JP4696104B2 - Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof - Google Patents
Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4696104B2 JP4696104B2 JP2007256228A JP2007256228A JP4696104B2 JP 4696104 B2 JP4696104 B2 JP 4696104B2 JP 2007256228 A JP2007256228 A JP 2007256228A JP 2007256228 A JP2007256228 A JP 2007256228A JP 4696104 B2 JP4696104 B2 JP 4696104B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- film
- imaging device
- state imaging
- manufacturing
- antireflection film
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims description 58
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 28
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 55
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 51
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 44
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 claims description 36
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 230000003667 anti-reflective effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 4
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical group [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003595 spectral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010408 sweeping Methods 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Light Receiving Elements (AREA)
Description
本発明は裏面照射型固体撮像素子及びその製造方法に係り、特に、光利用効率が高く高感度な撮影を行うのに好適な構造を備える裏面照射型固体撮像素子及びその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and a manufacturing method thereof, and more particularly to a back-illuminated solid-state imaging device having a structure suitable for performing high-sensitivity imaging with high light utilization efficiency and a manufacturing method thereof.
CMOSイメージセンサやCCDイメージセンサ等の固体撮像素子には、表面照射型と裏面照射型とがある。イメージセンサの主要電子素子である信号読出回路(CMOSイメージセンサであればトランジスタ回路及び配線層,CCDイメージセンサであれば配線を含む電荷転送路)が形成された半導体基板の一面側(この面を「表面側」ということにする。)と同一面で、被写体からの入射光を受光する構造になっているものが表面照射型である。 Solid-state imaging devices such as a CMOS image sensor and a CCD image sensor include a front side illumination type and a back side illumination type. One side of a semiconductor substrate on which a signal readout circuit (a transistor circuit and wiring layer for a CMOS image sensor, a charge transfer path including wiring for a CCD image sensor), which is a main electronic element of an image sensor, is formed (this surface is The surface irradiation type is the same plane as “front side” and has a structure for receiving incident light from a subject.
これに対し、裏面照射型とは、例えば下記特許文献1に記載されている様に、信号読出回路が形成された半導体基板表面側と反対側の面、すなわち、裏面で被写体からの入射光を受光する構造のものをいう。裏面照射型は、受光面積を表面照射型に比べて広くすることができ、また、光利用効率が高く高感度であるという利点がある。
On the other hand, the back-illuminated type, as described in, for example,
しかしながら、裏面照射型固体撮像素子は、表面照射型固体撮像素子に比較して光利用効率が高く高感度であるといっても、画素の微細化が進む近年の固体撮像素子では、更なる光利用効率の高効率化を図る必要がある。 However, even though the back-illuminated solid-state image sensor has higher light utilization efficiency and higher sensitivity than the front-illuminated solid-state image sensor, in recent solid-state image sensors that have advanced pixel miniaturization, further light It is necessary to increase the use efficiency.
本発明の目的は、光利用効率が高く高感度な裏面照射型固体撮像素子及びその製造方法を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a back-illuminated solid-state imaging device with high light utilization efficiency and high sensitivity, and a method for manufacturing the same.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、半導体基板の表面部に複数の画素が二次元アレイ状に形成され該半導体基板の裏面側から入射する被写界光の入射光量に応じて発生する信号電荷を前記画素が蓄積する裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法において、前記半導体基板の前記裏面側に反射防止膜を積層し、前記半導体基板の受光面の中央部分に設ける前記反射防止膜の膜厚を厚く、周辺部分に設ける前記反射防止膜の膜厚を薄く形成したことを特徴とする According to the method of manufacturing the backside illumination type solid-state imaging device of the present invention, a plurality of pixels are formed in a two-dimensional array on the surface portion of the semiconductor substrate, and the incident light of the field light incident from the backside of the semiconductor substrate is used. In the method of manufacturing a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device in which the pixel stores generated signal charges, the antireflection film is provided on a central portion of the light receiving surface of the semiconductor substrate by stacking an antireflection film on the backside of the semiconductor substrate. The film thickness of the film is thick, and the film thickness of the antireflection film provided in the peripheral portion is thin.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記受光面を中央部分から周辺部分にかけて複数の領域に分け、該領域毎に前記反射防止膜の膜厚を制御することを特徴とする。
The method for manufacturing a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the present invention is characterized in that the light receiving surface is divided into a plurality of regions from a central portion to a peripheral portion, and the film thickness of the antireflection film is controlled for each region .
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法の前記膜厚は、該反射防止膜を透過する光の光路長が該光の波長をλとしたときλ/4またはその奇数倍となるように形成したことを特徴とする。 The film thickness of the backside illumination type solid-state imaging device of the present invention is such that the optical path length of the light transmitted through the antireflection film is λ / 4 or an odd multiple thereof when the wavelength of the light is λ. It is formed.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記反射防止膜の上にカラーフィルタが前記画素対応に形成され、該画素毎の前記反射防止膜の膜厚が該画素毎の前記カラーフィルタの色別に形成されることを特徴とする。 In the manufacturing method of the backside illumination type solid-state imaging device of the present invention, a color filter is formed on the antireflection film corresponding to the pixel, and the film thickness of the antireflection film for each pixel is the color filter for each pixel. It is characterized by being formed for each color.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記カラーフィルタを透過する光の波長が長いほど前記膜厚を厚くすることを特徴とする。 The method for manufacturing a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the present invention is characterized in that the film thickness is increased as the wavelength of light transmitted through the color filter is longer.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記カラーフィルタの或る色の画素に対応して設けた前記反射防止膜の膜厚をn・λ/4(nは奇数、λは入射光の波長)としたとき、該色と異なる色の前記カラーフィルタが設けられた隣接画素に対応して設けた前記反射防止膜の膜厚を、m・λ/4(m≠nの奇数)としたことを特徴とする。 In the manufacturing method of the backside illumination type solid-state imaging device of the present invention, the film thickness of the antireflection film provided corresponding to a certain color pixel of the color filter is set to n · λ / 4 (n is an odd number, λ is incident). Light wavelength), the film thickness of the antireflection film provided corresponding to the adjacent pixel provided with the color filter of a different color is m · λ / 4 (m ≠ n odd number) It is characterized by that.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記半導体基板から見て最初に形成する平坦化膜であって、前記反射防止膜の段差を吸収する平坦化膜を、該平坦化膜の上層,下層に設けられる材料の屈折率と該平坦化膜の屈折率との差が最も小さくなる層間に該平坦化膜を設けたことを特徴とする。 According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a method for manufacturing a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device, comprising: a planarizing film that is formed first when viewed from the semiconductor substrate, and a planarizing film that absorbs a step of the antireflection film is formed on the planarizing film. The planarizing film is provided between the layers where the difference between the refractive index of the material provided in the upper layer and the lower layer and the refractive index of the planarizing film is the smallest.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記半導体基板がシリコンであり、前記反射防止膜が窒化シリコンの単層膜であることを特徴とする。 In the method for manufacturing a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, the semiconductor substrate is silicon, and the antireflection film is a single layer film of silicon nitride.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記反射防止膜が多層膜であることを特徴とする。 In the method for manufacturing a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, the antireflection film is a multilayer film.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子の製造方法は、前記カラーフィルタの代わりに、該カラーフィルタが透過する光の波長のみ選択的に透過し他の波長域の光を反射する前記反射防止膜を設けたことを特徴とする。 In the manufacturing method of the backside illumination type solid-state imaging device of the present invention, instead of the color filter, the antireflection film that selectively transmits only the wavelength of light transmitted through the color filter and reflects light in other wavelength ranges is provided. It is provided.
本発明の裏面照射型固体撮像素子は、半導体基板の表面部に複数の画素が二次元アレイ状に形成され該半導体基板の裏面側から入射する被写界光の入射光量に応じて発生する信号電荷を前記画素が蓄積する裏面照射型固体撮像素子において、上記のいずれかに記載の製造方法で製造したことを特徴とする。 The back-illuminated solid-state imaging device of the present invention has a plurality of pixels formed in a two-dimensional array on the front surface of a semiconductor substrate, and a signal generated according to the amount of incident field light incident from the back surface of the semiconductor substrate. A back-illuminated solid-state imaging device in which charges are accumulated in the pixels is manufactured by any one of the manufacturing methods described above.
本発明によれば、反射防止膜を裏面側の受光面に設けたので、半導体基板の裏面側における入射光の反射率を抑制でき、より多くの入射光を半導体基板内の光電変換領域に導入できるため、光利用効率が高く高感度な撮像が可能となる。 According to the present invention, since the antireflection film is provided on the light receiving surface on the back side, the reflectance of incident light on the back side of the semiconductor substrate can be suppressed, and more incident light is introduced into the photoelectric conversion region in the semiconductor substrate. Therefore, it is possible to perform imaging with high light utilization efficiency and high sensitivity.
以下、本発明の一実施形態について、図面を参照して説明する。 Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
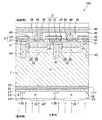
図1は、本発明の第1実施形態に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子の断面模式図である。本実施形態の裏面照射型固体撮像素子100は、インターライン型CCDであり、p型半導体基板1の表面側に垂直電荷転送路(VCCD)21とフォトダイオード22とが形成され、裏面側に、反射防止膜27、カラーフィルタ(赤(R),緑(G),青(B))層23及びマイクロレンズ24が積層される。
FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The backside illumination type solid-
半導体基板1の裏面側表面部には高濃度p++層25が形成され、この高濃度p++層25が接地される。高濃度p++層25の上には入射光に対して透明な酸化膜26が積層されており、その上に、本実施形態では、反射防止膜27が積層され、その上に、カラーフィルタ層23,マイクロレンズ(トップレンズ)層24が順に積層される。各マイクロレンズ24は、対向する位置に設けられた対応のフォトダイオード22の中心に焦点が合うように形成される。
A high-concentration p ++ layer 25 is formed on the back surface side surface portion of the
カラーフィルタ層23は画素(フォトダイオード)単位に区画され、カラーフィルタ層23の半導体基板1側の隣接区画間には、画素間の混色を防ぐための遮光部材28が設けられる。
The
半導体基板1の表面側に形成される垂直電荷転送路(VCCD)21は、n+層の埋め込みチャネル31と、半導体基板1の表面側最表面に形成されたシリコン酸化膜やONO(酸化膜―窒化膜―酸化膜)構造の絶縁膜でなるゲート絶縁層32を介して積層された転送電極膜33とで構成される。
The vertical charge transfer path (VCCD) 21 formed on the surface side of the
垂直電荷転送路21は、表面照射型固体撮像素子と同様に、図示しない水平電荷転送路(HCCD)が延びる方向に対して垂直方向に延びる様に形成され、且つ、複数本の垂直電荷転送路21が形成される。そして、隣接する垂直電荷転送路21間に、垂直電荷転送路21に沿う方向に複数のフォトダイオード22が所定ピッチで形成される。
The vertical
フォトダイオード22は、本実施形態では、p型半導体基板1の表面側に形成されたn層35とその下に形成されたn−層36とで構成される。そして、n層35の表面部に暗電流抑制用の薄いp型高濃度(p+)表面層38が形成され、表面層38の中央表面部に、コンタクト部としてn+層39が形成される。
In this embodiment, the
垂直電荷転送路21の埋め込みチャネル(n+層)31の下には基板1よりp濃度の高いp層41が形成されており、このn層31及びp層41と、図示の例では右隣のフォトダイオード22との間に、素子分離帯としてのp+領域42が形成される。各p層41の下には、半導体基板1より高濃度なp−領域42が設けられ、隣接するフォトダイオード22間の素子分離が図られる。各p−領域42は、上述した画素区画部分すなわち遮光部材28に対応する箇所に設けられる。
A
垂直電荷転送路21の埋め込みチャネル31の下に形成されたp層41は、図示の例では左隣のn層35の表面端部の上まで延び、この端部分のp+表面層38は、n層35の右端面位置より後退した位置になっている。そして、転送電極膜33の左端面は、p層41の左端面まで重なる様に延設され、n層35と、転送電極膜33及びp層41の表面端部とが若干オーバーラップする構成になっている。
The
この様なオーバーラップ構成が可能なのは、裏面照射型では半導体基板1の表面側に面積的な余裕があるためである。表面照射型では、面積的余裕がないため、転送電極膜の端部はフォトダイオードの端部に一致する位置までしか延設できず、間にp層を介在させることができない。
Such an overlap configuration is possible because the back-illuminated type has an area margin on the front surface side of the
本実施形態の様に、転送電極膜33とn層35との間にp層41を介在させると、転送電極膜(読出電極兼用)33に印加する読出電圧の低電圧化を図ることができ、CCD型固体撮像素子の低消費電力化を図ることが可能となる。
If the
半導体基板1の最表面に形成される絶縁層32の上に例えばポリシリコン膜でなる転送電極膜33が形成され、その上に、絶縁層45が積層される。そして、n+層39の上の絶縁層32,45に開口が開けられ、絶縁層45の上に金属電極46が積層されることで、n+層39と電極46とがコンタクトされる。電極46は、この裏面照射型固体撮像素子100のオーバーフロードレインとして機能する。
A
尚、上述した実施形態では、CCD型の裏面照射型固体撮像素子を説明したが、CMOS等のMOSタイプの裏面照射型固体撮像素子でも良い。MOSタイプとするには、図1に示す垂直電荷転送路21やオーバーフロードレイン等の代わりに、信号読出回路としてMOSトランジスタや配線層を基板1の表面側に形成れば良い。
In the above-described embodiment, the CCD type back-illuminated solid-state image sensor has been described. However, a MOS-type back-illuminated solid-state image sensor such as a CMOS may be used. For the MOS type, a MOS transistor or a wiring layer may be formed on the surface side of the
斯かる構造の裏面照射型固体撮像素子100で被写体画像を撮像する場合、被写界からの入射光は、半導体基板1の裏面側から入射する。この入射光はマイクロレンズ24で集光され、カラーフィルタ層23を通り、半導体基板1内に浸入する。本実施形態の場合、半導体基板1の裏面に反射防止膜27が設けられているため、入射光が高効率で半導体基板1内に進入することになる。
When a subject image is picked up by the backside illumination type solid-
マイクロレンズ24で集光された光が半導体基板1内に入射すると、この入射光は当該マイクロレンズ24及びカラーフィルタ23に対応するフォトダイオード22の方向に集光しながら進み、半導体基板1に光吸収され、光電変換されて正孔電子対が発生する。
When the light condensed by the
裏面照射型固体撮像素子100では、半導体基板1の裏面からフォトダイオードを構成するn領域22までの距離を、9μm程度の厚さにしているため、入射光が半導体基板1の表面側に設けたn+領域すなわち電荷転送路21に達するまでに全て基板1に吸収され光電変換されてしまう。従って、垂直電荷転送路21を遮光する必要がない。
In the back-illuminated solid-
各画素の光電変換領域(p++層25からn領域35までの領域)で発生した電子は、当該画素におけるn領域35に蓄積され、読出電極兼用の転送電極膜33に読出電圧が印加されると、n領域35から、図1に示す例では右隣の埋め込みチャネル31に読み出される。以後、垂直電荷転送路21に沿って図示しない水平電荷転送路(HCCD)まで転送され、次に水平電荷転送路に沿って図示しないアンプまで転送され、このアンプが信号電荷量に応じた電圧値信号を撮像画像信号として出力する。
Electrons generated in the photoelectric conversion region (region from the p ++ layer 25 to the n region 35) of each pixel are accumulated in the
p型半導体基板1の光電変換領域で発生した正孔(ホール)が基板1内でふらつくと、裏面照射型固体撮像素子100における受光面(撮像領域)の中央部分と周辺部分とでホール掃き出しムラが生じ、画素特性に差が生じてしまう。しかし、本実施形態の裏面照射型固体撮像素子100では、半導体基板1で発生したホールを裏面の略全面に設けられたp++層25で吸い取り、これを安定的にアースに掃き出すことができるため、このホール掃き出しムラによる画質劣化を回避できる。
When holes generated in the photoelectric conversion region of the p-
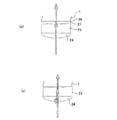
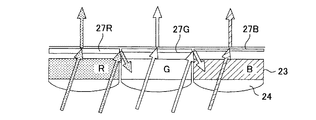
図2(a)は、図1に示す実施形態に係る反射防止膜部分の説明図である。反射防止膜及びカラーフィルタ,マイクロレンズ以外の図示は省略している。 FIG. 2A is an explanatory diagram of an antireflection film portion according to the embodiment shown in FIG. Illustrations other than the antireflection film, the color filter, and the microlens are omitted.
本実施形態の裏面照射型固体撮像素子100は、半導体基板1の光入射面に、反射防止膜27を設けたことを特徴とする。反射防止膜27を設けない図2(b)に示す構造では、屈折率“1.5”程度のマイクロレンズ24を通り、屈折率“1.6”程度のカラーフィルタ23を通過した入射光が屈折率“4”程度の半導体基板1に進入するとき、屈折率差が“4−1.6”と大きいためカラーフィルタ23と半導体基板1(酸化膜26の膜厚は小さいので考慮する必要がない。)との界面での反射率が高くなってしまう。
The backside illumination type solid-
これに対し、図2(a)に示す様に、反射防止膜27を上記の界面に設けることでこの界面での反射を防止でき、半導体基板1への光入射効率を高めることが可能となる。反射防止膜27の屈折率としては、シリコン半導体基板1の屈折率が“4”程度であるため“√4”すなわち“2”程度の材料が好適である。この屈折率を持つ材料としては、窒化シリコンがある。また、反射防止膜27の膜厚は反射を抑制する入射光の波長λの1/4すなわちλ/4(または、この奇数倍)が好適である。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 2A, by providing the
この様に、反射防止膜27を半導体基板1の光入射面に設けることで、入射光を高効率で半導体基板1内に取り込むことができ、更なる高感度撮影を行うことが可能となる。
In this manner, by providing the
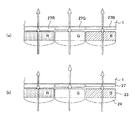
図3(a)は、本発明の第2実施形態に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子の反射防止膜部分の説明図である。その他の構成は図1と同様であり、図示は省略している(尚、以下の実施形態でも同様である。)。 FIG. 3A is an explanatory diagram of an antireflection film portion of the backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Other configurations are the same as those in FIG. 1, and the illustration is omitted (the same applies to the following embodiments).
図2(a)で説明した様に、反射防止膜27を設ければ、シリコン界面での反射を防止できる。単板式の固体撮像素子でカラー画像を撮像する場合には、各画素(フォトダイオード22)毎に赤色(R),緑色(G),青色(B)のカラーフィルタ23を積層することになるが、各カラーフィルタR,G,Bを透過して半導体基板1に入射する光の波長は、カラーフィルタの色毎に異なる。
As described with reference to FIG. 2A, if the
図3(b)に示す様に、このカラーフィルタR,G,Bの違いを無視し、各カラーフィルタR,G,Bで同一膜厚の反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bを用いても、反射防止膜のない図2(b)に示す固体撮像素子より半導体基板1への光入射率を改善できることは勿論である。
As shown in FIG. 3B, the difference between the color filters R, G, and B is ignored, and the
しかし、本実施形態では、図3(a)に示す様に、カラーフィルタR,G,Bの違いも考慮して、反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの夫々の膜厚を制御している。各カラーフィルタR,G,Bを透過する光の分光特性は釣り鐘状の山形になるため、赤色,緑色,青色それぞれの分光特性のピーク位置(あるいは各ピーク位置を中心とした所定範囲(色信号として取り出したい範囲)内の平均値)の波長λr,λg,λbの1/4(またはその奇数倍)に反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの各膜厚を制御する。
However, in the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 3A, the thicknesses of the
この様に、カラーフィルタの色毎に反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの膜厚をきめ細かく制御することで、各色画素毎の光入射率を高めることができると共に各色画素毎の光入射率の均一化も図ることが可能となる。
In this manner, by finely controlling the film thickness of the
反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bを夫々図2で説明した窒化シリコンの単層膜で製造すれば、膜厚の大小関係は、27R>27G>27Bとなる。しかし、反射防止膜は単層構造である必要はなく、多種材料の多層膜で形成することも可能である。多層膜で形成する場合の上記大小関係は単純な式にならないため、単層構造の場合と異なり、使用する材料によって制御するのが好ましい。
If the
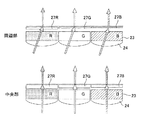
図4は、本発明の第3実施形態に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子の反射防止膜部分の説明図である。上述した第2実施形態では、カラーフィルタR,G,Bの色別に、当該色画素に設ける反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの膜厚を調整している。しかし、この膜厚は、膜表面に対して垂直方向の厚さで規定している。
FIG. 4 is an explanatory diagram of an antireflection film portion of a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the third embodiment of the present invention. In the second embodiment described above, the thicknesses of the
デジタルカメラ等に搭載する固体撮像素子の入射光は、撮影レンズを通して入射するため、撮影レンズの中心光軸上の光以外は、斜め入射光になる。つまり、撮像素子の受光面の中央領域には略垂直に入射するが、受光面の周辺領域には斜め入射光になる。 Incident light from a solid-state imaging device mounted on a digital camera or the like enters through a photographing lens, and therefore, light other than light on the central optical axis of the photographing lens becomes oblique incident light. That is, the light enters the central region of the light receiving surface of the image sensor substantially perpendicularly, but becomes obliquely incident light on the peripheral region of the light receiving surface.
反射防止膜が反射防止機能を持つには、膜厚をλ/4(またはその奇数倍)にしなければならない。しかし、このλ/4の長さは、実際には光路長で計算する必要があり、上記で「膜厚」としたのは、光が反射防止膜に垂直に入射することを前提としている。つまり、斜め入射光の場合には、反射防止膜の表面に垂直な「膜厚」は薄くても実際の光路長は確保可能となる。 In order for the antireflection film to have an antireflection function, the film thickness must be λ / 4 (or an odd multiple thereof). However, the length of λ / 4 actually needs to be calculated by the optical path length, and the above “film thickness” is based on the premise that light enters the antireflection film perpendicularly. That is, in the case of obliquely incident light, the actual optical path length can be secured even if the “film thickness” perpendicular to the surface of the antireflection film is thin.
従って、図4に示す実施形態では、固体撮像素子の受光面中央領域の反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの膜厚(表面に垂直な方向の膜厚)は厚く、周辺領域の膜厚は薄くすることで、斜め入射光でも受光面全面で最適な反射防止機能を得ることが可能となる。
Therefore, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4, the thickness of the
理想的には、受光面の位置毎,画素毎,色毎に入射角度を計算して反射防止膜の膜厚を規定するのが良いが、実際に画素毎に膜厚制御を行うと製造コスト的に割高になってしまう。このため、受光面を、例えば「中央部」「中間部」「周辺部」と複数領域に分割し、夫々で膜厚制御を行うのが好ましい。 Ideally, the film thickness of the antireflection film should be defined by calculating the incident angle for each position of the light receiving surface, for each pixel, and for each color. However, if the film thickness control is actually performed for each pixel, the manufacturing cost It becomes expensive. For this reason, it is preferable to divide the light receiving surface into a plurality of regions, for example, “central part”, “intermediate part” and “peripheral part”, and to control the film thickness respectively.
尚、本実施形態では、色毎でも膜厚制御を行ったが、図3(b)に示す様に、色毎の膜厚制御は行わずに、受光面の位置毎に膜厚制御をするだけでも良い。 In this embodiment, the film thickness control is performed for each color, but as shown in FIG. 3B, the film thickness control is performed for each position of the light receiving surface without performing the film thickness control for each color. Just fine.
図5は、本発明の第4実施形態に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子の反射防止膜部分の説明図である。単板式の固体撮像素子では、隣接する画素の色が異なる画素となる場合が生じる。この場合、赤色画素,緑色画素,青色画素が隣接していたとする。上述した実施形態では、nを奇数としたとき、赤色画素の反射防止膜27Rの膜厚をn・λr/4、緑色画素の反射防止膜27Gの膜厚をn・λg/4、青色画素の反射防止膜27Bの膜厚をn・λb/4とした。即ち、同一数nを用いた。
FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram of an antireflection film portion of a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the fourth embodiment of the present invention. In a single-plate solid-state imaging device, there are cases where adjacent pixels have different colors. In this case, it is assumed that the red pixel, the green pixel, and the blue pixel are adjacent to each other. In the embodiment described above, when n is an odd number, the red pixel
これに対し、本実施形態では、色が異なる隣接画素の反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの膜厚を、「n・λr/4」「m・λg/4」「q・λb/4」(ここで、n≠m≠qの奇数)とし、好適には、隣接画素のn,m,q間の数値が大きくずれる様にする。例えば、n=1,m=7,q=11とする。
On the other hand, in the present embodiment, the film thicknesses of the
但し、例えばλg/4のm倍が、λr,λbの1/4の奇数倍に一致するようなmは選択しないようにする。つまり、ある画素のカラーフィルタを透過した光が迷光となって隣接画素の反射防止膜内に入射としたとき、混色が起きてしまうが、このとき、隣接画素の反射防止膜内に入射した迷光が反射防止されずに反射率が大きくなる様にする。これにより、混色がより少なくなる。 However, for example, m is not selected such that m times λg / 4 matches an odd multiple of 1/4 of λr and λb. In other words, when light that has passed through the color filter of a certain pixel becomes stray light and enters the antireflection film of the adjacent pixel, color mixing occurs. At this time, stray light that has entered the antireflection film of the adjacent pixel The reflectance is increased without preventing reflection. Thereby, the color mixing is reduced.
図6は、本発明の第5実施形態に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子の反射防止膜部分の説明図である。 FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram of an antireflection film portion of a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the fifth embodiment of the present invention.
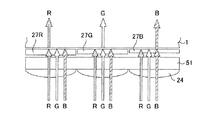
反射防止膜を上述した各実施形態の様に設けると、画素毎や位置毎に段差が生じる。このため、通常、段差が生じた部分に平坦化膜を積層して、その上にカラーフィルタ等を積層することになる。 When the antireflection film is provided as in the above-described embodiments, a step is generated for each pixel or for each position. For this reason, usually, a flattening film is laminated on the portion where the step is generated, and a color filter or the like is laminated thereon.
従来の場合には、図6(b)に示す様に、平坦化膜51は、段差が生じた原因となる反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bの直ぐ上(裏面側)に積層し、平坦化膜51の上下それぞれの材質について考慮しなかった。
In the conventional case, as shown in FIG. 6B, the flattening
しかし、本実施形態では、平坦化膜51を設ける位置を、図6(a)に示す様に、平坦化膜51とその上,下の材質の屈折率差が最も小さくなる位置に設ける。図示する実施形態では、平坦化膜51の屈折率が“1.4”程度であるため、屈折率1.5のマイクロレンズ24と、屈折率1.6のカラーフィルタ23との間に設けている。これにより、マイクロレンズから半導体基板1に入射する入射光のトータルとしての反射率を下げ透過率を上げることができる。
However, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6A, the position where the
図7は、本発明の第6実施形態に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子の反射防止膜部分の説明図である。本実施形態の反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bとして、特定波長成分のみ透過させる反射防止膜を用いる。
FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram of an antireflection film portion of a backside illumination type solid-state imaging device according to the sixth embodiment of the present invention. As the
つまり、赤色光を透過し他色光を遮断する反射防止膜27Rと、緑色光を透過し他色光を遮断する反射防止膜27Gと、青色光を透過し他色光を遮断する反射防止膜27Bとを用いる。
That is, an
例えば、3板式カラー固体撮像装置では、入射光をプリズムを用いてR光,G光,B光に3分割し、夫々の光を対応する固体撮像素子に入射させる構成となっているが、このプリズムに用いる反射膜材料を用いて上記の反射防止膜27R,27G,27Bを形成すれば、カラーフィルタが不要となる。
For example, in a three-plate color solid-state imaging device, incident light is divided into R light, G light, and B light using a prism, and each light is incident on a corresponding solid-state imaging device. If the
本発明に係る裏面照射型固体撮像素子は、入射光の半導体基板への入射光率が高いため、高感度撮影を行うデジタルカメラ等に搭載する固体撮像素子として有用である。 The back-illuminated solid-state imaging device according to the present invention is useful as a solid-state imaging device mounted on a digital camera or the like that performs high-sensitivity imaging because the incident light rate of incident light on a semiconductor substrate is high.
1 半導体基板
22 n領域(フォトダイオード)
23 カラーフィルタ
24 マイクロレンズ
27,27R,27G,27B 反射防止膜
28 遮光部材
51 平坦化膜
100 裏面照射型固体撮像素子
1 Semiconductor substrate 22 n region (photodiode)
23
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007256228A JP4696104B2 (en) | 2007-09-28 | 2007-09-28 | Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007256228A JP4696104B2 (en) | 2007-09-28 | 2007-09-28 | Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009088261A JP2009088261A (en) | 2009-04-23 |
| JP2009088261A5 JP2009088261A5 (en) | 2010-08-05 |
| JP4696104B2 true JP4696104B2 (en) | 2011-06-08 |
Family
ID=40661289
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007256228A Expired - Fee Related JP4696104B2 (en) | 2007-09-28 | 2007-09-28 | Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4696104B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5328207B2 (en) * | 2008-04-01 | 2013-10-30 | キヤノン株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device |
| KR101647779B1 (en) * | 2009-09-09 | 2016-08-11 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Image sensor, fabricating method thereof, and device comprising the image sensor |
| JP2016025602A (en) * | 2014-07-24 | 2016-02-08 | 学校法人立命館 | Imaging apparatus and processing apparatus |
| JP2018006696A (en) | 2016-07-08 | 2018-01-11 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | Storage device |
| WO2018092632A1 (en) * | 2016-11-21 | 2018-05-24 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Solid-state imaging element and manufacturing method |
| FR3065322B1 (en) * | 2017-04-18 | 2019-06-14 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | METHOD FOR PRODUCING A LED MATRIX DISPLAY DEVICE |
| JP2021168316A (en) * | 2018-07-13 | 2021-10-21 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Sensor element and electronic apparatus |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000001337A (en) * | 1998-06-08 | 2000-01-07 | Nippon Electric Glass Co Ltd | Window glass for optical semiconductor |
| JP2002203953A (en) * | 2001-01-05 | 2002-07-19 | Sony Corp | Solid image pickup element, and its manufacturing method |
| JP2004253630A (en) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | Solid state imaging device |
| JP2005142510A (en) * | 2003-11-10 | 2005-06-02 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Solid-state imaging device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2005234038A (en) * | 2004-02-17 | 2005-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Dielectric multilayer film filter and manufacturing method therefor, and solid-state imaging device |
| JP2005268643A (en) * | 2004-03-19 | 2005-09-29 | Sony Corp | Solid-state image pickup element, camera module, and electronic equipment module |
| JP2006245101A (en) * | 2005-03-01 | 2006-09-14 | Canon Inc | Imaging apparatus having color filter |
| JP2006351800A (en) * | 2005-06-15 | 2006-12-28 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Solid-state imaging device and camera |
| JP2007027603A (en) * | 2005-07-21 | 2007-02-01 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2007103401A (en) * | 2005-09-30 | 2007-04-19 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Image pickup device and image processor |
| JP2007165646A (en) * | 2005-12-14 | 2007-06-28 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for manufacturing solid-state imaging apparatus, and solid state imaging apparatus |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0569376A (en) * | 1991-09-09 | 1993-03-23 | Suzuki Motor Corp | Arm driving device |
| JP3242159B2 (en) * | 1992-07-09 | 2001-12-25 | ブラザー工業株式会社 | Electronics |
-
2007
- 2007-09-28 JP JP2007256228A patent/JP4696104B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000001337A (en) * | 1998-06-08 | 2000-01-07 | Nippon Electric Glass Co Ltd | Window glass for optical semiconductor |
| JP2002203953A (en) * | 2001-01-05 | 2002-07-19 | Sony Corp | Solid image pickup element, and its manufacturing method |
| JP2004253630A (en) * | 2003-02-20 | 2004-09-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | Solid state imaging device |
| JP2005142510A (en) * | 2003-11-10 | 2005-06-02 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Solid-state imaging device and its manufacturing method |
| JP2005234038A (en) * | 2004-02-17 | 2005-09-02 | Seiko Epson Corp | Dielectric multilayer film filter and manufacturing method therefor, and solid-state imaging device |
| JP2005268643A (en) * | 2004-03-19 | 2005-09-29 | Sony Corp | Solid-state image pickup element, camera module, and electronic equipment module |
| JP2006245101A (en) * | 2005-03-01 | 2006-09-14 | Canon Inc | Imaging apparatus having color filter |
| JP2006351800A (en) * | 2005-06-15 | 2006-12-28 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Solid-state imaging device and camera |
| JP2007027603A (en) * | 2005-07-21 | 2007-02-01 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Imaging apparatus |
| JP2007103401A (en) * | 2005-09-30 | 2007-04-19 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Image pickup device and image processor |
| JP2007165646A (en) * | 2005-12-14 | 2007-06-28 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for manufacturing solid-state imaging apparatus, and solid state imaging apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009088261A (en) | 2009-04-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9287423B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and method of manufacturing the solid-state imaging device | |
| JP4798232B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and electronic apparatus | |
| KR101358587B1 (en) | Solid-state image sensor and imaging system | |
| JP5651986B2 (en) | SOLID-STATE IMAGING DEVICE, ITS MANUFACTURING METHOD, ELECTRONIC DEVICE, AND CAMERA MODULE | |
| WO2016072281A1 (en) | Solid-state imaging element, method for manufacturing same, and electronic device | |
| JP4751865B2 (en) | Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US8633559B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4538353B2 (en) | Photoelectric conversion film stacked color solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2008227250A (en) | Compound type solid-state image pickup element | |
| JP2008227253A (en) | Back irradiation type solid-state image pickup element | |
| JP4696104B2 (en) | Back-illuminated solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5725123B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic device | |
| JP5360102B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic device | |
| JP4404561B2 (en) | MOS type color solid-state imaging device | |
| JP5504382B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and imaging apparatus | |
| JP2013207053A (en) | Solid state imaging device and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4495949B2 (en) | Two-plate color solid-state imaging device and digital camera | |
| JP5418527B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic device | |
| JP2014022649A (en) | Solid-state image sensor, imaging device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4070639B2 (en) | CCD color solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2006140413A (en) | Solid-state image sensing element | |
| JP2009049117A (en) | Method of forming color filter of solid-state image pickup device, solid-state image pickup device, and pattern mask set for solid-state image pickup device | |
| JP2007066962A (en) | Color solid-state imaging device and digital camera | |
| JP2007201047A (en) | Solid-state image pickup device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2011135100A (en) | Solid-state imaging device and electronic apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100212 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100623 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20100623 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20100708 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100907 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101027 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110201 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110228 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140304 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |