JP4933744B2 - Multi-pole magnetron sputtering deposition system - Google Patents
Multi-pole magnetron sputtering deposition system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4933744B2 JP4933744B2 JP2005127695A JP2005127695A JP4933744B2 JP 4933744 B2 JP4933744 B2 JP 4933744B2 JP 2005127695 A JP2005127695 A JP 2005127695A JP 2005127695 A JP2005127695 A JP 2005127695A JP 4933744 B2 JP4933744 B2 JP 4933744B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- target
- substrate
- magnet
- pole
- magnetron sputtering
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Physical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
Description
本発明は、被処理基板上に、薄膜を形成するための多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置及びその成膜方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus and a film forming method for forming a thin film on a substrate to be processed.
スパッタリング成膜方法は、膜の材料を含むターゲットに電離イオンを衝突させることによりターゲットから膜材料粒子を放出させ、これを被処理基板上に堆積成膜するための方法である。ターゲット表面の付近に磁界を形成したマグネトロンスパッタリング成膜方法は、成膜速度の向上と膜厚の面内均一性の向上とを同時に実現できる方法として広く用いられている。 The sputtering film forming method is a method for discharging film material particles from a target by colliding ionized ions with a target including a film material and depositing the film material particles on a substrate to be processed. A magnetron sputtering film forming method in which a magnetic field is formed in the vicinity of a target surface is widely used as a method capable of simultaneously realizing an improvement in film forming speed and an improvement in in-plane uniformity of film thickness.
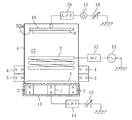
図11は、従来の代表的な平板マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置を示す概略図である。平板状のターゲット107の背面(非スパッタ面)107bに磁界発生手段101,102が配置されている。この磁界発生手段101,102の更に裏面側にヨーク111が設置され、磁力の閉回路が構成されている。ターゲット107に対向して被処理基板108が配設されている。このマグネトロンスパッタリング装置は、ターゲット107の裏面107b側に設けた磁石101,102によって、磁力線Qがターゲット107の裏面bから表面107a側に出て再びターゲット107側に戻るループを描くように磁界が形成される。その磁力線Qによって表面(スパッタ面)107a近傍に磁界Pを形成され、ターゲット107の中心を包囲するリング状、即ちドーナツ状の領域に対応してプラズマ密度が高くなるような電離状態が形成される。この磁界Pによって、真空チャンバー121内に導入したアルゴンガスなどの希ガス122と電子の衝突頻度を高めて、雰囲気ガスのイオン化を増進させ、プラズマがターゲット表面107a上に形成されて、ターゲット107がスパッタリングされて、ターゲット107中の膜材料粒子が放出される。この膜材料粒子が被処理基板108の表面108aに堆積成膜される。
FIG. 11 is a schematic view showing a conventional typical flat-plate magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus. Magnetic field generating means 101 and 102 are arranged on the back surface (non-sputtering surface) 107b of the
しかしながら、上記従来のマグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置では、磁力線Qがターゲット107の裏面107bから表面107a側に出て再びターゲット107側に戻るループを描くように磁界Pが形成されるので、ターゲット表面107aの磁場が弱く、プラズマ密度が十分高いとは言えない。
However, in the conventional magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus, the magnetic field P is formed so as to draw a loop in which the magnetic field lines Q are drawn from the
その上、上記ループ形状の磁力線Qによって形成されるドーナツ形状のプラズマ密度の高い領域は、膜厚の面内均一性を向上させるのに効果的である反面、ターゲット107の消耗が激しい優先的にスパッタされる部分が局部的に発生する。換言すると、ターゲット表面107a上における磁界の状態により、ターゲット107のスパッタされる割合の面内分布が決定されてしまう。従って、ターゲット107の利用面積が小さく、ターゲット107を有効的に消費できない点において問題がある。
In addition, the donut-shaped high plasma density region formed by the loop-shaped magnetic field lines Q is effective for improving the in-plane uniformity of the film thickness, but the
また、ターゲット107として磁性体を使用する場合には、ターゲット107に磁力が吸収されるため、ターゲット表面107aで発生する磁場が弱いと言う問題点を有し、磁性体のターゲット107の場合には、ターゲットを薄くしなければならなく、交換頻度が多いと言う欠点を有する。
Further, when a magnetic material is used as the
上述したように、通常のマグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置では、多くの解決課題を抱えている。その解決手段の1例として、本発明の発明者らによって、多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置が開発されている。この多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置を、図12によって説明する。なお、図11と同じものは同じ符号とする。 As described above, ordinary magnetron sputtering film forming apparatuses have many problems to be solved. As an example of the solution, a multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus has been developed by the inventors of the present invention. This multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus will be described with reference to FIG. The same components as those in FIG.
ターゲット107の表面側外周の外方位置に、外部磁石103が外周磁石102に対応して放射状に配置されている。ここからでる磁力線Tはターゲット裏面107bの中心磁石101のS極に引かれて入射する。このとき外部磁石103と外周磁石102は同極であることから反発しあい、磁力線Tが外周磁石102から中心磁石101へ向かう磁力線Rをターゲット表面107a近傍へ押しつける作用をする。これらの相互作用により、外部磁石103が無い通常のマグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置(図11)のものに比較して、ターゲット表面107a近傍部の磁力線密度を高くすることが出来、かつスパッタリングに有効なプラズマ密度の領域が広がる。
しかし、外部磁石103からでる磁力線Tは、一部はターゲット裏面の中心磁石101のS極に引かれて入射するが、中心磁石101に入射されずに他の方向に逃げてしまうものも少なくない。そのために、ターゲット表面107aのプラズマ密度としては、まだ不十分なものとなっている。
However, some of the magnetic field lines T generated from the
そのために、図13及び14図に示すように、第1外部磁石103に重なるように、第2外部磁石104を設けたもの(2段重ね)が知られている。即ち、中心磁石101は、ターゲット裏面107b側にS極を配し、4つの外周磁石102a〜102dはターゲット裏面107b側にN極を配し、4つの第1外部磁石103a〜103d、第2外部磁石104a〜104dは中心磁石101方向に向けてN極を配して、設置されている。
For this purpose, as shown in FIGS. 13 and 14, a structure in which a second
この構造では、第2外部磁石104a〜104dが第1外部磁石103a〜103dと同極であることから反発しあい、第1外部磁石103a〜103dから基板108側へ逃げる磁力線を抑えることができるので、ターゲット表面107aの磁界を飛躍的に強くすることができる。即ち、第1外部磁石103a〜103dからの磁力線が効率よく中心電極101側に向けられるので、ターゲット表面107a上での磁界を強く出来ると同時に、外周電極102から中心電極101に向かう磁力線Rがターゲット表面107aから離れるのを抑制できるので、この磁力線もターゲット表面107a上に集中させるのに効果的である。これらの相互作用によって、ターゲット表面107a上の磁力密度が高くなり、ターゲット表面107aの広い表面の範囲にわたって、且つイオン密度の高いプラズマを得られる(特許文献1)。
特許文献1に示されるような、第1外部磁石と第2外部磁石とを重ねて配設した、いわゆる2段重ねの多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置は、ターゲット表面の磁力線を増加し、該表面のプラズマ密度を大幅に高めている。このことによって、従来に比較して、成膜される薄膜の厚さの分布を一定に保つ、即ち面内均一性を比較的高くすることができるようになった。
As shown in
しかし、良好なデバイス特性や安定したプロセスを得るためには、高い面内均一性を確保する、成膜速度を高くする、均一で緻密な薄膜を形成することが重要であるが、これらの性能を満足するものではなかった。 However, in order to obtain good device characteristics and a stable process, it is important to ensure high in-plane uniformity, increase the deposition rate, and form a uniform and dense thin film. I was not satisfied.
発明者らは、更に、外部磁石を2段重ねにして多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング装置を突き詰めて研究した結果、ターゲット表面107a近傍において高密度のプラズマが発生するにもかかわらず、基板の薄膜形成が必ずしも高い性能のものになっていないことに疑問を抱いた。今までは、ターゲット表面の磁界を強くすること、ターゲット表面の広い範囲から膜材料を放出させ、高いエネルギを得ることに開発の主眼を置いて研究を進めてきたが、今度は着眼点を変更して、ターゲット表面に形成できた高いイオン密度のプラズマを無駄なく、効果的に基板まで移動させることについて、誠意研究を重ねた。
The inventors have further studied the multi-pole magnetron sputtering apparatus with two layers of external magnets, and as a result, despite the generation of high-density plasma in the vicinity of the
その結果、本発明者は、ターゲットの外側に第1外部磁石及び第2外部磁石を設けたことによって、第2外部磁石が第1外部磁石の磁力線の拡散を押さえ込み、中心磁石に向う磁力線を多くしているが、第2外部磁石の磁力線は、第1外部磁石と反発するので、1部は中心磁石に向うが、他の方向にも多く分布していることに着目し、中心磁石に向ってない第2外部磁石の磁力線を有効に活用することを考えたものであって、これらの磁力線を基板方向に向う磁力線として集約し、且つ磁力線を活性化してプラズマ密度を高めることを狙ったものである。 As a result, the present inventor has provided the first external magnet and the second external magnet outside the target, so that the second external magnet suppresses the diffusion of the magnetic force lines of the first external magnet and increases the magnetic force lines toward the central magnet. However, the magnetic field lines of the second external magnet are repelled from the first external magnet, so that one part faces the central magnet, but pays attention to the fact that many parts are distributed in other directions. It is intended to make effective use of the magnetic field lines of the second external magnet that is not present, and aims to consolidate these magnetic field lines as magnetic field lines toward the substrate and to activate the magnetic field lines to increase the plasma density It is.
請求項1の発明は、基板上に膜を形成するための多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置であって、
気密な処理室と、
上記処理室内に配設され且つ上記基板を支持するための保持面を有する第1保持部材と、
上記第1保持部材と対向するように上記処理室内に配設された第2保持部材と、
上記第1保持部材上に支持された上記基板と対向する表面を有するように、上記第2保持部材に保持されたターゲットと、
上記ターゲットの裏面側中央部に配設され該ターゲット裏面に一方の磁極が向けられた中心磁石と、
上記ターゲットの裏面側外周縁部に配設され該ターゲット裏面に他方の磁極が向けられた複数の外周磁石と、
上記ターゲットの表面側の該ターゲット外周縁よりも外側位置に配設され、上記外周磁石の他方の磁極と同じか異なる磁極が内側に向けられた複数の第1外部磁石と、
上記第1外部磁石に重なるように、上記第1外部磁石よりも上記基板側位置に配設され、当該第1外部磁石と同じように磁極が配向された複数の第2外部磁石と、
上記ターゲットと上記基板とを結ぶ方向を軸として巻回され、且つその中心が上記ターゲットと上記基板との空間に配置され、更に第2外部磁石4の位置と基板との間に配設されたコイルと、
上記コイルに高周波電力を付与する高周波電力付与手段と、
上記ターゲット及び上記基板間に電力を印加する電力印加手段とを備える構成である。
The invention of
An airtight processing chamber,
A first holding member disposed in the processing chamber and having a holding surface for supporting the substrate;
A second holding member disposed in the processing chamber so as to face the first holding member;
A target held by the second holding member so as to have a surface facing the substrate supported on the first holding member;
A central magnet disposed at the center of the back side of the target and having one magnetic pole directed to the back side of the target;
A plurality of outer peripheral magnets disposed on the outer peripheral edge of the back side of the target and having the other magnetic pole directed to the back surface of the target;
A plurality of first external magnets arranged at positions outside the outer peripheral edge of the target on the surface side of the target and having the same or different magnetic pole as the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet directed inward;
A plurality of second external magnets arranged at a position closer to the substrate than the first external magnet and having magnetic poles oriented in the same manner as the first external magnet so as to overlap the first external magnet;
It is wound around the direction connecting the target and the substrate, and the center thereof is disposed in the space between the target and the substrate, and is further disposed between the position of the second
High-frequency power applying means for applying high-frequency power to the coil;
And a power applying unit that applies power between the target and the substrate.
請求項2の発明は、請求項1記載の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置において、上記第1外部磁石は全て、上記外周磁石の上記他方の磁極と同じ磁極を上記内側に向けて配設されている構成である。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus according to the first aspect, all of the first external magnets are arranged with the same magnetic pole as the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet facing inward. It is the composition which is.
請求項3の発明は、請求項1記載の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置において、上記外周磁石の上記他方の磁極と同じ磁極を上記内側に向けた第1外部磁石と、上記外周磁石の上記他方の磁極とは異なる磁極を上記内側に向けた第1外部磁石とが交互に配設されている構成である。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus according to the first aspect, wherein the first external magnet has the same magnetic pole as the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet facing inward, and the other of the outer peripheral magnets. The first external magnets with the magnetic poles different from the magnetic poles facing inward are alternately arranged.
請求項4の発明は、請求項1ないし3のいずれか一に記載の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置において、
上記第1外部磁石及び第2外部磁石は、上記処理室の外壁の外側位置に該外壁に近接して又は接触して配設されている構成である。
The invention of
The first external magnet and the second external magnet are arranged in proximity to or in contact with the outer wall at a position outside the outer wall of the processing chamber.
請求項5の発明は、請求項1ないし4のいずれか一に記載の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置において、
上記電力印加手段は、上記ターゲットに電力を印加するターゲット電力印加手段と、上記基板に電力を印加する基板電力印加手段とを備え、上記ターゲット電力印加手段及び上記基板電力印加手段は印加する電力を可変できるようになっている構成である。
The invention of
The power application means includes target power application means for applying power to the target, and substrate power application means for applying power to the substrate, and the target power application means and the substrate power application means supply power to be applied. This is a configuration that can be varied.
請求項6の発明は、請求項1ないし5のいずれか一に記載の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置を使用した成膜方法であって、
上記第1保持部材の上記保持面上に上記基板を配置(載置)する工程と、次に、上記処理室内を排気しながら上記処理室内に処理ガスを供給することにより、上記処理室内を所定の減圧雰囲気に設定する工程と、次に、上記電力印加手段により上記ターゲット及び上記基板間に電界を形成して、上記コイルに高周波電力を付与して、上記ターゲットから上記膜材料粒子を放出させ、上記膜材料粒子を上記基板表面上に堆積させることにより上記基板表面に薄膜を形成する処理工程とを具備し、
上記第1外部磁石からは上記ターゲット表面に沿って上記中心磁石に向かう磁力線を有する磁界を形成し、上記第2外部磁石からは上記コイル内を通って基板に向かう磁力線及び上記中心磁石に向かう磁力線を有する磁界を形成する構成である。
Invention of Claim 6 is the film-forming method using the multiple magnetic pole magnetron sputtering film-forming apparatus as described in any one of
Placing (mounting) the substrate on the holding surface of the first holding member, and then supplying a processing gas into the processing chamber while evacuating the processing chamber; Next, the electric field is formed between the target and the substrate by the power application means, high frequency power is applied to the coil, and the film material particles are released from the target. And a treatment step of forming a thin film on the substrate surface by depositing the film material particles on the substrate surface,
A magnetic field having a magnetic field line extending from the first external magnet toward the central magnet along the target surface is formed. From the second external magnet, a magnetic field line flowing through the coil toward the substrate and a magnetic field line toward the central magnet. It is the structure which forms the magnetic field which has.
請求項7の発明は、請求項6に記載の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜方法において、上記ターゲット電力印加手段及び上記基板電力印加手段の電力値を調整して、上記膜の成膜状態を調整する構成である。 A seventh aspect of the present invention is the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming method according to the sixth aspect, wherein the power value of the target power applying means and the substrate power applying means is adjusted to adjust the film forming state of the film. It is a configuration.
請求項1の発明によれば、ターゲット表面の広い範囲で高い磁場を形成できるので、ターゲット表面のプラズマ密度を高い状態に維持でき、その上プラズマ密度の高い状態を基板の方まで拡大できる。その結果、ターゲット表面から放出された膜材料粒子(イオン)は、高速で且つ緻密状態で基板に入射させることことができ、高い面内均一性を確保することができ、高い成膜速度で基板に均一で緻密な膜が形成される。 According to the first aspect of the present invention, since a high magnetic field can be formed over a wide range of the target surface, the plasma density on the target surface can be maintained at a high level, and the high plasma density state can be expanded to the substrate. As a result, the film material particles (ions) released from the target surface can be incident on the substrate at high speed and in a dense state, and high in-plane uniformity can be ensured, and the substrate can be formed at a high film formation rate. A uniform and dense film is formed.
請求項2の発明によれば、ターゲット表面によりイオン密度の高いプラズマを生成でき、ターゲットの厚みを厚くしてもターゲット表面に磁場を確保できるので、ターゲットの交換頻度を少なく出来る。 According to the second aspect of the present invention, plasma having a high ion density can be generated on the target surface, and a magnetic field can be secured on the target surface even when the target is thickened.
請求項3の発明によれば、ターゲットのより広い範囲でイオン密度の高いプラズマを生成できるので、ターゲットの寿命が長く、より高い面内均一性を確保することができ、無駄なくターゲット表面を利用できる。
According to the invention of
請求項4の発明によれば、第1外部磁石及び第2外部磁石の位置や大きさを変更することが簡単であり、数を増やす・減らすことも簡単に出来る。また、既に設置されているマグネトロンスパッタリング装置も簡単に、多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング装置に変更できる。
According to the invention of
請求項5の発明によれば、ターゲットや基板に応じて、最適なターゲット電力及び基板電力を設定でき、必要な薄膜を得ることができる。いろいろのターゲット及び基板に対して利用でき、本装置の利用範囲が拡大できる。
According to the invention of
請求項6の発明によれば、ターゲット表面の広い範囲で高い磁場を形成できるので、ターゲット表面のプラズマ密度を高い状態に維持でき、その上プラズマ密度の高い状態を基板のほうまで拡大できる。その結果、ターゲット表面から放出された膜材料粒子(イオン)は、高速で且つ緻密状態で基板8に入射させることことができ、基板に均一で緻密な膜が形成される。特にスパッタ圧力が低圧力でも良いので、より緻密な膜を形成できる。スパッタ圧力は、得られる薄膜によって異なるが、1.33×10-1Paよりも低いほうが好ましく、特に、1×10-2Paよりも低くするとさらに好ましい。
According to the invention of claim 6, since a high magnetic field can be formed over a wide range of the target surface, the plasma density on the target surface can be maintained at a high level, and the high plasma density state can be expanded to the substrate. As a result, film material particles (ions) emitted from the target surface can be incident on the
請求項7の発明によれば、ターゲットや基板に応じて、必要な薄膜を得るための最適なターゲット電力及び基板電力を簡単に調整設定することができる。
According to the invention of
以下、本発明の実施形態を図面に基づいて説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
(実施形態1)
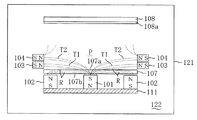
実施形態1の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置を、図1及び図2に基づき、説明する。略円筒形状の真空容器(処理室)21の下部に磁石内臓のターゲット台(保持部材)11が配設されている。ターゲット台11の上面に磁性体で構成された円板状ターゲット7が設置され、容器21の上方位置に配設された保持部材10の表面10aに被処理基板8が取付けられている。ターゲット台11内であって、ターゲット7の中心部に対応する位置に中心磁石1が配設され、ターゲット7の周囲に対応する位置には4つの外周磁石2(2a〜2d)が略90°間隔で配設されている。中心磁石1はターゲット裏面7bにS極を向けて配置されており、外周磁石2はターゲット裏面7bにN極を向けて配置されている。
(Embodiment 1)
The multi-pole magnetron sputtering film-forming apparatus of
ターゲット7より上側位置であって、且つ容器21の外壁の外側位置に、外周磁石2a〜2dに対応して4つの第1外部磁石3(3a〜3d)及び4つの第2外部磁石4(4a〜4d)が重なるように配設されている。第1外部磁石3及び第2外部磁石4は、夫々N極が内方を向くように配設されている。
Four first external magnets 3 (3a to 3d) and four second external magnets 4 (4a) corresponding to the peripheral magnets 2a to 2d are positioned above the
また、容器21内部には、ターゲット7の中心と基板8の中心とを結ぶ線を軸として巻回されたコイル5が、第2外部磁石4に近接した位置から基板方向に向けて延びて配設されている。このコイル5は、SUS304製パイプからなり、スパイラル状に3回巻かれ、一端がマッチング回路12を介して高周波電源13に接続されている。
Inside the
本実施形態では、コイルの他端はフリーでどこにも接続されてないが、アースや高周波電源に接続されるようにしても良い。ターゲット7には、ローパスフィルター14を介して可変直流電源15が接続されている。基板8には、ローパスフィルター16を介して可変直流電源18に接続されている。ローパスフィルター16と可変直流電源18の間には、電流を測定する電流測定手段17が設けられている。
In the present embodiment, the other end of the coil is free and not connected anywhere, but may be connected to ground or a high-frequency power source. A variable
次に、実施形態1の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置の作動状態を説明する。高周波電源13は、13.56Mzが設定されている。可変直流電源15及び18は、所定の電圧値にセットされる。容器21内には、図示を省略するが、その側壁等からアルゴン等のスパッタリングガスが所定圧力で導入され、排気されるようになっている。このことによって、図2に示すように、外周磁石2からターゲット裏面7bに向かう磁力線Rは一部が磁性体で出来たターゲット7内部に吸収されるが、一部はターゲット7を透過してターゲット表面7aを通って中心部磁石1のS極へ入射する。
Next, the operating state of the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus of
第1外部磁石3からでる磁力線T1は、第1外部磁石3と外周磁石2が同極であることから反発しあい、ターゲット裏面7bの中心磁石1のS極に引かれて入射し、磁力線Rをターゲット表面7a近傍方向に押付ける作用をする。なお、磁力線T1の一部はターゲット表面7a方向とは逆の方向へ回って自己回路を組もうとするが、第2外部磁石4の磁力線T2が中心磁石1のS極方向に引かれることによって、磁力線T1がターゲット表面7方向に押付けられるので、ターゲット表面7方向とは逆の方向へ回る磁力線は極力打ち消される。その結果、磁力線T1によって、磁力線Rがターゲット表面7近傍に集中するようになるとともに、磁力線T1及びT2もターゲット表面7に向かうので、ターゲット表面7では、強い磁界となり、イオン密度の高いプラズマが得られる。同時に、ターゲット表面7aの広い範囲において高いプラズマが得られる。
The magnetic force lines T1 generated from the first
第2外部磁石4の磁力線T2の一部は、通常では中心磁石1方向でなく、他の方向にも分散する傾向を有するが、本発明では、この分散する傾向にある磁力線を、コイル5を設けることによって集約し、且つ基板8方向に向かう磁力線T3として整流する。この磁力線T3の流れによって、ターゲット7から放出された膜材料粒子をできるだけ基板8方向に向かわせると同時に、膜材料粒子のその方向への速度を増加する。その上、コイル5には高周波電圧が印加されるので、コイル5近辺はプラズマの発生が促進され、プラズマ密度が上がっている。
A part of the magnetic field lines T2 of the second
この結果、第2外部磁石4を設置し、さらにコイル5を設けたことにより、広い範囲で高いプラズマ密度であるターゲット表面7aから膜材料粒子が活発に放出され、同時に活発状態にある膜材料粒子は、コイル5近辺の高いプラズマ密度領域を高速で通過できるので、基板8には均一で緻密な膜8aが形成される。特に、第2外部磁石4の磁力線T3及びコイル5でのプラズマ発生とによって、基板8方向に向う強力な磁場を形成することができ、電子が基板方向へスパイラル運動し、プラズマが基板の近傍まで広がることができるので、イオンを効率的に基板に入射させることができ、緻密で均一な膜を形成することができる。
As a result, by installing the second
(実施形態2)
図3及び図4により、本発明の実施形態2を説明する。実施形態1と同じものは同じ符号とし、説明は省略する。
(Embodiment 2)
A second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. The same components as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals, and description thereof is omitted.
実施形態1と異なる構成は、実施形態2では、ターゲット7の周囲に6つの外周磁石22が略60°間隔で、ターゲット裏面7bにN極を向けて配置され、6つの第1外部磁石23、23´及び6つの第2外部磁石24、24´が重なるように配設され、第1外部磁石23、23´及び第2外部磁石24、24´は、夫々N極とS極が交互に内方を向くように配設されていることである。
In the configuration different from the first embodiment, in the second embodiment, six outer
実施形態2の多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置の作動状態を説明する。外周磁石22からターゲット裏面7bに向かう磁力線Rは一部が磁性体で出来たターゲット7内部に吸収されるが、一部はターゲット7を透過してターゲット表面7aを通って中心部磁石1のS極へ入射する。第1外部磁石23からでる磁力線T1は、第1外部磁石23と外周磁石22が同極であることから反発しあい、ターゲット裏面7bの中心磁石1のS極に引かれて入射し、磁力線Rをターゲット表面7a近傍方向に押付ける作用をする。同様に、第2外部磁石24から出る磁力線T2は、磁力線T1及びRをターゲット表面7a近傍方向に押付ける作用をする。
The operating state of the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus of
一方、第1外部磁石23´はS極であり、外周磁石22や隣接する第1外部磁石23と異なる磁極であり、外周磁石22や第1外部磁石23からでる磁力線T4が、第1外部磁石23´に引かれる。同様に、第2外部磁石24´にも、外周磁石22や第2外部磁石24からでる磁力線T4が、第1外部磁石24´に引かれる。
On the other hand, the first
その結果、これらT1、T2、T4及びRの磁力線によって、ターゲット表面7a近傍に、広い範囲で強い磁場が形成されるので、ターゲット表面7a上で高い磁場を形成する。
As a result, a strong magnetic field is formed in a wide range in the vicinity of the
また、実施形態1と同様に、基板方向に向かう磁力線T3の流れによって、ターゲット7から離れた膜材料粒子をできるだけ基板8方向に向かわせると同時に、膜材料粒子のその方向への速度を増加する。その上、コイル5には高周波電圧がかかるので、コイル5近辺はプラズマの発生が促進され、プラズマ密度が上がっている。
Similarly to the first embodiment, the flow of the magnetic force lines T3 directed toward the substrate causes the film material particles separated from the
この結果、この実施形態2においても、プラズマが基板の近傍まで広がることができ、イオンを効率的に基板に入射させることができ、基板8に均一で緻密な膜8aを形成することができる。
As a result, also in the second embodiment, plasma can spread to the vicinity of the substrate, ions can be efficiently incident on the substrate, and a uniform and
次に、図5〜図8に基づいて、実施形態1及び2に示す多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置について実験した結果を説明する。 Next, based on FIGS. 5 to 8, results of experiments on the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus shown in the first and second embodiments will be described.
ターゲットには、Ni(直径200mm、厚さ5mm)、スパッタガスにAr(純度99.9999%)を用いた。圧力を4.0×10-5Paまで排気した後、ガスを導入して、放電圧力及びガス流量はそれぞれ、1.33×10-1 Pa、1sccm一定とした。146φの基板フォルダーを用い、ターゲットと基板間は150mmとした。基板に流れ込む電流の変化を測定した。設置したコイル5の中心部でターゲット7の表面から60mmの位置において、テスラメータを用いてターゲットと垂直方向の磁束密度を測定した結果を図5に示す。実施形態1、2では、高周波電源13の電圧を30Wとした。従来例1は、第1外部磁石、第2外部磁石及びコイルを設けてない、いわゆる代表的な平板マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置(図11)とした。
Ni (diameter 200 mm,
実施形態1及び2では、ターゲット表面7aの広い範囲で、通常の平板マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置(図11)に比べて高い磁束密度を得ることができる。これは、実施形態1及び2では、第1外部磁石、第2外部磁石及びコイルを設けたことにより、ターゲット表面の磁場を高め、さらに基板方向への磁力線が強く形成されているからであると考えられる。
In the first and second embodiments, a high magnetic flux density can be obtained over a wide range of the
ターゲット直流バイアス電圧(Vt)を−400Vの一定としたときの基板電流(A)と基板直流バイアス電圧(Vs)との関係を図6に示す。 FIG. 6 shows the relationship between the substrate current (A) and the substrate DC bias voltage (Vs) when the target DC bias voltage (Vt) is kept constant at −400V.
従来例1は図11に示す平板マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置であって、従来例2は図12に示す多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置(第1外部磁石のみ)であって、従来例3は図13及び図14に示す多重マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置(第1外部磁石及び第2外部磁石)である。 Conventional Example 1 is a flat-plate magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus shown in FIG. 11, Conventional Example 2 is a multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus (only the first external magnet) shown in FIG. 12, and Conventional Example 3 is shown in FIG. And a multiple magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus (first external magnet and second external magnet) shown in FIG.
図6に示すように、負の直流バイアス電圧を印加した領域でのイオンによる電流Aが、実施形態1及び2では、大きく増加している。基板直流バイアス電圧(Vs)=−100V、高周波電力=30Wのとき、従来例1に比較して、実施形態1及び2では、約3倍に増加している。これは、第1外部磁石、第2外部磁石及びコイルにより、基板方向への磁力線によりプラズマが基板方向へ引き出され、コイルによる誘導結合プラズマの効果でイオン化が助長され、イオン電流が増加していることも寄与しているからである。 As shown in FIG. 6, the current A due to ions in the region where the negative DC bias voltage is applied is greatly increased in the first and second embodiments. When the substrate DC bias voltage (Vs) = − 100 V and the high-frequency power = 30 W, the first and second embodiments increase about three times as compared with the conventional example 1. This is because the first external magnet, the second external magnet, and the coil draw plasma in the direction of the substrate due to the magnetic lines of force in the direction of the substrate, and the ionization is promoted by the effect of inductively coupled plasma by the coil, increasing the ionic current. It is because that also contributes.
基板直流バイアス電圧(Vs)を−80Vの一定としたときの基板電流(A)とターゲット直流バイアス電圧(Vt)との関係を図7に示す。 FIG. 7 shows the relationship between the substrate current (A) and the target DC bias voltage (Vt) when the substrate DC bias voltage (Vs) is kept constant at −80V.
Vt=−500Vで、高周波電力=30Wのとき、イオン電流Aは従来例1に比較して、実施形態1及び2では、約5倍に増加している。この結果より、本発明では、ターゲット直流バイアス電圧(Vt)の増加に伴い効率良くイオン化されていることがわかる。 When Vt = −500 V and high-frequency power = 30 W, the ion current A is increased about five times in the first and second embodiments compared to the first conventional example. From this result, it can be seen that in the present invention, ionization is efficiently performed as the target DC bias voltage (Vt) increases.
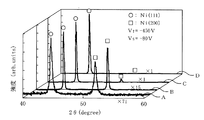
ターゲット直流バイアス電圧(Vt)を−450V、基板直流バイアス電圧(Vs)を−80Vの一定値とし、各スパッタ法において作製したNi薄膜のX線回折パターンを図8に示す。結晶構造は、基板にCorning社の1737ガラス基板(商品名)を用い、X線回折法(XRD、CuKα)により評価した。図8において、従来例1をA、従来例2をB、従来例3をC、実施形態1をDで示す。
FIG. 8 shows an X-ray diffraction pattern of the Ni thin film produced by each sputtering method with the target DC bias voltage (Vt) set to a constant value of −450 V and the substrate DC bias voltage (Vs) set to −80 V. The crystal structure was evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD, CuKα) using a Corning 1737 glass substrate (trade name) as the substrate. In FIG. 8, Conventional Example 1 is indicated by A, Conventional Example 2 is indicated by B, Conventional Example 3 is indicated by C, and
この結果より、従来例1〜3では、Ni(111)、Ni(200)のピークが観測される。それに対して、実施形態1では、Ni(200)のピークがほとんど観測されず、Ni(111)の相対強度が増加していることが解かる。即ち、本発明では、結晶配向性の良いNi膜が得られた。これは、ターゲット表面で高いプラズマが発生し、基板方向に向かう磁力線が強化され、更にコイル領域でのプラズマ発生の助長の効果によるものと考えられる。
From these results, Ni (111) and Ni (200) peaks are observed in Conventional Examples 1 to 3. On the other hand, in
なお、実施形態2についても、実施形態1と同様な結果が予測されるので、省略した。 The second embodiment is also omitted because the same result as that of the first embodiment is predicted.
(実施形態3)
実施形態3について、説明する。実施形態3では、ターゲットとしてFeを用いた点が実施形態2と異なるのみで、他は実施形態2と同じである。
(Embodiment 3)
ターゲットには、Fe(直径200mm、厚さ5mm、純度99.99%)を用いた。高周波(13.56MHz)電力は30Wとした。ガス流量は10sccm一定とした。ターゲットと基板間は150mmとした。圧力を4.0×10-5Paまで排気した後、ガスを導入して、スパッタ圧力を、8.0×10-2 Pa〜1.1 Paまで変化させた。 Fe (200 mm diameter, 5 mm thickness, purity 99.99%) was used as the target. The high frequency (13.56 MHz) power was 30 W. The gas flow rate was fixed at 10 sccm. The distance between the target and the substrate was 150 mm. After exhausting the pressure to 4.0 × 10 −5 Pa, gas was introduced to change the sputtering pressure from 8.0 × 10 −2 Pa to 1.1 Pa.
この実施形態3においても、実施形態2と同様に、第1外部磁石及び第2外部磁石、高周波コイルを備えているので、ターゲット表面の強磁界を確保でき、更に基板方向に向かった高いイオン密度のプラズマを維持できるので、基板近辺まで高密度プラズマを維持でき、基板表面に均一及び緻密に成膜できた。 In the third embodiment, similarly to the second embodiment, since the first external magnet, the second external magnet, and the high frequency coil are provided, a strong magnetic field on the target surface can be secured, and further, a high ion density toward the substrate. Therefore, it was possible to maintain a high-density plasma up to the vicinity of the substrate and to form a uniform and dense film on the surface of the substrate.
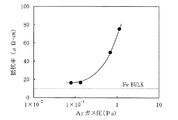
特に、この実施形態3では、基板の堆積膜の電気的特性とスパッタ圧力との関係を実験して観測した。電気的特性は、膜厚とシート抵抗から算出した抵抗率とした。この実験結果を図9に示すように、抵抗率は、スパッタ圧力の低下に伴って減少し、バルク値(10.1μΩ・cm)に近づいた。特に、8.0×10-2 Paのスパッタ圧力で堆積させた際の膜の抵抗率は約16μΩ・cmであった。
In particular, in
図10には、各スパッタ圧力で作成したFe薄膜のX線回折パターンを示す。スパッタ圧力が、1.1Paの場合には、Fe(110)、Fe(200)、Fe(211)のピークが観測され、これらの結晶構造が含まれていることを示す。また、スパッタ圧力が、6.7×10-1Paや1.3×10-1Paの場合には、Fe(110)のピークが強くなり、Fe(200)、Fe(211)のピークが弱くなっているが、Fe(220)のピークが新たに見られ、これらのこれらの結晶構造が含まれていることを示す。それに対して、スパッタ圧力が、8.0×10-2Paの場合には、Fe(110)のピークが強くなり、Fe(200)、Fe(211)、Fe(220)のピークはほとんど見られない。 FIG. 10 shows X-ray diffraction patterns of Fe thin films prepared at each sputtering pressure. When the sputtering pressure is 1.1 Pa, peaks of Fe (110), Fe (200), and Fe (211) are observed, indicating that these crystal structures are included. In addition, when the sputtering pressure is 6.7 × 10 −1 Pa or 1.3 × 10 −1 Pa, the peak of Fe (110) becomes strong and the peaks of Fe (200) and Fe (211) become weak. However, a new Fe (220) peak is seen, indicating that these crystal structures are included. On the other hand, when the sputtering pressure is 8.0 × 10 −2 Pa, the peak of Fe (110) becomes strong, and the peaks of Fe (200), Fe (211), and Fe (220) are almost seen. Absent.
これらの実験結果から、本発明では、スパッタ圧力が低圧力であってもプラズマ放電維持が可能なであり、基板に対し結晶配向性の良く緻密なFe膜が得られる。 From these experimental results, in the present invention, plasma discharge can be maintained even when the sputtering pressure is low, and a dense Fe film having good crystal orientation with respect to the substrate can be obtained.
本発明では、第1外部磁石、第2外部磁石及び高周波コイルからなる構成であり、ターゲット表面にイオン密度の高いプラズマを広い範囲で発生させ、高プラズマ状態を維持して基板表面に薄膜を形成できる構成をとっているので、スパッタ圧力を低圧力としても、上記状態を確保できるものである。特に、スパッタ圧力が低圧力で良いので、イオン化してないAr等のガス量が少なくて済み、ターゲット表面から放出された膜材料粒子を高速且つ効率的に基板に導くことができるとともに、それとともに、真空容器内壁等からの酸素成分等の不純物の析出を抑えることができるので、雰囲気ガスを高性能状態に維持でき、高純度のFe膜を得られる。基板に堆積されるFe膜中には酸素が含まれることが極端に少なくなっており、平滑で滑らかで緻密な成膜が形成できるので、さびにくいFe膜が得られる。 In the present invention, the first external magnet, the second external magnet, and the high-frequency coil are configured to generate a plasma having a high ion density on a target surface in a wide range and maintain a high plasma state to form a thin film on the substrate surface. Since such a configuration is adopted, the above state can be ensured even when the sputtering pressure is low. In particular, since the sputtering pressure may be low, the amount of non-ionized gas such as Ar can be reduced, and the film material particles released from the target surface can be guided to the substrate at high speed and efficiently. Moreover, since precipitation of impurities such as oxygen components from the inner wall of the vacuum vessel can be suppressed, the atmospheric gas can be maintained in a high performance state, and a high purity Fe film can be obtained. Since the Fe film deposited on the substrate contains extremely little oxygen, a smooth, smooth and dense film can be formed, and an Fe film that is not easily rusted can be obtained.
なお、上記実施形態1では外周磁石・第1外部磁石・第2外部磁石を4つとし、上記実施形態2では外周磁石・第1外部磁石・第2外部磁石を6つとして説明したが、これらの数に限られるものではなく、上記磁石は同じ数とであれば任意の数を設けられるものである。また中心磁石は1つとして説明したが、この数に限られるものではなく、ドーナツ上に多数配設した構造でも良い。 In the first embodiment, four outer magnets, first outer magnets, and second outer magnets are used. In the second embodiment, six outer magnets, first outer magnets, and second outer magnets are used. The number of magnets is not limited to this number, and any number can be provided as long as the number of the magnets is the same. In addition, although the number of central magnets has been described as one, the number is not limited to this, and a structure in which a large number of magnets are arranged on a donut may be used.
上記実施形態では、コイルは、第2外部磁石4に近接した位置から基板方向に向けて延びて配設されているが、ターゲットと基板との空間に配置すればよいものであって、例えば、基板に近い位置に配置しても良い。基板に近い位置に配置すれば、基板表面近傍でのイオン化を促進でき、実施形態のような位置に配設すれば空間内のプラズマ密度を向上できるので、ターゲット・基板、要求する薄膜の特性等に応じて、適切な位置に配設すればよい。コイルの材料は、ステンレスを用いたが、これに限定されるものではなく、他の材料でも良い。コイルの巻き数は3回に限らず、任意に設定すればよい。コイルに加える高周波電力は、13.56MHzに限られるものではなく、他の周波数でも良い。なお、上記コイルに関しては、ターゲット材、基板、得られる薄膜の特性等に応じて適切に設定すれば良いものである。
In the above embodiment, the coil is arranged extending from the position close to the second
ターゲットは、鉄、ニッケル、コバルト等の磁性体だけではなく、非磁性体でも良く、金属に限らずセラミックス等でも良い。 The target is not limited to a magnetic material such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, but may be a non-magnetic material, not limited to a metal, and may be ceramic.
ターゲットに印加する電位は直流でも交流でも良い。ターゲット及び基板に印加する電位は、設定値を自由に選択できるようにしておくと、ターゲット材・基板材等に応じて、設定値を選定できるので、好ましい。 The potential applied to the target may be direct current or alternating current. It is preferable that the potential applied to the target and the substrate can be selected freely according to the target material, the substrate material, and the like.
上記実施形態では、外部磁石を真空容器の外側に配設したが、真空容器内に配設しても良い。 In the above embodiment, the external magnet is disposed outside the vacuum vessel, but may be disposed within the vacuum vessel.
ターゲットを下部に、基板を上部に配設した構造としたが、逆にしても良い。 Although the structure is such that the target is disposed at the bottom and the substrate is disposed at the top, it may be reversed.
Fe−N薄膜、Fe−O2薄膜等のように、ArガスとN2、或いはArガスとO2の混合ガス中で反応性マグネトロンスパッタリングを行なうものにも適用できる。 The present invention can also be applied to those in which reactive magnetron sputtering is performed in a mixed gas of Ar gas and N2, or Ar gas and O2, such as a Fe-N thin film and a Fe-O2 thin film.
以上説明したように、本発明に関わる発明は、例えば導電膜、半導体膜、絶縁膜、磁気記録装置の磁気ヘッドの薄膜、耐磨耗性膜、耐食性膜などの薄膜を形成するための多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置に適用することができる。 As described above, the invention related to the present invention is a multiple magnetic pole for forming a thin film such as a conductive film, a semiconductor film, an insulating film, a thin film of a magnetic head of a magnetic recording device, a wear resistant film, a corrosion resistant film, etc. It can be applied to a magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus.
例えば、半導体ウエハへの半導体膜、パソコン・携帯電話に使われるマグネシウム合金への装飾性薄膜、電子部品に使われる各種プラスチック部品への電磁シールド性薄膜等に適用できる。 For example, it can be applied to semiconductor films on semiconductor wafers, decorative thin films on magnesium alloys used in personal computers and mobile phones, and electromagnetic shielding thin films on various plastic parts used in electronic parts.
1 中心磁石
2 外周磁石
3 第1外部磁石
4 第2外部磁石
5 コイル
7 ターゲット
8 基板
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (7)
気密な処理室と、
上記処理室内に配設され且つ上記基板を支持するための保持面を有する第1保持部材と、
上記第1保持部材と対向するように上記処理室内に配設された第2保持部材と、
上記第1保持部材上に支持された上記基板と対向する表面を有するように、上記第2保持部材に保持されたターゲットと、
上記ターゲットの裏面側中央部に配設され該ターゲット裏面に一方の磁極が向けられた中心磁石と、
上記ターゲットの裏面側外周縁部に配設され該ターゲット裏面に他方の磁極が向けられた複数の外周磁石と、
上記ターゲットの表面側の該ターゲット外周縁よりも外側位置に配設され、上記外周磁石の他方の磁極と同じか異なる磁極が内側に向けられた複数の第1外部磁石と、
上記第1外部磁石に重なるように、上記第1外部磁石よりも上記基板側位置に配設され、当該第1外部磁石と同じように磁極が配向された複数の第2外部磁石と、
上記ターゲットと上記基板とを結ぶ方向を軸として巻回され、且つその中心が上記ターゲットと上記基板との空間に配置され、更に第2外部磁石4の位置と基板との間に配設されたコイルと、
上記コイルに高周波電力を付与する高周波電力付与手段と、
上記ターゲット及び上記基板間に電力を印加する電力印加手段とを備えることを特徴とする多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜装置。 A multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus for forming a film on a substrate,
An airtight processing chamber,
A first holding member disposed in the processing chamber and having a holding surface for supporting the substrate;
A second holding member disposed in the processing chamber so as to face the first holding member;
A target held by the second holding member so as to have a surface facing the substrate supported on the first holding member;
A central magnet disposed at the center of the back side of the target and having one magnetic pole directed to the back side of the target;
A plurality of outer peripheral magnets disposed on the outer peripheral edge of the back side of the target and having the other magnetic pole directed to the back surface of the target;
A plurality of first external magnets arranged at positions outside the outer peripheral edge of the target on the surface side of the target and having the same or different magnetic pole as the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet directed inward;
A plurality of second external magnets arranged at a position closer to the substrate than the first external magnet and having magnetic poles oriented in the same manner as the first external magnet so as to overlap the first external magnet;
It is wound around the direction connecting the target and the substrate, and the center thereof is disposed in the space between the target and the substrate, and is further disposed between the position of the second external magnet 4 and the substrate . Coils,
High-frequency power applying means for applying high-frequency power to the coil;
A multi-pole magnetron sputtering film-forming apparatus, comprising: a power applying unit that applies power between the target and the substrate.
上記第1外部磁石は全て、上記外周磁石の上記他方の磁極と同じ磁極を上記内側に向けて配設されていることを特徴とする。 The multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus according to claim 1,
All of the first external magnets are arranged with the same magnetic pole as the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet facing inward.
上記外周磁石の上記他方の磁極と同じ磁極を上記内側に向けた第1外部磁石と、上記外周磁石の上記他方の磁極とは異なる磁極を上記内側に向けた第1外部磁石とが交互に配設されていることを特徴とする。 The multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus according to claim 1,
The first external magnet with the same magnetic pole as the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet facing inward and the first external magnet with the magnetic pole different from the other magnetic pole of the outer peripheral magnet facing inward are alternately arranged. It is provided.
上記第1外部磁石及び第2外部磁石は、上記処理室の外壁の外側位置に該外壁に近接して又は接触して配設されていることを特徴とする。 In the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The first external magnet and the second external magnet are arranged at positions outside the outer wall of the processing chamber in proximity to or in contact with the outer wall.
上記電力印加手段は、上記ターゲットに電力を印加するターゲット電力印加手段と、上記基板に電力を印加する基板電力印加手段とを備え、上記ターゲット電力印加手段及び上記基板電力印加手段は印加する電力を可変できるようになっていることを特徴とする。 In the multiple magnetic pole magnetron sputtering film-forming apparatus as described in any one of Claims 1 thru | or 4,
The power application means includes target power application means for applying power to the target, and substrate power application means for applying power to the substrate, and the target power application means and the substrate power application means supply power to be applied. It is characterized by being variable.
上記第1保持部材の上記保持面上に上記基板を配置(載置)する工程と、次に、上記処理室内を排気しながら上記処理室内に処理ガスを供給することにより、上記処理室内を所定の減圧雰囲気に設定する工程と、次に、上記電力印加手段により上記ターゲット及び上記基板間に電界を形成して、上記コイルに高周波電力を付与して、上記ターゲットから上記膜材料粒子を放出させ、上記膜材料粒子を上記基板表面上に堆積させることにより上記基板表面に薄膜を形成する処理工程とを具備し、
上記第1外部磁石からは上記ターゲット表面に沿って上記中心磁石に向かう磁力線を有する磁界を形成し、上記第2外部磁石からは上記コイル内を通って基板に向かう磁力線及び上記中心磁石に向かう磁力線を有する磁界を形成することを特徴とする多重磁極マグネトロンスパッタリング成膜方法。 A film forming method using the multi-pole magnetron sputtering film forming apparatus according to any one of claims 1 to 5,
Placing (mounting) the substrate on the holding surface of the first holding member, and then supplying a processing gas into the processing chamber while evacuating the processing chamber; Next, the electric field is formed between the target and the substrate by the power application means, high frequency power is applied to the coil, and the film material particles are released from the target. And a treatment step of forming a thin film on the substrate surface by depositing the film material particles on the substrate surface,
A magnetic field having a magnetic field line extending from the first external magnet toward the central magnet along the target surface is formed. A method of forming a multi-pole magnetron sputtering film, comprising: forming a magnetic field having:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005127695A JP4933744B2 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2005-04-26 | Multi-pole magnetron sputtering deposition system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005127695A JP4933744B2 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2005-04-26 | Multi-pole magnetron sputtering deposition system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006307243A JP2006307243A (en) | 2006-11-09 |
| JP4933744B2 true JP4933744B2 (en) | 2012-05-16 |
Family
ID=37474461
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005127695A Active JP4933744B2 (en) | 2005-04-26 | 2005-04-26 | Multi-pole magnetron sputtering deposition system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4933744B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9659758B2 (en) | 2005-03-22 | 2017-05-23 | Honeywell International Inc. | Coils utilized in vapor deposition applications and methods of production |
| JP2009062568A (en) * | 2007-09-05 | 2009-03-26 | Tsuru Gakuen | Magnetron sputtering film deposition system |
| JP5442286B2 (en) * | 2009-03-25 | 2014-03-12 | トーヨーエイテック株式会社 | Magnetron sputtering apparatus and electronic component manufacturing method |
| WO2013042355A1 (en) | 2011-09-22 | 2013-03-28 | 学校法人 芝浦工業大学 | Thin-film formation method, thin-film formation device, object to be treated having coating film formed thereon, die and tool |
| US11183373B2 (en) | 2017-10-11 | 2021-11-23 | Honeywell International Inc. | Multi-patterned sputter traps and methods of making |
| US20230141298A1 (en) * | 2021-11-05 | 2023-05-11 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Etch uniformity improvement for single turn internal coil pvd chamber |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS61190070A (en) * | 1985-02-20 | 1986-08-23 | Hitachi Ltd | Sputter device |
| JP4355036B2 (en) * | 1997-03-18 | 2009-10-28 | キヤノンアネルバ株式会社 | Ionization sputtering equipment |
| JP2003183828A (en) * | 2001-12-14 | 2003-07-03 | Asahi Seisakusho:Kk | Magnetron sputtering method with multiplex magnetic poles |
-
2005
- 2005-04-26 JP JP2005127695A patent/JP4933744B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006307243A (en) | 2006-11-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TW486718B (en) | High-density plasma source for ionized metal deposition | |
| TW436863B (en) | High-density plasma source for ionized metal | |
| TW497132B (en) | Coaxial electromagnet in a magnetron sputtering reactor | |
| JP4933744B2 (en) | Multi-pole magnetron sputtering deposition system | |
| JP4896164B2 (en) | Plasma processing equipment | |
| WO2012035603A1 (en) | Magnetic field generating device, magnetron cathode, and sputter device | |
| JP2005509747A (en) | Magnet array combined with rotating magnetron for plasma sputtering | |
| TW473556B (en) | Planer gas introducing unit of CCP reactor | |
| US8535494B2 (en) | Rotary magnet sputtering apparatus | |
| CN103374705A (en) | Magnetron sputtering device | |
| JP2012197463A (en) | Film deposition method | |
| KR20140019577A (en) | Apparatus of depositing thin film and method of depositing thin film using the same | |
| US6649036B2 (en) | Mirrortron sputtering apparatus | |
| JP2010248576A (en) | Magnetron sputtering apparatus | |
| JP2007529633A (en) | Sputtering apparatus for producing thin films | |
| JP2006233240A (en) | Sputtering cathode and sputtering system | |
| JP5645806B2 (en) | Film forming apparatus and method for manufacturing film forming body | |
| JP2009062568A (en) | Magnetron sputtering film deposition system | |
| JP4283360B2 (en) | Plasma processing equipment | |
| JP2008025001A (en) | Magnetron sputtering apparatus | |
| JP2007231401A (en) | Facing target sputtering system | |
| JP2018076561A (en) | Film deposition method and film deposition apparatus | |
| JP4854569B2 (en) | Mirrortron sputtering equipment | |
| JPH0159351B2 (en) | ||
| JPH1136063A (en) | Arc type evaporating source |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080222 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100531 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100608 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100805 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110308 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110419 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120124 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120217 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4933744 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150224 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |