JP5676759B2 - 安定した仮想周波数のための複数の動作点の管理 - Google Patents
安定した仮想周波数のための複数の動作点の管理 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5676759B2 JP5676759B2 JP2013516697A JP2013516697A JP5676759B2 JP 5676759 B2 JP5676759 B2 JP 5676759B2 JP 2013516697 A JP2013516697 A JP 2013516697A JP 2013516697 A JP2013516697 A JP 2013516697A JP 5676759 B2 JP5676759 B2 JP 5676759B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- state
- power consumption
- determining
- current
- power
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 claims description 26
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000004590 computer program Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 36
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000007726 management method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007619 statistical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 241000700605 Viruses Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009529 body temperature measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005265 energy consumption Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010295 mobile communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
- G06F1/3234—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken
- G06F1/324—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken by lowering clock frequency
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F1/00—Details not covered by groups G06F3/00 - G06F13/00 and G06F21/00
- G06F1/26—Power supply means, e.g. regulation thereof
- G06F1/32—Means for saving power
- G06F1/3203—Power management, i.e. event-based initiation of a power-saving mode
- G06F1/3234—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken
- G06F1/3296—Power saving characterised by the action undertaken by lowering the supply or operating voltage
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Power Sources (AREA)
Description
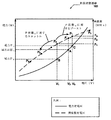
最新の集積回路(IC)の電力消費は、各世代の半導体チップに関して深刻化する設計問題になっている。電力消費が増加するにつれて、余分な熱を除去して、IC障害を防ぐために、より大きなファンおよび放熱板などの、より費用のかかる冷却システムが利用される。しかし、冷却システムはシステム費用を増大させる。ICの電力散逸制約は、ポータブルコンピュータおよびモバイル通信装置に関してのみならず、複数のプロセッサコア、またはコア、および1コア内に複数のパイプラインを含み得る、高性能のスーパースカラー(superscalar)マイクロプロセッサに関しても問題である。
Claims (20)
- それぞれのブロックの活動レベルに応じてデータを生成するように構成された、プロセッサコア内の1つ以上の機能ブロックであって、1つ以上の離散電力性能状態(離散P状態)で動作するように構成された機能ブロックと、
前記1つ以上の機能ブロックに接続された、前記プロセッサコア内の電力マネージャとを備え、
前記電力マネージャは、
所望の電力消費に対応する仮想P状態であって、サポートされた離散P状態ではない仮想P状態を決定し、
前記仮想P状態よりも低い低P状態及び前記仮想P状態よりも高い高P状態のそれぞれに用いられる、個々の最短滞留時間を決定し、
前記低P状態又は前記高P状態に対応する電力消費よりも前記所望の電力消費により緊密に一致する平均電力消費を経時的に生成するために、前記個々の最短滞留時間を用いて、前記低P状態及び前記高P状態を交互に選択し且つ伝達するように構成されている、
コンピューティングシステム。 - 前記電力マネージャは、
少なくとも現在のP状態の最短滞留時間が経過したのを判定したことに応じて、次のP状態を選択するように構成されている、請求項1に記載のコンピューティングシステム。 - 前記電力マネージャは、
前記データに少なくとも一部基づいて、前記1つ以上の機能ブロックのうち1つの機能ブロックに対して、所与の時間間隔中に平均電力消費を決定し、
前記平均電力消費が前記所望の電力消費を、少なくとも、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第1の変化量だけ超えているという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも低いP状態を選択し、
前記平均電力消費が前記所望の電力消費を、少なくとも、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第2の変化量だけ下回っているという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも高いP状態を選択するように構成されている、請求項1に記載のコンピューティングシステム。 - 前記所望の電力消費は、前記1つ以上の機能ブロックに対する熱設計電力値に対応する、請求項3に記載のコンピューティングシステム。
- 前記電力マネージャが、対応する閾値に達する率に基づき、前記現在のP状態から2状態以上離れたP状態を選択するようにさらに構成されている、請求項3に記載のコンピューティングシステム。
- 前記電力マネージャは、
前記所望の電力消費と複数の機能ブロックの電力消費値との間で、符号付き累算差分を経時的に決定し、
前記符号付き累算差分が、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第1の変化量より大きいという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも低いP状態を選択し、
前記符号付き累算差分が、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第2の変化量より少ないという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも高いP状態を選択するようにさらに構成されている、
請求項3に記載のコンピューティングシステム。 - 前記電力マネージャは、所与の期間の終わりに、前記符号付き累算差分をリセットするように構成されている、請求項6に記載のコンピューティングシステム。
- 前記時間間隔がN個の機能ブロックサンプル間隔の最大カウントを含み、前記電力マネージャが、前記符号付き累算差分の符号が変わったか、または前記カウントがNに達したかの検出に応じて、どちらが最初に起こったかにより、前記カウントをリセットするようにさらに構成された、請求項6に記載のコンピューティングシステム。
- 安定した仮想動作点を作成するために複数の離散動作点を管理するためのコンピューティングシステムによって実行される方法であって、
個々の電力性能状態(P状態)で動作する1つ以上の機能ブロックの活動レベルに応じて、データを生成することと、
所望の電力消費に対応する仮想P状態であって、サポートされた離散P状態と等しくない仮想P状態を決定することと、
前記仮想P状態よりも低い低P状態及び前記仮想P状態よりも高い高P状態のそれぞれに用いられる、個々の最短滞留時間を決定することと、
前記低P状態又は前記高P状態に対応する電力消費よりも前記所望の電力消費により緊密に一致する平均電力消費を経時的に生成するために、前記個々の最短滞留時間を用いて、前記低P状態及び前記高P状態を交互に選択し且つ伝達することと、
を含む方法。 - 少なくとも現在のP状態の最短滞留時間が経過したのを判定したことに応じて、次のP状態を選択することをさらに含む、請求項9に記載の方法。
- 前記データに少なくとも一部基づいて、前記1つ以上の機能ブロックのうち1つの機能ブロックに対して、所与の時間間隔中に平均電力消費を決定することと、
前記平均電力消費が前記所望の電力消費を、少なくとも、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第1の変化量だけ超えているという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも低いP状態を選択することと、
前記平均電力消費が前記所望の電力消費を、少なくとも、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第2の変化量だけ下回っているという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも高いP状態を選択することとをさらに含む、請求項9に記載の方法。 - 前記所望の電力消費は、前記1つ以上の機能ブロックに対する熱設計電力値に対応する、請求項11に記載の方法。
- 対応する閾値に達する率に基づき、前記現在のP状態から2状態以上離れたP状態を選択することをさらに含む、請求項11に記載の方法。
- 前記所望の電力消費と複数の機能ブロックの電力消費値との間で、符号付き累算差分を経時的に決定することと、
前記符号付き累算差分が、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第1の変化量より大きいという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも低いP状態を選択することと、
前記符号付き累算差分が、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第2の変化量より少ないという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも高いP状態を選択することとをさらに含む、
請求項11に記載の方法。 - 所与の期間の終わりに、前記符号付き累算差分をリセットすることをさらに含む、請求項14に記載の方法。
- 前記時間間隔は、N個の機能ブロックサンプル間隔の最大カウントを含み、
前記符号付き累算差分の符号が変わったか、または前記カウントがNに達したかの検出に応じて、どちらが最初に起こったかにより、前記カウントをリセットすることをさらに含む、請求項14に記載の方法。 - 安定した仮想動作点を作成するために複数の離散動作点を管理するように機能するプログラム命令を格納するコンピュータ可読記憶媒体であって、
前記プログラム命令は、
個々の電力性能状態(P状態)で動作する1つ以上の機能ブロックの活動レベルに応じて、データを生成し、
所望の電力消費に対応する仮想P状態であって、サポートされた離散P状態と等しくない仮想P状態を決定し、
前記仮想P状態よりも低い低P状態及び前記仮想P状態よりも高い高P状態のそれぞれに用いられる、個々の最短滞留時間を決定し、
前記低P状態又は前記高P状態に対応する電力消費よりも前記所望の電力消費により緊密に一致する平均電力消費を経時的に生成するために、前記個々の最短滞留時間を用いて、前記低P状態及び前記高P状態を交互に選択し且つ伝達する、ように実行可能である、
コンピュータ可読記憶媒体。 - 前記プログラム命令は、少なくとも現在のP状態の最短滞留時間が経過したのを判定したことに応じて、次のP状態を選択する、ようにさらに実行可能である、請求項17に記載のコンピュータ可読記憶媒体。
- 前記プログラム命令は、
前記データに少なくとも一部基づいて、前記1つ以上の機能ブロックのうち1つの機能ブロックに対して、所与の時間間隔中に平均電力消費を決定し、
前記平均電力消費が前記所望の電力消費を、少なくとも、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第1の変化量だけ超えているという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも低いP状態を選択し、
前記平均電力消費が前記所望の電力消費を、少なくとも、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第2の変化量だけ下回っているという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも高いP状態を選択する、ようにさらに実行可能である、請求項18に記載のコンピュータ可読記憶媒体。 - 前記プログラム命令は、
前記所望の電力消費と複数の機能ブロックの電力消費値との間で、符号付き累算差分を経時的に決定し、
前記符号付き累算差分が、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第1の変化量より大きいという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも低いP状態を選択し、
前記符号付き累算差分が、ゼロよりも大きい絶対値を有する第2の変化量より少ないという判断に応じて、現在のP状態よりも高いP状態を選択する、ようにさらに実行可能である、請求項19に記載のコンピュータ可読記憶媒体。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US12/819,777 US8504854B2 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2010-06-21 | Managing multiple operating points for stable virtual frequencies |
| US12/819,777 | 2010-06-21 | ||
| PCT/US2011/041291 WO2011163261A1 (en) | 2010-06-21 | 2011-06-21 | Managing multiple operating points for stable virtual frequencies |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013533548A JP2013533548A (ja) | 2013-08-22 |
| JP2013533548A5 JP2013533548A5 (ja) | 2014-08-07 |
| JP5676759B2 true JP5676759B2 (ja) | 2015-02-25 |
Family
ID=44546037
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013516697A Active JP5676759B2 (ja) | 2010-06-21 | 2011-06-21 | 安定した仮想周波数のための複数の動作点の管理 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8504854B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2583151B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5676759B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101718116B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102971687B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2011163261A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8510582B2 (en) * | 2010-07-21 | 2013-08-13 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Managing current and power in a computing system |
| US8984305B2 (en) | 2010-12-21 | 2015-03-17 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus to configure thermal design power in a microprocessor |
| US9442732B2 (en) * | 2012-03-19 | 2016-09-13 | Via Technologies, Inc. | Running state power saving via reduced instructions per clock operation |
| EP2725450A4 (en) * | 2012-08-30 | 2015-07-08 | Huawei Device Co Ltd | METHOD AND DEVICE FOR CONTROLLING A CENTRAL UNIT |
| US9218044B2 (en) * | 2012-11-27 | 2015-12-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Computing system frequency target monitor |
| US9323300B2 (en) * | 2012-11-27 | 2016-04-26 | International Business Machines Corporation | Computing system voltage control |
| JP5764150B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-16 | 2015-08-12 | レノボ・シンガポール・プライベート・リミテッド | パワー・オン状態から省電力状態に移行させる方法およびコンピュータ |
| US9436265B2 (en) * | 2013-10-24 | 2016-09-06 | Fujitsu Limited | Information processing apparatus and load control method |
| US9436263B2 (en) * | 2014-02-21 | 2016-09-06 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Systems and methods for power optimization using throughput feedback |
| US9934831B2 (en) | 2014-04-07 | 2018-04-03 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses and methods for storing and writing multiple parameter codes for memory operating parameters |
| JP6356502B2 (ja) * | 2014-06-20 | 2018-07-11 | 株式会社東芝 | 機器運転設定装置及び機器運転設定値決定プログラム |
| US10070390B2 (en) * | 2014-10-24 | 2018-09-04 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Power management of a wireless communication device |
| US9847662B2 (en) | 2014-10-27 | 2017-12-19 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Voltage slew rate throttling for reduction of anomalous charging current |
| US9880605B2 (en) * | 2014-10-27 | 2018-01-30 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Method and system for throttling power consumption |
| US9916087B2 (en) | 2014-10-27 | 2018-03-13 | Sandisk Technologies Llc | Method and system for throttling bandwidth based on temperature |
| FR3054949A1 (fr) | 2016-08-03 | 2018-02-09 | Stmicroelectronics (Crolles 2) Sas | Procede de reglage d'au moins un point de fonctionnement d'au moins un circuit integre d'un systeme sur puce, et systeme sur puce correspondant |
| FR3054885B1 (fr) | 2016-08-03 | 2018-09-07 | Stmicroelectronics (Crolles 2) Sas | Procede d'estimation d'un profil d'exploitation d'un circuit integre d'un systeme sur puce, et systeme sur puce correspondant |
| JP2020061124A (ja) * | 2018-10-05 | 2020-04-16 | 富士通株式会社 | 並列処理装置及び演算処理方法 |
| US11940859B2 (en) | 2018-11-16 | 2024-03-26 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Adjusting power consumption limits for processors of a server |
| US11409560B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2022-08-09 | Intel Corporation | System, apparatus and method for power license control of a processor |
| US11360827B2 (en) | 2019-06-04 | 2022-06-14 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Regulating core and un-core processor frequencies of computing node clusters |
Family Cites Families (60)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3382460A (en) | 1967-09-11 | 1968-05-07 | Sanders Associates Inc | Linearly swept frequency generator |
| GB1466603A (en) | 1974-11-06 | 1977-03-09 | Burroughs Corp | Flip-flop controlled clock gating system |
| JPS5941338B2 (ja) | 1976-05-10 | 1984-10-06 | 日本電気株式会社 | クロツクパルス再生回路 |
| US4186637A (en) | 1977-09-22 | 1980-02-05 | Norlin Industries, Inc. | Tone generating system for electronic musical instrument |
| US4191942A (en) | 1978-06-08 | 1980-03-04 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Single slope A/D converter with sample and hold |
| GB2041591B (en) | 1979-01-31 | 1983-05-05 | Philips Electronic Associated | Frequency divider |
| US4284906A (en) | 1979-10-03 | 1981-08-18 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Constant amplitude variable frequency synchronized linear ramp generator |
| US4471310A (en) | 1982-01-04 | 1984-09-11 | At&T Bell Laboratories | Pulse generator having variable pulse occurrence rate |
| US4573017A (en) | 1984-01-03 | 1986-02-25 | Motorola, Inc. | Unitary phase and frequency adjust network for a multiple frequency digital phase locked loop |
| US4855622A (en) | 1987-12-18 | 1989-08-08 | North American Philips Corporation, Signetics Division | TTL compatible switching circuit having controlled ramp output |
| US5517521A (en) | 1993-06-25 | 1996-05-14 | Digital Wireless Corporation | Method and apparatus for synchronization between real-time sampled audio applications operating full-duplex over a half-duplex radio link |
| US5600347A (en) | 1993-12-30 | 1997-02-04 | International Business Machines Corporation | Horizontal image expansion system for flat panel displays |
| US5485129A (en) | 1995-01-20 | 1996-01-16 | Motorola, Inc. | Method and apparatus for digital modulation using pulse deletion |
| US5764089A (en) | 1995-09-11 | 1998-06-09 | Altera Corporation | Dynamic latching device |
| US6473732B1 (en) | 1995-10-18 | 2002-10-29 | Motorola, Inc. | Signal analyzer and method thereof |
| US5740417A (en) | 1995-12-05 | 1998-04-14 | Motorola, Inc. | Pipelined processor operating in different power mode based on branch prediction state of branch history bit encoded as taken weakly not taken and strongly not taken states |
| US5712826A (en) | 1996-03-26 | 1998-01-27 | Intel Corporation | Apparatus and a method for embedding dynamic state machines in a static environment |
| US5825218A (en) | 1996-10-24 | 1998-10-20 | Stmicroelectronics, Inc. | Driver circuit including slew rate control system with improved voltage ramp generator |
| US5889436A (en) | 1996-11-01 | 1999-03-30 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Phase locked loop fractional pulse swallowing frequency synthesizer |
| US5917355A (en) | 1997-01-16 | 1999-06-29 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Edge-triggered staticized dynamic flip-flop with conditional shut-off mechanism |
| US5964881A (en) | 1997-11-11 | 1999-10-12 | Advanced Micro Devices | System and method to control microprocessor startup to reduce power supply bulk capacitance needs |
| US6043692A (en) | 1998-07-13 | 2000-03-28 | Xilinx, Inc. | Circuit and method for generating clock signals with an incrementally reduced effective frequency |
| JP3819166B2 (ja) | 1998-11-27 | 2006-09-06 | ヒタチグローバルストレージテクノロジーズネザーランドビーブイ | 消費エネルギー低減方法 |
| US6510525B1 (en) | 1999-04-26 | 2003-01-21 | Mediaq, Inc. | Method and apparatus to power up an integrated device from a low power state |
| US6289067B1 (en) | 1999-05-28 | 2001-09-11 | Dot Wireless, Inc. | Device and method for generating clock signals from a single reference frequency signal and for synchronizing data signals with a generated clock |
| US6457135B1 (en) * | 1999-08-10 | 2002-09-24 | Intel Corporation | System and method for managing a plurality of processor performance states |
| US6278308B1 (en) | 1999-10-08 | 2001-08-21 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Low-power flip-flop circuit employing an asymmetric differential stage |
| GB9925593D0 (en) | 1999-10-28 | 1999-12-29 | Sgs Thomson Microelectronics | Clock generator circuit |
| KR20020050270A (ko) * | 1999-11-09 | 2002-06-26 | 토토라노 제이. 빈센트 | 환경에 따른 프로세서의 작동 파라미터의 동적 조절방법 |
| US6711694B1 (en) | 2000-02-03 | 2004-03-23 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson(Publ) | Apparatus and method for generating a modulated clock signal including harmonics that exhibit a known sideband configuration |
| US6292062B1 (en) | 2000-02-10 | 2001-09-18 | Silicon Wave, Inc. | Method and apparatus for implementing a high-precision interval timer utilizing multiple oscillators including a non-optimal oscillator |
| US6629256B1 (en) | 2000-04-04 | 2003-09-30 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Apparatus for and method of generating a clock from an available clock of arbitrary frequency |
| JP4446568B2 (ja) | 2000-07-21 | 2010-04-07 | 富士通マイクロエレクトロニクス株式会社 | Pll周波数シンセサイザ回路 |
| US6988214B1 (en) | 2000-11-06 | 2006-01-17 | Dell Products L.P. | Processor power state transistions using separate logic control |
| EP1241788A1 (en) | 2001-03-13 | 2002-09-18 | STMicroelectronics Limited | Digital frequency divider |
| US7089437B2 (en) | 2001-06-18 | 2006-08-08 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Apparatus for determining power consumed by a bus of a digital signal processor using counted number of logic state transitions on bus |
| US6597620B1 (en) | 2001-07-18 | 2003-07-22 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Storage circuit with data retention during power down |
| US7111178B2 (en) | 2001-09-28 | 2006-09-19 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for adjusting the voltage and frequency to minimize power dissipation in a multiprocessor system |
| US7096145B2 (en) | 2002-01-02 | 2006-08-22 | Intel Corporation | Deterministic power-estimation for thermal control |
| US6611435B2 (en) | 2002-01-08 | 2003-08-26 | Intel Corporation | voltage regulator with voltage droop compensation |
| US6988217B1 (en) | 2002-02-27 | 2006-01-17 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Method and mechanism for generating a clock signal with a relatively linear increase or decrease in clock frequency |
| US6954864B2 (en) | 2002-03-29 | 2005-10-11 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for remotely placing a computing device into a low power state |
| US7152169B2 (en) | 2002-11-29 | 2006-12-19 | Intel Corporation | Method for providing power management on multi-threaded processor by using SMM mode to place a physical processor into lower power state |
| US7272732B2 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2007-09-18 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Controlling power consumption of at least one computer system |
| US7225349B2 (en) | 2003-07-25 | 2007-05-29 | Intel Corporation | Power supply voltage droop compensated clock modulation for microprocessors |
| US7426647B2 (en) * | 2003-09-18 | 2008-09-16 | Vulcan Portals Inc. | Low power media player for an electronic device |
| US7200762B2 (en) | 2003-09-30 | 2007-04-03 | Intel Corporation | Providing a low-power state processor voltage in accordance with a detected processor type |
| US7159766B2 (en) | 2004-01-20 | 2007-01-09 | Standard Microsystems Corporation | Peripheral device feature allowing processors to enter a low power state |
| US7301373B1 (en) | 2005-08-04 | 2007-11-27 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Asymmetric precharged flip flop |
| US7562234B2 (en) | 2005-08-25 | 2009-07-14 | Apple Inc. | Methods and apparatuses for dynamic power control |
| US7454637B2 (en) | 2005-09-02 | 2008-11-18 | Intel Corporation | Voltage regulator having reduced droop |
| US7498694B2 (en) | 2006-04-12 | 2009-03-03 | 02Micro International Ltd. | Power management system with multiple power sources |
| US7420378B2 (en) | 2006-07-11 | 2008-09-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | Power grid structure to optimize performance of a multiple core processor |
| US7681054B2 (en) * | 2006-10-03 | 2010-03-16 | International Business Machines Corporation | Processing performance improvement using activity factor headroom |
| US7673160B2 (en) | 2006-10-19 | 2010-03-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | System and method of power management for computer processor systems |
| US20090150696A1 (en) | 2007-12-10 | 2009-06-11 | Justin Song | Transitioning a processor package to a low power state |
| GB2455744B (en) | 2007-12-19 | 2012-03-14 | Advanced Risc Mach Ltd | Hardware driven processor state storage prior to entering a low power mode |
| US8028185B2 (en) * | 2008-03-11 | 2011-09-27 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Protocol for transitioning in and out of zero-power state |
| US8112647B2 (en) | 2008-08-27 | 2012-02-07 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Protocol for power state determination and demotion |
| US8156287B2 (en) * | 2009-01-15 | 2012-04-10 | International Business Machines Corporation | Adaptive data prefetch |
-
2010
- 2010-06-21 US US12/819,777 patent/US8504854B2/en active Active
-
2011
- 2011-06-21 EP EP11741709.7A patent/EP2583151B1/en active Active
- 2011-06-21 WO PCT/US2011/041291 patent/WO2011163261A1/en active Application Filing
- 2011-06-21 JP JP2013516697A patent/JP5676759B2/ja active Active
- 2011-06-21 CN CN201180033354.0A patent/CN102971687B/zh active Active
- 2011-06-21 KR KR1020137001294A patent/KR101718116B1/ko active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN102971687A (zh) | 2013-03-13 |
| EP2583151A1 (en) | 2013-04-24 |
| EP2583151B1 (en) | 2018-08-22 |
| KR101718116B1 (ko) | 2017-04-04 |
| JP2013533548A (ja) | 2013-08-22 |
| KR20130088132A (ko) | 2013-08-07 |
| US20110314312A1 (en) | 2011-12-22 |
| CN102971687B (zh) | 2016-08-03 |
| US8504854B2 (en) | 2013-08-06 |
| WO2011163261A1 (en) | 2011-12-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5676759B2 (ja) | 安定した仮想周波数のための複数の動作点の管理 | |
| US8942932B2 (en) | Determining transistor leakage for an integrated circuit | |
| US9652019B2 (en) | System and method for adjusting processor performance based on platform and ambient thermal conditions | |
| US8442786B2 (en) | Flexible power reporting in a computing system | |
| US8510582B2 (en) | Managing current and power in a computing system | |
| US9671767B2 (en) | Hybrid system and method for determining performance levels based on thermal conditions within a processor | |
| US9727435B2 (en) | Method and system of sampling to automatically scale digital power estimates with frequency | |
| US8793512B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for thermal control of processing nodes | |
| US9261949B2 (en) | Method for adaptive performance optimization of the soc | |
| JP5427981B2 (ja) | 処理ノードにおける電力消費を制御するための機構 | |
| US20120159198A1 (en) | Processor power limit management | |
| JP7014778B2 (ja) | 動的信頼性品質モニタリング | |
| WO2013082069A2 (en) | Method of power calculation for performance optimization | |
| CN112631414A (zh) | 一种风扇的控制方法、系统及介质 | |
| CN116235395A (zh) | 基于由电压调节器场效应晶体管的脉宽调制器切换所确定的相效率的切相 | |
| US12164353B2 (en) | Frequency/state based power management thresholds | |
| Sulaiman | Microprocessors thermal challenges for portable and embedded systems using thermal throttling technique | |
| CN116194863A (zh) | 老化电路的操作电压调节 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140623 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140623 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20140623 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20140728 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140730 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141029 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20141202 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20141225 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5676759 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |