JP4723870B2 - Method and apparatus for setting target pixel region for color tone control of printing and picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing press - Google Patents
Method and apparatus for setting target pixel region for color tone control of printing and picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing press Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4723870B2 JP4723870B2 JP2005029612A JP2005029612A JP4723870B2 JP 4723870 B2 JP4723870 B2 JP 4723870B2 JP 2005029612 A JP2005029612 A JP 2005029612A JP 2005029612 A JP2005029612 A JP 2005029612A JP 4723870 B2 JP4723870 B2 JP 4723870B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- target pixel
- pixel region
- color
- target
- region
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Facsimile Image Signal Circuits (AREA)
- Color Image Communication Systems (AREA)
- Inking, Control Or Cleaning Of Printing Machines (AREA)
- Spectrometry And Color Measurement (AREA)
Description
本発明は、センサを用い、特定の画素領域に着目して色調を制御する印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法及び装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a picture color tone control method and apparatus for a printing press that uses a sensor to control color tone by paying attention to a specific pixel region.
印刷機の絵柄の色調を制御する技術として、種々の技術が提案されている。
例えば、特許文献1及び特許文献2にて提案された技術では、次のような手順で色調制御を行なう。
まず、各色の印刷ユニットで印刷された絵柄の分光反射率を分光計にて測定する。そして、インキキーのキーゾーン毎に分光反射率(キーゾーン全体の平均分光反射率)を演算し、さらに各キーゾーンの分光反射率を国際照明委員会が提唱する色座標値(L*a*b*)に変換する。各色のインキ供給量を調整して試印刷を行い、所望の色調を有する印刷シート(以下、OKシートという)が得られたら、OKシートの各キーゾーンの色座標値を目標色座標値に設定する。次に、本印刷を開始してキーゾーン毎にOKシートと印刷シート(以下、本印刷で得られた印刷シートを本刷りシートという)との色座標値の差(色差)を算出し、色差に対する各印刷ユニットのインキキー開度の増減量を計算して、色差がゼロになるように各印刷ユニットの各インキキーの開度をオンライン制御によって調整する。
Various techniques have been proposed as techniques for controlling the color tone of a picture of a printing press.
For example, in the techniques proposed in
First, the spectral reflectance of the pattern printed by each color printing unit is measured with a spectrometer. Then, the spectral reflectance (average spectral reflectance of the entire key zone) is calculated for each key zone of the ink key, and the color coordinate value (L * a * b) proposed by the International Illumination Committee for the spectral reflectance of each key zone. *). Test printing is performed by adjusting the ink supply amount of each color, and when a print sheet having a desired color tone (hereinafter referred to as “OK sheet”) is obtained, the color coordinate value of each key zone of the OK sheet is set as the target color coordinate value. To do. Next, the actual printing is started, and the color coordinate value difference (color difference) between the OK sheet and the printing sheet (hereinafter, the printing sheet obtained by the main printing is referred to as the main printing sheet) is calculated for each key zone. The increase / decrease amount of the ink key opening of each printing unit with respect to is calculated, and the opening of each ink key of each printing unit is adjusted by online control so that the color difference becomes zero.
しかしながら、特許文献1,2に開示された技術では、計測手段として分光計を用いており、分光計はコストが高く、さらに、分光計は新聞用輪転機のように計測対象(この場合は印刷シート)が極めて高速で移動する場合には処理能力上追従することができない。また、上記方法では、OKシートが印刷されてから色調制御が開始されることになるため、立ち上がりからOKシートが印刷されるまでの間に多くの損紙が発生してしまう。また、上記方法では、インキキーのキーゾーン内の絵柄をキーゾーン全体で平均化してその平均分光反射率に基づいて色調制御を行なうため、キーゾーン内の絵柄の画線率が低い場合には、分光計の計測誤差が大きくなり、制御が不安定になりやすい。さらに、客先からの注文には、絵柄中の特定の注目点について特に厳しい色調管理を要求される場合があるが、このように特定の注目点について色調制御したい場合には、基準となる画像データとして上流の製版工程からCIP3〔CIP3(Cooperation for Integration of Prepress, Press, Postpress)規格のPPF(Print Production Format)データ〕等のデータをもらわなければならない。
However, in the techniques disclosed in
そこで、特許文献3には、これらの課題を解決すべく、次のような手順で色調制御を行なう技術が提案されている。
まず、印刷絵柄をインキ供給装置のインキ供給単位幅で分割したときのインキ供給単位幅毎の目標混色網濃度を設定する。なお、インキ供給装置のインキ供給単位幅とは、インキ供給装置がインキキー装置である場合には各インキキーのキー幅(キーゾーン)のことであり、インキ供給装置がデジタルポンプ装置である場合には各デジタルポンプのポンプ幅のことである。なお、目標混色網濃度の設定方法については、後述する。
In order to solve these problems, Patent Document 3 proposes a technique for performing color tone control according to the following procedure.
First, a target color mixture halftone density is set for each ink supply unit width when the printed pattern is divided by the ink supply unit width of the ink supply apparatus. The ink supply unit width of the ink supply device is the key width (key zone) of each ink key when the ink supply device is an ink key device, and when the ink supply device is a digital pump device. It is the pump width of each digital pump. A method for setting the target color mixture halftone density will be described later.
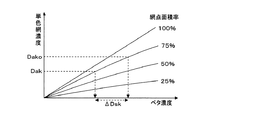
印刷を開始して本刷りシートが得られると、IRGB濃度計を用いて本刷りシートのインキ供給単位幅毎の実混色網濃度を計測する。そして、予め設定した各インキ色の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、実混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の実網点面積率を求める。実網点面積率を実混色網濃度から求める方法としては、各インキ色の網点面積率と混色網濃度との関係を記憶したデータベース、例えば、ISO/TC130国内委員会が制定した新聞印刷JapanColor基準の印刷物を印刷し、IRGB濃度計で実測したデータベースを用いてもよく、より簡単には、そのデータベースを利用して公知のノイゲバウアーの式で近似した値を利用することもできる。また、上記の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、目標混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の目標網点面積率も求めておく。目標網点面積率については、実網点面積率のように毎回求める必要はなく、目標混色網濃度が変わらない限りは一度求めておけばよい。例えば、目標混色網濃度を設定した時点で目標網点面積率も求めておいてもよい。 When printing is started and a main printing sheet is obtained, an actual color mixture halftone density for each ink supply unit width of the main printing sheet is measured using an IRGB densitometer. Then, the actual halftone dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the actual mixed color halftone density is obtained based on the correspondence relationship between the halftone dot area ratio of each ink color and the mixed color halftone density. As a method for obtaining the actual halftone dot area ratio from the actual mixed color halftone density, a database storing the relationship between the halftone dot area ratio of each ink color and the mixed color halftone density, for example, newspaper printing JapanColor established by the ISO / TC130 National Committee. A database obtained by printing a standard printed matter and actually measured by an IRGB densitometer may be used. More simply, a value approximated by a well-known Neugebauer equation can be used by using the database. Further, based on the correspondence between the halftone dot area ratio and the mixed color halftone density, the target halftone dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the target mixed color halftone density is also obtained. The target halftone dot area ratio does not need to be obtained every time as the actual halftone dot area ratio, and may be obtained once as long as the target mixed color halftone density does not change. For example, the target dot area ratio may also be obtained when the target color mixture halftone density is set.
次に、予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、実網点面積率に対応する実単色網濃度を求める。実単色網濃度を実網点面積率から求める方法としては、単色網濃度と網点面積率との関係を表すマップやテーブルを用意しておき、これらのマップやテーブルに実網点面積率を当てはめてもよく、より簡単には、公知のユールニールセンの式を用いて前記関係を近似して、それを利用して求めてもよい。また、上記の網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、目標網点面積率に対応する目標単色網濃度も求めておく。目標単色網濃度については、実単色網濃度のように毎回求める必要はなく、目標網点面積率が変わらない限りは一度求めておけばよい。例えば、目標網点面積率を設定した時点で目標単色網濃度も求めておいてもよい。 Next, an actual monochrome halftone density corresponding to the actual halftone dot area ratio is obtained based on a correspondence relationship between a preset halftone dot area ratio and the monochrome halftone density. As a method of obtaining the actual monochrome dot density from the actual dot area ratio, a map or table showing the relationship between the monochrome dot density and the dot area ratio is prepared, and the actual dot area ratio is set in these maps or tables. It may be applied, or more simply, the relationship may be approximated using a well-known Yule-Nielsen equation and used to determine the relationship. Further, based on the correspondence relationship between the halftone dot area ratio and the monochrome halftone density, a target monochrome halftone density corresponding to the target halftone dot area ratio is also obtained. The target monochromatic halftone density need not be obtained every time as in the case of the actual monochromatic halftone density, and may be obtained once as long as the target halftone dot area ratio does not change. For example, the target monochromatic halftone density may also be obtained when the target halftone dot area ratio is set.
次に、予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度とベタ濃度との対応関係に基づき、目標網点面積率のもとでの目標単色網濃度と実単色網濃度との偏差に対応するベタ濃度偏差を求める。ベタ濃度偏差を求める方法としては、上記体対応関係を表すマップやテーブルを用意しておき、これらのマップやテーブルに目標網点面積率,目標単色網濃度及び実単色網濃度を当てはめてもよく、より簡単には、公知のユールニールセンの式を用いて前記関係を近似して、それを利用して求めてもよい。そして、求めたベタ濃度偏差に基づきインキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整し、各色のインキの供給量をインキ供給単位幅毎に制御する。ベタ濃度偏差に基づくインキ供給量の調整量は、簡単には、公知のAPI(オートプリセットインキング)関数を用いて求めることができる。 Next, based on the correspondence relationship between the halftone dot area ratio, the monochrome halftone density, and the solid density set in advance, the solid color corresponding to the deviation between the target monochrome halftone density and the actual monochrome halftone density under the target halftone dot area ratio. Obtain the concentration deviation. As a method for calculating the solid density deviation, a map or table showing the above-mentioned body correspondence may be prepared, and the target halftone dot area ratio, the target monochromatic halftone density, and the actual monochromatic halftone density may be applied to these maps and tables. More simply, the relationship may be approximated using a well-known Yule-Nielsen equation and obtained using this equation. Then, the ink supply amount is adjusted for each ink supply unit width based on the obtained solid density deviation, and the ink supply amount for each color is controlled for each ink supply unit width. The adjustment amount of the ink supply amount based on the solid density deviation can be easily obtained using a known API (Auto Preset Inking) function.
このような絵柄色調制御方法によれば、分光計ではなくIRGB濃度計を用いて色調制御を行なうことができるので、計測手段にかかるコストが低減できるとともに新聞輪転機のような高速印刷機にも十分に対応することが可能となる。
また、外部(例えば、印刷依頼元等)から印刷対象絵柄のkcmy網点面積率データ(例えば、製版用の画像データ等)を取得できる場合の目標混色網濃度の設定手法として、以下の点が提案されている。
According to such a pattern color tone control method, the color tone control can be performed using an IRGB densitometer instead of a spectrometer, so that the cost for measuring means can be reduced and the high-speed printing machine such as a newspaper rotary press can be used. It becomes possible to respond sufficiently.
Further, as a method for setting a target color mixture halftone density when kcmy halftone dot area ratio data (for example, image data for plate making) of a print target pattern can be acquired from the outside (for example, a print request source), the following points are provided. Proposed.
まず、取得した画像データ(kcmy網点面積率データ)に対し、印刷対象絵柄を構成する画素の中からインキ供給単位幅毎に各インキ色に対応する注目画素(注目画素とは、一画素でもよく、連続する一塊の複数画素でもよい)をそれぞれ設定し、予め設定した網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき注目画素の網点面積率を混色網濃度に変換する。そして、注目画素の混色網濃度を目標混色網濃度として設定するとともに、設定した注目画素の実混色網濃度を計測する。 First, with respect to the acquired image data (kcmy halftone dot area ratio data), a pixel of interest corresponding to each ink color for each ink supply unit width among pixels constituting the pattern to be printed (a pixel of interest is a single pixel). (It may be a plurality of continuous pixels), and the halftone dot area ratio of the target pixel is converted into the mixed color halftone density based on the correspondence between the halftone dot area ratio and the mixed color halftone density. Then, the mixed color halftone density of the target pixel is set as the target mixed color halftone density, and the actual mixed color halftone density of the set target pixel is measured.
これによれば、JapanColorのデータベースを利用するなど画素単位で発色を推定できるのでOKシートが印刷されるのを待つまでもなく、印刷開始直後から絵柄の特定の注目点(注目画素)について色調制御を行なうことができる。なお、kcmy網点面積率データとしては、印刷対象絵柄のビットマップデータ(例えば、1bit−Tiff製版用データ)でもよく、ビットマップデータをCIP3データ相当の低解像度データに変換したものを用いてもよい。 According to this, since color development can be estimated on a pixel-by-pixel basis, such as using the JapanColor database, color tone control can be performed for a specific point of interest (attention pixel) of a pattern immediately after printing starts without waiting for an OK sheet to be printed. Can be performed. The kcmy halftone dot area ratio data may be bitmap data of a pattern to be printed (for example, 1-bit-Tiff plate-making data), or may be obtained by converting bitmap data into low resolution data equivalent to CIP3 data. Good.
なお、注目点の設定方法として、ビットマップデータを用いてタッチパネル等の表示装置上に印刷絵柄の画像を表示して、オペレータが任意に注目点を指定する方法や、インキ色毎に最も濃度感度の高い画素、或いは、インキ色毎に各画素の網点面積率に対して最も自己相関が大きい画素を演算して自動抽出し、注目画素として設定する方法が提案されている。また、注目画素の具体的な設定方法としては、自己相関感度Hを導入し、この自己相関感度Hが最も大きい画素を最も自己相関が大きい画素とし、この画素を注目画素として設定するようにしている。例えば、シアンの自己相関感度Hcは、各画素面積率データ(c,m,y,k)を用いて、“Hc=c2/(c+m+y+k)”で表すことができ、この自己相関感度Hcの値が最も高い画素がシアンの注目点となる。 Note that the point of interest can be set by displaying an image of a printed pattern on a display device such as a touch panel using bitmap data, and by the operator arbitrarily specifying the point of interest, or by using the most density sensitivity for each ink color. A method has been proposed in which a pixel having a high autocorrelation with respect to a halftone dot area ratio of each pixel is calculated and automatically extracted and set as a pixel of interest for each ink color. In addition, as a specific method of setting the target pixel, an autocorrelation sensitivity H is introduced, a pixel having the highest autocorrelation sensitivity H is set as a pixel having the highest autocorrelation, and this pixel is set as the target pixel. Yes. For example, the autocorrelation sensitivity Hc of cyan can be expressed by “Hc = c 2 / (c + m + y + k)” using each pixel area ratio data (c, m, y, k). The pixel with the highest value is the cyan attention point.
このように、インキ色毎に各画素の網点面積率に対して最も自己相関が大きい画素を演算して抽出し、これを注目画素として設定し、この注目画素に関して目標単色網濃度及び実単色網濃度を算出して実単色網濃度が目標単色網濃度に近づくようにインキ供給量をフィードバック制御することにより、より安定した色調制御を行なうことができる。
ところで、上記の技術では、自動で注目画素を設定する場合、自己相関が最も大きい画素(1画素、又は連続する一塊の複数画素)を注目画素としている。印刷する画素の基本的な単位は、製版データの画素単位であるが、実混色網濃度を計測するセンサであるIRGB濃度計は、印刷速度が速くなるほど単位時間当たりの反射光量が小さくなり、その影響を受けて計測エリアが小さいほど濃度計の計測精度は大幅に低下してしまう。 By the way, in the above technique, when the target pixel is automatically set, the pixel having the highest autocorrelation (one pixel or a plurality of continuous pixels) is set as the target pixel. The basic unit of pixels to be printed is the pixel unit of plate making data, but the IRGB densitometer, which is a sensor for measuring the actual mixed color halftone density, reduces the amount of reflected light per unit time as the printing speed increases. The measurement accuracy of the densitometer is greatly reduced as the measurement area is affected.
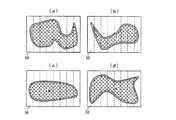
そこで、濃度計の解像度の最小単位を基本単位(これを、センサ画素単位又は1ブロックと呼ぶ)として、注目画素を設定することが必要になる。この場合、製版データの画素を多数集めたものがセンサ画素単位の1画素(1ブロック)に相当することになる。このような観点から、例えば、図13にC,M,Y,Kの符号を付して示すように、製版データから得られる製版面50中に、ブロックを設定し(実際のブロックはこれほど大きくはない)、このブロック単位で、注目画素を設定することが考えられる。
Therefore, it is necessary to set the pixel of interest using the minimum unit of resolution of the densitometer as a basic unit (this is called a sensor pixel unit or one block). In this case, a collection of a large number of pixels of plate making data corresponds to one pixel (one block) in sensor pixel units. From such a point of view, for example, as shown in FIG. 13 with the symbols C, M, Y, and K, blocks are set in the
一方、特許文献3の技術では、自己相関感度Hが最も大きい画素が、濃度感度が高く、且つ画像のエッジ部が含まれ難い特徴を持つ画素として注目画素に設定しているが、この自己相関感度Hには、自己相関が高いことと標準偏差が低いことの2つの条件が含まれる。このため、ブロック単位で注目画素を設定する場合、あるブロックにおいて、大部分が白紙である中に、ある色のインキのみが少量だけ印刷される場合があって、このようなブロックが、該当するインキ色の自己相関感度が最も高いブロックとなることがある。 On the other hand, in the technique of Patent Document 3, a pixel having the highest autocorrelation sensitivity H is set as a pixel of interest as a pixel having high density sensitivity and a characteristic that the edge portion of the image is difficult to be included. Sensitivity H includes two conditions: high autocorrelation and low standard deviation. For this reason, when setting a pixel of interest in block units, only a small amount of ink of a certain color may be printed while a majority of the block is blank paper. It may be the block with the highest autocorrelation sensitivity of the ink color.
このように選出された自己相関感度が最も高いブロックを注目画素に設定すると、ブロック内に僅かにしか印刷されない該当するインキ色の濃度を検出して色調制御をすることになり、濃度検出感度が低下して色調制御の精度が低下してしまうことがある。
そこで、より色調制御を精度良く実施することができるように注目画素を適切に設定したいが、例えば新聞印刷などの場合、紙面編集から印刷完了までを短時間で完了しなくてはならないので、注目画素の設定を適切にするだけでなく短時間で効率よく行なわれなくてはならない。
If the block with the highest autocorrelation sensitivity selected in this way is set as the pixel of interest, the density of the corresponding ink color that is printed only slightly in the block is detected and the tone control is performed, and the density detection sensitivity is increased. The accuracy of the color tone control may decrease due to the decrease.
Therefore, we would like to set the target pixel appropriately so that the color tone control can be carried out more accurately.For example, in the case of newspaper printing, it is necessary to complete the process from paper editing to printing completion in a short time. Not only is the pixel setting appropriate, it must be done efficiently in a short time.
本発明は、上述の課題に鑑み創案されたもので、制御のための注目個所(注目画素)を適切にしかも短時間で効率よく設定できるようにして、色調制御の精度を向上させることができるようにした、印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法及び装置並びに印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法及び装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been devised in view of the above-described problems, and can improve the accuracy of color tone control by appropriately setting a target location (target pixel) for control in a short time and efficiently. It is an object of the present invention to provide a method and apparatus for setting a target pixel area for color tone control of printing and a method and apparatus for controlling a picture color tone of a printing press.
上記目標を達成するため、本発明の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法は、印刷絵柄中の特定の画素領域に注目して印刷の色調をフィードバック制御する際に用いる各インキ色の注目画素領域を設定する方法であって、製版データ及び印刷用ジョブチケットデータの作成時に、上記ジョブチケットデータに上記製版データに対応した上記注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込む注目画素領域情報書き込みステップと、上記製版データ及び上記ジョブチケットデータに基づいて印刷を実施するに当たって、上記の書き込まれた注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて印刷絵柄中に上記注目画素領域を設定する注目画素領域設定ステップとを備え、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報は、上記注目画素領域としてベタ領域,網領域,平網領域のうち少なくとも何れか2つの領域の中から1つを選ぶ選択情報であることを特徴としている(請求項1)。なお、注目画素領域情報書き込みステップは、例えば紙面構成を担当する紙面デザイナーなどの紙面構成担当者等が行ない、注目画素領域設定ステップは印刷オペレータ等が行なう。
In order to achieve the above-described target, the target pixel region setting method for color tone control according to the present invention uses the target pixel region for each ink color to be used for feedback control of the color tone of printing by paying attention to a specific pixel region in a printed pattern. A method of setting, a pixel-of-interest area information writing step of writing information on the pixel-of-interest area corresponding to the plate-making data into the job ticket data when creating plate-making data and printing job ticket data; in carrying out the printing based on the job ticket data, and a noticed pixel region setting step for setting the noticed pixel region into printing picture based on information about the target pixel region written with the above, said pixel of interest There is little information about the area among the solid area, the net area, and the flat area. It is characterized in that also selection information to select one of the any two regions (claim 1). Note that the pixel-of-interest area information writing step is performed, for example, by a person in charge of paper configuration such as a paper designer who is in charge of paper configuration, and the pixel-of-interest region setting step is performed by a print operator or the like.
例えば、印刷絵柄には、一般的にベタ領域及び種々の網点面積率の網領域があるが、紙面構成担当者等は、印刷絵柄のうちの特にベタ領域の色調を重視して制御したければ、ジョブチケットデータにベタ領域を注目画素領域とする旨の情報を書き込み、印刷絵柄のうちの特に網領域の色調を重視して制御したければ、ジョブチケットデータに網領域を注目画素領域とする旨の情報を書き込めばよい。また、ベタ領域や平網領域は色調にムラが生じやすいので、このようなベタ領域や平網領域の色調ムラを解消したい場合には、紙面構成担当者等は、ジョブチケットデータに注目画素領域としてベタ領域或いは平網領域を設定する旨の情報を書き込めばよい。
For example, the printing picture, generally there is a solid area and halftone area of the various halftone dot area ratio, but the paper structure personnel, etc., in particular the control with an emphasis on the color tone of the solid area of the printing picture If it is desired to write information indicating that the solid area is the target pixel area in the job ticket data, and control the emphasis on the color tone of the print area, in particular, the net area is set to the job ticket data. It is only necessary to write information to that effect. In addition, since solid areas and flat mesh areas tend to have uneven color tone, if you want to eliminate such uneven color tones in solid areas or flat mesh areas, the person in charge of the page configuration, etc., should pay attention to the job ticket data in the target pixel area. Information for setting a solid area or a flat net area may be written.
さらに、上記平網領域は、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の画像微分値が予め設定された基準値以下の領域であることが好ましい(請求項2)。この場合の網点面積率の画像微分値とは、隣接画素との差分の値であり、また、網点面積率の画像微分値にかかる予め設定された基準値は、例えば1%とすることができる。
上記ベタ領域は、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が予め設定された基準値以上の領域であって、上記網領域は、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が上記基準値未満の領域であることが好ましい(請求項3)。この場合の網点面積率の値にかかる予め設定された基準値は、例えば70%とすることができる。
Further, the upper Kitaira network region is preferably image differential value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printing picture is a region below a preset reference value (claim 2). In this case, the image differential value of the halftone dot area ratio is a difference value from adjacent pixels, and the preset reference value for the image differential value of the halftone dot area ratio is, for example, 1%. Can do.
The solid area is an area where the value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printed pattern is equal to or greater than a preset reference value, and the halftone area of the printed pattern is less than the reference value The region is preferable (claim 3). In this case, a preset reference value for the value of the halftone dot area ratio can be set to 70%, for example.
また、上記注目画素領域設定ステップでは、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて上記注目画素領域を手動又は自動で設定することができる(請求項4)。手動の場合は、例えば印刷オペレータによって設定し、自動の場合は例えばコンピュータを用いて設定することができる。
上記の設定された注目画素領域のうちエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いたものを印刷の色調制御に用いる注目画素領域とすることが好ましい(請求項5)。
Further, in the target pixel region setting step, it can be set manually or automatically the noticed pixel region based on the information on the pixel of interest areas (Claim 4). In the case of manual, it can be set by, for example, a printing operator, and in the case of automatic, it can be set by using, for example, a computer.
It is preferable that the noticed pixel region to be used for color tone control of the printing of the minus edge portion of the above set noticed pixel region by a predetermined sensor pixels (claim 5).
上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて行なう上記注目画素領域設定ステップを第1の注目画素領域設定ステップとし、上記第1の注目画素領域設定ステップとは別に、製版データの網点面積率データに基づいて、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を、反射光量を計測するセンサのセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いた領域を、該当するインキ色の上記注目画素領域として設定する第2の注目画素領域設定ステップをさらにそなえていることが好ましい(請求項6)。
The target pixel region setting step performed based on the information on the target pixel region is set as a first target pixel region setting step, and, separately from the first target pixel region setting step , halftone dot area ratio data of plate making data is used. Based on this, a region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light, and the edge portion of the corresponding ink color is removed from the selected region by a predetermined sensor pixel. the area, preferably further comprising a second noticed pixel region setting step of setting as the target pixel area of the pertaining ink color (claim 6).
また、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて行なう上記注目画素領域設定ステップを第1の注目画素領域設定ステップとし、上記第1の注目画素領域設定ステップとは別に、製版データの網点面積率データに基づいて上記注目画素領域を設定するステップであって、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を、反射光量を計測するセンサのセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いても上記注目画素領域が存在する場合には、上記選定領域の中から上記エッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いた領域を、該当するインキ色の上記注目画素領域として設定し、上記のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除くと上記注目画素領域がなくなってしまう場合には、上記選定領域の中から上記エッジ部を除くことなく上記の自己相関が高い領域を、該当するインキ色の上記注目画素領域として設定する第2の注目画素領域設定ステップをさらにそなえていることが好ましい(請求項7)。
The target pixel region setting step performed based on the information regarding the target pixel region is a first target pixel region setting step, and the halftone dot area ratio of the plate making data is separated from the first target pixel region setting step. A step of setting the pixel region of interest based on data , wherein a region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of a sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light , and the corresponding ink is selected from the selected region; If the target pixel area exists even if the edge portion of the color is removed by the predetermined sensor pixel, the area obtained by removing the edge portion by the predetermined sensor pixel from the selected region is used as the corresponding ink color. In the case where the pixel region of interest disappears when the edge portion is removed by a predetermined number of sensor pixels, the selected region is set as the pixel region of interest. The region above the autocorrelation is high without excluding the edge portion, that further includes a second noticed pixel region setting step of setting as the target pixel area of the pertaining ink color preferred in (Claim 7 ).
上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップでは、上記選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を上記センサ画素単位で除く際に、上記センサ画素単位で1画素分だけ除くことが好ましい(請求項8)。
さらに、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて行なう上記注目画素領域設定ステップを第1の注目画素領域設定ステップとし、上記第1の注目画素領域設定ステップとは別に、製版データに基づいて、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を、反射光量を計測するセンサのセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を含むように上記自己相関が高い領域の外側まで膨らませた領域を、上記注目画素領域として設定する第2の注目画素領域設定ステップをさらにそなえていることが好ましい(請求項9)。
また、上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップでの上記自己相関が高い領域とは、各インキ色について予め設定された条件以上に自己相関が高い全ての画素群であって、上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップは、コンピュータを用いて上記画素群を自動抽出する注目画素領域自動設定ステップとして構成されることが好ましい(請求項10)。
In the second pixel-of-interest region setting step, it is preferable that when the corresponding ink color edge portion is removed from the selected region in the sensor pixel unit, only one pixel is removed in the sensor pixel unit. 8).
Et al is, the noticed pixel region setting step of performing on the basis of the information on the pixel of interest area are first noticed pixel region setting step, the above first noticed pixel region setting step separately, based on the plate making data A region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light, and the region having a high autocorrelation is selected from the selected region so as to include an edge portion of the corresponding ink color. an area inflated to the outside, preferably further comprising a second noticed pixel region setting step of setting as the target pixel regions (claim 9).
In addition, the region having a high autocorrelation in the second pixel-of-interest region setting step is a group of all pixels having an autocorrelation higher than a preset condition for each ink color. pixel region setting step, is preferably configured as a noticed pixel region automatically setting step of automatically extracting the pixel group by using a computer (claim 10).
上記第1の注目画素領域設定ステップによって設定された第1の注目画素領域と上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップによって設定された第2の注目画素領域との和の領域を注目画素領域に設定することが好ましい(請求項11)。
また、本発明の印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法(請求項12)は、請求項1〜11の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法を用いて設定された注目画素領域に注目して印刷の色調をフィードバック制御する印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法であって、上記注目画素領域に関する目標混色網濃度を設定する目標混色網濃度設定ステップと、上記センサを用いて、印刷で得られた本刷りシートのインキ供給単位幅毎の各インキ色の上記注目画素領域に関する実混色網濃度を計測する実混色網濃度計測ステップと、予め設定した網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の目標網点面積率を求める目標網点面積率算出ステップと、上記の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の実網点面積率を求める実網点面積率算出ステップと、予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標網点面積率に対応する目標単色網濃度を求める目標単色網濃度算出ステップと、上記の網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実網点面積率に対応する実単色網濃度を求める実単色網濃度算出ステップと、予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度とベタ濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記注目画素領域について、上記目標網点面積率のもとでの上記目標単色網濃度と上記実単色網濃度との偏差に対応するベタ濃度偏差を求めるベタ濃度偏差算出ステップと、上記ベタ濃度偏差に基づき上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整するインキ供給量調整ステップとをそなえていることを特徴としている。
The sum area of the first target pixel area set by the first target pixel area setting step and the second target pixel area set by the second target pixel area setting step is set as the target pixel area. (Claim 11 ).
The printing press picture color tone controlling method of the present invention (Claim 12), the target pixel area set by using the color tone control noticed pixel region setting method according to any one of
さらに、請求項6〜11の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法を用いるとともに、上記の目標混色網濃度設定ステップ,実混色網濃度計測ステップ,目標網点面積率算出ステップ,実網点面積率算出ステップ,目標単色網濃度算出ステップ,実単色網濃度算出ステップ,及びベタ濃度偏差算出ステップを、上記第1の注目画素領域設定ステップによって設定された第1の注目画素領域と上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップによって設定された第2の注目画素領域との双方に関して実施して、上記インキ供給量調整ステップでは、これらから得られる2つの上記ベタ濃度偏差に基づき上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整することが好ましい(請求項13)。 Further, the target pixel area setting method for color tone control according to any one of claims 6 to 11 is used, and the target mixed color halftone density setting step, the actual mixed color halftone density measuring step, and the target halftone dot area ratio calculating step are performed. , An actual halftone dot area ratio calculating step, a target monochromatic halftone density calculating step, an actual monochromatic halftone density calculating step, and a solid density deviation calculating step are set to the first target pixel area set by the first target pixel area setting step. And the second target pixel region set by the second target pixel region setting step, and the ink supply amount adjusting step performs the ink based on the two solid density deviations obtained from them. it is preferable to adjust the ink supplying amount for each supply unit width (claim 13).
また、上記インキ供給量調整ステップでは、上記第1の注目画素に関して得られた上記ベタ濃度偏差と、上記第2の注目画素に関して得られた上記ベタ濃度偏差とを、予め設定された重み付けに応じて加重平均して、この加重平均したベタ濃度偏差に基づき上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整することが好ましい(請求項14)。
本発明の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置(請求項15)は、印刷絵柄中の特定の画素領域に注目して印刷の色調をフィードバック制御する際に用いる各インキ色の注目画素領域を設定する装置であって、製版データ及び印刷用ジョブチケットデータに上記製版データに対応した上記注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込む書込手段と、上記製版データ及び上記ジョブチケットデータに基づいて印刷を制御するとともに上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて上記注目画素領域を自動で設定する演算装置とを備え、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報は、上記注目画素領域としてベタ領域,網領域,平網領域のうち少なくとも何れか2つの領域の中から1つを選ぶ選択情報であることを特徴としている。
In the ink supply amount adjustment step, the solid density deviation obtained for the first pixel of interest and the solid density deviation obtained for the second pixel of interest are set according to a preset weight. and weighted average Te, it is preferable to adjust the ink supplying amount for each of the ink supplying unit widths based on the weighted average solid density deviation (claim 14).
Tone control noticed pixel region setting apparatus of the printing of the present invention (Claim 15), the noticed pixel region for each ink color to be used for feedback control of the tone of interest to print a particular pixel region in the printing picture an apparatus for setting, controlling and writing means for writing information on the noticed pixel region corresponding to the plate making data to the plate making data and the print job ticket data, the printing based on the plate making data and the job ticket data And an arithmetic unit that automatically sets the target pixel area based on the information on the target pixel area, and the information on the target pixel area includes a solid area, a net area, and a flat net area as the target pixel area. It is the selection information which selects one from at least any two areas.
上記平網領域は、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の画像微分値が予め設定された基準値以下の領域であることが好ましい(請求項16)。 Upper Kitaira network region is preferably image differential value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printing picture is a region below a preset reference value (claim 16).
上記ベタ領域は、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が予め設定された基準値以上の領域であって、上記網領域は、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が上記基準値未満の領域であることが好ましい(請求項17)。
上記演算装置は、上記の設定された注目画素領域のうちエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いたものを印刷の色調制御に用いる注目画素領域とすることが好ましい(請求項18)。
The solid area is an area where the value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printed pattern is equal to or greater than a preset reference value, and the halftone area of the printed pattern is less than the reference value The region is preferable (claim 17 ).
The arithmetic unit is preferably in a noticed pixel region to be used for color tone control of the printing of the minus edge portion of the above set noticed pixel region by a predetermined sensor pixels (claim 18).
上記演算装置には、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて注目画素領域を設定する第1の注目画素領域設定手段と、上記第1の注目画素領域設定手段とは別に、製版データに基づいて、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を、反射光量を計測するセンサのセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いた領域を、上記注目画素として設定する第2の注目画素領域設定手段とそなえていることが好ましい(請求項19)。
上記演算装置には、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて注目画素領域を設定する第1の注目画素領域設定手段と、上記第1の注目画素領域設定手段とは別に、製版データに基づいて、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を、反射光量を計測するセンサのセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を含むように上記自己相関が高い領域の外側まで膨らませた領域を、上記注目画素領域として設定する第2の注目画素領域設定手段とそなえていることが好ましい(請求項20)。
The arithmetic unit includes a first target pixel region setting unit that sets a target pixel region based on the information about the target pixel region and a first target pixel region setting unit, based on plate making data. A region with a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor that measures the amount of reflected light, and a region obtained by removing the edge portion of the corresponding ink color from the selected region by a predetermined sensor pixel is selected. it is preferable that includes the second noticed pixel region setting means for setting as the target pixel (claim 19).
The upper SL computing device, a first noticed pixel region setting means for setting a noticed pixel region based on the information on the pixel of interest areas, apart from the first noticed pixel region setting means, based on the plate making data A region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light, and the region having a high autocorrelation is included from the selected region to include an edge portion of the corresponding ink color. of an area inflated to the outside, it is preferable that includes the second noticed pixel region setting means for setting as the target pixel regions (claim 20).
上記演算装置では、上記第1の注目画素領域設定手段によって設定された第1の注目画素領域と上記第2の注目画素領域設定手段によって設定された第2の注目画素領域との和の領域を注目画素領域に設定することが好ましい(請求項21)。
また、本発明の印刷機の絵柄色調制御装置(請求項22)は、請求項15〜21の何れか1項に記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置と、印刷で得られる本刷りシートの走行ライン上に配置されたセンサと、印刷幅方向に分割されたインキ供給単位幅毎の該注目画素領域に関する目標混色網濃度を設定する目標混色網濃度設定手段と、上記センサを操作して上記本刷りシートの上記インキ供給単位幅毎の実混色網濃度を計測する混色網濃度計測手段と、予め設定した網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の目標網点面積率を求める目標網点面積率演算手段と、上記の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の実網点面積率を求める実網点面積率演算手段と、予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標網点面積率に対応する目標単色網濃度を求める目標単色網濃度演算手段と、上記の網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実網点面積率に対応する実単色網濃度を求める実単色網濃度演算手段と、予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度とベタ濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標網点面積率のもとでの上記目標単色網濃度と上記実単色網濃度との偏差に対応するベタ濃度偏差を求めるベタ濃度偏差演算手段と、上記ベタ濃度偏差に基づくフィードバック制御により上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整するインキ供給量調整手段とを備えたことを特徴としている。
In the arithmetic device, a sum area of the first target pixel region set by the first target pixel region setting unit and the second target pixel region set by the second target pixel region setting unit is calculated. it is preferable to set the noticed pixel region (claim 21).
A picture color tone control device for a printing press according to the present invention (Claim 22 ) includes a target pixel region setting device for color tone control of printing according to any one of
なお、上記の目標混色網濃度の設定は、製版データから取得できるデータとして、例えば、製版用の画像データ等の印刷対象絵柄のkcmy網点面積率データを用いて、印刷対象絵柄を構成する画素の中からインキ供給単位幅毎に各インキ色に対応する注目画素をそれぞれ設定し、予め設定した網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき注目画素の網点面積率を混色網濃度に変換することができる。そして、注目画素の混色網濃度を目標混色網濃度として設定するとともに、設定した注目画素の実混色網濃度を計測する。これによれば、JapanColorのデータベースを利用するなどにより画素単位で発色を推定できるので、印刷開始直後から絵柄の設定した注目画素領域について色調制御を行ないながら適切に印刷を行なうことができる。 The target color mixture halftone density is set as the data that can be acquired from the plate making data , for example, by using the kcmy halftone dot area ratio data of the print target image such as image data for plate making, the pixels constituting the print target picture The target pixel corresponding to each ink color is set for each ink supply unit width, and the halftone dot area ratio of the target pixel is determined based on the relationship between the preset halftone dot area ratio and the mixed color halftone density. Can be converted to Then, the mixed color halftone density of the target pixel is set as the target mixed color halftone density, and the actual mixed color halftone density of the set target pixel is measured. According to this, since the color development can be estimated in units of pixels by using the JapanColor database or the like, it is possible to perform printing appropriately while performing color tone control on the pixel region of interest set with the pattern immediately after the start of printing.
なお、上述のkcmy網点面積率データとしては、印刷対象絵柄のビットマップデータ(例えば、1bit−Tiff製版用データ)、或いは50.8dpi相当のCIP4(International Cooperation for Integration of Processes in Prepress,Press,and Postpress)規格のJDF(Job Definition Format)データ、或いはそれと同程度の解像度変換したデータ(1200dpi或いは2400dpiの1bit−Tiffデータから50dpiの8bit−Tiffに変換したデータ)でもよく、ビットマップデータをJDFデータ相当の低解像度データに変換したものを用いてもよい。 As the above kcmy halftone dot area ratio data, bitmap data of a pattern to be printed (for example, data for 1-bit-Tiff plate making) or CIP4 equivalent to 50.8 dpi (International Cooperation for Integration of Processes in Prepress, Press, and Postpress) standard JDF (Job Definition Format) data, or the same resolution-converted data (1200 dpi or 2400 dpi 1-bit-Tiff data converted to 50 dpi 8-bit-Tiff), and bitmap data can be converted to JDF. Data converted into low-resolution data equivalent to data may be used.
さらに、予め設定した混色網濃度と色座標値との対応関係に基づき、センサで計測された注目画素の実混色網濃度に対応する実色座標値と、目標混色網濃度に対応する目標色座標値とを求めて、実色座標値と目標色座標値との色差を求め、上記実色座標値及び/又は上記色差を表示装置に表示するようにしてもよい。これによれば、オペレータに対して色がどれだけのレベルで合っているか直感的に分かりやすくすることができる。 Further, based on the correspondence between the preset color mixture halftone density and the color coordinate value, the actual color coordinate value corresponding to the actual color mixture halftone density of the target pixel measured by the sensor and the target color coordinate corresponding to the target color mixture halftone density The color difference between the actual color coordinate value and the target color coordinate value may be obtained by obtaining the value, and the actual color coordinate value and / or the color difference may be displayed on the display device. According to this, it is possible to intuitively understand how much the color matches the operator.
本発明の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法(請求項1)及び装置(請求項15)によれば、例えば、印刷する紙面のデザイナーなどの紙面構成担当者等が、製版データ及び印刷用ジョブチケットデータの作成時に、ジョブチケットデータに上記製版データに対応した上記注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込み、印刷時には、印刷オペレータは、書き込まれた注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて印刷絵柄中に注目画素領域を設定すればよく、注目画素領域の設定を、短時間にしかも適切に行なうことができる。このため、例えば新聞印刷などの、紙面編集から印刷完了までを短時間で完了しなくてはならない場合にも、注目画素領域の設定を適切に行なうことができ、この注目画素領域に基づいて印刷の色調制御を精度良く行なうことができる。 According to the method for setting a pixel area of interest for printing color tone control (Claim 1) and the apparatus (Claim 15 ) of the present invention, for example, a person in charge of page configuration, such as a designer of a page to print, makes plate making data and printing When creating the job ticket data, information related to the target pixel area corresponding to the plate making data is written in the job ticket data, and at the time of printing, the print operator adds the target pixel in the print pattern based on the information regarding the written target pixel area. The region may be set, and the target pixel region can be set appropriately in a short time. For this reason, even when it is necessary to complete a short period of time from paper editing to printing completion, such as newspaper printing, the target pixel area can be appropriately set, and printing is performed based on the target pixel area. Can be accurately controlled.
しかも、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報として、上記注目画素領域として例えばベタ領域,網領域,平網領域の各領域の中から1つを選ぶ選択情報とするので、印刷オペレータは、選択情報に基づいて各領域の中の一つを選択操作するだけで良く、注目画素領域の設定にかかる印刷オペレータの負担が軽減される(請求項1,15)。
さらに、上記平網領域を、上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の画像微分(隣接画素との差分)値が予め設定された基準値(例えば1%)以下の領域とすること(請求項2,16)や、上記ベタ領域を、上記ベタ領域を上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が予め設定された基準値(例えば70%)以上の領域とし、上記網領域を上記印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が上記基準値未満の領域とすること(請求項3,17)により、ベタ領域や網領域や平網領域の各領域の自動選定を容易に行なえるようになる。
In addition, as the information on the target pixel area, for example, selection information for selecting one of the areas of the solid area, the net area, and the flat net area is selected as the target pixel area. Thus, it is only necessary to select and operate one of the regions, and the burden on the printing operator for setting the pixel region of interest is reduced (
Further, the upper Kitaira network region, has the above printing picture images differentiation dot percent (the difference between the adjacent pixel) value previously set reference value (for example, 1%) or less in the region (claim 2 , 16) and, on the Symbol solid area, the solid area of the dot percent of the printing picture value preset reference value (e.g., 70%) as a more regions, the net area of the printing picture By setting the halftone dot area ratio to a region less than the reference value (Claims 3 and 17 ), it is possible to easily automatically select each of the solid region, the halftone region, and the flat halftone region.
また、注目画素領域設定ステップでは、演算装置によって、上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて上記注目画素領域を自動で設定すること(請求項4)により、注目画素領域の設定にかかる印刷オペレータの負担が一層軽減される。
また、注目画素領域のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いた領域を印刷の色調制御に用いる注目画素領域とすること(請求項5〜7,18,19)により、注目画素領域中に、白紙領域を含む他の領域が入らないようにすることができ、印刷速度上昇時やペースタ(自動紙継)時等に目標画像位置と現在画像位置とにずれが生じた場合にも、濃度検出感度の低下を防ぐことができ、色調制御の精度低下を抑制することができる。
In the target pixel region setting step, the calculation device automatically sets the target pixel region based on the information on the target pixel region (claim 4), so that the print operator for setting the target pixel region The burden is further reduced.
Further, by setting a region obtained by removing the edge portion of the target pixel region by a predetermined number of sensor pixels as a target pixel region used for printing tone control (
さらに、注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて行なう注目画素領域設定ステップ(第1の注目画素領域設定ステップ)とは別に、製版データの網点面積率データに基づいて、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域をセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いた領域を、上記注目画素として設定する第2の注目画素領域設定ステップをそなえること(請求項6,7)により、紙面構成の作成担当者等の注目点選出の尺度とは別の尺度(自己相関が高い領域)でも、注目画素領域を設定することができ、印刷時にオペレータ等が、紙面構成の作成担当者等とは異なる立場の印刷品質要求に対しても対応することができる。 Further, apart from the target pixel region setting step (first target pixel region setting step) performed based on the information regarding the target pixel region, the autocorrelation is high for each ink color based on the dot area ratio data of the plate making data. A second target pixel region setting step is provided in which a region is selected in units of sensor pixels, and a region obtained by removing a corresponding ink color edge from the selected region by a predetermined sensor pixel is set as the target pixel. you by (claim 6), but a different measure than the measure of the target point selection, such as the staff in charge of creation paper structure (region having a high autocorrelation), can be set noticed pixel region at the time of printing An operator or the like can respond to a print quality request in a different position from the person in charge of creating the paper configuration.
また、上記のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除くと上記注目画素がなくなってしまう場合には、上記選定領域の中から上記エッジ部を除くことなく上記の自己相関が高い領域を、該当するインキ色の上記注目画素として設定する第2の注目画素設定ステップをさらにそなえていること(請求項7)により、紙面構成の作成担当者等の注目点選出の尺度とは別の尺度(自己相関が高い領域)での注目画素領域の設定を、エッジ部を所定画素分だけ除くことによって注目画素がなくなってしまうような僅かな選定領域(自己相関が高い領域)に対しても実施することができる。
In addition, if the target pixel disappears when the edge portion is removed by a predetermined number of sensor pixels, the region having the high autocorrelation is excluded from the selected region without removing the edge portion. By further including a second target pixel setting step for setting the target pixel of the ink color (claim 7 ), a scale (autocorrelation) different from the scale for selecting the target point of the person in charge of creating the page configuration, etc. The target pixel region in the region where the target pixel is high) is also applied to a few selected regions (regions with high autocorrelation) where the target pixel disappears by removing the edge portion by a predetermined number of pixels. it can.
また、本発明の印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法(請求項12)及び装置(請求項22)によれば、分光計ではなく反射光量を計測するセンサを用いて色調制御を行なうことができるので、位置ズレに伴う計測手段にかかるコストが低減できるとともに新聞輪転機のような高速印刷機にも十分に対応することができる上、適切に設定された注目画素領域に基づいて印刷の色調をフィードバック制御するので、適切に色調制御を行なうことができる。 Further, according to the design color tone control method (claim 12 ) and apparatus (claim 22 ) of the printing press according to the present invention, the tone control can be performed using a sensor that measures the amount of reflected light instead of the spectrometer. It can reduce the cost of measuring means due to misregistration, and can sufficiently support high-speed printing presses such as a newspaper rotary press, and feedback control of the color tone of printing based on an appropriately set pixel area of interest. Therefore, it is possible to appropriately control the color tone.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施の形態を説明する。
図1は本発明の一実施形態にかかる新聞用オフセット輪転機の概略構成を示す図である。本実施形態の新聞用オフセット輪転機は多色刷りの両面印刷機であり、印刷シート8の搬送経路に沿って、インキ色〔墨(k)、藍(c)、紅(m)、黄(y)〕毎に印刷ユニット2a,2b,2c,2dが設置されている。本実施形態では、印刷ユニット2a,2b,2c,2dは、インキキー7とインキ元ローラ6からなるインキキー式のインキ供給装置を備えている。この形式のインキ供給装置では、インキキー7のインキ元ローラ6に対する隙間量(以下、この隙間量をインキキー開度という)によりインキ供給量を調整することができる。また、インキキー7は印刷幅方向に複数並置されており、インキキー7の幅単位(以下、インキキー7によるインキ供給単位幅をキーゾーンという)でインキ供給量を調整することができる。インキキー7により供給量を調整されたインキは、インキローラ群5内で適度に練られ、薄膜を形成した後に版胴4の版面に供給され、版面に付着したインキがブランケット胴3を介して絵柄として印刷シート8に転写される。なお、図1中では省略しているが、本実施形態の新聞用オフセット輪転機は両面刷りなので、各印刷ユニット2a,2b,2c,2dには、印刷シート8の搬送経路を挟むようにして一対のブランケット胴3,3が備えられ、各ブランケット胴3に対して版胴4やインキ供給装置が設けられている。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a schematic configuration of a newspaper offset rotary press according to an embodiment of the present invention. The newspaper web offset press of this embodiment is a multi-color printing duplex printing machine, and ink colors [black (k), indigo (c), red (m), yellow (y )] Is provided for each
本実施形態の新聞用オフセット輪転機は、最下流の印刷ユニット2dのさらに下流にラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計(センサ)1を備えている。ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1は印刷シート8上の絵柄の色を印刷幅方向ライン状にI(赤外光)、R(赤)、G(緑)、B(青)の反射濃度(混色網濃度)として計測する計測器であり、印刷シート8全体の反射濃度を計測したり、任意の位置の反射濃度を計測したりすることが可能である。本実施形態の新聞用オフセット輪転機は両面刷りなので、ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1は印刷シート8の搬送経路を挟むようにして表裏両側に配置され、表裏両面の反射濃度を計測できるようになっている。
The newspaper offset rotary press of this embodiment includes a line sensor type IRGB densitometer (sensor) 1 further downstream of the most
ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1により計測された反射濃度は演算装置(コンピュータ)10に送信される。演算装置10はインキ供給量の制御データを演算する装置であり、ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1で計測された反射濃度に基づいて演算を行い、印刷シート8の絵柄の色を目標色に一致させるためのインキキー7の開度を演算している。ここで、図2は本発明の一実施形態にかかる新聞用オフセット輪転機の絵柄色調制御装置の概略構成を示す図であると同時に、演算装置10の色調制御機能に着目した機能ブロック図である。
The reflection density measured by the line sensor
演算装置10は、印刷機とは離れて設置されたDSP(ディジタル・シグナル・プロセッサ)11とPC(パソコン)12とから構成され、PC12には色変換部14,インキ供給量演算部15,オンライン制御部16及びキー開度リミッタ演算部17としての機能が割り当てられている。演算装置10の入力側には、ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1が接続され、出力側には印刷機内蔵の制御装置20が接続されている。制御装置20は、インキキー7のキーゾーン毎にインキ供給量を調整するインキ供給量調整手段として機能するものであり、インキキー7を開閉させる図示しない開閉装置を制御しており、各印刷ユニット2a,2b,2c,2dのインキキー7毎に独立してキー開度を調整することができる。
The
また、演算装置10には、紙面に対する印刷絵柄を表示する表示装置(印刷エリアモニタ)が接続されており、この印刷エリアモニタ40がタッチパネルとしての機能も持っている。このタッチパネル40により、製版データを印刷シート8の印刷面を画像に変換したもの、又は、ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1で撮像された印刷シート8の印刷面が表示され、印刷面上の任意の領域を指で選択できるようになっている。
In addition, a display device (print area monitor) for displaying a printed pattern on the paper surface is connected to the
ところで、色調制御に先立って、注目画素領域(注目点ともいう)を設定するようになっており、この注目画素領域の設定に本発明の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法及び装置が適用されている。
ここで、本実施形態に係る印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法及び装置について説明する。図6に示すように、注目画素領域設定の処理ステップとして、紙面作成パートの処理ステップ(ステップA10〜A30)と、印刷パートの処理ステップ(ステップA40〜A80)とをそなえている。なお、全国紙の新聞であれば、紙面作成パートは主に基地局側で処理し、印刷パートは主に各地の印刷工場側で処理する。
Prior to color tone control, a target pixel region (also referred to as a target point) is set, and the target pixel region setting method and apparatus for color tone control of printing according to the present invention are applied to the setting of the target pixel region. Has been.
Here, a target pixel region setting method and apparatus for controlling color tone of printing according to the present embodiment will be described. As shown in FIG. 6, the processing steps for setting the target pixel area include processing steps for the paper surface creation part (steps A10 to A30) and processing steps for the printing part (steps A40 to A80). In the case of a national newspaper, the paper preparation part is processed mainly at the base station side, and the printing part is processed mainly at the printing factory in each region.
つまり、例えば基地局側の紙面作成パートでは、印刷する紙面のデザイナーなどの紙面構成担当者等が、印刷する紙面の構成を行ない(ステップA10)、これに基づいて製版データを作成し(ステップA20)、さらに、この印刷に係るジョブチケットデータに注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込む(ステップA30)。ジョブチケットデータは、印刷工程管理(Processes),製版(Prepress),印刷(Press),後加工(Postpress)の各属性や手順を記述した工程書に相当し、印刷全体を管理する担当者等が作成するが、このジョブチケットデータの一部に、注目画素領域に関する情報を書き加えるのである。 That is, for example, in the paper surface creation part on the base station side, the person in charge of the paper surface, such as the designer of the paper surface to be printed, configures the paper surface to be printed (step A10), and creates plate making data based on this (step A20). Further, information relating to the pixel region of interest is written in the job ticket data relating to this printing (step A30). Job ticket data corresponds to a process document that describes the attributes and procedures of printing process management (Processes), plate making (Prepress), printing (Press), and post-processing (Postpress). Although it is created, information on the target pixel region is added to a part of the job ticket data.
なお、ジョブチケットのデータ形式は、何ら制限されるものではないが、例えば、CIP4(International Cooperation for Integration of Processes in Prepress,Press,and Postpress)規格のJDF(Job Definition Format)では、XML言語を使うので、機械の制御指示のみならず、経営管理に反映させるための情報などより細かい情報まで組み込めるようになっており、注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込むことも容易である。したがって、CIP4規格のJDFデータのような汎用性のあるジョブチケットのデータ形式を採用することも好ましい。 The data format of the job ticket is not limited at all. For example, the JDF (Job Definition Format) of the CIP4 (International Cooperation for Integration of Processes in Prepress, Press, and Postpress) standard uses the XML language. Therefore, it is possible to incorporate not only machine control instructions but also more detailed information such as information to be reflected in business management, and it is easy to write information on the target pixel area. Therefore, it is also preferable to employ a versatile job ticket data format such as CIP4 standard JDF data.
ここで、「注目画素領域に関する情報」について説明する。「注目画素領域」を設定すると、その画素領域の各インキが目標濃度になるようにインキ供給が制御される。したがって、対象の印刷絵柄のうち特に精度良く色調制御を行ないたい部分を「注目画素領域」に設定すればよい。
例えば、印刷絵柄内は、網点面積率に着目すれば、ベタ領域と、網領域とに分類できる。さらに、網点面積率の変化に着目すれば、上記の網点面積率が均一の平網領域と、その他の領域とに分類できる。本実施形態では、ベタ領域と網領域と平網領域とのうちのいずれか重視したいものを注目画素領域に選択して、色調制御を行なうようになっている。
Here, “information on the target pixel region” will be described. When the “target pixel area” is set, the ink supply is controlled so that each ink in the pixel area has a target density. Therefore, it is only necessary to set a portion of the target print pattern for which color tone control is to be performed with high accuracy as the “target pixel region”.
For example, the printing picture, if attention is paid to the dot percent, Classification and base data area, in the network area. Further, paying attention to changes in the halftone dot area ratios can be classified into the above dot percentage uniform tint region, and other realm. In the present embodiment, by selecting what you want to emphasize one of the solid area and the Amiryo region and Hiraamiryo region to the target pixel region, thereby performing the color tone control.
絵柄の重たい部分を重視する場合にはベタ領域を、絵柄の軽い部分を重視する場合には網領域を、絵柄が均一な網領域部分を重視するには平網領域を、それぞれ選択すればよい。本来均一な色調であるべき平網領域は、僅かなインキ量の相違で色ムラが生じるので、これらを防止又は抑制するには平網領域を選択すればよい。また、ベタの色或いはハーフトーン(中間調)の色を高精度に合わせたい場合はベタ領域或いは網領域を選択すればよい。なお、網領域のなかでもハイライト部(網点面積率が極めて少ない部分)を除いて制御すれば、ハーフトーンをより高精度に出し易くなるので、網点面積率の上限(例えば70パーセント又は80パーセント)と下限(例えば20パーセント)とを設けて、網領域を定義しても良い。 Select a solid area when emphasizing the heavy part of the design, select a mesh area when emphasizing the light part of the design, and select a flat area when emphasizing the net region part with a uniform pattern. . The flat halftone area that should originally have a uniform color tone has uneven color due to a slight difference in the amount of ink. Therefore, in order to prevent or suppress these, the flat halftone area may be selected. In addition, when it is desired to match a solid color or a halftone (halftone) color with high accuracy, a solid area or a halftone area may be selected. It should be noted that if the control is performed by excluding a highlight portion (a portion having a very small halftone dot area ratio) in the halftone area, halftone can be easily obtained with higher accuracy, so the upper limit of the halftone dot area ratio (for example, 70 percent or 80%) and a lower limit (for example, 20%) may be provided to define the net region.
この場合、いずれを重視すべきかの判断は、客先からの要望を踏まえて紙面を作成する紙面デザイナーなどの紙面構成担当者等が適しており、紙面構成担当者等が、ベタ領域と網領域或いはクライアントが希望する領域とのいずれを注目画素領域にするかをジョブチケットデータの一部に書き加えるのである。
一方、例えば印刷工場側の印刷パートでは、紙面作成パートから送られたジョブチケットデータ(ステップA40)、及び、製版データを取得して(ステップA50)、製版パートでデザイナーが指定した色合わせ重視の製版データに対する座標がジョブチケットデータに書かれていない場合には、ステップA55の判定を経て、製版データに基づいてジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンス(即ち、色調制御のための注目画素領域に関する情報)に対応して色を合わせたい注目画素領域を選択し(ステップA60)、さらに、製版データに基づいて予め設定された設定基準に対応した積算制御ポイント(注目画素領域)を自動抽出する(ステップA70)。また、製版パートでデザイナーが指定した色合わせ重視の製版データに対する座標がジョブチケットデータに書かれていた場合には、このジョブチケットデータに書かれた座標を優先的に選んで、その位置を注目画素に選択する(ステップA90)。
In this case, the decision as to which should be emphasized is appropriate for the person responsible for the page composition, such as a page designer who creates the sheet based on the request from the customer, and the person responsible for the page composition, for example, the solid area and the network area Alternatively, an area desired by the client to be used as the target pixel area is added to a part of the job ticket data.
On the other hand, for example, in the printing part on the printing factory side, the job ticket data (step A40) sent from the paper surface creation part and the plate making data are acquired (step A50), and the color matching emphasis specified by the designer in the plate making part is emphasized. If the coordinates for the plate making data are not written in the job ticket data, after the determination in step A55, the guidance in the job ticket data based on the plate making data (that is, information on the target pixel region for color tone control) is used. Correspondingly, a pixel region of interest for which a color is to be matched is selected (step A60), and further, an integration control point (a pixel of interest region) corresponding to a preset setting criterion is automatically extracted based on the plate making data (step A70). . In addition, if the coordinates for the plate making data that emphasizes color matching specified by the designer in the plate making part are written in the job ticket data, the coordinates written in the job ticket data are preferentially selected, and the position is noted. A pixel is selected (step A90).
このように、注目画素領域の設定は、ジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンスに対応した設定(ステップA60:第1の注目画素領域を設定する第1の注目画素領域設定ステップ)と、予め設定された設定基準に対応した設定(ステップA70:第2の注目画素領域を設定する第2の注目画素領域設定ステップ)との二つの系統で、注目画素領域を設定し、これらの第1,第2の注目画素領域を複合して最終的な注目画素領域を設定するようになっている。そして、この第1,第2の注目画素領域を複合する際、設定された重み付けAに応じて、第1の注目画素領域と第2の注目画素領域とを加重平均して、色調制御を実施するようになっている。 As described above, the target pixel area is set according to the guidance in the job ticket data (step A60: first target pixel area setting step for setting the first target pixel area), and a preset setting. The target pixel area is set in two systems, corresponding to the reference (step A70: second target pixel area setting step for setting the second target pixel area), and the first and second attentions are set. The final pixel region of interest is set by combining the pixel regions. When the first and second target pixel regions are combined, the first tone pixel region and the second target pixel region are weighted and averaged according to the set weight A, and the tone control is performed. It is supposed to be.
ステップA60のジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンスに応じた第1の注目画素領域の設定についてさらに説明すると、印刷準備段階で、図7(b)に示すように、自動注目点候補の選択画面を、印刷エリアモニタ40又はその他のモニタに表示する。この選択画面には、手動注目点制御(注目画素領域を手動で設定し色調を制御する)と、ベタの色重視[注目画素領域をベタ領域に自動設定し色調を制御する、図7(c)参照]と、網の色重視[注目画素領域を網領域に自動設定し色調を制御する、図7(c)参照]と、平網(ベタ)の色重視[注目画素領域を平網領域に自動設定し色調を制御する、図8(b)参照]との、各チェック欄が設けられ、ジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンスに応じて、これらのチェック欄のいずれかを選択するようになっている。この際、オペレータによる手動でチェックしてもよく、PC12による自動でチェックするようにしても良い。なお、ここでは、初期状態では、手動注目点制御にチェックが入っており、ジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンスがない場合などは、オペレータによる手動で注目画素領域を設定することができる。さらに本実施形態では、製版パートでデザイナーが指定した色合わせ重視の製版データに対する座標をジョブチケットデータに書くことができるようになっており、ジョブチケットデータに色合わせ重視の製版データに対する座標が書かれていた場合は、前述のように優先的にその位置が注目画素に選択されるようになっている。
The setting of the first target pixel area according to the guidance in the job ticket data in step A60 will be further described. At the print preparation stage, as shown in FIG. 7B, an automatic target point candidate selection screen is printed. It is displayed on the area monitor 40 or other monitor. On this selection screen, manual attention point control (manually setting the target pixel region and controlling the color tone), solid color emphasis [automatically setting the target pixel region as a solid region and controlling the color tone, FIG. ) Reference] and emphasis on the color of the mesh [automatically set the pixel area of interest to the mesh area and control the color tone, see FIG. 7C] and emphasis on the color of the flat mesh (solid area of the pixel area of interest Are automatically set to control the color tone, see FIG. 8 (b)], and each check column is selected according to the guidance in the job ticket data. Yes. At this time, it may be checked manually by an operator or automatically by the
また、自動注目点指定網点面積率(ベタ領域と網領域との判定用網点面積率)X及び平網重視画素微分閾値[平網領域(ベタ領域も含む)の判定用網点面積率微分値]Yを設定変更できるようになっている。なお、ここでは、自動注目点指定網点面積率Xのデフォルト値を70パーセントとし、平網重視画素微分閾値Yのデフォルト値を1パーセント/n画素[単位画素あたりの網点面積率の変化量(パーセント単位)]としている。もちろんこれらのデフォルト値は、このような値に限定されない。 Also, an automatic attention point designation halftone dot area ratio (solid dot area ratio for solid area and halftone area) X and flat halftone weighted pixel differentiation threshold [a halftone dot area ratio for flat halftone area (including solid area)] The differential value] Y can be changed. Here, the default value of the automatic attention point designation halftone dot area ratio X is 70%, and the default value of the flat halftone weighted pixel differentiation threshold Y is 1% / n pixels [the amount of change in the halftone dot area ratio per unit pixel]. (Percentage)]. Of course, these default values are not limited to such values.
そして、ベタ領域又は網領域がチェック(選定)され、自動注目点指定網点面積率Xが適宜変更されると、図7(a)に示すように、まず、製版データから積算点抽出(各画素の網点面積率の抽出)が行なわれ(ステップB10)、網点面積率を自動注目点指定網点面積率Xと比較して、各インキの各画素に対して網点面積率がX以上のベタ領域かX未満の網領域かを判定しながら(ステップB20)、ベタの色重視(ベタ領域指定)なら該当する画素を注目点(注目画素)に選定(抽出)し、網の色重視(網領域指定)なら該当する画素を注目点(注目画素)に選定(抽出)し、印刷絵柄の全領域に対してこれを行なって、注目画素領域を選定する(ステップB30)。この結果、第1の注目画素領域(注目積算点)が存在するか否かに応じて(ステップB40)、第1の注目画素領域(注目積算点)が存在すれば、第1の注目画素領域と後述する第2の注目画素領域とを複合して注目画素領域を設定しこれに基づいて色調を制御(ステップB50:ハイブリッド制御)し、第1の注目画素領域(注目積算点)が存在しなければ、第2の注目画素領域に基づいて色調を制御する(ステップB60:通常積算制御)。 Then, when the solid area or halftone area is checked (selected) and the automatic attention point designation halftone dot area ratio X is appropriately changed, first, as shown in FIG. Extraction of the halftone dot area ratio of the pixel) (step B10), the halftone dot area ratio is compared with the automatic target point designated halftone dot area ratio X, and the halftone dot area ratio is X for each pixel of each ink. While determining whether the above-mentioned solid area or a halftone area less than X (step B20), if a solid color is important (solid area designation), the corresponding pixel is selected (extracted) as an attention point (attention pixel), and the color of the mesh If emphasis is given (designation of a halftone area), the corresponding pixel is selected (extracted) as a target point (target pixel), and this is performed on the entire area of the printed pattern to select the target pixel area (step B30). As a result, depending on whether or not the first target pixel region (target integration point) exists (step B40), if the first target pixel region (target integration point) exists, the first target pixel region And a second target pixel area to be described later are combined to set the target pixel area, and based on this, the color tone is controlled (step B50: hybrid control), and the first target pixel area (target integration point) exists. If not, the color tone is controlled based on the second target pixel region (step B60: normal integration control).
また、平網領域がチェック(選定)され、平網重視画素微分閾値Yが適宜変更されると、図8(a)に示すように、まず、製版データから積算点抽出(各画素の網点面積率の抽出)が行なわれ(ステップC10)、次に、各画素の網点面積率を網点位置で微分(網点面積率画像微分)する(ステップC20)。隣接する画素間で、網点面積率が変化すればその変化量に応じた網点面積率画像微分の値が算出されるが、平網やベタの領域では、隣接する画素間で、網点面積率はほとんど変化しないので、網点面積率画像微分の値は0又は略0となる(図8(b)参照)。そこで、この算出した網点面積率画像微分値(微分画素)を平網重視画素微分閾値Yと比較して、網点面積率画像微分値(微分画素)が微小ならば、その画素を注目画素とする(ステップC30)。そして、印刷絵柄の全領域に対してこれを行なって、注目画素領域を選定する。この結果、第1の注目画素領域(注目積算点)が存在するか否かに応じて(ステップC40)、第1の注目画素領域(注目積算点)が存在すれば、第1の注目画素領域と後述する第2の注目画素領域とを複合して注目画素領域を設定しこれに基づいて色調を制御(ステップC50:ハイブリッド制御)し、第1の注目画素領域(注目積算点)が存在しなければ、第2の注目画素領域に基づいて色調を制御する(ステップC60:通常積算制御)。 When the flat halftone area is checked (selected) and the flat halftone weighted pixel differentiation threshold Y is appropriately changed, as shown in FIG. 8A, first, an integration point is extracted from the plate-making data (halftone dot of each pixel). (Area ratio extraction) is performed (step C10), and then the halftone dot area ratio of each pixel is differentiated (halftone dot area ratio image differentiation) at the halftone dot position (step C20). If the halftone dot area ratio changes between adjacent pixels, the value of the halftone dot area ratio image derivative is calculated according to the amount of change, but in a flat halftone or solid area, halftone dots are calculated between adjacent pixels. Since the area ratio hardly changes, the value of the halftone dot area ratio image derivative is 0 or substantially 0 (see FIG. 8B). Thus, the calculated halftone dot area ratio image differential value (differential pixel) is compared with the flat halftone weighted pixel differential threshold Y, and if the halftone dot area ratio image differential value (differential pixel) is very small, that pixel is selected as the target pixel. (Step C30). Then, this is performed on the entire area of the printed pattern, and the target pixel area is selected. As a result, depending on whether or not the first target pixel region (target integration point) exists (step C40), if the first target pixel region (target integration point) exists, the first target pixel region And a second target pixel region to be described later are combined to set the target pixel region, and based on this, the color tone is controlled (step C50: hybrid control), and the first target pixel region (target integration point) exists. If not, the color tone is controlled based on the second target pixel region (step C60: normal integration control).
なお、このように設定した第1の注目画素領域は、製版データに基づいて設定されるので、極めて高精度に設定されることになるが、この第1の注目画素領域の外周のエッジ部はいずれの色も印刷されない白紙部分や他の領域(ベタ領域の隣の網領域とか、平網領域の隣の網領域など)と隣接している可能性がある点に着目して、例えば図3の(a)〜(d)にそれぞれ破線で示すように、第1の注目画素領域から斜線で示すエッジ部分を除いた領域(網掛け部分)を、第1の注目画素領域に設定するようにしている。ここでは、図4の拡大図に示すように、エッジ部分のセンサ画素単位の1画素分だけ(斜線部)を除いたもの(網掛け部)を、第1の注目画素領域に設定するようにしている。 Since the first target pixel area set in this way is set based on the plate making data, it is set with extremely high accuracy. However, the outer edge of the first target pixel area is Focusing on the fact that there is a possibility of being adjacent to a blank area or other area (such as a net area adjacent to a solid area or a net area adjacent to a flat net area) in which neither color is printed, for example, FIG. As shown by broken lines in (a) to (d) of FIG. 5, a region (shaded portion) obtained by removing the edge portion indicated by diagonal lines from the first target pixel region is set as the first target pixel region. ing. Here, as shown in the enlarged view of FIG. 4, a portion (shaded portion) excluding only one pixel (shaded portion) in the sensor pixel unit of the edge portion is set as the first target pixel region. ing.
次に、第2の注目画素領域の設定について説明する。
第2の注目画素領域の設定は、演算装置10のDSP11を通じて行なわれ、DSP11には、第2の注目画素領域を自動で設定する機能(第2の注目画素領域自動設定手段)がそなえられる。
つまり、演算装置10には、予め製版データが入力され、演算装置10のDSP11では、この製版データに基づいて得られるkcmy網点面積率データから、印刷絵柄をインキ供給装置のインキ供給単位幅で分割したときの上記インキ供給単位幅毎に、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を選定し、この選定領域の中から該当するインキ色のエッジ部を所定画素分だけ除いた領域を、各インキ色に対応する制御時の参照領域である注目画素領域としてそれぞれのインキ色毎に自動設定する(この機能が第2の注目画素領域設定手段の1つである注目画素領域自動設定手段に相当する)ようになっている。ここで、インキ供給装置のインキ供給単位幅とは、インキ供給装置がインキキー装置である場合には各インキキーのキー幅(キーゾーン)のことであり、インキ供給装置がデジタルポンプ装置である場合には各デジタルポンプのポンプ幅のことである。
Next, the setting of the second target pixel area will be described.
The setting of the second target pixel area is performed through the
That is, the plate making data is input to the
なお、製版データは、ビットマップデータとして与えられるが、第2の注目画素領域の設定に当たっては、ビットマップデータを印刷機のフォーマットに応じたCIP4規格のJDFデータ相当の低解像度データに変換した上で、且つ、以下のようなセンサの画素単位で処理を行なう。
つまり、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域とは、具体的には、自己相関感度Hが予め設定された所定値以上の領域であり、センサ(IRGB濃度計)1の画素単位の領域とする。センサの画素単位とは、センサ(IRGB濃度計)1の解像度の最小単位である。具体的には、製版データの画素を多数集めたものがセンサ画素単位の1画素(1ブロック)に相当することになる。例えば、CIP3のように解像度データが50.8dpi程度の低解像度であり、センサ1ブロックの解像度が2.54dpiなら製版データの縦20画素分,横20画素分の領域(製版データの画素単位でで、20×20=400画素分)がセンサ画素単位の1画素単位となる。
The plate-making data is given as bitmap data. In setting the second target pixel area, the bitmap data is converted into low-resolution data equivalent to CDF4 standard JDF data according to the format of the printing press. In addition, the following processing is performed in units of pixels of the sensor.
That is, the region where the autocorrelation is high for each ink color is specifically a region where the autocorrelation sensitivity H is equal to or higher than a predetermined value, and is defined as a pixel unit region of the sensor (IRGB densitometer) 1. . The pixel unit of the sensor is a minimum unit of resolution of the sensor (IRGB densitometer) 1. Specifically, a collection of a large number of pixels for plate making data corresponds to one pixel (one block) in sensor pixel units. For example, if the resolution data is a low resolution of about 50.8 dpi as in CIP3 and the resolution of the
自己相関感度Hは、例えば、シアンの自己相関感度Hcは、画素面積率データ(c,m,y,k)を用いて、“Hc=cn/(c+m+y+k)”で表すことができ、この自己相関感度Hcの値を、予め設定された基準自己相関感度値(所定値)H0と比較して、自己相関感度Hcが基準自己相関感度値H0以上ならシアンについて自己相関が高い領域となる。
他の色のインキについても同様に、自己相関感度Hの値を算出し、それぞれ予め設定された基準自己相関感度値(所定値)H0と比較する。
The autocorrelation sensitivity H, for example, the autocorrelation sensitivity Hc of cyan, using pixel area ratio data (c, m, y, k ) and can be represented by "Hc = c n / (c + m + y + k)", this When the autocorrelation sensitivity Hc is compared with a reference autocorrelation sensitivity value (predetermined value) H 0 set in advance and the autocorrelation sensitivity Hc is equal to or higher than the reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0 , Become.
Similarly, the other color inks, calculates the value of the autocorrelation sensitivity H, for preset reference autocorrelation sensitivity value respectively (predetermined value) H 0 Comparison.
なお、基準自己相関感度値H0は、オペレータの入力操作により設定できるようになっている。このため、基準自己相関感度値H0を高めに設定して、自己相関がかなり高い領域に絞って注目画素領域を設定することで、注目画素領域は減少するが該当するインキのトーンが強い点から濃度検出感度を上げて色調制御の精度の上げるようにしたり、基準自己相関感度値H0を低めに設定して、自己相関があまり高くない領域も含んで注目画素領域を設定することで、濃度検出感度は低下するが注目画素領域を広げることで色調制御の精度を上げるようにしたり、することができる。もちろん、基準自己相関感度値H0の推奨値(例えば絵柄全体の自己相関平均値)が予め入力されており、慣れないオペレータは、この推奨値を用いるようにすることができる。また、原則的には、基準自己相関感度値H0は各インキ色に対し共通の値とするが、インキ色によって、基準自己相関感度値H0を変えることも考えられる。 The reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0 can be set by an operator's input operation. Therefore, to set a higher reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0, by setting the target pixel region autocorrelation Search in fairly high region, the target pixel region decreases but the point strong pertaining ink tone or to raise accuracy of up to tone controlling the concentration detection sensitivity from the reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0 is set to low, by setting the noticed pixel region including even a region autocorrelation is not very high, Although the density detection sensitivity is lowered, it is possible to increase the accuracy of the color tone control by expanding the target pixel region. Of course, a recommended value of the reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0 (for example, the autocorrelation average value of the entire picture) is input in advance, and an operator who is not accustomed can use this recommended value. In principle, the reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0 is a common value for each ink color, but it is also conceivable to change the reference autocorrelation sensitivity value H 0 depending on the ink color.
このようにして、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域を選定すると、例えば図3の(a)〜(d)に示すように、製版面50中に、各インキ色毎に、自己相関が高い領域が得られる。このような自己相関が高い領域をそのまま、注目画素領域に設定してしまうと、前述のように、大部分が白紙の中に、ある色のインキのみが少量だけ印刷される場合を含むことになり、濃度検出感度が低下して色調制御の精度の低下を招き、特に、印刷速度上昇時やペースタ(自動紙継)時に、目標画像位置と現在画像位置とにずれが生じると、該当するインキ色の少量の印刷部分が、位置ずれして色調制御の精度が大幅に低下してしまうことがある。
Thus, when a region having a high autocorrelation is selected for each ink color, for example, as shown in FIGS. 3A to 3D, the autocorrelation is high for each ink color in the plate-making
そこで、この自己相関が高い領域の外周のエッジ部はいずれの色も印刷されない白紙部分と隣接している可能性がある点に着目して、例えば図3の(a)〜(d)にそれぞれ破線で示すように、自己相関が高い領域から、斜線で示すエッジ部分を除いた領域(網掛け部分)を、注目画素領域に設定するようにしている。ここでは、図4の拡大図に示すように、エッジ部分のセンサ画素単位の1画素分だけ(斜線部)を除いたもの(網掛け部)を、注目画素領域に設定するようにしている。 Therefore, paying attention to the fact that the edge portion on the outer periphery of the region having a high autocorrelation may be adjacent to a blank paper portion on which any color is not printed, for example, as shown in FIGS. As indicated by a broken line, a region (shaded portion) obtained by removing an edge portion indicated by oblique lines from a region having a high autocorrelation is set as a target pixel region. Here, as shown in the enlarged view of FIG. 4, an area (shaded portion) excluding only one pixel (shaded portion) in the sensor pixel unit of the edge portion is set as the target pixel region.
なお、自己相関が高い領域からそのエッジ部分について除く領域は、センサ画素単位の1画素分に限るものではないが、エッジ部分を除去することは、注目画素領域内に白紙部分が含まれることを抑え濃度検出感度の低下を抑制して色調制御の精度の低下を防ぐためであるが、この一方で、除去したエッジ部分だけ、注目画素領域から除かれることになり、それだけ注目画素領域が減ってしまうため、この面から色調制御の精度の低下を招くことが考えられる。これらの点を勘案すると、色調制御の精度を確保するためには、エッジ部分のセンサ画素単位の1画素分だけを除くことが好ましい。 Note that the region excluding the edge portion from the region having a high autocorrelation is not limited to one pixel in the sensor pixel unit, but removing the edge portion means that a blank page portion is included in the target pixel region. This is to prevent the decrease in density detection sensitivity by suppressing the decrease in density detection sensitivity. On the other hand, only the removed edge part is removed from the target pixel area, and the target pixel area is reduced accordingly. Therefore, it is conceivable that the accuracy of color tone control is reduced from this aspect. Considering these points, in order to ensure the accuracy of the color tone control, it is preferable to exclude only one pixel in the sensor pixel unit of the edge portion.
なお、このようにエッジ部分を注目画素領域から除く処理に代えて、エッジ部分を確実に含むように、注目画素領域を自己相関が高い領域の外側まで膨らませたものに設定しても同様の効果が得られる。つまり、濃度検出精度の低下は、検出時の微小な位置ズレによって自己相関が高い領域のエッジ部分が検出されたりされなかったりすることで起こる。したがって、検出時の微小な位置ズレがあってもエッジ部分の付近を常に検出しないように注目画素領域を狭めるようにする代わりに、検出時の微小な位置ズレがあってもエッジ部分の付近を常に検出するように注目画素領域を広げても濃度検出精度の低下を防ぐことができるのである。エッジ部分のセンサ画素単位の1画素分だけ削っても低画線では注目画素が無く場合があるが、このように注目画素領域を広げる手法では、このような不具合も招かず、低画線の場合に効果的である。 It should be noted that the same effect can be obtained by setting the target pixel region to be expanded outside the region having a high autocorrelation so as to surely include the edge portion instead of the process of removing the edge portion from the target pixel region in this way. Is obtained. That is, the decrease in density detection accuracy occurs when an edge portion of a region having a high autocorrelation is not detected due to a minute position shift at the time of detection. Therefore, instead of narrowing the pixel area of interest so that the vicinity of the edge portion is not always detected even if there is a minute positional shift at the time of detection, the vicinity of the edge portion is detected even if there is a small positional shift at the time of detection. Even if the pixel region of interest is expanded so that it is always detected, it is possible to prevent a decrease in density detection accuracy. Even if only one pixel of the sensor pixel unit in the edge portion is removed, there is a case where there is no target pixel in the low image line. However, such a method of expanding the target pixel region does not cause such a problem, It is effective in the case.
一方、本実施形態では、オペレータ自身が、タッチパネルとしての印刷エリアモニタ40に映し出された印刷面(製版データに基づく製版面50の印刷面が好ましい)上の任意の領域を第1の注目画素領域として指で選択できるようになっている。この第1の注目画素領域の手動設定は、例えば図5(a)〜(d)に斜線で示すように、各インキ色毎に行なう。演算装置10及び印刷エリアモニタ40のこのような注目画素領域の手動設定に係る機能が、第1の注目画素領域設定手段の1つである注目画素領域手動設定手段に相当する。この注目画素領域の手動設定の場合も、センサ画素単位で設定する。
On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the operator himself designates an arbitrary area on the print surface (preferably the print surface of the plate-making
このように、ジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンスに応じて或いはオペレータ自身の指定により設定された注目画素領域(第1の注目画素領域)と、注目画素領域自動設定手段により自動で設定された注目画素領域(第2の注目画素領域)との2系統で、注目画素領域を設定できるが、実際の色調制御には、これらの各注目画素領域に基づく制御量を加重平均して制御量を設定し、これに基づいて制御するようになっている。つまり、詳細は後述するが、色調制御には各インキのベタ濃度偏差を用いており、このベタ濃度偏差を、上記の第1の注目画素領域と第2の注目画素領域とのそれぞれに基づいて算出し、両ベタ濃度偏差を、予め設定された重み付けに応じて加重平均して、この加重平均したベタ濃度偏差に基づきインキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整することで、色調制御を行なうようになっている。 Thus, the target pixel region (first target pixel region) set according to the guidance in the job ticket data or designated by the operator itself, and the target pixel region automatically set by the target pixel region automatic setting unit The target pixel area can be set in two systems (second target pixel area), but in actual color tone control, the control amount based on each of these target pixel areas is set by weighted averaging, Control is based on this. That is, although details will be described later, the solid density deviation of each ink is used for color tone control, and this solid density deviation is based on each of the first target pixel area and the second target pixel area. The color tone control is performed by calculating and weighting and averaging both solid density deviations according to a preset weighting, and adjusting the ink supply amount for each ink supply unit width based on the weighted average density deviation. It is like that.
このため、演算装置10には、この加重平均の際の重み付けを設定する機能(重み付け設定手段)がそなえられ、オペレータは演算装置10に付設されたキーボード等によって、重み付けを任意に設定できるようになっている。例えば、自己相関に着目して設定された第2の注目画素領域の重み付けを0パーセントに設定すれば、ジョブチケットデータ内のガイダンス等に応じて設定された第1の注目画素領域のみに基づいてベタ濃度偏差が算出され色調制御が行なわれ、第2の注目画素領域の重み付けを100パーセントに設定すれば、第2の注目画素領域のみに基づいてベタ濃度偏差が算出され色調制御が行なわれるように設定することができる。
For this reason, the
もちろん、第1の注目画素領域の重み付けを0パーセントと100パーセントの間の適当な値に設定すれば、この割合で、ベタ濃度偏差が算出され色調制御が行なわれる。第2の注目画素領域の重み付けを50パーセントに設定すれば、第1の注目画素領域に基づくベタ濃度偏差と第2の注目画素領域に基づくベタ濃度偏差とを単純平均したベタ濃度偏差を用いて色調制御が行なわれる。 Of course, if the weight of the first target pixel region is set to an appropriate value between 0% and 100%, the solid density deviation is calculated and the color tone control is performed at this ratio. If the weight of the second target pixel area is set to 50%, a solid density deviation obtained by simply averaging the solid density deviation based on the first target pixel area and the solid density deviation based on the second target pixel area is used. Color control is performed.
このように、注目画素領域の設定を行なった上で、印刷絵柄をインキ供給装置のインキ供給単位幅で分割したときの各注目画素領域のインキ供給単位幅毎の目標混色網濃度を製版データの絵柄情報に基づいて設定する。 In this way, after setting the target pixel area, the target color mixture halftone density for each ink supply unit width of each target pixel area when the printed pattern is divided by the ink supply unit width of the ink supply device is set in the plate making data. Set based on picture information.
以下、図9,図10を参照して、色調制御の処理を順に説明する。
ここでは、図9に示すように、製版データ[新聞社の基地局からビットマップデータ(1bit−Tiff製版用データ)、或いは50.8dpi相当のJDFデータ、或いはそれと同程度の解像度変換したデータ(1200dpi或いは2400dpiの1bit−Tiffデータから50dpiの8bit−Tiffに変換したデータ)]の形式で印刷工場に送信されてくる新聞紙の紙面情報]を取得し(ステップD10)、送信されたビットマップデータを印刷機のフォーマットに応じたJDFデータ相当の低解像度データに変換し(ステップD20)、この低解像度データを画素面積率データとして用いる。この解像度の変換処理は一般的なJDFデータとの共用を図るためであるが、後の処理においてビットマップデータそのものを画素面積率データとして用いることも可能である。
Hereinafter, with reference to FIGS. 9 and 10, the color tone control process will be described in order.
Here, as shown in FIG. 9, plate-making data [bitmap data (1-bit-Tiff plate-making data) from a base station of a newspaper company, JDF data equivalent to 50.8 dpi, or data converted to the same resolution ( (Page data converted from 1-bit-Tiff data of 1200 dpi or 2400 dpi to 8-bit-Tiff of 50 dpi)]] is obtained (step D10), and the transmitted bitmap data is obtained. The data is converted into low resolution data equivalent to JDF data according to the format of the printing press (step D20), and this low resolution data is used as pixel area ratio data. This resolution conversion process is for sharing with general JDF data, but it is also possible to use the bitmap data itself as pixel area ratio data in subsequent processes.
ステップD30では、各インキ色に対応する第1の注目画素領域をそれぞれ上述のごとく自動設定する。
ステップD50では、データベース141に記録された変換テーブルを用いて、自動設定された各インキ色の注目画素の網点面積率ki,ci,mi,yiを混色網濃度に変換し、それを目標混色網濃度Ioa,Roa,Goa,Boaとして設定する。
In step D30, the first target pixel area corresponding to each ink color is automatically set as described above.
In step D50, using the conversion table recorded in the
また、ステップD30,D50と平行して、ステップD40では、インキ供給各インキ色に対応する第2の注目画素領域をそれぞれ上述のごとく自動設定し、ステップD60では、データベース141に記録された変換テーブルを用いて、手動設定された各インキ色の注目画素の網点面積率ki,ci,mi,yiを混色網濃度に変換し、それを目標混色網濃度Ioh,Roh,Goh,Bohとして設定する。
In parallel with steps D30 and D50, in step D40, the second pixel region of interest corresponding to each ink color is automatically set as described above. In step D60, the conversion table recorded in the
以上のように目標混色網濃度Io,Ro,Go,Boが設定されたら、図10に示すように、ステップS10以降の処理を繰り返し実行する。まず、ステップS10として、ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1が印刷シート8全面の一画素毎の反射光量i’,r’,g’,b’を計測する。IRGB濃度計1で計測された各画素の反射光量i’,r’,g’,b’はDSP11に入力される。
When the target color mixture halftone densities Io, Ro, Go, and Bo are set as described above, the processes after step S10 are repeatedly executed as shown in FIG. First, as step S10, the line sensor
DSP11は、ステップS20として、各画素の反射光量i’,r’,g’,b’について所定の印刷枚数単位で移動平均を行なうことで、ノイズ成分を除去した各画素の反射光量i,r,g,bを算出する。
そして、ステップS30aとして、ステップS20で演算された各画素の反射光量i,r,g,bを用いて各色の第1の注目画素の実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bを演算し、ステップS30bとして、ステップS20で演算された各画素の反射光量i,r,g,bを用いて各色の第2の注目画素の実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bを演算する。
In step S20, the
Then, as step S30a, the actual mixed color halftone densities I, R, G, B of the first target pixel of each color are calculated using the reflected light amounts i, r, g, b of each pixel calculated in step S20, In step S30b, the actual mixed color halftone densities I, R, G, and B of the second target pixel of each color are calculated using the reflected light amounts i, r, g, and b of each pixel calculated in step S20.
DSP11は、製版画像の注目点の反射光量i,r,g,bと白紙部分の反射光量とから目標混色網濃度Io,Ro,Go,Boを演算し、印刷シート(本刷りシート)8の注目点の反射光量i,r,g,bと白紙部分の反射光量とから実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bを演算する。なお、注目画素は、基本的に複数画素の集合であるので、反射光量i,r,g,bを、注目画素を構成する複数画素で平均処理する。例えば、白紙部分の赤外光の反射光量をipとし、キーゾーン内の赤外光の平均反射光量をikとすると、赤外光の実混色網濃度IはI=log10(ip/ik)として求められる。DSP11で演算されたキーゾーン毎の実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bは、PC12の色変換部14に入力される。
The
色変換部14は、ステップS40a,S50a及びS60aの処理と、ステップS40b,S50b及びS60bの処理とを行なう。
まず、ステップS40aとして、ステップD50で設定された各色の第1の注目画素の目標混色網濃度Io,Ro,Go,Bo、及びステップS30aで演算された各色の第1の注目画素の実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bに対応する各インキ色の網点面積率をそれぞれ演算する。また、ステップS40bとして、ステップD60で設定された各色の第2の注目画素の目標混色網濃度Io,Ro,Go,Bo、及びステップS30bで演算された各色の第2の注目画素の実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bに対応する各インキ色の網点面積率を、ステップS40aと同様にそれぞれ演算する。これらの演算にはデータベース141を用い、データベース141に記憶された対応関係に基づき、目標混色網濃度Io,Ro,Go,Boに対応する各インキ色の網点面積率を目標網点面積率ko,co,mo,yoとして演算し、実混色網濃度I,R,G,Bに対応する各インキ色の網点面積率を実網点面積率k,c,m,yとして演算する。
The
First, in step S40a, the target color mixture density Io, Ro, Go, Bo of the first target pixel of each color set in step D50 and the actual color mixture network of the first target pixel of each color calculated in step S30a. The dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the densities I, R, G, and B is calculated. In step S40b, the target color mixture density Io, Ro, Go, Bo of the second target pixel of each color set in step D60 and the actual color mixture network of the second target pixel of each color calculated in step S30b. The dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the densities I, R, G, B is calculated in the same manner as in step S40a. For these calculations, the
次に、色変換部14は、ステップS50aとして、ステップS40aで算出された目標網点面積率ko,co,mo,yo、及び実網点面積率k,c,m,yに対応する各インキ色の単色網濃度をそれぞれ演算する。また、ステップS50bとして、ステップS40bで算出された目標網点面積率ko,co,mo,yo、及び実網点面積率k,c,m,yに対応する各インキ色の単色網濃度をそれぞれ演算する。これらの演算には、図11に示すようなマップを用いる。図11は網点面積率を変化させた場合に実測される単色網濃度を特性曲線としてプロットしたマップの一例であり、事前に測定されたデータにより作成されている。図11に示す例では、墨色の目標網点面積率ko、実網点面積率kをマップに照らし合わせることで、マップ中の特性曲線からそれぞれ目標単色網濃度Dakoと実単色網濃度Dakとが求められている。このようにして、色変換部14は、各インキ色の目標単色網濃度Dako,Daco,Damo,Dayoと実単色網濃度Dak,Dac,Dam,Dayとを求める。
Next, in step S50a, the
次に、色変換部14は、ステップS60aとして、各色の第1の注目画素目標単色網濃度Dako,Daco,Damo,Dayoと実単色網濃度Dak,Dac,Dam,Dayとの偏差に対応する各インキ色のベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk1,ΔDsc1,ΔDsm1,ΔDsy1を演算する。また、ステップS60bとして、各色の第2の注目画素目標単色網濃度Dako,Daco,Damo,Dayoと実単色網濃度Dak,Dac,Dam,Dayとの偏差に対応する各インキ色のベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk2,ΔDsc2,ΔDsm2,ΔDsy2を演算する。
Next, in step S60a, the
なお、ベタ濃度は網点面積率にも依存しており、同単色網濃度に対しては、網点面積率が高いほどベタ濃度は低くなる。そこで、色変換部14は、図12に示すようなマップを用いて演算を行なう。図12は単色ベタ濃度を変化させた場合に実測される単色網濃度を網点面積率毎に特性曲線としてプロットしたマップの一例であり、事前に測定されたデータにより作成されている。色変換部14は、各インキ色について目標網点面積率ko,co,mo,yoに対応する特性曲線を図12に示すマップから選択し、選択した特性曲線に目標単色網濃度Dako,Daco,Damo,Dayoと実単色網濃度Dak,Dac,Dam,Dayとを対応させることにより、ベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk1,ΔDsc1,ΔDsm1,ΔDsy1,ΔDsk2,ΔDsc2,ΔDsm2,ΔDsy2を求める。図12に示す例では、墨色の目標網点面積率koが75%の場合に、目標単色網濃度Dako、実単色網濃度Dakをマップに照らし合わせることで、マップ中の75%特性曲線から墨色のベタ濃度偏差ΔDskが求められている。
The solid density also depends on the halftone dot area ratio. For the same monochrome halftone density, the higher the halftone dot area ratio, the lower the solid density. Therefore, the
このように、第1の注目画素に基づくベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk1,ΔDsc1,ΔDsm1,ΔDsy1と、第2の注目画素に基づくベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk2,ΔDsc2,ΔDsm2,ΔDsy2を算出したら、ステップS65として、両ベタ濃度偏差を、予め設定された重み付けに応じて加重平均し、ベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk,ΔDsc,ΔDsm,ΔDsyを取得する。ベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk,ΔDsc,ΔDsm,ΔDsyは、手動設定される第2の注目画素の重み付けをAパーセントに設定すれば、下式のように算出できる。
ΔDsk=(1−A)・ΔDsk1+A・ΔDsk2
ΔDsc=(1−A)・ΔDsc1+A・ΔDsc2
ΔDsm=(1−A)・ΔDsm1+A・ΔDsm2
ΔDsy=(1−A)・ΔDsy1+A・ΔDsy2
色変換部14で演算された各インキ色のベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk,ΔDsc,ΔDsm,ΔDsyは、インキ供給量演算部15に入力される。インキ供給量演算部15は、ステップS70として、ベタ濃度偏差ΔDsk,ΔDsc,ΔDsm,ΔDsyに対応するキー開度偏差量ΔKk,ΔKc,ΔKm,ΔKyを演算する。キー開度偏差量ΔKk,ΔKc,ΔKm,ΔKyは、各インキキー7の現在のキー開度Kk0,Kc0,Km0,Ky0(前回のステップS100の処理で印刷機の制御装置20に出力したキー開度Kk,Kc,Km,Ky)に対する増減量であり、インキ供給量演算部15は、公知のAPI関数(オートプリセットインキング関数)を用いて演算を行なう。API関数は基準濃度にするため各キーゾーンの画線率A(Ak,Ac,Am,Ay)とキー開度K(Kk,Kc,Km,Ky)との対応関係を示した関数である。画線率Aは、ステップS0で用いたものを用いることができる。具体的には、基準濃度Ds(Dsk,Dsc,Dsm,Dsy)に対するベタ濃度偏差ΔDs(ΔDsk,ΔDsc,ΔDsm,ΔDsy)の比率kd(kd=ΔDs/Ds)を求めるとともに、画線率Aに対する基準濃度にするためのキー開度Kを、API関数を使って求め、これらの積としてベタ濃度偏差ΔDsをゼロにするためのキー開度偏差量ΔK(ΔK=kd×K)を求める。
As described above, when the solid density deviations ΔDsk1, ΔDsc1, ΔDsm1, and ΔDsy1 based on the first target pixel and the solid density deviations ΔDsk2, ΔDsc2, ΔDsm2, and ΔDsy2 based on the second target pixel are calculated, both solids are obtained in step S65. The density deviations are weighted and averaged according to preset weights to obtain solid density deviations ΔDsk, ΔDsc, ΔDsm, and ΔDsy. The solid density deviations ΔDsk, ΔDsc, ΔDsm, and ΔDsy can be calculated by the following equation if the weight of the second target pixel that is manually set is set to A percent.
ΔDsk = (1−A) · ΔDsk1 + A · ΔDsk2
ΔDsc = (1−A) · ΔDsc1 + A · ΔDsc2
ΔDsm = (1−A) · ΔDsm1 + A · ΔDsm2
ΔDsy = (1−A) · ΔDsy1 + A · ΔDsy2
The solid density deviations ΔDsk, ΔDsc, ΔDsm, ΔDsy of each ink color calculated by the
次に、オンライン制御部16は、ステップS80として、色変換部14で演算されたキー開度偏差量ΔKk,ΔKc,ΔKm,ΔKyを、各印刷ユニット2a,2b,2c,2
dからラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計1までの無駄時間、時間あたりのインキキー7の反応時間、及び印刷速度を考慮して補正する。この補正は、キー開度信号が入力されてからインキキー7が動き、キー開度が変更されて印刷シートに供給されるインキ量が変化し、IRGB濃度計1に反射光量の変化として検出されるまでの時間遅れを考慮したものである。このようなむだ時間の大きいオンラインフィードバック制御系としては、例えばむだ時間補償付PI制御、ファジー制御、ロバスト制御等が最適である。オンライン制御部16は、補正後のキー開度偏差量(オンライン制御用キー開度偏差量)ΔKk,ΔKc,ΔKm,ΔKyに現在のキー開度Kk0,Kc0,Km0,Ky0を加算したオンライン制御用キー開度Kk1,Kc1,Km1,Ky1をキー開度リミッタ演算部17に入力する。
Next, in step S80, the
Correction is made in consideration of the dead time from d to the line sensor
キー開度リミッタ演算部17は、ステップS90として、オンライン制御部16で演算されたオンライン制御用キー開度Kk1,Kc1,Km1,Ky1に対して上限値を規制する補正を行なう。これは、特に低画線部における色変換アルゴリズム(ステップS40,S50,S60の処理)の推定誤差によりキー開度が異常に増大することを規制するための処理である。そして、キー開度リミッタ演算部17は、ステップS100として、上限値を規制したキー開度Kk,Kc,Km,Kyをキー開度信号として印刷機の制御装置20に送信する。
In step S90, the key opening
印刷機の制御装置20は、ステップS110として、演算装置10から送信されたキー開度信号Kk,Kc,Km,Kyに基づき各印刷ユニット2a,2b,2c,2dの各インキキー7の開度を調節する。これにより、各インキ色のインキ供給量は、キーゾーン毎に目標とする色調に見あったものにコントロールされることとなる。
In step S110, the
本実施形態にかかる印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法及び装置並びに色調制御方法及び装置によれば、印刷する紙面のデザイナーなどの紙面構成担当者等が、製版データ及び印刷用ジョブチケットデータの作成時に、ジョブチケットデータに上記製版データに対応した注目画素領域に関する情報(クライアントが指定した注目点或いはデザイナーが重要と思う注目点、ベタ,網,平網のいずれを選択するかの種別)を書き込むので、印刷時には、印刷オペレータは、書き込まれた注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいてチェック欄にチェックをすればよく、オペレータの負担が軽減され、注目画素領域の設定を、短時間にしかも適切に行なうことができる。また、クライアントが指定した注目点或いはデザイナーが重要と思う注目点が座標と腕具体的に指定されている場合には、この座標情報からそのまま注目画素領域を選定すれば良く、オペレータの負担がより軽減され、注目画素領域の設定を、より短時間に適切に行なうことができる。 According to the target pixel area setting method and apparatus for color tone control of printing and the color tone control method and apparatus according to the present embodiment, the person in charge of the page configuration such as the designer of the page to print the plate making data and the job ticket data for printing At the time of creation, information about the pixel area of interest corresponding to the above-mentioned plate making data (type of whether the point of interest specified by the client or the point of interest that the designer thinks important, solid, mesh, or flat screen) is selected in the job ticket data Since writing is performed, the printing operator only needs to check the check column based on the written information regarding the target pixel area at the time of printing, the burden on the operator is reduced, and the target pixel area can be set appropriately in a short time. Can be done. In addition, when the attention point designated by the client or the attention point considered important by the designer is specifically designated as coordinates and arms, the pixel area of interest can be selected as it is from this coordinate information, and the burden on the operator is further increased. Thus, the pixel region of interest can be set appropriately in a shorter time.
このため、例えば新聞印刷などの、紙面編集から印刷完了までを短時間で完了しなくてはならない場合にも、注目画素領域の設定を適切に行なうことができ、この注目画素領域に基づいて印刷の色調制御を精度良く行なうことができる。
また、PC12を用いて、上記のチェック欄へのチェックを自動で行なうことも可能であり、何ら人為的な処理を要さずに、注目画素領域の設定を適切に行なうことができる。
For this reason, even when it is necessary to complete a short period of time from paper editing to printing completion, such as newspaper printing, the target pixel area can be appropriately set, and printing is performed based on the target pixel area. Can be accurately controlled.
Also, it is possible to automatically check the above check column using the
特に、ベタ領域又は平網領域を、印刷絵柄の網点面積率の画像微分(隣接画素との差分)値が予め設定された基準値(例えば1%)以下の領域とすることや、ベタ領域を印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が予め設定された基準値(例えば70%)以上の領域とし、網領域を、印刷絵柄の網点面積率の値が基準値(例えば70%)未満の領域とすることにより、ベタ領域や網領域や平網領域の各領域の自動選定を容易に行なえ注目画素領域の自動設定に寄与する。 In particular, the solid area or the flat mesh area is set to an area in which the image differential (difference from adjacent pixels) value of the dot area ratio of the printed pattern is equal to or less than a preset reference value (for example, 1%). Is a region where the halftone dot area ratio of the printed pattern is equal to or greater than a preset reference value (for example, 70%), and the halftone dot area ratio of the printed pattern is less than the reference value (for example, 70%). By setting the area, automatic selection of each area of the solid area, the net area, and the flat net area can be easily performed, which contributes to the automatic setting of the target pixel area.
また、注目画素領域のエッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除いた領域を印刷の色調制御に用いる注目画素領域とすることにより、注目画素領域中に、白紙領域を含む他の領域が入らないようにすることができ、印刷速度上昇時やペースタ(自動紙継)時等に目標画像位置と現在画像位置とにずれが生じた場合にも、濃度検出感度の低下を防ぐことができ、色調制御の精度低下を抑制することができる。また、注目画素領域を自己相関が高い領域の外側まで膨らませたものに設定すれば、低画線の場合にも注目画素領域を確実に確保することができ、しかも、色調制御の精度低下を抑制することができる。 In addition, by setting an area obtained by removing the edge portion of the target pixel area by a predetermined number of sensor pixels as the target pixel area used for printing tone control, other areas including a blank area are not included in the target pixel area. It is possible to prevent a decrease in density detection sensitivity even when there is a difference between the target image position and the current image position when the printing speed is increased or when the paster (automatic paper splicing) is performed. Can be suppressed. In addition, if the target pixel area is set to be expanded outside the area with high autocorrelation, the target pixel area can be reliably secured even in the case of a low image line, and the decrease in accuracy of color tone control is suppressed. can do.
さらに、ジョブチケットデータ等に基づいて行なう第1の注目画素領域設定とは別に、製版データのkcmy網点面積率データに基づいて、各インキ色について自己相関が高い領域をIRGB濃度計のセンサ画素単位で選定し、この選定領域に基づいて第2の注目画素領域を設定するので、紙面構成の作成担当者等の注目点選出の尺度とは別の尺度(自己相関が高い領域)で、センシングから考えた場合に最も制御精度が向上する注目画素領域を設定することができ、制御性能を向上させることが出来る。第一の注目画素領域はあくまでも人間優先、第二の注目画素領域はコンピュータ優先であり、従って第二の注目点では、位置ずれの影響や色感度が低いという画素は選択されない特徴がある。 Further, apart from the first target pixel area setting based on job ticket data or the like, based on the kcmy halftone dot area ratio data of the plate making data, an area having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is determined as a sensor pixel of the IRGB densitometer. Since the second pixel-of-interest area is set based on this selected area, sensing is performed using a different scale (area with high autocorrelation) from the scale of attention point selection by the person in charge of creating the page configuration. Therefore, it is possible to set a pixel region of interest in which the control accuracy is most improved when considered from the above, and it is possible to improve the control performance. The first pixel-of-interest area has human priority, and the second pixel-of-interest area has computer priority. Therefore, at the second pixel-of-interest, there is a feature that a pixel having a low positional sensitivity or color sensitivity is not selected.
また、エッジ部を所定のセンサ画素分だけ除くと注目画素がなくなってしまう場合には、選定領域の中からエッジ部を除かずに自己相関が高い領域全てを、該当するインキ色の第2の注目画素領域に設定すれば、エッジ部を所定画素分だけ除くことによって注目画素がなくなってしまうような僅かな選定領域(自己相関が高い領域)に対しても実施することができる。 Further, if the target pixel disappears if the edge portion is removed by a predetermined number of sensor pixels, all the regions having high autocorrelation are excluded from the selected region without removing the edge portion. If the target pixel area is set, the present invention can be applied to a small selection area (area with high autocorrelation) in which the target pixel disappears by removing the edge portion by a predetermined number of pixels.
しかも、2系統で設定された注目画素領域を、重み付け設定により加重平均することで、オペレータの意図を適宜の割合で反映させることができる。
したがって、第1の注目画素領域の重み付けを100パーセント又はこれに近く設定すれば、紙面作成パートの意図が強く反映された色調制御(インキ供給量制御)を実施することができる。一方、紙面作成パートにあまり頼らないで制御をする場合には、第1の注目画素領域の重み付けを0パーセント又はこれに近く設定すれば、制御装置10による客観基準に従って自動設定された標準的な注目画素に基づく、適切な色調制御(インキ供給量制御)を実現できる。
In addition, the intention of the operator can be reflected at an appropriate ratio by performing weighted averaging of the target pixel region set in two systems by weighting setting.
Therefore, if the weight of the first target pixel region is set to 100% or close to this, color tone control (ink supply amount control) that strongly reflects the intention of the paper surface creation part can be performed. On the other hand, when the control is performed without relying much on the paper surface creation part, if the weighting of the first target pixel region is set to 0 percent or close to this, a standard automatically set according to the objective standard by the
(B)その他
以上、本発明の実施形態について説明したが、本発明の実施の形態は上記のものに限定されない。
例えば、本実施形態では、2系統で設定された注目画素領域を加重平均しており、加重平均にかかる重み付けは自由に設定できるようになっているが、よりシンプルに、紙面作成パート意思優先(第1の注目画素領域100パーセント)と、制御装置10による客観基準優先(第2の注目画素領域100パーセント)と、単純平均(両者50パーセント)との3パターンのみを選択できるようにしたり、より単純に、紙面作成パート意思優先(第1の注目画素領域100パーセント)と、制御装置10による客観基準優先(第2の注目画素領域100パーセント)とのいずれかを選択できるようにしたりしてもよい。また、第1の注目画素領域のみを採用しても、一定の効果を得ることができる。
(B) Others Although the embodiment of the present invention has been described above, the embodiment of the present invention is not limited to the above.
For example, in this embodiment, the pixel region of interest set in two systems is weighted average, and the weighting related to the weighted average can be set freely. It is possible to select only three patterns of the first target pixel area (100%), the objective reference priority by the control device 10 (second
さらに、重み付けによらず、第1の注目画素領域と第2の注目画素領域との単純和を注目画素領域としてもよい。
また、本実施形態では、各インキ色の網点面積率と混色網濃度とを関連付けるデータベース141を備える方法の他、各インキ色の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係を規定した公知のノイゲバウアーの式を記憶しておき、この式に各インキ色の網点面積率を当てはめることで混色網濃度を算出する方法を採ることもできる。
Furthermore, a simple sum of the first target pixel region and the second target pixel region may be used as the target pixel region regardless of weighting.
In this embodiment, in addition to a method including a
また、図12に示すようなマップを用いて目標単色網濃度と実単色網濃度との偏差に対応する各インキ色のベタ濃度偏差を求める方法の他、網点面積率と単色網濃度とベタ濃度との対応関係を規定した公知のユールニールセンの式を記憶しておき、この式に目標網点面積率、実網点面積率及び単色網濃度を当てはめることでベタ濃度偏差を算出する方法もある。 Further, in addition to a method for obtaining a solid density deviation of each ink color corresponding to the deviation between the target monochrome color density and the actual monochrome color density using a map as shown in FIG. 12, the dot area ratio, the monochrome color density, and the solid color are obtained. A method of calculating a solid density deviation by storing a known Yule-Nielsen formula that defines the correspondence with density and applying the target halftone dot area ratio, actual halftone dot area percentage, and monochrome halftone density to this formula is also available. is there.
また、実施形態では、濃度を計測するセンサとしてラインセンサ型のIRGB濃度計を用いているが、スポット型のIRGB濃度計を用いて印刷シート上を2次元的に走査するようにしてもよい。 In the embodiment, a line sensor type IRGB densitometer is used as a sensor for measuring density . However, a spot type IRGB densitometer may be used to scan the print sheet two-dimensionally.
1 ラインセンサ型IRGB濃度計
2a,2b,2c,2d 印刷ユニット
3 ブランケット胴
4 版胴
5 インキローラ群
6 インキ元ローラ
7 インキキー
8 印刷シート
10 演算装置
11 DSP
12 PC
14 色変換部
15 インキ供給量演算部
16 オンライン制御部
17 キー開度リミッタ演算部
20 印刷機内蔵の制御装置
30 タッチパネル
32 表示装置
40 印刷エリアモニタ(タッチパネル)
50 印刷面
DESCRIPTION OF
12 PC
14
50 printing side
Claims (22)
製版データ及び印刷用ジョブチケットデータの作成時に、上記ジョブチケットデータに上記製版データに対応した上記注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込む注目画素領域情報書き込みステップと、
上記製版データ及び上記ジョブチケットデータに基づいて印刷を実施するに当たって、上記の書き込まれた注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて印刷絵柄中に上記注目画素領域を設定する注目画素領域設定ステップとを備え、
上記の注目画素領域に関する情報は、上記注目画素領域としてベタ領域,網領域,平網領域のうち少なくとも何れか2つの領域の中から1つを選ぶ選択情報である
ことを特徴とする、色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 A method for setting a pixel region of interest for each ink color used in feedback control of a print color tone by paying attention to a specific pixel region in a printed pattern,
A pixel-of-interest area information writing step of writing information on the pixel-of-interest area corresponding to the plate-making data into the job ticket data when creating the plate-making data and printing job ticket data;
In performing printing based on the plate-making data and the job ticket data, the pixel-of-interest region setting step of setting the pixel-of-interest region in a printed pattern based on the information on the pixel-of-interest region written,
The information on the target pixel area is color tone control characterized in that it is selection information for selecting at least one of a solid area, a halftone area, and a flat halftone area as the target pixel area. Attention pixel region setting method.
ことを特徴とする、請求項1記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 Upper Kitaira network region, and wherein the image differential value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printing picture is a preset reference value or less in the region, according to claim 1, wherein the color tone controlling noticed pixel region setting method .
ことを特徴とする、請求項1記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 The solid area is an area where the value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printed pattern is equal to or greater than a preset reference value, and the halftone area of the printed pattern is less than the reference value The method for setting a target pixel region for color tone control according to claim 1, wherein the pixel region is a region.
ことを特徴とする、請求項1〜3の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 4. The color tone control according to claim 1, wherein in the target pixel region setting step, the target pixel region is manually or automatically set based on information on the target pixel region. Attention pixel region setting method.
ことを特徴とする、請求項1〜4の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 5. The pixel region of interest that is used for color tone control of printing is a region obtained by removing the edge portion of the set pixel region of interest by a predetermined number of sensor pixels. 6. 2. A method for setting a pixel area of interest for color tone control described in 1.
ことを特徴とする、請求項1〜5の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 The target pixel region setting step performed based on the information on the target pixel region is set as a first target pixel region setting step, and, separately from the first target pixel region setting step, halftone dot area ratio data of plate making data is used. Based on this, a region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light, and the edge portion of the corresponding ink color is removed from the selected region by a predetermined sensor pixel. 6. The color tone control device according to claim 1, further comprising a second target pixel region setting step of setting the region as the target pixel region of the corresponding ink color. Attention pixel area setting method.
ことを特徴とする、請求項1〜5の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 The target pixel region setting step performed based on the information on the target pixel region is set as a first target pixel region setting step, and, separately from the first target pixel region setting step, halftone dot area ratio data of plate making data is used. A step of setting the pixel region of interest based on the selected region, wherein a region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light, and the corresponding ink color is selected from the selected region. If the pixel region of interest exists even if the edge portion is removed by a predetermined sensor pixel, the region in which the edge portion is removed from the selected region by the predetermined sensor pixel is removed from the selected region. If it is set as the target pixel area and the edge part is removed by the predetermined sensor pixels, the target pixel area disappears. 2. The method according to claim 1, further comprising a second target pixel region setting step for setting the region having a high autocorrelation without removing the edge portion as the target pixel region of the corresponding ink color. 6. A method for setting a target pixel area for color tone control according to any one of items 1 to 5.
ことを特徴とする、請求項6又は7記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 In the second pixel-of-interest region setting step, when the corresponding ink color edge portion is removed from the selected region in the sensor pixel unit, only one pixel is removed in the sensor pixel unit. The method for setting a target pixel area for color tone control according to claim 6 or 7 .
ことを特徴とする、請求項1〜5の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 The target pixel region setting step performed based on the information on the target pixel region is set as a first target pixel region setting step. Separately from the first target pixel region setting step, each ink color is determined based on the plate making data. A region with a high autocorrelation was selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor that measures the amount of reflected light, and was expanded from the selected region to the outside of the region with a high autocorrelation so as to include the edge portion of the corresponding ink color. 6. The target pixel region setting method for color tone control according to any one of claims 1 to 5, further comprising a second target pixel region setting step for setting a region as the target pixel region. .
上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップは、コンピュータを用いて上記画素群を自動抽出する注目画素領域自動設定ステップとして構成される
ことを特徴とする、請求項7〜9の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 The region having a high autocorrelation in the second target pixel region setting step is a group of all pixels having a high autocorrelation higher than a preset condition for each ink color,
The second noticed pixel region setting step, characterized in that it is configured as a noticed pixel region automatically setting step of automatically extracting the pixel group by using a computer, according to any one of claims 7-9 Of interest pixel region setting method for color tone control.
ことを特徴とする、請求項7〜10の何れか1項に記載の色調制御用注目画素領域設定方法。 The sum area of the first target pixel area set by the first target pixel area setting step and the second target pixel area set by the second target pixel area setting step is set as the target pixel area. The method for setting a target pixel region for color tone control according to any one of claims 7 to 10 , wherein:
上記注目画素領域に関する目標混色網濃度を設定する目標混色網濃度設定ステップと、
センサを用いて、印刷で得られた本刷りシートのインキ供給単位幅毎の各インキ色の上記注目画素領域に関する実混色網濃度を計測する実混色網濃度計測ステップと、
予め設定した網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の目標網点面積率を求める目標網点面積率算出ステップと、
上記の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の実網点面積率を求める実網点面積率算出ステップと、
予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標網点面積率に対応する目標単色網濃度を求める目標単色網濃度算出ステップと、
上記の網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実網点面積率に対応する実単色網濃度を求める実単色網濃度算出ステップと、
予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度とベタ濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記注目画素領域について、上記目標網点面積率のもとでの上記目標単色網濃度と上記実単色網濃度との偏差に対応するベタ濃度偏差を求めるベタ濃度偏差算出ステップと、
上記ベタ濃度偏差に基づき上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整するインキ供給量調整ステップとをそなえている
ことを特徴とする、印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法。 There in claim 1 to 11 any one printing press picture color tone controlling method for feedback control of the color tone of interest to the printing target pixel area set by using the color tone control noticed pixel region setting method according to the And
A target color mixture halftone density setting step for setting a target color mixture halftone density relating to the target pixel region;
Using sensors, and the actual color mixture halftone density measurement step of measuring an actual color mixture halftone density regarding the noticed pixel region for each ink color for each Yi Nki supplying unit widths of the printing sheet obtained in printing,
A target halftone dot area ratio calculating step for obtaining a target halftone dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the target mixed color halftone density based on a correspondence relationship between a predetermined halftone dot area ratio and mixed color halftone density;
Based on the correspondence between the halftone dot area ratio and the mixed color halftone density, an actual halftone dot area ratio calculation step for obtaining the actual halftone dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the actual mixed color halftone density;
A target monochromatic halftone density calculating step for obtaining a target monochromatic halftone density corresponding to the target halftone dot area ratio based on a correspondence relationship between a predetermined halftone dot area ratio and a monochromatic halftone density;
An actual monochromatic halftone density calculating step for obtaining an actual monochromatic halftone density corresponding to the actual halftone dot area ratio based on the correspondence relationship between the halftone dot area ratio and the monochromatic halftone density;
Based on the correspondence relationship between the halftone dot area ratio, the monochrome halftone density, and the solid density set in advance, for the target pixel area, the target monochrome halftone density and the actual monochrome halftone density under the target halftone dot area ratio A solid density deviation calculating step for obtaining a solid density deviation corresponding to the deviation of
A picture color tone control method for a printing press, comprising: an ink supply amount adjusting step for adjusting an ink supply amount for each ink supply unit width based on the solid density deviation.
上記の目標混色網濃度設定ステップ,実混色網濃度計測ステップ,目標網点面積率算出ステップ,実網点面積率算出ステップ,目標単色網濃度算出ステップ,実単色網濃度算出ステップ,及びベタ濃度偏差算出ステップを、上記第1の注目画素領域設定ステップによって設定された第1の注目画素領域と上記第2の注目画素領域設定ステップによって設定された第2の注目画素領域との双方に関して実施して、上記インキ供給量調整ステップでは、これらから得られる2つの上記ベタ濃度偏差に基づき上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整する
ことを特徴とする、請求項12記載の印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法。 With use of the color tone control noticed pixel region setting method according to any one of claims 6-11,
The target mixed color halftone density setting step, the actual mixed color halftone density measuring step, the target halftone dot area ratio calculating step, the actual halftone dot area ratio calculating step, the target single color halftone density calculating step, the actual single color halftone density calculating step, and the solid density deviation The calculation step is performed for both the first target pixel region set by the first target pixel region setting step and the second target pixel region set by the second target pixel region setting step. 13. The pattern color tone of a printing press according to claim 12 , wherein, in the ink supply amount adjustment step, the ink supply amount is adjusted for each ink supply unit width based on the two solid density deviations obtained therefrom. Control method.
ことを特徴とする、請求項13記載の印刷機の絵柄色調制御方法。 In the ink supply amount adjustment step, the solid density deviation obtained with respect to the first target pixel area and the solid density deviation obtained with respect to the second target pixel area are set according to a preset weighting. 14. The pattern color tone control method for a printing press according to claim 13 , wherein the ink supply amount is adjusted for each of the ink supply unit widths based on the weighted average solid density deviation.
製版データ及び印刷用ジョブチケットデータに上記製版データに対応した上記注目画素領域に関する情報を書き込む書込手段と、
上記製版データ及び上記ジョブチケットデータに基づいて印刷を制御するとともに上記の注目画素領域に関する情報に基づいて上記注目画素領域を自動で設定する演算装置とを備え、
上記の注目画素領域に関する情報は、上記注目画素領域としてベタ領域,網領域,平網領域のうち少なくとも何れか2つの領域の中から1つを選ぶ選択情報である
ことを特徴とする、印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 An apparatus for setting a pixel region of interest for each ink color, which is used when feedback-controlling the color tone of printing by paying attention to a specific pixel region in a printed pattern,
A writing means for writing information on the noticed pixel region corresponding to the plate making data to the plate making data and the print job ticket data,
An arithmetic unit that controls printing based on the plate-making data and the job ticket data and automatically sets the pixel region of interest based on information on the pixel region of interest;
The information on the target pixel area is selection information for selecting at least one of a solid area, a halftone area, and a flat halftone area as the target pixel area. A target pixel area setting device for color tone control.
ことを特徴とする、請求項15記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 Upper Kitaira network region, and wherein the image differential value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printing picture is a region below a preset reference value, according to claim 15 tone control target pixel areas of the printing according Setting device.
ことを特徴とする、請求項16記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 The solid area is an area where the value of the halftone dot area ratio of the printed pattern is equal to or greater than a preset reference value, and the halftone area of the printed pattern is less than the reference value 17. The target pixel region setting device for color tone control of printing according to claim 16, wherein the pixel region is a region.
ことを特徴とする、請求項15〜17の何れか1項に記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 18. The arithmetic device according to claim 15 , wherein a pixel region in which an edge portion is removed by a predetermined number of sensor pixels from the set target pixel region is set as a target pixel region used for color tone control of printing. The target pixel region setting device for color tone control of printing according to any one of the above.
ことを特徴とする、請求項15〜18の何れか1項に記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 The arithmetic unit includes a first target pixel region setting unit that sets a target pixel region based on the information about the target pixel region and a first target pixel region setting unit, based on plate making data. A region with a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor that measures the amount of reflected light, and a region obtained by removing the edge portion of the corresponding ink color from the selected region by a predetermined sensor pixel is selected. 19. The target pixel region setting device for color tone control of printing according to claim 15 , further comprising second target pixel region setting means for setting as the target pixel region .
ことを特徴とする、請求項15〜17の何れか1項に記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 The arithmetic unit includes a first target pixel region setting unit that sets a target pixel region based on the information about the target pixel region and a first target pixel region setting unit, based on plate making data. A region having a high autocorrelation for each ink color is selected for each sensor pixel of the sensor for measuring the amount of reflected light, and the region having a high autocorrelation is selected from the selected region so as to include an edge portion of the corresponding ink color. The color tone control for printing according to any one of claims 15 to 17 , characterized in that an area expanded outward is provided with second target pixel area setting means for setting the target pixel area. Attention pixel area setting device.
ことを特徴とする、請求項19又は20記載の印刷の色調制御用注目画素領域設定装置。 In the arithmetic device, a sum area of the first target pixel region set by the first target pixel region setting unit and the second target pixel region set by the second target pixel region setting unit is calculated. 21. The target pixel region setting device for color tone control of printing according to claim 19 or 20 , wherein the target pixel region is set in a target pixel region.
印刷で得られる本刷りシートの走行ライン上に配置されたセンサと、
印刷幅方向に分割されたインキ供給単位幅毎の該注目画素領域に関する目標混色網濃度を設定する目標混色網濃度設定手段と、
上記センサを操作して上記本刷りシートの上記インキ供給単位幅毎の実混色網濃度を計測する混色網濃度計測手段と、
予め設定した網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の目標網点面積率を求める目標網点面積率演算手段と、
上記の網点面積率と混色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実混色網濃度に対応する各インキ色の実網点面積率を求める実網点面積率演算手段と、
予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標網点面積率に対応する目標単色網濃度を求める目標単色網濃度演算手段と、
上記の網点面積率と単色網濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記実網点面積率に対応する実単色網濃度を求める実単色網濃度演算手段と、
予め設定した網点面積率と単色網濃度とベタ濃度との対応関係に基づき、上記目標網点面積率のもとでの上記目標単色網濃度と上記実単色網濃度との偏差に対応するベタ濃度偏差を求めるベタ濃度偏差演算手段と、
上記ベタ濃度偏差に基づくフィードバック制御により上記インキ供給単位幅毎にインキ供給量を調整するインキ供給量調整手段とを備えた
ことを特徴とする、印刷機の絵柄色調制御装置。 A target pixel area setting device for color control of printing according to any one of claims 15 to 21 ,
A sensor arranged on the running line of the main printed sheet obtained by printing;
A target color mixture halftone density setting means for setting a target color mixture halftone density regarding the noticed pixel region of each divided Lee Nki supplying unit width in the print width direction,
A mixed color halftone density measuring means for measuring the actual mixed color halftone density for each ink supply unit width of the main printing sheet by operating the sensor;
A target halftone dot area ratio calculating means for obtaining a target halftone dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the target mixed color halftone density based on a correspondence relationship between a predetermined halftone dot area ratio and the mixed color halftone density;
Based on the correspondence between the halftone dot area ratio and the mixed color halftone density, an actual halftone dot area ratio calculating means for obtaining the actual halftone dot area ratio of each ink color corresponding to the actual mixed color halftone density,
A target monochromatic halftone density calculating means for obtaining a target monochromatic halftone density corresponding to the target halftone dot area ratio based on a correspondence relationship between a predetermined halftone dot area ratio and a monochromatic halftone density;
Based on the correspondence between the halftone dot area ratio and the monochromatic halftone density, an actual monochromatic halftone density calculating means for obtaining an actual monochromatic halftone density corresponding to the actual halftone dot area ratio;
Based on the correspondence relationship between the halftone dot area ratio, the monochrome halftone density, and the solid density set in advance, the solid corresponding to the deviation between the target monochrome halftone density and the actual monochrome halftone density under the target halftone dot area ratio. Solid density deviation calculating means for obtaining density deviation;
An image color tone control device for a printing press, comprising: an ink supply amount adjusting means for adjusting an ink supply amount for each ink supply unit width by feedback control based on the solid density deviation.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005029612A JP4723870B2 (en) | 2005-02-04 | 2005-02-04 | Method and apparatus for setting target pixel region for color tone control of printing and picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing press |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005029612A JP4723870B2 (en) | 2005-02-04 | 2005-02-04 | Method and apparatus for setting target pixel region for color tone control of printing and picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing press |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006212985A JP2006212985A (en) | 2006-08-17 |
| JP2006212985A5 JP2006212985A5 (en) | 2007-07-05 |
| JP4723870B2 true JP4723870B2 (en) | 2011-07-13 |
Family
ID=36976588
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005029612A Expired - Fee Related JP4723870B2 (en) | 2005-02-04 | 2005-02-04 | Method and apparatus for setting target pixel region for color tone control of printing and picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing press |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4723870B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5517470B2 (en) * | 2009-03-09 | 2014-06-11 | 三菱重工印刷紙工機械株式会社 | Color control method for printing press and color control device for printing press |
| JP5676610B2 (en) * | 2009-08-12 | 2015-02-25 | トムソン ライセンシングThomson Licensing | System and method for artifact reduction based on region of interest of image sequence |
| JP6107199B2 (en) * | 2013-02-14 | 2017-04-05 | 株式会社リコー | Image forming apparatus, color measurement method, and color measurement program |
| JP6310665B2 (en) * | 2013-09-24 | 2018-04-11 | アイマー・プランニング株式会社 | Can printing device |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4252793B2 (en) * | 2002-11-21 | 2009-04-08 | 大日本スクリーン製造株式会社 | Print management method, image data creation device, and image creation data |
-
2005
- 2005-02-04 JP JP2005029612A patent/JP4723870B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006212985A (en) | 2006-08-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4183711B2 (en) | Color tone confirmation method and device before printing of printing press, plate making method, pattern color tone control method and device of printing press | |
| JP3825427B2 (en) | Pattern color control method for printing machine and printing machine | |
| JPWO2008007746A1 (en) | Printing simulation method and apparatus for setting ink supply amount used for printing of printing machine, picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing machine, and printing machine | |
| JP5311716B2 (en) | Pattern color tone control device and pattern color tone control method for printing press | |
| JP4015670B2 (en) | Newspaper printing control method and newspaper printing system | |
| JP2006076191A (en) | Method and device for controlling color tone of pattern | |
| JP2006076191A5 (en) | ||
| JPWO2006054521A1 (en) | Pattern color tone control method and apparatus | |
| JP4365754B2 (en) | Pattern color tone control method and apparatus | |
| JPWO2006051903A1 (en) | Pattern color tone control method and apparatus | |
| JP4723870B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for setting target pixel region for color tone control of printing and picture color tone control method and apparatus of printing press | |
| JP2006068948A5 (en) | ||
| JP4801700B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for confirming pattern color of printing machine before printing | |
| JP4691116B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for checking color tone before printing of printing press and plate making method | |
| JP2007216691A (en) | Printing control method and printing system | |
| JP2006239955A (en) | Setting method and device of target compound color screen density of printing machine and controlling method and device of color tone of pattern of printing machine | |
| JP2006239955A5 (en) | ||
| JP5184295B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for setting target color mixing halftone density of printing press and picture color tone control method and apparatus for printing press | |
| JP3836107B2 (en) | Pattern color control method and apparatus for printing press | |
| JP4792537B2 (en) | PRINT PREPARATION METHOD, PRINT PREPARATION SYSTEM, PRINT PREPARATION SYSTEM TERMINAL DEVICE, PRINT PREPARATION SYSTEM PROGRAM, RECORDING MEDIUM, PRINT CONTROL SYSTEM AND PRINT SYSTEM | |
| JP2009241468A (en) | Method and apparatus for supporting control of printing color tone, and method and apparatus for managing printing color tone | |
| JP4264429B2 (en) | Ink strike-through estimation method and apparatus for printing press | |
| JP5591362B2 (en) | Pattern color tone control device and pattern color tone control method for printing press | |
| JP2006142672A (en) | Controlling method of color tone of pattern of printing machine and device | |
| JP2006159904A (en) | Method and device for texture color tone control of printing machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070518 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20070731 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080624 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080825 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20090929 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091228 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20100112 |
|
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20100402 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20100914 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110307 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110408 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140415 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |