質層23以外の部分に起因する引きはがしに要する力)に埋もれてしまう程度に低下している。
以上の「剥離強度」の評価結果から、上述の製造工程では、正極活物質層23の端縁位置と導電体層21の端縁位置との間隔(図3(b)において「W」で示す距離)が、2mm以下となるように、正極活物質層23の塗布幅を設定しているが、正極活物質層23の端縁位置と導電体層21の端縁位置との間隔が1mm以下となるように、正極活物質層23の塗布幅を設定することが、より好ましいものと言える。
FIG. 10 shows a graph of the relationship between “extrusion amount” and “peel strength” in Table 1.
The data of “peeling strength” in the region where the corresponding “extrusion amount” is a value of “0” or less is used to prevent a short circuit at the edge of the positive electrode
On the other hand, the data of “peel strength” in the region where the corresponding “protrusion amount” is a value larger than “0” indicates that the positive electrode
In the region where the “extrusion amount” exceeds 2.0 mm, the “peel strength” is a constant value, and the actual peel strength of the positive electrode
From the above evaluation results of “peel strength”, in the above-described manufacturing process, the interval between the edge position of the positive electrode
〔別実施形態〕
以下、本発明の別実施形態を列記する。
(1)上記実施の形態では、正極側電極を2条分について一括して製作する場合を例示しているが、例えば、図13に示すように、4条分について一括して導電体層21及び正極活物質層23等の形成を行い、最終工程において1点鎖線Cの位置で4条に切断分離するように構成しても良いし、更に多くの条数で作製しても良い。尚、図13においては、図5における各要素と対応するものには、図5と同一の符号を付している。
(2)上記実施の形態では、アルミニウム箔22の長手方向において、正極活物質層23と未塗工部3aとの境界部分の略全長に亘る範囲を上記活物質層はみ出し部として設定しているが、必ずしも全長である必要はなく、正極活物質層23の端縁位置を検出する必要のある部分だけでも良い。
(3)上記実施の形態では、光学的位置検出手段として、撮像装置にて正極活物質層23と未塗工部3aとの境界部分を撮像して、その撮像情報から正極活物質層23の端縁位置を検出する場合を例示しているが、例えば、ビーム光を正極活物質層23と未塗工部3aとの境界部分で走査して、その反射光を検出した光センサの検出情報に基づいて、反射光量の変化から正極活物質層23の端縁位置を検出する等、光学的位置検出手段の具体構成は、種々に変更可能である。
[Another embodiment]
Hereinafter, other embodiments of the present invention will be listed.
(1) In the above embodiment, the case where the positive electrode is manufactured in batches for two strips is illustrated, but for example, as shown in FIG. In addition, the positive electrode
(2) In the above embodiment, in the longitudinal direction of the
(3) In the above embodiment, as the optical position detection means, the boundary portion between the positive electrode
(4)上記実施の形態では、プレス加工処理として、正極側電極の湾曲抑制のためのプレス加工と、正極活物質層の高密度化等のためのプレス加工とを、順次に行った場合を例示しているが、2種類のプレス加工処理の間に、電極をロール状に巻き取る工程を設けても良い。又、正極活物質層の高密度化等のためのプレス加工を行った後に、正極側電極の湾曲抑制のためのプレス加工を行っても良い。
(5)上記実施の形態では、導電体層21を箔状正極板(正極側の箔状電極板)に形成する場合を例示して説明しているが、負極側電極42においても、箔状負極板(負極側の箔状電極板)と負極活物質との材質等の関係で、箔状負極板と負極活物質層との間に導電体層を配置する場合に、本発明を適用することができる。
(4) In the above embodiment, as the press processing, press processing for suppressing the bending of the positive electrode side electrode and press processing for increasing the density of the positive electrode active material layer are sequentially performed. Although illustrated, a step of winding the electrode in a roll shape may be provided between the two types of press processing. In addition, after performing press processing for increasing the density of the positive electrode active material layer, press processing for suppressing the bending of the positive electrode side electrode may be performed.
(5) In the above embodiment, the case where the
3a 未塗工部
21 導電体層
22 箔状電極板
23 活物質層
24 短絡防止層
3a
Claims (13)
前記活物質層の形成領域における前記未塗工部の存在側の端縁部の少なくとも一部において、上層側の前記活物質層の端縁が、下層側の前記導電体層の端縁よりも前記未塗工部側に位置する活物質層はみ出し部を形成する工程と、
前記活物質層はみ出し部において、光学的位置検出手段にて前記活物質層の存在位置を特定する工程とを有する電池用電極の製造方法。 A conductive layer and an active material layer are sequentially stacked and stacked so that an uncoated portion that exposes the surface of the foil electrode plate is formed on the conductive foil electrode plate. A method for producing an electrode for a battery,
In at least a part of the edge portion on the existing side of the uncoated portion in the active material layer formation region, the edge of the active material layer on the upper layer side is more than the edge of the conductor layer on the lower layer side. Forming an active material layer protrusion located on the uncoated part side;
And a step of identifying an existing position of the active material layer by optical position detection means at the protruding portion of the active material layer.
その検出した位置情報に基づいて、正極側の前記箔状電極板上における前記活物質層と前記未塗工部との境界部分の上に、前記箔状電極板よりも電気抵抗の大きい短絡防止層を形成する請求項1又は2記載の電池用電極の製造方法。 The optical position detection means detects the edge position of the active material layer in the protruding portion of the active material layer formed on the foil electrode plate on the positive electrode side,
On the basis of the detected position information, on the boundary portion between the active material layer and the uncoated portion on the foil-like electrode plate on the positive electrode side, a short circuit prevention having a larger electric resistance than the foil-like electrode plate The manufacturing method of the battery electrode of Claim 1 or 2 which forms a layer.
その検出した位置情報に基づいて、前記導電体層及び前記活物質層を積層した状態の前記箔状電極板の切断位置を設定する請求項1〜3のいずれか1項に記載の電池用電極の製造方法。 An edge position of the active material layer at the protruding portion of the active material layer is detected by the optical position detection means,
The battery electrode according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein a cutting position of the foil electrode plate in a state in which the conductor layer and the active material layer are laminated is set based on the detected position information. Manufacturing method.
前記活物質層と前記未塗工部との境界部分の略全長に亘る範囲が前記活物質層はみ出し部として設定されている請求項1〜4のいずれか1項に記載の電池用電極の製造方法。 The foil-like electrode plate is formed in a long band shape, and the conductor layer and the active material layer are in the state in which the uncoated portion is located at the widthwise end of the foil-like electrode plate. Formed in a strip shape extending in the longitudinal direction of the plate,
The manufacturing of the battery electrode according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein a range over a substantially entire length of a boundary portion between the active material layer and the uncoated portion is set as the protruding portion of the active material layer. Method.
前記活物質層の形成領域における前記未塗工部の存在側の端縁部の少なくとも一部において、上層側の前記活物質層の端縁が、下層側の前記導電体層の端縁よりも前記未塗工部側に位置する活物質層はみ出し部が形成されている電池用電極。 A battery in which a conductor layer and an active material layer are sequentially stacked on a conductive foil-like electrode plate in a region other than the formation position of an uncoated portion that exposes the surface of the foil-like electrode plate. Electrode,
In at least a part of the edge portion on the existing side of the uncoated portion in the active material layer formation region, the edge of the active material layer on the upper layer side is more than the edge of the conductor layer on the lower layer side. The battery electrode in which the active material layer protrusion part located in the said uncoated part side is formed.
前記箔状電極板の上に積層される導電体層と、
前記導電体層の上に積層される活物質層と、
前記箔状電極板が露出する未塗工部と、
前記活物質層が前記導電体層の形成位置から前記未塗工部側へはみ出した活物質層はみ出し部と、
を備える電池用電極。 A foil-like electrode plate having conductivity;
A conductor layer laminated on the foil electrode plate;
An active material layer laminated on the conductor layer;
An uncoated portion where the foil electrode plate is exposed;
An active material layer protruding part from which the active material layer protrudes from the formation position of the conductor layer to the uncoated part side;
A battery electrode comprising:
前記発電要素を収納する筐体と、 A housing for storing the power generation element;
を備える電池。A battery comprising:
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011186750A JP5772397B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2011-08-30 | Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode |
| US13/565,683 US9905838B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2012-08-02 | Electrode and method of manufacturing the same |
| KR1020120087249A KR101928376B1 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2012-08-09 | Electrode and method of manufacturing the same |
| CN201210305620.7A CN102969480B (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2012-08-24 | The manufacture method of electrode and electrode |
| DE102012215198A DE102012215198A1 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2012-08-27 | Electrode and process for its preparation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011186750A JP5772397B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2011-08-30 | Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013051035A JP2013051035A (en) | 2013-03-14 |
| JP2013051035A5 JP2013051035A5 (en) | 2014-10-16 |
| JP5772397B2 true JP5772397B2 (en) | 2015-09-02 |
Family
ID=48012947
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011186750A Active JP5772397B2 (en) | 2011-08-30 | 2011-08-30 | Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5772397B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023132531A1 (en) * | 2022-01-07 | 2023-07-13 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Lithium secondary battery electrode and manufacturing method therefor |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2014203424A1 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2014-12-24 | Necエナジーデバイス株式会社 | Secondary battery and electrode production method |
| JP6365175B2 (en) * | 2014-09-24 | 2018-08-01 | 株式会社Gsユアサ | Electricity storage element |
| JP2016186882A (en) * | 2015-03-27 | 2016-10-27 | 株式会社Gsユアサ | Electrode, and power storage element including electrode |
| JP6705126B2 (en) * | 2015-06-04 | 2020-06-03 | 株式会社Gsユアサ | Method for manufacturing electrode plate |
| JP6766338B2 (en) * | 2015-10-30 | 2020-10-14 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Electrode plate manufacturing method and secondary battery manufacturing method |
| JP6672706B2 (en) * | 2015-10-30 | 2020-03-25 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Method for manufacturing electrode plate and method for manufacturing secondary battery |
| JP7155881B2 (en) | 2018-10-31 | 2022-10-19 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Electrode plate, battery using same, method for manufacturing electrode plate, method for manufacturing battery using same, die head |
| CN113228340A (en) * | 2019-03-01 | 2021-08-06 | 积水化学工业株式会社 | Electrode for lithium ion secondary battery, and lithium ion secondary battery |
| WO2021186716A1 (en) * | 2020-03-19 | 2021-09-23 | 株式会社 東芝 | Electrode, multilayer body and secondary battery |
| WO2021199684A1 (en) * | 2020-03-30 | 2021-10-07 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Method for producing positive electrode plate for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and method for producing nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery |
| CN114023922A (en) * | 2021-11-02 | 2022-02-08 | 孚能科技(赣州)股份有限公司 | Lithium ion battery pole piece, manufacturing method thereof and lithium ion battery |
| CN118553853A (en) * | 2022-03-01 | 2024-08-27 | 珠海冠宇电池股份有限公司 | Pole piece, winding cell and battery |
| CN115332542B (en) * | 2022-10-12 | 2023-04-07 | 楚能新能源股份有限公司 | Battery core pole piece substrate and pole piece production equipment |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001185128A (en) * | 1999-12-24 | 2001-07-06 | Toshiba Battery Co Ltd | Electrode sheet cutting method and device thereof |
| JP4201619B2 (en) * | 2003-02-26 | 2008-12-24 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and method for producing electrode used therefor |
| US7251122B2 (en) * | 2003-12-22 | 2007-07-31 | Tdk Corporation | Electric chemical capacitor, and method and apparatus for manufacturing electrode for electric chemical capacitor |
| JP4487220B1 (en) * | 2009-01-26 | 2010-06-23 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Positive electrode for lithium secondary battery and method for producing the same |
| JP5590333B2 (en) * | 2011-02-25 | 2014-09-17 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | Lithium ion secondary battery and its positive electrode |
-
2011
- 2011-08-30 JP JP2011186750A patent/JP5772397B2/en active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2023132531A1 (en) * | 2022-01-07 | 2023-07-13 | 주식회사 엘지에너지솔루션 | Lithium secondary battery electrode and manufacturing method therefor |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013051035A (en) | 2013-03-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5776446B2 (en) | Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode | |
| JP5772397B2 (en) | Battery electrode manufacturing method and battery electrode | |
| KR101928376B1 (en) | Electrode and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP6521323B2 (en) | Secondary battery and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP4347759B2 (en) | Electrode manufacturing method | |
| JP6183348B2 (en) | Electrode body and method for producing electrode body | |
| JP6292678B2 (en) | Secondary battery and electrode manufacturing method | |
| JP2013187077A (en) | Wound type and stack type electrode battery | |
| JP5735096B2 (en) | Non-aqueous secondary battery manufacturing method and non-aqueous secondary battery manufacturing method | |
| JP6032628B2 (en) | Thin battery | |
| JP6038813B2 (en) | Electrode manufacturing method and non-aqueous electrolyte battery manufacturing method | |
| CN109891640B (en) | Electrode for nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery | |
| JPWO2018079817A1 (en) | Electrode for electrochemical device, electrochemical device, and production method thereof | |
| CN109478676B (en) | Electrode assembly and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP2013182677A (en) | Laminate type power storage device | |
| JP5678270B2 (en) | Power generation element and secondary battery | |
| JP2013161773A (en) | Pole plate and secondary battery | |
| JP2017216160A (en) | Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery | |
| JP2010205429A (en) | Nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery and electrode for the same | |
| JP3680809B2 (en) | Lithium ion polymer secondary battery and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4779352B2 (en) | Battery manufacturing method | |
| WO2013098968A1 (en) | Method for producing electrode and method for producing non-aqueous electrolyte battery | |
| JP5954339B2 (en) | Rectangular secondary battery and manufacturing method thereof | |
| CN117673495A (en) | Method for manufacturing battery | |
| CN112753111A (en) | Electrode for lithium ion secondary battery, method for producing same, and lithium ion secondary battery |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140826 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140902 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150410 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150421 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150515 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150602 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150615 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5772397 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |