JP5328169B2 - Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system - Google Patents
Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5328169B2 JP5328169B2 JP2008027664A JP2008027664A JP5328169B2 JP 5328169 B2 JP5328169 B2 JP 5328169B2 JP 2008027664 A JP2008027664 A JP 2008027664A JP 2008027664 A JP2008027664 A JP 2008027664A JP 5328169 B2 JP5328169 B2 JP 5328169B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- conversion element
- wiring
- thin film
- signal
- tft
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Light Receiving Elements (AREA)
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、薄膜トランジスタ(TFT)及び変換素子を有する撮像装置及びその製造方法、放射線撮像システムに関するものである。 The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus having a thin film transistor (TFT) and a conversion element, a manufacturing method thereof, and a radiation imaging system.
近年、TFT(薄膜トランジスタ)を用いた液晶パネルの製造技術は、可視光等の光やX線等の放射線を電気信号に変換する変換素子を有するエリアセンサーへと利用されている。 In recent years, a manufacturing technique of a liquid crystal panel using a TFT (thin film transistor) is used for an area sensor having a conversion element that converts light such as visible light or radiation such as X-rays into an electric signal.
特許文献1には、TFTアレー上に第一保護絶縁膜と、第一保護絶縁膜の上に接地配線に繋ぎ、その一部がTFTゾーンを遮蔽するように構成される容量電極と、第一保護絶縁膜の上に形成された容量電極を覆う第二保護絶縁膜が記載されている。そして、第二保護絶縁膜の上にTFTのドレイン電極に繋ぐように画像電極が形成された装置が記載されている。また、特許文献2には、光電変換素子に発生した信号電荷を受けるゲート及びゲートに蓄積された信号電荷に応じた信号を読み出すためのソース・ドレインを有する読出用電界効果トランジスタを配置した装置が記載されている。
しかしながら、従来の構成において、複数のTFTを配置した場合は、信号配線にゲート絶縁膜を介して交差する配線が増加し、寄生容量が増加する。そのため、S/Nが低下するという問題点があった。 However, in the conventional configuration, when a plurality of TFTs are arranged, the number of wirings that intersect the signal wiring via the gate insulating film increases, and the parasitic capacitance increases. Therefore, there is a problem that S / N decreases.
そのため、本発明の目的は、変換素子と複数のTFTとを有する画素が配列された撮像装置において、配線間の容量を低減し、高いS/Nが得られる撮像装置を提供することである。 Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an imaging device in which a capacitance between wirings is reduced and a high S / N can be obtained in an imaging device in which pixels having a conversion element and a plurality of TFTs are arranged.
本発明の撮像装置は、絶縁基板と、各々が、前記絶縁基板の上に配置された変換素子と、前記絶縁基板と前記変換素子との間に配置された複数の薄膜トランジスタと、を含み、前記複数の薄膜トランジスタが、前記変換素子にゲート電極が電気的に接続された読み出し用薄膜トランジスタと、前記読み出し用薄膜トランジスタのソース電極又はドレイン電極に電気的に接続された選択用薄膜トランジスタと、を含む複数の画素と、前記絶縁基板と前記変換素子との間に配置され、前記選択用薄膜トランジスタが選択されることにより入射した光又は放射線を前記変換素子が変換して得られる電荷に対応した信号が転送される信号配線と、前記選択用薄膜トランジスタのゲート電極に駆動信号を供給するゲート配線と、を含む撮像装置であって、前記複数の薄膜トランジスタ及び前記信号配線と前記変換素子との間に複数の絶縁膜が配置されており、前記ゲート配線は前記複数の絶縁膜の間に配置されていることを特徴とする。
The imaging apparatus of the present invention includes an insulating substrate , each of the conversion elements disposed on the insulating substrate, and a plurality of thin film transistors disposed between the insulating substrate and the conversion element, A plurality of pixels, wherein a plurality of thin film transistors includes a reading thin film transistor whose gate electrode is electrically connected to the conversion element, and a selection thin film transistor electrically connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the reading thin film transistor When the disposed between the insulating substrate and the transducer, signal corresponding to charge the transducer light or radiation incident is obtained by converting by said selection thin film transistor is selected to be transferred an imaging apparatus comprising a signal line, and a gate wiring for supplying a driving signal to the gate electrode of the selection TFT Wherein there is disposed a plurality of insulating films between the plurality of thin film transistors and the signal wiring and the conversion element, the gate line may be disposed between the plurality of insulating films.
なお、本願において、放射線はX線,α線,β線,γ線等を含む。 In the present application, radiation includes X-rays, α-rays, β-rays, γ-rays, and the like.
本発明によれば、上記の構成を有することにより、配線間の容量を低減し、高いS/Nが得られる撮像装置を提供することができる。 According to the present invention, by having the above-described configuration, it is possible to provide an imaging device that can reduce the capacitance between wirings and obtain high S / N.
本発明の撮像装置は可視光,赤外光等の光、又はX線、α線、β線、γ線等の放射線を電気信号に変換することができる。 The imaging apparatus of the present invention can convert light such as visible light and infrared light, or radiation such as X-rays, α-rays, β-rays, and γ-rays into electrical signals.
本発明の変換素子は、可視光、赤外光等の光、又はX線、α線、β線、γ線等の放射線を電荷に変換する。可視光等の光を電気信号に変換する場合は、例えば水素化アモルファスシリコンなどによる光電変換素子が用いられる。光電変換素子は、MIS型変換素子やPIN型変換素子が用いられる。X線、γ線、α線等の放射線を電気信号に変換する場合は、放射線を可視光等の光電変換可能な光に変換する波長変換層としてのシンチレーター層が光電変換素子に組み合わせられる。また、X線等の放射線を直接変換するアモルファスセレン、カドミウムテルル、ヨウ化鉛などによる直接変換素子が用いられる。 The conversion element of the present invention converts light such as visible light and infrared light, or radiation such as X-rays, α rays, β rays, and γ rays into electric charges. When light such as visible light is converted into an electrical signal, a photoelectric conversion element made of, for example, hydrogenated amorphous silicon is used. As the photoelectric conversion element, an MIS type conversion element or a PIN type conversion element is used. In the case of converting radiation such as X-rays, γ-rays, and α-rays into electrical signals, a scintillator layer as a wavelength conversion layer that converts the radiation into light capable of photoelectric conversion such as visible light is combined with the photoelectric conversion element. In addition, a direct conversion element made of amorphous selenium, cadmium tellurium, lead iodide or the like that directly converts radiation such as X-rays is used.
(第1の実施形態)
図1〜図12は、本発明に関わる第1の実施形態の、画素の平面図、断面図と簡易等価回路図を表したものである。
(First embodiment)
1 to 12 show a plan view, a sectional view, and a simplified equivalent circuit diagram of a pixel according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
本実施形態の要点は、第一に、スイッチ素子と変換素子との間には複数の絶縁膜が配置された積層構造を有しており、ゲート配線及び信号配線の少なくとも一方が、絶縁膜に挟まれた領域に配置されているということである。第二に、スイッチ素子は、複数の薄膜トランジスタによるソースフォロアー型の構成を有するということである。複数の薄膜トランジスタは、信号配線と電気的に接続された読み出し用薄膜トランジスタと、電源供給配線及び読み出し用薄膜トランジスタTFTと電気的に接続された選択用薄膜トランジスタと、で構成される。この2点は全ての実施形態に共通している。また、リセット配線と電気的に接続されたリセット用薄膜トランジスタを有する場合、変換素子内の電荷をリセットできるため好適である。 The main point of this embodiment is that, first, it has a laminated structure in which a plurality of insulating films are arranged between the switch element and the conversion element, and at least one of the gate wiring and the signal wiring is formed on the insulating film. That is, it is arranged in the sandwiched area. Secondly, the switch element has a source follower type configuration with a plurality of thin film transistors. The plurality of thin film transistors includes a reading thin film transistor electrically connected to the signal wiring, and a selection thin film transistor electrically connected to the power supply wiring and the reading thin film transistor TFT. These two points are common to all the embodiments. In addition, a reset thin film transistor electrically connected to the reset wiring is preferable because the charge in the conversion element can be reset.
図1は、本発明の第1の実施形態に関わる画素の平面図で、変換素子1と複数の薄膜トランジスタ(2、3、4)が対となる一画素を示したものである。不図示であるが、画素は、例えば、2000×2000個配列される等、数は限定されない。そして、例えば、行又は列毎に画素がそれぞれ配線に共通に接続される。ここで、図22を用いて、1本の信号配線sigの寄生容量の影響について、説明する。g1、g2は、ゲート配線を示す。Rsig1、Rsig2、・・・RsigNは、信号配線材料の抵抗成分及び配線の断面積や長さによる抵抗成分を示す。Csig1、Csig2、・・・CsigNは、信号配線と交差するゲート配線によって生ずる容量などで構成された信号配線の寄生容量を示す。Sは、信号処理回路を示す。本発明のような絶縁基板上に複数の画素を配列した大面積の撮像装置は、配線が20〜40cm程度の長さを有し、10μm程度の幅を有する。従って、半導体チップ上に形成される回路等の1μm以下の幅の微細配線の寄生容量の影響より大きくなる。更に、半導体チップの場合と異なり、信号配線と交差する変換素子の電極によって生ずる容量も加わる。撮像装置は、微少な電荷を転送するが、信号配線の抵抗や容量が増加すると、ノイズが増加しやすくなり、S/Nが低下してしまう。また、本実施形態に示すような、ソースフォロアー型の変換素子では、転送する信号が増幅されるため、転送速度が必要になる。このため、高速駆動する際などは、時定数となる信号配線の抵抗と容量の積(Rsig×Csig)を低減する事が必要になる。信号配線とゲート配線の間にゲート絶縁膜が配置される構成においては、0.1μm程度で形成されるTFTのゲート絶縁膜を厚くすることで配線の交差部に生ずる寄生容量を低減することができるが、TFTのオン特性が低下するため好ましくない。 FIG. 1 is a plan view of a pixel according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and shows a pixel in which a conversion element 1 and a plurality of thin film transistors (2, 3, 4) are paired. Although not shown, the number of pixels is not limited, for example, 2000 × 2000 pixels are arranged. For example, the pixels are commonly connected to the wiring for each row or column. Here, the influence of the parasitic capacitance of one signal wiring sig will be described with reference to FIG. g1 and g2 denote gate wirings. R sig1 , R sig2 ,... R sigN indicate the resistance component of the signal wiring material and the resistance component depending on the cross-sectional area and length of the wiring. C sig1 , C sig2 ,..., C sigN indicate the parasitic capacitance of the signal wiring configured by the capacitance generated by the gate wiring intersecting with the signal wiring. S indicates a signal processing circuit. In a large-area imaging device in which a plurality of pixels are arranged on an insulating substrate as in the present invention, the wiring has a length of about 20 to 40 cm and a width of about 10 μm. Therefore, it becomes larger than the influence of the parasitic capacitance of the fine wiring having a width of 1 μm or less such as a circuit formed on the semiconductor chip. Further, unlike the case of the semiconductor chip, a capacitance generated by the electrode of the conversion element intersecting with the signal wiring is also added. The imaging device transfers a minute charge. However, if the resistance and capacitance of the signal wiring increase, noise tends to increase and the S / N decreases. In addition, in the source follower type conversion element as shown in the present embodiment, since the signal to be transferred is amplified, a transfer speed is required. For this reason, when driving at high speed, it is necessary to reduce the product (Rsig × Csig) of the resistance and capacitance of the signal wiring, which becomes a time constant. In the configuration in which the gate insulating film is disposed between the signal wiring and the gate wiring, the parasitic capacitance generated at the intersection of the wiring can be reduced by increasing the thickness of the gate insulating film of the TFT formed with about 0.1 μm. However, it is not preferable because the on-characteristics of the TFT deteriorate.
図1に示すように、一画素には、読み出し用薄膜トランジスタ2と、電源供給配線13及び読み出し用TFTと電気的に接続する選択用薄膜トランジスタ3と、リセット配線と電気的に接続されたリセット用薄膜トランジスタ4の3つのTFTが配置されている。以下、読み出し用薄膜トランジスタ2は読み出し用TFT2と表記し、選択用薄膜トランジスタ3は選択用TFT3と表記し、リセット用薄膜トランジスタ4はリセット用TFT4と表記する。なお、以下の記載で薄膜トランジスタのソース電極及びドレイン電極は、電流の向きによって相互に読み替え可能である。
As shown in FIG. 1, one pixel includes a readout
読み出し用TFT2は、ゲート電極が変換素子の一方の電極に接続され、変換素子に入射した光や放射線の量に応じて動作する。ここで、変換素子の一方の電極とは、後述の図3で示される下部電極である第5の導電層51である。そして、読み出し用TFT2のソース電極18と信号配線12はスルーホール16を介して接続されている。選択用TFT3は、オンされて電源供給配線13から供給された電圧を変換素子1の電位に対応した電圧を信号配線12に供給する。そして、選択用TFT3のソース電極18はスルーホール16を介して電源供給配線13に接続されている。リセット用TFT4は、変換素子に蓄積された電荷が読出された後にオンされる。そして、リセット配線14から供給された電圧(リセット電位)により変換素子内の電荷がリセットされる。リセット用TFT4のソース電極18は、スルーホールを介してリセット配線14と接続されている。
The
変換素子1は、各TFTの上部に配置されている。変換素子1の下部電極は、スルーホール16を介して読み出し用TFT2のゲート電極17に接続されている。さらに、変換素子1の下部電極は、スルーホール16を介してリセット用TFT4のドレイン電極19に接続されている。ここで、変換素子の一方の電極とは、後述の図3で示される下部電極である第5の導電層51である。
The conversion element 1 is disposed above each TFT. The lower electrode of the conversion element 1 is connected to the
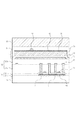
図2は、図1中のA−A’線に沿った断面図である。図示された読み出し用TFT2及び選択用TFT3は、非晶質シリコンを用いたボトムゲート型TFTであり、絶縁基板上に配置されている。各TFTは、ゲート電極である第1の導電層41、ゲート絶縁膜である第1の絶縁膜31、第1の半導体層61、第1の不純物半導体層62及び第2の導電層42から構成されている。図1における第1のゲート配線11a及び第2のゲート配線11bは、絶縁基板21と第1の絶縁膜31との間に配置されている(不図示)。第1のゲート配線11aは、選択用TFT3のゲート電極17に駆動信号を供給するゲート配線である。第2のゲート配線11bは、リセット用TFT4のゲート電極17に駆動信号を供給するゲート配線である。
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view taken along line A-A ′ in FIG. 1. The illustrated
変換素子1は、第5の導電層51、変換素子の絶縁膜33、第2の半導体層71、オーミックコンタクト層である第2の不純物半導体層72、透明電極層である第6の導電層52から成るMIS型変換素子である。第5の導電層51は、変換素子1の一方の電極である下部電極である。変換素子1は、複数の薄膜トランジスタ上に配置されている。バイアス配線である第7の導電層53は、変換素子1に電圧を印加するために配置されている。第6の導電層52がバイアス配線を兼ねる場合は、第7の導電層53は無くても良い。そして、保護層34、シンチレーター層35が変換素子1上に配置されている。
The conversion element 1 includes a fifth
第2の絶縁膜32は、変換素子と複数のTFTとの間に配置され、複数の絶縁膜(32a、32b)の積層膜からなる。信号配線、リセット配線及び電源供給配線は、第2の絶縁膜間に配置された第3の導電層43により構成されている。第2の絶縁膜32は、低誘電率でかつ、膜厚を厚く形成できる材料が望ましい。本実施形態の第2の絶縁膜32は、平坦性を有する有機系の絶縁膜である。このような構成は、画素内で大きい面積を有するTFTの特にチャネル領域、ソース電極及びドレイン電極と、上部に形成する各配線や変換素子との容量を低減するために有効である。そして、TFTが複数配置されている場合、配線数が増加し、配線の交差部が増加するが、配線間の容量の合計を低減するために有効である。さらに、TFT上部に形成する各配線の幅を広くしてTFTを覆う構成にして、配線抵抗を積極的に低減しようとした場合に、特に効果的である。この結果、配線間の容量を低減でき、また、図1に示すような各配線の線幅を無理のない線幅で形成することができる。本図では各配線は極端に太くする構成にはしていないが、例えば信号配線やリセット配線、電源供給配線をTFTのゲート電極に重なるような配置や、幅が広い配線とした場合であっても、第2の絶縁膜が間に配置されているため、容量の増加を抑制できる。このような構成によって、各配線の抵抗や容量を低減できるため、抵抗と容量の積からなる配線時定数を下げる事が可能となる。そして、信号配線の抵抗や容量の低減によって、ノイズの少ない画像を得ることができる。また、リセット配線及び電源供給配線の時定数の低減によって、二次元的にアーチファクトのない高品質な画像を得ることができる。ゲート配線についても同様である。ゲート配線を第3の導電層で配置し、信号配線、リセット配線及び電源供給配線を第1の導電層又は第2の導電層で配置し、各TFTや各配線に大胆にオーバーラップさせても、間に介在する第2の絶縁膜の効果により容量の低減や、抵抗の低減が可能となる。この結果、ゲート配線の配線時定数を低減することが可能となり、駆動速度を向上させることができるため、例えば動画撮影などで違和感のない高品質な動画像を提供することが可能となる。
The second insulating
第2の絶縁膜32の材質は、上部に積層する変換素子の製造プロセスを考慮し、耐熱性が高い、アクリル系・ポリイミド系・シロキサン系の膜が望ましい。そして、有機膜は、膜厚を厚くすることが容易であるため、複数の絶縁膜の各々は1μm以上10μm以下、より好ましくは2μm以上10μm以下、最も好ましくは3μm以上10μm以下で形成することが望ましい。また、複数の絶縁膜の合計膜厚が20μmを超えるほど厚くなると、感光性のフォトレジストをコーティングする際に、段差が大きいことでレジストの密着性が悪い領域が発生してしまう。また、段差部の凹部の箇所だけレジストの膜厚が厚くなり、その後の露光、現像プロセスでフォトレジストが感光しきれず、パターン残りが発生してしまう。従って、複数の絶縁膜の合計膜厚を20μm以下にする必要がある。また、変換素子の絶縁基板側とは反対側が放射線の入射側であるため、透明性は重要視されない。このため、耐熱性があれば光透過性はなくても良い。このため、例えば、有機膜の中に感光剤を含んでいても問題なく、感光性を有する有機膜を使用することで、フォトリソグラフィー法により加工でき、プロセスを簡略化できる。また、無機膜であれば、SiO2やTEOSなどのCVD膜で1μm以上形成することが望ましい。
The material of the second insulating
また、各TFTのソース電極、ドレイン電極及びチャネル領域は、第2の絶縁膜32で直接覆われているが、各TFTと第2の絶縁膜32との間にTFTの保護膜として無機の絶縁膜を配置してもよい。このような構成により、更にTFTの絶縁性の向上や不純物の特性への影響を低減することができる。この保護膜としての無機の絶縁膜は、薄い膜厚でTFTの保護が可能である。従って、容量を充分に低減するためには第2の絶縁膜を必要とする。
Further, the source electrode, drain electrode, and channel region of each TFT are directly covered with the second insulating
図3は、図1中のB−B’線に沿った断面図である。 FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view taken along line B-B ′ in FIG. 1.
図示されたリセット用TFT4は、非晶質シリコンを用いたボトムゲート型TFTであり、絶縁基板上に配置されている。コンタクト部45は、読み出し用TFT2のゲート電極17と同じ第1の導電層41の一部である。リセット用TFT4及びコンタクト部45は、それぞれスルーホール16を介して変換素子1の下部電極である第5の導電層51に接続されている。第2の絶縁膜のうち、絶縁膜32aのスルーホール16の位置は、絶縁膜32bのスルーホール16の位置とずれている。これは、リソグラフィー法で形成したスルーホール上に導電層を形成した際、条件によってはスルーホールの中央部で段差が形成され、この段差の上に更にスルーホールを形成すると加工が不安定になるためである。
The illustrated
図4は、図1中のF−F’線に沿った断面図である。 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line F-F ′ in FIG. 1.
図示された第1のゲート配線11aは、絶縁基板21上に配置されている。この第1のゲート配線11aと、信号配線12、電源供給配線13及びリセット配線14との間に第1の絶縁膜31と第2の絶縁膜32aとが配置されている。このように、ゲート絶縁膜である第1の絶縁膜31より厚くできる第2の絶縁膜32aを配線間に配置したため、配線の容量を低減することができる。
The illustrated
図5は、第1の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の平面図で、図1とは異なる例を示した画素の平面図である。 FIG. 5 is a plan view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the first embodiment, and is a plan view of a pixel showing an example different from FIG.
図1と異なる点は、第1のゲート配線11aがスルーホール16を介して選択用TFT3のゲート電極17に接続されているということである。そして、第2のゲート配線11bもスルーホール16を介してリセット用TFT4のゲート電極17に接続されている。
The difference from FIG. 1 is that the
図6は、図5中のG−G’線に沿った断面図である。 FIG. 6 is a cross-sectional view taken along line G-G ′ in FIG. 5.
図示された第1のゲート配線11aは、第2の絶縁膜32aと32bとの間に配置されている。信号配線12、電源供給配線13及びリセット配線14は、第1の絶縁膜31と第2の絶縁膜32aとの間に配置されている。図5、図6の構成においても、ゲート絶縁膜である第1の絶縁膜31より厚くできる第2の絶縁膜32aを配線間に配置したため、配線の容量を低減することができる。
The illustrated
図7は、第1の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の平面図で、図1とは異なる例を示した画素の平面図である。 FIG. 7 is a plan view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the first embodiment, and is a plan view of a pixel showing an example different from FIG.
図1と異なる点は、信号配線の配線幅が太いことである。撮像装置は、信号配線の配線抵抗を下げる事で、ノイズを低減することができ、S/Nを向上させることができる。従来の構成では、信号配線の線幅を太くすると、配線抵抗は低減できるが、配線容量が増加してしまうために、逆にS/Nの低下につながる場合がある。しかし、図2,図3のように、信号配線を第2の絶縁膜の複数の絶縁膜間に配置することで、信号配線は、TFTを構成する各電極と容量結合しないため、容量は増加せずに配線抵抗を低減でき、撮像装置のS/Nを向上することが可能となる。特に、層間絶縁膜が低誘電で膜厚が厚ければなお良い。また、信号配線を構成する金属膜の膜厚を厚くしても、その上部に形成する層間絶縁膜が平坦化性を有する事で金属膜の上に被覆性良く形成し、かつ段差なく成膜することが可能になるため、その後で形成する配線の断線や、絶縁膜の絶縁性などに影響しないため良い。 The difference from FIG. 1 is that the wiring width of the signal wiring is large. The imaging apparatus can reduce noise and improve S / N by reducing the wiring resistance of the signal wiring. In the conventional configuration, if the line width of the signal wiring is increased, the wiring resistance can be reduced. However, since the wiring capacity is increased, the S / N may be decreased. However, as shown in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the signal wiring is not capacitively coupled to each electrode constituting the TFT by arranging the signal wiring between the plurality of insulating films of the second insulating film, so that the capacity increases. Therefore, the wiring resistance can be reduced, and the S / N of the imaging apparatus can be improved. In particular, it is better if the interlayer insulating film has a low dielectric constant and a large film thickness. Even if the thickness of the metal film that forms the signal wiring is increased, the interlayer insulating film formed on the upper part of the metal film has a flatness so that it can be formed on the metal film with good coverage and can be formed without any step. Therefore, it is good because it does not affect the disconnection of the wiring to be formed later or the insulating property of the insulating film.
図8は、第1の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の平面図で、図1とは異なる例を示した画素の平面図である。 FIG. 8 is a plan view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the first embodiment, and is a plan view of a pixel showing an example different from FIG.
図1と異なる点は、変換素子に発生した電荷を蓄積する蓄積容量を画素に配置したことである。 The difference from FIG. 1 is that a storage capacitor for storing the charge generated in the conversion element is arranged in the pixel.
蓄積容量81はグランド電位が供給される一方の電極と、変換素子と読み出し用TFTとの間に電気的に接続された他方の電極とを有する。一方の電極は、隣接画素と共通にグランド用配線に接続されている。また、一方の電極は、グランド配線ではなく、リセット配線、バイアス配線又は電源供給配線に接続されてもよい。他方の電極は、読み出し用TFTのゲート電極と同一の導電層で構成されている。
The
蓄積容量は、蓄積容量の電極と、信号配線、リセット配線、バイアス配線及び電源供給配線との間に第2の絶縁膜が配置されているため、配線容量を増加させることなく画素内に配置できる。従って、ノイズを低減することができ、S/Nを向上させることができる。 The storage capacitor can be arranged in the pixel without increasing the wiring capacitance because the second insulating film is arranged between the electrode of the storage capacitor and the signal wiring, reset wiring, bias wiring, and power supply wiring. . Therefore, noise can be reduced and S / N can be improved.
図9は、第1の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の断面図で、図2とは異なる例を示した画素の断面図である。 FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the first embodiment, and is a cross-sectional view of a pixel that shows an example different from FIG.
図2と異なる点は、第2の絶縁膜を3層の積層膜で配置したことである。 The difference from FIG. 2 is that the second insulating film is arranged as a laminated film of three layers.
図9は、図1のA−A’断面線に相当する位置における画素の断面図である。第2の絶縁膜32の絶縁膜32bと絶縁膜32cとの間に選択用TFTに接続された第1のゲート配線11aが配置されている。第1のゲート配線11aは、第4の導電層44により形成されている。このような構成によって、配線の容量を低減することができる。
FIG. 9 is a cross-sectional view of the pixel at a position corresponding to the A-A ′ cross-sectional line of FIG. 1. Between the insulating
図10は、第1の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の断面図で、図9とは異なる例を示した画素の断面図である。 FIG. 10 is a cross-sectional view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the first embodiment, and is a cross-sectional view of a pixel illustrating an example different from FIG.
図9と異なる点は、ゲート配線は図2と同様に第1の導電層で配置し、第2の絶縁膜の2ヶ所の層間部に信号配線を配置したことである。 The difference from FIG. 9 is that the gate wiring is arranged in the first conductive layer as in FIG. 2, and the signal wiring is arranged in two interlayer portions of the second insulating film.
図10は、図1のA−A’断面線に相当する位置における画素の断面図である。第2の絶縁膜32の絶縁膜32aと絶縁膜32bとの間に信号配線12aが配置されている。さらに、絶縁膜32bと絶縁膜32cとの間に信号配線12bが配置されている。このような構成によって、配線の容量を低減とともに、2系統の読み出し経路を配置することができる。従って、例えば列方向に配置された2画素の信号の転送が可能になる。
FIG. 10 is a cross-sectional view of the pixel at a position corresponding to the A-A ′ cross-sectional line of FIG. 1. The
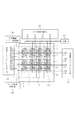
図11は、図10に示される画素を有する撮像装置の基板内の画素領域と周辺回路との関係を示す概念図である。 FIG. 11 is a conceptual diagram showing a relationship between a pixel region in a substrate and a peripheral circuit of the imaging device having the pixel shown in FIG.
基板内に変換素子が配置された領域と、周辺に配置された信号処理回路部、ゲートドライバ回路部との接続状態を表している。図10で示したような変換素子を複数の区域に分け、それぞれの区域毎に専用の信号配線を配置してなる撮像装置を、別の構成で示した配置例である。 The connection state of the area | region where the conversion element is arrange | positioned in a board | substrate, the signal processing circuit part arrange | positioned at the periphery, and a gate driver circuit part is represented. FIG. 11 is an arrangement example showing another configuration of an imaging apparatus in which the conversion element as shown in FIG. 10 is divided into a plurality of areas and a dedicated signal wiring is arranged for each area.
図11では、基板内に配置した変換素子を、区域1〜4の4つの区域に分割し、それぞれに専用の信号配線を配置している。基板の外には、上部の2つの区域から信号を取り込むことができる第一の信号処理回路部162と、下部の2つの区域から信号を取り込むことができる第二の信号処理回路部163と、を配置している。さらに、それぞれの区域に配置されたゲート電極を制御する第一のゲートドライバ回路部164、第二のゲートドライバ回路部165を配置している。図には示していないが、変換素子に電圧を印加する共通電極ドライバ回路部及び電源は、前述の信号処理回路部又はゲートドライバ回路部内に配置している。
In FIG. 11, the conversion element arranged in the substrate is divided into four areas 1 to 4, and dedicated signal wirings are arranged in each of the areas. Outside the substrate, a first signal
このように、画素領域を大きく4つに分けることで、1本の信号配線と接続されるTFTの個数を1/4にすることが可能である。これにより、特にTFT部のソース電極−ゲート電極間で形成する容量が少なくなり、信号配線の総容量を小さくすることができる。このとき、例えば区域2から第一の信号処理回路部162に引き回す配線は、少なくとも区域1を通過する箇所においては上下を絶縁膜である有機材料で挟み込むことで、例えばその上部に変換素子を配置しても形成される容量を小さくすることができる。このため、変換素子の開口率を大きく確保しながら、信号配線の総容量を小さく抑えることができる。また、各区域から一つ選択されたゲート配線4本を同時に駆動し信号処理回路に同時に送ることで、高速駆動を行うことも可能である。
In this manner, the number of TFTs connected to one signal wiring can be reduced to ¼ by dividing the pixel region into four. As a result, the capacitance formed between the source electrode and the gate electrode of the TFT portion is reduced, and the total capacitance of the signal wiring can be reduced. At this time, for example, the wiring routed from the
ゲート配線については、第一のゲートドライバ回路部164と第二のゲートドライバ回路部165が、基板内に配置されたゲート配線により互いに接続されていても構わないし、ゲート配線が中央で左右に分離されていても構わない。
With respect to the gate wiring, the first gate
図12は、図1に示す画素が配置されたパネルと周辺回路を含む撮像装置の簡易等価回路図である。絶縁基板21には、変換素子1と複数のTFT(2、3、4)が対となる画素がマトリックス状に配置されており、各行又は各列に対応した本数の信号配線又はゲート配線が配置されている。複数のTFTは、変換素子1で変換された電荷に応じた信号を読み出すための読み出し用TFT2と、読み出す画素を選択するための選択用TFT3と、読み出した後に変換素子内の残存電荷をリセットするためのリセット用TFT4を有する。ここで、読み出し用TFT2は、ゲート電極が変換素子1に接続されたソースフォロアー型のTFTである。信号処理回路部150は、信号配線12により転送された信号を処理する。ゲートドライバー回路部は、第一の駆動回路部と第2の駆動回路部を含み、駆動信号を転送するためにゲート配線と接続されている。第一の駆動回路151は、選択用TFTを制御する。第二の駆動回路152は、リセット用TFTを制御する。共通電極ドライバー回路156は、バイアス配線15にバイアス電圧を供給する。電源153は、電源供給配線13に電圧もしくは電流を供給する。リセット制御回路部154は、リセット配線14に電圧を供給する。また、ソースフォロアー型の読み出し用TFT2と選択用TFT3の接続関係を入れ替えても良い。すなわち、選択用TFT3のソース電極18と読み出し用TFT2のドレイン電極19を接続し、選択用TFT3のドレイン電極19と信号配線12と接続した撮像装置は、同様に動作する。
FIG. 12 is a simplified equivalent circuit diagram of an imaging apparatus including a panel on which the pixels shown in FIG. 1 are arranged and a peripheral circuit. On the insulating
以上に述べたように、変換素子と複数のTFTからなる撮像装置において、行もしくは列方向に交差して配置された各配線間に、第2の絶縁膜を構成する少なくとも1層の絶縁膜を挟む構造にすることで、配線の容量を低減することができる。また、レイアウトの自由度が向上することで配線幅を太くし抵抗を下げる事が可能となる。この結果、配線数が多くなっても、配線容量や抵抗の増加に関わる特性不良の発生を防止する事が可能となる。なお、上記の各構成は、自由に組合せ可能である。 As described above, in the imaging device including the conversion element and the plurality of TFTs, at least one insulating film constituting the second insulating film is provided between the wirings arranged to intersect in the row or column direction. With the sandwiched structure, the wiring capacity can be reduced. In addition, since the flexibility of layout is improved, the wiring width can be increased and the resistance can be reduced. As a result, even when the number of wirings increases, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of characteristic defects related to increases in wiring capacity and resistance. Each of the above configurations can be freely combined.
(第2の実施形態)
図13〜図21は、本発明に係る第2の実施形態の、撮像装置の画素の平面図、断面図である。
(Second Embodiment)
13 to 21 are a plan view and a cross-sectional view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
本実施形態の要点は、TFTがトップゲート型の多結晶シリコンTFTである場合においても、ゲート配線及び信号配線の少なくとも一方が、TFTと変換素子との間に配置された複数の絶縁膜に挟まれた領域に配置されているということである。 The main point of this embodiment is that even when the TFT is a top gate type polycrystalline silicon TFT, at least one of the gate wiring and the signal wiring is sandwiched between a plurality of insulating films arranged between the TFT and the conversion element. It is that it is arranged in the area.
図13は、本発明の第2の実施形態に係る撮像装置の画素の平面図である。 FIG. 13 is a plan view of a pixel of an imaging apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
図13に示すように、第1の実施形態と同様に、一画素には、読み出し用TFT2と、電源供給配線13及び読み出し用TFT2とを電気的に接続する選択用TFT3と、リセット配線14と電気的に接続されたリセット用TFT4の3つのTFTが配置されている。変換素子、各TFT、各配線の接続関係は第1の実施形態と同様である。
As shown in FIG. 13, as in the first embodiment, one pixel includes a
図14は、図13のC−C′線に沿った断面図である。 14 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line CC ′ of FIG.
図示された読み出し用TFT2及び選択用TFT3は、多結晶シリコンを用いたトップゲート型TFTであり、絶縁基板上に配置された第1の絶縁膜31a上に配置されている。各TFTは、チャネル領域及び不純物領域を有する多結晶シリコン層61、ゲート絶縁膜である第1の絶縁膜31b、ゲート電極17である第1の導電層41、ソース電極及びドレイン電極を構成する第2の導電層42から構成されている。図13における第1のゲート配線11a及び第2のゲート配線11bは、第1の絶縁膜31bと第2の絶縁膜32aの間に配置されている(不図示)。前述の第1の実施形態では、ボトムゲート型のTFTを用いているが、ボトムゲート型のTFTが非晶質シリコンを用いて形成された場合、TFTの移動度が小さいため、TFTの抵抗を下げるためにチャネル幅を大きくしなければならない。このため、TFTの各電極間の容量が増加し、この各電極に接続された配線の容量が増加してしまう。そこで、本実施例に示すように、多結晶シリコンを用いたTFTを使用することで、移動度が向上し、TFTのチャネル幅を小さくする事が可能となり、TFTの各電極間の容量を低減し、結果、配線抵抗を小さくする事ができる。各TFTは、ゲート電極に対向する位置に1つのチャネル領域を有するが、例えばダブルゲート型のTFTとすることでリーク電流を更に低減することができる。また、リセット用TFT4や選択用TFT3など、高い電圧を供給するTFTにダブルゲート構造を用いる事で、ソース・ドレイン電極間の電気的な耐圧を更に向上できる。また、微弱電流を扱う信号配線に接続されるTFTも、ダブルゲート構造にすることでリーク電流を更に低減することができるため、撮像装置のS/Nを向上できる。
The illustrated
変換素子1は、第5の導電層51、変換素子の絶縁膜33、第2の半導体層71、オーミックコンタクト層である第2の不純物半導体層72、透明電極層である第6の導電層52から成るMIS型変換素子である。第7の導電層53は、変換素子1に電圧を印加するためのバイアス配線である。第6の導電層52がバイアス配線を兼ねる場合は、無くても良い。
The conversion element 1 includes a fifth
第2の絶縁膜32は、変換素子と複数のTFTとの間に配置され、複数の絶縁膜(32a、32b)の積層膜からなる。信号配線12、電源供給配線13及びリセット配線14は、第2の絶縁膜間に配置された第2の導電層42により構成されている。第2の絶縁膜32は、低誘電率でかつ、膜厚を厚く形成できる膜が望ましく、本実施形態の第2の絶縁膜32は、平坦性を有する有機系の絶縁膜である。第2の絶縁膜32の複数の絶縁膜の各々は1μm以上10μm以下、より好ましくは2μm以上10μm以下、最も好ましくは3μm以上10μm以下で形成することが望ましい。また、無機膜であれば、SiO2やTEOSなどのCVD膜で1μm以上形成することが望ましい。また、複数の絶縁膜32の合計膜厚が20μmを超えるほど厚くなると、感光性のフォトレジストをコーティングする際に、段差が大きいことでレジストの密着性が悪い領域が発生してしまう。また、段差部の凹部の箇所だけレジストの膜厚が厚くなり、その後の露光、現像プロセスでフォトレジストが感光しきれず、パターン残りが発生してしまう。従って、複数の絶縁膜32の合計膜厚を20μm以下にする必要がある。このような構成は、画素内で大きい面積を有するTFTの特にチャネル領域やソース電極及びドレイン電極と、上部に形成する各配線や変換素子との容量を低減するために有効である。そして、TFTが複数配置されている場合、配線数が増加し、配線の交差部が増加するが、配線間の容量の合計を低減するために有効である。さらに、TFT上部に形成する各配線の幅を広くしてTFTを覆う構成にして、配線抵抗を積極的に低減しようとした場合に、特に効果的である。この結果、配線間の容量を低減でき、また、図13に示すような各配線の線幅を無理のない線幅で形成することができる。また、配線からの微弱なリーク電流を防止するために、信号配線12を無機の絶縁膜で挟み込む構成にしても構わない。
The second insulating
図15は、図13中のD−D’線に沿った断面図である。 FIG. 15 is a sectional view taken along line D-D ′ in FIG. 13.
図示されたリセット用TFT4は、多結晶シリコンを用いたトップゲート型TFTであり、第1の絶縁膜31a上に配置されている。コンタクト部45は、読み出し用TFT2のゲート電極17と同じ第1の導電層41の一部である。リセット用TFT4及びコンタクト部45は、それぞれスルーホール16を介して変換素子1の下部電極である第5の導電層51に接続されている。第2の絶縁膜32aのスルーホールの位置は、第2の絶縁膜32bのスルーホールの位置とずれている。これは、リソグラフィー法で形成したスルーホール上に導電層を形成した際、条件によってはスルーホールの中央部で段差が形成され、この段差部上に更にスルーホールを形成すると加工が不安定になるためである。
The illustrated
図16は、第2の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の平面図で、図13とは異なる例を示した画素の平面図である。 FIG. 16 is a plan view of pixels of the imaging apparatus according to the second embodiment, and is a plan view of pixels illustrating an example different from FIG.
図13に示す画素と異なる点は、第2の絶縁膜が光を吸収する領域と透過する領域を有することである。 The difference from the pixel shown in FIG. 13 is that the second insulating film has a region that absorbs light and a region that transmits light.
図17は、図16の開口平面図に示したE−E’部の断面図である。第2の絶縁膜32aは、可視光を吸収するブラックマトリックス材料を用いている。第2の絶縁膜32bは、可視光を透過する透明な材料を用いている。同時に、変換素子の下部電極である第5の導電層51には、ITOなどの透明導電膜を用いている。ブラックマトリックス材料を用いる事で、変換素子の上部電極である第6の導電層側から可視光が入射された時、可視光が画素と画素の隙間からの透過を低減し、光学的なクロストークを低減できるため、解像度(MTF)を向上することができる。更に、絶縁基板21の変換素子1とは反対側に発光体(不図示)を配置した場合、発光体が発した光は第2の絶縁膜32aの開口82から変換素子1に照射できる。この結果、変換素子1内に蓄積された残存キャリアを、光照射により再結合し除去する事が可能になる。
17 is a cross-sectional view of the E-E ′ portion shown in the opening plan view of FIG. 16. The second
このように、配線を第2の絶縁膜の間に挟み込むことにより、配線抵抗や容量を低減できる。さらに、レイアウトの自由度が向上する。また、第2の絶縁膜32に光吸収領域と透過領域を設けることで、MTFの向上と光リセット機能を有することによる感度の向上が可能になる。
In this manner, the wiring resistance and capacitance can be reduced by sandwiching the wiring between the second insulating films. Furthermore, the degree of freedom in layout is improved. Further, by providing a light absorption region and a transmission region in the second insulating
図18は、第2の実施形態に関わる撮像装置の画素の平面図で、図13とは異なる例を示した画素の平面図である。 FIG. 18 is a plan view of a pixel of the imaging apparatus according to the second embodiment, and is a plan view of a pixel showing an example different from FIG.
図13に示す画素と異なる点は、変換素子1で変換された電荷を増幅せずに読み出す転送用薄膜トランジスタ(以下、転送用TFT)を配置した点である。 A difference from the pixel shown in FIG. 13 is that a transfer thin film transistor (hereinafter referred to as a transfer TFT) that reads the electric charge converted by the conversion element 1 without amplifying it is arranged.
図18は、図13で示した平面構造に、更に信号配線12と変換素子1とを直接接続する転送用TFT5が配置されている。転送用TFT5は、ソースフォロアー型TFTとは異なり、変換素子1で変換された電荷を直接読み出すために配置されたもので、ソースフォロアー型のように信号を増幅する機能はないものの、微弱電流を高階調で読み出すことができる。例えば、静止画撮影時に高階調な画像を得る場合等に使うと良く、用途に応じた使い分けが可能になるため転送用TFT5は静止画用TFTとして用いられる。この場合、信号配線12に供給される電流もしくは電圧が小さくなるため、信号配線12と接続される不図示の信号処理回路部等に、ゲインを切り替える切り替え回路を設ける必要が出てくる。また、転送用TFT5は特に微弱な電流を取り扱うため、ダブルゲート構造にすると良い。
In FIG. 18, a
図19は、図18に示す画素を用いたパネルと周辺回路を含む撮像装置の簡易等価回路図である。変換素子1と複数のTFT(2、3、4、5)が対となる画素はマトリックス状に配置されている。そして、画素の配列に対応した信号配線12、第1のゲート配線11a及び第2のゲート配線11bとを含む基板と、周囲に配置された信号処理回路150、ゲートドライバー回路151、152と、を有し、撮像装置を構成している。共通電極ドライバー回路部156は、バイアス配線15にバイアス電圧を供給する。電源153は、電源供給配線に電流又は電圧を供給する。リセット制御回路部154は、リセット配線14に電圧を供給する。変換素子1で変換された電荷に応じた信号を読み出すための読み出し用TFT2と、読み出す画素を選択するための選択用TFT3と、読み出した後に変換素子内の残存電荷をリセットするためのリセット用TFT4を配置している。ここで、読み出し用TFT2は、ゲート電極17が変換素子1に接続されたソースフォロアー型のTFTである。図12と異なるのは、変換素子1と信号配線12を直接接続する転送用TFT5を配置している点である。この転送用TFT5を設ける事で、転送される信号量は減少するものの、高階調で信号を読み出す事が可能になり、用途に応じて使い分けができるようになる。ソースフォロアー型の読み出し用TFT2と選択用TFT3の接続関係を入れ替えて、選択用TFT3のソース電極18と読み出し用TFT2のドレイン電極19を接続し、選択用TFT3のドレイン電極19と信号配線12と接続した撮像装置は、同様に動作する。
FIG. 19 is a simplified equivalent circuit diagram of an imaging device including a panel using the pixels shown in FIG. 18 and peripheral circuits. Pixels in which the conversion element 1 and a plurality of TFTs (2, 3, 4, 5) are paired are arranged in a matrix. Then, a substrate including the
図20は、図19とは異なる簡易等価回路図である。図19と異なる点は、ソースフォロアー型の読み出し用TFTを、2つの選択用TFT3(第1の選択用薄膜トランジスタ3a、第2の選択用薄膜トランジスタ3b)で挟み込んだ点である。信号配線12にソースフォロアー型のTFTが直接接続されていると、変換素子1に外部から電磁波等のノイズ成分が入射すると、読み出し用TFT2のゲート電極17の電位が変動する。そして、TFTの空乏状態もしくは蓄積状態が変化し、ソース電極18及びドレイン電極19とゲート電極17の間の容量が微少に変化する。その結果、画素内もしくは信号配線12の容量分布が発生し、画像のアーチファクトとして見える可能性がある。読み出し用TFT2と選択用TFT3とが逆の配置であっても同様の影響が発生し、変換素子1と読み出し用TFT2を直接接続すると、光が入射した場合に、画素内の容量分布が発生し、画像のアーチファクトとして見える可能性がある。よって、この様に、読み出し用TFT2を2つの選択用TFT(3a、3b)の間に接続することで、変換素子1に電磁波等のノイズ成分が入射しても、画像のアーチファクトを防止できる。また、このような構成は、レイアウトの自由度があるために配置可能で、配線とTFTをオーバーラップしても特性不良につながらない構造であるがゆえに可能になる。なお、第1の実施形態、第2の実施形態に記載した各構成は、自由に組合せ可能である。
FIG. 20 is a simplified equivalent circuit diagram different from FIG. A difference from FIG. 19 is that a source follower type reading TFT is sandwiched between two selection TFTs 3 (a first selection thin film transistor 3a and a second selection thin film transistor 3b). When a source follower type TFT is directly connected to the
(応用例)
図21は本発明の好適な実施の形態に係る放射線撮像装置を放射線撮像システムへ適用した場合の応用例を示したものである。
(Application examples)
FIG. 21 shows an application example when the radiation imaging apparatus according to the preferred embodiment of the present invention is applied to a radiation imaging system.
放射線源であるX線チューブ6050で発生したX線6060は患者あるいは被験者6061の胸部6062を透過し、シンチレーターが上部に配置された放射線撮像装置6040に入射する。放射線撮像装置6040はイメージセンサーを含みうる。この入射したX線には患者6061の体内部の情報が含まれている。X線の入射に対応してシンチレーターは発光し、これを光電変換して、電気的情報を得る。この情報はディジタルに変換され信号処理手段となるイメージプロセッサ6070により画像処理され制御室の表示手段となるディスプレイ6080で観察できる。
X-rays 6060 generated by an
また、この情報は電話回線6090等の伝送処理手段により遠隔地へ転送でき、別の場所のドクタールームなど表示手段となるディスプレイ6081に表示もしくは光ディスク等の記録手段に保存することができ、遠隔地の医師が診断することも可能である。また記録手段となるフィルムプロセッサ6100により記録媒体となるフィルム6110に記録することもできる。
Further, this information can be transferred to a remote place by transmission processing means such as a
1 変換素子
2 読み出し用薄膜トランジスタ
3(3a、3b) 選択用薄膜トランジスタ
4 リセット用薄膜トランジスタ
5 転送用薄膜トランジスタ
11(11a、11b、11c) ゲート配線
12 信号配線
13 電源供給配線
14 リセット配線
16 スルーホール
17 ゲート電極
18 ソース電極
19 ドレイン電極
21 絶縁基板
31(31a、31b) 第1の絶縁膜
32(32a、32b、33c) 第2の絶縁膜
33 絶縁膜
41 第1の導電層
42 第2の導電層
43 第3の導電層
44 第4の導電層
51 第5の導電層
52 第6の導電層
53 第7の導電層
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (9)
各々が、前記絶縁基板の上に配置された変換素子と、前記絶縁基板と前記変換素子との間に配置された複数の薄膜トランジスタと、を含み、前記複数の薄膜トランジスタが、前記変換素子にゲート電極が電気的に接続された読み出し用薄膜トランジスタと、前記読み出し用薄膜トランジスタのソース電極又はドレイン電極に電気的に接続された選択用薄膜トランジスタと、を含む複数の画素と、
前記絶縁基板と前記変換素子との間に配置され、前記選択用薄膜トランジスタが選択されることにより入射した光又は放射線を前記変換素子が変換して得られる電荷に対応した信号が転送される信号配線と、
前記選択用薄膜トランジスタのゲート電極に駆動信号を供給するゲート配線と、
を含む撮像装置であって、
前記複数の薄膜トランジスタ及び前記信号配線と前記変換素子との間に複数の絶縁膜が配置されており、
前記ゲート配線は前記複数の絶縁膜の間に配置されていることを特徴とする撮像装置。 An insulating substrate ;
Each including a conversion element disposed on the insulating substrate, and a plurality of thin film transistors disposed between the insulating substrate and the conversion element, the plurality of thin film transistors being connected to the conversion element by a gate electrode A plurality of pixels, each including a readout thin film transistor electrically connected to the source thin film transistor and a selection thin film transistor electrically connected to a source electrode or a drain electrode of the readout thin film transistor;
Wherein disposed between the insulating substrate and the transducer, signal signal corresponding to the electric charge the transducer light or radiation incident is obtained by converting by said selection thin film transistor is selected to be transferred wire When,
A gate wiring for supplying a driving signal to the gate electrode of the selection TFT,
An imaging device comprising:
A plurality of insulating films are disposed between the plurality of thin film transistors and the signal wiring and the conversion element,
The image pickup apparatus, wherein the gate wiring is disposed between the plurality of insulating films.
前記読み出し用薄膜トランジスタのソース電極及びドレイン電極のそれぞれに前記第1の選択用薄膜トランジスタ及び前記第2の選択用薄膜トランジスタのいずれかが電気的に接続されたことを特徴とする撮像装置。 The imaging device according to claim 1, wherein the pixel includes a second selection thin film transistor electrically connected to the gate wiring,
One of the first selection thin film transistor and the second selection thin film transistor is electrically connected to a source electrode and a drain electrode of the readout thin film transistor, respectively.
前記撮像装置からの信号を処理する信号処理手段と、
前記信号処理手段からの信号を記録するための記録手段と、
前記信号処理手段からの信号を表示するための表示手段と、
前記信号処理手段からの信号を伝送するための伝送処理手段と、を有することを特徴とする放射線撮像システム。 The imaging device according to any one of claims 1 to 8,
Signal processing means for processing a signal from the imaging device;
Recording means for recording a signal from the signal processing means;
Display means for displaying a signal from the signal processing means;
A radiation imaging system comprising: a transmission processing unit for transmitting a signal from the signal processing unit.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008027664A JP5328169B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2008-02-07 | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system |
| US12/034,969 US7638772B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2008-02-21 | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system |
| US12/543,542 US20090302229A1 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2009-08-19 | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007049368 | 2007-02-28 | ||
| JP2007049368 | 2007-02-28 | ||
| JP2008027664A JP5328169B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2008-02-07 | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008244445A JP2008244445A (en) | 2008-10-09 |
| JP2008244445A5 JP2008244445A5 (en) | 2011-01-27 |
| JP5328169B2 true JP5328169B2 (en) | 2013-10-30 |
Family
ID=39915344
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008027664A Active JP5328169B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2008-02-07 | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5328169B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5400507B2 (en) * | 2009-07-13 | 2014-01-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system |
| JP5700973B2 (en) | 2010-08-05 | 2015-04-15 | キヤノン株式会社 | Detection apparatus and radiation detection system |
| JP2012114166A (en) * | 2010-11-22 | 2012-06-14 | Canon Inc | Detection device and radiation detection system |
| JP5925475B2 (en) * | 2010-12-09 | 2016-05-25 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Photodetection circuit |
| JP5709709B2 (en) * | 2011-05-31 | 2015-04-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Detection device manufacturing method, detection device and detection system |
| JP5954983B2 (en) * | 2011-12-21 | 2016-07-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, radiation imaging system, and manufacturing method of imaging apparatus |
| WO2013164720A1 (en) * | 2012-04-30 | 2013-11-07 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Imaging detector with anti-aliasing filter in the readout electronics and/or photosensor |
| JP5974654B2 (en) * | 2012-06-13 | 2016-08-23 | ソニー株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and imaging display system |
| JP5709810B2 (en) * | 2012-10-02 | 2015-04-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Detection device manufacturing method, detection device and detection system |
| JP6282363B2 (en) * | 2017-02-09 | 2018-02-21 | キヤノン株式会社 | Detection device and detection system |
| CN110111753B (en) * | 2019-04-10 | 2020-10-27 | 深圳市华星光电半导体显示技术有限公司 | Driving method and device of display panel |
| JP2023131411A (en) * | 2022-03-09 | 2023-09-22 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Energy line detection system |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4255527B2 (en) * | 1997-10-20 | 2009-04-15 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | Semiconductor device |
| CN1227893C (en) * | 2000-02-04 | 2005-11-16 | 皇家菲利浦电子有限公司 | Active pixel sensor |
| JP2003023144A (en) * | 2001-07-06 | 2003-01-24 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | Semiconductor device |
| JP5207583B2 (en) * | 2005-07-25 | 2013-06-12 | キヤノン株式会社 | Radiation detection apparatus and radiation detection system |
-
2008
- 2008-02-07 JP JP2008027664A patent/JP5328169B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2008244445A (en) | 2008-10-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5328169B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system | |
| US7638772B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system | |
| US7435968B2 (en) | Radiation detecting apparatus, radiation imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system | |
| KR100755287B1 (en) | Radiation image pickup device | |
| JP5043373B2 (en) | Conversion device, radiation detection device, and radiation detection system | |
| JP5406473B2 (en) | Radiation detector | |
| JP5043374B2 (en) | Conversion device, radiation detection device, and radiation detection system | |
| JP5489542B2 (en) | Radiation detection apparatus and radiation imaging system | |
| US8497562B2 (en) | Solid-state image pickup device | |
| JP5235350B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging system | |
| EP1420453B1 (en) | Image pickup apparatus, radiation image pickup apparatus and radiation image pickup system | |
| US20100277630A1 (en) | Imaging apparatus and radiation imaging apparatus | |
| US20060255239A1 (en) | Image pick-up apparatus and manufacturing method thereof, radiation image pick-up apparatus, and radiation image pick-up system | |
| US7550731B2 (en) | Coversion apparatus and imaging system | |
| US20120080600A1 (en) | Detection apparatus and radiation detection system | |
| JP2004296654A (en) | Radiation imaging device | |
| JP2004265932A (en) | Radiation imaging device | |
| US6600157B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, and radiation detection device and radiation detection system having same | |
| JP5677353B2 (en) | Radiation detection apparatus and radiation imaging system | |
| JP4393085B2 (en) | Radiation detector | |
| JP2004265933A (en) | Radiation detector | |
| JP2006186031A (en) | Photoelectric conversion device and radiation imager | |
| JP2001326340A (en) | Photoelectric converter and radiation imaging system | |
| JP2002124684A (en) | Semiconductor device, system and device for detecting radiation comprising it |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20100201 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101201 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101201 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121030 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20121031 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121227 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130625 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130723 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5328169 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |