JP5257826B2 - Fuel cell stack, fuel cell stack unit and fuel cell - Google Patents
Fuel cell stack, fuel cell stack unit and fuel cell Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5257826B2 JP5257826B2 JP2007165030A JP2007165030A JP5257826B2 JP 5257826 B2 JP5257826 B2 JP 5257826B2 JP 2007165030 A JP2007165030 A JP 2007165030A JP 2007165030 A JP2007165030 A JP 2007165030A JP 5257826 B2 JP5257826 B2 JP 5257826B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- fuel cell
- fuel
- cell stack
- surface portion
- air
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/30—Hydrogen technology
- Y02E60/50—Fuel cells
Landscapes
- Fuel Cell (AREA)
Description
本発明は、固体酸化物形の燃料電池(SOFC)の燃料電池セルスタックに関し、更に詳細には、絶縁性で多孔質の基体と、基体の周囲を管状に覆い且つ互いに電気的に直列に接続された複数の燃料電池セルを含むように基体の上に積層された管状部分とを有する燃料電池セルスタックに関する。 The present invention relates to a fuel cell stack of a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC), and more particularly, an insulating and porous substrate, a tube covering the periphery of the substrate, and electrically connected to each other in series. The present invention relates to a fuel cell stack having a tubular portion laminated on a base so as to include a plurality of fuel cells that are formed.
また、本発明は、複数の上記燃料電池セルスタックと、それらが取付けられたマニホールドとを有する燃料電池セルスタックユニットに関する。また、本発明は、複数の上記燃料電池セルスタックと、それらを収容したケースとを有する燃料電池に関する。 The present invention also relates to a fuel cell stack unit having a plurality of the above fuel cell stacks and a manifold to which they are attached. The present invention also relates to a fuel cell having a plurality of the above fuel cell stacks and a case containing them.
従来から、絶縁性で多孔質の基体と、基体の周囲を管状に覆い且つ互いに電気的に直列に接続された複数の燃料電池セルを含むように基体の上に積層された管状部分とを有する燃料電池セルスタックが知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。燃料電池セルスタックは、複数の燃料電池セルを組合せた構造体である。各燃料電池セルは、燃料極と空気極とを有し、燃料極に水素を含む燃料ガスを作用させ、且つ、空気極に酸素を含む空気を作用させることによって発電させる。上記管状部分を有する燃料電池の場合、一般的には、管状部分の内側に燃料極が配置され、その外側に空気極が配置される。 Conventionally, it has an insulating and porous substrate, and a tubular portion laminated on the substrate so as to include a plurality of fuel cells that cover the periphery of the substrate in a tubular shape and are electrically connected to each other in series. A fuel cell stack is known (for example, see Patent Document 1). The fuel cell stack is a structure in which a plurality of fuel cells are combined. Each fuel cell has a fuel electrode and an air electrode, and generates electric power by causing a fuel gas containing hydrogen to act on the fuel electrode and causing air containing oxygen to act on the air electrode. In the case of a fuel cell having the tubular portion, generally, a fuel electrode is disposed inside the tubular portion and an air electrode is disposed outside the fuel electrode.
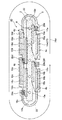
複数の燃料電池セルを組合せた燃料電池セルスタックの一例を、特許文献1に記載されている燃料電池セルスタックを参照して説明する。図15は、特許文献1に記載された燃料電池セルスタックの斜視図である。
An example of a fuel cell stack in which a plurality of fuel cells are combined will be described with reference to the fuel cell stack described in
特許文献1に記載されている燃料電池セルスタック100は、絶縁性で多孔質の基体102と、基体102の周囲を管状に覆い且つ互いに電気的に直列に接続された複数の燃料電池セル104を含むように基体102の上に積層された管状部分106とを有している。燃料電池セルスタック1の断面形状は、扁平であり、互いに対向する平面部分108を有している。複数の燃料電池セル104は、平面部分108に形成され、管状部分106の一方の端部101aから他方の端部101bに向かって1列に配列されている。また、各燃料電池セル104の面積は、一方の端部101aから他方の端部101bに向かって次第に大きくなっている。
A fuel cell stack 100 described in
燃料ガスを管状部分106の内側の基体102に一方の端部101aから他方の端部101bに向かって流し、空気を管状部分106の外側に流すことによって、燃料電池セル100を作動させる。燃料ガスを一方の端部101aから他方の端部101bに向かって流すと、燃料ガス中の水素が一方の端部の側の燃料電池セル104から使われるので、燃料ガスは他方の端部に向かうにつれて薄まる。もし、同じ面積の燃料電池セルが配置されていれば、他方の端部に向かうほど、発生電圧が低下する。更に、発生電圧の異なる燃料電池セルが直列に配置されていることにより、発生電圧の小さい燃料電池セルに強制的に電流が流れ、かかる燃料電池セルが劣化する。しかしながら、特許文献1に開示された燃料電池セルスタック100では、燃料電池セル104の面積が他方の端部に向かうにつれて大きくなっているので、各燃料電池セル104の発生電圧を一定に維持することができる。また、燃料電池セル104の劣化を防止することができる。
The fuel cell 100 is operated by flowing the fuel gas through the base 102 inside the tubular portion 106 from one end 101 a toward the other end 101 b and flowing air outside the tubular portion 106. When the fuel gas flows from one end 101a toward the other end 101b, hydrogen in the fuel gas is used from the fuel cell 104 on the one end side, so that the fuel gas flows to the other end. It fades as it goes. If fuel cells having the same area are arranged, the generated voltage decreases toward the other end. Furthermore, since the fuel cells having different generated voltages are arranged in series, a current flows forcibly through the fuel cells having a small generated voltage, and the fuel cells deteriorate. However, in the fuel cell stack 100 disclosed in
上述した燃料電池セルスタック100において、燃料ガスの水素が完全に消費されて、他方の端部の燃料電池セル104に全く水素が供給されない状態、所謂燃料枯れが生じ得る。この場合、他方の端部の燃料電池セルが不良になり、その結果、燃料電池セルが電気的に直列に接続された燃料電池セルスタック全体が機能しなくなる。従って、燃料枯れが生じても、燃料電池セルが不良にならず、燃料電池セルスタック全体の機能が維持されるように信頼性を向上させる余地がある。 In the fuel cell stack 100 described above, hydrogen in the fuel gas is completely consumed, and so-called fuel depletion may occur, in which no hydrogen is supplied to the fuel cell 104 at the other end. In this case, the fuel cell at the other end becomes defective, and as a result, the entire fuel cell stack in which the fuel cells are electrically connected in series does not function. Therefore, there is room for improving the reliability so that the fuel cell does not become defective and the function of the entire fuel cell stack is maintained even if the fuel runs out.
また、各燃料電池セル104の面積は、燃料ガスの流量や濃度等に応じて決定されるので、燃料電池セルの仕様設計が困難である。 In addition, since the area of each fuel cell 104 is determined according to the flow rate and concentration of the fuel gas, it is difficult to design the specifications of the fuel cell.
そこで、本発明は、絶縁性で多孔質の基体と、基体の周囲を管状に覆い且つ互いに電気的に直列に接続された複数の燃料電池セルを含むように基体の上に積層された管状部分とを有する燃料電池セルスタックの信頼性を向上させること、及び、上記燃料電池セルスタックを含む燃料電池セルスタックユニット及び燃料電池を提供することを第1の目的としている。 Accordingly, the present invention provides a tubular portion laminated on a base so as to include an insulating porous base and a plurality of fuel cells that cover the base in a tubular shape and are electrically connected to each other in series. It is a first object of the present invention to improve the reliability of a fuel cell stack having the above, and to provide a fuel cell stack unit and a fuel cell including the fuel cell stack.
本発明は、更に、絶縁性で多孔質の基体と、基体の周囲を管状に覆い且つ互いに電気的に直列に接続された複数の燃料電池セルを含むように基体の上に積層された管状部分とを有する燃料電池セルスタックの信頼性を向上させることができ且つその仕様設計を容易にすること、及び、上記燃料電池セルスタックを含む燃料電池セルスタックユニット及び燃料電池を提供することを第2の目的としている。 The present invention further includes a tubular portion laminated on the base so as to include an insulating and porous base and a plurality of fuel cells that cover the periphery of the base and are electrically connected to each other in series. And to provide a fuel cell stack unit and a fuel cell including the fuel cell stack, and to provide a fuel cell stack unit including the fuel cell stack. The purpose is.
上記の目的を達成するために、本発明は、基体上に複数の燃料電池セルを積層した燃料電池セルスタックを複数個電気的に接続した燃料電池セルスタックユニットであって、基体は、長手方向に延びると共に長手方向に直交する断面が幅に対し厚さが小さい形状であり且つその内部に長手方向に沿って一端から他端まで貫通する孔を有し、燃料電池セルの各々は、燃料極、電解質及び空気極を有する燃料電池セルスタックユニットにおいて、空気及び燃料ガスの一方が、基体の孔の一端から他端に流れ、且つ、空気及び燃料ガスの他方が、燃料電池セルスタックの外側に流れ、燃料電池セルスタックの各々は、燃料電池セルの燃料極及び空気極のそれぞれに電気的に接続された燃料極端子及び空気極端子を有し、基体は、基体の厚み方向の互いに反対側に位置する第一周面部分及び第二周面部分、並びに、基体の幅方向の互いに反対側に位置し第一周面部分及び第二周面部分を接続する第一接続面部分及び第二接続面部分からなる周面を有し、燃料電池セルスタックの各々は、燃料電池セルスタックの各々の燃料極端子及び空気極端子に電気的に接続され且つ基体の第1周面部分又は第2周面部分に沿って離間して設けられた複数の電極接続部を介して、互いに電気的に直列に接続されており、複数の上記電極接続部が上記燃料電池セルの燃料電池セルスタックの中央部寄りに設けられていることを特徴としている。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a fuel cell stack unit in which a plurality of fuel cell stacks in which a plurality of fuel cells are stacked on a substrate are electrically connected, wherein the substrate has a longitudinal direction. The cross section orthogonal to the longitudinal direction has a shape with a small thickness with respect to the width, and has a hole penetrating from one end to the other end along the longitudinal direction. In the fuel cell stack unit having an electrolyte and an air electrode, one of air and fuel gas flows from one end of the hole of the base to the other end, and the other of air and fuel gas is outside the fuel cell stack. Each of the fuel cell stacks has a fuel electrode terminal and an air electrode terminal electrically connected to the fuel electrode and the air electrode of the fuel cell, respectively. The first peripheral surface portion and the second peripheral surface portion that are located on the opposite sides of the substrate, and the first connection surface portion that is located on the opposite sides in the width direction of the base and connects the first peripheral surface portion and the second peripheral surface portion. And each of the fuel cell stacks is electrically connected to each fuel electrode terminal and air electrode terminal of the fuel cell stack, and the first peripheral surface portion of the base body. Alternatively, the plurality of electrode connection portions are electrically connected in series via a plurality of electrode connection portions provided apart from each other along the second peripheral surface portion, and the plurality of electrode connection portions are fuel cells of the fuel cell. It is provided near the center of the stack .
本発明において、好ましくは、複数の電極接続部は、基体の第1周面部又は第2周面部の中央部を挟んで設けられている。In the present invention, preferably, the plurality of electrode connection portions are provided with the central portion of the first peripheral surface portion or the second peripheral surface portion of the base interposed therebetween.
本発明において、好ましくは、燃料電池セルスタックの各々は、基体の第一周面部分側の燃料極端子から第二周面部分側の空気極端子に向けて第一接続面部分に沿って電流を流し、第二周面部分側の燃料極端子から第一周面部分側の空気極端子に向けて第二接続面部分に沿って電流を流すように構成されている。 In the present invention, preferably, each of the fuel cell stacks has a current along the first connection surface portion from the fuel electrode terminal on the first peripheral surface portion side to the air electrode terminal on the second peripheral surface portion side. And a current is caused to flow along the second connection surface portion from the fuel electrode terminal on the second peripheral surface portion side toward the air electrode terminal on the first peripheral surface portion side.
本発明によれば、信頼性を向上させた燃料電池セルスタックユニットを提供することができる。 According to the present invention, a fuel cell stack unit with improved reliability can be provided.
以下、図面を参照して本発明による燃料電池セルスタックの参考例及び実施形態を説明する。ここで、燃料電池セルスタックとは、複数の燃料電池セルを含む1つの構造体をいう。 Hereinafter, reference examples and embodiments of a fuel cell stack according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Here, the fuel cell stack refers to one structure including a plurality of fuel cells.
図1は、本発明による燃料電池スタックの参考例の概略的な斜視図である。また、図2は、図1の線II−IIにおける図式的な断面図である。 FIG. 1 is a schematic perspective view of a reference example of a fuel cell stack according to the present invention. FIG. 2 is a schematic cross-sectional view taken along line II-II in FIG.
図1に示すように、本発明の参考例である燃料電池セルスタック1は、絶縁性で多孔質の基体2と、基体2の周囲を管状に覆い、且つ複数の燃料電池セル4を含むように基体2の上に積層された管状部分6とを有している。この燃料電池セルスタック1では、空気及び燃料ガスの一方が、管状部分6の内側に位置する基体2の中を一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bに流され、空気及び燃料ガスの他方が管状部分6の外側に流される。
以下、例示として、管状部分6の内側に位置する基体2の中を燃料ガスが流れる構造の燃料電池セルスタック1を説明する。また、燃料ガスが流れる方向を管内ガス流れ方向Fと称する。基体2は、管内ガス流れ方向Fと垂直な細長い断面を有し、また、管内ガス流れ方向Fに貫通する複数の孔8を有している。基体2は、例えば、CaやY等の希土類元素から選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたジルコニア、マグネシア、スピネル、フォルステライトなどの少なくとも一種から形成されることが好ましい。
As shown in FIG. 1, a
Hereinafter, as an example, a
図2に示すように、管状部分6が積層された基体2の周面は、互いに反対側に位置する2つの平面部分10a、10cと、それらを互いに連結し且つ互いに反対側に位置する2つの接続面部分10b、10dとを有している。本参考例では、一方の平面部分10aに2つの燃料電池セル4a、4bが形成され、他方の平面部分10bに2つの燃料電池セル4c、4dが形成されている。各燃料電池セル4a〜4dは、同様の構造を有している。以下、燃料電池セル4aの構成要素に符号aを付してそれを説明し、それに対応する他の燃料電池セル4b〜4dの構成要素にそれぞれ符号b〜dを付して、それらの説明を省略する。なお、図2において、燃料電池セル4a〜4dの構成要素を説明するために、それらの厚さを基体2の厚さに比べて大きくして表している。
As shown in FIG. 2, the peripheral surface of the
燃料電池セル4aは、基体2の上に積層された燃料極12aと、燃料極12aを覆うように積層された電解質14aと、電解質14aの上に積層された空気極16aと、空気極16aの上に積層された集電層18aとを有している。電解質14aは、空気又は燃料ガスを透過させない緻密材料で形成され、燃料極12a及び基体2を覆った管状の構造を有している。なお、電解質14a〜14bは、分離しているわけではなく、一体の層14を構成している。
The
燃料極12aは、例えば、Niと、CaやY、Sc等の希土類元素から選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたジルコニアとの混合体、Niと、希土類元素から選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたセリアとの混合体、Niと、Sr、Mg、Co、Fe、Cuから選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたランタンガレートとの混合体、の少なくとも一種から形成される。
The
電解質14aは、例えば、Y、Sc等の希土類元素から選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたジルコニア、希土類元素から選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたセリア、Sr、Mgから選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたランタンガレート、の少なくとも一種から形成される。
The
空気極16aは、例えば、Sr、Caから選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたランタンマンガナイト、Sr、Co、Ni、Cuから選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたランタンフェライト、Sr、Fe、Ni、Cuから選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたサマリウムコバルト、銀、などの少なくとも一種から形成される。
The
集電層18aは、導電性及び空気透過性という観点から、銀を含有する多孔質導電性膜であることが好ましい。
The
基体2の厚さTは、例えば、2mmであり、燃料極12aの厚さは、例えば、50μmであり、電解質14aの厚さは、例えば、30μmであり、空気極16aの厚さは、例えば、30μmであり、集電層18aの厚さは、例えば10μmである。基体2の幅Wは、例えば、30mmであり、基体2の長さLは、例えば、80mmである(図1参照)。
The thickness T of the
燃料電池セルスタック1は、更に、燃料電池セル4a〜4dを直列に接続するためのインターコネクタ20a〜20d及び延長集電層22を有している。
The
インターコネクタ20a〜20dはそれぞれ、各燃料電池セル4a〜4dの燃料極12から電解質14を貫いて突出し、且つ、空気極16及び集電層18と離間している。インターコネクタ20a〜20dは、例えば、Sr、Ca、Mgから選ばれる少なくとも一種をドープしたランタンクロマイト、銀ろう、銀及び銀を含む合金、銀とガラスの混合体、などの少なくとも一種から形成される。インターコネクタ20a〜20dの厚さは、例えば、60μmである。
The interconnectors 20 a to 20 d protrude from the fuel electrode 12 of each
延長集電層22は、一方の接続面部分10bの電解質14の上に積層されている。延長集電層22は、電気的接続という観点から、銀を含有する導電性部材であることが好ましく、集電層18と同一の材料であっても良いし、インターコネクタ20a〜dと同一の材料であっても良い。延長集電層22の厚さは、例えば、20μmである。
The extended
図1に示すように、各燃料電池セル4a〜4d、インターコネクタ20a〜20d及び延長集電層22は、一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bまで延びる形態を有している。図1には、燃料電池セル4a、4bの集電層18a、18b、インターコネクタ20a及び延長集電層22が見えている。燃料極12a〜12d、空気極16a〜16d及び集電層18a〜18dは、矩形に積層されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, each of the
4つの燃料電池セル4a〜4dは、管状部分6の周方向に1列に配列されると共に、互いに電気的に直列に接続されている。具体的には、図2に示すように、第1の燃料電池セル4aの空気極16a及び集電層18aと第2の燃料電池セル4bの燃料極12bとがインターコネクタ20bを介して接続され、第2の燃料電池セル4bの集電層18と第3の燃料電池セル4cの燃料極12cとが延長集電層22及びインターコネクタ20cを介して接続され、第3の燃料電池セル4cの空気極16c及び集電層18cと第4の燃料電池セル4dの燃料極12dとがインターコネクタ20dを介して接続されている。それにより、第4の燃料電池セル4dから第3及び第2の燃料電池セル4c、4bを介して第1の燃料電池セル4aまで延びる直列接続セルグループ、即ち、互いに直列に接続された一連の燃料電池セル4のグループ24aが構成される。本参考例では、燃料電池セルスタック1は、単一の直列接続セルグループ24aを有している。直列接続セルグループ24aにおいて、インターコネクタ20aは、燃料極端子26として作用し、第4の燃料電池セル4dの集電層18dは、空気極端子27として作用し、燃料極端子26と空気極端子27との間の電圧が取り出される。上記接続はすべて、一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bにわたってなされている。
The four
第1の燃料電池セル4aの空気極16a及び第3の燃料電池セル4cの空気極16cはそれぞれ、インターコネクタ20b、20dに接続されていなくてもよい。しかしながら、図2に示すように、空気極16a、16cは、集電層18a、18cと共にインターコネクタ20b、20dに接続されるように配置されることが好ましい。それにより、空気極16a、16cとインターコネクタ20b、20dとの間の電気的接続の信頼性を確保することができると共に、集電層18a、18cを介して露出される空気極16a、16cの面積を広くして、発電出力を増大させることができる。
The
次に、本発明の参考例による燃料電池セルスタック作り方の一例を説明する。 Next, an example of how to make a fuel cell stack according to a reference example of the present invention will be described.
先ず、絶縁性の基体原料粉末を押出し成形することによって、多孔性の基体2を形成する。多孔の程度を調整するという観点から、原料粉末に球状粒子のセルロースや繊維状のグラファイト等の造孔材などを添加してもよい。
First, a
次いで、燃料極12a〜12dを基体2の上にスクリーン印刷する。スクリーン印刷は、基体2を周方向に回すように行い、両方の平面部分10a、10cについて行う。燃料極12a〜12dをスクリーン印刷する代わりに、例えば、予めシート状に成形した燃料極12a〜12dを基体2の上にドクターブレード法によって貼り付けてもよい。
Next, the
次いで、インターコネクタ20a〜20dが形成される部分をマスキングして、電解質14をスラリーコートし、基体2と燃料極12a〜12dと電解質14とを、例えば、1400℃で共焼成する。
Next, portions where the
次いで、空気極16a〜16dを、燃料極12a〜12dと同様にしてスクリーン印刷し、例えば、1100℃で焼成する。空気極16a〜16dをスクリーン印刷する代わりに、例えば、予めシート状に成形した空気極16a〜16dを電解質14の上にドクターブレード法によって貼り付けてもよい。
Next, the
次いで、インターコネクタ20a〜20dをスクリーン印刷によって形成する。インターコネクタ20a〜20dをスクリーン印刷する変わりに、例えば、インターコネクタ粉末をペースト化して直接塗布してもよい。インターコネクタ20a〜20dは、空気極16a〜16dと直接接続されるように形成されることが好ましい。
Next, the
最後に、集電層18a〜18d及び延長集電層22をスクリーン印刷によって形成し、インターコネクタ20a〜20d、集電層18a〜18d及び延長集電層22を、例えば、800℃で共焼成する。集電層18a〜18d及び延長集電層22をスクリーン印刷する代わりに、例えば、予めシート状に成形した集電層18a〜18dを空気極16a〜16d及びインターコネクタ20b〜20dの上にドクターブレード法によって貼り付けてもよい。
Finally, the current collecting layers 18a to 18d and the extended
次に、本発明の参考例による燃料電池セルの動作を説明する。 Next, the operation of the fuel cell according to the reference example of the present invention will be described.
基体2の孔8に一方の端部1aから燃料ガスを供給する。基体2が多孔質であるため、燃料ガスは、孔8だけでなく、基体2全体に行き渡る。燃料ガスは、水素や、炭化水素燃料を改質した改質ガス等を含み、燃料極12と作用する。燃料ガスは、発電反応により、他方の端部1bに向かうにつれて薄まる。
Fuel gas is supplied to the
また、燃料電池セルスタック1の管状部分6の周りに且つ他方の端部1bに向かって、空気を供給する。空気は、酸素を含み、多孔質である集電層18を通り抜けて空気極16と作用する。空気は、発電反応により、他方の端部1bに向かうにつれて薄まるけれども、空気は、通常、燃料電池の作動温度をコントロールする目的で、比較的大量に供給される。
Air is supplied around the
燃料極端子26、即ち、インターコネクタ20aと、空気極端子27、即ち、第4の燃料電池セル4dの集電層18dとを電気的に接続することにより、燃料電池セルスタック1の発電効果が得られる。
By electrically connecting the
燃料極12a〜12dと作用しなかった燃料ガスは、他方の端部1bから出たところで、空気中の酸素と共に燃焼される。
The fuel gas that has not acted on the
本発明の参考例による燃料電池セルスタック1では、他方の端部1bにおいて燃料枯れが生じた場合であっても、一方の端部1aにおいて各燃料電池セル4が機能しているため、燃料電池セル4自体が不良になることはない。その結果、燃料電池セルスタック1の発電効果が維持され、信頼性が高い燃料電池セルスタック1を提供することができる。
In the
また、他方の端部1bにおいて燃料枯れが生じた場合、各燃料電池セル4の発電効率は低下するけれども、燃料電池セル4が管内ガス流れ方向Fに対して垂直な周方向に1列に配列されているので、電気的に直列に接続された各燃料電池セル4a〜4dの発電効率の低下はほぼ同じである。従って、各燃料電池セル4a〜4dによる発生電圧はほぼ一定であり、各燃料電池セル4a〜4dの劣化が防止され、即ち、耐久性が向上する。
In addition, when fuel withering occurs at the
また、本発の参考例による燃料電池セルスタック1は、従来技術の燃料電池セルスタックと異なり、燃料極12a〜12d、空気極16a〜16d、集電層18a〜18dの面積を各燃料電池セル4a〜4dにおいて同じにすることができるので、設計及び製造が容易になる。例えば、燃料電池セルスタック1の発生電圧を増加させたい場合には、セル数を増やせばよく、その電流を増加させたい場合には、燃料極12a〜12d及び空気極16a〜16dの面積を広げればよい。従って、本発明の参考例による燃料電池セルスタック1によれば、小型であっても、比較的高い電圧発生させることが容易である。
Also, the
次に、本発明による燃料電池セルスタックの第1の実施形態を説明する。図3は、本発明による燃料電池セルスタックの第1の実施形態の図2と同様の断面図である。 Next, a first embodiment of a fuel cell stack according to the present invention. FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view similar to FIG. 2 of the first embodiment of the fuel cell stack according to the present invention.
図3に示すように、本発明の第1の実施形態である燃料電池セルスタック30は、燃料電池セル4a〜4dの接続の仕方が異なること以外、参考例である燃料電池セルスタック1と同様の構造を有している。概略的には、第2と第3の燃料電池セル4b、4cが電気的に直列に接続され、第4と第1の燃料電池セル4d、4aが電気的に直列に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
詳細には、第2の燃料電池セル4bの集電層18bと第3の燃料電池セル4cの燃料極12cとが、一方の接続面部分10bの電解質14の上に積層された延長集電層22及びインターコネクタ20cを介して接続されている。それにより、第3の燃料電池セル4cから第2の燃料電池セル4bまで延びる第1の直列接続セルグループ24bが構成される。第1の直列接続セルグループ24bにおいて、インターコネクタ20bは、燃料極端子26aとして作用し、第3の燃料電池セル4cの集電層18cは、空気極端子27aとして作用し、燃料極端子26aと空気極端子27aとの間の電圧が取り出される。
Specifically, the extended current collecting layer in which the
また、第4の燃料電池セル4dの集電層18dと第1の燃料電池セル4aの燃料極12aとが、他方の接続面部分10dの電解質14の上に積層された延長集電層23及びインターコネクタ20aを介して接続されている。それにより、第1の燃料電池セル4aから第4の燃料電池セル4dまで延びる第2の直列接続セルグループ24cが構成される。第2の直列接続セルグループ24cは、第1の直列接続セルグループ24bに対して絶縁されている。第2の直列接続セルグループ24cにおいて、インターコネクタ20dは、燃料極端子26bとして作用し、第1の燃料電池セル4aの集電層18aは、空気極端子27bとして作用し、燃料極端子26bと空気極端子27bとの間の電圧が取り出される。
Also, an extended
かくして、本実施形態では、燃料電池セルスタック30は、2つの直列接続セルグループ24b、24cを有している。第1の直列接続セルグループ24bの燃料極端子26a及び第2の直列接続セルグループ24cの空気極端子27bが、一方の平面部分10aに配置され、第1の直列接続セルグループ24bの空気極端子27b及び第2の直列接続セルグループ24cの燃料極端子26bが他方の平面部分10cに配置されることが好ましい。
Thus, in the present embodiment, the
次に、燃料電池セルスタックの第2の実施形態を説明する。図4は、本発明による燃料電池セルスタックの第2の実施形態の図2と同様の断面図である。 Next, a second embodiment of the fuel cell stack will be described. FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view similar to FIG. 2 of the second embodiment of the fuel cell stack according to the present invention.
図4に示すように、本発明の第2の実施形態である燃料電池セルスタック40は、燃料電池セル4a〜4dの接続の仕方が異なること以外、参考例である燃料電池セルスタック1と同様の構造を有している。概略的には、第2〜第4と第1の燃料電池セル4b、4c、4d、4aが電気的に直列に接続されている。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
詳細には、図4に示すように、第2の燃料電池セル4bの集電層18dと第3の燃料電池セル4cの燃料極12cとが延長集電層22及びインターコネクタ20cを介して接続され、第3の燃料電池セル4cの空気極16c及び集電層18cと第4の燃料電池セル4dの燃料極12dとがインターコネクタ20dを介して接続され、第4の燃料電池セル4dの集電層18dと第1の燃料電池セル4aの燃料極12aとが延長集電層23及びインターコネクタ20aを介して接続されている。それにより、第1の燃料電池セル4aから第4及び第3の燃料電池セル4d、4cを介して第2の燃料電池セル4bまで延びる直列接続セルグループ24dが構成される。本実施形態では、燃料電池セルスタック40は、単一の直列接続セルグループ24dを有している。直列接続セルグループ24dにおいて、インターコネクタ20bは、燃料極端子26として作用し、第1の燃料電池セル4aの集電層18aは、空気極端子27として作用し、燃料極端子26と空気極端子27との間の電圧が取り出される。
Specifically, as shown in FIG. 4, the
次に、燃料電池セルスタックユニットの参考例を説明する。図5は、本発明による燃料電池セルスタックユニットの参考例の斜視図である。 Next, a reference example of the fuel cell stack unit will be described. FIG. 5 is a perspective view of a reference example of the fuel cell stack unit according to the present invention.
本発明の参考例である燃料電池セルスタックユニット50は、燃料ガスマニホールド52と、その上に配置された25個の参考例の燃料電池セルスタック1とを有している。
A fuel
燃料ガスマニホールド52は、横長の直方体形状の密封箱であり、その内部に、燃料ガスが充填される燃料ガス空間54を有している。燃料ガス空間54は、各燃料電池セルスタック1の孔8と連通している。燃料ガス空間54には、燃料ガス供給管(図示せず)から燃料ガスが供給される。燃料ガス供給管(図示せず)は、改質ガス装置(図示せず)に接続されることが好ましい。
The
燃料電池セルスタック1は、隣接した燃料電池セル1の平面部分10a、10bが対向するように且つ1列に燃料ガスマニホールド52の上にロウ付け又はガラスを用いて気密に固定されている。隣接した燃料電池セル1は、電極接続部材56を介して電気的に直列に接続されている。
The
図6は、電極接続部材を取付けた燃料電池セルスタックの斜視図である。図7は、電極接続部材の斜視図である。図8は、燃料電池セルスタックユニットの電流の流れを示す概略図である。 FIG. 6 is a perspective view of a fuel cell stack having an electrode connecting member attached thereto. FIG. 7 is a perspective view of the electrode connection member. FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram showing the flow of current in the fuel cell stack unit.
図6及び図7に示すように、電極接続部材56は、燃料電池セルスタック1の他方の端部1bに取付けることが可能な取付け部56aと、取付け部から下方に延びる接続部56bとを有している。取付け部56aは、燃料電池セルスタック1の他方の端部1bを締め付けるように嵌め込み可能なC字形断面形状を有している。接続部56bは、隣接した燃料電池セルスタック1の間で押圧されて撓み可能なU字形断面形状を有している。接続部56bは、互いに隣接した一方の燃料電池セルスタック1の第1の燃料電池セル4aのインターコネクタ20と他方の燃料電池セルスタック1の第4の燃料電池セル4dの集電層18とに押付けられ、一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bにわたって接触している。それにより、隣接した燃料電池セルスタック1が電気的に直列に且つ確実に接続されている。
かくして、図8に示すように、燃料電池セルスタックユニット60の燃料極端子26u及び空気極端子27uはそれぞれ、一方の側の燃料電池セルスタック1の燃料極端子26及び他方の側の空気極端子27であり、電流が矢印A1で示す経路で流れる。電極接続部材56と燃料電池セルスタック1をより確実に接続するという観点から、電極接続部材56と燃料電池セルスタック1との間に導電性接着剤や銀とガラスの混合体を介在させてもよい。
As shown in FIGS. 6 and 7, the
Thus, as shown in FIG. 8, the
電極接続部材56は、例えば、銀やランタンクロマイトやランタンコバルタイトなどで被覆された各種金属、ステンレス鋼、ニッケル基合金、クロム基合金などの耐熱金属を、板金加工等することによって形成されることが好ましい。また、電極接続部材56はU字部厚さ方向に電流が流れるという観点、燃料電池セルスタック1の外側に流れる反応ガスの流れを整流するという観点から、緻密体であることが好ましい。
The
電極接続部材56は、対向した燃料電池セル4の間で一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bにわたって延びているので、その一部分で接触不良があっても、燃料電池セル4の電気的な接続状態が維持され、燃料電池セルスタックユニット50の信頼性が向上する。
Since the
図9及び図10は、電極接続部材の実施形態及び変形例を示す斜視図である。 9 and 10 are perspective views showing an embodiment and a modification of the electrode connecting member.
図9に示すように、実施形態の電極接続部材58は、電極部材56の接続部56bと同様、隣接した燃料電池セルスタック1の間で押圧されて撓み可能にY字形状に折り曲げられた金属シートである。変形例の電極接続部材58は、それを隣接した燃料電池セルスタック1の間に押し込むことによってそれらの間に且つ一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bにわたって取付けられる。電極接続部材58と燃料電池セルスタック1をより確実に接続するという観点から、電極接続部材58と燃料電池セルスタック1との間に導電性接着剤や銀とガラスの混合体を介在させてもよい。
As shown in FIG. 9, the
図10に示すように、変形例の電極接続部材60は、撓み可能な材料で形成されると共に、例えば、銀やランタンクロマイトやランタンコバルタイトなどで被覆された各種金属、ステンレス鋼、ニッケル基合金、クロム基合金などの耐熱金属のスポンジ状やフェルト状、ランタンクロマイトなどのセラミック多孔質材料で形成される。変形例の電極接続部材60は、それを隣接した燃料電池セルスタック1の間に押し込むことによってそれらの間に且つ一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bにわたって取付けられる。電極接続部材60と燃料電池セルスタック1をより確実に接続するという観点から、電極接続部材60と燃料電池セルスタック1との間に導電性接着剤や銀とガラスの混合体を介在させてもよい。
As shown in FIG. 10, the
図11は、燃料電池セルスタックユニットの実施形態の電流の流れを示す概略図である。 FIG. 11 is a schematic diagram illustrating a current flow in the embodiment of the fuel cell stack unit.
図11に示すように、実施形態の燃料電池セルスタックユニット62では、複数の第1の実施形態の燃料電池セルスタック30と、1つの第2の実施形態の燃料電池セルスタック40とが燃料ガスマニホールドの上に固定され、それらが実施形態の電極接続部材58によって電気的に直列に接続されている。具体的には、電極接続部材58は、互いに隣接した一方の燃料電池セルスタック30の第1の直列接続セルグループ24bの空気極端子27aと他方の燃料電池セルスタック30の第1の直列接続セルグループ24bの燃料極端子26aとに押付けられ、接触している。また、電極接続部材58は、互いに隣接した一方の燃料電池セルスタック30の第2の直列接続セルグループ24cの燃料極端子26bと他方の燃料電池セルスタック30の第2の直列接続セルグループ24cの空気極端子27bとに押付けられ、接触している。かくして、電流は、図11に示す矢印A2の経路で流れる。
As shown in FIG. 11, in the fuel
この場合、燃料電池セルスタックユニット62の燃料極端子26u及び空気極端子27uはそれぞれ、第2の実施形態の燃料電池セルスタック40から最も遠くに位置する第1の実施形態の燃料電池セルスタック30の燃料極端子26a及び空気極端子27bになる。従って、燃料極端子26u及び空気極端子27uへの配線作業が、燃料電池セルスタック30の数に係わらず共通になるので、燃料電池セルスタック30の組立てるとき及びその数を増減させるときの作業が容易になる。
In this case, the
次に、燃料電池セルスタックユニットの実施形態を説明する。図12は、本発明による燃料電池セルスタックユニットの実施形態の斜視図である。 Next, an embodiment of the fuel cell stack unit will be described. FIG. 12 is a perspective view of an embodiment of a fuel cell stack unit according to the present invention.
本発明の実施形態である燃料電池セルスタックユニット70は、燃料ガスマニホールド72と、その側面72a、72bに配置された4個の燃料電池セルスタック76とを有している。
The fuel
燃料電池セルスタック76は、上述した参考例の燃料電池セルスタック1の変形形態であり、平面部分10a、10cのそれぞれに配置した燃料電池セル4の個数が5つであること以外、燃料電池セルスタック1と同様の構造を有している。
The
燃料ガスマニホールド72は、横長の直方体形状の密封箱であり、その内部に、燃料ガスが充填される燃料ガス空間74を有している。燃料ガス空間74は、各燃料電池セルスタック76の孔8と燃料ガス空間74とが連通している。燃料ガス空間74には、燃料ガス供給管(図示せず)から燃料ガスが供給される。燃料ガス供給管(図示せず)は、改質ガス装置(図示せず)に接続されることが好ましい。
The
2つの燃料電池セルスタック76は、その一方の平面部分10aとその他方の平面部分10bとが対向するように、燃料ガスマニホールド72の一方の側面72aにロウ付け又はガラスを用いて気密に固定されている。また、他の2つの燃料電池セルスタック76は、その一方の平面部分10aと他方の平面部分10bとが対向するように、燃料ガスマニホールド72の他方の側面72bにロウ付け又はガラスを用いて気密に固定されている。
隣接した燃料電池セル76は、上述した電極接続部材58、60(図示せず)を介して電気的に直列に接続されている。
The two fuel cell stacks 76 are airtightly fixed to one
燃料電池セルスタックユニット70は、上下方向寸法が小さい燃料電池セルスタックの配置を可能にする。
The fuel
次に、参考例の燃料電池セルスタックユニットを用いた燃料電池の一例を説明する。図13は、本発明による燃料電池の第1の実施形態の概略的な正面図である。 Next, an example of a fuel cell using the fuel cell stack unit of the reference example will be described. FIG. 13 is a schematic front view of a first embodiment of a fuel cell according to the present invention.
図13に示すように、本発明の第1の実施形態である燃料電池80は、上述した燃料電池セルスタックユニット50(図13では、燃料電池セルスタック1の個数を6つに省略して示している。)と、それを収容するケース81とを有している。燃料ガスHは、ケース81の外部からケース81内に配置された改質器82を通して燃料ガスマニホールド52に供給され、燃料電池セルスタック1の内側を一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bに向かって流れる。空気Oは、ケース91の外部からケース91内に設けられた通路93、94を通って、燃料電池セルスタック1の外側全体にわたって流れる。均一な電流分布を得るという観点から、空気は燃料電池セルスタック1の下方より送風し、燃料電池セルスタック1の管外を下方から上方に向かって流れることが好ましい。空気を燃料電池セルスタック1の下方より送風することで、燃料電池セルスタック1の下方を冷却する効果を得る。すなわち、燃料電池セルスタック1の下方に集中しやすい電流分布を、温度差により、燃料電池セルスタック1全体に行き渡らせることができるからである。かくして、燃料ガスHと空気Oとは、燃料電池セルスタック1の他方の端部1bに隣接した燃焼領域85で混合され且つ燃焼され、それによって生じた燃焼ガスCは、ケース81に設けられた通路96を通って排出口97から排出される。改質器92は、燃料ガスHと空気Oの燃焼によって生じた熱を利用するために、燃焼領域85に配置されることが好ましい。
As shown in FIG. 13, the
次に、実施形態の燃料電池セルスタックユニットを用いた燃料電池の一例を説明する。図14は、本発明による燃料電池の第2の実施形態の概略的な平面図である。 Next, an example of a fuel cell using the fuel cell stack unit embodiment will be described. FIG. 14 is a schematic plan view of a second embodiment of the fuel cell according to the present invention.
図14に示すように、本発明の第2の実施形態である燃料電池90は、上述した燃料電池セルスタックユニット70(図14では、燃料電池セルスタック70の1つの平面部分10aに設けられた燃料電池セル4の個数を2つに省略して示している。)と、それを収容するケース91とを有している。燃料ガスHは、ケース91の外部からケース91内に配置された改質器92を通して燃料ガスマニホールド72に供給され、燃料電池セルスタック76の内側を一方の端部1aから他方の端部1bに向かって流れる。空気Oは、ケース91の外部からケース91内に配置された空気熱交換器93を通して空気マニホールド94に供給され、燃料電池セルスタック76の外側全体にわたって流れる。燃料ガスHと空気Oとは、燃料電池セルスタック76の他方の端部1bに隣接した燃焼領域95で混合され且つ燃焼され、それによって生じた燃焼ガスCは、ケース91に設けられた排出口96から排出される。改質器92及び空気熱交換器93は、燃料ガスHと空気Oの燃焼によって生じた熱を利用するために、燃焼領域95に配置されることが好ましい。
As shown in FIG. 14, the
以上、本発明の実施形態を説明したが、本発明は、以上の実施の形態に限定されることなく、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明の範囲内で種々の変更が可能であり、それらも本発明の範囲内に包含されるものであることはいうまでもない。 Although the embodiments of the present invention have been described above, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and various modifications are possible within the scope of the invention described in the claims. Needless to say, these are also included within the scope of the present invention.
上記実施形態では、燃料電池セル4の管状部分6の内側を流れるガスは、水素又は炭化水素燃料等を改質した改質ガス等の燃料ガスであり、燃料電池セル4の管状部分6の外側を流れるガスは、酸素を含む空気であったが、内側を流れるガスと外側を流れるガスを交換してもよい。
In the above embodiment, the gas flowing inside the
また、上記実施形態では、燃料電池セル4を断面が扁平状であったが、断面形状は任意であり、楕円状のフラットチューブ形であってもよい。
Moreover, in the said embodiment, although the cross section of the
燃料電池セルスタック1に設けられる燃料電池セル4の形状及び個数は任意である。それに応じて、燃料電池セルスタック1は、管内ガス流れ方向Fを縦方向としてみたときに、縦長になってもよいし、横長になってもよい。縦長の場合には、電流を増加させたいとき、すなわち燃料電池セル4の面積を大きくするのに好適である。また、横長の場合には、電圧を増加させたいとき、すなわち燃料電池セル4の数を増やすときに好適である。
The shape and number of the
1、30、40 燃料電池セルスタック
1a 一方の端部
1b 他方の端部
2 基体
4、4a〜4d 燃料電池セル
6 管状部分
10a、10c 平面部分
10b、10d 接続面部分
12a〜12d 燃料極
14(14a〜14d) 電解質
16a〜16d 空気極
18a〜18d 集電層
20a〜20d インターコネクタ
22、23 延長集電層
24a〜24d 直列接続セルグループ
50、70 燃料電池セルスタックユニット
52、72 燃料ガスマニホールド
80、90 燃料電池
81、91 ケース
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (3)
空気及び燃料ガスの一方が、上記基体の孔の一端から他端に流れ、且つ、空気及び燃料ガスの他方が、上記燃料電池セルスタックの外側に流れ、
上記燃料電池セルスタックの各々は、上記燃料電池セルの燃料極及び空気極のそれぞれに電気的に接続された燃料極端子及び空気極端子を有し、
上記基体は、基体の厚み方向の互いに反対側に位置する第一周面部分及び第二周面部分、並びに、基体の幅方向の互いに反対側に位置し第一周面部分及び第二周面部分を接続する第一接続面部分及び第二接続面部分からなる周面を有し、
上記燃料電池セルスタックの各々は、上記燃料電池セルスタックの各々の燃料極端子及び空気極端子に電気的に接続され且つ上記基体の第1周面部分又は第2周面部分に沿って離間して設けられた複数の電極接続部を介して、互いに電気的に直列に接続されており、複数の上記電極接続部が上記燃料電池セルの上記燃料電池セルスタックの中央部寄りに設けられていることを特徴とする燃料電池セルスタックユニット。 A fuel cell stack unit in which a plurality of fuel cell stacks in which a plurality of fuel cells are stacked on a substrate are electrically connected, wherein the substrate extends in the longitudinal direction and has a cross section perpendicular to the longitudinal direction in width. A fuel cell stack having a shape with a small thickness and having a hole penetrating from one end to the other end along the longitudinal direction inside the fuel cell, each of which includes a fuel electrode, an electrolyte, and an air electrode In the unit
One of air and fuel gas flows from one end of the hole in the base to the other end, and the other of air and fuel gas flows outside the fuel cell stack,
Each of the fuel cell stacks has a fuel electrode terminal and an air electrode terminal electrically connected to the fuel electrode and the air electrode of the fuel cell,
The base body includes a first peripheral surface portion and a second peripheral surface portion located on opposite sides in the thickness direction of the base body, and a first peripheral surface portion and a second peripheral surface located on opposite sides in the width direction of the base body. Having a peripheral surface composed of a first connecting surface portion and a second connecting surface portion connecting the portions;
Each of the fuel cell stacks is electrically connected to the fuel electrode terminal and the air electrode terminal of each of the fuel cell stacks, and is separated along the first peripheral surface portion or the second peripheral surface portion of the base. Are connected in series with each other via a plurality of electrode connection portions provided, and the plurality of electrode connection portions are provided near the center of the fuel cell stack of the fuel cell . A fuel cell stack unit characterized by that.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007165030A JP5257826B2 (en) | 2007-06-22 | 2007-06-22 | Fuel cell stack, fuel cell stack unit and fuel cell |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007165030A JP5257826B2 (en) | 2007-06-22 | 2007-06-22 | Fuel cell stack, fuel cell stack unit and fuel cell |
Related Child Applications (6)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010215258A Division JP5257856B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2010-09-27 | Fuel cell stack unit |
| JP2010215262A Division JP5317025B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2010-09-27 | Fuel cell stack unit |
| JP2010215259A Division JP5257857B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2010-09-27 | Fuel cell stack unit |
| JP2010215257A Division JP5257855B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2010-09-27 | Fuel cell stack unit |
| JP2010215260A Division JP5317024B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2010-09-27 | Fuel cell stack unit |
| JP2010215261A Division JP5257858B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2010-09-27 | Fuel cell stack unit |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009004251A JP2009004251A (en) | 2009-01-08 |
| JP2009004251A5 JP2009004251A5 (en) | 2010-11-18 |
| JP5257826B2 true JP5257826B2 (en) | 2013-08-07 |
Family
ID=40320403
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007165030A Expired - Fee Related JP5257826B2 (en) | 2007-06-22 | 2007-06-22 | Fuel cell stack, fuel cell stack unit and fuel cell |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5257826B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5159382B2 (en) * | 2008-03-19 | 2013-03-06 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Electrochemical cell |
| JP2011054478A (en) * | 2009-09-03 | 2011-03-17 | Toto Ltd | Fuel cell stack assembly and fuel cell module |
| JP5480656B2 (en) * | 2010-02-15 | 2014-04-23 | 京セラ株式会社 | Horizontal stripe solid oxide fuel cell bundle and fuel cell |
| JP2011204392A (en) * | 2010-03-24 | 2011-10-13 | Kyocera Corp | Horizontal stripe type solid-oxide fuel cell bundle and fuel cell |
| JP5449076B2 (en) * | 2010-07-28 | 2014-03-19 | 京セラ株式会社 | Fuel cell |
| EP2600456B1 (en) * | 2010-07-29 | 2016-11-30 | Kyocera Corporation | Fuel cell bundle and fuel cell module provided with same |
| JP5738651B2 (en) * | 2011-03-29 | 2015-06-24 | 東京瓦斯株式会社 | Flat tube type vertically and horizontally striped solid oxide fuel cell bundle |
| JP5108987B1 (en) * | 2011-10-25 | 2012-12-26 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Fuel cell structure |
| JP5646779B2 (en) * | 2013-04-19 | 2014-12-24 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Fuel cell |
| US10038209B2 (en) * | 2013-11-28 | 2018-07-31 | Kyocera Corporation | Cell stack device, module, and module housing device |
| JP6578415B1 (en) * | 2018-06-12 | 2019-09-18 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Metal member for electrochemical cell, cell stack and cell stack apparatus |
| JP6582097B1 (en) * | 2018-06-12 | 2019-09-25 | 日本碍子株式会社 | Metal member for electrochemical cell, cell stack and cell stack apparatus |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5132878B2 (en) * | 2005-11-11 | 2013-01-30 | 京セラ株式会社 | Fuel cell, fuel cell stack and fuel cell |
-
2007
- 2007-06-22 JP JP2007165030A patent/JP5257826B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009004251A (en) | 2009-01-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5257826B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack, fuel cell stack unit and fuel cell | |
| EP1304755B1 (en) | Fuel cell interconnect with integrated flowpaths and method for making same | |
| JP5158556B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack and fuel cell including the same | |
| JP4826992B2 (en) | Fuel cell plate, fuel cell cylindrical cell, fuel cell stack, fuel cell module, fuel cell unit and fuel cell system | |
| TW201419646A (en) | Systems and methods for suppressing chromium poisoning in fuel cells | |
| JP5254588B2 (en) | Solid oxide fuel cell module | |
| KR20220157519A (en) | Electrochemical element, electrochemical module, electrochemical device, and energy system | |
| JP5155362B2 (en) | Current collecting member, fuel cell stack and fuel cell | |
| JP5317024B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack unit | |
| WO2019116839A1 (en) | Fuel cell and cell stack device | |
| JP4758074B2 (en) | Fuel cell assembly and fuel cell | |
| JP5257856B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack unit | |
| JP5026017B2 (en) | Flat type solid oxide fuel cell separator | |
| JP5373668B2 (en) | Single cell for solid oxide fuel cell and solid oxide fuel cell | |
| JP5257858B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack unit | |
| JP5257857B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack unit | |
| JP5257855B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack unit | |
| JP5317025B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack unit | |
| WO2020012699A1 (en) | Cell stack device | |
| JP5245205B2 (en) | Solid oxide fuel cell | |
| WO2020095472A1 (en) | Fuel cell and cell stack device | |
| JP6239707B1 (en) | Fuel cell stack and fuel cell | |
| JP2016039004A (en) | Fuel battery | |
| JP2005346989A (en) | Current-collecting member, fuel battery cell stack, and fuel battery | |
| WO2018043387A1 (en) | Fuel cell stack and fuel cell |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100616 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100930 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20121219 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130107 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130308 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130401 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160502 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5257826 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130414 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |