JP5561453B2 - AD converter, mechanical quantity detector, and electronic equipment. - Google Patents
AD converter, mechanical quantity detector, and electronic equipment. Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5561453B2 JP5561453B2 JP2008110198A JP2008110198A JP5561453B2 JP 5561453 B2 JP5561453 B2 JP 5561453B2 JP 2008110198 A JP2008110198 A JP 2008110198A JP 2008110198 A JP2008110198 A JP 2008110198A JP 5561453 B2 JP5561453 B2 JP 5561453B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- filter
- signal
- conversion
- clock signal
- discrete
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Gyroscopes (AREA)
- Analogue/Digital Conversion (AREA)
Description
本発明は、AD変換装置、力学量検出装置及び電子機器に関する。 The present invention relates to an AD conversion device, a mechanical quantity detection device, and an electronic apparatus.
ジャイロセンサーはある一定の回転軸を中心とした回転運動に対する回転の速さ(回転角速度)を計測するセンサーである。今日広く使われているのは「振動ジャイロセンサー」であり「コリオリの力」を利用して回転角速度を検出する。 The gyro sensor is a sensor that measures a rotation speed (rotational angular velocity) with respect to a rotational motion around a certain rotation axis. The “vibration gyro sensor” widely used today detects the angular velocity using the “Coriolis force”.
例えば圧電効果を利用して動作する振動ジャイロスコープでは、ジャイロ素子(水晶等の振動体)に交流電圧を加えるとコリオリ力が発生し、回転率や角速度に応じて電流が発生する。電流信号をジャイロセンサー内部で増幅し、角速度に比例した電圧が出力される。ジャイロセンサーの出力電圧は、A/D変換装置によってデジタル信号に変換されてマイクロコンピュータに取り込まれ、マイクロコンピュータによる様々な制御が行われる。例えば、ジャイロセンサーは携帯電話やデジタルカメラ等の電子機器に搭載されており、手ぶれ補正等に利用されている。 For example, in a vibrating gyroscope that operates using the piezoelectric effect, when an AC voltage is applied to a gyro element (vibrating body such as a crystal), a Coriolis force is generated, and a current is generated according to the rotation rate and angular velocity. The current signal is amplified inside the gyro sensor, and a voltage proportional to the angular velocity is output. The output voltage of the gyro sensor is converted into a digital signal by an A / D converter and taken into a microcomputer, and various controls are performed by the microcomputer. For example, a gyro sensor is mounted on an electronic device such as a mobile phone or a digital camera, and is used for camera shake correction or the like.
また、最近では、ジャイロセンサーがアナログフロントエンド回路やA/D変換回路とともにパッケージ化されたデジタル出力のジャイロセンサーモジュールも存在する。
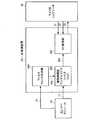
図16は、従来のセンサーシステムの構成例を示す図である。センサーモジュール(力学量検出装置)とマイクロコンピュータの間にAD変換装置が接続されており、AD変換装置はアンチエリアスフィルタとAD変換回路により構成されている。 FIG. 16 is a diagram illustrating a configuration example of a conventional sensor system. An AD converter is connected between the sensor module (mechanical quantity detector) and the microcomputer, and the AD converter is composed of an anti-alias filter and an AD converter circuit.
ここで、アンチエリアスフィルタには連続時間型のローパスフィルタが使用される。すなわち、アンチエリアスフィルタは抵抗器、コンデンサ、トランジスタ、オペアンプ等の部品により構成される。そのため、これらの部品の精度ばらつきにより、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性にばらつきが出やすく、調整しにくいという問題があった。 Here, a continuous-time low-pass filter is used as the anti-alias filter. That is, the anti-alias filter is composed of components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and operational amplifiers. For this reason, there is a problem in that the gain characteristics and phase characteristics of the anti-alias filter tend to vary due to variations in accuracy of these components, and adjustment is difficult.
また、AD変換回路のサンプリングタイミング(チップイネーブル信号)はマイクロコンピュータが決定するたため、マイクロコンピュータのタスクにおいてAD変換回路の制御オペレーションが占める割合が無視できず、システムの負荷を増大させる要因となっていた。 In addition, since the sampling timing (chip enable signal) of the AD conversion circuit is determined by the microcomputer, the proportion of the control operation of the AD conversion circuit in the microcomputer task cannot be ignored, which increases the system load. It was.
さらに、AD変換回路のサンプリングタイミングをマイクロコンピュータが決定するとサンプリングジッターが発生するため、AD変換の精度を向上させることが難しくなる場合もあった。そのため、センサーモジュールの検出精度が高くてもセンサーモジュールとAD変換装置を含むセンサーシステム全体としては高い検出精度を維持することが困難な場合もあった。 Further, when the microcomputer determines the sampling timing of the AD conversion circuit, sampling jitter occurs, and it may be difficult to improve the AD conversion accuracy. Therefore, even if the detection accuracy of the sensor module is high, it may be difficult to maintain high detection accuracy for the entire sensor system including the sensor module and the AD converter.
本発明は、以上のような問題点に鑑みてなされたものであり、アンチエリアスフィルタの調整を容易にするとともに、センサーシステム全体としての高い検出精度を維持させることができるAD変換装置及び力学量検出装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the problems as described above, and makes it possible to easily adjust an anti-alias filter and maintain high detection accuracy as a whole sensor system and a mechanical quantity. An object is to provide a detection device.
(1)本発明は、
力学量を検出する力学量検出装置が出力する検出結果のアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換するAD変換装置であって、
前記検出結果のアナログ信号をサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行う離散時間型フィルタと、
前記離散時間型フィルタによってフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換するAD変換処理を行うAD変換部と、を含み、
前記離散時間型フィルタは、
前記力学量検出装置が出力する同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理を行うことを特徴とする。
(1) The present invention
The analog signal of the detection result of the physical quantity detection device for detecting the dynamics volume outputs an AD converter for converting a digital signal,
A discrete-time filter that performs sampling by sampling an analog signal of the detection result; and
An AD conversion unit that performs an AD conversion process for converting an analog signal filtered by the discrete-time filter into a digital signal;
The discrete time filter is:
Filter processing as an anti-alias filter for the AD conversion processing is performed based on a synchronous clock signal output from the mechanical quantity detection device.
力学量検出装置は、例えば、加速度センサーや角速度センサー(ジャイロセンサー)であってもよい。
The dynamics amount detecting device may be, for example, an acceleration sensor or an angular velocity sensor (gyro sensor).
離散時間型フィルタは、検出結果のアナログ信号を同期クロック信号でサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行ってもよいし、検出結果のアナログ信号を同期クロック信号を分周したクロック信号でサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行ってもよい。 The discrete-time filter may perform the filtering process by sampling the analog signal of the detection result with the synchronous clock signal, or perform the filtering process by sampling the analog signal of the detection result with the clock signal obtained by dividing the synchronous clock signal. You may go.
AD変換処理のアンチエリアスフィルタを抵抗器、コンデンサ、トランジスタ、オペアンプ等の部品を使用して連続時間型フィルタとして構成した場合、これらの部品の精度ばらつきにより、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性にばらつきが出やすく調整しにくい。しかし、本発明によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタを周波数精度が比較的高くジッタの小さい同期クロック信号に基づいて動作する離散時間型フィルタとして構成するので、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性のばらつきを小さくすることができる。従って、本発明によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタの調整を容易にするとともに、センサーシステム全体としての高い検出精度を維持させることができる。 When an anti-alias filter for AD conversion processing is configured as a continuous-time filter using components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and operational amplifiers, the gain characteristics and phase characteristics of the anti-alias filter are affected by variations in the accuracy of these components. Difficult to adjust and difficult to adjust. However, according to the present invention, since the anti-alias filter is configured as a discrete-time filter that operates based on a synchronous clock signal with relatively high frequency accuracy and low jitter, variations in gain characteristics and phase characteristics of the anti-alias filter are reduced. Can be small. Therefore, according to the present invention, it is possible to easily adjust the anti-alias filter and maintain high detection accuracy as the entire sensor system.
(2)本発明のAD変換装置は、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記離散時間型フィルタが前記検出結果のアナログ信号をサンプリングするためのフィルタクロック信号を生成するフィルタクロック生成部を含み、
前記フィルタクロック生成部は、
外部からの設定値に基づいて前記同期クロック信号を分周した前記フィルタクロック信号を生成するようにしてもよい。
(2) The AD converter of the present invention
A filter clock generator for generating a filter clock signal for sampling the analog signal of the detection result by the discrete-time filter based on the synchronous clock signal;
The filter clock generator is
The filter clock signal obtained by dividing the synchronous clock signal based on a set value from the outside may be generated.
例えば、前記フィルタクロック生成部は、前記同期クロック信号を分周して前記フィルタクロック信号を生成するクロック分周回路を含み、当該クロック分周回路の分周比は外部から可変に設定されるようにしてもよい。 For example, the filter clock generation unit includes a clock frequency dividing circuit that divides the synchronous clock signal to generate the filter clock signal, and the frequency dividing ratio of the clock frequency dividing circuit is variably set from the outside. It may be.
本発明によれば、フィルタクロック信号の周波数を外部から設定することにより、離散時間型フィルタのカットオフ周波数が所望の周波数になるように調整することができる。従って、AD変換部によるAD変換処理の周期を変化させた場合でも、その周期変化に合わせて離散時間型フィルタのカットオフ周波数を調整することによりアンチエリアスフィルタとしての機能を確保することができる。 According to the present invention, the cutoff frequency of the discrete-time filter can be adjusted to a desired frequency by setting the frequency of the filter clock signal from the outside. Therefore, even when the AD conversion processing cycle by the AD converter is changed, the function as an anti-alias filter can be secured by adjusting the cutoff frequency of the discrete-time filter in accordance with the cycle change.
(3)本発明のAD変換装置は、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換処理のタイミングを制御するAD変換制御部を含むようにしてもよい。
(3) The AD converter of the present invention
An AD conversion control unit that controls the timing of the AD conversion processing based on the synchronous clock signal may be included.
AD変換制御部は、AD変換処理のタイミングを同期クロック信号で制御するようにしてもよいし、AD変換処理のタイミングを同期クロック信号を分周したクロック信号で制御するようにしてもよい。 The AD conversion control unit may control the timing of AD conversion processing with a synchronous clock signal, or may control the timing of AD conversion processing with a clock signal obtained by dividing the synchronous clock signal.
本発明によれば、AD変換制御部がAD変換部によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御するので、外部のマイクロコンピュータのタスクにおいてAD変換部の制御オペレーションが占める割合をより小さくすることができる。従って、システムの負荷をより減少させることができる。 According to the present invention, since the AD conversion control unit controls the timing of AD conversion processing by the AD conversion unit, the ratio of the control operation of the AD conversion unit in the task of the external microcomputer can be further reduced. Therefore, the load on the system can be further reduced.
また、AD変換部のサンプリングタイミングをマイクロコンピュータが決定するとサンプリングジッターが発生するためAD変換の精度を向上させることが難しくなるが、本発明によれば、力学量検出装置が出力する同期クロック信号に基づいてAD変換処理のタイミングが制御されるので、同期クロック信号の周波数精度でセンサーシステム全体としての検出処理を行うことができる。 In addition, when the microcomputer determines the sampling timing of the AD conversion unit, it is difficult to improve the accuracy of AD conversion because sampling jitter occurs. However, according to the present invention, the synchronous clock signal output from the mechanical quantity detection device can be reduced. Since the timing of the AD conversion processing is controlled based on this, the detection processing of the entire sensor system can be performed with the frequency accuracy of the synchronous clock signal.
(4)本発明のAD変換装置において、
前記AD変換制御部は、
外部からの設定値に基づいた周期で前記AD変換処理が行われるように制御するようにしてもよい。
(4) In the AD converter of the present invention,
The AD conversion control unit
You may make it control so that the said AD conversion process is performed with the period based on the setting value from the outside.
例えば、前記AD変換制御部は、前記同期クロック信号に基づいてカウント動作をするカウンタ回路を含み、当該カウンタ回路のカウント値に基づいて前記AD変換処理のタイミングを制御し、当該カウンタ回路のカウント数は外部から可変に設定されるようにしてもよい。 For example, the AD conversion control unit includes a counter circuit that performs a counting operation based on the synchronous clock signal, controls the timing of the AD conversion processing based on the count value of the counter circuit, and counts the counter circuit May be variably set from the outside.
また、例えば、AD変換装置は、前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換制御部を動作させるためのAD変換制御クロック信号を生成するAD変換制御クロック生成部を含み、前記AD変換制御クロック生成部は、前記同期クロック信号を分周して前記AD変換制御クロック信号を生成するクロック分周回路を含み、当該クロック分周回路の分周比は外部から可変に設定されるようにしてもよい。 Further, for example, the AD conversion apparatus includes an AD conversion control clock generation unit that generates an AD conversion control clock signal for operating the AD conversion control unit based on the synchronous clock signal, and the AD conversion control clock generation The unit may include a clock frequency dividing circuit that divides the synchronous clock signal to generate the AD conversion control clock signal, and the frequency dividing ratio of the clock frequency dividing circuit may be variably set from the outside. .
本発明によれば、外部からの設定値に基づいてAD変換部によるAD変換処理の周期を簡単に変更することができる。従って、外部のマイクロコンピュータからの設定値によって、AD変換の精度を上げたい時はAD変換処理の周期を短くし、AD変換の精度を下げてもよい時はAD変換処理の周期を長くすることにより、マイクロコンピュータのタスクにおいてAD変換部の制御オペレーションが占める割合をリアルタイムに変化させることができる。従って、システムの負荷を最適な状態に近づけることができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to easily change the period of AD conversion processing by the AD conversion unit based on a set value from the outside. Therefore, the AD conversion processing cycle is shortened when it is desired to increase the AD conversion accuracy by a set value from an external microcomputer, and the AD conversion processing cycle is lengthened when the AD conversion accuracy may be lowered. Thus, the ratio of the control operation of the AD conversion unit in the task of the microcomputer can be changed in real time. Therefore, the system load can be brought close to the optimum state.
(5)本発明のAD変換装置において、
前記離散時間型フィルタは、スイッチトキャパシタフィルタであってもよい。
(5) In the AD converter of the present invention,
The discrete time filter may be a switched capacitor filter.
(6)本発明のAD変換装置において、
n(n≧2)個の前記力学量検出装置の各々に対応して設けられたn個の前記離散時間型フィルタと、
n個の前記離散時間型フィルタによってフィルタ処理されたn個のアナログ信号から時分割に1のアナログ信号を順に選択するフィルタ選択部を含み、
前記AD変換部は、
前記フィルタ選択部によって時分割に順に選択されたアナログ信号に対して前記AD変換処理を行い、
n個の前記離散時間型フィルタは、
n個の前記力学量検出装置が略同じタイミングでそれぞれ検出したn個のアナログ信号に対してそれぞれフィルタ処理したn個のアナログ信号が前記フィルタ選択部によって時分割に順に選択されるように、それぞれ位相遅延が調整されているようにしてもよう。
(6) In the AD converter of the present invention,
n discrete time filters provided corresponding to each of the n (n ≧ 2) mechanical quantity detection devices;
a filter selection unit that sequentially selects one analog signal in time division from n analog signals filtered by the n discrete-time filters;
The AD converter is
Performing the AD conversion processing on the analog signals sequentially selected by the filter selection unit in a time-sharing manner,
The n discrete time filters are:
The n analog signals obtained by filtering the n analog signals respectively detected by the n mechanical quantity detection devices at substantially the same timing are sequentially selected by the filter selection unit in a time division manner. Even if the phase delay is adjusted.
本発明によれば、n個の力学量検出装置の検出結果に対して1つのAD変換部が時分割にAD変換処理を行うことができる。従って、AD変換装置に使用される部品の数やチップの面積を削減することができる。 According to the present invention, one AD conversion unit can perform AD conversion processing in a time division manner on the detection results of n pieces of mechanical quantity detection devices. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the number of parts used in the AD converter and the area of the chip.
(7)本発明は、
上記のいずれかに記載のAD変換装置と、
前記力学量検出装置と、
前記AD変換装置により前記検出結果のアナログ信号がAD変換されたデジタル信号に基づいて処理を行う処理部と、を含むことを特徴とする電子機器である。
(7) The present invention
An AD conversion device according to any of the above,
The mechanical quantity detection device;
An electronic apparatus comprising: a processing unit that performs processing based on a digital signal obtained by AD-converting an analog signal of the detection result by the AD conversion device.
(8)本発明は、
駆動信号に基づいて振動し、外部から加えられた力学量に応じて変調されたアナログ信号を出力する振動子と、
前記駆動信号と同じ周波数の同期クロック信号を生成する同期クロック生成回路と、
前記振動子が出力するアナログ信号又は当該アナログ信号を増幅した信号に対して前記同期クロック信号に基づいて同期検波を行い、力学量に応じて復調された信号成分を含むアナログ信号を生成する同期検波回路と、
前記同期検波回路が出力するアナログ信号をサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行う離散時間型フィルタと、
前記離散時間型フィルタによってフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換するAD変換処理を行うAD変換部と、を含み、
前記離散時間型フィルタは、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記同期検波により発生する不要信号を減衰させるためのフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理と、前記AD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理を行うことを特徴とする力学量検出装置である。
(8) The present invention
A vibrator that vibrates based on a driving signal and outputs an analog signal modulated according to a mechanical quantity applied from the outside;
A synchronous clock generation circuit for generating a synchronous clock signal having the same frequency as the drive signal;
Synchronous detection for performing analog detection on the analog signal output from the vibrator or the amplified signal based on the synchronous clock signal and generating an analog signal including a signal component demodulated according to a dynamic quantity Circuit,
A discrete-time filter that performs filtering by sampling an analog signal output by the synchronous detection circuit; and
An AD conversion unit that performs an AD conversion process for converting an analog signal filtered by the discrete-time filter into a digital signal;
The discrete time filter is:
Based on the synchronous clock signal, a mechanical quantity detection characterized by performing a filter process as a filter for attenuating an unnecessary signal generated by the synchronous detection and a filter process as an anti-alias filter for the AD conversion process Device.
力学量検出装置は、
前記振動子が出力するアナログ信号を増幅する増幅回路を含み、
前記同期検波回路は、
前記増幅回路が出力する信号に対して前記同期検波を行うようにしてもよい。
The mechanical quantity detection device
Including an amplifier circuit for amplifying an analog signal output from the vibrator;
The synchronous detection circuit is
You may make it perform the said synchronous detection with respect to the signal which the said amplifier circuit outputs.
AD変換処理のアンチエリアスフィルタを抵抗器、コンデンサ、トランジスタ、オペアンプ等の部品を使用して連続時間型フィルタとして構成した場合、これらの部品の精度ばらつきにより、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性にばらつきが出やすく調整しにくい。しかし、本発明によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタを同期クロック信号に基づいて動作する離散時間型フィルタとして構成するので、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性のばらつきを小さくすることができる。従って、本発明によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタの調整を容易にするとともに、センサーシステム全体としての高い検出精度を維持させることができる。 When an anti-alias filter for AD conversion processing is configured as a continuous-time filter using components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and operational amplifiers, the gain characteristics and phase characteristics of the anti-alias filter are affected by variations in the accuracy of these components. Difficult to adjust and difficult to adjust. However, according to the present invention, since the anti-alias filter is configured as a discrete-time filter that operates based on the synchronous clock signal, variations in gain characteristics and phase characteristics of the anti-alias filter can be reduced. Therefore, according to the present invention, it is possible to easily adjust the anti-alias filter and maintain high detection accuracy as the entire sensor system.
また、本発明によれば、離散時間型フィルタは、同期検波により発生する不要信号を減衰させるためのフィルタとAD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタの両方の機能を果たす。従って、力学量検出装置に使用される部品の数やチップの面積を削減することができる。 In addition, according to the present invention, the discrete-time filter functions as both a filter for attenuating unnecessary signals generated by synchronous detection and an anti-alias filter for AD conversion processing. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the number of parts and the chip area used in the mechanical quantity detection device.
(9)本発明の力学量検出装置は、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記離散時間型フィルタが前記検出結果のアナログ信号をサンプリングするためのフィルタクロック信号を生成するフィルタクロック生成部を含み、
前記フィルタクロック生成部は、
外部からの設定値に対応する周波数を有する前記フィルタクロック信号を生成するようにしてもよい。
(9) The mechanical quantity detection device of the present invention includes:
A filter clock generator for generating a filter clock signal for sampling the analog signal of the detection result by the discrete-time filter based on the synchronous clock signal;
The filter clock generator is
The filter clock signal having a frequency corresponding to a set value from the outside may be generated.
(10)本発明の力学量検出装置は、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換処理のタイミングを制御するAD変換制御部を含むようにしてもよい。
(10) The mechanical quantity detection device of the present invention includes:
An AD conversion control unit that controls the timing of the AD conversion processing based on the synchronous clock signal may be included.
(11)本発明の力学量検出装置において、
前記AD変換制御部は、
外部からの設定値に対応する分周比で前記同期クロックを分周した周期で前記AD変換処理が行われるように制御するようにしてもよい。
(11) In the mechanical quantity detection device of the present invention,
The AD conversion control unit
You may make it control so that the said AD conversion process may be performed with the period which divided the said synchronous clock by the frequency division ratio corresponding to the setting value from the outside.
(12)本発明の力学量検出装置において、
前記離散時間型フィルタは、スイッチトキャパシタフィルタであってもよい。
(12) In the mechanical quantity detection device of the present invention,
The discrete time filter may be a switched capacitor filter.
(13)本発明は、
上記のいずれかに記載の力学量検出装置と、
前記力学量検出装置の検出結果に基づいて処理を行う処理部と、を含むことを特徴とする電子機器である。
(13) The present invention provides:
A mechanical quantity detection device according to any of the above,
And a processing unit that performs processing based on a detection result of the mechanical quantity detection device.
以下、本発明の好適な実施形態について図面を用いて詳細に説明する。なお、以下に説明する実施の形態は、特許請求の範囲に記載された本発明の内容を不当に限定するものではない。また以下で説明される構成の全てが本発明の必須構成要件であるとは限らない。 DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. The embodiments described below do not unduly limit the contents of the present invention described in the claims. Also, not all of the configurations described below are essential constituent requirements of the present invention.
1.AD変換装置
1−1.対象となる力学量検出装置
図1は、本実施形態のAD変換装置によるAD変換処理のターゲットとなるアナログ信号を生成する力学量検出装置について説明するための図である。
1. 1. AD converter 1-1. FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining a mechanical quantity detection device that generates an analog signal that is a target of AD conversion processing by the AD conversion apparatus of the present embodiment.
力学量検出装置(センサーモジュール)10は、駆動信号102、104に基づいて振動する振動子110によって力学量を検出し、検出データ信号12(検出結果のアナログ信号)を出力する。駆動信号102、104は、例えば、発振回路100(例えば、水晶発振器やセラミックレゾネータによる発振回路)が出力する発振信号であってもよい。
The mechanical quantity detection device (sensor module) 10 detects the mechanical quantity by the
振動子110は、発振回路100の発振周波数(駆動信号102、104の周波数(駆動周波数))で振動することにより、差動信号112、114として、例えば、角速度や加速度等の力学量を検出する。ここで、差動信号112、114は、力学量に応じた変調度で駆動信号102、104が変調された信号である。例えば、振動子110は、振動方向と直交する方向に加わる力(コリオリ力)により、駆動信号102、104と位相が±π/2ずれて振幅変調(AM変調)された差動信号102、104を出力する。
The
プリアンプ120は差動信号102、104を差動増幅して増幅信号122を出力する。
The
発振クロック106は、位相調整回路150によって位相をπ/2遅延し、同期クロック信号14を出力する。
The phase of the
同期検波回路130は、AM変調された増幅信号122に対して、発振回路100が出力する発振クロック106をπ/2遅延させた同期クロック信号14(駆動周波数を有するクロック信号)により同期検波(狭義には乗算)を行い、同期検波信号132を出力する。ここで、同期検波によりDC付近の周波数帯域に検波信号が生成されるが、同時に、駆動周波数の2倍の周波数帯域に不要な信号が発生する。すなわち、同期検波信号132は、DC付近の周波数帯域の検波信号成分と駆動周波数の2倍の周波数帯域の不要な信号成分を含んでいる。
The
同期検波用フィルタ140は、同期検波信号132からこの不要な信号成分を除去した検出データ信号12(アナログ信号)を生成するローパスフィルタとして機能する。同期検波用フィルタ140は、連続時間型フィルタであってもよいし、離散時間型フィルタであってもよい。例えば、同期検波用フィルタ140は、同期クロック信号14により動作するスイッチトキャパシタフィルタ(Switched Capacitor Filter(SCF))として構成することができる。
The
発振回路100を水晶発振器による発振回路として構成した場合、駆動信号102、104のジッタが極めて小さい。また、駆動信号102、104に同期した同期クロック信号14のジッタも極めて小さい。従って、力学量検出装置10(センサーモジュール)は高い検出精度で検出データ信号12を生成することができる。
When the
1−2.AD変換装置の第1構成例
図2は、本実施形態のAD変換装置の第1の構成例について説明するための図である。
1-2. First Configuration Example of AD Converter FIG. 2 is a diagram for describing a first configuration example of the AD converter according to the present embodiment.
AD変換装置20−1は、センサーモジュール10が出力する検出結果のアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換する処理を行う。
The AD conversion apparatus 20-1 performs processing for converting an analog signal as a detection result output from the
センサーモジュール10は、駆動信号に基づいて振動する振動子によって力学量を検出する力学量検出装置であり、例えば、図1のように構成されている。センサーモジュール10としては、角速度センサー(ジャイロセンサー)モジュールや、加速度センサーモジュール等が考えられる。
The
AD変換装置20−1は、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200、AD変換部300及びフィルタクロック生成部400を含む。
The AD conversion apparatus 20-1 includes a discrete-
離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200は、AD変換部300の前段に配置され、センサーモジュール10が出力する検出結果のアナログ信号(図1の検出データ信号12)をサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行う。離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200は、センサーモジュール10が出力する同期クロック信号14(図1の同期クロック信号14)に基づいて、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理を行い、AD変換器300のサンプリングによりDC付近の周波数帯域に折り返すノイズをあらかじめ無視できる程度にまで減衰させたアナログ信号202を出力する。離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200は、例えば、スイッチトキャパシタフィルタ(SCF)であってもよい。
The discrete-time
AD変換部300は、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200によってフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号202をNビットのデジタル信号22に変換するAD変換処理を行う。AD変換部300は、マイクロコンピュータ30が出力するチップイネーブル信号(CE)31及びクロック信号32によりAD変換処理のタイミングが制御される。すなわち、AD変換部300は、例えば、チップイネーブル信号(CE)31がローレベルにある期間において、クロック信号32に同期してアナログ信号202をサンプリングし、AD変換処理を行ってデジタル信号22を生成する。
The
AD変換部300は、フラッシュ型(並列比較型)、パイプライン型、逐次比較型、デルタシグマ方式等の既知の様々なタイプのAD変換回路により構成することができる。
The
マイクロコンピュータ30は、チップイネーブル信号(CE)31をハイレベルからローレベルに変化させた後、デジタル信号22を取り込む。AD変換部300がAD変換処理を終了するまでウェイトしてからチップイネーブル信号(CE)31をローレベルからハイレベルに変化させてデジタル信号の取り込みを終了する。すなわち、チップイネーブル信号(CE)31は、マイクロコンピュータ30がAD変換部300によるAD変換処理の期間を制御する。
The
フィルタクロック生成部400は、同期クロック信号14に基づいて、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200がセンサーモジュール10の検出結果のアナログ信号12をサンプリングするためのフィルタクロック信号402を生成する。
Based on the
図3は、AD変換装置の第1の構成例におけるフィルタクロック生成部の構成例について説明するための図である。 FIG. 3 is a diagram for explaining a configuration example of the filter clock generation unit in the first configuration example of the AD conversion apparatus.
フィルタクロック生成部400は、例えば、プリセットデータ410、ダウンカウンタ420、デコーダ430等により構成することができる。
The filter
ダウンカウンタ420は、例えば、同期クロック信号14の立ち上がりエッジに同期してダウンカウントする処理を行う。
For example, the
デコーダ430は、ダウンカウンタ420のカウント値422をデコードしてフィルタクロック信号402を生成する処理を行う。また、ダウンカウンタ420のカウント値422が0の時にロード信号432を生成する。ダウンカウンタ420は、同期クロック信号14の立ち上がりエッジに同期してロード信号432を検出するとプリセットデータ410をロードし、カウント値422が0になるまでダウンカウントする処理を繰り返す。
The
すなわち、フィルタクロック生成部400は、ダウンカウンタ420がプリセットデータ410の値(m−1)から0までダウンカウントする処理を繰り返すことにより、同期クロック信号14をm分周してフィルタクロック信号402を生成するクロック分周回路として機能する。
That is, the filter
なお、プリセットデータ410が2k−1−1(k≧2)である場合は、ダウンカウンタ420(バイナリカウンタ)が0までダウンカウントすると自動的に2k−1−1に戻るので、ダウンカウンタ420の最上位ビットの信号をフィルタクロック信号402(同期クロック信号14の2k−1分周クロック信号)とすればデコーダ430は不要である。
When the
一般に、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理のアンチエリアスフィルタを抵抗器、コンデンサ、トランジスタ、オペアンプ等の部品を使用して連続時間型フィルタとして構成した場合、これらの部品の精度ばらつきにより、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性にばらつきが出やすく調整しにくい。しかし、本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタを周波数精度が比較的高くジッタの小さい同期クロック信号14に基づいて動作する離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200として構成するので、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性のばらつきを小さくすることができる。従って、本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタの調整を容易にするとともに、センサーシステム全体としての高い検出精度を維持させることができる。
In general, when an anti-alias filter for AD conversion processing by the
1−3.AD変換装置の第2構成例
図4は、本実施形態のAD変換装置の第2の構成例について説明するための図である。
1-3. Second Configuration Example of AD Converter FIG. 4 is a diagram for describing a second configuration example of the AD converter according to the present embodiment.
AD変換装置20−2は、図2のAD変換装置20−1のフィルタクロック生成部400をフィルタクロック生成部450に置き換えた構成になっている。
The AD conversion apparatus 20-2 has a configuration in which the filter
フィルタクロック生成部450は、マイクロコンピュータ30からの設定値34に対応する周波数を有するフィルタクロック信号452を生成する。
The filter
AD変換装置20−2のフィルタクロック生成部450以外の構成は図2のAD変換装置20−1と同じ構成であるため同じ番号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
Since the configuration other than the filter
図5は、AD変換装置の第2の構成例におけるフィルタクロック生成部の構成例について説明するための図である。 FIG. 5 is a diagram for describing a configuration example of the filter clock generation unit in the second configuration example of the AD conversion apparatus.
フィルタクロック生成部450は、例えば、ダウンカウンタ420、デコーダ430、セレクタ460等により構成することができる。デコーダ430の構成は、図3のデコーダ430と同じ構成であるため同じ番号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
The filter
ダウンカウンタ420は、図3のダウンカウンタ420と同じ構成であるため同じ番号が付されているが、同期クロック信号14の立ち上がりエッジに同期してロード信号432を検出するとプリセットデータ設定値34をロードする処理において図3のダウンカウンタ420の処理と異なる。すなわち、プリセットデータ設定値34に応じてダウンカウンタ420のダウンカウント周期が変化する。その結果、デコーダ430が出力する分周クロック信号434の分周比もプリセットデータ設定値34に応じて変化する。
Since the
セレクタ460はプリセットデータ設定値34に応じて同期クロック信号14又は分周クロック信号434のいずれかを選択してフィルタクロック信号452を生成する。例えば、同期クロック信号14をm分周したフィルタクロック信号452を生成するためのプリセットデータ設定値34をm−1とすると、セレクタ460は、プリセットデータ設定値34が0の時は同期クロック信号14を選択し、プリセットデータ設定値34が1以上の時は分周クロック信号434を選択するように構成してもよい。
The selector 460 selects either the
すなわち、フィルタクロック生成部450は、マイクロコンピュータ30から入力されるプリセットデータ値34に対応する周波数を有するフィルタクロック信号452を生成する。
That is, the filter
なお、プリセットデータ設定値34が2k−1−1(k≧2)である場合は、ダウンカウンタ420(バイナリカウンタ)が0までダウンカウントすると自動的に2k−1−1に戻るので、ダウンカウンタ420の最上位ビットの信号を分周クロック信号434(同期クロック信号14の2k−1分周クロック信号)とすればデコーダ430は不要である。
When the preset
本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、フィルタクロック信号452の周波数(同期クロック信号14に対する分周比)を外部から設定することにより、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200のカットオフ周波数が所望の周波数になるように調整することができる。従って、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理の周期を変化させた場合でも、その周期変化に合わせて離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200のカットオフ周波数を調整することによりアンチエリアスフィルタとしての機能を確保することができる。
According to the AD conversion apparatus of this embodiment, the cutoff frequency of the discrete-
1−4.AD変換装置の第3構成例
図6は、本実施形態のAD変換装置の第3の構成例について説明するための図である。
1-4. Third Configuration Example of AD Converter FIG. 6 is a diagram for describing a third configuration example of the AD converter according to the present embodiment.
AD変換装置20−3は、図2のAD変換装置20−1にAD変換制御部500が追加されている。
In the AD conversion apparatus 20-3, an AD
AD変換制御部500は、同期クロック信号14に基づいて、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。より具体的には、AD変換制御部500は、同期クロック信号14に同期してAD変換部300のチップイネーブル信号(CE)502及びストローブ信号24を生成し、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。すなわち、AD変換制御部500は、チップイネーブル信号(CE)502をハイレベルからローレベルに変化させた後、AD変換部300がAD変換処理を終了するまでウェイトしてからチップイネーブル信号(CE)502をローレベルからハイレベルに変化させる。また、ストローブ信号24の立ち上がりエッジまたは立ち下がりエッジをトリガとして、AD変換部300はデジタル信号22を出力する。また、マイクロコンピュータ30はストローブ信号24を使ってデジタル信号22を受信する。すなわち、図2のAD変換装置20−1のようにマイクロコンピュータ30がAD変換処理のタイミングを制御するのではなく、AD変換制御部500がAD変換部300によるAD変換処理の期間を制御する。
The AD
AD変換部300が出力するデジタル信号22はストローブ信号24に同期してマイクロコンピュータ30のポートに送信される。マイクロコンピュータ30は、当該ポートがフル状態になると割り込みを発生させてAD変換結果を取り込む。すなわち、マイクロコンピュータ30は、AD変換部300がAD変換処理を行っている間ウェイトする必要がないため、CPU(図示しない)が他のタスクを実行することができる。
The
さらに、マイクロコンピュータ30にDMA(Direct Memory Access)コントローラを組み込んでおき、デジタル信号22が入力されるポートがフルになり割り込みが発生すると、DMAコントローラがバスを占有してポートに蓄えられたデータをメモリに転送する処理を行うようにすれば、AD変換処理によるCPUの負荷をなくすことができる。
Furthermore, when a DMA (Direct Memory Access) controller is incorporated in the
AD変換装置20−3のAD変換制御部500以外の構成は図2のAD変換装置20−1と同じ構成であるため同じ番号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
The configuration other than the AD
図7は、AD変換装置の第3の構成例におけるAD変換制御部の構成例について説明するための図である。 FIG. 7 is a diagram for describing a configuration example of the AD conversion control unit in the third configuration example of the AD conversion apparatus.
AD変換制御部500は、例えば、プリセットデータ510、タイマー(ダウンカウンタ)520、ステートマシン530、デコーダ540等により構成することができる。
The AD
タイマー520は、例えば、同期クロック信号14の立ち上がりエッジに同期してダウンカウントすることにより、プリセットデータ510に対応する時間を計測する処理を行う。タイマー520は、プリセットデータ510に対応する時間を計測する毎に計測時間終了信号522を生成する。
For example, the
ステートマシン530は、タイマー520が生成する計測時間終了信号522をトリガとして状態(ステート)を遷移させる。ステートマシン530は、現在のステートを示すステート信号532を出力する。
The
デコーダ540は、ステート信号532をデコードし、ステートマシン530が所定のステートにある時にAD変換部300のチップイネーブル信号(CE)502及びストローブ信号24を生成する処理を行う。
The
AD変換部300はチップイネーブル信号(CE)502がローレベルにある期間において、ストローブ信号24の立ち上がりエッジまたは立ち下がりエッジをトリガとして、デジタル信号22を出力する。
The
本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、AD変換制御部500がAD変換部300によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御するので、外部のマイクロコンピュータ30のタスクにおいてAD変換部300の制御オペレーションが占める割合をより小さくすることができる。従って、システムの負荷をより減少させることができる。
According to the AD conversion apparatus of this embodiment, since the AD
また、AD変換部300のサンプリングタイミングをマイクロコンピュータ30が決定するとサンプリングジッターが発生するためAD変換の精度を向上させることが難しくなるが、本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、センサーモジュール10が出力する同期クロック信号14に基づいてAD変換処理のタイミングが制御されるので、同期クロック信号14の周波数精度でセンサーシステム全体としての検出処理を行うことができる。
Further, when the
1−5.AD変換装置の第4構成例
図8は、本実施形態のAD変換装置の第4の構成例について説明するための図である。
1-5. Fourth Configuration Example of AD Converter FIG. 8 is a diagram for describing a fourth configuration example of the AD converter according to the present embodiment.
AD変換装置20−4は、図6のAD変換装置20−3のフィルタクロック生成部400及びAD変換制御部500を、それぞれフィルタクロック生成部450及びAD変換制御部550に置き換えた構成になっている。
The AD conversion device 20-4 has a configuration in which the filter
フィルタクロック生成部450は、図4及び図5で説明したフィルタクロック生成部450と同じ構成であり、その説明を省略する。
The filter
AD変換制御部550は、マイクロコンピュータ30からの設定値(同期クロック信号14に対する分周比)36に対応する周期でAD変換部300によるAD変換処理が行われるように制御する。
The AD
AD変換装置20−4のフィルタクロック生成部450及びAD変換制御部550以外の構成は図6のAD変換装置20−3と同じ構成であるため同じ番号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
The configurations other than the filter
図9は、AD変換装置の第4の構成例におけるAD変換制御部の構成例について説明するための図である。 FIG. 9 is a diagram for describing a configuration example of the AD conversion control unit in the fourth configuration example of the AD conversion apparatus.
AD変換制御部550は、例えば、タイマー(ダウンカウンタ)520、ステートマシン530、デコーダ540等により構成することができる。ステートマシン530及びデコーダ540の構成は、図7のステートマシン530及びデコーダ540と同じ構成であるため同じ番号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
The AD
タイマー520は、図7のタイマー520と同じ構成であるため同じ番号が付されているが、同期クロック信号14の立ち上がりエッジに同期してプリセットデータ設定値36をロードする処理において図7のタイマー520の処理と異なる。すなわち、プリセットデータ設定値36に応じてタイマー520のダウンカウント周期が変化する。その結果、デコーダ540が出力するAD変換部300のチップイネーブル信号(CE)552がローにある期間及びストローブ信号24もプリセットデータ設定値36に応じて変化する。
The
すなわち、AD変換制御部550は、マイクロコンピュータ30から入力されるプリセットデータ設定値(同期クロック信号14に対する分周比)36に対応する周期でAD変換部300によるAD変換処理が行われるように制御する。
That is, the AD
本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、外部のマイクロコンピュータ30からの設定値36に基づいてAD変換部300によるAD変換処理の周期を簡単に変更することができる。従って、マイクロコンピュータ30からの設定値36によって、AD変換の精度を上げたい時はAD変換処理の周期を短くし、AD変換の精度を下げてもよい時はAD変換処理の周期を長くすることにより、マイクロコンピュータ30のタスクにおいてAD変換部300の制御オペレーションが占める割合をリアルタイムに変化させることができる。従って、システムの負荷を最適な状態に近づけることができる。
According to the AD conversion apparatus of this embodiment, the AD conversion processing cycle by the
また、本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理の周期を変化させた場合でも、それに合わせてフィルタクロック信号452の周波数を外部から設定することにより、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200のカットオフ周波数が所望の周波数になるように調整することができる。従って、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理の周期を変化させた場合でも、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200を最適なアンチエリアスフィルタとして機能させることができる。
In addition, according to the AD conversion apparatus of the present embodiment, even when the AD conversion processing cycle by the
1−6.AD変換装置の第5構成例
図10は、本実施形態のAD変換装置の第5の構成例について説明するための図である。
1-6. Fifth Configuration Example of AD Conversion Device FIG. 10 is a diagram for describing a fifth configuration example of the AD conversion device of the present embodiment.
AD変換装置20−5は、n(n≧2)個の離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−n、AD変換部300、n個のフィルタクロック生成部450−1〜450−n、AD変換制御部550、マルチプレクサ700等により構成されている。
The AD conversion apparatus 20-5 includes n (n ≧ 2) discrete-time antialias filters 200-1 to 200-n, an
離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−nは、n個のセンサーモジュール10−1〜10−nの各々に対応して設けられ、センサーモジュール10−1〜10−nがそれぞれ出力する検出結果のアナログ信号12−1〜12−nをそれぞれサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行う。 The discrete-time anti-alias filters 200-1 to 200-n are provided corresponding to each of the n sensor modules 10-1 to 10-n, and detections output from the sensor modules 10-1 to 10-n, respectively. The resulting analog signals 12-1 to 12-n are sampled and filtered.
フィルタクロック生成部450−1〜450−nは、センサーモジュール10−1〜10−nがそれぞれ出力する同期クロック信号14−1〜14−nに基づいて、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−nがアナログ信号12−1〜12−nをサンプリングするためのフィルタクロック信号452−1〜452−nをぞれぞれ生成する処理を行う。また、フィルタクロック生成部450−1〜450−nは、マイクロコンピュータ30からの設定値34−1〜34−nに対応する周波数を有するフィルタクロック信号452−1〜452−nをぞれぞれ生成するように構成されていてもよい。例えば、フィルタクロック生成部450−1〜450−nの各々は、図5と同じ構成であってもよい。
The filter clock generation units 450-1 to 450-n are discrete-time antialias filters 200-1 to 200-n based on the synchronous clock signals 14-1 to 14-n output from the sensor modules 10-1 to 10-n, respectively. 200-n performs processing for generating filter clock signals 452-1 to 452-n for sampling the analog signals 12-1 to 12-n, respectively. The filter clock generators 450-1 to 450-n respectively output filter clock signals 452-1 to 452-n having frequencies corresponding to the set values 34-1 to 34-n from the
AD変換制御部550は、同期クロック信号14−1〜14−nのいずれか(例えば、同期クロック信号14−1)に基づいて、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。より具体的には、AD変換制御部550は、例えば、同期クロック信号14−1に同期してAD変換部300のチップイネーブル信号(CE)552及びストローブ信号24を生成し、AD変換部300によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。また、AD変換制御部550は、マイクロコンピュータ30からの設定値(同期クロック信号14−1に対する分周比)36に対応する周期でAD変換部300によるAD変換処理が行われるように制御するように構成されていてもよい。例えば、AD変換制御部550は、図9と同じ構成であってもよい。
The AD
また、AD変換制御部550は、マルチプレクサ700のデータ選択信号554を生成するようにしてもよい。例えば、AD変換制御部550は、図9に示す構成のデコーダ540においてデータ選択信号554を生成するようにしてもよい。
Further, the AD
マルチプレクサ700は、フィルタ選択部として機能し、離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−nによってそれぞれフィルタ処理されたn個のアナログ信号202−1〜202−nから時分割に1のアナログ信号を順に選択して選択アナログ信号702を生成する処理を行う。ここで、マルチプレクサ700は、データ選択信号554に従い、アナログ信号202−1〜202−nから時分割に1のアナログ信号を順に選択して選択アナログ信号702を生成する。マルチプレクサ700は、例えば、データ選択信号554が0〜n−1の値である時にそれぞれアナログ信号202−1〜202−nが選択されるように構成されていてもよい。
The
AD変換部300は、マルチプレクサ700が選択した選択アナログ信号702をNビットのデジタル信号22に変換するAD変換処理を行う。
The
すなわち、AD変換装置20−5は、センサーモジュール10−1〜10−nの検出結果のアナログ信号12−1〜12−nを時分割に順にAD変換してデジタル信号22を出力する。
That is, the AD conversion apparatus 20-5 performs AD conversion on the analog signals 12-1 to 12-n as the detection results of the sensor modules 10-1 to 10-n in order in a time division manner, and outputs the
図11は、第5の構成例のAD変換装置の動作タイミングについて説明するためのタイミングチャート図である。 FIG. 11 is a timing chart for explaining the operation timing of the AD converter of the fifth configuration example.
図10で説明したように、AD変換装置20−5は、センサーモジュール10−1〜10−nの検出結果のアナログ信号12−1〜12−nを時分割に順にAD変換してデジタル信号22を出力する。
As described with reference to FIG. 10, the AD conversion apparatus 20-5 performs AD conversion on the analog signals 12-1 to 12-n as detection results of the sensor modules 10-1 to 10-n sequentially in a time-sharing manner, so that the
例えば、時刻t0〜t1におけるセンサーモジュール10−1〜10−nの検出結果のアナログ信号12−1〜12−nが時分割にAD変換の対象となる。そのため、アナログ信号12−1〜12−nがアンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−nによってそれぞれフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号202−1〜202−nが、例えば、それぞれ時刻t1〜t2、時刻t2〜t3、・・・、時刻t4〜t5においてAD変換の対象となるように、マルチプレクサ700のデータ選択信号554は、時刻t1〜t2、時刻t2〜t3、・・・、時刻t4〜t5においてそれぞれ、0、1、・・・、n−1になる。
For example, the target of the AD converting analog signals 12-1 to 12-n of the sensor module 10-1 to 10-n of the detection result of the time division at time t 0 ~t 1. Therefore, the analog signals 202-1 to 202-n obtained by filtering the analog signals 12-1 to 12-n by the anti-alias filters 200-1 to 200-n are, for example, time t 1 to t 2 , time t 2 ~t 3, ···, so that the target of the AD conversion at time t 4 ~t 5, the
ここで、マルチプレクサ700はデータ選択信号554に従って時刻t1〜t2においてアナログ信号202−1を選択するので、時刻t1〜t2におけるアナログ信号202−1は時刻t0〜t1におけるアナログ信号12−1がフィルタ処理された信号である必要がある。そこで、アンチエリアスフィルタ200−1の位相遅延pd1がt1−t0にほぼ等しくなるように調整される。
Here, the
また、マルチプレクサ700はデータ選択信号554に従って時刻t2〜t3においてアナログ信号202−2を選択するので、時刻t2〜t3におけるアナログ信号202−2は時刻t0〜t1におけるアナログ信号12−2がフィルタ処理された信号である必要がある。そこで、アンチエリアスフィルタ200−2の位相遅延pd2がt2−t0にほぼ等しくなるように調整される。同様に、アンチエリアスフィルタ200−nの位相遅延pdnがtn−t0にほぼ等しくなるように調整される。
Further, the
次に、時刻t5〜t6におけるセンサーモジュール10−1〜10−nの検出結果のアナログ信号12−1〜12−nがそれぞれ時刻t6〜t7、時刻t7〜t8、・・・、時刻t9〜t10においてAD変換の対象となり、時分割にAD変換処理が行われる。 Next, the sensor module 10-1 to 10-n of the detection result of the analog signal 12-1 to 12-n are respectively the time t 6 ~t 7 at time t 5 ~t 6, time t 7 ~t 8, ·· -, subject to the AD conversion at time t 9 ~t 10, AD conversion processing is performed in time division.
ここで、例えば、フィルタクロック信号452−1〜452−nの周波数を変更(すなわち、SCF回路のスイッチング周期を変更)することにより、アンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−nの位相遅延を調整するようにしてもよい。また、例えば、SCF回路の容量値を変更することによりアンチエリアスフィルタ200−1〜200−nの位相遅延を調整するようにしてもよい。 Here, for example, the phase delay of the anti-alias filters 200-1 to 200-n is adjusted by changing the frequency of the filter clock signals 452-1 to 452-n (that is, changing the switching period of the SCF circuit). You may do it. Further, for example, the phase delay of the anti-alias filters 200-1 to 200-n may be adjusted by changing the capacitance value of the SCF circuit.
本実施形態のAD変換装置によれば、n個のセンサーモジュール10−1〜10−nの検出結果12−1〜12−nに対して1つのAD変換部300が時分割にAD変換処理を行うことができる。従って、本実施形態のAD変換装置に使用される部品の数やチップの面積を削減することができる。
According to the AD conversion apparatus of this embodiment, one
2.力学量検出装置
図12は、本実施形態の力学量検出装置の構成例について説明するための図である。
2. Mechanical Quantity Detection Device FIG. 12 is a diagram for explaining a configuration example of the mechanical quantity detection device of the present embodiment.
力学量検出装置(センサーモジュール)800は、駆動信号812、814に基づいて振動する振動子820によって力学量を検出し、検出データ信号802(デジタル信号)を出力する。駆動信号812、814は、例えば、発振回路810(例えば、水晶発振器やセラミックレゾネータによる発振回路)が出力する発振信号であってもよい。
The mechanical quantity detection device (sensor module) 800 detects the mechanical quantity by the
発振回路810は、駆動信号812、814に同期した発振クロック816を生成する処理を行う。発振回路810は、発振クロック生成回路として機能する。
The
振動子820に、駆動信号812と、それに位相がπずれた逆位相の駆動信号814が入力されると、図示しない振動片が振動する。この振動を駆動振動とする。そして振動片に角速度が生じた場合、駆動振動と直交する方向にコリオリ力が働く。コリオリ力によって、駆動振動に対して位相がπ/2遅れた検出対象振動が生じる。振動子820は、圧電効果を利用して振動を電流や電圧に変換してアナログ信号(差動信号822、824)を出力する。この際、アナログ信号には、検出対象振動に起因する信号のほか、駆動振動が漏れることに起因する信号が重畳された信号が出力される。
When a
以上のようにして、振動子820は外部から加えられた角速度に応じて駆動信号812および814と位相がπ/2ずれた変調されたアナログ信号(差動信号822、824)を出力する。
As described above, the
プリアンプ830は差動信号822、824を差動増幅して増幅信号832を出力する。
The
同期検波回路840は、AM変調された増幅信号832に対して、発振回路810が出力する発振クロック816の位相をπ/2遅延させた同期クロック信号882により同期検波(狭義には乗算)を行い、同期検波信号842を出力する。発振クロック816をπ/2遅延させるのは位相調整回路880が行う。ここで、同期検波によりDC付近の周波数帯域に検波信号が生成されるが、同時に、駆動周波数の2倍の周波数帯域に不要な信号が発生する。すなわち、同期検波信号842は、DC付近の周波数帯域の検波信号成分と駆動周波数の2倍の周波数帯域の不要な信号成分を含んでいる。
The
離散時間型フィルタ850は、ローパスフィルタとして機能する。また、離散時間型フィルタ850は、AD変換回路860のサンプリングによりDC付近の周波数帯域に折り返すノイズをあらかじめ無視できる程度にまで低減するアンチエリアスフィルタとしても機能する。離散時間型フィルタ850は、例えば、スイッチトキャパシタフィルタ(SCF)であってもよい。
The
AD変換回路860は、離散時間型フィルタ850によってフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号852をNビットのデジタル信号862に変換するAD変換処理を行う。AD変換回路860は、フラッシュ型(並列比較型)、パイプライン型、逐次比較型、デルタシグマ方式等の既知の様々なタイプのAD変換回路により構成することができる。
The
AD変換制御回路870は、同期クロック信号882に基づいて、AD変換回路860によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。より具体的には、AD変換制御回路870は、同期クロック信号882に基づいてAD変換回路860のチップイネーブル信号(CE)872及びクロック信号874を生成し、AD変換回路860によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。すなわち、AD変換制御回路870は、チップイネーブル信号(CE)872をハイレベルからローレベルに変化させた後、AD変換回路860がAD変換処理を終了するまでウェイトしてからチップイネーブル信号(CE)872をローレベルからハイレベルに変化させる。すなわち、AD変換制御回路870がAD変換回路860によるAD変換処理のタイミングを制御する。
The AD
また、AD変換制御回路870は、AD変換回路860が出力するデジタル信号862をシリアルデータ802に変換してストローブ信号804とともにマイクロコンピュータ900のポートに送信するようにしてもよい。マイクロコンピュータ900は、当該ポートがフル状態になると割り込みを発生させてAD変換結果を取り込む。すなわち、マイクロコンピュータ900は、AD変換回路860がAD変換処理を行っている間ウェイトする必要がないため、CPU(図示しない)が他のタスクを実行することができる。
Further, the AD
なお、同期検波回路840が出力するアナログ信号842に対してAD変換処理を行う回路(806)の構成は、例えば、図1〜図11で説明したAD変換装置20−1〜20−5と同じ構成に置き換えてもよい。
The configuration of the circuit (806) that performs AD conversion processing on the
一般に、AD変換回路860によるAD変換処理のアンチエリアスフィルタを抵抗器、コンデンサ、トランジスタ、オペアンプ等の部品を使用して連続時間型フィルタとして構成した場合、これらの部品の精度ばらつきにより、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性にばらつきが出やすく調整しにくい。しかし、本実施形態の力学量検出装置によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタを周波数精度が比較的高くジッタの小さい同期クロック信号882に基づいて動作する離散時間型フィルタ850として構成するので、アンチエリアスフィルタのゲイン特性や位相特性のばらつきを小さくすることができる。従って、本実施形態の力学量検出装置によれば、アンチエリアスフィルタの調整を容易にするとともに、センサーシステム全体としての高い検出精度を維持させることができる。
In general, when an anti-alias filter for AD conversion processing by the
また、本実施形態の力学量検出装置によれば、離散時間型フィルタ850は、ローパスフィルタの機能とAD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタの両方の機能を果たす。従って、本実施形態の力学量検出装置に使用される部品の数やチップの面積を削減することができる。
Further, according to the mechanical quantity detection device of the present embodiment, the discrete-
また、本実施形態の力学量検出装置によれば、離散時間型フィルタ850やAD変換回路870に供給されるクロック信号は、マイクロコンピュータ900から供給されるのではなく、同期クロック信号882に基づいて生成される。従って、本実施形態の力学量検出装置の検出精度を同期クロック信号882の周波数精度で保証することができる。また、マイクロコンピュータ900からクロック信号を供給する必要がないので、本実施形態の力学量検出装置を1チップで実現する場合にはピン数を削減することができる。
Further, according to the mechanical quantity detection device of this embodiment, the clock signal supplied to the
図13(A)、図13(B)は、力学量検出装置の構成例における位相調整回路によるサンプリングタイミングの調整について説明するための図である。 FIG. 13A and FIG. 13B are diagrams for explaining the adjustment of the sampling timing by the phase adjustment circuit in the configuration example of the mechanical quantity detection device.
図13(A)は、同期検波回路840の入力信号832及び同期クロック信号882の波形の一例を示す図である。
FIG. 13A is a diagram illustrating an example of waveforms of the
同期検波回路840の入力信号832には、同期クロック信号882の周波数帯域において、検出対象信号(変調信号)834以外に検出振動に対して位相がπ/2進んだ駆動振動が漏れることに起因して発生する不要信号836が含まれる。不要信号836は、検出対象信号834に対してπ/2の位相が進んでいる。
This is because the
図13(B)は、同期検波回路840の出力信号842の波形の一例を示す図である。
FIG. 13B is a diagram illustrating an example of the waveform of the
同期検波回路840の出力信号842は、DC付近の周波数帯域において検出対象信号844を含み、同期クロック信号882の周波数(駆動周波数)の2倍の周波数帯域において不要信号846を含む。離散時間型フィルタ850によって正の成分と負の成分が打ち消すあうことで不要信号を除去している。
The
本実施形態の力学量検出装置によれば、離散時間型フィルタ850が、同期検波回路840の出力信号842をサンプリングする際に、同期クロック信号882の周波数の2倍の周波数帯域の不要信号に伴う折り返しノイズを効果的に減衰させることができる。従って、センサーシステム全体としての検出精度を向上させることができる。
According to the mechanical quantity detection device of this embodiment, when the discrete-
3.電子機器
図14に、本実施の形態の電子機器のブロック図の一例を示す。本電子機器1000は、マイクロコンピュータ910、入力部920、メモリ930、電源生成部940、出力部950、アナログ出力センサーモジュール960、AD変換装置970を含む。
3. Electronic Device FIG. 14 shows an example of a block diagram of the electronic device of this embodiment. The electronic apparatus 1000 includes a
入力部920は、種々のデータを入力するためのものである。
The
センサーモジュール960は、駆動信号に基づいて振動する振動子によって力学量を検出し、検出結果のアナログ信号をAD変換装置970に出力する処理を行う。
The
AD変換装置970は、センサーモジュール960が出力する検出結果のアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換する処理を行う。
The
マイクロコンピュータ910は、入力部920により入力されたデータに基づいて種々の処理を行う。また、マイクロコンピュータ910は、センサーモジュール960の検出結果のアナログ信号がAD変換装置970によりAD変換されたデジタル信号に基づいて検出結果の解析処理等を行う。
The
メモリ930は、マイクロコンピュータ910などの作業領域となるものである。
The
電源生成部940は、電子機器1000で使用される各種電源を生成するためのものである。
The
出力部950は、マイクロコンピュータ910の解析処理結果等を出力するためのものである。
The
AD変換装置970として本実施の形態のAD変換装置を組み込むことにより、コストパフォーマンスの高い電子機器を提供することができる。
By incorporating the AD converter of this embodiment as the
図15に、本実施の形態の電子機器のブロック図の他の一例を示す。本電子機器1100は図14の電子機器1000のアナログ出力センサーモジュール960及びAD変換装置970をデジタル出力センサーモジュール980に置き換えた構成になっている。
FIG. 15 illustrates another example of a block diagram of the electronic device of this embodiment. The electronic apparatus 1100 has a configuration in which the analog
センサーモジュール980は、駆動信号に基づいて振動する振動子によって力学量を検出し、検出結果のデジタル信号をマイクロコンピュータ910に出力する処理を行う。マイクロコンピュータ910は、センサーモジュール980の検出結果のデジタル信号に基づいて検出結果の解析処理等を行う。
The
電子機器1100のセンサーモジュール980以外の構成は図14の電子機器1000と同じ構成であるため同じ番号を付しており、その説明を省略する。
Since the configuration of the electronic device 1100 other than the
センサーモジュール980として本実施の形態の力学量検出装置を組み込むことにより、コストパフォーマンスの高い電子機器を提供することができる。
By incorporating the mechanical quantity detection device of this embodiment as the
図14及び図15に示した本実施形態を利用できる電子機器としては、移動体やロボットの姿勢検出や姿勢制御を行う装置、バーチャルリアリティ等に使用されるヘッドマウントディスプレイ、頭の姿勢角度を検出するトラッカー、3Dゲームパッド等を使用するゲーム機、デジタルカメラ、携帯電話機、携帯型情報端末、カーナビゲーションシステム等の種々の電子機器を考えることができる。 Electronic devices that can use this embodiment shown in FIG. 14 and FIG. 15 include devices that perform posture detection and posture control of moving bodies and robots, head-mounted displays used in virtual reality, and head posture angles. Various electronic devices such as a game machine using a tracker, a 3D game pad, a digital camera, a mobile phone, a portable information terminal, and a car navigation system can be considered.
なお、本発明は本実施形態に限定されず、本発明の要旨の範囲内で種々の変形実施が可能である。 In addition, this invention is not limited to this embodiment, A various deformation | transformation implementation is possible within the range of the summary of this invention.
本発明は、実施の形態で説明した構成と実質的に同一の構成(例えば、機能、方法及び結果が同一の構成、あるいは目的及び効果が同一の構成)を含む。また、本発明は、実施の形態で説明した構成の本質的でない部分を置き換えた構成を含む。また、本発明は、実施の形態で説明した構成と同一の作用効果を奏する構成又は同一の目的を達成することができる構成を含む。また、本発明は、実施の形態で説明した構成に公知技術を付加した構成を含む。 The present invention includes configurations that are substantially the same as the configurations described in the embodiments (for example, configurations that have the same functions, methods, and results, or configurations that have the same objects and effects). In addition, the invention includes a configuration in which a non-essential part of the configuration described in the embodiment is replaced. In addition, the present invention includes a configuration that exhibits the same operational effects as the configuration described in the embodiment or a configuration that can achieve the same object. Further, the invention includes a configuration in which a known technique is added to the configuration described in the embodiment.
10 力学量検出装置(センサーモジュール)、10−1〜10−n センサーモジュール、12 検出データ信号、12−1〜12−n 検出データ信号、14 同期クロック信号、14−1〜14−n 同期クロック信号、20−1〜20−5 AD変換装置、22 デジタル信号、24 ストローブ信号、30 マイクロコンピュータ、31 チップイネーブル信号、32 クロック信号、34 プリセットデータ設定値、34−1〜34−n プリセットデータ設定値、36 プリセットデータ設定値、100 発振回路、102 駆動信号、104駆動信号、106 発振クロック、110 振動子、112 差動信号、114 差動信号、120 プリアンプ、122 増幅信号、130 同期検波回路、132 同期検波信号、140 同期検波用フィルタ、150 位相調整回路、200 離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ、200−1〜200−n 離散時間型アンチエリアスフィルタ、202 アナログ信号、202−1〜202−n アナログ信号、300 AD変換部、400 フィルタクロック生成部、402 フィルタクロック信号、410 プリセットデータ、420 ダウンカウンタ、422 カウント値、430 デコーダ、432 ロード信号、450 フィルタクロック生成部、450−1〜450−n フィルタクロック生成部、452 フィルタクロック信号、452−1〜452−n フィルタクロック信号、460 セレクタ、500 AD変換制御部、502 チップイネーブル信号、510 プリセットデータ、520 タイマー、522 計測時間終了信号、530 ステートマシン、532 ステート信号、540 デコーダ、550 AD変換制御部、552 チップイネーブル信号、554 データ選択信号、700 マルチプレクサ、702 選択アナログ信号、800 力学量検出装置(センサーモジュール)、802 シリアルデータ、804 ストローブ信号、810 発振回路、812 駆動信号、814駆動信号、816 発振クロック、820 振動子、822 差動信号、824 差動信号、830 プリアンプ、832 増幅信号、834 検出対象信号、836 不要信号、840 同期検波回路、842 同期検波信号、844 検出対象信号、846 不要信号、850 離散時間型フィルタ、852 アナログ信号、860 AD変換部、862 デジタル信号、870 AD変換制御回路、872 チップイネーブル信号、874 クロック信号、880 位相調整回路、882 同期クロック信号、900 マイクロコンピュータ、910 マイクロコンピュータ、920 入力部、930 メモリ、940 電源生成部、950 出力部、960 センサーモジュール、970 AD変換装置、980 センサーモジュール、1000 電子機器、1100 電子機器 DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 10 Mechanical quantity detection apparatus (sensor module), 10-1 to 10-n sensor module, 12 detection data signal, 12-1 to 12-n detection data signal, 14 synchronous clock signal, 14-1 to 14-n synchronous clock Signal, 20-1 to 20-5 AD converter, 22 digital signal, 24 strobe signal, 30 microcomputer, 31 chip enable signal, 32 clock signal, 34 preset data setting value, 34-1 to 34-n preset data setting Value, 36 preset data setting value, 100 oscillation circuit, 102 drive signal, 104 drive signal, 106 oscillation clock, 110 oscillator, 112 differential signal, 114 differential signal, 120 preamplifier, 122 amplified signal, 130 synchronous detection circuit, 132 Synchronous detection signal, 140 Synchronous detection Filter, 150 phase adjustment circuit, 200 discrete-time antialias filter, 200-1 to 200-n discrete-time antialias filter, 202 analog signal, 202-1 to 202-n analog signal, 300 AD converter, 400 Filter clock generation unit, 402 Filter clock signal, 410 preset data, 420 down counter, 422 count value, 430 decoder, 432 load signal, 450 filter clock generation unit, 450-1 to 450-n filter clock generation unit, 452 Filter clock Signal, 452-1 to 452-n filter clock signal, 460 selector, 500 AD conversion control unit, 502 chip enable signal, 510 preset data, 520 timer, 522 measurement time end signal, 530 state machine, 532 state signal, 540 decoder, 550 AD conversion control unit, 552 chip enable signal, 554 data selection signal, 700 multiplexer, 702 selection analog signal, 800 mechanical quantity detection device (sensor module), 802 serial data, 804 Strobe signal, 810 oscillation circuit, 812 drive signal, 814 drive signal, 816 oscillation clock, 820 vibrator, 822 differential signal, 824 differential signal, 830 preamplifier, 832 amplified signal, 834 detection target signal, 836 unnecessary signal, 840 Synchronous detection circuit, 842 Synchronous detection signal, 844 Detection target signal, 846 Unnecessary signal, 850 Discrete time filter, 852 Analog signal, 860 AD conversion unit, 862 Digital signal, 870 AD conversion control Path, 872 chip enable signal, 874 clock signal, 880 phase adjustment circuit, 882 synchronization clock signal, 900 microcomputer, 910 microcomputer, 920 input section, 930 memory, 940 power generation section, 950 output section, 960 sensor module, 970 AD converter, 980 sensor module, 1000 electronic device, 1100 electronic device
Claims (11)
前記検出結果のアナログ信号をサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行う離散時間型フィルタと、
前記離散時間型フィルタによってフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換するAD変換処理を行うAD変換部と、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換処理のタイミングを制御するAD変換制御部と、を含み、
前記離散時間型フィルタは、
前記力学量検出装置が出力する同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理を行うことを特徴とするAD変換装置。 An AD converter that converts an analog signal of a detection result output by a mechanical quantity detection device that detects a mechanical quantity into a digital signal,
A discrete-time filter that performs sampling by sampling an analog signal of the detection result; and
An AD converter that performs an AD conversion process for converting the analog signal filtered by the discrete-time filter into a digital signal;
An AD conversion control unit that controls the timing of the AD conversion processing based on the synchronous clock signal ,
The discrete time filter is:
An AD conversion apparatus that performs filter processing as an anti-alias filter for the AD conversion processing based on a synchronous clock signal output from the mechanical quantity detection device.
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記離散時間型フィルタが前記検出結果のアナログ信号をサンプリングするためのフィルタクロック信号を生成するフィルタクロック生成部を含み、
前記フィルタクロック生成部は、
外部からの設定値に基づいて前記同期クロック信号を分周した前記フィルタクロック信号を生成することを特徴とするAD変換装置。 In claim 1,
A filter clock generator for generating a filter clock signal for sampling the analog signal of the detection result by the discrete-time filter based on the synchronous clock signal;
The filter clock generator is
An AD conversion apparatus that generates the filter clock signal obtained by dividing the synchronous clock signal based on an externally set value.
前記AD変換制御部は、
外部からの設定値に基づいた周期で前記AD変換処理が行われるように制御することを特徴とするAD変換装置。 In claim 1 or 2 ,
The AD conversion control unit
An AD conversion apparatus, wherein the AD conversion processing is controlled to be performed at a cycle based on a set value from the outside.
前記離散時間型フィルタは、スイッチトキャパシタフィルタであることを特徴とするAD変換装置。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 3 ,
The AD converter according to claim 1, wherein the discrete-time filter is a switched capacitor filter.
n(n≧2)個の前記力学量検出装置の各々に対応して設けられたn個の前記離散時間型フィルタと、
n個の前記離散時間型フィルタによってフィルタ処理されたn個のアナログ信号から時分割に1のアナログ信号を順に選択するフィルタ選択部を含み、
前記AD変換部は、
前記フィルタ選択部によって時分割に順に選択されたアナログ信号に対して前記AD変換処理を行い、
n個の前記離散時間型フィルタは、
n個の前記力学量検出装置が略同じタイミングでそれぞれ検出したn個のアナログ信号に対してそれぞれフィルタ処理したn個のアナログ信号が前記フィルタ選択部によって時分割に順に選択されるように、それぞれ位相遅延が調整されていることを特徴とするAD変換装置。 In any one of Claims 1 thru | or 4 ,
n discrete time filters provided corresponding to each of the n (n ≧ 2) mechanical quantity detection devices;
a filter selection unit that sequentially selects one analog signal in time division from n analog signals filtered by the n discrete-time filters;
The AD converter is
Performing the AD conversion processing on the analog signals sequentially selected by the filter selection unit in a time-sharing manner,
The n discrete time filters are:
The n analog signals obtained by filtering the n analog signals respectively detected by the n mechanical quantity detection devices at substantially the same timing are sequentially selected by the filter selection unit in a time division manner. An AD converter characterized in that a phase delay is adjusted.
前記力学量検出装置と、
前記AD変換装置により前記検出結果のアナログ信号がAD変換されたデジタル信号に基づいて処理を行う処理部と、を含むことを特徴とする電子機器。 An AD converter according to any one of claims 1 to 5 ,
The mechanical quantity detection device;
An electronic device comprising: a processing unit that performs processing based on a digital signal obtained by AD-converting the analog signal of the detection result by the AD conversion device.
前記駆動信号と同じ周波数の同期クロック信号を生成する同期クロック生成回路と、
前記振動子が出力するアナログ信号又は当該アナログ信号を増幅した信号に対して前記同期クロック信号に基づいて同期検波を行い、力学量に応じて復調された信号成分を含むアナログ信号を生成する同期検波回路と、
前記同期検波回路が出力するアナログ信号をサンプリングしてフィルタ処理を行う離散時間型フィルタと、
前記離散時間型フィルタによってフィルタ処理されたアナログ信号をデジタル信号に変換するAD変換処理を行うAD変換部と、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記AD変換処理のタイミングを制御するAD変換制御部と、を含み、
前記離散時間型フィルタは、
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記同期検波により発生する不要信号を減衰させるためのフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理と、前記AD変換処理に対するアンチエリアスフィルタとしてのフィルタ処理を行うことを特徴とする力学量検出装置。 A vibrator that vibrates based on a driving signal and outputs an analog signal modulated according to a mechanical quantity applied from the outside;
A synchronous clock generation circuit for generating a synchronous clock signal having the same frequency as the drive signal;
Synchronous detection for performing analog detection on the analog signal output from the vibrator or the amplified signal based on the synchronous clock signal and generating an analog signal including a signal component demodulated according to a dynamic quantity Circuit,
A discrete-time filter that performs filtering by sampling an analog signal output by the synchronous detection circuit; and
An AD converter that performs an AD conversion process for converting the analog signal filtered by the discrete-time filter into a digital signal;
An AD conversion control unit that controls the timing of the AD conversion processing based on the synchronous clock signal ,
The discrete time filter is:
Based on the synchronous clock signal, a mechanical quantity detection characterized by performing a filter process as a filter for attenuating an unnecessary signal generated by the synchronous detection and a filter process as an anti-alias filter for the AD conversion process apparatus.
前記同期クロック信号に基づいて、前記離散時間型フィルタが、前記同期検波回路が出力する前記アナログ信号をサンプリングするためのフィルタクロック信号を生成するフィルタクロック生成部を含み、
前記フィルタクロック生成部は、
外部からの設定値に対応する周波数を有する前記フィルタクロック信号を生成することを特徴とする力学量検出装置。 In claim 7 ,
Based on the synchronous clock signal, the discrete-time filter includes a filter clock generation unit that generates a filter clock signal for sampling the analog signal output by the synchronous detection circuit,
The filter clock generator is
A mechanical quantity detection device that generates the filter clock signal having a frequency corresponding to a set value from the outside.
前記AD変換制御部は、
外部からの設定値に対応する分周比で前記同期クロックを分周した周期で前記AD変換処理が行われるように制御することを特徴とする力学量検出装置。 In claim 7 or 8 ,
The AD conversion control unit
An apparatus for detecting a mechanical quantity, wherein the AD conversion process is performed in a cycle in which the synchronous clock is divided by a division ratio corresponding to an externally set value.
前記離散時間型フィルタは、スイッチトキャパシタフィルタであることを特徴とする力学量検出装置。 In any one of Claims 7 thru | or 9 ,
The discrete time filter is a switched capacitor filter.
前記力学量検出装置の検出結果に基づいて処理を行う処理部と、を含むことを特徴とする電子機器。 The mechanical quantity detection device according to any one of claims 7 to 10 ,
And a processing unit that performs processing based on a detection result of the mechanical quantity detection device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008110198A JP5561453B2 (en) | 2008-04-21 | 2008-04-21 | AD converter, mechanical quantity detector, and electronic equipment. |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008110198A JP5561453B2 (en) | 2008-04-21 | 2008-04-21 | AD converter, mechanical quantity detector, and electronic equipment. |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009258047A JP2009258047A (en) | 2009-11-05 |
| JP2009258047A5 JP2009258047A5 (en) | 2011-04-14 |
| JP5561453B2 true JP5561453B2 (en) | 2014-07-30 |
Family
ID=41385641
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008110198A Active JP5561453B2 (en) | 2008-04-21 | 2008-04-21 | AD converter, mechanical quantity detector, and electronic equipment. |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5561453B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11611349B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2023-03-21 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | Analog-to-digital converter, sensor system , and test system |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012023202A (en) * | 2010-07-14 | 2012-02-02 | Tamagawa Seiki Co Ltd | Soc having high resolution a/d converter input port for imu signal |
| JP2014109507A (en) * | 2012-12-03 | 2014-06-12 | Murata Mfg Co Ltd | Gyro device and angular velocity detection system |
| JP6524673B2 (en) * | 2015-01-22 | 2019-06-05 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Circuit device, physical quantity detection device, electronic device and moving body |
| JP2017225031A (en) * | 2016-06-16 | 2017-12-21 | 国立大学法人大阪大学 | A/d converter and electronic apparatus |
| JP6805188B2 (en) | 2018-01-26 | 2020-12-23 | 株式会社東芝 | Detector |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS60250500A (en) * | 1984-05-25 | 1985-12-11 | 横河メディカルシステム株式会社 | Multi-point current measuring apparatus |
| JPS6326033A (en) * | 1986-07-17 | 1988-02-03 | Nec Ic Microcomput Syst Ltd | Analog-digital converter |
| JP3385725B2 (en) * | 1994-06-21 | 2003-03-10 | ソニー株式会社 | Audio playback device with video |
| JP4032681B2 (en) * | 2001-08-27 | 2008-01-16 | 株式会社デンソー | Synchronous detection method and apparatus, and sensor signal detection apparatus |
| US7062403B2 (en) * | 2003-06-30 | 2006-06-13 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Rotational speed sensor comprising a vibrating gyroscope and method for equalizing the rotational speed sensor |
| JP4396725B2 (en) * | 2006-05-12 | 2010-01-13 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Detection device, gyro sensor, and electronic device |
-
2008
- 2008-04-21 JP JP2008110198A patent/JP5561453B2/en active Active
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11611349B2 (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2023-03-21 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | Analog-to-digital converter, sensor system , and test system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009258047A (en) | 2009-11-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5561453B2 (en) | AD converter, mechanical quantity detector, and electronic equipment. | |
| TWI576566B (en) | Inertial force sensor | |
| JP5286676B2 (en) | Detection device, sensor and electronic device | |
| US9602117B2 (en) | Detection device, sensor, electronic apparatus, and moving object | |
| JP6641712B2 (en) | Circuit device, electronic equipment and moving object | |
| US10018468B2 (en) | Physical-quantity detection circuit, physical-quantity sensor, and electronic device | |
| JP6307840B2 (en) | Detection device, sensor, electronic device, and moving object | |
| JP2015108566A (en) | Detector, sensor, electronic apparatus, and movable body | |
| WO2009128188A1 (en) | Physical quantity detection circuit, physical quantity sensor device | |
| JP2009229152A (en) | Angular velocity sensor | |
| JP2015102406A (en) | Detection device, sensor, electronic apparatus, and moving body | |
| TW201740084A (en) | Method for processing signals and device | |
| JP4836985B2 (en) | Physical quantity detection circuit | |
| JP6844310B2 (en) | Frequency ratio measuring device and physical quantity sensor | |
| US20210333104A1 (en) | Detector | |
| JP2017050664A (en) | Analog reference voltage generating circuit, circuit device, physical quantity sensor, electronic device and moving object | |
| US20140290361A1 (en) | Apparatus for driving gyroscope sensor | |
| KR101204205B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for driving inertial sensor | |
| JP2016153744A (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity detection device, electronic apparatus and mobile body | |
| JP6524673B2 (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity detection device, electronic device and moving body | |
| JP6561702B2 (en) | Physical quantity detection system, electronic device and moving object | |
| CN110296697B (en) | Circuit device, physical quantity measuring device, electronic apparatus, and moving object | |
| CN214666889U (en) | Laser gyroscope jitter offset frequency control device based on frequency modulation | |
| JP2010286371A (en) | Physical quantity detector, abnormality diagnosis system of the same, and abnormality diagnosis method of the same | |
| JP2009168588A (en) | Detection circuit, physical quantity measuring device, gyro sensor, and electronic device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20110729 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20110729 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110819 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120829 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120905 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121102 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130731 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130927 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140514 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140527 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5561453 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |