JP4790177B2 - Especially solenoid valve for slip control type hydraulic brake device - Google Patents
Especially solenoid valve for slip control type hydraulic brake device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4790177B2 JP4790177B2 JP2001506898A JP2001506898A JP4790177B2 JP 4790177 B2 JP4790177 B2 JP 4790177B2 JP 2001506898 A JP2001506898 A JP 2001506898A JP 2001506898 A JP2001506898 A JP 2001506898A JP 4790177 B2 JP4790177 B2 JP 4790177B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- valve
- valve seat
- housing
- magnetic armature
- solenoid valve
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60T—VEHICLE BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF; BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF, IN GENERAL; ARRANGEMENT OF BRAKING ELEMENTS ON VEHICLES IN GENERAL; PORTABLE DEVICES FOR PREVENTING UNWANTED MOVEMENT OF VEHICLES; VEHICLE MODIFICATIONS TO FACILITATE COOLING OF BRAKES
- B60T8/00—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force
- B60T8/32—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration
- B60T8/34—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration having a fluid pressure regulator responsive to a speed condition
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60T—VEHICLE BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF; BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF, IN GENERAL; ARRANGEMENT OF BRAKING ELEMENTS ON VEHICLES IN GENERAL; PORTABLE DEVICES FOR PREVENTING UNWANTED MOVEMENT OF VEHICLES; VEHICLE MODIFICATIONS TO FACILITATE COOLING OF BRAKES
- B60T8/00—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force
- B60T8/32—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration
- B60T8/34—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration having a fluid pressure regulator responsive to a speed condition
- B60T8/36—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration having a fluid pressure regulator responsive to a speed condition including a pilot valve responding to an electromagnetic force
- B60T8/3615—Electromagnetic valves specially adapted for anti-lock brake and traction control systems
- B60T8/363—Electromagnetic valves specially adapted for anti-lock brake and traction control systems in hydraulic systems
- B60T8/365—Electromagnetic valves specially adapted for anti-lock brake and traction control systems in hydraulic systems combining a plurality of functions in one unit, e.g. pressure relief
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60T—VEHICLE BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF; BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF, IN GENERAL; ARRANGEMENT OF BRAKING ELEMENTS ON VEHICLES IN GENERAL; PORTABLE DEVICES FOR PREVENTING UNWANTED MOVEMENT OF VEHICLES; VEHICLE MODIFICATIONS TO FACILITATE COOLING OF BRAKES
- B60T15/00—Construction arrangement, or operation of valves incorporated in power brake systems and not covered by groups B60T11/00 or B60T13/00
- B60T15/02—Application and release valves
- B60T15/025—Electrically controlled valves
- B60T15/028—Electrically controlled valves in hydraulic systems
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60T—VEHICLE BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF; BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEMS OR PARTS THEREOF, IN GENERAL; ARRANGEMENT OF BRAKING ELEMENTS ON VEHICLES IN GENERAL; PORTABLE DEVICES FOR PREVENTING UNWANTED MOVEMENT OF VEHICLES; VEHICLE MODIFICATIONS TO FACILITATE COOLING OF BRAKES
- B60T8/00—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force
- B60T8/32—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration
- B60T8/34—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration having a fluid pressure regulator responsive to a speed condition
- B60T8/36—Arrangements for adjusting wheel-braking force to meet varying vehicular or ground-surface conditions, e.g. limiting or varying distribution of braking force responsive to a speed condition, e.g. acceleration or deceleration having a fluid pressure regulator responsive to a speed condition including a pilot valve responding to an electromagnetic force
- B60T8/3615—Electromagnetic valves specially adapted for anti-lock brake and traction control systems
- B60T8/363—Electromagnetic valves specially adapted for anti-lock brake and traction control systems in hydraulic systems
Description
【0001】
本発明は、請求項1の前提部分に記載した、特にスリップコントロール式液圧ブレーキ装置のための電磁弁に関する。
【0002】
スリップコントロール式液圧ブレーキ装置において流体の流れを制御するための、公知公用のこのような弁は、実際に多彩に使用されている。
【0003】
ドイツ連邦共和国特許出願公開第19808826号公報により既に、スリップコントロール式液圧ブレーキ装置のための、基本位置で開放する電磁弁が知られている。この電磁弁の弁ケースはカートリッジ構造体として形成されている。このカートリッジ構造体は特に、快削鋼から作られた旋削部品として、ブロック状の弁収容体内でくさび止めされる。弁座を形成する弁板も、比較的に頑丈で、特に同様に快削鋼からなる旋削部品から製作されている。この旋削部品は弁ケーシングの下端範囲においてかしめによって保持される。弁座と協働する弁突棒は弁ケーシング内を案内され、中実円筒体からなる頑丈なシャフト部分である。このシャフト部分は調節ブッシュと関連して磁気アーマチュアの端面に支持される。この磁気アーマチュアは弁ケーシング上の弁スリーブ区間内で案内されている。電磁弁の基本位置で弁突棒を弁座から持ち上げ保持するために、弁突棒と同軸にいわゆる戻しばねが設けられている。この戻しばねはその一端が弁突棒を調節ブッシュと共に磁気アーマチュアの方に押している。
【0004】
基本位置で閉じる種類の電磁弁も既に知られている。この電磁弁は例えばドイツ連邦共和国特許出願公開第19727654号公報に記載されている。既に述べた、基本位置で開放する弁と異なり、基本位置で閉じる弁の場合には、中実体から製作された弁突棒は、実質的に独立して取扱操作可能な、磁気アーマチュアを備えたサブアセンブリを形成している。このサブアセンブリは磁気アーマチュアに支持された圧縮ばねによって弁座の方に向けられ、電磁弁の上記の基本位置で弁座を閉鎖保持する。
【0005】
上述の電磁弁の場合、弁の細部を製作するためおよび機能するアセンブリ全体を弁収容体内に挿入するために必要な製作コストが、比較的に高くつくという欠点がある。
【0006】
そこで、本発明の課題は、信頼性が保証されかつ比較的に簡単に製作される構造が維持されると共に、製作コストが大幅に低減されるように、基本位置で開放する実施形または基本位置で閉じる実施形の電磁弁を改良することである。
【0007】
この課題は、冒頭に述べた種類の電磁弁において、本発明に従い請求項1の特徴部分に記載した特徴によって解決される。
【0008】
従属請求項に記載された手段により、合目的な実施の形態が提供される。次に、本発明の他の特徴および効果と関連して、図1a〜3に基づいて、この実施の形態を詳しく図示および説明する。
【0009】
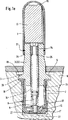
先ず最初に、図1aに基づいて、基本位置で開放する電磁弁の基本的な全体構造を説明する。縦断面を示した電磁弁は、ブッシュ状の弁ケーシング3を備えている。この弁ケーシングは両端範囲に案内面3a,3bを備えている。それによって、ドーム状の弁スリーブ1を保持し、他端で鉢状の弁座−収容体7を保持することができる。従って、弁ケーシング3は上記の部品に適した中央体を形成している。この中央体は同時に磁気コア25の機能を受け持つ。上記の部品をできるだけ低コストで製作するために、弁ケーシング3は冷間押出しプレス部品によって形成され、弁スリーブ1と鉢状の弁座−収容体7は深絞り部品として形成されている。この場合、弁座−収容体7は鉢状の底部に、スタンピング法によって、逆止弁10のための弁座面と、弁突棒4に取付けられた弁閉鎖部材9のための弁座面を備えている。製作技術的および機能的に重要な他の構造は、弁突棒4を薄壁状のスリーブ部品として形成することによって生じる。このスリーブ部品はロータリスエージング部品としてあるいは場合によっては深絞り部品として精密にかつきわめて低コストで製作可能である。弁突棒4の薄壁状のスリーブ輪郭によって決まる簡単な輪郭は、図1aの形状に従って、戻しばね8のきわめて所望な配置を可能にする。この戻しばねは弁突棒4に同心的に保持されるので、ばねの一方の巻線端部は突棒の漏斗状拡大部に支持され、他方の巻線端部は鉢状の弁座−収容体7の底部に支持される。弁閉鎖部材9は図示の実施形では、弁突棒4の端部範囲において舌片状に取り囲まれる鋼球によって形成されている。弁閉鎖部材9と反対の側において、鉢状の弁座−収容体7の底には更に、既に述べた逆止弁10が設けられ、同様に鋼球として形成されている。この鋼球は弁座−収容体7に嵌合された鉢状フィルタ11によって、その位置が、第2の弁座を有する鉢底部のバイパス穴12上に固定されている。弁突棒4内には調節ピン2が設けられている。この調節ピンは弁突棒4から磁気アーマチュア13の方向に突出している。調節ピン2は多角形の形材からなっている。この形材はA−A断面に従って、三角形の横断面を有し、磁気アーマチュア残留空隙を調節するために、突棒管内で摺動可能であり、この突棒管と共にプレスばめ部を形成する。
【0010】
補足的に指摘すると、勿論、調節ピン2を完全に調節した後で、適当な摩擦連結手段およびまたは形状補完的な連結手段によって弁突棒4内で上記部品の付加的な位置固定を行うことができる。
【0011】
同様に冷間押出しプレス部品によって製作された磁気アーマチュア13が、電磁弁を低コストで製作するために寄与する。この磁気アーマチュアは図示のごとく、磁気コア25として作用する弁ケーシング3の上方において、弁スリーブ1内に延びている。磁気アーマチュア13も多角形の形材として製作可能である。磁気アーマチュア13が弁突棒4の位置に関係なく弁スリーブ1内で調節可能であると有利である。従って、磁気アーマチュア13と弁突棒4は互いに独立した部品を形成し、軸方向の力伝達部材として連結され、半径方向において互いに独立して作用する。弁突棒4が基本的には管として形成され、調節ピン2と場合によって磁気アーマチュア13が多角形の形材からなっていることにより、横方向通路14を有する弁突棒4内でおよび弁スリーブ1内で圧力のつりあいが生じ、この圧力が弁ケーシング3の両側にある中空室15,16に達する。これによってカートリッジとして形成された電磁弁は、ブロック状の弁支持体6内で固定するためにのみ、かしめ部17の範囲において比較的に肉厚の壁状の、肩部5の形をした弁ケーシング3の部分を備えている。この弁ケーシングの部分では、弁支持体6に加えられる軸方向のかしめ力により、弁支持体6の収容穴18内で電磁弁のほぼ摩擦連結が行われる。収容穴18は段付き穴として形成されている。この場合、かしめ作業が終了した後で、弁ケース3の肩部5と弁支持体6の段部19との間に、鉢状の弁座−収容体7の縁部20が液体を漏らさぬように挟持されている。鉢状の弁座−収容体7内に延びる、弁ケーシング3の案内面3bを備えた突出部31は、弁座−収容体が鉢状フィルタ11およびその中にある逆止弁10と共に弁支持体6内に挿入される前に、弁ケーシング3上での弁座−収容体7の確実な予備組立てと取扱操作を生じる。例えば、弁スリーブ1は弁ケース3の案内面3aを有する円筒状の突出部上に嵌合されるだけでなく、完全に調節した後で溶接連結19によって永久的に固定される。溶接連結19の代わりに勿論、代替的な摩擦連結固定法と形状補完的連結固定法を用いることができる。弁内の側方に設けた逆止弁を除いて、その他の上記部品はすべて、弁縦軸線に対して同心的に配置されている。
【0012】
図1aに示した上記の実施の形態と異なり、図示した電磁弁の次の構造的変形では、図1aと異なる細部について説明する。それぞれの弁変形のすべての細部が説明されない場合には、この細部は図1aの実施の形態に一致するので、この細部は前述の説明から明らかである。
【0013】
図1bは図1aと異なり、弁座−収容体7内にプレスばめ部を備えた別個のスリーブ体22が、鉢状の弁座−収容体7に圧入されている電磁弁を示している。このスリーブ体は弁閉鎖部材9寄りの端面に、弁座として作用する球状シール面を備えている。この場合更に、スリーブ体22は磁気アーマチュア残留空隙を調節するために、図1aに示した調節ピン2の機能を有する。というのは、管状の弁突棒4が図1と異なり、図1bでは磁気アーマチュア13の端面に直接載っているからである。
【0014】
図1cの電磁弁の実施の形態でも、図1bに基づいて説明したスリーブ体22が使用される。しかし、このスリーブ体がフィルタ底の方に延長した弁ケーシング3内に直接圧入されている点が異なっている。それによって、図1a,1bの図示と異なり、弁座−収容体7は弁ケーシング3の一体部品を形成している。
【0015】
図1dに示す電磁弁は図1bの実施の形態の電磁弁によく似ている。この電磁弁の鉢状の弁座−収容体7は、中実のスリーブ体22の範囲に、きわめてスリムなスリーブ状区間を備えている。このスリーブ状区間には鉢状フィルタ11が嵌合されている。鉢状フィルタ11内には同時に、逆止弁とこの逆止弁10に所属するバイパス通路12が巧みに設けられている。弁ケーシング3における弁座−収容体7の固定は、外側から薄壁状の弁座−収容体7の案内面に形成される半径方向かしめ部によって行われる。この半径方向かしめ部はこの断面図で、弁ケーシング3の突出部31の方に向いた突起23として示してある。
【0016】
上述のすべての電磁弁は、きわめて簡単な方法で、圧力制御弁(逃がし弁)の機能を有することができる。この機能について次に図1eに基づいて例示的に説明する。管状の弁突棒4が大まかに採寸された円筒状の中空室を備えていることにより、弁閉鎖部材9の上述の固定配置の代わりに、弁閉鎖部材9が弁突棒4上に軸方向に移動可能に配置されている。そのために、弁閉鎖部材9はプランジャの形をして上側から弁突棒4の中空室内に挿入され、その円錐状の当接肩部が先細の突棒端部に載り、同時に弁閉鎖部材4の開放した端部分から突出するその閉鎖体がばねで付勢されてスリーブ体22または弁座−収容体7の方に向いている。逃がし弁の機能を左右する開放圧力は、弁ばね24によって決定される。この弁ばねは弁閉鎖部材9と、弁突棒4内に圧入されたストッパーとの間で圧縮挿入されている。それによって、電磁的に励起された弁の閉鎖位置で、先ず最初に公知のごとく、弁閉鎖部材9が圧力を漏らさぬように弁座−収容体7に接触する。この接触は、弁座−収容体7の下方で生じる液圧が弁ばね24によって弁閉鎖部材9に加えられる圧力を上回るまで行われる。それによって、弁閉鎖部材9はその弁座から離れ、従って逃がし弁機能を達成する。
【0017】
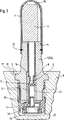
次に、通常のごとく基本位置で閉じる電磁弁に基づいて本発明の重要な特徴を図2aに従って明確に説明する。この説明に続いて、図2b〜2dに基づいて弁の部品の変形を説明する。
【0018】
図2aの電磁弁は図1a〜1eの電磁弁と同様に、冷間押出しプレス部品として製作された磁気アーマチュア13と、冷間押出しプレス部品から製作された磁気コア25と、弁ケーシング3に固定された鉢状の弁座−収容体7を備えている。薄壁状のスリーブ部品が使用される場合には、このスリーブ部品は、前述の実施の形態と同様に、好ましくは深絞り部品としてあるいは場合によってはロータリスエージング部品として形成される。これに関連して、図2aは深絞り部品として形成されたスリーブ状の弁ケーシング3を示している。この弁ケーシングの両端は案内面3a,3bを形成し、この案内面は一方の側が磁気コア25によって画成され、他方の側が鉢状の弁座−収容体7によって画成されている。スリーブ状弁ケーシング3に取付けられた両部品25,7は特に溶接継手19によって永久的に固定されている。上記の部品内には磁気アーマチュア13が設けられている。この磁気アーマチュアはその壁に、図1のように、圧力平衡溝または角ばった断面を有する。それによって、弁内の液圧の釣合いが妨害されることなく保証される。既に図1に関連し述べたように、磁気アーマチュア13と磁気コア25は冷間押出しプレス部品として形成されている。そのために特に、識別コードX8Cr17の材料またはその代わりに識別コードX6Cr17の材料が適している。スリーブ状弁ケーシング3は特に、1.43.03クラスのオーステナイト鋼からなっている。同じ材料が鉢状の弁座−収容体7のために使用される。この材料の選択は図1a〜1eに示した電磁弁の上記のスリーブ部品についても適用される。図2aの電磁弁では、鉢状の弁座−収容体7の縁部20が外側かしめによって弁支持体6を直接固定されている。弁座−収容体7の鉢部は、前述のすべての実施の形態と同様に、少なくとも1つの半径方向穴と軸方向穴を備えている。この場合、弁縦軸線に沿って配置された穴はスタンピング法によって、弁閉鎖部材9のための弁座−収容体7に形成され、それに対して横方向に弁座−収容体7を貫通する穴は一般的に止り穴として形成されている。それによって、開放した弁切換え位置で、弁閉鎖部材9の下方と上方にある弁支持体6の穴の間で、圧力媒体接続が行われる。弁閉鎖部材9としては特に、磁気アーマチュア13内にかしめられて固定された球が使用される。この球は磁気アーマチュア13と磁気コア25の間にある戻しばね8の作用を受けて、弁閉鎖体9の弁座面に押し付けられている。弁支持体6の段付き穴内での鉢状の弁座−収容体7のシールは、弁座−収容体7と弁支持体6の間に配置されたOリング28によって行うことができる。リングフィルタ29は弁座−収容体7に沿ってOリング28まで延びているので、弁支持体6の段付き穴内での本来の組立ての前に、Oリング28が付加的に保持され、場合によっては運搬時に保護される。電磁弁は外側に対して弁支持体6内での簡単な外側かしめ部を介してのみシールおよび固定されている。一方、Oリング28によって行われる、弁支持体6内での下側のシールは、弁閉鎖部材9の下方で弁支持体6に開口する通路と、リングフィルタの高さ位置にある横方向通路との間の流れの短絡を防止する。磁気コア25はスリーブ状弁ケーシング3の開放した範囲内に栓のように圧入され、必要な調節の後で溶接継ぎ目によって永久的に固定される。磁気コア25または磁気アーマチュア13に設けることができる、この磁気コアと磁気アーマチュアの間の突起によって、いわゆる磁気アーマチュア接着が防止される。戻しばねの省スペース的な収容および案内のために、図に示すように、磁気アーマチュア13は長穴を備えている。上記のすべての部品は同軸位置にある。
【0019】
次に、図2aに基づいて、異なる細部を説明する。この細部は図2aの図示の代替部または補足部である。
【0020】
図2bは図2aの電磁弁に基づいて、弁ケーシング3の詳細な変形を示している。この弁ケーシングのスリーブ状区間は弁閉鎖部材9の下方まで延び、そこで鉢状の弁座−収容体7を収容している。この弁座−収容体は図2aのように弁ケーシング3に溶接されていないで、弁ケーシング3の段部上のストッパーまで圧入されている。この範囲において弁ケーシング3の切刃状の突起31が弁支持体6の下側の通路接続口内まで延びているときには、この弁ケーシングは希望される場合または必要な場合に、金属的なシールを生じることができる。このシールは図示に従って断面の左側半部に示してある。弁縦軸線の右側では、図2aに既に示したOリング28がシール手段として示してある。しかし、これは付加的なコストを必要とする。弁支持体6にかしめられた環状部分32は弁をシールおよび固定するために弁ケーシング3に溶接されている。
【0021】
図2cは両スリーブ部分の縁曲げ部の形をした二分割実施形を示している。この場合、縁曲げ継手の外側の縁部20は同時に、弁支持体6内の電磁弁のかしめ範囲を形成している。その他のすべての細部は図2a,2bの図示と一致している。
【0022】
図2dは基本位置で閉じる構造の電磁弁を示している。この電磁弁はいわゆる二段弁の形の機能拡張部を備えている。そのために、磁気アーマチュア13に取付けられた弁閉鎖部材9は弁支持体6にかしめられた弁座−収容体7に直接載っていないで、上記の弁座─収容体7内で移動可能に案内された第2の弁座─収容体7′に載っている。両弁座─収容体7,7′の間には、弁ばね24が圧縮されて配置されている。磁気アーマチュア13を励磁する際、弁座─収容体7′の両側で圧力平衡が生じると、上記弁ばねの作用により、中間鉢状部材として形成された弁座─収容体7′が磁気アーマチュア13の運動に追随する。それによって、内側の弁−収容体7′は磁気アーマチュア13の弁閉鎖部材9上にとどまり、従って比較的に小さな弁座穴は球状の弁閉鎖部材9によって閉じたままである。垂直に開口する圧力媒体通路と水平に開口する圧力媒体通路の間の圧力媒体接続は、磁気アーマチュア13の励磁状態で、比較的に大きな弁座横断面にわたって強制的に行われる。この弁座横断面は両弁座−収容体7,7′の間に設けられている。弁閉鎖部材9の上方に生じる液圧が、弁閉鎖部材9の下方の液圧よりも大きい場合には、磁気アーマチュア13の励磁の際にも、内側の弁座−収容体7′のシール面が外側の弁座−収容体7に押し付けられる。それによって、専ら内側の弁座−収容体7′の比較的小さな弁座穴が弁閉鎖部材9によって開放される。外側と内側の弁座−収容体7,7′は冷間押出しプレス部品または深絞り部品として形成されているので、きわめて小さく簡単で精密に製作される部品が弁支持体6の収容穴内に挿入される。外側の弁座−収容体7に類似して、内側の弁座−収容体7′も、大まかに採寸された圧力媒体穴26と鉢状拡張部の範囲内の滑り面を備えている。それによって、内側の弁座−収容体7の確実な案内が保証される。
【0023】
図3の電磁弁は最も似ている図1cの弁構造と異なり、長さが幾分短縮された中空円筒状の弁ケーシング3を備えている。この弁ケーシングの下端の中空室16には、特に深絞り部品として形成されたスリーブ体22が圧入されている。このスリーブ体は一方では弁閉鎖部材9の方に向いた端部に弁座形状部を備え、他方では反対側の端部に逆止弁10用の他の弁座形状部を備えている。逆止弁10を落下しないように保持し、逆止弁を位置決めするために、スリーブ部分35が、スリーブ体22に侵入した圧力媒体穴27に下側から挿入されている。このスリーブ部分は本実施の形態では小さく選定された開放横断面によって、固定オリフィスの機能を有する。スリーブ部分35はスリーブ体22内でのその圧入長さの外側で、軸方向と半径方向に突出した端部を備えている。球状の逆止弁10が突出した端部と、弁座形状部を有するスリーブ体22の拡張した範囲との間に保持されている。図示した実施の形態では、半径方向に突出した端部は、深絞り部品として形成されたスリーブ部分35の舌片36として示してある。従って、スリーブ部分35は逆止弁10およびスリーブ体22と共に、予め組立てられたユニットを形成する。このユニットは弁ストロークを調節するために必要な寸法だけ、通路に似た中空室16内に圧入される。図1cに示したバイパス穴12はプレスばめ連結範囲内においてスリーブ体22の外周に沿って中空室16内に縦方向溝として延びている。スリーブ部分35から突出する段付きスリーブ体22の端部には、鉢状フィルタ11が嵌められているので、液体を漏らさない固定が行われる。図3の弁の説明していないすべての細部は、図1cの弁の説明または図1a,1b,1dまたは1eの変形の1つと一致している。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】図1a〜1eは基本位置で開放する電磁弁を形成するための合目的な実施の形態を示す図である。
【図2】図2a〜2dは基本位置で閉じる電磁弁のいろいろな構造的な実施の形態を示す図である。
【図3】図1a〜1eに示した電磁弁の変形を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 弁スリーブ
2 調節ピン
3 弁ケーシング
4 弁突棒
5 肩部
6 弁支持体
7,7′ 弁座−収容体
8 戻しばね
9 弁閉鎖部材
10 逆止弁
11 鉢状フィルタ
12 バイパス穴
13 磁気アーマチュア
14 横方向通路
15 中空室
16 中空室
17 かしめ部
18 収容穴
19 段部
20 縁部
21 溶接連結部
22 スリーブ体
23 突起
24 弁ばね
25 磁気コア
26 圧力媒体穴
27 圧力媒体穴
28 Oリング
29 リングフィルタ
30 突起
31 突出部
32 環状部分
33 弁座穴
34 ストッパー
35 スリーブ部分
36 舌片[0001]
The invention relates to a solenoid valve, in particular for a slip-controlled hydraulic brake device, as defined in the preamble of
[0002]
Such publicly known valves for controlling the flow of fluid in a slip control type hydraulic brake device are actually used in various ways.
[0003]
German Patent Application No. 1980826 discloses an electromagnetic valve that opens in a basic position for a slip-controlled hydraulic brake device. The valve case of this electromagnetic valve is formed as a cartridge structure. This cartridge structure is particularly wedged in a block-shaped valve housing as a turning part made from free-cutting steel. The valve plate forming the valve seat is also relatively strong and is produced in particular from turning parts made of free-cutting steel as well. This turning part is held by caulking in the lower end region of the valve casing. The valve stem, which cooperates with the valve seat, is guided in the valve casing and is a sturdy shaft part consisting of a solid cylinder. This shaft portion is supported on the end face of the magnetic armature in association with the adjusting bush. This magnetic armature is guided in a valve sleeve section on the valve casing. In order to lift and hold the valve protruding rod from the valve seat at the basic position of the electromagnetic valve, a so-called return spring is provided coaxially with the valve protruding rod. One end of the return spring pushes the valve stem with the adjusting bush toward the magnetic armature.
[0004]
The kind of solenoid valve that closes in the basic position is already known. This solenoid valve is described, for example, in German Published Patent Application No. 19727654. Unlike the previously described valve that opens in the basic position, in the case of the valve that closes in the basic position, the valve stem made from the solid body has a magnetic armature that can be handled and operated substantially independently. A subassembly is formed. This subassembly is directed towards the valve seat by a compression spring supported on a magnetic armature, and holds the valve seat closed in the above basic position of the solenoid valve.
[0005]
The solenoid valve described above has the disadvantage that the manufacturing costs required to fabricate the details of the valve and to insert the entire functional assembly into the valve housing are relatively high.
[0006]
Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an embodiment or a basic position that is opened at the basic position so that the structure in which reliability is ensured and the structure can be manufactured relatively easily is maintained and the manufacturing cost is greatly reduced. It is an improvement of the solenoid valve of the embodiment that is closed with.
[0007]
This problem is solved by the features described in the characterizing part of
[0008]
Suitable means are provided by the means described in the dependent claims. This embodiment will now be illustrated and described in detail based on FIGS. 1a-3 in connection with other features and advantages of the present invention.
[0009]
First, the basic overall structure of the solenoid valve opened at the basic position will be described with reference to FIG. 1a. The electromagnetic valve shown in the longitudinal section includes a bush-
[0010]
In addition, it should be pointed out that, of course, after the
[0011]
Similarly, a
[0012]
Unlike the above-described embodiment shown in FIG. 1a, in the next structural modification of the illustrated solenoid valve, details different from FIG. If all the details of the respective valve deformation are not explained, this detail is clear from the foregoing description, since this detail corresponds to the embodiment of FIG. 1a.
[0013]
FIG. 1b differs from FIG. 1a in that it shows a solenoid valve in which a
[0014]
Also in the embodiment of the solenoid valve of FIG. 1c, the
[0015]
The solenoid valve shown in FIG. 1d is very similar to the solenoid valve of the embodiment of FIG. 1b. This bowl-shaped valve seat-
[0016]
All the solenoid valves described above can have the function of a pressure control valve (relief valve) in a very simple manner. This function will now be described by way of example with reference to FIG. 1e. Instead of the above-described fixed arrangement of the
[0017]
The important features of the present invention will now be described clearly with reference to FIG. 2a on the basis of a solenoid valve closing in the basic position as usual. Following this description, the deformation of the valve components will be described with reference to FIGS.
[0018]
The solenoid valve shown in FIG. 2a is fixed to the
[0019]
The different details will now be described with reference to FIG. 2a. This detail is the alternative or supplement shown in FIG. 2a.
[0020]
FIG. 2b shows a detailed variant of the
[0021]
FIG. 2c shows a two-part embodiment in the form of an edge bend in both sleeve portions. In this case, the
[0022]
FIG. 2d shows a solenoid valve that is closed in the basic position. This solenoid valve has a function expansion part in the form of a so-called two-stage valve. For this purpose, the
[0023]
3 differs from the most similar valve structure of FIG. 1c in that it comprises a hollow
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIGS. 1a to 1e show a preferred embodiment for forming a solenoid valve that opens in a basic position.
2a to 2d show various structural embodiments of a solenoid valve closing in a basic position. FIG.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a modification of the electromagnetic valve shown in FIGS. 1a to 1e.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (8)
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19928750.3 | 1999-06-23 | ||
| DE19928750 | 1999-06-23 | ||
| DE19936711A DE19936711A1 (en) | 1999-06-23 | 1999-08-06 | Solenoid valve, especially for hydraulic brake systems with slip control |
| DE19936711.6 | 1999-08-06 | ||
| PCT/EP2000/005653 WO2001000473A1 (en) | 1999-06-23 | 2000-06-20 | Solenoid valve, especially for hydraulic brake systems with slip control |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003503260A JP2003503260A (en) | 2003-01-28 |
| JP2003503260A5 JP2003503260A5 (en) | 2007-07-12 |
| JP4790177B2 true JP4790177B2 (en) | 2011-10-12 |
Family
ID=7912255
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001506898A Expired - Fee Related JP4790177B2 (en) | 1999-06-23 | 2000-06-20 | Especially solenoid valve for slip control type hydraulic brake device |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4790177B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR100642022B1 (en) |
| DE (2) | DE19936711A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (52)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10004518A1 (en) * | 2000-02-02 | 2001-08-09 | Continental Teves Ag & Co Ohg | Braking system |
| DE10047399A1 (en) * | 2000-09-26 | 2002-04-11 | Continental Teves Ag & Co Ohg | Electromagnetic valve, especially for hydraulic brake system with slip control, has restoring spring supported on stop arranged near joint between valve seat body and valve housing |
| WO2002035125A1 (en) * | 2000-10-20 | 2002-05-02 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Closure device |
| DE10102593B4 (en) * | 2000-10-20 | 2007-12-13 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Closure device and method for fastening a closure body in a housing |
| EP1347907B1 (en) | 2000-12-27 | 2005-06-08 | Continental Teves AG & Co. oHG | Valve mechanism, especially for an anti-skid automotive brake systems |
| DE10141134A1 (en) * | 2001-01-12 | 2002-07-18 | Continental Teves Ag & Co Ohg | Electromagnetic valve for use in anti-skid braking systems has annular filter housing mounted below valve seat, filter cup containing filter plate being releasably attached to housing, forming premounted unit |
| JP3716219B2 (en) * | 2001-08-21 | 2005-11-16 | マンド コーポレーション | Solenoid valve for brake system |
| DE10203325A1 (en) * | 2001-08-30 | 2003-03-20 | Continental Teves Ag & Co Ohg | Electromagnetic valve, especially for hydraulic brake systems with slip control, has plate filter in bore coaxial to ring filter housing forming one-piece filter unit with ring filter housing |
| DE10205854B4 (en) * | 2001-10-04 | 2010-09-02 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Solenoid valve, in particular for hydraulic brake systems |
| KR100612738B1 (en) * | 2001-11-05 | 2006-08-18 | 주식회사 만도 | Solenoid valve for brake system |
| DE10212040A1 (en) * | 2002-01-14 | 2003-07-24 | Continental Teves Ag & Co Ohg | Electromagnetic valve for controlling through-flow of fluids operates in motor vehicle hydraulic brake units with regulated slippage. |
| KR100751230B1 (en) * | 2002-05-08 | 2007-08-23 | 주식회사 만도 | Solenoid valve for brake system |
| EP1636518A2 (en) * | 2002-12-13 | 2006-03-22 | Continental Teves AG & Co. oHG | Electromagnetic valve |
| JP4038452B2 (en) * | 2003-04-18 | 2008-01-23 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Proportional solenoid valve |
| DE10322904B4 (en) * | 2003-05-21 | 2008-08-28 | Zf Lenksysteme Gmbh | Valve for flow control |
| JP2005132347A (en) * | 2003-10-10 | 2005-05-26 | Advics:Kk | Braking fluid control device |
| DE102005061352A1 (en) * | 2005-09-15 | 2007-03-22 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Electromagnetic valve, in particular for slip-controlled motor vehicle brake systems |
| JP4597027B2 (en) * | 2005-10-17 | 2010-12-15 | タイム技研株式会社 | solenoid valve |
| KR101023673B1 (en) * | 2005-12-12 | 2011-03-25 | 주식회사 만도 | Solenoid valve for brake system |
| DE102006019464A1 (en) * | 2006-03-21 | 2007-09-27 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Solenoid valve |
| DE102006054184A1 (en) * | 2006-11-16 | 2008-05-21 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | magnetic valve |
| DE102006054185A1 (en) * | 2006-11-16 | 2008-05-21 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | magnetic valve |
| JP2008190574A (en) * | 2007-02-02 | 2008-08-21 | Nissin Kogyo Co Ltd | Solenoid valve |
| KR100848265B1 (en) * | 2007-03-30 | 2008-07-25 | 주식회사 만도 | Valve for anti-lock brake system |
| DE102007028516A1 (en) * | 2007-06-21 | 2008-12-24 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | magnetic valve |
| DE102007040691B4 (en) | 2007-08-29 | 2019-02-07 | Schaeffler Technologies AG & Co. KG | Solenoid valve and method of manufacturing a solenoid valve |
| KR100860482B1 (en) * | 2007-10-11 | 2008-09-26 | 주식회사 만도 | Solenoid valve for brake system |
| KR100867559B1 (en) * | 2007-10-11 | 2008-11-10 | 주식회사 만도 | Solenoid valve for break system |
| US8267334B2 (en) | 2007-10-11 | 2012-09-18 | Mando Corporation | Solenoid valve for brake system |
| JP5341433B2 (en) * | 2008-08-26 | 2013-11-13 | 株式会社不二工機 | 3-way selector valve |
| JP5487836B2 (en) | 2009-09-17 | 2014-05-14 | 株式会社アドヴィックス | Hydraulic device with solenoid valve |
| DE102009029670A1 (en) * | 2009-09-22 | 2011-03-24 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Check valve with two closing bodies |
| DE102009055279A1 (en) * | 2009-12-23 | 2011-06-30 | Robert Bosch GmbH, 70469 | Solenoid valve and driver assistance device |
| DE102010002284A1 (en) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-08-25 | Continental Teves AG & Co. OHG, 60488 | Valve arrangement, particularly for slip-controlled motor vehicle braking system, has hydraulically controlled non-return valve in non-return valve housing, where valve closure unit is arranged in tubular housing body |
| KR101683855B1 (en) * | 2010-07-01 | 2016-12-08 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Solenoid valve |
| KR101683858B1 (en) * | 2010-07-02 | 2016-12-07 | 현대모비스 주식회사 | Solenoid valve for oil pressure control |
| JP5710299B2 (en) * | 2011-02-04 | 2015-04-30 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | Brake device |
| US8684029B2 (en) | 2011-03-11 | 2014-04-01 | Mando Corporation | Check valve of hydraulic brake system |
| KR101237320B1 (en) * | 2011-03-11 | 2013-02-28 | 주식회사 만도 | Check Valve of Hydraulic break system |
| DE102012206282A1 (en) * | 2011-05-17 | 2012-11-22 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Electromagnetic valve, in particular for slip-controlled motor vehicle brake systems |
| DE102012222725A1 (en) * | 2012-12-11 | 2014-06-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Valve unit for hydraulic system of motor car, has valve ports provided at downstream side of non-return valve associated with filter that is assigned to main valve, so that downstream side of non-return valve is unfiltered |
| DE102013200533B4 (en) * | 2013-01-16 | 2016-01-21 | Rausch & Pausch Gmbh | VALVE CARTRIDGE |
| DE102013217580A1 (en) * | 2013-09-04 | 2015-03-05 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Electromagnetic valve, in particular for slip-controlled motor vehicle brake system |
| JP6347444B2 (en) * | 2014-09-12 | 2018-06-27 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | solenoid valve |
| JP6467223B2 (en) * | 2014-12-25 | 2019-02-06 | ヴィオニア日信ブレーキシステムジャパン株式会社 | Normally closed solenoid valve, vehicle brake fluid pressure control device, and assembly method of normally closed solenoid valve |
| JP6333776B2 (en) * | 2015-06-18 | 2018-05-30 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Poppet valve, hydraulic machine and regenerative energy generator |
| JP6333230B2 (en) * | 2015-11-17 | 2018-05-30 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | Valve block, fluid machine and renewable energy power generator |
| DE102016220348A1 (en) * | 2016-10-18 | 2018-04-19 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Solenoid valve for controlling the brake pressure of a wheel brake |
| CN108644389B (en) | 2017-06-14 | 2019-09-24 | 京西重工(上海)有限公司 | Regulated brake device electromagnetic valve component |
| DE102018101767A1 (en) * | 2018-01-26 | 2019-08-01 | Rausch & Pausch Gmbh | PRESSURE RELEASE SOLENOID VALVE |
| DE102018220673A1 (en) * | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-18 | Continental Teves Ag & Co. Ohg | Solenoid valve, in particular for slip-controlled motor vehicle brake systems |
| DE102021206310A1 (en) | 2021-06-21 | 2022-12-22 | Continental Automotive Technologies GmbH | Electromagnetic valve, in particular for slip-controlled motor vehicle brake systems |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998009855A1 (en) * | 1996-09-03 | 1998-03-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Electromagnetic valve for an automotive hydraulic braking system with traction control |
| JPH11160274A (en) * | 1997-11-28 | 1999-06-18 | Ngk Spark Plug Co Ltd | Gas sensor |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19700405A1 (en) * | 1997-01-09 | 1998-07-16 | Teves Gmbh Alfred | Solenoid valve for vehicle ABS braking systems |
| DE19710353A1 (en) * | 1997-03-13 | 1998-09-17 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Solenoid valve with integrated check valve |
| DE19711375A1 (en) * | 1997-03-19 | 1998-09-24 | Itt Mfg Enterprises Inc | Valve arrangement for regulated hydraulic braking systems |
-
1999
- 1999-08-06 DE DE19936711A patent/DE19936711A1/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2000
- 2000-06-20 KR KR1020017016400A patent/KR100642022B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2000-06-20 JP JP2001506898A patent/JP4790177B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-06-20 DE DE50010522T patent/DE50010522D1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1998009855A1 (en) * | 1996-09-03 | 1998-03-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Electromagnetic valve for an automotive hydraulic braking system with traction control |
| JP2000517263A (en) * | 1996-09-03 | 2000-12-26 | ローベルト ボツシユ ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | Solenoid valve for slip-controlled hydraulic vehicle brake system |
| JPH11160274A (en) * | 1997-11-28 | 1999-06-18 | Ngk Spark Plug Co Ltd | Gas sensor |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003503260A (en) | 2003-01-28 |
| DE50010522D1 (en) | 2005-07-14 |
| KR20020021134A (en) | 2002-03-18 |
| DE19936711A1 (en) | 2001-01-11 |
| KR100642022B1 (en) | 2006-11-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4790177B2 (en) | Especially solenoid valve for slip control type hydraulic brake device | |
| US6268784B1 (en) | Magnetic valve | |
| US6644623B1 (en) | Electromagnetic valve | |
| JP3787392B2 (en) | solenoid valve | |
| JP2838626B2 (en) | Solenoid valve device | |
| US9038984B2 (en) | Solenoid valve, in particular for slip-controlled motor vehicle braking systems | |
| US5496100A (en) | Pressure limited solenoid valve for a brake system | |
| KR100507939B1 (en) | Electrovalve for an anti-slip automotive hydraulic braking system | |
| US5356211A (en) | Magnet valve | |
| US6318703B1 (en) | Electromagnetic valve and process for setting the stroke of an electromagnetic valve | |
| US8579251B2 (en) | Solenoid valve | |
| US6065495A (en) | Two-position, three-way solenoid-actuated valve | |
| JPH07167337A (en) | Solenoid operating valve | |
| JP2011503459A (en) | Valve cartridge for solenoid valve and associated solenoid valve | |
| JP4432681B2 (en) | Brake fluid control system | |
| JP4778204B2 (en) | Solenoid operated valve | |
| JP5546645B2 (en) | Solenoid valve and method of manufacturing solenoid valve | |
| US6523913B1 (en) | Pressure control valve | |
| US5718489A (en) | Hydraulic unit for traction-controlled motor vehicle brake systems | |
| EP2334962B1 (en) | Valve for distributing fluids | |
| JP4012792B2 (en) | solenoid valve | |
| JP2005524806A (en) | Seat valve | |
| JP2006516703A (en) | solenoid valve | |
| JP2002510021A (en) | Solenoid valve | |
| JPH0958433A (en) | Solenoid valve, particularly solenoid valve used for hydraulic type brake gear having slip control function for automobile |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070522 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070522 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20100519 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100520 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100622 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20100917 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20100928 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101021 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110621 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110720 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140729 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4790177 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |