JP5284635B2 - Electron multiplier - Google Patents
Electron multiplier Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5284635B2 JP5284635B2 JP2007330337A JP2007330337A JP5284635B2 JP 5284635 B2 JP5284635 B2 JP 5284635B2 JP 2007330337 A JP2007330337 A JP 2007330337A JP 2007330337 A JP2007330337 A JP 2007330337A JP 5284635 B2 JP5284635 B2 JP 5284635B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- dynode
- wiring portion
- dynodes
- electron multiplier
- spacer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
Description
本発明は、多段に積層させたダイノードからなる電子増倍部によって入射電子流を増倍する電子増倍管に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an electron multiplier that multiplies an incident electron current by an electron multiplier made of dynodes stacked in multiple stages.
従来、ダイノードが積層された構造の電子増倍部を有する電子増倍装置として、複数のダイノードを互いに分離して配置させるために、チャンネルを形成する孔が形成された導電層とライン状のセパレータ層とが交互に配置された装置が知られている(下記特許文献1参照)。また、このような装置においてセパレータに抵抗性材料を用いた場合には、中間電極の電位を設定する外部抵抗或いは外部装置を省略することができることが明らかにされている。
しかしながら、上述した電子増倍装置においては、抵抗性のセパレータとした場合にそのセパレータが電子増倍部の内部空間に露出されているため、増倍電子がセパレータに入射してしまうことでセパレータに対してダメージを与え、セパレータの抵抗値が変化してしまう可能性がある。その結果、各ダイノードへの印加電圧が変化し、電子の増倍効率や検出効率を変化させる場合があった。例えば、セパレータの抵抗値が著しく上昇した場合は、各電極への電荷の供給量が少なくなり電子の増倍効率が小さくなるし、セパレータの抵抗値が著しく低下した場合は、ダイノード間の電位差が低くなり電子の増倍効率が小さくなる。つまり、同じ大きさの入力に対して、得られる出力が変化してしまい、検出感度が不安定になる場合があった。 However, in the above-described electron multiplier, when the separator is a resistive separator, the separator is exposed in the internal space of the electron multiplier, so that the multiplier electrons are incident on the separator. On the other hand, damage may be caused and the resistance value of the separator may change. As a result, the voltage applied to each dynode may change, changing the electron multiplication efficiency and detection efficiency in some cases. For example, when the resistance value of the separator is remarkably increased, the amount of charge supplied to each electrode is reduced and the electron multiplication efficiency is reduced. When the resistance value of the separator is remarkably reduced, the potential difference between the dynodes is reduced. The electron multiplication efficiency becomes lower. In other words, for the same size input, the obtained output changes, and the detection sensitivity may become unstable.
そこで、本発明は、かかる課題に鑑みて為されたものであり、電子増倍部における給電部を削減することで電子増倍部を小型化しつつ検出感度を安定化することが可能な電子増倍管を提供することを目的とする。 Accordingly, the present invention has been made in view of such problems, and by reducing the power feeding section in the electron multiplier section, the electron multiplier capable of stabilizing the detection sensitivity while reducing the size of the electron multiplier section. The purpose is to provide a double tube.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明の電子増倍管は、入射電子を増倍する電子増倍孔を有する平板電極であるダイノードが複数段に積層された電子増倍部を備えた電子増倍管であって、隣接する2段のダイノードの間には、それぞれ、2段のダイノードの間を電気的に接続する導電路を有する絶縁性の枠状部材であるスペーサが配置されており、導電路の一部は、絶縁体によって覆われた抵抗体によって形成されていることを特徴とする。 In order to solve the above problems, an electron multiplier of the present invention is an electron multiplier having an electron multiplier section in which dynodes, which are plate electrodes having electron multiplier holes for multiplying incident electrons, are stacked in a plurality of stages. Between the adjacent two-stage dynodes, spacers, which are insulating frame-like members having conductive paths that electrically connect the two-stage dynodes, are arranged between the adjacent two-stage dynodes. A part of the path is formed by a resistor covered with an insulator.
このような電子増倍管によれば、複数段のダイノードからなる電子増倍部のうちの2つの隣接するダイノードが、それらの間に配置されたスペーサの導電路によって抵抗体を介して電気的に接続されるので、直列的に接続された複数段のダイノードの両端に電圧を印加することにより隣接するダイノード間に所望の電位差を生じさせることができる結果、電子増倍部における給電部を削減することができる。また、その抵抗体は絶縁体によって覆われており管内の空間に対して露出していないので、増倍電子の影響による抵抗体の抵抗値の変化を抑制することができ、電子増倍効率の安定化が可能になる。これにより、電子増倍部を小型化しながら検出感度を安定化することができる。 According to such an electron multiplier, two adjacent dynodes in the electron multiplier section composed of a plurality of dynodes are electrically connected via a resistor by a conductive path of a spacer disposed between them. As a result, it is possible to generate a desired potential difference between adjacent dynodes by applying a voltage across the dynodes of a plurality of stages connected in series. can do. In addition, since the resistor is covered with an insulator and not exposed to the space in the tube, a change in the resistance value of the resistor due to the influence of the multiplying electrons can be suppressed, and the electron multiplication efficiency can be reduced. Stabilization is possible. Thereby, it is possible to stabilize the detection sensitivity while reducing the size of the electron multiplier.
導電路は、2段のダイノードのうちの一方と電気的に接続するための第1接続部と、2段のダイノードのうちの他方と電気的に接続するための第2接続部と、第1接続部と第2の接続部とを抵抗体を介して電気的に接続する、絶縁体で覆われた配線部と、を含むことが好ましい。この場合、導電路が、隣接する2段のダイノードのそれぞれと接続部において接続され、これらの2段のダイノードが、絶縁体で覆われた配線部によって抵抗体を介して接続されるので、配線部への電子入射によるノイズの発生を抑制し、検出感度を安定化することができる。 The conductive path has a first connection portion for electrically connecting with one of the two-stage dynodes, a second connection portion for electrically connecting with the other of the two-stage dynodes, It is preferable that the wiring part covered with the insulator which electrically connects a connection part and a 2nd connection part via a resistor is included. In this case, the conductive path is connected to each of the adjacent two-stage dynodes at the connection portion, and these two-stage dynodes are connected via the resistor by the wiring portion covered with the insulator. The generation of noise due to the incidence of electrons on the part can be suppressed, and the detection sensitivity can be stabilized.
また、第1接続部及び第2接続部は複数である、ことも好ましい。接続部を複数設けることで、確実に隣接する2段のダイノードと電気的に接続されるので、安定した電位供給を行うことができ、検出感度をさらに安定することができる。 It is also preferable that there are a plurality of first connection portions and second connection portions. By providing a plurality of connection portions, it is surely electrically connected to two adjacent dynodes, so that a stable potential can be supplied and detection sensitivity can be further stabilized.
また、配線部は、複数の第1接続部を連結する第1の配線部と、複数の第2接続部を連結する第2の配線部と、第1の配線部と第2の配線部とを接続する中間配線部とを含み、抵抗体は、中間配線部の一部を形成していることも好ましい。かかる構成を備えれば、スペーサと隣接する2段のダイノードとを電気的に接続するための複数の第1接続部及び第2接続部が、第1及び第2の配線部によって連結され、第1及び第2の配線部が抵抗体を含む中間配線部によって接続されているので、第1の接続部および第2の接続部と抵抗体との接続構造が簡略化される。 The wiring unit includes a first wiring unit that couples the plurality of first connection units, a second wiring unit that couples the plurality of second connection units, a first wiring unit, and a second wiring unit. It is also preferable that the resistor forms a part of the intermediate wiring portion. With such a configuration, a plurality of first connection portions and second connection portions for electrically connecting the spacer and the adjacent two-stage dynodes are connected by the first and second wiring portions, Since the 1st and 2nd wiring part is connected by the intermediate | middle wiring part containing a resistor, the connection structure of a 1st connection part and a 2nd connection part, and a resistor is simplified.
また、スペーサは、ダイノードの電子増倍孔が形成された領域を取り囲むような枠状の形状を有することも好ましい。こうすれば、ダイノード間の距離を安定して保持することにより、検出感度を安定化することができる。 It is also preferable that the spacer has a frame shape surrounding the region where the electron multiplying holes of the dynode are formed. In this way, the detection sensitivity can be stabilized by stably maintaining the distance between the dynodes.
また、第1接続部及び第2接続部には窪み又は突起が形成され、2段のダイノードのそれぞれには、少なくとも1つの突起又は窪みが形成されており、2段のダイノードのうち一方のダイノードの突起又は窪みが、第1接続部の窪み又は突起に嵌め合わされることにより、一方のダイノードと配線部とが電気的に接続され、2段のダイノードのうち他方のダイノードの突起又は窪みが、第2接続部の窪み又は突起に嵌め合わされることにより、他方のダイノードと配線部とが電気的に接続されることも好ましい。こうすれば、隣接する2段のダイノードに形成された突起又は窪みが、1つのスペーサに設けられた接続部に嵌め合わされるので、ダイノード同士の位置決めが容易となり検出感度のより一層な安定化が可能になる。 The first connection portion and the second connection portion are formed with depressions or protrusions, and each of the two-stage dynodes is formed with at least one protrusion or depression, and one dynode of the two-stage dynodes. Are fitted into the depressions or protrusions of the first connection part, so that one dynode and the wiring part are electrically connected, and the protrusions or depressions of the other dynode of the two-stage dynodes are It is also preferable that the other dynode and the wiring portion are electrically connected by being fitted in the recess or protrusion of the second connection portion. In this way, since the protrusions or depressions formed in the two adjacent dynodes are fitted into the connecting portion provided in one spacer, the positioning of the dynodes is facilitated, and the detection sensitivity is further stabilized. It becomes possible.
スペーサは、2段のダイノードのうちの一方のダイノード側に設けられ、一方のダイノードと電気的に接続するための第1接続部を含む第1の絶縁部材と、2段のダイノードのうちの他方のダイノード側に設けられ、他方のダイノードと電気的に接続するための第2接続部を含む第2の絶縁部材と、第1及び第2の絶縁部材の間に把持された第3の絶縁部材と、第1の絶縁部材と第3の絶縁部材との間に設けられ、第1接続部に電気的に接続された第1の配線部と、第2の絶縁部材と第3の絶縁部材との間に設けられ、第2接続部に電気的に接続された第2の配線部と、第3の絶縁部材を貫通して設けられ、第1の配線部と第2の配線部とを接続する中間配線部とを有し、中間配線部の一部は、抵抗体によって形成されている、ことが好ましい。この場合、抵抗体は確実に絶縁部材で包囲されるため、検出感度を安定化することができる。 The spacer is provided on one dynode side of the two-stage dynodes, and includes a first insulating member including a first connection portion for electrically connecting to the one dynode, and the other of the two-stage dynodes. A second insulating member provided on the dynode side and including a second connecting portion for electrically connecting to the other dynode, and a third insulating member held between the first and second insulating members A first wiring portion provided between the first insulating member and the third insulating member and electrically connected to the first connecting portion, a second insulating member, and a third insulating member Between the second wiring part electrically connected to the second connecting part and the third insulating member, and connecting the first wiring part and the second wiring part. It is preferable that a part of the intermediate wiring part is formed by a resistor. . In this case, since the resistor is surely surrounded by the insulating member, the detection sensitivity can be stabilized.
また、第1の配線部、第2の配線部、及び中間配線部は、第3の絶縁部材に形成されていることも好ましい。かかる構成を採れば、スペーサにおける導電路の形成が容易となり製造効率が向上する。 Moreover, it is also preferable that the first wiring portion, the second wiring portion, and the intermediate wiring portion are formed on the third insulating member. By adopting such a configuration, it is easy to form a conductive path in the spacer, and the manufacturing efficiency is improved.
本発明によれば、電子増倍部における給電部を削減することで電子増倍部を小型化しつつ検出感度を安定化することが可能な電子増倍管を提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the electron multiplier which can stabilize a detection sensitivity can be provided, reducing an electron multiplier part by reducing the electric power feeding part in an electron multiplier part.
以下、図面を参照しつつ本発明に係る電子増倍管の好適な実施形態について詳細に説明する。なお、図面の説明においては同一又は相当部分には同一符号を付し、重複する説明を省略する。 Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of an electron multiplier according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the description of the drawings, the same or corresponding parts are denoted by the same reference numerals, and redundant description is omitted.
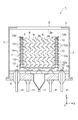
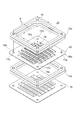
図1は、本発明の好適な一実施形態に係る電子増倍管である光電子増倍管1の管軸方向に沿った端面図である。この光電子増倍管1は、入射光を受ける円形状の透光性を有する受光面板2、その受光面板2の外縁部に取り付けられた円筒状の金属側管3、及び金属側管3を挟んで受光面板2に対面して配置された円形のステム4によって構成された真空容器5と、この真空容器5内に配設された収束電極6、電子増倍部7、及びアノード8とを備えている。この光電子増倍管1のサイズとしては特定のサイズには限定されないが、例えば、真空容器5の管軸Z方向の長さが12mm、管軸Zに垂直な方向の幅が15mmである。
FIG. 1 is an end view along a tube axis direction of a
受光面板2の内面には、光電陰極2aが設けられ、この光電陰極2aと電子増倍部7との間において、管軸Z方向に対して垂直な方向(図1のX軸方向)に略等間隔に並ぶように線状の収束電極6が設けられている。この収束電極6は、外部から受光面板2への光の入射に伴い光電陰極2aから真空容器5内に放出された光電子を、その軌道を収束させることにより電子増倍部7に入射させる。
A
電子増倍部7は、多数の電子増倍孔9を有するダイノード10が、管軸Z方向に複数段で積層されて構成されており、最終段のダイノード10の後段側には、最終段のダイノード10の電子増倍孔9に対向して略矩形状のアノード8が配設されている。また、ステム4には、外部のブリーダ回路と接続して、光電陰極2a、収束電極6、電子増倍部7、及びアノード8に所定の電圧を印加するステムピン11が貫通して設けられている。
The
このダイノード10の段数及びステムピン11への印加電圧は様々に設定されうるが、例えば、ダイノード10は8段で積層され、光電陰極2a、収束電極6、各ダイノード10、及びアノード8への印加電圧は、それぞれ、-900V、-900V、-800〜-100V(100V間隔)、0V(グラウンド電位)と、光電陰極2aからアノード8に向かうに従って高くなるように設定されている。これにより、入射電子流は、電子増倍経路における上流から下流に向かうにつれて、具体的には最前段のダイノード10から最後段のダイノード10に向かうにつれて増倍されて、アノード8で検出信号として外部に取り出される。
The number of stages of the
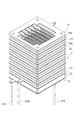
各ダイノード10は、略矩形状のステンレスや、アルミニウム等の金属製の平板電極に、管軸Z方向に対して垂直な方向(図1のY軸方向)に沿って互いに並列にスリット状の電子増倍孔9が複数形成されて成る。そして、これらの複数のダイノード10が、枠状のスペーサ12aを介して互いに所定の間隔を空けて積み重ねられている。例えば、ダイノード10は、9mm四方、厚さ0.1mmのステンレス平板に1mm間隔で電子増倍孔9が形成され、0.8mmピッチで積層される。このとき、隣接する2つのダイノード10は、スペーサ12aを介して積み重ねられることにより、管軸Zに対して垂直な平面(X−Y平面)に沿った方向及び管軸Zに沿った方向に互いに位置合わせされる。これにより、ダイノード10に形成された電子増倍孔9は、その前段側(収束電極6側)の開口9aが前段のダイノード10の電子増倍孔9の後段側(アノード8側)の開口9bの延長線上に位置するように設定され、管軸Z方向に沿ったジグザグ状の電子増倍用チャネルを並列に形成する。
Each
最前段のダイノード10と収束電極6とは、スペーサ12bを介して積み重ねられることにより、X−Y平面に沿った方向及びZ軸に沿った方向に互いに位置合わせされている。同様に、最後段のダイノード10とアノード8とは、スペーサ13を介して積み重ねられることにより、X−Y平面に沿った方向及びZ軸に沿った方向に互いに位置合わせされている。なお、スペーサ12a,12bは、後述するように、セラミック等の絶縁材料からなる3層構造の枠状の絶縁体の内部に導電路が形成された構造を有する一方で、スペーサ13は、1層構造の全体がセラミック等の絶縁材料からなる枠状の絶縁部材である。
The
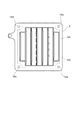
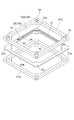
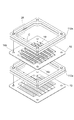
次に、図2及び図3を参照して、電子増倍部7の積層構造について詳細に説明する。図2は、図1の収束電極6を含む電子増倍部7の平面図、図3は、図1の収束電極6及び電子増倍部7の一部を示す分解斜視図である。
Next, with reference to FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the laminated structure of the
収束電極6の受光面板2側の表面6aの辺縁部の四隅のうちの対角線上の二隅には、2つの略円形状の突起部14a,14bが形成され、表面6aの別の対角線上に位置する辺縁部の二隅には、2つの略円形状の窪み部15c,15dが形成されている。また、収束電極6の電子増倍部7側の表面6bにおける突起部14a,14bに対して反対側の位置には、それぞれ、突起部14a,14bとほぼ同一の大きさを有する略円形状の窪み部15a,15bが形成され、表面6bにおける窪み部15c,15dに対して反対側の位置には、それぞれ、窪み部15c,15dとほぼ同一の大きさを有する略円形状の突起部14c,14dが形成されている。
Two substantially
同様に、ダイノード10の前段側の表面10aの辺縁部の四隅のうちの対角線上の二隅には、2つの略円形状の突起部16a,16bが形成され、表面10aの別の対角線上に位置する辺縁部の二隅には、2つの略円形状の窪み部17c,17dが形成されている。また、同一のダイノード10の後段側の表面10bにおける突起部16a,16bに対して反対側の位置には、それぞれ、突起部16a,16bとほぼ同一の大きさを有する略円形状の窪み部17a,17bが形成され、表面10bにおける窪み部17c,17dに対して反対側の位置には、それぞれ、窪み部17c,17dとほぼ同一の大きさを有する略円形状の突起部16c,16dが形成されている。
Similarly, two substantially
スペーサ12a,12bは、収束電極6及びダイノード10の縁形状とほぼ同一の縁形状を有する枠状部材である。このスペーサ12a及びスペーサ12bは、それぞれ、2つのダイノード10の間及び収束電極6と最前段のダイノード10との間に配置された際に電子増倍部7の電子増倍孔9が形成された領域A(図1参照)にかからないように、当該領域Aを取り囲むのに十分な大きさでその中央部が矩形状に切り抜かれている。また、このスペーサ12bには、収束電極6とダイノード10との間に配置される際に突起部14c,14d,16a,16bに対向する隅部において円形状の穴部(窪み)18が穿たれている。同様に、スペーサ12aには、2つのダイノード10間に配置される際に突起部16a,16b,16c,16dに対向する隅部において円形状の穴部(窪み)19が穿たれている。これらの穴部18,19は、それぞれ、スペーサ12b,12aの隅部の両面に形成されている。
The
上述した形状を有する2つのダイノード10がスペーサ12aを介して積層される際には、前段のダイノード10の突起部16c,16dが、スペーサ12aの対角線上の2つの穴部19に嵌め合わされ、後段のダイノード10の突起部16a,16bが、スペーサ12aの別の対角線上の2つの穴部19に嵌め合わされることによって互いに積み重ねられる。また、収束電極6と最前段のダイノード10とがスペーサ12bを介して積層される際には、ダイノード10の突起部16a,16bが、スペーサ12bの対角線上の2つの穴部18に嵌め合わされ、収束電極6の突起部14c,14dが、スペーサ12bの別の対角線上の2つの穴部18に嵌め合わされることによって互いに積み重ねられる。これにより、収束電極6と複数段のダイノード10とは、互いに管軸Zに垂直な方向及び管軸Zに沿った方向において位置合わせがなされる。このようにして、収束電極6から最終段のダイノード10までがスペーサ12a,12bを介して積み重ねられている。
When the two
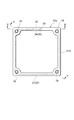
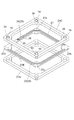
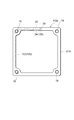
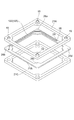
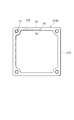
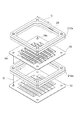
次に、スペーサ12a(スペーサ12b)の詳細構成について説明する。図4は、スペーサ12aの平面図、図5は、図4のスペーサ12aのV-V線に沿った断面図、図6は、図4のスペーサ12aのVI-VI線に沿った断面図、図7は、図4のスペーサ12aを上方から見た斜視図、図8は、図4のスペーサ12aを下方から見た斜視図である。なお、スペーサ12bは、スペーサ12aとその厚さにおいて異なるが基本構成は同一であるので、その説明を省略する。
Next, a detailed configuration of the
スペーサ12aは、3つの矩形枠状の絶縁部材21A,21B,21Cが重ね合わされて、互いの融着により一体化されて成り、絶縁部材21Aは、前段のダイノード10側に配置され、絶縁部材21Cは、後段側のダイノード10側に配置され、絶縁部材21Bは、2つの絶縁部材21A,21Cの間に把持される。絶縁部材21Bの両面及び貫通孔内部には、第1配線部22、第2配線部23、及び中間配線部24からなる配線部を含み、スペーサ12aを挟む2段のダイノード10の間を電気的に接続する導電路25が形成されている。さらに、導電路25には、絶縁部材21Aの四隅に形成され、前段のダイノード10と第1配線部22とを電気的に接続するための4つの穴部19(第1接続部)と、絶縁部材21Cの四隅に形成され、後段のダイノード10と第2配線部23とを電気的に接続するための4つの穴部19(第2接続部)とが、それぞれ設けられている。
The
第1配線部22は、絶縁部材21Bの前段のダイノード10側の面26上に、1つの辺の中間部から3つの隅部26a,26b,26cを経由して他の隅部26dに至るまで、面26からはみ出ることなく面26の外縁に沿って形成され(図7)、第2配線部23は、絶縁部材21Bの後段のダイノード10側の面27上に、1つの辺の中間部から3つの隅部27a,27b,27cを経由して他の隅部27dに至るまで、面27からはみ出ることなく面27の外縁に沿って形成されている(図8)。
The
また、第2配線部23の隅部27aと隅部27dとの間の端部には、スクリーン印刷により面27からはみ出ることなく形成された抵抗体28と、絶縁部材21Bの両面26,27の間に貫通して形成された層間接続用のスルーホール29とから成る中間配線部24が接続されている(図6、図8)。この抵抗体28の一端は第2配線部23の端部に接続され、抵抗体28の他端は面27上においてスルーホール29に接続され、スルーホール29は、さらに面26上において第1配線部22の端部に接続されている(図6)。すなわち、中間配線部24は、第1配線部22と第2配線部23とを抵抗体28を介して電気的に接続する機能を有する。
In addition, a
絶縁部材21Aに形成された穴部19は、その内面から絶縁部材21Bの面26側にかけて導電性材料30でコーティングされており、この導電性材料30が第1配線部22に接触することにより、穴部19と第1配線部22とが電気的に接続される。同様に、絶縁部材21Cに形成された穴部19は、その内面から絶縁部材21Bの面27側にかけて導電性材料30でコーティングされており、この導電性材料30が第2配線部23に接触することにより、穴部19と第2配線部23とが電気的に接続される(図5)。これにより、第1配線部22及び第2配線部23は、絶縁部材21Aの4つの穴部19及び絶縁部材21Cの4つの穴部19のそれぞれを連結して接続することによって、絶縁部材21Aの穴部19と絶縁部材21Cの穴部19とを抵抗体28を介して接続する。
The
図9を参照して、上記構成のスペーサ12aが2つのダイノード10の間に配置された場合のダイノード間の給電方向について説明する。同図の矢印Bに示すように、前段のダイノード10の突起部16c,16dとスペーサ12aの2つの穴部19とが接続されることにより、前段のダイノード10からスペーサ12aの2つの隅部に電荷が流れ込む。2つの隅部に流れ込んだ電荷は、第1配線部22、抵抗体28を含む中間配線部24及び第2配線部23を経由して、後段のダイノード10側の4つ穴部19に到達する。そして、穴部19に到達した電荷は、その穴部19に嵌め込まれた突起部16a,16bを伝わって後段側のダイノード10に流れ込む。このようにして、隣接する2つのダイノード10間においては、抵抗体28を経由して電荷が供給されることがわかる。このとき、2つのダイノード10間に挟まれたスペーサ12aにおいては、第1配線部22、抵抗体28を含む中間配線部24及び第2配線部23が、絶縁部材21A,21B,21Cに覆われることになり、真空容器5の内部空間に露出されることはない。ここでは、1つのダイノード10と導電路25とが2点で接続されているが、穴部19に形成された導電性材料30がダイノード10の窪み部17a,17b,17c,17dの周辺と接触することにより、4点で接続することも可能である。
With reference to FIG. 9, the feeding direction between dynodes when the
なお、絶縁部材21Bの面27上に形成された抵抗体28は、レーザトリミング加工により抵抗値の調整を施されてもよい。その際、絶縁部材21A,21B,21Cを重ね合わせてスペーサ12aとして形成された時点での調整が好ましいために、絶縁部材21Cの抵抗体28に対向する部分に開口を設け、その開口を介して抵抗値の調整を行った後、抵抗体28を増倍電子等からより確実に保護するために、絶縁部材21Cの開口をガラス材等の絶縁材によって充填又はコーティングするのが好ましい。
Note that the resistance value of the
以上説明した光電子増倍管1によれば、電子増倍部7を構成する複数段のダイノード10のうちの2つの隣接するダイノード10が、それらの間に配置されたスペーサ12aの導電路25によって抵抗体28を介して電気的に接続されるので、直列的に接続された複数段のダイノード10の両端に電圧を印加することにより隣接するダイノード10間に所望の電位差を生じさせることができる結果、ダイノード10に電圧を印加するための給電部としての接続端子数を削減することができ、電子増倍部7を小型化することができる。例えば、収束電極6、複数段のダイノード10からなる電子増倍部7、及びアノード8の組立図である図10に示すように、ステムピン11(図1参照)のいずれかである接続ピン31A、接続ピン31B、接続ピン31Cを、それぞれ収束電極6、最後段のダイノード10、アノード8に接続して、スペーサ12a,12bに内蔵される抵抗体28の抵抗値を約100kΩ〜数100kΩに設定する。この場合、接続ピン31Aと接続ピン31Bとの間に電圧を印加すれば、抵抗体28が分圧(分電圧)抵抗として機能することにより、最後段以外の各ダイノード10に外部から直接電圧を印加することなく所定電圧に設定することができる。よって、接続端子数の削減による電子増倍部7の小型化とともに、真空容器5内でのステムピン11用の空間およびステム4に対してのステムピン11の占有面積を非常に小さくできるため、結果として、真空容器5の大きさに対する有効面積(電子増倍部7の電子増倍孔9が形成された領域A(図1参照))を大きくすることができる。勿論、ピン数の少ない電子管とすることができコストも削減できる。なお、収束電極6を不要とする場合は、最前段と最後段のダイノード10に接続された接続ピン31Aと接続ピン31Bに電圧を印加する。
According to the
また、抵抗体28は絶縁部材21B,21Cによって覆われており真空容器5内の空間に対して露出していないので、増倍電子の影響による抵抗体28の抵抗値の変化を抑制することができ、電子増倍効率の安定化が可能になる。また、光電子増倍管1の場合、光電陰極2aを形成する際のアルカリ物質が抵抗体28に付着した場合、その影響により抵抗体28の抵抗値が変化してしまう可能性があるが、それも抑制することができ、電子増倍効率の安定化が可能になる。さらに、この抵抗体28は、絶縁部材21B上にスクリーン印刷で形成されるので、所望の抵抗値に容易に設定することができる。一方、ダイノード10の段間距離は、絶縁部材21A,21B,21C自体の厚さで容易に調整することができる。つまり、スペーサ全体で抵抗値を発生する場合に比べ、ダイノード10の段間距離と抵抗値との間に関連性を持つことなく、それぞれが最適な状態を選択することが可能となる。これにより、電子増倍部7を小型化しながら検出感度を安定化することができる。
Further, since the
また、導電路25が、隣接する2段のダイノード10の複数の接続点(接続部)と連結して接続され、これらの2段のダイノード10が、絶縁体で覆われた第1配線部22、第2配線部23、及び中間配線部24によって抵抗体28を介して互いに接続されるので、各配線部への電子入射によるノイズの発生や配線部のはがれを抑制することができる。また、各ダイノード10に対して複数の接続部を有することから、例えばダイノード10に反り等が生じた場合であっても、確実に接点を保つことができ、安定した電位供給を行うことができるとともに、ダイノード全体に亘ってより均一な電位を設定することができる。また、形成されたスペーサ12a,12bに関して表裏なく使用することができ、装置全体の製造効率が向上する。さらに、複数の接続部が第1配線部22、第2配線部23によって連結され、それらが互いに中間配線部24によって抵抗体28を介して互いに接続されるので、各接続部ごとに抵抗体28まで配線を設けることなく、各接続部と抵抗体28との接続構造が簡略されるとともに、配線部全体の長さが短縮化されて、ダイノード全体に亘ってより均一な電位を設定することができる。これらにより、結果として、検出感度を安定化することができる。
In addition, the
さらに、スペーサ12a,12bは、ダイノード10の電子増倍孔9が形成された領域Aを取り囲むような枠状の形状を有するので、ダイノード10の辺縁部との接触面積の増加によってダイノード10間の距離を安定して保持することにより、複数段のダイノード10による電子増倍機能を維持し、検出感度を安定化することができる。また、外部衝撃等への耐震性も高く、ダイノード10を積層して電子増倍部7を組上げる際にも、容易に組上げることができ、装置全体の製造効率が向上する。さらに、電子増倍部7の内部の電子増倍空間をダイノード10等とともに密閉することで、電子が電子増倍部7の外へ出てしまうことに起因するノイズを抑制することができる。
Furthermore, since the
またさらに、スペーサ12a,12bは、絶縁部材21A,21B,21Cの3層構造であり、絶縁部材21Bに形成された抵抗体28を含む中間配線部24、第1配線部22、及び第2配線部23がこれらの絶縁部材21A,21B,21Cによって覆われていることで、抵抗体28を含む配線部をスペーサ12a,12b内部で絶縁体によって確実に包囲することができるので、検出感度を安定化することができる。また、抵抗体28を含む配線部が絶縁部材21Bに一括に形成されているので、製造時の導電路25の形成が容易となり、装置全体の製造効率が向上する。また、抵抗体28の抵抗値を変更したスペーサ12a,12bを作成する場合にも、絶縁部材21Bを交換するのみで対応可能であることから、抵抗値の変更したスペーサの作成も容易に行うことができる。さらに、絶縁部材21A,21B,21Cの接合に関しては、接着剤等を介することなく絶縁部材同士の融着で行われているために、接着剤等による抵抗体28および各配線部への影響やガス放出といった問題を生じることもない。
Furthermore, the
さらにまた、前段側のダイノード10の突起部16c,16dが、スペーサ12aの前段側の穴部19に嵌め合わされ、後段側のダイノード10の突起部16a,16bが、スペーサ12aの後段側の穴部19に嵌め合わされることにより、2段のダイノード10とスペーサ12aの導電路25とが電気的に接続されるので、ダイノード10同士およびダイノード10とスペーサ12aとの位置決めが容易となると同時に確実かつ安定な電気的接続が為される。ダイノード同士の位置関係の変化は各チャンネルの出力の変化につながり、ダイノード10とスペーサ12aとの位置関係の変化は、両者の電気的接続状態の変化(例えば接続部における接触面積の変化による電気的抵抗の変化)にもつながるため、検出感度のより一層な安定化が可能になる。
Furthermore, the
なお、本発明は、前述した実施形態に限定されるものではない。例えば、スペーサに形成される導電路の形状としては、以下の様々な変形態様を採ることができる。 In addition, this invention is not limited to embodiment mentioned above. For example, the following various modifications can be employed as the shape of the conductive path formed in the spacer.
図11〜13には、本発明の第1の変形例であるスペーサ112aを示す。このスペーサ112aにおいては、第1配線部122が、絶縁部材21Bの面26上に1つの辺の中間部から隅部26aを経由して隅部26bに至るまで略L字状に形成され(図12)、第2配線部123は、絶縁部材21Bの面27上に1つの辺の中間部から隅部27aを経由して隅部27bに至るまで略L字状で形成されている(図13)。そして、これらの配線部122,123が、抵抗体28とスルーホール29とから成る中間配線部24によって接続される。図14を参照して、上記構成のスペーサ112aが2つのダイノード10の間に配置された場合のダイノード間の給電方向について説明する。同図の矢印Cに示すように、前段のダイノード10の突起部16cとスペーサ112aの穴部19とが接続されることにより、前段のダイノード10からスペーサ112aの1つの隅部に電荷が流れ込む。隅部に流れ込んだ電荷は、第1配線部122、抵抗体28を含む中間配線部24及び第2配線部123を経由して、後段のダイノード10側の2つの穴部19に到達する。そして、穴部19に到達した電荷は、その穴部19に嵌め込まれた突起部16bを伝わって後段側のダイノード10に流れ込む。このことから、スペーサ112aによっても、隣接する2つのダイノード10間において抵抗体28を経由して電荷を流れ込ませることが可能である。ここで、スペーサ112aの各面の四隅の穴部19のうちの1箇所がダイノード10に接続されれば済むため、それ以外の三隅にある穴部19の内部は導電コーティングが省略されてもよい。
11 to 13 show a
また、図15には、本発明の第2の変形例であるスペーサ212aを示す。このスペーサ212aにおいては、2つの配線部と抵抗体28及びスルーホール29を含む中間配線部24とから成る導電路225が、絶縁部材21Bの辺の中間部から1つの隅部に至るまで略直線状に形成されている。このようなスペーサ212aを用いた場合のダイノード間の給電方向は、図16の矢印Dに示すようになる。具体的には、前段のダイノード10からスペーサ212aの1つの隅部に電荷が流れ込み、その電荷は、抵抗体28を含む導電路225、及び後段のダイノード10側に接続された1つの穴部19を経由して後段側のダイノード10に流れ込む。本変形例においても、第1の変形例と同様に、スペーサ212aの各面の四隅の穴部19のうちの1箇所がダイノード10に接続されれば済むため、それ以外の三隅にある穴部19の内部は導電コーティングが省略されてもよい。
FIG. 15 shows a
さらに、図17及び図18に示す本発明の第3の変形例であるスペーサ312aのように、絶縁部材21A,21Cを含む2層構造とし、絶縁部材21Aに形成された穴部19の底面と絶縁部材21Cに形成された穴部19の底面との間に抵抗体328を埋め込ませてもよい。このようなスペーサ312aによっても、隣接する2段のダイノード10を抵抗体を介して接続することができる。なお、本変形例においても絶縁部材21Bに抵抗体328を埋め込むようにすることで3層構造としてもよい。また、スペーサ212aの各面の四隅の穴部19の全てに抵抗体328を埋め込ませてもよく、一部の穴部19でも良い。その場合、抵抗体328を埋め込ませていない穴部19の内部は導電コーティングは省略されてもよい。
Further, like a
また、図19に示す本発明の第4の変形例であるスペーサ412aのように、絶縁部材による1層構造を採用してもよい。このようなスペーサ412aでは、絶縁部材21Bの第1配線部22が形成された面26、及び第2配線部23と中間配線部24とが形成された面27のうち、少なくとも抵抗体28を、好ましくは面26および面27の両面をガラス材等の絶縁材でコーティングすればよい。
Moreover, you may employ | adopt the 1 layer structure by an insulating member like the
また、ダイノードがエッチング加工により製造されるような場合であってダイノードに突起を形成することが困難なときは、スペーサ側に突起を、ダイノード側に窪み又は孔を形成してもよい。図20は、このような場合の本発明の第5の変形例であるスペーサ512aの斜視図である。同図に示すスペーサ512aでは、絶縁部材21Bの両面においてそれぞれ異なる対角線上の隅部に配線部425と電気的に接続された導電性の突起部419が設けられ、その絶縁部材21Bの両面の突起部419を除いた領域が、ガラス材によってコーティングされている。このような構造によっても、抵抗体28の抵抗値の変化を防ぎつつ、ダイノード間を配線部425を介して接続することができる。
In the case where the dynode is manufactured by etching and it is difficult to form the protrusion on the dynode, the protrusion may be formed on the spacer side, and the depression or hole may be formed on the dynode side. FIG. 20 is a perspective view of a
また、光電子増倍管1におけるダイノード10とアノード8との配置関係は図10に示すものには限定されず、アノード8の後段に1段以上のダイノード10が配置されてもよい。その場合は、アノード8の前段側及び後段側のダイノード10との間には別途抵抗を設ける必要がある。例えば、アノード8とアノード8の前段側及び後段側に配置されたダイノード10との間は、絶縁体のみから成るスペーサが設けられ、ダイノード10に対してのステムピン11は、最前段、アノード8の前段側及び後段側のダイノード10に接続される。そして、アノード8の前段側のダイノード10に接続されたステムピン11と、アノード8の後段側のダイノード10に接続されたステムピン11との間において、別途ブリーダ抵抗等の抵抗体を設けることで、各ダイノード10への分圧(分電圧)を行う。
Further, the arrangement relationship between the
また、以上説明した実施形態では、電子増倍部を備えた電子増倍管として光電子増倍管を示したが、それ以外にも光電陰極を有さない電子増倍管、入力光像を輝度増幅するイメージ増倍管等の電子増倍部を備えた電子増倍管であってもよい。 In the embodiment described above, the photomultiplier tube is shown as the electron multiplier tube provided with the electron multiplier section. However, the electron multiplier tube having no other photocathode, the input light image has a luminance. It may be an electron multiplier provided with an electron multiplier such as an image multiplier to be amplified.
1…光電子増倍管、2a…光電陰極、7…電子増倍部、9…電子増倍孔、10…ダイノード、12a,12b,112a,212a,312a,412a,512a…スペーサ、16a,16b,16c,16d…突起部、18,19…穴部(第1又は第2接続部)、21A,21B,21C…絶縁部材、22,122…第1の配線部(配線部)、23,123…第2の配線部(配線部)、24…中間配線部(配線部)、25,225,425…導電路、28,328…抵抗体。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
隣接する2段の前記ダイノードの間には、それぞれ、前記2段のダイノードの間を電気的に接続する導電路を有する絶縁性の枠状部材であるスペーサが配置されており、
前記導電路の一部は、絶縁体によって覆われた抵抗体によって形成されている、
ことを特徴とする電子増倍管。 An electron multiplier having an electron multiplier section in which dynodes, which are plate electrodes having electron multiplier holes for multiplying incident electrons, are stacked in a plurality of stages,
Between the adjacent two-stage dynodes, spacers that are insulating frame-like members each having a conductive path that electrically connects the two-stage dynodes are disposed,
A part of the conductive path is formed by a resistor covered with an insulator,
An electron multiplier characterized by that.
前記2段のダイノードのうちの一方と電気的に接続するための第1接続部と、
前記2段のダイノードのうちの他方と電気的に接続するための第2接続部と、
前記第1接続部と前記第2の接続部とを前記抵抗体を介して電気的に接続する、絶縁体で覆われた配線部と、
を含むことを特徴とする請求項1記載の電子増倍管。 The conductive path is
A first connection for electrically connecting to one of the two-stage dynodes;
A second connection for electrically connecting to the other of the two-stage dynodes;
A wiring portion covered with an insulator for electrically connecting the first connection portion and the second connection portion via the resistor;
The electron multiplier according to claim 1, comprising:
ことを特徴とする請求項2記載の電子増倍管。 The first connection part and the second connection part are plural.
The electron multiplier according to claim 2, wherein:
前記複数の第1接続部を連結する第1の配線部と、
前記複数の第2接続部を連結する第2の配線部と、
前記第1の配線部と前記第2の配線部とを接続する中間配線部とを含み、
前記抵抗体は、前記中間配線部の一部を形成している、
ことを特徴とする請求項3記載の電子増倍管。 The wiring part is
A first wiring portion connecting the plurality of first connection portions;
A second wiring portion connecting the plurality of second connection portions;
An intermediate wiring portion connecting the first wiring portion and the second wiring portion;
The resistor forms a part of the intermediate wiring portion.
The electron multiplier as claimed in claim 3.
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜4のいずれか一項に記載の電子増倍管。 The spacer has a frame shape surrounding the region where the electron multiplier hole of the dynode is formed.
The electron multiplier as described in any one of Claims 1-4 characterized by the above-mentioned.
前記2段のダイノードのそれぞれには、少なくとも1つの突起又は窪みが形成されており、
前記2段のダイノードのうち一方のダイノードの前記突起又は前記窪みが、前記第1接続部の前記窪み又は前記突起に嵌め合わされることにより、前記一方のダイノードと前記配線部とが電気的に接続され、
前記2段のダイノードのうち他方のダイノードの前記突起又は前記窪みが、前記第2接続部の前記窪み又は前記突起に嵌め合わされることにより、前記他方のダイノードと前記配線部とが電気的に接続される、
ことを特徴とする請求項2〜5のいずれか1項に記載の電子増倍管。 A depression or a protrusion is formed in the first connection portion and the second connection portion,
Each of the two-stage dynodes is formed with at least one protrusion or depression,
The one dynode and the wiring portion are electrically connected by fitting the protrusion or the recess of one dynode of the two-stage dynodes to the recess or the protrusion of the first connection portion. And
The other dynode and the wiring portion are electrically connected by fitting the protrusion or the recess of the other dynode of the two-stage dynodes to the recess or the protrusion of the second connection portion. To be
The electron multiplier tube according to claim 2, wherein the electron multiplier tube is provided.
前記2段のダイノードのうちの一方のダイノード側に設けられ、前記一方のダイノードと電気的に接続するための前記第1接続部を含む第1の絶縁部材と、
前記2段のダイノードのうちの他方のダイノード側に設けられ、前記他方のダイノードと電気的に接続するための前記第2接続部を含む第2の絶縁部材と、
前記第1及び第2の絶縁部材の間に把持された第3の絶縁部材と、
前記第1の絶縁部材と前記第3の絶縁部材との間に設けられ、前記第1接続部に電気的に接続された第1の配線部と、
前記第2の絶縁部材と前記第3の絶縁部材との間に設けられ、前記第2接続部に電気的に接続された第2の配線部と、
前記第3の絶縁部材を貫通して設けられ、前記第1の配線部と前記第2の配線部とを接続する中間配線部とを有し、
前記中間配線部の一部は、抵抗体によって形成されている、
ことを特徴とする請求項2又は3に記載の電子増倍管。 The spacer is
A first insulating member provided on one dynode side of the two-stage dynodes and including the first connecting portion for electrically connecting to the one dynode;
A second insulating member provided on the other dynode side of the two-stage dynodes and including the second connecting portion for electrically connecting to the other dynode;
A third insulating member gripped between the first and second insulating members;
A first wiring portion provided between the first insulating member and the third insulating member and electrically connected to the first connecting portion;
A second wiring portion provided between the second insulating member and the third insulating member and electrically connected to the second connecting portion;
An intermediate wiring portion provided through the third insulating member and connecting the first wiring portion and the second wiring portion;
A part of the intermediate wiring part is formed of a resistor.
The electron multiplier according to claim 2 or 3, wherein
ことを特徴とする請求項7記載の電子増倍管。 The first wiring portion, the second wiring portion, and the intermediate wiring portion are formed on the third insulating member,
The electron multiplier according to claim 7.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007330337A JP5284635B2 (en) | 2007-12-21 | 2007-12-21 | Electron multiplier |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007330337A JP5284635B2 (en) | 2007-12-21 | 2007-12-21 | Electron multiplier |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009152121A JP2009152121A (en) | 2009-07-09 |
| JP5284635B2 true JP5284635B2 (en) | 2013-09-11 |
Family
ID=40921009
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007330337A Active JP5284635B2 (en) | 2007-12-21 | 2007-12-21 | Electron multiplier |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5284635B2 (en) |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1402549A (en) * | 1971-12-23 | 1975-08-13 | Mullard Ltd | Electron multipliers |
| FR2566175B1 (en) * | 1984-05-09 | 1986-10-10 | Anvar | ELECTRON MULTIPLIER DEVICE, LOCATED BY THE ELECTRIC FIELD |
| JPH04359855A (en) * | 1991-06-06 | 1992-12-14 | Hamamatsu Photonics Kk | Secondary electron multiplier |
| JP3260902B2 (en) * | 1993-04-28 | 2002-02-25 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Electron multiplier |
| JP3260901B2 (en) * | 1993-04-28 | 2002-02-25 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Electron multiplier |
| JP3630456B2 (en) * | 1994-11-30 | 2005-03-16 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Electron multiplier |
| JP4744844B2 (en) * | 2004-10-29 | 2011-08-10 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Photomultiplier tube and radiation detector |
| JP4921248B2 (en) * | 2007-05-28 | 2012-04-25 | 浜松ホトニクス株式会社 | Electron tube |
-
2007
- 2007-12-21 JP JP2007330337A patent/JP5284635B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009152121A (en) | 2009-07-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5290804B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| US8022606B2 (en) | Electron multipler and electron detector | |
| WO2007099958A1 (en) | Photomultiplier, radiation sensor, and photomultiplier fabricating method | |
| US5532551A (en) | Photomultiplier for cascade-multiplying photoelectrons | |
| JP5290805B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JP2009289693A (en) | Charged-particle detector | |
| WO2001075933A1 (en) | Electron multiplier and photomultiplier | |
| WO2007099959A1 (en) | Photomultiplier and radiation detecting apparatus | |
| JP5284635B2 (en) | Electron multiplier | |
| JP5330083B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JP4921248B2 (en) | Electron tube | |
| US8587196B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JPH07335174A (en) | Electron multiplier tube | |
| JP4402478B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JP5154717B2 (en) | Electron multiplier and photomultiplier tube including the same | |
| US12431342B2 (en) | Charged particle detector | |
| JP5789021B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JP2009200044A (en) | Photomultiplier | |
| JP2018097925A (en) | Ultraviolet detector | |
| JP3312770B2 (en) | Electron multiplier | |
| JP5518364B2 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JP3630456B2 (en) | Electron multiplier | |
| EP2442347B1 (en) | Photomultiplier tube | |
| JP4816271B2 (en) | Plasma display panel | |
| EP1727183A1 (en) | Image display device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101207 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120315 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120321 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121127 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130121 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130528 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130530 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5284635 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |