JP5233478B2 - Light emitting device - Google Patents
Light emitting device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5233478B2 JP5233478B2 JP2008195484A JP2008195484A JP5233478B2 JP 5233478 B2 JP5233478 B2 JP 5233478B2 JP 2008195484 A JP2008195484 A JP 2008195484A JP 2008195484 A JP2008195484 A JP 2008195484A JP 5233478 B2 JP5233478 B2 JP 5233478B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- light emitting
- package
- opening
- light
- emitting device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000012778 molding material Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000002845 discoloration Methods 0.000 description 12
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 5
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000017525 heat dissipation Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004954 Polyphthalamide Substances 0.000 description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 3
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920006375 polyphtalamide Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229920002050 silicone resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 229910052688 Gadolinium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052765 Lutetium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulphide Chemical compound [S-2] UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052771 Terbium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002223 garnet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052746 lanthanum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 2
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052706 scandium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910002704 AlGaN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910015363 Au—Sn Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000906 Bronze Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052684 Cerium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004606 Fillers/Extenders Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001218 Gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001030 Iron–nickel alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052777 Praseodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052772 Samarium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920001807 Urea-formaldehyde Polymers 0.000 description 1
- WAAQUBJIWXTCPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O-2].[Al+3].P.[Y+3] Chemical compound [O-2].[Al+3].P.[Y+3] WAAQUBJIWXTCPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910002113 barium titanate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JRPBQTZRNDNNOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N barium titanate Chemical compound [Ba+2].[Ba+2].[O-][Ti]([O-])([O-])[O-] JRPBQTZRNDNNOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052790 beryllium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005219 brazing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010974 bronze Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- KUNSUQLRTQLHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N copper tin Chemical compound [Cu].[Sn] KUNSUQLRTQLHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004049 embossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005496 eutectics Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052735 hafnium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000009832 plasma treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- -1 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002952 polymeric resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006126 semicrystalline polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 1
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N yttrium atom Chemical compound [Y] VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
- H01L2224/48091—Arched
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/484—Connecting portions
- H01L2224/48463—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a ball bond
- H01L2224/48465—Connecting portions the connecting portion on the bonding area of the semiconductor or solid-state body being a ball bond the other connecting portion not on the bonding area being a wedge bond, i.e. ball-to-wedge, regular stitch
Landscapes
- Led Device Packages (AREA)
Description
本発明は、発光素子を用いた発光装置に関し、特に液晶ディスプレイのバックライト等に用いられる薄型の発光装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a light emitting device using a light emitting element, and more particularly to a thin light emitting device used for a backlight of a liquid crystal display.
近年、高輝度、高出力の発光素子及び小型の発光装置が開発され種々の分野に利用されている。このような発光装置は、小型、低消費電力や軽量等の特徴を生かして、例えば、携帯電話及び液晶バックライトの光源、各種メータの光源及び各種読み取りセンサ等に利用されている。 In recent years, light emitting elements with high brightness and high output and small light emitting devices have been developed and used in various fields. Such a light emitting device is utilized for, for example, a light source of a mobile phone and a liquid crystal backlight, a light source of various meters, various reading sensors, and the like, taking advantage of features such as small size, low power consumption and light weight.
例えば、バックライトに用いられる光源は、パッケージの開口部に発光素子が載置され、この発光素子を覆うように蛍光体を含む透光性樹脂を充填することにより構成される。
このような従来の光源(発光装置)のパッケージに用いられる樹脂は耐光性が低い。そのため、発光素子から開口部の側面に向けて出射された光により、開口部の側面が変色する事で、光効率が減少する。それに伴い、製品寿命が短くなるという問題があった。
また、従来の発光装置は、パッケージに用いられる樹脂の耐熱性が低いため、発光素子から発生した熱によって、パッケージが変形したり、変色したりするという問題があった。
For example, a light source used for a backlight is configured by placing a light emitting element in an opening of a package and filling a light-transmitting resin containing a phosphor so as to cover the light emitting element.
The resin used for the package of such a conventional light source (light emitting device) has low light resistance. For this reason, the light emitted from the light emitting element toward the side surface of the opening changes the color of the side surface of the opening, thereby reducing the light efficiency. Accordingly, there has been a problem that the product life is shortened.
In addition, the conventional light emitting device has a problem that the package is deformed or discolored by heat generated from the light emitting element because the resin used for the package has low heat resistance.
そのために、例えば図4に示したように、リードフレーム400の一部を屈曲し、パッケージの変色の顕著であった部分を羽根部401、403で覆って、発光素子からの光による変色防止、発光素子から発生した熱を放熱している(例えば特許文献1)。
Therefore, for example, as shown in FIG. 4, a part of the
しかし、図4に示した形態では、上記の問題を解決できるが、羽根部401、403の上端面406をパッケージ405により覆ったのみでは、金属である羽根部401、403とパッケージ405との熱膨張率の違いにより、羽根部とパッケージとの界面において、剥離する懸念がある。
However, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4, the above problem can be solved, but the heat of the
そこで、リードフレームとパッケージとの密着性をより強くし、リードフレームとパッケージとの界面剥離を防止しつつ、且つ発光素子からの光によるパッケージの変色防止、発光素子から発生した熱を効率よく放熱できる発光装置を提供する事を目的とする。 Therefore, the adhesion between the lead frame and the package is strengthened, the interface between the lead frame and the package is prevented from peeling, the discoloration of the package due to the light from the light emitting element is prevented, and the heat generated from the light emitting element is efficiently radiated. An object of the present invention is to provide a light-emitting device that can be used.
以上の目的を達成するために、本発明は、側面と底面を備えた開口部を有するパッケージと、前記底面に露出されたリードフレームと、を備えた発光装置であって、前記リードフレームは、前記側面に、屈曲された反射部を有し、該反射部の内壁面の一部が前記パッケージの内部に位置する事を特徴とする。
このような構成により形成された発光装置は、発光素子からの光は、反射率の高い反射部により反射され、パッケージが変色するのを防止することができる。また、反射部の内壁面の一部が、パッケージの内部にあることで、反射部とパッケージとの密着力がより強化できる。従って、反射部とパッケージとの界面において、剥離するのを防止する事が可能となる。
In order to achieve the above object, the present invention is a light emitting device including a package having an opening having a side surface and a bottom surface, and a lead frame exposed on the bottom surface, wherein the lead frame includes: A bent reflection part is provided on the side surface, and a part of the inner wall surface of the reflection part is located inside the package.
In the light-emitting device formed with such a structure, light from the light-emitting element is reflected by a reflective portion having a high reflectance, and the package can be prevented from being discolored. In addition, since a part of the inner wall surface of the reflecting portion is inside the package, the adhesion between the reflecting portion and the package can be further strengthened. Therefore, it is possible to prevent peeling at the interface between the reflective portion and the package.
また、本発明において、前記開口部の側面は、前記内壁面の一部を覆う部分よりも前記開口部の上面側において、前記底面に対する傾斜角が、前記反射部の前記底面に対する傾斜角より小さい面を有する事が好ましい。
このような構成により、開口部上面側において、発光素子からの光が直接当たらないようにする事ができ、よりパッケージの変色を防止する事ができる。
In the present invention, the side surface of the opening has an inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface that is smaller than the inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface of the reflection portion on the upper surface side of the opening portion than the portion covering a part of the inner wall surface. It is preferable to have a surface.
With such a configuration, the light from the light emitting element can be prevented from being directly applied on the upper surface side of the opening, and the discoloration of the package can be further prevented.
また、本発明において、前記開口部内に蛍光体を含む封止部材を有し、前記蛍光体は、少なくとも前記内壁面の一部を覆う部分よりも前記底面側に配置される事が好ましい。
このような構成により、蛍光体より発生した熱を反射部及び開口部の底面に露出されたリードフレームを通して外部へと放熱する事が可能となる。
Moreover, in this invention, it has a sealing member containing fluorescent substance in the said opening part, and it is preferable that the said fluorescent substance is arrange | positioned at the said bottom face side rather than the part which covers a part of said inner wall surface.
With such a configuration, heat generated from the phosphor can be radiated to the outside through the lead frame exposed on the bottom surface of the reflecting portion and the opening.
本発明によれば、リードフレームの一部を屈曲した反射部とパッケージとの密着性をより強くでき、反射部とパッケージとの界面において剥離するのを防止しつつ、発光素子からの光によるパッケージの変色防止、発光素子及び蛍光体から発生した熱を効率よく放熱できる発光装置を提供する事ができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to further enhance the adhesion between the reflection part obtained by bending a part of the lead frame and the package, and prevent the peeling at the interface between the reflection part and the package, and the package by light from the light emitting element. It is possible to provide a light-emitting device that can prevent discoloration and efficiently dissipate heat generated from the light-emitting element and the phosphor.
本発明を実施するための最良の形態を、以下に図面を参照しながら説明する。但し、以下に示す形態は、一例であって、本発明は、発光装置を以下の発光装置に限定するものではない。さらに、以下の説明において、同一の名称、符号については同一若しくは同質の部材を示しており、詳細な説明を適宜省略する。 The best mode for carrying out the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. However, the form shown below is an example and this invention does not limit a light-emitting device to the following light-emitting devices. Further, in the following description, the same name and reference sign indicate the same or the same members, and detailed description will be omitted as appropriate.
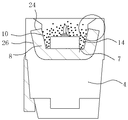
図1Aは、本発明の発光装置を示す斜視図である。図1Bは、本発明の発光装置のリードフレームの斜視図である。図1Cは、図1AのA−A断面図である。図1Dは、図1Cの一部拡大図である。図1Eは、図1Bの一部拡大図である。図2Aは、本発明の他の発光装置を示す正面図である。図2Bは、図2Aの背面図である。図2Cは、図2Aの平面図である。図2Eは、図2Aの右側面図である。図2Dは、図2Aの底面図である。図2Fは、図2Aの左側面図である。図2Gは、図1Aを斜め上から見た斜視図である。図2Hは、図2Aを斜め後ろから見た斜視図である。図2Iは、図2AのA−A断面図である。図2Jは、図2Aの封止部材を斜線で示した正面図である。図2Kは、図2Aの封止部材が充填されていない状態を示した正面図である。そして、図3A〜図3Fは、本発明の発光装置の製造方法を示す概略断面図である。 FIG. 1A is a perspective view showing a light emitting device of the present invention. FIG. 1B is a perspective view of the lead frame of the light emitting device of the present invention. 1C is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA in FIG. 1A. FIG. 1D is a partially enlarged view of FIG. 1C. FIG. 1E is a partially enlarged view of FIG. 1B. FIG. 2A is a front view showing another light emitting device of the present invention. FIG. 2B is a rear view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2C is a plan view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2E is a right side view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2D is a bottom view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2F is a left side view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2G is a perspective view of FIG. 1A viewed from obliquely above. FIG. 2H is a perspective view of FIG. 2A as viewed obliquely from behind. FIG. 2I is a cross-sectional view taken along line AA in FIG. 2A. FIG. 2J is a front view of the sealing member in FIG. 2A indicated by oblique lines. FIG. 2K is a front view showing a state where the sealing member of FIG. 2A is not filled. 3A to 3F are schematic cross-sectional views illustrating the method for manufacturing the light emitting device of the present invention.
本発明の発光装置1は、図1に示したように、側面と底面を備えた開口部2を有するパッケージ4と、開口部2の底面7に露出されたリードフレーム6とを有する発光装置である。本発明において、リードフレーム6は、開口部の側面に、屈曲された反射部8を有し、反射部8の内壁面10の一部がパッケージ4の内部に位置する。
ここで、反射部8において、内壁面10は、主として発光素子から出射された光を反射する面であり、開口部の側面において露出される側の面を言う。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
Here, in the reflecting
(開口部2)
開口部2は、パッケージ4に形成される。開口部2の底面7には、露出されたリードフレーム6を有する。
(Opening 2)
The opening 2 is formed in the
本発明では、開口部の形状は、長方形状であり、開口部の発光素子に近い方の側面において、反射部の内壁面を覆う部分をその他の部分より肉厚に形成され、開口部の発光素子に遠い方の側面は略同じ肉厚に形成されてある。しかし、特に限定されるものではなく、開口部の底面に電気的な接続をとるリードフレーム6の一部表面を露出するものであれば、開口部の形状が、円、楕円、三角、四角又はこれらに近似する形状等いずれでもよい。
また、開口部2の深さは、載置する発光素子12の数、ボンディング方法によって適宜調整することができる。開口部2の大きさは、より広配光を得るため、大きい方が好ましい。なお、この開口部2の底面及び/又は側面は、エンボス加工又はプラズマ処理などで、接着表面積を増加させ、封止部材との密着性を向上させる事が好ましい。
In the present invention, the shape of the opening is rectangular, and on the side surface of the opening close to the light emitting element, the portion covering the inner wall surface of the reflecting portion is formed thicker than the other portions, and the light emission of the opening The side surface far from the element is formed with substantially the same thickness. However, it is not particularly limited, and the shape of the opening may be a circle, an ellipse, a triangle, a square, or the like, as long as a part of the surface of the
Further, the depth of the opening 2 can be adjusted as appropriate depending on the number of light-emitting
本実施形態において、図1に示すように、開口部の側面に、屈曲された反射部8を有し、反射部8の内壁面10の一部はパッケージ4の内部に位置する。
これにより、発光素子からの光を反射率の高い反射部8の内壁面10で反射し、効率よく光を取り出すことができる。それと共に、開口部の側面は金属材料より形成された反射部8が形成されるため、発光素子12から出射された光によるパッケージ4の変色を防止する事ができる。また、反射部8の内壁面10の一部がパッケージ4の内部に位置する事により、パッケージと反射部との密着力を強化する事ができ、パッケージと反射部との界面において、剥離するのを防止する事ができる。
In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 1, a
Thereby, the light from a light emitting element can be reflected by the
内壁面10は、内壁面の上端から内壁面全面の10%以上であり、発光素子の高さより上までパッケージにより覆われる事が好ましいく、内壁面全面の一部でも、パッケージにより覆われる事がより好ましい。
これにより、反射部とパッケージとの密着力を上げることができ、反射部とパッケージとの界面において剥離するのを防止する事が可能となる。
なお、内壁面10は、パッケージにより全て覆われてしまうと、開口部の側面は、耐光性の低いパッケージ成型材料により覆われる事となり、発光素子からの光による劣化を防げない。
The
As a result, the adhesion between the reflecting portion and the package can be increased, and peeling at the interface between the reflecting portion and the package can be prevented.
If the
また、図1に示すように、反射部8の内壁面10と隣接する上面24と、上面24と隣接し、且つ内壁面10と対向する外壁面26はパッケージにより各々全面を覆われる事が好ましい。
これにより、パッケージと反射部との密着性を強化でき、パッケージと反射部との界面において、剥離する事を防止する事ができる。
Moreover, as shown in FIG. 1, it is preferable that the
Thereby, the adhesiveness of a package and a reflection part can be strengthened, and it can prevent peeling at the interface of a package and a reflection part.
また、図1Dに示すように、開口部2の側面は、内壁面10の一部を覆う部分(以下、係止部とも言う)よりも開口部の上面側において、開口部2の底面に対する傾斜角θ1が、反射部8の開口部2の底面に対する傾斜角θ2より小さい面16(以下、傾斜面とも言う)を有することが好ましい。これにより、開口部の上面側において、発光素子からの光が直接当たらないようにする事ができ、よりパッケージの変色を防止する事ができる。
傾斜面16の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ1は30度〜90度が好ましい。そして、反射部8の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ2は、60度〜90度が好ましい。これにより、発光素子からの光を直接当たることなく、内壁面10を支持する事ができる。
なお、傾斜面は少なくとも一面有していればよく複数面有していても良い。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 1D, the side surface of the opening 2 is inclined with respect to the bottom surface of the opening 2 on the upper surface side of the opening rather than a portion that covers a part of the inner wall surface 10 (hereinafter also referred to as a locking portion). It is preferable that the angle θ 1 has a surface 16 (hereinafter also referred to as an inclined surface) that is smaller than the inclination angle θ 2 with respect to the bottom surface of the opening 2 of the reflecting
Inclination angle theta 1 is 30 degrees to 90 degrees relative to the bottom surface of the opening portion of the
Note that the inclined surface may have at least one surface and may have a plurality of surfaces.
(パッケージ4)
本発明におけるパッケージ4は、図1に示すように、開口部2を有し、開口部2の底面にリードフレーム6を有する。さらに、パッケージ4は、発光素子12が載置されるリードフレーム6を固定保持する支持体として働き、発光素子12を外部環境から保護する機能も有する。
(Package 4)
As shown in FIG. 1, the
本発明で用いられるパッケージの成形材料は特に限定されず、液晶ポリマー、ポリフタルアミド樹脂、ポリブチレンテレフタレート(PBT)等、従来から知られているあらゆる熱可塑性樹脂を用いることができる。特に、ポリフタルアミド樹脂のように高融点結晶が含有されてなる半結晶性ポリマー樹脂を用いると、表面エネルギーが大きく、開口内部に設けることができる封止部材や後付することができる導光板等との密着性が良好なパッケージが得られる。これにより、封止部材を充填し硬化する工程において、冷却過程でのパッケージと封止部材との界面に剥離が発生することを抑制することができる。また、発光素子からの光を効率よく反射させるために、パッケージ成形部材中に酸化チタンなどの白色顔料などを混合させることができる。
パッケージ4の正面は面一でなくてもよく、段差部を有するものであってもよい。なお、本発明では、図1Aに示すように、パッケージ4の正面は段差部を有している。
The molding material for the package used in the present invention is not particularly limited, and any conventionally known thermoplastic resin such as liquid crystal polymer, polyphthalamide resin, polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), or the like can be used. In particular, when a semi-crystalline polymer resin containing a high melting point crystal such as polyphthalamide resin is used, a sealing member that can be provided inside the opening and a light guide plate that can be retrofitted with a large surface energy. Thus, a package having good adhesion with the above can be obtained. Thereby, in the process of filling and curing the sealing member, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of peeling at the interface between the package and the sealing member in the cooling process. Moreover, in order to reflect the light from a light emitting element efficiently, white pigments, such as a titanium oxide, can be mixed in a package shaping | molding member.
The front surface of the
(反射部8)
反射部8は、リードフレームの一部であり、開口部の側面に、屈曲して形成されている。反射部8は、内壁面10と、内壁面と隣接する上面24と、上面24と隣接し、且つ内壁面10と対向する外壁面26と、を有する。そして、反射部8の上面24及び外壁面26は、パッケージにより各々全面を覆われ、内壁面10の一部は、パッケージ4の内部に位置する。
(Reflection part 8)
The
本発明において、反射部8は、発光素子を挟むように、且つ発光素子からの光により変色されやすい、発光素子に最も近い両側面に形成される。
これにより、パッケージ両側面において、発光素子からの光による劣化されやすい部分を反射部により覆う事ができるため、パッケージの劣化を防止する事が可能となる。
In the present invention, the reflecting
As a result, on both sides of the package, it is possible to cover the portions that are easily deteriorated by the light from the light emitting elements with the reflecting portions, and thus it is possible to prevent the package from being deteriorated.
反射部8は、少なくも1つ形成されればよいが、2つ設けられるのが好ましい。2つ設ける場合、発光素子12に対して角度、幅、高さ等対称に形成される事が好ましい。反射部8を発光素子に対して対称に形成すると、対称性を有する配光を得ることが可能となる。
また、反射部8は、発光素子に対して対称/若しくは非対称に2つ以上形成する事もできる。
Although at least one reflecting
Also, two or more reflecting
また、反射部8の外壁面26に溝若しくは凹凸を設けてパッケージと反射部8とが接触する表面積を多くする事が好ましい。これにより、よりパッケージと反射部との密着性を上げる事が可能となり、パッケージと反射部との界面において剥離する問題を解決する事が可能となる。
Moreover, it is preferable to provide a groove or unevenness on the
また、内壁面10の上面24側に切欠き又は溝を設けて、その切欠き又は溝がパッケージにより覆われる事が好ましい。これにより、パッケージ4と反射部8とが接触する表面積を多くする事が可能となり、よりパッケージと反射部との密着性が上がり、パッケージと反射部との界面において剥離する問題を解決する事が可能となる。
Moreover, it is preferable to provide a notch or a groove on the
図1に示したように、反射部8の幅W1は、発光素子の幅W2に対して、100%以上が好ましい。これにより、発光素子からの光によるパッケージの変色されやすい箇所を反射部により覆うことができるため、パッケージの変色を防止する事が可能となる。
As shown in FIG. 1, the width W1 of the reflecting
また、反射部の高さH1は、パッケージの高さH2に対して、50%〜90%程度、別の観点から、発光素子の高さH3に対して、100%以上が好ましい。これにより、発光素子からの光によるパッケージの変色されやすい箇所を反射部により覆うため、パッケージの変色を防止する事ができる。 Further, the height H1 of the reflecting portion is preferably about 50% to 90% with respect to the height H2 of the package, and from another viewpoint, it is preferably 100% or more with respect to the height H3 of the light emitting element. As a result, the portion that is likely to be discolored by the light from the light emitting element is covered by the reflecting portion, so that discoloration of the package can be prevented.
また、反射部の厚さT1は、リードフレームの反射部以外の部分の厚さと略同じにする事が好ましいが、リードフレームの反射部以外の部分の厚さより薄くする事がより好ましい。反射部の厚さT1を、それ以外のリードフレームの厚さよりも薄くすると、リードフレームの一部を屈曲した反射部を形成する際に、屈曲しやすくなると共に成形しやすくなる。 In addition, the thickness T1 of the reflecting portion is preferably substantially the same as the thickness of the portion other than the reflecting portion of the lead frame, but is more preferably thinner than the thickness of the portion other than the reflecting portion of the lead frame. If the thickness T1 of the reflecting portion is made thinner than the thickness of the other lead frame, it becomes easy to bend and form when the reflecting portion is formed by bending a part of the lead frame.
また、図1Dに示すように、内壁面の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ2は、60度〜90度が好ましい。これにより、所望の配光特性を実現しつつ、内壁面により、発光素子からの光を反射する事で、パッケージの変色を防止する事ができる。 Moreover, as shown to FIG. 1D, 60 degrees-90 degrees are preferable for inclination | tilt angle (theta) 2 with respect to the bottom face of the opening part of an inner wall surface. Thereby, discoloration of the package can be prevented by reflecting light from the light emitting element by the inner wall surface while realizing a desired light distribution characteristic.
(リードフレーム6)
リードフレーム6は、発光素子と電気的に接続するための電極である。
本発明のリードフレーム6は、前述したように、開口部2の側面に、屈曲された反射部8を有する。
(Lead frame 6)
The
As described above, the
リードフレームは、実質的に板状であればよく、波形板状を有する板状であってもよい。その膜厚は均一であってもよいし、部分的に厚膜又は薄膜であってもよい。材料は特に限定されず、熱伝導率の比較的大きな材料で形成することが好ましい。このような材料で形成することにより、発光素子で発生する熱を効率的に逃がすことができる。例えば、200W/(m・K)程度以上の熱伝導率を有しているもの、比較的大きい機械的強度を有するもの、あるいは打ち抜きプレス加工又はエッチング加工等が容易な材料が好ましい。具体的には、銅、アルミニウム、金、銀、タングステン、鉄、ニッケル等の金属又は鉄−ニッケル合金、燐青銅等の合金等が挙げられる。また、リードフレームの表面には、搭載される発光素子からの光を効率よく取り出すために反射メッキが施されていることが好ましい。 The lead frame may be substantially plate-shaped, and may be plate-shaped having a corrugated plate shape. The film thickness may be uniform or partially thick or thin. The material is not particularly limited, and it is preferably formed of a material having a relatively large thermal conductivity. By forming with such a material, heat generated in the light emitting element can be efficiently released. For example, a material having a thermal conductivity of about 200 W / (m · K) or more, a material having a relatively large mechanical strength, or a material that can be easily punched or etched is preferable. Specific examples include metals such as copper, aluminum, gold, silver, tungsten, iron and nickel, and alloys such as iron-nickel alloys and phosphor bronze. Further, it is preferable that the surface of the lead frame is subjected to reflection plating in order to efficiently extract light from the light emitting element to be mounted.
また、図1Aに示すように、開口部2の底面のリードフレーム6に切欠き9を設けて、開口部の底面において、パッケージが露出するようにする事が好ましい。これにより、開口部に充填される後述する封止部材とパッケージとの密着性が向上する。封止部材とパッケージとの密着性が良いと、発光装置の外部より、硫化性ガスの浸入を防ぐ事ができ、硫化性ガスによるリードフレームの変色を防止する効果が得られる。また、外部より水の浸入を防ぐ事も可能である。
なお、切欠き9は、1つ設けることが好ましいが、図1Aに示すように、複数設けるとより好ましい。複数の切欠き9を設ける事で、開口部の底面において露出したパッケージと封止部材との密着性がより向上する。
Further, as shown in FIG. 1A, it is preferable to provide a
In addition, although it is preferable to provide one
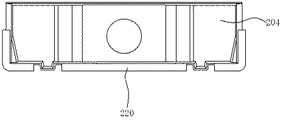
また、リードフレームに、図2に示すように、放熱端子220を設ける事が好ましい。放熱端子を設ける事で、より発光素子212及び蛍光体(図示せず)から発生した熱を効率的に放熱する事ができる。
なお、放熱端子は、実装する際に、実装される側の面に形成されることが好ましい。
Moreover, it is preferable to provide the
In addition, it is preferable to form a thermal radiation terminal in the surface by the side of mounting, when mounting.
(発光素子12)
開口部2に載置される発光素子12は、いわゆる発光ダイオードと呼ばれる素子であればどのような半導体材料からなるものでもよい。例えば、基板上に、InN、AlN、GaN、InGaN、AlGaN、InGaAlN等の窒化物半導体、III―V族化合物半導体、II―IV族化合物半導体等、種々の半導体によって、活性層を含む積層構造が形成されたものが挙げられる。
(Light emitting element 12)
The
本発明においては、発光素子12は、一つのみならず、複数個搭載されてもよい。この場合、光度を向上させるために、同じ発光色の光を発する発光素子を複数個組み合わせても良い。また、例えば、RGBに対応するように、発光色の異なる発光素子を複数個組み合わせることにより、色再現性を向上させることができる。
In the present invention, not only one
これらの発光素子12は、図1に示すように、パッケージ4の開口部2の底面にあるリードフレーム6に、接合部材(図示せず)によって載置される。このような接合部材は、例えば、絶縁性基板(サファイア基板)上に窒化物半導体を成長させて形成された発光素子の場合には、エポキシ樹脂、シリコーン等を用いることができる。また、発光素子からの光や熱による劣化を考慮して、発光素子裏面にAlメッキをし、Au−Sn共晶などの半田、低融点金属等のろう材、導電性ペーストなどを接合部材として用いてもよい。また、導電性基板(GaAs等)からなり、赤色に発光する発光素子のように、両面に電極が形成された発光素子の場合には、銀、金、パラジウムなどの導電性ペースト等によって載置される。
As shown in FIG. 1, these
本発明の発光装置には、発光素子の他、保護素子が搭載されていてもよい。保護素子は発光素子が載置される開口部内に搭載されてもよいし、パッケージに別の開口部を形成して搭載してもよい。発光素子が搭載されるリードフレームの裏面に搭載して、パッケージ成形材料で被覆してパッケージと一体に形成してもよい。また、保護素子は、1つでもよいし、2つ以上の複数個でもよい。ここで、保護素子は、特に限定されるものではなく、発光装置に搭載される公知のもののいずれでもよい。具体的には、ツェナーダイオード、トランジスタのダイオード等が利用できる。 In the light emitting device of the present invention, a protective element may be mounted in addition to the light emitting element. The protective element may be mounted in the opening where the light emitting element is placed, or may be mounted by forming another opening in the package. It may be mounted on the back surface of the lead frame on which the light emitting element is mounted, and covered with a package molding material to be formed integrally with the package. Further, the number of protective elements may be one, or two or more. Here, the protective element is not particularly limited, and may be any known element mounted on the light emitting device. Specifically, a Zener diode, a transistor diode, or the like can be used.
発光素子は、通常、基板上に形成された正極及び負極に、それぞれ導電性ワイヤにより接続されている。
導電性ワイヤは、発光素子の電極とのオーミック性、機械的接続性、電気伝導性及び熱伝導性がよいものが求められる。熱伝導度としては、0.01cal/(s)(cm2)(℃/cm)以上が好ましく、より好ましくは0.5cal/(s)(cm2)(℃/cm)以上である。また、作業性などを考慮して導電性ワイヤの直径は、好ましくは、Φ10μm以上、Φ45μm以下である。導電性ワイヤの直径は、25μm以上がより好ましく、発光素子の発光面積の確保や扱い易さの観点から35μm以下がより好ましい。このような導電性ワイヤとして具体的には、金、銅、白金、アルミニウム等の金属及びそれらの合金を用いた導電性ワイヤが挙げられる。
発光素子は、ワイヤーボンディングの他、半田等の導電性接着部材を用いてフリップチップボンディングしてもよい。
The light emitting element is usually connected to a positive electrode and a negative electrode formed on a substrate, respectively, by conductive wires.
The conductive wire is required to have good ohmic properties, mechanical connectivity, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity with the electrode of the light emitting element. The thermal conductivity, 0.01cal / (s) (cm 2) (℃ / cm) or more, is more preferably 0.5cal / (s) (cm 2 ) (℃ / cm) or more. In consideration of workability and the like, the diameter of the conductive wire is preferably Φ10 μm or more and Φ45 μm or less. The diameter of the conductive wire is more preferably 25 μm or more, and more preferably 35 μm or less from the viewpoint of securing the light emitting area of the light emitting element and ease of handling. Specific examples of such conductive wires include conductive wires using metals such as gold, copper, platinum, and aluminum, and alloys thereof.
The light emitting element may be flip-chip bonded using a conductive adhesive member such as solder in addition to wire bonding.
(封止部材14)
封止部材は、発光素子12を外部環境から保護するものである。発光素子12を覆うようにパッケージの開口部2内に充填した封止部材の材料を硬化させることにより発光素子12等を封止部材にて被覆する。
また、本発明において、図1Cに示すように、開口部に蛍光体を含む封止部材14が形成され、蛍光体は、少なくとも内壁面10の一部を覆う部分より開口部の底面7側に有する事が好ましい。
これにより、蛍光体から発生した熱を反射部8へと伝熱し、リードフレーム6を通して外部へと放熱する事ができる。
(Sealing member 14)
The sealing member protects the
In the present invention, as shown in FIG. 1C, a sealing
Thereby, the heat generated from the phosphor can be transferred to the reflecting
封止部材は、例えば、シリコーン樹脂、エポキシ樹脂、ユリア樹脂、フッ素樹脂、及び、それらの樹脂を少なくとも一種以上含むハイブリッド樹脂等、耐候性に優れたものを用いることができる。また、封止部材は、有機物に限られず、ガラス、シリカゲルなどの耐光性に優れた無機物を用いることもできる。また、本発明において、封止部材に、粘度増量剤、光拡散剤、顔料など、用途に応じてあらゆる部材を添加する事ができる。光拡散剤として例えば、チタン酸バリウム、酸化チタン、酸化アルミニウム、二酸化珪素、炭酸カルシウム、及び、それらを少なくとも一種以上含む混合物などを挙げることができる。更にまた、封止部材の光出射面側を所望の形状にすることによってレンズ効果を持たせることができる。具体的には凸レンズ形状、凹レンズ形状さらには、発光観測面から見て楕円形状やそれらを複数組み合わせた形状にすることができる As the sealing member, for example, a silicone resin, an epoxy resin, a urea resin, a fluororesin, and a hybrid resin including at least one kind of those resins can be used. The sealing member is not limited to an organic material, and an inorganic material having excellent light resistance such as glass and silica gel can also be used. Moreover, in this invention, all members, such as a viscosity extender, a light diffusing agent, and a pigment, can be added to a sealing member according to a use. Examples of the light diffusing agent include barium titanate, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, calcium carbonate, and a mixture containing at least one of them. Furthermore, a lens effect can be given by making the light emission surface side of the sealing member a desired shape. Specifically, it can be a convex lens shape, a concave lens shape, an elliptical shape when viewed from the light emission observation surface, or a shape obtained by combining a plurality of them.
(蛍光体)
本発明において、発光素子からの光の波長を変換させる蛍光体を含有させる事ができる。このような蛍光体の一例として、以下に述べる希土類元素を含有する蛍光体がある。
(Phosphor)
In this invention, the fluorescent substance which converts the wavelength of the light from a light emitting element can be contained. As an example of such a phosphor, there is a phosphor containing a rare earth element described below.
具体的には、Y、Lu、Sc、La、Gd、TbおよびSmの群から選択される少なくとも1つの元素と、Al、Ga、およびInの群から選択される少なくとも1つの元素とを有するガーネット(石榴石)型蛍光体が挙げられる。特に、アルミニウム・ガーネット系蛍光体は、AlとY、Lu、Sc、La、Gd、Tb、Eu、Ga、In及びSmから選択された少なくとも一つの元素とを含み、かつ希土類元素から選択された少なくとも一つの元素で付活された蛍光体であり、発光素子から出射された可視光や紫外線で励起されて発光する蛍光体である。例えば、イットリウム・アルミニウム酸化物系蛍光体(YAG系蛍光体)の他、Tb2.95Ce0.05Al5O12、Y2.90Ce0.05Tb0.05Al5O12、Y2.94Ce0.05Pr0.01Al5O12、Y2.90Ce0.05Pr0.05Al5O12等が挙げられる。これらのうち、特に本発明において、Yを含み、かつCeあるいはPrで付活され組成の異なる2種類以上のイットリウム・アルミニウム酸化物系蛍光体が利用される。 Specifically, a garnet having at least one element selected from the group of Y, Lu, Sc, La, Gd, Tb, and Sm, and at least one element selected from the group of Al, Ga, and In (Steorite) type phosphor. In particular, the aluminum garnet phosphor includes Al and at least one element selected from Y, Lu, Sc, La, Gd, Tb, Eu, Ga, In, and Sm, and is selected from rare earth elements. It is a phosphor activated by at least one element, and is a phosphor that emits light when excited by visible light or ultraviolet light emitted from a light emitting element. For example, in addition to yttrium-aluminum oxide phosphor (YAG phosphor), Tb 2.95 Ce 0.05 Al 5 O 12 , Y 2.90 Ce 0.05 Tb 0.05 Al 5 O 12 , Y 2.94 Ce 0.05 Pr 0.01 Al 5 O 12 , Y 2.90 Ce 0.05 Pr 0.05 Al 5 O 12 and the like. Among these, particularly in the present invention, two or more kinds of yttrium / aluminum oxide phosphors containing Y and activated by Ce or Pr and having different compositions are used.
また、窒化物系蛍光体は、Nを含み、かつBe、Mg、Ca、Sr、Ba、及びZnから選択された少なくとも一つの元素と、C、Si、Ge、Sn、Ti、Zr、及びHfから選択された少なくとも一つの元素とを含み、希土類元素から選択された少なくとも一つの元素で付活された蛍光体である。窒化物系蛍光体として、例えば、(Sr0.97Eu0.03)2Si5N8、(Ca0.985Eu0.015)2Si5N8、(Sr0.679Ca0.291Eu0.03)2Si5N8、等が挙げられる。 In addition, the nitride-based phosphor contains N and at least one element selected from Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Zn, and C, Si, Ge, Sn, Ti, Zr, and Hf And a phosphor activated by at least one element selected from rare earth elements. Examples of the nitride phosphor include (Sr 0.97 Eu 0.03 ) 2 Si 5 N 8 , (Ca 0.985 Eu 0.015 ) 2 Si 5 N 8 , (Sr 0.679 Ca 0.291). Eu 0.03 ) 2 Si 5 N 8 , and the like.
以下に本発明の発光装置1の製造方法を図3A〜図3Fを参照しながら説明する。
まず、金属平板に打ち抜き加工を施して、その表面に金属メッキを施して、図3Aに示すように、後にリードフレームとなるリードフレーム平板201を形成する。次に、後に反射部となる部分を実線Bの位置でZ方向に屈曲して、図3Bに示すリードフレーム平板201が得られる。続いて、図3Cに示すように、リードフレーム6及びリードフレームの一部である反射部8を、上下に分割されたパッケージ成型用のモールド金型346、348の間に配置して、挟み込む。上側の金型は、後に反射部8の内壁面10の一部を覆われるようにするための凹部(図示せず)が形成されている。その後、図3Dのように、下側の金型348の材料注入ゲートより、金型346、348の空洞内へ成形材料を注入する。次に、図3Eに示すように、金型346、348内の成形材料を硬化させ、図3Fに示すように、まず下側の金型348を外し、上側の金型346を矢印の方向に外す。
Below, the manufacturing method of the light-emitting
First, a metal flat plate is punched and subjected to metal plating to form a lead frame
以下、本発明に係る実施例について詳述する。なお、本発明は以下に示す実施例にのみ限定されないことは言うまでもない。
(実施例1)
本実施例の発光装置1は、図1Cに示すように、開口部2を有するパッケージ4と、開口部2の底面にリードフレーム6を有する発光装置である。本実施例においては、リードフレーム6は、リードフレームの一部を開口部の側面に、屈曲した反射部8を有し、反射部8の内壁面10の一部がパッケージ4の内部に位置する。そして、開口部の側面は、反射部8の内壁面10の一部を覆う部分よりも開口部上面側において、開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ1が、反射部の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ2よりも小さい傾斜面16を有する。
Examples according to the present invention will be described in detail below. Needless to say, the present invention is not limited to the following examples.
(Example 1)
The
本実施例において、まず、厚さ0.11mm鉄入り銅からなる金属板の表面に銀メッキを施したリードフレーム平板を形成する。そして、後に反射部となる部分をリードフレーム平板の表面に対して60度となるよう屈曲形成する。このようにして得られたリードフレーム平板を金型内に配置し、成型材料として、ポリフタルアミド樹脂を注入し、硬化させて金型を外す。そして、得られたパッケージのリードフレームに窒化物半導体からなる発光素子12をエポキシ樹脂により接着し固定する。次に、固定された発光素子の電極と、リードフレームとをそれぞれAuを主な材料とする導電性ワイヤにて接続する。
In this embodiment, first, a lead frame flat plate is formed by applying silver plating to the surface of a metal plate made of iron-containing copper having a thickness of 0.11 mm. Then, a portion that will later become a reflective portion is bent and formed at 60 degrees with respect to the surface of the lead frame flat plate. The lead frame flat plate thus obtained is placed in a mold, polyphthalamide resin is injected as a molding material, and cured to remove the mold. Then, the
次に、エポキシ樹脂とシリコーン樹脂を混ぜた変性シリコーン樹脂にYAG蛍光体を所定の割合(5〜30重量%)で混合し、開口部2に充填し、熱風オーブンにて硬化し(硬化条件:150℃、4時間)、封止部材14を形成した。
Next, a YAG phosphor is mixed at a predetermined ratio (5 to 30% by weight) with a modified silicone resin in which an epoxy resin and a silicone resin are mixed, filled in the opening 2, and cured in a hot air oven (curing conditions: 150 degreeC, 4 hours), and the sealing
本実施例において、反射部の幅W1は、0.85mm、反射部の高さH1は、0.23mm、反射部の厚さは、0.11mmで形成された。
また、発光素子の幅W2は、0.5mm、高さH3は、0.12mmで形成された。
そして、パッケージの高さH2は、1mmで形成された。
In this example, the width W1 of the reflecting portion was 0.85 mm, the height H1 of the reflecting portion was 0.23 mm, and the thickness of the reflecting portion was 0.11 mm.
The width W2 of the light emitting element was 0.5 mm, and the height H3 was 0.12 mm.
The package height H2 was 1 mm.
得られた発光装置1は、開口部2を有しており、開口部の底面にリードフレーム6を有し、リードフレーム6は、開口部の側面に、屈曲された反射部8を有し、反射部8の内壁面10の一部がパッケージ4の内部に位置している。反射部8の内壁面10は、内壁面の上端から内壁面全体の10%をパッケージにより覆っている。
これにより、発光素子からの光は、反射率の高い反射部8により反射され、パッケージ4が変色するのを防止することができる。また、反射部8の内壁面10がパッケージ4の内部にあることで、反射部8とパッケージ4との密着力がより強化でき、反射部8とパッケージ4との界面において、剥離するのを防止する事が可能となる。
The obtained light emitting
Thereby, the light from the light emitting element is reflected by the
また、本実施例において、開口部の側面は、内壁面の一部を覆う部分よりも開口部の上面側において、開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ1が、反射部の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ2より小さい傾斜面16を有する。傾斜面の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ1は、30度で、反射部の開口部の底面に対する傾斜角θ2は、60度で形成された。
このような構成により、開口部の上面側において、発光素子からの光が直接当たらないようにする事ができ、よりパッケージの変色を防止する事ができる。
Further, in the present embodiment, the side surface of the opening portion has an inclination angle θ 1 with respect to the bottom surface of the opening portion on the upper surface side of the opening portion rather than the portion covering a part of the inner wall surface, and the inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface of the opening portion of the reflecting portion It has a corner theta 2 is smaller than the
With such a configuration, it is possible to prevent light from the light emitting element from being directly applied to the upper surface side of the opening, and to further prevent discoloration of the package.
さらに、本実施例において、開口部2に蛍光体を含む封止部材14が形成され、蛍光体は、少なくとも内壁面の一部を覆う部分よりも開口部の底面側に有する事が好ましい。これにより、蛍光体から発生した熱を反射部8へと伝熱し、リードフレームを通して外部へと放熱する事ができる。
Furthermore, in the present embodiment, it is preferable that a sealing
(実施例2)
図2Aは、本発明の他の発光装置を示す正面図である。図2Bは、図2Aの背面図である。図2Cは、図2Aの平面図である。図2Eは、図2Aの右側面図である。図2Fは、図2Aの左側面図である。図2Gは、図1Aを斜め上から見た斜視図である。図2Hは、図2Aを斜め後ろから見た斜視図である。図2Iは、図2AのA−A断面図である。図2Jは、図2Aの封止部材を斜線で示した正面図である。図2Kは、図2Aの封止部材が充填されていない状態を示した正面図である。
(Example 2)
FIG. 2A is a front view showing another light emitting device of the present invention. FIG. 2B is a rear view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2C is a plan view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2E is a right side view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2F is a left side view of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2G is a perspective view of FIG. 1A viewed from obliquely above. FIG. 2H is a perspective view of FIG. 2A as viewed obliquely from behind. FIG. 2I is a cross-sectional view taken along the line AA of FIG. 2A. FIG. 2J is a front view of the sealing member in FIG. 2A indicated by oblique lines. FIG. 2K is a front view showing a state where the sealing member of FIG. 2A is not filled.
実施例2の発光装置201は、放熱端子220が形成されている。放熱端子220は、発光装置201を実装する際に、実装される側の面に形成されている。実装される側の面に放熱端子を形成する事で、高い放熱性を得ることができる。これにより、発光素子から発生した熱を効率的に放熱する事ができ、変色を防止する事が可能となる。また、放熱端子220が実装される側の面に設けられる分、実装される面側に重心がくるため、実装性が良くなる。
In the
それ以外の部分については実施例1の発光装置と実質的に同様の構成である。 Other parts are substantially the same as those of the light emitting device of Example 1.
本発明の半導体装置は、液晶のバックライト用光源、各種インジケーター用光源、パネルメーター、表示灯や面発光スイッチおよび光学センサなどに利用可能である。 The semiconductor device of the present invention can be used for a liquid crystal backlight light source, various indicator light sources, panel meters, indicator lamps, surface emitting switches, optical sensors, and the like.
1 発光装置
2 開口部
4 パッケージ
6 リードフレーム
8 反射部
10 内壁面
12 発光素子
14 封止部材
16 傾斜面
301 リードフレーム平板
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (7)
前記リードフレームは、前記側面に、屈曲された反射部を有し、該反射部の内壁面の一部が前記パッケージの成形材料に覆われている発光装置。 A light emitting device comprising: a package having an opening having a side surface and a bottom surface; and a lead frame exposed on the bottom surface,
The lead frame has a bent reflecting portion on the side surface, and a part of an inner wall surface of the reflecting portion is covered with a molding material of the package.
前記リードフレームは、前記側面に、屈曲された反射部を有し、
前記開口部の側面は、前記パッケージと前記反射部の内壁面との界面よりも前記開口部の上面側において、前記底面に対する傾斜角が、前記反射部の前記底面に対する傾斜角より小さい面を有する発光装置。 A light emitting device comprising: a package having an opening having a side surface and a bottom surface; and a lead frame exposed on the bottom surface,
The lead frame has a bent reflecting portion on the side surface,
The side surface of the opening portion has a surface whose inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface is smaller than the inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface of the reflection portion on the upper surface side of the opening portion with respect to the interface between the package and the inner wall surface of the reflection portion. Light emitting device.
前記リードフレームは、前記側面に、屈曲された反射部を有し、The lead frame has a bent reflecting portion on the side surface,
前記開口部の側面は、前記反射部よりも前記開口部の上面側において、前記底面に対する傾斜角が、前記反射部の前記底面に対する傾斜角より小さい面を有する発光装置。The light emitting device, wherein the side surface of the opening portion has a surface with an inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface smaller than an inclination angle with respect to the bottom surface of the reflection portion on the upper surface side of the opening portion with respect to the reflection portion.
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195484A JP5233478B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Light emitting device |
| TW098121659A TWI456784B (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-06-26 | Light emitting device |
| CN200980129910.7A CN102113139B (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-07-08 | Light-emitting device |
| PCT/JP2009/003192 WO2010013396A1 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-07-08 | Light-emitting device |
| KR1020117004530A KR101602977B1 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-07-08 | Light-emitting device |
| BRPI0916438 BRPI0916438B1 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-07-08 | light emitting device |
| EP09802646.1A EP2315263B1 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-07-08 | Light-emitting device |
| US13/056,580 US8525208B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2009-07-08 | Light emitting device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195484A JP5233478B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Light emitting device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010034325A JP2010034325A (en) | 2010-02-12 |
| JP2010034325A5 JP2010034325A5 (en) | 2011-09-08 |
| JP5233478B2 true JP5233478B2 (en) | 2013-07-10 |
Family
ID=41738453
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008195484A Active JP5233478B2 (en) | 2008-07-29 | 2008-07-29 | Light emitting device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5233478B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012079723A (en) | 2010-09-30 | 2012-04-19 | Toyoda Gosei Co Ltd | Light-emitting device |
| DE102013214877A1 (en) * | 2013-07-30 | 2015-02-19 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | Method for producing a cover element and an optoelectronic component, cover element and optoelectronic component |
| KR102101400B1 (en) * | 2013-08-20 | 2020-04-16 | 엘지디스플레이 주식회사 | Light emitting diode package and liquid crystal display device using the same |
| JP6583297B2 (en) | 2017-01-20 | 2019-10-02 | 日亜化学工業株式会社 | Composite substrate for light emitting device and method for manufacturing light emitting device |
| JP7057512B2 (en) * | 2019-08-30 | 2022-04-20 | 日亜化学工業株式会社 | Light emitting device |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100550856B1 (en) * | 2003-06-03 | 2006-02-10 | 삼성전기주식회사 | Method for manufacturing light emitting diode device |
| JP2007317974A (en) * | 2006-05-29 | 2007-12-06 | Enomoto Co Ltd | Side-view led device and its manufacturing method |
| KR100772433B1 (en) * | 2006-08-23 | 2007-11-01 | 서울반도체 주식회사 | Light emitting diode package employing lead terminal with reflecting surface |
| JP4914710B2 (en) * | 2006-12-27 | 2012-04-11 | 日立ケーブルプレシジョン株式会社 | Lead frame for light emitting element mounting package and method for manufacturing the same |
-
2008
- 2008-07-29 JP JP2008195484A patent/JP5233478B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010034325A (en) | 2010-02-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101602977B1 (en) | Light-emitting device | |
| US10115876B2 (en) | Light emitting device mount, leadframe, and light emitting apparatus | |
| JP5333237B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP5119621B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| EP2819192B1 (en) | Package for light emitting apparatus and light emitting apparatus including the same | |
| JP5444654B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP5978572B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP6414427B2 (en) | Light emitting device mounting structure | |
| JP5710088B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| JP5233478B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP5233992B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP2004165308A (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP4544361B2 (en) | Light emitting device | |
| JP5722759B2 (en) | Light emitting device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110725 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110725 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20121204 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130204 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130226 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130311 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5233478 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160405 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |