JP5633592B2 - Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium - Google Patents
Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5633592B2 JP5633592B2 JP2013060156A JP2013060156A JP5633592B2 JP 5633592 B2 JP5633592 B2 JP 5633592B2 JP 2013060156 A JP2013060156 A JP 2013060156A JP 2013060156 A JP2013060156 A JP 2013060156A JP 5633592 B2 JP5633592 B2 JP 5633592B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- protective layer
- layer
- resin
- epoxy
- base material
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Description
本発明は、保護層転写シート、及び中間転写媒体に関する。 The present invention relates to a protective layer transfer sheet and an intermediate transfer medium.
透明性に優れ、中間色の再現性や階調性が高く、従来のフルカラー写真画像と同等の高品質画像が簡易に形成できるという理由から、昇華転写方式により被転写体上に熱転写画像を形成することが広く行われている。被転写体上に熱転写画像が形成された印画物としては、デジタル写真や、身分証明書、運転免許証、会員証等多く分野で使用されているIDカードが知られている。 Forms a thermal transfer image on the transfer material by the sublimation transfer method because it is excellent in transparency, has high reproducibility and gradation of intermediate colors, and can easily form a high-quality image equivalent to a conventional full-color photographic image. It is widely done. As a printed matter in which a thermal transfer image is formed on a transfer object, an ID card used in many fields such as a digital photograph, an identification card, a driver's license, and a membership card is known.
昇華転写方式による熱転写画像の形成には、基材の一方の面に染料層が設けられた熱転写シートと、被転写体、例えば、他の基材の一方の面に受容層が設けられた熱転写受像シートが使用される。そして、被転写体と、熱転写シートの染料層とを重ね合わせ、サーマルヘッドにより、熱転写シートの背面側から熱を印加して3色または4色の多数の色ドットを、被転写体上に移行させることにより、被転写体上に熱転写画像が形成された印画物を得ることができる。このような昇華転写方式によれば、熱転写シートに印加するエネルギー量によって染料の移行量を制御出来るため濃度階調が可能であることから、画像が非常に鮮明であり、且つ透明性、中間調の色再現性、階調性に優れフルカラー写真画像に匹敵する高品質の印画物を形成することができる。 For the formation of a thermal transfer image by a sublimation transfer method, a thermal transfer sheet in which a dye layer is provided on one side of a substrate and a transfer target, for example, a thermal transfer in which a receiving layer is provided on one side of another substrate An image receiving sheet is used. Then, the transferred object and the dye layer of the thermal transfer sheet are overlapped, and heat is applied from the back side of the thermal transfer sheet by the thermal head to transfer a large number of three or four color dots onto the transferred object. By doing so, it is possible to obtain a printed matter in which a thermal transfer image is formed on the transfer target. According to such a sublimation transfer method, since the amount of dye transfer can be controlled by the amount of energy applied to the thermal transfer sheet, density gradation is possible, so that the image is very clear and has transparency and halftone. Therefore, it is possible to form a high-quality printed product comparable to a full-color photographic image.
近時、熱転写受像シート以外の任意の被転写体上に、熱転写画像が形成された印画物を得たいとの要求に対応すべく、基材上に受容層が剥離可能に設けられた中間転写媒体が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1)。この中間転写媒体によれば、熱転写シートの染料層の染料を、中間転写媒体の受容層上に転写して熱転写画像を形成し、その後に中間転写媒体の背面側を加熱して、受容層を任意の被転写体上に転写することができ、任意の被転写体上に熱転写画像が形成された印画物を得ることができる。 Recently, an intermediate transfer in which a receiving layer is provided on a substrate in a peelable manner to meet the demand for obtaining a printed material on which a thermal transfer image is formed on an arbitrary transfer target other than a thermal transfer image receiving sheet. A medium has been proposed (for example, Patent Document 1). According to this intermediate transfer medium, the dye of the dye layer of the thermal transfer sheet is transferred onto the receiving layer of the intermediate transfer medium to form a thermal transfer image, and then the back side of the intermediate transfer medium is heated to form the receiving layer. The image can be transferred onto an arbitrary transfer medium, and a printed material having a thermal transfer image formed on the transfer medium can be obtained.
昇華転写方式により熱転写受像シートの受容層上に熱転写画像を形成することで得られる印画物、或いは、昇華転写方式により中間転写媒体の受容層に熱転写画像を形成し、この受容層を任意の被転写体上に再転写することで得られる印画物は、当該印画物の最表面に、熱転写画像が形成された受容層が位置することとなる。しかしながら、昇華転写方式で受容層上に形成される熱転写画像は、上記の如く階調性画像の形成に優れるものの、形成された印画物は通常の印刷インキによるものとは異なり、染料が顔料でなく比較的低分子量の染料であり且つビヒクルが存在しないため、耐可塑剤性、耐摩耗性、耐溶剤性等の耐久性に劣るといった欠点を有する。 A print obtained by forming a thermal transfer image on the receiving layer of the thermal transfer image-receiving sheet by the sublimation transfer method, or a thermal transfer image is formed on the receiving layer of the intermediate transfer medium by the sublimation transfer method, and this receiving layer is applied to any receiving layer. In the printed matter obtained by retransferring onto the transfer body, the receiving layer on which the thermal transfer image is formed is located on the outermost surface of the printed matter. However, although the thermal transfer image formed on the receiving layer by the sublimation transfer method is excellent in the formation of a gradation image as described above, the formed printed matter is different from the one using ordinary printing ink, and the dye is a pigment. In addition, since it is a relatively low molecular weight dye and no vehicle is present, it has the disadvantage of poor durability such as plasticizer resistance, abrasion resistance, and solvent resistance.
そこで、近時、熱転写画像が形成された熱転写受像シートの受容層と、保護層を有する保護層転写シートを重ね合わせ、サーマルヘッドや加熱ロール等を用いて保護層を転写させ、熱転写画像が形成された受容層上にさらに保護層を形成する方法が用いられている。このように熱転写画像が形成された受容層上にさらに保護層を形成することで、熱転写画像の耐久性を向上させることができる。例えば、特許文献2には、基材上に、剥離層、保護層、受容層兼接着層が設けられた中間転写媒体が提案されている。この中間転写媒体によれば、任意の基材上に、熱転写画像が形成された受容層、保護層を転写した時に、熱転写画像が形成された受容層の表面に保護層が位置することから、熱転写画像に耐久性を付与することができる。
Therefore, recently, the receiving layer of the thermal transfer image-receiving sheet on which the thermal transfer image is formed and the protective layer transfer sheet having the protective layer are overlapped, and the protective layer is transferred using a thermal head or a heating roll to form a thermal transfer image. A method in which a protective layer is further formed on the formed receiving layer is used. By further forming a protective layer on the receiving layer on which the thermal transfer image is thus formed, the durability of the thermal transfer image can be improved. For example,
しかしながら、耐久性の向上を主目的とする保護層を用いた場合には、保護層の箔切れ性が悪く、保護層転写シートの保護層、或いは熱転写画像が形成された中間転写媒体の受容層、及び保護層を、被転写体上に転写する際、転写される保護層に尾引きの発生や、転写部分の端部で転写不良が生じることとなる。箔切れ性を向上させるために、保護層の膜厚を下げることも考えられるが、保護層の膜厚を下げた場合には、耐久性が低下してしまう問題が生ずることとなる。 However, when a protective layer whose main purpose is to improve durability is used, the foil of the protective layer is poor and the protective layer of the protective layer transfer sheet or the receiving layer of the intermediate transfer medium on which the thermal transfer image is formed When the protective layer is transferred onto the transfer target, tailing occurs in the transferred protective layer, or transfer failure occurs at the end of the transfer portion. Although it is conceivable to reduce the film thickness of the protective layer in order to improve the foil cutting property, when the film thickness of the protective layer is reduced, there arises a problem that durability is lowered.
保護層に要求される重要な機能としては耐久性とともに箔切れ性が挙げられるものの、上記のように耐久性と箔切れ性はトレードオフの関係にあり、保護層の耐久性を向上させようとした場合には保護層の箔切れ性が低下する。このことから、1つの保護層で耐久性と箔切れ性の双方を満足させることができていないのが現状である。 Although important features required for the protective layer include durability and foil breakability, as described above, durability and foil tearability are in a trade-off relationship, and it is intended to improve the durability of the protective layer. In such a case, the foil breakability of the protective layer is lowered. From this, it is the present condition that both durability and foil tearability cannot be satisfied with one protective layer.
本発明はこのような状況に鑑みてなされたものであり、転写時の保護層の箔切れ性が良好で、かつ熱転写画像に十分な耐久性を付与することができる保護層転写シート、及び中間転写媒体を提供することを主たる課題とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such a situation, and a protective layer transfer sheet that has good foil tearability of the protective layer during transfer and can impart sufficient durability to a thermal transfer image, and an intermediate layer. It is a main problem to provide a transfer medium.
上記課題を解決するための本発明は、基材の一方の面に、当該基材から剥離可能な保護層が設けられた保護層転写シートであって、前記保護層は、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有しており、前記反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であり、前記反応性樹脂が、アミノ変性アクリル樹脂であることを特徴とする。 The present invention for solving the above problems is a protective layer transfer sheet in which a protective layer that can be peeled off from the base material is provided on one surface of the base material, and the protective layer reacts with an epoxy group. the reactive resin having a functional group, which contains the epoxy curing resin was allowed curing reaction with an epoxy curing agent state, and are the glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or more of the reactive resin, the reactive resin Is an amino-modified acrylic resin .
また、前記反応性樹脂の重量平均分子量(Mw)が15000以上70000以下であってもよい。 Moreover, 15000 or more and 70000 or less may be sufficient as the weight average molecular weight (Mw) of the said reactive resin.
また、前記基材と前記保護層との間に、当該基材から剥離可能な剥離層が設けられていてもよい。 Moreover, the peeling layer which can peel from the said base material may be provided between the said base material and the said protective layer.
上記課題を解決するための本発明は、基材の一方の面に、当該基材から剥離可能な保護層、受容層が積層された中間転写媒体であって、前記保護層は、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有しており、前記反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であり、前記反応性樹脂が、アミノ変性アクリル樹脂であることを特徴とする。
The present invention for solving the above problems is an intermediate transfer medium in which a protective layer that can be peeled off from the base material and a receiving layer are laminated on one surface of the base material, the protective layer comprising an epoxy group and the reactive resin having a reactive functional group, which contains the epoxy curing resin was allowed curing reaction with an epoxy curing agent state, and are the glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or more of the reactive resin, said reaction The resin is an amino-modified acrylic resin .
本発明の保護層転写シート、及び中間転写媒体によれば、当該保護層転写シート、及び中間転写媒体に含まれる保護層に、トレードオフの関係にある箔切れ性と、耐久性の双方を付与することができ、保護層転写シートにおいては、熱転写画像が形成された受容層上に保護層を転写する際の保護層の箔切れ性が良好であり、熱転写画像が形成された印画物に高い耐久性を付与することができる。また、中間転写媒体においては、熱転写画像が形成された受容層、及び保護層を、任意の基材上に転写する際の保護層の箔切れ性が良好で、かつ受容層上に形成された熱転写画像に高い耐久性を付与することができる。 According to the protective layer transfer sheet and the intermediate transfer medium of the present invention, the protective layer transfer sheet and the protective layer included in the intermediate transfer medium are provided with both the foil breakability and durability that are in a trade-off relationship. In the protective layer transfer sheet, the foil of the protective layer is good when the protective layer is transferred onto the receiving layer on which the thermal transfer image is formed, and the printed matter on which the thermal transfer image is formed is high. Durability can be imparted. In addition, in the intermediate transfer medium, the receiving layer on which the thermal transfer image was formed and the protective layer had good foil breakability when transferred onto an arbitrary substrate, and were formed on the receiving layer. High durability can be imparted to the thermal transfer image.
<<保護層転写シート>>
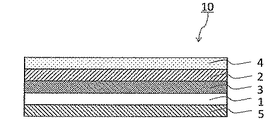
以下に、本発明の保護層転写シート10について詳細に説明する。図1は、本発明の保護層転写シートの一例を示す概略断面図である。図1、図2に示すように、本発明の保護層転写シート10は、基材1の一方の面上に、当該基材1から剥離可能な保護層2が設けられた構成をとる。基材1、及び保護層2は、本発明の保護層転写シート10における必須の構成である。なお、本発明の保護層転写シート10は、これら必須の構成に加え、図2に示すように、任意の層が設けられていてもよい。なお、図2は、基材1と保護層2との間に任意の層である剥離層3が設けられており、保護層2上に任意の層である接着層4が設けられており、基材1の他方の面上に任意の層である背面層5が設けられている。以下、本発明の保護層転写シート10の各構成について具体的に説明する。
<< Protective layer transfer sheet >>
Below, the protective
(基材)
基材1は本発明の保護層転写シート10における必須の構成であり、保護層2、或いは基材1と保護層2との間に任意に設けられる剥離層3、及び基材1の他方の面上に任意に設けられる背面層5を保持するために設けられる。基材1の材料については特に限定されないが、保護層2を被転写体上に転写する際に加えられる熱に耐え、取り扱い上支障のない機械的特性を有することが望ましい。このような基材1として、例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタレート等のポリエステル、ポリアリレート、ポリカーボネート、ポリウレタン、ポリイミド、ポリエーテルイミド、セルロース誘導体、ポリエチレン、エチレン・酢酸ビニル共重合体、ポリプロピレン、ポリスチレン、アクリル、ポリ塩化ビニル、ポリ塩化ビニリデン、ポリビニルアルコール、ポリビニルブチラール、ナイロン、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン、ポリサルフォン、ポリエーテルサルフォン、テトラフルオロエチレン・パーフルオロアルキルビニルエーテル、ポリビニルフルオライド、テトラフルオロエチレン・エチレン、テトラフルオロエチレン・ヘキサフルオロプロピレン、ポリクロロトリフルオロエチレン、ポリビニリデンフルオライド等の各種プラスチックフィルムまたはシートを挙げることができる。また、基材1の厚さは、その強度及び耐熱性が適切になるように材料に応じて適宜設定することができ、2.5〜100μm程度が一般的である。
(Base material)
The
(保護層)
基材1の一方の面上には、当該基材1から剥離可能な保護層2が設けられている。保護層2は、本発明の保護層転写シート10における必須の構成であり、熱転写時に基材1から剥離され被転写体に転写される層である。
(Protective layer)
A
本発明では、基材1から剥離可能に設けられている保護層2が、以下の(1)、(2)に示す条件を満たしている。
In this invention, the
条件1;保護層2が、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂をエポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有していること。
条件2;上記反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であること。
Condition 1: The
Condition 2: The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the reactive resin is 60 ° C. or higher.
上記条件1は、主として、保護層2の耐久性の向上を目的としており、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂をエポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を、保護層2に含有せしめることで保護層2に耐久性を付与している。
The
なお、上記条件1において、エポキシ硬化剤による硬化の進行にともない、エポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有している保護層は脆くなる傾向にあり、耐久性を十分に向上させるべく、硬化の度合いを高めていった場合には、耐久性の向上に相反し、保護層の箔切れ性が低下していく。また、エポキシ硬化剤と反応する反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)によっては、エポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有している保護層の耐久性を十分に満足させることができなくなる。
In the
そこで、本発明では、条件2に示されるように、エポキシ硬化剤によって反応性樹脂を硬化したことで付与される耐久性を低下させることなく、かつ箔切れ性を同時に満足させるために、上記エポキシ基と反応する反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上に規定されている。ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上の反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を保護層2に含有させることで、耐久性を十分に向上させるべく、エポキシ硬化剤と反応性樹脂との硬化を十分に進行させていった場合であっても、保護層2の箔切れ性を満足させることができる。なお、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃未満の反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を保護層に含有させた場合には、保護層2が脆くなり箔切れ性は低下する。また、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上の反応性樹脂を用いた場合と比較して耐久性も低くなる。
Therefore, in the present invention, as shown in
つまり、条件1、条件2を満たすエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有する保護層2によれば、トレードオフの関係にある、耐久性と、箔切れ性の双方の要求を同時に満足させることができる。なお、本願明細書において、ガラス転移温度とは、Foxの理論計算式に基づき求められる温度(ケルビン(K))を、摂氏(℃)に換算したものである。
That is, according to the
以下、エポキシ硬化剤、及びガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上の反応性樹脂について説明する。 Hereinafter, the epoxy curing agent and the reactive resin having a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or higher will be described.
<エポキシ硬化剤>
本願明細書でいうエポキシ硬化剤とは、「1分子中に少なくとも2つ以上のエポキシ基を有する硬化剤」のことを意味する。また、エポキシ硬化型樹脂とは、「エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂を、当該エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応させることで得られる樹脂」のことを意味する。エポキシ硬化剤について特に限定はなく、例えば、ビスフェノールA型エポキシ樹脂、ビスフェノールF型エポキシ樹脂等のビスフェノール型エポキシ樹脂、クレゾールノボラック型エポキシ樹脂、フェノールノボラック型エポキシ樹脂、環状脂肪族系エポキシ樹脂、グリシジルエステル系エポキシ樹脂、グリシジルアミン系エポキシ樹脂、複素環式エポキシ樹脂などを挙げることができる。
<Epoxy curing agent>
The term “epoxy curing agent” as used herein means “a curing agent having at least two epoxy groups in one molecule”. Moreover, an epoxy curable resin means "resin obtained by carrying out the hardening reaction of the reactive resin which has a functional group which reacts with an epoxy group with the said epoxy hardening agent." There is no particular limitation on the epoxy curing agent, for example, bisphenol type epoxy resin such as bisphenol A type epoxy resin, bisphenol F type epoxy resin, cresol novolac type epoxy resin, phenol novolac type epoxy resin, cyclic aliphatic epoxy resin, glycidyl ester And epoxy resin, glycidylamine epoxy resin, and heterocyclic epoxy resin.
<反応性樹脂>
反応性樹脂は、上記で説明したようにガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であるとの条件を満たし、かつ、上記エポキシ硬化剤のエポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する樹脂である。反応性樹脂が有する官能基は、エポキシ硬化剤のエポキシ基と反応するものであればよく、特に限定はない。本発明では、この条件を満たす反応性樹脂を、上記エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂が、保護層2に含有されている。
<Reactive resin>
As described above, the reactive resin satisfies the condition that the glass transition temperature (Tg) is 60 ° C. or higher, and has a functional group that reacts with the epoxy group of the epoxy curing agent. The functional group that the reactive resin has is not particularly limited as long as it reacts with the epoxy group of the epoxy curing agent. In the present invention, the
保護層2中に含有されている硬化型樹脂が、エポキシ硬化剤と、反応性樹脂との硬化反応によって得られたエポキシ硬化型樹脂であるかは、エポキシ硬化剤とエポキシ反応性樹脂との反応後の構造のFT−IR分析、例えば、エポキシ基−アミノ基やエポキシ−水酸基などの反応後の吸収の有無や残留エポキシ基の吸収などを調べることによって特定することができる。また、NMRやGPCなどの分析機器を用いることで、硬化物のさらに詳しい分析をすることができる。
Whether the curable resin contained in the
エポキシ基と反応する官能基としては、例えば、アミノ基、イソシアネート基、カルボキシル基、フェノール性水酸基、水酸基、酸無水物、チオール基、及びアミド基等を挙げることができる。 Examples of functional groups that react with epoxy groups include amino groups, isocyanate groups, carboxyl groups, phenolic hydroxyl groups, hydroxyl groups, acid anhydrides, thiol groups, and amide groups.
具体的な例としては、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上の条件を満たす、アミノ変性アクリル樹脂、水酸基含有樹脂、カルボキシル基含有樹脂などを挙げることができる。中でも、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上のアミノ変性アクリル樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂は、耐久性や、箔切れ性に極めて優れる点で、反応性樹脂として好適である。 Specific examples include an amino-modified acrylic resin, a hydroxyl group-containing resin, a carboxyl group-containing resin and the like that satisfy a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or higher. Among them, an epoxy curable resin obtained by curing an amino-modified acrylic resin having a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or higher with an epoxy curing agent is suitable as a reactive resin because it is extremely excellent in durability and foil breakability. It is.
上記反応性樹脂の分子量について特に限定はないが、反応性樹脂の重量平均分子量(Mw)が15000未満である場合には、保護層2の耐久性が低下する傾向にある。一方、反応性樹脂の重量平均分子量(Mw)が70000を超える場合には、保護層2を転写した際の箔切れ性が低下する傾向にある。この点を考慮すると、保護層2には、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であり、かつ重量平均分子量が(Mw)が15000以上70000以下の反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめた硬化型エポキシ樹脂が含有されていることが好ましい。なお、このことは、反応性樹脂の分子量を限定するものではなく、上記好ましい範囲外の分子量であっても、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃未満の反応性樹脂を保護層に含有せしめた場合と比較して、保護層2に付与される耐久性や、箔切れ性は良好となる。なお、重量平均分子量(Mw)は、ゲル浸透クロマトグラフィー(GPC)により測定したポリスチレン換算値を意味する。
Although there is no limitation in particular about the molecular weight of the said reactive resin, when the weight average molecular weight (Mw) of a reactive resin is less than 15000, it exists in the tendency for durability of the
本発明では、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以下の反応性樹脂をエポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめていることから、十分に硬化を進行させた場合であっても、箔切れ性を満足させることができる。なお、反応性樹脂が有する官能基によっては、反応の進行に伴い箔切れ性が僅かながら低下していく場合もあることから、選択される反応性樹脂に応じて、適宜硬化の度合を調整することが好ましい。 In the present invention, a reactive resin having a glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or lower is cured by an epoxy curing agent, so that the foil breakability is satisfied even when curing is sufficiently advanced. Can do. Depending on the functional group of the reactive resin, the foil breakage may slightly decrease with the progress of the reaction, so the degree of curing is appropriately adjusted according to the selected reactive resin. It is preferable.
好ましい例としては、反応性樹脂が有する官能基(以下官能基Aと言う場合がある。)と、エポキシ硬化剤が有するエポキシ基とのモル当量比(−A/−エポキシ基)が、1.0以上3.0以上の範囲内である。特に、反応性樹脂が、上記で例示したアミノ変性アクリル樹脂である場合には、当量比がこの範囲内となるように、アミノ変性アクリル樹脂をエポキシ硬化剤によって硬化せしめることで、耐久性、及び箔切れ性に極めて優れた保護層2とすることができる。
As a preferred example, the molar equivalent ratio (-A / -epoxy group) between the functional group of the reactive resin (hereinafter sometimes referred to as functional group A) and the epoxy group of the epoxy curing agent is 1. It is in the range of 0 or more and 3.0 or more. In particular, when the reactive resin is the amino-modified acrylic resin exemplified above, the amino-modified acrylic resin is cured with an epoxy curing agent so that the equivalent ratio falls within this range, and the durability, and It can be set as the
保護層2の固形分総量に対する、エポキシ硬化型樹脂の含有量について特に限定はなく、他の任意の成分等の含有量に応じて適宜設定することができる。なお、保護層2の固形分総量に対する、エポキシ硬化型樹脂の含有量が50質量%未満である場合には、耐久性を十分に満足させることができない場合があり、また、他の任意の成分によっては箔切れ性が低下する場合がある。この点を考慮すると、エポキシ硬化型樹脂は、保護層2の固形分総量に対し50質量%以上の割合で含有されていることが好ましい。なお、上限値について特に限定はなく、100質量%である。
There is no restriction | limiting in particular about content of an epoxy curable resin with respect to solid content total amount of the
(他の任意の成分)
保護層2には、エポキシ硬化型樹脂とともに、他の任意の成分が含有されていてもよい。例えば、図1に示す形態では、保護層2に、基材1からの剥離性、被転写体との接着性が要求される。したがって、この形態では、保護層2に、剥離性を有する成分や、接着性を有する成分が含有されていることが好ましい。また、図1に示す形態では、当該保護層転写シート10を用いて保護層2を転写した時に、当該保護層2が、保護層が転写された被転写体の最表面に位置することから、保護層2には耐擦過性(スリップ性という場合もある。)を有する成分が含有されていることが好ましい。なお、被転写体側に、保護層2との接着性を満たす対応をとる、例えば、被転写体上に接着層を設けることもでき、この場合には、保護層2に接着性を有する材料が含まれていることを必ずしも要しない。また、後述するように、図1に示す形態における保護層2に要求される役割を、図2に示すように、別途の層によって補うこともできる。例えば、基材1と保護層2との間に、剥離性や、耐擦過性に対する要求を満たすことができる剥離層3を設け、保護層2上に、被転写体との接着性に対する要求を満たすことができる接着層4を設ける場合には、基材からの剥離性を有する成分、被転写体との接着性を有する成分、耐擦過性を有する成分を保護層2に含有させることを必ずしも要しない。
(Other optional ingredients)
The
また、図1、図2に示す構成にかえて、保護層2上に接着層4を設け、保護層2に、剥離性と耐擦過性を有する成分を含有せしめた構成としてもよい。この場合には、保護層2に接着性を有する成分を含有させなくとも、被転写体上に、保護層2を良好に転写することができる。また、図1、図2に示す構成にかえて、基材1と保護層2との間に剥離層3を設け、保護層2に接着性を有する成分を含有せしめた構成とすることもできる。この場合には、保護層2に剥離性や、耐擦過性を有する成分を含有させなくとも、保護層2が転写された印画物に耐久性や、耐擦過性を付与することができる。
Moreover, it is good also as a structure which provided the
なお、任意の成分は、エポキシ硬化型樹脂によって付与される箔切れ性や、耐久性を損なわない範囲で含有されていることが必要であり、具体的には、任意の成分の含有量は、保護層2の固形分総量に対し、50質量%以下であることが好ましい。以下、任意の成分について説明する。
In addition, it is necessary that the optional component is contained within a range that does not impair the durability and durability of the foil imparted by the epoxy curable resin. Specifically, the content of the optional component is: The total solid content of the
「耐擦過性を有する成分」
耐擦過性を有する成分としては、例えば、メタクリル酸エステル共重合体、塩化ビニル/酢酸ビニル共重合体、ポリエステル樹脂、ポリカーボネート樹脂、アクリル樹脂、紫外線吸収性樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、ポリスチレン樹脂、ポリウレタン樹脂、アクリルウレタン樹脂、これらの各樹脂をシリコーン変性させた樹脂、これらの各樹脂の混合物、電離放射線硬化性樹脂、紫外線吸収性樹脂等が挙げられる。なかでも、紫外線吸収性樹脂は、耐擦過性に特に優れる点で好適に使用することができる。
"Ingredients with scratch resistance"
Examples of the scratch-resistant component include, for example, a methacrylate ester copolymer, a vinyl chloride / vinyl acetate copolymer, a polyester resin, a polycarbonate resin, an acrylic resin, an ultraviolet absorbing resin, an epoxy resin, a polystyrene resin, a polyurethane resin, Examples thereof include acrylic urethane resins, resins obtained by modifying these resins with silicone, mixtures of these resins, ionizing radiation curable resins, ultraviolet absorbing resins, and the like. Of these, the UV-absorbing resin can be suitably used because it is particularly excellent in scratch resistance.
紫外線吸収性樹脂としては、例えば、反応性紫外線吸収剤を熱可塑性樹脂又は上記の電離放射線硬化性樹脂に反応、結合させて得た樹脂を使用することができる。より具体的には、サリシレート系、ベンゾフェノン系、ベンゾトリアゾール系、置換アクリロニトリル系、ニッケルキレート系、ヒンダートアミン系のような従来公知の非反応性の有機系紫外線吸収剤に、付加重合性二重結合(例えばビニル基、アクリロイル基、メタアクリロイル基など)、アルコール性水酸基、アミノ基、カルボキシル基、エポキシ基、イソシアネート基のような反応性基を導入したものが挙げられる。 As the ultraviolet absorbing resin, for example, a resin obtained by reacting and bonding a reactive ultraviolet absorbent to a thermoplastic resin or the above ionizing radiation curable resin can be used. More specifically, addition-polymerizable double-reactive organic UV absorbers such as salicylates, benzophenones, benzotriazoles, substituted acrylonitriles, nickel chelates, hindered amines, etc. Examples thereof include a bond (for example, a vinyl group, an acryloyl group, a methacryloyl group, etc.), an alcoholic hydroxyl group, an amino group, a carboxyl group, an epoxy group, and a reactive group such as an isocyanate group.
「基材からの剥離性を有する成分」
また、基材1からの剥離性に優れる成分としては、例えば、ポリエチレンワックス、シリコーンワックス等のワックス類、シリコーン樹脂、シリコーン変性樹脂、フッ素樹脂、フッ素変性樹脂、ポリビニルアルコール、アクリル樹脂、熱架橋性エポキシ−アミノ樹脂及び熱架橋性アルキッド−アミノ樹脂等が挙げられる。
"Ingredients with peelability from substrate"
In addition, examples of components having excellent releasability from the
「被転写体との接着性を有する成分」
被転写体との接着性を有する成分としては、例えば、アクリル系樹脂、ビニル系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ウレタン系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、エポキシ系樹脂、ゴム系樹脂、アイオノマー樹脂等を主成分とする従来既知の接着剤が広く使用できる。
“Ingredients having adhesiveness to the transfer target”
As a component having adhesiveness to the transfer target, for example, acrylic resin, vinyl resin, polyester resin, urethane resin, polyamide resin, epoxy resin, rubber resin, ionomer resin, etc. are the main components. Conventionally known adhesives can be widely used.
「その他任意の成分」
また、保護層2には、上記で例示した任意の成分以外に、他の任意の成分が含有されていてもよい。他の任意の成分としては、例えば、ベンゾフェノン系、ベンゾトリアゾール系、ベンゾエート系、トリアジン系、酸化チタン、酸化亜鉛などの公知の紫外線吸収剤、ヒンダードアミン系、Niキレート系などの光安定剤、ヒンダードフェノール系、硫黄系、リン系、ラクトン系などの酸化防止剤等を挙げることができる。これらの任意の成分は、1種を単独で用いてもよく、2種以上を併用して用いることもできる。
"Other optional ingredients"
The
また、保護層2の耐擦過性の更なる向上を目的として、保護層2に滑剤を含有してもよい。滑剤としては、例えば、変性シリコーンオイル、シリコーン変性樹脂などのシリコーン類、ステアリン酸亜鉛、ステアリルリン酸亜鉛、ステアリン酸カルシウム、ステアリン酸マグネシウムなどの金属石鹸類、脂肪酸アミド、ポリエチレンワックス、カルバナワックス、パラフィンワックスなどを挙げることができる。
Further, for the purpose of further improving the scratch resistance of the
保護層2の形成方法については特に制限はなく、エポキシ硬化剤、ガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上の反応性樹脂、必要に応じて添加される任意の成分を、適当な溶剤に溶解または分散させた保護層用塗工液を調製し、この保護層用塗工液を、基材1、又は基材1上に任意に設けられる層上に、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、グラビア版を用いたリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。保護層2の厚みについて特に限定はなく、エポキシ硬化型樹脂による耐久性を十分に発揮でき、また、箔切れ等を良好な状態とすることができる厚みの範囲内で適宜設定することができる。好ましくは、0.5μm以上10μm以下の範囲内である。
There is no restriction | limiting in particular about the formation method of the
上記では、図1に示す構成の保護層転写シートにおいて、保護層2に、基材1からの剥離性や、被転写体との接着性を付与した構成を中心に説明を行ったが、図2に示すように、これらの役割を別途の層に付与する構成としてもよい。つまり、本発明の保護層転写シートにおいて、図1に示すように被転写体上に保護層のみが転写される単層構成の転写層としてもよく、図2に示すように、保護層2と任意の層が被転写体上に転写される積層構成の転写層とすることもできる。転写層とは、被転写体上に転写される層を意味し、本発明では、必須の層である保護層2が含まれている。図2では、基材1と保護層2との間に剥離層3が設けられ、保護層2上に接着層4が設けられた構成をとる保護層転写シートの一例を示す概略断面図である。以下、任意の各層について説明する。
In the above, in the protective layer transfer sheet having the configuration shown in FIG. 1, the description has been made mainly on the configuration in which the
(剥離層)
図2に示すように、基材1と保護層2との間に剥離層3を設けてもよい。剥離層3の成分としては、上記「耐擦過性を有する成分」、「基材からの剥離性を有する成分」で例示した材料を適宜選択して用いることができる。なお、この剥離層3は、通常保護層2とともに、被転写体上に転写される層であるが、基材1側に残存する層としてもよい。被転写体側に転写される場合には、当該剥離層が、転写後の最表面に位置することから、この場合、剥離層に「耐擦過性を有する成分」が含有されていることが好ましい。一方、基材1側に残存する場合には、保護層2が転写後の最表面に位置することから、この場合には、上記で説明したように、保護層2に「耐擦過性を有する成分」が含有されていることが好ましい。剥離層3が、保護層2とともに被転写体上に転写される場合には、上記で例示した滑剤等を剥離層3に含有させることにより耐擦過性の更なる向上を図ることができる。
(Peeling layer)
As shown in FIG. 2, a
剥離層3の形成方法としては、上記「耐擦過性を有する成分」、「基材からの剥離性を有する成分」を適当な溶剤に溶解または分散させた剥離層用塗工液を調製し、この剥離層用塗工液を、基材1上に、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、グラビア版を用いたリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。剥離層3の厚みは、0.5μm〜5μm程度が一般的である。
As a method for forming the
(耐可塑剤性層)
保護層2が転写された印画物の耐可塑剤性を向上させるために、基材1と保護層2との間や、剥離層3を設ける場合には剥離層3と保護層4との間に耐可塑剤性層(図示しない)を設けてもよい。
(Plasticizer resistant layer)
In order to improve the plasticizer resistance of the printed material to which the
耐可塑剤性層としては、可塑剤成分を弾く材料や、可塑剤成分が画像に到達しにくい材料を好ましく使用することができる。可塑剤成分を弾く材料としては、ポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂、ポリビニルピロリドン樹脂等を挙げることができる。可塑剤成分が画像に到達しにくい材料としては、カチオン性のウレタンエマルジョン等のカチオン性樹脂を挙げることができる。これらの材料は単独で用いてもよく、2種以上を混合して用いることもできる。 As the plasticizer-resistant layer, a material that repels the plasticizer component or a material that does not easily reach the image can be preferably used. Examples of the material that repels the plasticizer component include polyvinyl alcohol resin, polyvinyl butyral resin, polyvinyl acetal resin, polyvinyl pyrrolidone resin, and the like. Examples of the material in which the plasticizer component hardly reaches the image include cationic resins such as a cationic urethane emulsion. These materials may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
また、可塑剤成分を弾く材料として例示したポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂は、ケン化度が30〜100%のものが好ましく、60〜100%のものが更に好ましい。ケン化度がこの範囲のポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂を耐可塑剤性層に含有させることで、保護層2を含む転写層の耐可塑剤性を更に向上させることができる。なお、本発明におけるケン化度とは、ポリマー中のビニルアルコール構造のモル数を、ポリマー中の全モノマーのモル数で割った値をいう。可塑剤成分を弾く材料や、可塑剤成分が画像に到達しにくい材料は、耐可塑剤性層の固形分総量に対し20質量%〜100質量%の範囲内で含有されていることが好ましい。
In addition, the polyvinyl alcohol resin, polyvinyl butyral resin, and polyvinyl acetal resin exemplified as materials for repelling the plasticizer component preferably have a saponification degree of 30 to 100%, and more preferably 60 to 100%. By including a polyvinyl alcohol resin, a polyvinyl butyral resin, or a polyvinyl acetal resin having a saponification degree within this range in the plasticizer-resistant layer, the plasticizer resistance of the transfer layer including the
また、耐可塑剤性層には、必要に応じて、例えば、滑剤、可塑剤、充填剤、帯電防止剤、アンチブロッキング剤、架橋剤、酸化防止剤、紫外線吸収剤、光安定剤、染料、顔料等の着色剤、蛍光増白剤、その他の添加剤等を添加してもよい。 In addition, the plasticizer-resistant layer may include, for example, a lubricant, a plasticizer, a filler, an antistatic agent, an antiblocking agent, a crosslinking agent, an antioxidant, an ultraviolet absorber, a light stabilizer, a dye, Colorants such as pigments, fluorescent brighteners, other additives, and the like may be added.
必要に応じて設けられる耐可塑剤性層は、上記で例示した材料の1種又は2種以上と、必要に応じて添加される各種材料を適当な溶剤により溶解または分散させて耐可塑剤性層用塗工液を調製し、これを基材1、あるいは必要に応じて設けられる剥離層3上に塗工・乾燥して形成することができる。耐可塑剤性層の厚さについて特に限定はないが、通常は乾燥後の厚みで0.1μm〜50μmであり、好ましくは1μm〜20μm程度である。
The plasticizer-resistant layer provided as necessary is a plasticizer-resistant material prepared by dissolving or dispersing one or more of the above-exemplified materials and various materials added as necessary with an appropriate solvent. A layer coating solution can be prepared, and this can be applied and dried on the
(接着層)
図2に示すように、保護層2上に接着層4を設けてもよい。接着層4の成分としては、上記「被転写体との接着性を有する成分」で例示した成分等を適宜選択して用いることができる。なお、被転写体側で、保護層2との接着性を満足させる対応をとる場合には、接着層4を設けることを必ずしも要しない。
(Adhesive layer)
As shown in FIG. 2, an
接着層4の形成方法としては、上記「被転写体との接着性を有する成分」を適当な溶剤に溶解または分散させた接着層用塗工液を調製し、この剥離層用塗工液を、保護層2上に、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、グラビア版を用いたリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。接着層4の厚みは、0.5μm〜10μm程度が一般的である。
As a method for forming the
上記では、積層構成の転写層の一例として、転写層が、必須の層である保護層2とともに、任意の層である剥離層、耐可塑剤性層、接着層を含む場合を例に挙げ説明を行ったが、転写層を構成する任意の層に含有されている成分によっては、例えば、剥離層、耐可塑剤性層、接着層に含有されている成分によっては、それぞれの層単独での箔切れ性が不十分となる場合がある。本発明では、転写層が積層構成を呈する場合であっても、当該転写層に含まれ、被転写体上に転写される必須の層である保護層2が上記で説明したように箔切れ性に優れることから、保護層2とともに転写される任意の層の箔切れ性が低い場合であっても、保護層2と任意の層と含む転写層全体としての箔切れ性を向上させることができる。
In the above description, as an example of a transfer layer having a laminated structure, the transfer layer includes, as an example, a
(背面層)
また、図2に示すように、基材1の保護層2が設けられている面とは異なる面上に、耐熱性、及び印画時におけるサーマルヘッドの走行性等を向上させるための背面層5を設けてもよい。なお、背面層5は本発明の保護層転写シート10における任意の構成である。
(Back layer)
In addition, as shown in FIG. 2, a
背面層5は、従来公知の熱可塑性樹脂等を適宜選択して形成することができる。このような、熱可塑性樹脂として、例えば、ポリエステル系樹脂、ポリアクリル酸エステル系樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル系樹脂、スチレンアクリレート系樹脂、ポリウレタン系樹脂、ポリエチレン系樹脂、ポリプロピレン系樹脂等のポリオレフィン系樹脂、ポリスチレン系樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニル系樹脂、ポリエーテル系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、ポリイミド系樹脂、ポリアミドイミド系樹脂、ポリカーボネート系樹脂、ポリアクリルアミド樹脂、ポリビニルクロリド樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセトアセタール樹脂等のポリビニルアセタール樹脂等の熱可塑性樹脂、これらのシリコーン変性物等が挙げられる。中でも、耐熱性等の点から、ポリアミドイミド系樹脂又はそのシリコーン変性物等を好ましく用いることができる。
The
また、背面層5には、上記熱可塑性樹脂に加え、スリップ性を向上させる目的で、ワックス、高級脂肪酸アミド、リン酸エステル化合物、金属石鹸、シリコーンオイル、界面活性剤等の離型剤、フッ素樹脂等の有機粉末、シリカ、クレー、タルク、炭酸カルシウム等の無機粒子等の各種添加剤が含有されていることが好ましく、リン酸エステル又は金属石鹸の少なくとも1種が含有されていることが特に好ましい。
In addition to the above thermoplastic resin, the
背面層5は、例えば、上記熱可塑性樹脂、必要に応じて添加される各種添加剤を適当な溶媒に分散又は溶解させた塗工液を、基材1上に、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、グラビア版を用いたリバースロールコーティング印刷法等の公知の手段により、塗工し、乾燥することにより形成することができる。背面層5の厚みは、耐熱性等の向上等の点から、0.1g/m2〜5g/m2程度が好ましく、0.3g/m2〜2.0g/m2程度がより好ましい。
For example, the
以上、本発明の保護層転写シート10について説明を行ったが、本発明の保護層転写シートは本発明の趣旨を妨げない範囲内での種々の態様をとることができる。例えば、基材1の保護層2が設けられた面と同一面上に、染料層を面順次に設けた染料層一体型の保護層転写シート(図示しない)とすることもできる。この染料層は単一の染料層であってもよく、例えば、イエロー染料層、マゼンタ染料層、シアン染料層がこの順で面順次に設けられた構成とすることもできる。
The protective
<<中間転写媒体>>
次に、図3、図4を用いて本発明の中間転写媒体100について説明する。本発明の中間転写媒体100は、基材1の一方の面上に、当該基材1から剥離可能な保護層2、受容層50が積層された構成をとる。基材1、保護層2、受容層50は、本発明の中間転写媒体100における必須の構成である。なお、本発明の中間転写媒体100は、図4に示すように、基材1と保護層2との間に剥離層3が設けられ、基材1の他方の面上に背面層5が設けられていてもよい。また、受容層50上に図示しない接着層が設けられていてもよい。以下、本発明の中間転写媒体100の各構成について具体的に説明する。
<< Intermediate transfer medium >>
Next, the
(基材)
基材1は、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10の基材1と同様のものを用いることができ、ここでの詳細な説明は省略する。
(Base material)
As the
(保護層)
基材1上には、当該基材1から剥離可能な保護層2が設けられている。本発明の中間転写媒体100では、保護層2が、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有していることを特徴とする。この特徴を有する本発明によれば、受容層50上に熱転写画像を形成した後に、本発明の中間転写媒体100の受容層50、及び保護層2を、任意の被転写体上に転写することで、受容層50に形成された熱転写画像に高い耐久性が付与された印画物を得ることができる。また、本発明では、受容層50、保護層2を被転写体上に転写する際の保護層2の箔切れ性にも優れる。
(Protective layer)
On the
本発明の中間転写媒体100によってもたらされる上記効果は、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10の保護層2と同様の理由によるものであり、ここでの詳細な説明は省略する。したがって、本発明の中間転写媒体100においては、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10で説明した保護層2をそのまま用いることができる。なお、本発明では、保護層2上に設けられる受容層50が、被転写体と直接的、又は接着層4等の任意の層を介して間接的に積層されることから保護層2が接着性を有していることを特に要しない。
The above-mentioned effect brought about by the
また、本発明の中間転写媒体においても、図3に示すように保護層2に「基材からの剥離性を有する成分」を含有せしめ、剥離層の機能を兼ね備える保護層2(剥離層兼保護層)としてもよく、基材からの剥離性を別途の層を設けることで担保する、例えば、図4に示すように、基材1と保護層2との間に剥離層3を設けることとしてもよい。剥離層3についても、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10で説明したものをそのまま用いることができ、ここでの詳細な説明は省略する。
Also in the intermediate transfer medium of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 3, the
(受容層)
図3、図4に示すように、保護層2上には受容層50が設けられている。この受容層上には、熱転写画像が形成される。そして、画像が形成された受容層50は、保護層2とともに被転写体上に転写され、その結果、印画物が形成される。受容層50を形成するための材料としては、昇華性染料または熱溶融性インキ等の熱移行性の色材を受容し易い従来公知の樹脂材料を使用することができる。例えば、ポリプロピレン等のポリオレフィン系樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニルもしくはポリ塩化ビニリデン等のハロゲン化樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル、塩化ビニル−酢酸ビニル系共重合体、エチレン−酢酸ビニル共重合体もしくはポリアクリル酸エステル等のビニル系樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレートもしくはポリブチレンテレフタレート等のポリエステル樹脂、ポリスチレン系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、エチレンもしくはプロピレン等のオレフィンと他のビニルポリマーとの共重合体系樹脂、アイオノマーもしくはセルロースジアスターゼ等のセルロース系樹脂、ポリカーボネート等が挙げられ、特に、塩化ビニル系樹脂、アクリル−スチレン系樹脂またはポリエステル樹脂が好ましい。
(Receptive layer)
As shown in FIGS. 3 and 4, a receiving
受容層50が接着層を介して被転写体に転写される場合には、受容層50自体の接着性は必ずしも要求されない。しかし、受容層50が接着層を介さないで被転写体に転写される場合には、塩化ビニル−酢酸ビニル共重合体などの接着性を有する樹脂材料を用いて受容層50を形成することが好ましい。
When the receiving
受容層50は、上述の材料の中から選択された単独または複数の材料および必要に応じて各種添加剤等を加え、水または有機溶剤等の適当な溶剤に溶解または分散させて受容層用塗工液を調製し、これをグラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法またはグラビア版を用いたリバースコーティング法等の手段により、塗布、乾燥して形成することができる。その厚さは、乾燥状態で1〜10g/m2程度である。
The receiving
受容層50が接着性を有しない場合には、当該受容層50上に接着層(図示しない)を設けることとしてもよい。接着層は、本発明の中間転写媒体100における任意の構成であり、被転写体側に接着処理等が施されている場合には、接着層を設けることを要しない。受容層50上に任意に設けられる接着層としては、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10の接着層4をそのまま用いることができ、ここでの詳細な説明は省略する。
When the receiving
(背面層)
また、図4に示すように基材1の他方の面上に背面層5が設けられていてもよい。背面層5としては、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10の保護層5をそのまま用いることができ、ここでの詳細な説明は省略する。
(Back layer)
Moreover, as shown in FIG. 4, the
また、本発明の中間転写媒体においても、上記本発明の保護層転写シートと同様に、基材1と保護層2との間に、剥離層や、耐可塑剤性層が設けられていてもよい。
In the intermediate transfer medium of the present invention, a release layer or a plasticizer-resistant layer may be provided between the
(画像形成方法)
本発明の中間転写媒体を用いて、受容層50上に画像形成を行う方法としては、特に限定されず、公知の熱転写方式にて行うことができる。
(Image forming method)
A method for forming an image on the receiving
また、上記画像形成の際に使用する熱転写シートとしては、例えば、ポリエステルフィルム等の基材の一方の面に熱転写性色材層が設けられ、基材の他方の面に背面層が設けられた従来公知の熱転写シートを使用することができる。以下、熱転写シートについて説明する。 Further, as the thermal transfer sheet used in the image formation, for example, a heat transferable color material layer is provided on one surface of a substrate such as a polyester film, and a back layer is provided on the other surface of the substrate. A conventionally known thermal transfer sheet can be used. Hereinafter, the thermal transfer sheet will be described.
(熱転写シートの基材)
熱転写シートの基材としては、従来公知のある程度の耐熱性と強度を有するものであればいずれのものでもよく、例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタレートフィルム、1,4−ポリシクロヘキシレンジメチレンテレフタレートフィルム、ポリエチレンナフタレートフィルム、ポリフェニレンサルフィドフィルム、ポリスチレンフィルム、ポリプロピレンフィルム、ポリサルホンフィルム、アラミドフィルム、ポリカーボネートフィルム、ポリビニルアルコールフィルム、セロハン、酢酸セルロース等のセルロース誘導体、ポリエチレンフィルム、ポリ塩化ビニルフィルム、ナイロンフィルム、ポリイミドフィルム、アイオノマーフィルム等の樹脂フィルム;コンデンサー紙、パラフィン紙、合成紙等の紙類;不織布;紙や不織布と樹脂との複合体等が挙げられる。
(Thermal transfer sheet base material)
The base material of the thermal transfer sheet may be any material as long as it has a conventionally known heat resistance and strength. For example, polyethylene terephthalate film, 1,4-polycyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate film, polyethylene naphthalate Film, polyphenylene sulfide film, polystyrene film, polypropylene film, polysulfone film, aramid film, polycarbonate film, polyvinyl alcohol film, cellophane, cellulose derivatives such as cellulose acetate, polyethylene film, polyvinyl chloride film, nylon film, polyimide film, ionomer Resin film such as film; paper such as condenser paper, paraffin paper, synthetic paper; non-woven fabric; composite of paper or non-woven fabric and resin And the like.
基材の厚みについて特に限定はないが、通常0.5μm〜50μmであり、好ましくは約1.5〜10μmである。 Although there is no limitation in particular about the thickness of a base material, it is 0.5-50 micrometers normally, Preferably it is about 1.5-10 micrometers.
基材は、隣接する層との接着性を向上させるため、表面処理が施されていてもよい。表面処理としては、コロナ放電処理、火炎処理、オゾン処理、紫外線処理、放射線処理、粗面化処理、化学薬品処理、プラズマ処理、グラフト化処理等、公知の樹脂表面改質技術を適用することができる。上記表面処理は、1種のみ行ってもよいし、2種以上行ってもよい。また、必要に応じ、その一方の面又は両面に下引き層(プライマー層)が設けられていてもよい。 The base material may be surface-treated in order to improve the adhesiveness with an adjacent layer. As the surface treatment, known resin surface modification techniques such as corona discharge treatment, flame treatment, ozone treatment, ultraviolet treatment, radiation treatment, surface roughening treatment, chemical treatment, plasma treatment, grafting treatment, etc. can be applied. it can. Only one type of surface treatment may be performed, or two or more types may be performed. Moreover, the undercoat layer (primer layer) may be provided in the one surface or both surfaces as needed.
(熱転写性色材層)
熱転写性色材層は、熱転写シートが昇華型熱転写シートの場合には、昇華性染料を含有する層となり、熱溶融型熱転写シートの場合には、着色剤を含む熱溶融組成物を含有する層となる。また、昇華性染料を含有する層領域と、着色剤を含む熱溶融組成物からなる熱溶融性のインクを含有する層領域とを連続した1枚の基材上に面順次に設けられた熱転写シートを用いることもできる。以下、熱転写シートが、昇華型熱転写シートである場合を中心に説明するが、本発明の中間転写媒体100は、昇華型熱転写シートと組み合されて用いられることに限定されるものではない。
(Heat transferable color material layer)
The thermal transfer colorant layer is a layer containing a sublimation dye when the thermal transfer sheet is a sublimation type thermal transfer sheet, and a layer containing a thermal melt composition containing a colorant in the case of a thermal melt type thermal transfer sheet. It becomes. Also, thermal transfer in which a layer region containing a sublimable dye and a layer region containing a heat-meltable ink comprising a heat-melting composition containing a colorant are provided on a single continuous substrate in a surface sequential manner. A sheet can also be used. Hereinafter, although the case where the thermal transfer sheet is a sublimation type thermal transfer sheet will be mainly described, the
昇華性染料としては、例えば、ジアリールメタン系染料;トリアリールメタン系染料;チアゾール系染料;メロシアニン染料;ピラゾロン染料;メチン系染料;インドアニリン系染料;アセトフェノンアゾメチン、ピラゾロアゾメチン、イミダゾルアゾメチン、イミダゾアゾメチン、ピリドンアゾメチン等のアゾメチン系染料;キサンテン系染料;オキサジン系染料;ジシアノスチレン、トリシアノスチレン等のシアノスチレン系染料;チアジン系染料;アジン系染料;アクリジン系染料;ベンゼンアゾ系染料;ピリドンアゾ、チオフェンアゾ、イソチアゾールアゾ、ピロールアゾ、ピラゾールアゾ、イミダゾールアゾ、チアジアゾールアゾ、トリアゾールアゾ、ジスアゾ等のアゾ系染料;スピロピラン系染料;インドリノスピロピラン系染料;フルオラン系染料;ローダミンラクタム系染料;ナフトキノン系染料;アントラキノン系染料;キノフタロン系染料;等が挙げられ、更に具体的には、特開平7−149062号公報に例示の化合物等が挙げられる。上記熱転写性色材層において、昇華性染料は熱転写性色材層の全固形分に対し5〜90重量%、好ましくは10〜70重量%の量である。昇華性染料の使用量が、上記範囲未満であると印字濃度が低くなることがあり、上記範囲を越えると保存性等が低下することがある。 Examples of sublimation dyes include diarylmethane dyes; triarylmethane dyes; thiazole dyes; merocyanine dyes; pyrazolone dyes; methine dyes; indoaniline dyes; Azomethine dyes such as azomethine and pyridone azomethine; xanthene dyes; oxazine dyes; cyanostyrene dyes such as dicyanostyrene and tricyanostyrene; thiazine dyes; azine dyes; acridine dyes; benzeneazo dyes; Azo dyes such as azo, isothiazole azo, pyrrole azo, pyrazole azo, imidazole azo, thiadiazole azo, triazole azo, disazo; spiropyran dyes; indolinospiropyran dyes ; Fluoran dyes; rhodamine lactam dyes; naphthoquinone dyes; anthraquinone dyes; quinophthalone dyes; and the like, and more specifically, the compounds exemplified in JP-A-7-149062 and the like. In the heat transferable color material layer, the sublimation dye is 5 to 90% by weight, preferably 10 to 70% by weight, based on the total solid content of the heat transferable color material layer. If the amount of sublimable dye used is less than the above range, the print density may be low, and if it exceeds the above range, the storage stability may be lowered.
上記染料を担持するためのバインダー樹脂としては、例えば、エチルセルロース樹脂、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース樹脂、エチルヒドロキシセルロース樹脂、メチルセルロース樹脂、ニトロセルロース樹脂、酢酸セルロース樹脂等のセルロース系樹脂、ポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂、ポリビニルピロリドン等のビニル系樹脂、ポリ(メタ)アクリレート、ポリ(メタ)アクリルアミド等のアクリル系樹脂、ポリウレタン系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、フェノキシ樹脂、フェノール樹脂、エポキシ樹脂等が挙げられる。これらの中でも、セルロース系、ビニル系、アクリル系、ポリウレタン系、ポリエステル系等の樹脂が耐熱性、染料の移行性等の点から好ましい。 Examples of the binder resin for supporting the dye include cellulose resins such as ethyl cellulose resin, hydroxyethyl cellulose resin, ethyl hydroxy cellulose resin, methyl cellulose resin, nitrocellulose resin, and cellulose acetate resin, polyvinyl alcohol resin, and polyvinyl acetate resin. , Polyvinyl butyral resin, polyvinyl acetal resin, vinyl resins such as polyvinyl pyrrolidone, acrylic resins such as poly (meth) acrylate and poly (meth) acrylamide, polyurethane resins, polyamide resins, polyester resins, phenoxy resins, phenols Examples thereof include resins and epoxy resins. Among these, cellulose-based, vinyl-based, acrylic-based, polyurethane-based, and polyester-based resins are preferable from the viewpoints of heat resistance, dye transferability, and the like.
また、熱転写性色材層は、離型剤、無機微粒子、有機微粒子等を含有していてもよい。離型剤としては、シリコーンオイル、ポリエチレンワックス、リン酸エステル等が挙げられる。シリコーンオイルとしては、ストレートシリコーンオイル、および変性シリコーンオイルやその硬化物等が挙げられる。シリコーンオイルは反応性のものでもよいし、非反応性のものでも良い。無機微粒子としては、カーボンブラック、アルミニウム、二硫化モリブデン等が挙げられる。変性シリコーンオイルは、反応性シリコーンオイルと非反応性シリコーンオイルに分類できる。反応性シリコーンオイルには、アミノ変性、エポキシ変性、カルボキシル変性、ヒドロキシ変性、メタクリル変性、メルカプト変性、フェノール変性、片末端反応性・異種官能基変性がある。非反応性シリコーンオイルとしては、ポリエーテル変性、メチルスチリル変性、アルキル変性、高級脂肪酸エステル変性、親水性特殊変性、高級アルコキシ変性、フッ素変性等がある。シリコーンオイルの添加量は、バインダーの質量に対し、0.1〜15質量%が好ましく、更に好ましくは0.3〜10質量%である。また、上記有機微粒子としては、ポリエチレンワックス等が挙げられる。 The heat transferable color material layer may contain a release agent, inorganic fine particles, organic fine particles and the like. Examples of the mold release agent include silicone oil, polyethylene wax, and phosphate ester. Examples of the silicone oil include straight silicone oil, modified silicone oil, and cured products thereof. The silicone oil may be reactive or non-reactive. Inorganic fine particles include carbon black, aluminum, molybdenum disulfide and the like. The modified silicone oil can be classified into a reactive silicone oil and a non-reactive silicone oil. The reactive silicone oil includes amino modification, epoxy modification, carboxyl modification, hydroxy modification, methacryl modification, mercapto modification, phenol modification, one-terminal reactivity and heterofunctional modification. Non-reactive silicone oils include polyether modification, methylstyryl modification, alkyl modification, higher fatty acid ester modification, hydrophilic special modification, higher alkoxy modification, fluorine modification and the like. The amount of silicone oil added is preferably 0.1 to 15% by mass, more preferably 0.3 to 10% by mass, based on the mass of the binder. Examples of the organic fine particles include polyethylene wax.
熱転写性色材層は、例えば、昇華性染料、バインダー樹脂、及び必要に応じて任意に添加される各種の成分を、適当な溶媒に分散、或いは溶解した熱転写性色材層用塗工液を、基材上に、従来公知の塗工方法を用いて、塗工・乾燥することで形成することができる。従来公知の塗工方法としては、グラビア印刷法、グラビア版を用いたリバースロールコーティング法、ロールコーター、バーコーター等が挙げられる。また、溶媒としては、トルエン、メチルエチルケトン、エタノール、イソプロピルアルコール、シクロヘキサノン、ジメチルホルムアミド〔DMF〕等が挙げられる。 The heat transferable color material layer is, for example, a coating solution for a heat transferable color material layer in which a sublimable dye, a binder resin, and various components optionally added as necessary are dispersed or dissolved in an appropriate solvent. It can be formed on a substrate by coating and drying using a conventionally known coating method. Conventionally known coating methods include a gravure printing method, a reverse roll coating method using a gravure plate, a roll coater, a bar coater and the like. Examples of the solvent include toluene, methyl ethyl ketone, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, cyclohexanone, dimethylformamide [DMF] and the like.
熱転写性色材層の厚みについて特に限定はなく、通常0.2μm〜5μm程度である。 There is no limitation in particular about the thickness of a heat transferable color material layer, and it is about 0.2 micrometer-5 micrometers normally.
(熱転写シートの背面層)
また、基材の他方の面上に、耐熱性、及び印画時におけるサーマルヘッドの走行性等を向上させるための背面層が設けられていてもよい。熱転写シートの背面層としては、上記本発明の保護層転写シート10の背面層5をそのまま用いることができる。
(Back layer of thermal transfer sheet)
In addition, a back layer for improving heat resistance, running performance of the thermal head during printing, and the like may be provided on the other surface of the substrate. As the back layer of the thermal transfer sheet, the
次に実施例及び比較例を挙げて本発明を更に具体的に説明する。以下、特に断りのない限り、部または%は質量基準である。また、Tgはガラス転移温度を、Mwは重量平均分子量を意味する。 Next, the present invention will be described more specifically with reference to examples and comparative examples. Hereinafter, unless otherwise specified, parts or% is based on mass. Tg means glass transition temperature, and Mw means weight average molecular weight.
(実施例1)
基材として厚さ12μmのポリエチレンテレフタレートフィルム(東レ株式会社製、ルミラー)を用い、該基材上に下記組成の剥離層用塗工液を乾燥状態で1.0g/m2の厚さとなるように塗工し剥離層を形成した。次いで、剥離層上に下記組成の保護層用塗工液1を、乾燥状態で2.0g/m2の厚さとなるように塗工し保護層を形成した。更に該保護層の上に下記組成の受容層用塗工液を、乾燥状態で1.0g/m2の厚さとなるように塗工し受容層を形成して実施例1の中間転写媒体を得た。なお、上記の剥離層用塗工液、保護層用塗工液1、受容層用塗工液は、全てグラビアコーティングにて塗工した。
Example 1
A polyethylene terephthalate film (Lumirror, manufactured by Toray Industries, Inc.) having a thickness of 12 μm is used as a substrate, and a coating solution for a release layer having the following composition is dried on the substrate to a thickness of 1.0 g / m 2 Was applied to form a release layer. Subsequently, the protective
<剥離層用塗工液>
・アクリル樹脂 80部
(BR−87、三菱レイヨン(株)製)
・ポリエステル樹脂 5部
(バイロン200、東洋紡(株)製)
・ポリエチレンワックス 5部 (ポリワックス1000 東洋アドレ(株)製)
・紫外線吸収アクリル樹脂 10部
(PUVA−50M−40TM、大塚化学(株)製)
・トルエン 200部
・MEK 200部
<Coating liquid for release layer>
・ Acrylic resin 80 parts (BR-87, manufactured by Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd.)
・
・ 5 parts of polyethylene wax
・ Ultraviolet-absorbing
・ Toluene 200 parts ・ MEK 200 parts
<保護層用塗工液1>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):0.5
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分40%、Tg75℃、Mw53000) 100部
(LK−730 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 2.1部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<Protective
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 0.5
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 40%, Tg 75 ° C., Mw 53000) 100 parts (LK-730 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
・ Epoxy curing agent 2.1 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
<受容層用塗工液>
・塩化ビニル−酢酸ビニル共重合体 95部
(CNL、日信化学工業(株)製)
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル 5部
(KP−1800U、信越化学工業(株)製)
・トルエン 200部
・MEK 200部
<Coating liquid for receiving layer>
・ 95 parts of vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymer (CNL, manufactured by Nissin Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.)
・ Epoxy-modified
・ Toluene 200 parts ・ MEK 200 parts
(実施例2)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液2に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例2の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Example 2)
An intermediate transfer medium of Example 2 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液2>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):1.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分40%、Tg75℃、Mw53000) 100部
(LK−730 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 4.25部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<Protective
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 1.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 40%, Tg 75 ° C., Mw 53000) 100 parts (LK-730 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
Epoxy curing agent 4.25 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(実施例3)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液3に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例3の中間転写媒体を得た。
Example 3
An intermediate transfer medium of Example 3 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液3>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):2.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分40%、Tg75℃、Mw53000) 100部
(LK−730 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 8.5部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 2.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 40%, Tg 75 ° C., Mw 53000) 100 parts (LK-730 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
・ Epoxy curing agent 8.5 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(実施例4)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液4に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例4の中間転写媒体を得た。
Example 4
An intermediate transfer medium of Example 4 was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液4>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):3.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分40%、Tg75℃、Mw53000) 100部
(LK−730 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 12.75部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 3.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 40%, Tg 75 ° C., Mw 53000) 100 parts (LK-730 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
-Epoxy curing agent 12.75 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(実施例5)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液5に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例5の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Example 5)
An intermediate transfer medium of Example 5 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液5>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):1.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分50%、Tg63℃、Mw31000) 100部
(LK−723 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 3.23部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 1.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (
・ Epoxy curing agent 3.23 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(実施例6)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液6に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例6の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Example 6)
An intermediate transfer medium of Example 6 was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液6>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):2.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分50%、Tg63℃、Mw31000) 100部
(LK−723 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 6.46部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<Coating liquid 6 for protective layer>
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 2.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (
・ Epoxy curing agent 6.46 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(実施例7)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液7に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例7の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Example 7)
An intermediate transfer medium of Example 7 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液7>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):2.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分50%、Tg62℃、Mw25000) 100部
(LK−714 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 6.46部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<Coating liquid 7 for protective layer>
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 2.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (
・ Epoxy curing agent 6.46 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(実施例8)
剥離層を形成せず、保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の剥離層兼保護層用塗工液1に変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして実施例8の中間転写媒体を得た。なお、剥離層兼保護層用塗工液は、乾燥状態で3.0g/m2の厚さとなるように塗工した。
(Example 8)
The intermediate transfer medium of Example 8 was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the release layer was not formed and the protective
<剥離層兼保護層用塗工液1>
モル当量比(−アミノ基/−エポキシ基):1.0
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分40%、Tg75℃、Mw53000) 200部
(LK−730 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 8.5部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・ポリエチレンワックス 5部 (ポリワックス1000 東洋アドレ(株)製)
・紫外線吸収アクリル樹脂 10部
(PUVA−50M−40TM、大塚化学(株)製)
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 200部
<
Molar equivalent ratio (-amino group / -epoxy group): 1.0
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 40%, Tg 75 ° C., Mw 53000) 200 parts (LK-730 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
・ Epoxy curing agent 8.5 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ 5 parts of polyethylene wax
・ Ultraviolet-absorbing
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 200 parts
(比較例1)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液Aに変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして比較例1の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Comparative Example 1)
An intermediate transfer medium of Comparative Example 1 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液A>
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分40%、Tg75℃、Mw53000) 100部
(LK−730 東レファインケミカル(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<Coating liquid A for protective layer>
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 40%, Tg 75 ° C., Mw 53000) 100 parts (LK-730 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(比較例2)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液Bに変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして比較例2の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Comparative Example 2)
An intermediate transfer medium of Comparative Example 2 was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液B>
・アミノ変性アクリル樹脂(固形分55%、Tg59℃、Mw13000) 100部
(LK−707 東レファインケミカル(株))
・エポキシ硬化剤 7.14部
(デナコール EX−612) ナガセケムテックス(株))
・トルエン/イソブタノール=1/1混合溶剤 100部
<Coating liquid B for protective layer>
Amino-modified acrylic resin (solid content 55%, Tg 59 ° C., Mw 13000) 100 parts (LK-707 Toray Fine Chemical Co., Ltd.)
・ Epoxy curing agent 7.14 parts (Denacol EX-612) Nagase ChemteX Corporation)
・ Toluene / isobutanol = 1/1 mixed solvent 100 parts
(比較例3)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液Cに変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして比較例3の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Comparative Example 3)
An intermediate transfer medium of Comparative Example 3 was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液C>
・ポリエステル樹脂 20部
(バイロン200 東洋紡(株))
・MEK/トルエン=1/1混合溶剤 80部
<Coating liquid C for protective layer>
・ Polyester resin 20 parts (Byron 200 Toyobo Co., Ltd.)
MEK / toluene = 1/1 mixed solvent 80 parts
(比較例4)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液Dに変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして比較例4の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Comparative Example 4)
An intermediate transfer medium of Comparative Example 4 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液D>
・ポリエステル樹脂 20部
(バイロン600 東洋紡(株))
・MEK/トルエン=1/1混合溶剤 80部
<Coating liquid D for protective layer>
・ Polyester resin 20 parts (Byron 600 Toyobo Co., Ltd.)
MEK / toluene = 1/1 mixed solvent 80 parts
(比較例5)
保護層用塗工液1を下記組成の保護層用塗工液Eに変更した以外は、全て実施例1と同様にして比較例5の中間転写媒体を得た。
(Comparative Example 5)
An intermediate transfer medium of Comparative Example 5 was obtained in the same manner as Example 1 except that the protective
<保護層用塗工液E>
・アクリル系樹脂 20部
(ダイヤナールBR−87 三菱レイヨン(株))
・MEK/トルエン=1/1混合溶剤 80部
<Coating liquid E for protective layer>
・ Acrylic resin 20 parts (Dianar BR-87 Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd.)
MEK / toluene = 1/1 mixed solvent 80 parts
(印画物の形成)
HDP−600(HID社)プリンタと、該プリンタ専用インクリボンを用いて、デフォルト条件下で各実施例、及び比較例の中間転写媒体の受容層へ黒ベタ画像を形成し、次いで、同プリンタを用いて塩ビカード(DNP社製)上に、175℃、2sec/inchの再転写条件で、黒ベタ画像形成後の受容層、保護層、及び剥離層を転写させ(実施例8については剥離層兼保護層を転写させ)、実施例1〜8、比較例1〜5の印画物を得た。
(Formation of prints)
Using an HDP-600 (HID) printer and an ink ribbon dedicated to the printer, a black solid image was formed on the receiving layer of the intermediate transfer medium of each example and comparative example under the default conditions. The receiving layer, protective layer, and release layer after black solid image formation were transferred onto a PVC card (manufactured by DNP) under re-transfer conditions of 175 ° C. and 2 sec / inch (for Example 8, release layer) The prints of Examples 1 to 8 and Comparative Examples 1 to 5 were obtained.
(箔切れ性評価)
各実施例及び比較例の箔切れ性の評価として、印画物の尾引きの確認を目視にて行い、以下の評価基準で評価を行った。評価結果を表1に示す。なお、尾引きとは、転写層の転写領域と非転写領域の境界を起点とし、該境界から非転写領域側にはみ出した転写層の長さを意味する。
<評価基準>
○:尾引きが0.3mm未満である。
×:尾引きが0.3mm以上である。
(Foil tearing evaluation)
As an evaluation of the foil breakability of each example and comparative example, the tailing of the printed material was visually confirmed and evaluated according to the following evaluation criteria. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1. The tailing means the length of the transfer layer that starts from the boundary between the transfer region and the non-transfer region of the transfer layer and protrudes from the boundary to the non-transfer region side.
<Evaluation criteria>
○: The tailing is less than 0.3 mm.
X: The tailing is 0.3 mm or more.
(耐可塑剤性評価)
各実施例及び比較例の印画物上に、可塑剤(DOP)を添加した後に、PETフィルムでカバーをし、40℃ 8h後の印画物の表面状態を目視で観察し、以下の評価基準で評価試験を行った。評価試験結果を表1に示す。
<評価基準>
○:画像にダメ―ジが見られない。
△:画像に僅かなダメージが見られるが使用上問題ないレベルである。
×:使用上問題となる画像のダメージが見られる。
(Evaluation of plasticizer resistance)
After the plasticizer (DOP) was added on the prints of each Example and Comparative Example, the PET film was covered and the surface condition of the prints after 8 hours at 40 ° C. was visually observed. An evaluation test was conducted. The evaluation test results are shown in Table 1.
<Evaluation criteria>
○: No damage is seen in the image.
(Triangle | delta): Although a slight damage is seen in an image, it is a level which does not have a problem in use.
X: Damage to the image causing a problem in use is observed.
(耐溶剤性評価)
各実施例及び比較例の印画物を、メチルエチルケトン(MEK)に浸した綿棒で30回往復した後の画像の状態を目視で確認を行い、以下の評価基準に基づいて耐溶剤性の評価を行った。評価結果を表1に示す。
<評価基準>
○:画像にダメ―ジが見られない。
△:画像に僅かなダメージが見られるが使用上問題ないレベルである。
×:使用上問題となる画像のダメージが見られる。
(Solvent resistance evaluation)
The prints of each Example and Comparative Example were visually checked for the state of the image after 30 reciprocations with a cotton swab dipped in methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), and the solvent resistance was evaluated based on the following evaluation criteria. It was. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
<Evaluation criteria>
○: No damage is seen in the image.
(Triangle | delta): Although a slight damage is seen in an image, it is a level which does not have a problem in use.
X: Damage to the image causing a problem in use is observed.
(耐摩耗性評価)
各実施例及び比較例の印画物を、磨耗輪CS−10Fを用いて荷重500gで250回磨耗し、摩耗後の表面状態を目視で観察し、以下の評価基準で評価試験を行った。評価試験結果を表1に示す。
<評価基準>
○・・・印画物に全くキズが生じていない。
△・・・印画物に少しキズが生じているが使用上問題ないレベルである。
×・・・印画物に大きくキズが生じている。
(Abrasion resistance evaluation)
The printed matter of each Example and Comparative Example was worn 250 times with a load of 500 g using a wear wheel CS-10F, the surface condition after wear was visually observed, and an evaluation test was performed according to the following evaluation criteria. The evaluation test results are shown in Table 1.
<Evaluation criteria>
○: There is no scratch on the printed material.
Δ: Slightly scratched on the printed material, but at a level where there is no problem in use.
X: The print product is greatly scratched.
1…基材
2…保護層
3…剥離層
4…接着層
5…背面層
10…保護層転写シート
50…受容層
100…中間転写媒体
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
前記保護層は、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有しており、
前記反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であり、
前記反応性樹脂が、アミノ変性アクリル樹脂であることを特徴とする保護層転写シート。 A protective layer transfer sheet provided on one surface of the base material with a protective layer that can be peeled off from the base material,
The protective layer contains an epoxy curable resin in which a reactive resin having a functional group that reacts with an epoxy group is cured and reacted with an epoxy curing agent,
Ri Der glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60 ° C. or more of the reactive resin,
The protective layer transfer sheet , wherein the reactive resin is an amino-modified acrylic resin .
前記保護層は、エポキシ基と反応する官能基を有する反応性樹脂を、エポキシ硬化剤によって硬化反応せしめたエポキシ硬化型樹脂を含有しており、 The protective layer contains an epoxy curable resin in which a reactive resin having a functional group that reacts with an epoxy group is cured and reacted with an epoxy curing agent,
前記反応性樹脂のガラス転移温度(Tg)が60℃以上であり、 The glass transition temperature (Tg) of the reactive resin is 60 ° C. or higher,
前記反応性樹脂が、アミノ変性アクリル樹脂であることを特徴とする中間転写媒体。 An intermediate transfer medium, wherein the reactive resin is an amino-modified acrylic resin.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013060156A JP5633592B2 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2013-03-22 | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium |
| US14/779,137 US9387653B2 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2014-03-20 | Protective layer transfer sheet, and the intermediate transfer medium |
| PCT/JP2014/057888 WO2014148631A1 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2014-03-20 | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium |
| EP14768399.9A EP2987642B1 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2014-03-20 | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013060156A JP5633592B2 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2013-03-22 | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014184615A JP2014184615A (en) | 2014-10-02 |
| JP2014184615A5 JP2014184615A5 (en) | 2014-11-13 |
| JP5633592B2 true JP5633592B2 (en) | 2014-12-03 |
Family
ID=51832654
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013060156A Active JP5633592B2 (en) | 2013-03-22 | 2013-03-22 | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5633592B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10071566B2 (en) * | 2015-04-03 | 2018-09-11 | Canon Finetech Nisca Inc. | Transfer material, recorded matter, method of manufacturing recorded matter, image-recording apparatus, and apparatus for manufacturing recorded matter |
| JP7283141B2 (en) * | 2019-03-11 | 2023-05-30 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Intermediate transfer medium and coating solution for forming receiving layer |
| JP6849031B2 (en) * | 2019-08-30 | 2021-03-24 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Thermal transfer sheet, intermediate transfer medium, printed matter produced by using the thermal transfer sheet or the intermediate transfer medium, manufacturing method of printed matter, and printed matter manufacturing system. |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04344289A (en) * | 1991-05-20 | 1992-11-30 | Konica Corp | Image recording medium and image recording medium preparation as well as image recording medium preparation device |
| JP2010221400A (en) * | 2009-03-19 | 2010-10-07 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Thermal transfer image receiving sheet |
-
2013
- 2013-03-22 JP JP2013060156A patent/JP5633592B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014184615A (en) | 2014-10-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5699384B1 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| WO2014157678A1 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| JP5447557B2 (en) | Thermal transfer sheet | |
| EP2762323B1 (en) | Thermal transfer sheet | |
| JP5699385B1 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| EP2746057A1 (en) | Thermal transfer sheet | |
| JP6387670B2 (en) | Combination of intermediate transfer medium and thermal transfer sheet, and method for forming printed matter | |
| JP5874188B2 (en) | Image forming method | |
| JP5633592B2 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| JP5699380B2 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| JP5573274B2 (en) | Thermal transfer sheet | |
| JP6102998B2 (en) | Thermal transfer sheet | |
| WO2014148631A1 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| KR102478352B1 (en) | Sublimation type thermal transfer sheet | |
| WO2013129415A1 (en) | Intermediate transfer medium | |
| JP5794080B2 (en) | Image forming method, combination of thermal transfer sheet and thermal transfer image receiving sheet | |
| JP5633593B2 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet and intermediate transfer medium | |
| JP6024513B2 (en) | Intermediate transfer medium | |
| JP5794082B2 (en) | Thermal transfer sheet manufacturing method and thermal transfer sheet | |
| JP5880511B2 (en) | Protective layer transfer sheet | |
| JP2018176567A (en) | Thermal transfer image-receiving sheet | |
| JP2014198427A (en) | Set of thermal transfer ink sheet and thermal transfer image receiving sheet and image formation method using the same | |
| JP2013212608A (en) | Thermal transfer sheet | |
| JP2018171840A (en) | Thermal transfer image-receiving sheet, thermal transfer sheet, coating liquid for receiving layer, method of forming thermal transfer image-receiving sheet, and method of forming printed matter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140808 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140808 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20140808 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20140905 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140916 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140929 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5633592 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |