JP5511767B2 - Vapor deposition equipment - Google Patents
Vapor deposition equipment Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5511767B2 JP5511767B2 JP2011236147A JP2011236147A JP5511767B2 JP 5511767 B2 JP5511767 B2 JP 5511767B2 JP 2011236147 A JP2011236147 A JP 2011236147A JP 2011236147 A JP2011236147 A JP 2011236147A JP 5511767 B2 JP5511767 B2 JP 5511767B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vapor
- vapor deposition
- chamber
- steam
- processing chamber
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 title claims description 105
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 72
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 66
- 239000012159 carrier gas Substances 0.000 claims description 31
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 63
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 57
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 27
- 238000005401 electroluminescence Methods 0.000 description 25
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 13
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005525 hole transport Effects 0.000 description 2
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910001316 Ag alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000861 Mg alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009125 cardiac resynchronization therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007772 electrode material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000010935 stainless steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007738 vacuum evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005019 vapor deposition process Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Electroluminescent Light Sources (AREA)
- Physical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
Description
本発明は、蒸着により被処理体を成膜処理する蒸着装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a vapor deposition apparatus that performs film formation on an object to be processed by vapor deposition.
近年、エレクトロルミネッセンス(EL;ELectroluminescence)を利用した有機EL素子が開発されている。有機EL素子は、熱をほとんど出さないのでブラウン管などに比べて消費電力が小さく、また、自発光なので、液晶ディスプレー(LCD)などに比べて視野角に優れている等の利点があり、今後の発展が期待されている。 In recent years, organic EL elements using electroluminescence (EL) have been developed. Organic EL elements generate little heat, so they consume less power than CRTs, etc., and because they emit light, they have advantages such as better viewing angles than liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Development is expected.
この有機EL素子のもっとも基本的な構造は、ガラス基板上にアノード(陽極)層、発光層およびカソード(陰極)層を重ねて形成したサンドイッチ構造である。発光層の光を外に取り出すために、ガラス基板上のアノード層には、ITO(Indium Tin Oxide)からなる透明電極が用いられる。かかる有機EL素子は、表面にITO層(アノード層)が予め形成されたガラス基板上に、発光層とカソード層を順に成膜することによって製造されるのが一般的である。 The most basic structure of this organic EL element is a sandwich structure in which an anode (anode) layer, a light emitting layer and a cathode (cathode) layer are formed on a glass substrate. In order to extract light from the light emitting layer to the outside, a transparent electrode made of ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) is used for the anode layer on the glass substrate. Such an organic EL element is generally manufactured by sequentially forming a light emitting layer and a cathode layer on a glass substrate on which an ITO layer (anode layer) is formed in advance.
以上のような有機EL素子の発光層を成膜させる装置としては、例えば特許文献1に示す真空蒸着装置が知られている。 As an apparatus for forming the light emitting layer of the organic EL element as described above, for example, a vacuum evaporation apparatus shown in Patent Document 1 is known.
ところで、有機EL素子の発光層を成膜させる工程では、処理容器内を所定の圧力まで減圧させることが行われる。その理由は、上記のように有機EL素子の発光層を成膜させる場合、蒸着ヘッドから200℃〜500℃程度の高温にした成膜材料の蒸気を供給して、基板表面に成膜材料を蒸着させるのであるが、仮に大気中で成膜処理すると、気化させた成膜材料の蒸気の熱が処理容器内の空気を伝わることにより、処理室内に配置された各種センサ等の部品を高温にさせ、それら部品の特性を悪化させたり、部品自体の破損を招いてしまうからである。そこで、有機EL素子の発光層を成膜させる工程では、処理容器内を所定の圧力まで減圧させ、成膜材料の蒸気の熱が逃げないように維持している(真空断熱)。 By the way, in the step of forming the light emitting layer of the organic EL element, the inside of the processing container is depressurized to a predetermined pressure. The reason for this is that when the light emitting layer of the organic EL element is formed as described above, vapor of the film forming material heated to about 200 ° C. to 500 ° C. is supplied from the vapor deposition head, and the film forming material is applied to the substrate surface. If the film is deposited in the atmosphere, the vaporized vapor of the film-forming material is transferred to the air in the processing container, so that various sensors and other components placed in the processing chamber are heated to a high temperature. This is because the characteristics of these parts are deteriorated or the parts themselves are damaged. Therefore, in the step of forming the light emitting layer of the organic EL element, the inside of the processing container is depressurized to a predetermined pressure and maintained so that the heat of the vapor of the film forming material does not escape (vacuum insulation).
一方、成膜材料を蒸発させる蒸気発生部や、蒸気発生部で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を蒸着ヘッドに送る配管、成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御する制御弁などは、成膜材料の補充、メンテナンス等の理由から、処理容器の外部に置かれるのが一般的である。しかしながら、仮にこれら蒸気発生部、配管、制御弁などを大気圧下に配置した場合、空気中を通じて放熱することにより、蒸気発生部で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を、蒸着ヘッドに送るまでの間、所望の温度に保ちにくいといった問題を生じる。例えば、蒸着ヘッドに送るまでの間に、成膜材料の蒸気が設定温度以下となると、成膜材料が配管中などで析出し、蒸着ヘッドに十分に送られなくなってしまう。そのため、蒸着ヘッドからの蒸気の供給量が減少し、蒸着速度が低下してしまう。 On the other hand, the vapor generating part for evaporating the film forming material, the piping for sending the vapor of the film forming material generated in the vapor generating part to the vapor deposition head, the control valve for controlling the supply of the vapor of the film forming material, etc. Generally, it is placed outside the processing container for reasons such as replenishment and maintenance. However, if these vapor generating parts, piping, control valves, etc. are arranged under atmospheric pressure, the heat of the film forming material generated in the vapor generating part can be transferred to the vapor deposition head by radiating heat through the air. In the meantime, there arises a problem that it is difficult to maintain a desired temperature. For example, if the vapor of the film forming material falls below the set temperature before being sent to the vapor deposition head, the film forming material is deposited in a pipe or the like and cannot be sufficiently sent to the vapor deposition head. For this reason, the amount of vapor supplied from the vapor deposition head decreases, and the vapor deposition rate decreases.
従って本発明の目的は、蒸気発生部で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を温度低下させること無く蒸着ヘッドに送ることができる蒸着装置を提供することにある。 Accordingly, an object of the present invention is to provide a vapor deposition apparatus that can send vapor of a film forming material generated in a vapor generating section to a vapor deposition head without lowering the temperature.
本発明によれば、蒸着により被処理体を成膜処理する蒸着装置であって、被処理体を成膜処理する減圧可能な処理室と、前記処理室と隣接して配置される減圧可能な蒸気発生室と、前記処理室の内部に露出し、前記処理室の内部に向けて蒸気を噴出する蒸気噴出口と、前記蒸気噴出口が任意の面に形成された蒸着ヘッドと、前記蒸気発生室に配置され、成膜材料を蒸発させる蒸気発生部と、前記蒸気発生室内に少なくともその一部が配置され、前記蒸気発生部と前記蒸気噴出口を連通させる配管と、前記配管に設けられ、成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御する制御弁と、前記蒸気発生部で蒸発させた成膜材料の蒸気を前記蒸気噴出口に供給させるためのキャリアガスを、前記蒸気発生部に供給するキャリアガス供給配管とを備え、前記蒸気発生部は、全体を一体的に加熱可能なヒータブロックを有し、前記ヒータブロックの内部に、成膜材料を充填可能な材料容器と、前記キャリアガス供給配管から供給されたキャリアガスを前記材料容器に通すキャリアガス経路を配置し、前記蒸着ヘッドを、前記蒸気噴出口が形成された面を前記処理室内に露出させた姿勢で前記処理室と前記蒸気発生室とを仕切る隔壁に支持し、前記配管は、前記処理室の外部及び前記蒸気発生室の外部に露出しないことを特徴とする、蒸着装置が提供される。 According to the present invention, there is provided a vapor deposition apparatus for performing a film forming process on an object to be processed by vapor deposition, a process chamber capable of performing a film forming process on the object to be processed, and a pressure reducing process disposed adjacent to the process chamber. A steam generating chamber; a steam outlet that is exposed to the inside of the processing chamber and jets steam toward the inside of the processing chamber ; a vapor deposition head in which the steam outlet is formed on an arbitrary surface; and the steam generation Disposed in the chamber, the vapor generating part for evaporating the film forming material, at least a part of the vapor generating part is disposed in the steam generating chamber, and provided in the pipe for communicating the vapor generating part and the vapor outlet, A control valve for controlling the supply of vapor of the film forming material, and a carrier gas for supplying the vapor generating part with a carrier gas for supplying the vapor of the film forming material evaporated in the vapor generating part to the vapor outlet and a supply pipe, the steam generating unit And a heater block that can be integrally heated, and a material container that can be filled with a film-forming material and a carrier gas supplied from the carrier gas supply pipe are passed through the heater container. A carrier gas path is disposed, and the vapor deposition head is supported by a partition wall that partitions the processing chamber and the vapor generation chamber in a posture in which the surface on which the vapor jet port is formed is exposed in the processing chamber, A vapor deposition apparatus is provided that is not exposed to the outside of the processing chamber and the outside of the vapor generation chamber.
前記隔壁の少なくとも一部を断熱材とすると良い。また、前記蒸気発生部と前記制御弁を、前記蒸着ヘッドに支持させても良い。 At least a portion of the pre-Symbol partition wall may be a heat insulating material. The vapor generation unit and the control valve may be supported by the vapor deposition head.
前記成膜材料は、例えば、有機EL素子の発光層の成膜材料である。また、前記制御弁は、例えば、ベローズ弁またはダイアフラム弁である。また、前記排気機構は、前記処理室と前記蒸気発生室にそれぞれ設けられていても良い。また、前記蒸気発生部で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を前記蒸着ヘッドに供給する輸送路が設けられ、前記輸送路には、複数の蒸気発生部が取り付けられていても良い。また、前記流路にはヒータを備えなくても良い。 The film forming material is, for example, a film forming material for a light emitting layer of an organic EL element. The control valve is, for example, a bellows valve or a diaphragm valve. The exhaust mechanism may be provided in each of the processing chamber and the steam generation chamber. In addition, a transport path for supplying the vapor of the film forming material generated by the steam generating section to the vapor deposition head may be provided, and a plurality of steam generating sections may be attached to the transport path. Further, the flow path may not include a heater.
本発明によれば、蒸気発生部で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を、処理室と蒸気発生室の外部に出さずに、蒸気噴出口に供給させることにより、真空断熱の状態で成膜材料の蒸気を温度低下させること無く蒸着ヘッドに送ることができる。このため、配管中などにおける成膜材料の析出を防止でき、蒸着ヘッドからの蒸気の供給量が安定し、蒸着速度の低下が回避される。 According to the present invention, the film-forming material generated in the vapor generation section is supplied to the vapor outlet without being discharged to the outside of the processing chamber and the vapor generation chamber. Can be sent to the vapor deposition head without lowering the temperature. For this reason, the deposition of the film forming material in the pipe or the like can be prevented, the amount of vapor supplied from the vapor deposition head is stabilized, and a decrease in the vapor deposition rate is avoided.
また、蒸着ヘッドに蒸気発生部と制御弁を支持させた一体的な構造とすれば、蒸着ユニットがコンパクトになり、処理室と蒸気発生室の内部の真空断熱により、蒸着ユニット全体の温度制御性、温度均一性が向上する。蒸着ヘッドに蒸気発生部と制御弁を一体化させることにより、各部の継目が無くなり、温度低下が緩和される。また、蒸着ユニットを一体的に取り出すことにより、メンテナンスも容易になる。更に、蒸気発生部を一体的に加熱可能なヒータブロックとし、このヒータブロックの内部に材料容器とキャリアガス経路を配置すれば、キャリアガスのプリヒートのためのヒータも省略でき、全体の省スペース化が図れる。 Also, if the vapor deposition head supports the vapor generation unit and the control valve, the vapor deposition unit becomes compact, and the temperature controllability of the entire vapor deposition unit is achieved by vacuum insulation inside the processing chamber and the vapor generation chamber. , Temperature uniformity is improved. By integrating the vapor generating part and the control valve into the vapor deposition head, the joints between the parts are eliminated, and the temperature drop is alleviated. Moreover, maintenance is also facilitated by taking out the vapor deposition unit integrally. Furthermore, if the steam generating part is a heater block that can be integrally heated, and if a material container and a carrier gas path are arranged inside the heater block, the heater for preheating the carrier gas can be omitted, thus saving the overall space. Can be planned.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、図面を参照にして説明する。以下の実施の形態では、蒸着処理の一例として、被処理体としてのガラス基板G上にアノード(陽極)層1、発光層3およびカソード(陰極)層2を成膜して有機EL素子Aを製造する処理システム10を例にして具体的に説明する。なお、本明細書及び図面において、実質的に同一の機能構成を有する構成要素については、同一の符号を付することにより重複説明を省略する。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. In the following embodiment, as an example of the vapor deposition process, an anode (anode) layer 1, a
先ず、図1は、本発明の実施の形態において製造される有機EL素子Aの説明図である。有機EL素子Aのもっとも基本となる構造は、陽極1と陰極2との間に発光層3を挟んだサンドイッチ構造である。陽極1はガラス基板G上に形成されている。陽極1には、発光層3の光を透過させることが可能な、例えばITO(Indium Tin Oxide)からなる透明電極が用いられる。
First, FIG. 1 is an explanatory diagram of an organic EL element A manufactured in the embodiment of the present invention. The most basic structure of the organic EL element A is a sandwich structure in which the
発光層3である有機層は一層から多層のものまであるが、図1では、第1層a1〜第6層a6を積層した6層構成である。第1層a1はホール輸送層、第2層a2は非発光層(電子ブロック層)、第3層a3は青発光層、第4層a4は赤発光層、第5層a5は緑発光層、第6層a6は電子輸送層である。かかる有機EL素子Aは、後述するように、ガラス基板G表面の陽極1の上に、発光層3(第1層a1〜第6層a6)を順次成膜し、仕事関数調整層(図示せず)を介在させた後、Ag、Mg/Ag合金などの陰極2を形成し、最後に、全体を窒化膜(図示せず)などで封止して、製造される。
Although the organic layer which is the
図2は、有機EL素子Aを製造するための成膜システム10の説明図である。この成膜システム10は、基板Gの搬送方向(図2において右向き)に沿って、ローダ11、トランスファーチャンバ12、発光層3の蒸着装置13、トランスファーチャンバ14、仕事関数調整層の成膜装置15、トランスファーチャンバ16、エッチング装置17、トランスファーチャンバ18、スパッタリング装置19、トランスファーチャンバ20、CVD装置21、トランスファーチャンバ22、アンローダ23を直列に順に並べた構成である。ローダ11は、基板Gを成膜システム10内に搬入するための装置である。トランスファーチャンバ12、14、16、18、20、22は、各処理装置間で基板Gを受け渡しするための装置である。アンローダ23は、基板Gを成膜システム10外に搬出するための装置である。
FIG. 2 is an explanatory diagram of the
ここで、本発明の実施の形態にかかる蒸着装置13について、更に詳細に説明する。図3は、蒸着装置13の構成を概略的に示した断面図、図4は、蒸着装置13が備える蒸着ユニット55(56,57,58,59,60)の斜視図、図5は、蒸着ユニット55(56,57,58,59,60)の回路図、図6は、蒸気発生部70,71,72の斜視図である。
Here, the
この蒸着装置13は、内部において基板Gを成膜処理するための処理室30と、成膜材料を蒸発させる蒸気発生室31とを上下に隣接させて配置した構成である。これら処理室30と蒸気発生室31は、アルミニウム、ステンレススチール等で構成された容器本体32の内部に形成されており、処理室30と蒸気発生室31の間は、断熱材で構成された隔壁33によって仕切られている。
The
処理室30の底面には、排気孔35が開口しており、排気孔35には、容器本体32の外部に配置された排気機構である真空ポンプ36が、排気管37を介して接続されている。この真空ポンプ36の稼動により、処理室30の内部は所定の圧力に減圧される。
An
同様に、蒸気発生室31の底面には、排気孔40が開口しており、排気孔40には、容器本体32の外部に配置された排気機構である真空ポンプ41が、排気管42を介して接続されている。この真空ポンプ41の稼動により、蒸気発生室31の内部は所定の圧力に減圧される。
Similarly, an
処理室30の上方には、ガイド部材45と、このガイド部材45に沿って適宜の駆動源(図示せず)によって移動する支持部材46が設けられている。支持部材46には、静電チャックなどの基板保持部47が取り付けられており、成膜対象である基板Gは基板保持部47の下面に水平に保持される。
Above the
処理室30の側面には、搬入口50と搬出口51が形成されている。この蒸着装置13では、搬入口50から搬入された基板Gが、基板保持部47で保持されて、処理室30内において図3中の右向きに搬送され、搬出口51から搬出される。
A carry-in
処理室30と蒸気発生室31の間を仕切っている隔壁33には、成膜材料の蒸気を供給する6個の蒸着ユニット55,56,57,58,59,60が、基板Gの搬送方向に沿って配置されている。これら蒸着ユニット55〜60は、ホール輸送層を蒸着させる第1の蒸着ユニット55、非発光層を蒸着させる第2の蒸着ユニット56、青発光層を蒸着させる第3の蒸着ユニット57、赤発光層を蒸着させる第4の蒸着ユニット58、緑発光層を蒸着させる第5の蒸着ユニット59、電子輸送層を蒸着させる第6の蒸着ユニット60からなり、基板保持部47によって保持されながら搬送されていく基板Gの下面に対して成膜材料の蒸気を順に成膜させるようになっている。また、各蒸着ユニット55〜60の間には、蒸気仕切り壁61が配置されており、各蒸着ユニット55〜60から供給される成膜材料の蒸気が互いに混合せずに、基板Gの下面に順に成膜されるようになっている。
Six
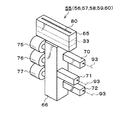
各蒸着ユニット55〜60は、いずれも同様の構成を有しているので代表して第1の蒸着ユニット55について説明する。図4に示すように、蒸着ユニット55は、蒸着ヘッド65の下方に配管ケース(輸送路)66を取り付け、この配管ケース66の両側面に、3つの蒸気発生部70,71,72と3つの制御弁75、76,77を取り付けた構成である。
Since each of the
蒸着ヘッド65の上面には、有機EL素子Aの発光層3の成膜材料の蒸気を噴出させる蒸気噴出口80が形成されている。蒸気噴出口80は、基板Gの搬送方向に直交する方向に沿ってスリット形状に配置されており、基板Gの幅と同じか僅かに長い長さを有している。このスリット形状の蒸気噴出口80から成膜材料の蒸気を噴出させながら、上述の基板保持部47によって基板Gを搬送することにより、基板Gの下面全体に成膜させるようになっている。
On the upper surface of the
蒸着ヘッド65は、蒸気噴出口80が形成された上面を処理室30内に露出させた姿勢で、処理室30と蒸気発生室31とを仕切る隔壁33に支持されている。蒸着ヘッド65の下面は、蒸気発生室31内に露出しており、この蒸着ヘッド65の下面に取り付けられた配管ケース(輸送路)66と、配管ケース66に取り付けられた蒸気発生部70,71,72および制御弁75、76,77がいずれも蒸気発生室31に配置されている。
The
3つの蒸気発生部70,71,72と3つの制御弁75、76,77は互いに対応した関係であり、制御弁75は、蒸気発生部70で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御し、制御弁76は、蒸気発生部71で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御し、制御弁77は、蒸気発生部72で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御するようになっている。配管ケース66の内部には、各蒸気発生部70〜72と各制御弁75〜77を接続する枝配管81,82,83と、各蒸気発生部70〜72から各制御弁75〜77を経て供給された成膜材料の蒸気を、合流させて蒸着ヘッド65に供給する合流配管85が設けられている。
The three
各蒸気発生部70〜72は、いずれも同様の構成を有しており、図6に示すように、蒸気発生部70〜72は、側面に複数のヒータ90が取り付けられた、全体を一体的に加熱可能なヒータブロック91を有している。ヒータブロック91全体は、ヒータ90によって、成膜材料を蒸発させることができる温度に加熱される。
Each of the
ヒータブロック91の内部中央には、有機EL素子Aの発光層3の成膜材料(蒸着材料)を充填可能な材料容器92が配置されており、ヒータブロック91の熱によって、この材料容器92に充填された成膜材料が蒸発させられるようになっている。また、ヒータブロック91の側面には、Arなどのキャリアガスを供給するキャリアガス供給配管93が接続されている。ヒータブロック91の内部には、このキャリアガス供給配管93から供給されたキャリアガスを、ヒータブロック91の内部において迂回させ、十分な距離を通過した後、材料容器92に供給させるキャリアガス経路94が形成されている。このため、キャリアガス供給配管93から供給されたキャリアガスは、キャリアガス経路94を通過することにより、ほぼヒータブロック91と同温度にまで昇温されてから、材料容器92に供給されるようになっている。なお、成膜材料を充填する場合、容器本体32の下部に形成されたゲートバルブ等(図示せず)を介して蒸気発生室31内を一旦大気開放し、各蒸気発生部70〜72の材料容器92に対する成膜材料の補充を行う。但し、処理室30と蒸気発生室31は上述の隔壁33によって仕切られているので、このような成膜材料の充填時においても、処理室30内は減圧されており、真空断熱状態が維持される。
In the center of the
各制御弁75〜77は、開閉操作を行うことにより、各蒸気発生部70〜72で蒸発させられてキャリアガスと一緒に各枝配管81〜83を経て供給される成膜材料の蒸気を、合流配管85側に供給する状態と、供給しない状態とに適宜切り替えることが可能である。制御弁75〜77には、ベローズ弁、ダイアフラム弁などを用いることができる。この制御弁75〜77の開閉操作によって、各蒸気発生部70〜72で蒸発させられた成膜材料の蒸気が、任意の組み合わせで合流配管85にて合流されるようになっている。そして、こうして合流配管85にて合流された成膜材料の蒸気が、処理室30と蒸気発生室31の外部に出ることなく、そのまま、蒸着ヘッド65上面の蒸気噴出口80から噴出させられるようになっている。なお、代表して第1の蒸着ユニット55について説明したが、他の蒸着ユニット56〜60も同様の構成である。
Each of the
その他、図2に示す仕事関数調整層の成膜装置15は、蒸着によって基板Gの表面に対して仕事関数調整層を成膜するように構成されている。エッチング装置17は、成膜された各層などをエッチングするように構成されている。スパッタリング装置19は、Agなどの電極材料をスパッタリングして、陰極2を形成させるように構成されている。CVD装置21は、窒化膜などからなる封止膜を、CVD等によって成膜し有機EL素子Aの封止を行うものである。
In addition, the work function adjusting
さて、以上のように構成された成膜システム10において、ローダ11を介して搬入された基板Gが、トランスファーチャンバ12によって、先ず、蒸着装置13に搬入される。この場合、基板Gの表面には、例えばITOからなる陽極1が所定のパターンで予め形成されている。
In the
そして、蒸着装置13では、表面(成膜面)を下に向けた姿勢にして基板保持部47で基板Gが保持される。なお、このように基板Gが蒸着装置13に搬入される前に、蒸着装置13の処理室30と蒸気発生室31の内部は、真空ポンプ36、41の稼動により、いずれも予め所定の圧力に減圧されている。
In the
そして、減圧された蒸気発生室31内において、各蒸気発生部70〜72で蒸発させられた成膜材料の蒸気が、制御弁75〜77の開閉操作によって、任意の組み合わせで合流配管85にて合流され、蒸気発生室31の外部に出ることなく、そのまま蒸着ヘッド65に供給される。こうして蒸着ヘッド65に供給された成膜材料の蒸気が、処理室30内において、蒸着ヘッド65上面の蒸気噴出口80から噴出される。
Then, in the decompressed
また一方、減圧された処理室30内においては、基板保持部47で保持された基板Gが、図3中の右向きに搬送されていく。そして、移動中に、蒸着ヘッド65上面の蒸気噴出口80から成膜材料の蒸気が供給されて、基板Gの表面に発光層3が成膜・積層されていく。
On the other hand, the substrate G held by the
そして、蒸着装置13において発光層3を成膜させた基板Gは、トランスファーチャンバ14によって、次に、成膜装置15に搬入される。こうして、成膜装置15では、基板Gの表面に仕事関数調整層が成膜される。
Then, the substrate G on which the
次に、トランスファーチャンバ16によって、基板Gはエッチング装置17に搬入され、各成膜の形状等が調整される。次に、トランスファーチャンバ18によって、基板Gはスパッタリング装置19に搬入され、陰極2が形成される。次に、トランスファーチャンバ20によって、基板GはCVD装置21に搬入され、有機EL素子Aの封止が行われる。こうして製造された有機EL素子Aが、トランスファーチャンバ22、アンローダ23を介して、成膜システム10外に搬出される。
Next, the substrate G is carried into the
以上の成膜システム10にあっては、蒸着装置13において、蒸気発生部70〜72で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を、処理室30と蒸気発生室31の外部に出さずに蒸気噴出口80に供給させることができ、成膜材料の蒸気を真空断熱の状態を維持して温度低下させること無く蒸着ヘッド65に送ることができる。このため、枝配管81,82,83や各制御弁75〜77、合流配管85などにおける成膜材料の析出を防止でき、蒸着ヘッド65からの蒸気の供給量が安定し、蒸着速度の低下が回避される。また、配管ケース66を一体的に加熱することによって、枝配管81,82,83や各制御弁75〜77、合流配管85などを加熱するヒータも省略でき、装置コスト、ランニングコストを低くでき、装置も小型にできる。
In the above
また、図示のように蒸着ヘッド65の下方に配管ケース66、蒸気発生部70,71,72、制御弁75、76,77を一体的に取り付けた蒸着ユニット55〜60を採用すれば、各蒸着ユニット55〜60をコンパクトに構成できる。また、各蒸着ユニット55〜60をそれぞれ一体的に取り出すことにより、メンテナンスも容易になる。
Moreover, if the vapor deposition units 55-60 which integrally attached the piping
また、図6に示したように、蒸気発生部70,71,72を一体的に加熱可能なヒータブロック91とし、このヒータブロック91の内部に材料容器92とキャリアガス経路94を配置すれば、キャリアガスのプリヒートのためのヒータも省略でき、省スペース化が図れる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 6, if the
以上、本発明の好ましい実施の形態の一例を説明したが、本発明は図示の形態に限定されない。当業者であれば、特許請求の範囲に記載された思想の範疇内において、各種の変更例または修正例に相到し得ることは明らかであり、それらについても当然に本発明の技術的範囲に属するものと了解される。例えば、有機EL素子Aの発光層3の蒸着装置13に基づいて説明したが、本発明は、その他の各種電子デバイス等の処理に利用される蒸着装置に適用することができる。
As mentioned above, although an example of preferable embodiment of this invention was demonstrated, this invention is not limited to the form of illustration. It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various changes or modifications can be made within the scope of the ideas described in the claims, and these are naturally within the technical scope of the present invention. It is understood that it belongs. For example, although it demonstrated based on the
処理の対象となる基板Gは、ガラス基板、シリコン基板、角形、丸形等の基板など、各種基板に適用できる。また、基板以外の被処理体にも適用できる。
The substrate G to be processed can be applied to various substrates such as a glass substrate, a silicon substrate, a square shape, a round shape, and the like. Further, the present invention can be applied to a target object other than the substrate.
図2では、基板Gの搬送方向に沿って、ローダ11、トランスファーチャンバ12、発光層3の蒸着装置13、トランスファーチャンバ14、仕事関数調整層の成膜装置15、トランスファーチャンバ16、エッチング装置17、トランスファーチャンバ18、スパッタリング装置19、トランスファーチャンバ20、CVD装置21、トランスファーチャンバ22、アンローダ23を直列に順に並べた構成の成膜システム10を示した。しかし、図7に示すように、トランスファーチャンバ100の周囲に、例えば、基板ロードロック装置101、スパッタリング蒸着成膜装置102、アライメント装置103、エッチング装置104、マスクロードロック装置105、CVD装置106、基板反転装置107、蒸着成膜装置108を配置した構成の成膜システム109としても良い。各処理装置の台数・配置は任意に変更可能である。
In FIG. 2, along the transport direction of the substrate G, a
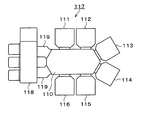
例えば、図8に示すように、トランスファーチャンバ110の周りに6台の処理装置111〜116を設けた処理システム117において本発明を適用することも可能である。なお、この図8に示す処理システム117では、搬入出部118から、2つのロードロック室119を介して、基板Gをトランスファーチャンバ110に搬入出させ、トランスファーチャンバ110によって、各処理装置111〜116に対して基板Gを搬入出させるようになっている。
For example, as shown in FIG. 8, the present invention can be applied to a
また例えば、図9に示すように、搬入出部120からロードロック室121を介して、各処理装置122、122に対して基板Gを直接(トランスファーチャンバを介さずに)搬入出させるように構成された処理システム123において本発明を適用することも可能である。このように、処理システムに設ける処理装置の台数、配置は任意である。
Further, for example, as shown in FIG. 9, the substrate G is configured to be directly loaded into and unloaded from the loading /
また、蒸着装置13内において、搬入口50から処理室30内に搬入された基板Gが、処理後、搬出口51から搬出される例を示した。しかし、搬入口と搬出口を兼用する搬入出口を設け、搬入出口から処理室30内に搬入された基板Gが、処理後、再び搬入出口から搬出されても良い。なお、処理後は、なるべく短時間で基板Gを処理室30内から搬出できるような搬送経路とすることが好ましい。
Moreover, in the
なお、各蒸着ユニット55〜60の蒸着ヘッド65から噴出される材料は同じでも異なっていても良い。また、蒸着ユニットの連数は6つに限らず、任意である。また、蒸着ユニットに設けられる蒸気発生部や制御弁の数も任意である。
In addition, the material ejected from the
本発明は、例えば有機EL素子の製造分野に適用できる。 The present invention can be applied to the field of manufacturing organic EL elements, for example.
A 有機EL素子
G ガラス基板
10 処理システム
11 ローダ11
12、14、16、18、20、22 トランスファーチャンバ
13 発光層の蒸着装置
15 仕事関数調整層の成膜装置
17 エッチング装置
19 スパッタリング装置
21 CVD装置
23 アンローダ
30 処理室
31 蒸気発生室
32 容器本体
33 隔壁
35、40 排気孔
36、41 真空ポンプ
45 ガイド部材
47 基板保持部
55〜60 蒸着ユニット
65 蒸着ヘッド
66 配管ケース
70〜72 蒸気発生部
75〜77 制御弁
80 蒸気噴出口
81〜83 枝配管
85 合流配管
90 ヒータ
91 ヒータブロック
92 材料容器
93 キャリアガス供給配管
94 キャリアガス経路
A Organic EL element
12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22
Claims (11)
被処理体を成膜処理する減圧可能な処理室と、
前記処理室と隣接して配置される減圧可能な蒸気発生室と、
前記処理室の内部に露出し、前記処理室の内部に向けて蒸気を噴出する蒸気噴出口と、
前記蒸気噴出口が任意の面に形成された蒸着ヘッドと、
前記蒸気発生室に配置され、成膜材料を蒸発させる蒸気発生部と、
前記蒸気発生室内に少なくともその一部が配置され、前記蒸気発生部と前記蒸気噴出口を連通させる配管と、
前記配管に設けられ、成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御する制御弁と、
前記蒸気発生部で蒸発させた成膜材料の蒸気を前記蒸気噴出口に供給させるためのキャリアガスを、前記蒸気発生部に供給するキャリアガス供給配管とを備え、
前記蒸気発生部は、全体を一体的に加熱可能なヒータブロックを有し、前記ヒータブロックの内部に、成膜材料を充填可能な材料容器と、前記キャリアガス供給配管から供給されたキャリアガスを前記材料容器に通すキャリアガス経路を配置し、
前記蒸着ヘッドを、前記蒸気噴出口が形成された面を前記処理室内に露出させた姿勢で前記処理室と前記蒸気発生室とを仕切る隔壁に支持し、
前記配管は、前記処理室の外部及び前記蒸気発生室の外部に露出しないことを特徴とする、蒸着装置。 A vapor deposition apparatus for performing a film formation process on an object to be processed by vapor deposition,
A processing chamber capable of depressurization for film-forming the object to be processed;
A depressurizable steam generation chamber disposed adjacent to the processing chamber;
A steam outlet that is exposed to the inside of the processing chamber and jets steam toward the inside of the processing chamber;
A vapor deposition head in which the vapor outlet is formed on an arbitrary surface;
A vapor generation unit disposed in the vapor generation chamber for evaporating the film forming material;
At least a part of the steam generation chamber is disposed, and a pipe for communicating the steam generation unit and the steam outlet;
A control valve provided in the pipe for controlling the supply of vapor of the film forming material ;
A carrier gas for supplying the vapor of the film-forming material evaporated in the vapor generation part to the vapor outlet, and a carrier gas supply pipe for supplying the vapor generation part ,
The steam generation unit includes a heater block capable of integrally heating the whole, and a material container that can be filled with a film forming material inside the heater block and a carrier gas supplied from the carrier gas supply pipe. Arrange a carrier gas path through the material container;
The vapor deposition head is supported by a partition wall that partitions the processing chamber and the vapor generation chamber in a posture in which the surface on which the vapor ejection port is formed is exposed in the processing chamber,
The said piping is not exposed to the exterior of the said process chamber, and the said vapor generation chamber, The vapor deposition apparatus characterized by the above-mentioned.
被処理体を成膜処理する処理室と、成膜材料を蒸発させる蒸気発生室とを隣接させて配置し、
前記処理室の内部と前記蒸気発生室の内部を減圧させる排気機構と、
前記処理室の内部に成膜材料の蒸気を供給する蒸着ユニットとを設け、
前記蒸着ユニットは、
前記処理室の内部に向けて蒸気を噴出する蒸気噴出口と、
前記蒸気噴出口が任意の面に形成された蒸着ヘッドと、
前記蒸気発生室に成膜材料を蒸発させる蒸気発生部と、
成膜材料の蒸気の供給を制御する制御弁と、
前記蒸気発生部で発生させた成膜材料の蒸気を、前記処理室と前記蒸気発生室の外部に出さずに、前記蒸気噴出口に供給させる流路と
前記蒸気発生部で蒸発させた成膜材料の蒸気を前記蒸気噴出口に供給させるためのキャリアガスを、前記蒸気発生部に供給するキャリアガス供給配管とを備え、
前記蒸気発生部は、全体を一体的に加熱可能なヒータブロックを有し、前記ヒータブロックの内部に、成膜材料を充填可能な材料容器と、前記キャリアガス供給配管から供給されたキャリアガスを前記材料容器に通すキャリアガス経路を配置し、
前記蒸着ヘッドを、前記蒸気噴出口が形成された面を前記処理室内に露出させた姿勢で前記処理室と前記蒸気発生室とを仕切る隔壁に支持することを特徴とする、蒸着装置。 A vapor deposition apparatus for performing a film formation process on an object to be processed by vapor deposition,
A processing chamber for forming a film to be processed and a vapor generation chamber for evaporating a film forming material are disposed adjacent to each other,
An exhaust mechanism for depressurizing the interior of the processing chamber and the interior of the steam generation chamber;
An evaporation unit for supplying vapor of a film forming material to the inside of the processing chamber;
The vapor deposition unit includes:
A steam outlet for ejecting steam toward the inside of the processing chamber;
A vapor deposition head in which the vapor outlet is formed on an arbitrary surface;
A vapor generating section for evaporating the film forming material in the vapor generating chamber;
A control valve for controlling the supply of vapor of the film forming material;
A flow path for supplying the vapor of the film-forming material generated in the vapor generating section to the vapor outlet without taking the vapor out of the processing chamber and the vapor generation chamber;
A carrier gas for supplying the vapor of the film-forming material evaporated in the vapor generation part to the vapor outlet, and a carrier gas supply pipe for supplying the vapor generation part ,
The steam generation unit includes a heater block capable of integrally heating the whole, and a material container that can be filled with a film forming material inside the heater block and a carrier gas supplied from the carrier gas supply pipe. Arrange a carrier gas path through the material container;
The vapor deposition apparatus, wherein the vapor deposition head is supported by a partition wall that partitions the processing chamber and the vapor generation chamber in a posture in which a surface on which the vapor jet port is formed is exposed in the processing chamber .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011236147A JP5511767B2 (en) | 2011-10-27 | 2011-10-27 | Vapor deposition equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011236147A JP5511767B2 (en) | 2011-10-27 | 2011-10-27 | Vapor deposition equipment |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006269085A Division JP5173175B2 (en) | 2006-09-29 | 2006-09-29 | Vapor deposition equipment |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012026041A JP2012026041A (en) | 2012-02-09 |
| JP2012026041A5 JP2012026041A5 (en) | 2012-12-13 |
| JP5511767B2 true JP5511767B2 (en) | 2014-06-04 |
Family
ID=45779301
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011236147A Active JP5511767B2 (en) | 2011-10-27 | 2011-10-27 | Vapor deposition equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5511767B2 (en) |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001308082A (en) * | 2000-04-20 | 2001-11-02 | Nec Corp | Method of vaporizing liquid organic material and method of growing insulation film |
| JP3684343B2 (en) * | 2001-09-25 | 2005-08-17 | 株式会社日本ビーテック | Molecular beam source cell for thin film deposition |
| JP2003193224A (en) * | 2001-12-21 | 2003-07-09 | Sharp Corp | Thin film manufacturing apparatus, thin film multiple layer apparatus using the same, and thin film manufacturing method |
| JP2004010990A (en) * | 2002-06-10 | 2004-01-15 | Sony Corp | Thin-film forming apparatus |
| US7067170B2 (en) * | 2002-09-23 | 2006-06-27 | Eastman Kodak Company | Depositing layers in OLED devices using viscous flow |
| JP4013859B2 (en) * | 2003-07-17 | 2007-11-28 | 富士電機ホールディングス株式会社 | Organic thin film manufacturing equipment |
| JP4366226B2 (en) * | 2004-03-30 | 2009-11-18 | 東北パイオニア株式会社 | Organic EL panel manufacturing method, organic EL panel film forming apparatus |
| JP2006057173A (en) * | 2004-08-24 | 2006-03-02 | Tohoku Pioneer Corp | Film deposition source, vacuum film deposition apparatus and method for producing organic el panel |
| JP2006104497A (en) * | 2004-10-01 | 2006-04-20 | Hitachi Zosen Corp | Vapor deposition apparatus |
-
2011
- 2011-10-27 JP JP2011236147A patent/JP5511767B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012026041A (en) | 2012-02-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5173175B2 (en) | Vapor deposition equipment | |
| JP5043394B2 (en) | Vapor deposition apparatus and operation method thereof | |
| KR101230997B1 (en) | Substrate processing system | |
| KR101113128B1 (en) | Method for controlling film forming apparatus, film forming method, film forming apparatus, organic el electronic device and storage medium having program for controlling film forming apparatus stored therein | |
| JP5203584B2 (en) | Film forming apparatus, film forming system, and film forming method | |
| WO2012039383A1 (en) | Vacuum processing apparatus and method for forming organic thin film | |
| WO2010113659A1 (en) | Film forming device, film forming method, and organic el element | |
| US20100259162A1 (en) | Film forming device control method, film forming method, film forming device, organic el electronic device, and recording medium storing its control program | |
| KR101088828B1 (en) | Deposition apparatus for organic el and evaporating apparatus | |
| KR20080098813A (en) | Temperature control unit of canister, device for supplying organic and apparatus for organic vapor deposition by using the same | |
| JP2008038224A (en) | Film deposition apparatus, film deposition system, and film deposition method | |
| JP5511767B2 (en) | Vapor deposition equipment | |
| JP5411243B2 (en) | Vapor deposition equipment | |
| JP5051870B2 (en) | Light emitting element manufacturing apparatus and light emitting element manufacturing method | |
| JP2004220852A (en) | Film forming device and manufacturing device of organic el element | |
| KR20090015380A (en) | Canister for providing organic compounds in chamber | |
| JP5697500B2 (en) | Vacuum deposition apparatus and thin film forming method | |
| WO2011040538A1 (en) | Substrate processing system | |
| JP2010242175A (en) | Film deposition system | |
| JP2010144212A (en) | Material supply apparatus and material supply method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20111027 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121030 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130502 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131022 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131212 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140311 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140325 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5511767 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |